Genetic engineering strain high in yield of phenazine-1-formamide and construction method thereof
The technology of a genetically engineered strain and construction method is applied in the field of genetically engineered strains and its construction for high-yielding phenazine-1-carboxamide, which can solve the problems of low yield and efficiency of phenazine-1-carboxamide, and achieve increased yield, The effect of effective biological control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0050] Embodiment 1, the construction of lon gene in vitro mutant
[0051] Primers were designed according to the lon gene and its upstream and downstream sequences in the Pseudomonas chloropinus HT66 genome (see Table 1):
[0052] Table 1
[0053]
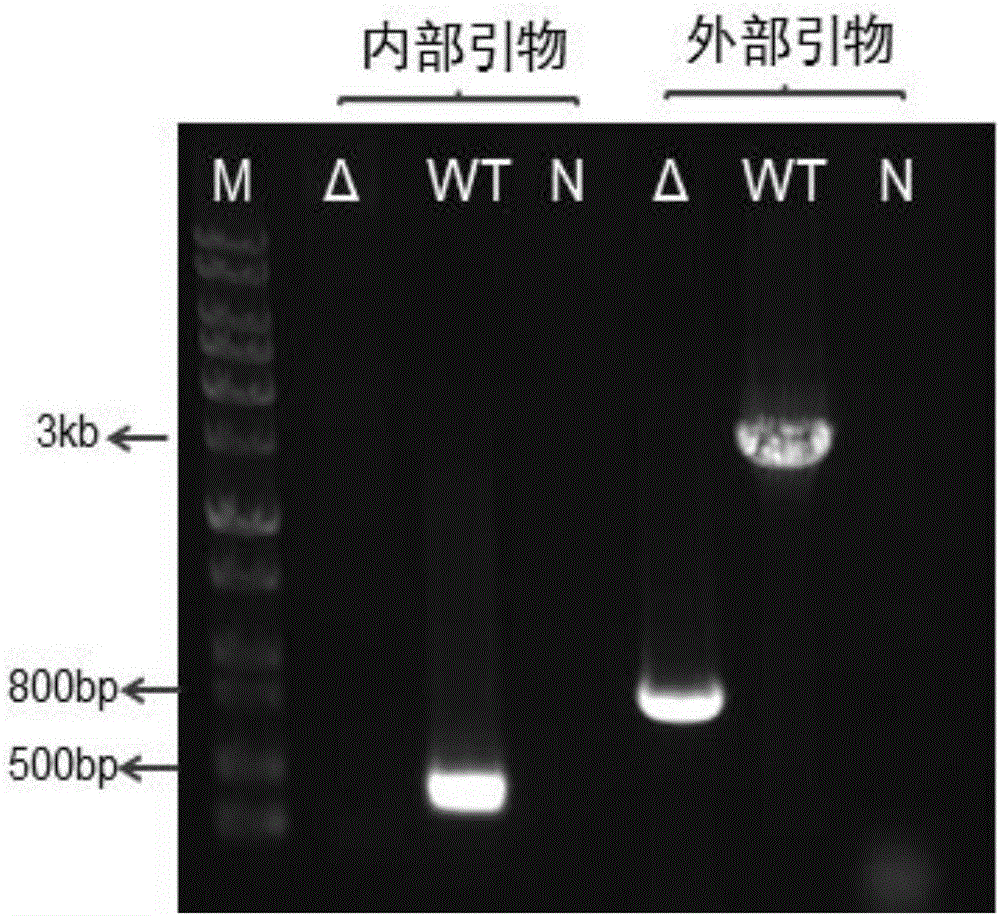
[0054] Using the genomic DNA as a template, the corresponding fragment in the genome is amplified.
[0055] The upstream and downstream PCR products were ligated by fusion PCR, and the fusion PCR product and the pK18mobsacB vector were respectively digested with EcoRI and XbaI, recovered through the column, and ligated with T4 ligase to obtain in vitro mutant plasmids.
[0056] Escherichia coli S17 was transformed with the in vitro mutant plasmid. The S17 strain carrying the recombinant plasmid was fully activated, inoculated in LB medium containing 50 mg / L kanamycin, and cultured at 37°C and 180 rpm for 12 hours. The fully activated HT66 strain was inoculated in LB medium and cultured at 28°C and 180 rpm for 12h. Collect...
Embodiment 2
[0058] Embodiment 2, construction of parS gene in vitro mutant
[0059] Primers were designed according to the parS and upstream and downstream sequences in the Pseudomonas chloropinus HT66 genome (see Table 2):
[0060] Table 2
[0061]
[0062] Using the genomic DNA as a template, the corresponding fragment in the genome is amplified.
[0063] The upstream and downstream PCR products were ligated by fusion PCR, and the fusion PCR product and the pK18mobsacB vector were respectively digested with BamHI and HindIII, recovered by column, and ligated with T4 ligase to obtain in vitro mutant plasmids.
[0064] Escherichia coli S17 was transformed with the obtained in vitro mutant plasmid. The S17 strain carrying the recombinant plasmid was fully activated, inoculated in LB medium containing 50 mg / L kanamycin, and cultured at 37°C and 180 rpm for 12 hours. The fully activated HT66 strain was inoculated in LB medium and cultured at 28°C and 180 rpm for 12 hours. Collect an...
Embodiment 3
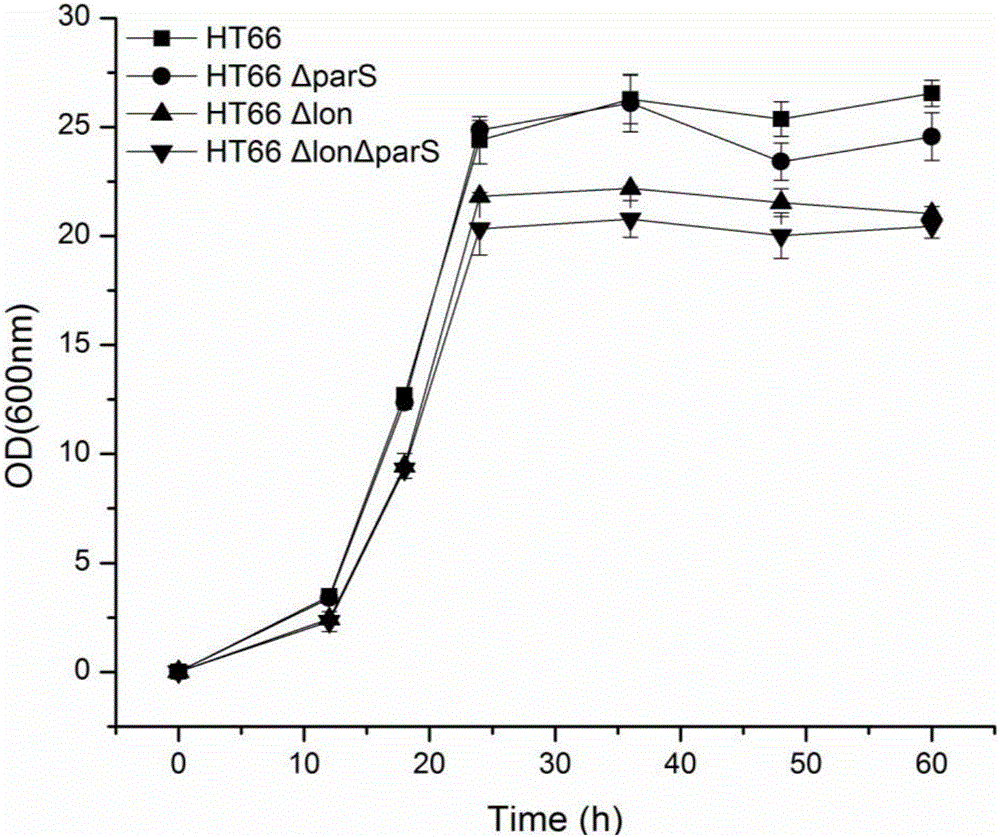
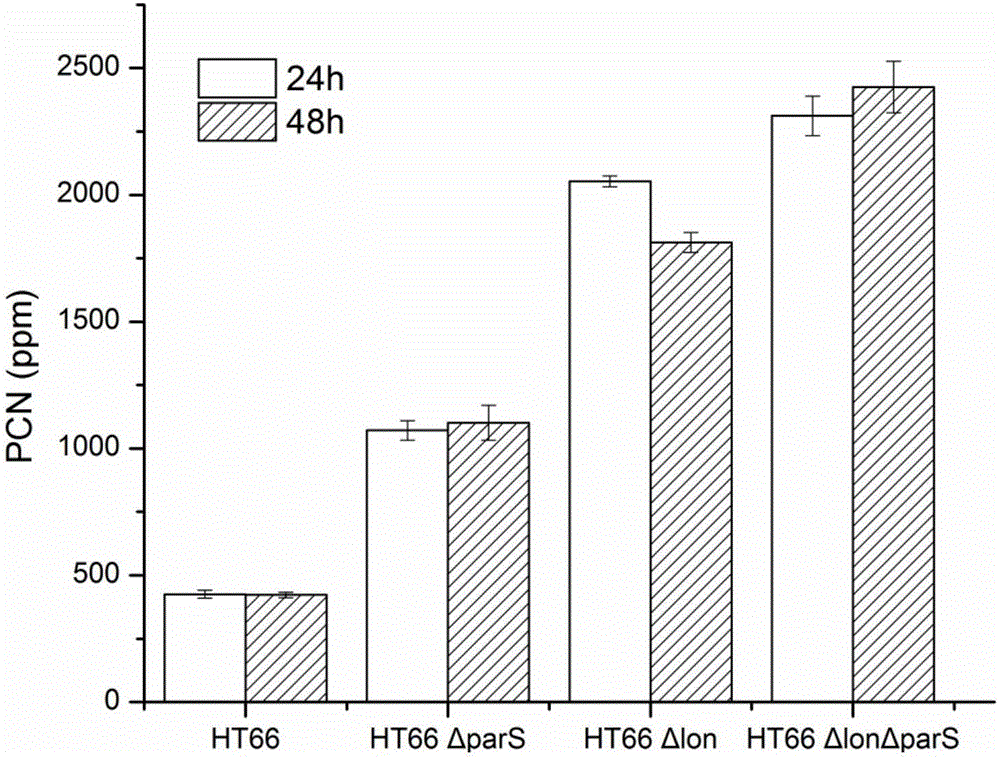
[0065] Example 3, Construction of lon and parS double mutant strain HT66ΔlonΔparS
[0066] The S17 strain carrying the parS recombinant plasmid was fully activated, inoculated in LB medium containing 50 mg / L kanamycin, and cultured at 180 rpm at 37°C for 12 hours. The fully activated HT66Δlon strain was inoculated in LB medium and cultured at 28°C and 180 rpm for 12 hours. Collect and wash the two kinds of bacteria at 5000 rpm, resuspend in LB medium and mix with EP tube at a concentration ratio of HT66Δlon:S17 of 3:1, let it stand for 1 hour; take the mixed bacteria solution and spot it on the LB plate, Cultivate at 28°C for 24 hours; scrape and resuspend the mixed colonies grown in LB, dilute and spread on LB plates with kanamycin 50mg / L and ampicillin 100mg / L, culture at 28°C for 2-3 days and then pick Coat the single clone on a 10% sucrose plate, culture at 28°C for 1-2 days; pick the single clone on the sucrose plate, spot it on the kanamycin 50 mg / L resistant LB plate...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com