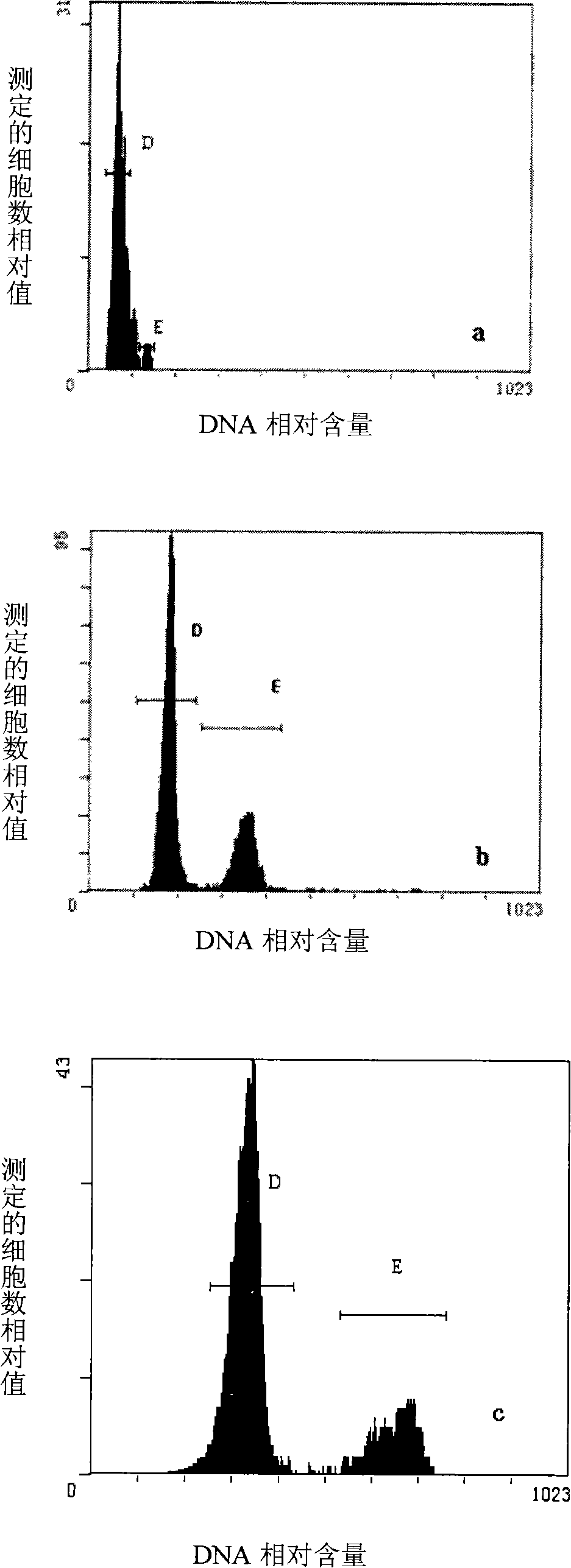
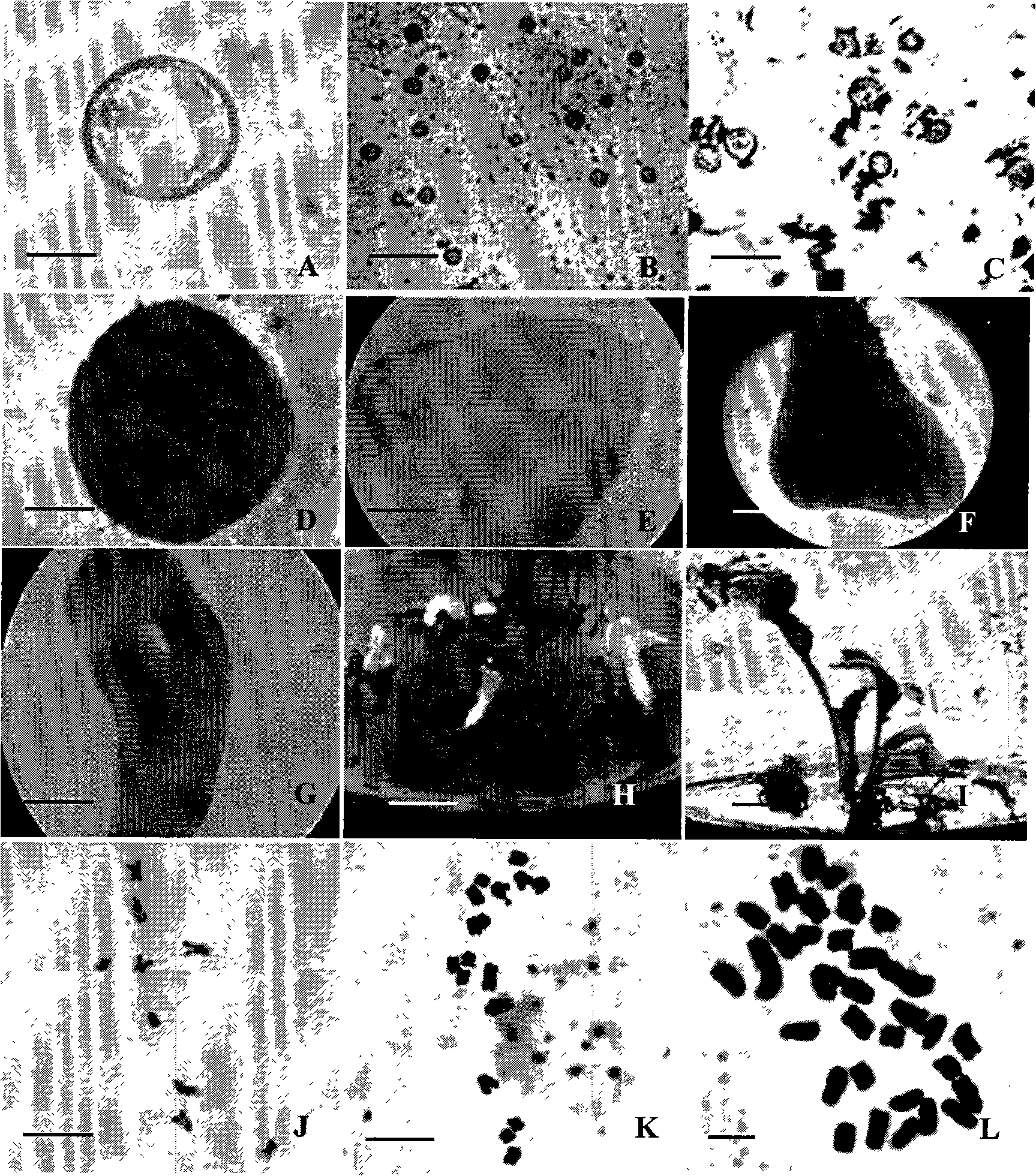Breeding process of obtaining radish haploidy
A single and ploidy radish technology, applied in the field of plant genetics and breeding, can solve the problems of low embryo emergence rate and limited number of regenerated plants, and achieve the effects of improving selection efficiency, speeding up the breeding process, and shortening the time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0025] (1) Culture of microspores
[0026]Donor plants from radish material NAU-xxxs-03 (Wang Wei, Liu Liwang, Gong Yiqin, et al. Analysis of enzyme activities related to carbohydrate and sucrose metabolism in the process of radish fleshy root swelling. Acta Horticultural Science, 2007, 34(5): 1313-1316) Select flower buds of about 1.5-5.0 mm above, use the petal-to-drug ratio (petal length / anther length), select flower buds with the same length as the petal-to-drug ratio or slightly shorter than the anther, and disinfect the buds with 75% alcohol for 60 seconds, and then use 8 % sodium hypochlorite solution surface disinfection for 15 minutes, rinsed with sterile water 3 times. Put the flower buds in a sterilized mortar to add 0.015% Ca by mass 2+ , pH 5.8 B 5 -13 liquid medium (B 5 +13% sucrose, B 5 See Gamborg, O.L.; Miller, R.A.; Ojima, K. Nutrient requirements of suspension cultures of soybean root cells. Exp Cell Res. 50: 151-158; 1968) as the washing solution, and f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com