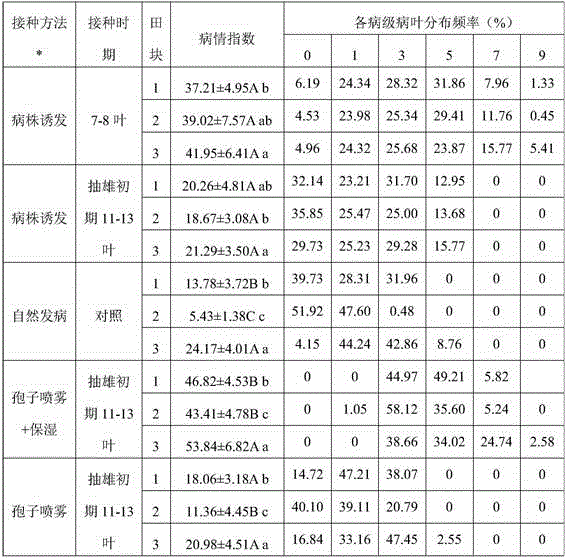
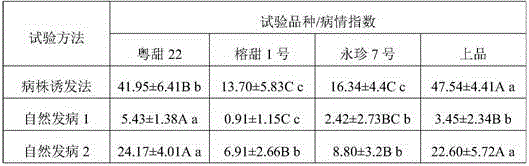
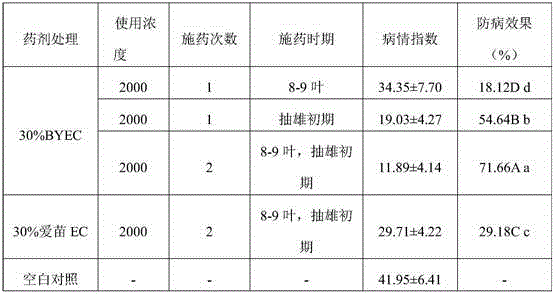
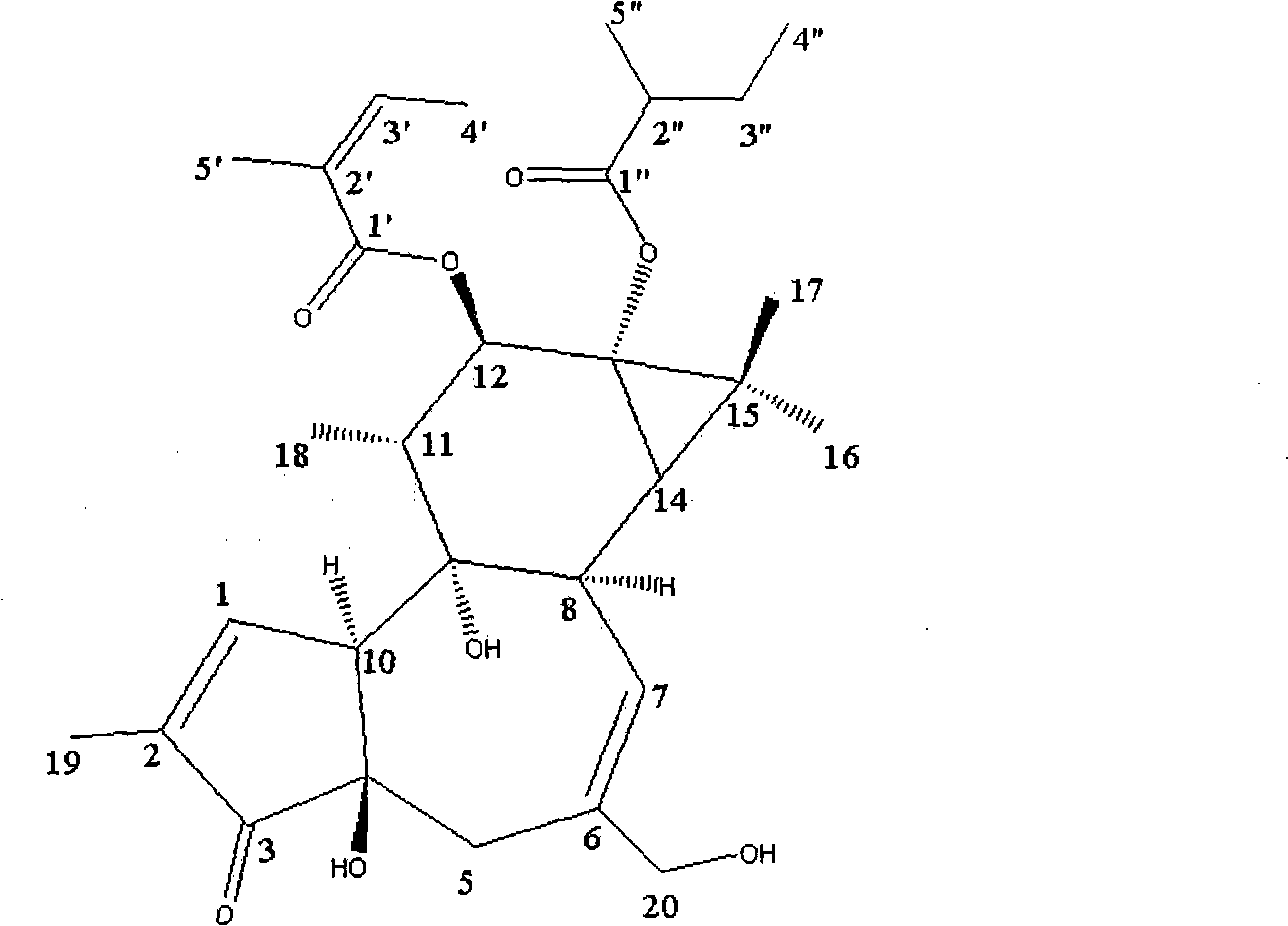
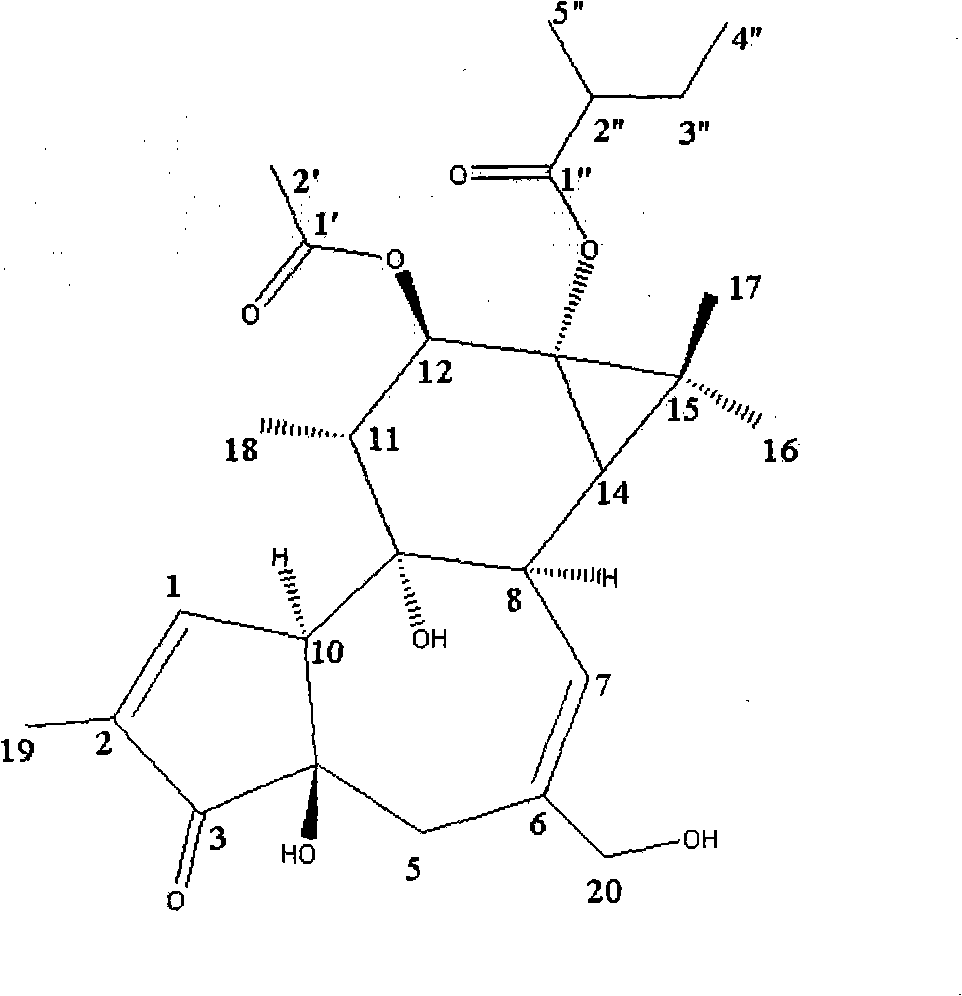
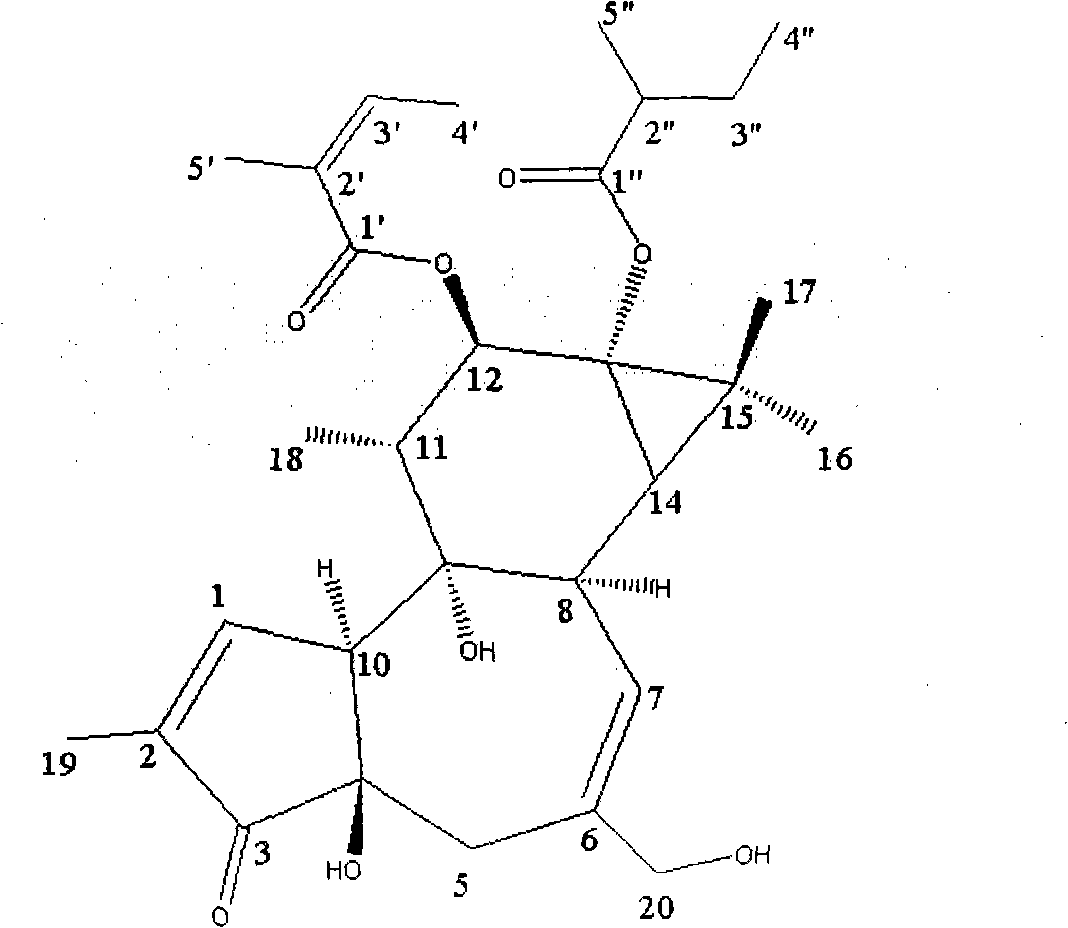
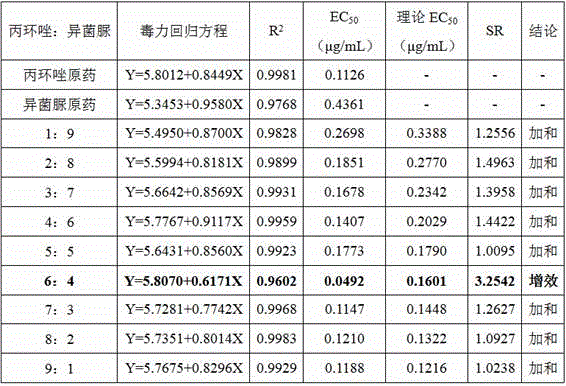
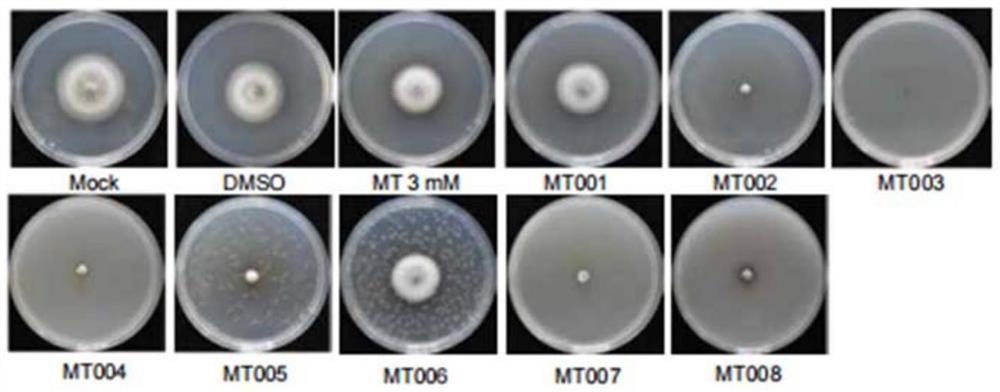
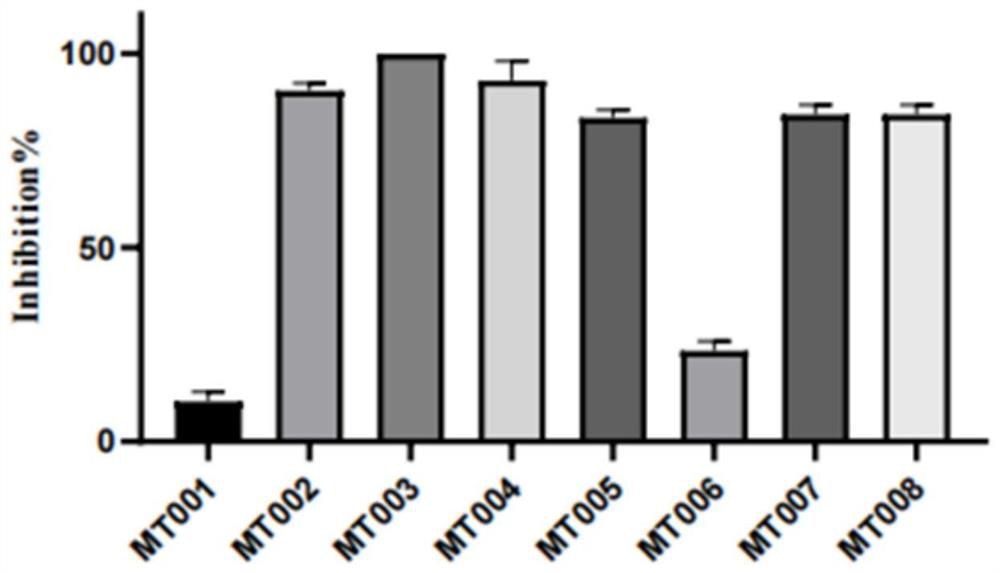
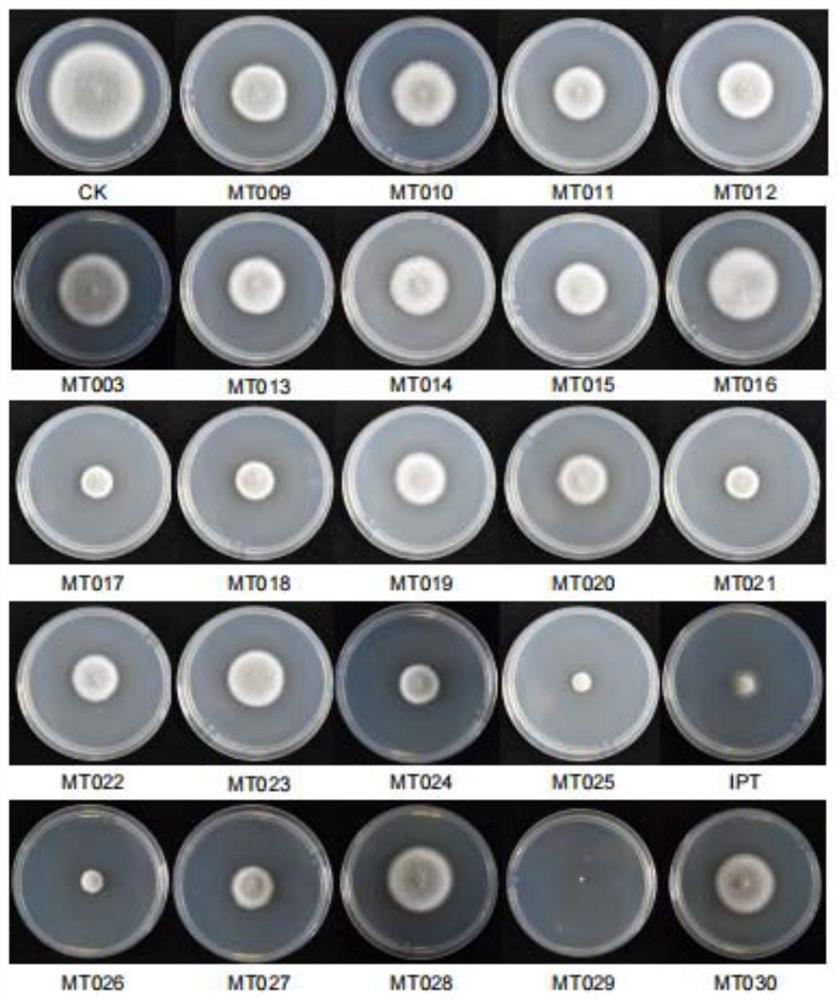
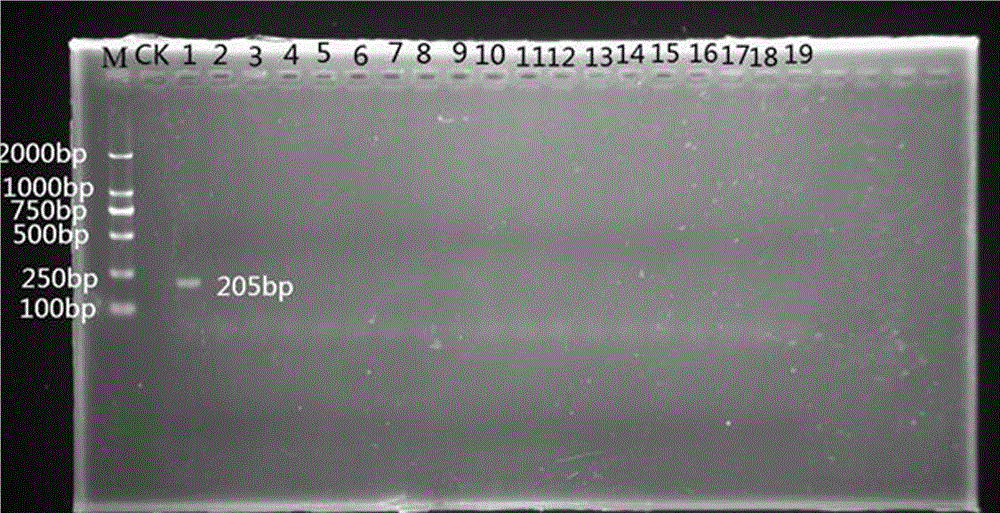
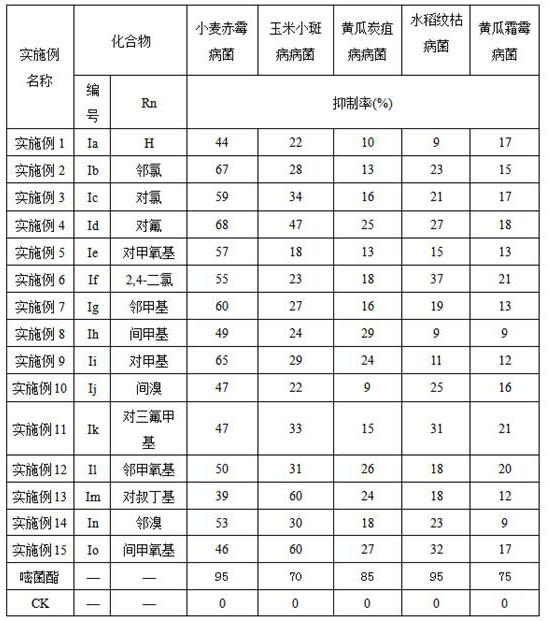
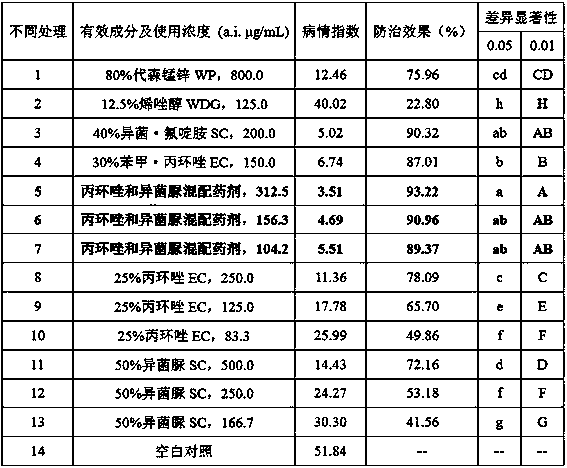
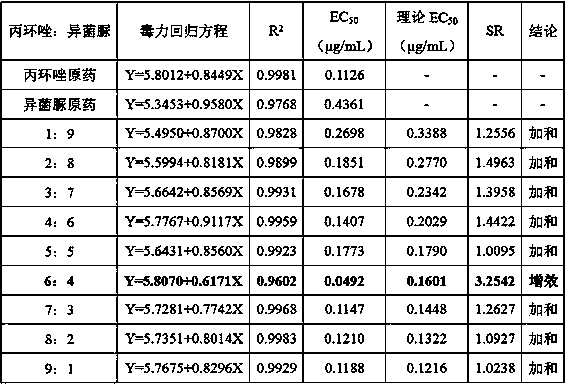
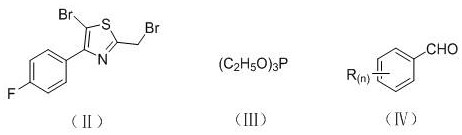Patents
Literature
48 results about "Bipolaris maydis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
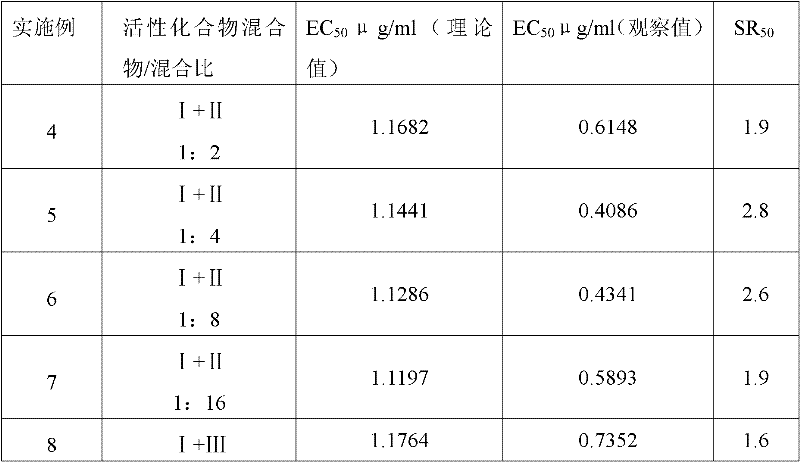
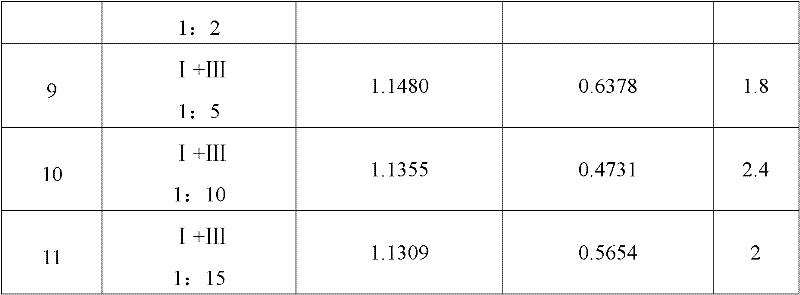
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Southern corn leaf blight (SCLB) is a fungal disease of maize caused by the plant pathogen Bipolaris maydis (also known as Cochliobolus heterostrophus in its teleomorph state). The fungus is an Ascomycete and can use conidia or ascospores to infect.
Pseudomonas chlororaphis for preventing and treating crop fusarium disease and applications thereof
The invention provides pseudomonas chlororaphis for preventing and treating the crop fusarium disease and applications thereof. The preservation number of the pseudomonas chlororaphis is CGMCC No. 7729. The Pcho01 bacterium strain of the pseudomonas chlororaphis has a high effective antagonistic action, is capable of being applied to the preventing and treating wheat scab caused by fusarium, and the preventing and treating efficiency in the field is maintained above 60%. The Pcho01 bacterium strain also has a very good antagonistic action on botrytis cinerea, rice sheath blight fungus, bipolaris maydis, pythium wltmum, rhizopus, and pseudomonas solanacearum, and can be used to prevent and treat the diseases caused by those bacteria mentioned above.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Alpine grassland pasture endogenous serratia plymuthica strain GH010 and application thereof as well as microbial agent prepared from same and preparation method
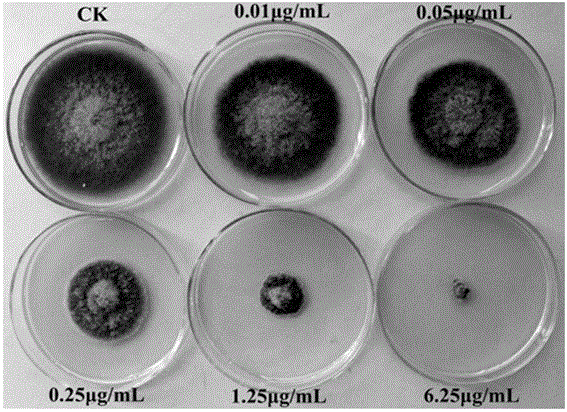
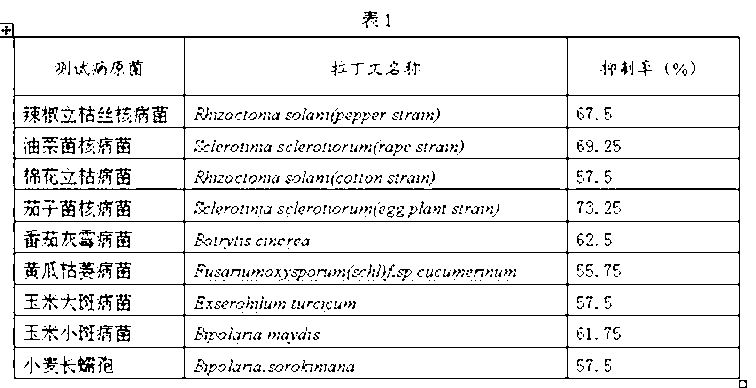
The invention discloses an alpine grassland pasture endogenous serratia plymuthica strain GH010 capable of inhibiting various pathogenic bacteria and discloses a microbial agent prepared from the alpine grassland pasture endogenous serratia plymuthica strain GH010 and a preparation method thereof. The alpine grassland pasture endogenous serratia plymuthica strain GH010 and the microbial agent prepared from the same disclosed by the invention have the beneficial effects of having good inhibition effects on the various pathogenic bacteria; the inhibition effect is 67.5% of chili rhizoctonia solani and 69.5% of rape sclerotinia sclerotiorum; the bacteriostasis rates of cotton rhizoctonia solani, eggplant sclerotinia sclerotiorum, tomato botrytis cinerea, fusarium wilt of cucumber, exserohilum turcicum, bipolaris maydis or bipolaristriticola are more than or equal to 57.5%; and the strain has growth-promoting effects on crops including alfalfa and the like, and the environmental protection properties of a microbial pesticide and a microbial fertilizer prepared from the strain are good, the resistance to drugs is unlikely to generate and the safety is good.
Owner:GANSU AGRI UNIV
Sterilization composite containing metalaxyl-M and application thereof
ActiveCN102204550ASynergisticIncrease productionBiocideFungicidesPhytophthora sp.Exserohilum species
The invention discloses a sterilization composite containing metalaxyl-M and application thereof. The sterilization composite containing metalaxyl-M comprises two active components A and B, the component A is metalaxyl-M and the component B is propineb or metiram. The composite is efficient, safe and environmentally-friendly, has synergy, can be used for increasing crop production and fruit quality and lowering cost and is beneficial to the postponement of the generation of drug resistance of harmful bacteria. The composite also can be used for preventing and controlling crop banded sclerotial blight, damping off, root rot, rice blast, exserohilum turcicum, bipolaris maydis, downy mildew, phytophthora blight, leaf spot, gray mold, alternaria leaf spot, anthracnose, ring spot, powdery mildew, Leptosphaeria maculans and late blight.
Owner:JIANGSU BAOLING CHEM
Preparation method and use of agricultural bactericide containing parthenolide
ActiveCN105815326AStrong inhibitory activityRaw materials are easy to getBiocideDead animal preservationPlant diseasePollution
The invention relates to a botanical pesticide bactericide and a preparation method thereof. The bactericide is obtained through extracting whole herb of Dendranthema lauandulifolium and through processing. Main active components of the bactericide comprise 5-20wt% of parthenolide, water and a surfactant, and are processed to prepare an emulsion in water, and the emulsion in water is used to prevent and control various crop diseases after being diluted. The bactericide has the advantages of easily available raw materials, simple process, low cost, good prevention and control effect on rice bacterial leaf blight, rice bacterial streak, Bipolaris maydis and other diseases, high safety to crops, and no pollution to environment, and is a biological pesticide preparation suitable for Chinese nuisance-free agricultural product production requirements.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY JIANGSU PROVINCE & CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
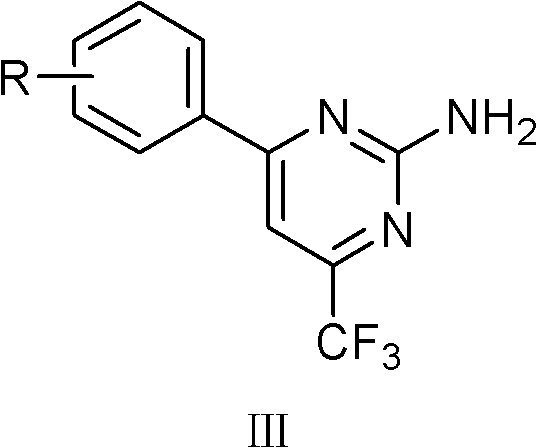
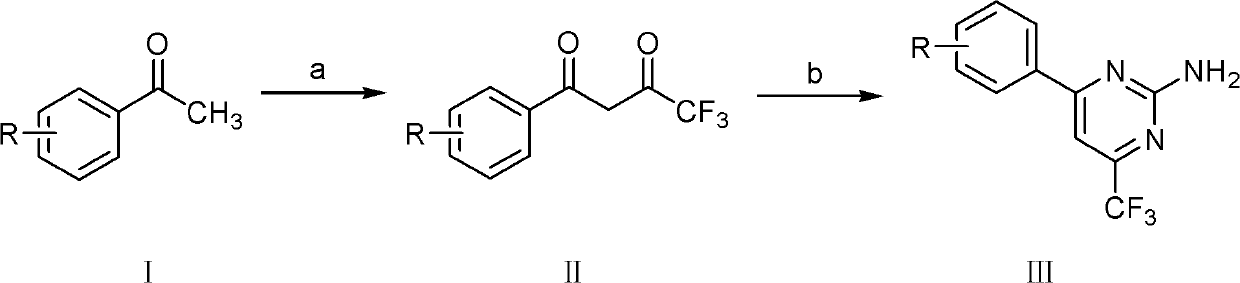
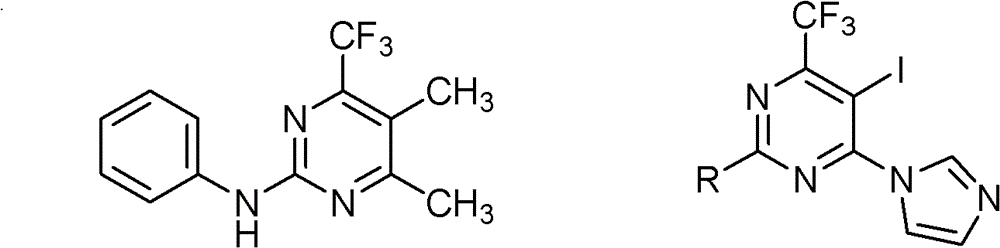
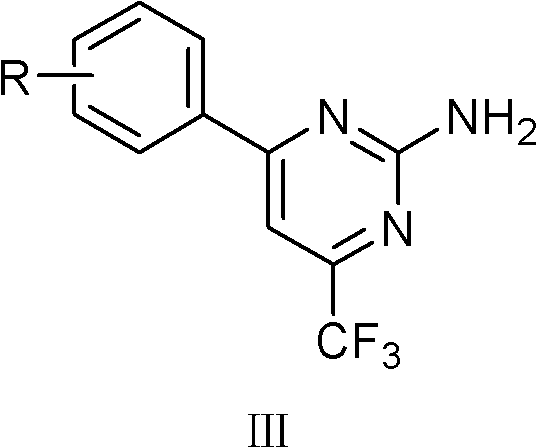
Trifluoromethyl-containing pyrimidinamine compound, preparation method thereof, and application of trifluoromethyl-containing pyrimidinamine compound used as bacteriacide
The invention relates to a 4-substituted phenyl-6-trifluoromethyl-2-amino pyrimidinamine compound which has a novel chemical structure and a general formula III, a synthesis method for the compound and the application of the compound used as bacteriacide. The method comprises the following steps of: reacting substituted phenyl methyl ketone used as an initial raw material and trifluoroacetic acid ethyl ester under catalysis of sodium alcoholate to generate 4,4,4-trifluoro-1-substituded phenylbutane-1,3-diketone, and reacting 4,4,4-trifluoro-1-substituded phenylbutane-1,3-diketone and guanidinium salt under an alkaline condition to generate a III series compound with the general formula III. The compound with the general formula III can inhibit growth of pathogenic bacteria such as rice sheath blight, rice bakanae disease, exserohilum turcicum, bipolaris maydis, curvulavia lunata, corn kernel rot, corn top rot pathogenic bacteria, fusarium graminearum, cotton anthracnose, bean fusarium, rape sclerotinia rot, botrytis cinerea, cucumber fusarium wilt pathogenic bacteria, cucumber brown rot pathogenic bacteria, cucumber scab pathogenic bacteria, hot pepper root rot pathogenic bacteria, kidney bean anthracnose bacteria, and pythium aphanidermatum. In the formula III, R is methyl, ethyl, methoxy group, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, trifluoromethyl and other groups, and the number of R is 1 to 3.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
Bacillus subtilis and application thereof to prevention and treatment of bipolaris maydis
The invention discloses bacillus subtilis and application thereof to prevention and treatment of bipolaris maydis. The strain of the bacillus subtilis for preventing and treating bipolaris maydis is DZSY21, the preservation name is bacillus subtilis, the bacillus subtilis is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) which is located in #3, No.1 Courtyard, West Beichen Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, the preservation date is November 27, 2015, and the preservation No. is CGMCC NO.11749. The 16S rDNA gene sequence of the bacillus subtilis is a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID No.1, and the gyrB gene sequence of the bacillus subtilis is a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID No.2. The bacillus subtilis is high in growth speed, large in sporulation quantity, good in stress resistance and good in antibacterial property, and can be quantitatively colonized in leaves of corn plants.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Corn southern leaf blight field natural inducement technology and application of technology
InactiveCN106416654AEasy to getFully reflect the ability to resist diseases and expand vertically upwardsPlant cultivationCultivating equipmentsDiseased plantPlastic mulch
The invention relates to the technical field of crop disease research, in particular to a corn southern leaf blight field natural inducement technology and application of the technology. The technology basically includes the steps that plastic film mulching is conducted; individual core seedlings which all have 3-4 leaves and 1 core are planted in two rows, wherein the line spacing is 0.4-0.5 m; in the stage when each corn plant in the field has 7-8 leaves, fresh corn southern leaf blight diseased plants artificially inoculated in a greenhouse serve as a field inducement bacterium source and horizontally placed on moist surfaces between the corn plants, and field normal irrigation is used for keeping soil moist. The infected corn southern leaf blight diseased plants which are artificially inoculated serve as the inducement bacterium source, operation is easy, and the inducement bacterium source is easy to obtain. The structure of the inducement bacterium source is similar to that of a wild bipolaris maydis population, and the pathogenic ability is reliable. Good and stable pathogen conditions can be provided. The technology is applicable to corn southern leaf blight resistance screening of corn germplasm and also applicable to screening of disease prevention insecticides and technical research.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION FAAS
Maize sheath surface paenibacillus polymyxa strain and application thereof
ActiveCN112322555ABlight control effect is obviousBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBiotechnologyPaenibacillus polymyxa
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological prevention and control of maize diseases, and discloses a maize sheath surface paenibacillus polymyxa strain and application thereof. The maize sheath surface paenibacillus polymyxa strain disclosed by the invention is paenibacillus polymyxa SF05; the strain is collected in China Center for Type Culture Collection on July 31, 2020, the collection number is CCTCC NO: M 2020384, and the collection address is Wuhan University, Wuhan, China. The maize sheath surface paenibacillus polymyxa strain can effectively inhibit the growth of rhizoctonia solani, exserohilum turcicum, bipolaris maydis and fusurium verticillioides, and can induce up-regulation of the expression level of maize disease resistance-related genes, enhances maize disease resistance, and can effectively control the maize sheath blight in production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
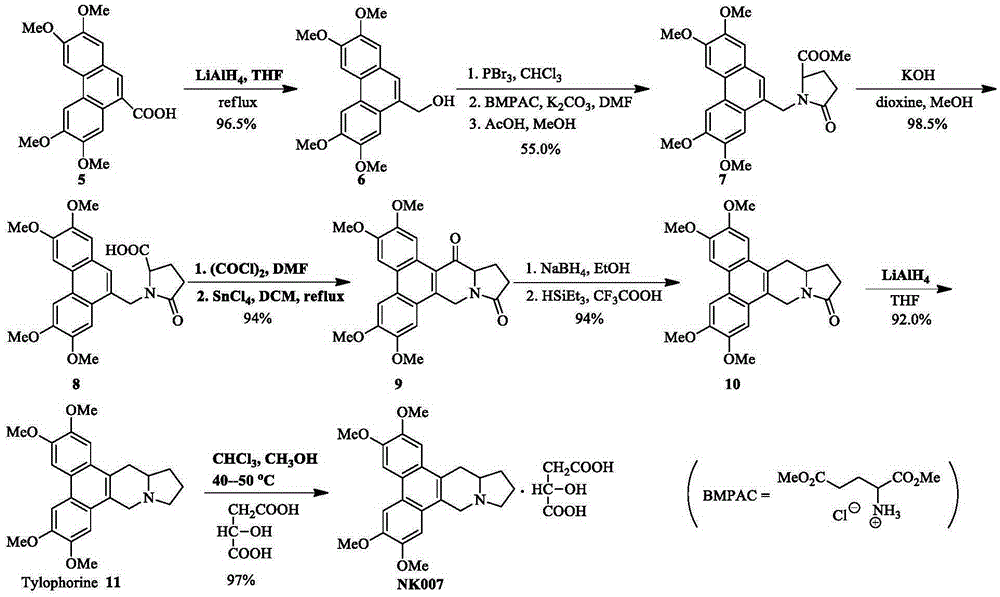
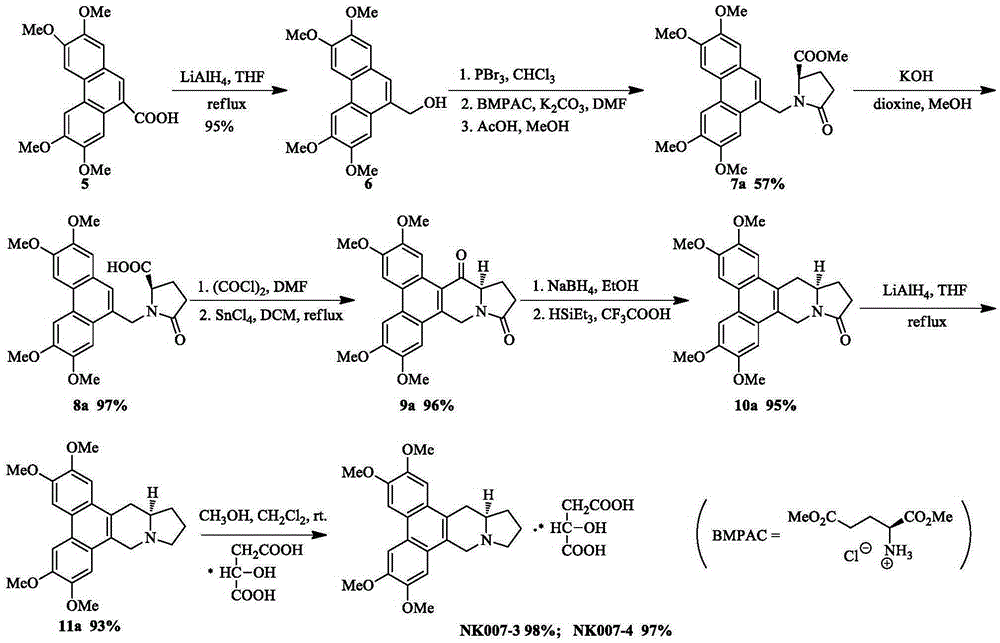
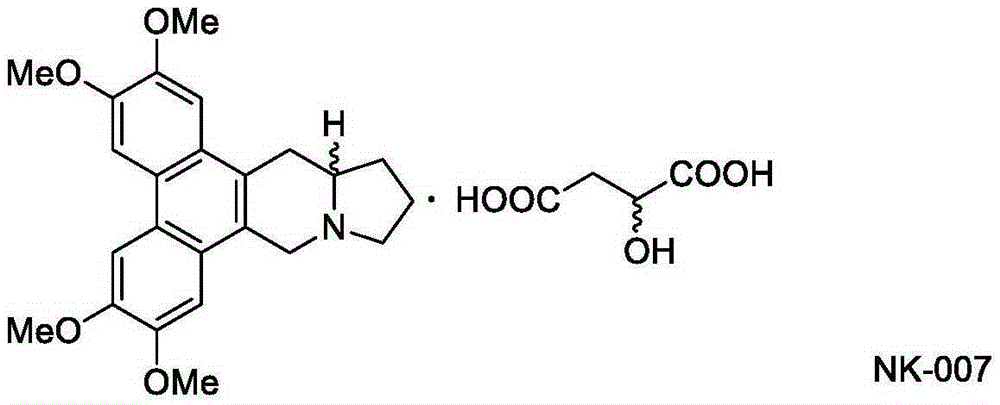
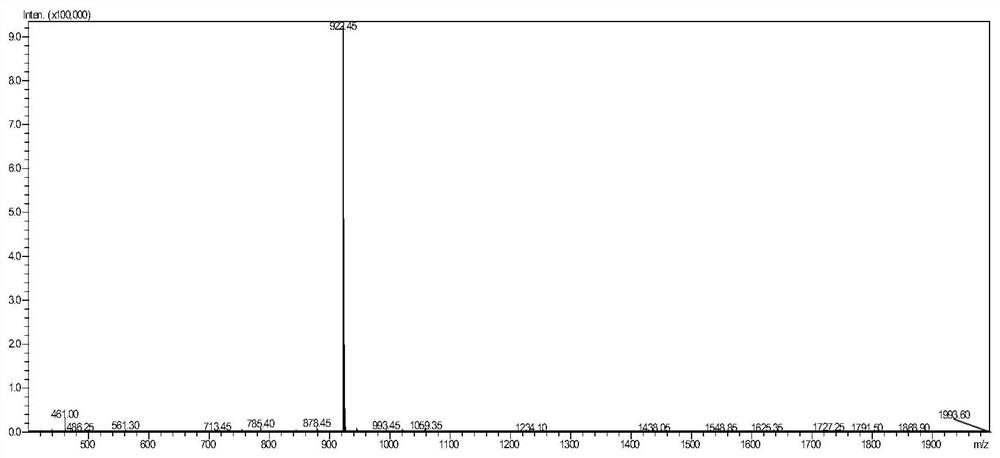
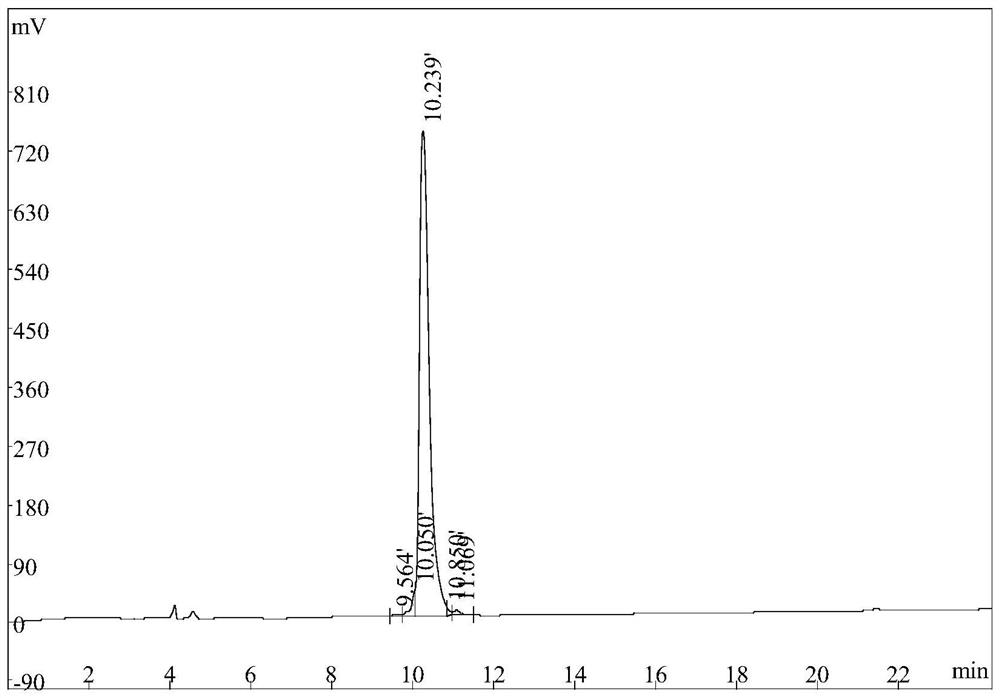
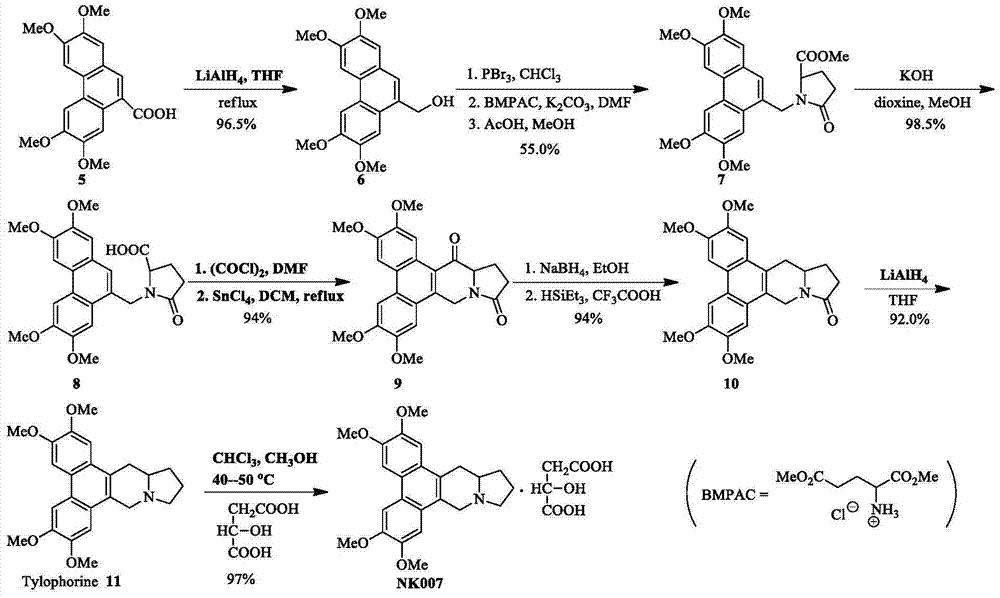
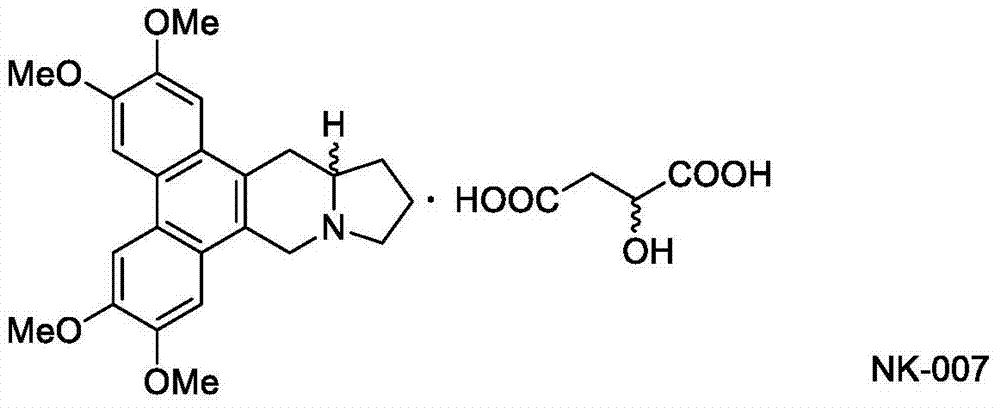
Two optically pure isomers of NK007 and bactericidal applications
The invention relates to two optically pure isomers of NK007 for short and applications in a bactericidal aspect. Compounds NK007-3 and NK007-4 have good bactericidal activity, can be used for treating plant bacteria diseases selected from fusarium wilt of cucumber, cercospora brown spot of peanut, apple ring spot, alternaria solani, puccinia polysora, rice bakanae disease, sclerotinia rot of colza, phytophthora capsici disease, wheat sharp eyespot, bipolaris maydis, watermelon anthracnose, potato late blight, rice sheath blight disease and cucumber gray mold.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Efficient disease-resistant authenticated inoculum for corn leaf blight and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108251497AGood for sporulationHigh sporulationMicrobiological testing/measurementSodium phosphatesGnat
The invention provides an efficient disease-resistant authenticated inoculum for corn leaf blight and a preparation method thereof. The inoculum comprises the following raw materials in proportion byweight: 100 g of sorghum, 0.20 to 0.25 g of magnesium sulfate, 0.20 to 0.25 g of sodium phosphate and 15 to 30 g of corn leaves. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) screening ofcorn leaf blight virulent bacterial strains; (2) storage of corn leaf blight virulent bacterial strains; (3) preparation of secondary cultures; (4) preparation of the inoculum; and (5) cultivation ofthe inoculum. The inoculum has the advantages that the obtained bacterial strains for authenticating corn leaf blight disease resistance are bacterial strains with high pathogenicity, high purity andhigh activity, and guarantees are provided for authenticating corn disease resistance inoculation; the work efficiency is greatly improved compared with a plate medium; the infection of gnats and infectious microbes is avoided, so that the high-quality inoculum finished product is obtained; the cultivation of the inoculum and a cultivation condition thereof are beneficial for generation of corn leaf blight germ conidium, so that the inoculum is high in spore formation speed, large in spore formation quantity and long in spore formation period.
Owner:GUANGXI AGRI VOCATIONAL COLLEGE
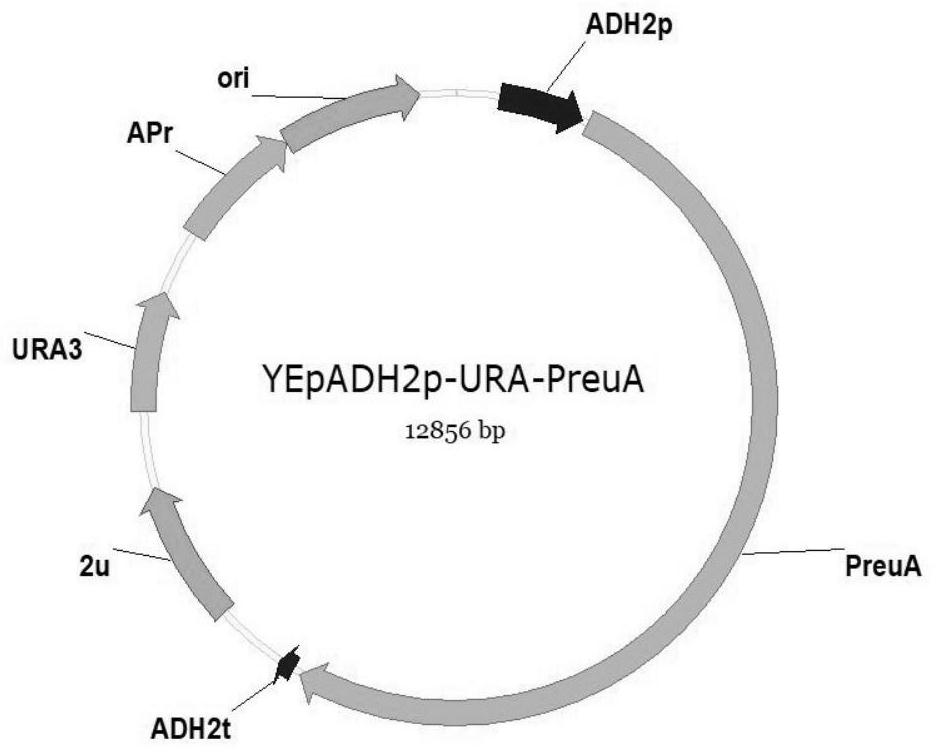
Polyketide synthase PreuA and application thereof in preparation of red powder moss acid
The invention relates to a polyketide synthase and an application thereof in preparation of red powder moss acid, and belongs to the technical field of microbial chemistry. According to the invention, the polyketide synthase PreuA related to synthesis of the rubrorubicacid is cloned from the phorbia fungus for the first time, and a yeast mutant strain capable of efficiently producing the rubrorubicacid is constructed based on a saccharomyces cerevisiae heterologous expression technology; and the prepared red powder moss acid is taken as an object, and the inhibitory activity of the red powder moss acid on seven kinds of crop pathogenic fungi is researched. Research finds that the red powder moss acid has different degrees of inhibition effects on four crop pathogenic fungi including apple ring spot bacteria, corn bipolaris maydis, potato verticillium wilt bacteria and sclerotium rolfsii, and has a very strong antagonistic effect (MIC, 25 [mu]g / mL) on the apple ring spot bacteria. The invention greatly enriches the production source of the red powder moss acid, and has important scientific value and application prospect for expanding the derivatization approach of the red powder moss acid and researching and developing novel biopesticides.
Owner:SOUTH CENTRAL UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
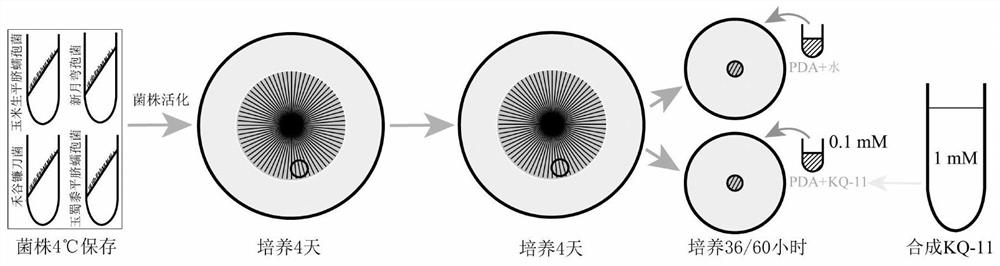
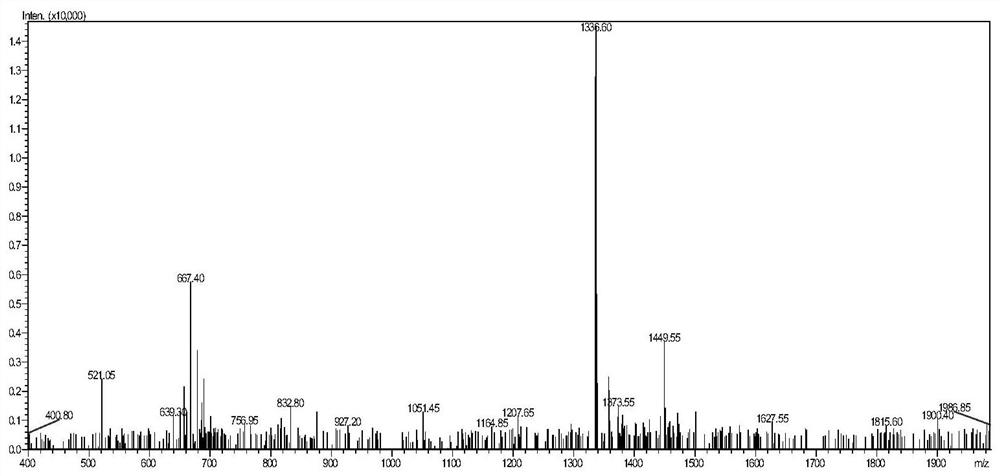
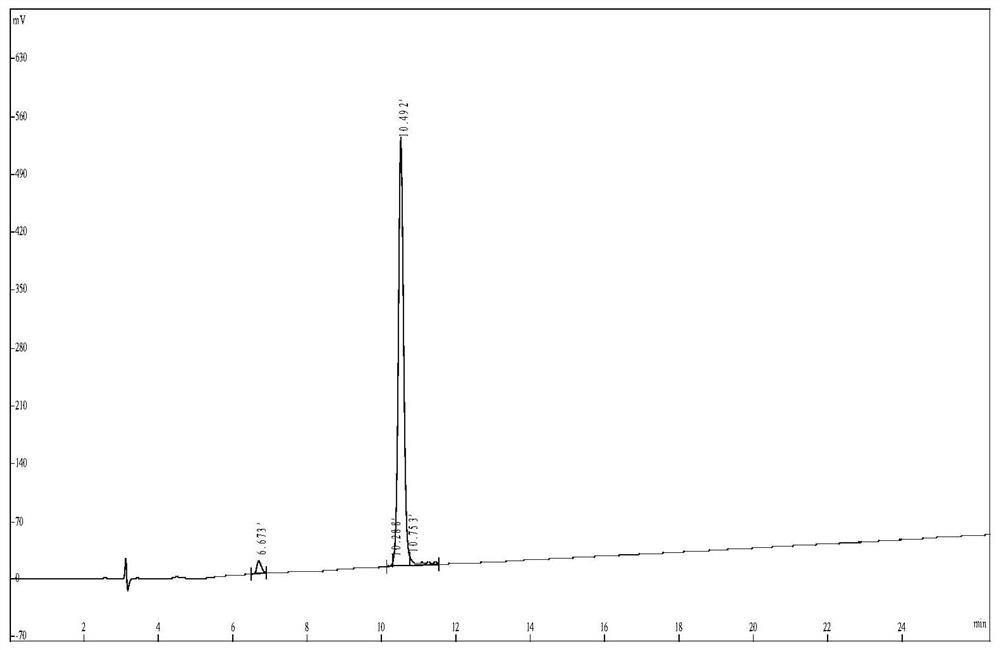
Non-traditional peptide KQ-11 and application thereof
The invention discloses a non-traditional peptide KQ-11. The amino acid sequence of the peptide KQ-11 is KQRKKILGCTY. A broad-spectrum antifungal activity experiment of the non-traditional peptide KQ-11 shows that the KQ-11 achieves an inhibition effect on fungi mainly through hypha aggregation. The highest inhibition rates of the peptide KQ-11 on the Bipolaris zeicola, Curvularia lunata, Fusarium graminearum and Bipolaris maydis are 60.4 percent, 61.9 percent, 45.1 percent and 39.9 percent respectively.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
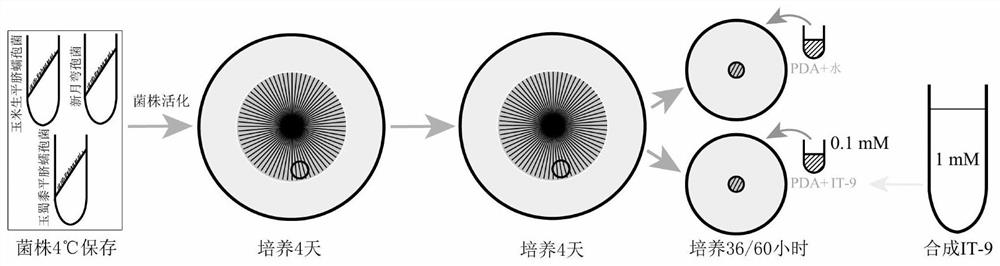
Novel small peptide IT-9 and application thereof
The invention discloses a novel small peptide IT-9. The amino acid sequence of the peptide IT-9 is ITACVHLPA. A broad-spectrum antifungal activity experiment of the peptide IT-9 shows that hyphae of Bipolaris zeicola and Curvularia lunata growing on a culture medium containing the peptide IT-9 have an abnormal branching phenomenon, but the phenomenon is not observed in a control culture medium without the peptide; it is indicated that the peptide IT-9 can achieve the inhibition effect on Bipolaris zeicola and Curvularia lunata by causing abnormal branches of hyphae. The peptide IT-9 has the highest inhibition rates of 83.6%, 79.8% and 59.2% respectively on Bipolaris zeicola, Curvularia lunata, and Bipolaris maydis.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Breeding method of waxy corn variety with high resistance against diseases and pests
The invention discloses a breeding method of a waxy corn variety with high resistance against diseases and pests, belonging to the technical field of corn disease-resistant breeding. In the invention, high-yield high-quality waxy corn variety, high-resistance bipolaris maydis variety, high-resistance sphacelotheca reiliana variety, high-resistance ostrinia nubilalis variety and high-resistance puccinia polysora variety are adopted as parents; and through hybridization and backcrossing polymerization and multiple generations of seed waxiness and disease resistance identification and screening, a hybrid waxy corn variety with high resistance against 4 diseases and pests, good waxiness and excellent agricultural and yield traits is obtained.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
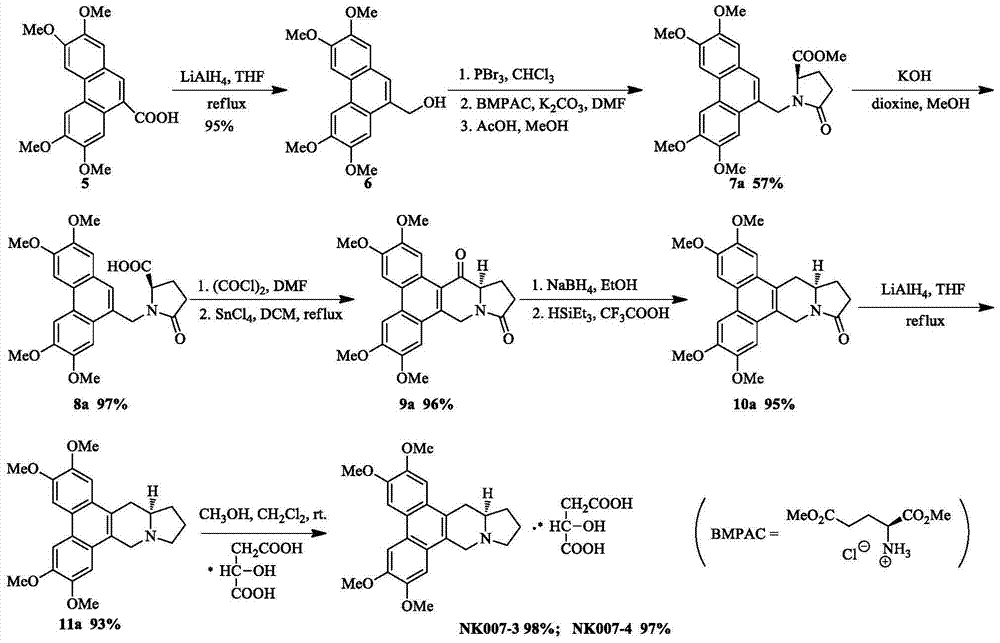
Two optically pure isomers of nk007 and their bactericidal applications
The invention relates to two optically pure isomers of NK007 for short and applications in a bactericidal aspect. Compounds NK007-3 and NK007-4 have good bactericidal activity, can be used for treating plant bacteria diseases selected from fusarium wilt of cucumber, cercospora brown spot of peanut, apple ring spot, alternaria solani, puccinia polysora, rice bakanae disease, sclerotinia rot of colza, phytophthora capsici disease, wheat sharp eyespot, bipolaris maydis, watermelon anthracnose, potato late blight, rice sheath blight disease and cucumber gray mold.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
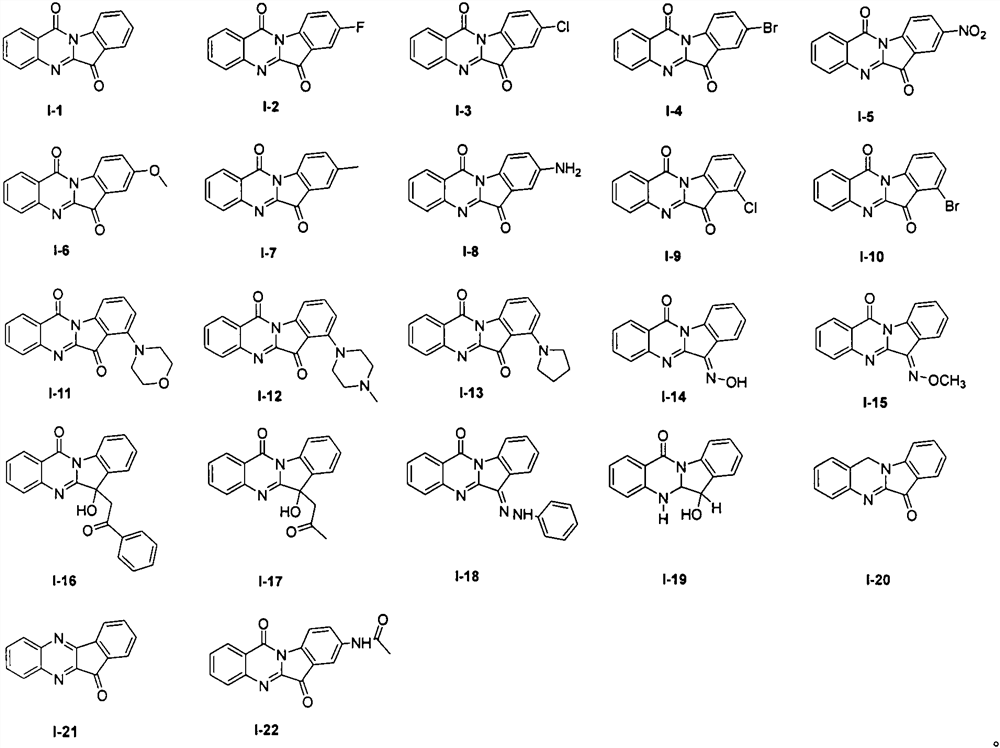
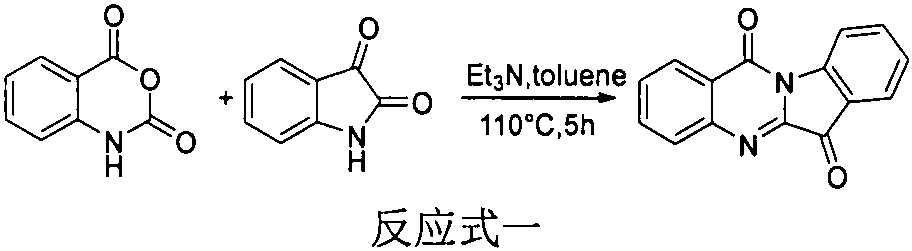
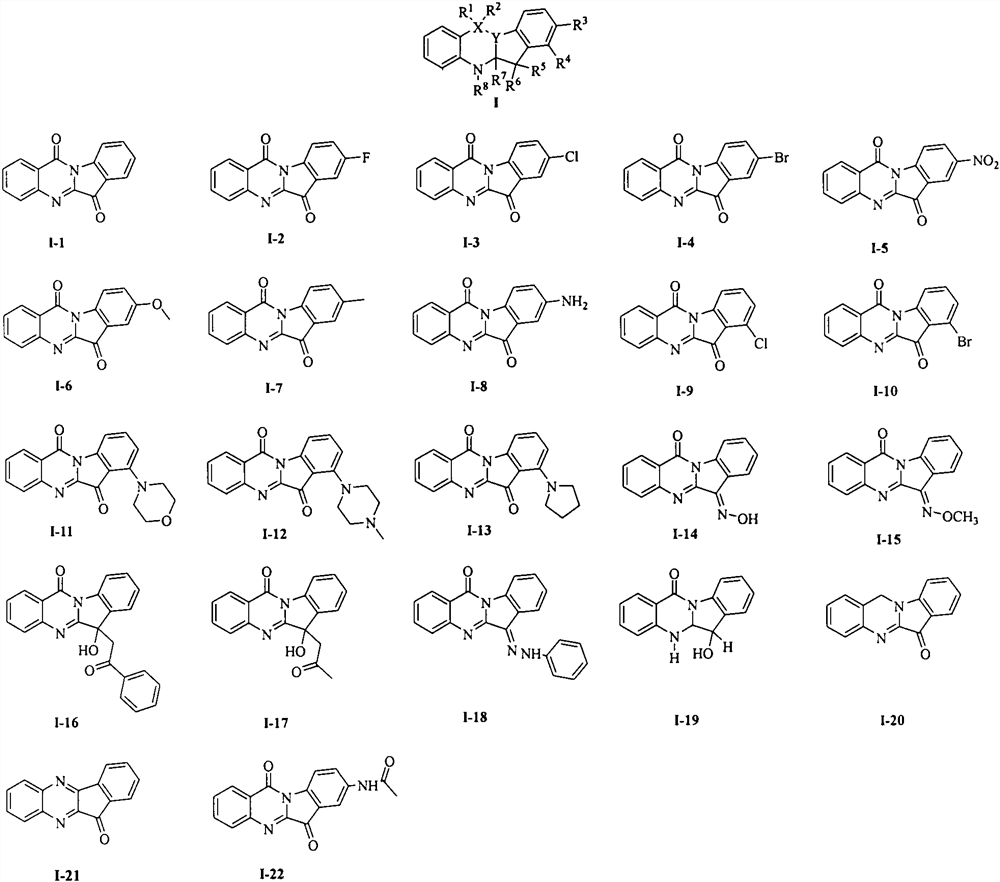
Application of tryptanthrin derivatives in treatment of plant viruses and germs
ActiveCN113016814ASuppress witheringHigh activityBiocideFungicidesTobacco mosaic virusPhytophthora capsici
The invention relates to application of tryptanthrin derivatives in treatment of plant viruses and germs. According to the invention, it is found that the tryptanthrin derivatives I-1 to I-22 show good anti-plant virus and germ activity for the first time, and can well inhibit 14 kinds of plant germs such as tobacco mosaic virus (TMV), cucumber fusarium wilt, peanut brown spot, apple ring spot, wheat sheath blight, corn bipolaris maydis, watermelon anthracnose, rice bakanae disease, tomato early blight, wheat gibberellic disease, rice blast, phytophthora capsici, sclerotium of rape, cucumber gray mold and rice sheath blight.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Diterpene compound extracted from branches and leaves of croton and use thereof
InactiveCN102050731AAvoid infectionPrevent proliferationBiocideOrganic compound preparationNicotiana tabacumTobacco mosaic virus
The invention discloses a diterpene compound extracted from branches and leaves of croton. The diterpene compound comprises 12-O-Tigloylphorbol-13-(2-methy lbutyrate) and 12-O-Acetylphorbol-13-(2-methy lbutyrate). The invention further discloses the use of the diterpene compound in preparing biopesticide for killing tobacco mosaic virus and phytopathogen. Experiments prove that the diterpene compound extracted from branches and leaves of croton, including the 12-O-Tigloylphorbol-13-(2-methy lbutyrate) and the 12-O-Acetylphorbol-13-(2-methy lbutyrate), can remarkably stop tobacco mosaic virus from invasion and proliferation and restrain cucumber wilt disease fungus, wheat scab pathogen, magnaporthe grisea, thanatephorus cucumeris, bipolaris maydis, exserohilum turcicum and other phytopathogens.
Owner:马英
Mixed medicament and application thereof to prevention and treatment of bipolaris maydis
ActiveCN105638713ALong-lasting effectGood control effectBiocideDead animal preservationPropiconazoleMedicine
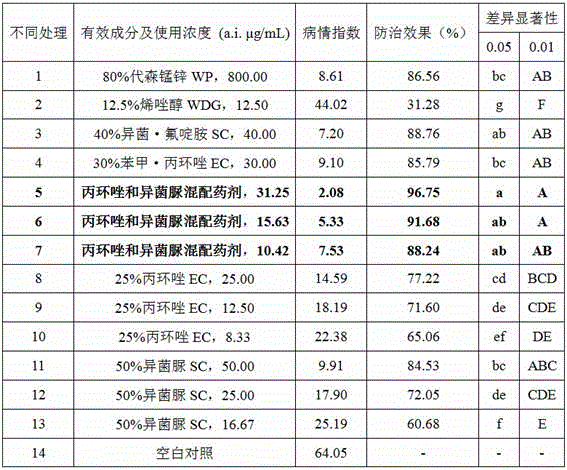
The invention belongs to the technical field of pesticides and discloses a mixed medicament and application thereof to prevention and treatment of bipolaris maydis. The mixed medicament comprises active ingredients including propiconazole and iprodione in a weight ratio of 6:4. By mixing of bactericides with different function mechanisms, the novel medicament for prevention and treatment of bipolaris maydis is obtained and conducive to delaying of field drug resistance, is capable of improving prevention and treatment effects and reducing medicament consumption and utilization cost and has potential social, economic and ecological benefits.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION FAAS
Sterilization composite containing metalaxyl-M and application thereof
ActiveCN102204550BSynergisticIncrease productionBiocideFungicidesPhytophthora sp.Exserohilum species
The invention discloses a sterilization composite containing metalaxyl-M and application thereof. The sterilization composite containing metalaxyl-M comprises two active components A and B, the component A is metalaxyl-M and the component B is propineb or metiram. The composite is efficient, safe and environmentally-friendly, has synergy, can be used for increasing crop production and fruit quality and lowering cost and is beneficial to the postponement of the generation of drug resistance of harmful bacteria. The composite also can be used for preventing and controlling crop banded sclerotial blight, damping off, root rot, rice blast, exserohilum turcicum, bipolaris maydis, downy mildew, phytophthora blight, leaf spot, gray mold, alternaria leaf spot, anthracnose, ring spot, powdery mildew, Leptosphaeria maculans and late blight.
Owner:JIANGSU BAOLING CHEM
Application of melatonin derivative in prevention and treatment of plant fungal diseases
ActiveCN114680114AStrong inhibitory activityGood broad spectrumBiocideOrganic chemistryBiotechnologyMonilinia
The invention discloses application of a melatonin derivative to prevention and treatment of plant fungal diseases, and belongs to the field of pesticides. According to the present invention, the compound has characteristics of strong inhibition activity on the pathogenicity of Magnaporthe oryzae, good broad spectrum, and good inhibition effect on Fusarium graminearum, Botrytis cinerea, Sclerotinia sclerotiorum, Pestalotiopsis, Monilinia fruticosa, Bipolaris maydis, and Rhizoctonia solani, and is the potential broad spectrum pesticide antibacterial molecule, and can be used for the preparation of the antibacterial agent, such that the antibacterial agent can be used for the preparation of the antibacterial agent, and can be used for the preparation of the antibacterial agent, such that the antibacterial agent can be used for the preparation of the antibacterial agent, and the antibacterial agent can be used for the preparation of the antibacterial agent, and can be used for the preparation of the antibacterial agent, and can be used for the preparation of the antibacterial agent.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
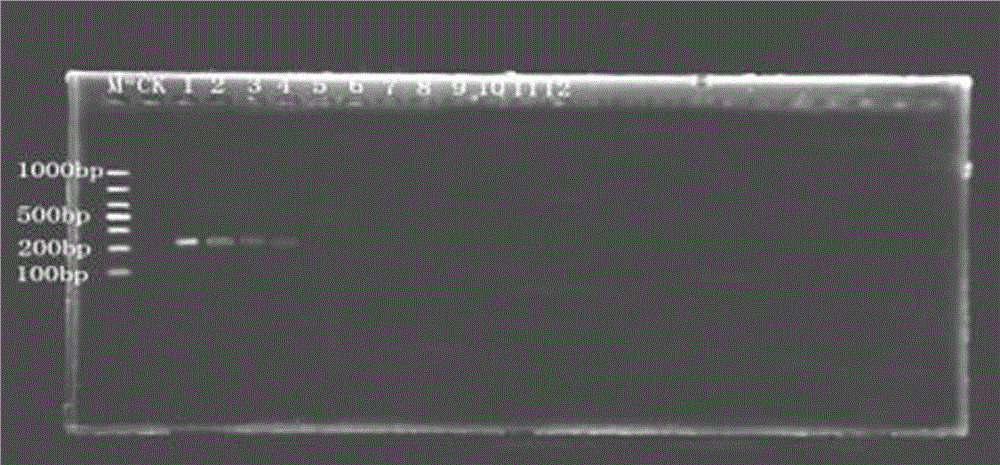
Rapid detection method of pathogens of corn southern leaf blight
InactiveCN105543382AMonitor for latent infestationTake early and effective preventive measuresMicrobiological testing/measurementForward primerA-DNA
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene engineering, relates to a method for rapidly detecting pathogens by a specific primer, and in particular relates to the specific primer for rapidly detecting corn southern leaf blight and a detection method of the corn southern leaf blight. A rapid detection method of pathogens of the corn southern leaf blight comprises the following steps: (1) collecting fungal hyphae; (2) extracting fungal DNAs; (3) carrying out PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification, wherein a PCR system is as follows: 1 microliter of a forward primer X-EF, 1 microliter of a reverse primer X-ER, 1 microliter of a DNA template, 12.5 microliters of Taq PCR Master Mix, and the balance of ddH2O which is added until the volume is 25 microliters; a PCR procedure: pre-denaturing for 3 minutes at 94 DEG C; denaturing for 30 seconds at 94 DEG C, annealing for 30 seconds at 52.9 DEG C, and extending for 30 seconds at 72 DEG C, circulating for 32 times; extending for 10 minutes at 72 DEG C and preserving at 4 DEG C. In order to provide evidences for rapidly and accurately monitoring whether corn leaves are latently infected by bipolaris maydis or not, prevention and control measures can be easily and effectively adopted as soon as possible.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Trifluoromethylpyrimidine-containing ammonia compound, preparation method and use as bactericide
The invention relates to a 4-substituted phenyl-6-trifluoromethyl-2-amino pyrimidinamine compound which has a novel chemical structure and a general formula III, a synthesis method for the compound and the application of the compound used as bacteriacide. The method comprises the following steps of: reacting substituted phenyl methyl ketone used as an initial raw material and trifluoroacetic acid ethyl ester under catalysis of sodium alcoholate to generate 4,4,4-trifluoro-1-substituded phenylbutane-1,3-diketone, and reacting 4,4,4-trifluoro-1-substituded phenylbutane-1,3-diketone and guanidinium salt under an alkaline condition to generate a III series compound with the general formula III. The compound with the general formula III can inhibit growth of pathogenic bacteria such as rice sheath blight, rice bakanae disease, exserohilum turcicum, bipolaris maydis, curvulavia lunata, corn kernel rot, corn top rot pathogenic bacteria, fusarium graminearum, cotton anthracnose, bean fusarium, rape sclerotinia rot, botrytis cinerea, cucumber fusarium wilt pathogenic bacteria, cucumber brown rot pathogenic bacteria, cucumber scab pathogenic bacteria, hot pepper root rot pathogenic bacteria, kidney bean anthracnose bacteria, and pythium aphanidermatum. In the formula III, R is methyl, ethyl, methoxy group, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, trifluoromethyl and other groups, and the number of R is 1 to 3.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
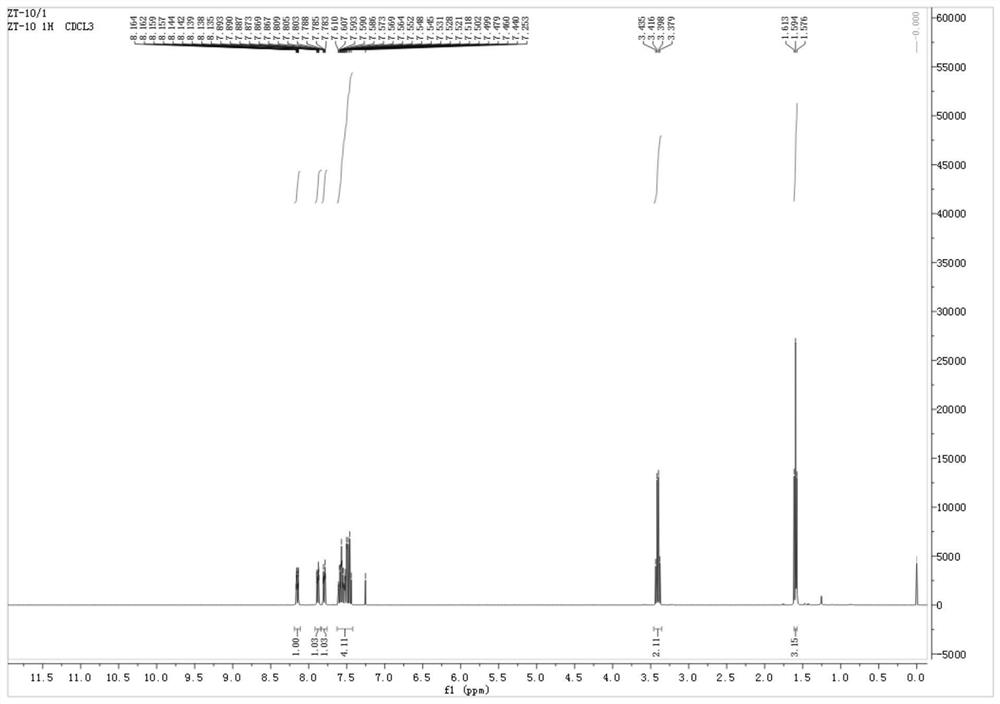
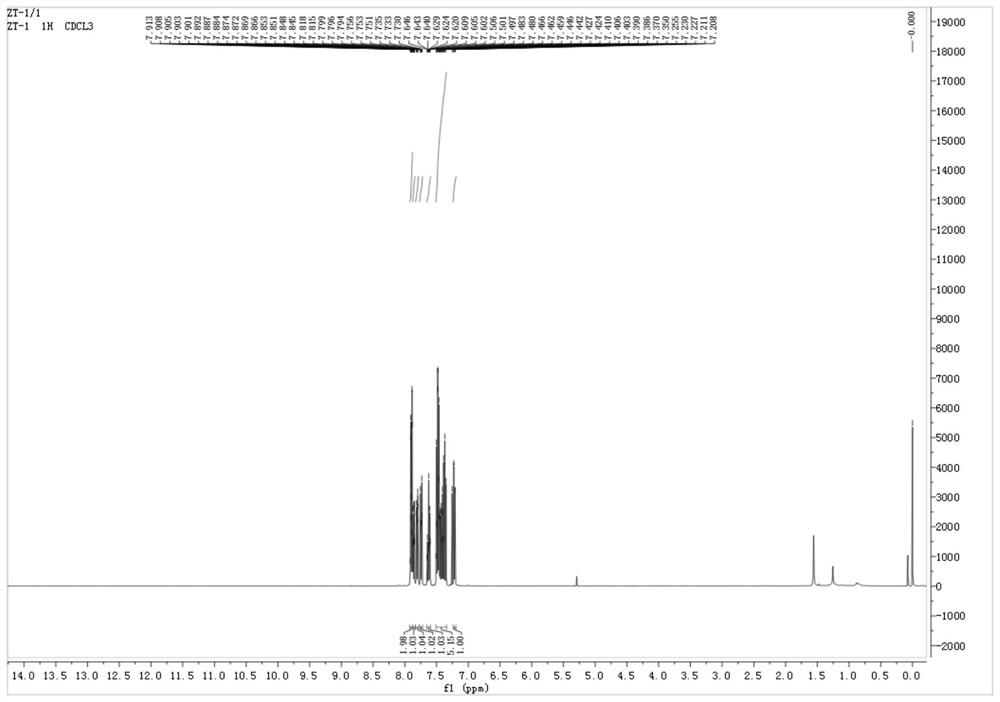
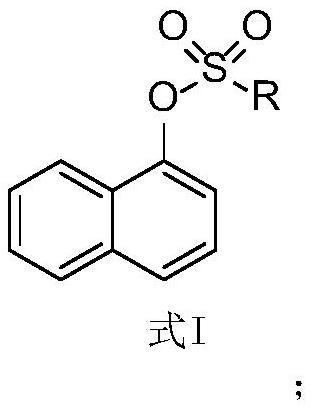
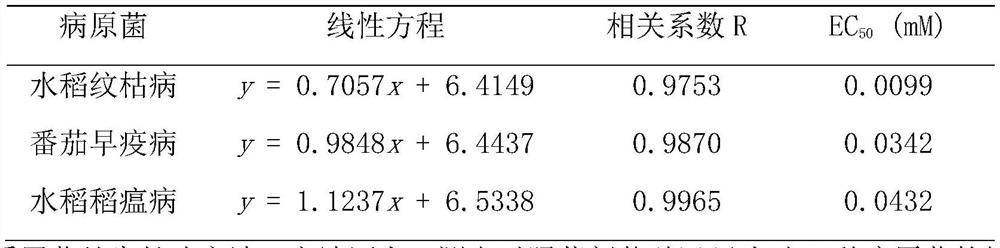
Application of 1-sulfonyl naphthol derivative in prevention and treatment of plant pathogenic fungi and antibacterial agent
The invention relates to application of a 1-sulfonyl naphthol derivative in prevention and treatment of plant pathogenic fungi and an antibacterial agent, and belongs to the technical field of antibacterial agents. In the application of the 1-sulfonyl naphthol derivative, the 1-sulfonyl naphthol derivative has a structure shown as a formula I, and in the formula I, R is C1-C6 alkyl, aryl or heteroaryl, wherein the aryl is phenyl, substituent substituted phenyl or naphthyl. In the application of the 1-sulfonyl naphthol derivative of the present invention, the 1-sulfonyl naphthol derivative canbe used for detecting 16 plant pathogenic fungi such as fusarium graminearum, wheat root rot fungi, wheat stem rot fungi, magnaporthe oryzae, setosphaeria turcica, bipolaris maydis, maize curvularia leaf spot, oilseed rape sclerotinia sclerotiorum, tobacco fusarium oxysporum, phytophthora nicotianae, alternaria alternata, cotton fusarium oxysporum, cucumber fusarium oxysporum and botrytis cina, alternaria brassicae and phytophthora capsici, and shows good antibacterial activity.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
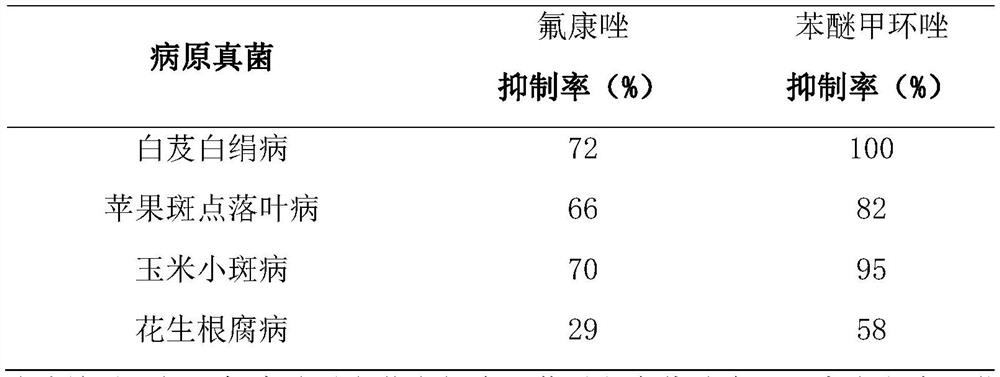
The new application of antifungal medicine in the control of crop diseases
The invention discloses a novel application of an antifungal medicine to prevention and control of crop diseases and belongs to the field of agricultural fungicides. The antifungal medicine is fluconazole and can prevent and control rice sheath blight disease, tomato early blight, rice blast, wheat powdery mildew, wheat stripe rust, rhizoma bletillae southern blight, apple alternaria leaf spots, bipolaris maydis and peanut root rot. Discovered that the fluconazole is relatively high in activity to various crop fungal diseases, the activities of some fluconazole are even higher than the activities of the triazole agricultural commercial fungicide used now, and the fluconazole can realize the novel application to prevention and control of the crop diseases.
Owner:YANGTZE UNIVERSITY
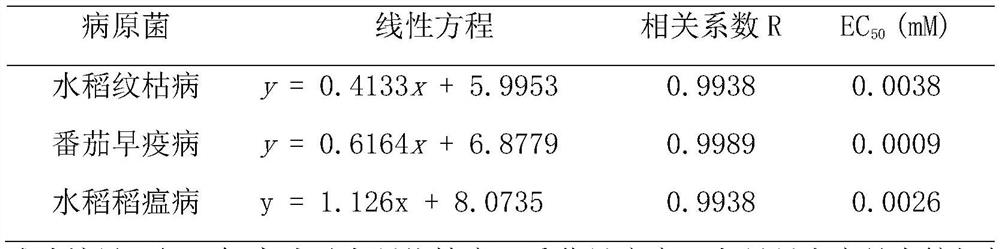
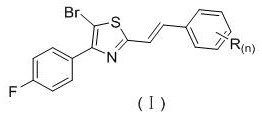
Application of a stilbene analog containing a thiazole ring structure as a fungicide
The invention discloses the application of a Stilbene analog containing a thiazole ring structure as a fungicide. The structural formula of the Stilbene analog containing a thiazole ring structure is shown in formula (I): in formula (I), the H on the benzene ring is The substituent R is mono-substituted, di-substituted or unsubstituted; n is an integer from 0 to 2, and n represents the number of substituent R on the benzene ring; when n=0, it means that the H on the benzene ring is not substituted; n= When 1, it means that the H on the benzene ring is monosubstituted by the substituent R; when n=2, it means that the H on the benzene ring is disubstituted by the substituent R, and the substituents R on different substitution positions are the same or different; the substituents R is hydrogen, C1~C4 alkyl, C1~C3 haloalkyl, methoxy or halogen. The Stilbene analog containing the thiazole ring structure of the present invention has a good inhibitory effect on wheat head blight and maize spot fungus.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
A kind of mixed agent and its application in preventing and treating small spot of corn
ActiveCN105638713BLong-lasting effectGood control effectBiocideDead animal preservationPropiconazoleMedicine
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION FAAS
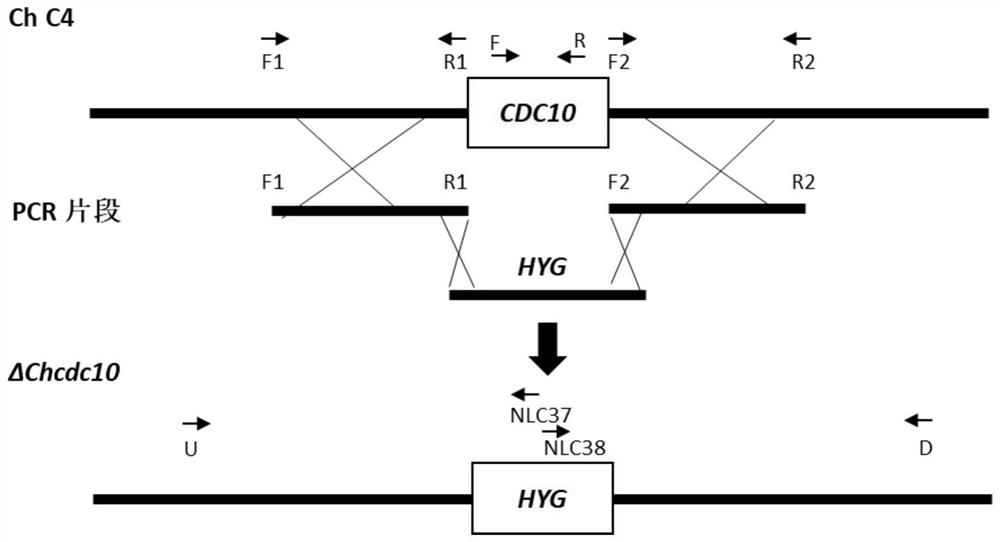
A kind of chcdc10 gene of Pseudomonas maize and its application
ActiveCN110257402BReduce pathogenicityMicroorganism based processesDepsipeptidesBiotechnologyMicrobial genetics
A kind of ChCDC10 gene of small spot bacterium maize and its application belong to the technical field of microbial genetic engineering. The ChCDC10 gene which is from the control of conidia formation, ascospore formation and pathogenicity of the small spot of corn provided by the invention, its DNA sequence is as SEQ Shown in ID No: 1; The protein encoded by the ChCDC10 gene provided, its amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID No: 2; ChCDC10 gene can be applied in the field of genetic engineering of plant resistance to maize spot disease; The protein ChCDC10, which controls the formation of conidia and ascospores and pathogenicity, is deleted, mutated or modified, so that the formation of conidia and ascospores is restricted and the pathogenicity is reduced, which can be used as a target in the design and screening of resistant maize It is safe for plants to be used in small spot disease agents, especially since such proteins do not exist in plants.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Streptomyces A2 strain with strong bacteriostatic effect and application thereof
ActiveCN112574902AInhibit expansionReduce the amount of formationBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyClavibacter michiganense
The invention discloses a streptomyces A2 strain with a strong bacteriostatic effect and an application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of streptomyces A2 strains and an application thereof. The streptomyces strain A2 is obtained by separation through a conventional dilution plate method, the strain A2 is inoculated into a PD culture medium and cultured for 3 days at the temperature of28 DEG C and the speed of 160 r / min to prepare a seed solution, then the seed solution is inoculated into a liquid fermentation culture medium with the pH value of 7.3, shaking culture is conducted for 7 days at the temperature of 28 DEG C and the speed of 160 r / min, and the biological agent is obtained, which has a high inhibition effect for Sclerotium rolfsii, In addition, the bacterial strainalso has a certain inhibition effect on colletotrichum gloeosporioides, botrytis cinerea and bipolaris maydis. A strain preparation is environment-friendly and non-toxic in source, has small influenceon the ecological environment and low requirements on culture conditions, and has good development and application prospects.
Owner:ZHONGKAI UNIV OF AGRI & ENG
Breeding method of a waxy corn variety with high resistance to diseases and insect pests
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Trichothecium roseum and veratridine combined bio-control agent, and application thereof in control of Bipolaris maydis
The invention discloses a Trichothecium roseum and veratridine combined bio-control agent, and an application thereof in the control of Bipolaris maydis, and belongs to the technical field of plant protection. The use amounts of the Trichothecium roseum and veratridine in the bio-control agent meet the following conditions: the concentration of the Trichothecium roseum is 0.25-0.45 mg / L, and the concentration of the veratridine is 1.0 * 10<6> spores / mL. Data of application of the bio-control agent formed by compounding the Trichothecium roseum with veratridine shows that the bio-control agentformed by compounding the Trichothecium roseum with veratridine has synergistic effects on the control of Bipolaris maydis, and has a most significant inhibition effect on the Bipolaris maydis when the final concentration of veratridine is 0.35 mg / L and the concentration of the Trichothecium roseum is 1.0 * 10<6> spores / mL.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com