Application of plumbagin for inhibiting growth of staphylococcus aureus biofilm
A technology of plumbagin and staphylococcus, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve the problem that the anti-biofilm activity is seldom studied, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Microdilution drug susceptibility test - Determination of minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) of plumbagin on suspended bacteria of Staphylococcus aureus: pick a single colony from a preserved strain of Staphylococcus aureus agar plate , inoculated in Muller-Hinton broth (MHB) medium, and cultured overnight at 37 °C with shaking. Use MHB medium to adjust the concentration of the bacterial solution so that the OD600 value is 0.4 (~5×10 8 CFU / ml), and diluted to 1×10 6 CFU / ml. Dilute the drug solution with MHB medium to make the final concentration of the drug solution 1024 μg / ml. Add 200 μl of the drug solution with a final concentration of 1024 μg / ml to the first well of each row of a sterile 96-well microtiter plate, and add 100 μl of MHB medium to the second to tenth wells. In each row, use a 100 μl pipette to remove 100 μl of liquid from the first well of each row and add it to the second well of each row for dilut...
Embodiment 2
[0021] Plate swabbing drug susceptibility test - Determination of minimum inhibitory biofilm growth concentration (MBIC) and minimum biofilm concentration (MBBC) of plumbagin on Staphylococcus aureus biofilm: solid tryptone soybean broth (TSB) culture plate Pick the single bacteria into a test tube containing 5 ml TSB, put it in a shaker at 37 °C at 180 r / min for overnight culture; take the bacterial solution and dilute it with TSB (containing 0.5% glucose) medium to an OD600 of 0.4 (equivalent to 5×10 8 CFU / ml), and further diluted to a concentration of 10 5 CFU / ml; Carefully add 200 μl of diluted bacterial solution to each well of a 96-well plate, and place it in a 37°C incubator for static culture for 24 hours. After the biofilm is formed, discard the suspension, add 250 μl PBS to each well to gently wash away the free bacteria, serially dilute the drug twice with TSB medium (0.0625-512 μg / ml) and add it to each well. DMSO content is less than 1%. Incubate at 37°C for 4...
Embodiment 3
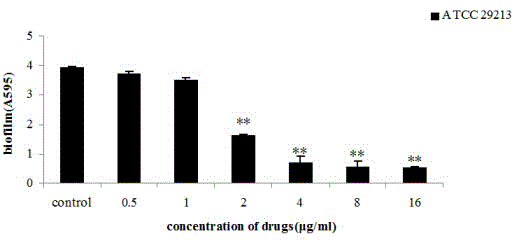
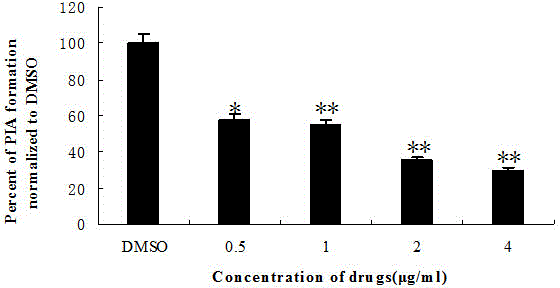
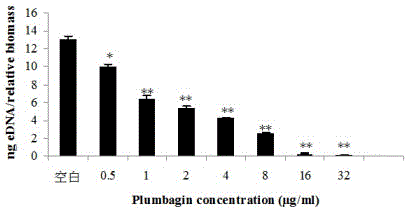
[0024] Semi-quantitative experiment of crystal violet-the effect of plumbagin on biofilm formation ability: Staphylococcus aureus was cultured overnight in TSB medium (TSBg) containing 0.5% glucose and diluted with TSBg medium to OD600 of 0.4 (equivalent to 5×10 8 CFU / ml), and further diluted to a concentration of 10 6 CFU / ml, add 100 μl per well into a 96-well plate, dilute plumbagin 2 times, so that the final concentration is 1 / 8MIC~2MIC (0.5~8 μg / ml), and use the culture medium as a blank control. Add 100 μl to the well, and incubate at 37°C for 24 h; wash with PBS to remove planktonic bacteria, add Bouin's fixative solution to fix for 1 h; wash with PBS for 3 times, add 1% crystal violet for staining for 30 min, wash with tap water to remove floating color; Wells were dissolved with 200 μl ethanol:acetone=80:20 (v / v), and detected at a wavelength of 570nm. The test used TSB broth as a blank control, and the same test was repeated three times. Quantitative results were...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com