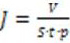Patents
Literature
30 results about "Protein retention" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In general, protein retention in the Golgi can perhaps best be viewed as a dynamic process in which one or more features of a Golgi resident protein contributes, to varying degrees, to its steady-state retention in a particular subcompartment.
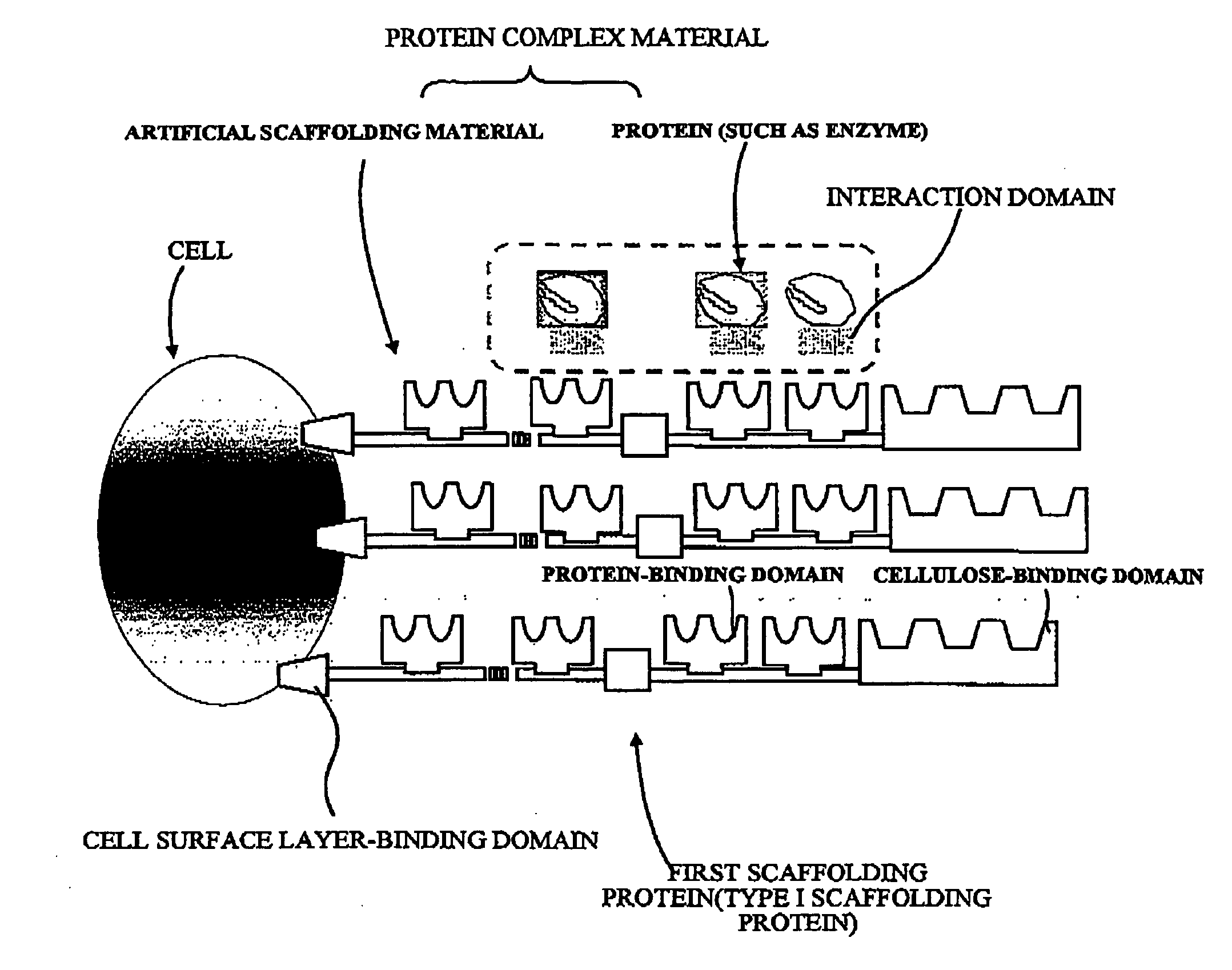
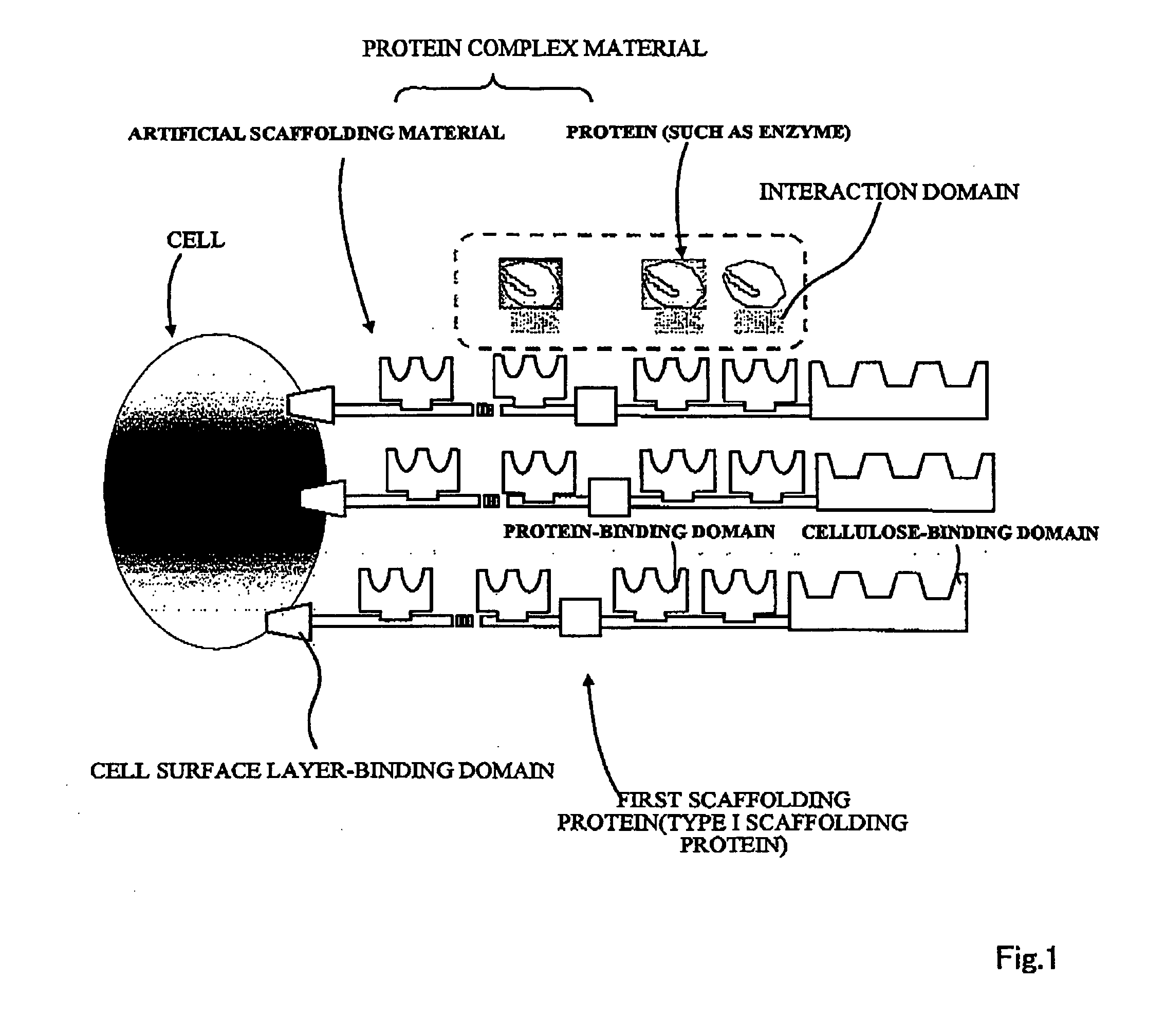
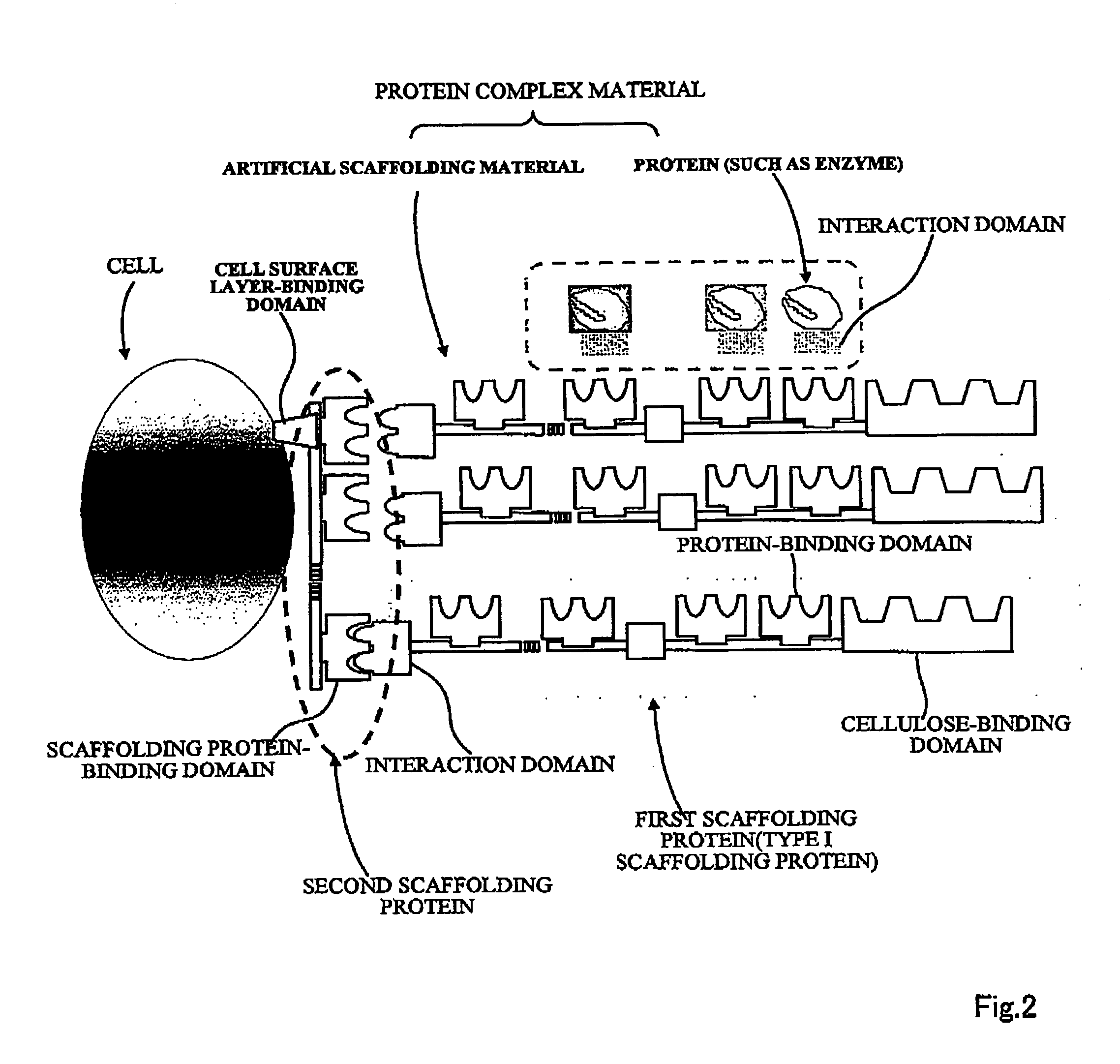
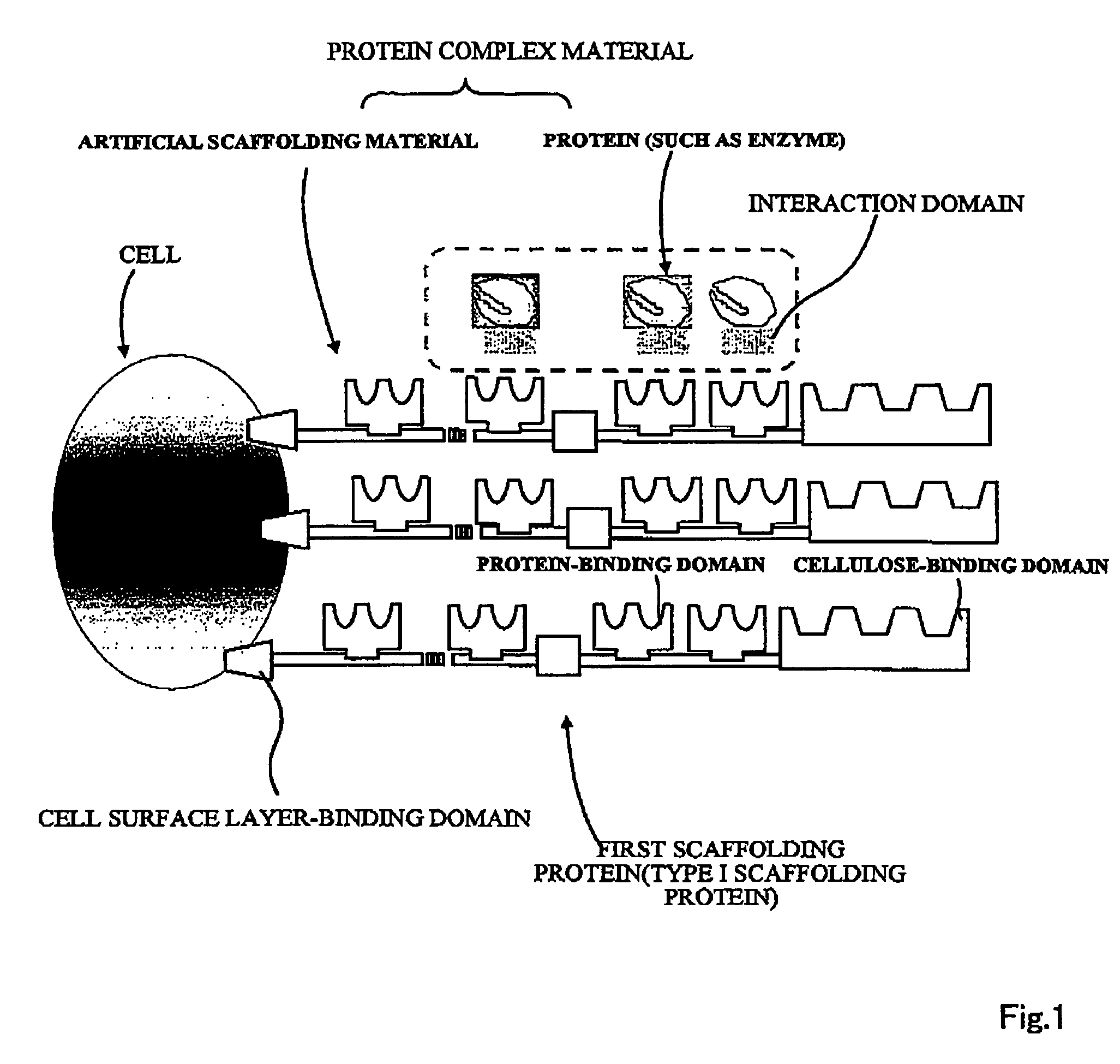
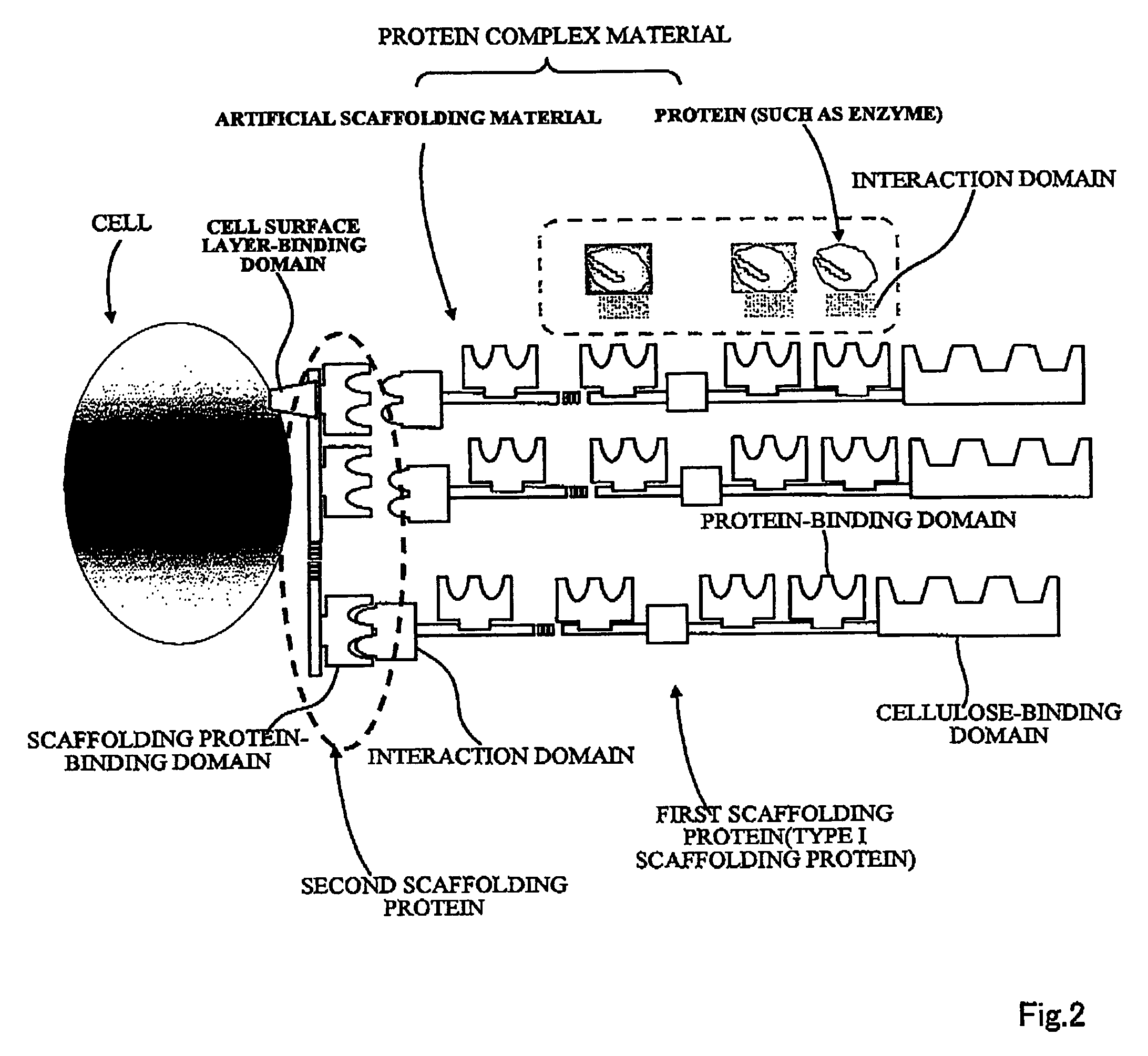
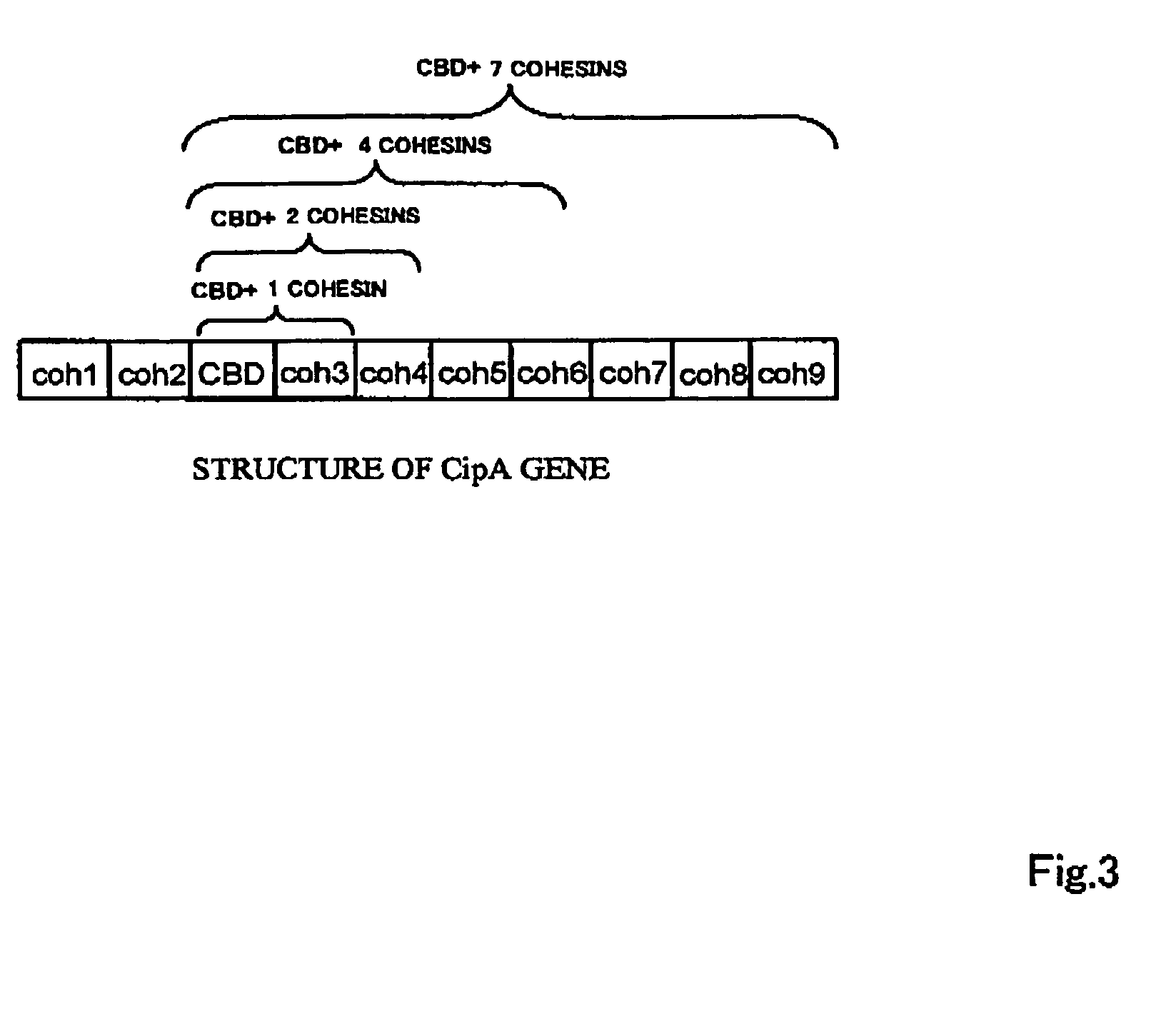
Artificial scaffolding material for protein retention and use of the same
The present invention provides an artificial scaffolding material for retaining proteins suitable for placing contiguously one species or two or more species of proteins such as enzymes. To this end, the artificial scaffolding material for retaining proteins is provided with a cell and scaffolding proteins heterologous to the cell and placed on the surface layer side of the cell at an extent that allows aggregation properties to be conferred to the cell, and provided with a plurality of non-covalently binding protein-binding domains arranged in tandem.
Owner:TOYOTA CENT RES & DEV LAB INC +1
Stabilized proteins
InactiveUS7037894B2Prevent undesired cross-linkControl cross-link reactionHormone peptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsTyrosineProtein retention
Isolated polypeptides or polypeptide chains are modified by di-tyrosine cross-linking such that the retain at least one functional activity. In one embodiment, the isolated polypeptide or polypeptide chains comprise at least one di-tyrosine cross-link, wherein at least one tyrosine of the di-tyrosine cross-link originates from a point mutation to tyrosine, and wherein the di-tyrosine cross-linked protein retains at least one function displayed by the protein in the absence of di-tyrosine cross-linking. In another embodiment, the di-tyrosine cross-linked polypeptide or polypeptide chain has enhanced stability compared to the same polypeptide or polypeptide chain in the absence of di-tyrosine cross-linking. A method for stabilization of a polypeptide or polypeptide complex, by the introduction of intra-polypeptide and / or inter-polypeptide di-tyrosine bonds, which simultaneously maintains the structure and function of the polypeptide or polypeptide complex is also described.
Owner:CALDER BIOSCI INC
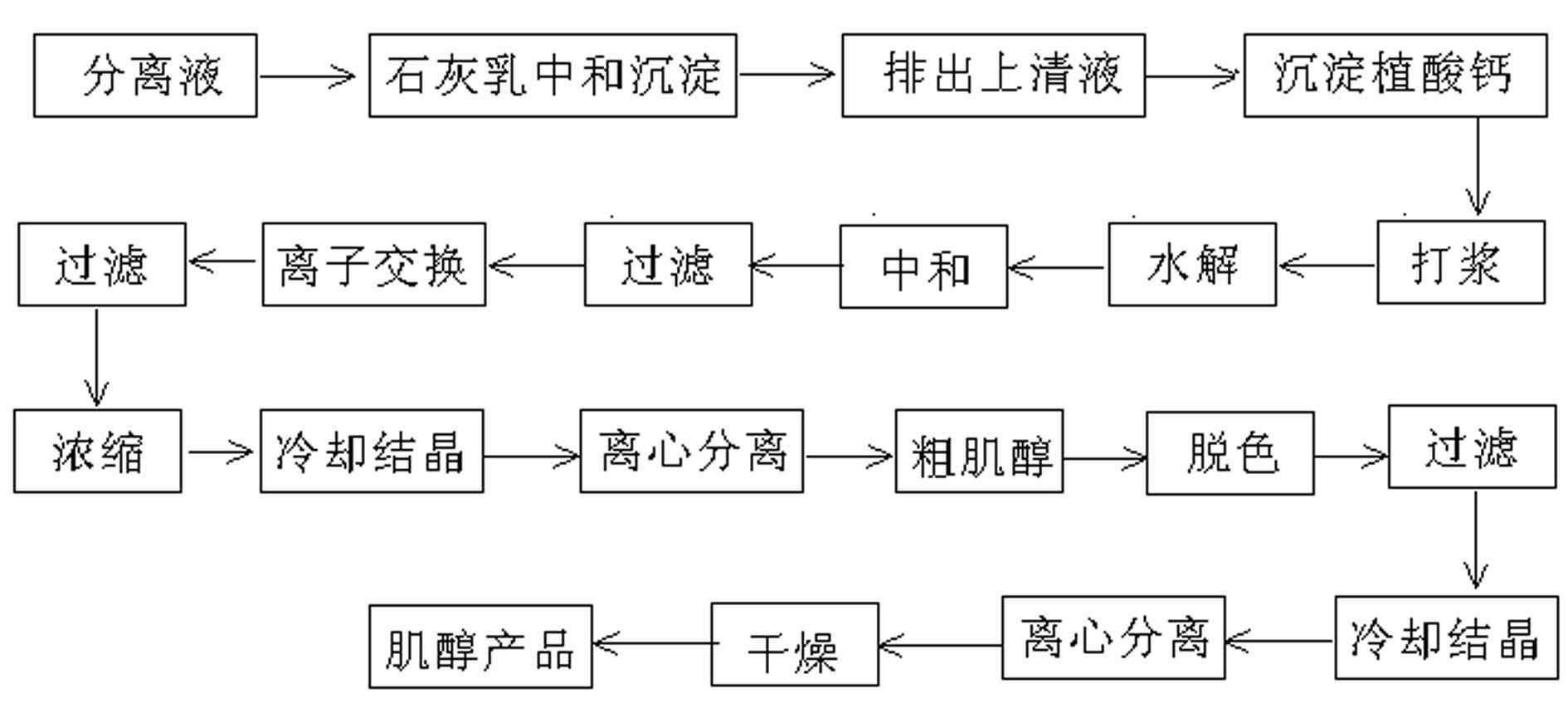
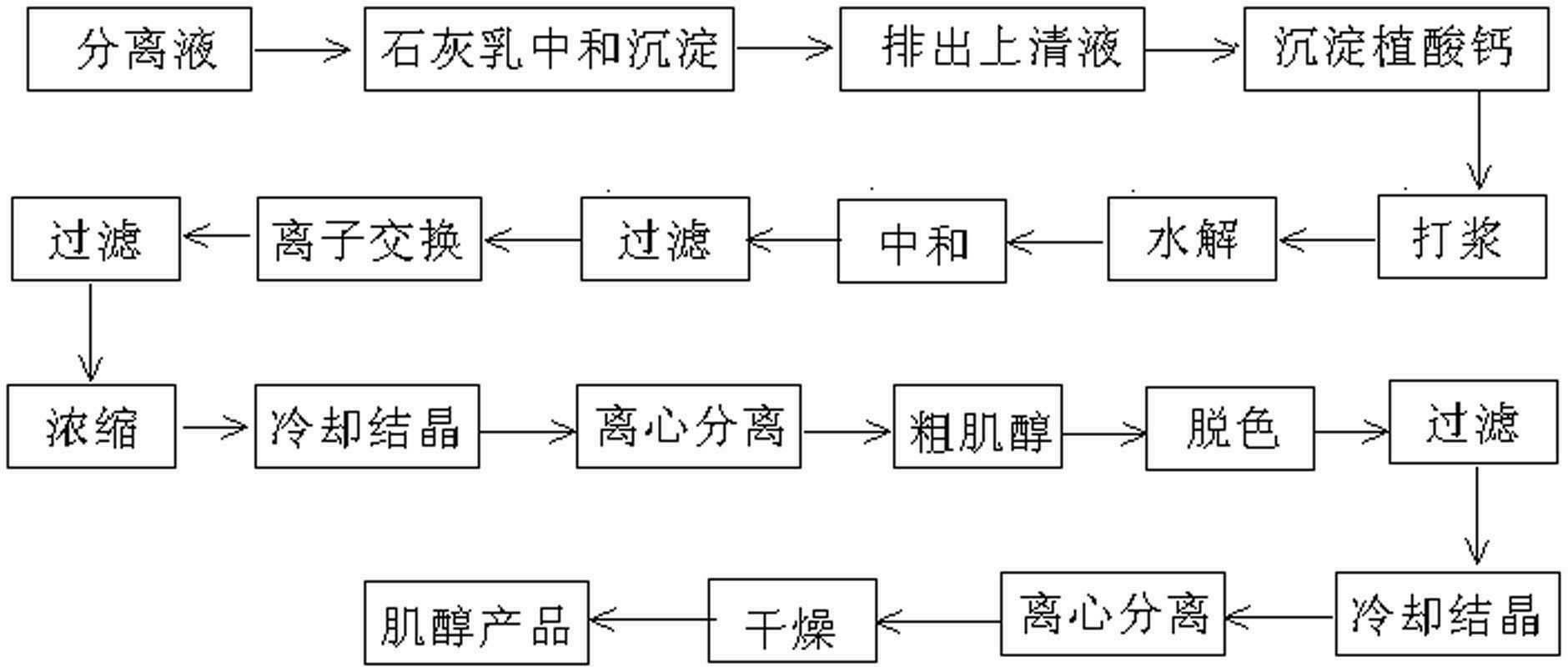
Method for preparing inositol from corn steep liquor
InactiveCN102603487AImprove concentrationHigh retention rateOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound separation/purificationAlkaline earth metalFiltration
Owner:HENAN XINYUAN BIOTECH CO LTD
Laminated casing or netting for proteinaceous products
A casing for containment of a proteinaceous product during or following processing is described. The casing has controlled porosity which permits close control of product drying with protein retention, providing good product color and surface texture, patterned and / or shaped products, high protein content and high peelability. The casing is a hollow tubular laminate of an outer lamina having high strength and, optionally, surface pattern-producing capability, and an inner laminate of controlled porosity which is permeable by vapors and, in most cases, also aqueous and organic liquids, but which is not permeable to solids such as proteins or fats. The laminae are adhered by an adhesive (preferably thermally activated) or by surface interlocking. Accessory materials such as liquid flavorants, colorants, release agents and anti-microbial agents can be incorporated into the laminae and from there imparted to the product. Applicable proteinaceous products include meat, poultry, seafood, soya and cheese.
Owner:JIF PAK MFG
Peanut polypeptide liquid and peanut protein polypeptide beverage prepared from the peanut polypeptide liquid
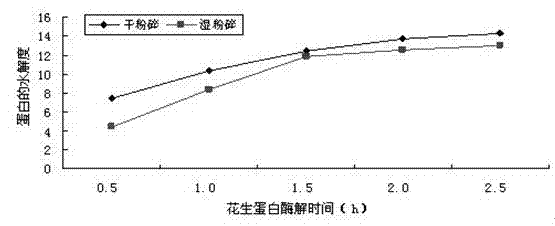
The invention discloses peanut polypeptide liquid and a peanut protein polypeptide beverage prepared from the peanut polypeptide liquid. A preparation method of the peanut polypeptide liquid comprises the following steps of drying peanut kernels by an oven, removing red skin, carrying out ultra-fine crushing to obtain peanut butter, adding the peanut butter into hot water having a temperature above 75 DEG C for dissolution according to a weight ratio of 1: (7 to 27), adjusting a pH value to of the peanut butter solution to a pH value of 7.0 to 8.5, based on the weight of the peanut butter, adding 0.3 to 0.9 wt% of peanut composite protease into the peanut butter solution, carrying out enzymolysis at a temperature of 45 to 65 DEG C for 0.5 to 2.5 hours, deactivating the peanut composite protease, and filtering to obtain the peanut polypeptide liquid. The preparation method of the peanut polypeptide liquid is simple, saves time and has a low cost. Dry ultra-fine crushing is utilized in raw material treatment so that a peanut protein retention ratio is high and an enzymolysis speed is fast. The peanut composite protease is utilized in proteolysis so that a degree of hydrolysis, the concentration of a trichloroacetic acid soluble protein, and a polypeptide yield are high. The peanut protein polypeptide beverage prepared from the peanut polypeptide liquid, white sugar and peanut protein liquid prepared from peanut butter which is subjected to dry ultra-fine crushing and is dissolved in water has the advantages of rich nutrient, specific fragrance belonging to peanut, smooth andfine mouthfeel, and no bitter taste.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY +1
Compositions and methods for proteomic investigations
Abstract of the Disclosure The present invention provides a variety of related proteomics analytical modalities that are open-ended, rapid, convenient and suitable for implementation in a high throughput parallel assay system. Specificity-determining compositions and methods are disclosed for use in proteomics. These compositions and methods provide a protein resolved from other protein species contained in a sample fluid, in its native, biologically functional conformation. The present invention provides a specificity-determining substrate that forms a complex with a protein molecule in a homogenous fashion. The specificity-determining substrate includes a specificity-determining ligand bound to a support, wherein optionally the substrate further includes a spacer bound between the ligand and the support. In addition a complex is provided that includes a specificity-determining substrate and a protein molecule. Furthermore, an array including a plurality of loci is provided, in which each locus includes a specificity-determining substrate of the invention. These substrates, complexes and arrays may be employed in a method of resolving a first protein from a fluid including one or more species of native, biologically active protein molecules, wherein the first protein retains its native structure and its biological activity; in a method of purifying one or more first proteins from a fluid including one or more species of native, biologically active protein molecules, wherein the purified first protein retains its native structure and its biological activity; in a method of characterizing one or more proteins in a fluid including one or more species of protein molecule; and in a method of identifying one or more proteins in a sample fluid wherein the concentration of the one or more proteins in the sample fluid differs from the concentration of the one or more proteins in a reference fluid.
Owner:ROY SWAPAN +2
Gene of human vascular endothelial growth factor monoclonal antibody and use thereof
InactiveCN101487005AGood saveHigh cost of mass productionImmunoglobulins against growth factorsFermentationEscherichia coliNucleotide
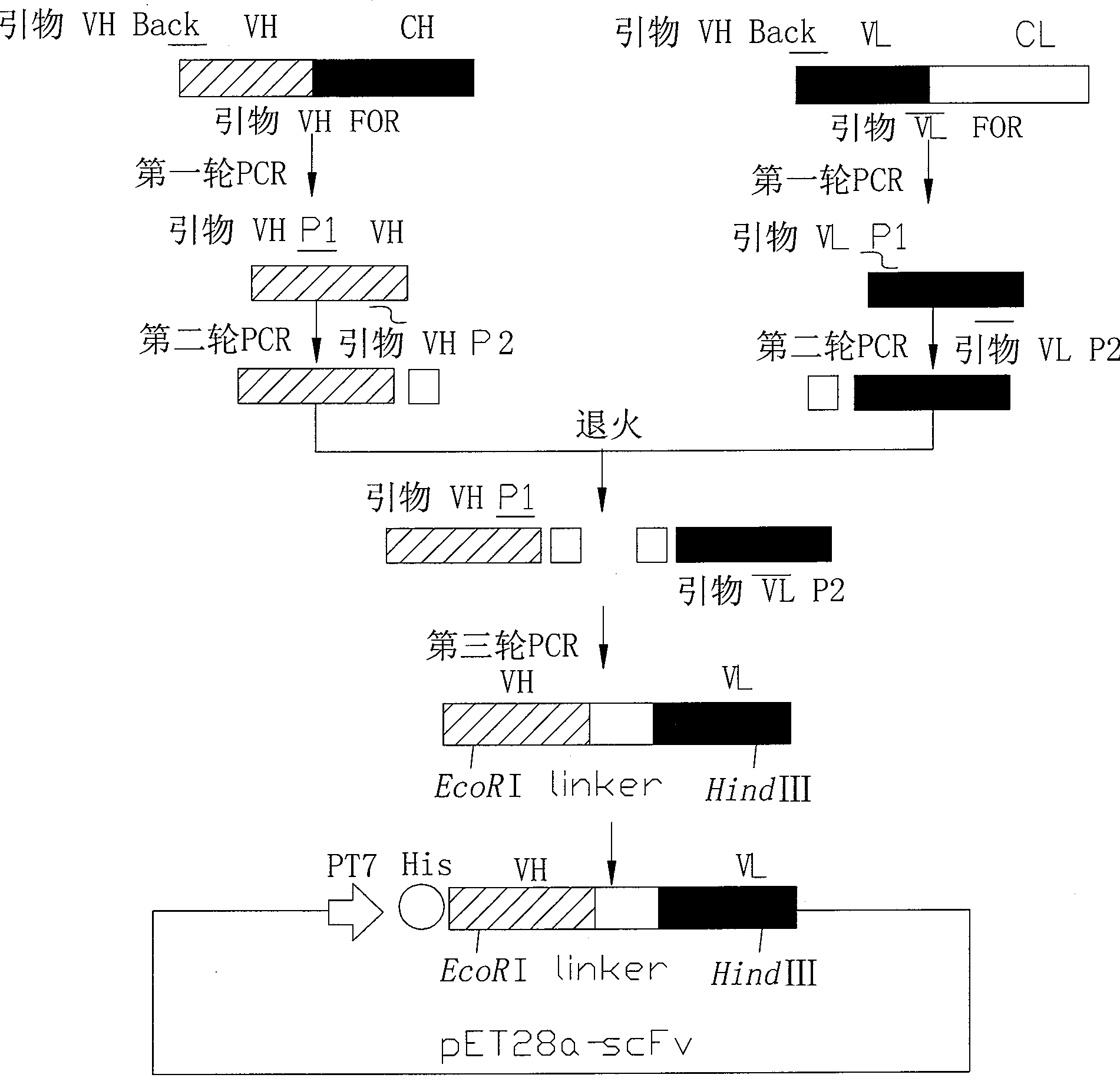
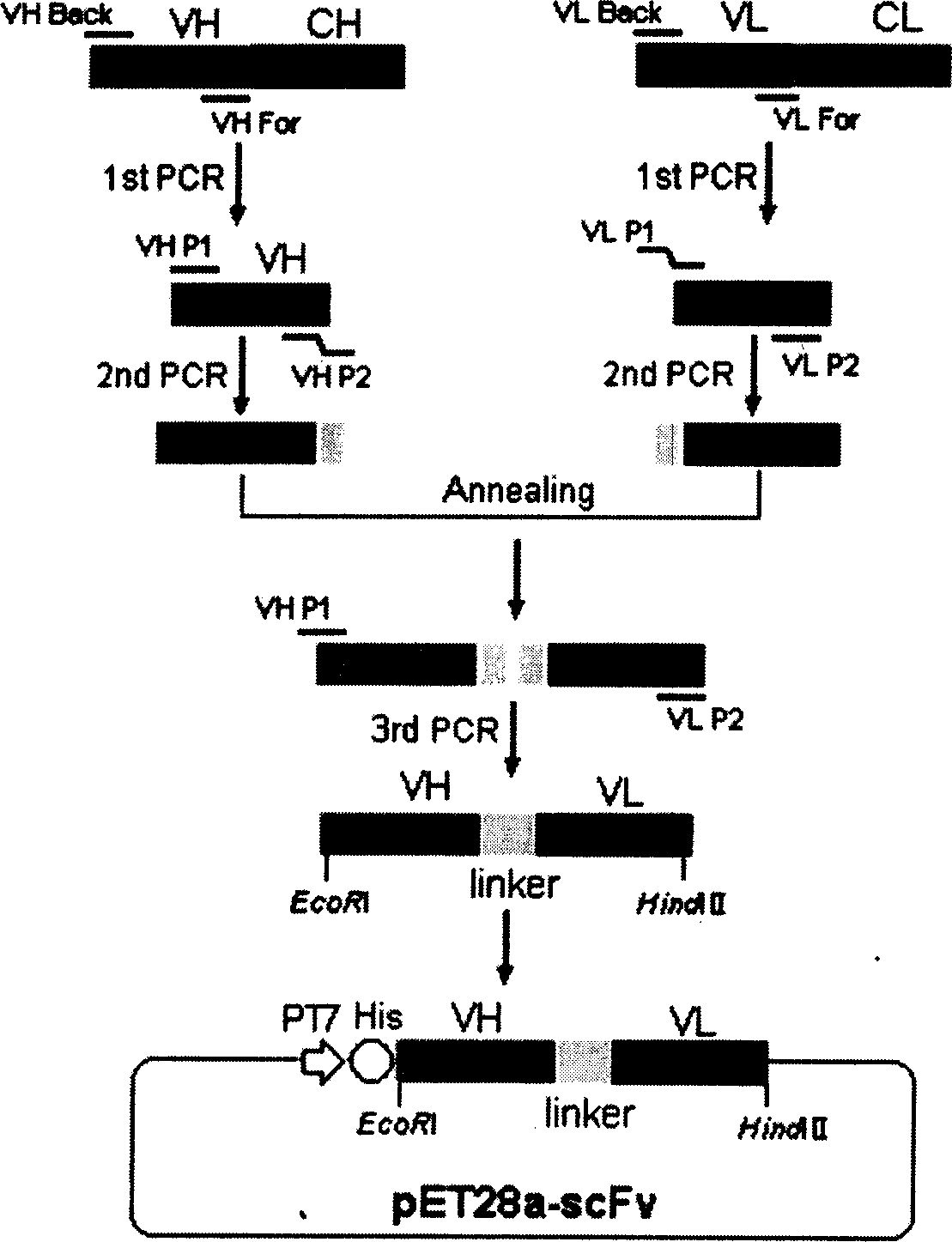
The invention relates to heavy chain and light chain variable region genes of a monoclonal antibody of a human vascular endothelial growth factor, a polypeptide that is encoded by the genes, a carrier that contains the genes, and application of the genes and the polypeptide in the preparation of a clinical testing agent of VEGF-related tumors. The invention utilizes gene engineering means to firstly obtain the heavy chain and light chain variable region genes of the monoclonal antibody from a hybridoma cell strain of the monoclonal antibody with VEGF165 secretion, the heavy chain variable region gene has the nucleotide sequence with SEQ ID NO of 1, the light chain variable region gene has the nucleotide sequence with SEQ ID NO of 3, and the genes are combined with scFv small molecule antibody and cloned into a pET28a expression carrier, have high-efficiency expression in colon bacillus and generate protein that has reserved antibody combination capability and VEGF165 action function. Through the modification with gene engineering techniques, the invention establishes the foundation for biological missile construction, has ultra-convenient antibody production and greatly lowered cost, and is favorable for industrial production.
Owner:林植华
Laminated casing having multiple porosities
Owner:JIF PAK MFG
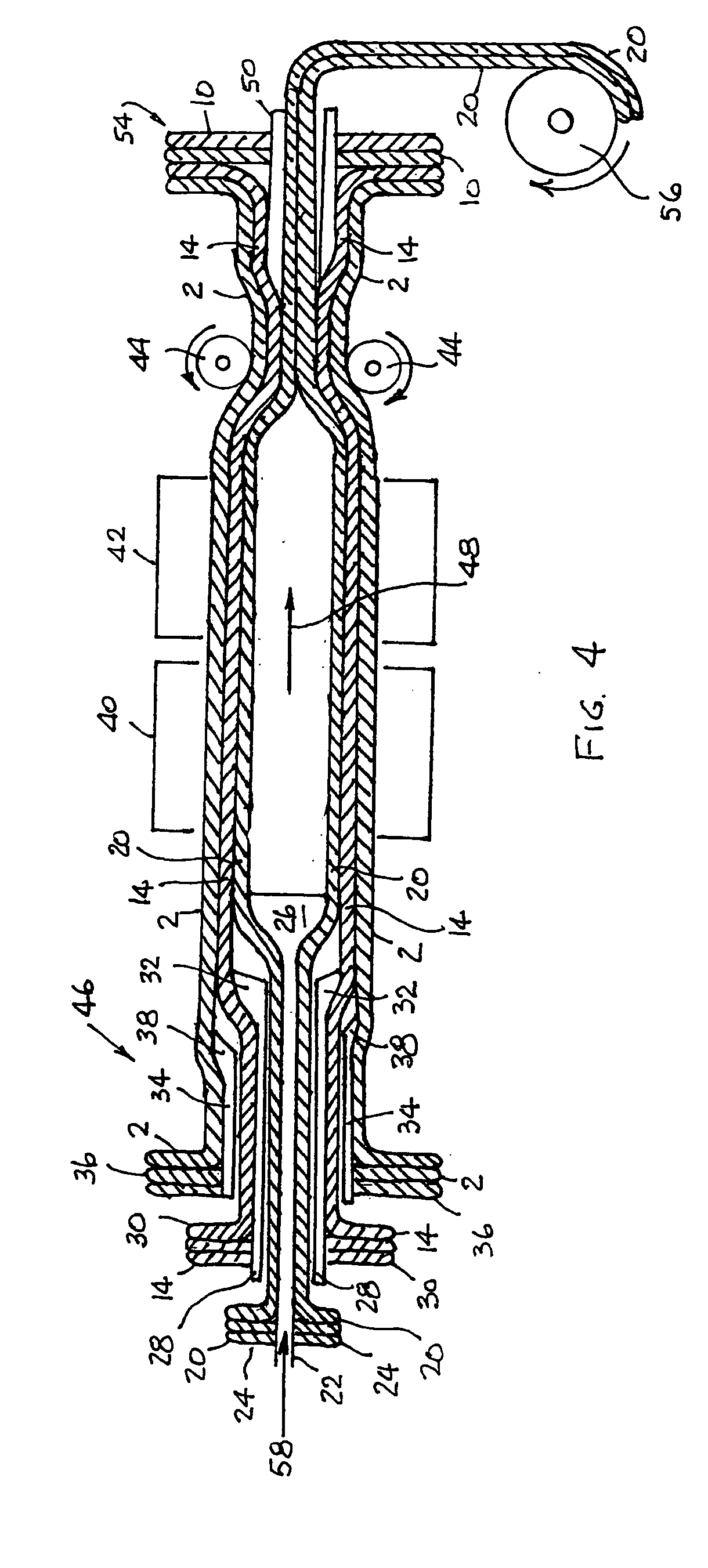
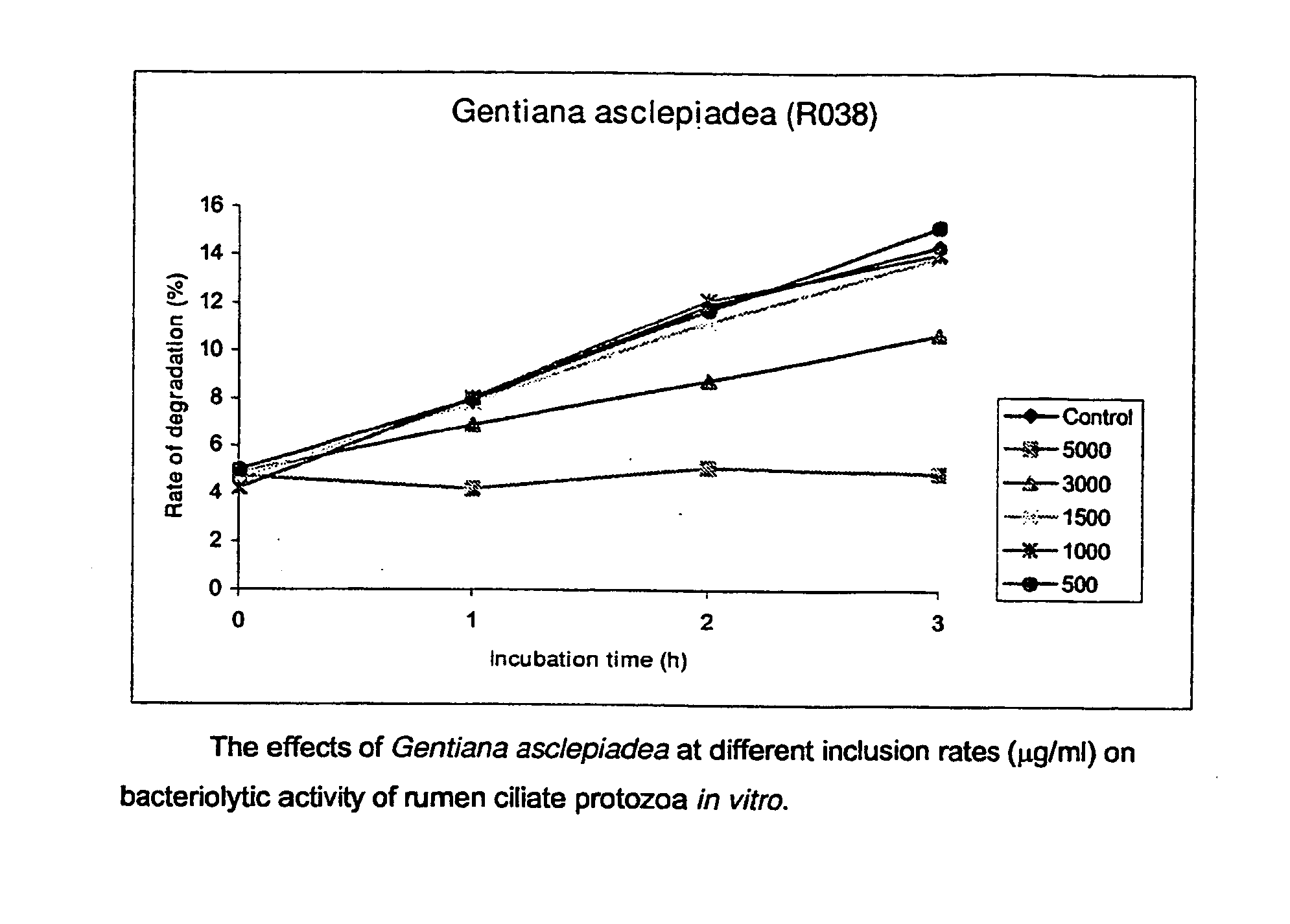
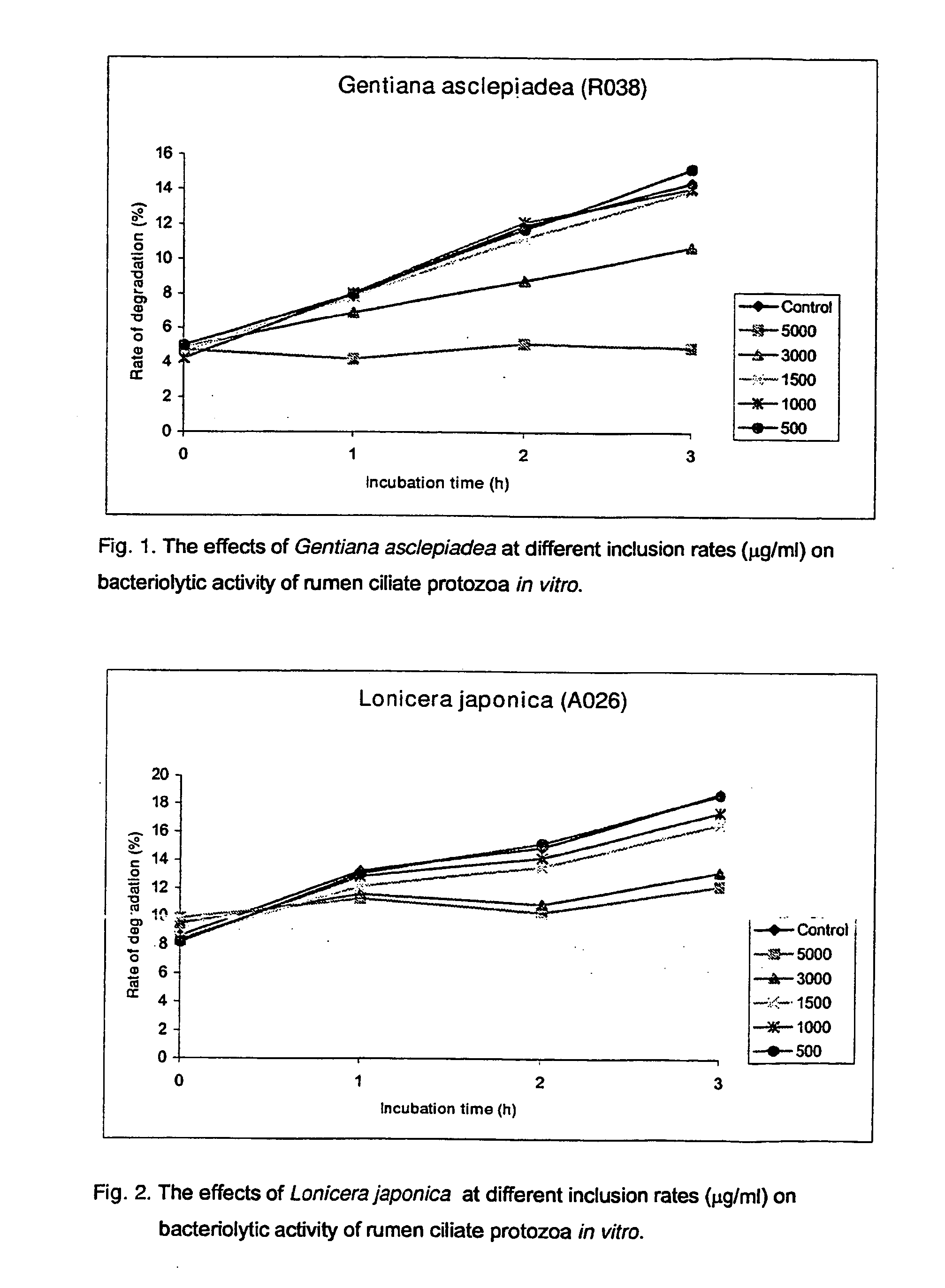
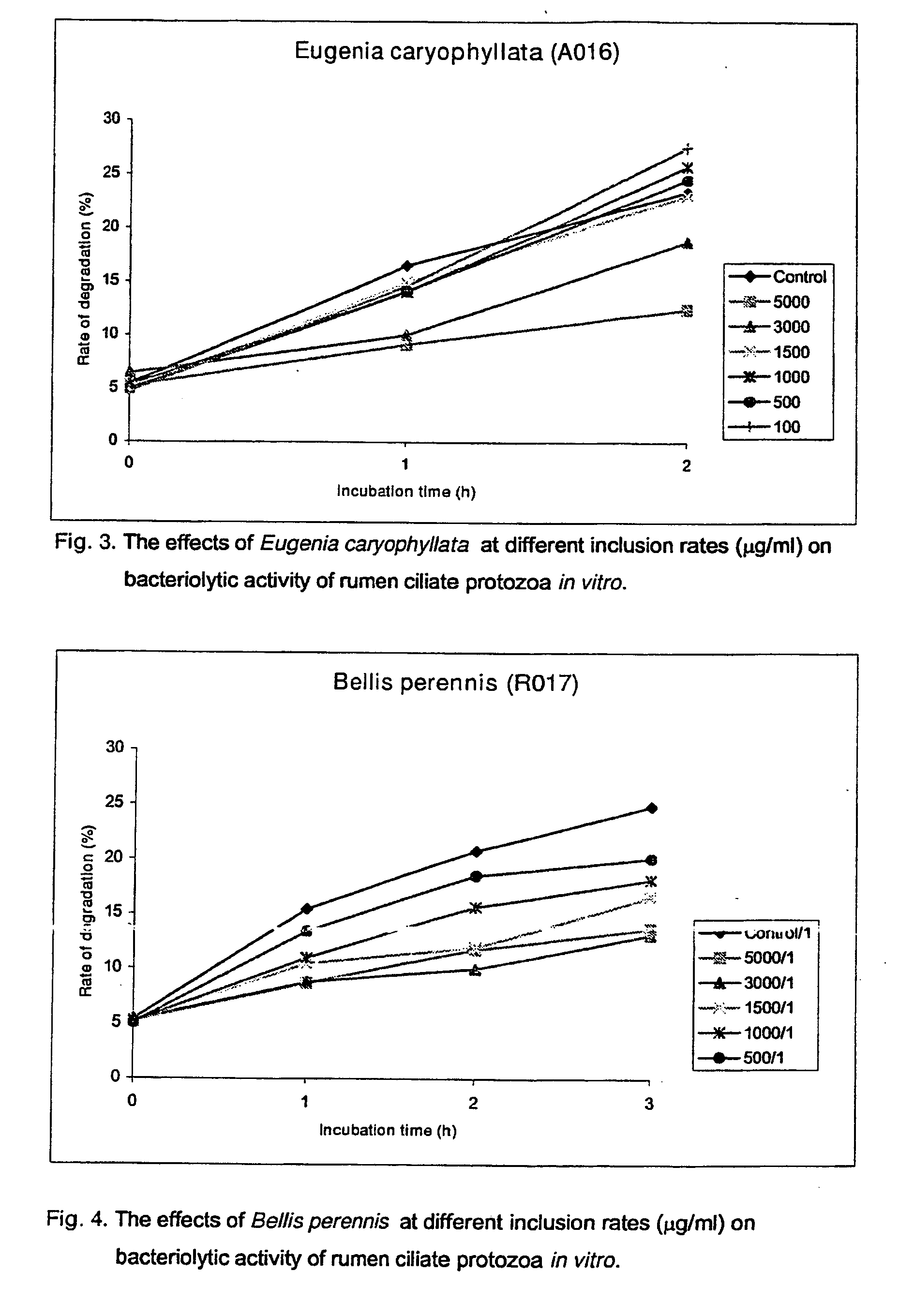
Use Of Plants, Plant Extracts And Nature-Identical Components From Plants To Affect The Rumen Fermentation And To Improve The Energy And Protein Retention Of Ruminants
InactiveUS20080008774A1Reduce failureLimit methanogenesisBiocideAnimal feeding stuffRheum nobileProtein retention
Use of an plant materials, plant extracts or nature-identical components selected from Lonicera japonica, Gentiana asclepidea, Gentiana lutea, Eugenia caryophyllata, Bellis perennis, Olea europaea, Symphytum officinale, Carduus pycnocephalus, Paeoniae alba radix, Populus tremula, Prunus avium, Salix caprea, Rheum nobile, Helianthemum canum, Arctostaphylos uva-ursi, Peltiphyllum peltatum, Epilobium montanum, Knautia arvensis, Latuca sativa and Urtica dioica and extracts thereof, and beta-myrcene to affect the rumen fermentation and to increase the availability of energy and nitrogen source for a ruminant.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Artificial scaffolding material for protein retention and use of the same
The present invention provides an artificial scaffolding material for retaining proteins suitable for placing contiguously one species or two or more species of proteins such as enzymes. To this end, the artificial scaffolding material for retaining proteins is provided with a cell and scaffolding proteins heterologous to the cell and placed on the surface layer side of the cell at an extent that allows aggregation properties to be conferred to the cell, and provided with a plurality of non-covalently binding protein-binding domains arranged in tandem.
Owner:TOYOTA CENT RES & DEV LAB INC +1
Process for manufacturing a soy protein concentrate having high isoflavone content
InactiveUS7083819B2High indexWort preparationProtein composition from vegetable seedsAdditive ingredientUltrafiltration
Owner:SOLAE LLC
Cellulose acetate/chitosan blood dialysis membrane and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105148740AGood pass rateGood for degradation and absorptionSemi-permeable membranesHollow fibreDialysis membranes
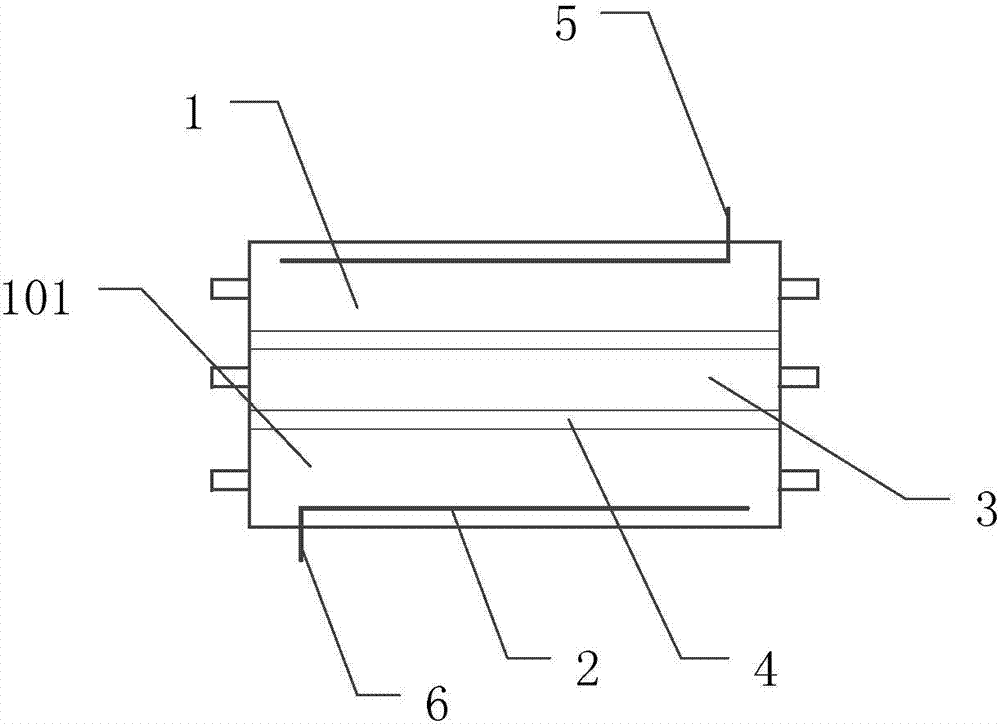
The invention discloses a cellulose acetate / chitosan blood dialysis membrane and a preparation method thereof, and relates to the field of biomaterials. The cellulose acetate / chitosan blood dialysis membrane is a hollow fiber film with hollow fiber diameter of 0.4-4 microns, aperture sizes of 2.2-4.8 microns and wall thickness of 40-80 microns. The dialysis membrane is prepared from 33-56 parts by mass of cellulose acetate, 12-18 parts by mass of chitosan, 5-10 parts by mass of phosphoric acid, 3-10 parts by mass of polyvinyl alcohol, 12-22 parts by mass of tetrahydrofuran and 8-16 parts by mass of dimethyl acetamide. The preparation method comprises 1, spinning liquid preparation and 2, electrostatic spinning. The cellulose acetate / chitosan blood dialysis membrane has good biocompatibility and good biofunctionability, has a high macromolecular protein retention rate and a high urea and water passing rate, and is an ideal dialysis membrane material.
Owner:SUZHOU BEC BIOLOGICAL TECH
Process for producing functional non-naturally occurring proteins, and method for site-specific modification and immobilization of the proteins
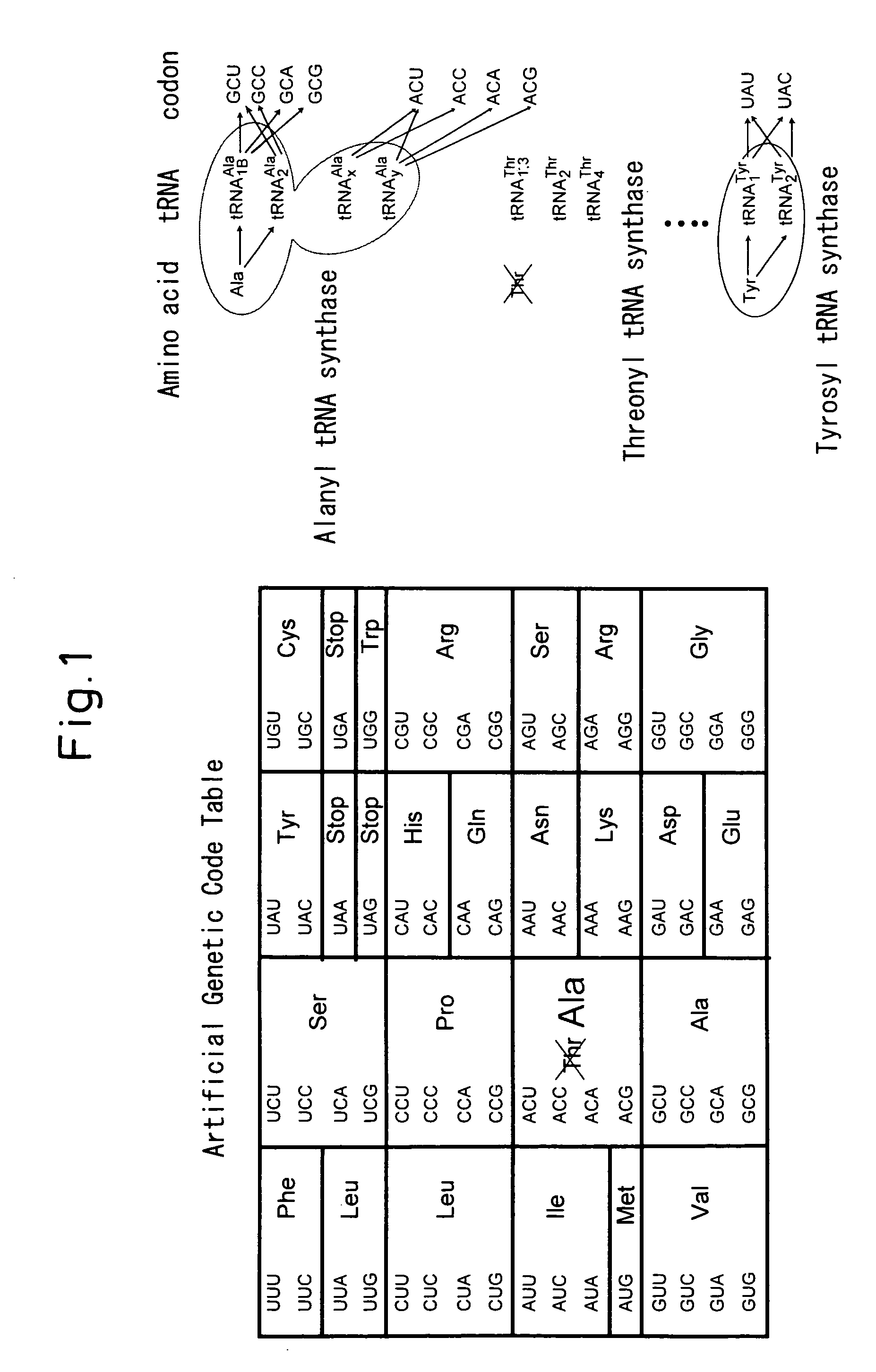
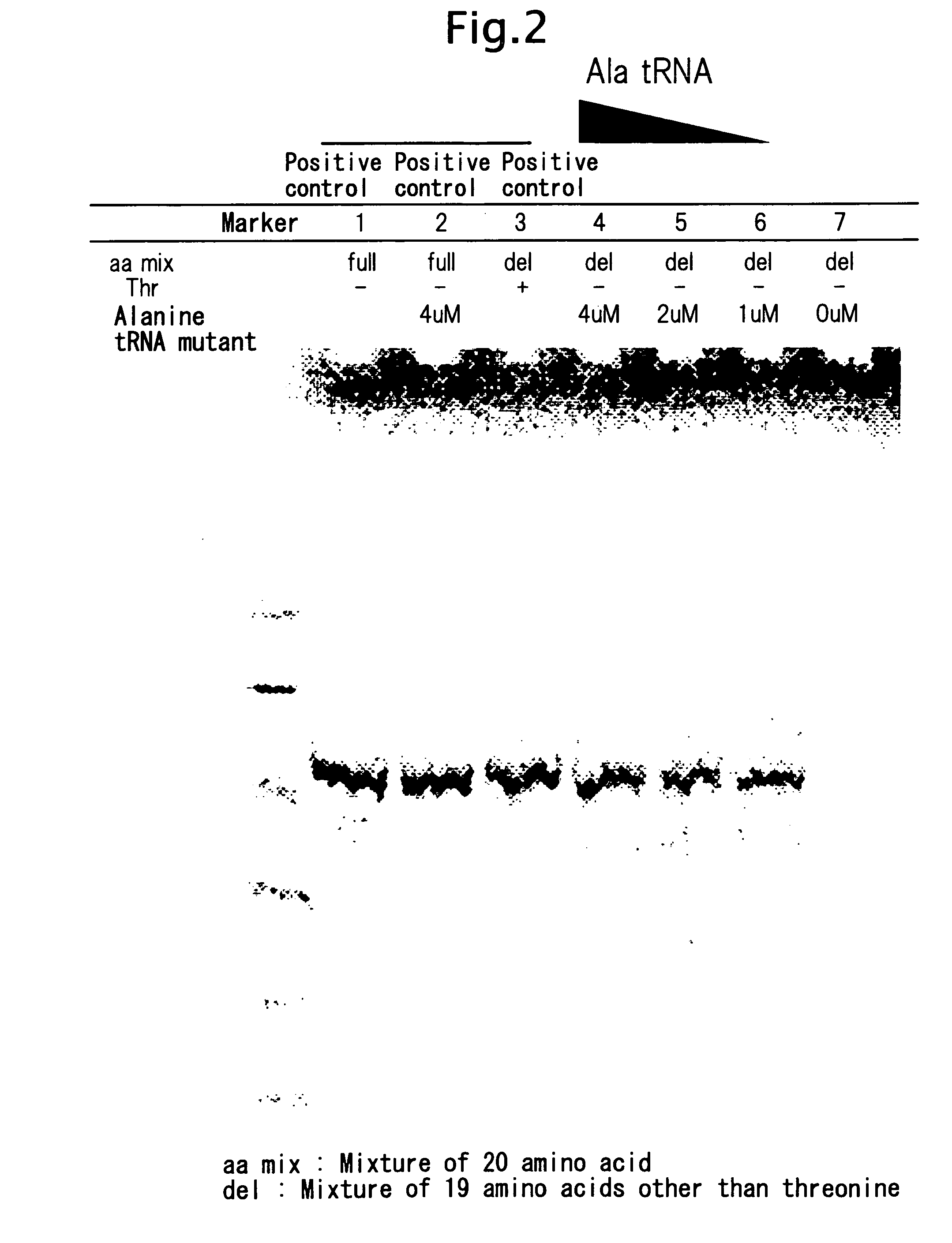
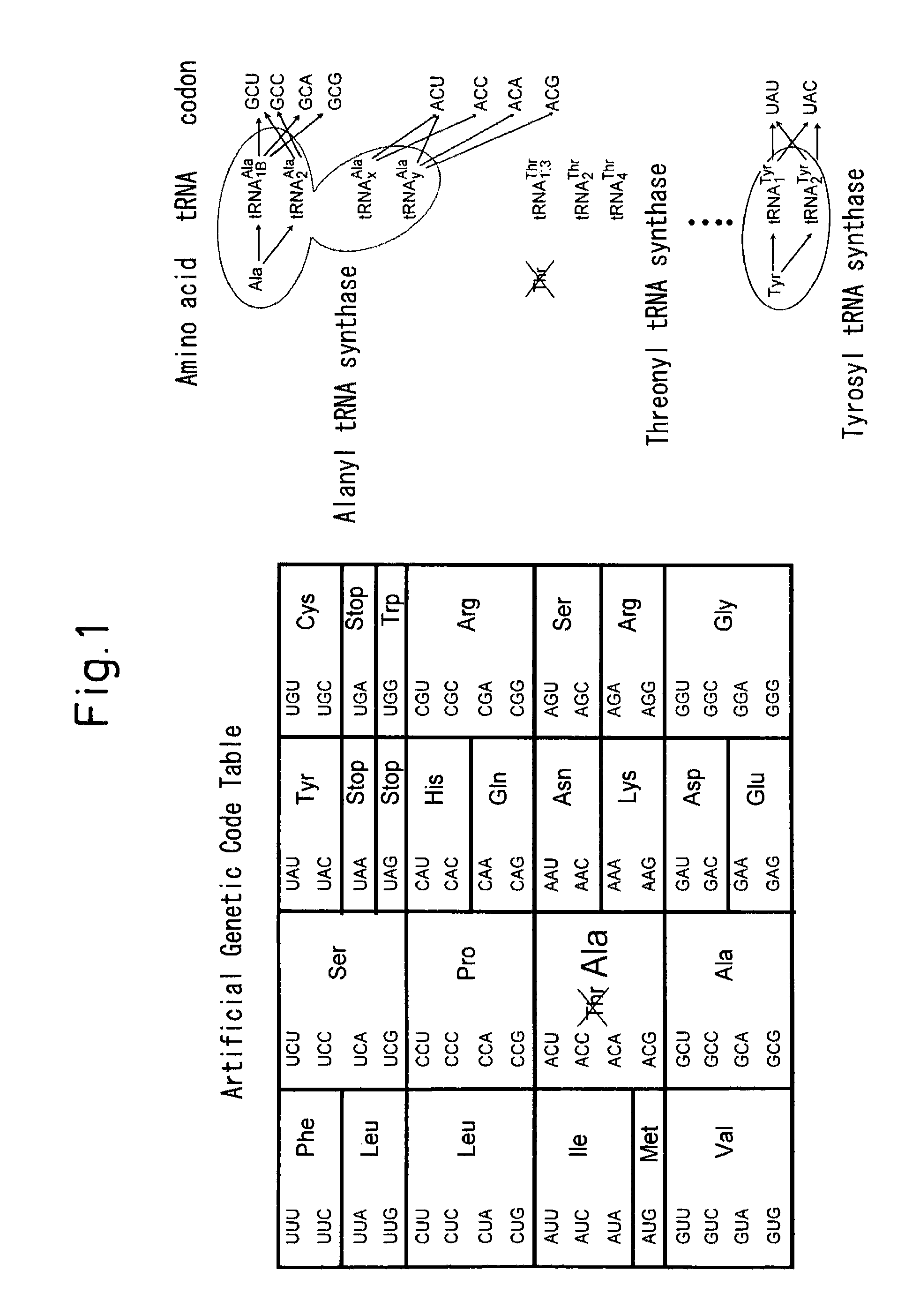
ActiveUS20090011459A1Inexpensive to mass produceSugar derivativesPeptide preparation methodsNucleotideProtein retention
There is provided a process for industrial production of non-naturally occurring proteins composed of less than 20 amino acids, wherein the proteins retain their original functions while being capable of site-specific modification or immobilization, or having new functions not found in nature in addition to the original functions of the proteins.Specifically there are provided a process for producing a functional non-naturally occurring protein having a specific amino acid type(s) replaced with a natural amino acid(s) other than the amino acid type(s), the process comprising:a) matching a nucleic acid portion having a nucleotide sequence reflecting the genotype with a protein portion that is the translation product of the nucleic acid portion;b) selecting the matched molecule obtained in step a);c) introducing mutation into the nucleic acid portion of the matched molecule obtained in step b);d) amplifying the nucleic acid portion obtained in step c);e) providing the nucleic acid portion obtained in step d) to step a), to match the nucleic acid portion with a protein portion that is the translation product of the nucleic acid portion; andf) selecting the matched molecule obtained in step e), to produce a functional non-naturally occurring protein;and a method for site-specific modification and site-immobilization of a functional non-naturally occurring protein.
Owner:WASEDA UNIV
Heavy chain and light chain variable region gene of human B lymphocyte stimulation factor monoclonal antibody and its application
InactiveCN1654654AGood saveHigh cost of mass productionImmunoglobulins against cytokines/lymphokines/interferonsBiological testingDiseaseNucleotide
The present invention relates to human B lymphocyte exciting factor monoclonal antibody heavy chain and light chain variable region gene, the gene coded polypeptide, vector containing the gene, the application of the gene and the polypeptide in preparing clinical detecting reagent for BLyS relative diseases and autoimmune diseases, and the preparation process. The heavy chain variable region gene has full length of 342 bp, nucleotide sequence shown in <400>1, and coded amino acid shown in <400>3; and the light chain variable region gene has full length of 321 bp, nucleotide sequence shown in <400>2, and coded amino acid shown in <400>4. The gene engineering expression produced protein has the antibody combining ability maintained and small scFv molecule, is easy to combine with other effector molecule via gene engineering process. The present invention lays foundation for constituting biological missile, has low cost and is favorable to industrial production.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
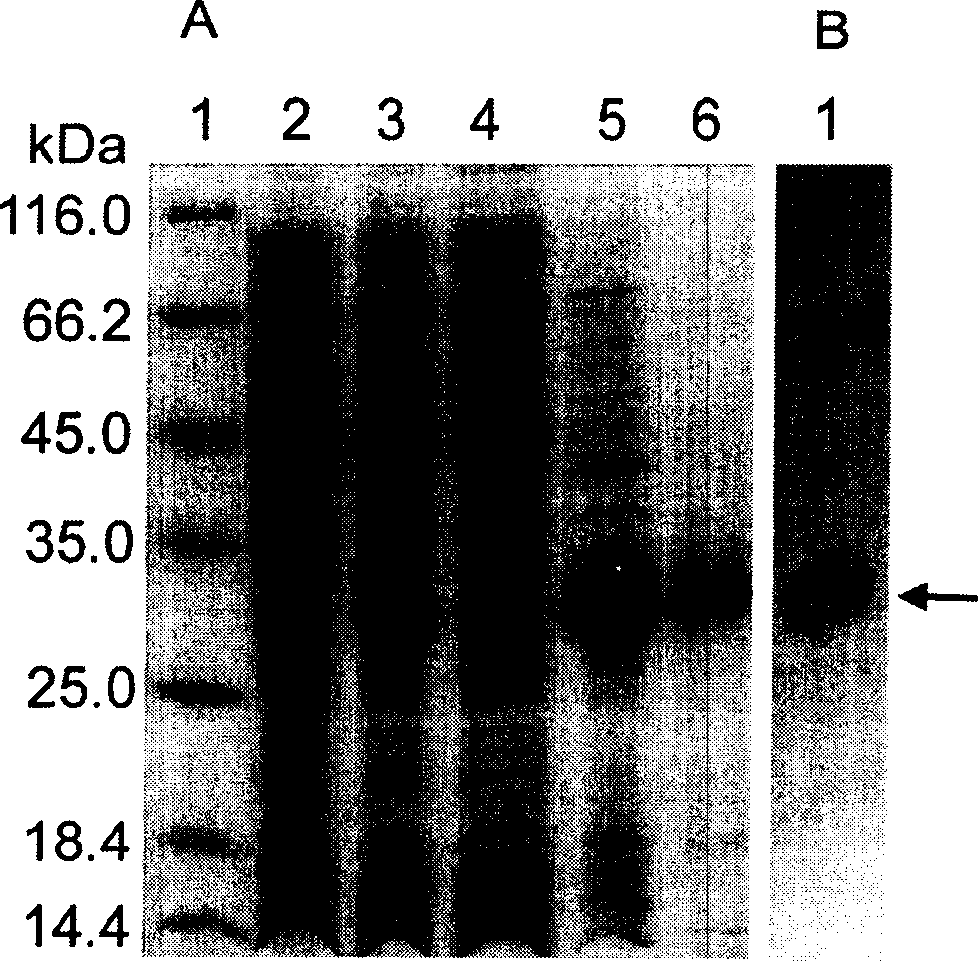
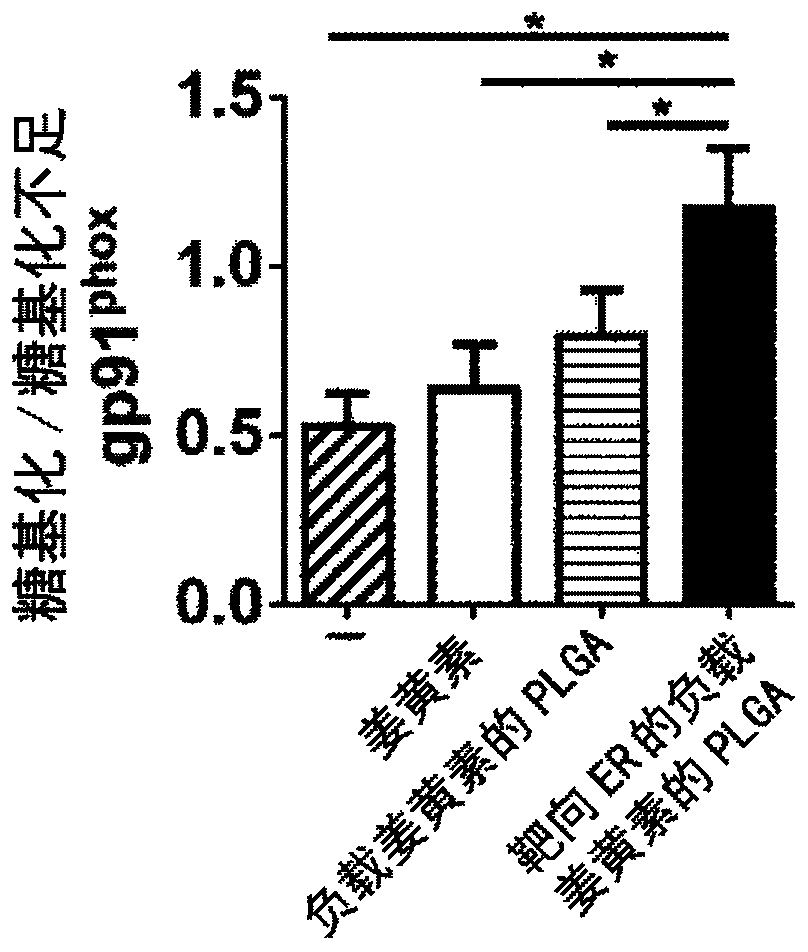
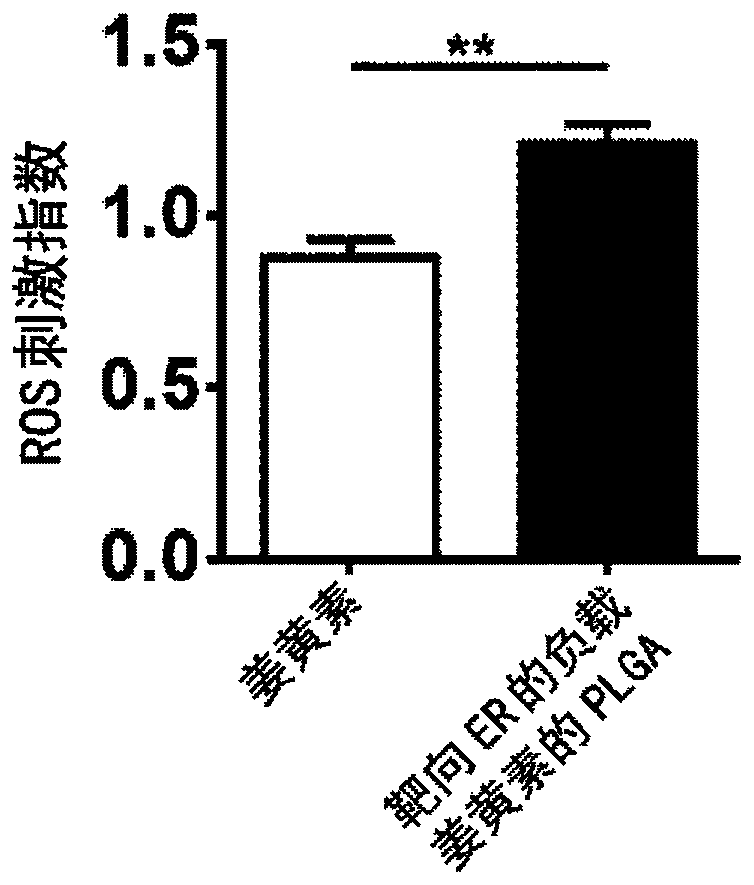
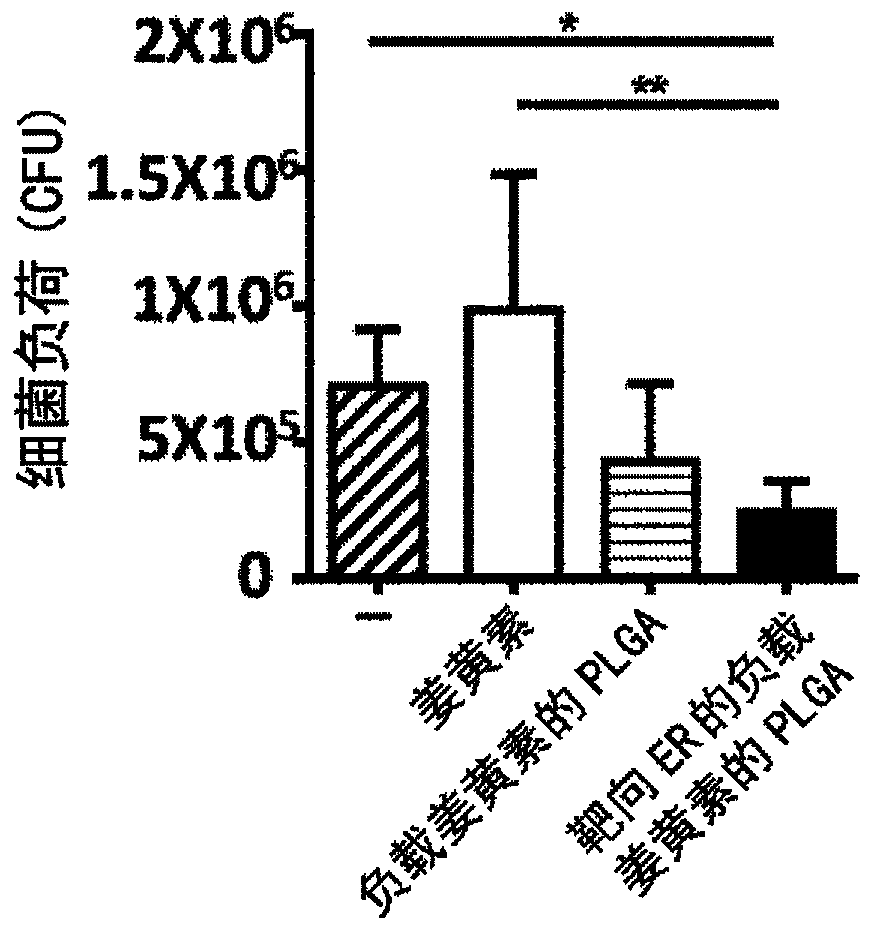
Endoplasmic Reticulum-Targeting Nanovehicles and Methods for Use Thereof
A method for treating a disease caused by protein retention in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) with a sarcoplasmic / endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase pump inhibitor encapsulated in a polymer nanoparticle. The polymer nanoparticle is surface modified such that it is targeted to the ER. The inhibitor reduces protein retention in the ER and the encapsulation lowers side effects of the inhibitor, e.g., cytotoxicity, as compared to administering the inhibitor without encapsulation. Also disclosed is a pharmaceutical composition that can be used for carrying out the method. Further provided is a transgenic mouse carrying in its genome a heterologous nucleic acid that encodes an H338Y mutant gp9lphx protein. The transgenic mouse can serve as a model for human chronic granulomatous disease.
Owner:NAT CHENG KUNG UNIV
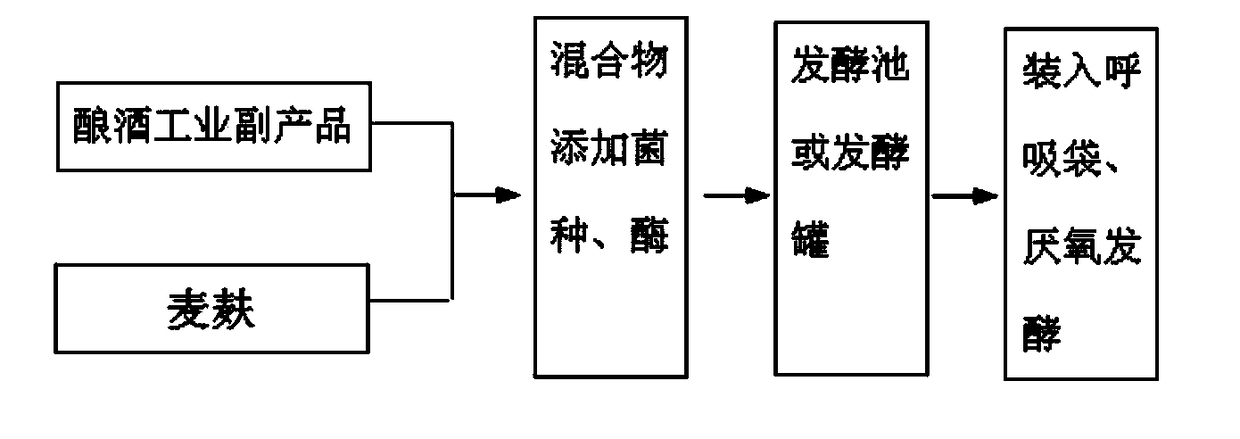
Preparation method of biological feed through reinforced denaturation of wine brewing industrial by-products
InactiveCN109480057AEasy to purifySupplement vitamin AFood processingAnimal feeding stuffCelluloseProtein retention
The invention relates to a preparation method of a biological feed through reinforced denaturation of wine brewing industrial by-products. The preparation method comprises the following steps of mixing the wine brewing industrial by-products with wheat bran, tapioca, traditional Chinese medicine powder and milk powder; and uniformly spraying activated bacillus FY99-01 strains and a compound enzymepreparation in mixed materials, performing aerobic fermentation, and after fermentation is completed, adding anaerobic strains so as to obtain the denaturation feed. According to the making technology disclosed by the invention, crude protein which cannot be absorbed in by-products can be converted into micromolecular water-soluble protein, so that absorption by intestinal tracts of livestock andpoultry can be promoted, protein retention in excrement can be substantially reduced, the balanced compounding ratio of amino acids and leucine in materials can be improved, absorption of nutrient substances by the livestock and the poultry can be promoted, the problems of higher cellulose expansion coefficient and a certain bonding degree of the by-products are solved, and digestion and absorption of nutrients are promoted.
Owner:海南汇萃生物科技有限公司
Conductance of improperly folded proteins through the secretory pathway and related methods for treating disease
InactiveUS8058314B2Reduced activityReduce expressionHalogenated hydrocarbon active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseMedicine
This invention provides the methodology and agents for treating any disease or clinical condition which is at least partly the result of endoplasmic reticulum-associated retention of proteins. Thus, the methods and agents of the present invention provide for the release of normally retained proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum. The present invention is particularly useful for treating any disease or clinical condition which is at least partly the result of endoplasmic reticulum-associated retention or degradation of mis-assembled or mis-folded proteins.
Owner:N FOLD LLC
Alfalfa spiral-type hay bundle processing technology in severe cold pasturing area
InactiveCN102630441BThe processing and modulation method is simpleEasy to operateAgriculture tools and machinesHarvested fruit hanging devicesProtein retentionPastoral area
The invention discloses an alpine-pastoral-area alfalfa spiral-type hay bundle processing technology in a severe cold pasturing area, which comprises the following steps of: (1) selection of variety; (2) harvesting; (3) forming the spiral type; (4) airing; and (5) storage. The alfalfa spiral-type hay bundle processing technology has the advantages of long pasture storage time, low requirement in water content, simplicity and easiness in operation and completeness in protein reservation.
Owner:GANSU AGRI UNIV
A kind of hydrophilic film and preparation method thereof
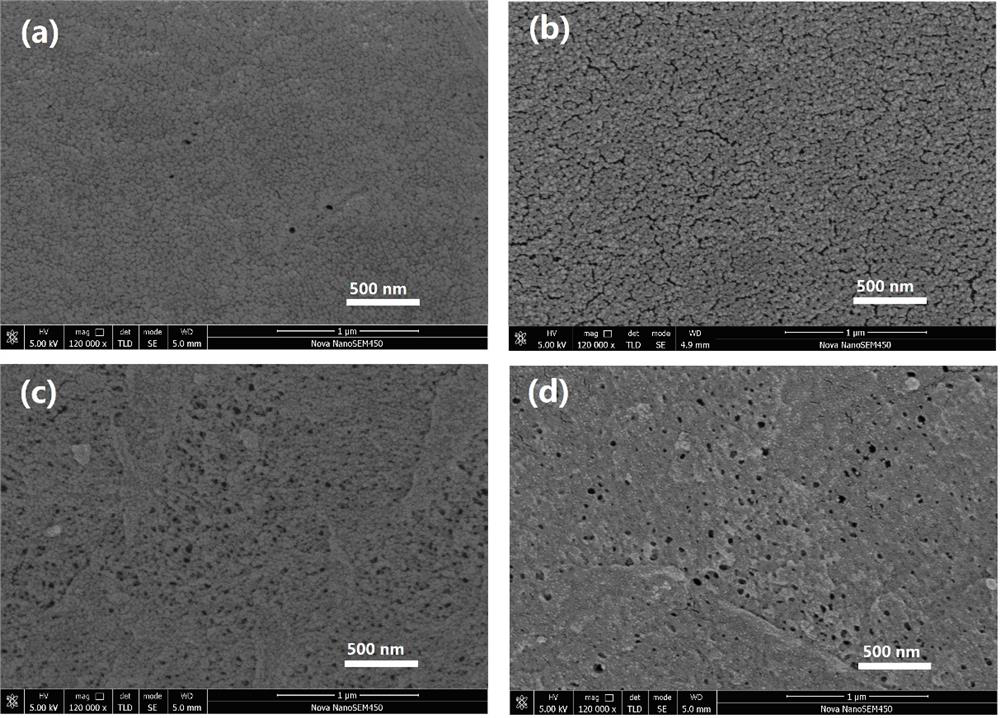
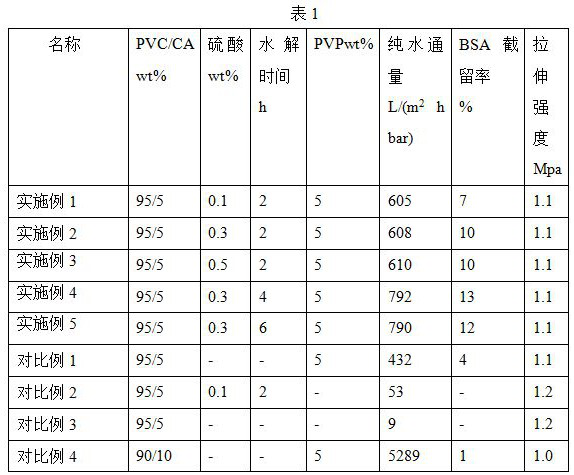
ActiveCN112452161BImprove filtering effectImprove pollutionMembranesSemi-permeable membranesFluid phaseCellulose acetate
The invention discloses a hydrophilic membrane and a preparation method thereof. Mix the membrane, then immerse the pretreated blend membrane in dilute sulfuric acid at 50-60°C for 2-6 hours, take it out, wash it and dry it to get a hydrophilic hydrolyzed membrane, wherein the hydrophobic raw material is polyvinyl chloride or chlorinated polyvinyl chloride . In the present invention, the hydrophobic raw material and cellulose acetate are added to the porogen to cast the film, and then the film is subjected to acid hydrolysis treatment, so that the pure water flux and the protein retention rate of the film are improved, and on the basis of maintaining the mechanical properties of the blended film, It greatly improves the filtration performance and anti-fouling ability of the membrane.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
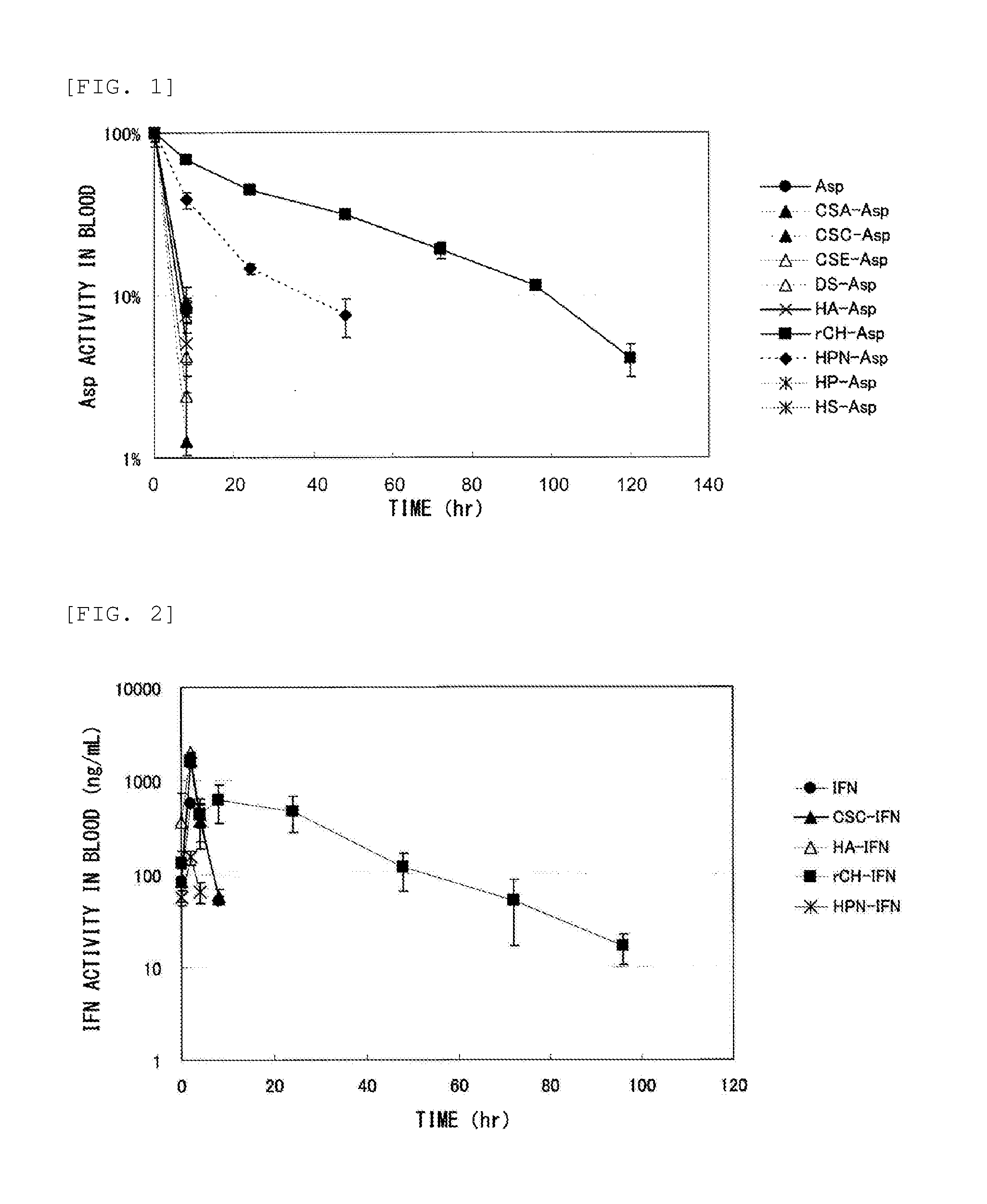
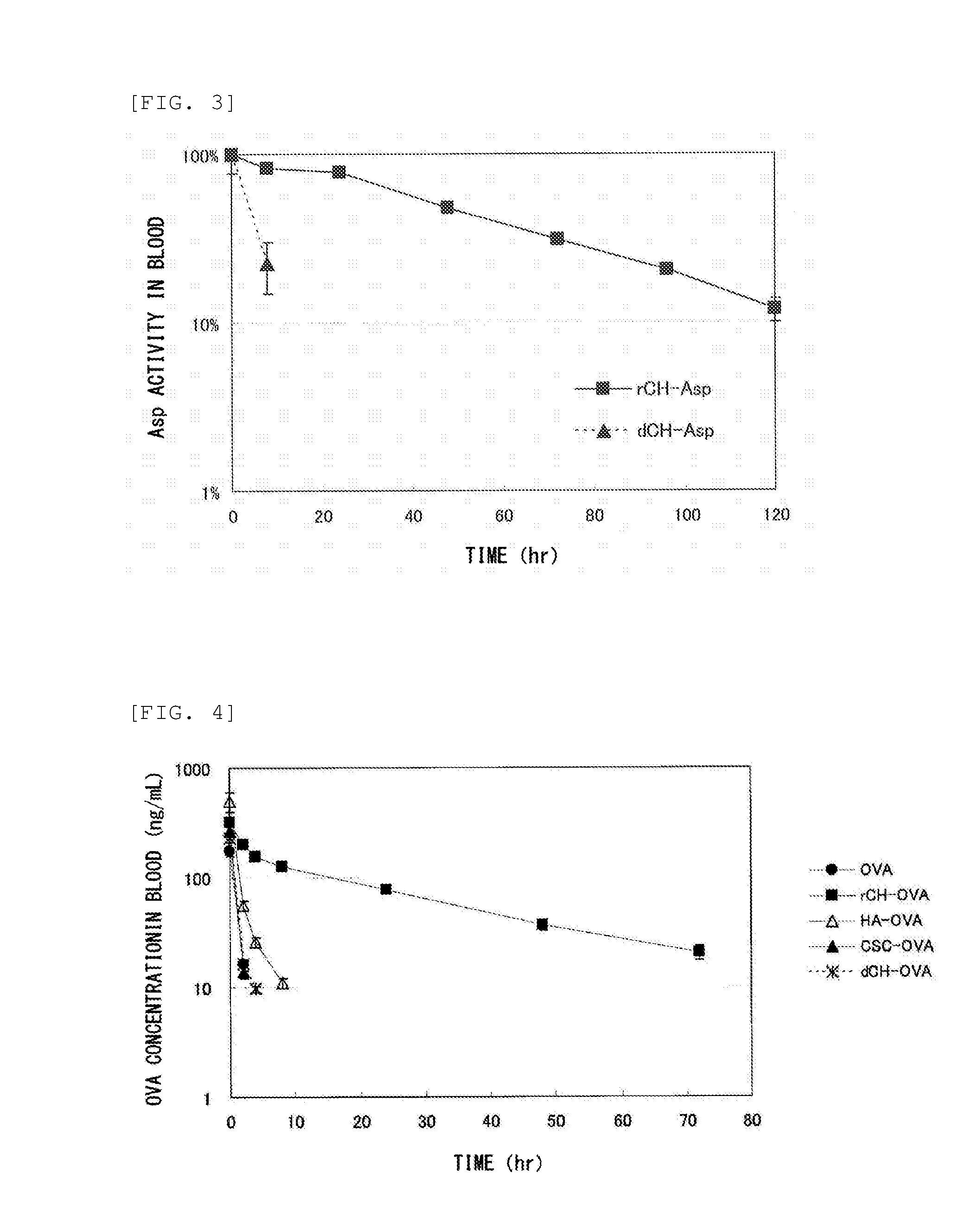
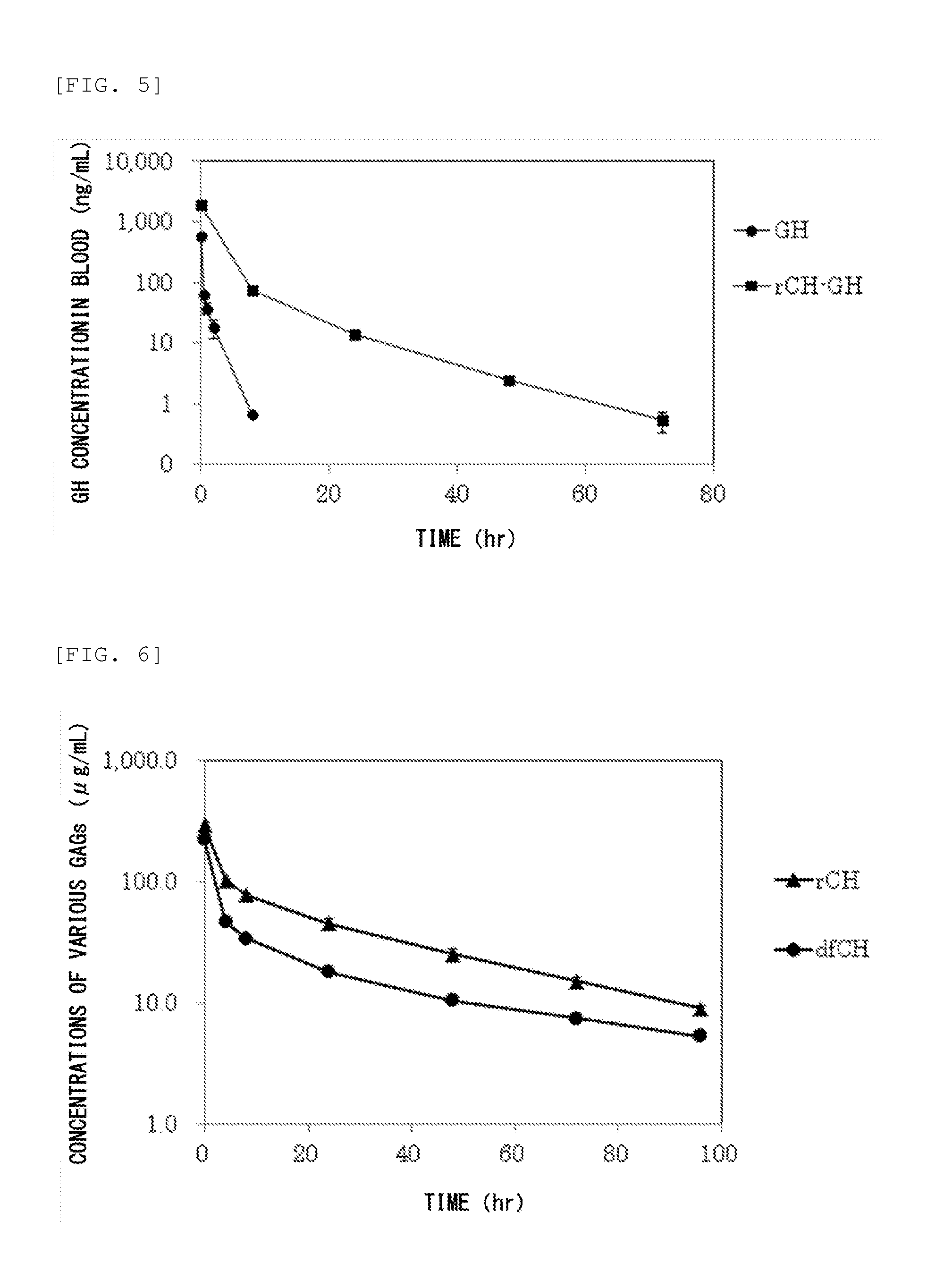
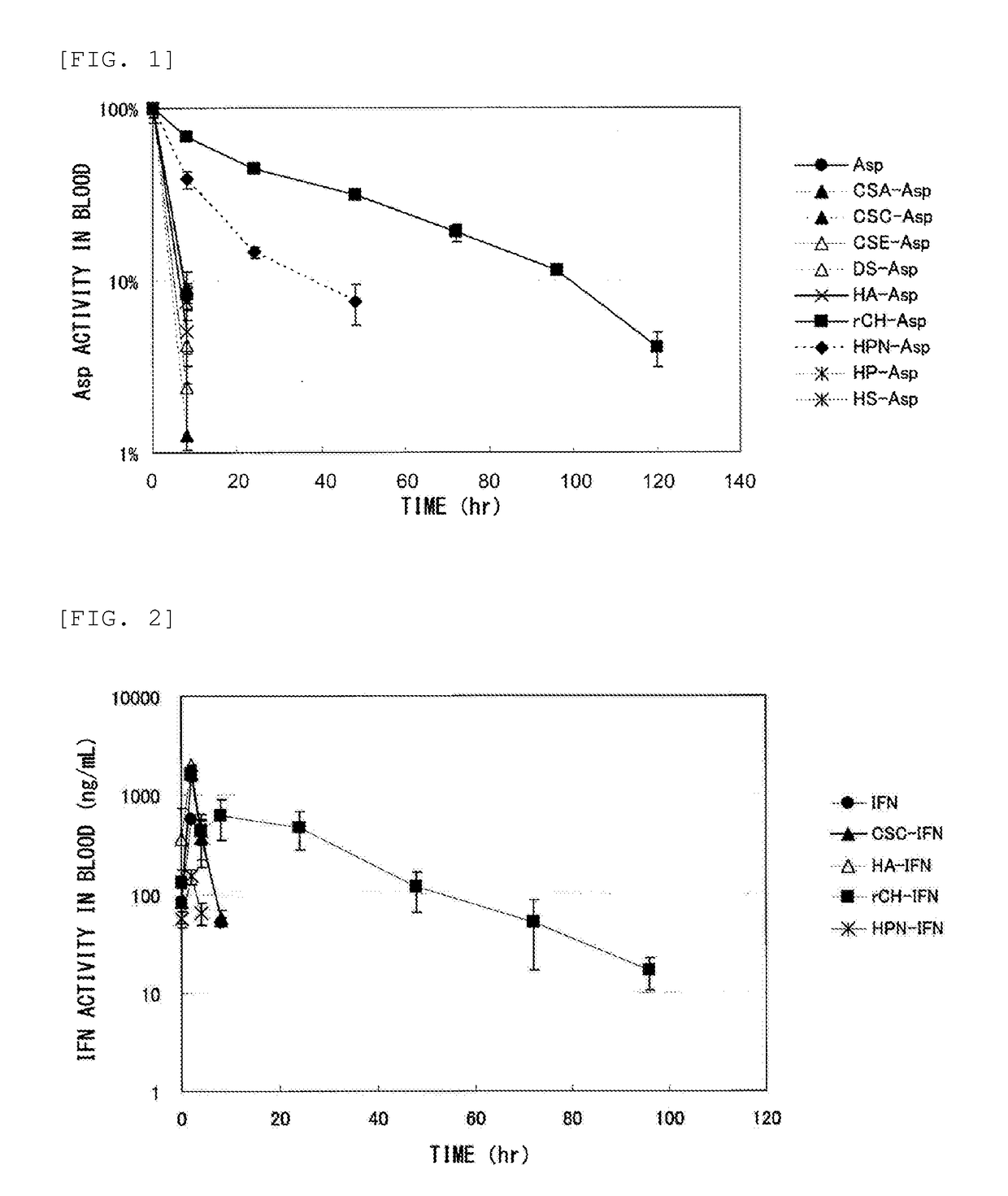
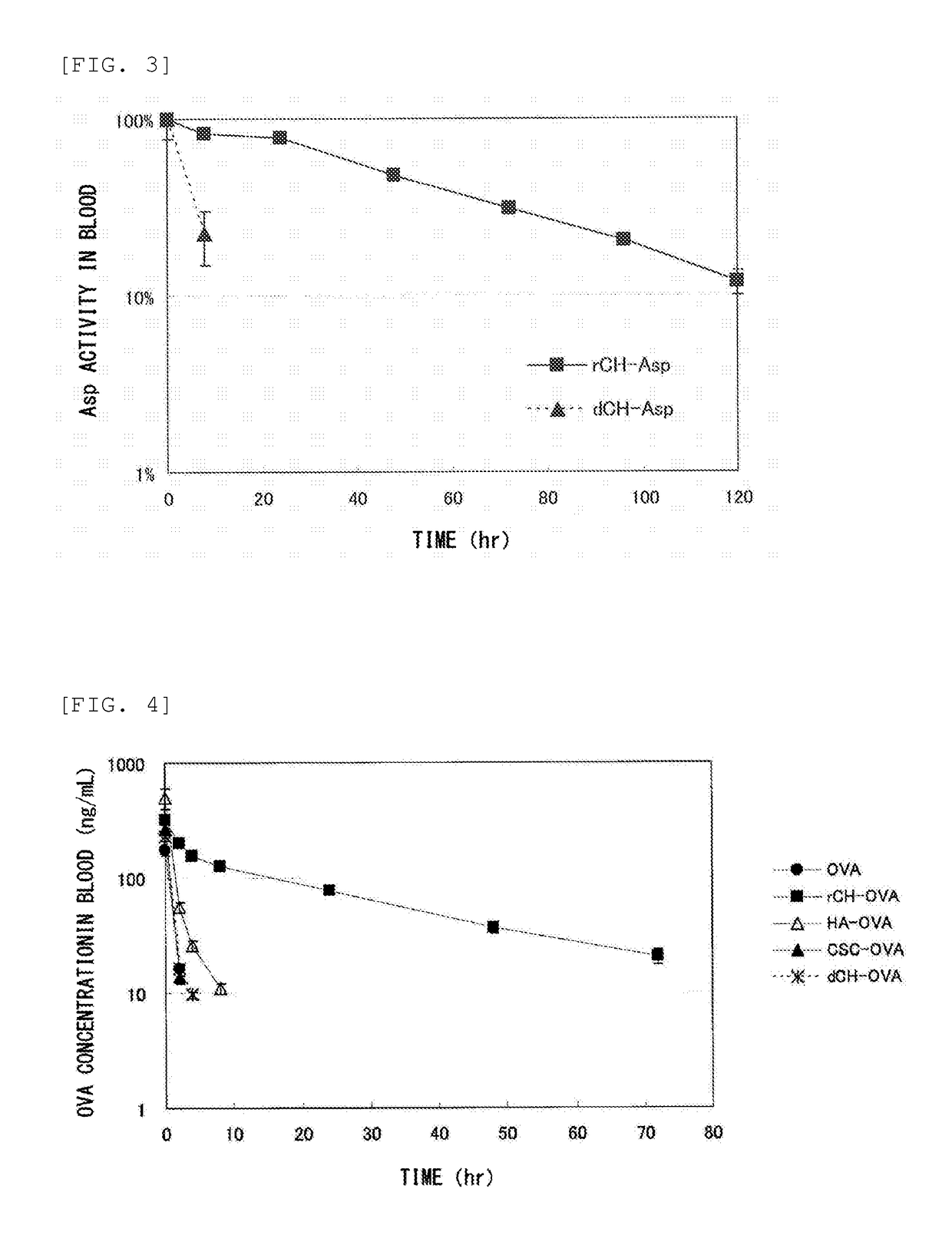
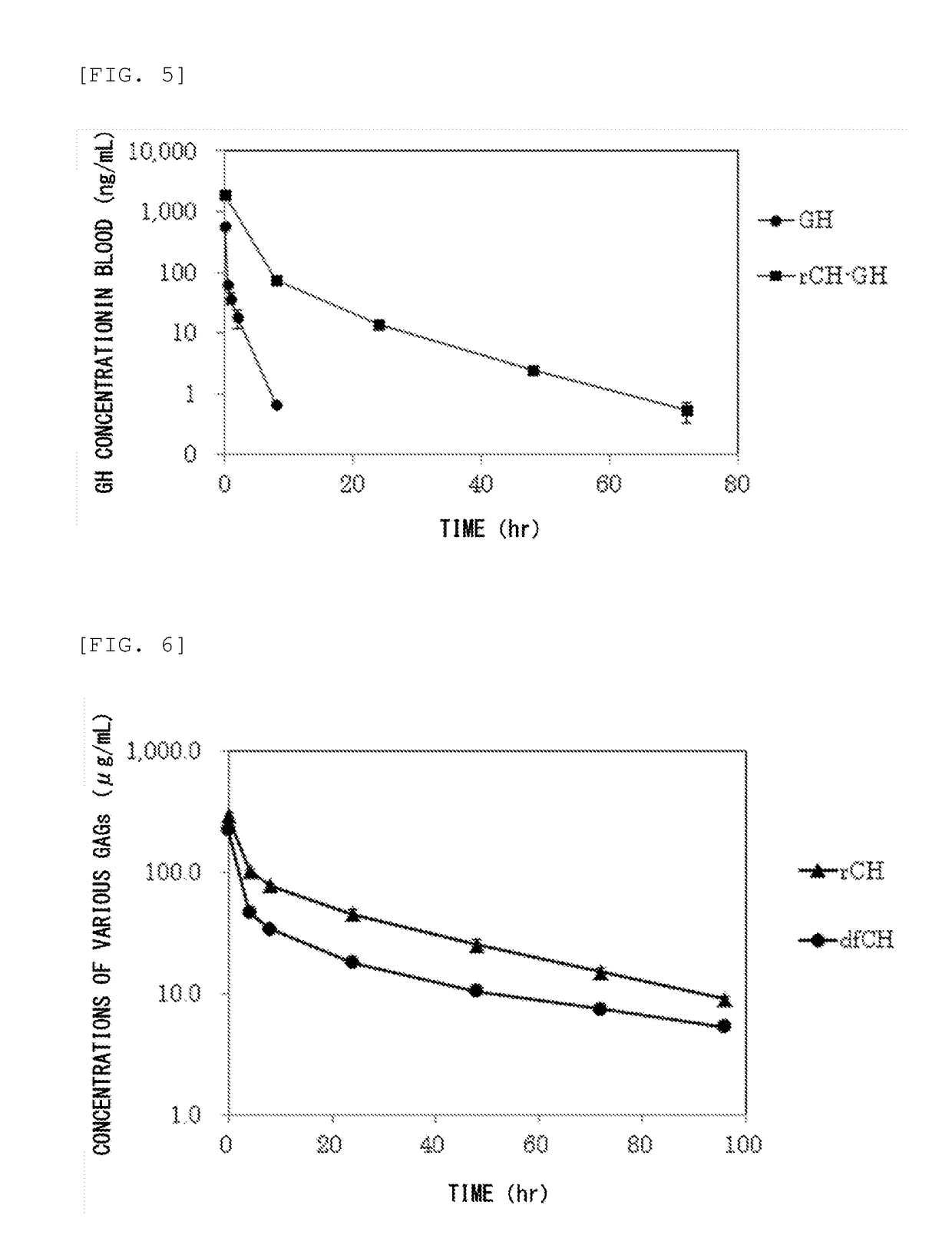
Method for improving blood persistence of protein
ActiveUS20160235857A1Increasing protein retentionLong retentionHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsProtein retentionChondroitin synthase
Provided herein is a means for increasing protein retention in blood. The protein retention in blood is increased by forming a conjugate of a protein and chondroitin produced by a microorganism having chondroitin-producing capability and / or chondroitin synthesized with a chondroitin synthase.
Owner:SEIKAGAKU KOGYO CO LTD
Preparing method of protein concentrate of sacha inchi fruits
InactiveCN105707407AHigh retention rateSimple processProtein composition from vegetable seedsBiotechnologyAcid water
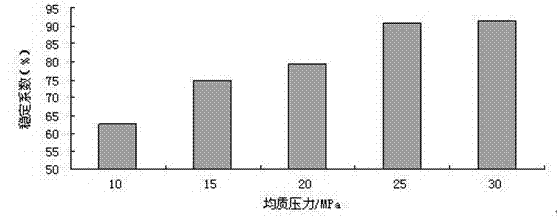
The invention discloses a preparing method of protein concentrate of sacha inchi fruits. By using the characteristics that the dissolving rates of the protein of sacha inchi fruits and micromolecule impurities in an ethanol solution and an acid aqueous solution are different, sacha inchi fruit meal is extracted with an ethanol solution, alcohol soluble impurities are separated, precipitation is extracted with acid water, acid water soluble impurities are separated, the precipitation is added with water to regulate the pH to be neutral, and the protein concentrate of sacha inchi fruits can be obtained through high-pressure homogenization and spray drying. The preparing method of the protein concentrate of sacha inchi fruits is low in cost, and the protein concentrate is white in color, free of acerbity, edible, high in yield and protein retention rate and capable of achieving mechanization.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
protein retention extension microscopy
ActiveCN108139408BPreparing sample for investigationBiological material analysisProtein retentionStreptavidin
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Preparation method of peanut peptide
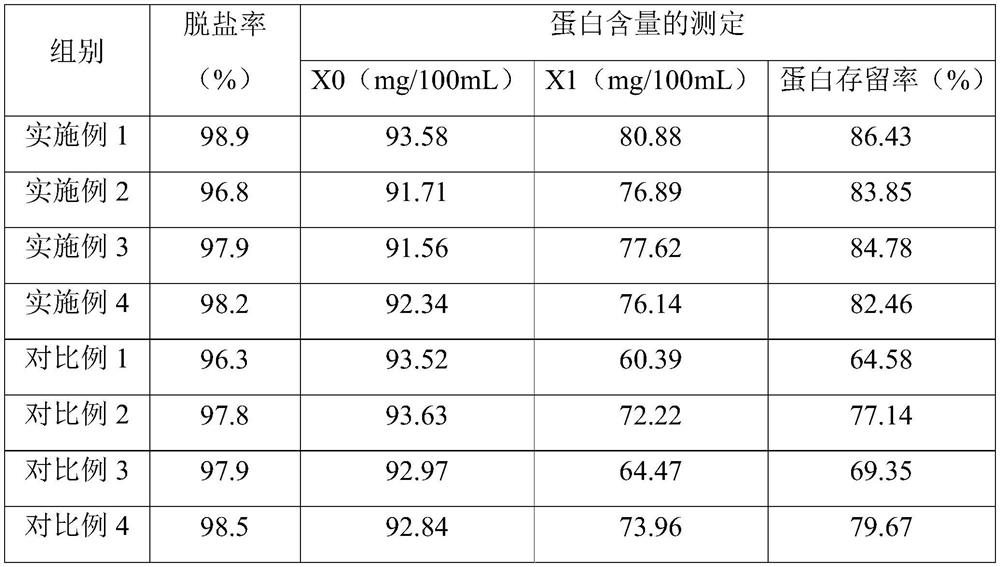
ActiveCN112501231AHigh desalination rateHigh protein contentPeptide preparation methodsFermentationDC - Direct currentUltrasonic assisted
The invention belongs to the technical field of peanut protein processing, and particularly relates to a preparation method of peanut peptide. The preparation method of the peanut peptide comprises the following steps of: S1) preparing peanut protein isolate; S2) performing ultrasonic enzymolysis treatment to obtain enzymatic hydrolysate; S3) performing electrodialysis desalination: adding the enzymatic hydrolysate obtained in the step S2 into a fresh water chamber of an electrodialysis device, adding 8-12g / L of a sodium sulfate aqueous solution into an electrode water chamber, adding a compound solution into a concentrated water chamber, applying 20-30V direct current voltage to electrodes on two sides of the electrodialysis device, and stopping when the conductivity is reduced to 100 microseconds / cm; and S4) performing drying: collecting feed liquid in the fresh water chamber in the step S3, and performing drying to obtain the peanut peptide. According to the preparation method disclosed by the invention, peanut meal is sequentially subjected to the steps of alkali extraction, acid extraction, ultrasonic assisted enzymolysis and electrodialysis desalination to obtain the peanut peptide, so that the protein retention rate of the peanut peptide is greatly increased, and the peanut peptide is good in antioxidant activity.
Owner:GUANGZHOU TIANQI BIO TECH
Process for producing functional non-naturally occurring proteins, and method for site-specific modification and immobilization of the proteins
ActiveUS8227209B2Sugar derivativesPeptide preparation methodsProtein retentionAmino acid composition
Owner:WASEDA UNIV
Method for improving blood persistence of protein
Owner:SEIKAGAKU KOGYO CO LTD
A kind of preparation method of peanut peptide
ActiveCN112501231BHigh desalination rateHigh protein contentPeptide preparation methodsFermentationProtein isolatePeanut meal
The invention belongs to the technical field of peanut protein processing, and in particular relates to a preparation method of peanut peptide. The preparation method of the peanut peptide of the present invention comprises the following steps: S1) preparation of peanut protein isolate; S2) ultrasonic enzymolysis treatment to obtain an enzymatic hydrolysis solution; S3) electrodialysis desalination: adding the enzymatic hydrolysis solution of step S2 to the fresh water of the electrodialysis device In the chamber, 8-12g / L sodium sulfate aqueous solution is added to the polar water chamber, and the compound solution is added to the concentrated water chamber. The electrodes on both sides of the electrodialysis device are connected with 20-30V DC voltage, and stop when the conductivity drops to 100μs / cm; S4) Drying: collect the feed liquid in the fresh water chamber in step S3, and dry it to obtain the peanut peptide. The present invention sequentially adopts the steps of alkali extraction, acid extraction, ultrasonic-assisted enzymolysis and electrodialysis desalination to peanut meal to prepare peanut peptide, which greatly improves the protein retention rate of peanut peptide and has good antioxidant activity.
Owner:GUANGZHOU TIANQI BIO TECH
Ultrafiltration device for drug binding studies
InactiveUS20050266577A1Improve protein retentionSimple and flexibleMembranesPreparing sample for investigationUltrafiltrationMedicine
The combination of a supported UF membrane having low non-specific binding (NSB) and high protein retention of the tested chemical entity (CE) in a device that is SBS complaint. The membrane is heat sealed to form one or more integral wells that are used to reduce NSB and improve protein retention and provides a simple, flexible way to reduce CE, such as drug and drug candidate (and other small molecule) NSB so that drug binding studies may more closely predict the behavior of these compounds in vivo.
Owner:MILLIPORE CORP
A kind of manufacture method of inchi fruit concentrated protein
InactiveCN105707407BHigh retention rateSimple processProtein composition from vegetable seedsProtein retentionHigh pressure
The invention discloses a preparing method of protein concentrate of sacha inchi fruits. By using the characteristics that the dissolving rates of the protein of sacha inchi fruits and micromolecule impurities in an ethanol solution and an acid aqueous solution are different, sacha inchi fruit meal is extracted with an ethanol solution, alcohol soluble impurities are separated, precipitation is extracted with acid water, acid water soluble impurities are separated, the precipitation is added with water to regulate the pH to be neutral, and the protein concentrate of sacha inchi fruits can be obtained through high-pressure homogenization and spray drying. The preparing method of the protein concentrate of sacha inchi fruits is low in cost, and the protein concentrate is white in color, free of acerbity, edible, high in yield and protein retention rate and capable of achieving mechanization.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Isoelectric protein purification device and method
PendingCN107245093AWon't changeLow costPeptide preparation methodsProtein targetConcentration polarization
The invention discloses a method and device for carrying out protein purification on the basis of isoelectric point difference of proteins. A principle of the method and the device is as follows: during electrophoresis, a target protein hardly swims in a buffer solution, of which isoelectric points are the same as those of the target protein. Impurity proteins swim to the positive pole or negative pole of an electrophoresis bath due to negative charges or positive charges and are concentrated on electrode bath areas, so as to be separated from the target protein. A sample is isolated from positive and negative pole areas of the electrophoresis bath by adopting a microporous material, so that the target protein can be reserved in a sample pool after electrophoresis. Meanwhile, the buffer solution in an electrode bath is uninterruptedly updated during electrophoresis, so that the condition that the swimming of the impurity proteins stops and the impurity proteins and polarized accumulated ions are taken away due to pH polarization and the concentration polarization of various charged ions is avoided.
Owner:赖兵
A kind of fermentation medium comprising waste bean curd yellow pulp water and waste bean dregs and its application
ActiveCN108410782BReduce pollutionReduce energy consumptionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCelluloseProtein retention
The invention discloses a fermentation medium containing waste bean curd yellow pulp and waste bean dregs and its application. Each liter of the fermentation medium includes the following components: 500 mL-1000 mL of treated waste bean curd yellow pulp, The final treated waste okara is 60-80 g, the inorganic salt is 0.25-30 g, and the pH is 6.5-7.5. The present invention adopts the combination treatment method of enzymatic hydrolysis and ceramic membrane filtration to treat waste bean curd yellow slurry water, and can obtain protein retention rate of 78%~85%, and total sugar penetration rate of 92%~96%; A large amount of cellulose in the fermentation process is hydrolyzed into glucose, which is the carbon source required for the fermentation of Corynebacterium glutamicum. The present invention can utilize the wastes in production such as bean curd yellow pulp water and bean dregs, which can not only reduce the cost of industrial production, avoid the waste of waste resources, but also reduce the pollution of waste materials to the environment, and at the same time increase the production of glutamic acid. The biomass of Corynebacterium acid and the production of L-ornithine.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com