Patents
Literature
44 results about "Extracellular dna" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
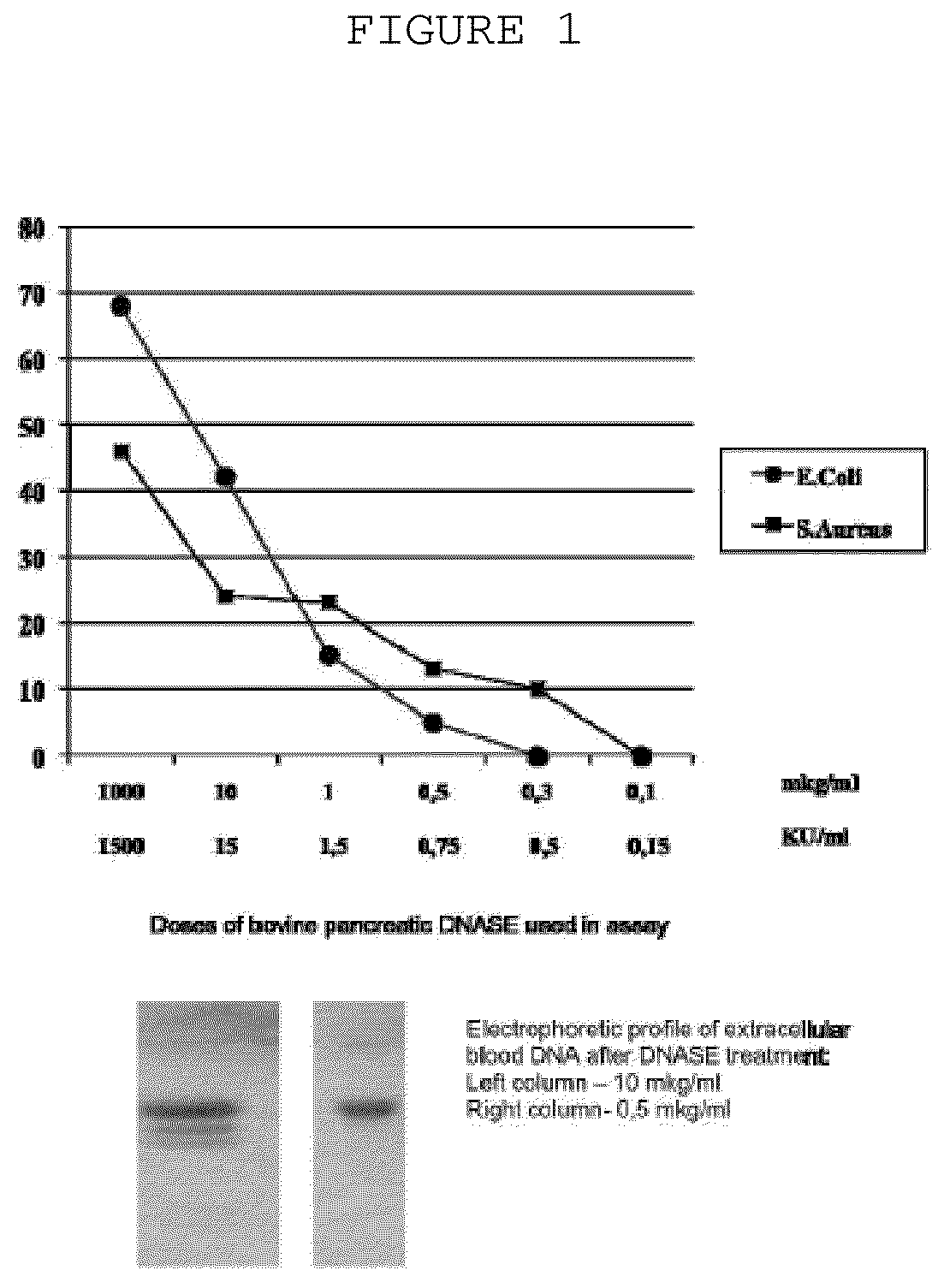
Extracellular DNA Bacteria can organize into structured communities, called biofilms, that protect them from antibiotics and from immune attack by the host. ... The extracellular DNA is thought to be derived from membrane vesicles. They propose that DNase I treatment may be beneficial to prevent biofilm formation in infection-linked diseases such as cystic fibrosis.
Non-invasive detection of fetal genetic traits
InactiveUS20050164241A1Facilitates non-invasive detectionComponent separationOther chemical processesPregnancyNon invasive
Blood plasma of pregnant women contains fetal and (generally>90%) maternal circulatory extracellular DNA. Most of said fetal DNA contains ≦500 base pairs, said maternal DNA having a greater size. Separation of circulatory extracellular DNA of <500 base pairs results in separation of fetal from maternal DNA. A fraction of a blood plasma or serum sample of a pregnant woman containing, due to size separation (e.g. by chromatography, density gradient centrifugation or nanotechnological methods), extracellular DNA substantially comprising ≦500 base pairs is useful for non-invasive detection of fetal genetic traits (including the fetal RhD gene in pregnancies at risk for HDN; fetal Y chromosome-specific sequences in pregnancies at risk for X chromosome-linked disorders; chromosomal aberrations; hereditary Mendelian genetic disorders and corresponding genetic markers; and traits decisive for paternity determination) by e.g. PCR, ligand chain reaction or probe hybridization techniques, or nucleic acid arrays.
Owner:SEQUENOM INC
Non-invasive detection of fetal genetic traits
ActiveUS20080071076A1Facilitates non-invasive detectionSugar derivativesOther chemical processesPregnancyNon invasive
Blood plasma of pregnant women contains fetal and (generally>90%) maternal circulatory extracellular DNA. Most of said fetal DNA contains .Itoreq.500 base pairs, said maternal DNA having a greater size. Separation of circulatory extracellular DNA of .Itoreq.500 base pairs results in separation of fetal from maternal DNA. A fraction of a blood plasma or serum sample of a pregnant woman containing, due to size separation (e.g. by chromatography, density gradient centrifugation or nanotechnological methods), extracellular DNA substantially comprising .Itoreq.500 base pairs is useful for non-invasive detection of fetal genetic traits (including the fetal RhD gene in pregnancies at risk for HDN; fetal Y chromosome-specific sequences in pregnancies at risk for X chromosome-linked disorders; chromosomal aberrations; hereditary Mendelian genetic disorders and corresponding genetic markers; and traits decisive for paternity determination) by e.g. PCR, ligand chain reaction or probe hybridization techniques, or nucleic acid arrays.
Owner:SEQUENOM INC
Method for treating oncological diseases
ActiveUS7612032B2Promote growthImprove efficiencyPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesDiseaseWhole body
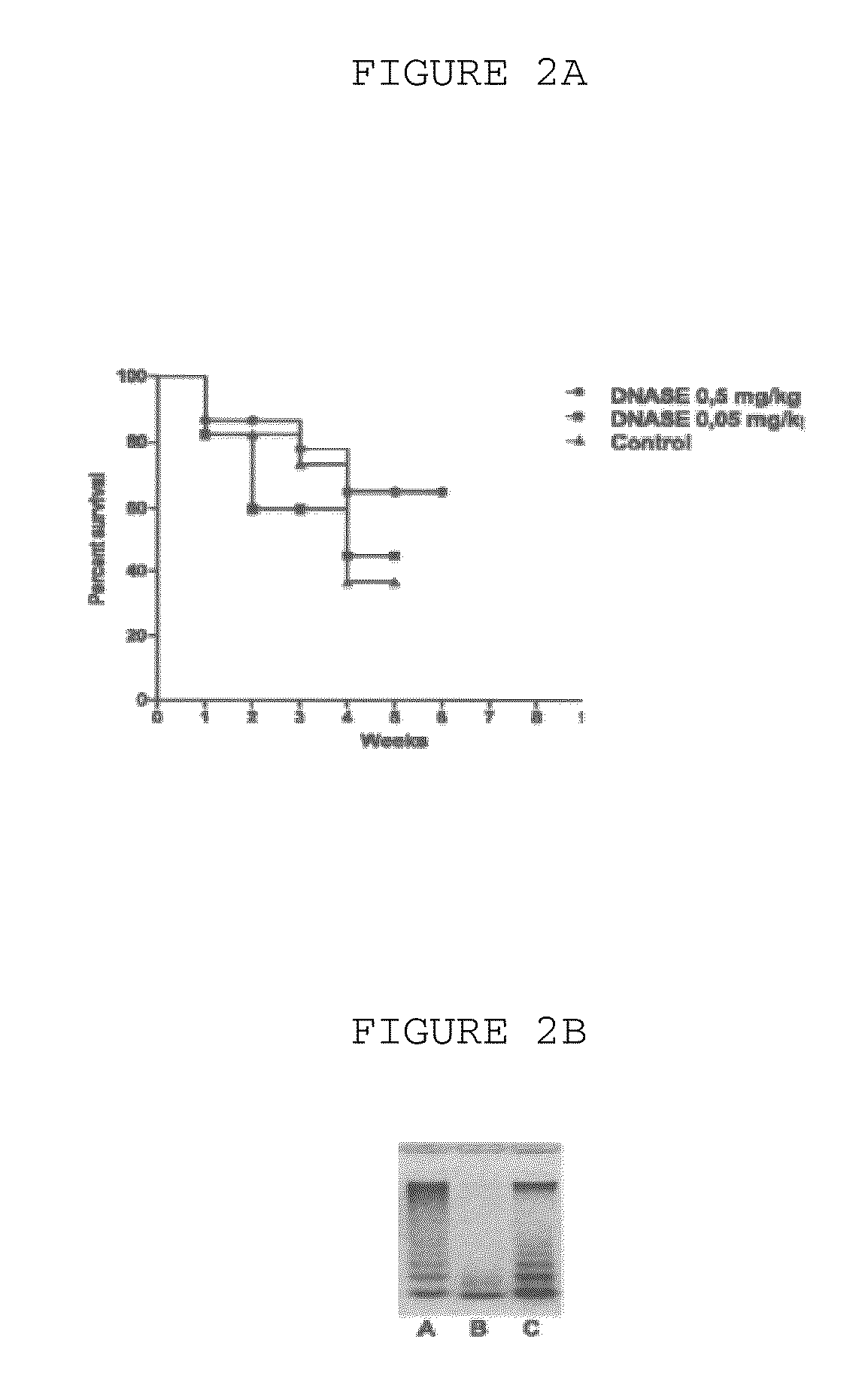
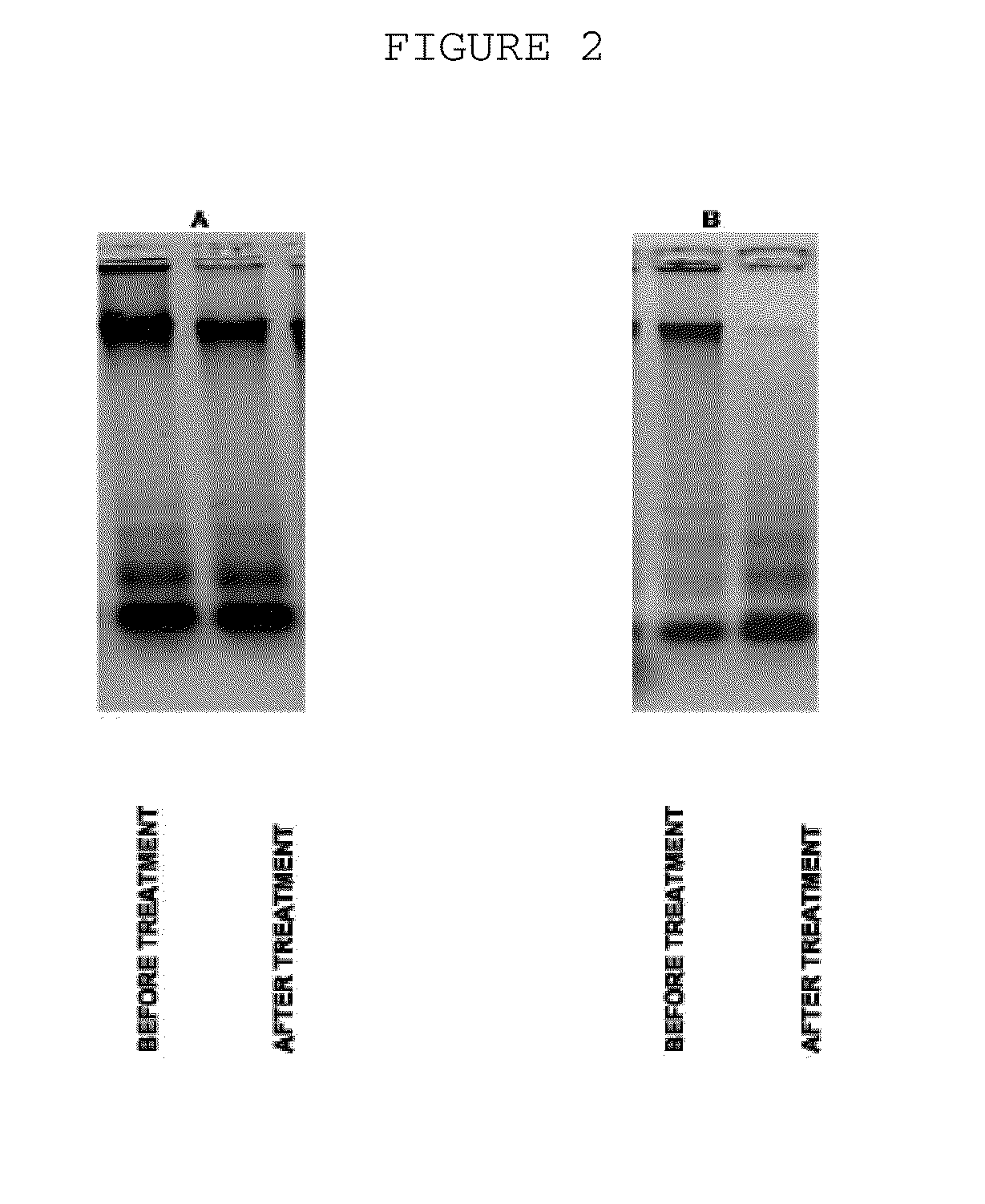
A method to treat solid tumors and other oncological diseases consists of parenterally injecting an agent which destroy's blood's extracellular DNA into the systemic blood circulation of a cancer patient to slow down malignant. The agent is embodied in the form of a DNAse enzyme and, more particularly, as a bovine pancreatic DNAse. Doses from 50,000-250,000,000 Kunz units / day are injected for 5-360 days. A binding agent or an agent that modifies the chemical composition of the blood extracellular DNA is additionally injected into the blood. This modifying agent is preferably an enzyme-ribonuclease.
Owner:CLS THERAPEUTICS
Method for treating systemic bacterial, fungal and protozoan infection
ActiveUS8431123B2Low-toxicLower Level RequirementsHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsBacteroidesProtozoa
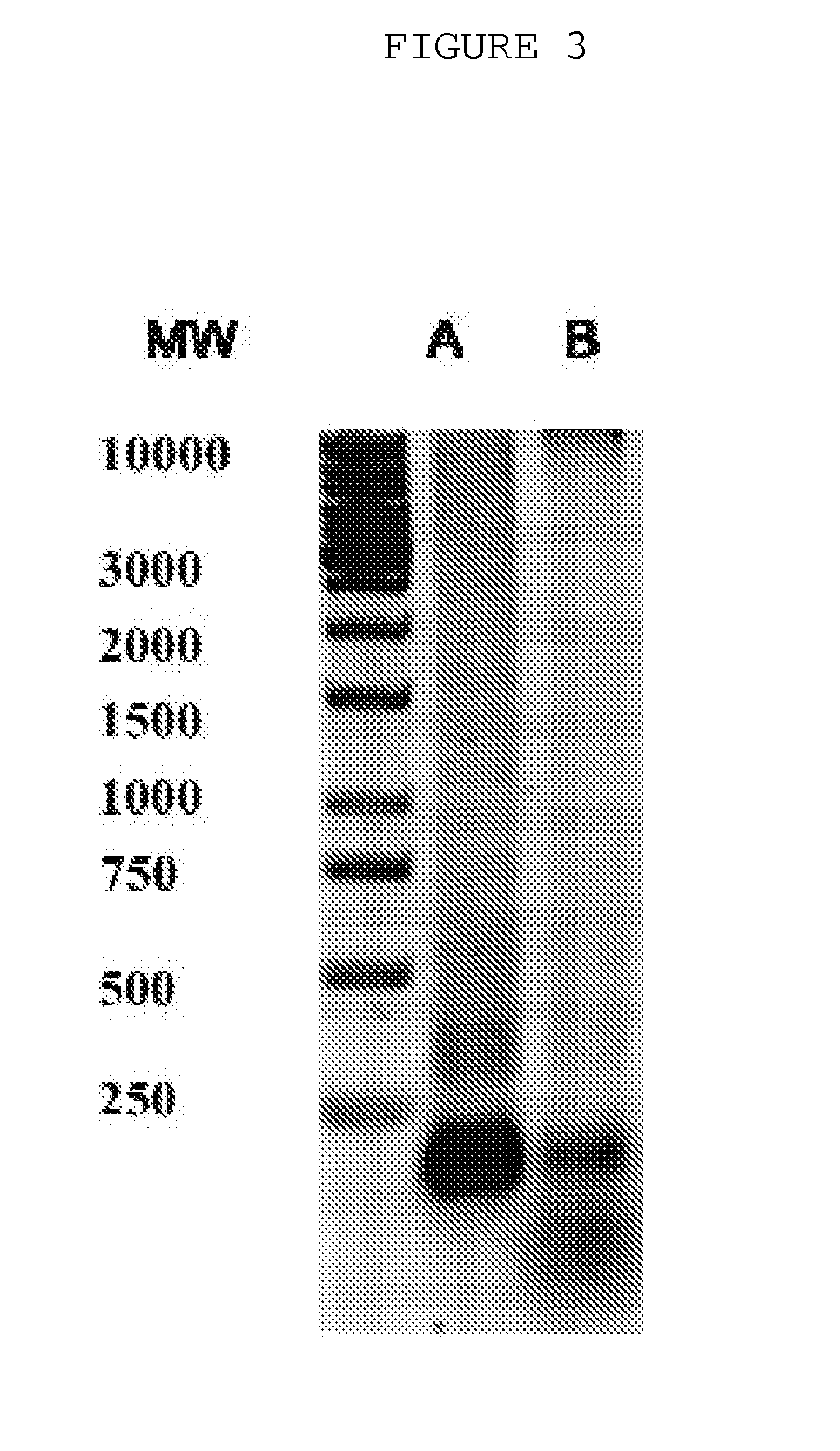
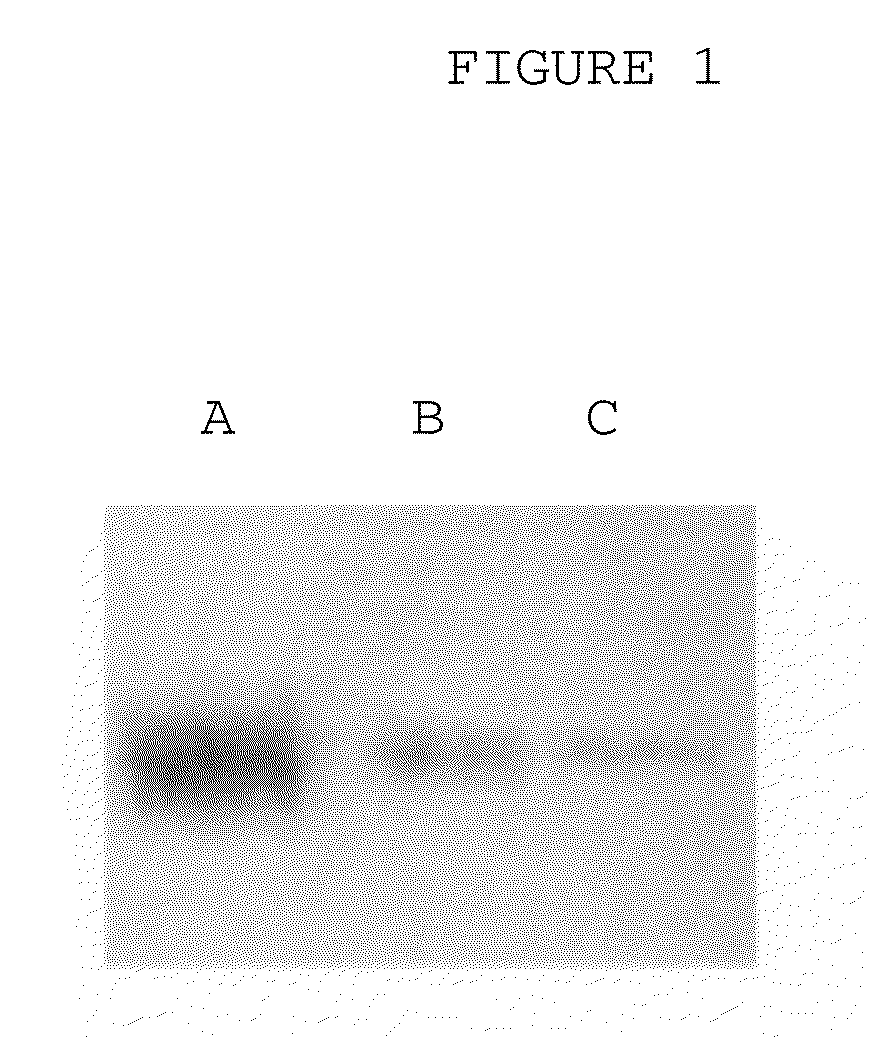
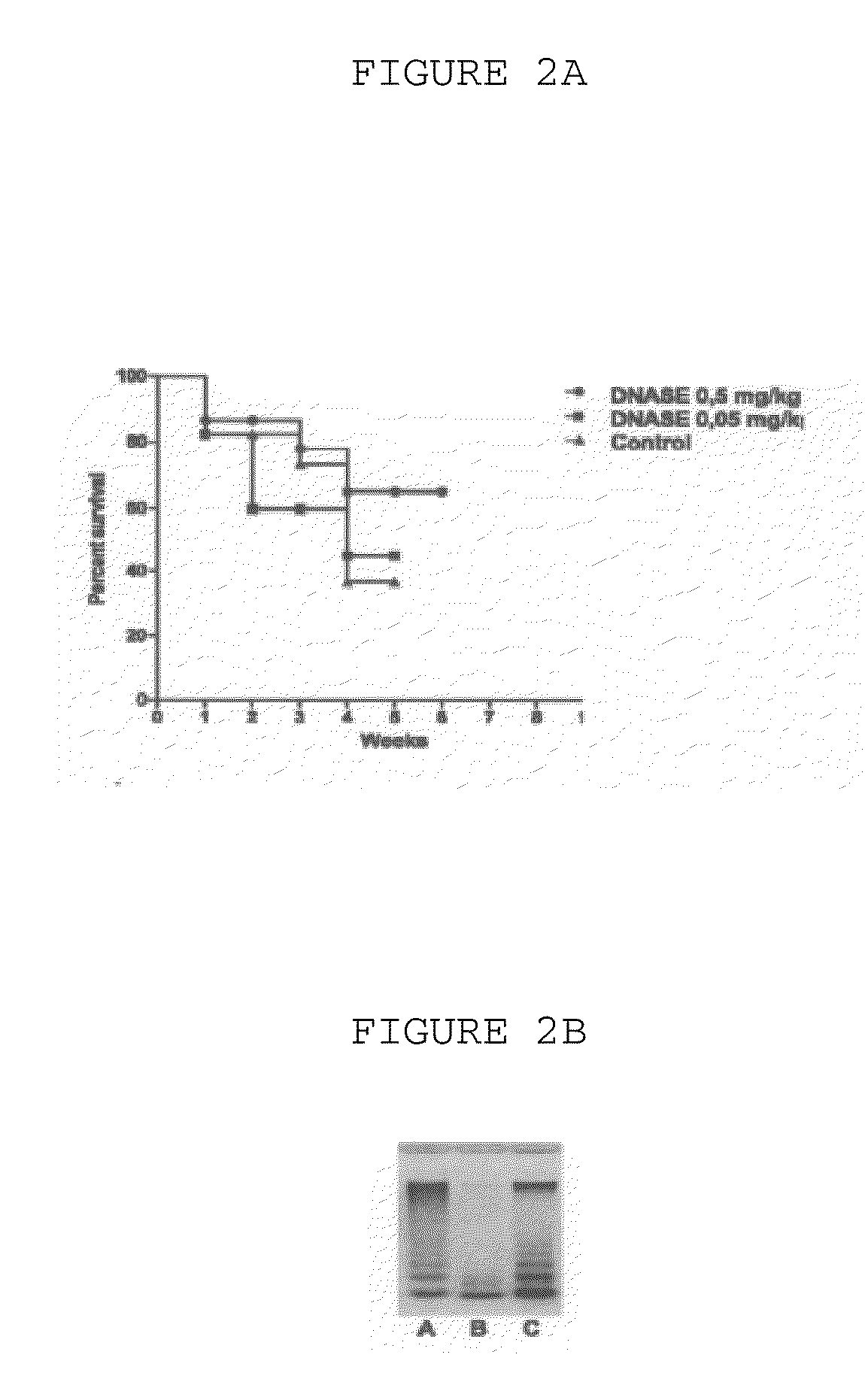
The invention is directed to a treatment of diseases that are accompanied by quantitative and / or qualitative changes of blood extracellular DNA and, more particularly, to a treatment of systemic bacterial, fungal and protozoan infections. The inventive method comprises introducing a treatment agent into a circulating blood system of a patient diagnosed with systemic infection caused by bacteria, fungi or protozoa, wherein said treatment agent destroys extracellular DNA in said blood of said patient and wherein said treatment agent used to destroy said extracellular DNA is a DNase enzyme: said agent being administered in doses and regimens which are sufficient to decrease the average molecular weight of circulating extracellular blood DNA in the blood of said patient; such decrease in the average molecular weight can be measured by gel electrophoresis of extracellular blood DNA fraction from the blood of said patient. A DNase enzyme may be applied in a dose and regimen that provide a DNase DNA hydrolytic activity measured in blood plasma that exceeds 1.5 Kunitz units per 1 ml of blood plasma for more than 12 hours within a period of 24 hours.
Owner:CLS THERAPEUTICS
Method for treating systemic DNA mutation disease
ActiveUS8388951B2Lower Level RequirementsGood treatment effectPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesDiseaseA-DNA
A treatment for systemic DNA mutation diseases accompanied with development of somatic mosaicism and elevation of blood extracellular DNA and, more particularly, to a treatment of diabetes mellitus and atherosclerosis. The inventive method consist from introducing a treatment agent into a circulating blood system of a patient diagnosed with systemic DNA mutation diseases when said treatment agent destroys extracellular DNA in said blood of said patient and wherein said treatment agent used to destroy said extracellular DNA is a DNASE enzyme: said agent might be administered in doses and regimens which sufficient to decrease number average molecular weight of circulating extracellular blood DNA in the blood of said patient; such decrease of number average molecular weight might be measured by gel electrophoresis of extracellular blood DNA fraction from the blood of said patient. A DNASE enzyme may be further applied in a dose and regime that provide a DNA hydrolytic activity measured in blood plasma exceeding 1.5 Kunitz units per 1 ml of blood plasma for more than 12 hours within a period of 24 hours.
Owner:CLS THERAPEUTICS
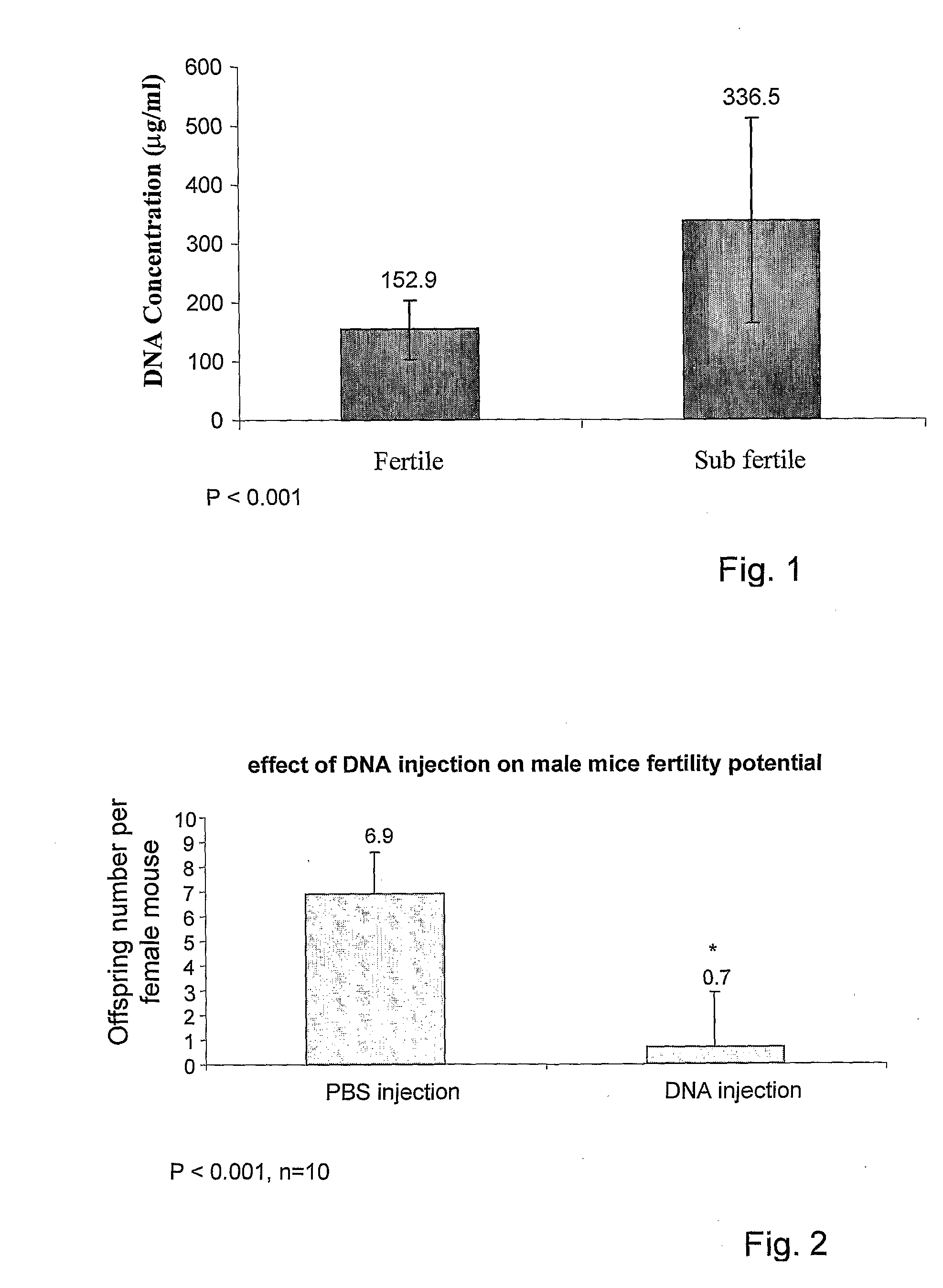
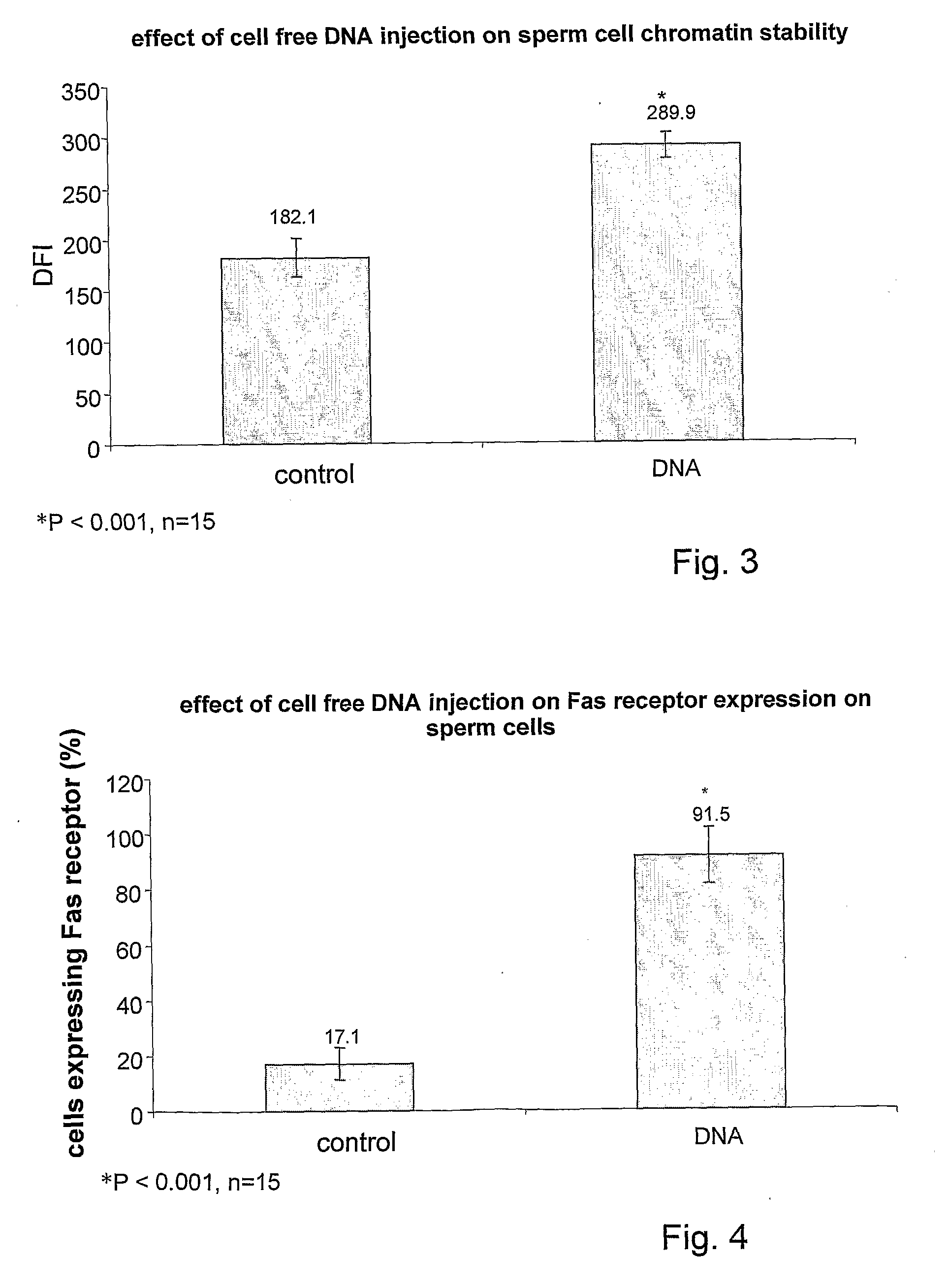
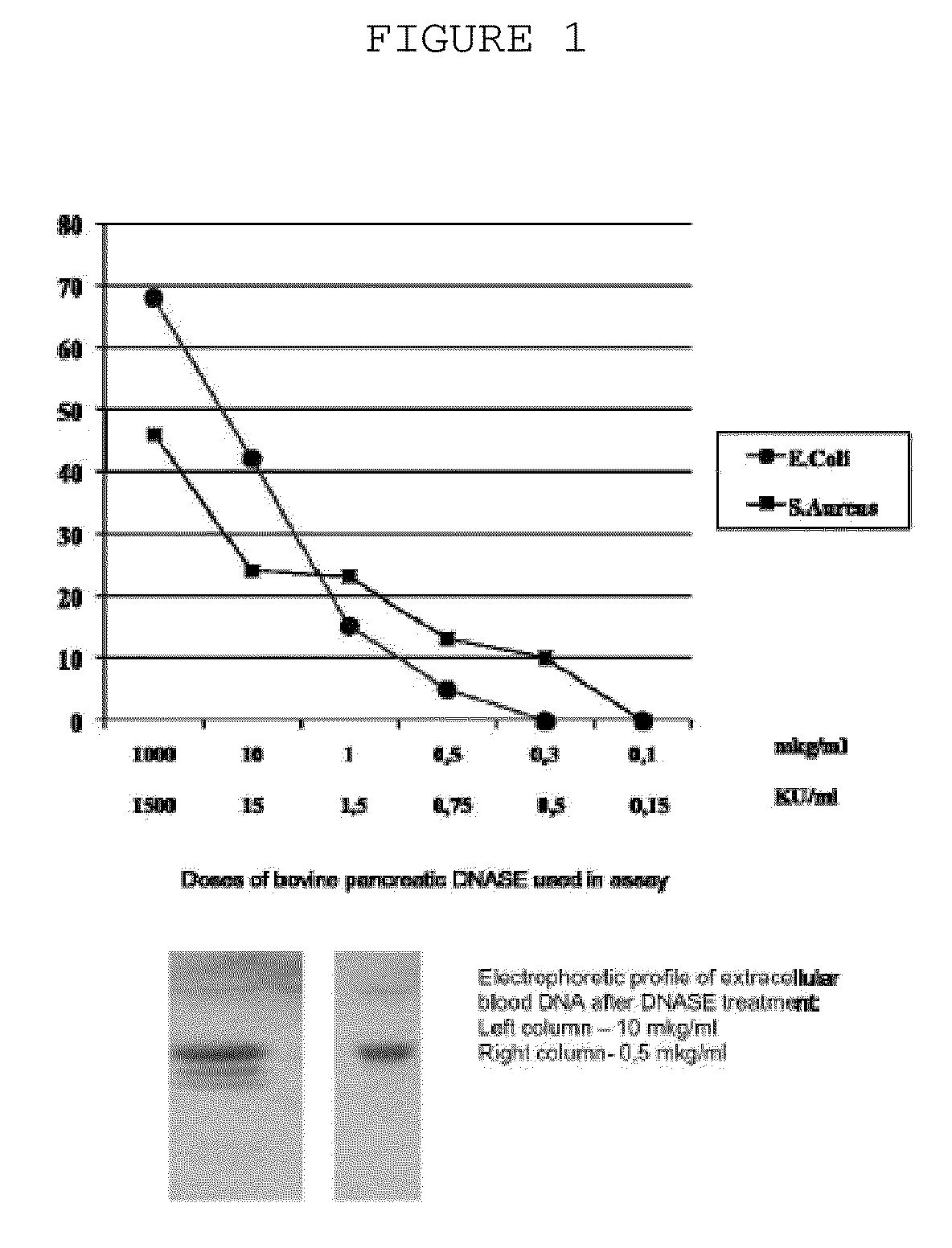
Method and pharmacological composition for the diagnosis and treatment of male
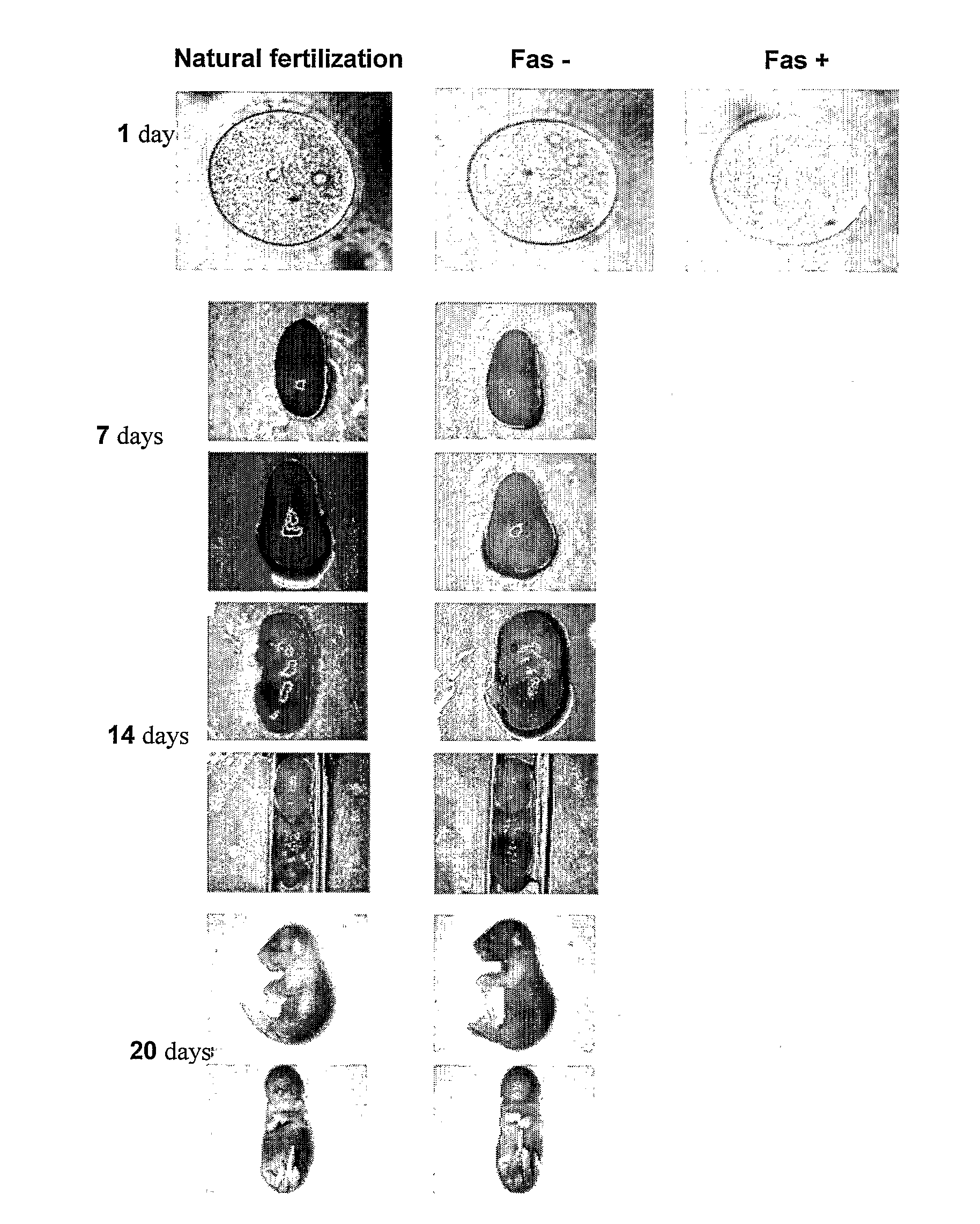
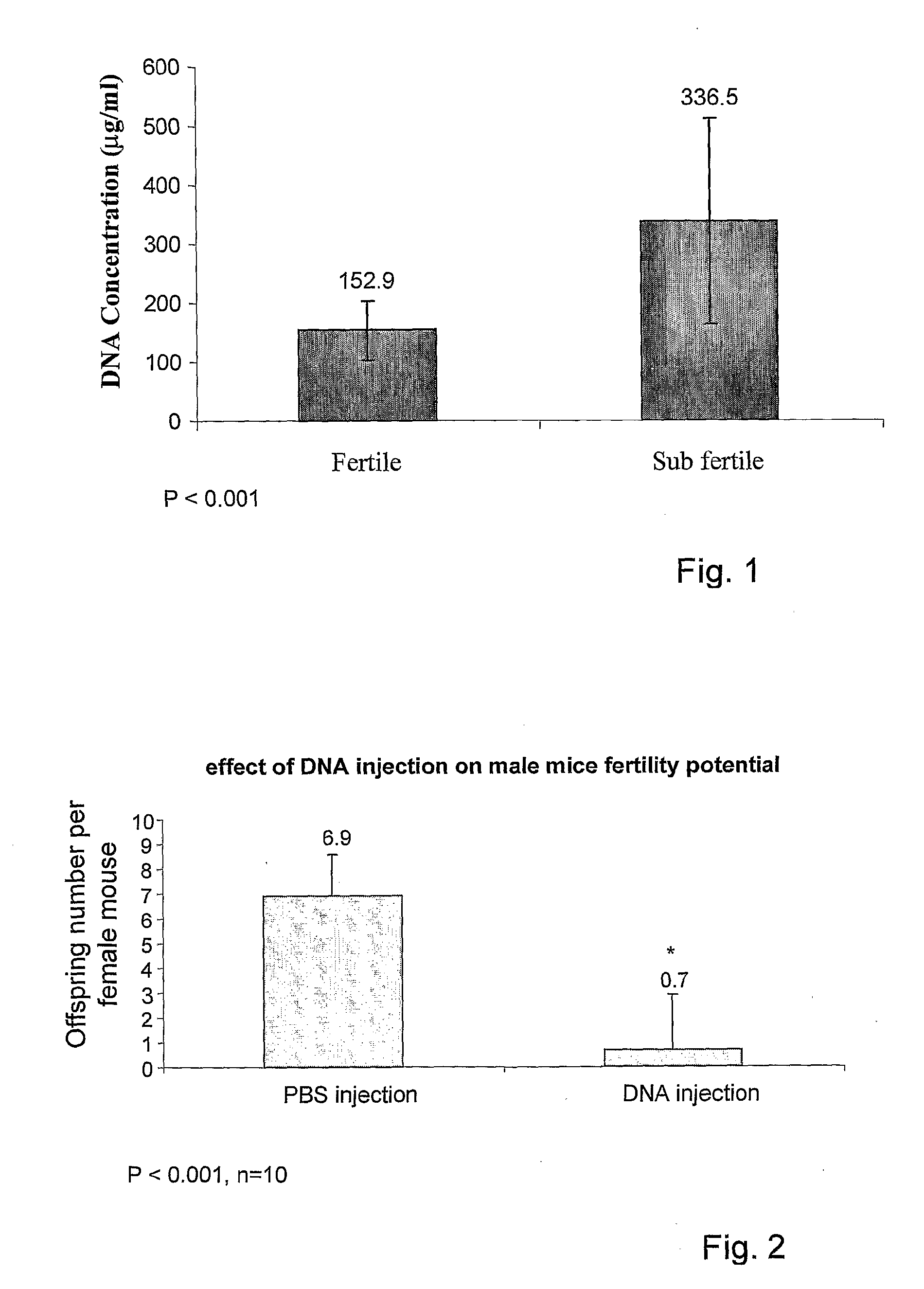
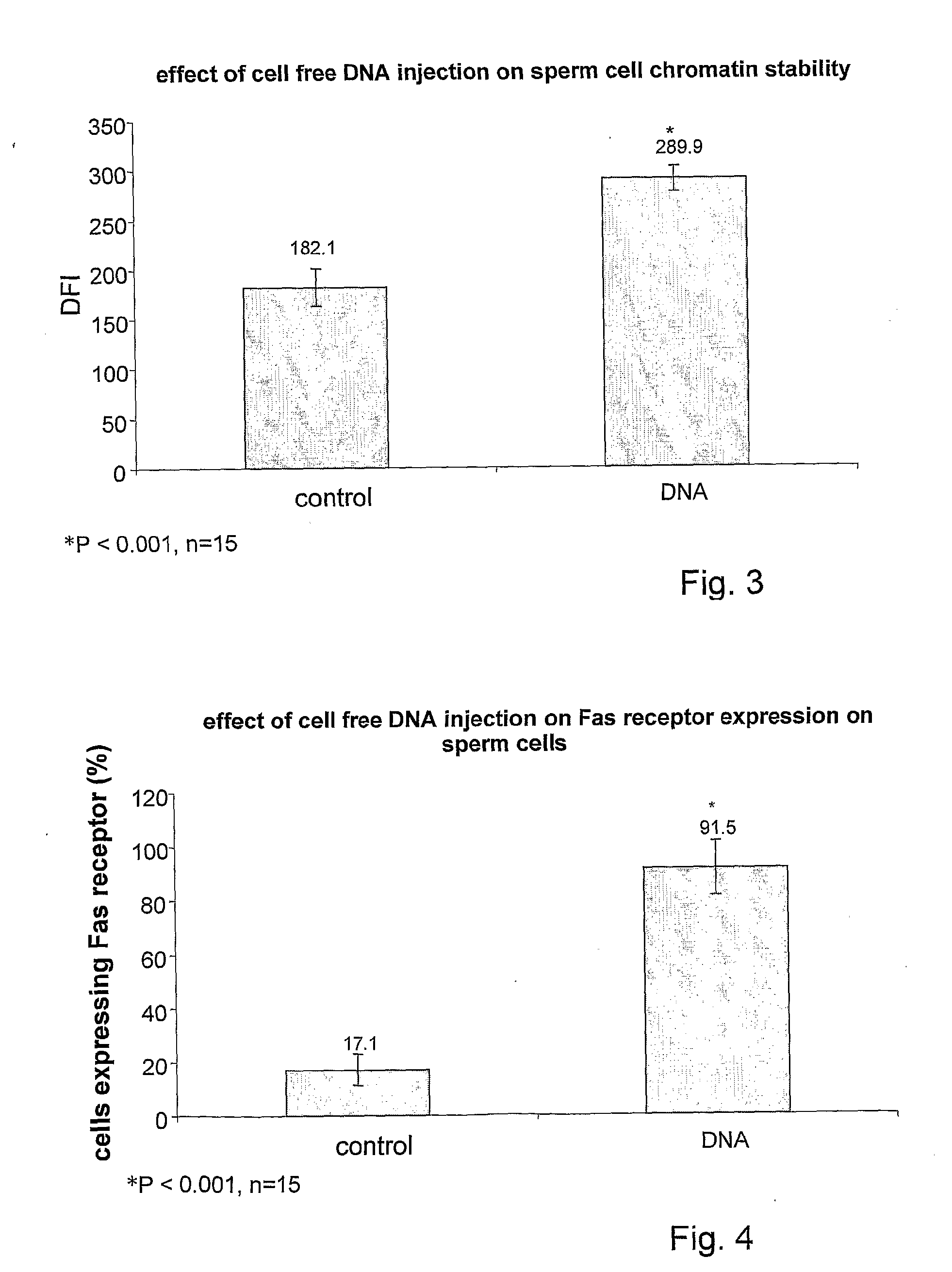
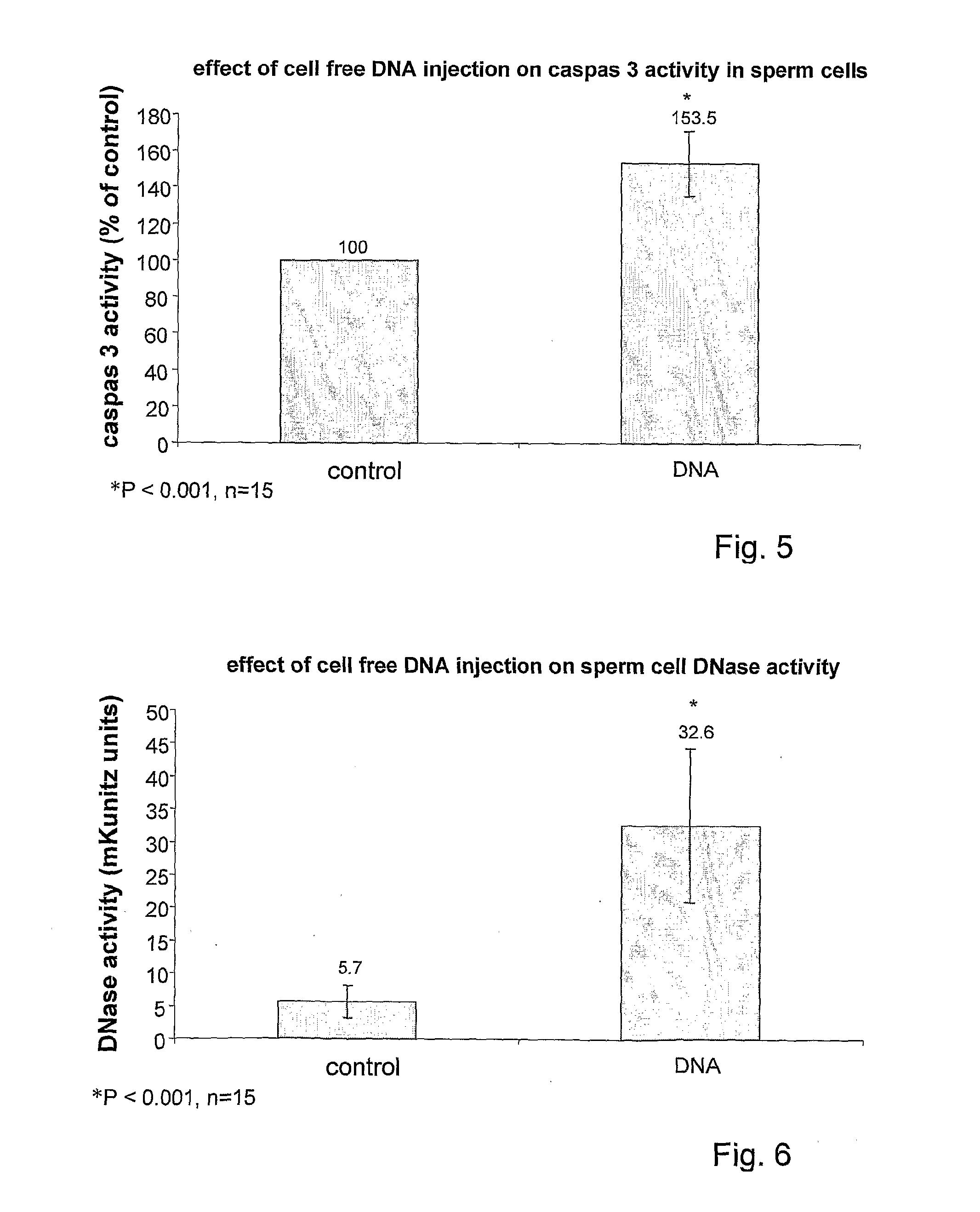
Pharmaceutical compositions for treating male sub-fertility that include an agent that causes a reduction in an effect of extracellular DNA on sperm cells, are provided. The agent may be, for example, an enzyme that degrades DNA such as DNase, a substance that blocks the interaction between cell free DNA and sperm cell surface receptors, a substance that binds to DNA, a substance that inhibits endogenous sperm cell DNase, a substance that inhibits a member of a signal transduction pathway mediated by DNA binding to sperm cell surface receptors, or an agent that stimulates production of an endogenous substance that causes a reduction in an antifertility effect of cell free DNA on sperm cells. Also provided are methods for treating male sub-fertility by administering the pharmaceutical composition to a subject in need thereof. Further provided are methods for determining a fertility status in a male subject, methods for assisted reproduction, methods for selecting an assisted reproduction technique (ART), and methods for selecting sperm cells in a sperm cell population for use in an assisted reproduction technique.
Owner:PERINESS LTD
Method for Treating Oncological Diseases
ActiveUS20100150903A1Promote growthImprove efficiencyPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesDiseaseChemical composition
A method to treat solid tumors and other oncological diseases consists of parenterally injecting an agent which destroy's blood's extracellular DNA into the systemic blood circulation of a cancer patient to slow down malignant. The agent is embodied in the form of a DNAse enzyme and, more particularly, as a bovine pancreatic DNAse. Doses from 50,000-250,000,000 Kunz units / day are injected for 5-360 days. A binding agent or an agent that modifies the chemical composition of the blood extracellular DNA is additionally injected into the blood. This modifying agent is preferably an enzyme-ribonuclease.
Owner:CLS THERAPEUTICS
Method for Treating Systemic Bacterial, Fungal and Protozoan Infection
ActiveUS20110189156A1Low-toxicLower Level RequirementsAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsDiseaseBacteroides
A treatment for the diseases that are accompanied by quantitative and qualitative changes of blood extracellular DNA and, more particularly, to a treatment of systemic bacterial, fungal and protozoan infections. The inventive method consist from introducing a treatment agent into a circulating blood system of a patient diagnosed with systemic infection caused by bacteria, fungi or protozoa when said treatment agent destroys extracellular DNA in said blood of said patient and wherein said treatment agent used to destroy said extracellular DNA is a DNASE enzyme: said agent must be administered in doses and regimens which sufficient to decrease number average molecular weight of circulating extracellular blood DNA in the blood of said patient; such decrease of number average molecular weight might be measured by gel electrophoresis of extracellular blood DNA fraction from the blood of said patient. A DNASE enzyme may be further applied in a dose and regime that provide a DNA hydrolytic activity measured in blood plasma exceeding 1.5 Kunitz units per 1 ml of blood plasma for more than 12 hours within a period of 24 hours.
Owner:CLS THERAPEUTICS
Method for Treating Systemic DNA Mutation Disease
ActiveUS20100303796A1Lower Level RequirementsGood treatment effectHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsA-DNABlood plasma
A treatment for systemic DNA mutation diseases accompanied with development of somatic mosaicism and elevation of blood extracellular DNA and, more particularly, to a treatment of diabetes mellitus and atherosclerosis. The inventive method consist from introducing a treatment agent into a circulating blood system of a patient diagnosed with systemic DNA mutation diseases when said treatment agent destroys extracellular DNA in said blood of said patient and wherein said treatment agent used to destroy said extracellular DNA is a DNASE enzyme: said agent might be administered in doses and regimens which sufficient to decrease number average molecular weight of circulating extracellular blood DNA in the blood of said patient;such decrease of number average molecular weight might be measured by gel electrophoresis of extracellular blood DNA fraction from the blood of said patient. A DNASE enzyme may be further applied in a dose and regime that provide a DNA hydrolytic activity measured in blood plasma exceeding 1.5 Kunitz units per 1 ml of blood plasma for more than 12 hours within a period of 24 hours.
Owner:CLS THERAPEUTICS
Detection of extracellular tumor-associated nucleic acid in blood plasma or serum
InactiveUS8048629B2Enabling detectionFacilitates selection and monitoringMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic material ingredientsReceptor tyrosine kinase inhibitorBlood plasma
This invention relates to detection of specific extracellular DNA in plasma or serum fractions of human or animal blood associated with neoplastic, pre-malignant or proliferative disease. Specifically, the invention relates to detection tumor-associated DNA, and to those methods of detecting and monitoring tumor-associated DNA found in the plasma or serum fraction of blood by using DNA extraction and amplification with or without enrichment for DNA. The invention allows the selection and monitoring of patients for various cancer therapies including receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapies.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
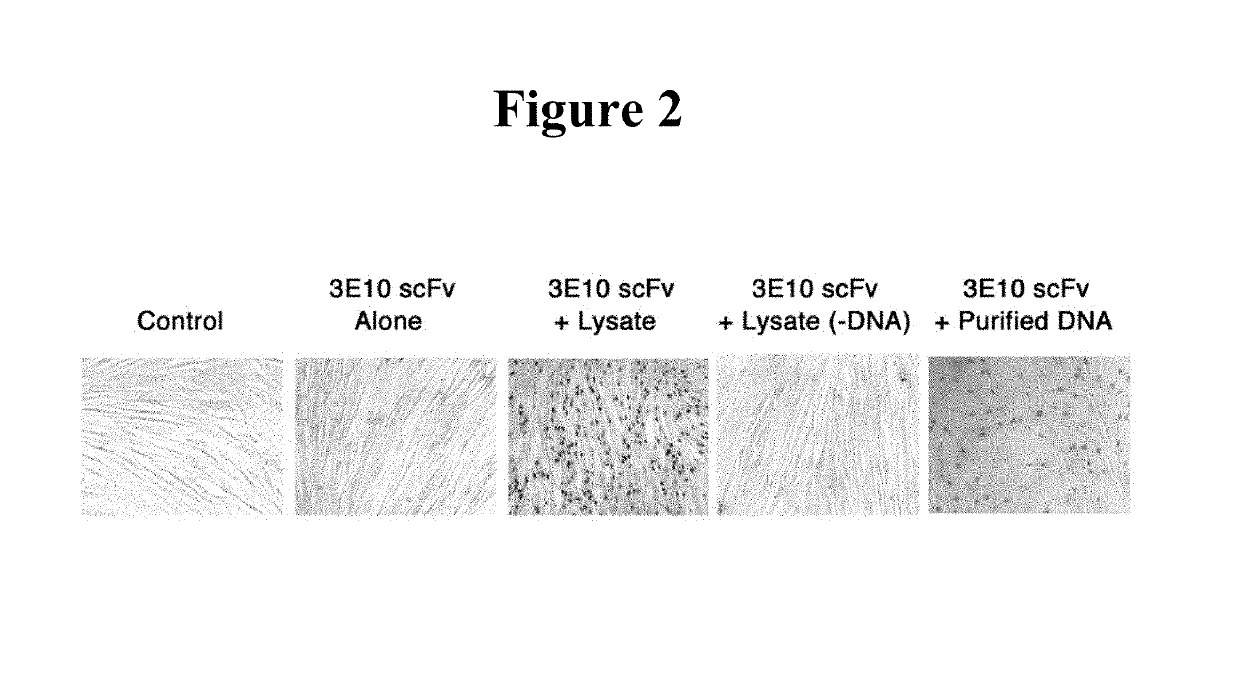
Methods for dna-dependent targeting of a cell permeant antibody
ActiveUS20160235859A1Peptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansExtracellularCell penetration
The invention provides methods for selective targeting of live cells, which have undergone or are undergoing radiation or chemotherapy, at a site of interest with a cell-penetrating polypeptide. In one embodiment of the invention, the method comprises contacting the live cells with a cell-penetrating polypeptide comprising cell-penetrating determinants so that the cell-penetrating polypeptide binds extracellular DNA near or around the live cells so as to form a complex or association therewith such that the complex or associated polypeptide-DNA so bound bind the live cells and penetrates the live cells thereby selectively targeting live cells at a site of interest with a cell-penetrating polypeptide.
Owner:U S GOVERNMENT REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS
Method for simultaneously extracting microbial intracellular and extracellular DNAs (deoxyribonucleic acids) in sewage biological treatment water sample
The invention relates to a method for simultaneously extracting microbial intracellular and extracellular DNAs (deoxyribonucleic acids) in a sewage biological treatment water sample, belonging to the technical field of sewage treatment. The method comprises the following steps: pretreating; and separating intracellular and extracellular DNAs, and respectively extracting and purifying the intracellular DNA and extracellular DNA. The method can simultaneously extract the intracellular and extracellular DNAs from a biological treatment sewage sample of an activated sludge process or the like and perform accurate quantification, has the advantages of high yield, high purity and low thallus cracking cross contamination, is simple and easy to implement, is very suitable for performing contrast experiments and scientific research on the sewage sample containing abundant microbes, and has application prospects for developing and processing business analysis kits.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Soil DNA extracting method for evaluating diversity of microbial community of plant root system
InactiveCN101709298AEasy to operateLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationPlant rootsDna recovery
The invention discloses a soil DNA extracting method for evaluating diversity of a microbial community of a plant root system. In the method, pretreatment is carried out on a sample before cell splitting, extracellular DNA and humic substances are removed, and the problems of difficult removal of the humic substances and low DNA recovery rate existing in a purification step are solved. In the extraction process of the method, phenol or chloroform is not used so as to reduce harm on the health of experimenters, obtain complete DNA and molecular fragments greater than 10kb and achieve high yield. OD260 / OD230 and OD260 / OD280 of the extracted soil microorganism DNA are close to standard values and can be directly applied to molecular operation so as to evaluate the diversity of the microbial community of the plant root system.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
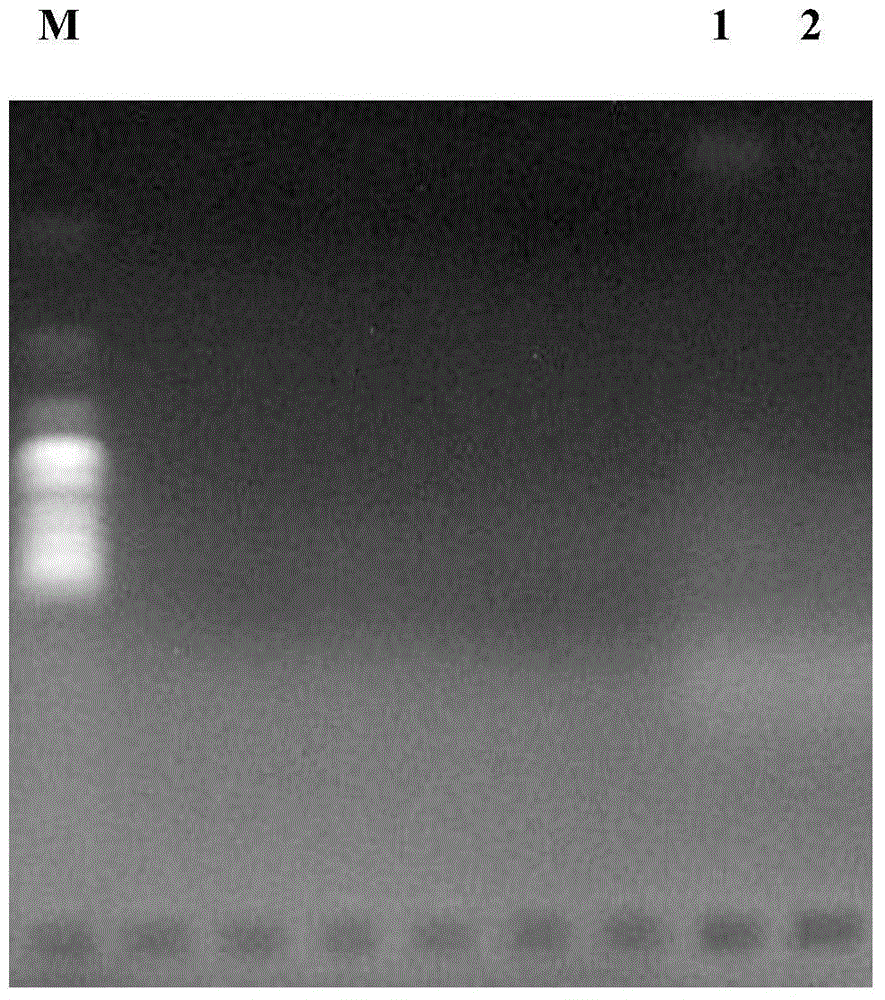
Method for treating diseases associated with changes of qualitative and/quantitative composition of blood extracellular dna
The invention relates to medicine and veterinary science and can be used for treating diseases associated with changes of the qualitative and / quantitative composition of blood extracellular DNA, namely generalised infection diseases provoked by bacteria, diseases provoked by fungi and protozoa, atherosclerosis, pancreatic diabetes, allergic diseases associated with delayed response hypersensitivity and diseases due to somatic cell gene mutations. The inventive method for treating diseases associated with modifications of the qualitative and / or quantitative composition of blood extracellular DNA, namely generalised infection diseases provoked by bacteria, diseases provoked by fungi and protozoa, atherosclerosis, pancreatic diabetes, allergic diseases associated with delayed response hypersensitivity and diseases due to somatic cell gene mutations consists in injecting an agent destroying blood extracellular DNA. DNAse enzyme injected into a systemic blood circulation in doses which modify the electrophoretic profile of the blood extracellular DNA definable by pulse-electrophoresis can be used in the form of an agent destroying said blood extracellular DNA. Said DNAse enzyme can be injected in doses and at regimes ensuring the level of a blood plasma DNA-hydrolytic activity which is measured in the blood plasma and is higher than 150 Kunz units per litre of plasma during a total time higher than 12 hours a day. The inventive method makes it possible to develop a high-efficient and low-toxic method for treating diseases associated with modifications of qualitative and / or quantitative composition of blood extracellular DNA individually or in combination thereof.
Owner:CLS THERAPEUTICS
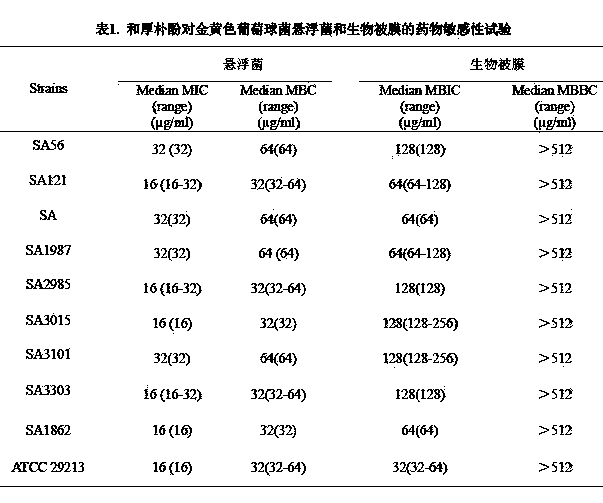
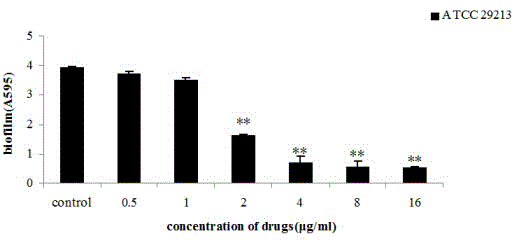
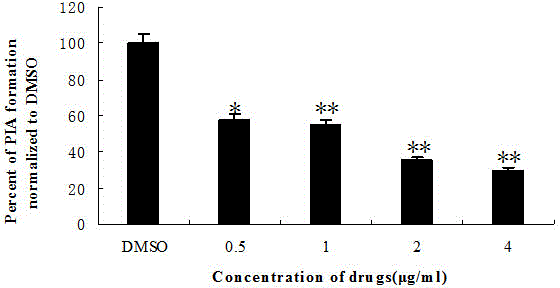
Application of honokiol in inhibiting staphylococcus aureus biofilm
InactiveCN104173324AInhibition effect verificationAntibacterial agentsHydroxy compound active ingredientsKill curveStaphyloccocus aureus
The invention discloses an application of honokiol in preparing medicines for inhibiting staphylococcus biofilms. Drug susceptibility test is utilized to detect the inhibiting effect of honokiol respectively on floating bacteria of staphylococcus aureus and biofilms, and the inhibiting effect of honokiol is further verified by drawing a killing curve and adopting a crystal violet semiquantitative method. Furthermore, the influence on polysaccharide intercellular adhesion (PIA) synthesis and extracellular DNA (eDNA) release and investigations on the transcriptional level of coding fibronectin-binding protein genes fnbA and fnbB indicate that the honokiol has an excellent effect for inhibiting growth of staphylococcus aureus biofilms.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
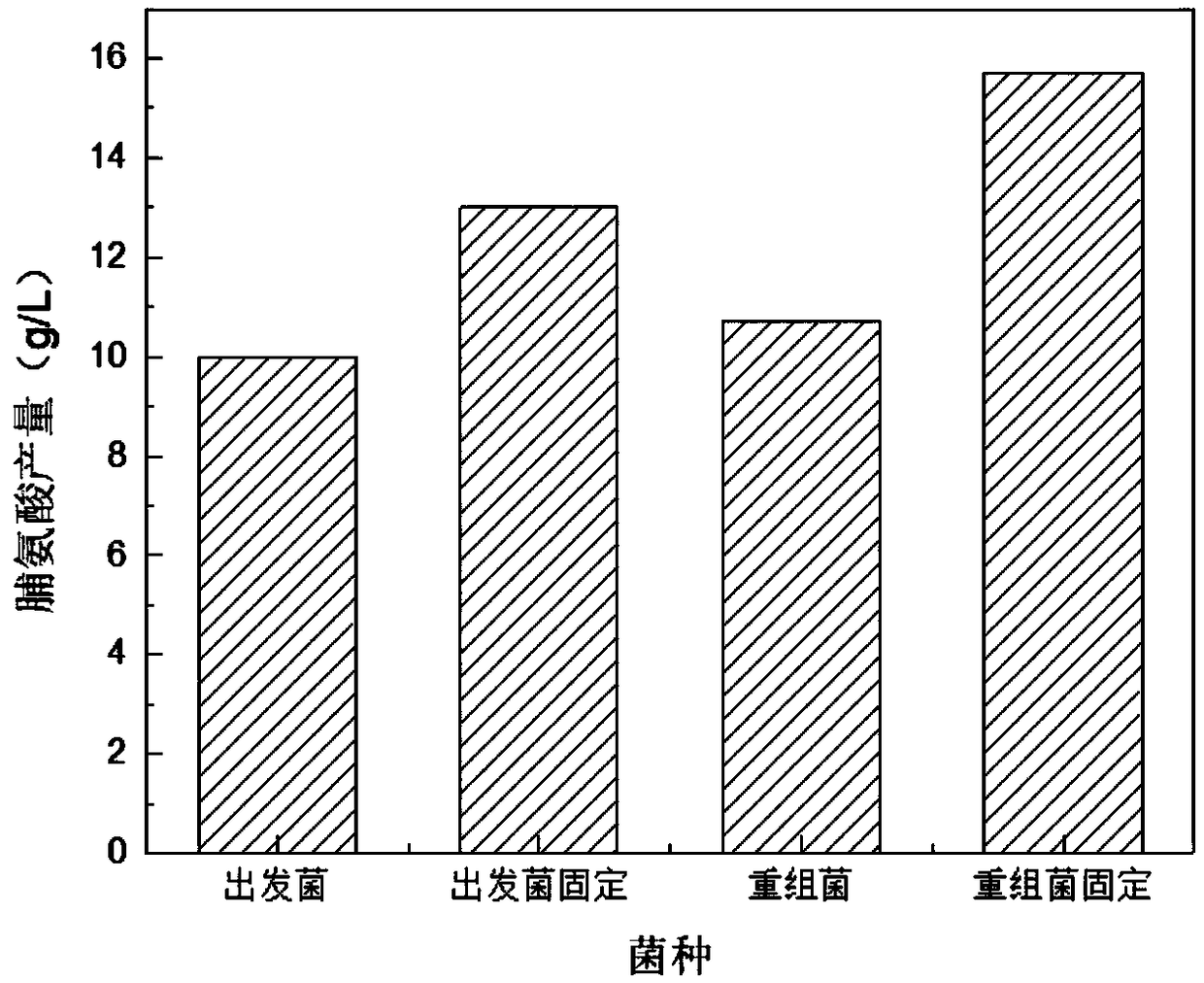
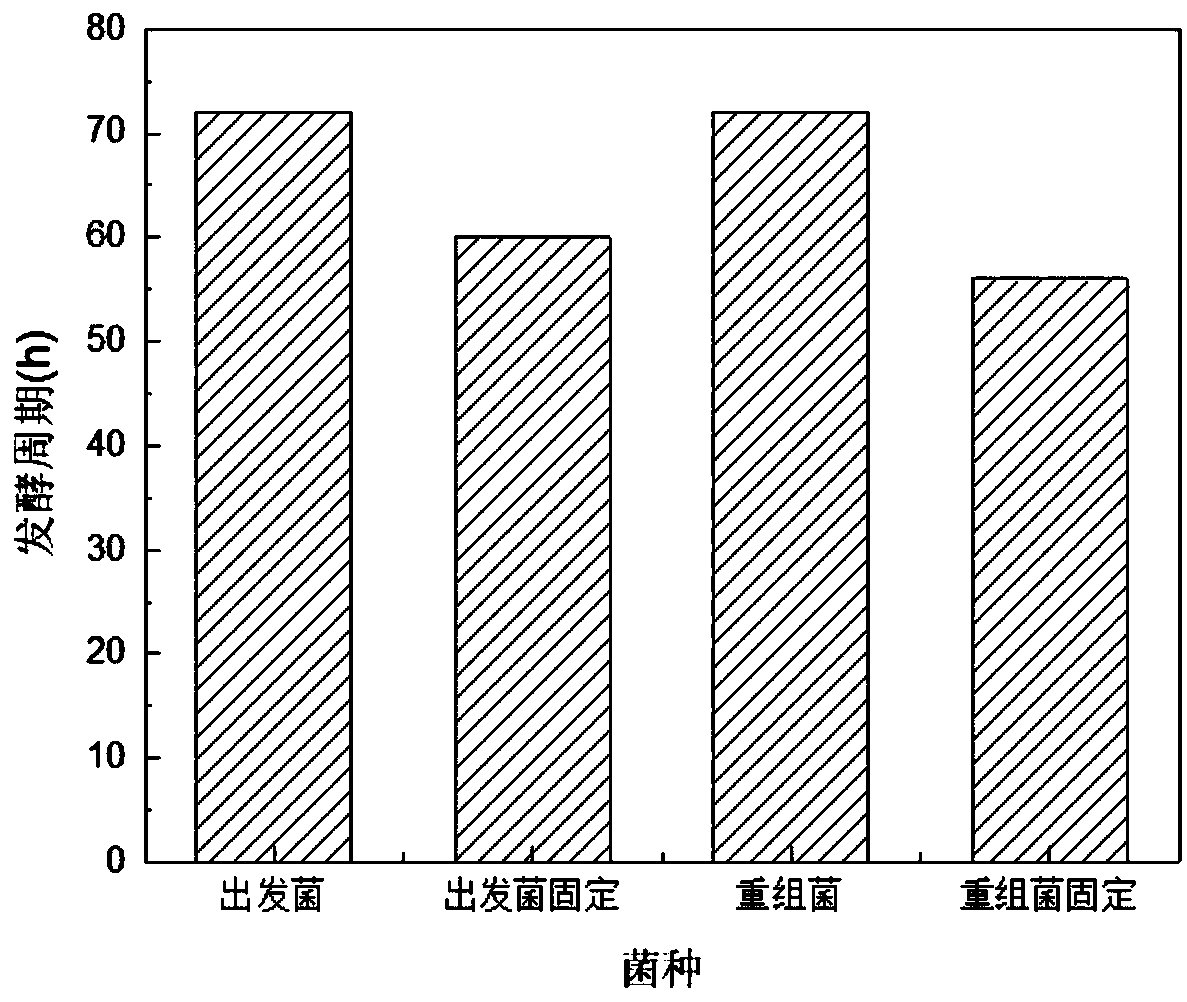
Corynebacterium glutamicum overexpressing adenosine triphosphatase, construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN109207418AEnhanced initial adhesionImprove stabilityBacteriaHydrolasesBacteroidesAdenosine triphosphatase
The invention discloses a Corynebacterium glutamicum overexpressing adenosine triphosphatase, wherein the gene sequence of the adenosine triphosphatase is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1. As that adenosine triphosphatase ATPase is overexpress in Corynebacterium glutamicum, the invention provides energy for the intermediate convert protein VirB11, causes the pili to fall off to form a type IV secretion pathway, increases the amount of extracellular DNA secretion, improves the initial adhesion ability of the bacteria, and improves the stability of the biofilm structure.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Detection of Extracellular Tumor-Associated Nucleic Acid in Blood Plasma or Serum
InactiveUS20080038743A1Enabling detectionFacilitates selection and monitoringMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationAbnormal tissue growthExtracellular
This invention relates to detection of specific extracellular DNA in plasma or serum fractions of human or animal blood associated with neoplastic, pre-malignant or proliferative disease. Specifically, the invention relates to detection tumor-associated DNA, and to those methods of detecting and monitoring tumor-associated DNA found in the plasma or serum fraction of blood by using DNA extraction and amplification with or without enrichment for DNA. The invention allows the selection and monitoring of patients for various cancer therapies including receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapies.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
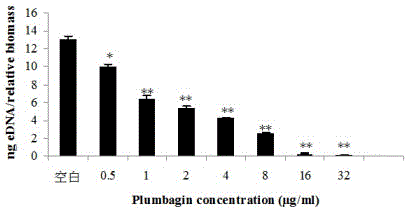
Application of plumbagin for inhibiting growth of staphylococcus aureus biofilm
The invention discloses an application of plumbagin for inhibiting growth of a staphylococcus aureus biofilm. Under the subinhibitory concentration of 1 / 8 MIC (minimal inhibitory concentration)-1 / 2 MIC, the inhibiting effect of plumbagin on staphylococcus aureus can be ignored, PIA (polysaccharide intercellular adhesion) synthesis and extracellular DNA (eDNA) release can be inhibited, the biofilm forming is effectively inhibited, the biofilm forming capacity is reduced with increase of drug concentration, dose dependency is shown, and when the concentration of plumbagin is up to and higher than MIC, the inhibiting effect of plumbagin on the biofilm approximately tends to be stable. According to the invention, the foundation is established for research of a generation mechanism of the biofilm.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
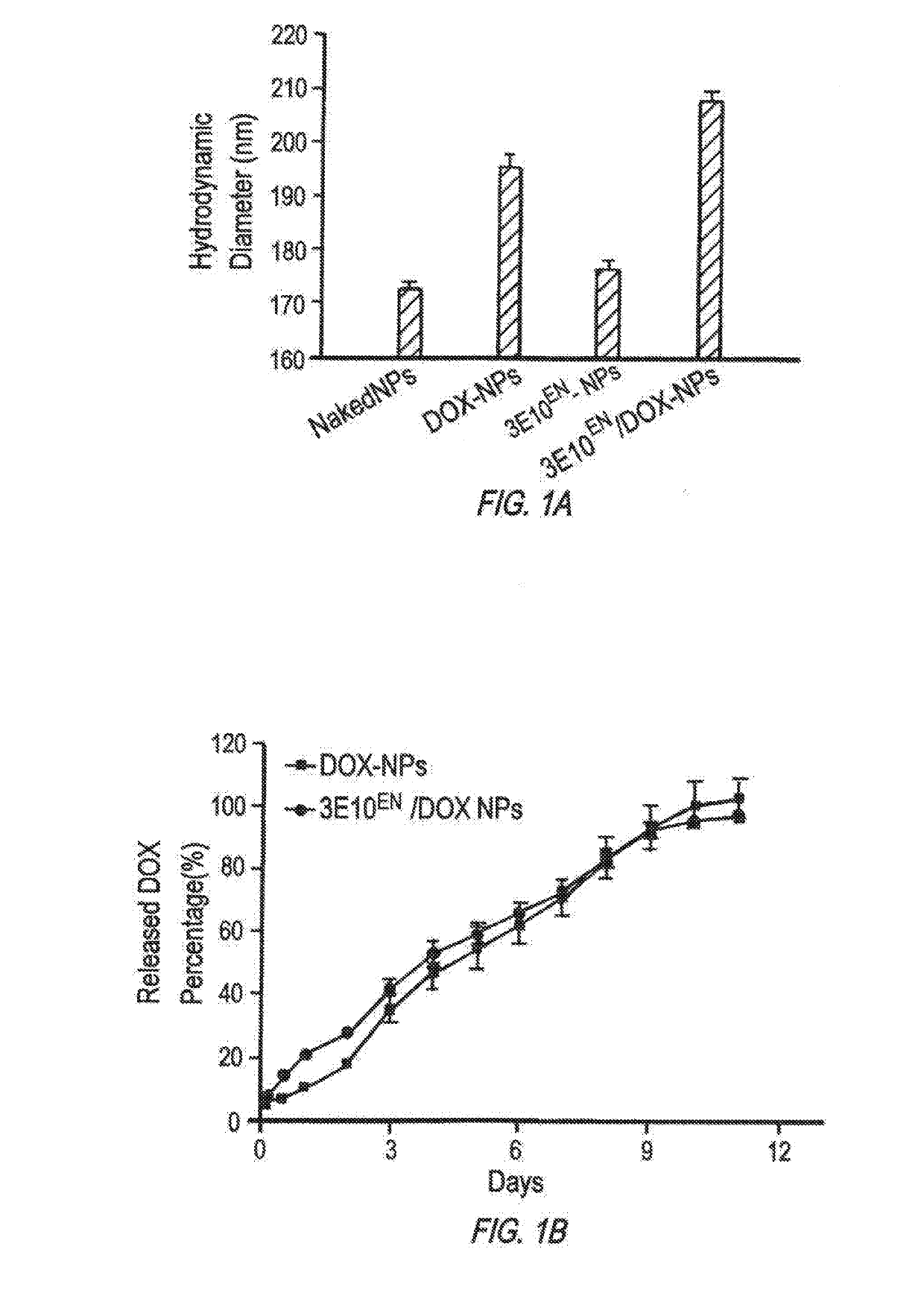
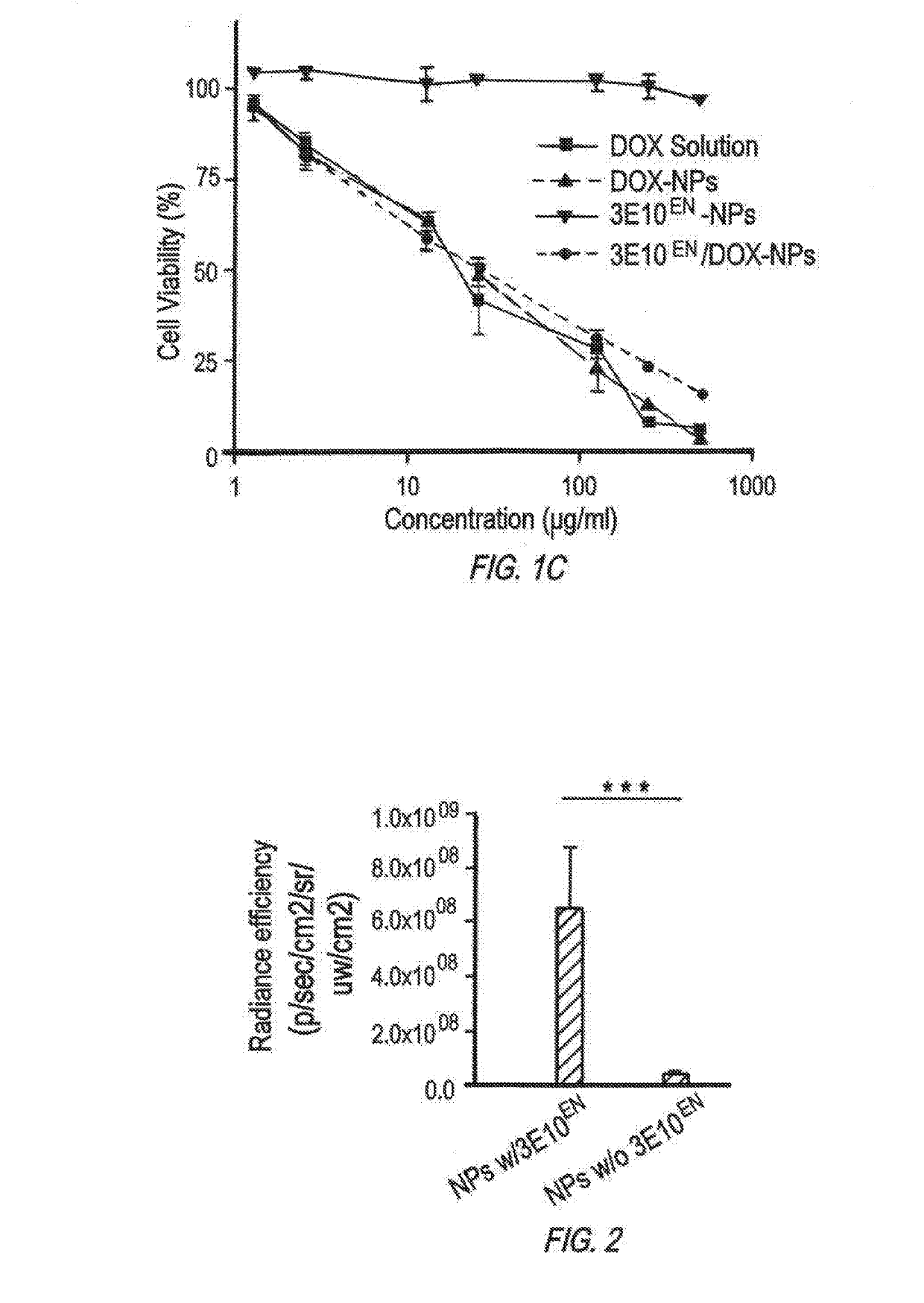
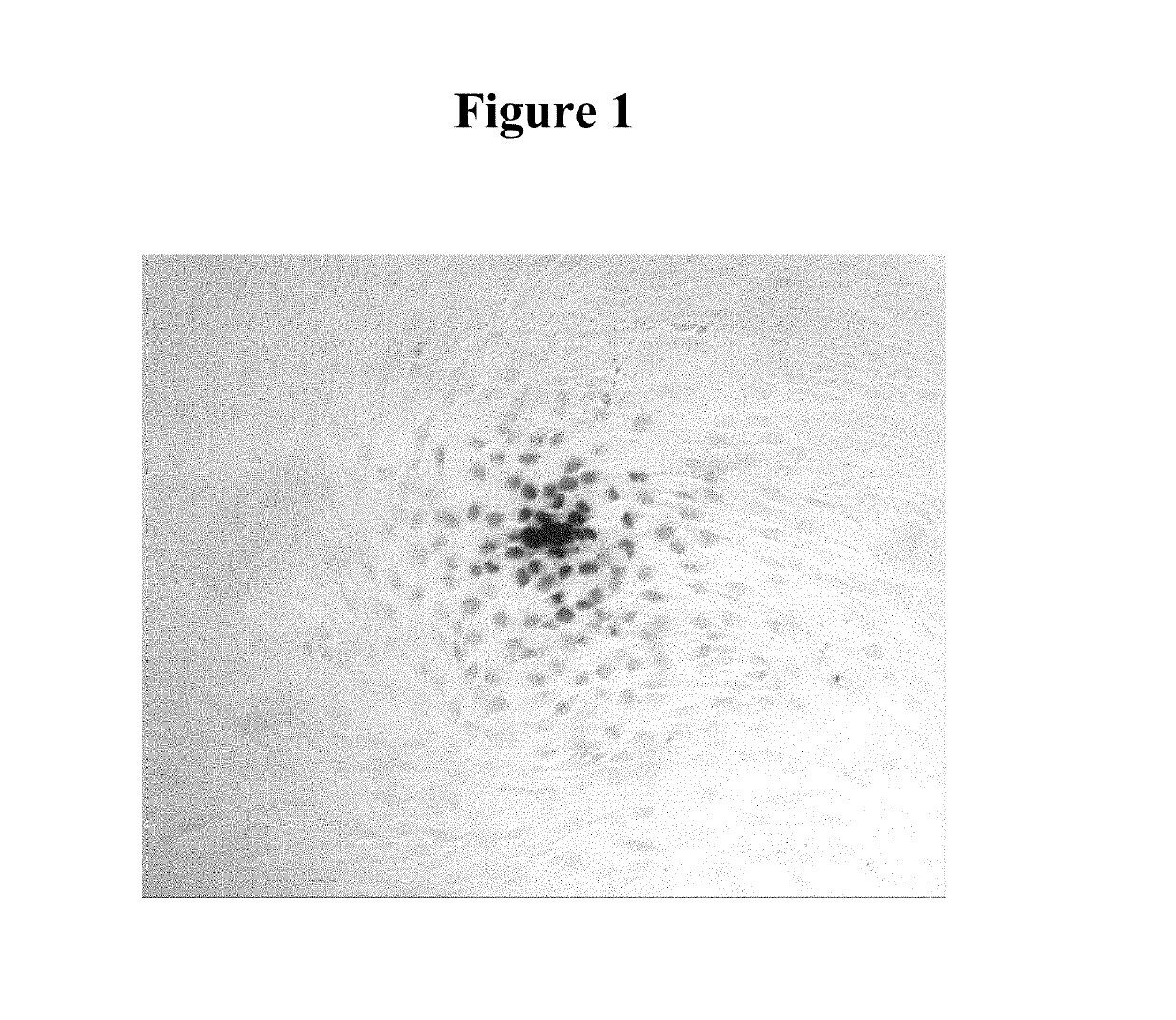
Antibody-mediated autocatalytic, targeted delivery of nanocarriers to tumors
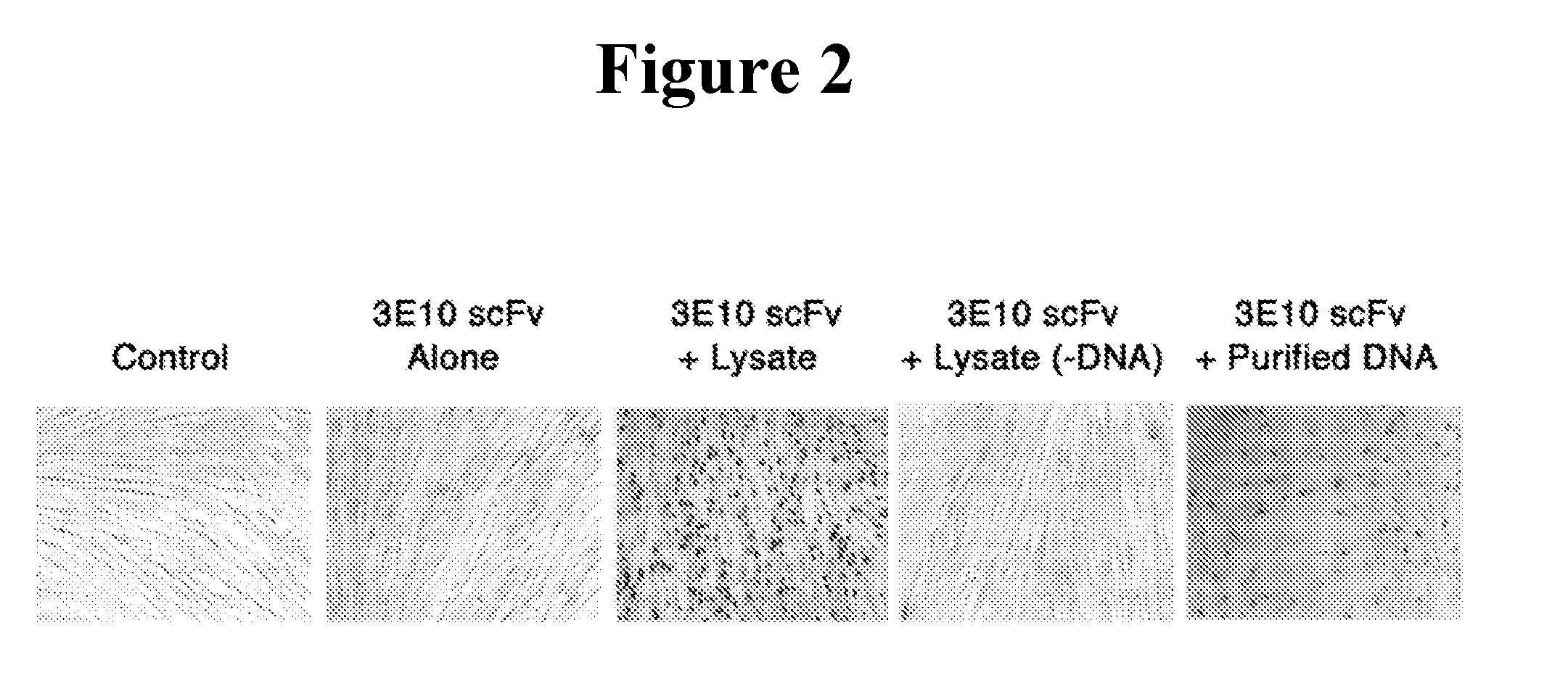
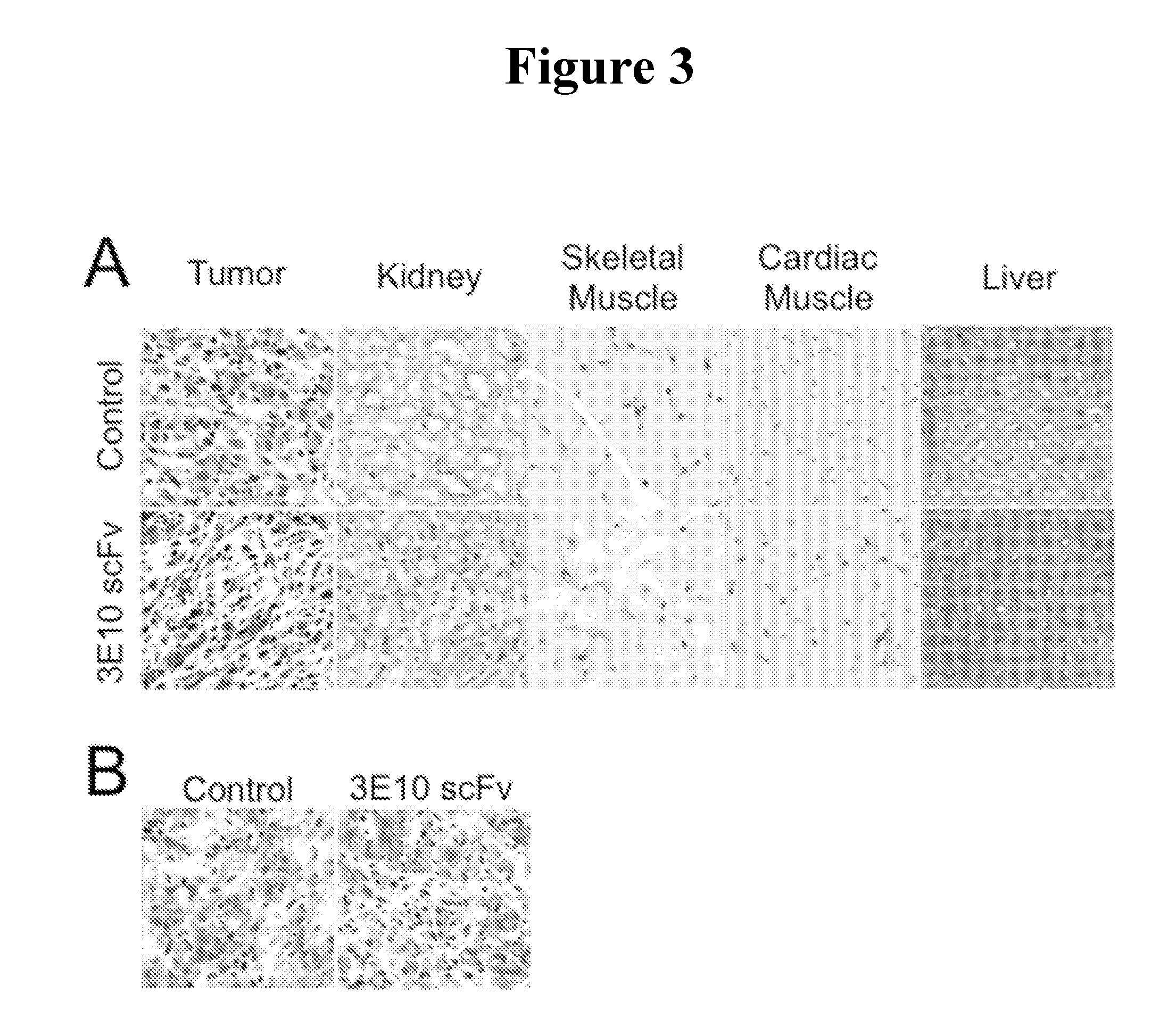
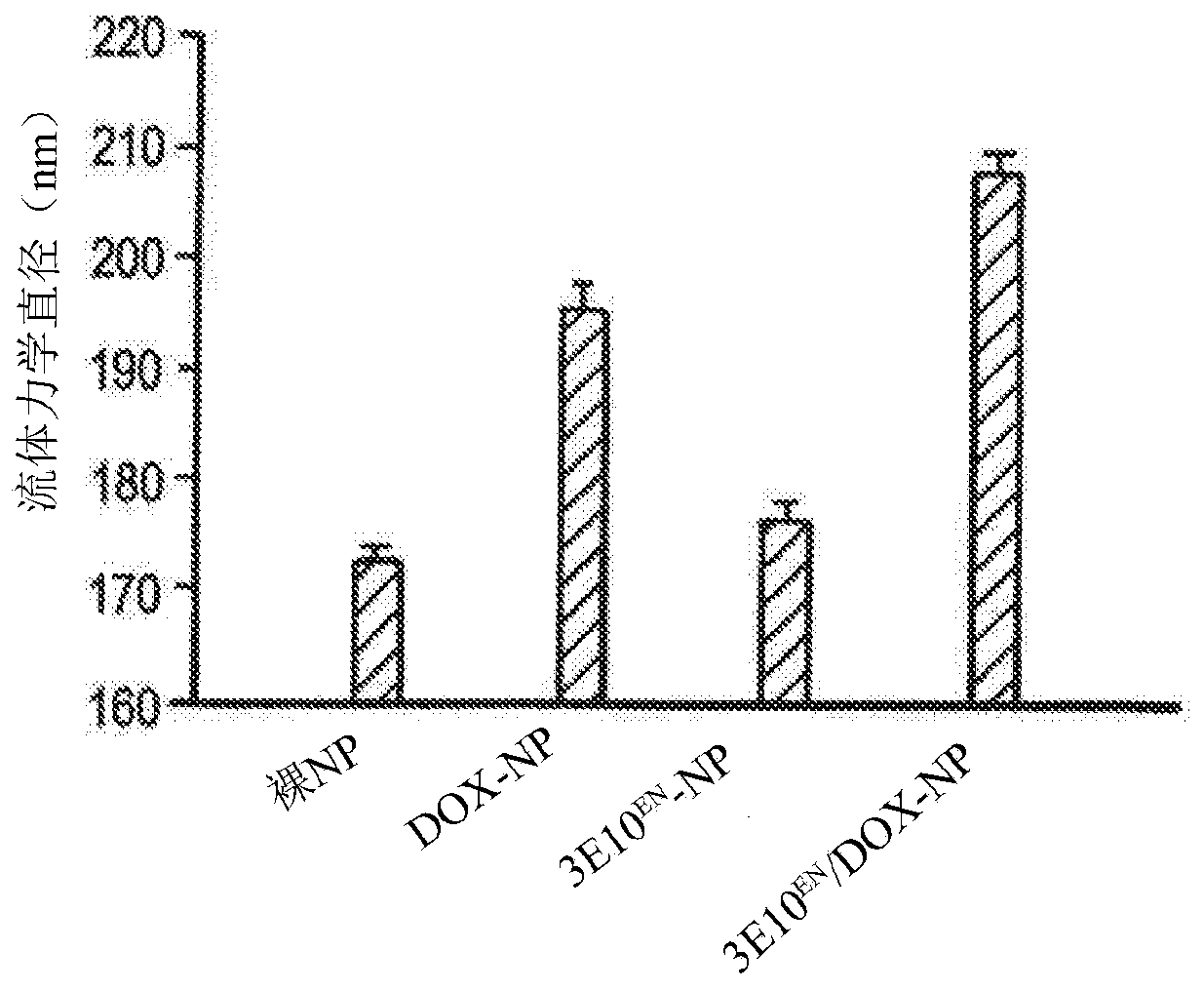
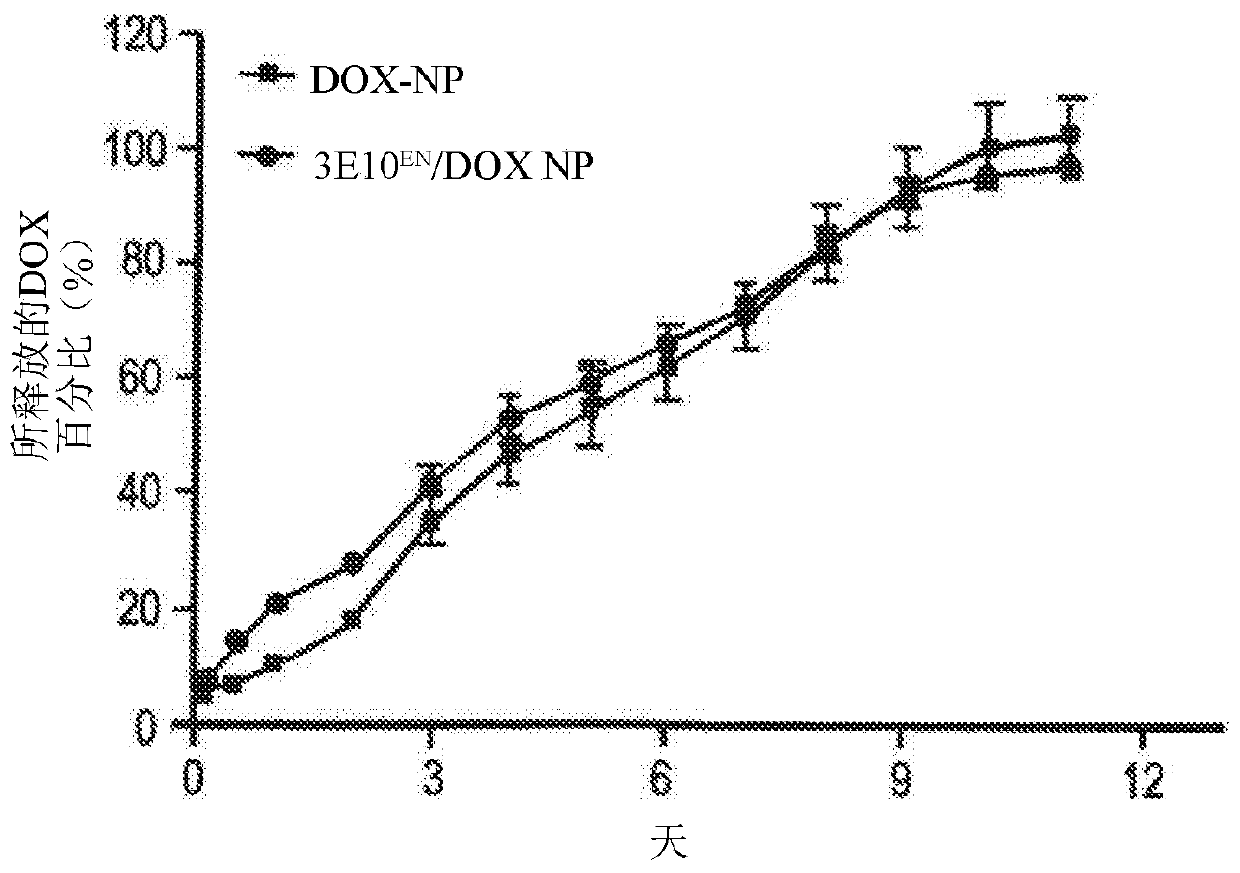
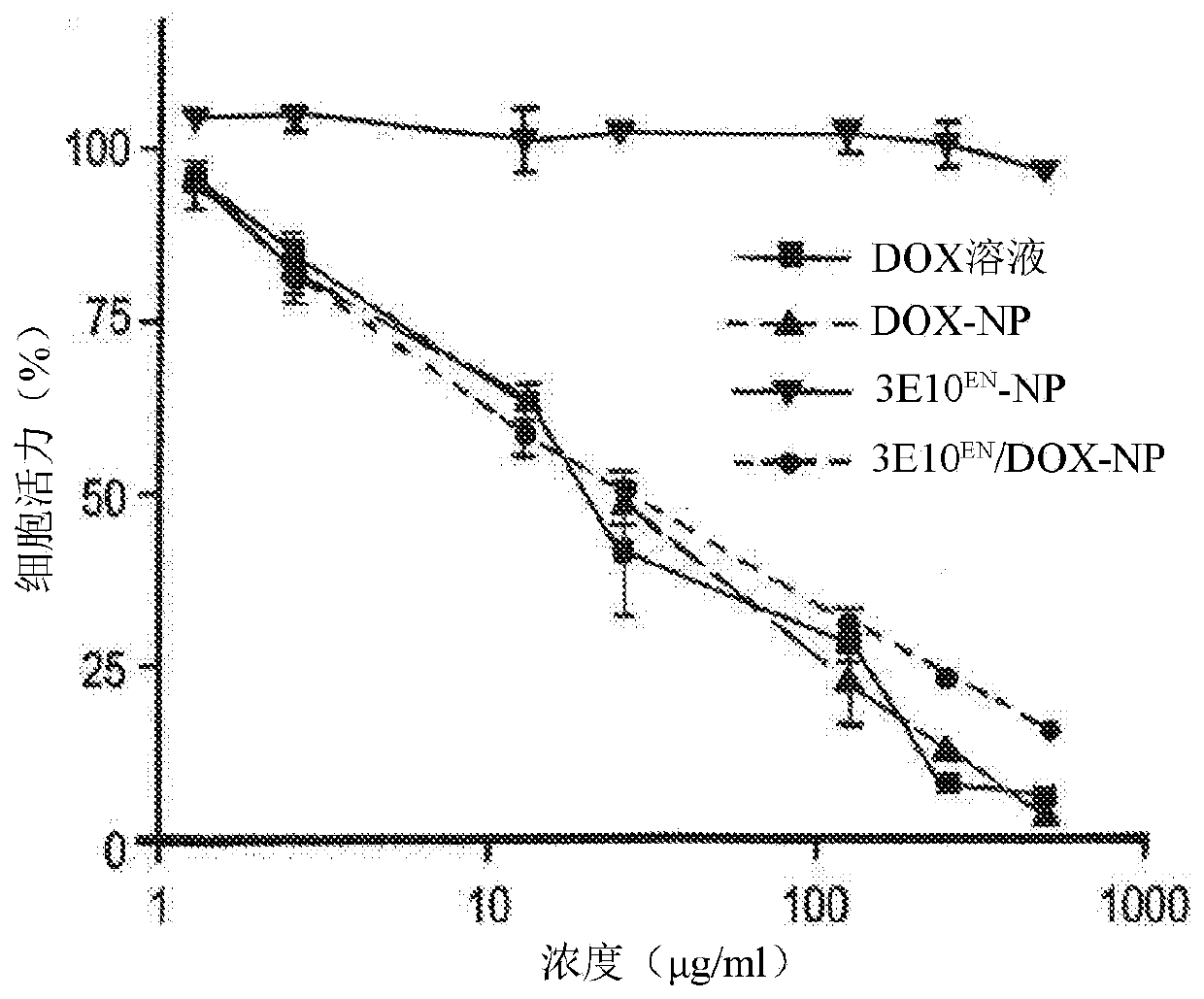
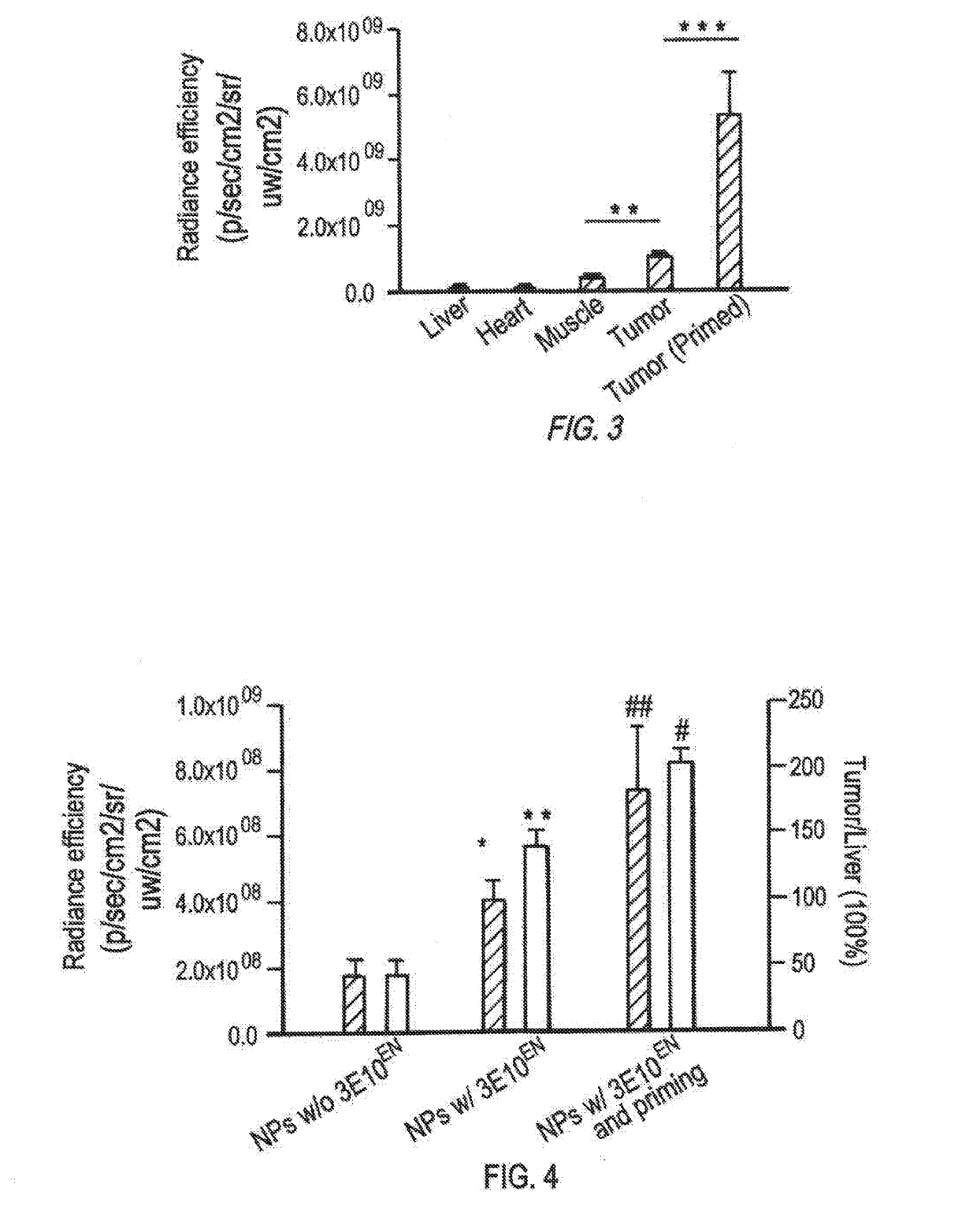
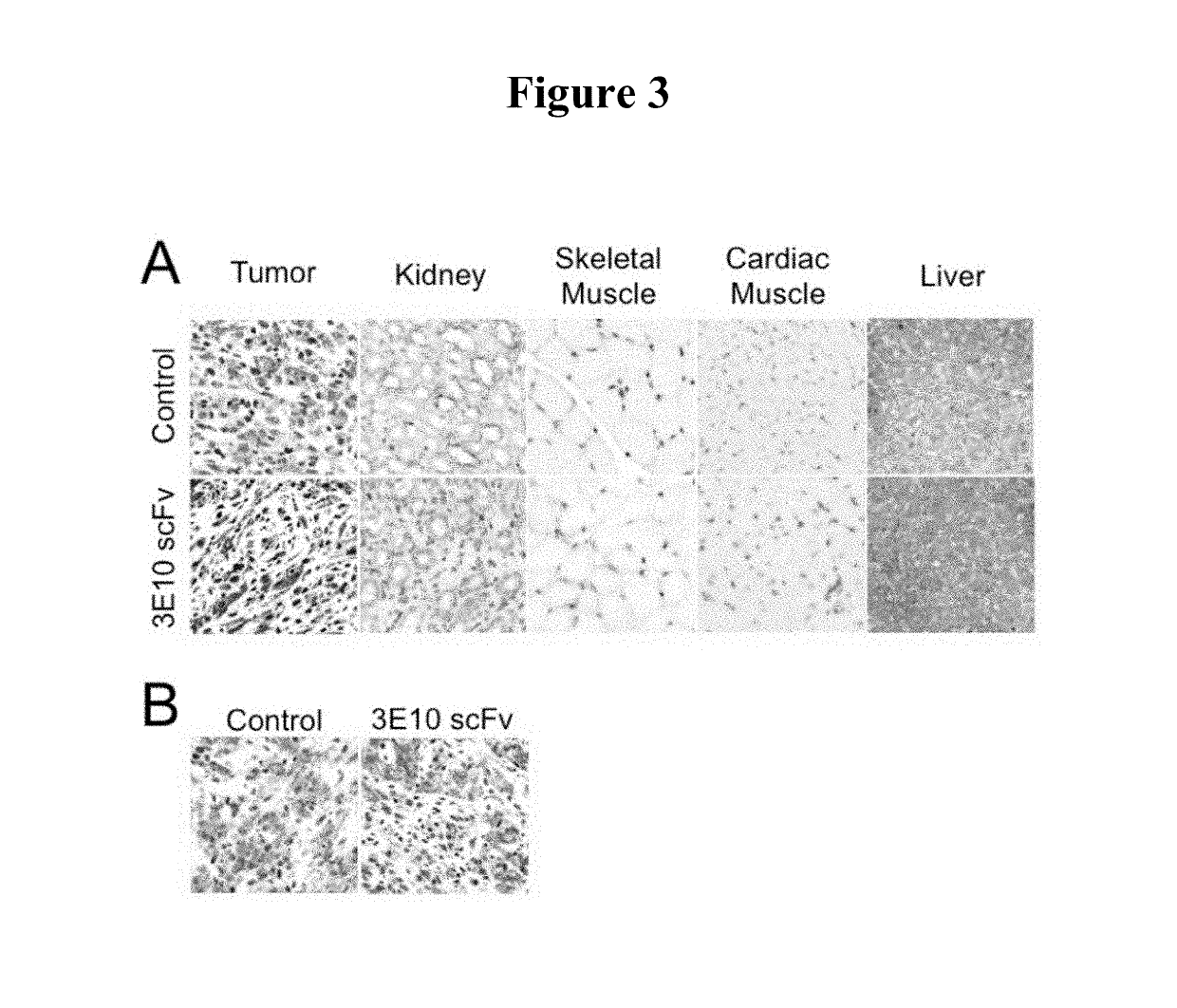
The present invention provides DNA-targeted nanocarriers for encapsulating an active agent and delivering it to extracellular DNA. The nanocarriers, for example, polymeric particles, liposomes, and multilamellar vesicles have targeting moiety that targets DNA conjugated thereto. The targeting moiety that targets DNA is typically an antibody, or variant, fragment, or fusion protein derived therefrom that binds to DNA or nucleosomes. The targeting moiety can be a circulating autoantibody that binds DNA such as those commonly found in patients with SLE. In some embodiments, the targeting moiety is antibody 3E10 or a variant, fragment, or fusion protein derived therefrom. Pharmaceutical compositions, methods of use, and dosage regimens are also provided.
Owner:YALE UNIV
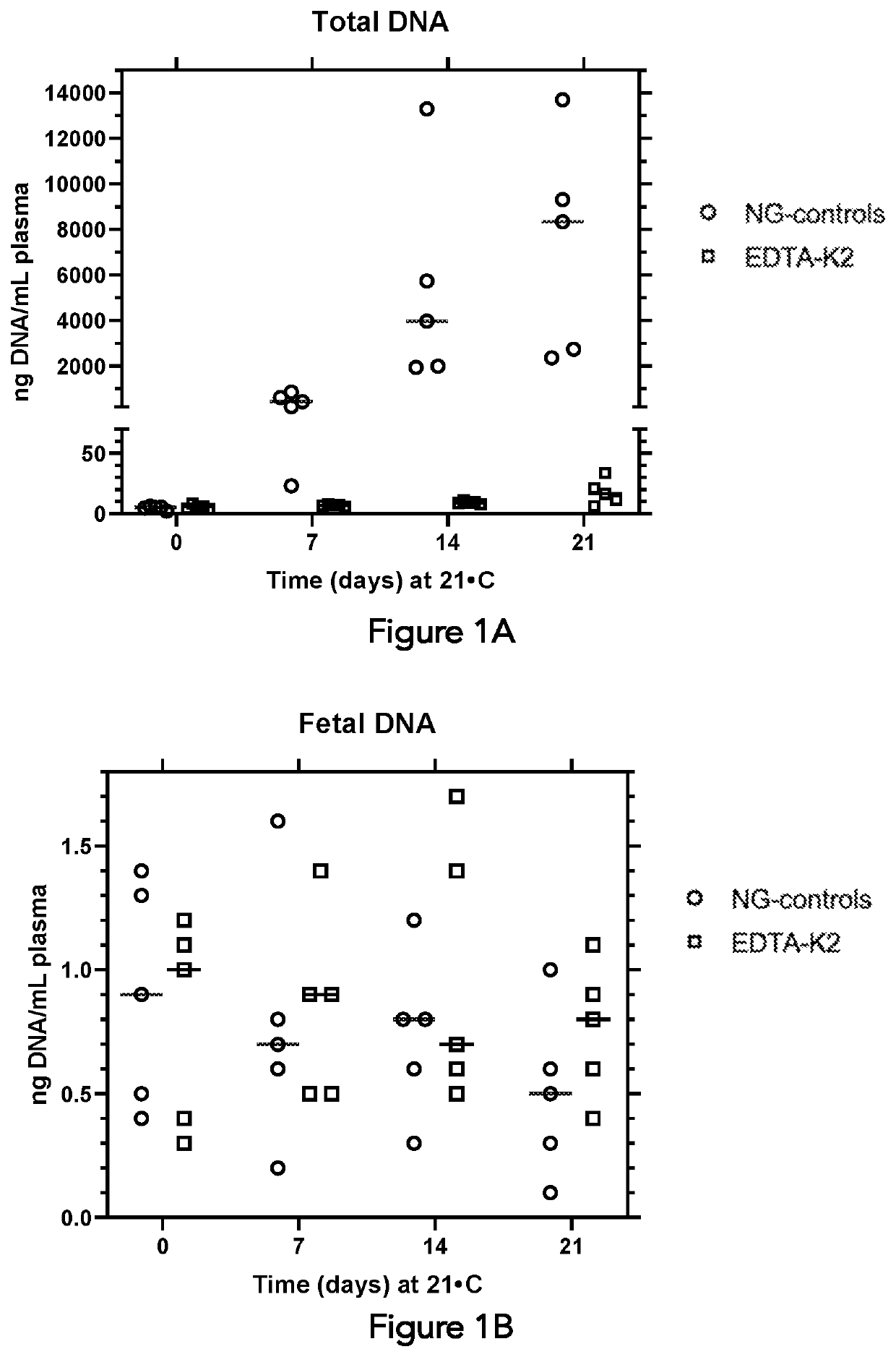
Composition and method for segregating extracellular DNA in blood
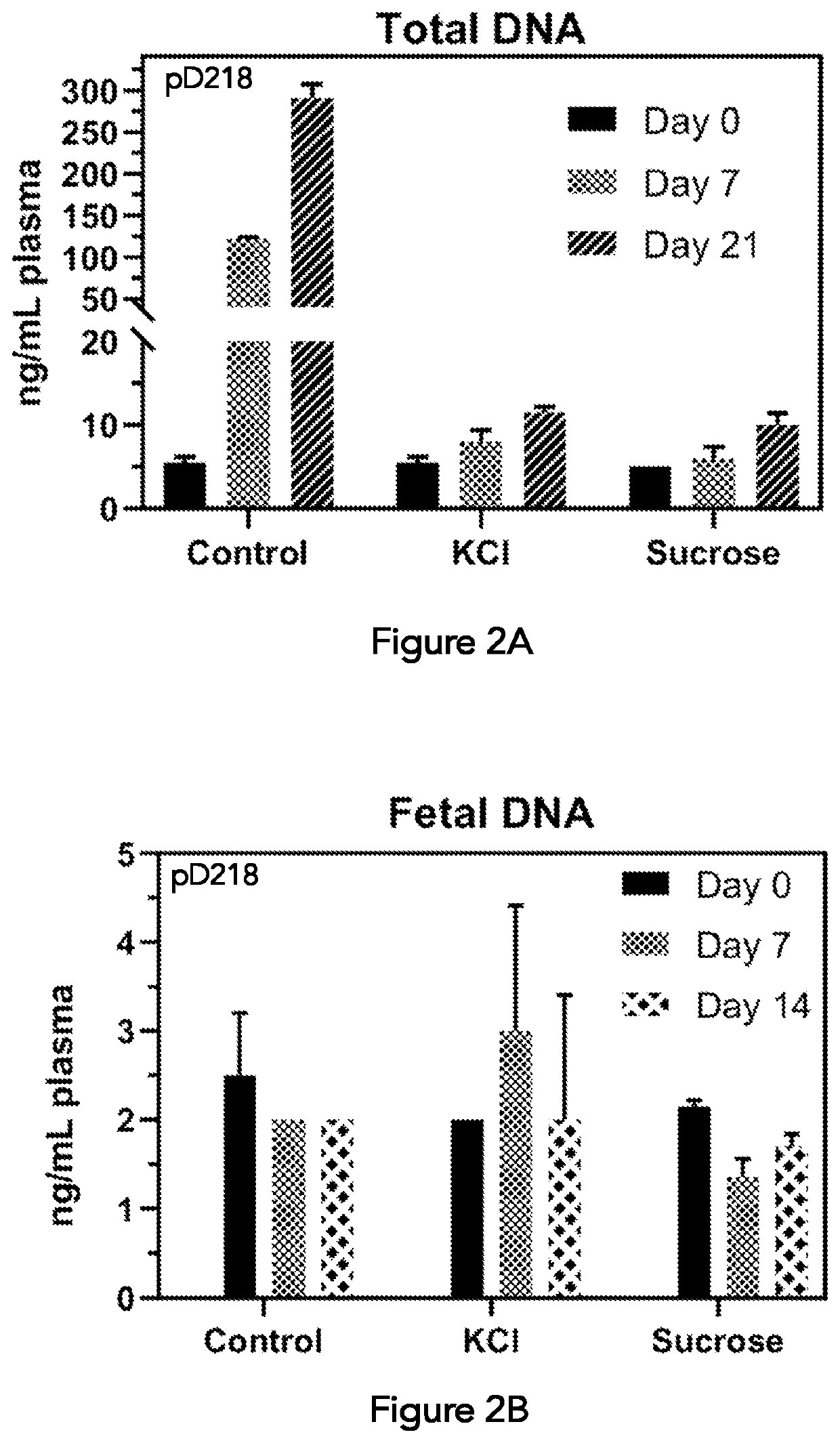
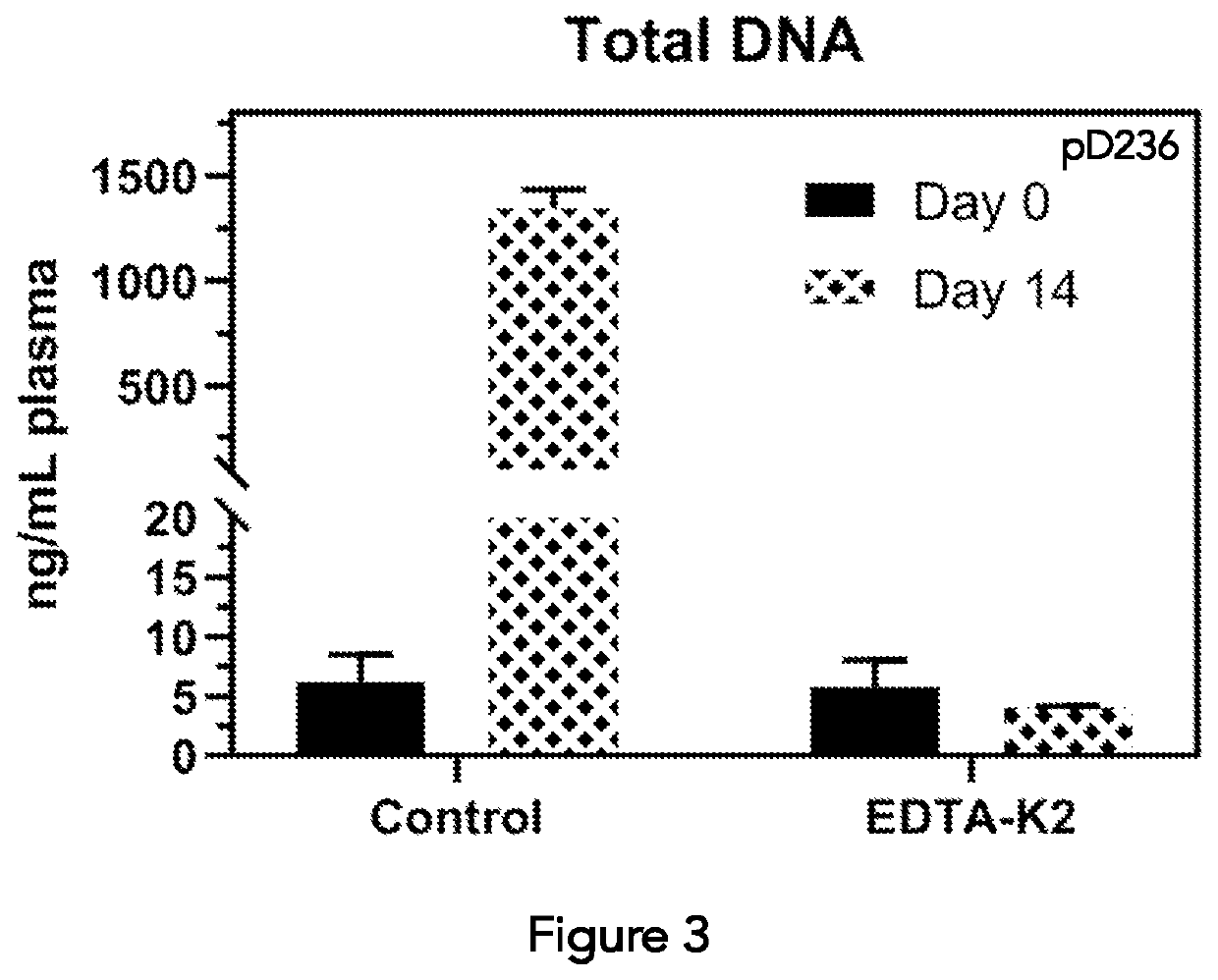
PendingUS20200196594A1Microbiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationExtracellularIntracellular
A composition and method suitable for separating and segregating extracellular DNA in a cell-containing sample, in particular, a blood sample is described. The composition comprising a thixotropic barrier gel and a stabilizing agent in aqueous solution at a concentration of at least 400 mM is capable of establishing and maintaining separation between intracellular and extracellular DNA in blood over time by means of physical barrier wherein when the composition is mixed with whole blood and centrifuged, plasma is separated from the packed cell layer by the thixotropic barrier gel and the blood cells are separated away from the plasma.
Owner:DELTADNA BIOSCIENCES INC
Antibody-mediated autocatalytic, targeted delivery of nanocarriers to tumors
ActiveUS20190247515A1Improve the effectiveness of treatmentImprove efficiencyOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryRegimenNanocarriers
DNA-targeted nanocarriers for encapsulating an active agent and delivering it to extracellular DNA are provided. The nanocarriers, for example, polymeric particles, liposomes, and multilamellar vesicles have targeting moiety that targets DNA conjugated thereto. The targeting moiety that targets DNA is typically an antibody, or variant, fragment, or fusion protein derived therefrom that binds to DNA or nucleosomes. The targeting moiety can be a circulating autoantibody that binds DNA such as those commonly found in patients with SLE. In some embodiments, the targeting moiety is antibody 3E10 or a variant, fragment, or fusion protein derived therefrom. Pharmaceutical compositions, methods of use, and dosage regimens are also provided.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Method for Treating Oncological Diseases
ActiveUS20130209443A9Promote growthImprove efficiencyHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseChemical composition
A method to treat solid tumors and other oncological diseases consists of parenterally injecting an agent which destroy's blood's extracellular DNA into the systemic blood circulation of a cancer patient to slow down malignant. The agent is embodied in the form of a DNAse enzyme and, more particularly, as a bovine pancreatic DNAse. Doses from 50,000-250,000,000 Kunz units / day are injected for 5-360 days. A binding agent or an agent that modifies the chemical composition of the blood extracellular DNA is additionally injected into the blood. This modifying agent is preferably an enzyme-ribonuclease.
Owner:CLS THERAPEUTICS
Electricity-generating Shewanella engineering strain, construction method and application
InactiveCN110699309AImprove adhesionPromote formationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyNucleotide
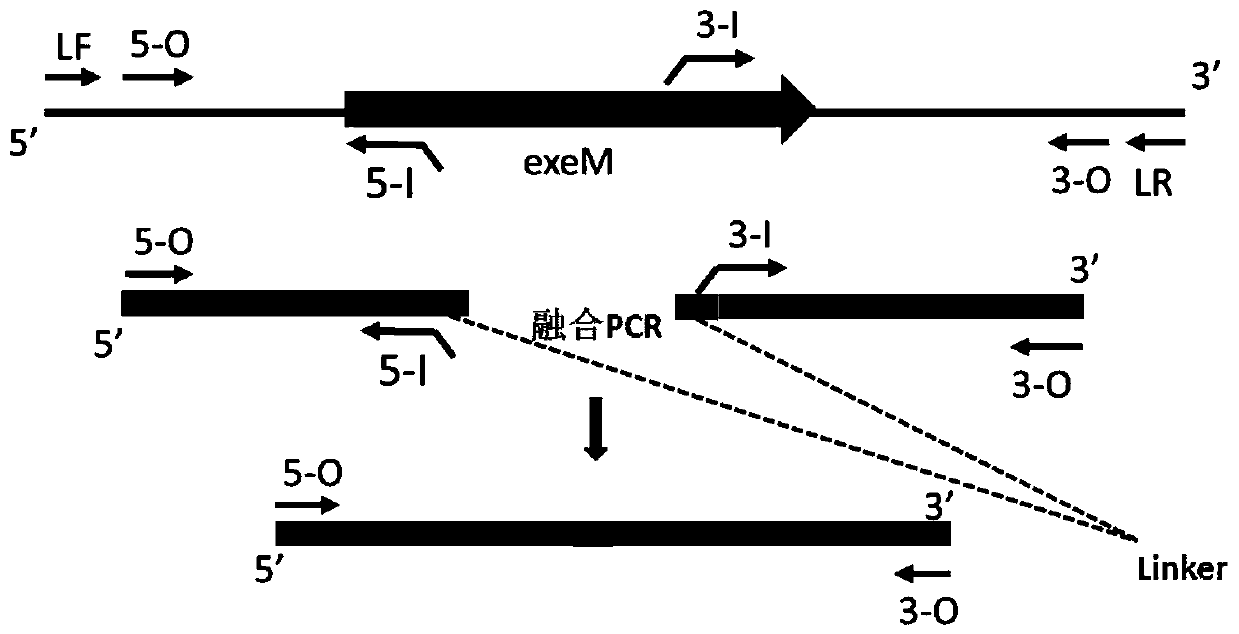
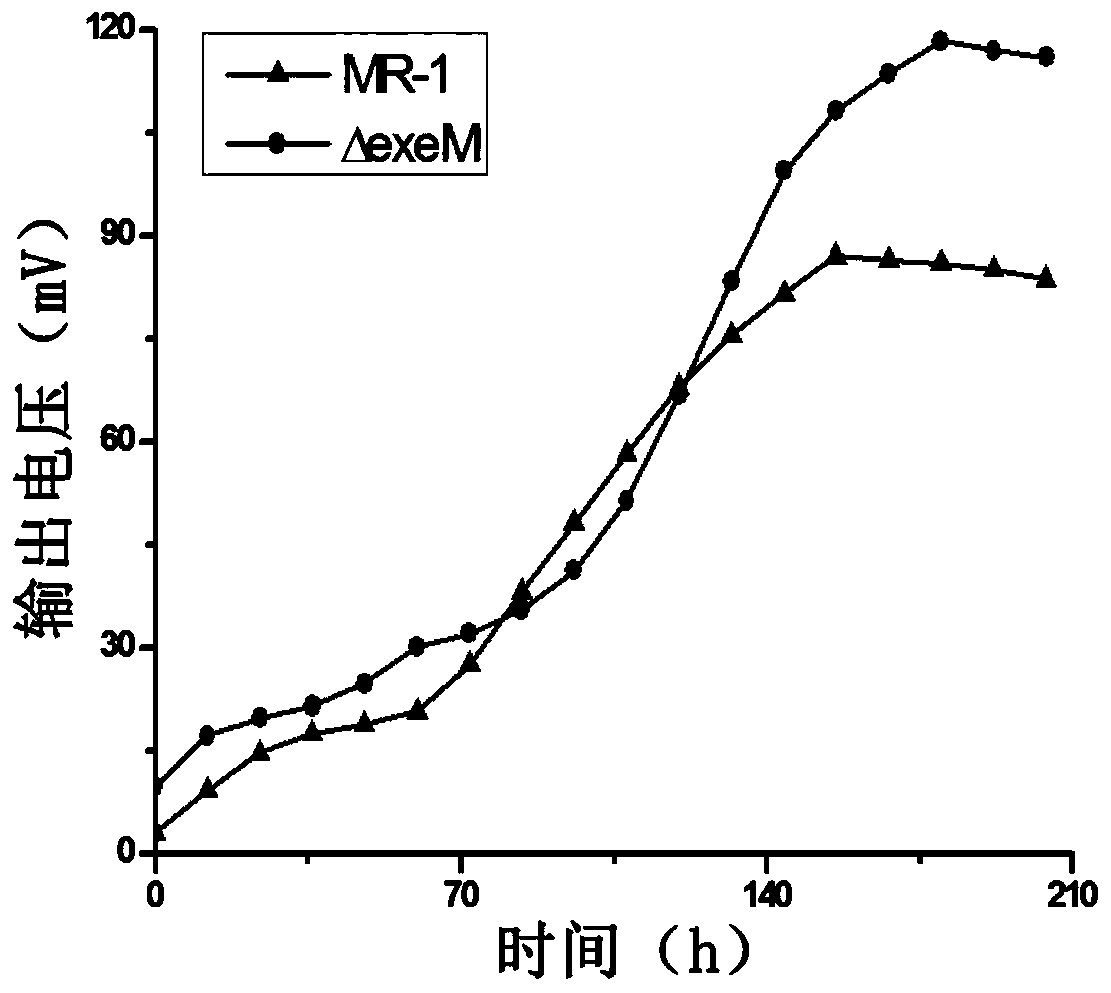
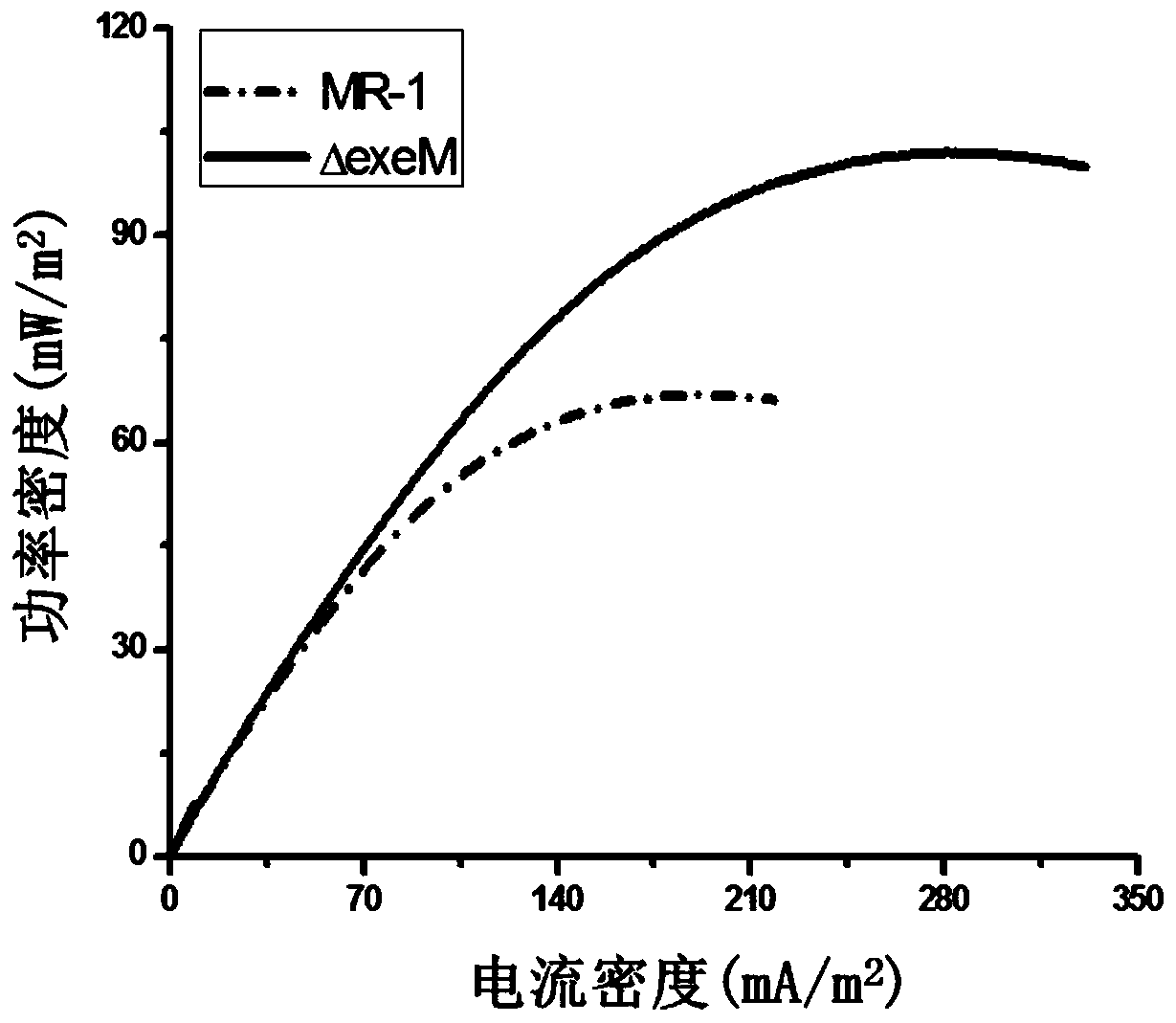
The invention discloses an electricity-generating Shewanella engineering strain, a construction method and application. The construction method of the electricity-generating Shewanella engineering strain includes the following steps that a target gene exeM of a wild-type Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 is knocked out, an electricity-generating Shewanella engineering strain [delta]exeM is obtained, anda nucleotide sequence of the gene exeM is shown in SEQ ID NO15. The electricity-generating Shewanella engineering strain [delta]exeM constructed by the construction method is a gene-deficient strain,the strain can produce more extracellular DNA (eDNA), the eDNA promotes bacterial adhesion, aggregation and biofilm formation, furthermore, extracellular electron transfer is enhanced, and the power density of microbial fuel cells is increased.
Owner:天津大学前沿技术研究院
A strain of Corynebacterium glutamicum overexpressing adenosine triphosphate and its construction method and application
The invention discloses a Corynebacterium glutamicum overexpressing adenosine triphosphatase, wherein the gene sequence of the adenosine triphosphatase is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1. As that adenosine triphosphatase ATPase is overexpress in Corynebacterium glutamicum, the invention provides energy for the intermediate convert protein VirB11, causes the pili to fall off to form a type IV secretion pathway, increases the amount of extracellular DNA secretion, improves the initial adhesion ability of the bacteria, and improves the stability of the biofilm structure.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
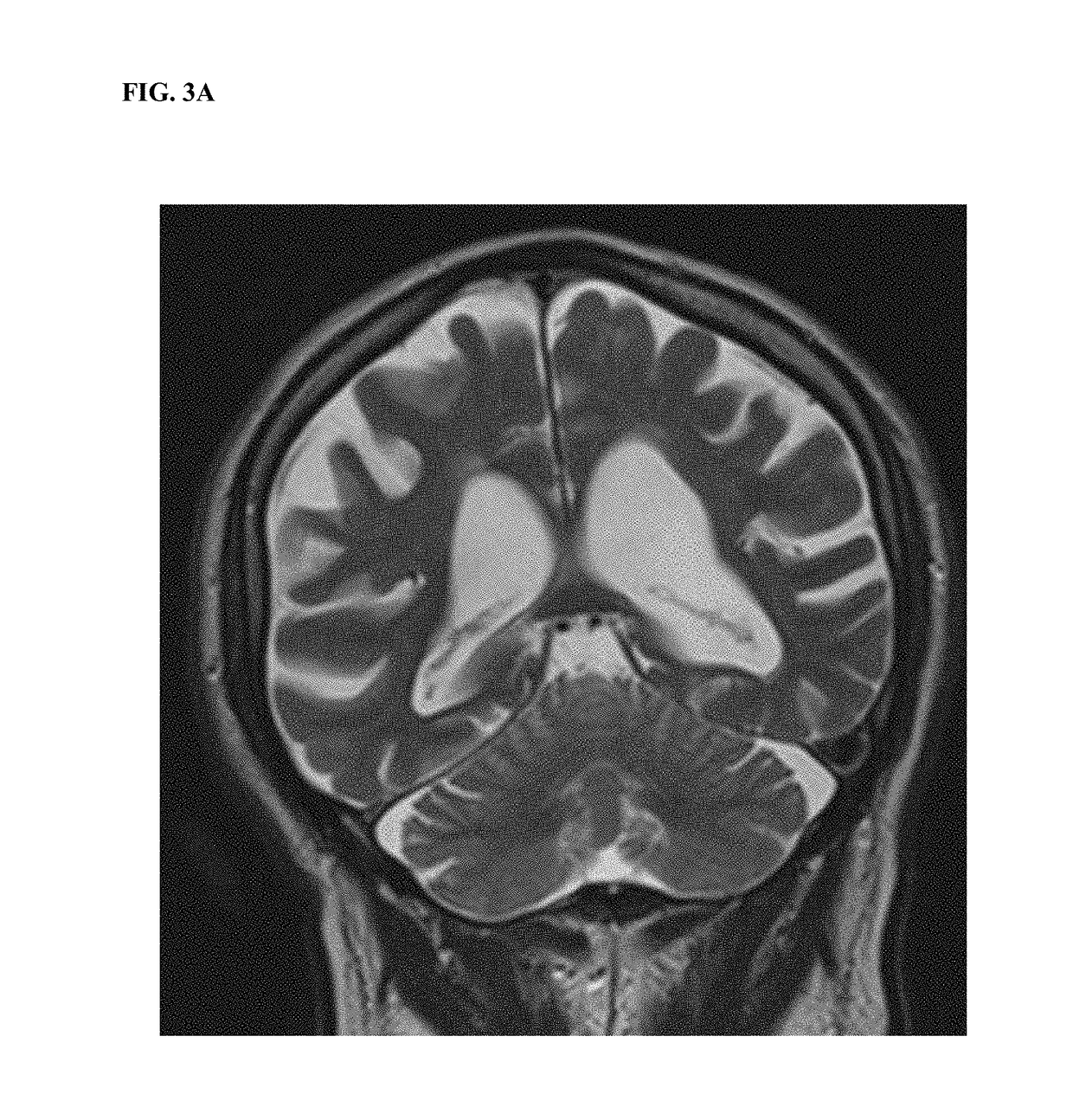
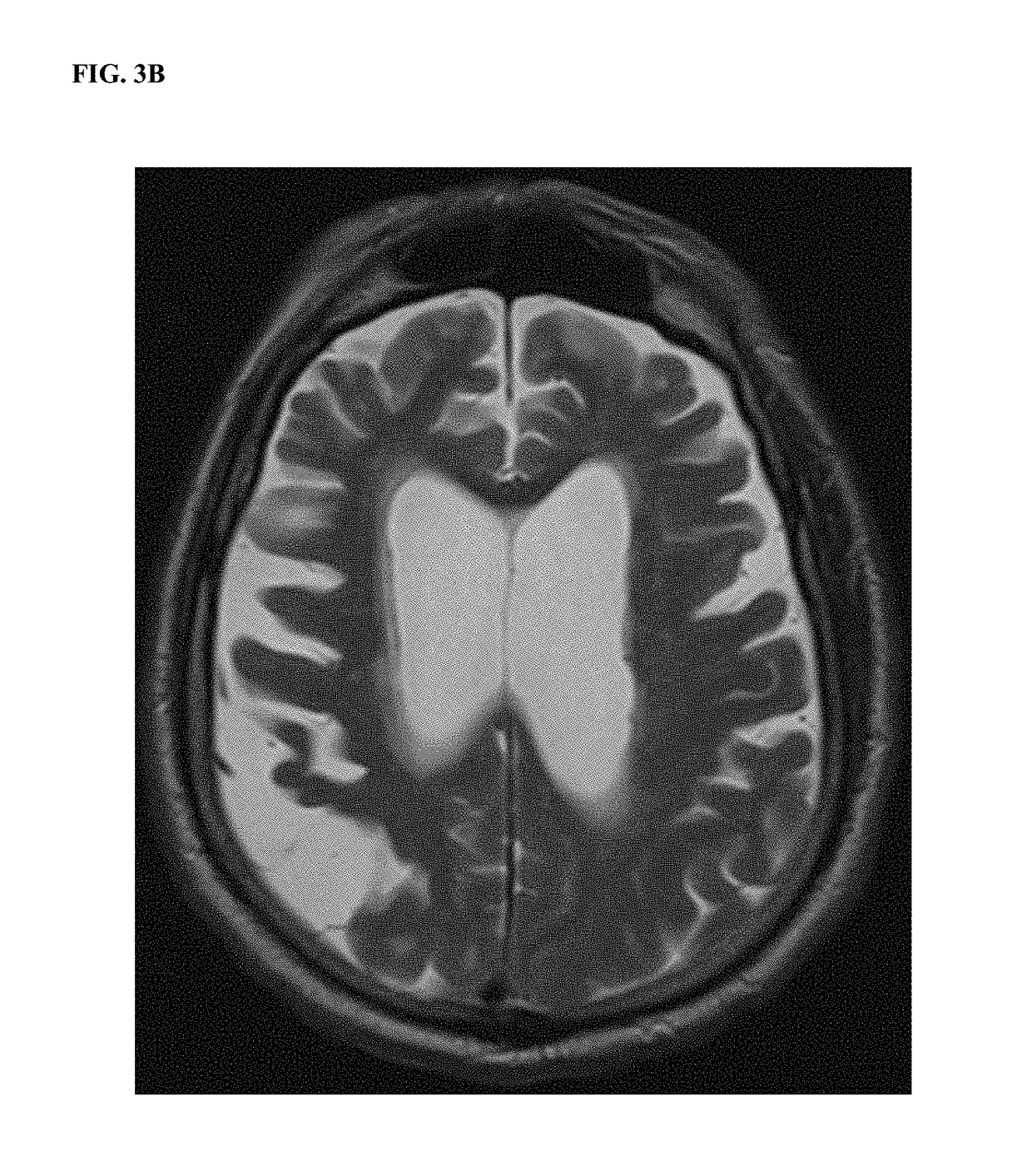
Extracellular DNA as a therapeutic target in neurodegeneration
ActiveUS20180360925A1Reduce molecular weightNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsMedicineDNase activity
The invention relates to the use of deoxyribonuclease (DNase) enzyme for inhibiting progression and for prevention and treatment of neurodegeneration.
Owner:CLS THERAPEUTICS
Methods for DNA-dependent targeting of a cell permeant antibody
The invention provides methods for selective targeting of live cells, which have undergone or are undergoing radiation or chemotherapy, at a site of interest with a cell-penetrating polypeptide. In one embodiment of the invention, the method comprises contacting the live cells with a cell-penetrating polypeptide comprising cell-penetrating determinants so that the cell-penetrating polypeptide binds extracellular DNA near or around the live cells so as to form a complex or association therewith such that the complex or associated polypeptide-DNA so bound bind the live cells and penetrates the live cells thereby selectively targeting live cells at a site of interest with a cell-penetrating polypeptide.
Owner:U S GOVERNMENT REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS
Method and pharmacological composition for the diagnosis and treatment of male sub-fertility
ActiveUS20130121985A1Quality improvementImprove fertilityBiocideHydrolasesCell freeReceptor-Mediated Signal Transduction
Methods for treating male sub-fertility by administering a pharmaceutical composition to a subject in need thereof are provided. The pharmaceutical compositions include an agent that causes a reduction in an effect of extracellular DNA on sperm cells. The agent may be, for example, an enzyme that degrades DNA such as DNase, a substance that blocks the interaction between cell free DNA and sperm cell surface receptors, a substance that binds to DNA, a substance that inhibits endogenous sperm cell DNase, a substance that inhibits a member of a signal transduction pathway mediated by DNA binding to sperm cell surface receptors, or an agent that stimulates production of an endogenous substance that causes a reduction in an antifertility effect of cell free DNA on sperm cells.
Owner:PERINESS LTD
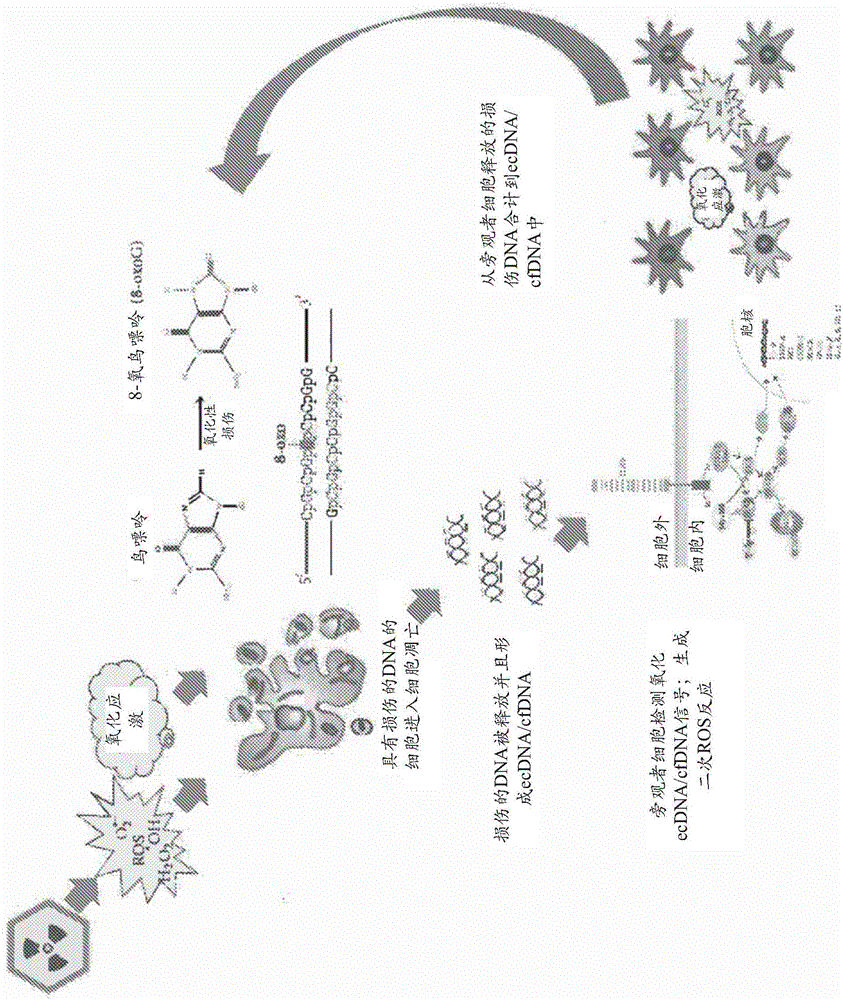
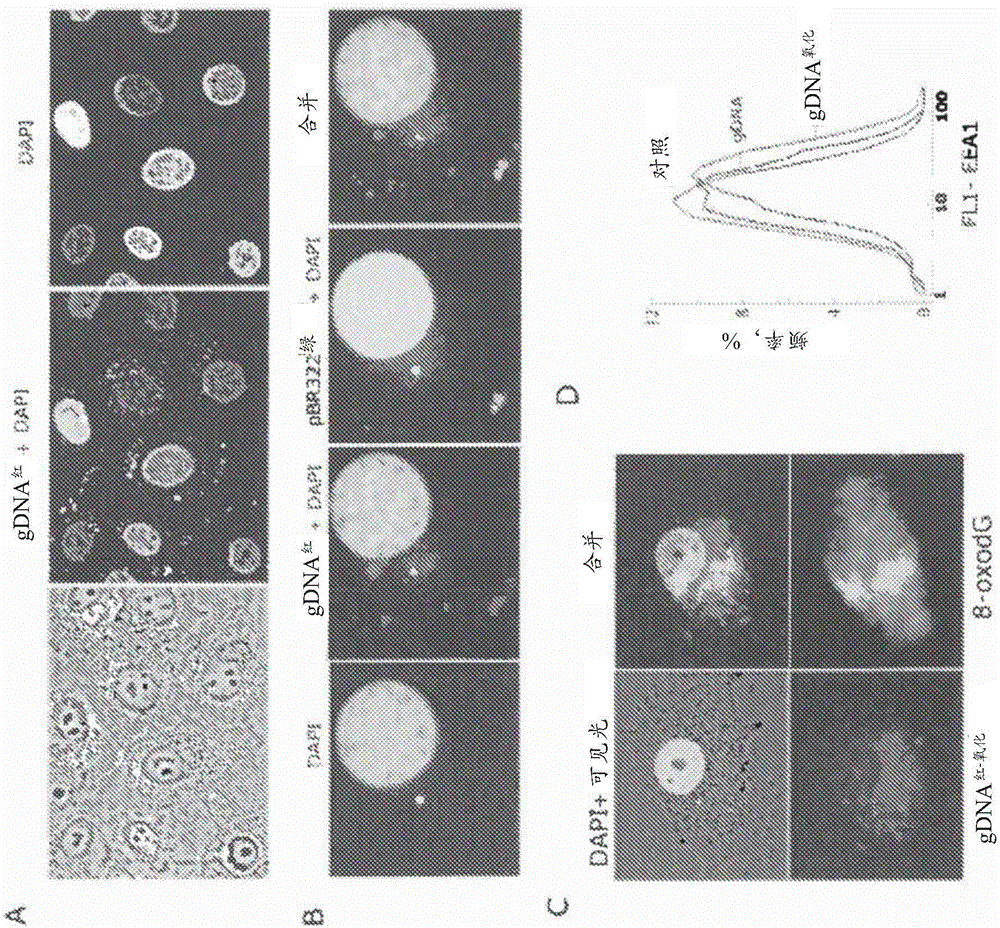
Oxidized fraction of extracellular dna as a biomarker of stress and methods for using the same
The present invention relates to methods of treating and diagnosing oxidative damage in a subject comprising administering an agent that binds oxidized extracellular nucleic acid, and methods of treating diseases and conditions in a subject comprising administering an adjuvant therapy comprising an agent that binds oxidized extracellular nucleic acid. The oxidized fraction of extracellular DNA can also be detected through electrochemical methods or by mass- spectrometry.
Owner:安娜·巴兰诺娃 +2
Methods of treating diseases related to net formation with parenteral administration of polysialylated dnase i
InactiveUS20190083636A1High hydrolytic activityNervous disorderHydrolasesDiseaseParenteral nutrition
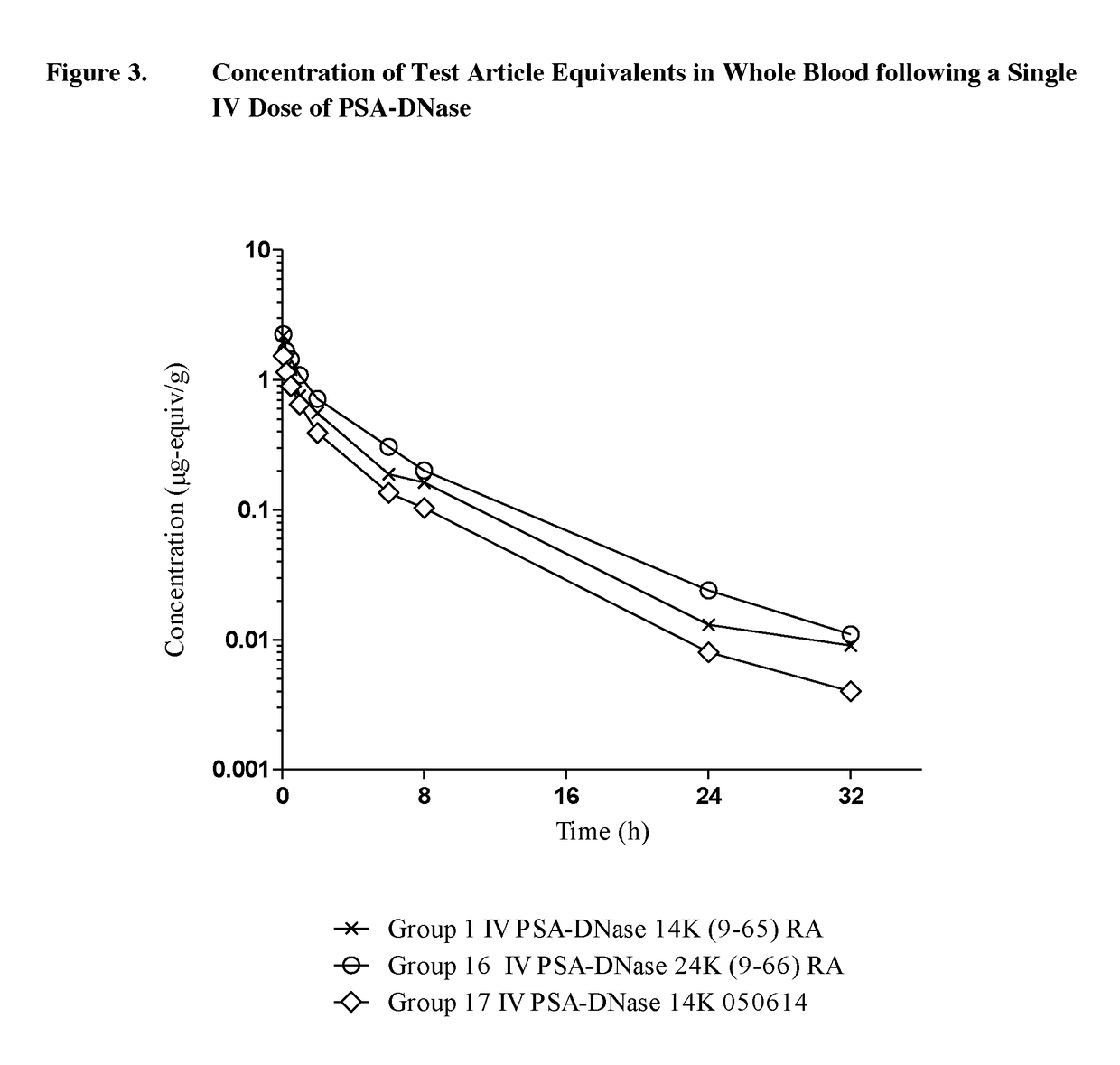
The present invention provides conjugates of deoxyribonuclease enzymes with water soluble polymers such as PSA having improved pharmacokinetic attributes. These modifications provide unexpectedly high levels of DNA hydrolytic activity in blood and other bodily tissues over the time due to markedly increased distribution phase and reduced clearance of DNase conjugates after delivery to blood circulation relative to the unconjugated compounds, while half-life and residence time of conjugates remains almost unchanged compared to the unconjugated DNase compounds. The compositions of the invention are used for parenteral treatment of diseases related to NET formation and the presence of extracellular DNA.
Owner:LIPOXEN TECHNOLOGIES LTD
A method for efficiently extracting intestinal contents and extracellular DNA of earthworms
ActiveCN114277029BImprove extraction qualityEfficient separationBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyGenetic Materials
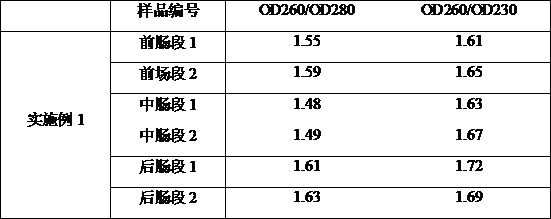
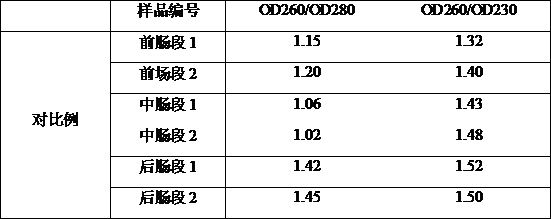
The invention discloses a method for efficiently extracting earthworm gut content and its extracellular DNA. The steps are as follows: rapid acquisition of earthworm gut content; construction and preparation of the extracellular genome internal standard gene; Extra DNA extraction. On the one hand, the method of the present invention can quickly take out the intestinal contents of individual tiny Eisenia chinensis, with simple steps and short time-consuming; on the other hand, it can also effectively separate and purify the extracellular eDNA in the intestinal contents, The extraction effect is stable, reliable and repeatable, and the extraction efficiency can reach 61%. The OD260 / OD280 of the extracted eDNA can reach 1.63, and the OD260 / OD230 can reach 1.72 through the detection of a nucleic acid protein analyzer, and subsequent molecular operations can be performed. The extraction method of the invention greatly improves the extraction quality of the intestinal content of the earthworm, and lays a foundation for the subsequent research on the extracellular genetic material of the earthworm intestinal tract.
Owner:AGRO ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION INST OF MIN OF AGRI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com