Method for mutually promoting growth of Bradyrhizobium japonicum and Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
A technology of soybean rhizobia and rhizobia, applied in the field of biological hydrogen production, can solve the problems of algae biomass accumulation and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
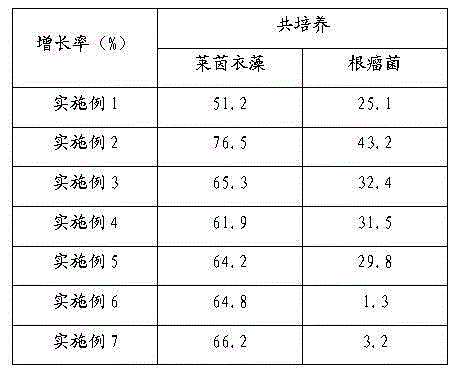
Embodiment 1
[0011] Co-cultivation in the normal medium of embodiment 1
[0012] The transgenic Chlamydomonas reinhardtii hemHc-lbac was grown to mid-log phase (OD 750 The value is about 2.0), and the rhizobia were cultured in the YEM medium to the late logarithmic phase (OD 600 value is about 1.0), centrifuged at 4000g for 5 minutes, and washed with TAP medium for 3 times to remove the influence of the original TAP medium and YEM medium; according to the volume mixing ratio of algal liquid and bacterial liquid of 20:1, the rhizobia and Chlamydomonas reinhardtii were added to the Erlenmeyer flask for mixed culture. The culture conditions are: temperature 25℃±1℃, light intensity 60μmol·m -2 ·s -1 .
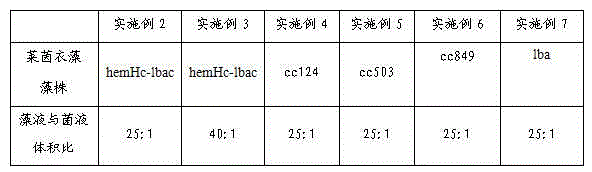
Embodiment 2-7
[0014] Except the following table parameter, other is the same as embodiment 1
[0015]
[0016] The Chlamydomonas strains of Examples 6 and 7 are derived from patent 201210007835
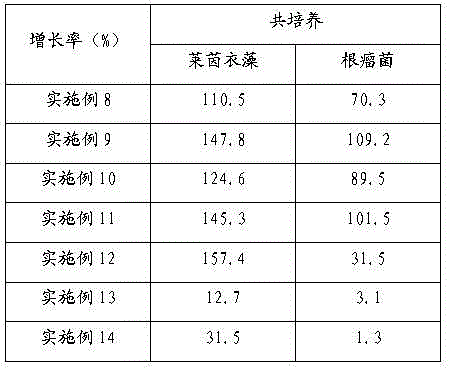
Embodiment 8
[0018] will be cultured in normal TAP medium to saturation phase (OD 750 value is about 3.0), centrifuge at 4000 r / min for 5 min, remove the supernatant, and wash with sulfur-deficient medium for 3 times to completely remove the sulfur element in the original medium [3] , and then Chlamydomonas reinhardtii according to the concentration OD 750 The value is about 2.0 and transferred to a 60ml hydrogen production culture tube. Will be cultured in YEM medium to late logarithmic phase (OD 600 About 1.0) rhizobia, centrifuge at 4000r / min for 5 minutes, remove the supernatant, wash with sulfur-deficient medium for 3 times, and then add it to the above-mentioned culture tube with Chlamydomonas reinhardtii according to the volume ratio of bacteria and algae at 20:1 In the medium, adjust the volume to 45ml with sulfur-deficient medium, and finally seal the nozzle with a rubber stopper. At a temperature of 25°C±1°C, the hydrogen production tube was shaded and incubated in the dark fo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com