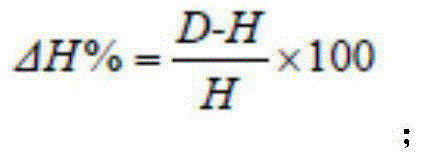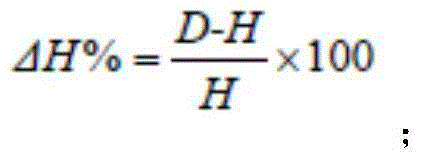Method for analyzing root domain soil microbial community structure of soft-rot diseased amorphophallus konjac plant
A soil microbial and community structure technology, applied in the field of soil microbial community structure analysis in the root zone of konjac soft rot plants, can solve the problems of unreported micro-ecological mechanisms and few studies on community structure changes.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0030] The technical solutions of the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with specific embodiments.
[0031] 1.1 Materials
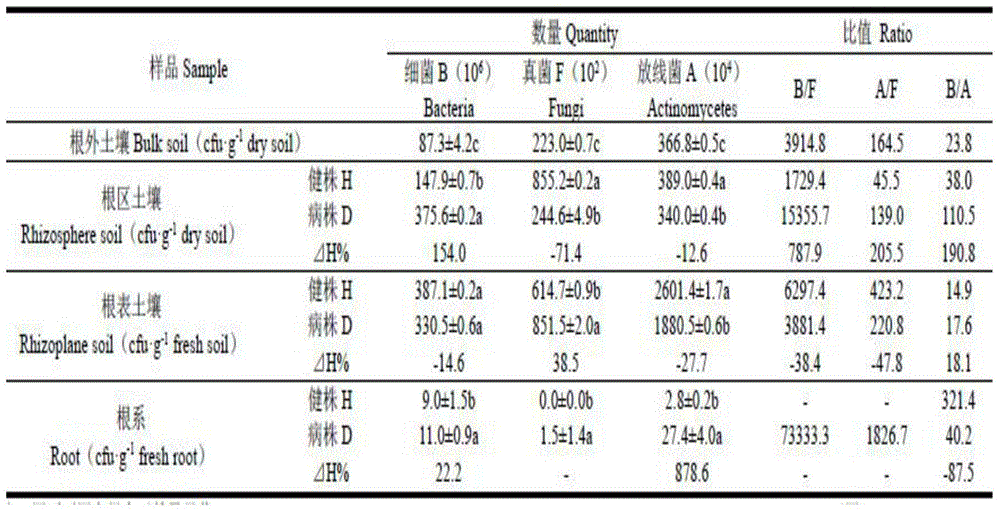
[0032] Samples for testing: 2011-08-2, in the konjac planting base of the 4th year of continuous cropping in Lixin Village, Linhe Township, Langao County, Shaanxi Province, the health (Healthy, H) and typical soft rot symptoms (Diseased, D) For the whole plant of Konjac and its BulkSoi, Rhizosphere Soil, Rhizoplane Soil and Root, the sample collection and processing refer to the method of Zhou Yongqiang et al.
[0033] Medium: beef extract peptone (BPA), potato sucrose (PDA) and Gao's No. 1 medium (GA)
[0034] 1.2 Method
[0035] 1.2.1 Separation and counting of microorganisms: the number of microorganisms was separated and counted by the dilution plate smear method. Bacteria, fungi and actinomycetes were respectively used beef extract peptone, potato sucrose and Goose No. 1 agar medium, each with 3 dilutions, each dil...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com