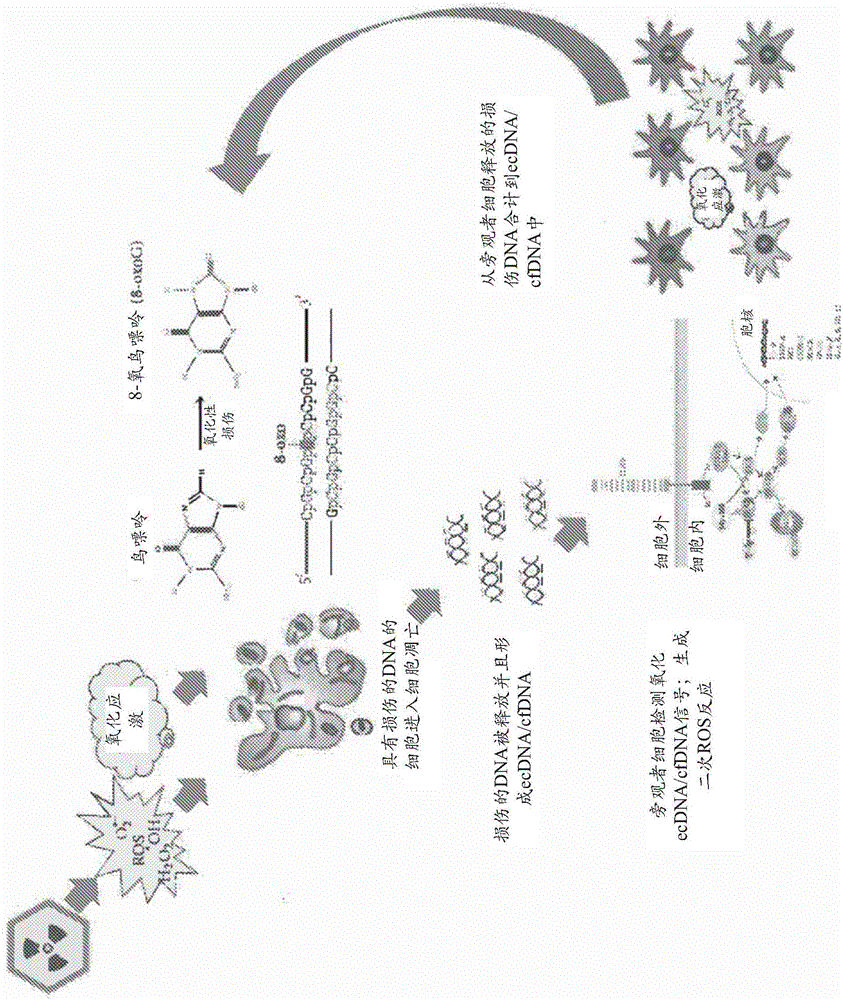
Oxidized fraction of extracellular dna as a biomarker of stress and methods for using the same
A cellular, oxidative technology, applied in the direction of biochemical equipment and methods, extracellular fluid diseases, chemical instruments and methods, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0133] cell culture
[0134] ER / PR-positive MCF-7 breast cancer cells were purchased at ATCC, Manassas, USA (catalogue number: HTB-22). Human embryonic lung fibroblasts were retrieved from the biological sample collection maintained by the Research Center for Medical Genetics (Russian Academy of Medical Sciences collection) and grown as described in [7]. Ethical approval for the use of primary human cells was obtained from the Committee for Medical and Health Research Ethics of Research Center for Medical Genetics, Russian Academy of Medical Sciences (2012, approval number 5).
[0135] MCF-7 cells were cultured in DMEM medium supplemented with 10% (v / v) fetal calf serum, 2 mM L-glutamine, 100 units / mL penicillin, and 100 μg / mL streptomycin. cells in a 5% CO 2 Grow at 37 °C under a humidified atmosphere of air. Cells were grown in slide flasks for 24h or 72h before treatment with DNA probes.
example 2
[0137] Flow Cytometry
[0138] Before flow cytometry, cells were washed in EDTA solution and then treated with 0.25% trypsin under controlled light microscopy. Cells were transferred to Eppendorf tubes, washed with medium, then centrifuged and resuspended in PBS. Cell staining using various antibodies was performed as follows. Briefly, to fix cells, paraformaldehyde (Sigma) was added at a final concentration of 2% for 10 minutes at 37°C. Cells were washed three times with 0.5% BSA-PBS and permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 (Sigma) in PBS or with 70% ethanol for 15 minutes at 4°C. Cells (approximately 50×10 3 ) were washed three times with 0.5% BSA-PBS and washed with 1-2 μg / mL FITC-γH2AX (Ser139) antibody (Temecula California), FITC-Ki-67 antibody, PCNA, 8 -oxodG, EEA1, AIM2, TLR9, NRF2, NF-κB (p65), S529NF-κB (p65) and STAT3 antibody (Abcam) were stained for 3h, then washed again three times with 0.5% BSA-PBS, and Staining was performed with 1 μg / mL of a secondary FITC...
example 3
[0142] fluorescence microscope
[0143] Cell images were acquired using an AxioScope Al microscope (Carl Zeiss).
[0144] Immunocytochemistry.
[0145] MCF-7 cells were fixed in 3% formaldehyde (4°C) for 20 minutes, washed with PBS and then permeabilized with 0.1% Triton X-100 in PBS for 15 minutes at room temperature, then blocked with 0.5% BSA in PBS 1 h, and incubated overnight at 4°C with FITC-γH2AX (Ser139), 8-oxodG, NRF2, STAT3, NF-κB (p65), AIM2 antibodies. After washing with 0.01% Triton X-100 in PBS, MCF-7 cells were incubated with FITC / PE goat anti-mouse IgG for 2 h at room temperature, washed with PBS and then stained with DAPI.
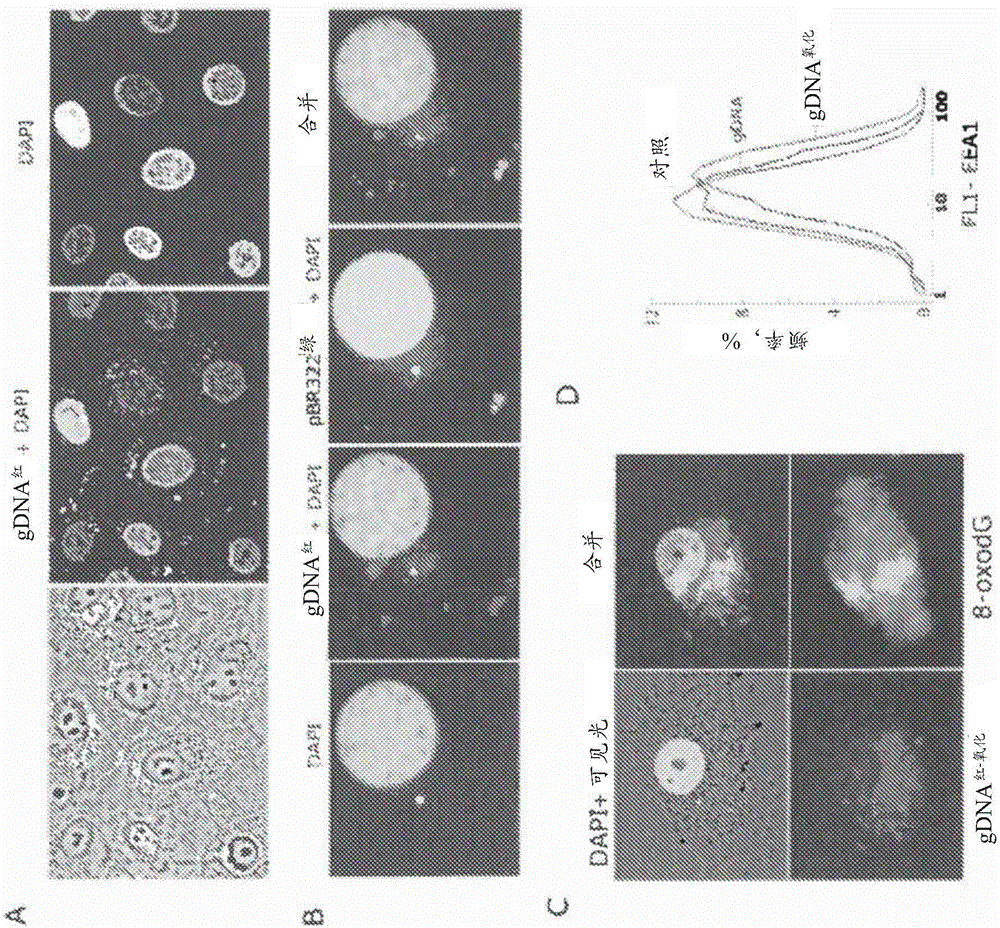
[0146] Intracellular localization of labeled DNA fragments.
[0147] gDNA 红 , gDNA 红-氧化 and pBR322 绿 The labeled fraction (50 ng / ml) was added to the culture medium for 30 minutes. Cells were washed three times with PBS, fixed in 3% paraformaldehyde (4°C) for 20 minutes, washed with PBS and stained with 2 μg / mL DAPI. To analyze the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com