Culturing method of eurytropic bolting-resisting spring Chinese cabbage free microspores
A technology of microspore culture and culture method, which is applied in the field of culture of free microspores of spring cabbage with broad adaptability and resistance to bolting, can solve problems such as gaps in spring cabbage breeding practices, and achieve the purpose of broadening the selection range of donor plants, improving breeding efficiency, Effects that increase the chance of obtaining
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
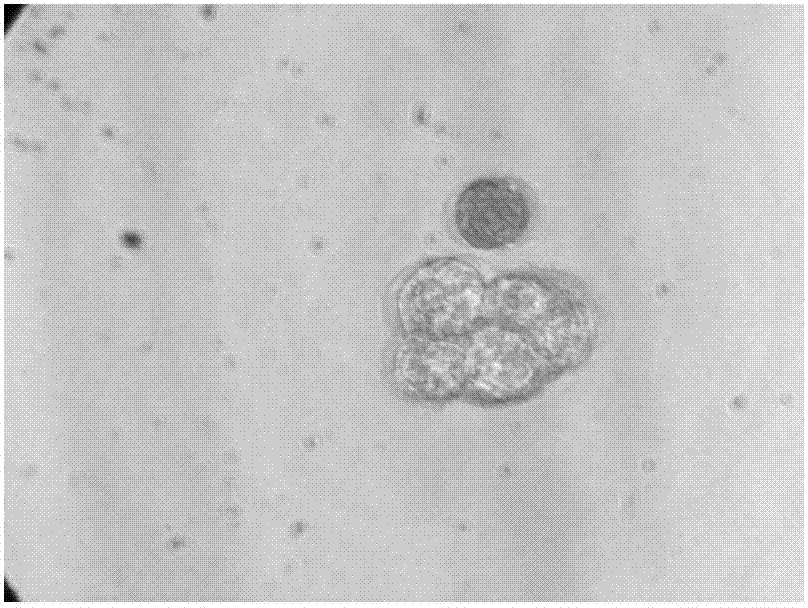
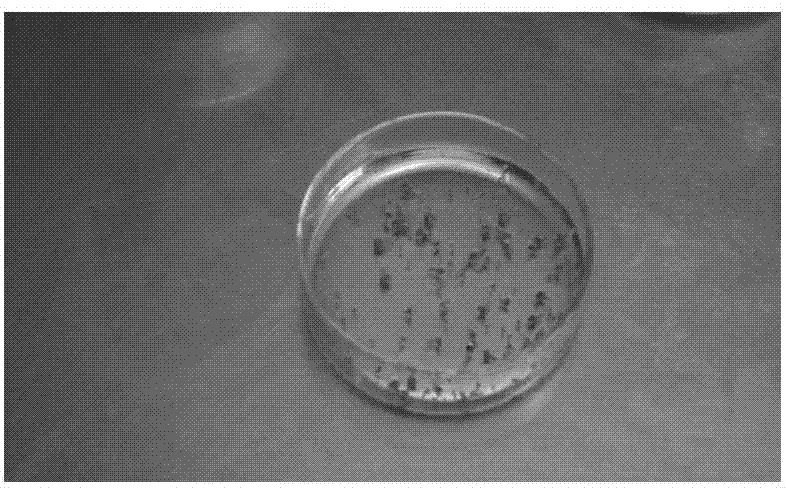
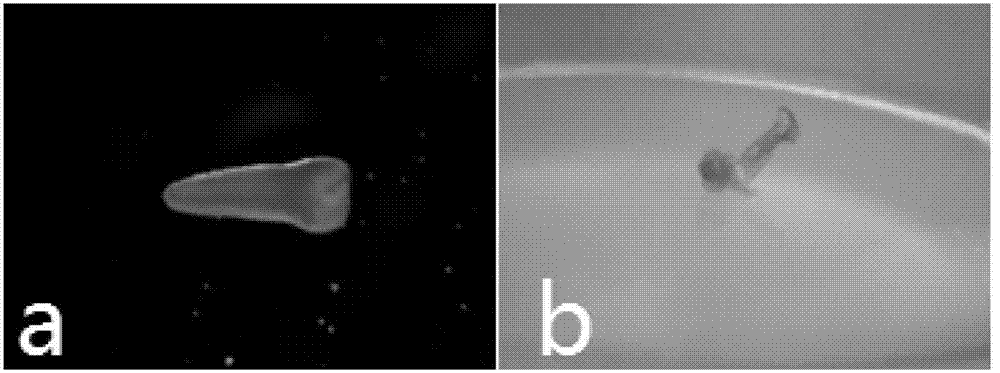
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Example 1 Preparation of hybrid combination of different spring cabbage materials and high-generation inbred line materials
[0024] 1.1 Selection and cultivation of test materials
[0025] The test materials included four commercially available spring cabbage varieties and four high-generation inbred line materials. The spring cabbage varieties were one Japanese spring cabbage variety Jujin and three copies (Korea spring cabbage varieties Yangchun, Sambo, Strong, Gao The generation inbred line materials were summer cabbage material 94610, early autumn material J3 and 06-21-1, and spring cabbage material 06-101-4.
[0026] According to the forecast of bolting resistance, the materials and varieties will be bred in 3 batches from late November to mid-December. They will be planted in 50-mesh insect-proof net sheds on March 10 of the following year. The ground will be covered with mulch, and they will bloom in late March. The hybrid combination was prepared by manual hybridizat...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Example 2 Free microspore culture of different spring cabbage materials, high-generation inbred line materials and their cross combinations
[0030] 2.1 Planting of various materials (see 1.1 in Example 1)
[0031] 2.2 Preparation of various media
[0032] Microspore extract and microspore lotion B5W: B5 liquid medium with 13% sucrose, pH 5.8, autoclaved.
[0033] Microspore heat shock treatment culture broth NLN-13: NLN liquid medium plus 13% sucrose, pH 5.8, 0.22μm microporous membrane filter sterilization.
[0034] Microspore dark culture medium NLN-10: NLN liquid medium with 10% sucrose, pH5.8, 0.22μm microporous membrane filter sterilization.
[0035] Microspore embryo growth medium B5G: B5 solid medium supplemented with 6-BA0.2mg / mL+NAA0.02mg / mL+3% sucrose, pH5.8, autoclaved.
[0036] Rooting medium for regenerated plants MS0: MS solid medium, without any hormone added, pH 5.8, autoclaved.
[0037] Please refer to [Guan Chunyun, Li Wei, Li Wenbin, Biotechnology of Brassica Pla...
Embodiment 3
[0048] Example 3 Identification of bolting resistance of regenerated plants cultured with free microspores of 07-ZY4
[0049] 3.1 Domestication, transplantation and selfing of regenerated plants
[0050] After the regenerated plants take root, the medium from which the roots are washed is transferred to a vermiculite: peat = 1:1 matrix to moisturize for 3-5 days for domestication. After the domestication is completed, the plants are transplanted into insect-proof nets for normal management, and transferred to the solar greenhouse at the end of November. After flowering, a single plant with normal pollen is selected to pick buds for self-pollination. Plants that can harvest seeds normally are DH regenerated plants. Seven of the nine regenerated plants of 07-ZY4 harvested selfed seeds, that is, seven double haploid lines (numbered from 09-552 to 09-558).
[0051] 3.2 Identification of bolting resistance of regenerated plants
[0052] In autumn, the double haploid strains and the contro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com