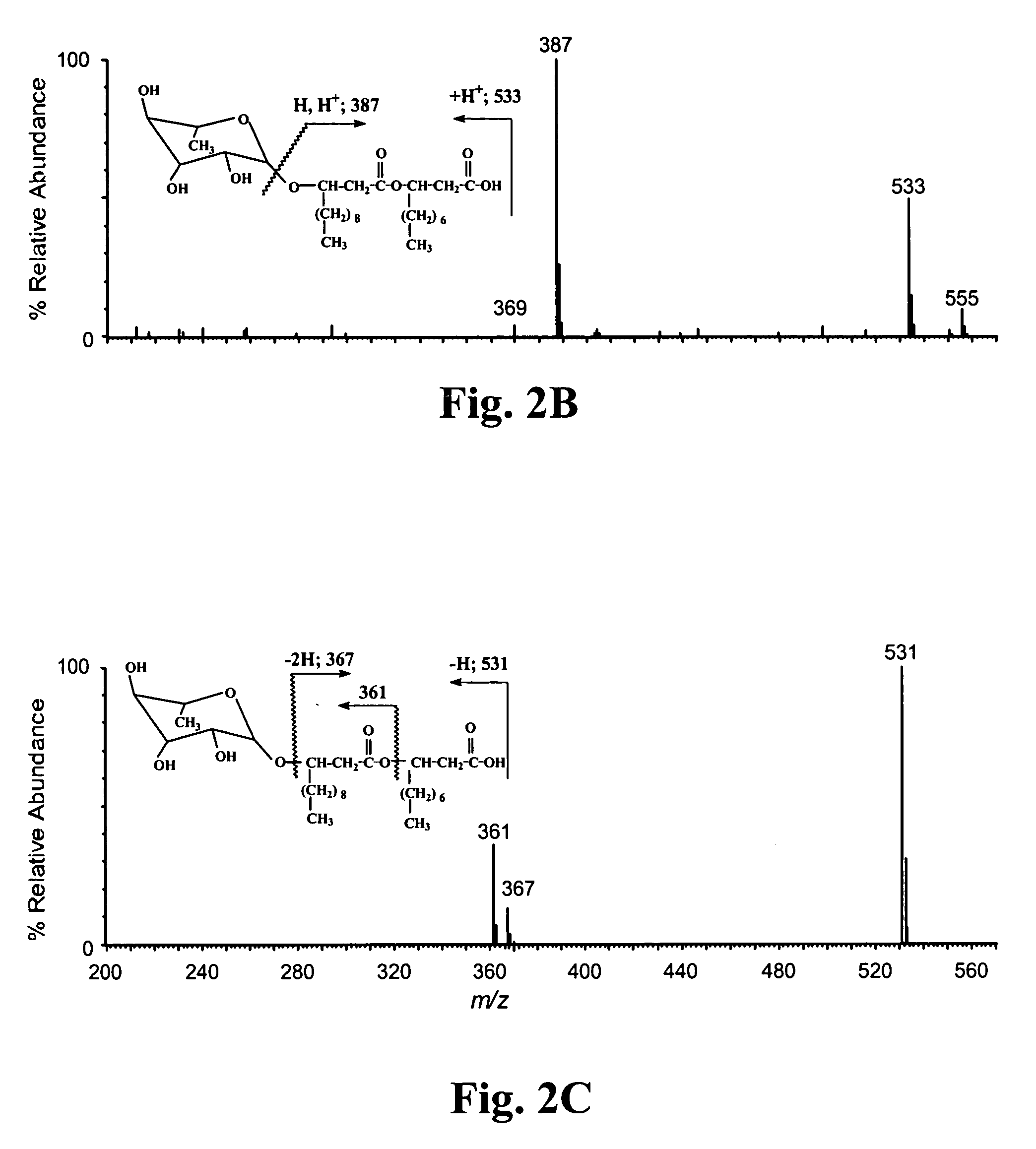
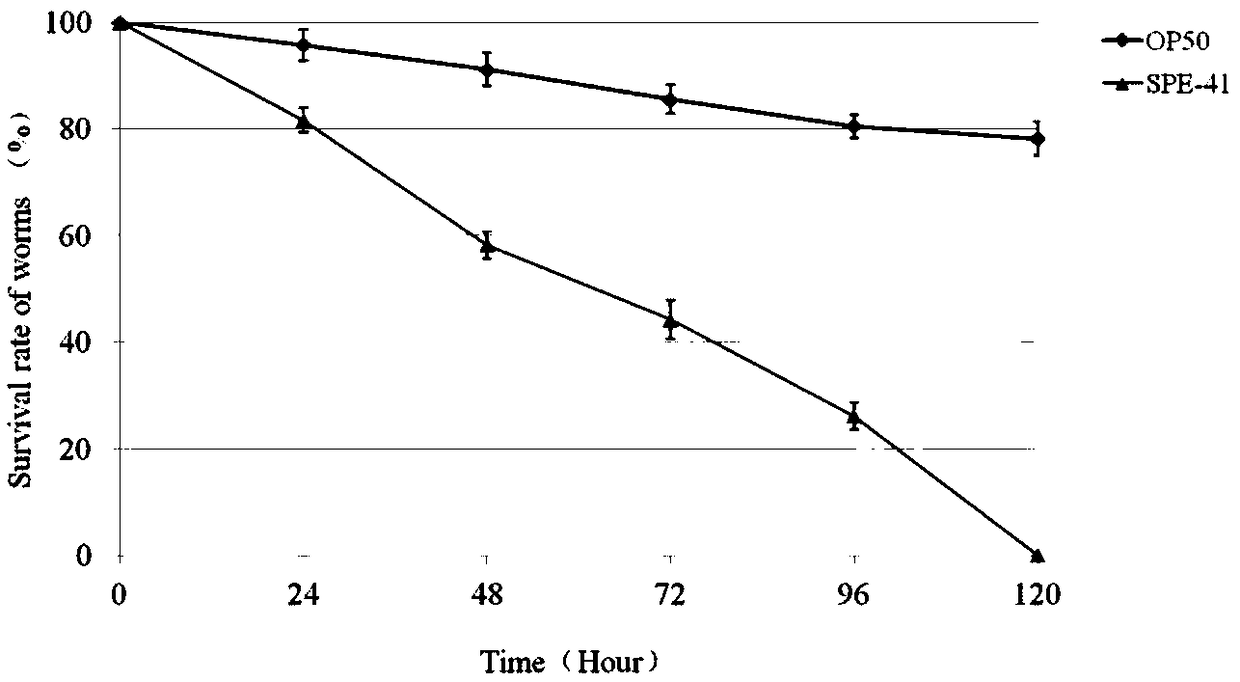
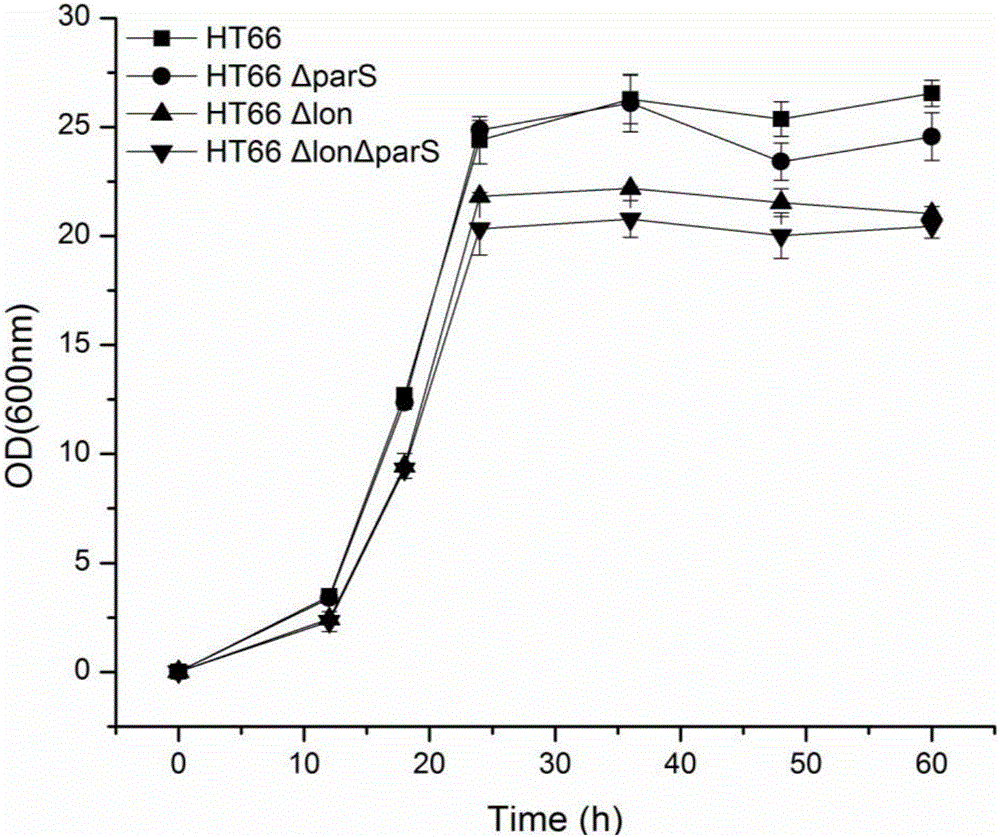
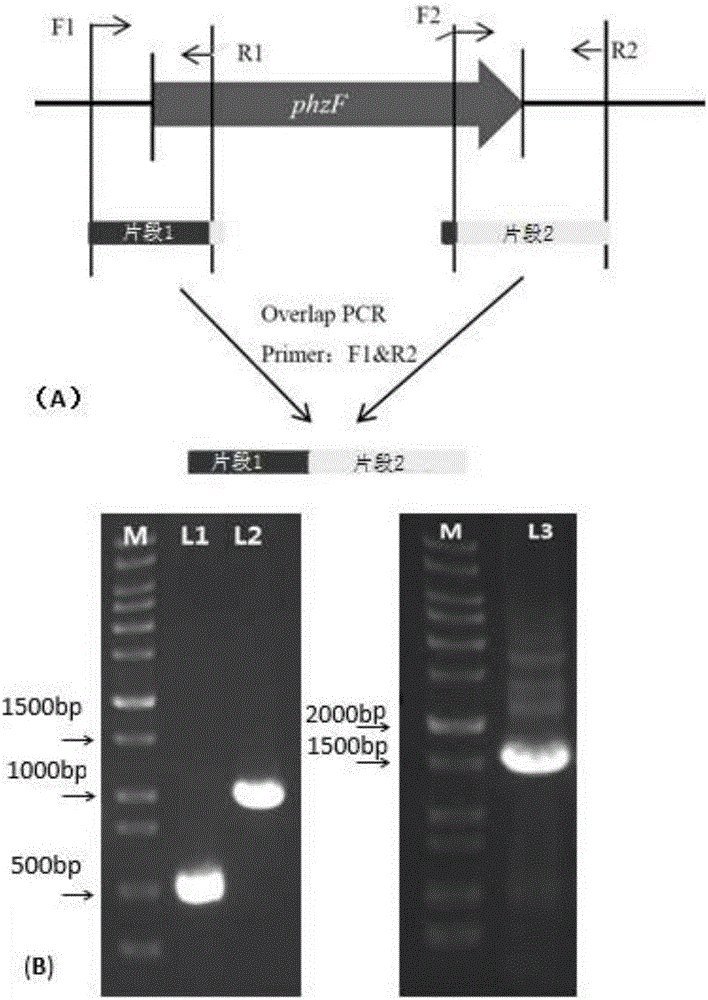
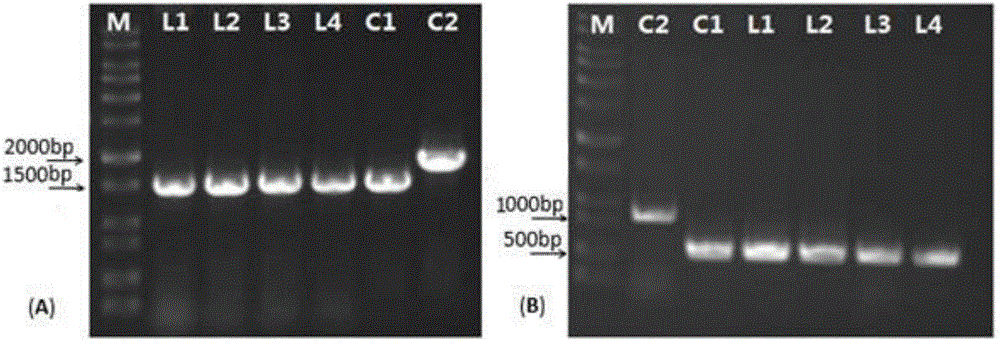
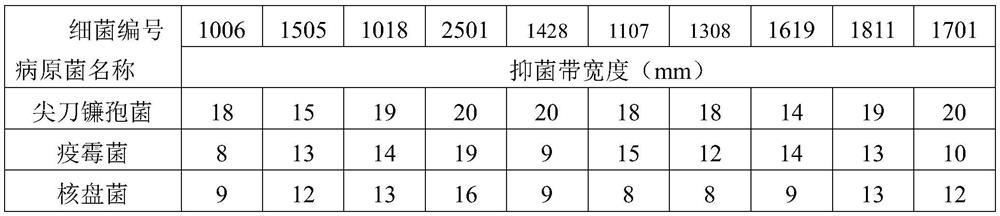
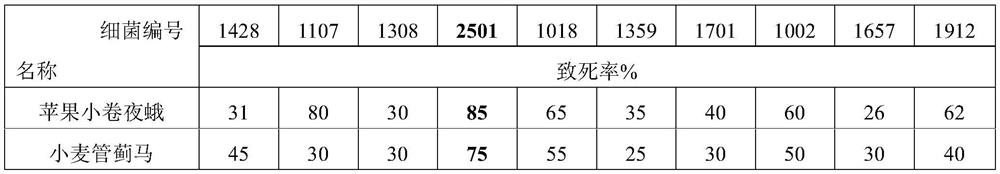
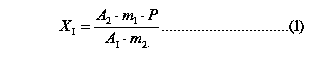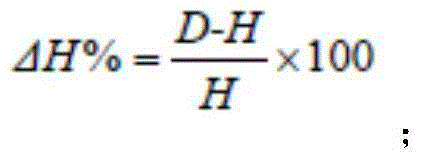Patents
Literature
72 results about "Pseudomonas chlororaphis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
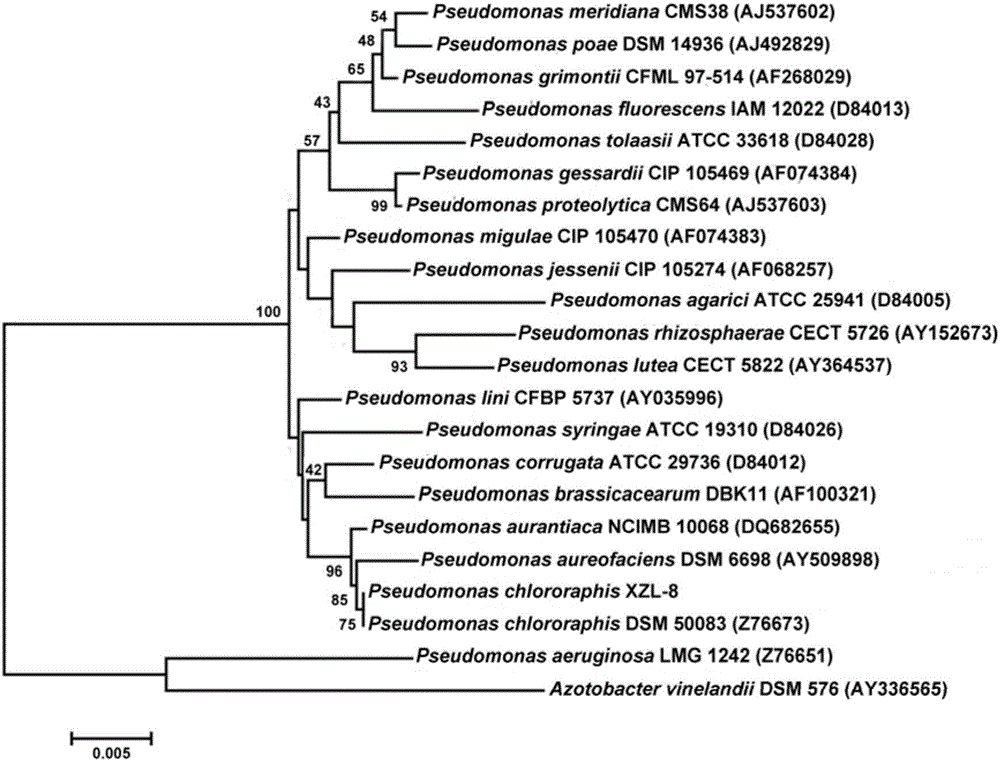
Pseudomonas chlororaphis is a bacterium used as a soil inoculant in agriculture and horticulture. It can act as a biocontrol agent against certain fungal plant pathogens via production of phenazine-type antibiotics. Based on 16S rRNA analysis, similar species have been placed in its group.
Prepn process of strain and prepn for controlling blight of vegetable biologically
The present invention relates to preparation process of strain and preparation for controlling blight of vegetable biologically. One kind of Pseudomonas chlororaphis GP72 is cultured and screened with sweet pepper rhizoid and its attached soil sample and KMB culture medium with antibiotic added, and preserved in the number of CGMCC No. 1748. The freeze preserved strain is activated and amplifying cultured to obtain microbial preparation, which may be used for preventing and controlling blight of chili, cucumber, wax gourd, etc; for preventing and controlling rape sclerotinia rot, cucumber fusarium wilt, water melon fusarium wilt, etc; and as vegetable growth promoter to raise the yield of vegetable.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Pseudomonas chlororaphis with wide-spectrum antimicrobial activity and application thereof
ActiveCN107099474AHas broad-spectrum antimicrobial activityStrong broad-spectrum antibacterial activityBiocideBacteriaDiseaseAntibacterial activity
The invention relates to Pseudomonas chlororaphis with wide-spectrum antimicrobial activity and application of Pseudomonas chlororaphis to prevention and treatment of diseases attacking fruit trees and field crops, belonging to the field of biotechnology. The Pseudomonas chlororaphis with wide-spectrum antimicrobial activity is classified and named as Pseudomonas chlororaphis YTBTa14, with an accession number of CCTCC No. M2016099, and the 16SrDNA sequence of the Pseudomonas chlororaphis is as shown in a sequence table in the specification. The thallus and fermentation broth of the Pseudomonas chlororaphis with wide-spectrum antimicrobial activity in the invention both have good wide-spectrum antimicrobial activity to fungal diseases attacking fruit trees, have long-lasting and stable antimicrobial effect, show great potential in development into novel high-efficiency wide-spectrum bio-control fungicides, and provide a novel approach for application of microbes to biological control.
Owner:SHANDONG YANTAI AGRI SCI & TECH INST
Pseudomonas chlororaphis for preventing and treating crop fusarium disease and applications thereof
The invention provides pseudomonas chlororaphis for preventing and treating the crop fusarium disease and applications thereof. The preservation number of the pseudomonas chlororaphis is CGMCC No. 7729. The Pcho01 bacterium strain of the pseudomonas chlororaphis has a high effective antagonistic action, is capable of being applied to the preventing and treating wheat scab caused by fusarium, and the preventing and treating efficiency in the field is maintained above 60%. The Pcho01 bacterium strain also has a very good antagonistic action on botrytis cinerea, rice sheath blight fungus, bipolaris maydis, pythium wltmum, rhizopus, and pseudomonas solanacearum, and can be used to prevent and treat the diseases caused by those bacteria mentioned above.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
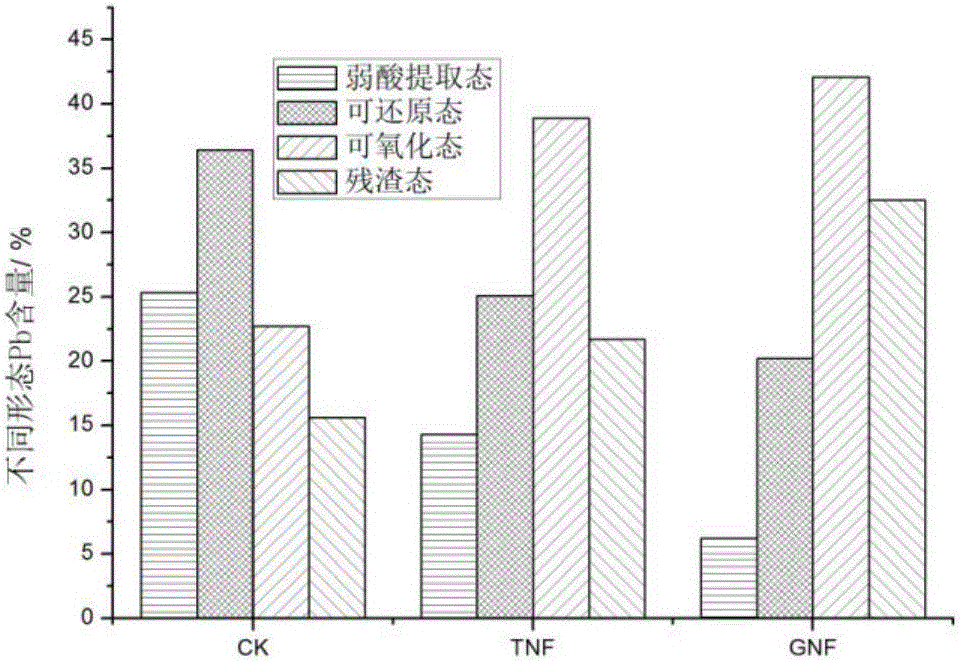
Charcoal loaded PSB passivator preparation and method for restoring Pb polluted soil through charcoal loaded PSB passivator
ActiveCN105734041AHigh removal rateImprove repair effectContaminated soil reclamationOn/in organic carrierPseudomonas tolaasiiFermentation
The invention discloses a preparation method of charcoal loaded PSB passivator, belongs to the technical field of soil restoration and further provides a method for restoring Pb polluted soil through the charcoal loaded PSB passivator. Green needle pseudomonades are adopted and immobilized; with charcoal as a carrier, the green needle pseudomonades cultured for the logarithmic phase are inoculated into a fermentation tank, charcoal is added for fermentation culture, then, immobilization is conducted, and the charcoal loaded PSB passivator is obtained. The preparation method is simple, easy to operation and suitable for large-scale production, the restoration capability of the charcoal loaded PSB passivator to soil is high, and the removing rate of lead is high.
Owner:INST OF HYDROGEOLOGY & ENVIRONMENTAL GEOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF GEOLOGICAL SCI
Processes for the production of rhamnolipids
A process for producing rhamnolipids involving culturing Pseudomonas chlororaphis strain NRRL B-30761 in a first aqueous culture medium containing about 0.3% NH4H2PO4, about 0.2% K2HPO4, about 0.2% carbon source, about 0.5 mg / L FeSO4, and about 0.1% MgSO4 for about 24–about 48 hours at about 25°–about 30° C. with orbital shaking, and then culturing Pseudomonas chlororaphis strain NRRL B-30761 in a static second aqueous culture medium containing per liter about 2% carbon source, about 0.7 g KH2PO4, about 0.9 g Na2HPO4, about 2 g NaNO3, about 0.4 g MgSO4.7H2O, and about 0.1 g CaCl2.2H2O for at least about 72 hours at about 20°–about 23° C., wherein the first and second aqueous culture medium contains only one source of carbon.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
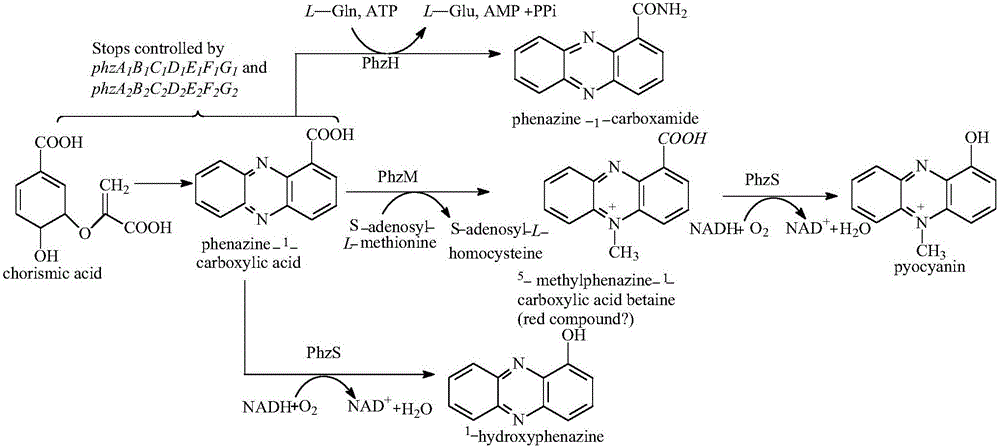
Genetic engineering strain for producing phenazine-1-carboxylic acid and application of genetic engineering strain
InactiveCN105087455ARaise the level of fermentationRaw materials are easy to obtainBiocideBacteriaFungicideSecondary metabolite
The invention discloses a genetic engineering strain for producing phenazine-1-carboxylic acid, which is produced by taking pseudomonas chlororaphis as a culture, as well as application of the genetic engineering strain; the genetic engineering strain is obtained by knocking out a phzH gene in pseudomonas chlororaphis genome. The genetic engineering strain for producing phenazine-1-carboxylic acid is finally prepared by deleting the phzH gene in the genome of the strain by virtue of insertion mutation or marker-less deletion from pseudomonas chlororaphis HT66 CCTCC NO: M2013467 which can naturally secrete phenazine-1-formamide as well as derivatives of the pseudomonas chlororaphis so as to convert a secondary metabolite from the phenazine-1-formamide into the phenazine-1-carboxylic acid. The invention also discloses a preparation method and a detection method of the fungicide.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Genetic engineering strain used for producing 2-hydroxyphenazine and preparation method and application genetic engineering strain
InactiveCN106635938ANutritional Requirements SimpleShort fermentation cycleBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationMicrobiology
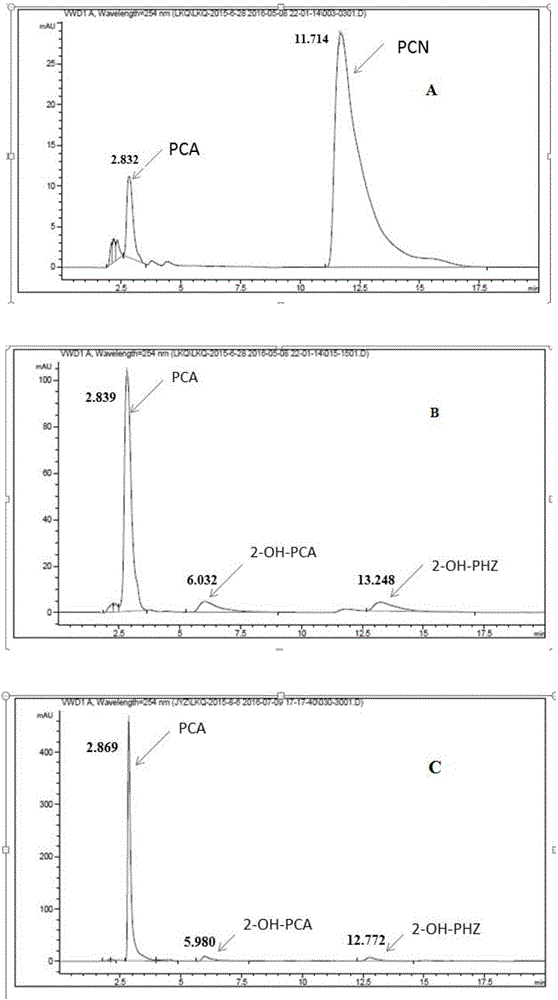
The invention provides a genetic engineering strain used for producing 2-hydroxyphenazine and a preparation method and application of the genetic engineering strain. The genetic engineering strain is prepared through the following step of replacing a phzH gene in a genome of Pseudomonas chlororaphis HT66 CCTCCNO: M2013467 and a derivative with an exogenous phzO gene. The preparation method comprises the following steps of constructing a recombinant plasmid, hybridizing parents and screening a gene replaced mutant strain. The high-level phenazine synthesis capability of the strain HT66 is utilized, the phzH gene in the strain HT66 is replaced with the exogenous phzO gene, the high-concentration phenazine-1-carboxylic acid is taken as a substrate, and is further transformed into 2-hydroxyphenazine under the action of a phzO protein. The genetic engineering strain is high in stability, produces less by-products, is short in fermentation period, and is favorable for the industrialized production of 2-hydroxyphenazine.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
A genetic engineering strain used for producing phenazine-1-carboxamide, a preparing method thereof and uses of the strain
InactiveCN107043730AIncrease productionGood stabilityBacteriaTransferasesGenetic engineeringMutant strain
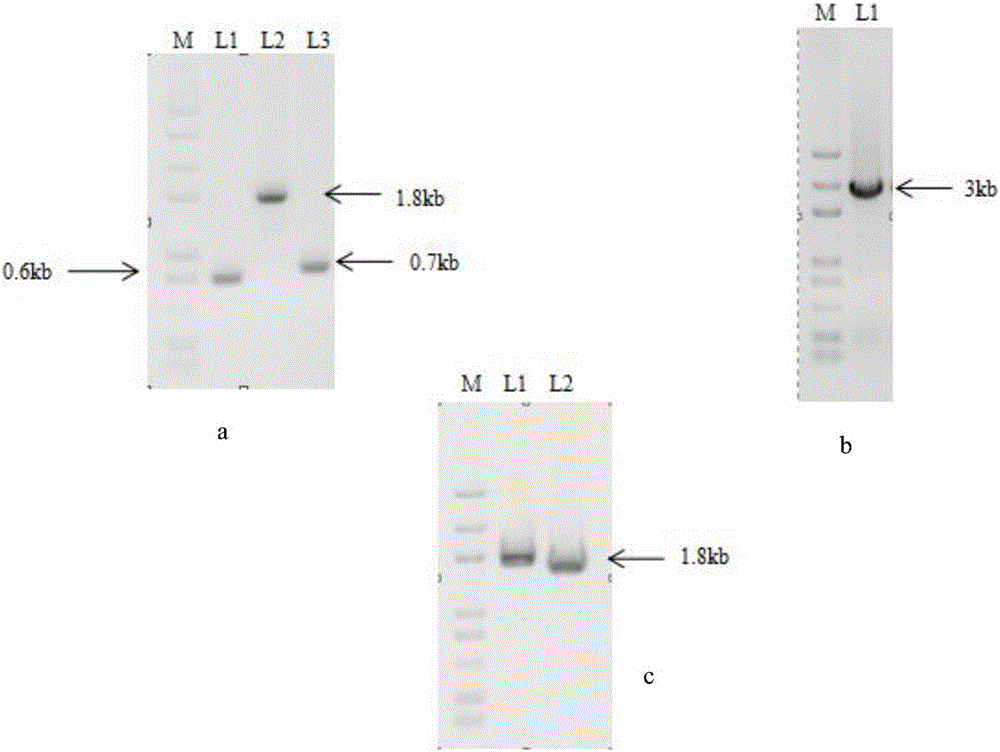
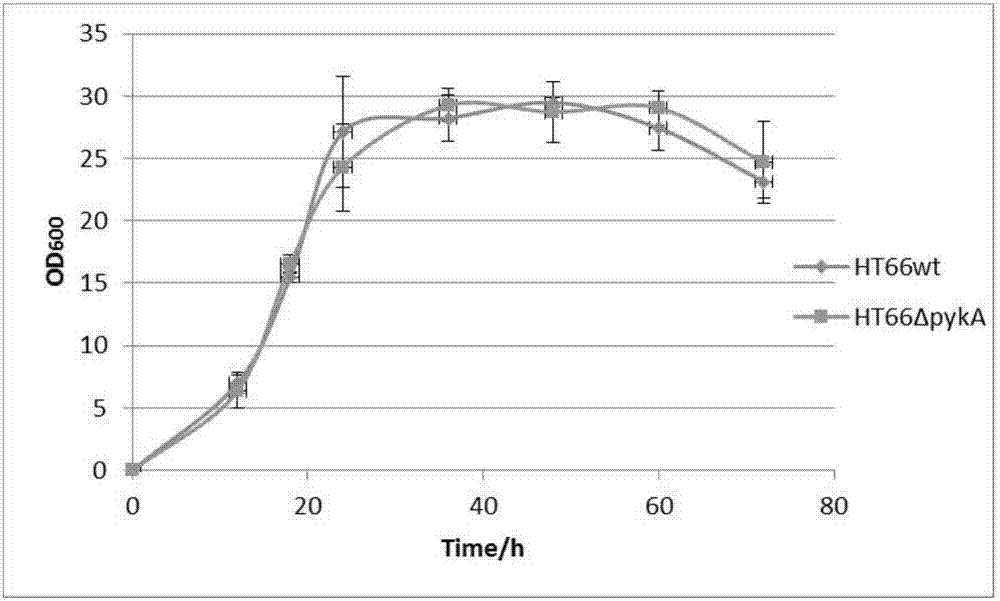
A genetic engineering strain used for producing phenazine-1-carboxamide (PCN), a preparing method thereof and uses of the strain are provided. The strain is prepared by knocking a pykA gene out from pseudomonas chlororaphis HT66 CCTCC NO:M 2013467 and derivatives thereof. The method includes steps of designing primers, constructing a recombinant plasmid and screening a mutant strain. Compared with the prior art, beneficial effects of the strain, the method and the uses are that a novel regulating strategy is adopted, flow directions of metabolic substances in cells are changed, the yield of the PCN is greatly increased, and the strain is safe, reliable and good in stability and can significantly promote agricultural and industrial applications of the PCN.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Application of pseudomonas chlororaphis subsp.aureofaciens in preventing and controlling nematode
InactiveCN109258695ANo pollution in the processNo pesticide residueBiocideNematocidesPesticide residueNematode
The invention relates to an application of pseudomonas chlororaphis subsp.aureofaciens in preventing and controlling nematode. The pseudomonas chlororaphis subsp.aureofaciens is chlororaphis subsp.aureofaciens GDMCC NO. 60273. The invention relates to the application of pseudomonas chlororaphis subsp.aureofaciens in preparing a biological bacteriostatic agent for preventing and controlling nematode. The biological bacteriostatic agent includes the chlororaphis subsp.aureofaciens served as an active ingredient and a carrier. The biological bacteriostatic agent is chlororaphis subsp.aureofaciensfermentation liquor. A method for preventing and controlling nematode comprises the step of spraying the biological bacteriostatic agent containing chlororaphis subsp.aureofaciens in claim 1 and / or fermentation liquor thereof onto an affected part. According to the application of pseudomonas chlororaphis subsp.aureofaciens in preventing and controlling nematode provided by the invention, chlororaphis subsp.aureofaciens used for preventing and controlling nematode is free from pesticide residue, free from environmental pollution and safe to human and livestock. Application of pseudomonas chlororaphis subsp.aureofaciens in preparing the biological bacteriostatic agent for preventing and controlling nematode is characterized by simple preparation process, low cost, excellent effect and convenience in use.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Genetic engineering strain high in yield of phenazine-1-formamide and construction method thereof
PendingCN106635937AIncrease productionEffective biological controlBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPseudomonas tolaasiiSingle mutation
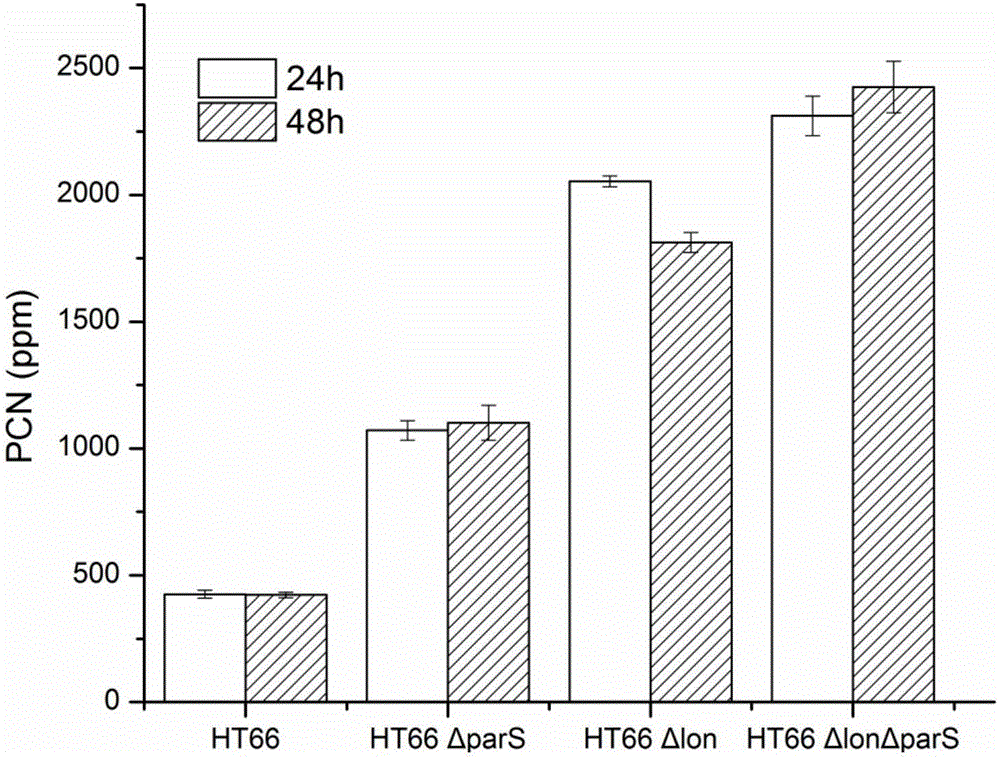
The invention discloses a genetic engineering strain high in yield of phenazine-1-formamide and a construction method thereof. The genetic engineering strain is a genetic engineering strain obtained by knocking out one or two of lon gene and parS gene of HT66CCTCC NO: M 2013467 genome of Pseudomonas chlororaphis, or a genetic engineering strain obtained by knocking out one or two of lon gene and parS gene of HT66CCTCC NO: M 2013467 rpeA and psrA single mutation strain or amphimutation strain genome of Pseudomonas chlororaphis, wherein single mutation strain is HT66 Delta rpeA and HT66 Delta psrA, and amphimutation strain is HT66 Delta rpeA Delta psrA. Compared with the prior art, the genetic engineering strain has the advantages that after lon and parS genes are delected from the genome of Pseudomonas chlororaphis, fermentation yield of phenazine-1-formamide is up to 2425mg / L, and the genetic engineering strain can be used for industrial production and agricultural application of phenazine-1-formamide.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Preparation method for formamide phenazine biological fungicide
The invention discloses a preparation method for formamide phenazine biological fungicide. The preparation method comprises the steps of (1) irradiating pseudomonas chlororaphis vegetation under ultraviolet light to obtain mutant strains; (2) mixing soybean powder, yeast powder and tap water, heating and filtering; (3) adding glucose, peptone, potassium dihydrogen phosphate and magnesium sulfate in the filtrate, dissolving with stirring, regulating a pH value with sodium hydroxide, loading into a triangular flask and heating to a temperature of 120-125 DEG C for sterilization; (4) inoculating the mutant strains on a loop-ramp lawn to obtain strains containing formamide phenazine single component; and (5) screening strains with the highest content of the formamide phenazine single component by using high performance liquid chromatography and drug-containing plate method. The formamide phenazine biological fungicide is suitable for preventing plant pathogenic fungi producing a lot of spores, such as fungi diseases caused by botrytis cinerea pers. and fulvia fulva; a conventional foliar spraying method is adopted to carry out field control; and control efficiency can reach 70-80%.
Owner:JIANGXI POROR CROPS ENG
Pseudomonas chloroaphis with effects of effective zea mays sheath blight control and zea mays growth promotion
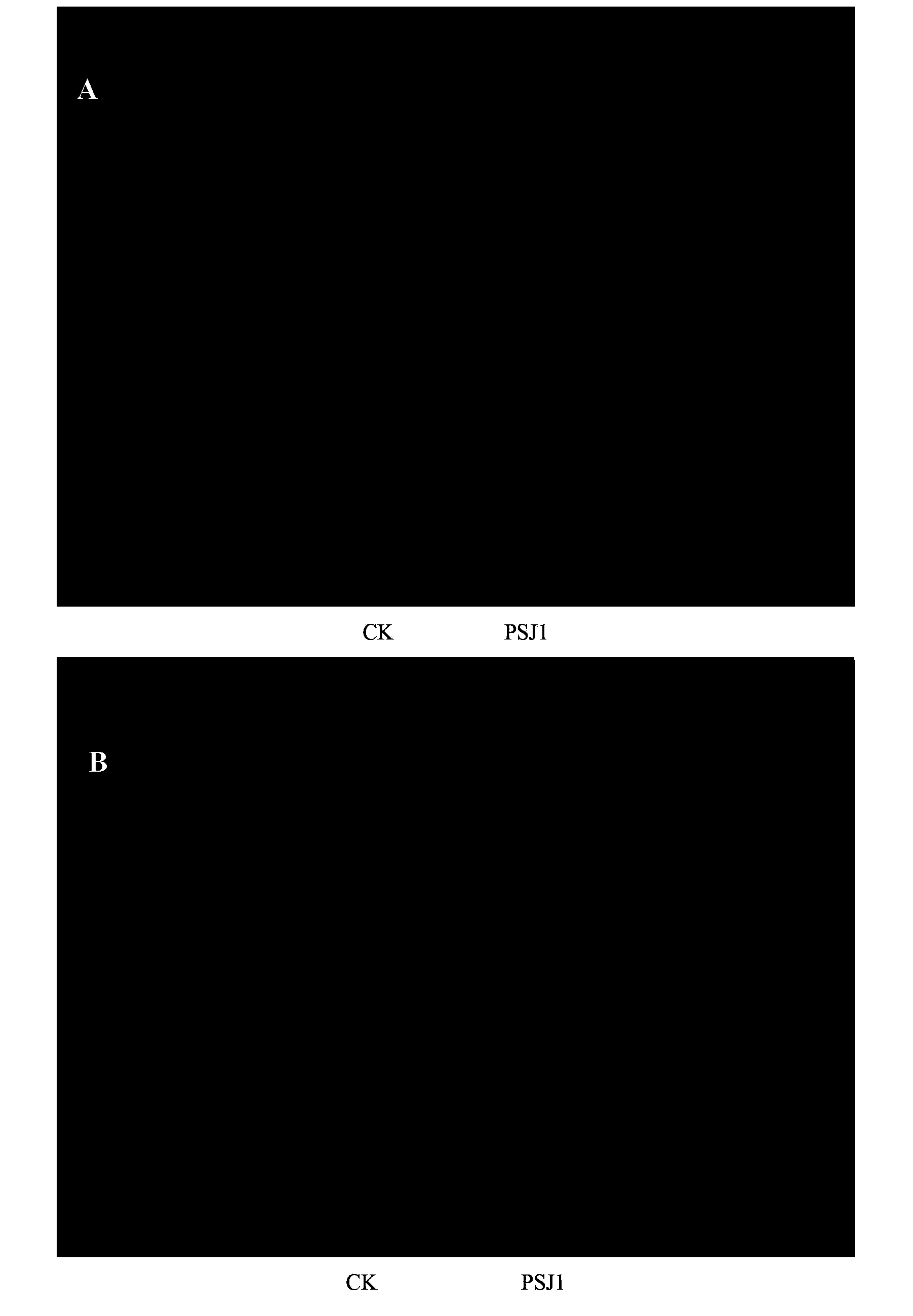
The invention relates to a strain of Pseudomonas chloroaphis with effects of effective zea mays sheath blight control and zea mays growth promotion, and belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. The strain is Pseudomonas chloroaphis PSJ1, is isolated from wheat rhizosphere, and has the preservation number of CGMCC NO.7932. The Pseudomonas chloroaphis PSJ1 has effects of zea mays growth promotion, Rhizoctonia solani growth inhibition, and sheath blight occurrence reduction.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Pseudomonas chlororaphis and application thereof in prevention and treatment of tomato stolonidium leaf spot
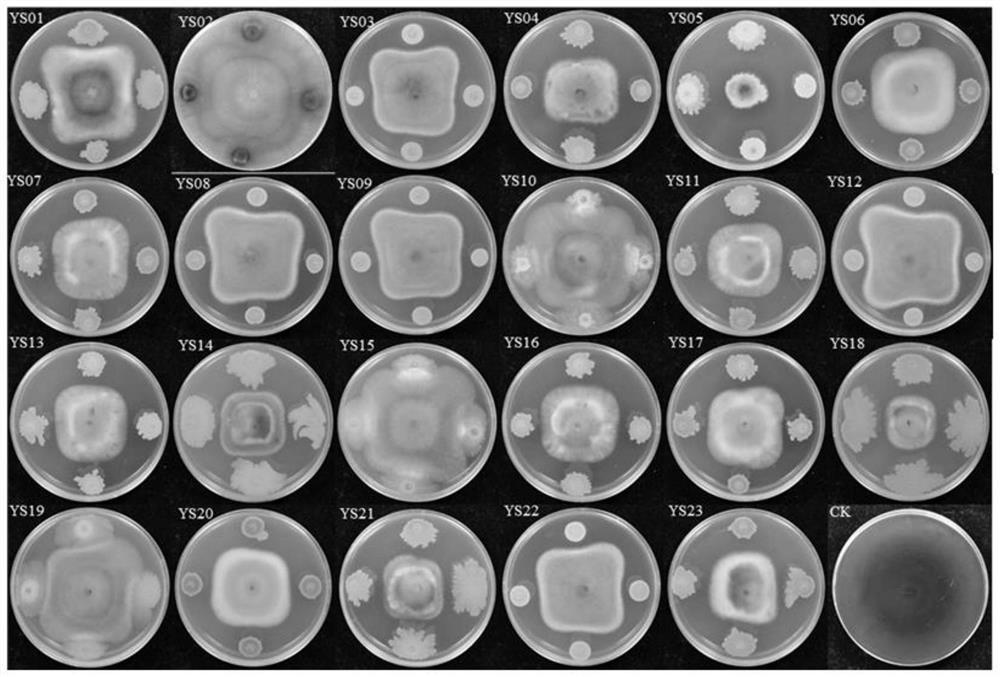
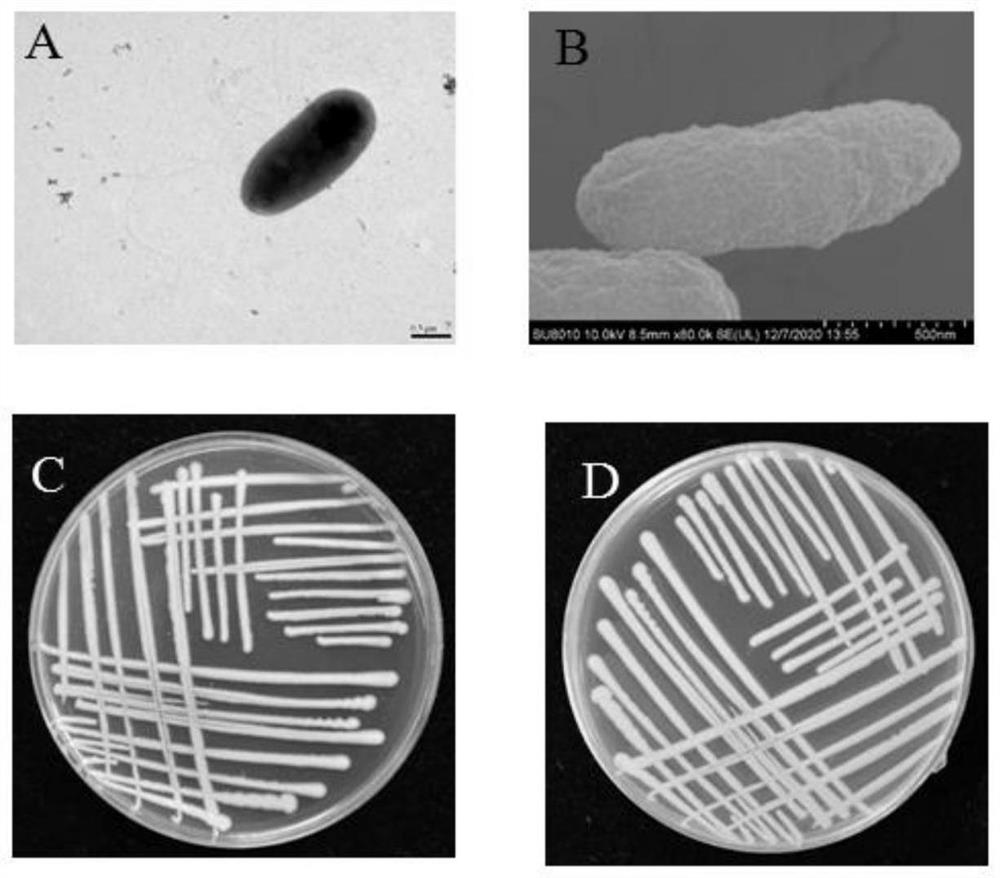
The invention discloses pseudomonas chlororaphis and application of the pseudomonas chlororaphis in prevention and treatment of tomato stolonidium leaf spot. The pseudomonas chlororaphis is pseudomonas chlororaphis YS05 and is preserved in the general microbiological center of the China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms on July 8, 2020, and the preservation number of the pseudomonas chlororaphis YS05 is CGMCC No.20323. The invention also discloses an application of the pseudomonas chlororaphis YS05 in inhibition of pathogenic bacteria. In bacteriostatic spectrum determination, the strain YS05 shows broad-spectrum resistance and has an antagonistic effect on 9 pathogenic fungi and 3 pathogenic bacteria. In a greenhouse potting control effect determination test, the control effect of the strain YS05 on the tomato Stemphylium leaf spot disease reaches 61.27%. In a test for determining the control effect on the in-vitro leaves of the tomato stolonifer, the control effect of the strain YS05 on the tomato gray leaf spot disease is 71.52%. Therefore, the strain YS05 has a good application prospect.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
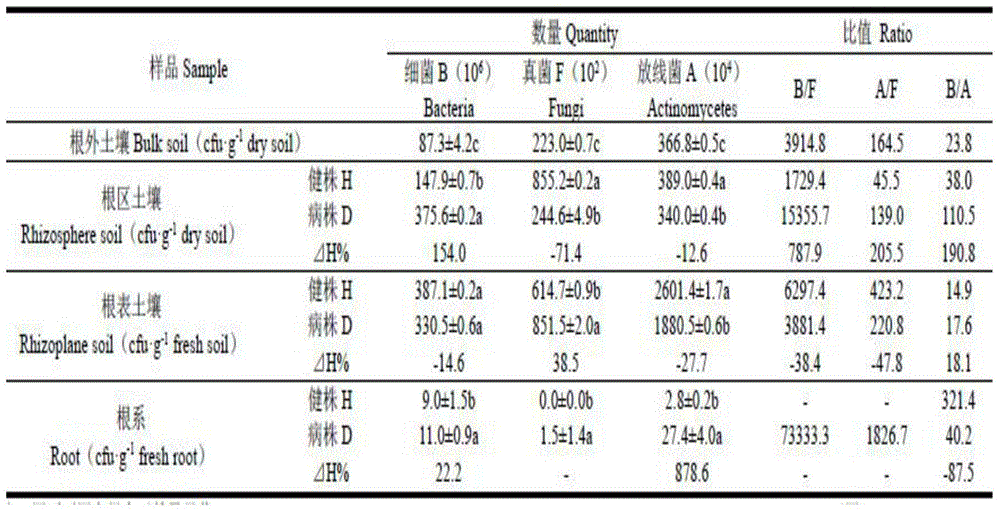
Method for analyzing root domain soil microbial community structure of soft-rot diseased amorphophallus konjac plant
The invention discloses a method for analyzing a root domain soil microbial community structure of a soft-rot diseased amorphophallus konjac plant. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring and treating a test sample, preparing a culture medium, performing microorganism isolation and enumeration, identifying dominant strains, testing the pH and the nutrition of soil, and processing data. By adopting the method for analyzing the root domain soil microbial community structure of the soft-rot diseased amorphophallus konjac plant, the change of the soil microbial community structure with the amorphophallus konjac soft-rot disease is studied, relevant micro-ecology mechanisms of the amorphophallus konjac soft-rot disease can be studied for a first time, and great significance is achieved. The study of the method for analyzing the root domain soil microbial community structure of the soft-rot diseased amorphophallus konjac plant shows that 9 dominant microorganisms, namely, 3 dominant bacteria including pseudomonas plecoglossicida, pseudomonas chlororaphis subsp.aureofaciens and stenotrophomonas pavanii, 4 dominant bacteria including fusarium solani, fusarium oxysporum, penicillium canescens and penucillium, and 2 dominant actionmycetes including streptomyces scabiei and streptomyces cellulosae, massively exist at the root domain of the soft-rot diseased amorphophallus konjac plant.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
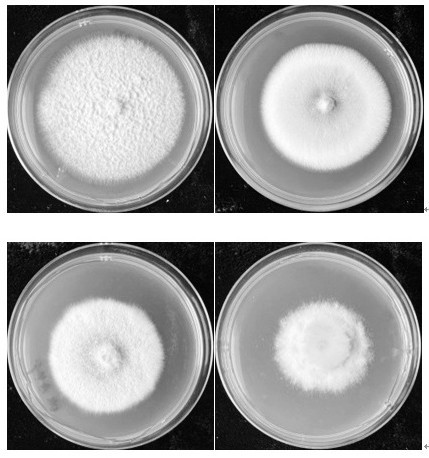
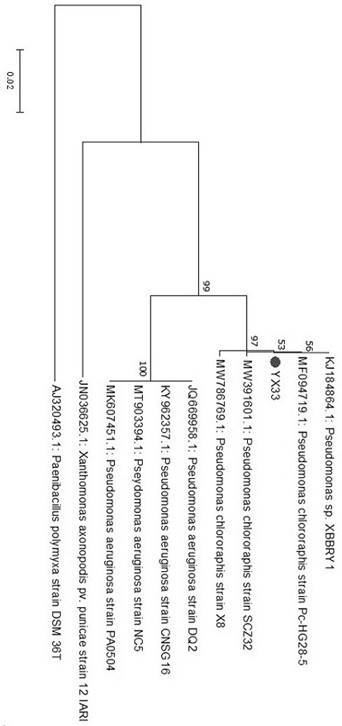
Pseudomonas chlororaphis YX33 and application thereof in prevention and treatment of tobacco fusarium root rot and growth promotion
PendingCN114703100APromote growth and developmentGood antibacterial effectBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologySporeling
The invention belongs to the technical field of tobacco disease prevention and treatment, and particularly relates to pseudomonas chlororaphis YX33 and application thereof in prevention and treatment of tobacco fusarium root rot and growth promotion, and test materials used in a test comprise a test soil sample, a test strain, a test tobacco variety and a test culture medium; the invention discloses Pseudomonas chlororaphis YZ33 which has an obvious antagonistic effect on tobacco fusarium root rot, the bacteriostatic mechanism and the growth promoting characteristic of the Pseudomonas chlororaphis YZ33 are preliminarily analyzed, and the Pseudomonas chlororaphis YZ33 is wide in bacteriostatic spectrum for main root and stem diseases of tobacco and has a good application prospect. The antibiotic generated by the thalli is mainly used for inhibiting spore germination and mycelial growth to generate a relatively strong antibacterial effect on tobacco fusarium oxysporum and fusarium solani, the growth and development of tobacco plants can be promoted, and a foundation is laid for subsequent research and application of field biological control.
Owner:TOBACCO RES INST HENAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Synthetic method of lipopeptide based on pseudomonas chlororaphis
ActiveCN106467922ALearn about synthesisUnderstand regulationMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyPseudomonas chlororaphis
The invention provides a synthetic method of lipopeptide based on pseudomonas chlororaphis. The method specifically comprises the following steps: pseudomonas chlororaphis undergoes fermental cultivation to obtain a fermentation broth containing peptidolipid. The conditions of the fermental cultivation are as follows: 25-30 DEG C; 200-300 r / min; and 25-50 mL / 250 mL of loading sample volume. In allusion to defects of the prior art, according to the corresponding relationship between fermentation temperature, rotating speed, loading sample volume and lipopeptide yield, practical application problems, such as how to obtain high-yield lipopeptide and how to obtain lipopeptide within a short period of time, are solved; and finally, lipopeptide yield is remarkably enhanced.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Genetic engineering strain for producing 1-hydroxyphenazine as well as preparation method and applications of genetic engineering strain
InactiveCN106399214AShort fermentation cycleNutritional Requirements SimpleBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationCarboxylic acid
The invention provides a genetic engineering strain for producing 1-hydroxyphenazine as well as a preparation method and applications of the genetic engineering strain. The genetic engineering strain is obtained through the following method: the phzH gene in Pseudomonas chlororaphis HT66 CCTCC NO:M2013467 and the genome of the derivative of the phzH gene is replaced by the exogenous phzS gene. The preparation method comprises the following steps: construction of recombinant plasmids, biparental hybridization, and screening of gene substitution mutant strains. For the first time, the exogenous phzS gene replaces the phzH gene in the strain HT66, the obtained genetic engineering strain can produce high-concentration phenazine-1-carboxylic acid through fermentation by taking natural agricultural and sideline products as raw materials, the high-concentration phenazine-1-carboxylic acid is taken as a substrate and is converted, and thus the high-level 1-hydroxyphenazine is obtained. The genetic engineering strain is safe and reliable, is friendly to the environment, and can be used for preparing 1-hydroxyphenazine.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Microbial agent for preventing and treating apple ring rot and preparation method thereof
PendingCN110317802APlay a sustained release roleGood effectBiocideFungiBiotechnologyStreptomyces hygroscopicus
The invention provides a microbial agent for preventing and treating apple ring rot and a preparation method thereof. The microbial agent is obtained by using a gel carrier loaded with compound microbial powder. The compound microbial agent comprises bacillus cereus ACCC03288 powder, trichoderma harzianum ACCC30371 powder, pseudomonas chlororaphis ACCC19853 powder, paecilomyces lilacinus ACCC30639powder and thorn spore streptomyces hygroscopicus ACCC40018 powder. The growth and reproduction of apple ring rot germs are synergistically inhibited, nutrition support is provided for apple trees, and the growth of apples is promoted. The gel carrier is obtained by utilizing a cross-linking reaction of acrylamide and sodium acrylate, cross-linking sodium alginate and calcium chloride and introducing polyvinyl alcohol, can be naturally degraded, has a slow release effect on the compound microbial powder, and provides nutrition support for the microbial growth, so that the compound microbial powder has a better control effect. The microbial agent only needs to be applied once, thereby reducing the labor intensity.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION SHANDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Genetic engineering strain for producing DHHA (2,3-dihydro-3-hydroxyanthranilic acid) and application thereof
InactiveCN106754590AEfficient synthesisRaise the level of fermentationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMetaboliteOrganic synthesis
The invention discloses a genetic engineering strain for producing DHHA (2,3-dihydro-3-hydroxyanthranilic acid) and the application thereof. On the basis of pseudomonas chlororaphis HT66 CCTCC NO: M2013467 secreting phenazinyl-1-carboxamide, a gene phzF in genomes of the strain and derivatives thereof is knocked out in the phenazine synthesizing route, so that an intermediate metabolite DHHA is accumulated and a phenazine compound is not synthesized any more. The genetic engineering strain can be applied to the preparation of the DHHA. The DHHA can be used as an important organic synthetic intermediate and a chiral catalyst, and has an important application value. The genetic engineering strain is safe, reliable, good in stability and short in fermentation period, and is conducive to biosynthesis and industrial application of the DHHA.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Pseudomonas chlororaphis subsp.aurantiaca as well as preparation and application of microbial agent thereof
The invention discloses a pseudomonas chlororaphis subsp.aurantiaca as well as preparation and application of a microbial agent thereof. The pseudomonas chlororaphis subsp.aurantiaca 2501 disclosed bythe invention not only has a sterilization function, but also has an insecticidal function, and fills the blank that pseudomonas chlororaphis found at present only has a single biocontrol function. The invention also discloses a liquid microbial agent II of the pseudomonas chlororaphis subsp.aurantiaca 2501. The liquid microbial agent II comprises the following components: Tween 80, trehalose, sucrose, orange peel essential oil and a 2501 liquid microbial agent I; a solid microbial agent II of the pseudomonas chlororaphis subsp.aurantiaca 2501 comprises the following components: glucose, beanpulp powder, potassium fulvate and a 2501 solid microbial agent I; and the remarkable application effect is achieved through a field experiment.
Owner:山东五福生生态工程有限公司
Humic acid biological fertilizer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108640756ARich in nutrientsIncrease profitAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserAmmonium orthophosphate fertilisersPhosphateMonopotassium phosphate
The invention relates to humic acid biological fertilizer and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the field of fertilizer. The humic acid biological fertilizer is mainly prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: humic acid, a biological bacterium agent, auxin, cytokinin, active small peptide, potassium dihydrogen phosphate, potassium sulfate, urea, borax and a microcapsule enzyme. The biological bacterium agent is prepared from streptomyces jingyangensis, bacillus subtilis, trichoderma koningii, acetobacter diazotrophicus, pseudomonas fluorescens and pseudomonas chlororaphis. An enzyme in the microcapsule enzyme is prepared from nitrate reductase, metalloprotease and anti-oxidization dismutase. The humic acid biological fertilizer provided by the invention has abundant nutrient elements; the utilization rate of all nutrient substances is high and the humic acid biological fertilizer is applicable to various crops; the yield and quality of the crops can be effectively improved, and the humic acid biological fertilizer is green and environmentally friendly. The preparation method of the humic acid biological fertilizer comprises the step of mixing the rawmaterials according to the ratio. The method is simple and easy to operate and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:李兴耀
Disease-resistant organic fertilizer microorganism inoculant
InactiveCN106007958AHas specificityExcrement fertilisersBioloigcal waste fertilisersEcological environmentCrop
The invention relates to a disease-resistant organic fertilizer microorganism inoculant. The disease-resistant organic fertilizer microorganism inoculant is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 5 to 10 parts of bacillus thuringiensis, 5 to 10 parts of bacillus amyloliquefaciens, 5 to 10 parts of streptomyces microflavus, 3 to 5 parts of thermophilic sporotrichum, 3 to 5 parts of pseudomonas chlororaphis, 20 to 40 parts of modified zeolite powder, 1.5 to 5 parts of fulvic acid potassium powder, 0.5 to 5 parts of sodium alga acid, 0.5 to 1 parts of water-retaining agent, 1 to 3 parts of polyaspartic acid, 3 to 6 parts of corn starch, 0.5 to 3 parts of tea saponin, 0.5 to 2 parts of complex enzyme preparation, 1 to 5 parts of sodium lignin sulfonate, 0.5 to 1 parts of citric acid, and 0.5 to 1 parts of sodium hydrogen sulfite. The disease-resistant organic fertilizer microorganism inoculant has the advantages that the disease-resistant property and immunity of crops are improved, the soil is loosened, the ecological environment is improved, the pesticide residue and macromolecule organic matter are effectively degraded, and the output and quality of crops are improved.
Owner:SHANDONG AIFUDI BIOLOGICAL TECH
Bacterial strain with effects of degrading inorganic phosphorus and antagonizing cytospora chrysosperma and application of bacterial strain
ActiveCN105950516AGrowth inhibitionPromote growthBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologyBacterial strain
The invention discloses a bacterial strain with effects of degrading inorganic phosphorus and antagonizing cytospora chrysosperma and application of the bacterial strain. The strain provided by the invention is pseudomonas chlororaphis XZL-8 and has the microbial preservation number of CGMCC NO.12555, wherein the pseudomonas chlororaphis XZL-8 is isolated from the rhizosphere soil of poplar, can decompose the insoluble inorganic phosphorus into rapid available phosphorus which can be absorbed and utilized by plants, can produce HCN, protease and esterase, and can prevent cytospora chrysosperma caused by cytospora chrysosperma; bacteriostatic volatiles produced by the pseudomonas aeruginosa can also inhibit the growth of cytospora chrysosperma. The pseudomonas chlororaphis XZL-8 is a biological control potential strain with capability to degrade phosphorus, excellent antagonistic effect, high control effect and good environmental safety, and has good prospects of development and application.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY +1
Genetic manipulation method of sacB-mediated Pseudomonas chlororaphis
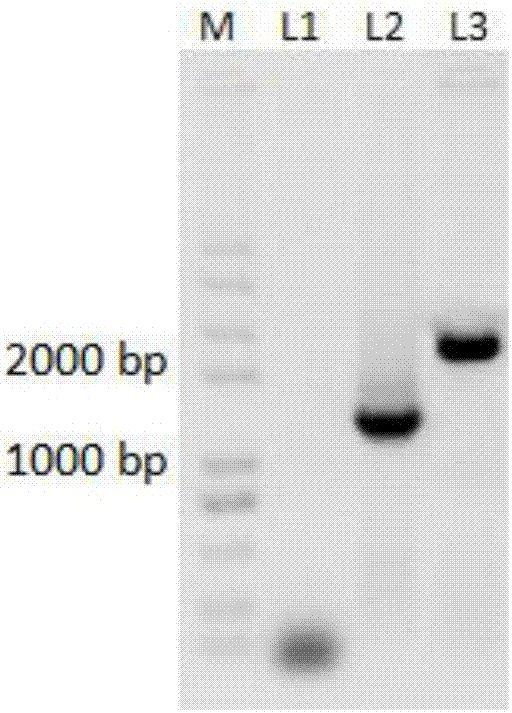
ActiveCN109913491AMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliWild type
The invention discloses a genetic manipulation method of sacB-mediated Pseudomonas chlororaphis and belongs to the technical field of biology. Pseudomonas chlororaphis is used as a start material; flanking sequences of upstream and downstream ends of a target gene are selected and subjected to gradient PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification respectively; two amplified fragments and conjugative suicide plasmid pEX18 are subjected to restriction digestion and connection respectively; a recombinant plasmid is constructed; the recombinant plasmid is converted to Escherichia coli and subjected to amphiphilic mating with wild Pseudomonas chlororaphis; deletion of the target gene is successfully achieved. The genetic manipulation method of sacB-mediated Pseudomonas chlororaphis is constructed successfully herein, which is suitable for acting mechanism and function researches for related genes and gene clusters of Pseudomonas chlororaphis antibacterial active materials.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Genetic engineering strain capable of highly producing phenazine-1-carboxylic acid, and construction method and applications thereof
ActiveCN112126611AIncrease productionPromote growthBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhenazineCarboxylic acid
The invention provides a genetic engineering strain capable of highly producing phenazine-1-carboxylic acid, and a construction method and applications thereof, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. Relatively safe pseudomonas chlororaphis Qlu-1 is taken as an original strain; phzO genes,binary regulation related genes and central carbon metabolism pathway regulation genes areknocked out in the Qlu-1 strain genome through a genetic engineering technology; and the corresponding genetic engineering strain is constructed, so that the yield of the phenazine-1-carboxylic acidcan be greatly increased, and the strain can be more effectively used for biological control. Through experimental verification, the genetic engineering strain QPCA-7 has excellent effects; PCA yieldcan reach up to 7854 mg / L; good growth performance can be achieved; and thus, the strain has good practical application values.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
Salvia miltiorrhiza bunge endophyte having phenolic acid accumulation inducing effect, and uses thereof
ActiveCN104830714APromote accumulationIncrease contentBiocidePlant growth regulatorsSalvia miltiorrhizaActive component
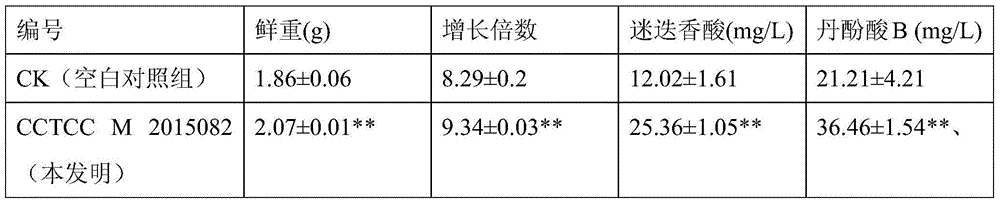
The present invention relates to a nature medicinal plant endophyte salvia miltiorrhiza bunge endophyte, and uses thereof, specifically to a salvia miltiorrhiza bunge endophyte, which is Pseudomonas chlororaphis LG1, and has the preservation number of CCTCC NO:M 2015082. The present invention further discloses the uses of the salvia miltiorrhiza bunge endophyte, wherein the salvia miltiorrhiza bunge endophyte can promote accumulation of phenolic acid substances in salvia miltiorrhiza bunge hairy roots. With the salvia miltiorrhiza bunge endophyte, the problems of low active component content and instable quality during the salvia miltiorrhiza bunge hairy root culture process can be solved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Specific strain and application thereof
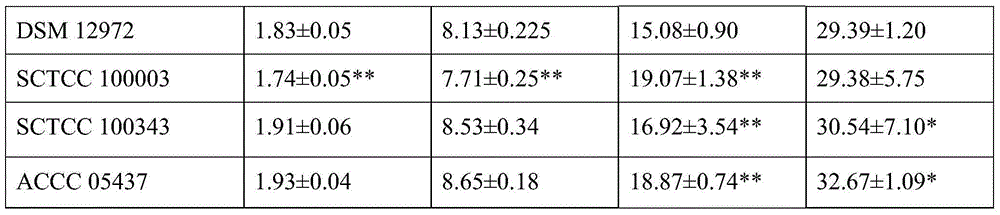
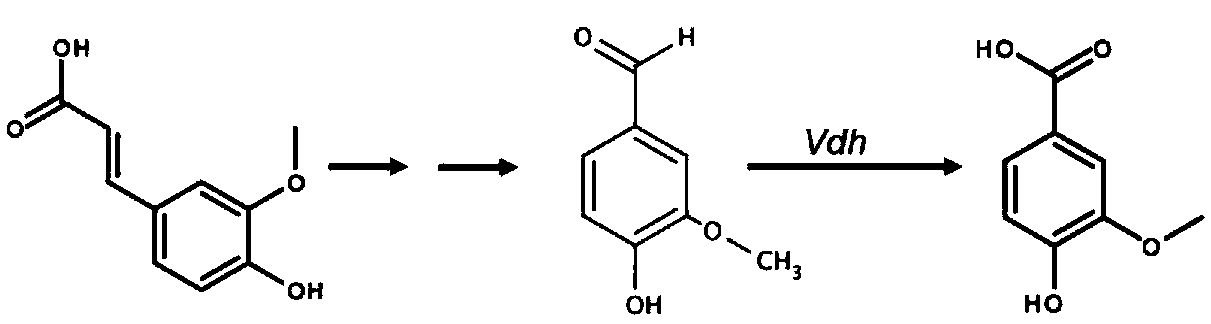
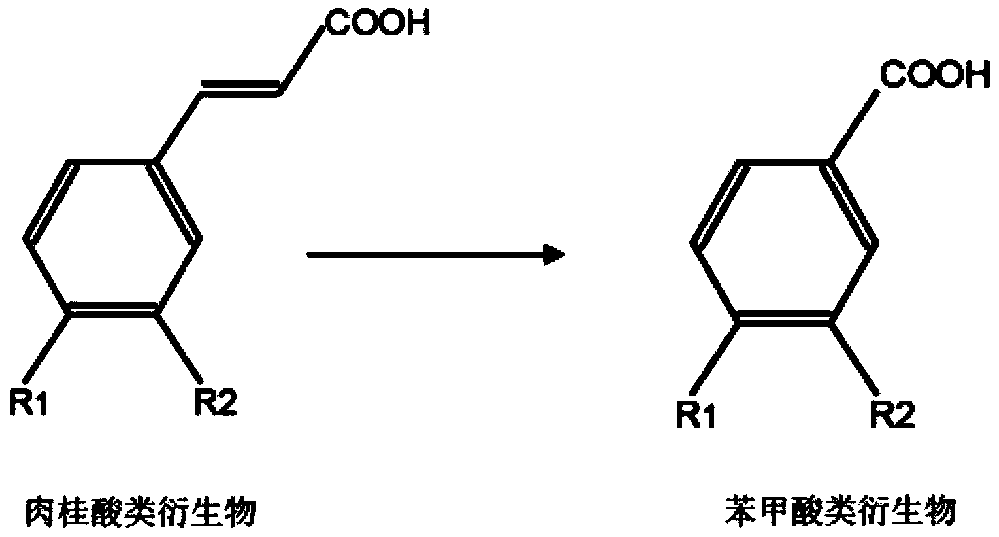
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, and particularly relates to a specific strain and application thereof. Pseudomonas chlororaphis can generate vanillic acid by using ferulic acid as substrate through biotransformation. Aspergillus niger having a preservation number of CCTCC NO:M 2016767 is obtained by screening, has the content of vanillic acid being more than 10g / L. The strain with higher specificity can directly utilize vegetation raw materials, and the concentration of vanillic acid can be 0.43g / L.
Owner:BOTON SHANGHAI BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
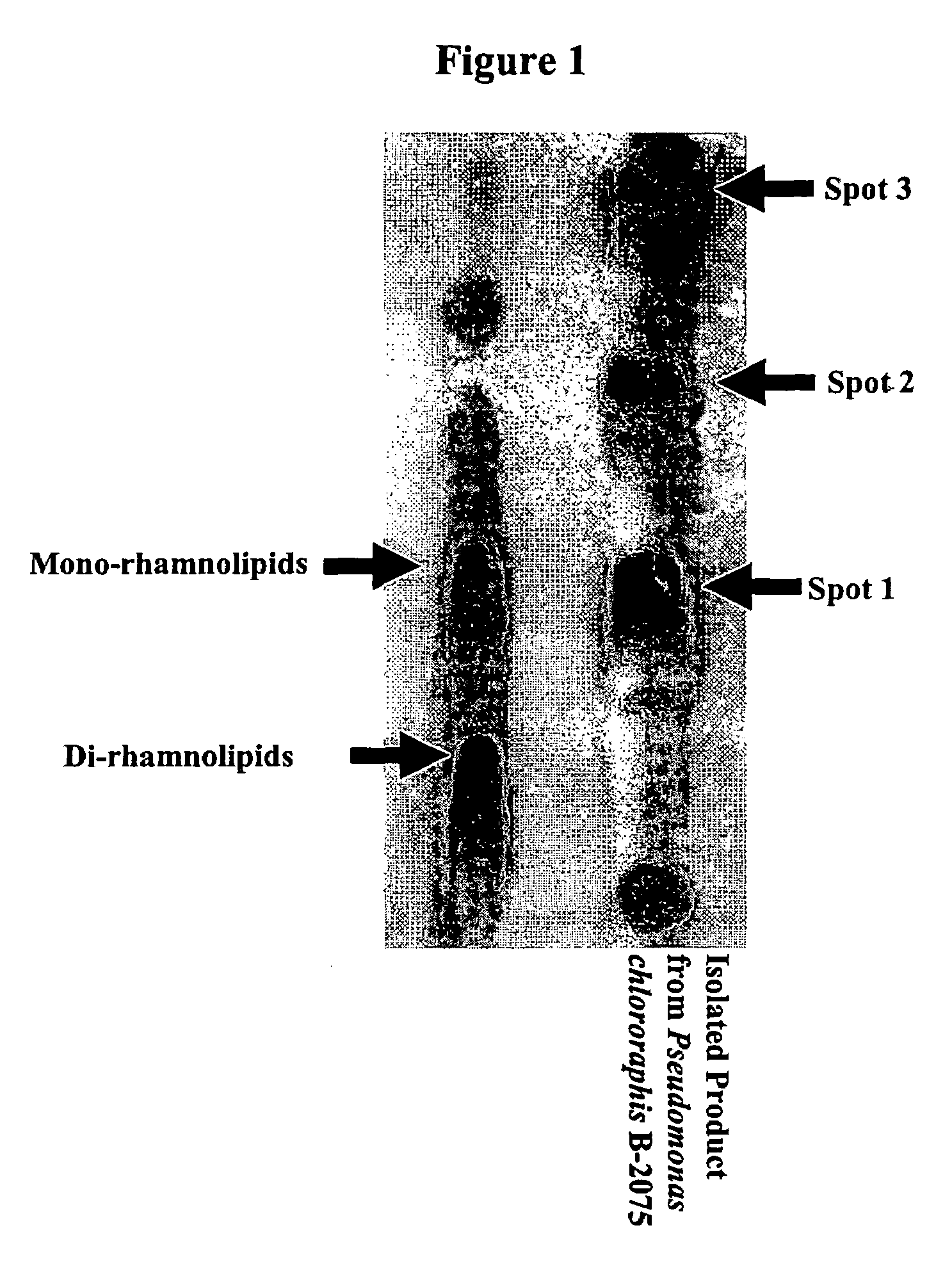
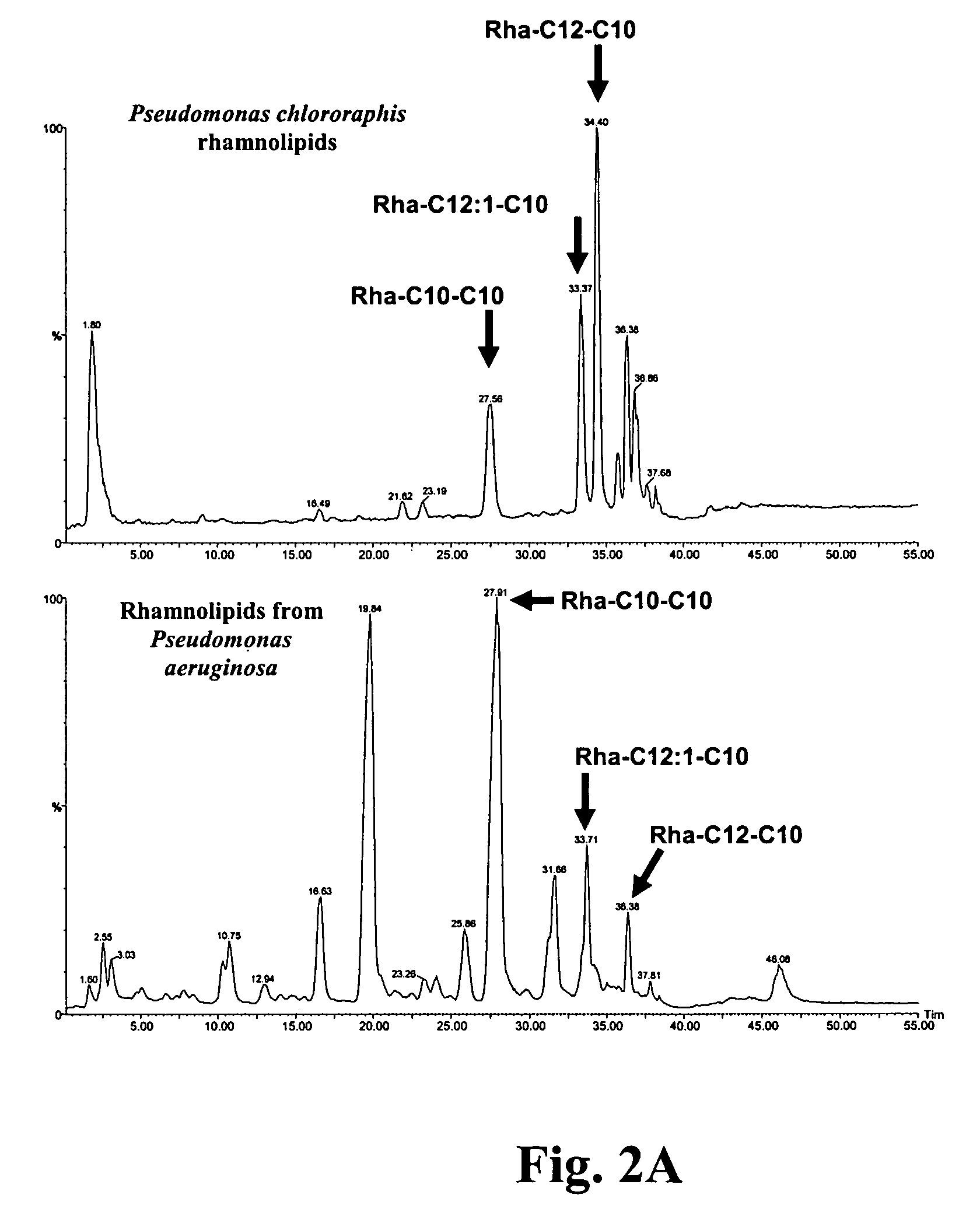
Production of dirhamnose-lipid in recombinant nonpathogenic bacterium Pseudomonas chlororaphis
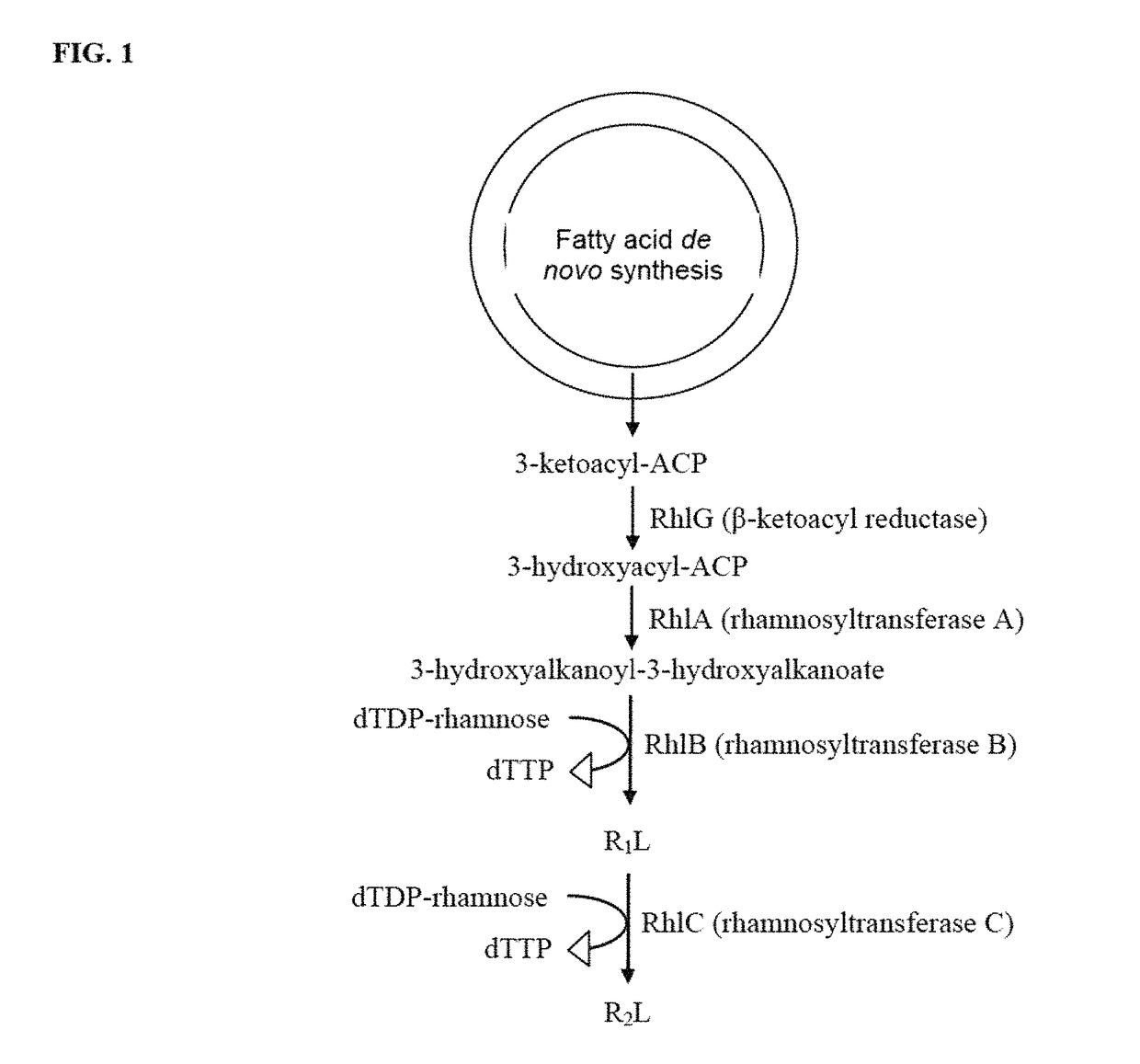
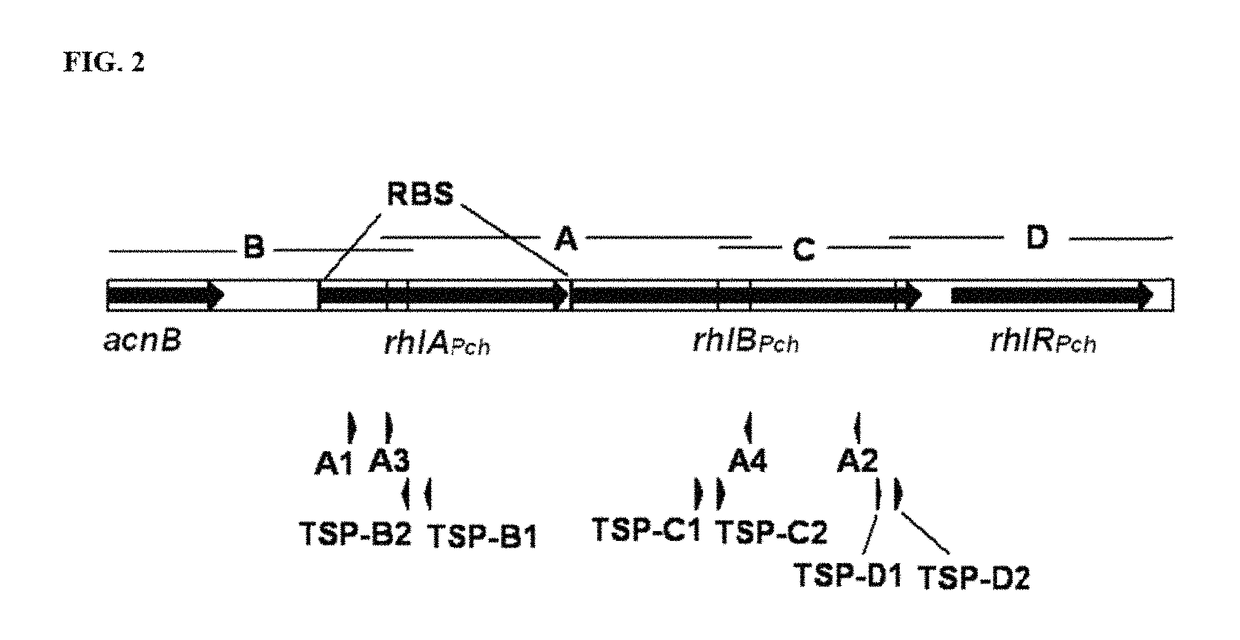
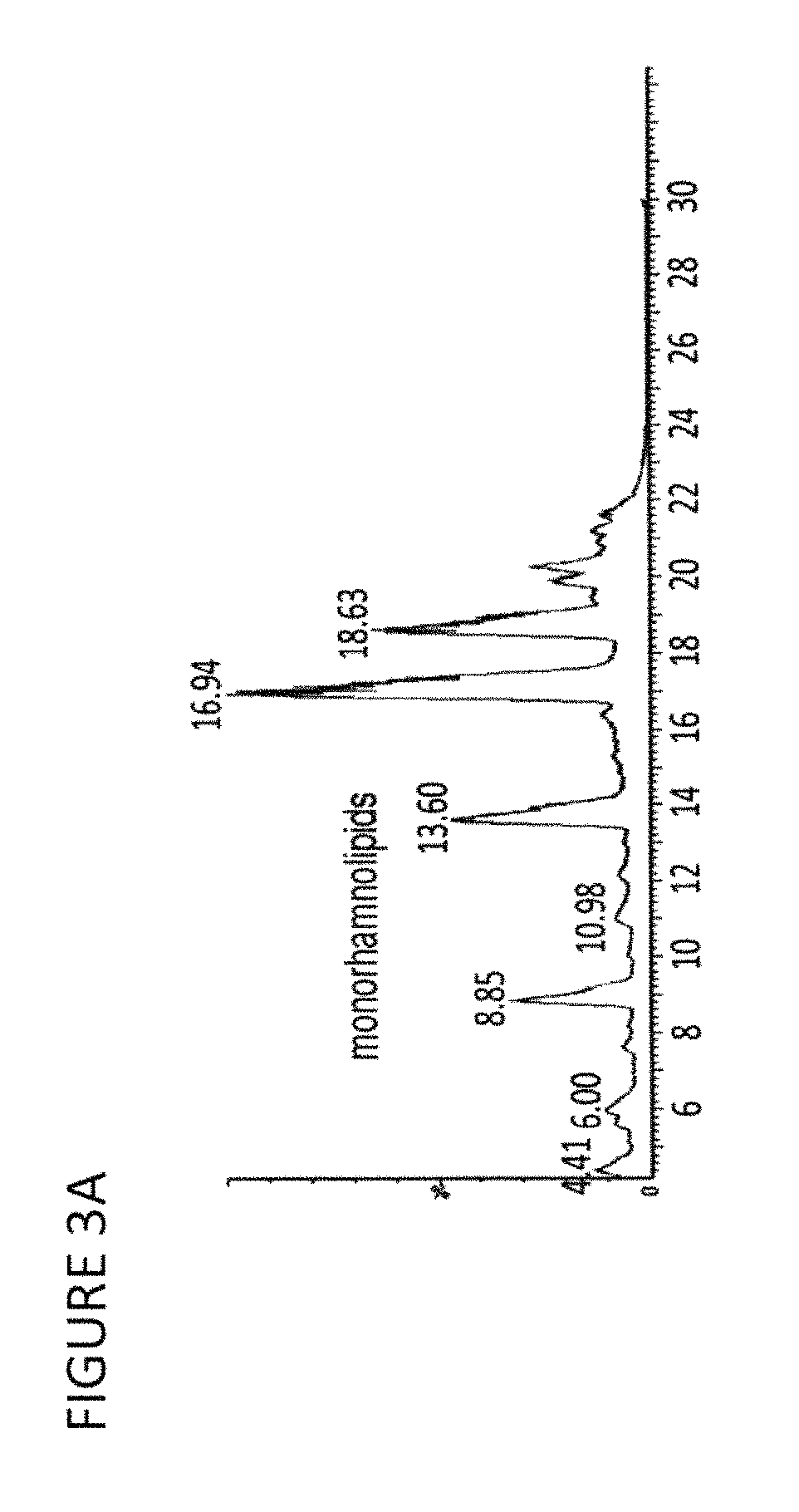
Pseudomonas chlororaphis NRRL B-30761 produces monorhamnolipids with predominantly 3-hydroxydodecenoyl-3-hydroxydecanoate (C12:1-C10) or 3-hydroxydodecanoyl-3-hydroxydecanoate (C12-C10) as the lipid moiety under static growth conditions. The cloning and sequencing of three genes and proteins involved in the biosynthesis of monorhamnose-lipid (R1L) is described. Expression of two of these genes, i.e., rhlA and rhlB, together in P. chlororaphis NRRL B-30761 increases R1L production by at least 10-fold. Also the generation of a recombinant P. chlororaphis NRRL B-30761 capable of synthesizing dirhamnose-lipid (R2L) is described. Characterization of R1L and R2L produced by the recombinant P. chlororaphis NRRL B-30761 is also described.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Pseudomonas chlororaphis and culture method and applications thereof
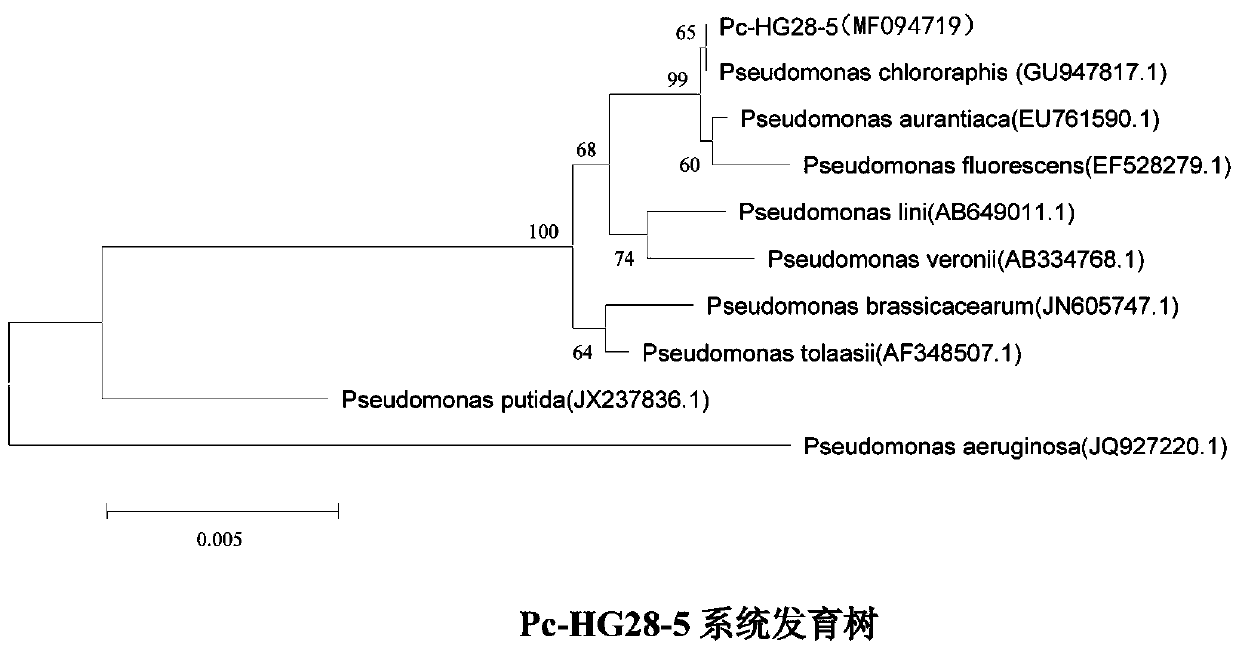
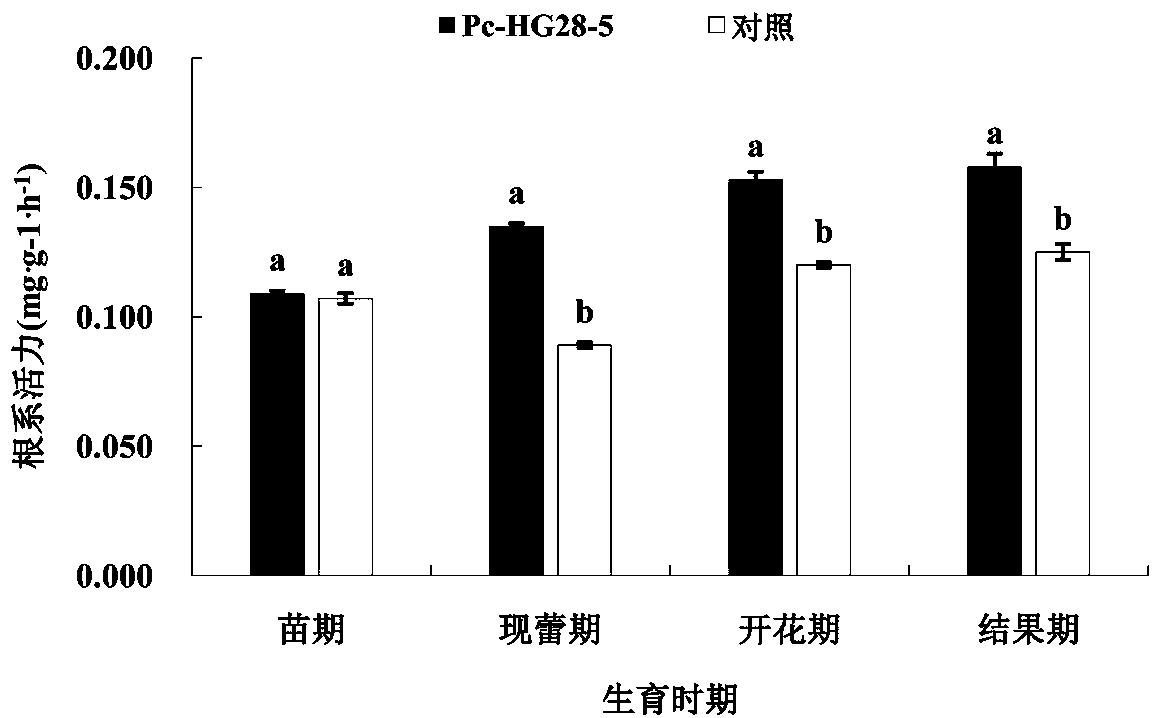
ActiveCN110144301AInhibition of germinationPrevent intrusionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPlant growthCulture mediums
The invention provides pseudomonas chlororaphis. The pseudomonas chlororaphis is pseudomonas chlororaphis Pc-HG28-5, and is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, wherein the preservation number is CGMCC No.14208. The pseudomonas chlororaphis is a plant growth promoting rhizobacterium which is separated and screened out from wheat roots, and can be cultured in apeptone culture medium. The pseudomonas chlororaphis can reduce a side effect of a seed coating agent, prevent epidemic disease, and reduce the number of harmful fungi in plant rhizosphere soil.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Breeding method of strain with high yield of phenazine-1-formamide based on genome shuffling
InactiveCN106399158AIncrease productionImprove the efficiency of restructuringBacteriaMutant preparationGenome shufflingPhenazine
The invention relates to a breeding method of a strain with high yield of phenazine-1-formamide based on genome shuffling. The breeding method comprises the following steps: by taking pseudomonas chlororaphis HT66 as an initial strain, carrying out mutagenesis treatment, thus obtaining a genome library containing various different positive mutations, and screening out a plurality of mutant strains with high PCN yield; and carrying out protoplast preparation and protoplast fusion on the mutant strains, and screening out fusants with high PCN yield. The breeding method has the beneficial effects that the mutant strains of pseudomonas chlororaphis HT66 are screened by adopting the method combining mutagenesis treatment with the genome shuffling technology, the relevant parameters of protoplast preparation and fusion are optimized, the genome shuffling efficiency is improved, the strain with high yield of phenazine-1-formamide is obtained, and compared with that of the initial strain, the yield of phenazine-1-formamide of the obtained strain is improved by 2.8 times to the maximum. The method provided by the invention is easy to operate, and the parent strain does not need to be labeled, so that the labor cost is greatly reduced, and the screening period is shortened.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com