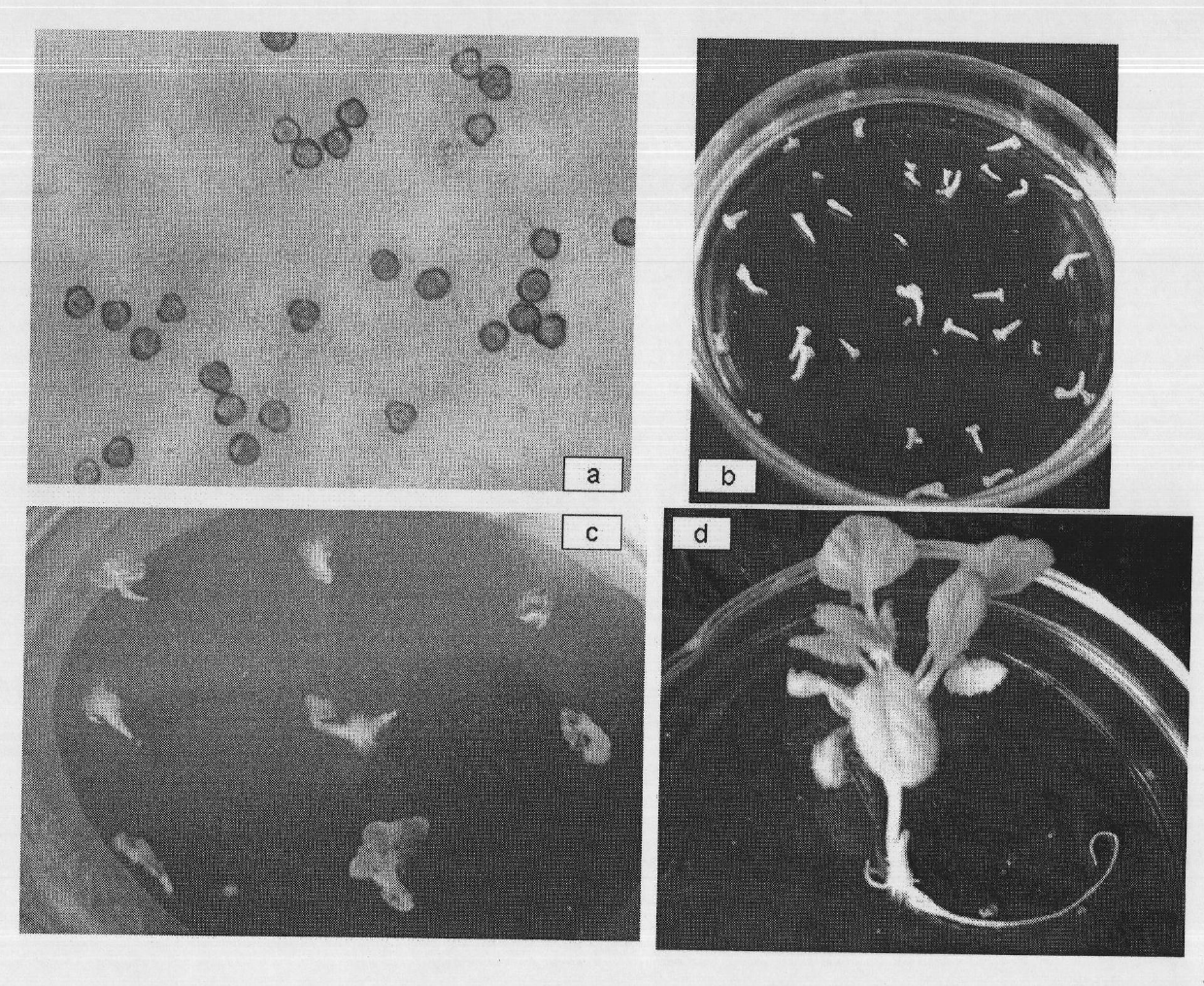
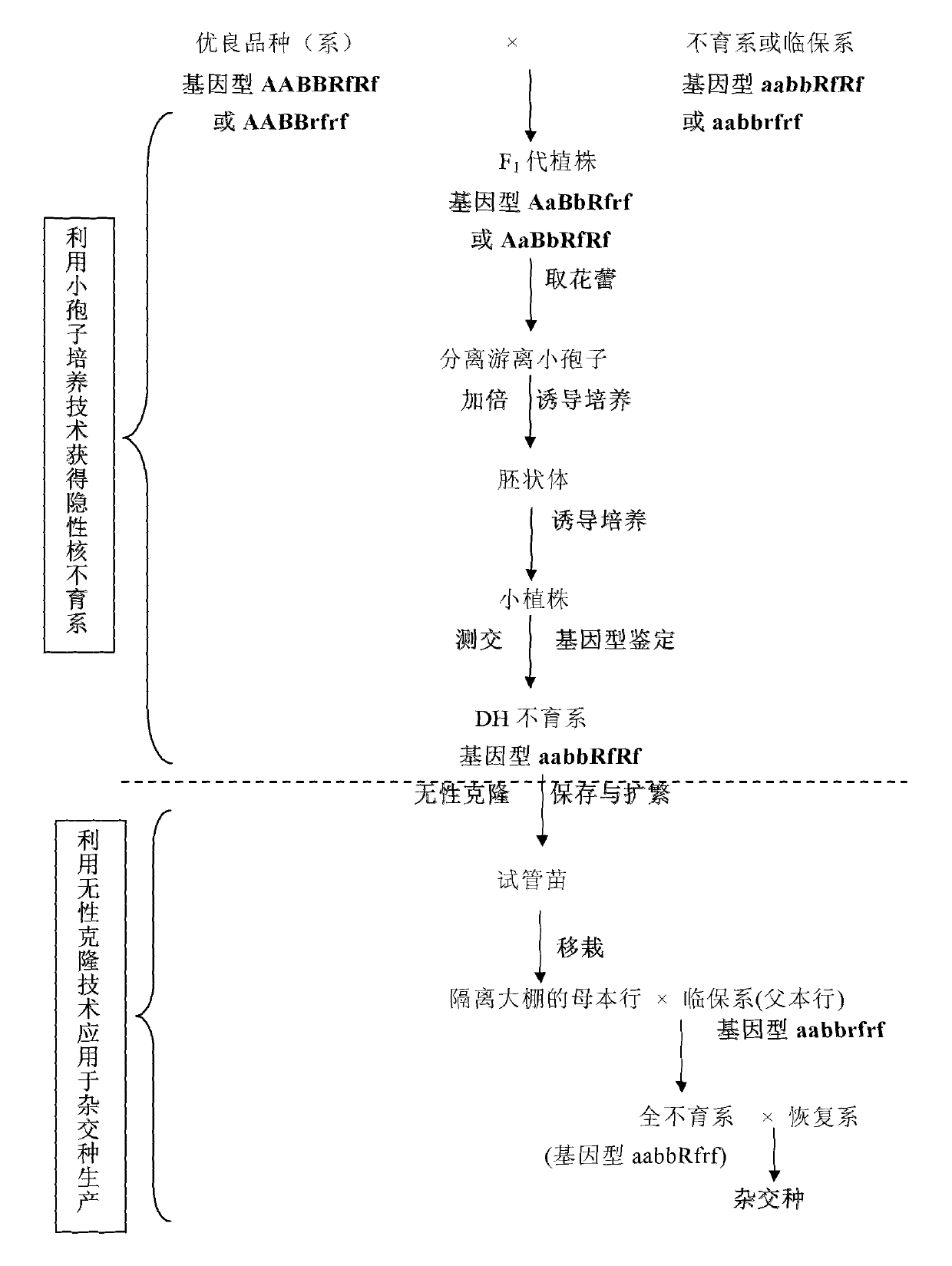
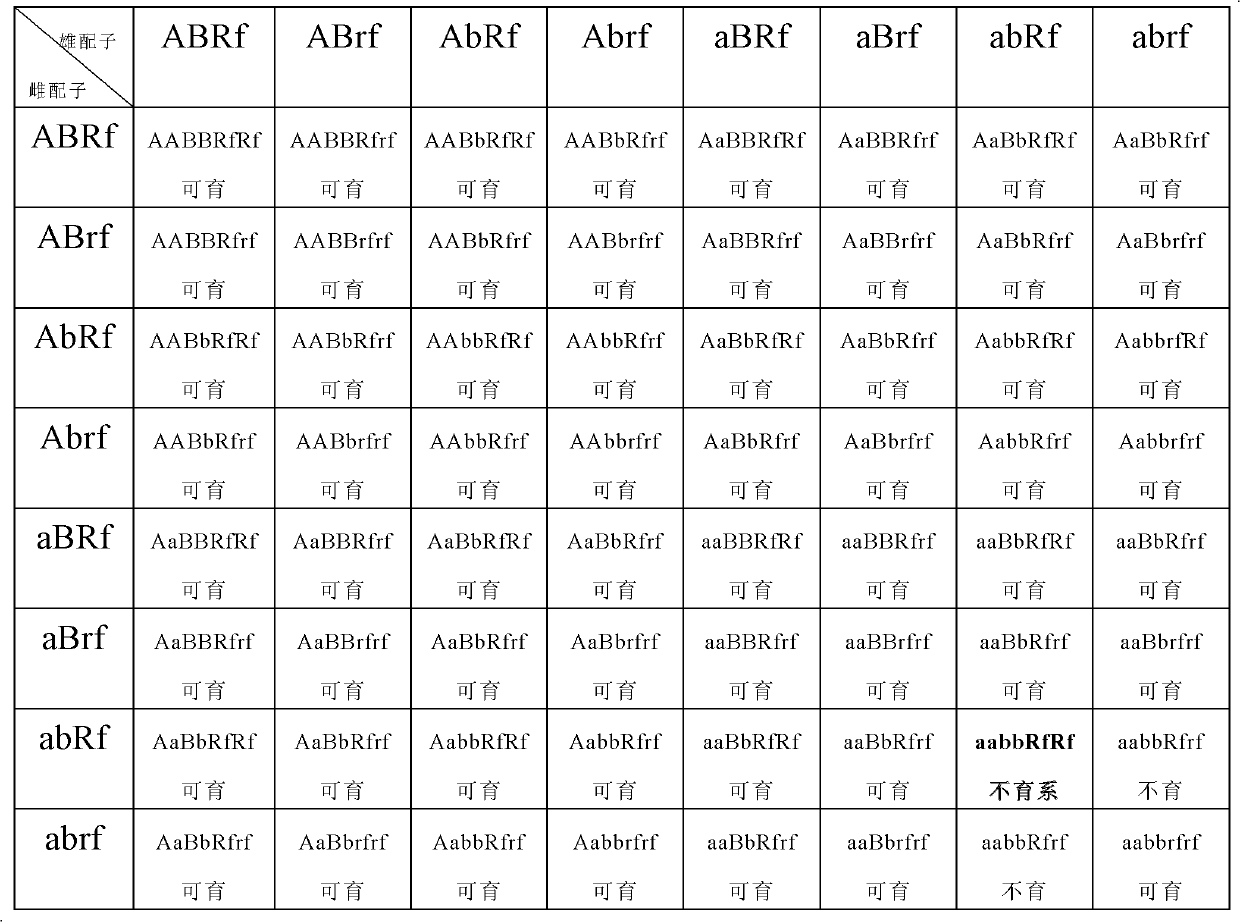
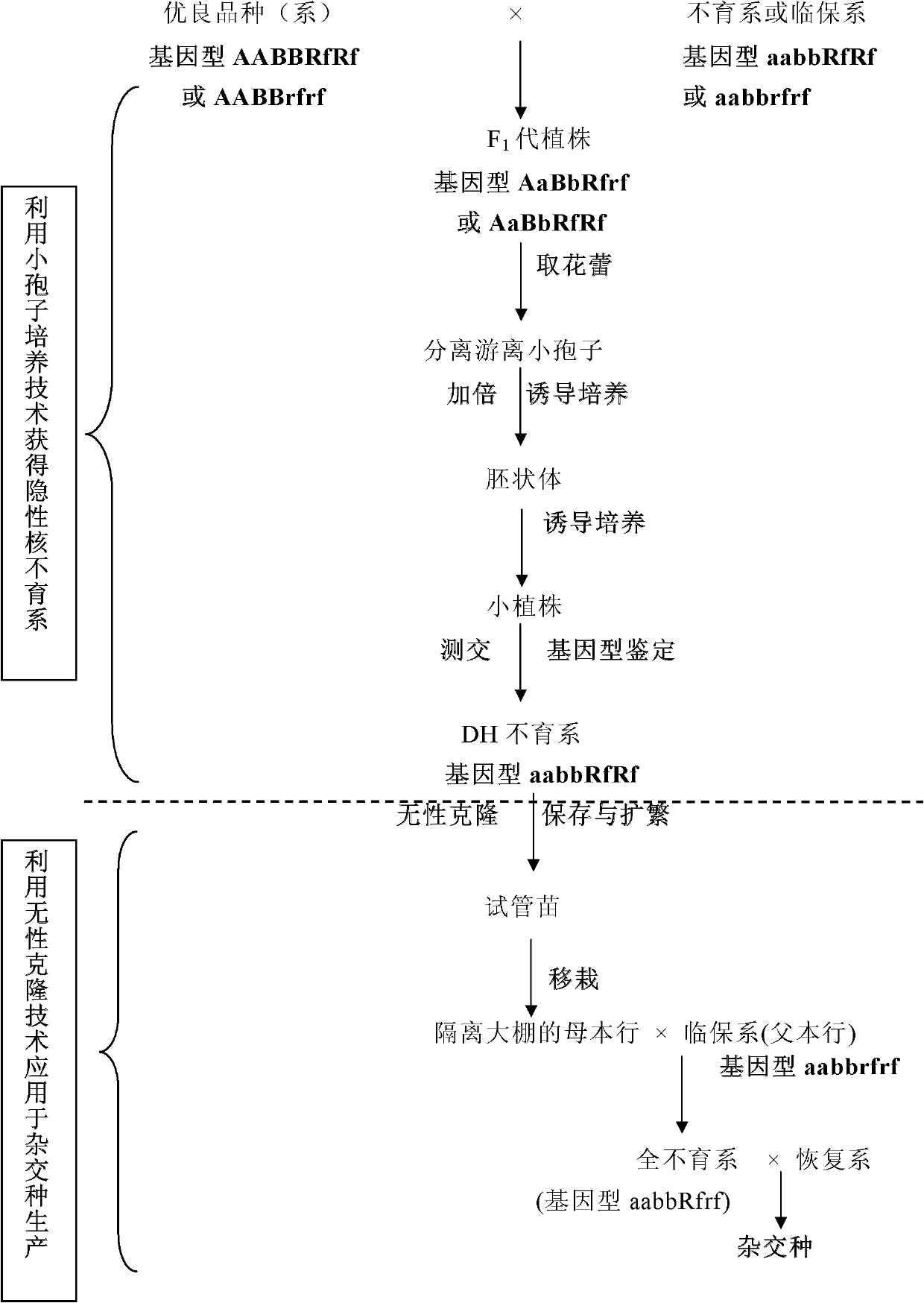
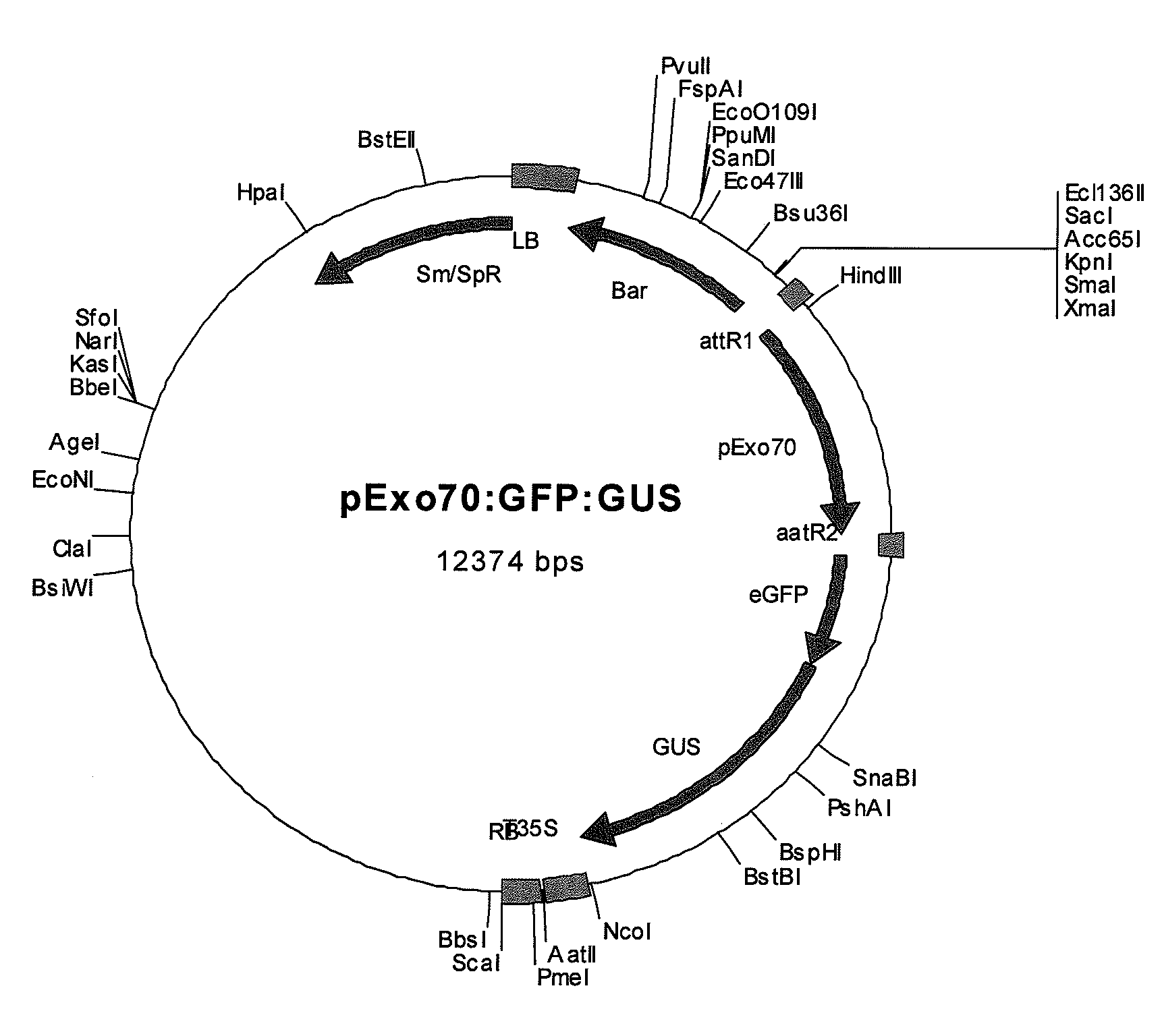
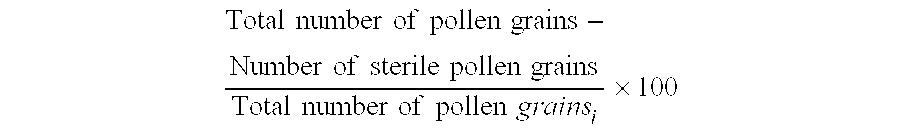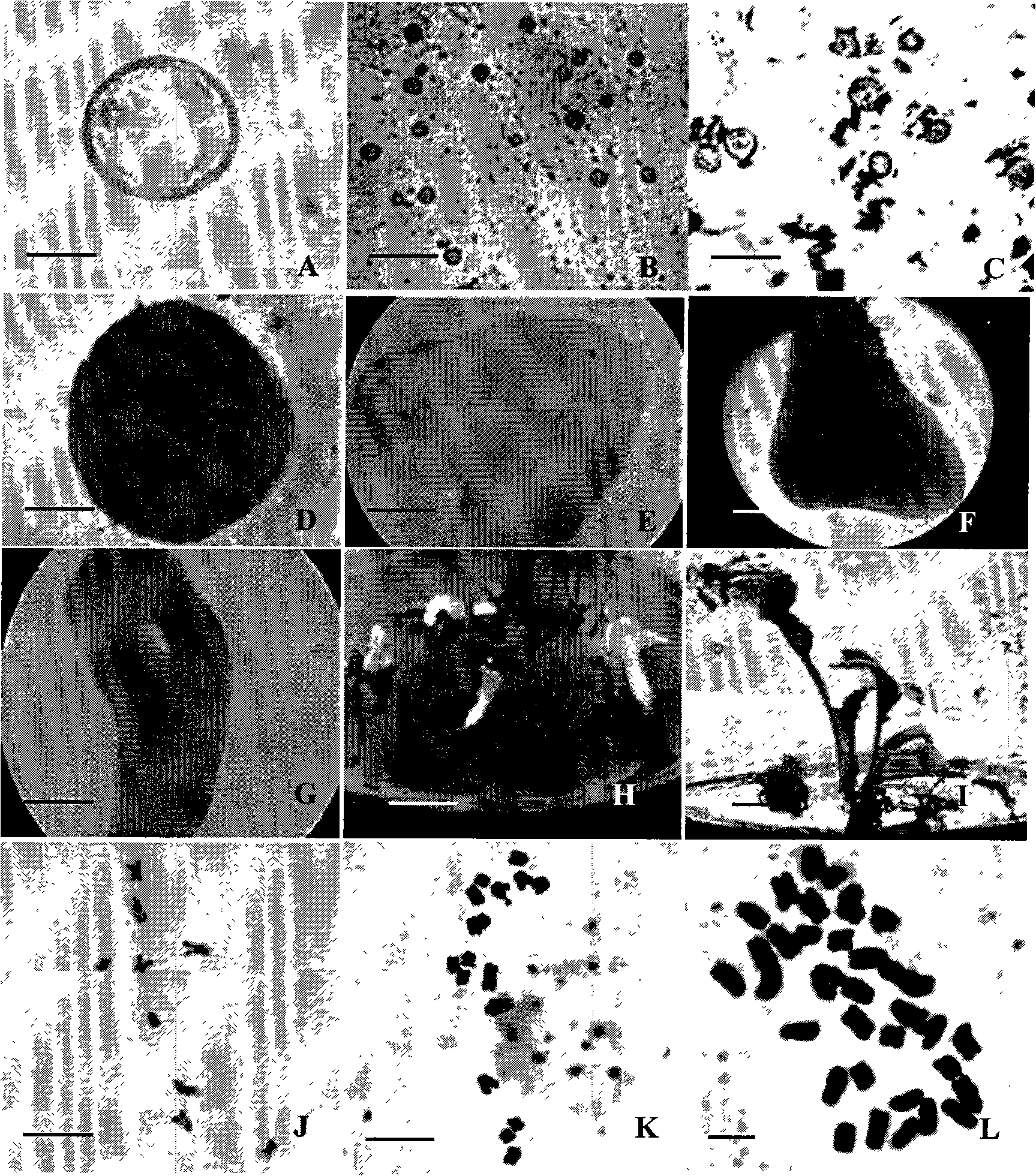Patents
Literature
219 results about "Plant Microspores" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Microspores are land plant spores that develop into male gametophytes, whereas megaspores develop into female gametophytes. The male gametophyte gives rise to sperm cells, which are used for fertilization of an egg cell to form a zygote.
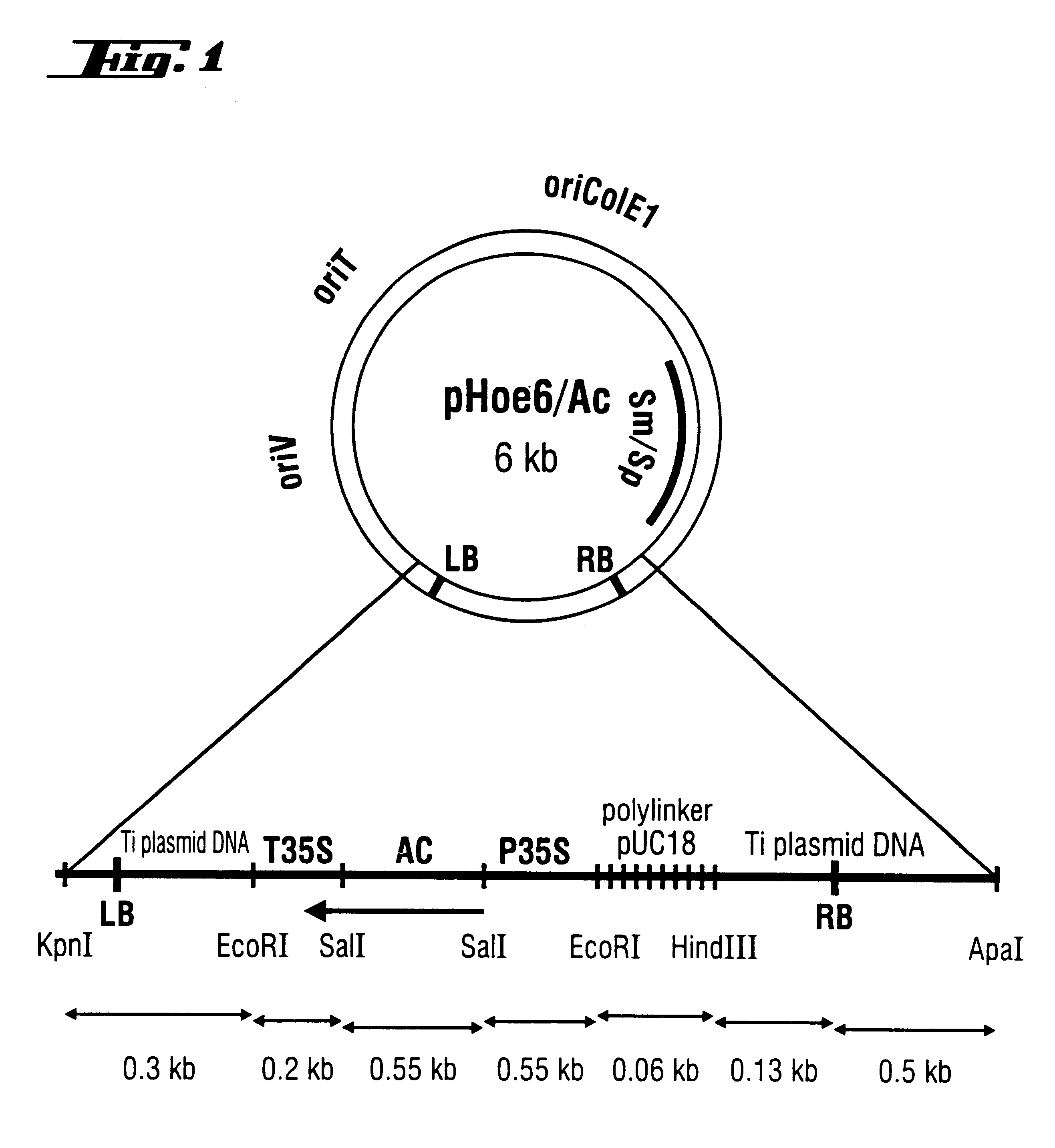
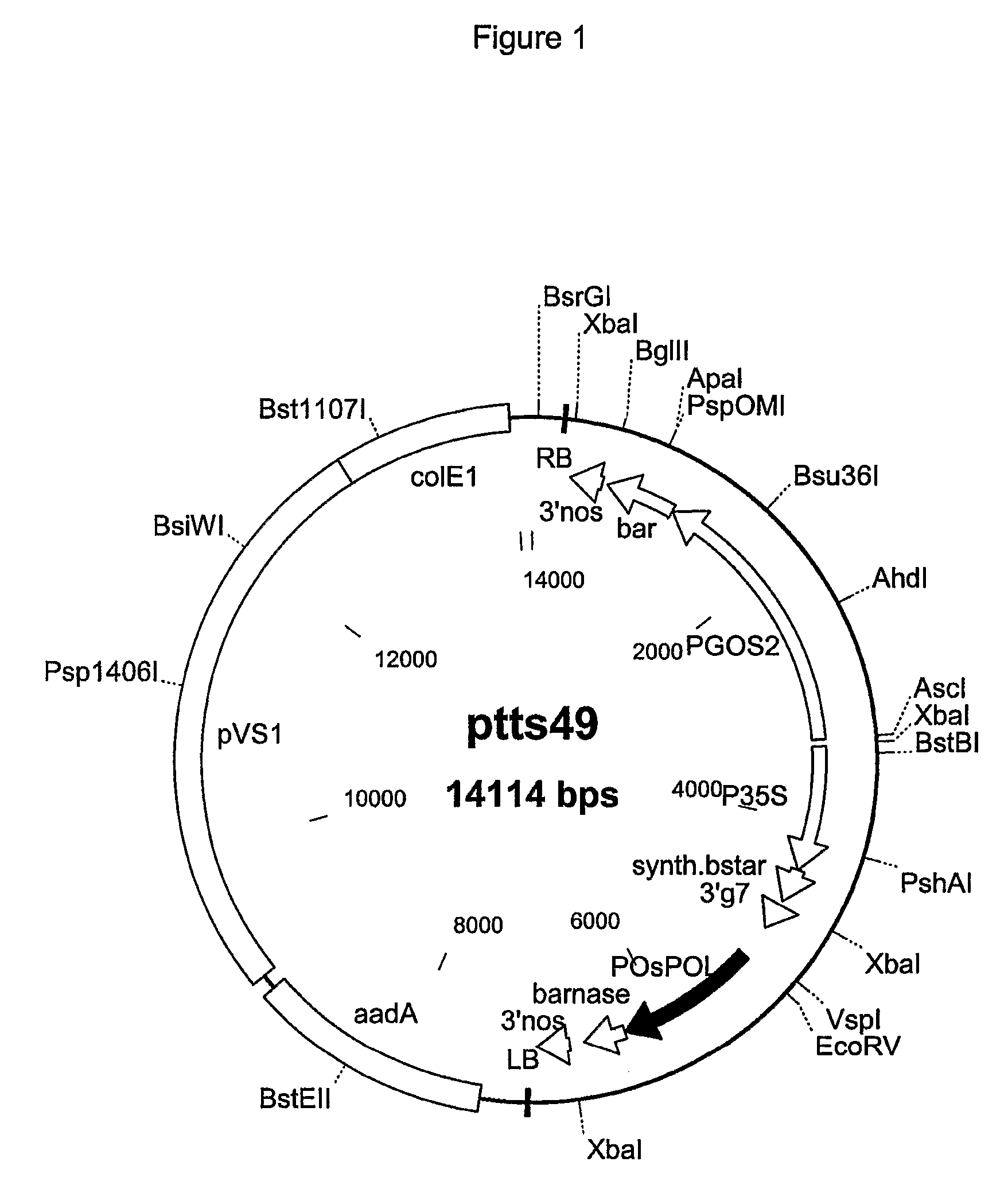
Transformed embryogenic microspores for the generation of fertile homozygous plants
InactiveUS6316694B1Increase the number ofImprove conversion efficiencyBryophytesOther foreign material introduction processesEmbryogenesisRegulatory control
The invention relates to transformed, embryogenic microspores and progeny thereof characterized by being transformed by Agrobacterium tumefaciens, capable of leading to non-chimeric transformed haploid or doubled haploid embryos that develop into fertile homozygous plants within one generation and containing stably integrated into their genome a foreign DNA, said DNA being characterized in that it comprises at least one gene of interest and at least base pairs within the right border sequence of Agrobacterium T-DNA. The invention furthermore relates to a method for the incorporation of foreign DNA into chromosomes of microspores comprising the following steps: a) infecting of embryogenic microspores with Agrobacteria, which contain plasmid carrying a gene of interest under regulatory control of initiation and termination regions bordered by at least one T-DNA border, b) Washing out and killing the Agrobacteria after co-cultivation.
Owner:AGREVO CANADA
Active carbon fiber in hollow morphological structure, and preparation method
InactiveCN1760414AImprove adsorption capacityGood molding effectHollow filament manufactureHollow fibreCarbonization
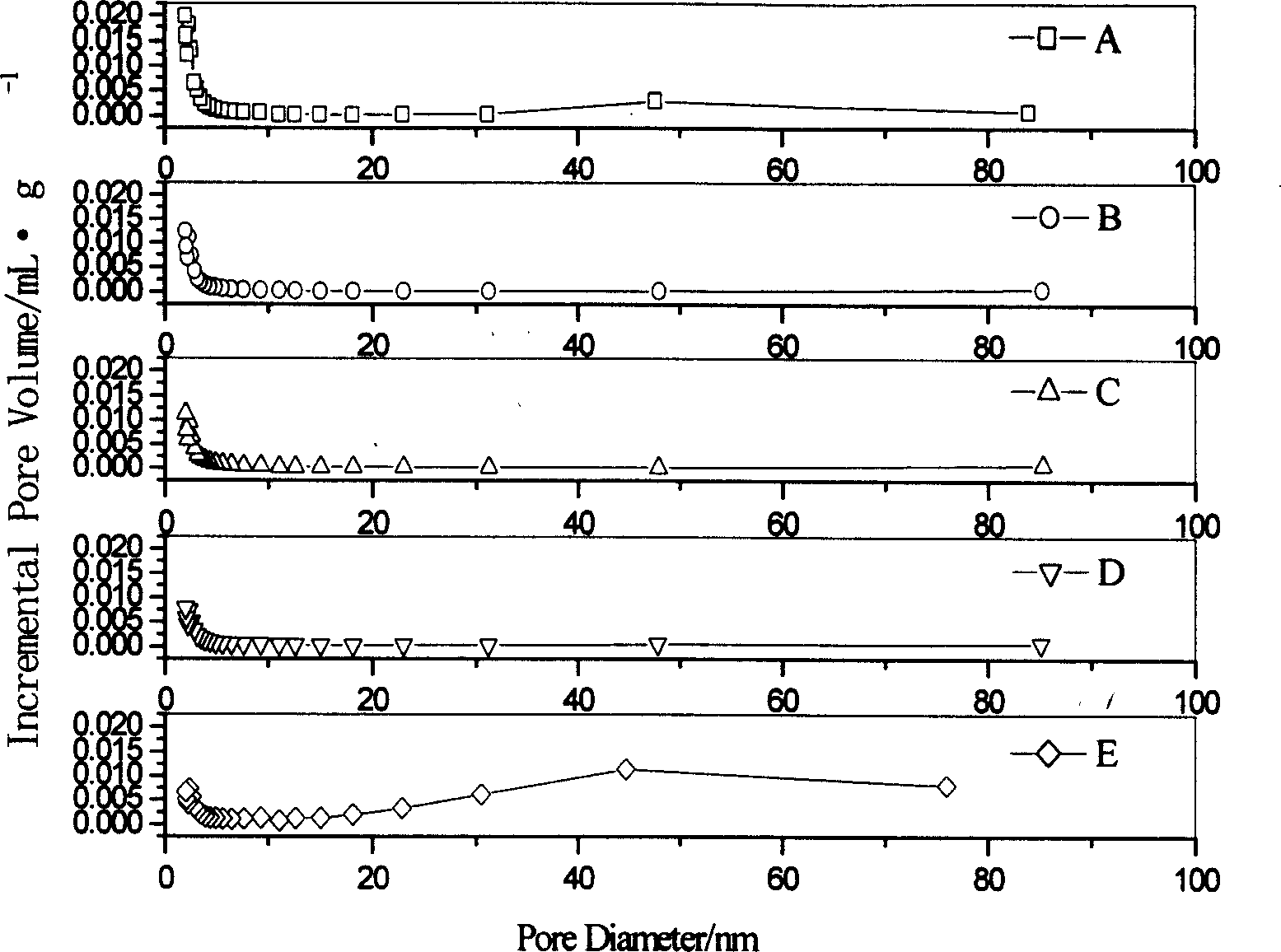
The present invention relates to an active carbon fibre adopting hollow morphological structure and its preparation method. The pose size distribution of its microspore and mid-pore is 2-90nm, and the pore size distribution of the mid-pore is 2-5nm. The invention uses medical polyacrylonitrile hollow fibre as raw material and adopts the following steps: soaking the raw material in solution containing phosphide to make pretreatment, preliminary heat treatment in oxidizing, carbonization and activation to obtain the invented product.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Rapid multi-target property polymerization breeding method for rape
InactiveCN102224801AImprove breeding levelShorten the breeding cyclePlant genotype modificationSporeGreenhouse
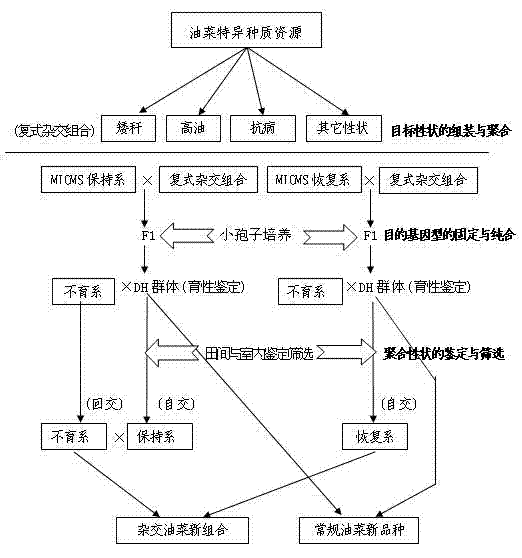
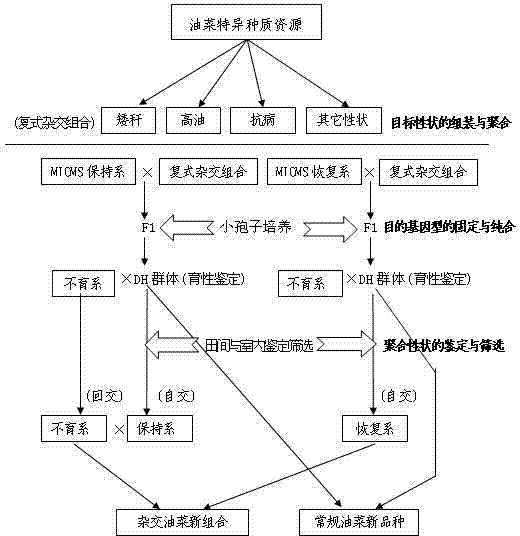
The invention provides a rapid multi-target property polymerization breeding method for rape, belonging to a plant breeding method, and comprising the following steps of: selecting excellent breeding target properties requiring to be polymerized, preparing single-cross combinations at room temperature in winter locally, preparing multi-parent complicated cross combinations in summer at different places, and assembling and polymerizing the multiple parents with excellent target properties based on the breeding requirements; performing microspore seedling cultivation on the complex filial generation for which multi-target property breeding restructuring polymerization is already realized, constructing a dihaploid (DH) breeding group, and realizing rapid fixation and homozygosis of the target genotypes of the generation of the multi-target property polymerization; and performing effective field and indoor identification and screening on the target genotypes of the generation for which the multi-target property polymerization is realized based on the property characteristics, performing molecular marker assistant selection on important target properties, and breeding new materials conforming to the breeding targets.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Rice pollen-preferential promoters and uses thereof
The present invention relates to rice genomic promoter sequences which promote transcription preferentially in microspores and / or pollen of plants. Also provided are chimeric genes comprising these promoter sequences, and plant transformation vectors comprising these chimeric genes. The present invention also discloses plant cells, plant tissues, plants, seeds and grains comprising these chimeric genes. The invention further discloses methods for expressing foreign nucleic acid sequences preferentially in pollen and for producing plants with modified pollen fertility.
Owner:BAYER CROPSCIENCE NV
Use of the BNM3 transcriptional activator to control plant embryogenesis and regeneration processes
InactiveUS7151170B1Improve regenerative abilityImprove planting effectSugar derivativesClimate change adaptationPlant cellEmbryo
The present invention provides for a gene obtained during the induction of microspore embryogenisis. The protein encoded by this gene renders plant cells embryongenic, and increases the regenerative capacity of the plant cell. Also disclosed is the regulatory region of this gene and its use for directing the expression of a gene of interest within a suitable host cell.
Owner:STICHTING WAGENINGEN RES +1
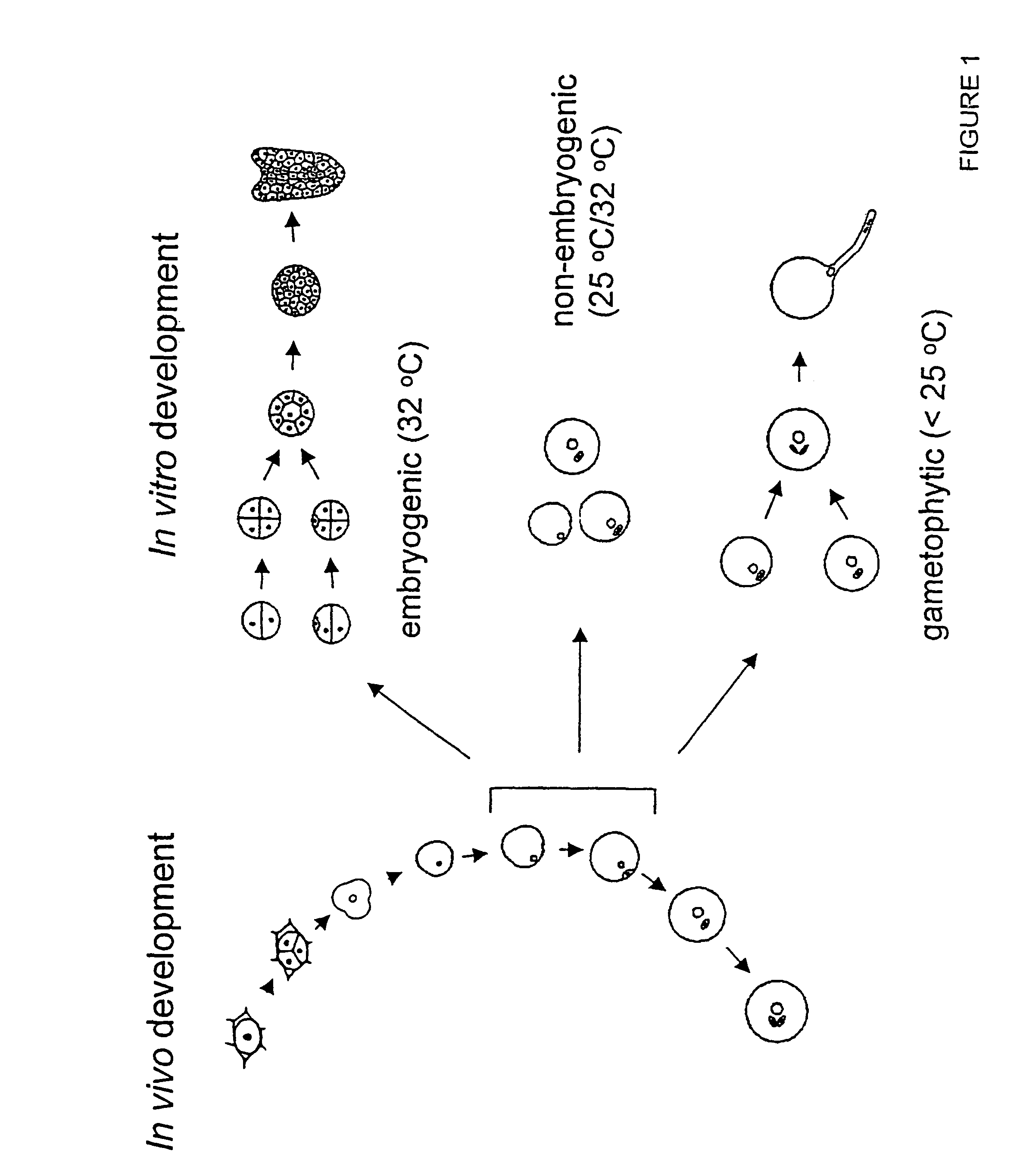
Induction of embryogenesis from plant microspores
Embryogenesis from plant microspores is routinely induced with a 16-24 h temperature treatment of 32.5° C. Continuous culture at 25° C. results in pollen development. However, microspore treatment with anti-cytoskeletal agents, or protein synthesis inhibitors, at the non-inductive temperature of 25° C., can induce embryogenesis, thus demonstrating that heat shock is not required for embryogenic induction. Furthermore, when anti-microtubule agents (e.g. colchicine) are used, embryo induction and chromosome doubling occur simultaneously, thus generating doubled haploids, whereas heat induction generates haploids. Thus, the use of microtubule inhibitors will provide a simple one-step process to simultaneously induce embryogenesis and chromosome doubling for the production of fertile plants, thus providing minimal manipulation which will be very advantageous for genetic studies and plant breeding programs. As noted, heat shock induces haploids. A low level of chromosome doubling can be obtained by adding colchicine to microspore cultures during the heat treatment. However, the use of trifluralin with the heat treatment, to generate doubled haploid plants results in an improved recovery of fertile doubled haploid plants than previously shown in the prior art.
Owner:AGRI & AGRI FOOD
Compositions and methods for plant genetic modification
Mixed duplex oligonucleotides (MDON) are used to effect site-specific genetic alterations in a target DNA sequence of a plant. The MDON are introduced by electroporation into microspores. Thereafter, plants having a desired genetic alteration are produced by germinating the microspores.
Owner:CIBUS
Method for quickly culturing barley anther and used culture media
InactiveCN102577946AReduce dosageReduce workloadPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsSporeHordeum vulgare
The invention discloses a barley anther culture medium, which comprises a pretreatment culture medium, an inducing culture medium and a differentiating / rooting culture medium. The invention further provides a method for rapidly culturing barley anther by using the barley anther culture medium. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) taking a wheat ear of which a microspore develops at a mononuclear metaphase from a field, taking anther out of the wheat ear, putting onto the pretreatment culturing medium, and culturing in a dark environment for 3-5 days; (2) transferring the pretreated anther onto the inducing culture medium, and culturing in a dark environment for 4-5 weeks; (2) transferring callus and a seedling obtained by inducing in the step (2) onto the differentiating / rooting culture medium, performing illumination culturing at the temperature of 22-25 DEG C and at the illumination intensity of 40-60 mumol / m<2> / s for 3-4 weeks, 12 hours every day, to obtain a rooting green seeding. Due to the adoption of the method disclosed by the invention, the culturing efficiency of the barley anther can be increased remarkably.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Method for preparing sustained-release material coating agent
InactiveCN102504171AReduced release rateGood slow releaseFertilizer mixturesMaterials sciencePolymer
The invention relates to a method for preparing a sustained-release material coating agent, which is characterized in that: (1) the sustained-release material coating agent comprises the following components in part by weight: 30 to 65 parts of cashew nut oil, 0.5 to 3.5 parts of hexamine, 30 to 50 parts of polyol and 15 to 20 parts of polyisocyanate; and (2) the sustained-release material coating agent is prepared by mixing the cashew nut oil and hexamine in a reaction kettle, stirring mixture uniformly, heating the mixture, keeping the temperature, cooling the mixture, adding the polyol andpolyisocyanate, stirring and mixing the new mixture uniformly, and cooling the new mixture to room temperature. A coated fertilizer can be manufactured by placing a granular fertilizer into a fluidized bed coating machine and spraying the coating agent onto rolling fertilizer granules. When the coating agent provided by the invention is used, a polymer microspore film can be formed on the surfaceof the granular fertilizer. In a fertilizer application process, the release rate of nutrients is slowed through natural temperature difference, humidity difference and coating internal and external concentration difference, and the sustained release effect is obvious. Meanwhile, the production process is simple, the application range of the coating agent is wide, the cost of the coating agent islow and the coating agent can be promoted easily.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
Method for assist-breeding low erucic acid, low sulfuric glucoside cabbage type rape self-incompatible line with microspore cultivation and SSR making
InactiveCN101248753AShort termSave human effortVector-based foreign material introductionPlant genotype modificationSporeInflorescence
The invention belongs to the technology field of the cole breeding, in particular to the method of the seed selection of the Brassica napus self incompatible line with low erucidic acid and sulfuric glucoside utilizing microspore culture and SSR marker assistance. The method is characterized in selecting the Brassica napus self incompatible line S-1300 as the female parent and maintenance line 04P63 External-52 as the male parent, crossbreeding and obtaining F1, microspore culture F1 and obtaining double haploid (DH) self incompatible line; further screening and obtaining the DH material of the Brassica napus self incompatible line with low erucidic acid and sulfuric glucoside; analyzing the variation of the self incompatible double haploid (DH) line by using the SSR markers, studying six major traits of the self incompatible double haploid (DH) line including the plant height, the first branch number, the first branch silique number, main inflorescence length, main inflorescence silique number and yield per plant; screening the double-low Brassica napus self incompatible double haploid (DH) line superior to the S-1300 in production, related trait and general combining ability. The seed selection provides an easy, rapid and effective method of the double-low Brassica napus inbred incompatible double haploid (DH) line.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
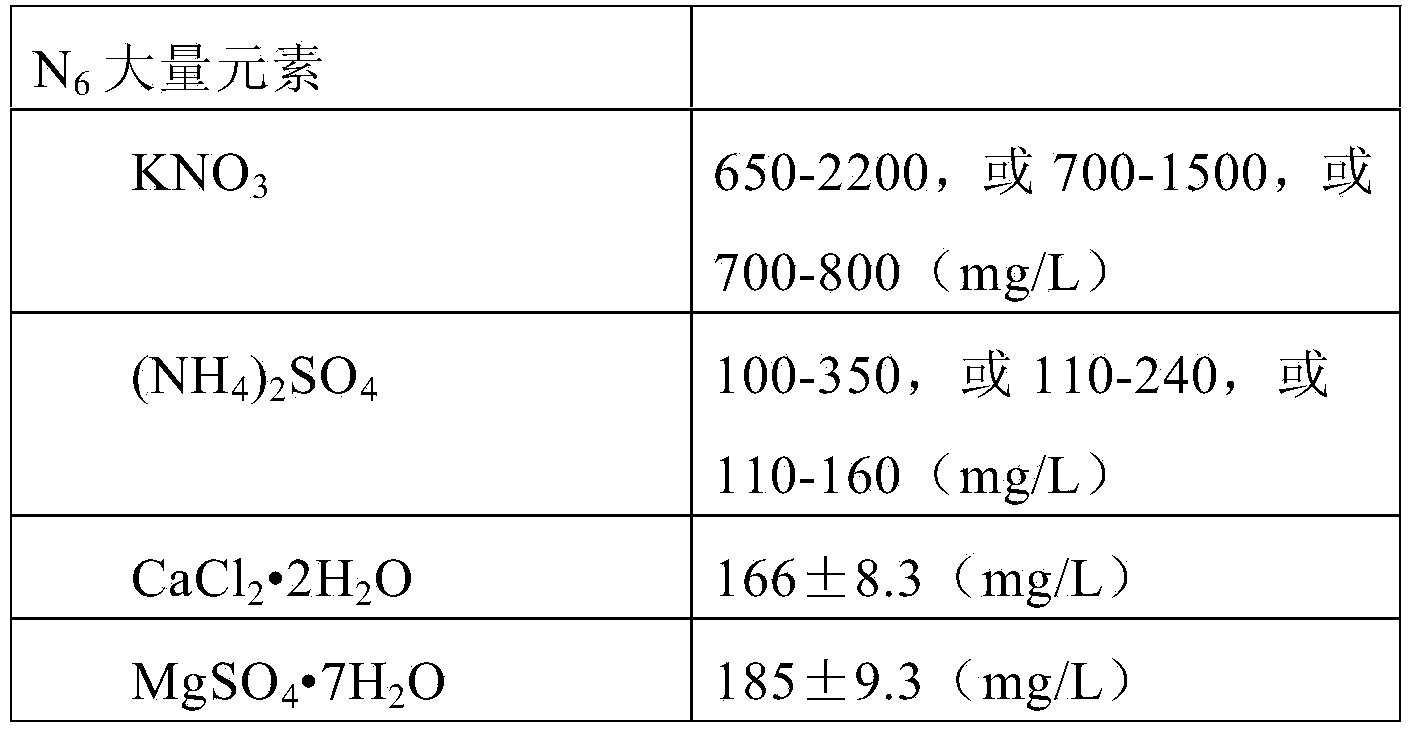
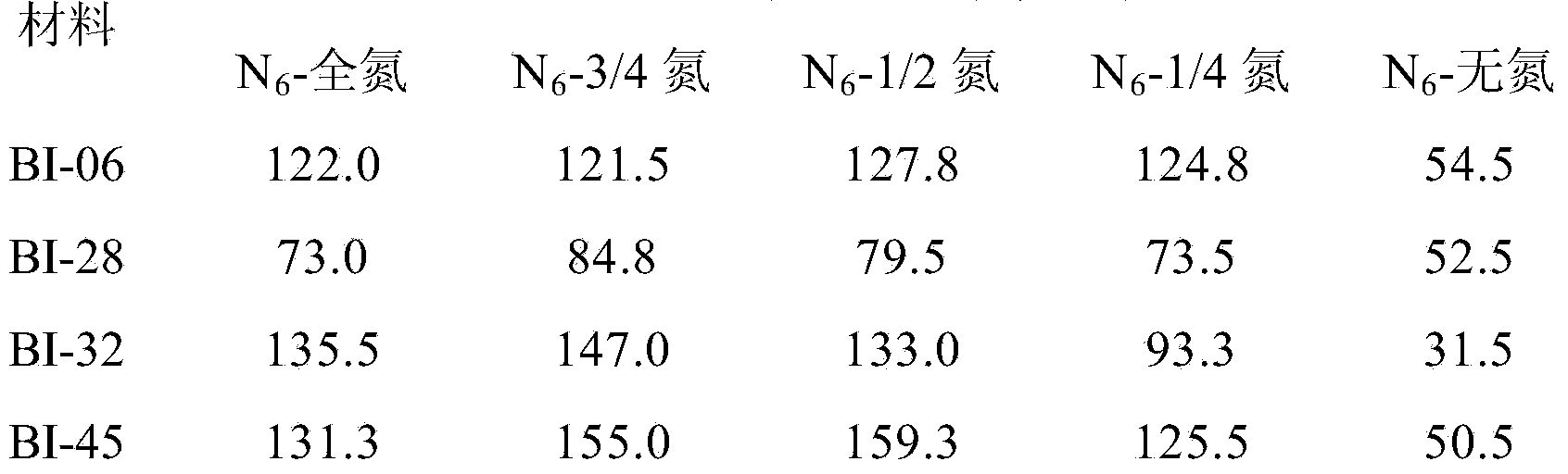
Induction medium for culturing callus of barley microspore
The invention provides an induction medium for culturing a callus of a barley microspore. The induction medium is prepared on the basis of a formula of an N6 culture medium, but the callus induction medium has the KNO3 concentration of 0-2500mg / L, the (NH4) SO4 concentration of 0-400mg / L, and is added with 400-2500mg / L of casein hydrolyzate and / or 400-2500mg / L of glutamine. The invention also provides a method for culturing the callus of the barley microspore and obtaining regenerated plants, and a kit containing the induction medium, an optional differential medium and a rooting and seedling-strengthening medium. The whole process is carried out under controlled conditions in a laboratory; results are real and reliable; after differentiation of the obtained callus, plenty of homozygous regenerated plants can be obtained.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Breeding and cultivating method for early-matured, disease-resistant and loose purple cauliflowers
ActiveCN103975849AOvercoming developmental abnormalitiesImprove developmentPlant genotype modificationSporeSource material
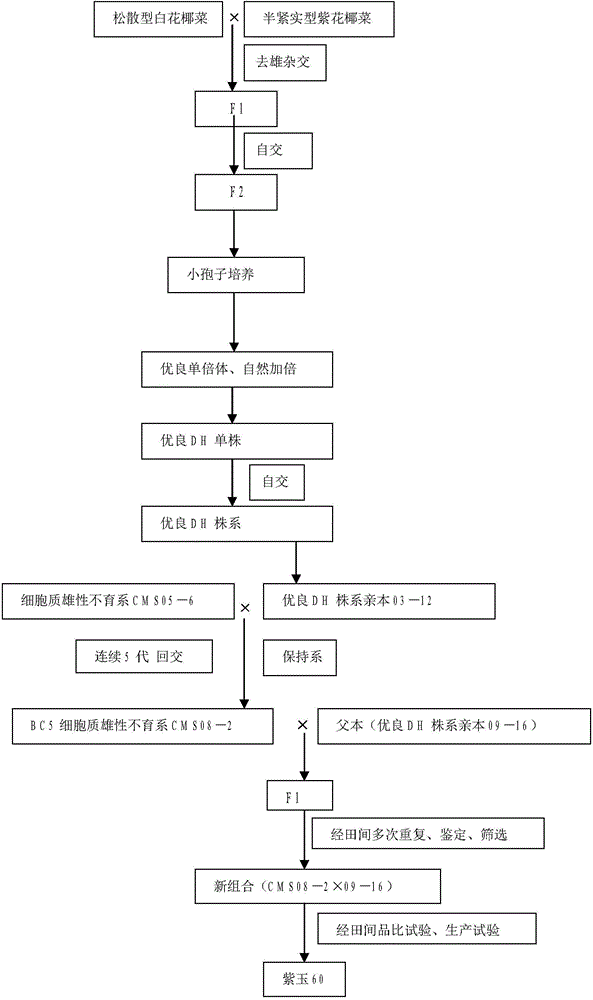
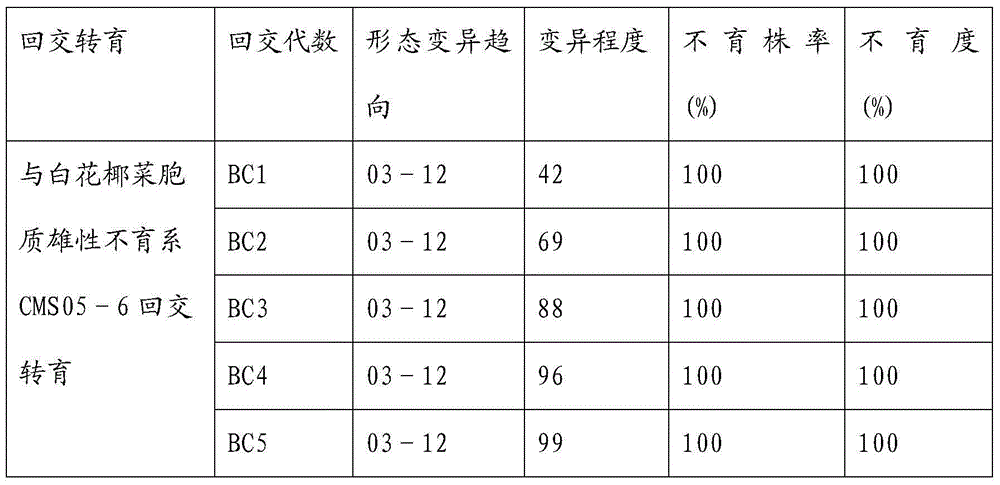
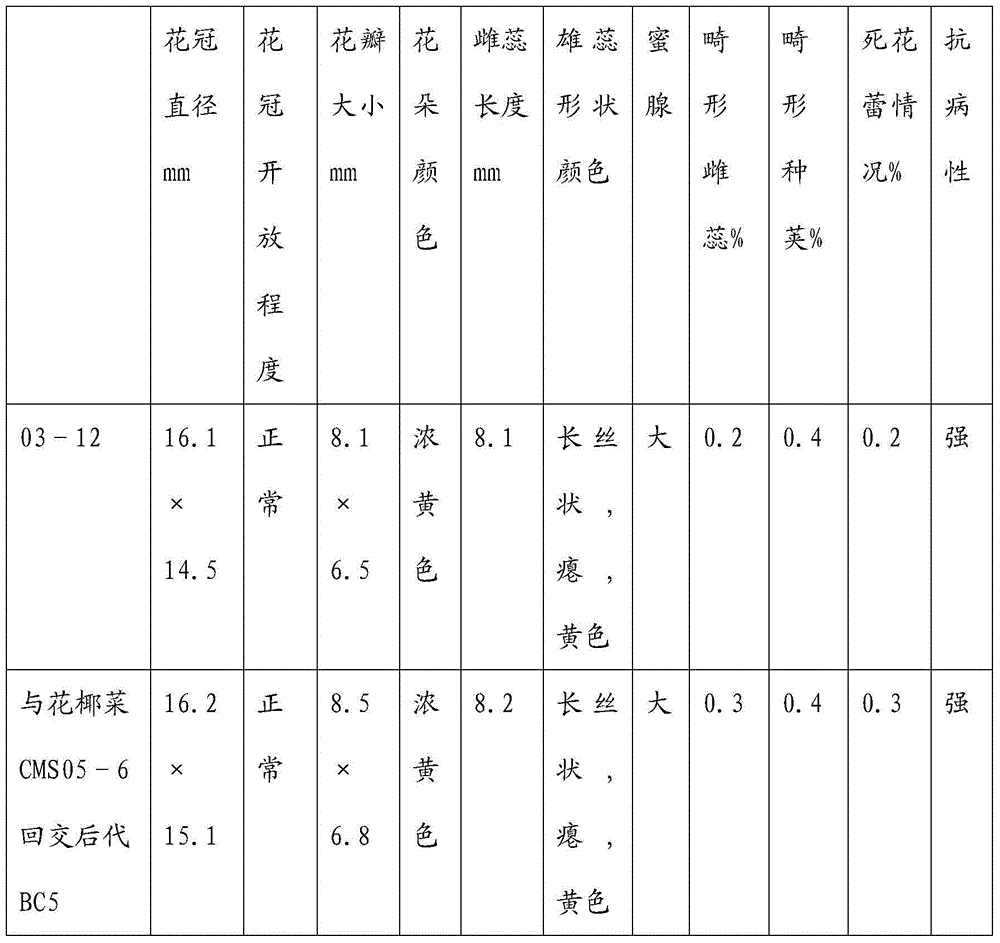
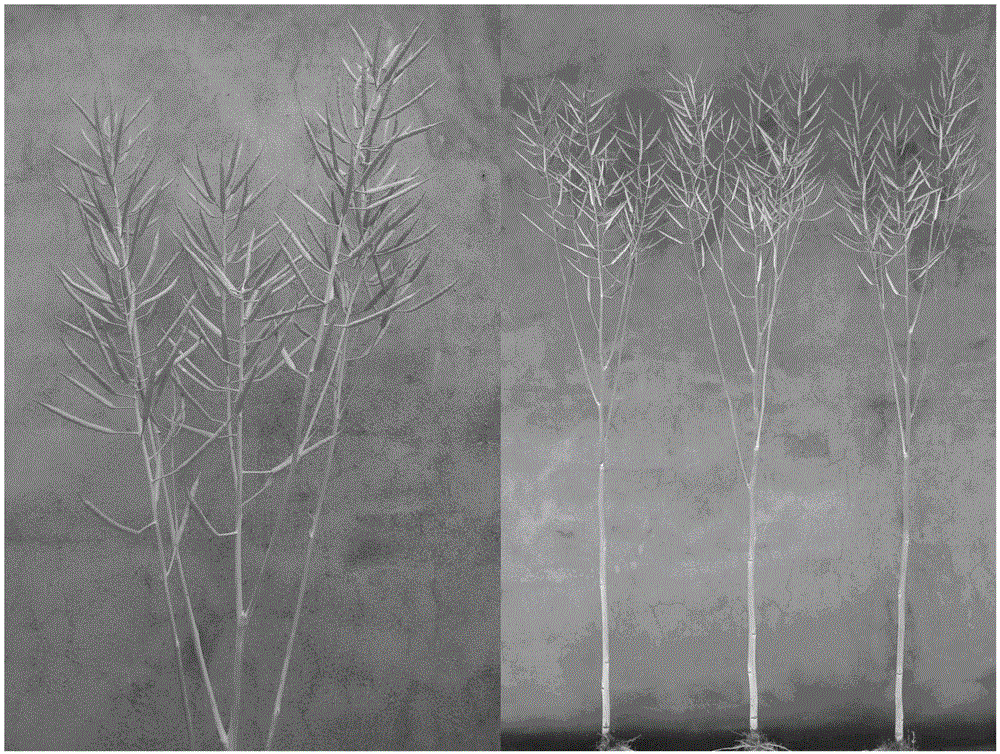
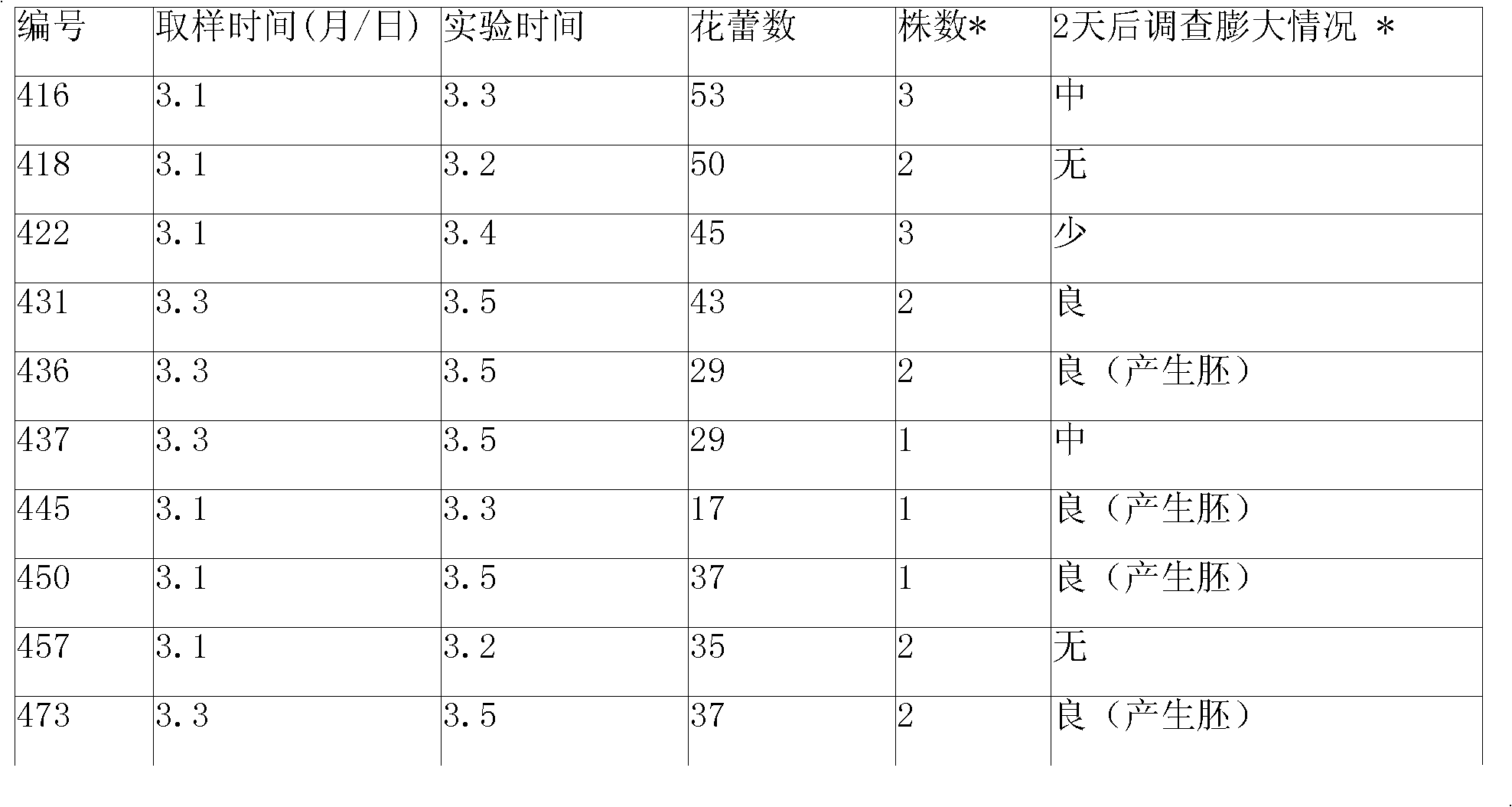
The invention relates to a breeding and cultivating method for a plant, in particular relates to a breeding and cultivating method for loose purple cauliflowers, and belongs to the technical field of plant cultivation. The breeding and cultivating method comprises the steps of hybridizing a loose purple cauliflower breeding material with a semi-compact purple cauliflower breeding material to obtain seeds F1, and selfing single strains with high comprehensive agronomic characters after the seeds F1 are sowed to obtain seeds F2; performing microspore culture on single loose purple cauliflowers through flower buds suitable for the microspore culture from the mononuclear edging stage to the double-core early stage to grow a large number of normal regenerated plants, selfing excellent DH plants of the loose purple cauliflowers to obtain a loose purple cauliflower excellent DH strain 03-12 serving as a recurrent parent which is hybridized with a cauliflower cytoplasmic male sterility source material CMS05-6, performing five generations of backcross transformation and selection to form a cytoplasmic male sterile line CMS08-2, and hybridizing the DH strain serving as a parent with the excellent cytoplasmic male sterile line CMS08-2.
Owner:杨广林
Seed breeding method of naturally-capped dwarf compact cabbage-type rape
InactiveCN105123510AImprove efficiencyExcellent homozygous germplasmPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsSporeF1 generation
The invention discloses a seed breeding method of a cabbage-type rape, wherein the seed breeding method is suitable for mechanical harvest and the cabbage-type rape is naturally capped in main inflorescence, is limited in siliques and is dwarf and compact in character. The seed breeding method includes following steps: (1) with the cabbage-type dwarf rapes 3H004 and compact-plant rapes 7399-8 as parents to performing hybridization to obtain an F1-generation; (2) in an early blooming period, selecting the buds being 3.0-4.0 mm in length on the main inflorescence and upper branched inflorescences of the F1 plant, perforning mutagenesis with EMS (ethyl methylsulfonate) and then performing colchicines doubling and microspore induction culture to obtain a DH separated population; (3) with plant height, branch characters, main inflorescence length, total silique number, growth period and oil-containing quantity and the like main characters, performing multi-year and multi-point in-field phenotype character identification to the DH separated population; and (4) selecting the variation materials which is naturally capped in main inflorescence, is limited in siliques, is lower than the upper branched inflorescences in height, is concentrated in blossom period and silique layers, and is dwarf and compact. The method can be used for obtaining the rape which is naturally capped in main inflorescence, is limited in siliques and is dwarf and compact in character. The method, when being popularized, can reduce planting cost of rapes and achieves excellent economical benefit.
Owner:陕西省杂交油菜研究中心
Breeding design and identification method for short-haulm compact type cole suitable for mechanized harvest
InactiveCN101292626AQuickly and effectively design breeding technology systemReduce planting costsMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationStem lengthMolecular identification
The invention pertains to the field of rape breeding and discloses a method for seed selection and identification of a novel dwarf compact type rape adapting to high-density planting and mechanized harvesting. The rape of Variety 5148-2 with apreservation number of CCTCC-P200601 that is bred by Huazhong Agricultural University and yellow-seed rape of DH series YN90-1016 that is synthesized artificially in Canada are taken as seed-parents and crossbred to obtain F1. In inflorescence, the main anthotaxy of an F1 plant and the flower buds with a size ranging from 2.8mm to 3.8mm at the upper branches of the P1 plant are selected, and then chromosome doubling with colchicine and microspore culture are carried out successively to obtain the segregation populations of double haploid. Filed phenotypic characteristic identification are applied for years in various spots to the segregation populations; variant rape materials with five major traits, namely, stem length, branch trait, length of anthotaxy, quantity of silique and growth period differing from those of the common rape and dwarf, compact plant, smallish and acervate branches and main anthotaxy, concentrative florescence and compact pod bearing layers phenotypes are selected to obtain the novel dwarf compact type rape adapting to mechanized harvesting. The invention also discloses a method for molecular identification.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Cultivation method for cabbage type rape Isolated microspore plant strain
InactiveCN101243776ASolve the problem of low induction rateImprove induction efficiencyPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsSporeBrassica
The invention discloses a cultivating method of the isolated microspores of brassica napus, which aims to solve the drawback of embryo index unavailable in prior art that, the production of microspore embryos can not be judged in the early stage. The invention is characterized in that, a whole filtered and sterilized NLN-13 hormone-free liquid culture medium comprising 45 to 55 mg / L colchicine is added to the prepared isolated microspores of brassica napus; the microspores are cultured in dark under a high temperature raging from 30 deg C to 35 deg C for two days; the materials having the microspore swell ratio large than 50% are chosen for subsequent induction culture. The cultivating method has the advantages that, the microspores having the microspore swell ratio large than 50% are chosen for subsequent induction culture, so the early rejection of the microspores that cannot produce embryos is facilitated; the workload is greatly reduced; the induction efficiency is improved, and the waste of time and resources is avoided.
Owner:贵州省生物技术研究所
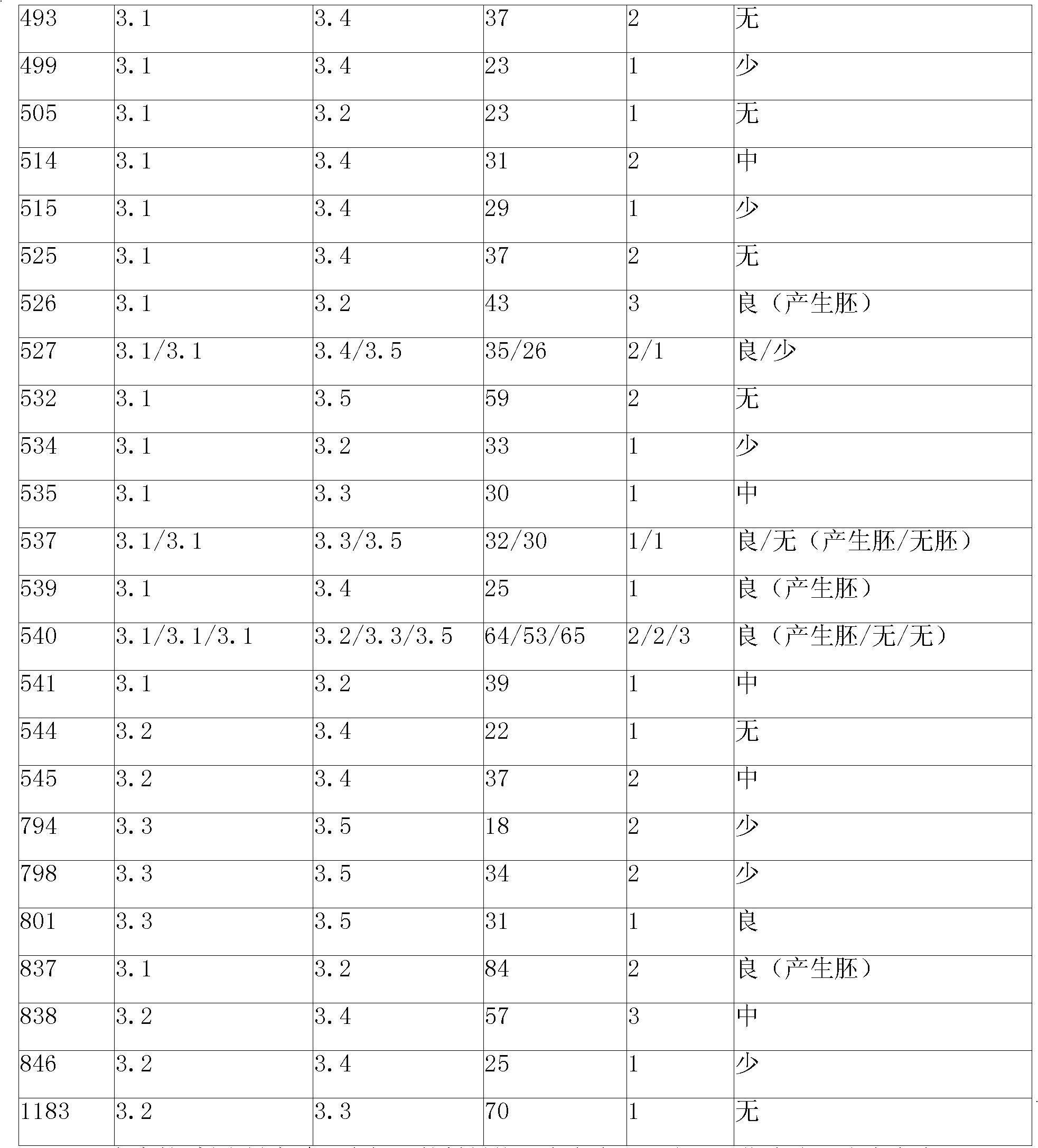
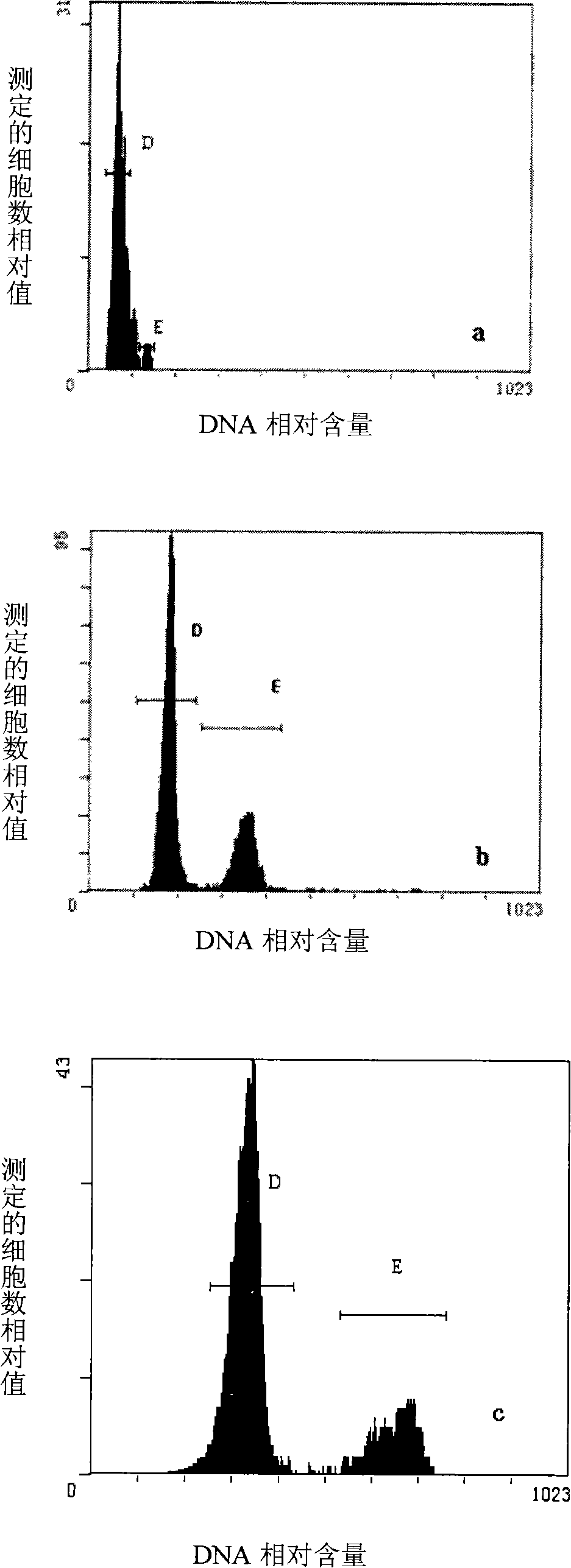
Ploidy appraising method of isolated microspore regeneration plant strain of non-heading Chinese cabbage
ActiveCN101135642AEasy to identifySimple sample preparationFluorescence/phosphorescencePloidy analysisSingle cell suspension
The method comprises: preparing single cell suspension liquid; using a flow cytometer produced by US BeckMAN COULTER company to make the flow cytometer ploidy analysis; using 488nm argon ion air cooling laser to measure the DNA molecule fluorescence intensity; if the peak value of the plant to be measured is close to 140, it is considered as a diploid; if it is close to 70 and 280, it is considered as haploid and tetraploid.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Culture method for improving embryonic birth rate of cabbage stalk
InactiveCN102577962AImprove embryo emergence rateImprove utilization efficiencyPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsSporeRapeseed
The invention relates to a culture method for improving embryonic birth rate of crops and particularly relates to a culture method for improving the embryonic birth rate of cabbage stalk, belonging to the technical field of plant culture. According to the culture method disclosed by the invention, a microspore culture technology is utilized for co-culture of the cabbage stalk and rapeseed microspores, so that the germ extraction rate of the cabbage stalk can be significantly improved and the problem of low embryogenesis frequency of microspore culture of the cabbage stalk is further solved.
Owner:ZHENJIANG AGRI SCI INST JIANGSU HILLY AREAS +1
Method for breeding recessive nuclear sterile temporary maintainer line by utilizing Brassica napus microspore culture technology
InactiveCN101766118AHigh frequencyImprove efficiencyPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsBrassicaSpore
The invention discloses a method for breeding a recessive nuclear sterile temporary maintainer line by utilizing a Brassica napus microspore culture technology, which comprises the following steps of: crossing by taking a good variety / strain as a female parent and taking a recessive nuclear sterile temporary maintainer line as a male parent to obtain an F1 generation; then carrying out inducing culture on the isolated microspore of the plant of the F1 generation by a Brassica napus microspore culture technology, thereby obtaining a DH strain; carrying out self cross on the DH strain and carrying out test cross on the heat exchange and a sterile line, wherein the test cross variety is completely sterile, and the corresponding DH strain is the recessive nuclear sterile temporary maintainer line. The good temporary maintainer line with a good genetic background can be rapidly obtained by the method and is applied to Brassica napus recessive nuclear sterile cross breeding.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
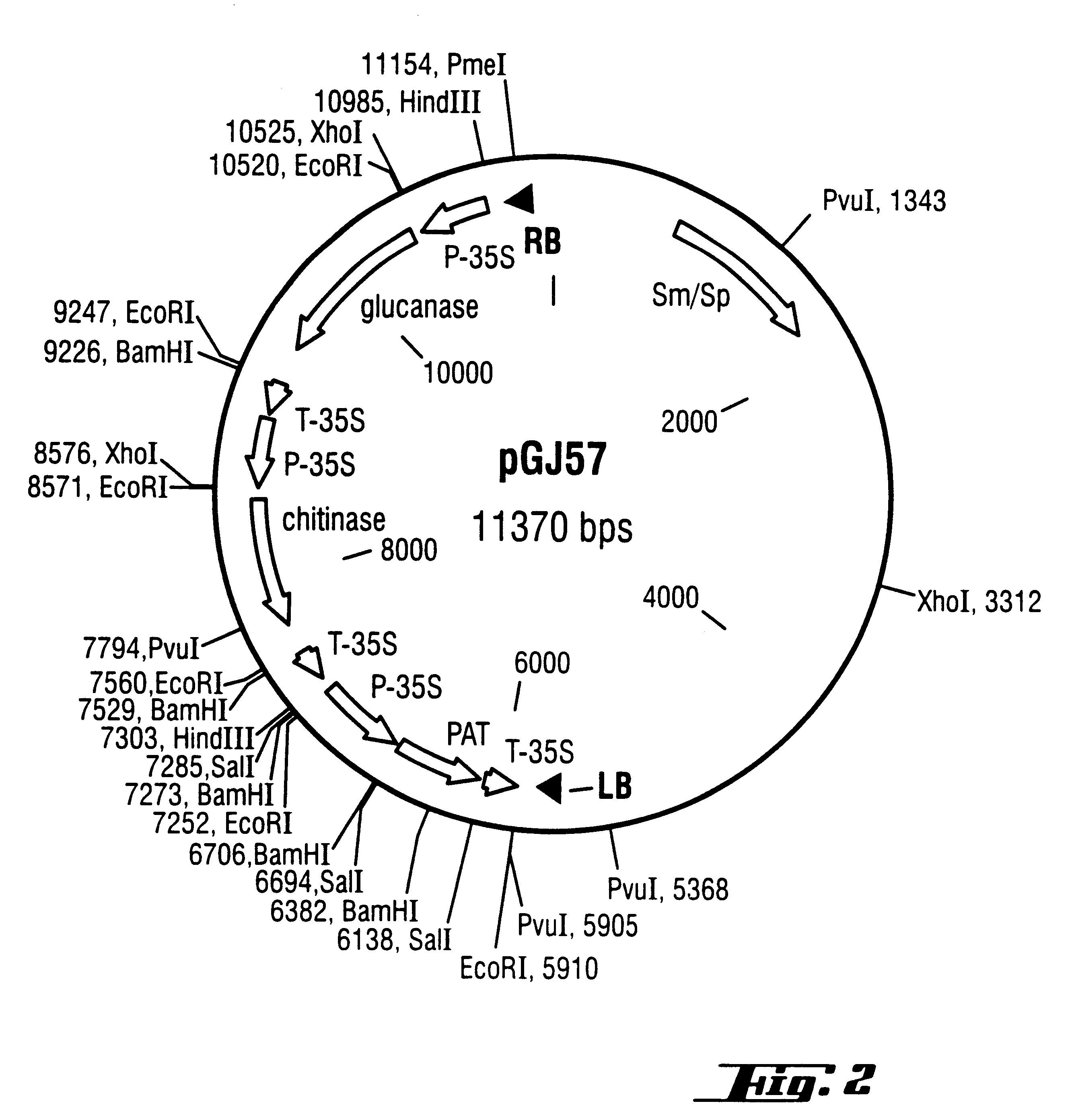
Microprojectile bombardment transformation of brassica
ActiveUS20070107077A1Increase varietyOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationBrassicaAspidosperma parvifolium
The invention relates to the genetic manipulation of plants, particularly plants of the genus Brassica. Methods are provided for producing transgenic Brassica plants involving the introduction of a DNA construct by microprojectile bombardment into pre-incubated microspores, microspore-derived embryos and microspore-derived hypocotyls. The methods find use in the development of improved agricultural varieties of Brassica plants through the incorporation of desirable agronomic traits.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Method for selecting and breeding Brassica napus recessive genic-male-sterile line through microspore culture technology and cloning technology
InactiveCN101946715ABreeding is more efficient thanShorten the breeding cyclePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsBrassicaSpore
The invention discloses a method for selecting and breeding Brassica napus recessive genic-male-sterile (GMS) line through the microspore culture technology and the cloning technology. The method comprises the following steps: a fine variety / line is hybridized with a recessive GMS line or temporary maintaining line to obtain the F1 generation; then the Brassica napus microspore culture technology is adopted to perform inducing culture to the isolated microspores of the F1 generation plant and obtain a DH strain; and then the DH strain with the sterile character is test-crossed with the temporary maintaining line, 100% of the tester strain is sterile, the corresponding sterile DH strain is the recessive GMS line; and then the cloning technology is used to rapidly obtain a large number of plants of the sterile line which are used for the complete sterile line production. By using the method of the invention, the sterile line with stable and excellent genetic background can be rapidly obtained and used in the Brassica napus recessive GMS cross-breeding.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
Method for inducing dissociate microspore callus of eggplant and regenerating plant strain
InactiveCN101371650AEliminate uncontrollable influencesNo competition issuesHorticulture methodsPlant tissue culturePlant cellBud
The invention is a method of inducement of isolated microspore callus of eggplant and plant regeneration. The major procedures are as follows. Appropriate anther is selected for pre-cultivation. Then dissociation and collection of microspore are carried out. And then static shallow pan dark culture is carried out in fluid nutrient medium. After 20 to 30 days, callus emerges successively. Callus is taken for cultivation under sunlight after emergence. When the callus grows to the size with the diameter of 2 to 6 millimeters, callus is transferred to solid regeneration culture medium for further cultivation. After 30 to 45 days, callus begins to differentiate to form buds. When bud grows to size of 1 to 3 centimeters, callus is transferred to rooting culture medium. After 10 to 15 days, strong root is developed. By adopting the method, the probability of obtaining haploid is high and frequency of microspore callus genesis is high. The invention is not only the technological breakthrough of eggplant haploid breeding, the inducing system of isolated microspore for cultivation of embryoid can also be a good experimental system for carrying out research on plant cell differentiation and development, molecular marker and gene map.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Breeding process of obtaining radish haploidy
InactiveCN101283674AIncreased induction rate of embryoid bodiesImprove selection efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementCultivating equipmentsSporeRoot tip
The invention discloses a rapid breeding method of monoploid radish and belongs to the field of plant genetics and breeding. The method comprises the following steps: culturing radish microspores that are subjected to heat treatment at 32.5 DEG C in a constant-temperature incubator for 48 hours to obtain cotyledonous embryoids, culturing the cotyledonous embryoids for 5-7 days at 25 DEG C under 4000Lx light illumination (16 h / d), transferring to a subculture medium for germination until the embryoids turn green, transferring to a rooting medium for plant regeneration, and identifying the regenerated plants by root tip cell chromosome count method or flow cytometry. The method is successful in the culture of regenerated plant of monoploid radish and increases the induction rate of embryoid from microspore up to 17.03 / 105. The self-bred line of monoploid plant of radish cultured by microspore culture method is obtained by chromosome doubling and is used for genetic improvement and new variety breeding of radish.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for obtaining chilli embryoid by microspore induction
InactiveCN1836496AThe method steps are simpleThe method steps are practicalPlant genotype modificationPlant cellsSporePlant cell
The culture process of inducing chilli microspore to obtain embryoid belongs to the field of plant cell engineering. The process includes the steps of trialing material, selecting bud, pre-treating bud, preparing liquid culture medium and solid culture medium, sterilizing and packing liquid culture medium and solid culture medium, sterilizing bud, abacterial stripping of anther, inoculating anther, culturing anther, naturally separating microspore, forming embryoid, etc. The process can obtain microspore embryoid with capacity of growing normally in high seedling forming rate, and has a period of about 8 weeks. Applying the process in breeding variety can speed the breeding process, raise the selecting effect and speed the pure variety breeding.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Method for increasing embryoid induction rate in culture of isolated microspores of hot (sweet) pepper
InactiveCN101822213APractical methodSpecific stepsPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsSporeHot peppers
The invention discloses a method for increasing the embryoid induction rate in the culture of isolated microspores of hot (sweet) pepper, which belongs to the technical field of the utilization of the theory of cytogenetics and breeding. On the basis of the published culturing method for obtaining embryoids by culturing isolated microspores of hot pepper, the quality of buds for culture is increased, bud sampling, preprocessing, disinfection and anther picking are controlled under lower temperature, anthers are precultured under the temperature of 7 DEG C in the darkness for one week and then cultured under the temperature of 28 DEG C in the darkness, and consequently, up to 8.4 embryoids / anther can be obtained, 1.3 embryoids / anther in average, and are higher than 1 embryoid / anther in the published patent technology and up to 1.83 embryoids / anther in the recently reported domestic research. The invention is characterized in that: the method is practical, the steps are specific, the method is applicable to a wide range of genotypes, the repeatability is good, and the method can ensure that the culture of isolated microspores of hot (sweet) pepper can be widely applied to haploid breeding and the establishment of genetic mapping populations.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
Method Of Producing Haploid And Doubled Haploid Plant Embryos, And Embryos, Plants, Progeny, Cells, Tissues And Seeds Obtainable By Method
The invention relates to a method for producing haploid plant embryos, comprising providing microspores or pollen that comprise cell division inducing molecules; pollinating an embryo sac cell, in particular an egg cell, of the plant of which the haploid embryo is to be made with the microspores or pollen; allowing the microspores or pollen to discharge the cell division inducing molecules in or in the vicinity of the embryo sac cell, in particular the egg cell, to trigger division thereof to obtain a haploid plant embryo. When doubled haploid plant embryos are to be produced doubling of the chromosome number takes place at a certain stage after pollination, in particular during cell division or after obtaining the embryo. The invention further relates to the embryos thus obtained, plants regenerated therefrom and progeny thereof.
Owner:RIJK ZWAAN ZAADTEELT & ZAADHANDEL BV
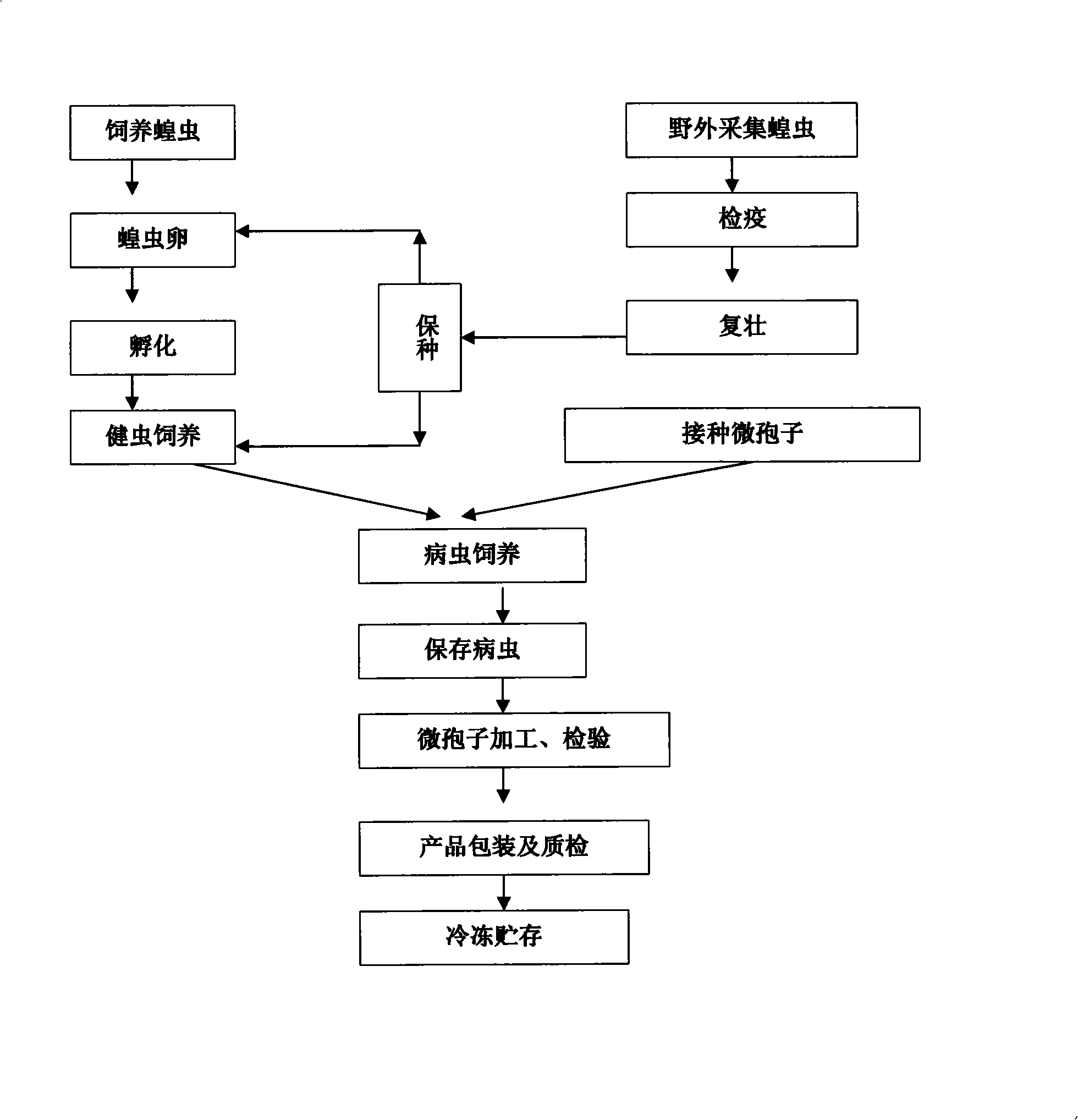
Microspore preparation and its production technique
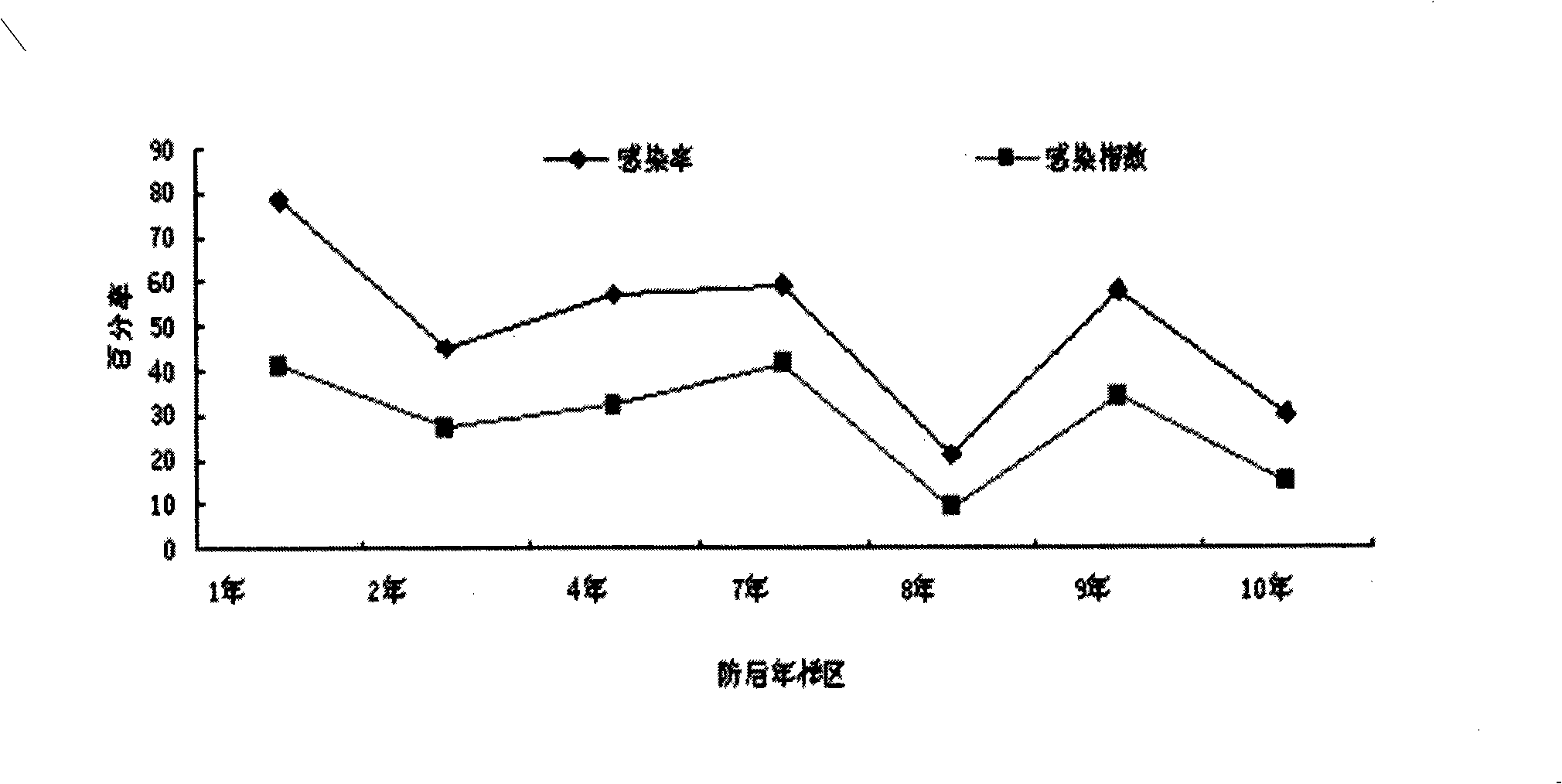
The invention provides a preparation containing 8-year-old microspores (P8) and 9-year-old microspores (P9) separated from Oedaleus asiaticus, and the preparation method thereof. The microspore preparation can be used for preventing and treating dozens of locusts such as farmland migratory locusts, grassland migratory locusts, Oedaleus asiaticus, bamboo locusts, rice locusts, etc, and can remarkably improve the locust control effect and ensure the stable prevention effect.
Owner:BEIJING MAMMOTH SEED
Simplified efficient culture method for brassica napus microspores
InactiveCN102217532AImprove utilization efficiencyReduce in quantityPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsSporeBrassica
The invention relates to a rape microspore culture method and discloses a simplified efficient culture method for brassica napus microspores, belonging to a new plant variety breeding method. Aiming at the problems in conventional brassica napus microspore culture, the technical aspects of sampling period, time and mode, an extracting solution, a culture method, a doubling method, long-distance sterile transportation and the like are respectively improved, so that the efficiency of the brassica napus microspore culture is greatly improved, the culture method and the culture program are simplified, the culture cost is reduced, and the method disclosed by the invention is convenient for popularization and application.
Owner:HENAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Anther development control gene and use thereof in realizing male sterility in Arabidopsis thaliana
ActiveCN102140131AAccording to Mendelian inheritanceIn line with the law of inheritancePlant peptidesFermentationNucleotideWild type
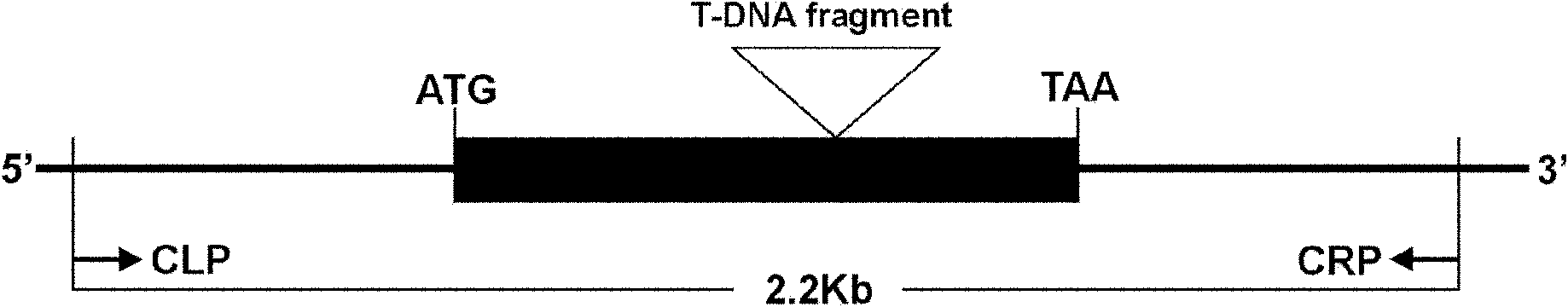
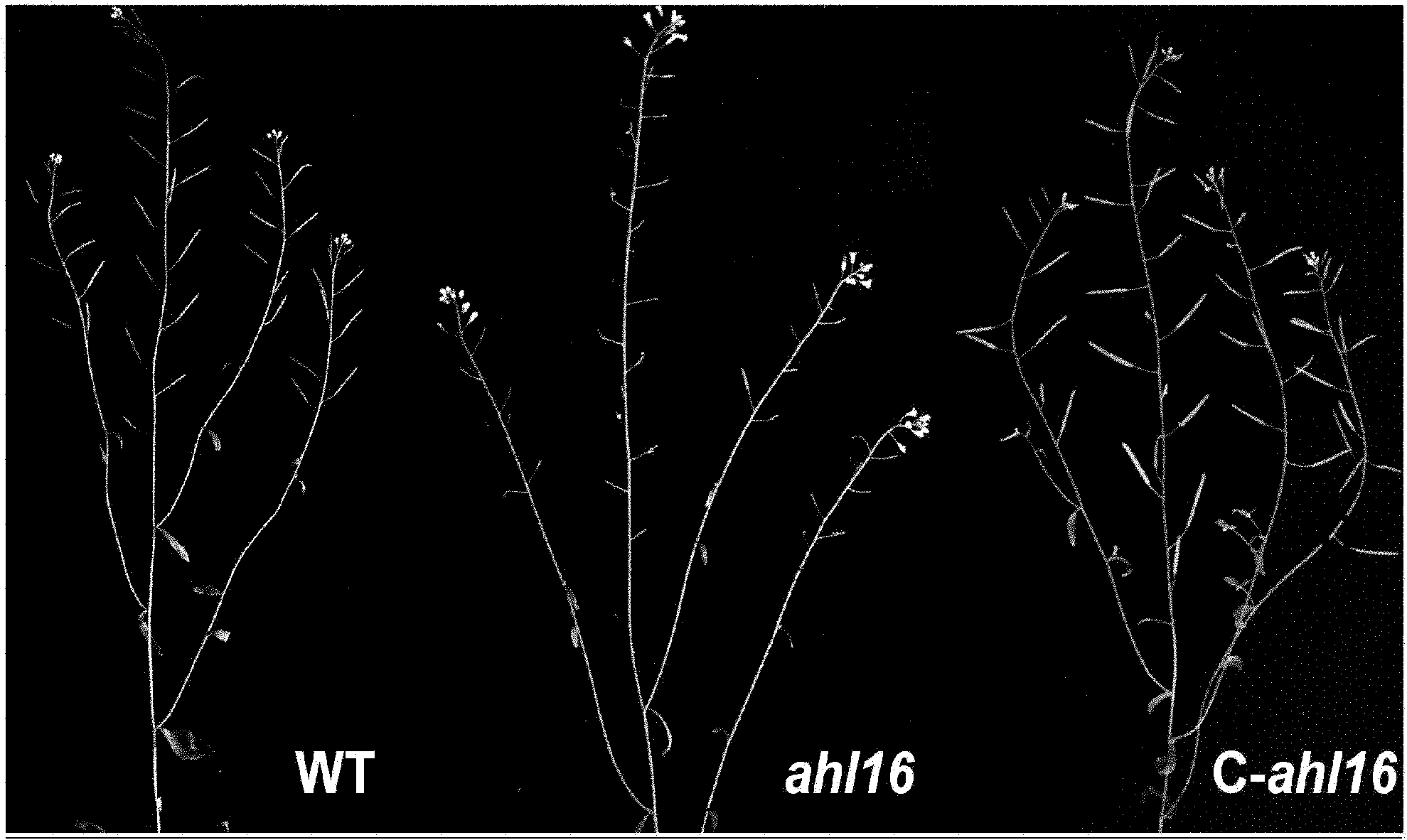
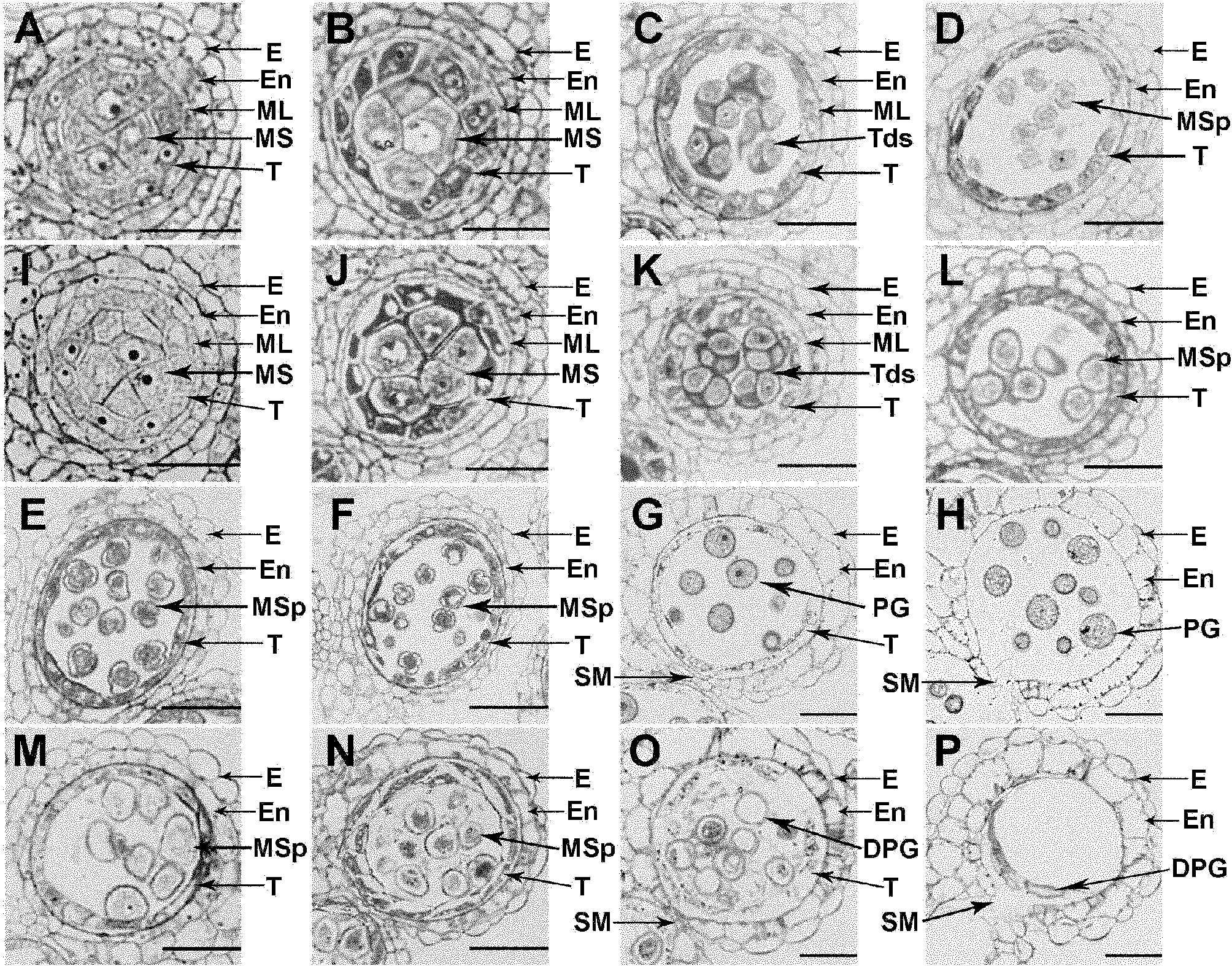
The invention relates to an anther development control gene and use thereof in realizing male sterility in Arabidopsis thaliana. An Arabidopsis thaliana male sterile mutant ahl16 is screened out from T-DNA-inserted mutant population, a gene AHL16 controlling the fertility of Arabidopsis thaliana is cloned and identified, the nucleotide sequence of the gene AHL16 is represented by SEQ ID N0.1, and genetic complement experiments prove that the AHL16 gene in a wild type can restore the male sterile phenotype. Amino acid sequence analysis and subcellular localization experiments indicate that the AHL16 gene codes proteins of an AT-hookmotif nuclear localized protein family and is located in the nucleus. In Arabidopsis thaliana, the mutation of the gene leads to complete male sterility. The gene has a very important application value in aspects of explanation of influences of the growth of the inner layers of the outer walls of microspores and the structures of the inner walls on the fertility of plants and improvement on yield by hybrid seed production.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for increasing inductivity and direct planting percent of Chinese cabbage and green Chinese cabbage hybrid microspore-derived embryo
InactiveCN101946700AHigh induction rateReduce menstrual healingHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureSporeEmbryo
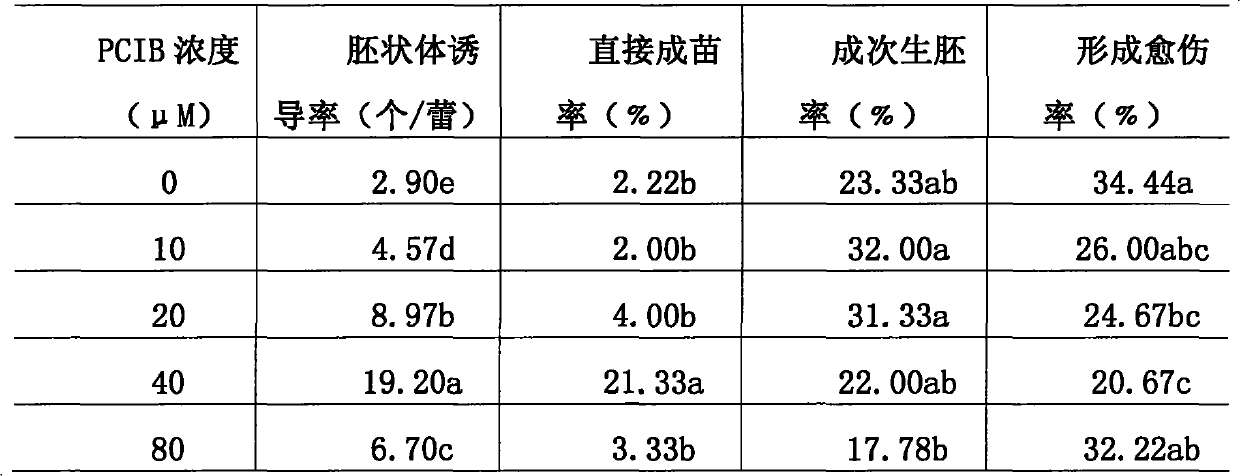
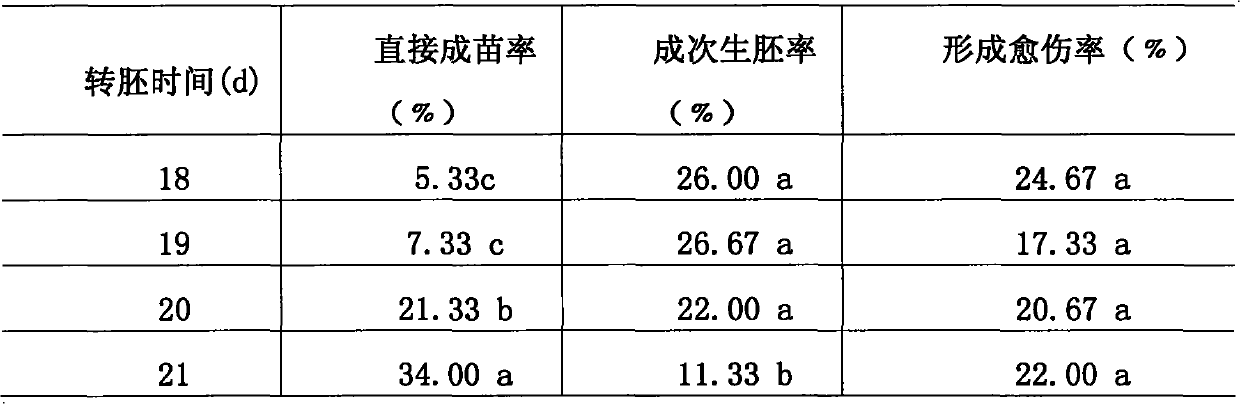
The invention discloses a method for increasing the inductivity and direct planting percent of Chinese cabbage and green Chinese cabbage hybrid free microspore culture embryoid and aims to solve the problems of low inductivity and planting percent and long culture period of the microspore embryoid in the prior art. In the method, the inductivity of the embryoid is increased by 6.2 times by using an NLN culture medium to which 40 mu m anti-auxin, namely, 2-(4-chlorophenoxy) isobutyric acid and 130 g.L<-1> cane sugar are added and the direct planting percent is up to 34.00 percent by transferring the embryoid to a hormone-free MS culture medium when the embryoid is mature at the 21st day after inoculation. In the method, only about 40 days are needed from the inoculation of a microspore to the acquisition of a regeneration plant, the embryoid which does not growth to a plant grows to a plant after primary secondary culture and the final planting percent is up to 80 percent. The method of the invention has the advantages of greatly saving time, improving the efficiency of microspore culture, accelerating a breeding process, lowering high cost caused by secondary culture, reducing thepollution to valuable materials and laying a basis for rapid and mass creation of high-quality breeding materials, along with simpleness and practicability.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
Culturing method of eurytropic bolting-resisting spring Chinese cabbage free microspores
InactiveCN103299896AImprove purification efficiencyImprove breeding efficiencyPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsSporeGreenhouse
The invention discloses a culturing method of eurytropic bolting-resisting spring Chinese cabbage free microspores. The culturing method comprises the following steps of: (1) taking a high-generation selfing line material which can easily carry out free microspore cultivation and carrying out hybridization on bolting-resisting spring Chinese cabbage materials of the microspores to be cultured to obtain hybridized seeds; and (2) sowing the hybridized seeds into a nutrition pot and naturally vernalizing in a greenhouse; from the end of March to the last ten days of April of the next year, taking flower buds at a bolting and flowering period to carry out the free microspore cultivation according to a conventional method to obtain a regenerated plant. According to the culturing method disclosed by the invention, a simple hybridization method is adopted to hybridize spring Chinese cabbages with different backgrounds in the market and the selfing line material which can easily carry out the free microspore cultivation, so that a donor plant gene type state is effectively improved, and a donor plant selection range of the cultivation of the bolting-resisting spring Chinese cabbage free microspores is obviously expanded; and the culturing method is beneficial for improving the obtaining possibility of double haploid materials of the spring Chinese cabbages with the different backgrounds, and the breeding efficiency of the spring Chinese cabbages is greatly improved.
Owner:VEGETABLE RES INST OF SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com