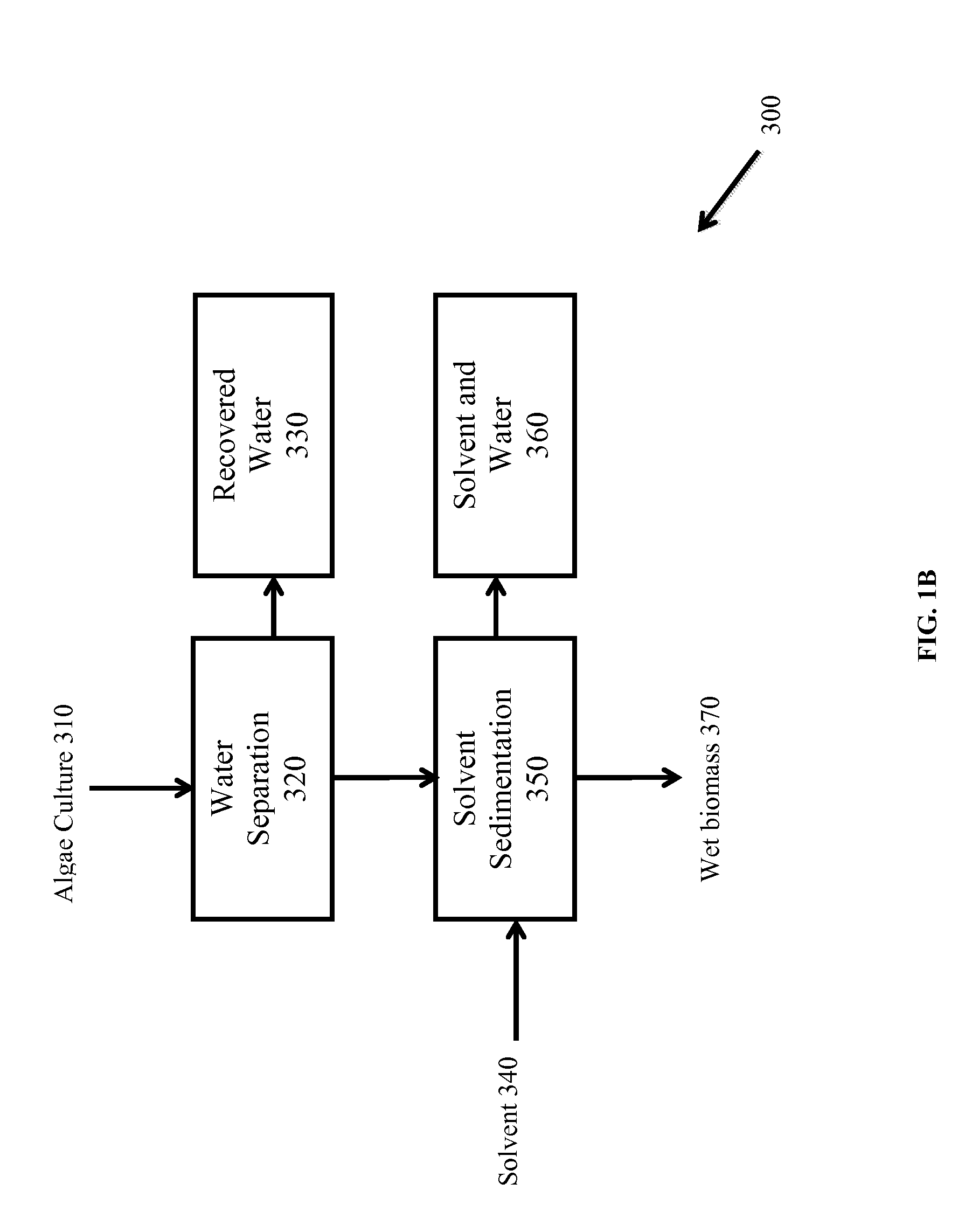
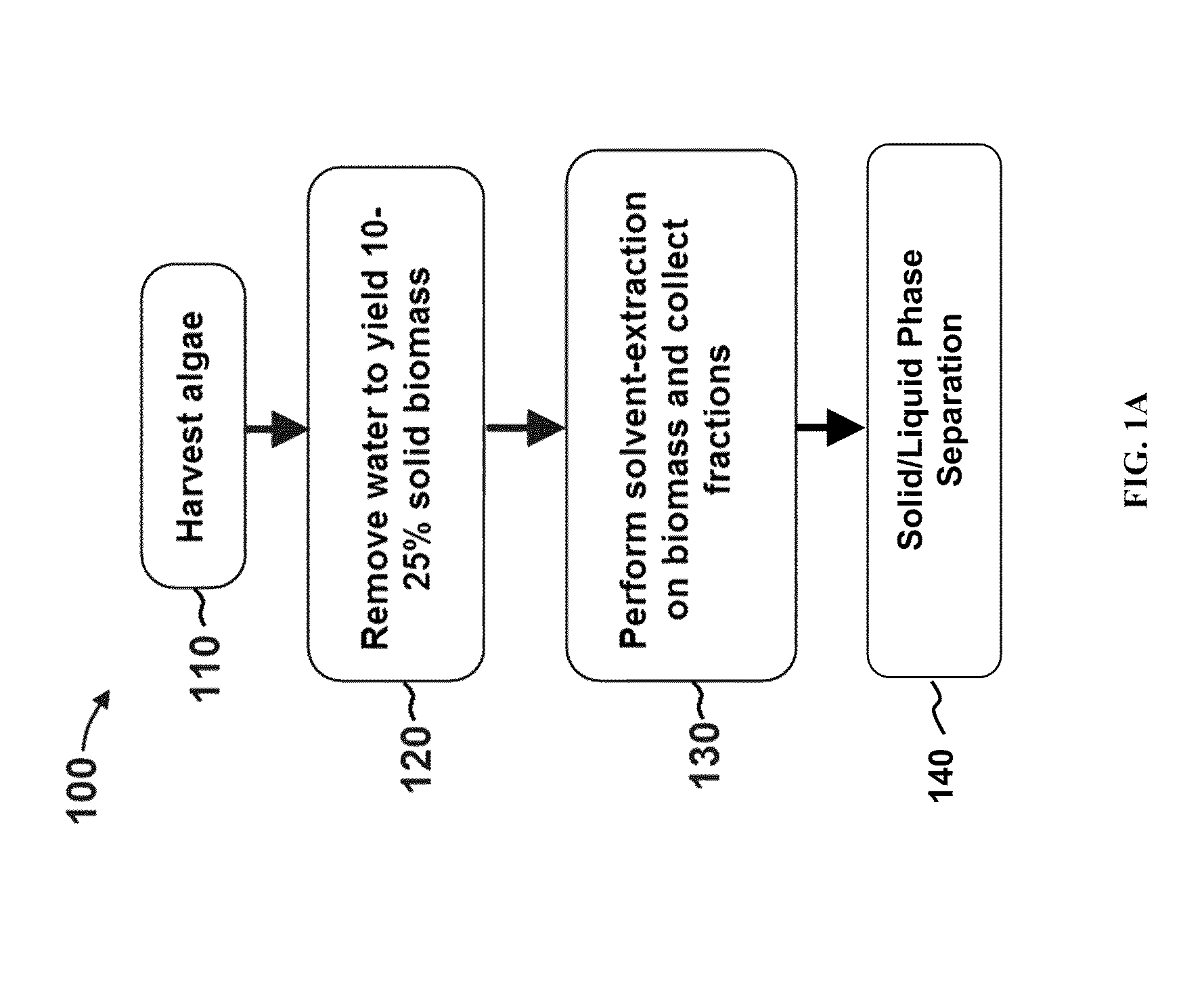
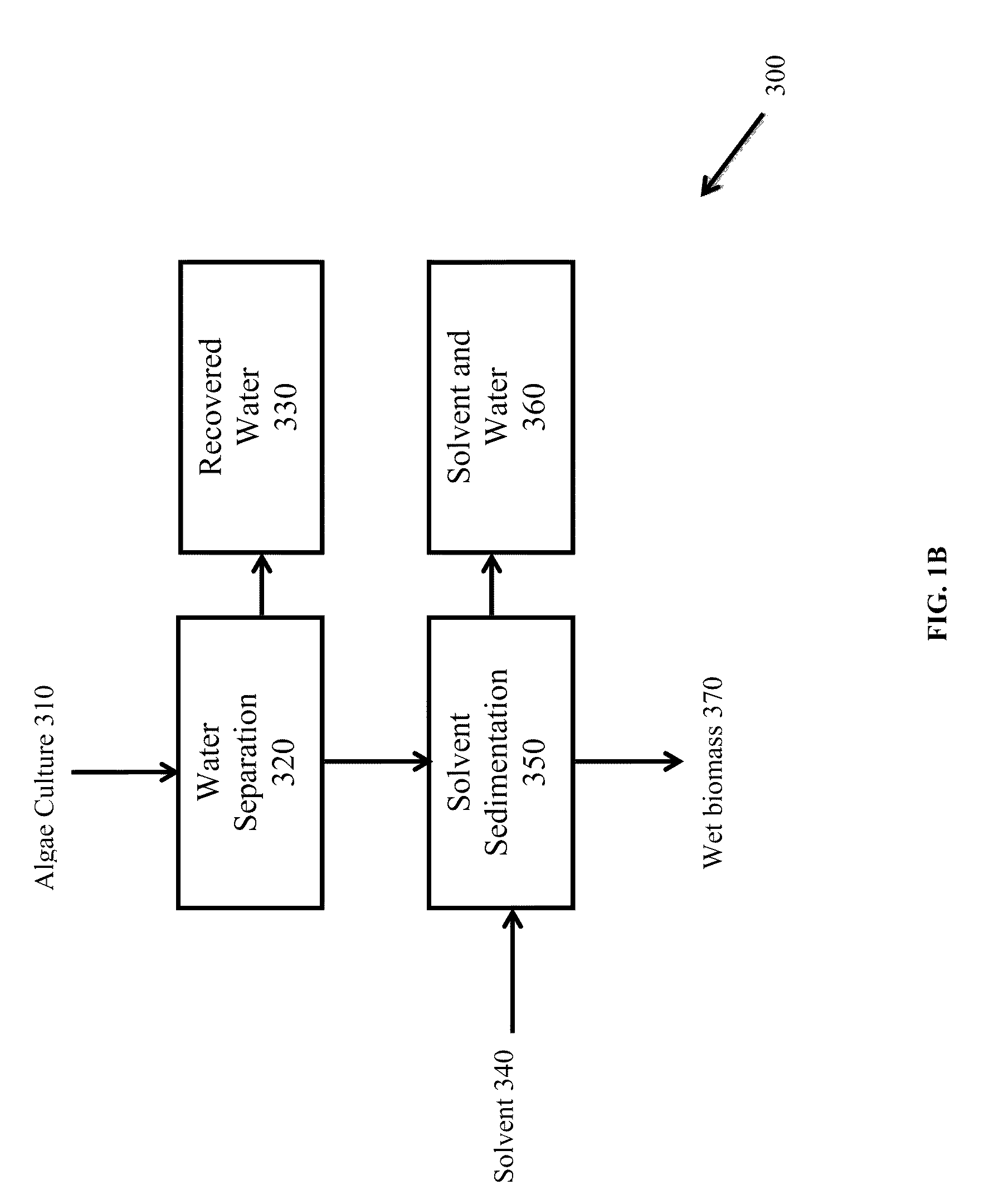
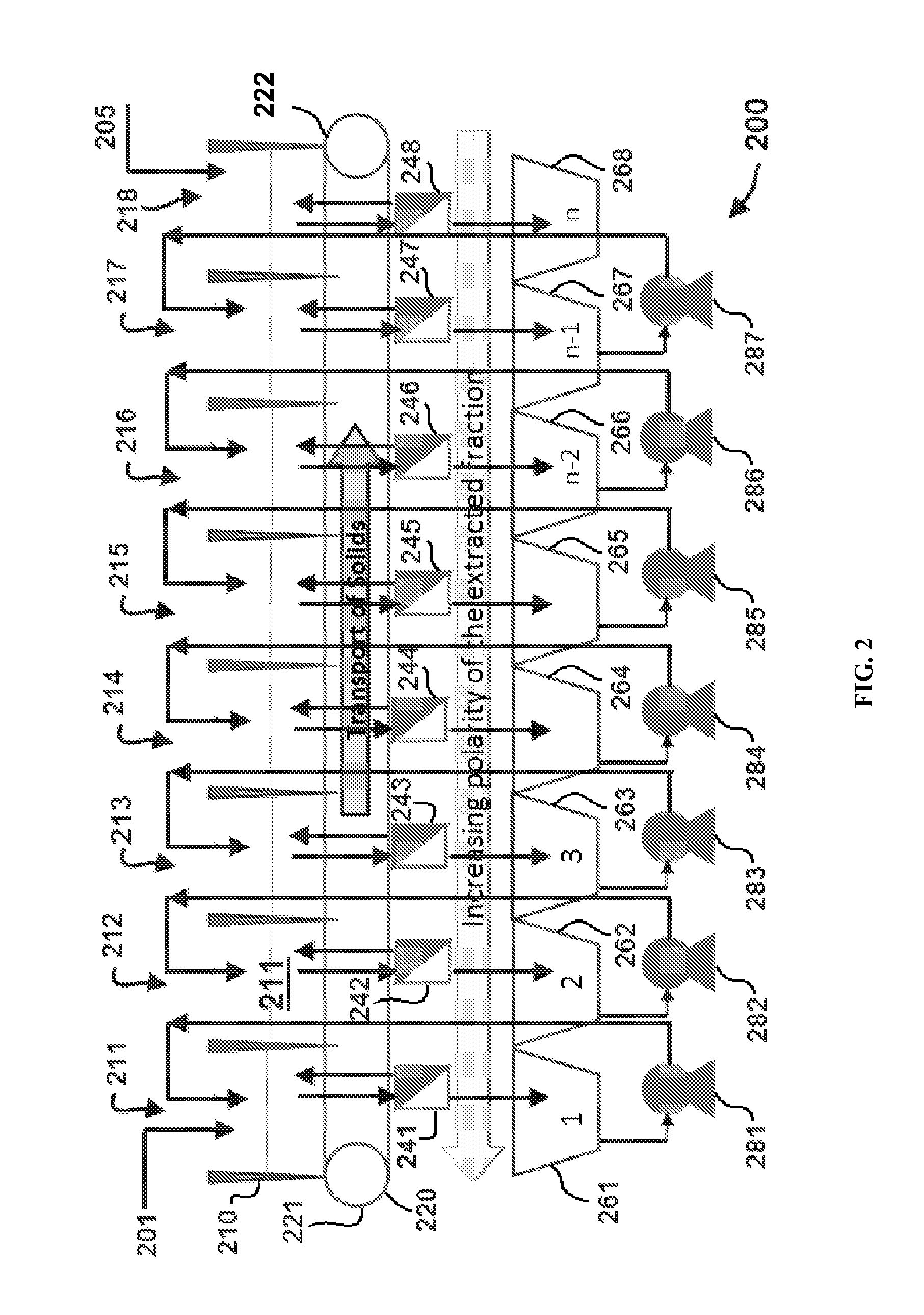
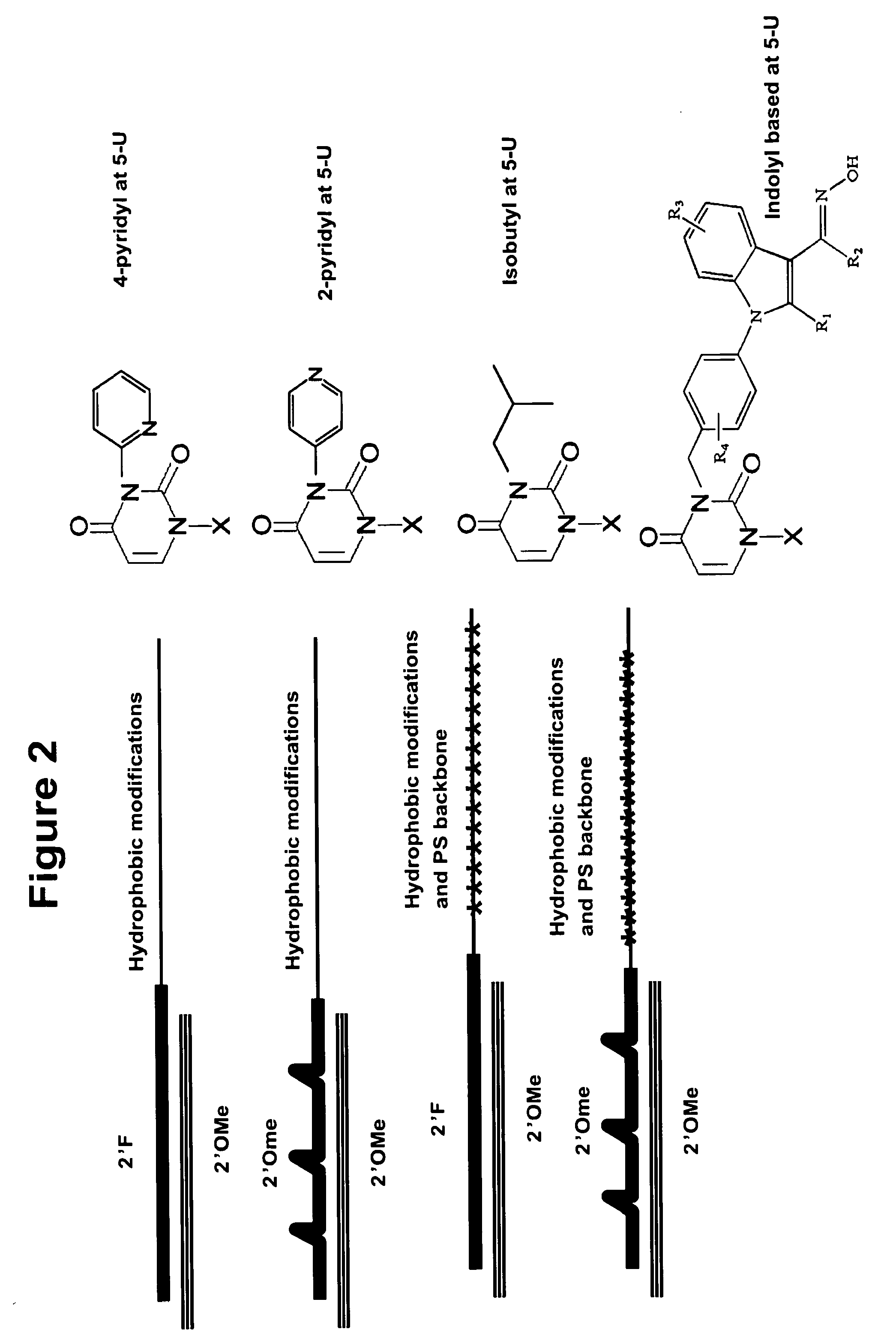
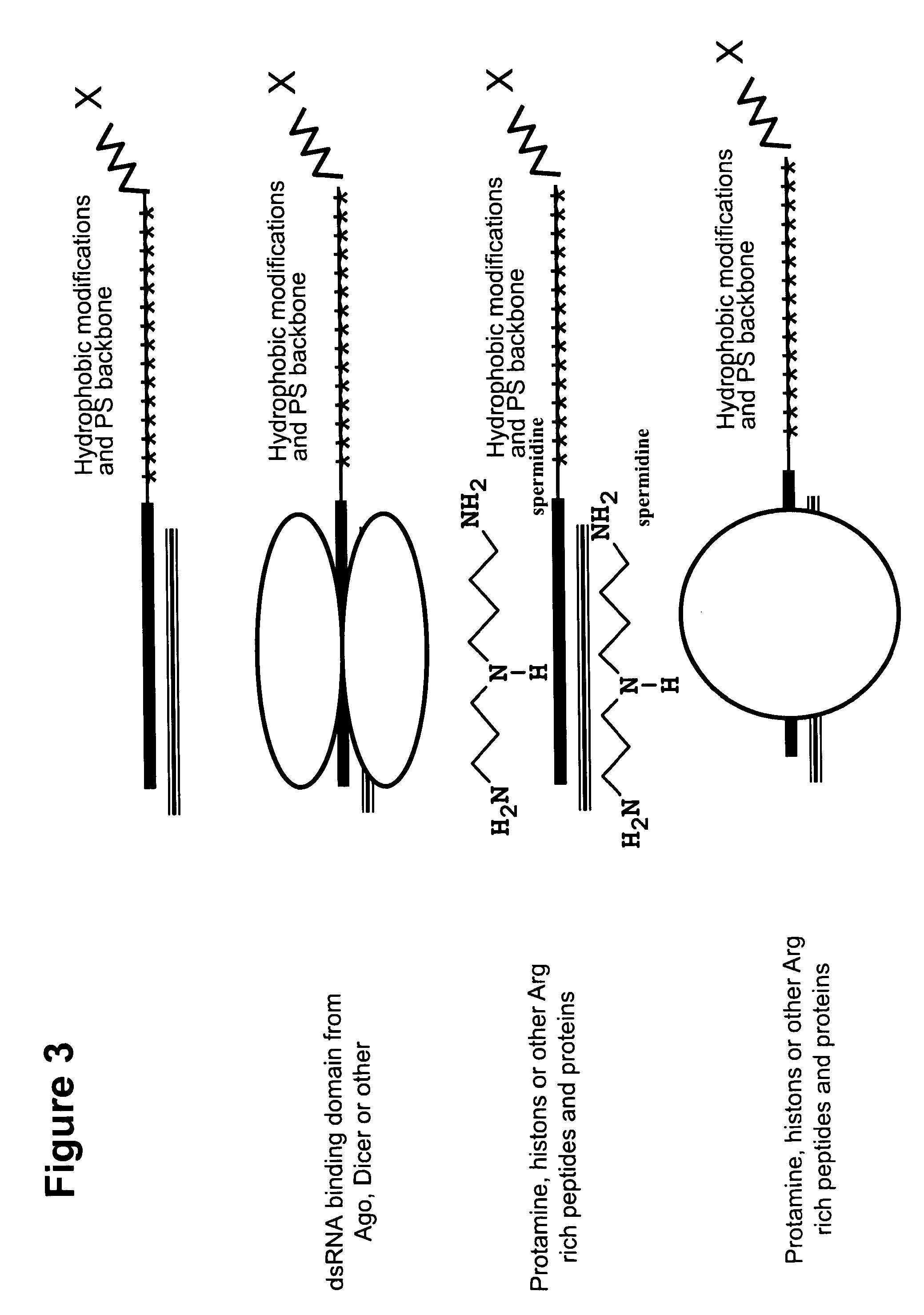
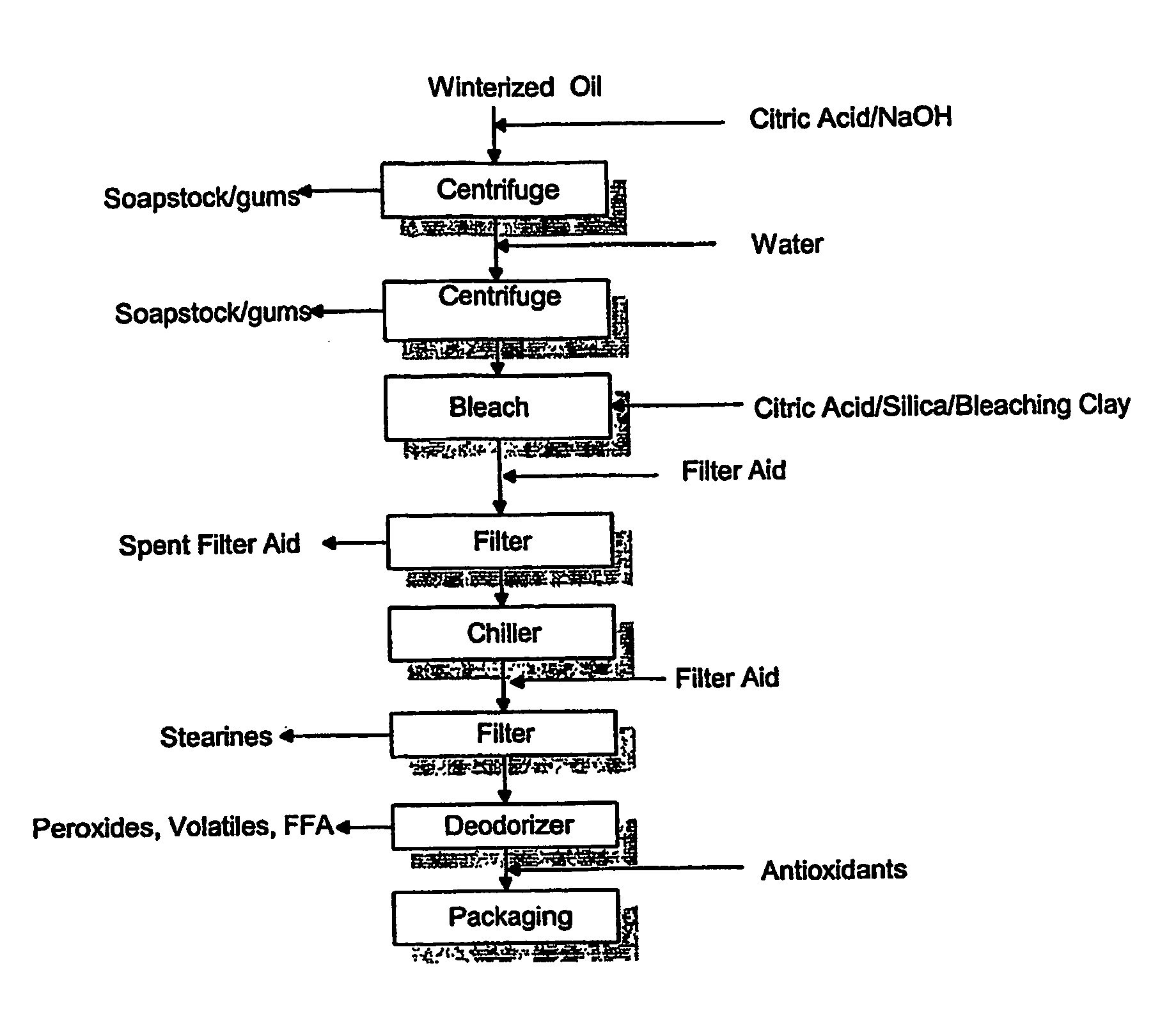
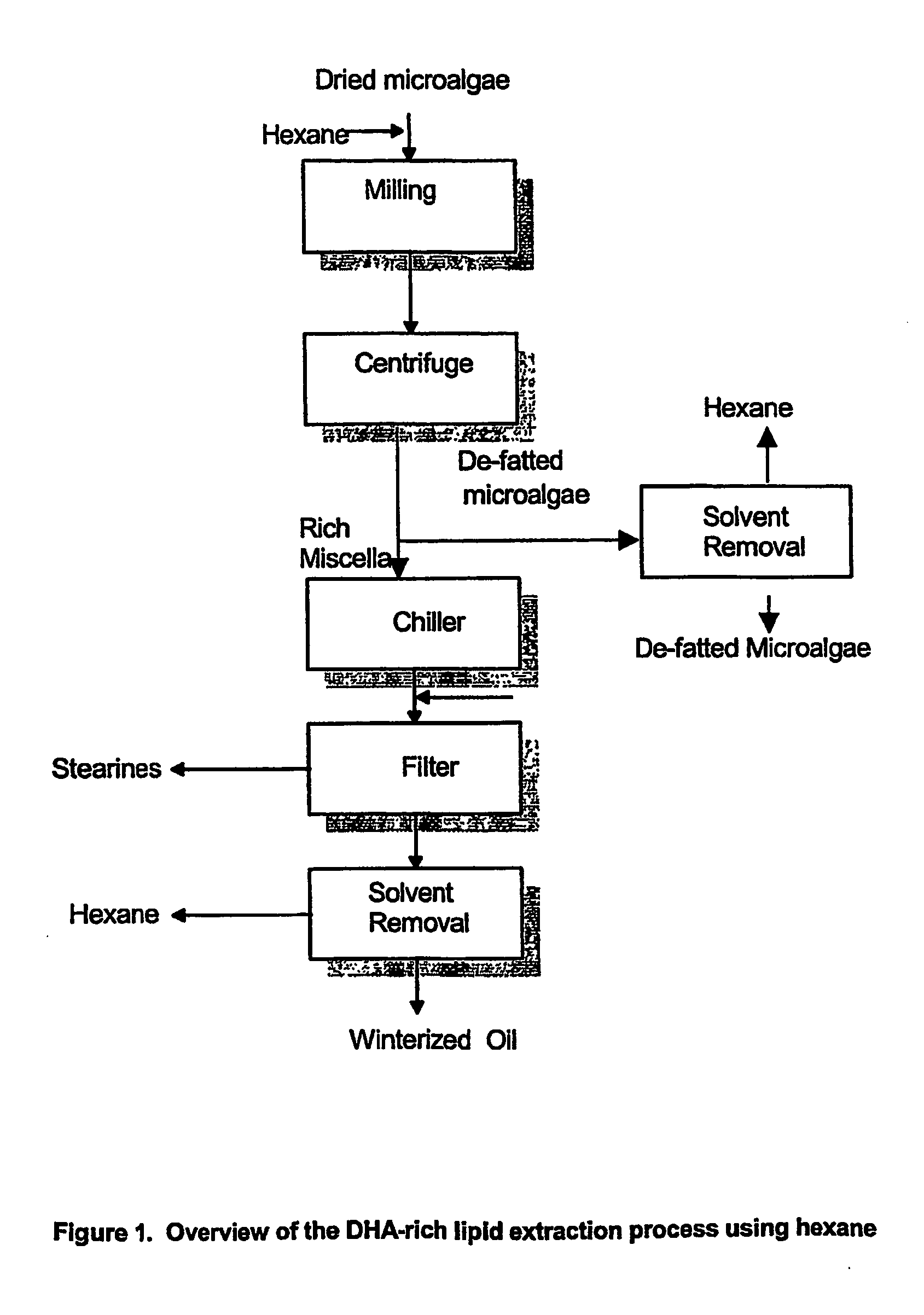
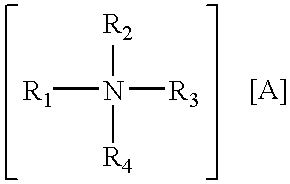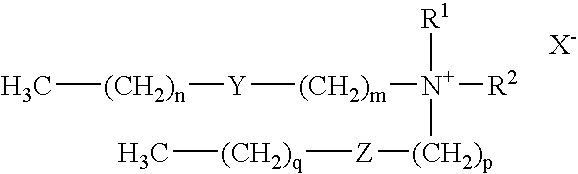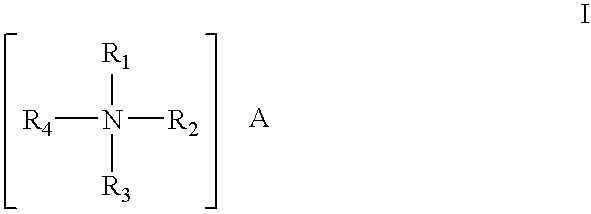Patents
Literature
164 results about "Neutral lipid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Neutral lipid storage disease with myopathy is a condition in which fats (lipids) are stored abnormally in organs and tissues throughout the body. People with this condition have muscle weakness (myopathy) due to the accumulation of fats in muscle tissue.
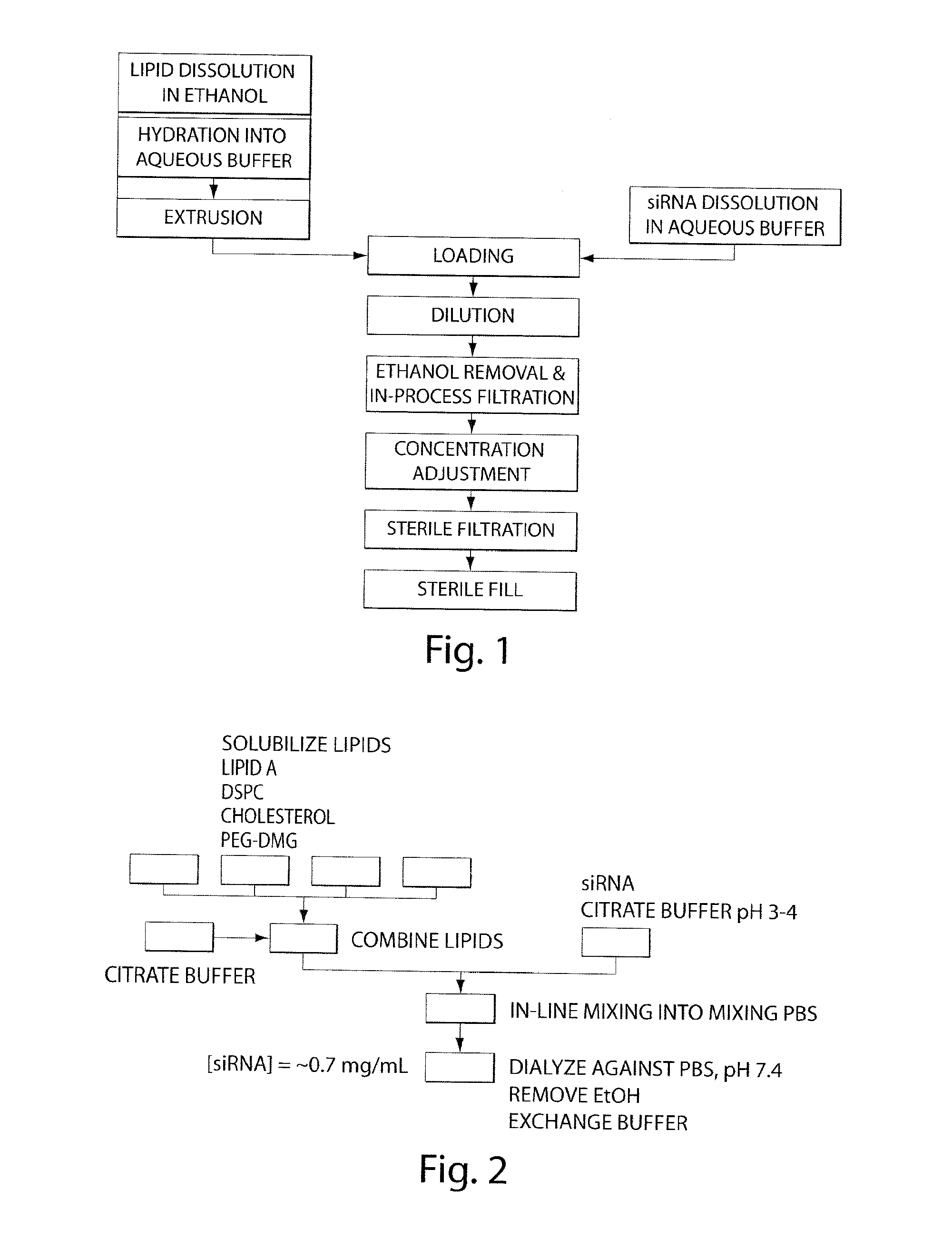
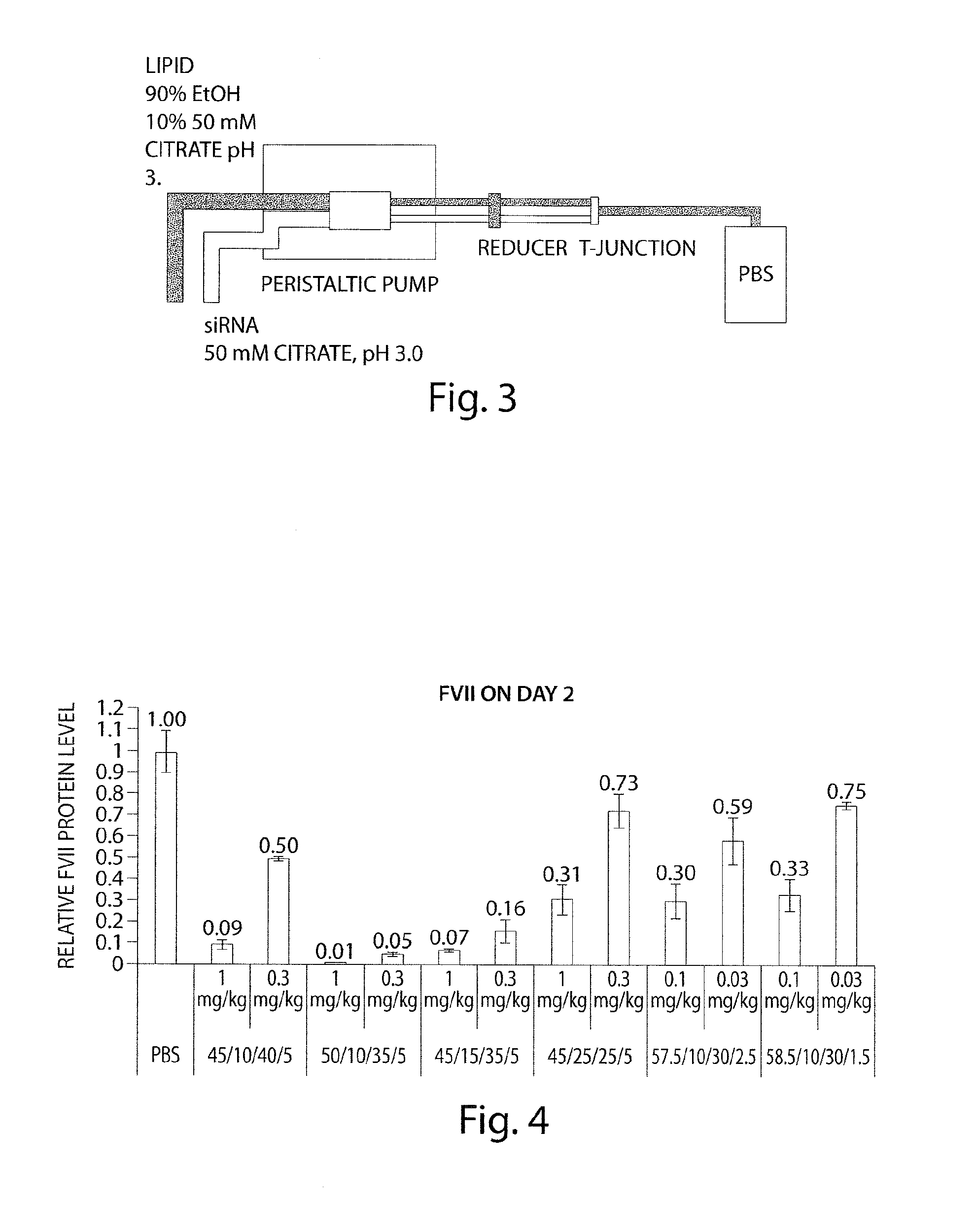
Lipid compositions
Disclosed herein are lipid compositions comprising a cationic lipid of formula (I), a neutral lipid, a sterol and a PEG or PEG-modified lipid, wherein formula (I) is (F). Also disclosed are methods of producing the cationic lipid of formula (I).
Owner:ARBUTUS BIOPHARMA CORPORAT ION
Lipid formulation
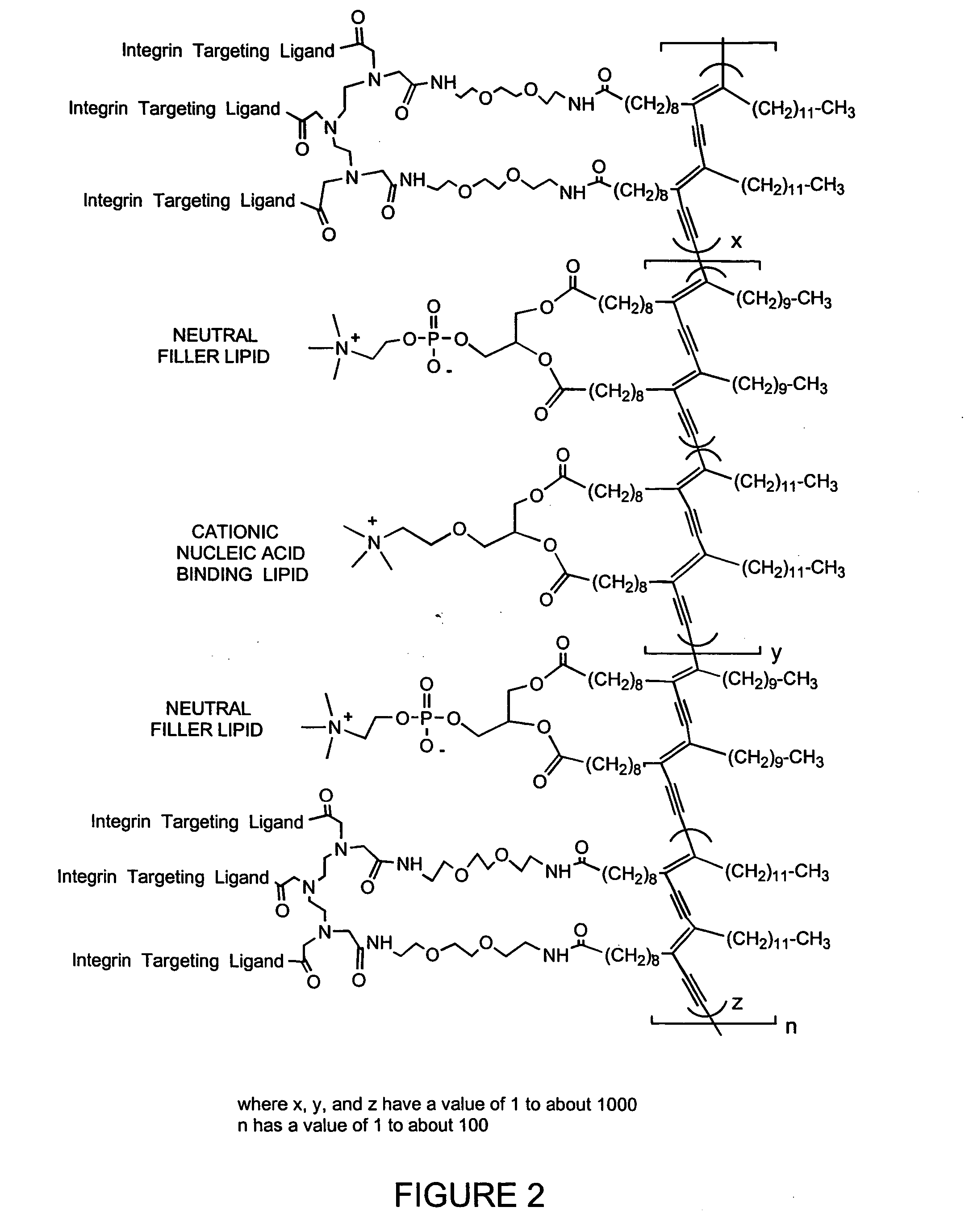
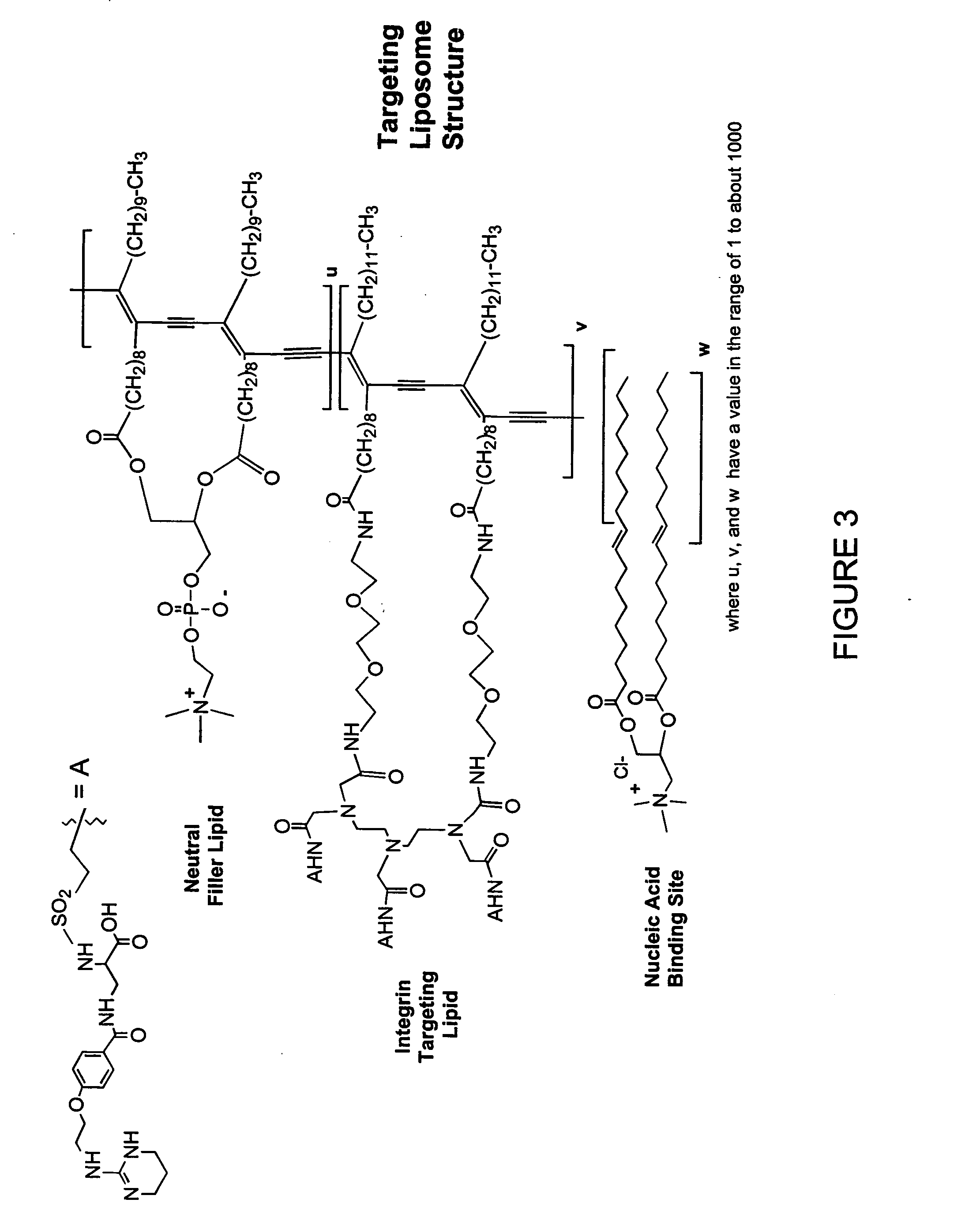
The invention features an improved lipid formulation comprising a cationic lipid of formula (A), a neutral lipid, a sterol and a PEG or PEG-modified lipid, where R1 and R2 are independently alkyl, alkenyl or alkynyl, each can be optionally substituted, and R3 and R4 are independently lower alkyl or R3 and R4 can be taken together to form an optionally substituted heterocyclic ring. In one embodiment, R1 and R2 are independently selected from oleoyl, pamitoyl, steroyl, linoleyl and R3 and R4 are methyl. Also disclosed are targeting lipids, and specific lipid formulations comprising such targeting lipids.
Owner:ARBUTUS BIOPHARMA CORPORAT ION
Bioeffective krill oil compositions
InactiveUS20080274203A1Increasing flesh colorationPromote growthBiocideMetabolism disorderInsulin resistanceAnti oxidant
This invention discloses new krill oil compositions characterized by having high amounts of phospholipids, astaxanthin esters and / or omega-3 contents. The krill oils are obtained from krill meal using supercritical fluid extraction in a two stage process. Stage 1 removes the neutral lipid by extracting with neat supercritical CO2 or CO2 plus approximately 5% of a co-solvent. Stage 2 extracts the actual krill oils by using supercritical CO2 in combination with approximately 20% ethanol. The krill oil materials obtained are compared with commercially available krill oil and found to be more bioeffective in a number of areas such as anti-inflammation, anti-oxidant effects, improving insulin resistances and improving blood lipid profile.
Owner:AKER BIOMARINE ANTARCTIC
Lipid compositions
Disclosed herein are lipid compositions comprising a cationic lipid of formula (I), a neutral lipid, a sterol and a PEG or PEG-modified lipid, wherein formula (I) isAlso disclosed are methods of producing the cationic lipid of formula (I).
Owner:ARBUTUS BIOPHARMA CORPORAT ION
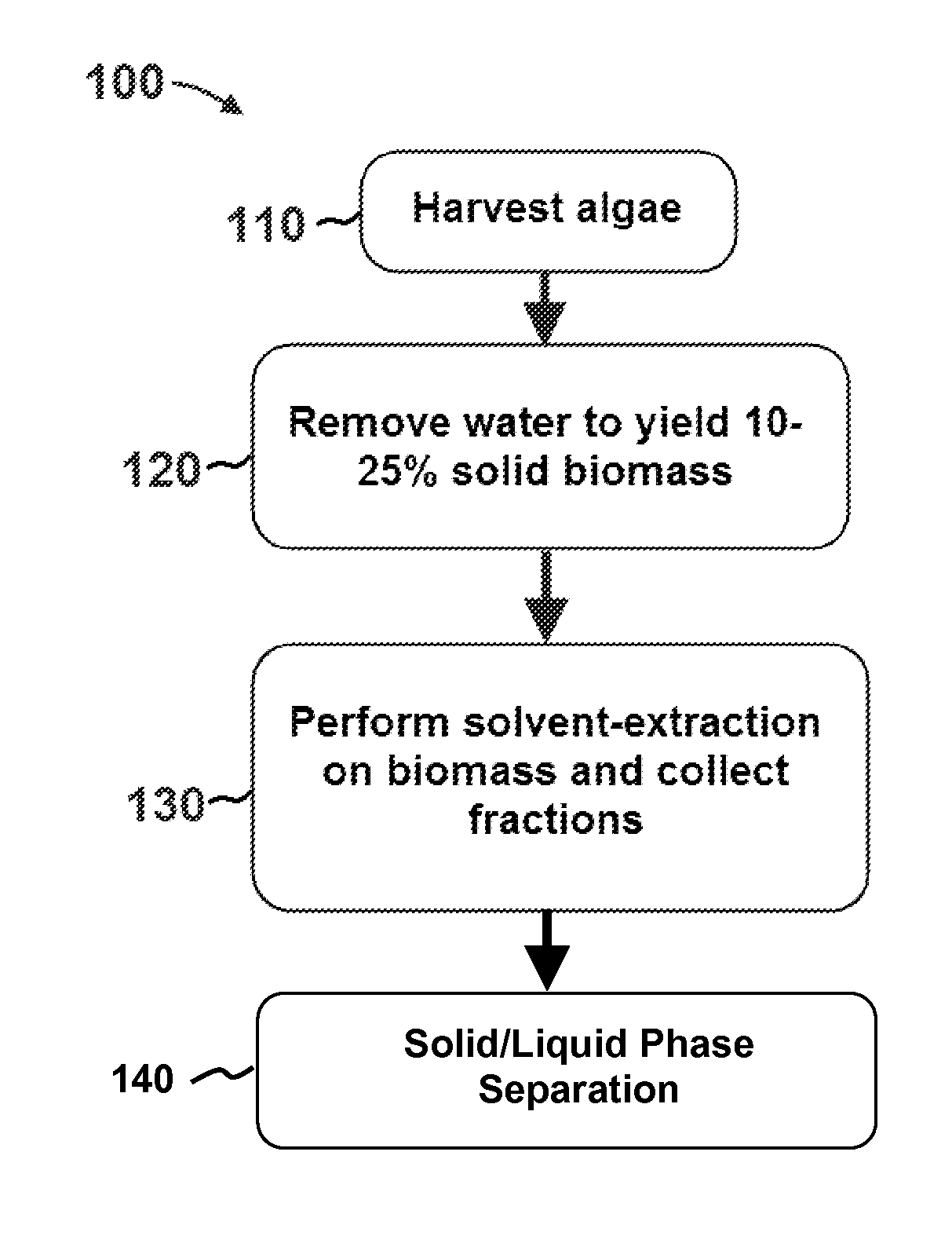
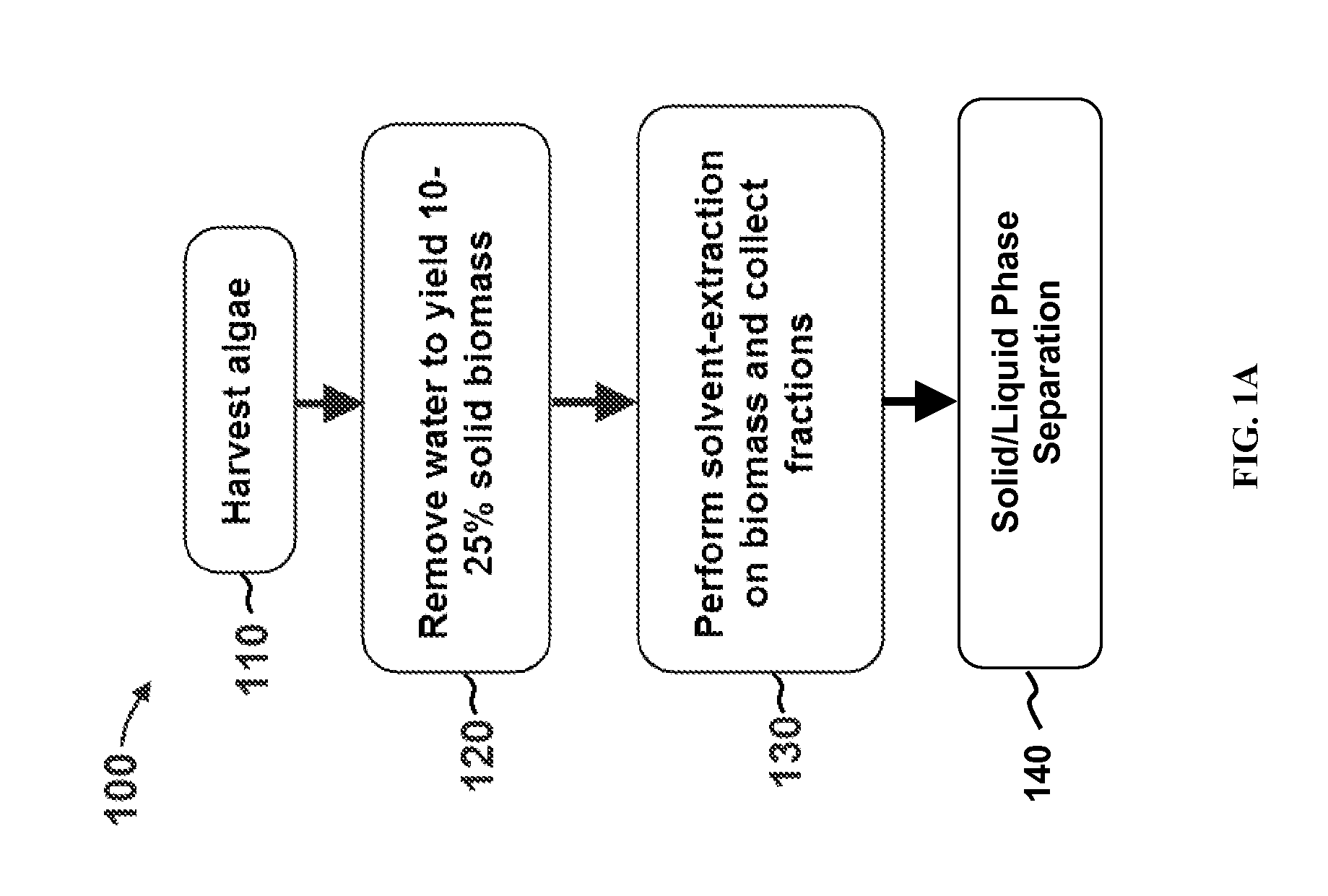
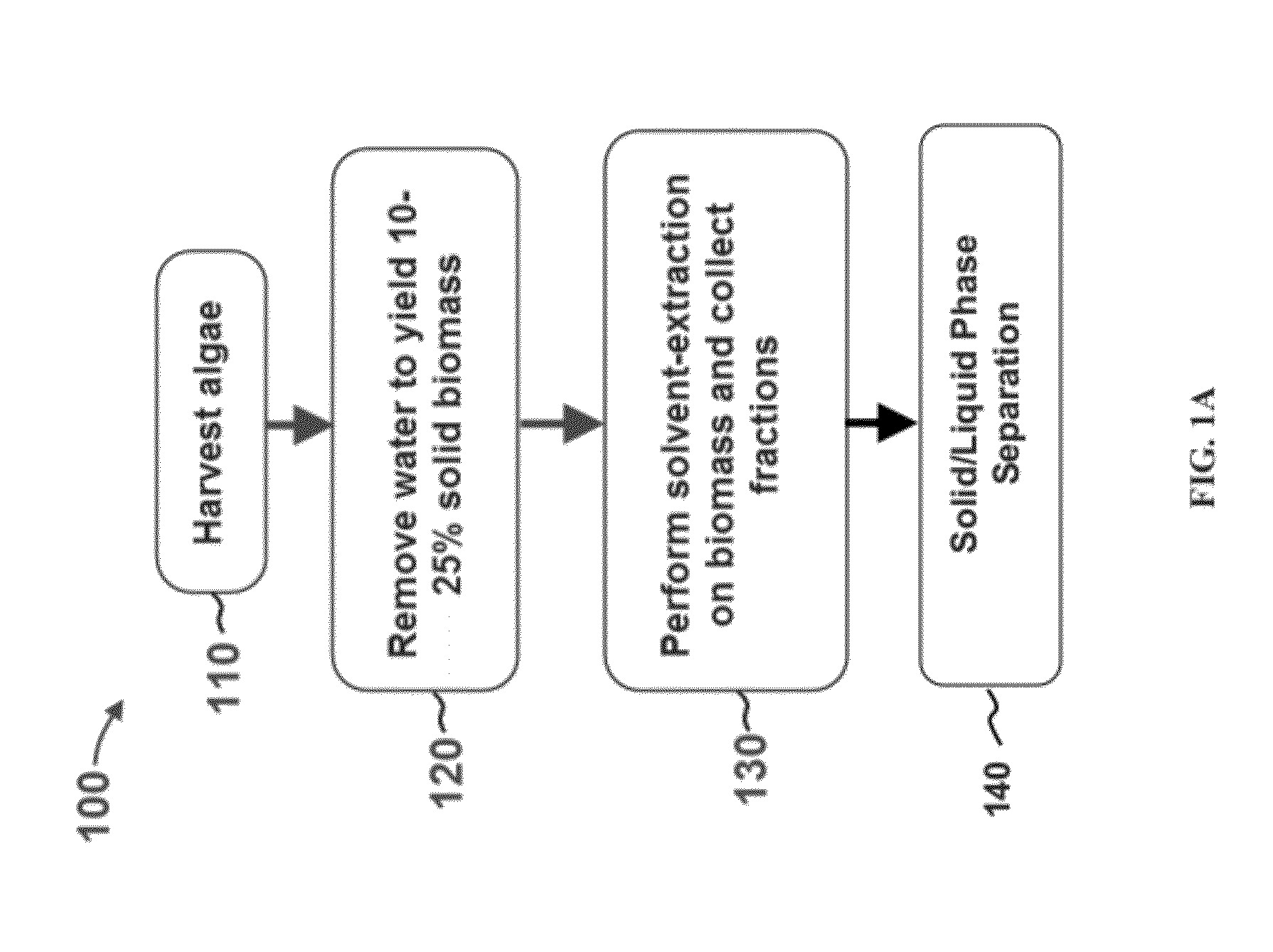
Extraction with fractionation of oil and proteinaceous material from oleaginous material
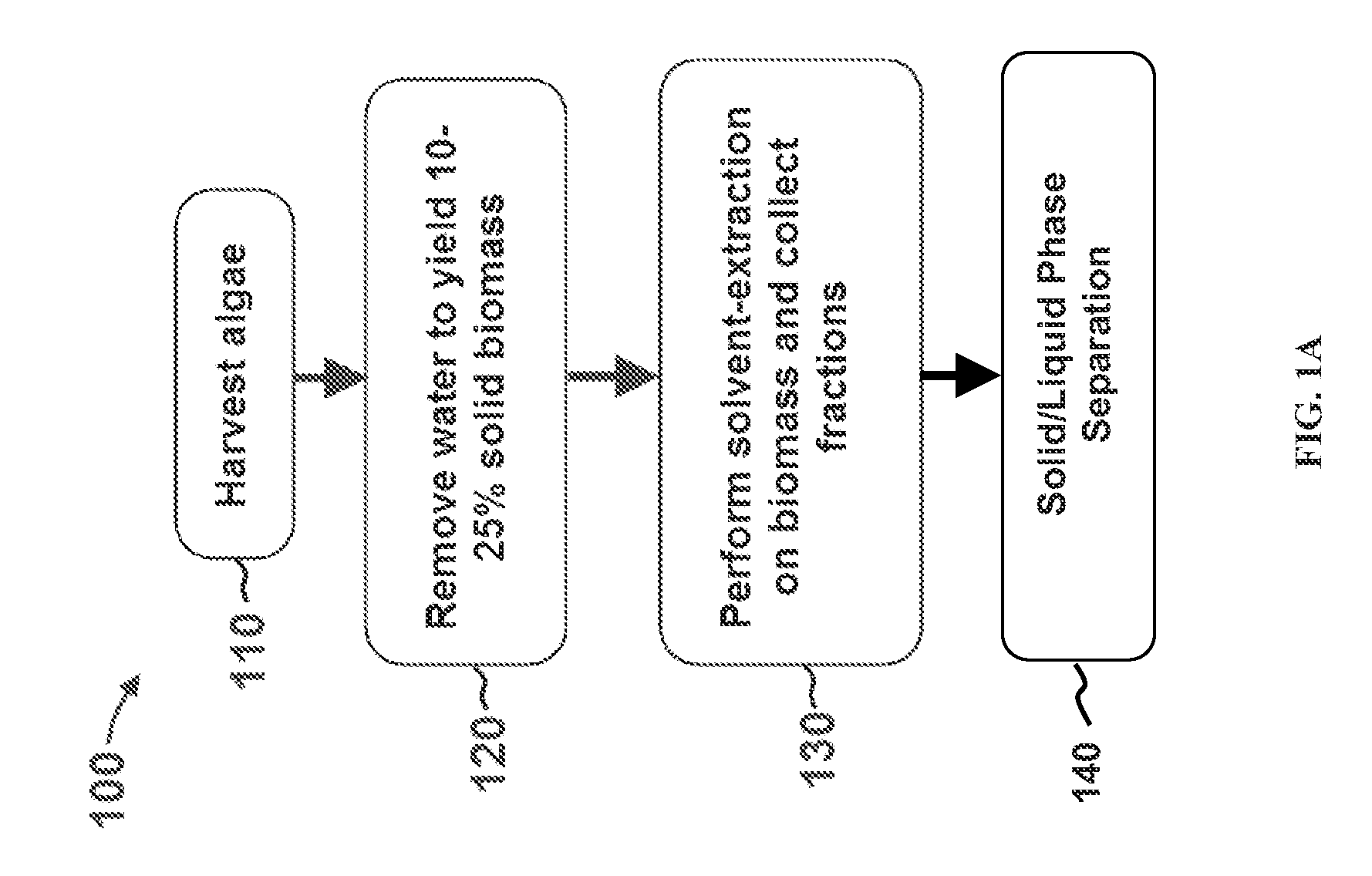
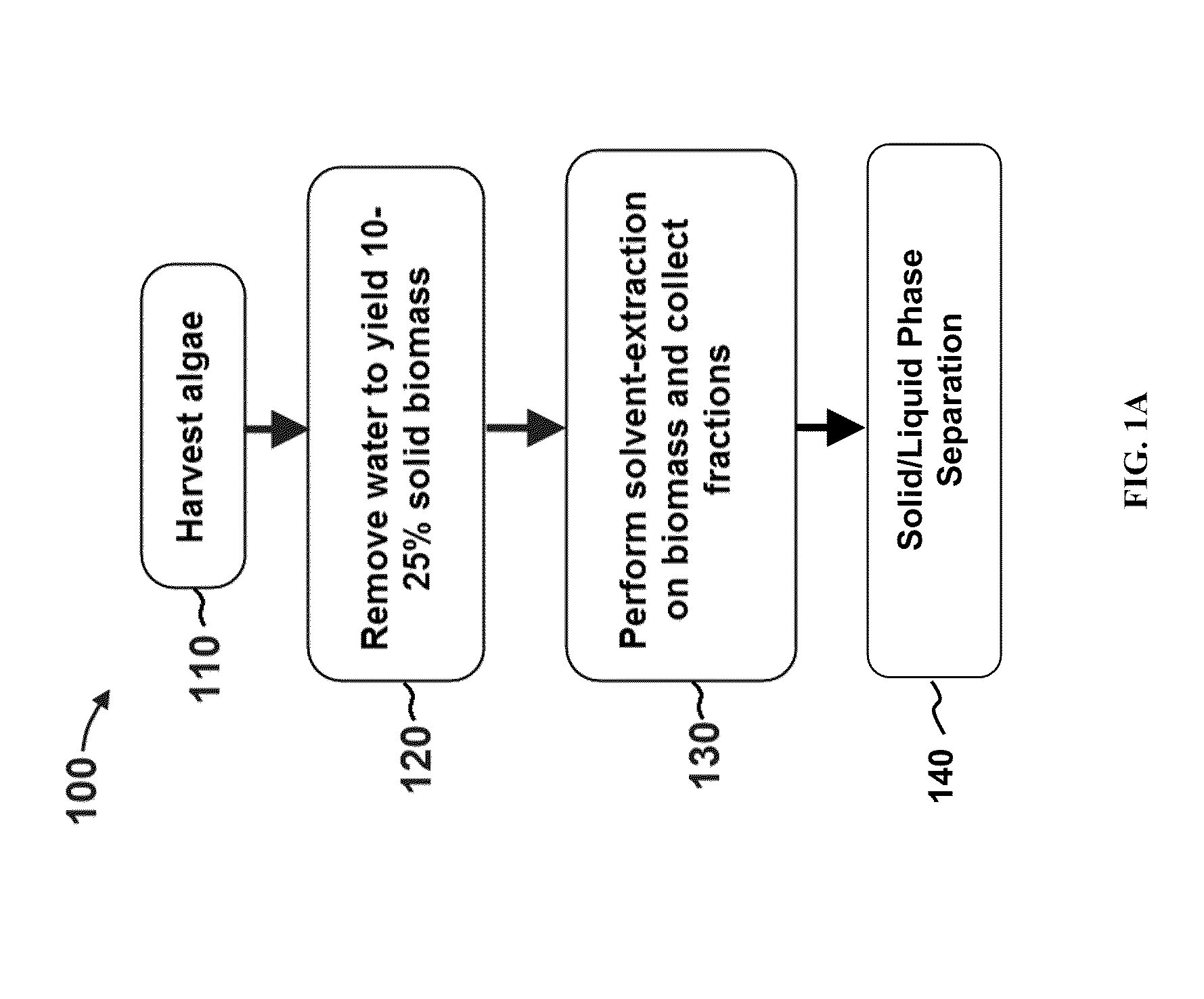
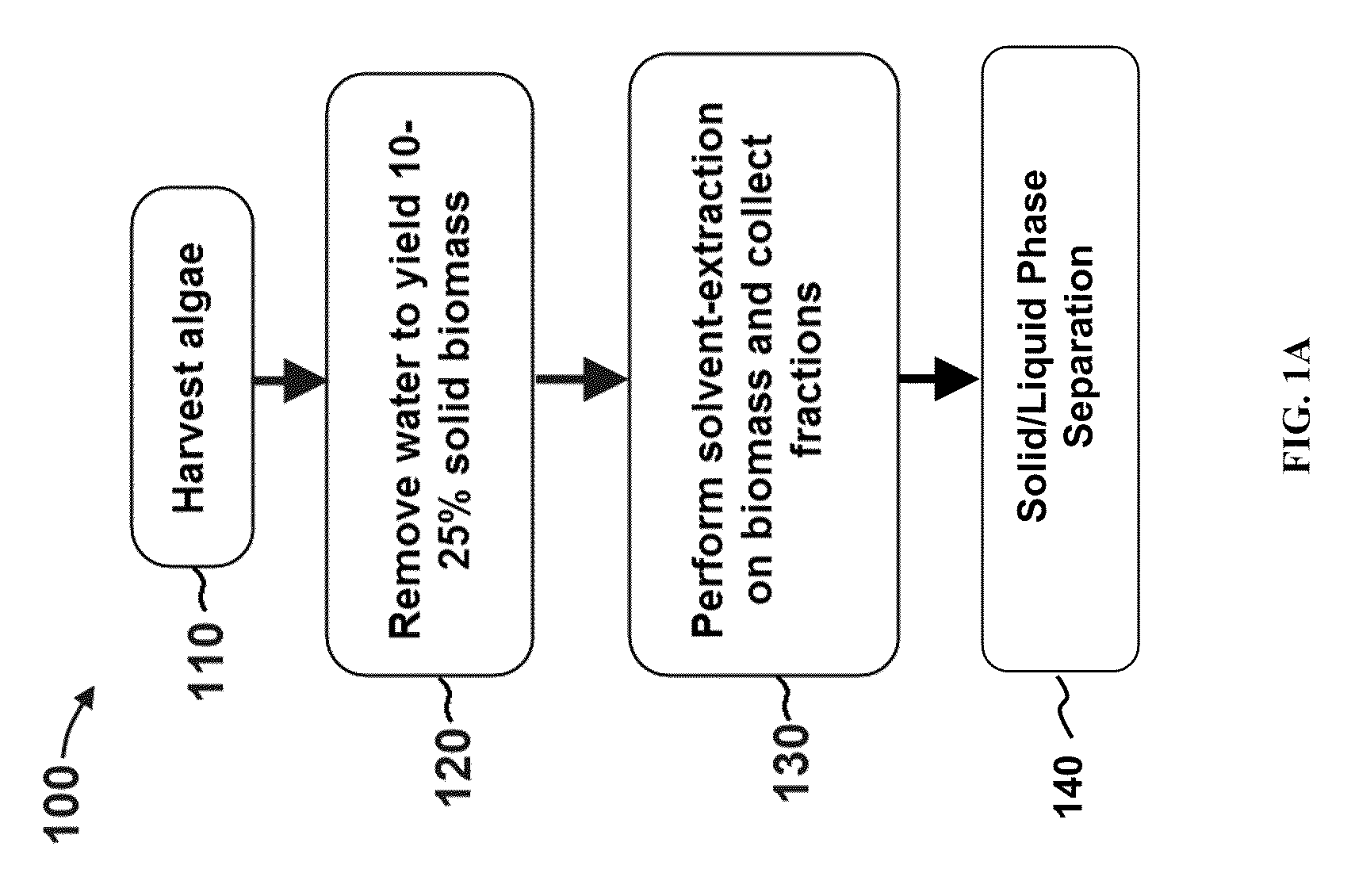
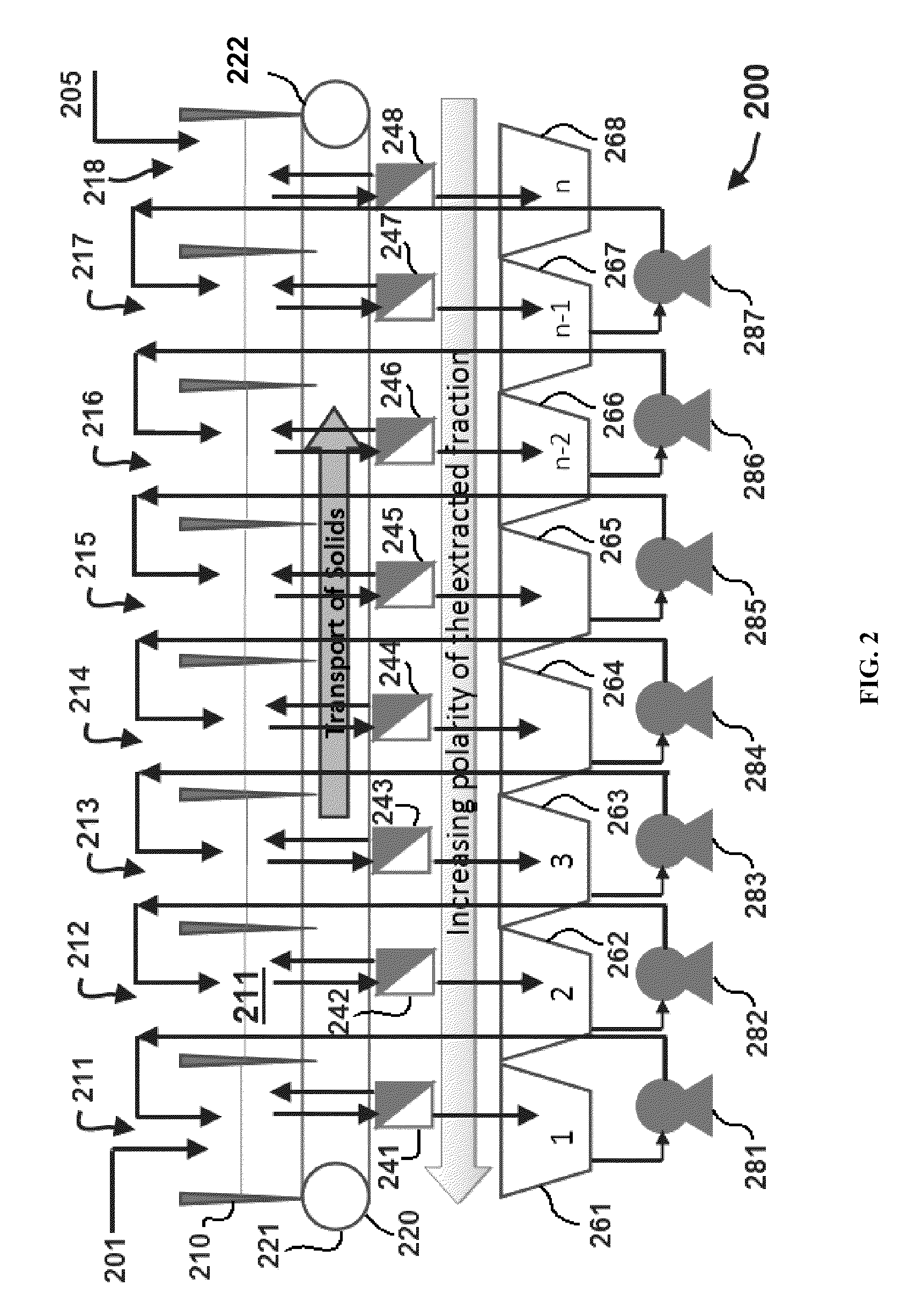
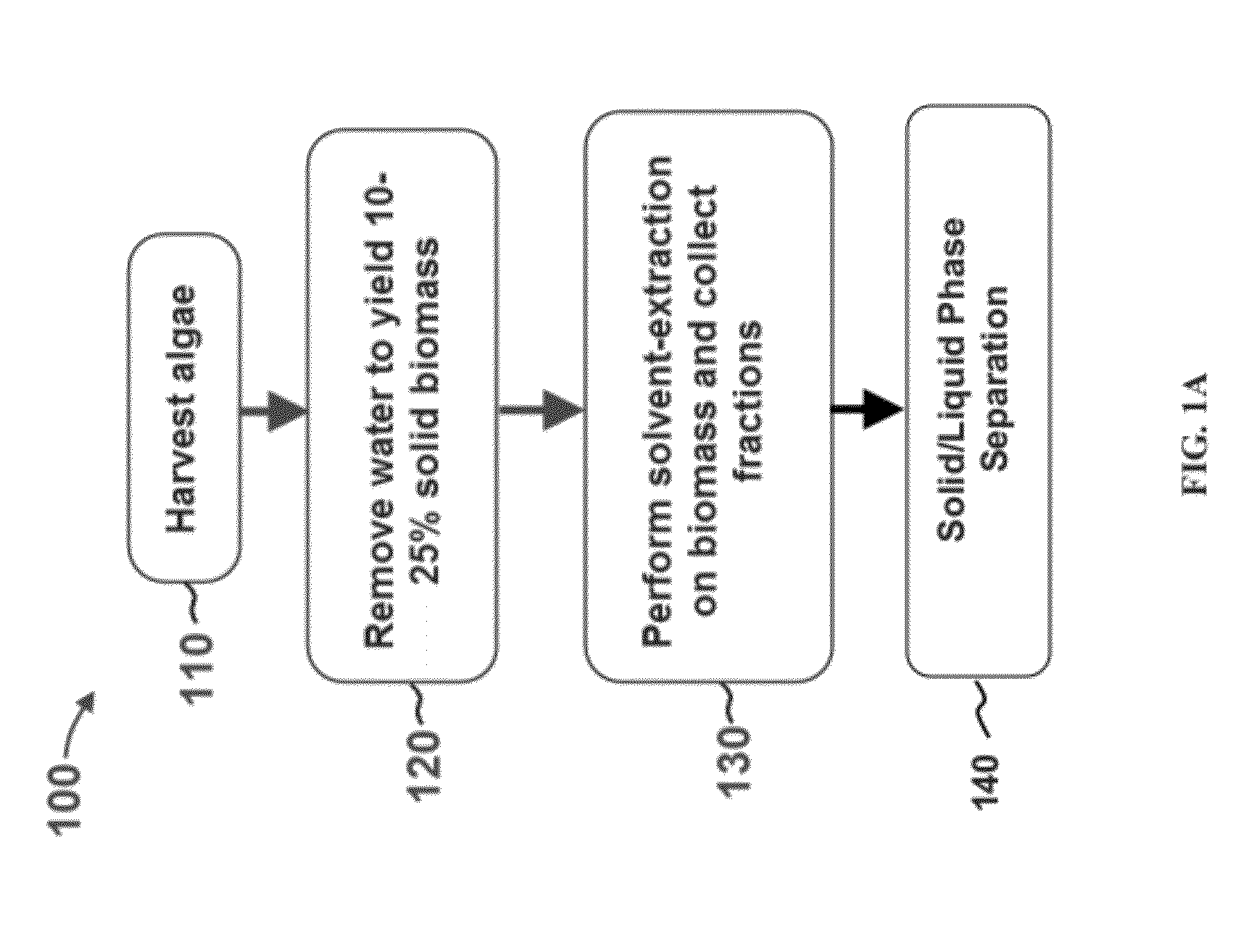
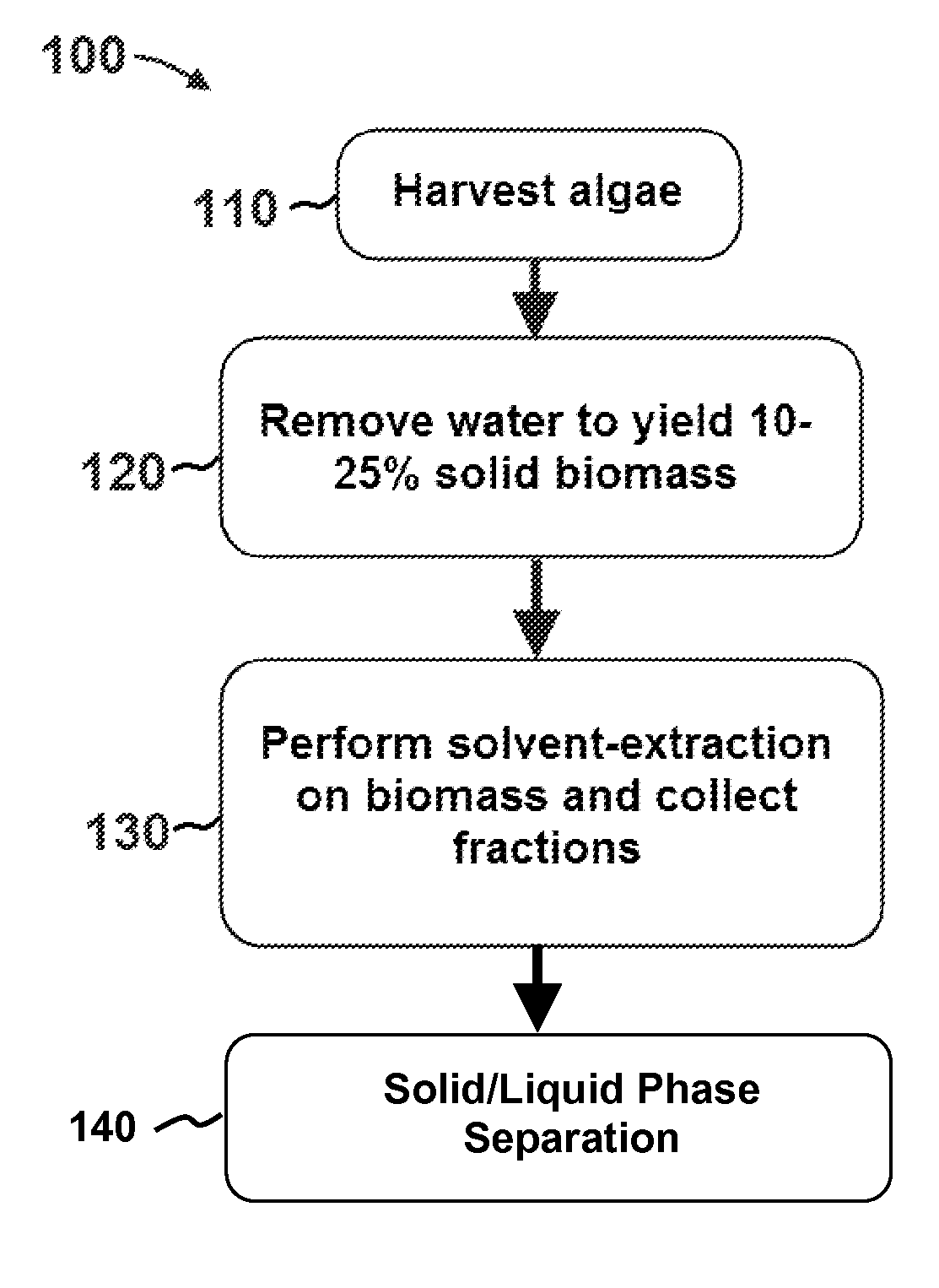
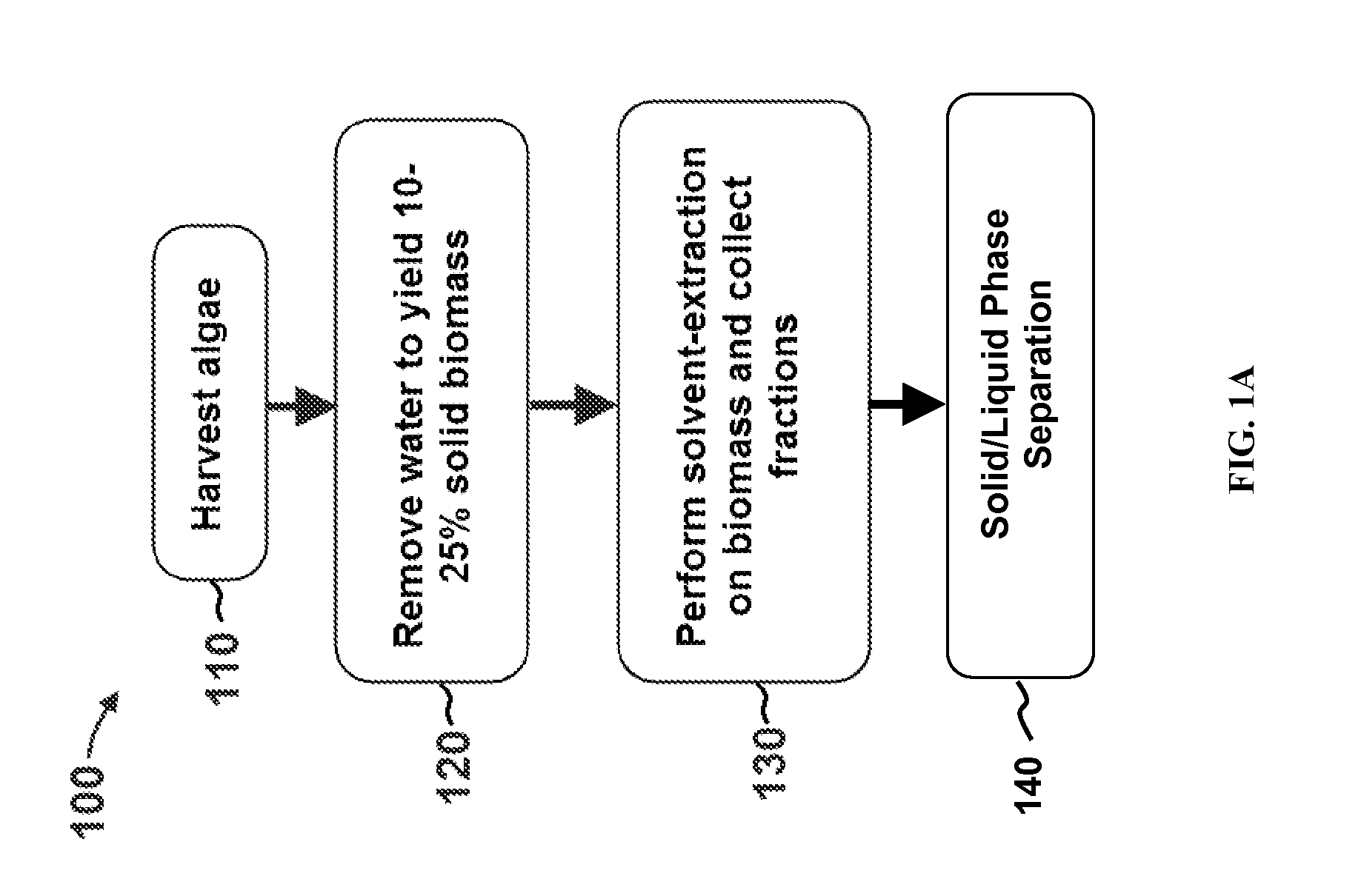
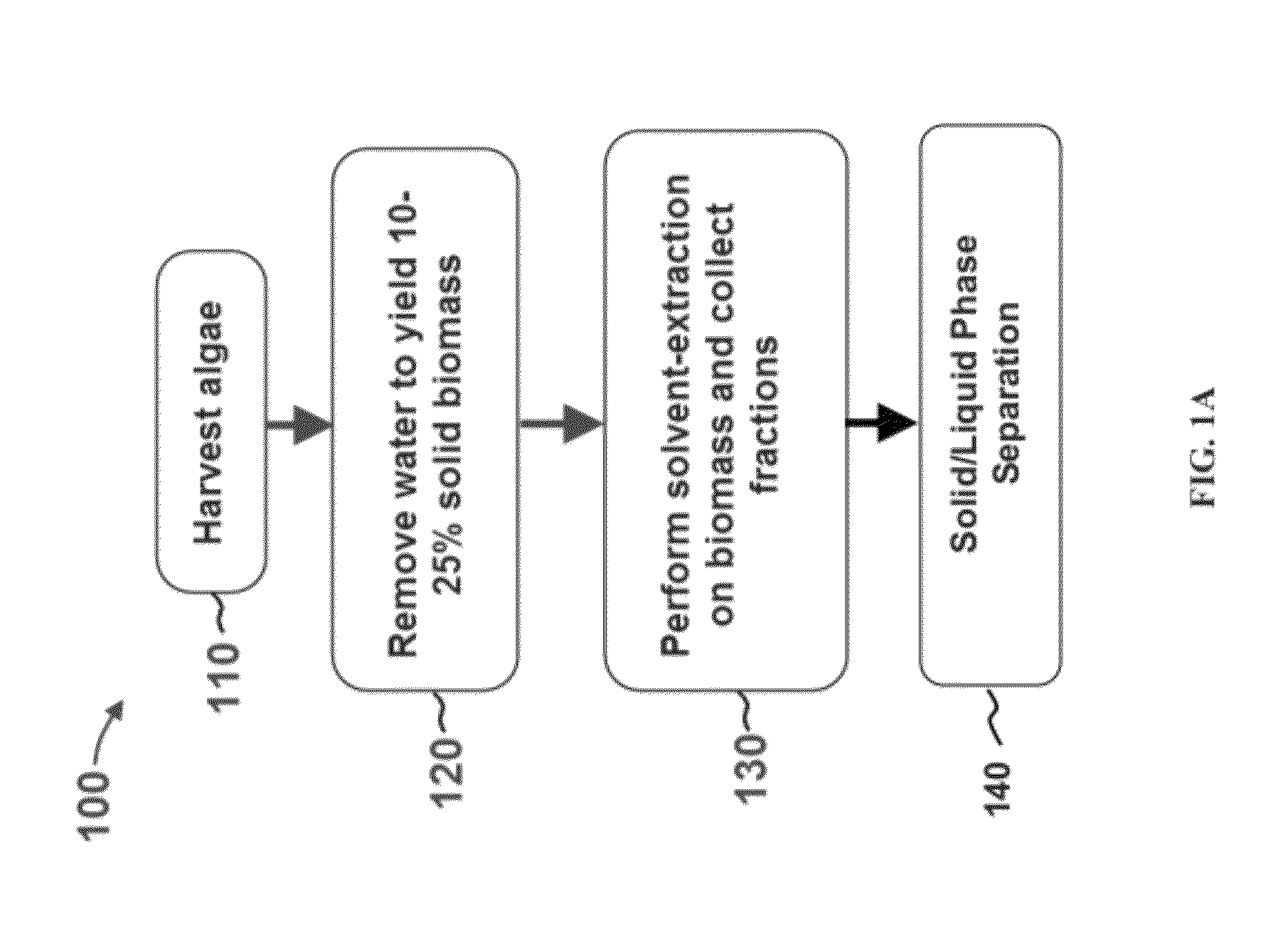
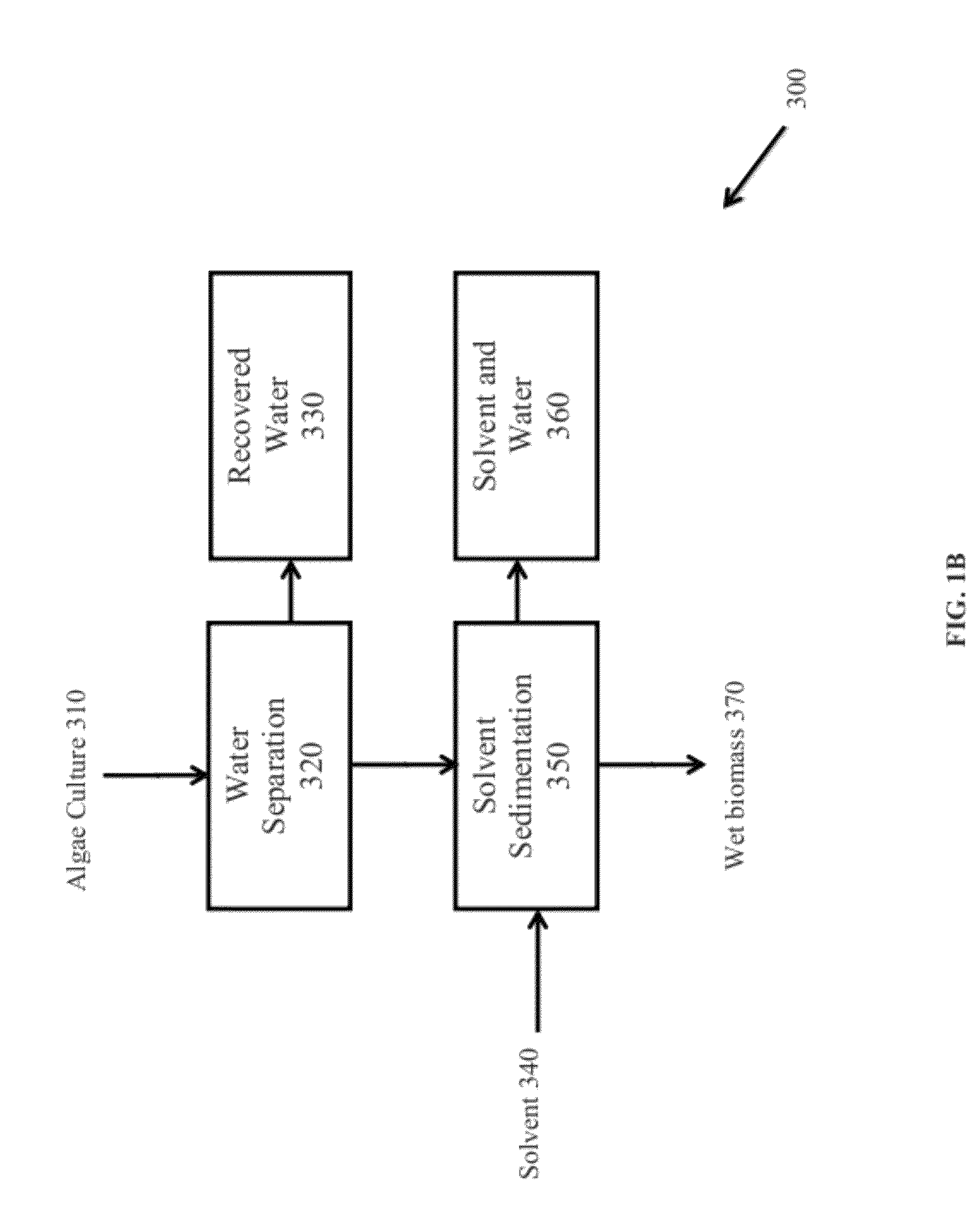
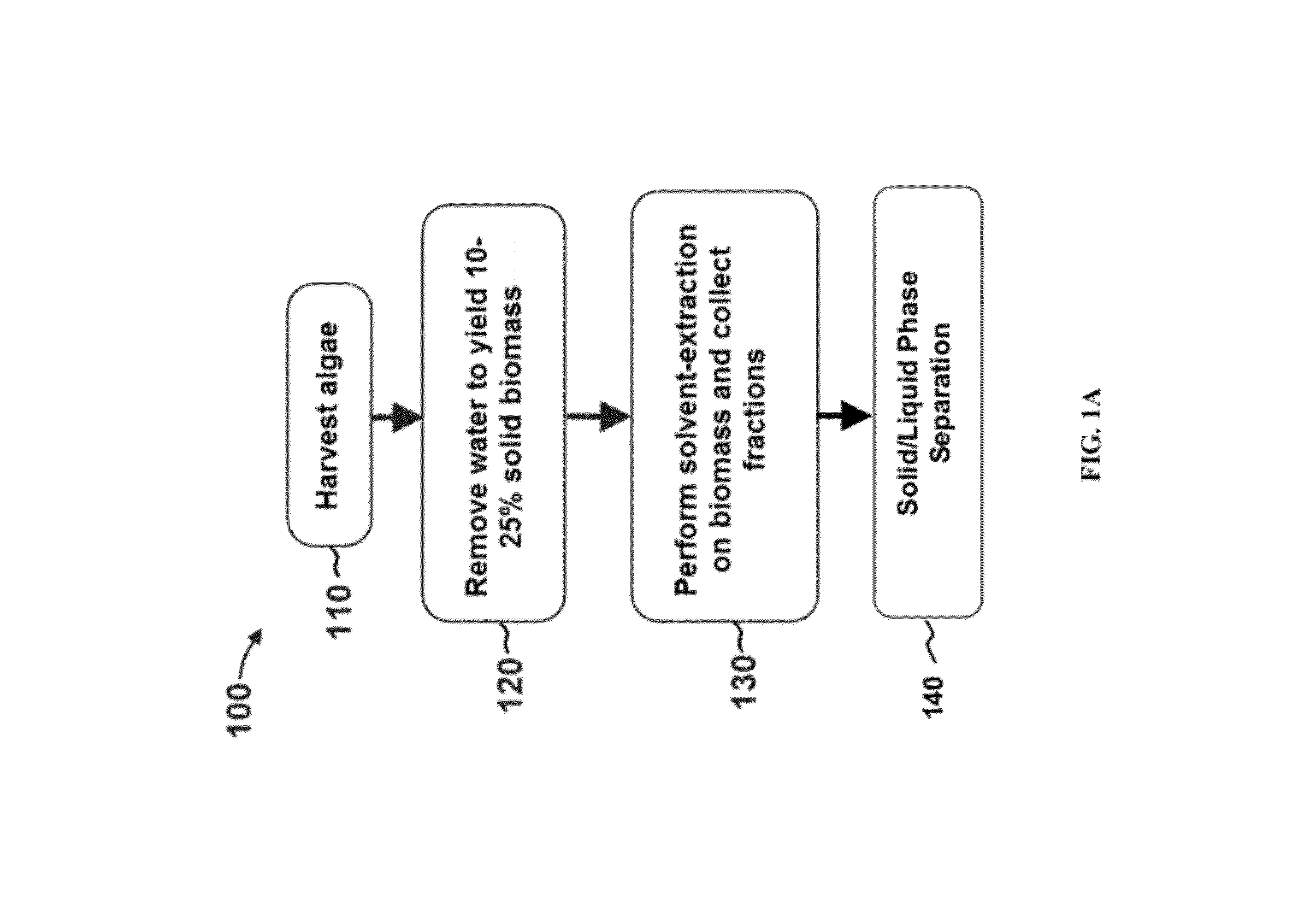
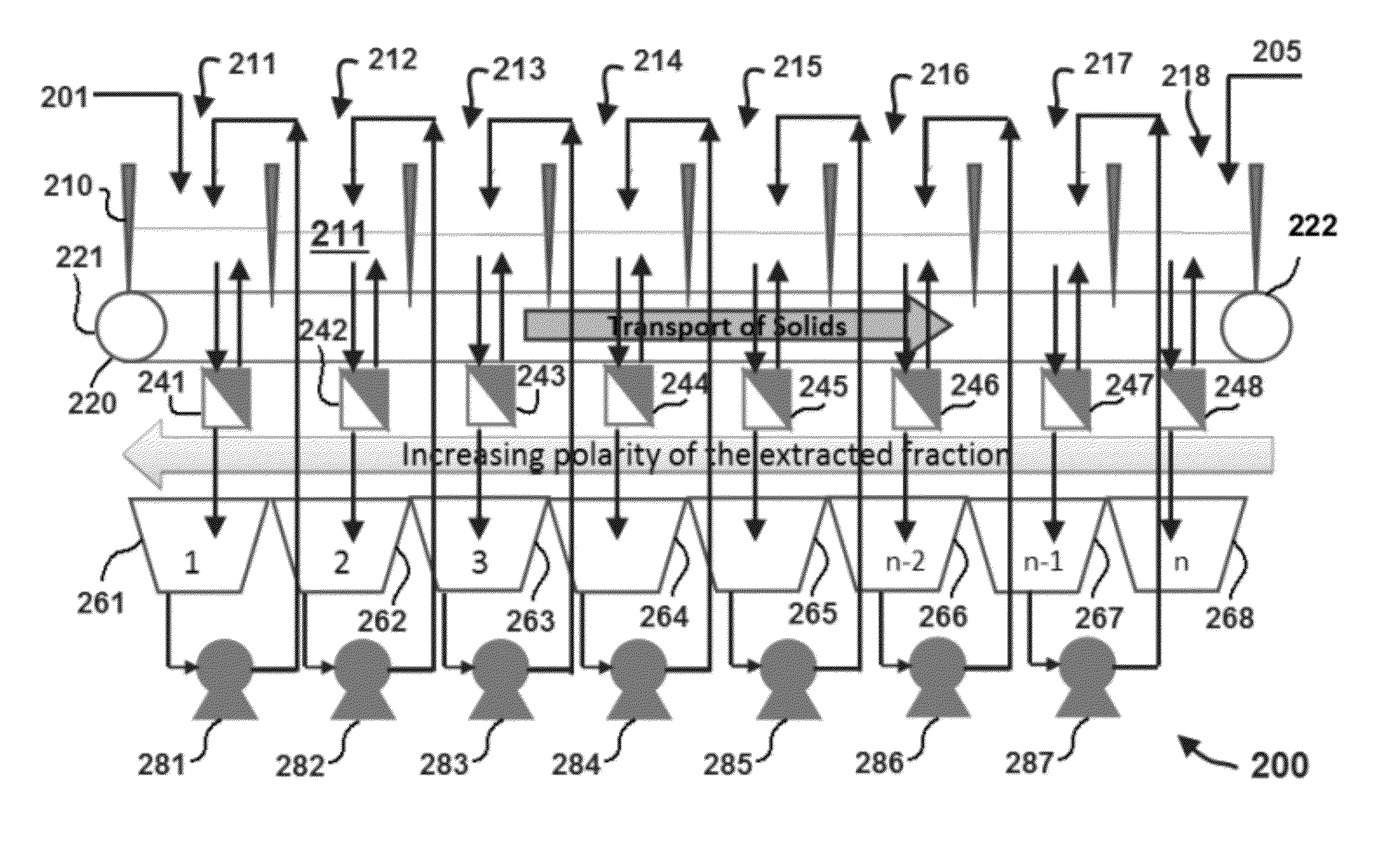
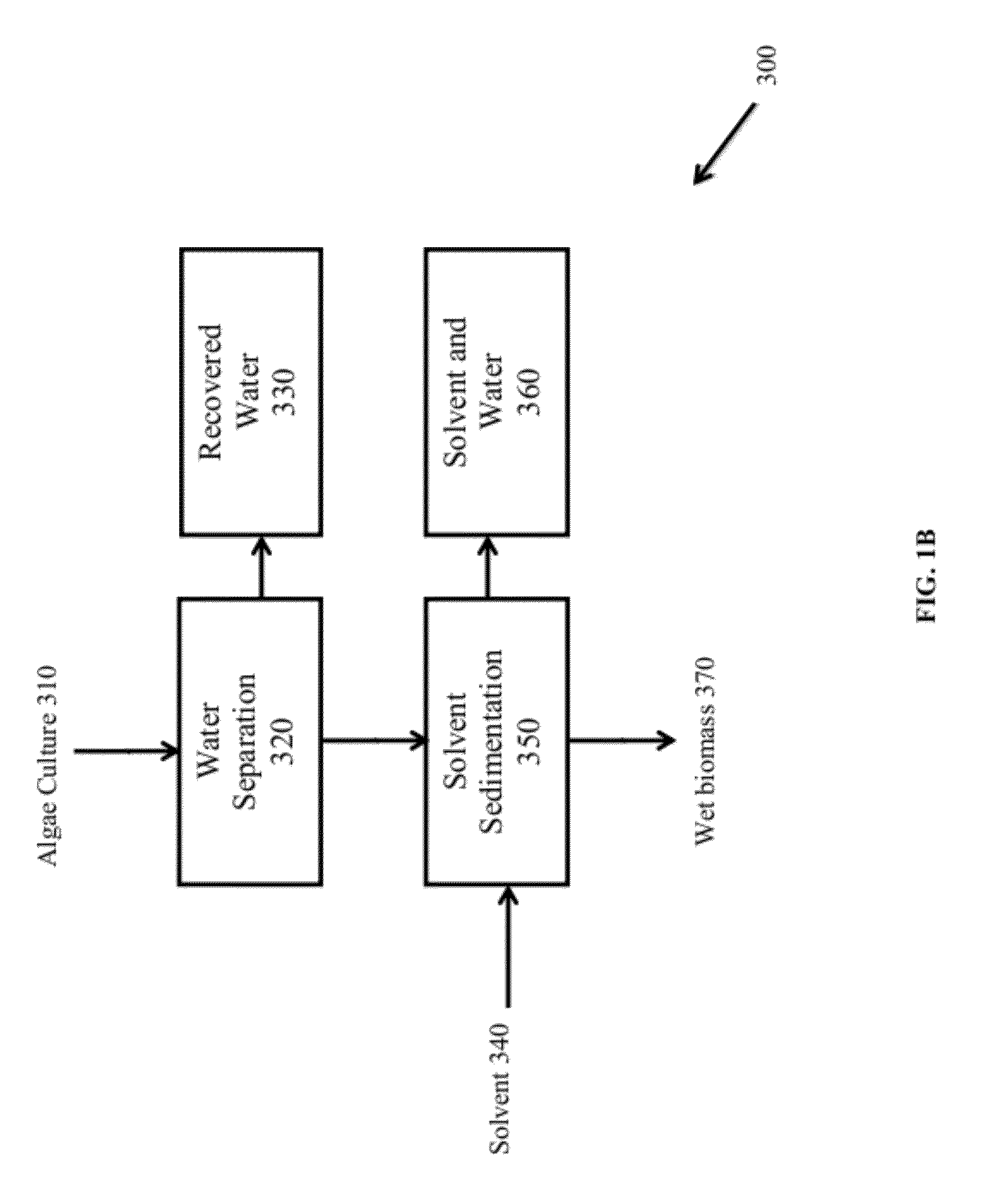
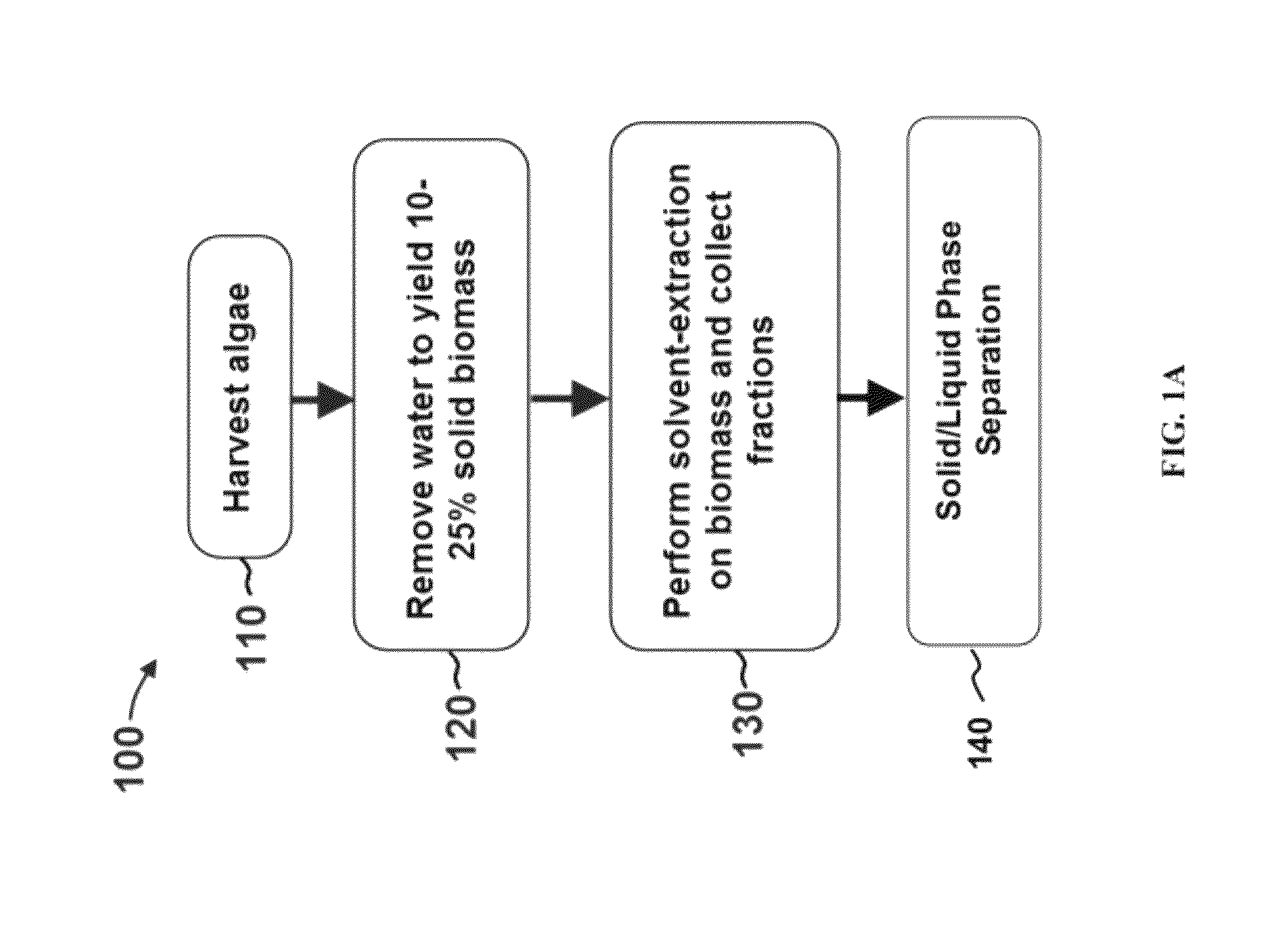
Methods for selective extraction and fractionation of algal lipids and algal products are disclosed. A method of selective removal of products from an algal biomass provides for single and multistep extraction processes which enable efficient separation of algal components. Among these components are neutral lipids synthesized by algae, which are extracted by the methods disclosed herein for the production of renewable fuels.
Owner:HELIAE DEVMENT
Methods of producing biofuels, chlorophylls and carotenoids
InactiveUS20110263886A1Fatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationWater insolubleBiofuel
A method for producing biofuels along with valuable food and neutraceutical products is provided. A method of making biofuels includes dewatering substantially intact algal cells to make an algal biomass, extracting neutral lipids along with carotenoids and chlorophylls from the algal biomass, and separation of the carotenoids and chlorophylls using adsorption or membrane diafiltration or other methods. The remaining neutral lipids are esterified with a catalyst in the presence of an alcohol. The method also includes separating a water soluble fraction comprising glycerin from a water insoluble fraction comprising fuel esters and distilling the fuel esters under vacuum to obtain a C16 or shorter fuel esters fraction, a C16 or longer fuel ester fraction, and a residue comprising omega-3 fatty acids esters and remaining carotenoids. The method further includes hydrogenating and deoxygenating at least one of (i) the C16 or shorter fuel esters to obtain a jet fuel blend stock and (ii) the C16 or longer fuel esters to obtain a diesel blend stock.
Owner:HELIAE DEVMENT
Lipid compositions
Disclosed herein are lipid compositions comprising a cationic lipid of formula (I), a neutral lipid, a sterol and a PEG or PEG-modified lipid, wherein formula (I) is (F). Also disclosed are methods of producing the cationic lipid of formula (I).
Owner:ARBUTUS BIOPHARMA CORPORAT ION
Multiple-layered liposome and preparation method thereof
InactiveUS20070082042A1Good skin permeabilityImprove stabilityDermatological disorderLiposomal deliverySterolIntercellular space
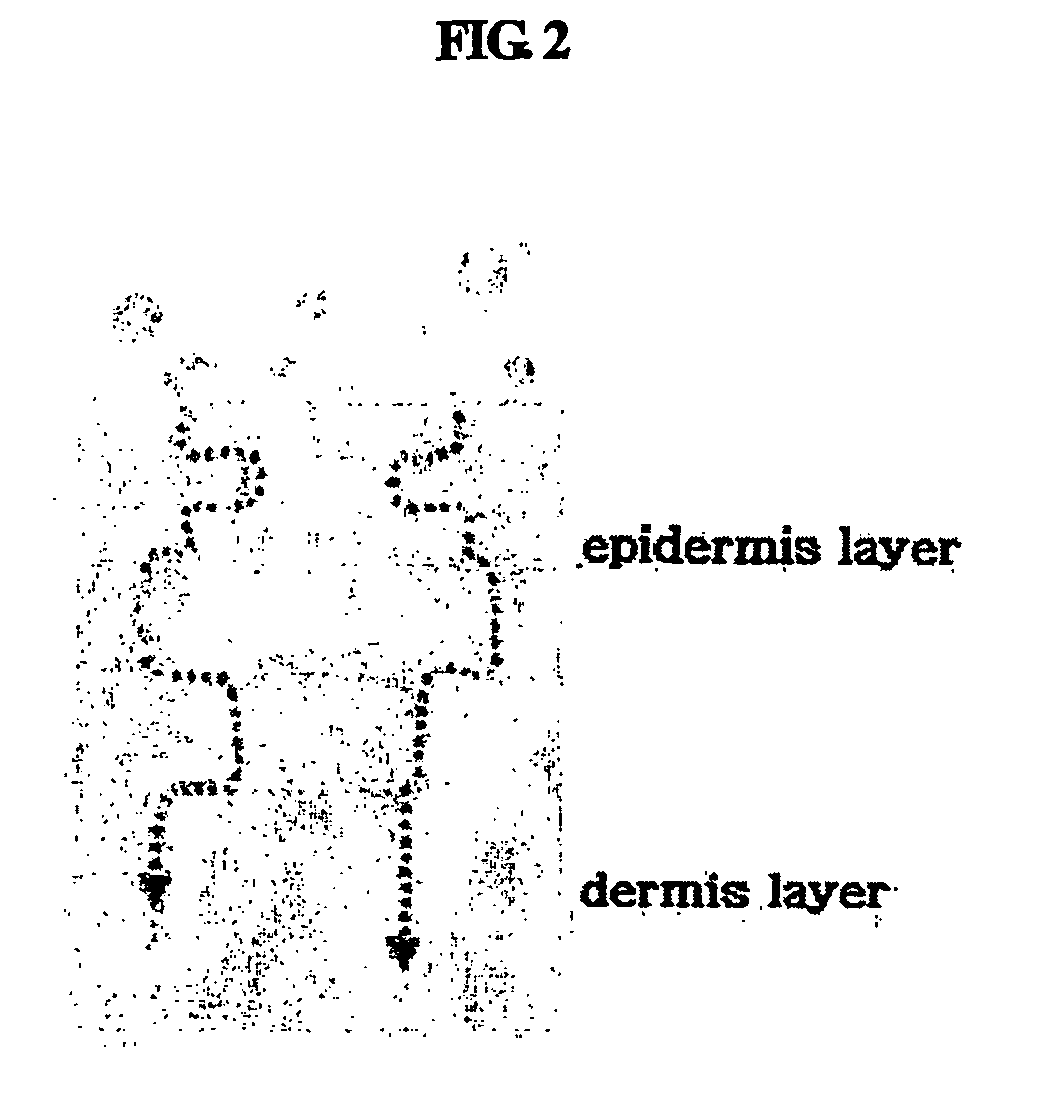
Disclosed are multilayered liposomes for transdermal absorption and a method of preparing the liposomes. The multilayered liposomes are prepared using a mixture of oil-phase components comprising squalane, sterols, ceramides, neutral lipids or oils, fatty acids and lecithins, is 200 to 5000 nm in particle size, and is capable of entrapping a physiologically active substance. The multilayered liposomes entrap a larger amount of a physiologically active substance and are structurally stable when encapsulating the physiologically active substance, compared to unilamellar liposomes. Also, they are prepared by a simple and cost-effective process not using a high-pressure homogenizer but using a general homo mixer. Further, since the multilayered liposomes are prepared in a larger size than the intercellular spaces in the stratum corneum, they overcome the tension of surrounding cells when passing through the intercellular spaces and are thus able to penetrate into the dermal layer, compared to nano-sized unilamellar liposomes. Thus, the multilayered liposomes are useful for enhancing the transdermal absorption of physiologically active substances.
Owner:BIOSPECTRUM
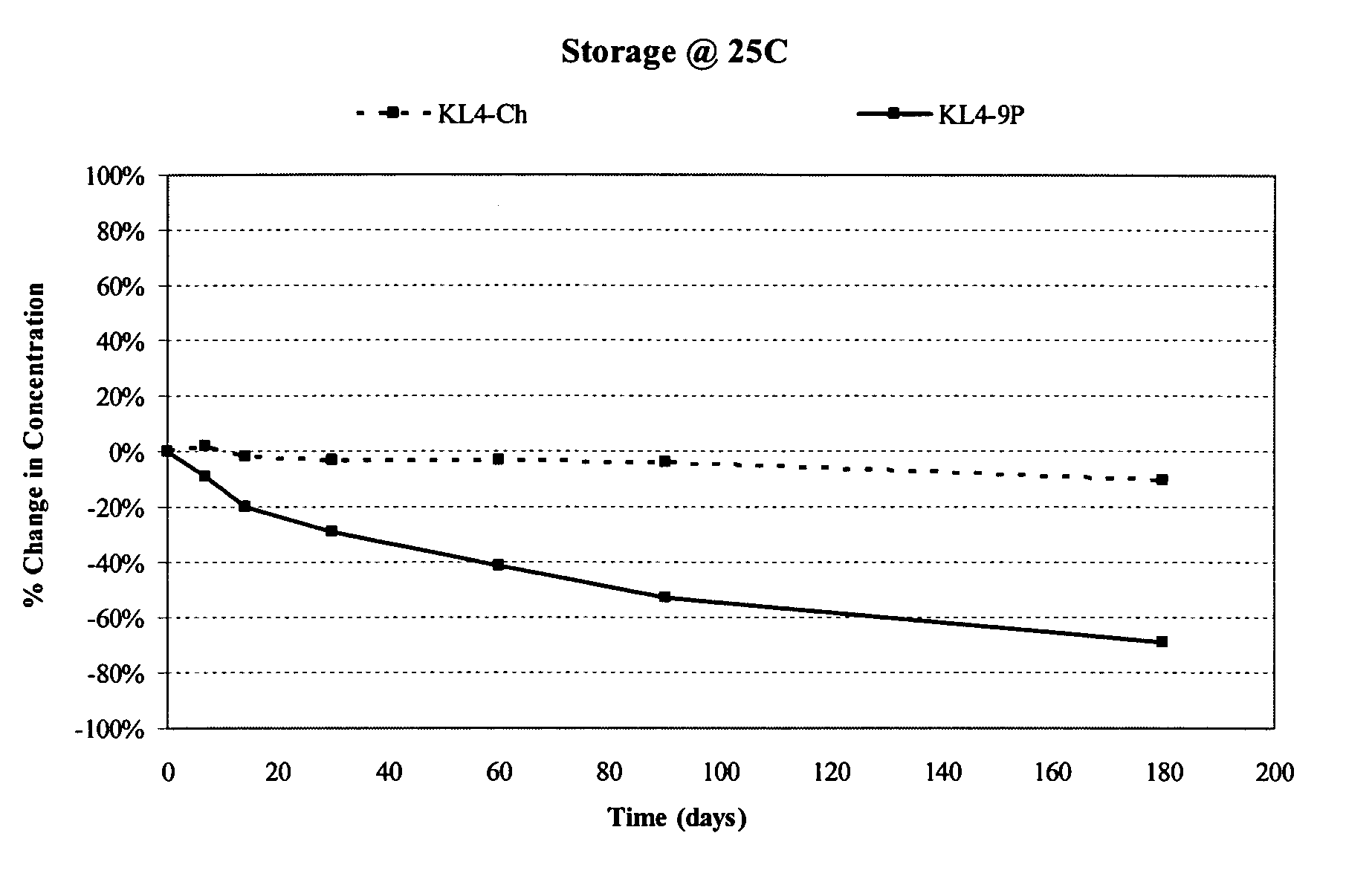
Systems for treating pulmonary infections
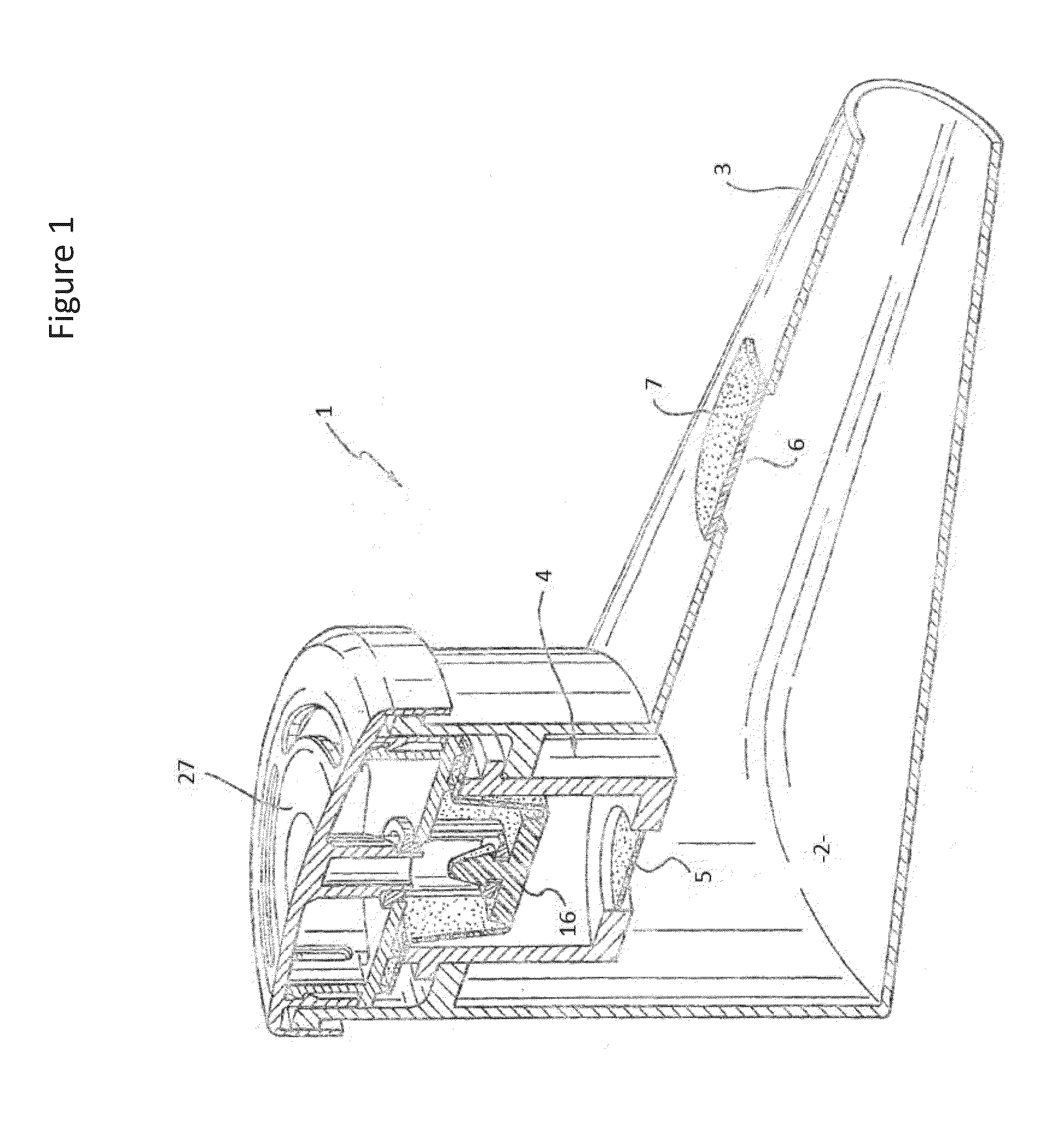
Provided herein are systems for treating a subject with a pulmonary infection, for example, a nontuberculous mycobacterial pulmonary infection, a Burkholderia pulmonary infection, a pulmonary infection associated with bronchiectasis, or a Pseudomonas pulmonary infection. The system includes a pharmaceutical formulation comprising a liposomal aminoglycoside dispersion, and the lipid component of the liposomes consist essentially of electrically neutral lipids. The system also includes a nebulizer which generates an aerosol of the pharmaceutical formulation at a rate greater than about 0.53 gram per minute. The aerosol is delivered to the subject via inhalation for the treatment of the pulmonary infection.
Owner:INSMED INC
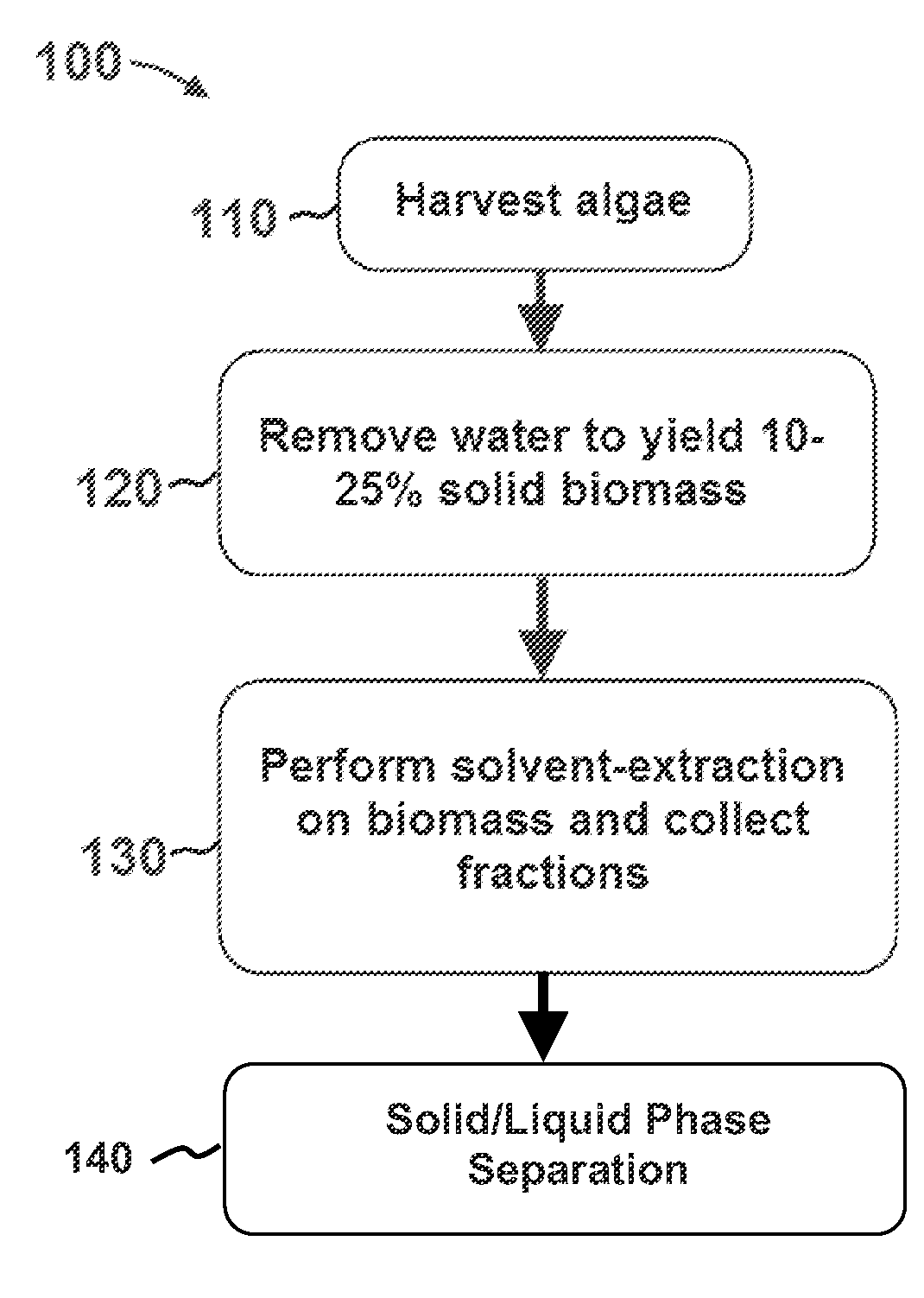
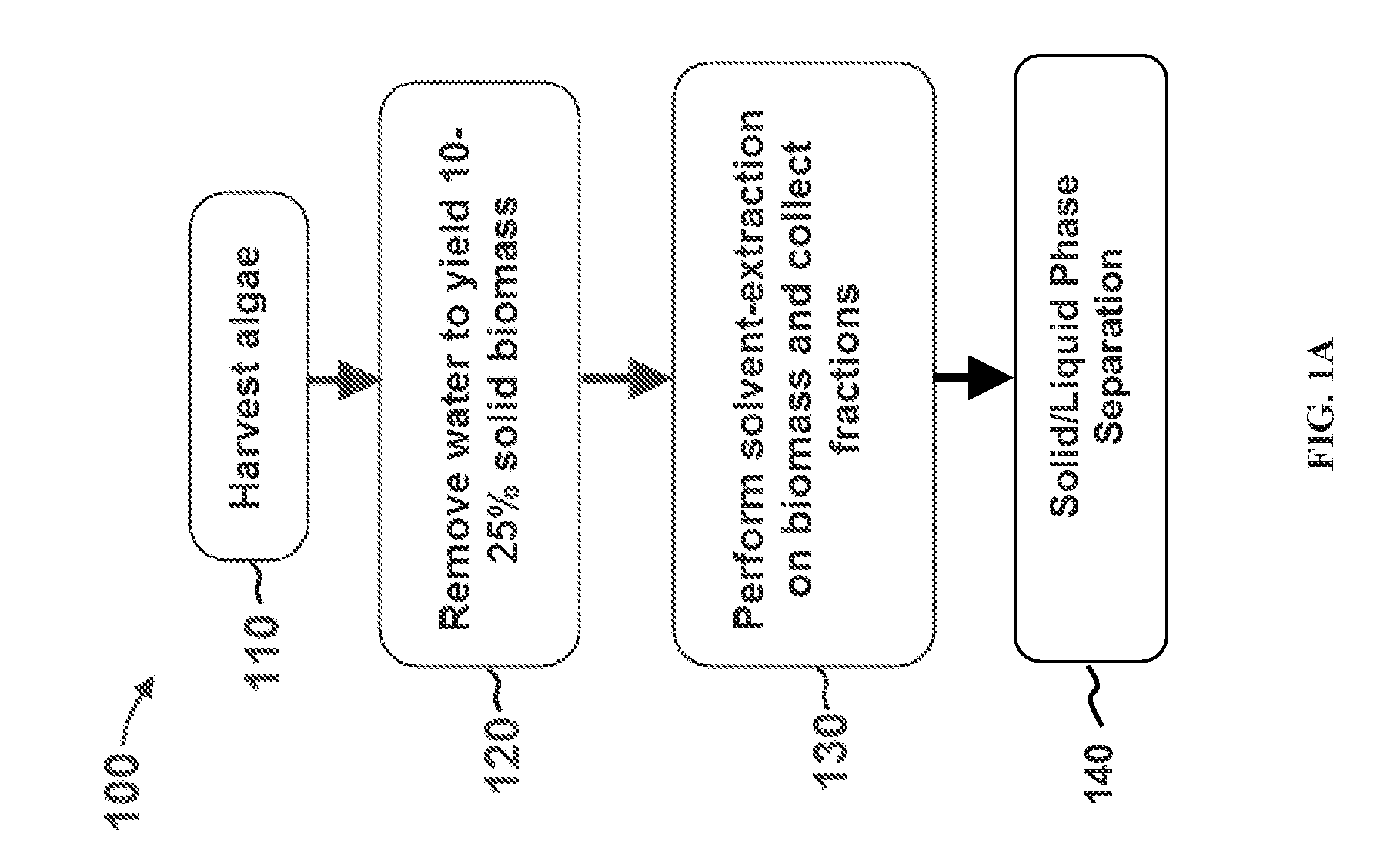
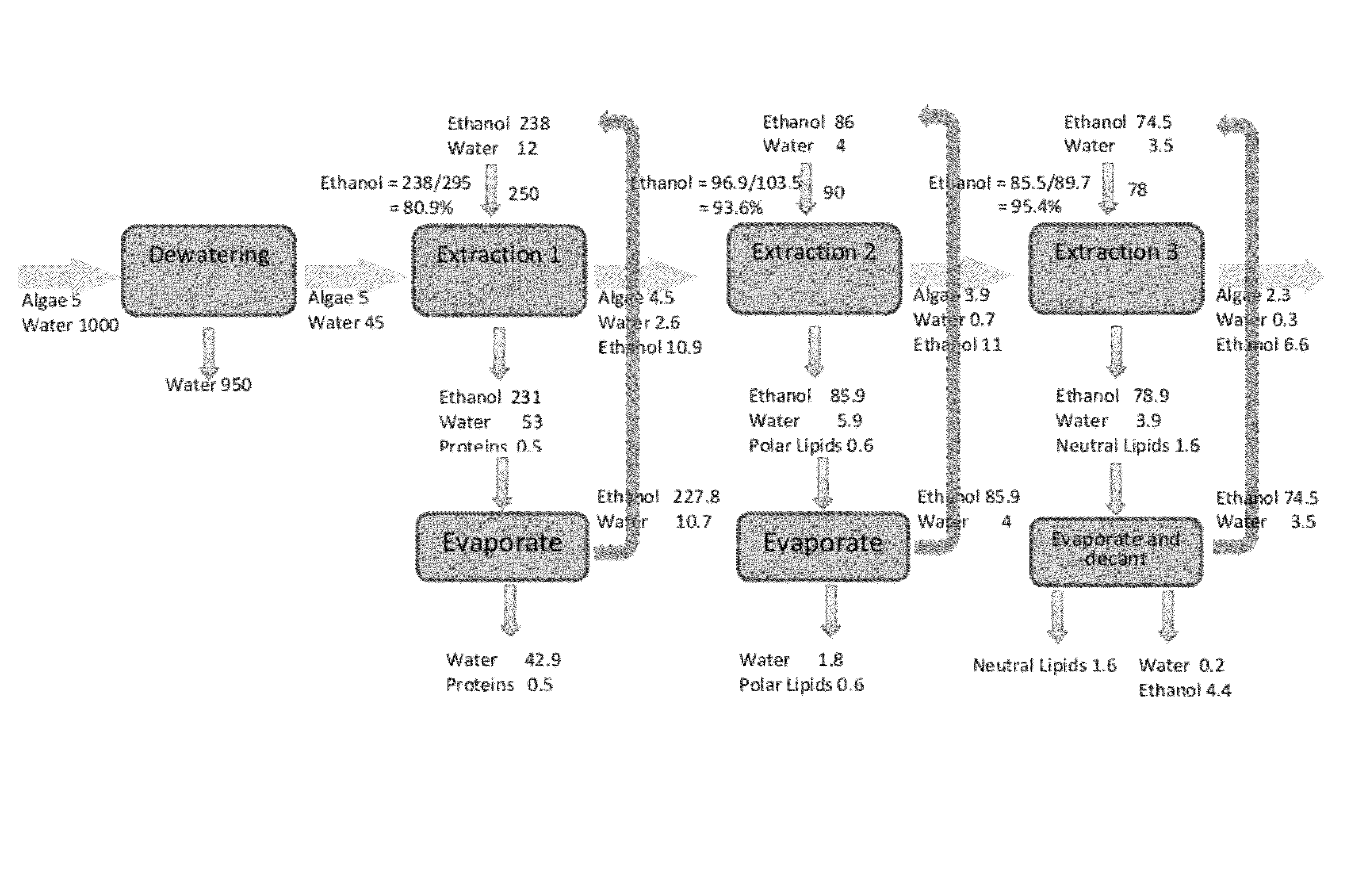
Methods of and Systems for Isolating Nutraceutical Products from Algae
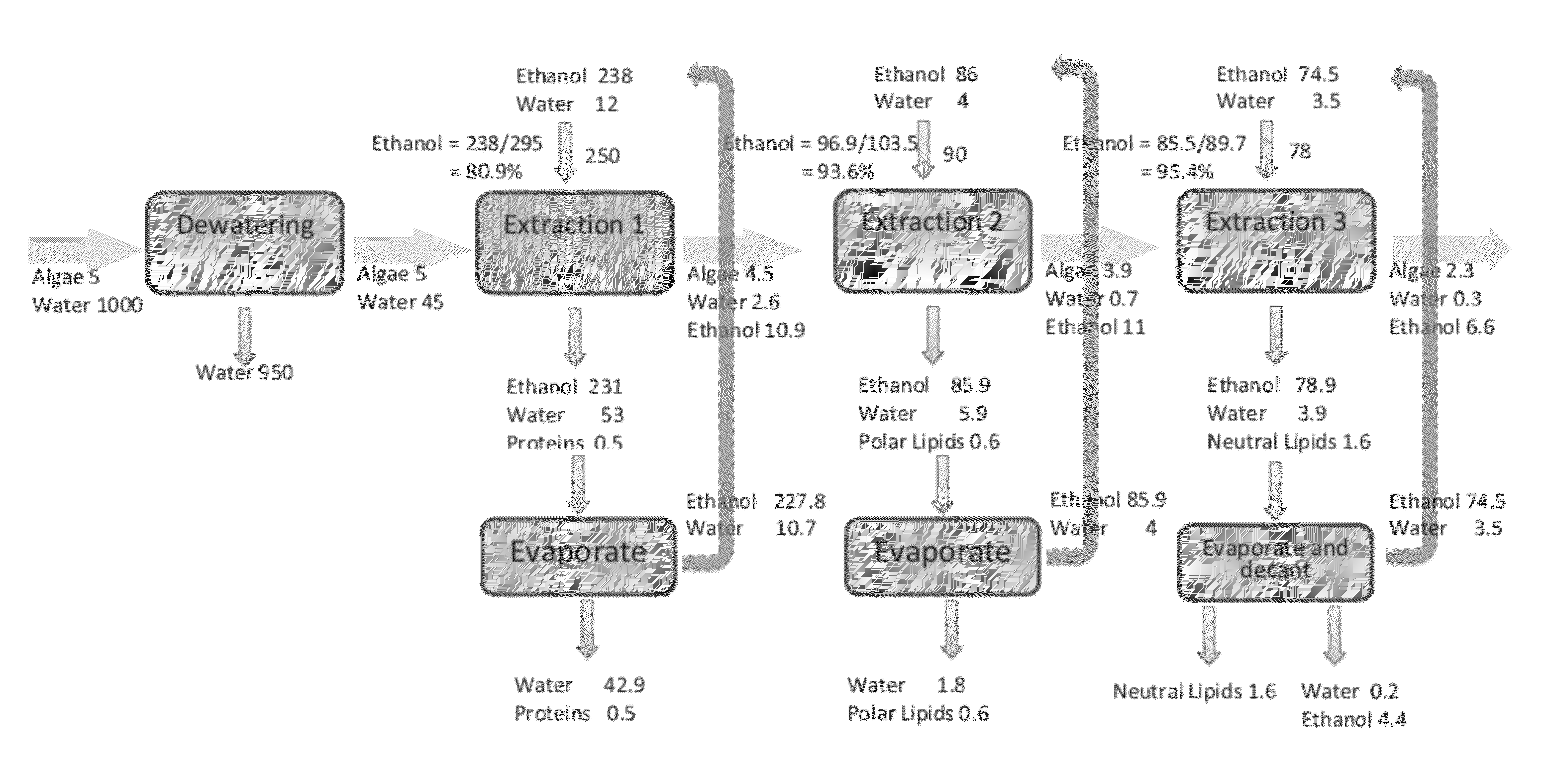
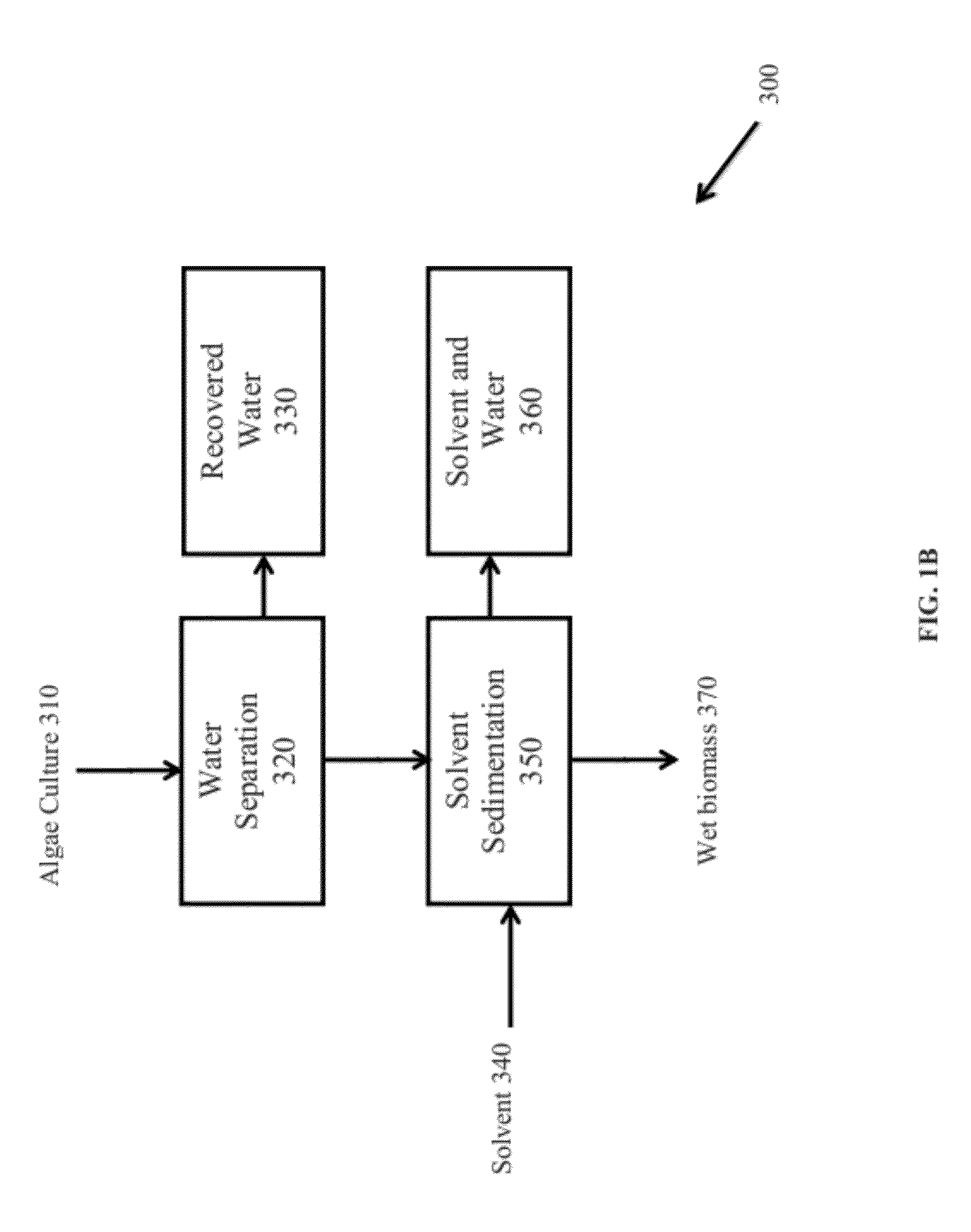
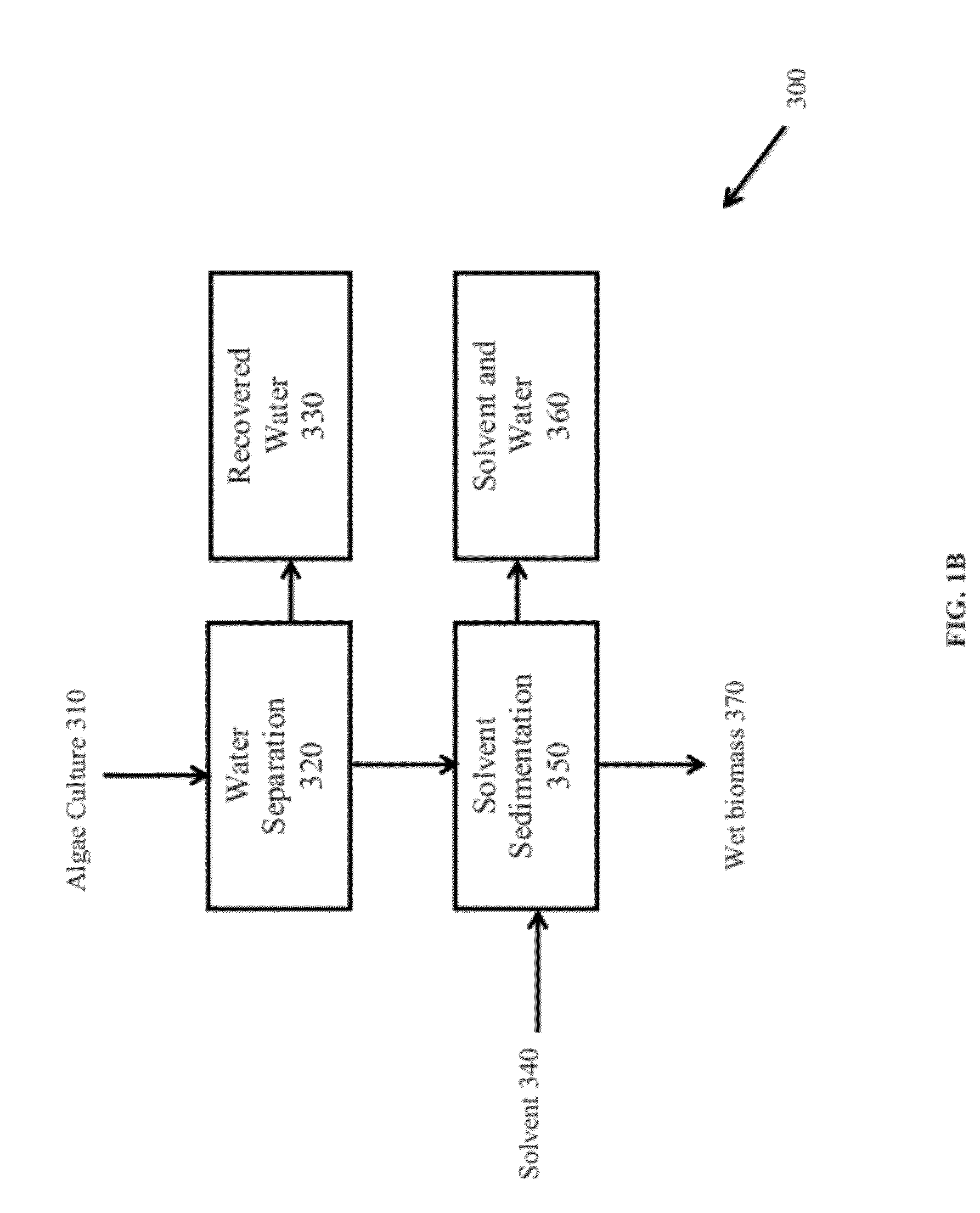
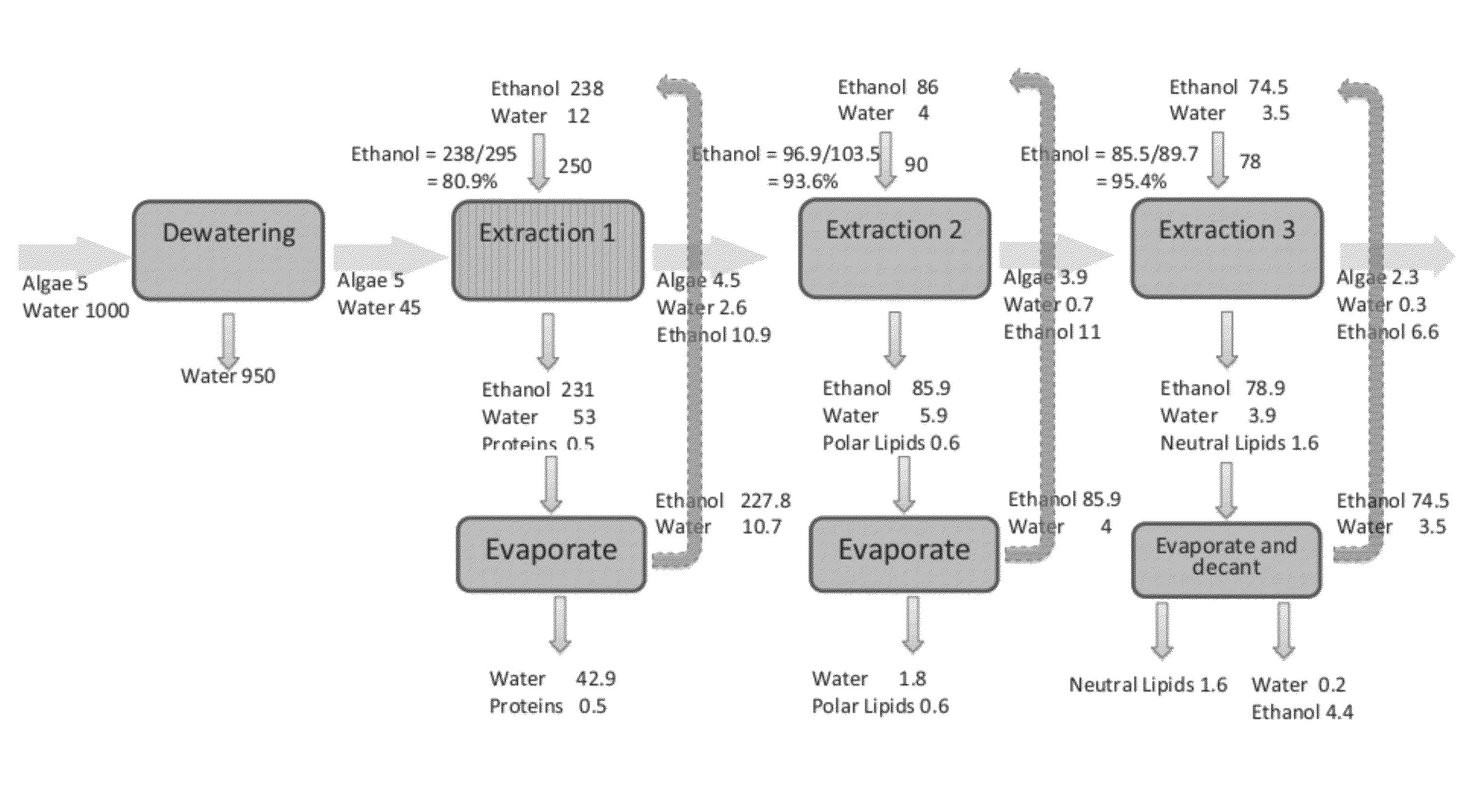
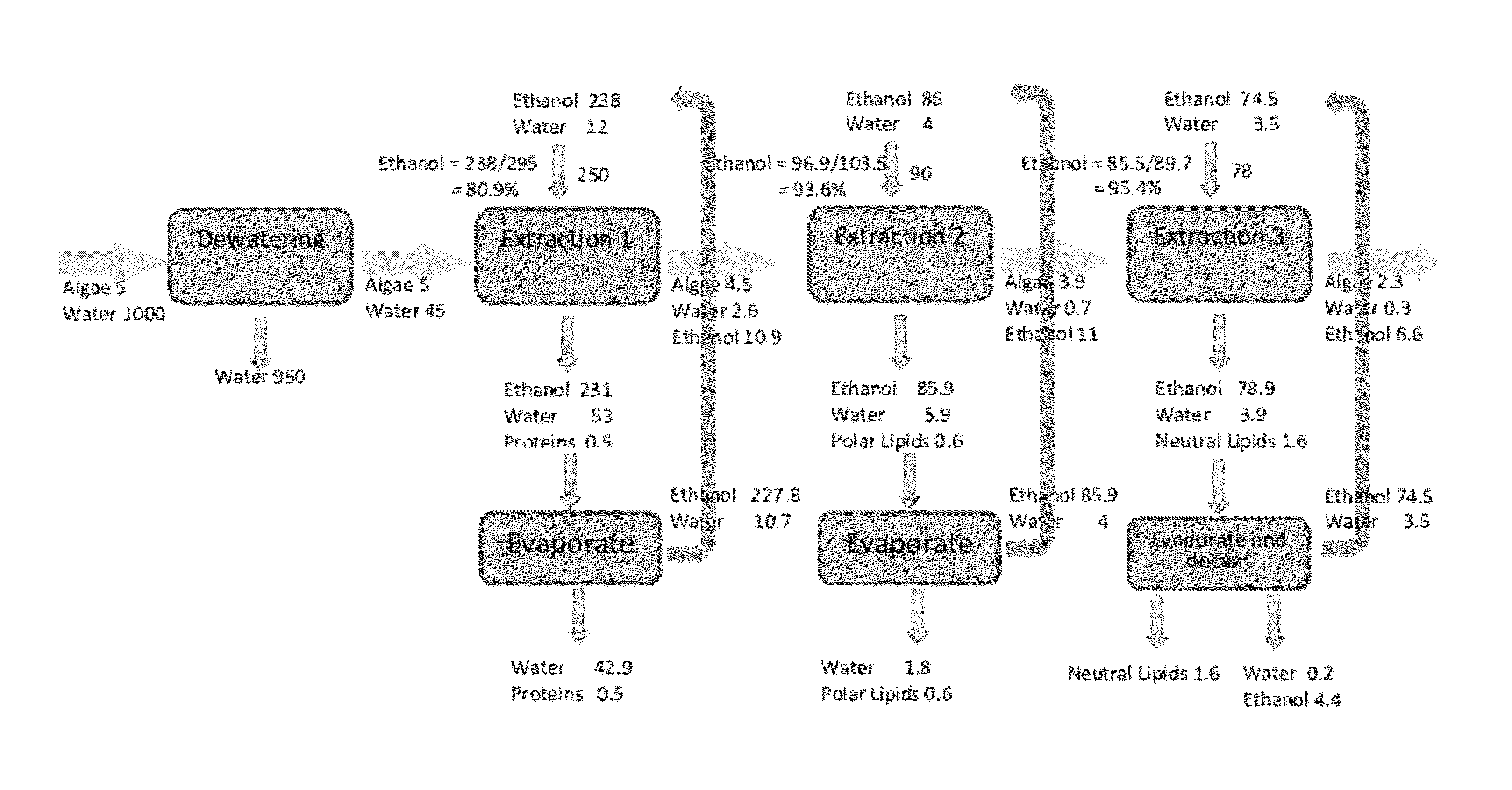
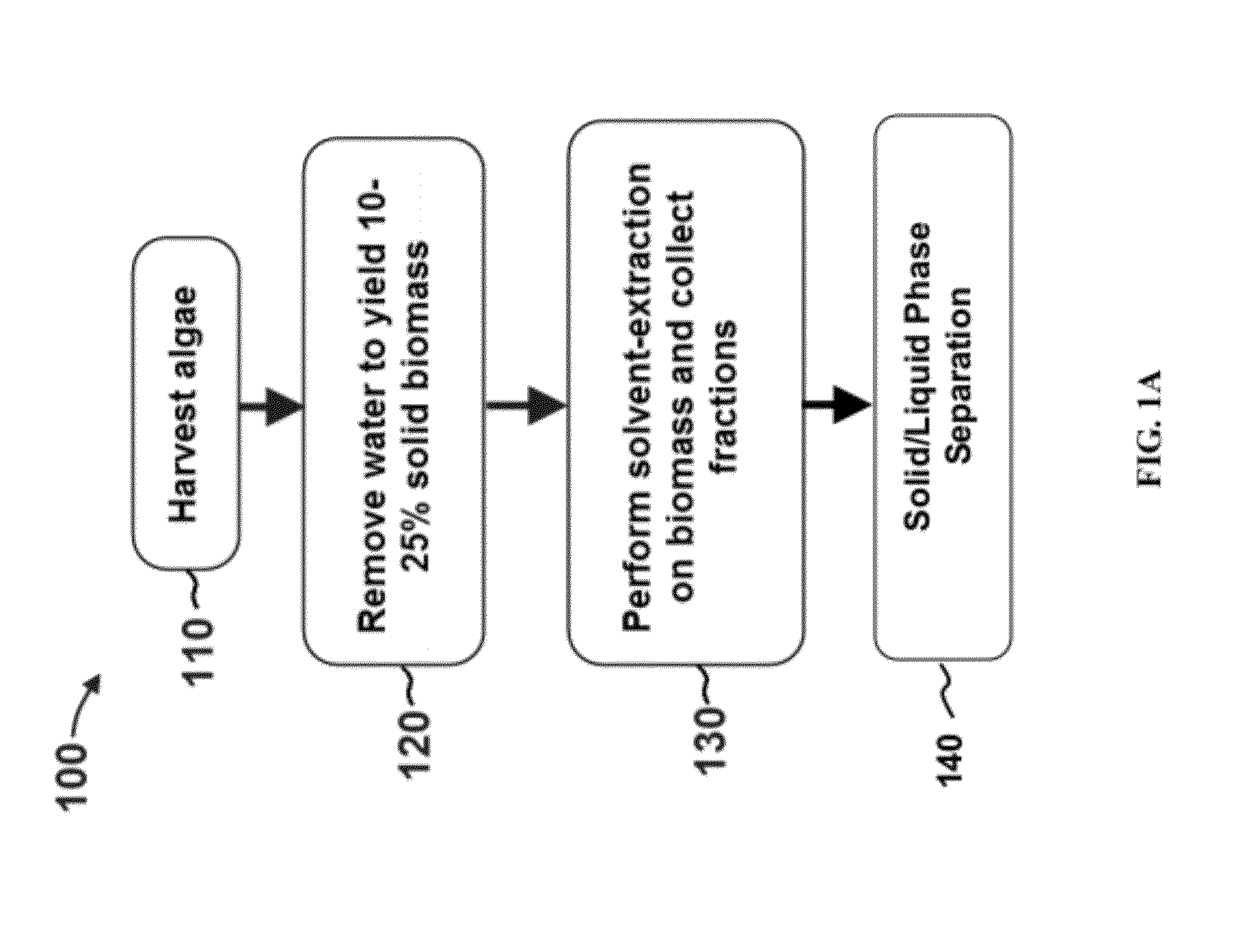
A method of isolating nutraceuticals products from algae is provided. A method of isolating carotenoids and omega-3 rich oil from algae includes dewatering substantially intact algal cells to make an algal biomass and adding a first ethanol fraction to the algal biomass. The method also includes separating a first substantially solid biomass fraction from a first substantially liquid fraction comprising proteins and combining the first substantially solid biomass fraction with a second ethanol fraction. The method further includes separating a second substantially solid biomass fraction from a second substantially liquid fraction comprising polar lipids and combining the second substantially solid biomass fraction with a third ethanol solvent fraction. The method also includes separating a third substantially solid biomass fraction from a third substantially liquid fraction comprising neutral lipids, wherein the third substantially solid biomass fraction comprises carbohydrates and separating the neutral lipids into carotenoids and omega-3 rich oil.
Owner:HELIAE DEVMENT
Methods of producing biofuels, chlorophylls and carotenoids
InactiveUS8115022B2Fatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acid esterificationWater insolubleBiofuel
A method for producing biofuels along with valuable food and neutraceutical products is provided. A method of making biofuels includes dewatering substantially intact algal cells to make an algal biomass, extracting neutral lipids along with carotenoids and chlorophylls from the algal biomass, and separation of the carotenoids and chlorophylls using adsorption or membrane diafiltration or other methods. The remaining neutral lipids are esterified with a catalyst in the presence of an alcohol. The method also includes separating a water soluble fraction comprising glycerin from a water insoluble fraction comprising fuel esters and distilling the fuel esters under vacuum to obtain a C16 or shorter fuel esters fraction, a C16 or longer fuel ester fraction, and a residue comprising omega-3 fatty acids esters and remaining carotenoids. The method further includes hydrogenating and deoxygenating at least one of (i) the C16 or shorter fuel esters to obtain a jet fuel blend stock and (ii) the C16 or longer fuel esters to obtain a diesel blend stock.
Owner:HELIAE DEVMENT
Methods of and systems for isolating nutraceutical products from algae
A method of isolating nutraceuticals products from algae is provided. A method of isolating carotenoids and omega-3 rich oil from algae includes dewatering substantially intact algal cells to make an algal biomass and adding a first ethanol fraction to the algal biomass. The method also includes separating a first substantially solid biomass fraction from a first substantially liquid fraction comprising proteins and combining the first substantially solid biomass fraction with a second ethanol fraction. The method further includes separating a second substantially solid biomass fraction from a second substantially liquid fraction comprising polar lipids and combining the second substantially solid biomass fraction with a third ethanol solvent fraction. The method also includes separating a third substantially solid biomass fraction from a third substantially liquid fraction comprising neutral lipids, wherein the third substantially solid biomass fraction comprises carbohydrates and separating the neutral lipids into carotenoids and omega-3 rich oil.
Owner:HELIAE DEVMENT
Invasomes for therapy of disorders, their preparation and use
The invention relates to invasomes comprising a lipid mixture comprising one or more lipids, preferably neutral lipids, one or more lysophosphatides and at least one pharmacological agent, preferably an immunomodulator, to the preparation thereof and to the use thereof for the therapy of disorders, preferably of disorders which can be treated by modulation of the immune system.
Owner:VECTRON THERAPEUTICS
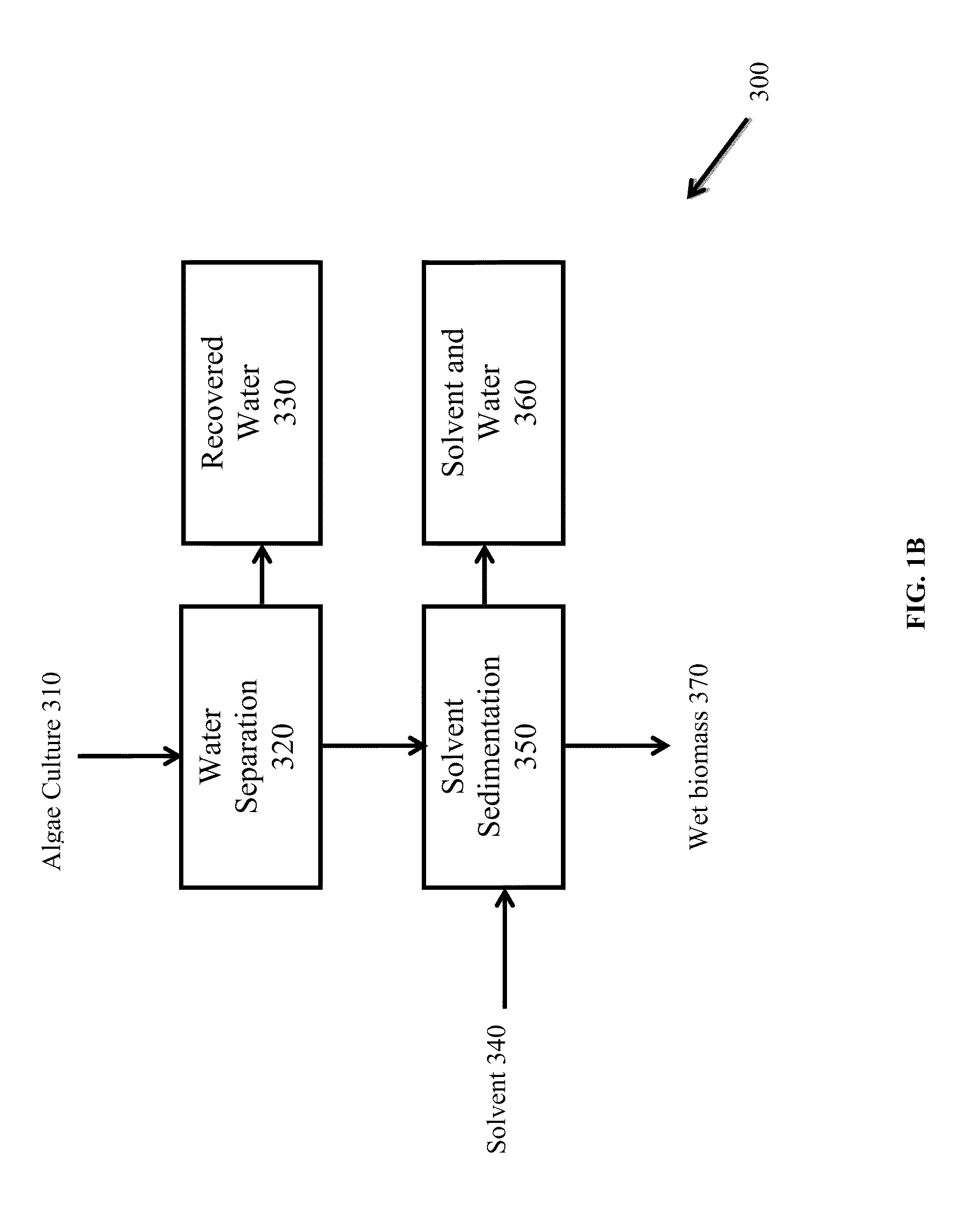
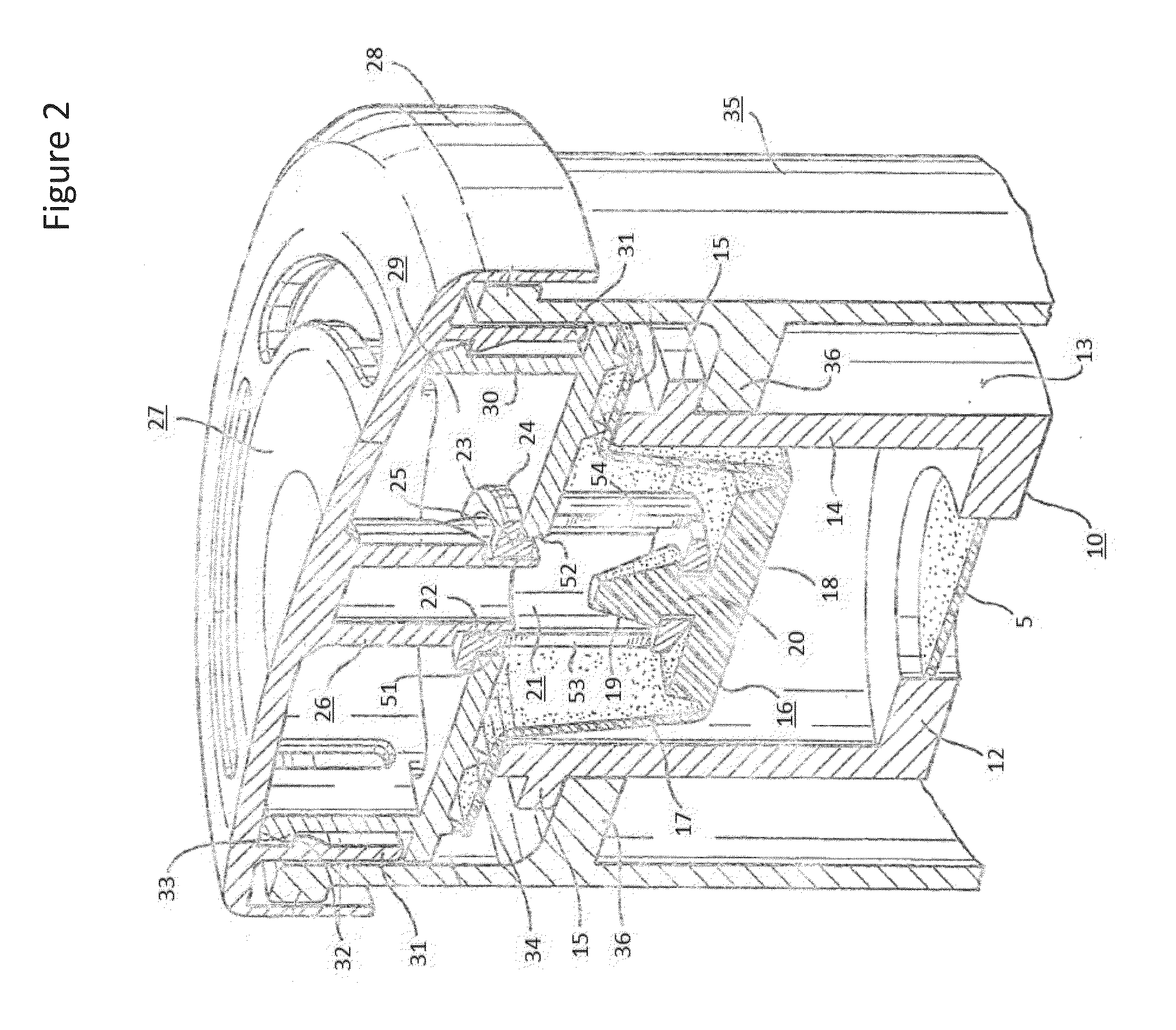
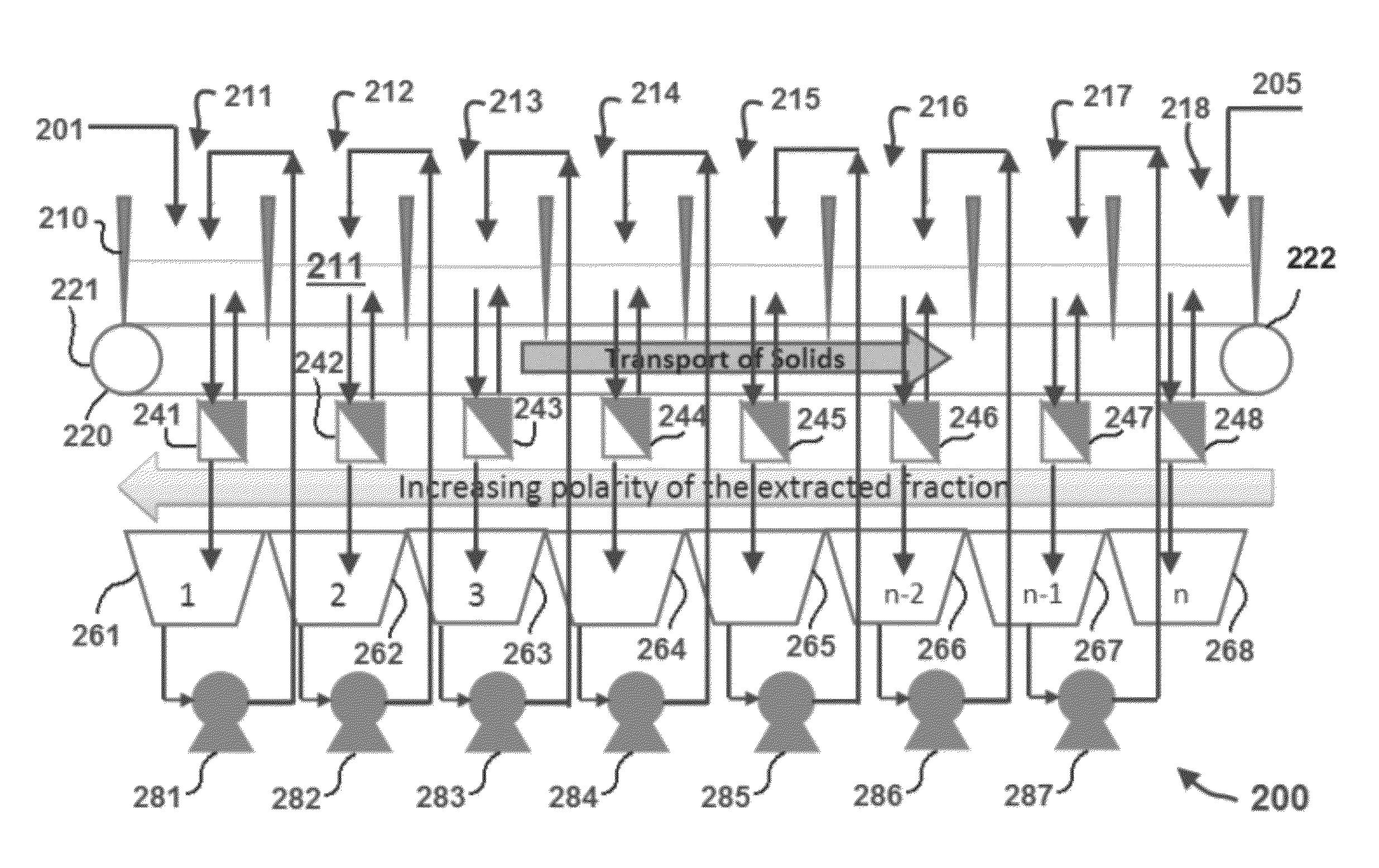
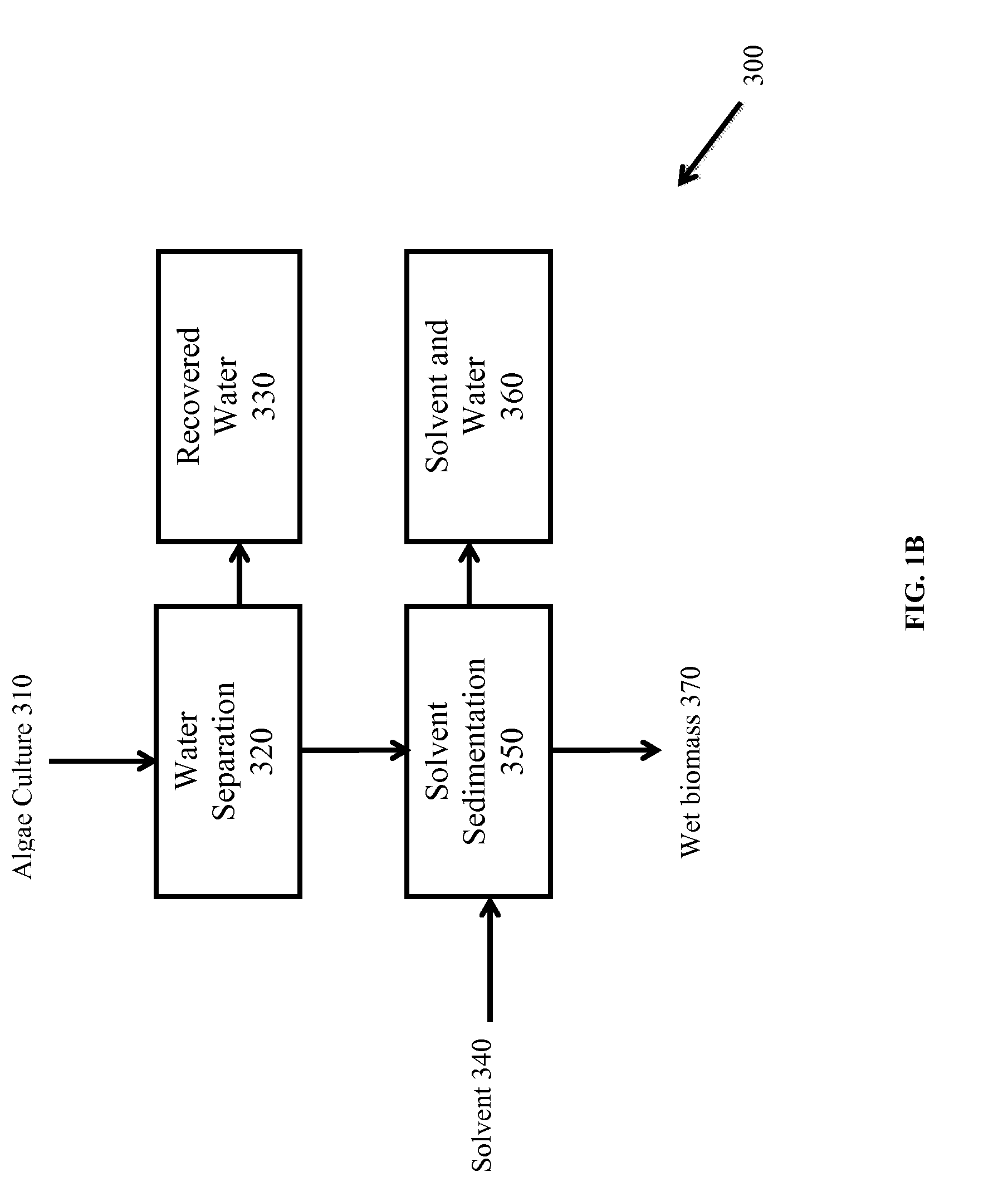
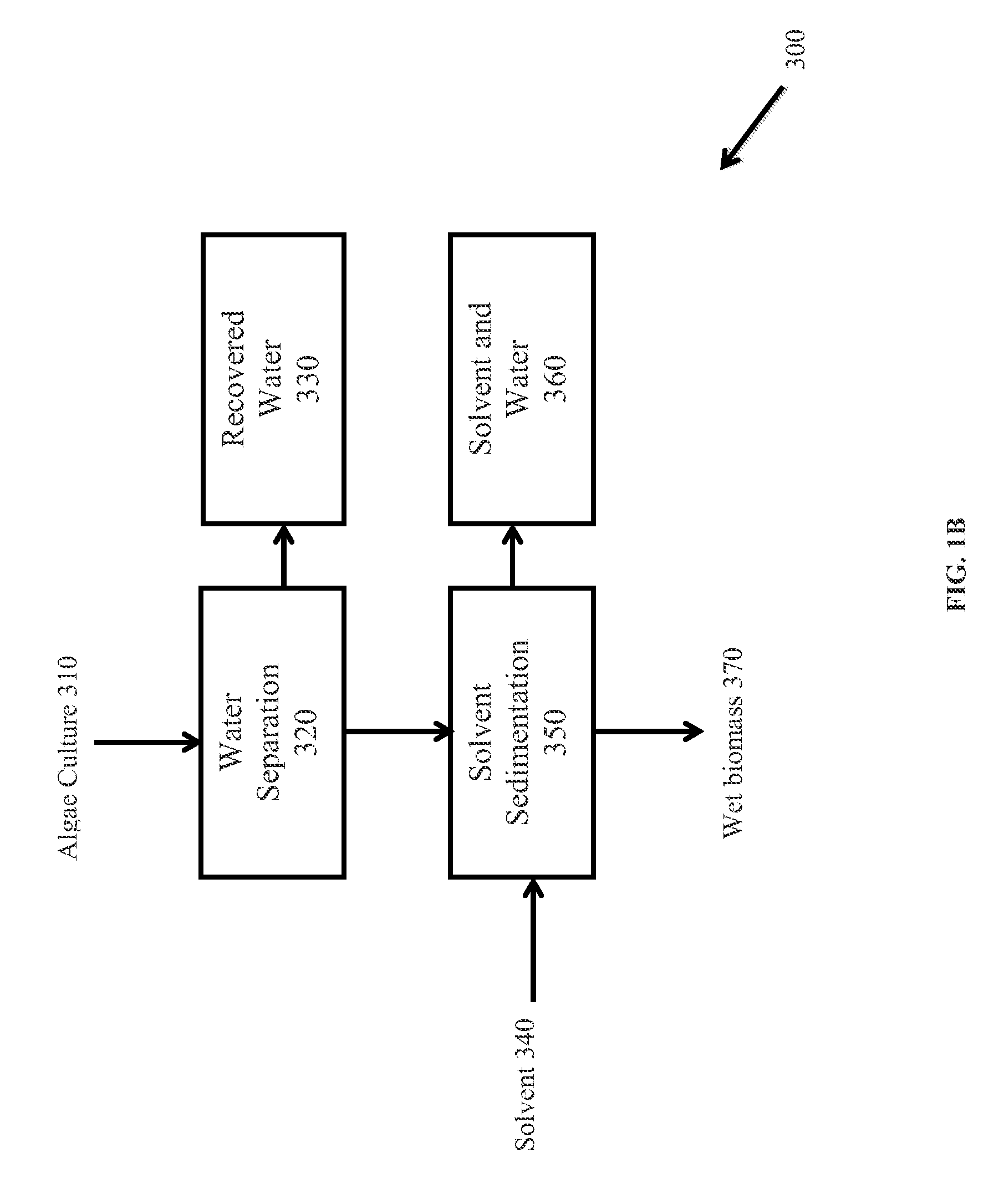
Extraction of neutral lipids by a two solvent method
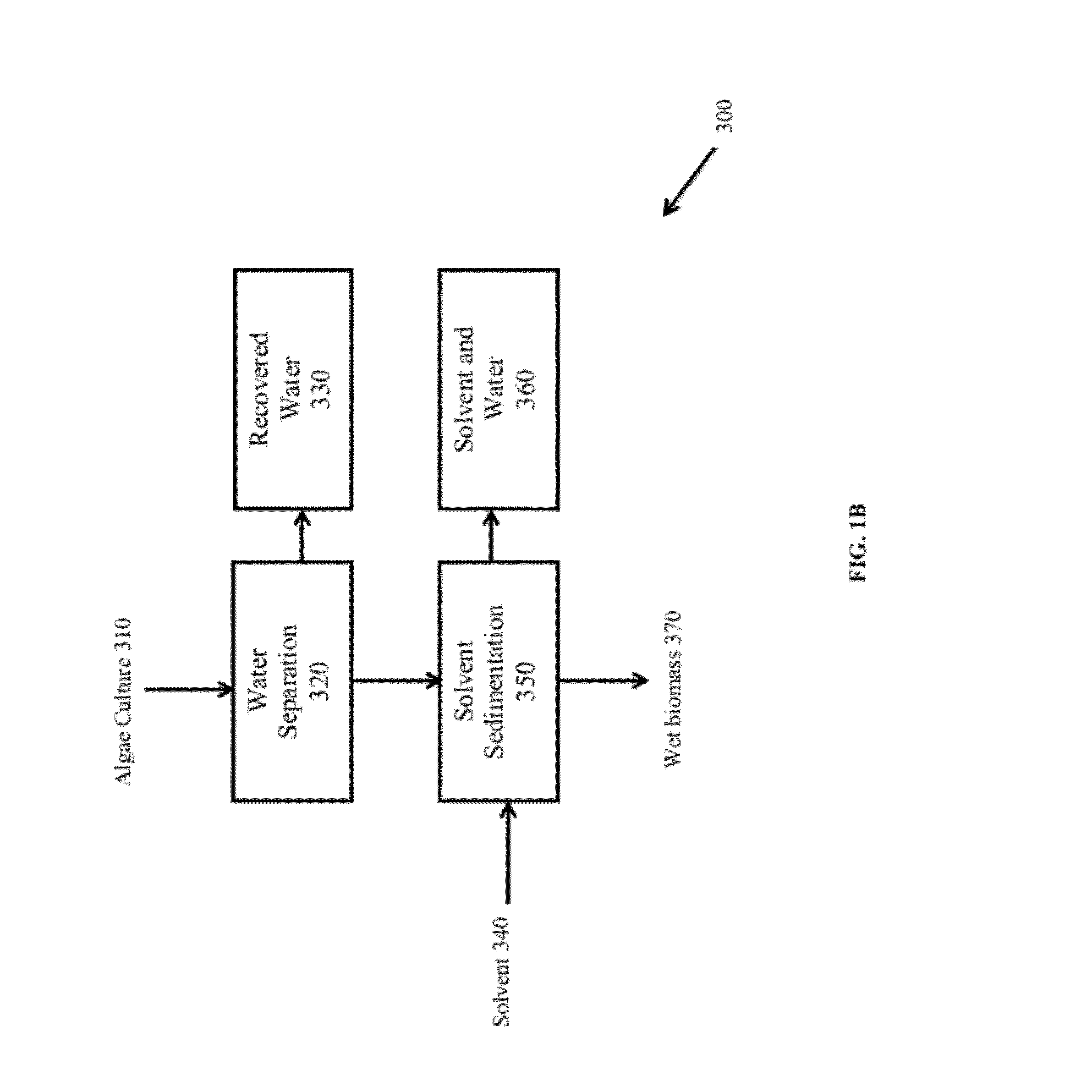
InactiveUS8202425B2Quantity minimizationReduce processing latencyWater/sewage treatment by centrifugal separationSemi-permeable membranesSolventPolar lipids
Owner:HELIAE DEVMENT
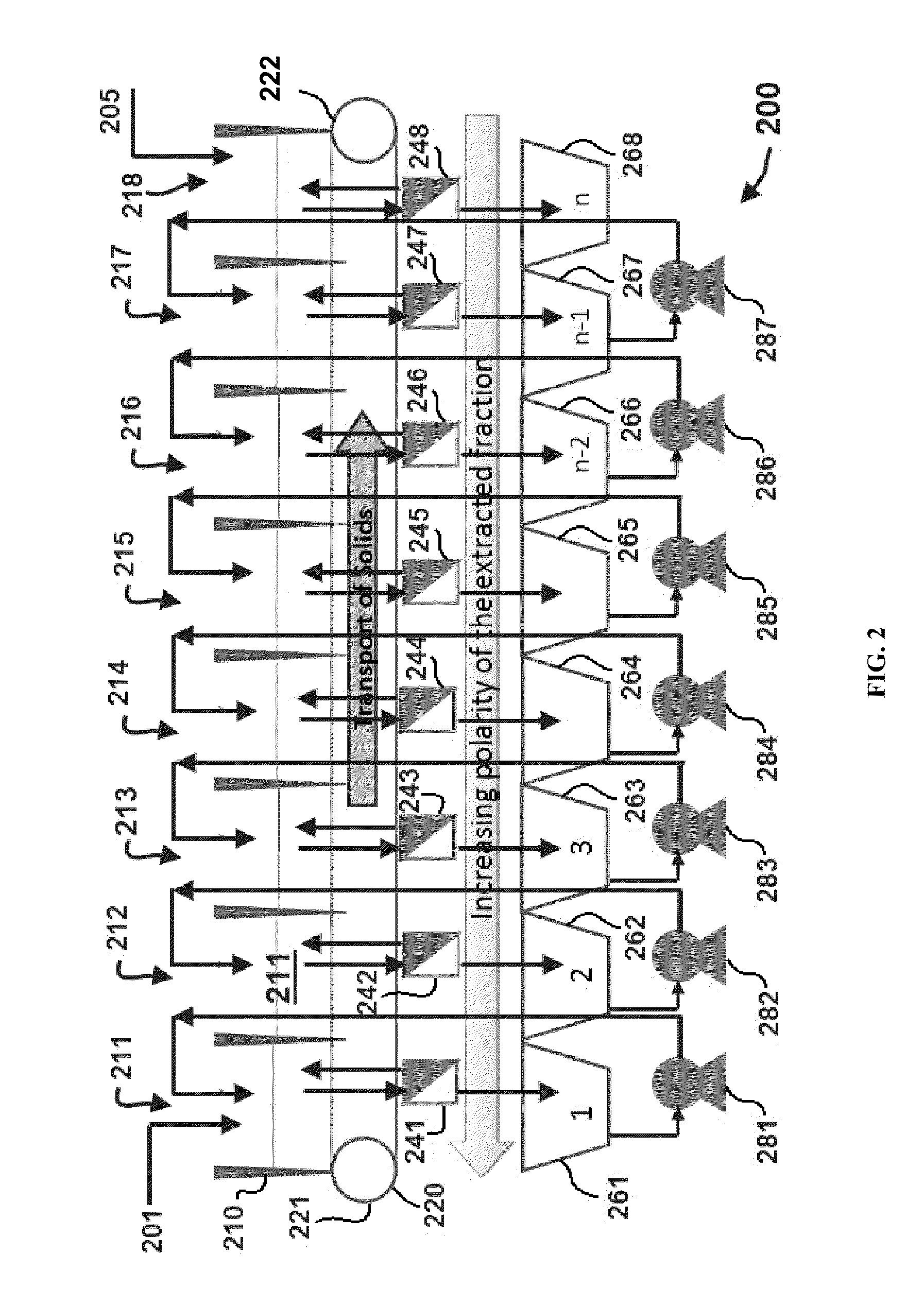
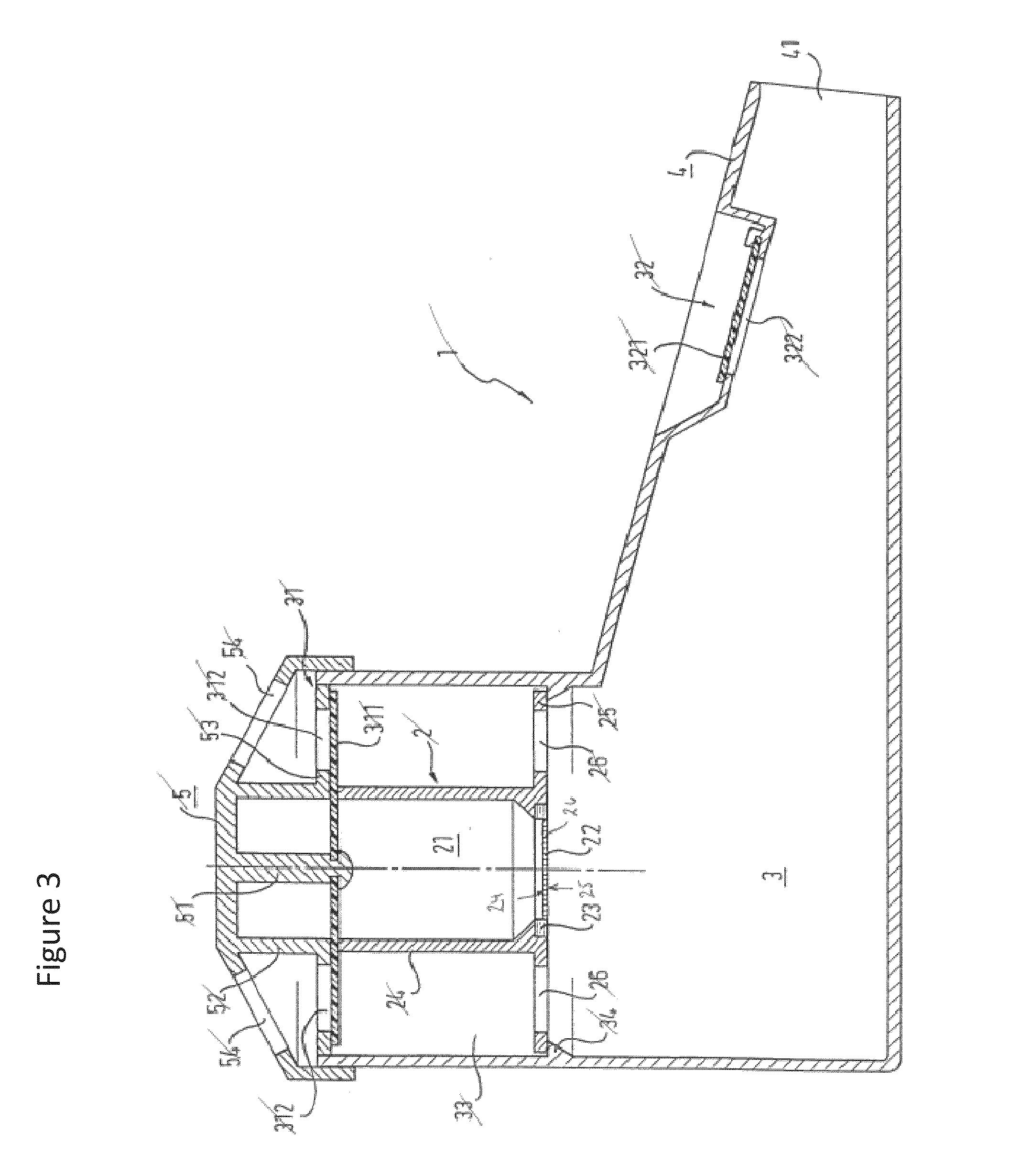
Extraction of polar lipids by a two solvent method
InactiveUS20120053357A1Reduce processing latencyQuantity minimizationWater/sewage treatment by centrifugal separationSemi-permeable membranesFood additiveSolvent
Owner:HELIAE DEVMENT
Methods of and Systems for Producing Biofuels
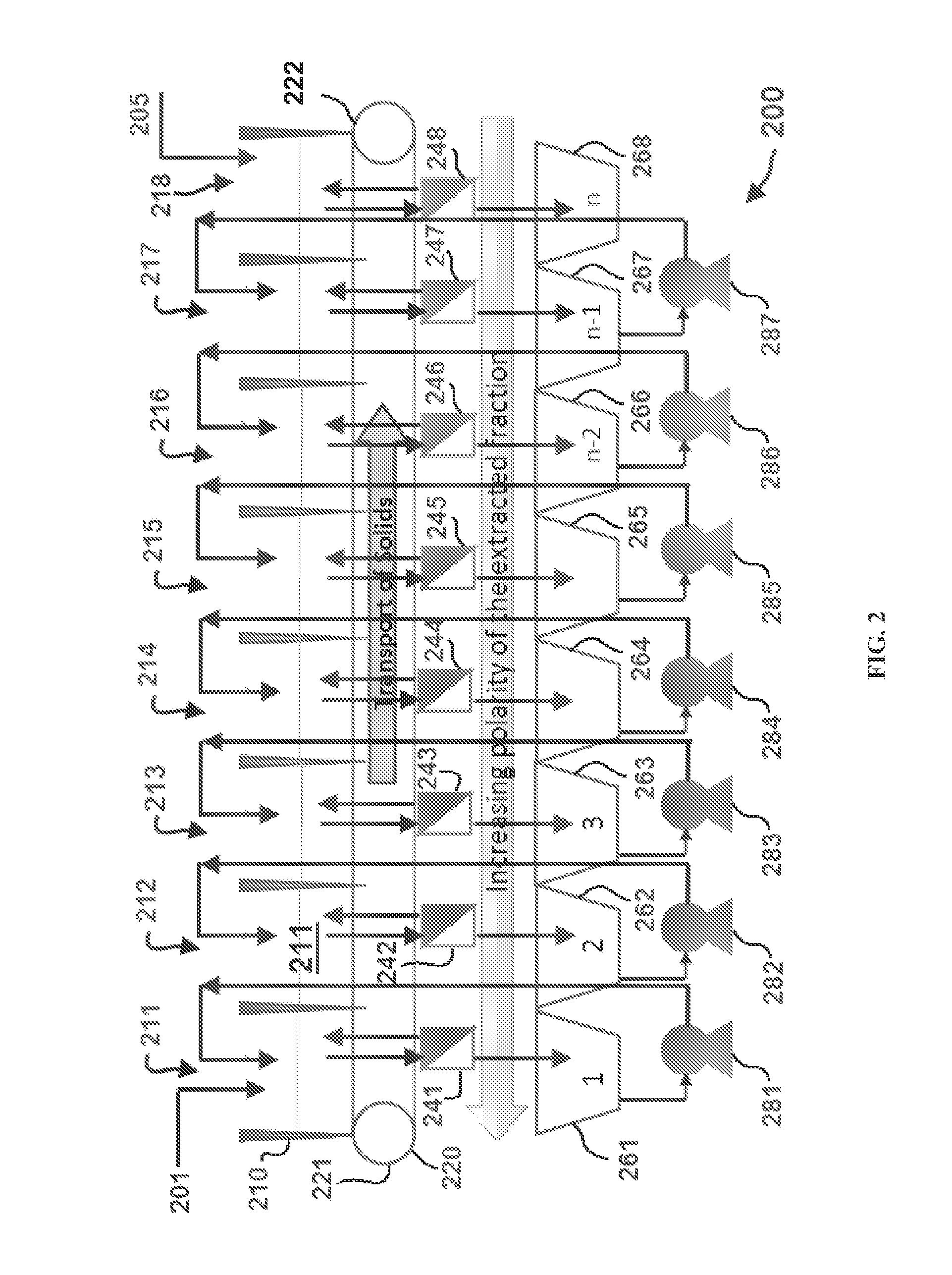
A method for producing biofuels is provided. A method of making biofuels includes dewatering substantially intact algal cells to make an algal biomass, sequentially adding solvent sets to the algal biomass, and sequentially separating solid biomass fractions from liquid fractions to arrive at a liquid fraction comprising neutral lipids. The method also includes esterifying the neutral lipids, separating a water miscible fraction comprising glycerin from a water immiscible fraction comprising fuel esters, carotenoids, and omega-3 fatty acids. The method also includes obtaining a C16 or shorter fuel esters fraction, a C16 or longer fuel ester fraction, and a residue comprising carotenoids and omega-3 fatty acids. The method includes hydrogenating and deoxygenating at least one of (i) the C16 or shorter fuel esters to obtain a jet fuel blend stock and (ii) the C16 or longer fuel esters to obtain a diesel blend stock.
Owner:HELIAE DEVMENT
Neutral nanotransporters
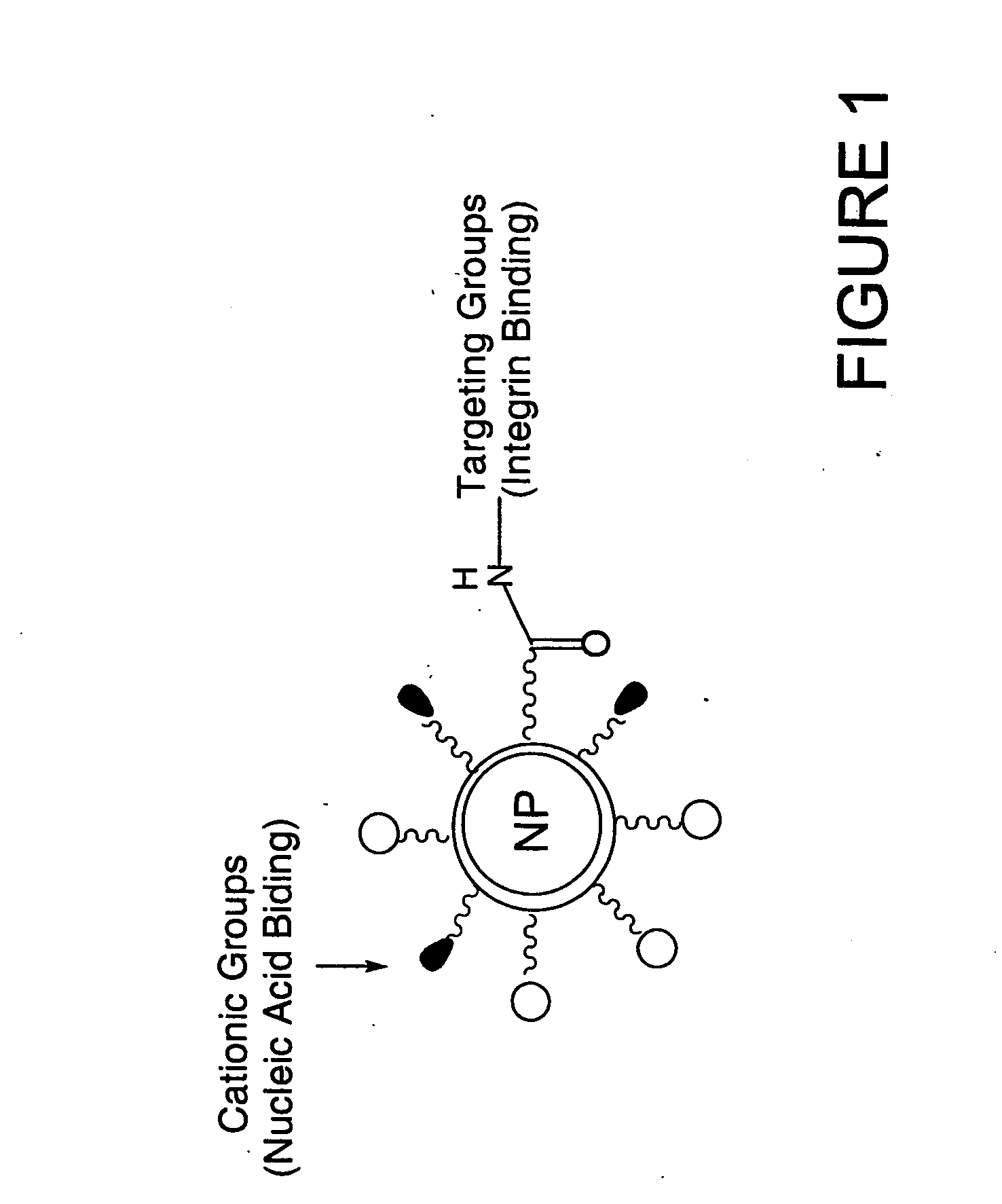
ActiveUS20110237522A1Efficient loadingImprove hydrophobicityOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderPolynucleotideNeutral lipid
Neutral lipid formulations for nucleic acid delivery are provided according to the invention. The neutral lipid formulations include hydrophobically modified polynucleotides and fat mixtures. Methods of using the neutral lipid formulations are also provided.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL) +1
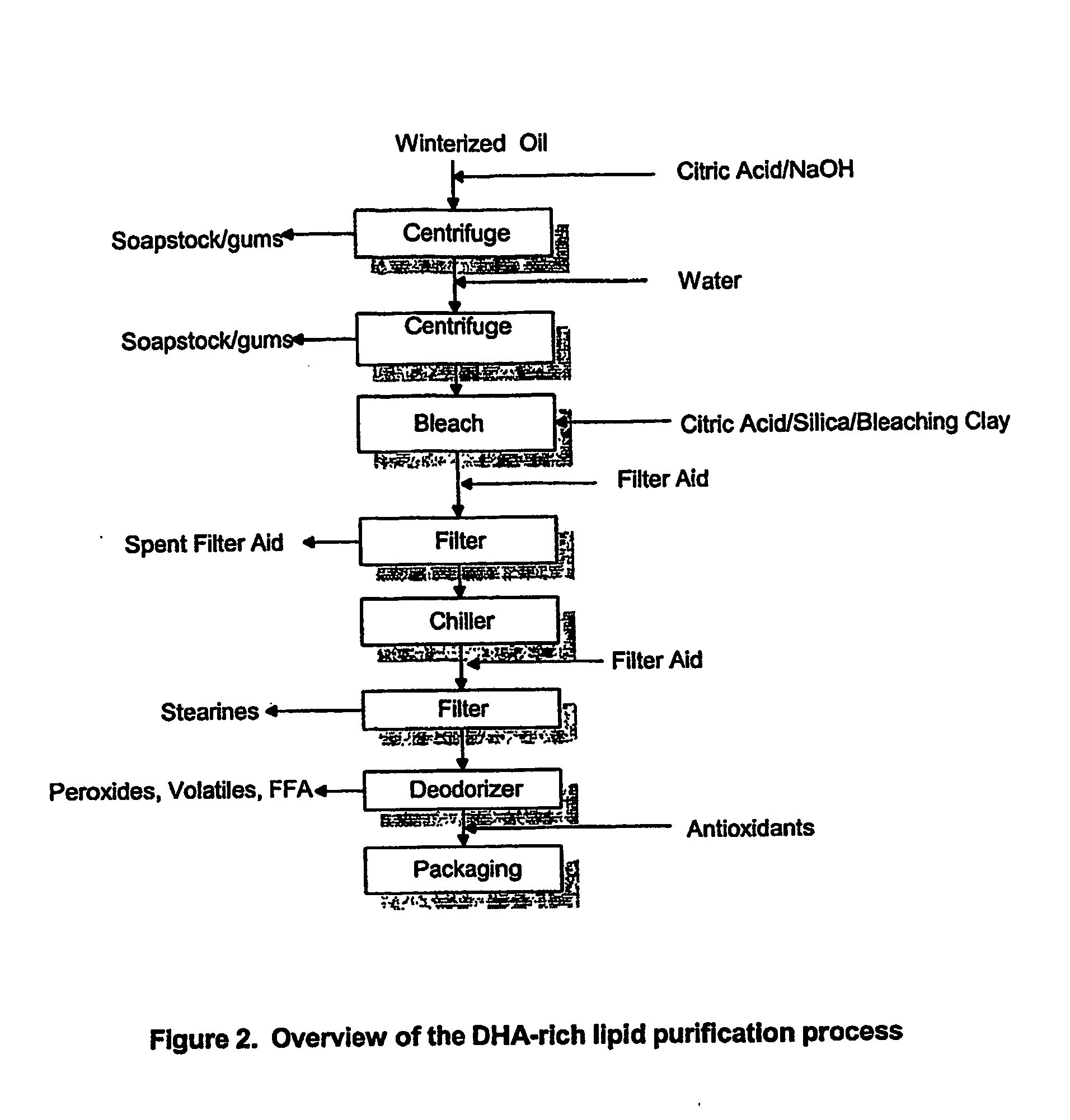
Extraction and winterization of lipids from oilseed and microbial sources
ActiveUS20050115897A1Solve many processesReduce degummingFatty-oils/fats refiningMicroorganism based processesLipid formationMicroorganism
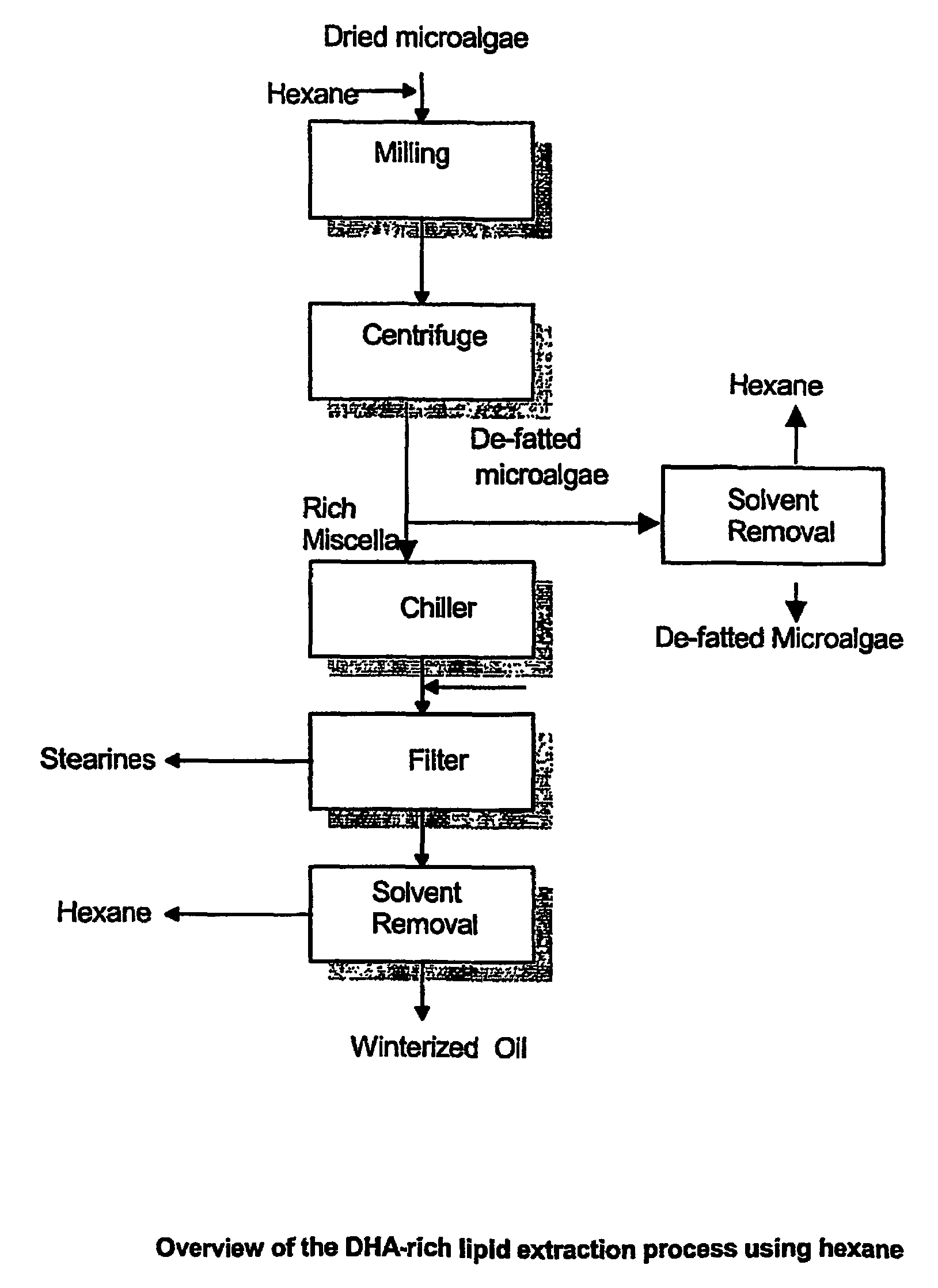
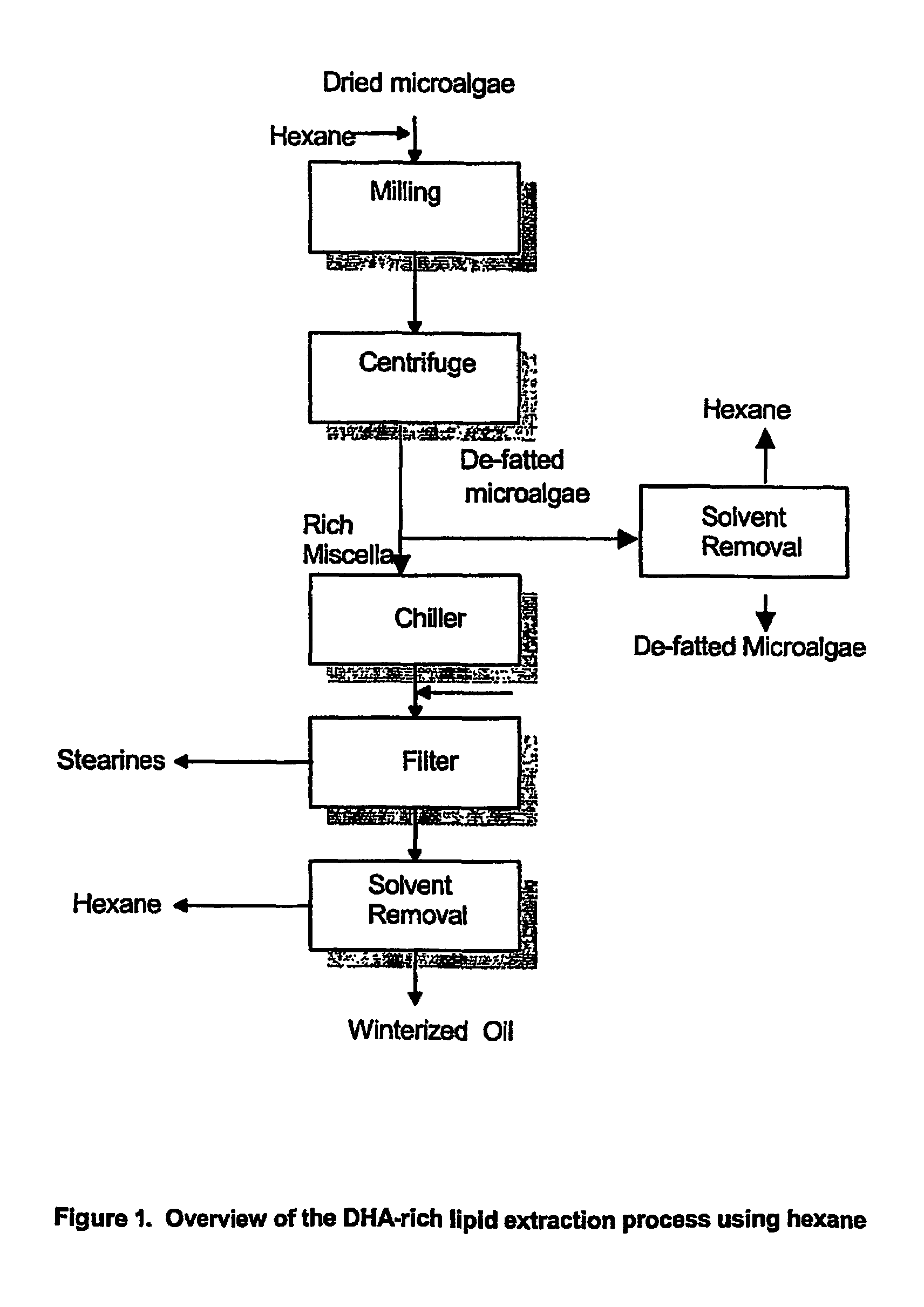
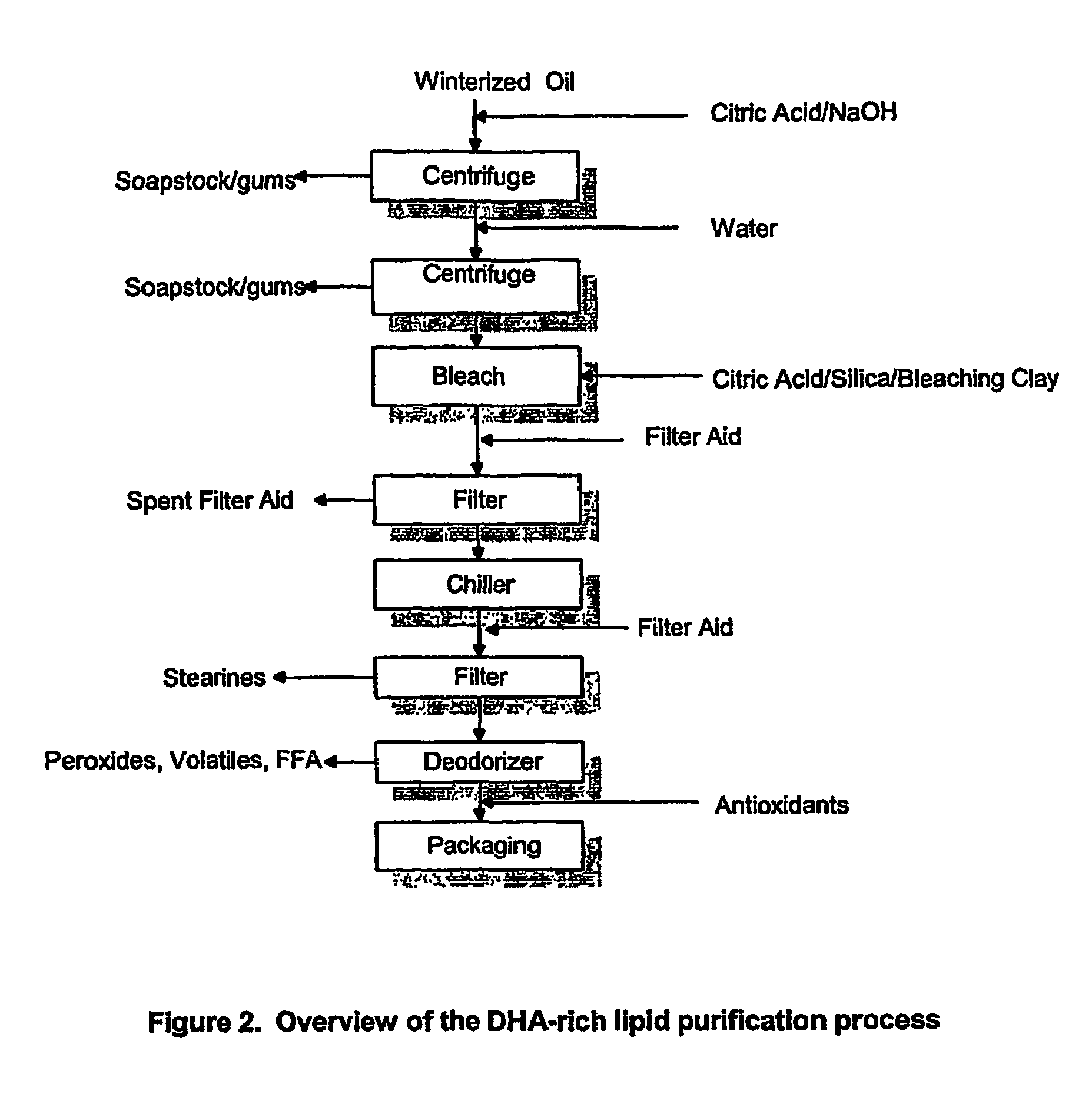
A process for purifying a lipid composition having predominantly neutral lipid components having at least one long chain polyunsaturated fatty acid is disclosed. The process employs contacting the lipid composition with a polar solvent, such as acetone, wherein the solvent is selected such that the contaminants are less soluble in the solvent than in the long chain polyunsaturated fatty acid. The process is typically conducted at cooler temperatures including about 0° C. Upon precipitation of the contaminants from the lipid composition, a separation is conducted to remove the precipitated material from the lipid composition. The long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids can include ARA, DPA, EPA and / or DHA. The process effectively winterizes lipid compositions, thereby reducing the tendency of such compositions to become hazy.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Extraction of neutral lipids by a two solvent method
InactiveUS20120046477A1Quantity minimizationReduce processing latencyWater/sewage treatment by centrifugal separationSemi-permeable membranesSolventPolar lipids
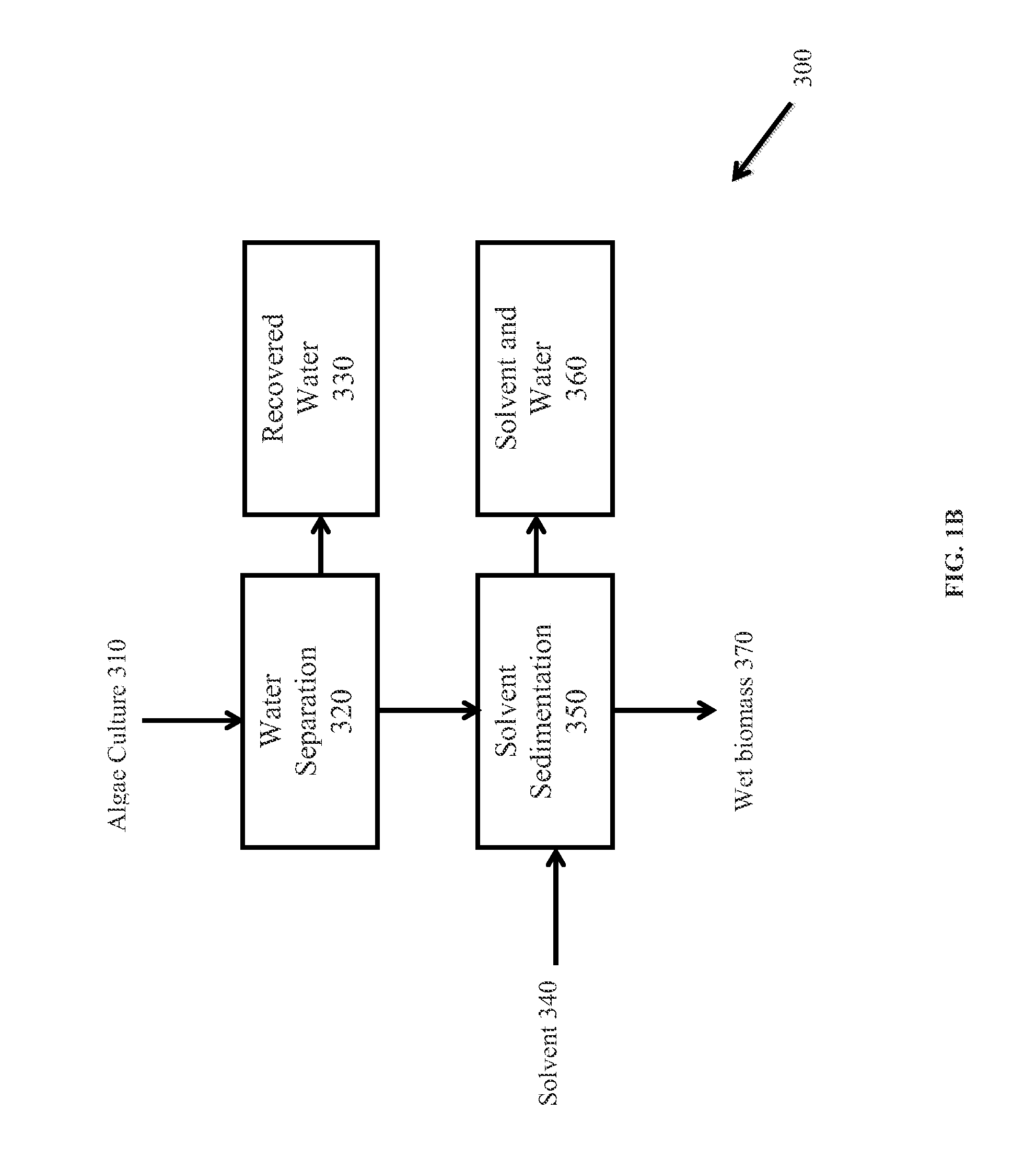
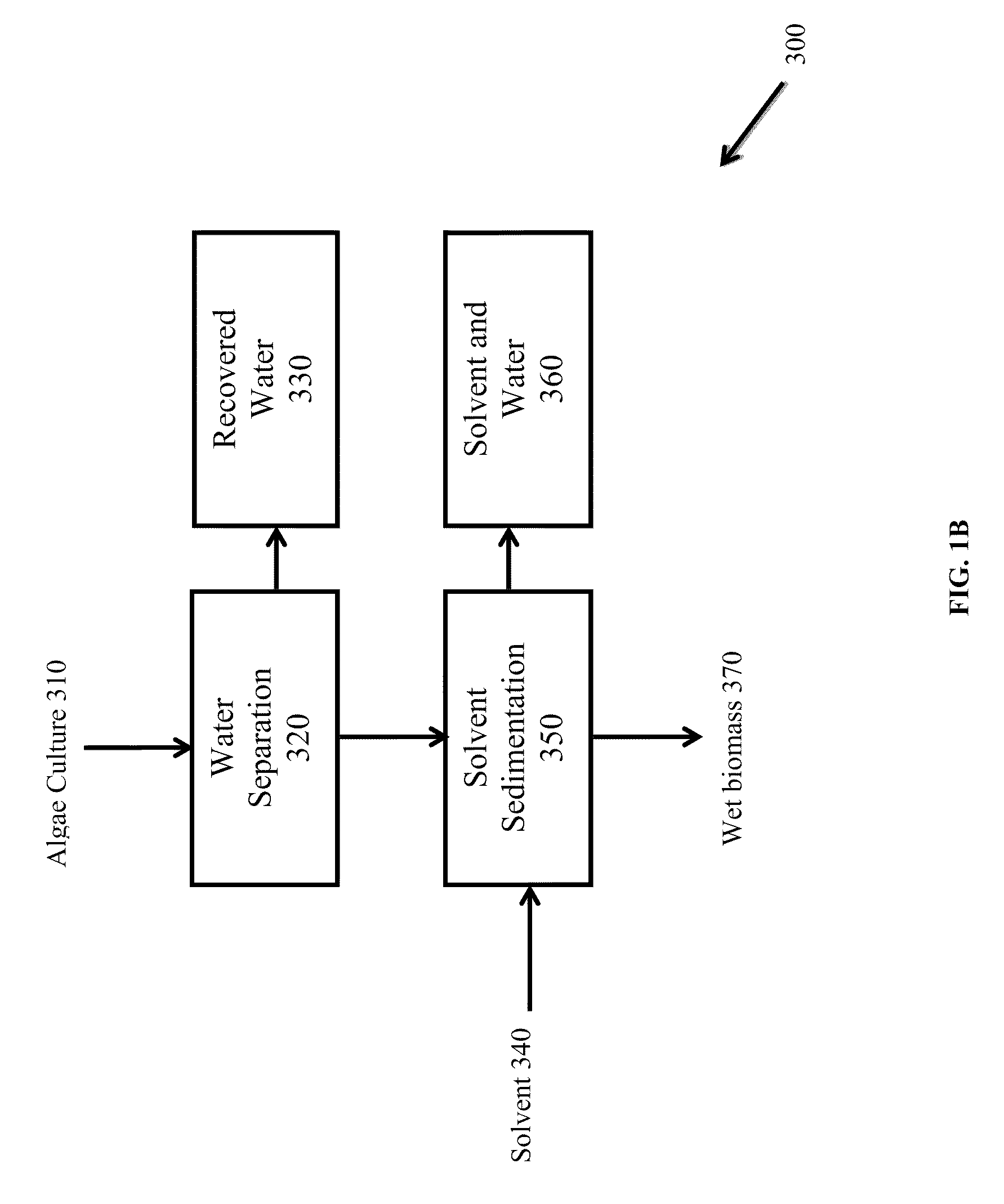
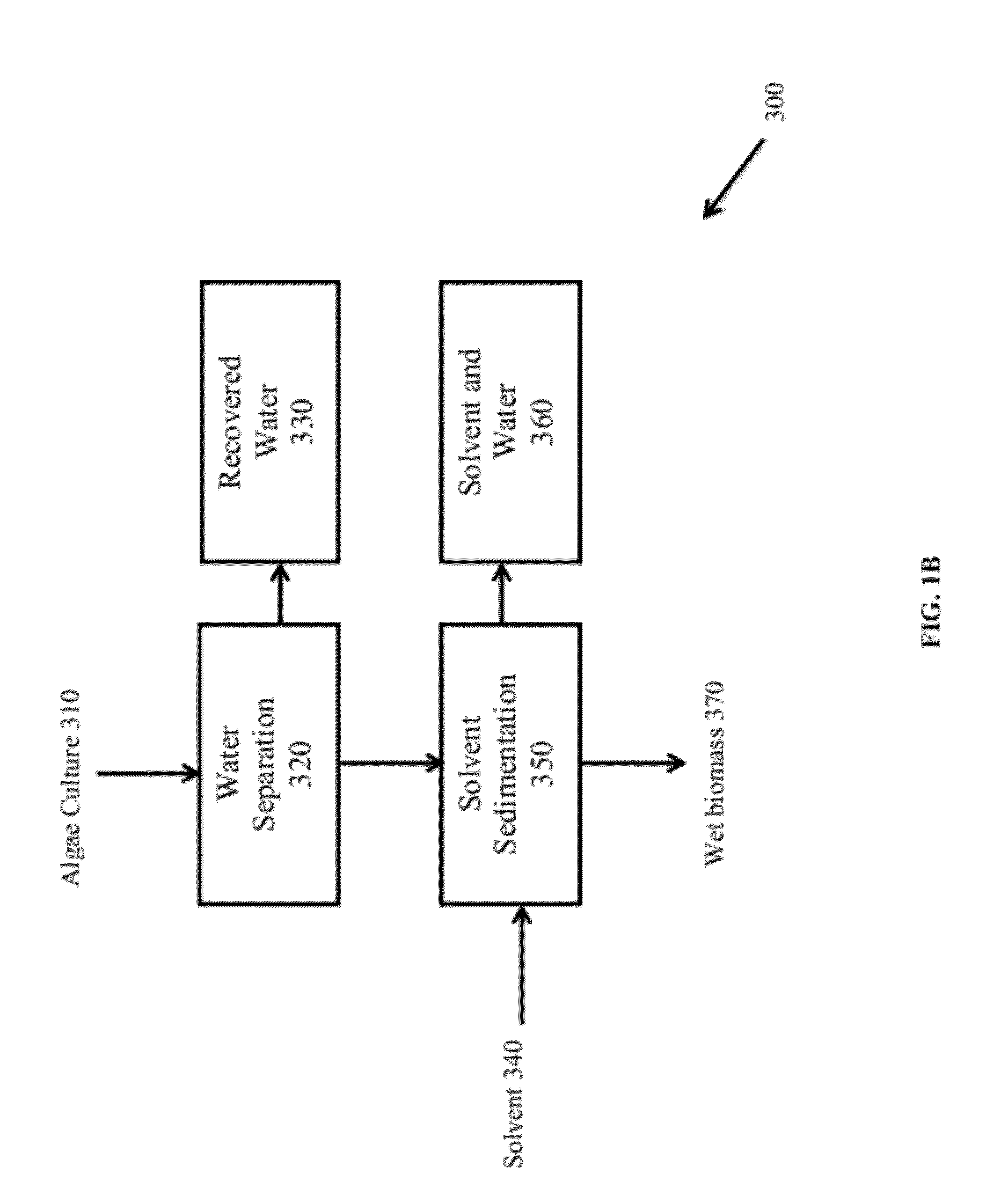
A method for separating neutral lipids from plant material, in particular, intact algal cells, using an amphipathic solvent set and a hydrophobic solvent set. Some embodiments include dewatering intact algal cells and then extracting neutral lipids from the algal cells. The methods provide for single and multistep extraction processes which allow for efficient separation of algal neutral lipids from a wet algal biomass while avoiding emulsification of extraction mixtures. The neutral lipids are removed after first removing a polar lipid fraction and a protein fraction. These neutral lipids can be used to generate renewable fuels as well as food products and supplements.
Owner:HELIAE DEVMENT
Extraction and winterization of lipids from oilseed and microbial sources
ActiveUS7419596B2Solve many processesReduce degummingFatty-oils/fats refiningMicroorganism based processesLipid formationSolubility
A process for purifying a lipid composition having predominantly neutral lipid components having at least one long chain polyunsaturated fatty acid is disclosed. The process employs contacting the lipid composition with a polar solvent, such as acetone, wherein the solvent is selected such that the contaminants are less soluble in the solvent than in the long chain polyunsaturated fatty acid. The process is typically conducted at cooler temperatures including about 0° C. Upon precipitation of the contaminants from the lipid composition, a separation is conducted to remove the precipitated material from the lipid composition. The long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids can include ARA, DPA, EPA and / or DHA. The process effectively winterizes lipid compositions, thereby reducing the tendency of such compositions to become hazy.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Method for introducing antisense oligonucleotides into eucaryotic cells
InactiveUS20060147514A1Efficient deliveryInduce cytotoxicityOrganic active ingredientsFungiLipid formationEucaryotic cell
The present invention relates to a method for introducing one or more antisense oligonucleotides into one or more eucaryotic cells using one or more lipid formulations comprising one or more cationic lipids of Formula I and optionally at least one neutral lipid. In particular, the present invention relates to a method for introducing one or more antisense oligonucleotides into one or more eucaryotic cells using a lipid formulation comprising dimethyldioctadecylammonium bromide (DDAB) and at least one neutral lipid, especially dioleylphosphatidylethanolamine (DOPE). The invention also relates to kits for carrying out the invention, compositions for carrying out the invention, and compositions formed while carrying out the invention. Further, the present invention relates to a method for inhibiting or preventing cell growth or proliferation, and a method for inhibiting or preventing expression of one or more proteins.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Extraction of polar lipids by a two solvent method
InactiveUS8211308B2Quantity minimizationReduce processing latencyWater/sewage treatment by centrifugal separationSemi-permeable membranesFood additiveSolvent
A method for separating polar lipids from plant material, in particular, intact algal cells, using an amphipathic solvent set and a hydrophobic solvent set. Some embodiments include dewatering intact algal cells and then extracting polar lipids from the algal cells. The methods provide for single and multistep extraction processes which allow for efficient separation of algal polar lipids from a wet algal biomass while avoiding emulsification of extraction mixtures. These polar lipids are high value products which can be used as surfactants, detergents, and food additives. Neutral lipids remaining in the algal biomass after extraction of polar lipids can be used to generate renewable fuels.
Owner:HELIAE DEVMENT
Pulmonary surfactant formulations
InactiveUS20060286038A1Increase ratingsImprove drug stabilityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseDipalmitoyl Phosphatidylcholine
Synthetic pulmonary surfactant compositions comprising dipalmitoyl phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylglycerol, and essentially neutral lipid, and having essentially no 1-palmitoyl 2-oleoyl phosphatidylglycerol and essentially no palmitic acid are provided. Methods for treating respiratory disease are also provided comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of a synthetic pulmonary surfactant comprising dipalmitoyl phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylglycerol, and essentially neutral lipid, and having essentially no 1-palmitoyl 2-oleoyl phosphatidylglycerol and essentially no palmitic acid.
Owner:DISCOVERY LABORATORIES INC
Extraction of neutral lipids by a two solvent method
InactiveUS8273248B1Reduce processing latencyQuantity minimizationTreatment involving filtrationSolid sorbent liquid separationSolventPolar lipids
A method for separating neutral lipids from plant material, in particular, intact algal cells, using an amphipathic solvent set and a hydrophobic solvent set. Some embodiments include dewatering intact algal cells and then extracting neutral lipids from the algal cells. The methods provide for single and multistep extraction processes which allow for efficient separation of algal neutral lipids from a wet algal biomass while avoiding emulsification of extraction mixtures. The neutral lipids are removed after first removing a polar lipid fraction and a protein fraction. These neutral lipids can be used to generate renewable fuels as well as food products and supplements.
Owner:HELIAE DEVMENT
Delivery system for nucleic acids
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST +1
Extraction of polar lipids by a two solvent method
InactiveUS20120277450A1Reduce processing latencyQuantity minimizationFatty-oils/fats productionFood additiveSolvent
A method for separating polar lipids from plant material, in particular, intact algal cells, using an amphipathic solvent set and a hydrophobic solvent set. Some embodiments include dewatering intact algal cells and then extracting polar lipids from the algal cells. The methods provide for single and multistep extraction processes which allow for efficient separation of algal polar lipids from a wet algal biomass while avoiding emulsification of extraction mixtures. These polar lipids are high value products which can be used as surfactants, detergents, and food additives. Neutral lipids remaining in the algal biomass after extraction of polar lipids can be used to generate renewable fuels.
Owner:HELIAE DEVMENT
Delivery of Sirna by Neutral Lipid Compositions
ActiveUS20090012021A1Efficient deliveryLarge deliveryOrganic active ingredientsSpecial deliveryDiseaseLiposome
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Extraction of proteins by a two solvent method
InactiveUS20130072661A1Quantity minimizationReduce processing latencyFatty acid esterificationMicroorganism lysisFood additiveSolvent
A method for separating proteins from plant material, in particular, intact algal cells, using an amphipathic solvent set and a hydrophobic solvent set. Some embodiments include dewatering intact algal cells and then extracting proteins from the algal cells. The methods provide for single and multistep extraction processes which allow for efficient separation of algal proteins from a wet algal biomass. These proteins are high value products which can be used as renewable sources of food and food additives. Neutral lipids remaining in the algal biomass after extraction of proteins can be used to generate renewable fuels.
Owner:HELIAE DEVELOPMENT LLC
Novel cationic liposome nucleic acid pharmaceutical preparation as well as preparation method and application thereof
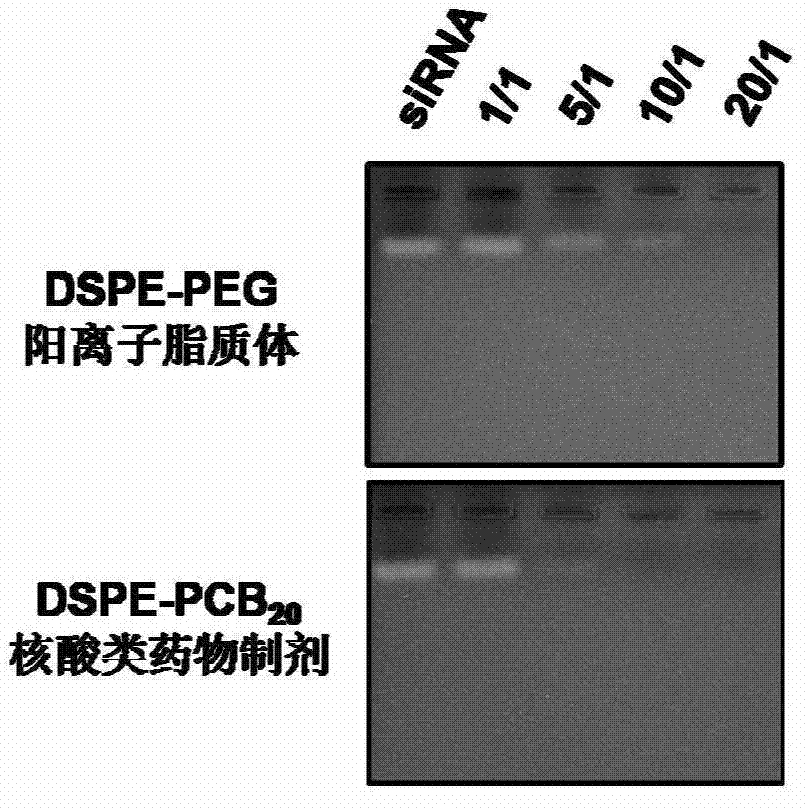
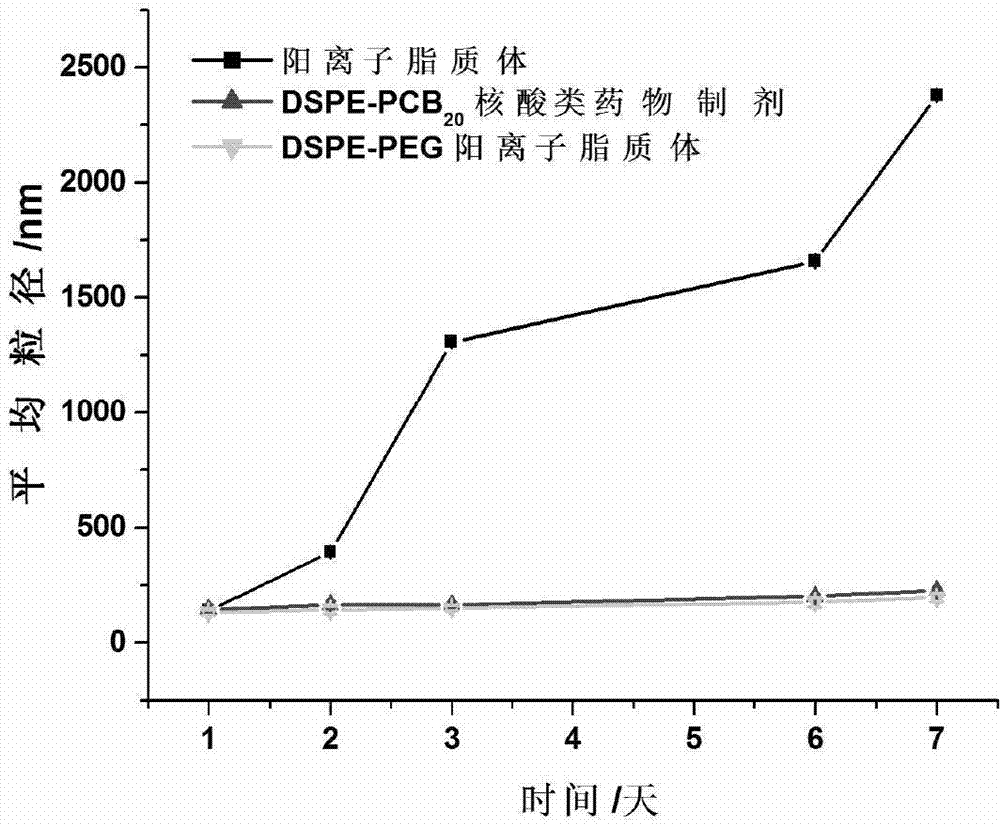
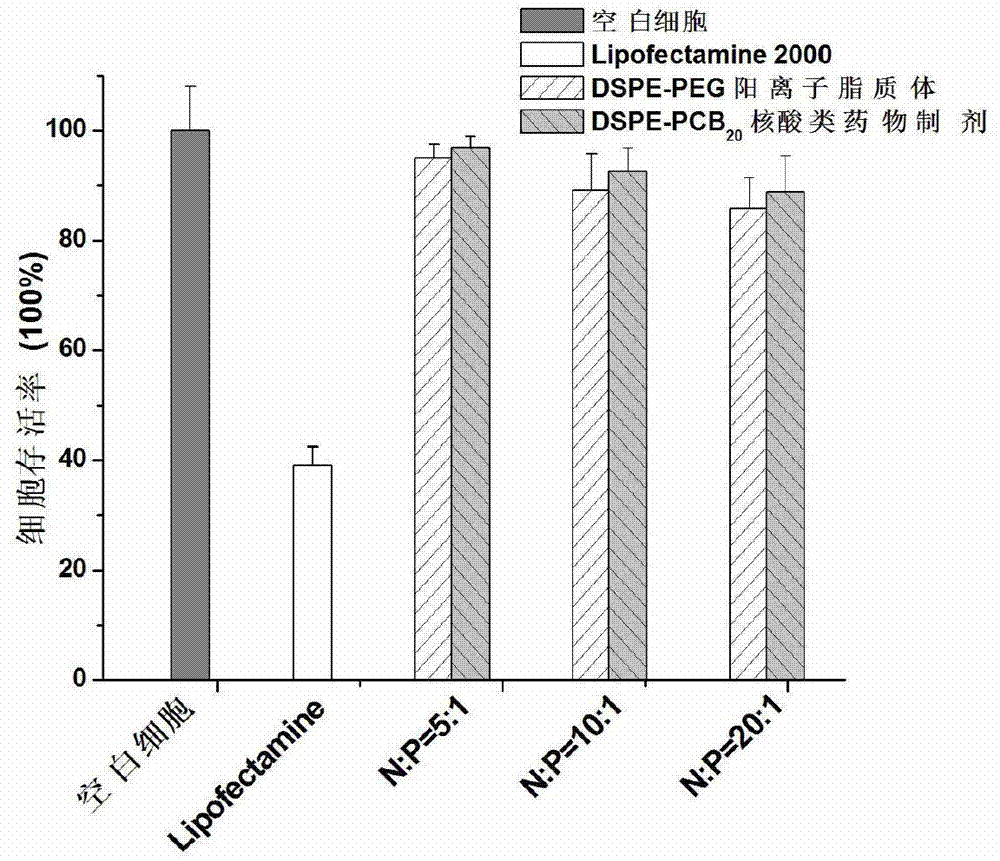
ActiveCN103194489APromote escapeIncrease serum stabilityOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticBetaineLipid molecule
The invention discloses a novel cationic liposome, a cationic liposome nucleic acid pharmaceutical preparation having the same as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The cationic liposome comprises cationic lipid, assisted lipo, polycarboxyl betaine lipid molecule and a freezing protective agent. The cationic liposome nucleic acid pharmaceutical preparation comprises cationic liposome modified by neutral lipid of polycarboxyl betaine and nucleic acid pharmaceutical preparation working solution. According to the cationic liposome, the defects of high toxicity, bad blood stability and low transfection efficiency are overcome and the pharmaceutical effects of the nucleic acid drugs are effectively improved; and at the same time, as the preparation is undisturbed by blood serum during the use, the operations in the experiment and the treatment are simplified.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +2
Methods of and systems for producing biofuels from algal oil
A method for producing biofuels is provided that includes dewatering intact algal cells to make an algal biomass, extracting neutral lipids from the algal biomass, and esterifying the neutral lipids with a catalyst in the presence of an alcohol. The method also includes separating a water soluble fraction comprising glycerin from a water insoluble fraction comprising fuel esters and distilling the fuel esters under vacuum to obtain a C16 or shorter fuel esters fraction, a C16 or longer fuel ester fraction, and a residue comprising carotenoids and omega-3 fatty acids. The method further includes hydrodeoxygenating at least one of (i) the C16 or shorter fuel esters to obtain a jet fuel blend stock and (ii) the C16 or longer fuel esters to obtain a diesel blend stock. The method further includes supplying the hydrogenation and deoxygenation processes with hydrogen produced from reformed light hydrocarbons or an algae culture.
Owner:HELIAE DEVMENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com