Glufosinate dehydrogenase mutant and application thereof
A glufosinate-ammonium and dehydrogenase technology, applied in the field of glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase mutants, can solve the problems of low asymmetric reduction activity and low substrate concentration, and achieve the effect of good industrial application prospects.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] Embodiment 1 Construction and screening of glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase mutant library
[0052] The glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase gene (amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID No.2 and nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID No.1) derived from baiji was constructed as expression vector pETDuet-1-lvPDH, transformed into Escherichia coli, The starting strain E.coli BL21(DE3) / pETDuet-1-lvPDH was obtained.
[0053] The glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase mutant library was prepared by three rounds of site-directed saturation mutagenesis, and the primers were designed as shown in Table 1.
[0054] In the first round, using the vector pETDuet-1-lvPDH as a template, using the site-directed saturation mutation primers K90-F and K90-R in Table 1 as primers, through saturation mutation PCR, the glufosinate-ammonium shown in SEQ ID No.2 was removed. The 90th lysine in the hydrogenase amino acid sequence was mutated into the remaining 19 amino acids, and transformed, plated, and...
Embodiment 2
[0065] Embodiment 2 Induced expression of glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase parent, mutant and glucose dehydrogenase
[0066] Glucose dehydrogenase gene gdh (nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID No.3, amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID No.4) is synthesized from the whole gene and obtained from recombinant glucose dehydrogenase of the genus Exiguobacterium sibiricum Strain E. coli BL21(DE3) / pET28b-GDH.
[0067] Example 1 departure bacterial strain E.coli BL21(DE3) / pETDuet-1-lvPDH and glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase mutant strain and recombinant glucose dehydrogenase bacterial strain E.coli BL21(DE3) / pET28b-GDH were respectively inoculated into containing In LB liquid medium with a final concentration of 50 μg / mL ampicillin and kanamycin, culture at 37°C for 9 hours, and inoculate into fresh ampicillin containing a final concentration of 50 μg / mL at a volume fraction of 2% (v / v). In the LB liquid medium of kanamycin and kanamycin, culture at 37°C and 180 rpm for 1.5 hours, ...
Embodiment 3
[0068] Embodiment 3 mutation library screening
[0069] Mix the wet cells of the mutant strain induced and expressed in Example 2 and the wet cells of glucose dehydrogenase at a mass ratio of 3:1, and add the amount of 50 g / L of the total amount of cells into pH 7.5, 100 mM phosphate buffer for resuspension , ultrasonic crushing on ice-water mixture for 10 minutes, ultrasonic crushing conditions: power of 400W, crushing for 1 second, pausing for 1 second, to obtain the crude enzyme solution of the mutant strain. Under the same conditions, replace the wet cells of the mutant strain with the starting strain to prepare the crude enzyme solution of the starting strain.
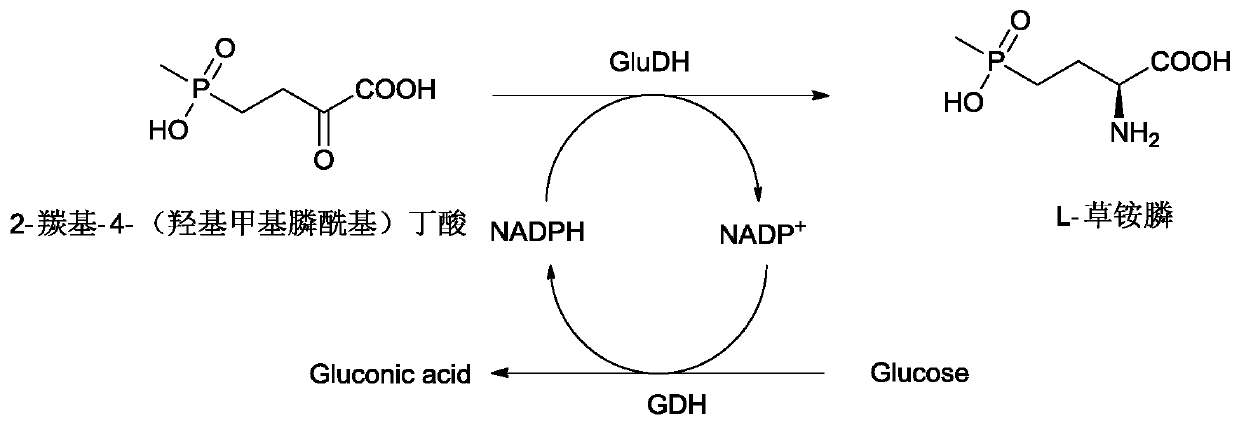
[0070] The crude enzyme solution of the mutant strain or the crude enzyme solution of the original strain is used as a catalyst, 2-carbonyl-4-(hydroxymethylphosphono)butyric acid is used as a substrate, glucose is used as an auxiliary substrate, and no exogenous NADPH or NADP is added. + , using the endogenous NA...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com