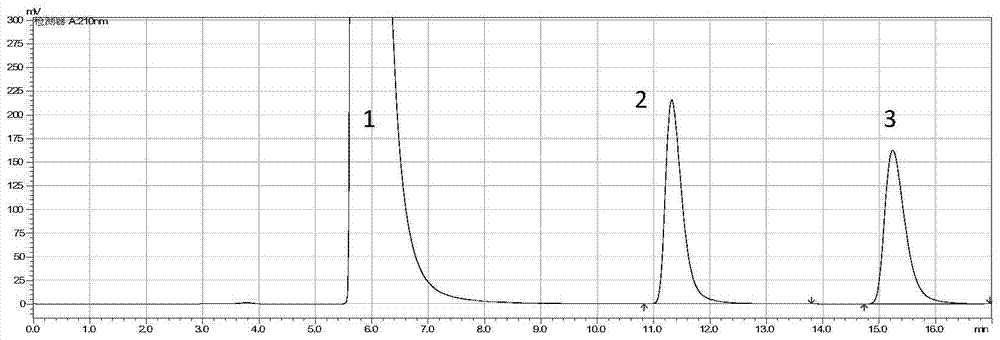
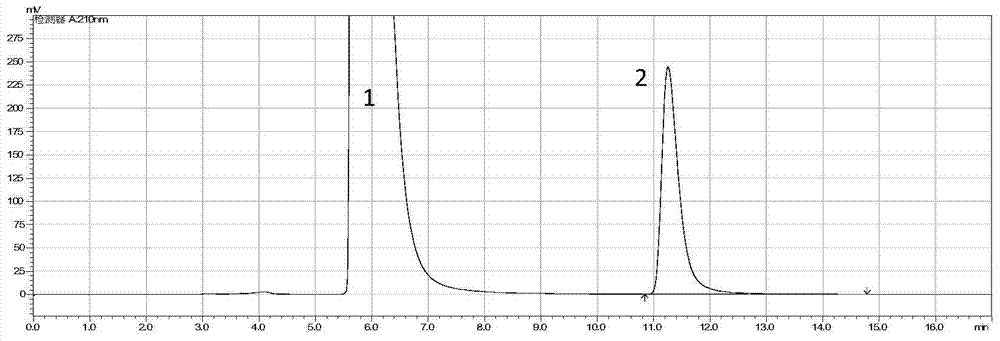
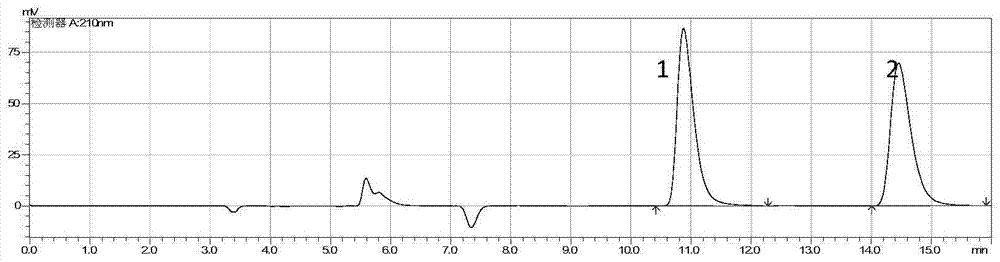
Method for whole-cell splitting of racemate beta-lactam by using Bradyrhizobium japonicum
A technology of bradyrhizobium and lactam, applied in the field of separation, can solve the problems of many reaction steps, cumbersome operation, limited enzymes and microorganisms, etc., and achieve the effects of low environmental pollution, high reaction efficiency and high purity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] This example is a whole cell of Bradyrhizobium soybean for splitting 3-hydroxy-4-phenyl-2-azetidinone.
[0039] The method comprises the steps of:
[0040] (1) Strain selection: Bradyrhizobium japonicum was selected as the strain, and the strain preservation number was CGMCC No.1.2550; the strain was preserved at -80°C;
[0041] (2) Fermentation broth preparation: inoculate the Bradyrhizobium soybean species into the rhizobia culture medium at a volume ratio of 0.1% to 0.5%, and vibrate at 20°C to 30°C at 220 rpm for 96 to 168 hours;
[0042] Rhizobium liquid fermentation medium: yeast extract 1.0g, mannitol 10.0g, soil extract 200ml, distilled water 800ml, pH7.2;
[0043] Among them, soil extract: 25g soil, add 100ml deionized water, cook at 105kPa for 1 hour, add water after filtering to make up to the volume before cooking;
[0044]The specific preparation method is: dissolve yeast extract, mannitol, and soil extract in deionized water, adjust the pH value to 7.2 w...
Embodiment 2
[0057] This example is a method for producing (-) β-lactam using Bradyrhizobium soybean as the strain.
[0058] The preferred scheme on the basis of the method in example 1, the improvements are:
[0059] (2) In the step, the temperature of the shaking culture is 28°C, the time is 168h, and the rotation speed is 220rpm;
[0060] (3) In the step, the bacterial fermentation liquid after culturing for 168 hours is fully mixed with a phosphate buffer solution with a pH value of 7.0 to obtain a diluted fermentation liquid; the mixing volume ratio of the fermentation liquid and a phosphate buffer solution with a pH value of 7.0 is 1: 1. After fully mixing, centrifuge at 11000rpm for 10min to collect the bacterial sediment; freeze it in a -20°C refrigerator for a certain period of time and then thaw it, then centrifuge at 11000rpm for 10min to collect the wet bacteria and use it as a biocatalyst;
[0061] (4) In the step, the wet bacteria are mixed with 1g / L racemic β-lactam solutio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com