Application of 1-sulfonyl naphthol derivative in prevention and treatment of plant pathogenic fungi and antibacterial agent
A technology of phytopathogenic fungi, sulfonyl naphthol, applied in biocides, plant growth regulators, chemicals for biological control, etc., to achieve good antibacterial activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0057] The application of the 1-sulfonylnaphthol derivatives in this example in the control of phytopathogenic fungi is the application of compounds 1-16 in Table 1 in the control of phytopathogenic fungi.
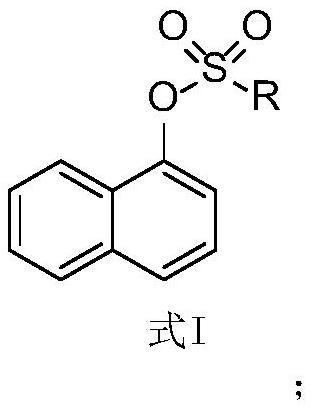
[0058] The concrete structural formula of compound 1~16 of table 1 and the R group in the corresponding structural formula I
[0059]
[0060]
[0061]
[0062] The above compounds 1-16 are prepared by a method comprising the following steps:
[0063] 1) In a 100mL flask, add 5mmol of 1-naphthol, 5.5mmol of substituted sulfonyl chloride (i.e. compound of formula II), and add 20mL of dichloromethane to dissolve it completely, then slowly drop triethylamine (6mmol, Et 3 N) dichloromethane solution, stirring reaction at room temperature (r.t.) after dropping, TLC tracking monitoring to the end of the reaction;
[0064] 2) After the reaction is over, add 20mL of water to the reaction system, then use dichloromethane to carry out multiple extractions, combine the orga...
Embodiment 2
[0184] The antibacterial agent for preventing and treating phytopathogenic fungi of this embodiment, wherein the active ingredient is any one of compounds 1-16 in Table 1. When preparing the antibacterial agent for controlling plant pathogenic fungi in this example, refer to the preparation method of the existing antibacterial agent, and only replace the active ingredient with the compound selected as the active ingredient among compounds 1-16. For example, the active ingredient in the commercial antibacterial agent Hymexazol can be replaced with the compound selected as the active ingredient among compounds 1-16 at an equal concentration.
experiment example
[0186] This experimental example is an activity test for inhibiting plant pathogenic fungi:
[0187] 1. Plant pathogenic fungi tested (16 species in total): wheat scab [Fusarium graminearum Schw.], wheat root rot [Bipolaris sorokiniana (Sacc.) Shoem], wheat stem rot [Fusariumpseudogramminearum, Fpg], rice Rice blast fungus [Pyricularia oryzae Cav.], corn large spot fungus [Exserohilum turcicum (Pass.) Leonard et Suggs], corn small spot fungus [Helminthosporium maydis Nisik&Miy], corn Currularia lunata (Boed) Wakker], Sclerotinia sclerotiorum (Lib.) de Bary], Fusarium oxysporum (Schlecht) f.sp. nicotianae (Johns.) Snyder et Hansen], Phytophoranicotianae Breda de Haan Tuker, Alternaria alternata Keissler, Fusarium oxysporium f.sp.Vasinfectum synder et Hansen, Fusarium oxysporium f.sp cucumbererinum Owen, Botrytis cinereaPers., Black cabbage Spot fungus [Alternaria brassicae Sacc.] and Capsicum phytophthora [Phytophthoracapsici Leonian] were provided by the Laboratory of Plant P...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com