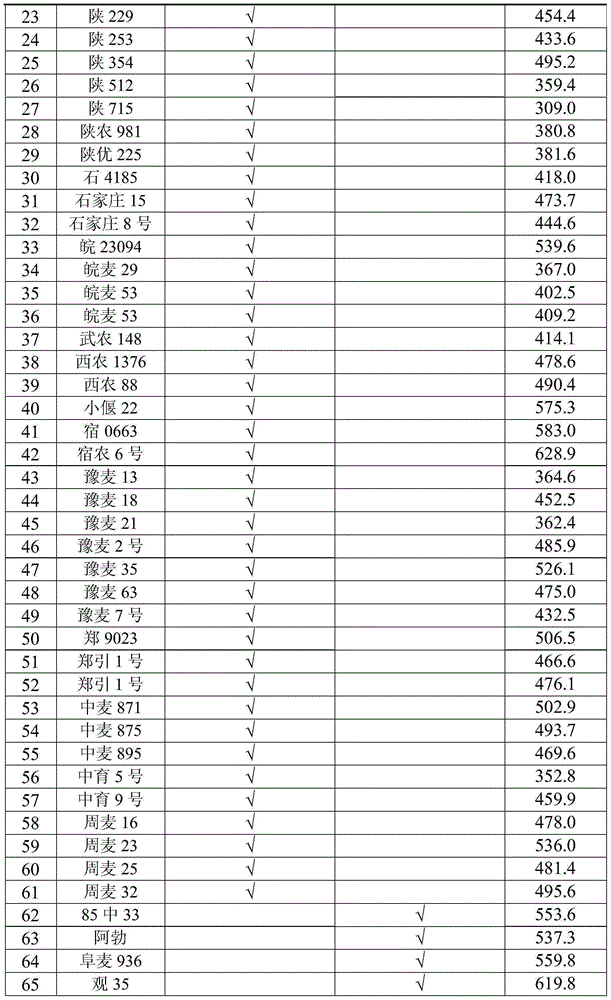
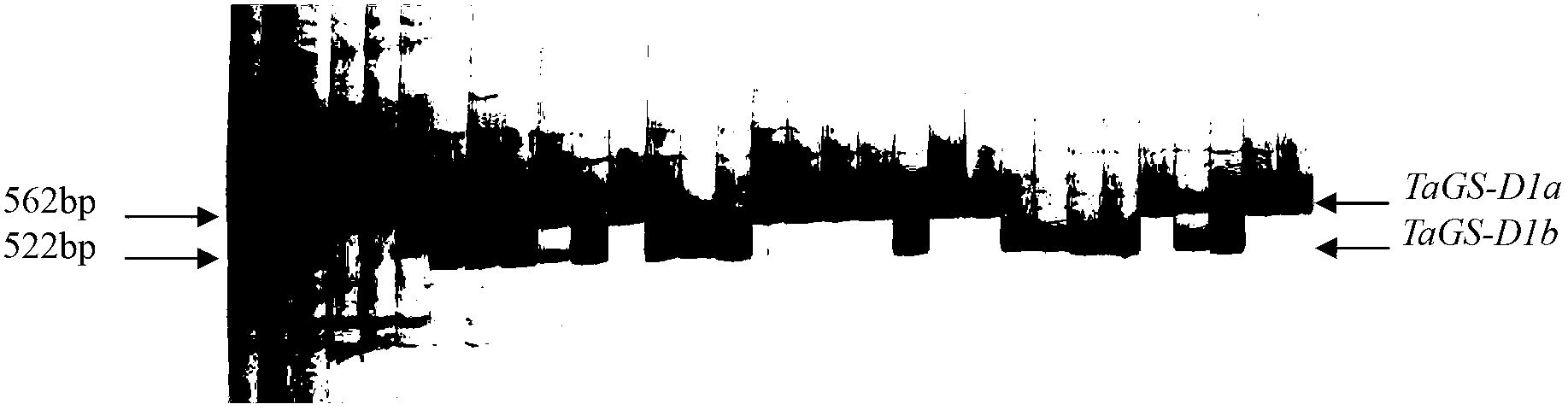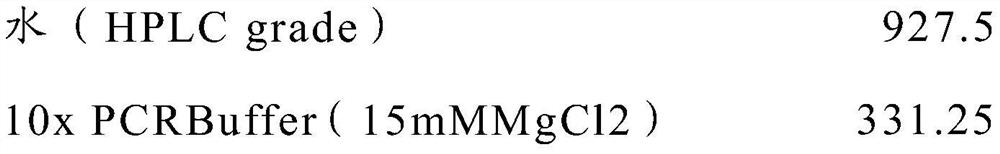Patents
Literature
54results about How to "Accelerate the pace of breeding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Flavonoid 3',5'-hydroxylase gene functional marker for screening high-dihydroxyl catechin-content tea plant, as well as application and application method thereof
ActiveCN106755308AQuick filterAccelerate the pace of breedingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationHydroxylase genePlant variety
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, particularly relates to a flavonoid 3',5'-hydroxylase gene functional marker for screening a high-dihydroxyl catechin-content tea plant, as well as application and an application method thereof, and discloses a functional marker for identifying the high-dihydroxyl catechin-content tea plant. The functional marker is applied to molecular marker-assisted selection, and can be used for rapidly screening a tea plant material with high dihydroxyl catechin content, thereby accelerating cultivation of a high-quality team plant variety. The functional marker has great theoretical significance and high economic value for molecular marker-assisted selection of a high-dihydroxyl catechin-content tea plant variety.
Owner:TEA RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Primer pair for assaying thousand-grain weight of wheat and related molecular marker
InactiveCN103060319AAccelerate the pace of breedingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGrain weightSingle strand dna
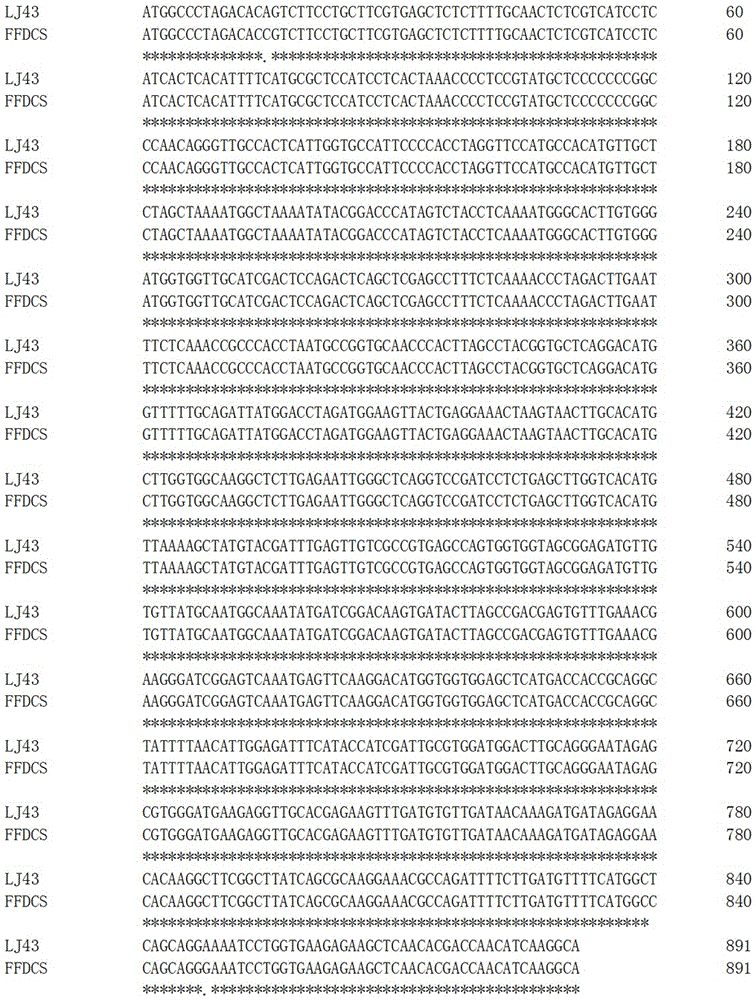
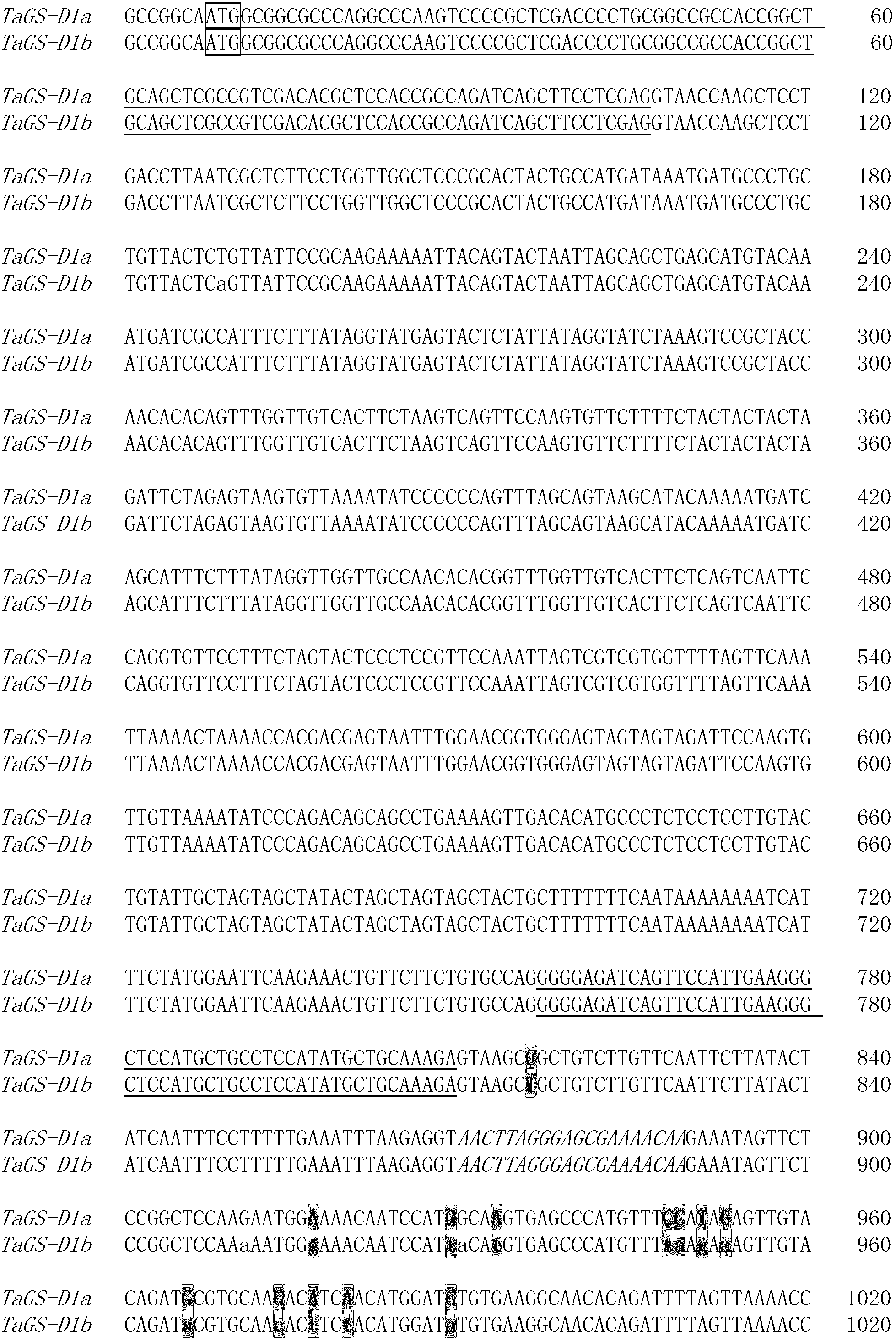
The invention discloses a primer pair for assaying the thousand-grain weight of wheat and a related molecular marker. The specific primer pair disclosed by the invention consists of a single-stranded DNA fragment shown in a sequence 3 of a sequence table and a single-stranded DNA fragment shown in a sequence 4 of the sequence table. The invention discloses allelic variation sequences, namely TaGS-D1a and TaGS-D1b, of an ordinary wheat gene TaGS and provides functional markers for assaying the allelic variation of the TaGS-D1a and the TaGS-D1b and the relationship between the functional markers and the thousand-grain weight of the wheat. Through applying the functional markers provided by the invention to molecular-marker-assisted selection, wheat varieties (materials) with higher thousand-grain weight can be quickly screened out, and thus, the pace for breeding new high-yielding wheat varieties is accelerated. The primer pair and the related molecular marker have important theoretical significance and economic value in the molecular-marker-assisted selection of the high-yielding wheat varieties.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Rapid breeding method for walnut improved varieties
InactiveCN103518543AAccelerate the pace of breedingConducive to the development of planting industryHorticultureWalnut NutRootstock
The invention relates to a walnut tree breeding method and provides a rapid breeding method for walnut improved varieties. The method comprises the processes of rootstock breeding, improved-variety scion breeding, grafting and field management after grafting. The rootstock breeding process includes that soil deep ploughing is carried out in winter in the current year, bedding and seeding are carried out after unfreezing in spring in the next year, and a walnut tree seedling is cultivated. Compared with a traditional grafting method, the rapid breeding method is characterized in that 1) when improved-variety seed trees or cutting orchard young sprouts grow to 30-40cm, 3-4 buds are reserved, pinching is carried out, and thin and weak buds on base portions of branches are removed in time after pinching and sprouting; 2) the grafting is carried out when the thickness of the walnut tree seedling 20cm away from the ground reaches more than 0.7cm. According to the rapid breeding method for the walnut improved varieties, new breakthroughs of current-year seeding, current-year grafting and current-year transplantation of walnut breeding are achieved, transplantation and garden building are higher than common grafting and breeding than 1-2 years, the problem of overhigh production cost of walnut tree planting is resolved, the step of walnut variety improving can be quickened, economic benefits are produced as soon as possible, and industrialized development of walnut planting is facilitated.
Owner:河南恒盈懿丰农牧有限公司
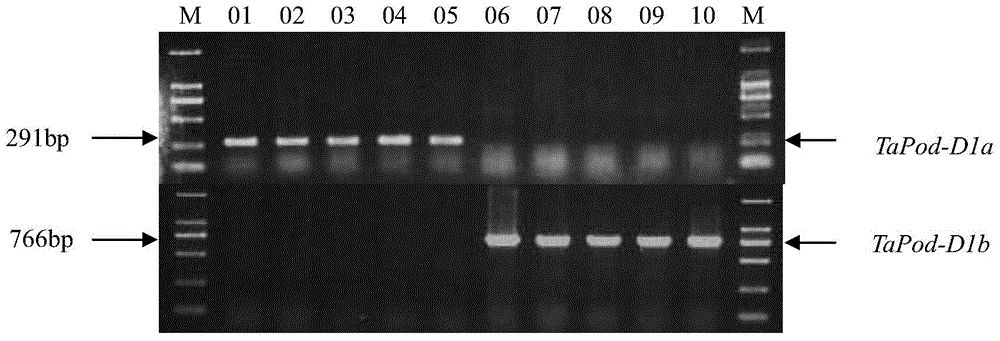
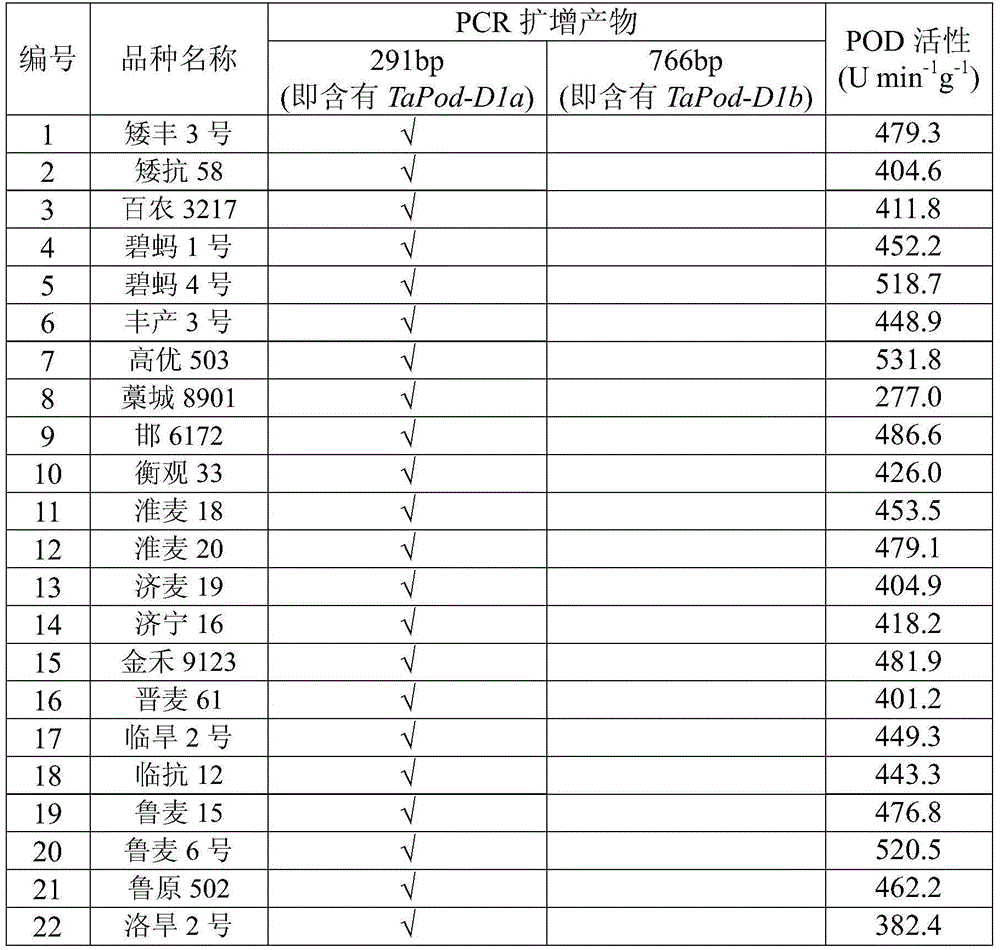
Molecular marker used for identifying POD (peroxidase) activity of wheat grain and application of molecular marker
ActiveCN104561299AHigh POD activityAccelerate the pace of breedingMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant cultivationAgricultural sciencePeroxidase
The invention discloses a molecular marker used for identifying POD (peroxidase) activity of a wheat grain and an application of the molecular marker. The molecular marker comprises primer pairs shown in (1) and (2) as follows: (1) represents a primer pair 1 comprising single-chain DNA shown in SEQ ID No.1 and single-chain DNA shown in SEQ ID No.2; (2) represents a primer pair 2 comprising single-chain DNA shown in a SEQ ID No.3 and single-chain DNA shown in SEQ ID NO.4. As is proven by an experiment, the molecular marker can be used for quickly identifying TaPod-D1a and TaPod-D1b allelic variations and correlation between TaPod-D1a and TaPod-D1b allelic variations and POD activity of wheat, a wheat variety with relatively high POD activity is screened out, the cultivation speed of the new high-quality wheat variety is increased, and the molecular marker has great theoretical significance and economical value in assisting in selection of the wheat variety with high POD activity.
Owner:XINJIANG AGRI UNIV +1
Molecular marker and specific primer for identifying wheat grain germination traits and application thereof
ActiveCN105861667ALow germination indexEar germination resistance is goodMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceTriticeae
The invention discloses a molecular marker and a specific primer for identifying wheat grain germination traits and application thereof. The invention provides a specific primer pair. The specific primer pair comprises two primers; amplification products comprise specific DNA molecules; the specific DNA molecules are target sequences of a primer F and a primer R in a wheat genome; the primer F is a single-chain DNA molecule shown as a sequence 3 of a sequence table; the primer R is a single-chain DNA molecule shown as a sequence 4 of the sequence table. The invention also provides a molecular marker related to a wheat germination index; the molecular marker is a DNA fragment prepared by taking the genome DNA of the to-be-detected wheat as a template and amplifying by using the specific primers. The molecular marker and the specific primer have important theoretical significance and economic value for assistant selection of wheat variety with preharvest sprouting resistance through the molecular marker.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for obtaining haploid regenerated plant by eggplant anther culturing
InactiveCN104041415AReduce browningInduction frequency is highHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureCell buddingAgriculture
Owner:NANJING INST OF VEGETABLE SCI
Walnut planting method
InactiveCN104737824AAccelerate the pace of breedingImprove qualityGraftingSeed and root treatmentEconomic benefitsGrafting
The invention discloses a walnut planting method. The method mainly comprises the following steps of germination accelerating and breeding-grafting-fertilizer and water managing-field managing. According to the walnut planting method, walnut fine seeds are rapidly bred, the new breakthroughs of the walnut breeding of current year seeding, current year grafting and current year outplanting are achieved. The outplanting and the field establishing are one to two years earlier than normal grafting and breeding, the problem that former walnut-trees are high in planting and producing cost is solved, the pace of walnut improving planting is accelerated, the planted walnut is high in quality, the yield is increased, and the economic benefit is improved.
Owner:重庆市丰都县三耀农业综合开发股份合作社
Culture medium prescription of regenerated plant from isolated microspore of brassica
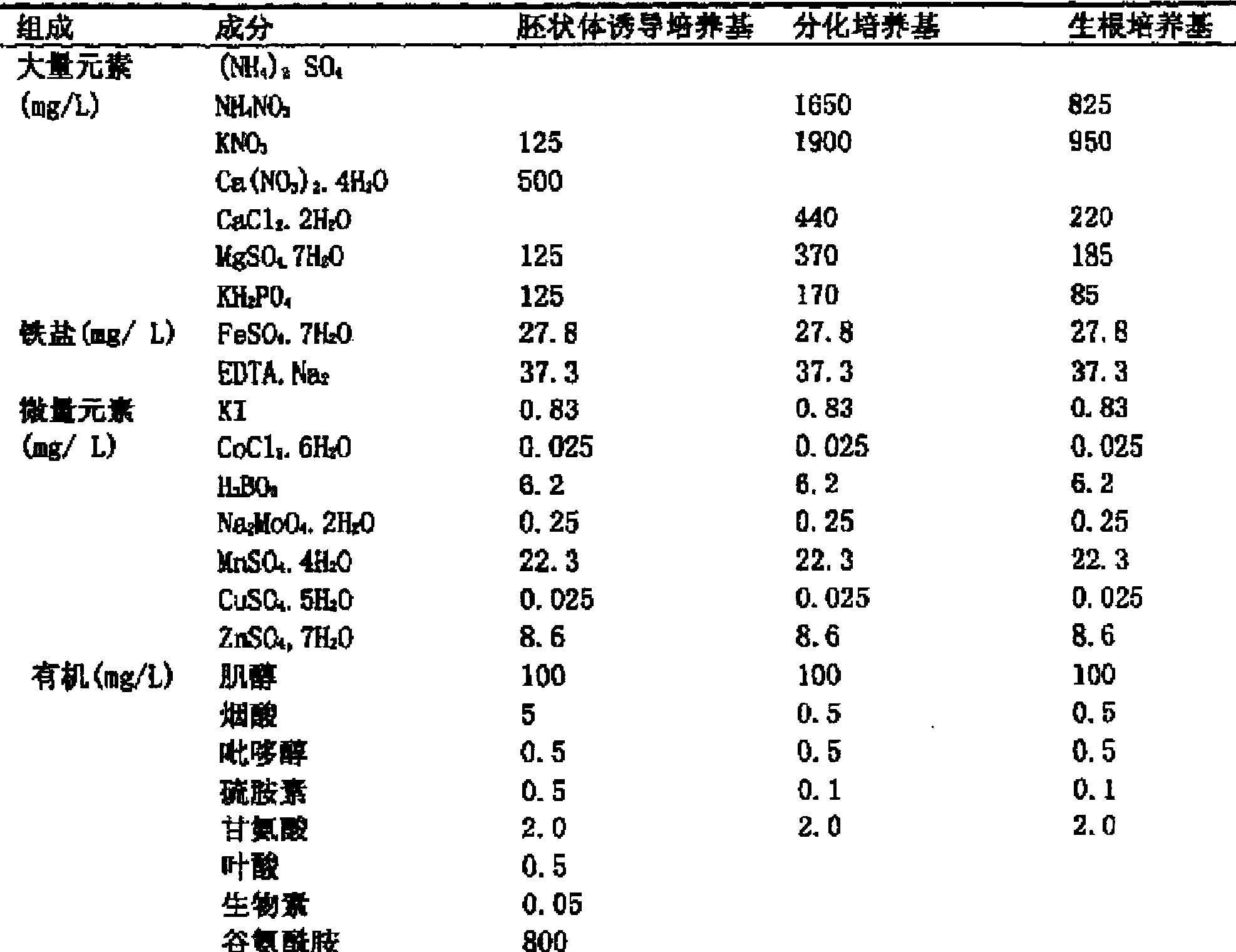
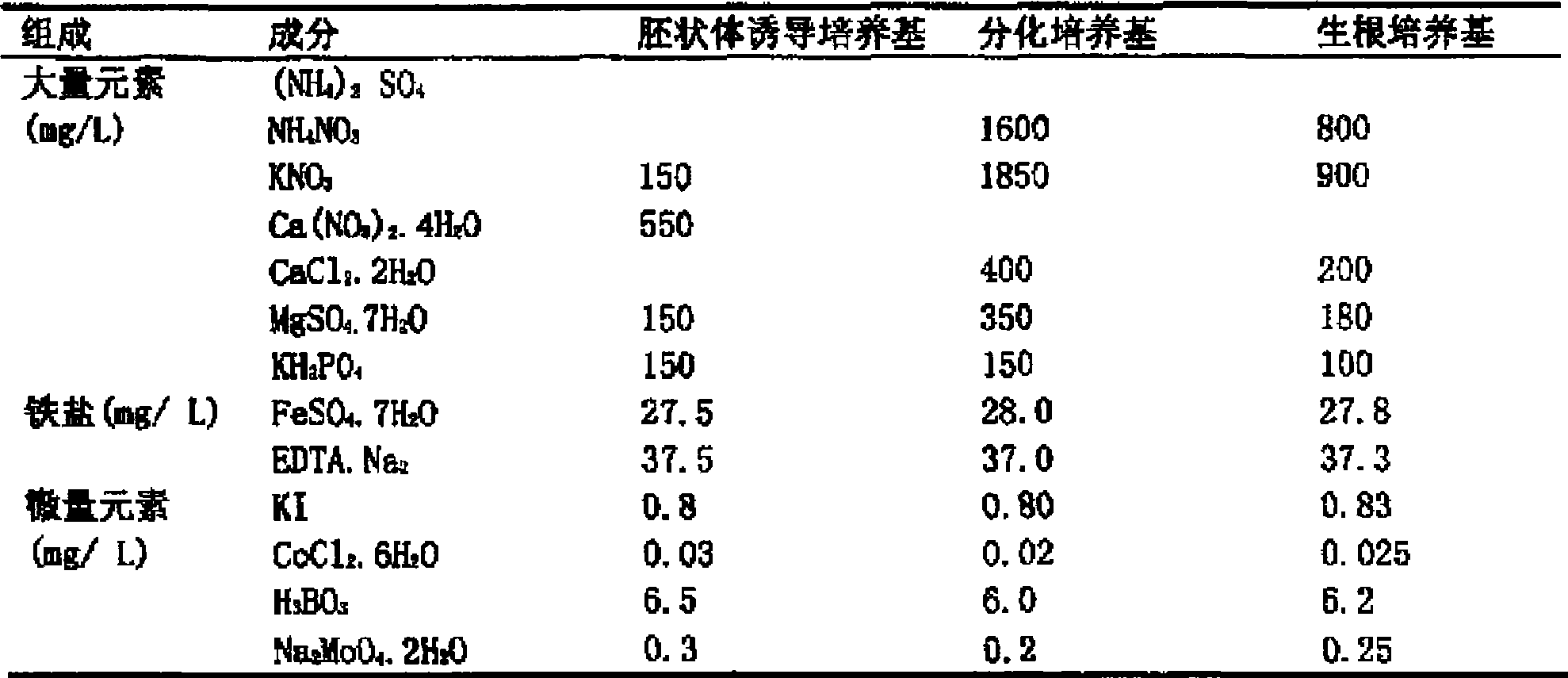
InactiveCN101433184AWide adaptabilityRich breeding resourcesPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsSporeBrassica
The invention provides a culture medium formulation for regenerated plantlets of Brassica isolated microspores, which relates to improvement of a culture medium formulation for regenerated plantlets of Brassica microspores as horticultural crops, and belongs to the field of bioengineering. The invention provides the culture medium formulation for regenerated plantlets of Brassica isolated microspores, which is high in induced embryo formation rate and differentiation rate. A culture medium of the invention comprises an embryoid induction culture medium, a differentiation culture medium and a rooting culture medium, wherein the embryoid induction culture medium, the differentiation culture medium and the rooting culture medium all comprise macroelements, trace elements and organic elements. The formulation has the advantages of providing a large number of new genotype pure lines for breeding and greatly enriching breeding resources of Brassica.
Owner:刘祥军
Molecular marker for identifying peroxidase activity of wheat grains and application of molecular marker
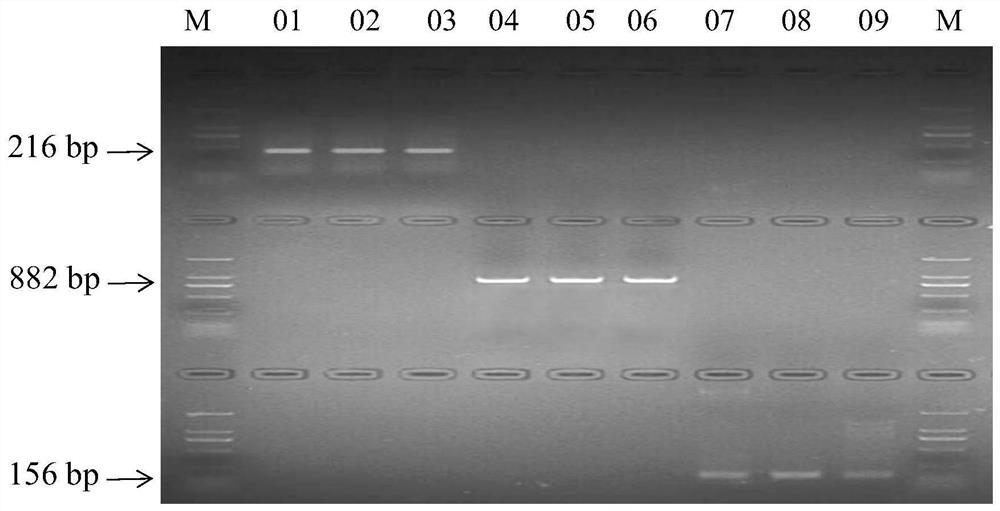
ActiveCN111733281AHigh POD activityAccelerate the pace of breedingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationWheat peroxidaseSingle strand
The invention discloses a molecular marker for identifying the peroxidase activity of wheat grains and an application of the molecular marker. The invention provides a complete set of primers for identifying the peroxidase activity of wheat. The complete set of primers consists of a primer pair 1, a primer pair 2 and a primer pair 3, wherein the primer pair 1 is composed of single-stranded DNA asshown in a sequence 1 and a sequence 2; the primer pair 2 is composed of single-stranded DNA as shown in a sequence 3 and a sequence 4; and the primer pair 3 is composed of single-stranded DNA as shown in a sequence 5 and a sequence 6. The molecular marker disclosed by the invention can be used for rapidly identifying allelic variation of TaPod-A3a, TaPod-A3b and TaPod-A3c and a correlation relationship between the allelic variation and the POD activity of the wheat, and screening out a wheat variety with relatively high POD activity, so that the breeding pace of a new high-quality wheat variety is accelerated, and the molecular marker has important theoretical significance and economic value in molecular marker-assisted selection of wheat varieties with high POD activity.
Owner:XINJIANG AGRI UNIV +1
Two-generation in one year reproduction method for konjac cross breeding
InactiveCN102763597AAccelerated selection of generationsHigh reproductive coefficientHorticulture methodsPlant tissue culturePlant tissueCross breeding
The invention relates to a two-generation in one year reproduction method for konjac cross breeding and belongs to the technical field of agricultural breeding. The method is characterized in that when 1 / 3-2 / 3 of the berry peel outside cross breeding seeds formed in the current year through konjac conventional cross breeding is turned from green into reddish orange or blue, the berry peel is stripped to obtain the seeds, the seeds are cultivated through an existing plant tissue cultivation method, seedlings with roots are planted on a seedbed in the same year, the seedlings grow more than three months, and single plant screening is performed. The seeds obtained by the method are induced and cultivated, seedling emergence percentage of the seeds reaches 65%-90%, and the seedling emergence percentage of mature seeds through induction and cultivation is 0. The two-generation in one year reproduction method for the konjac cross breeding achieves the purpose of two-generation in one year reproduction, improves reproduction coefficient, accelerates breeding step, and improves breeding efficiency.
Owner:云南省农业科学院生物技术与种质资源研究所 +2
Method for culturing cauliflower regenerative tree by free microspore culture technology
InactiveCN1552198ARich breeding resourcesAccelerate the pace of breedingPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsEcologySucrose
A method for culturing the regenerative plant of couliflower by free microspore culturing technique includes such steps as culturing until the microspore is generated, culturing at 25 deg.C and under 4000 LX for illumination (12-16 hr per day) until it becomes green, and culturing on non-hormone solid culture medium MS containing cane sugar (3%) until young seedling is grown up. It features that said solid culture medium contains also three auxins: kinin, 6-benzylpurine and naphthalene acetic acid. Its advantages are broad breeding resources and short breeding time.
Owner:TIANJIN RES INST OF VEGETABLE
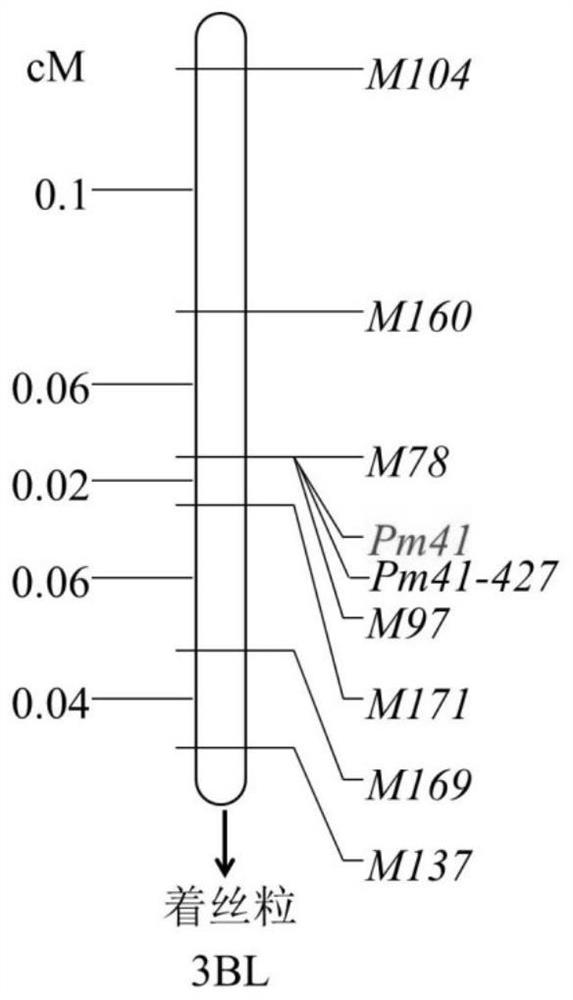
Functional molecular marker of triticum aestivum L. anti-blumeria graminis relevant gene Pm41, and application of functional molecular marker
ActiveCN112176083AAccelerate the pace of breedingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSingle strandA-DNA
The invention discloses a functional molecular marker of a triticum aestivum L. anti-blumeria graminis relevant gene Pm41, and application of the functional molecular marker. The genome DNA of triticum aestivum L. is taken as a template, and a DNA fragment obtained by amplification of a primer pair formed by a primer F and a primer R is a molecular marker Pm41-427. The primer F is a single-stranded DNA molecule disclosed by a sequence 8 of a sequence table, and the primer R is a single-stranded DNA molecule disclosed by a sequence 9 of the sequence table. When the molecular marker Pm41-427 provided by the invention is applied, a triticum aestivum L. material with blumeria graminis resistance can be quickly screened so as to quicken a breeding pace of a new variety of the triticum aestivumL.. The functional molecular marker has an important theoretical meaning and economic value.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
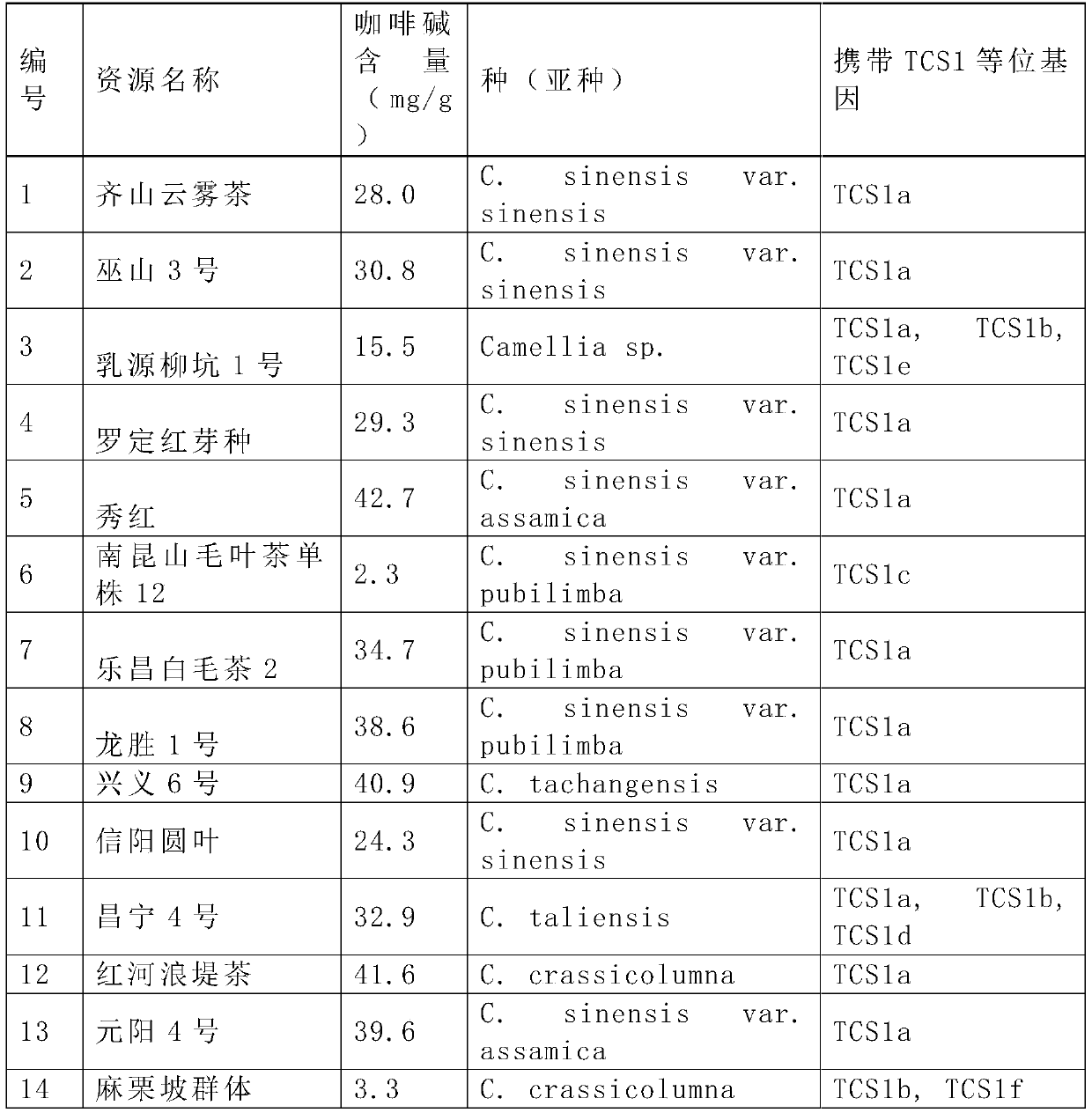
Specific primer pair, allele and molecular marker for screening thea section with low caffeine trait and screening method
ActiveCN105505957AQuick filterAccelerate the pace of breedingMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationPhenotypic traitScreening method
The present invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and relates to a specific primer pair, an allele and a molecular marker for screening thea section with low caffeine trait and a screening method. The present invention discloses allelic variation TCS1a, TCS1b, TCS1c, TCS1d, TCS1e and TCS1f sequence fragments of thea section TCS1 gene, and provides a functional marker for identification of low caffeine thea section, and the functional marker is used for molecular marker-assisted selection for quickly screening a low caffeine thea section material so as to speed up the pace of breeding of low caffeine tea tree varieties. The molecular marker-assisted selection of the low caffeine tea tree varieties has important theoretical significance and economic value.
Owner:TEA RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for breeding high-quality wheat
InactiveCN102440181AOvercome the phenomenon that emasculation is difficult to completeAccelerate the pace of breedingPlant genotype modificationDiseaseF1 generation
The invention relates to a method for breeding high-quality wheat. The method comprises the following steps of: hybridizing by selecting Zhengmai 005 as a female parent and Aizao 781 as a male parent, screening later generations of the Zhengmai 005 and the Aizao 781 to obtain Xufeng 998, and hybridizing by selecting Meisheng 0308 as a female parent and the Xufeng 998 as a male parent to obtain F1generation; back-crossing the F1 generation of plants and the wheat material, namely the Xufeng 998, and screening plants which are short in stalk, premature, more in tiller and good in disease resistance from one half of sterile plants; carrying out back-crossing for many times of the screened sterile plants and the wheat material, namely the Xufeng 998, and obtaining the screened wheat, namely the high-quality wheat. The bred high-quality wheat disclosed by the invention has the advantages of being hard in grain cutin, short in stalk, premature, more in tiller and good in disease resistanceand stress resistance.
Owner:河南许丰种业有限公司
Method for identifying salt-resistant capability of cotton by using death rate of leaf lower epidermic cells
InactiveCN102879341ASpeed up breedingImprove identification efficiencyColor/spectral properties measurementsDead cellCuticle
The invention relates to a method for identifying salt-resistant capability of cotton by using death rate of leaf lower epidermic cells. The method comprises the steps of selecting leaves with identical thickness in a cotyledon stage of the cotton, and tearing the lower epidermis from the leaves gently; putting the prepared lower epidermis in a NaCl solution with a concentration of 3.5 M, and treating for 10-15 min; staining the epidermis treated by the salt solution for 5-10 min by using a 0.03-0.05% neutral red solution; immersing the intravitally stained epidermis in tap-water with a pH value a little higher than 7 for 3-5 min; observing death situation of the epidermic cells under an optical microscope; recording the deaths of the cells in the same area according to a principle that living cells are stained into cherry-red color while the dead cells cannot stained; and determining the salt-resistant capability of the cotton through the salt-resistant capability of leaf lower epidermic cells. The method can determine genotype salt-resistant capability rapidly and accurately, is labor-saving and time-saving time, is not influenced by seasons and environment, and increases identification efficiency.
Owner:COASTAL AGRI RES INST HEBEI ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
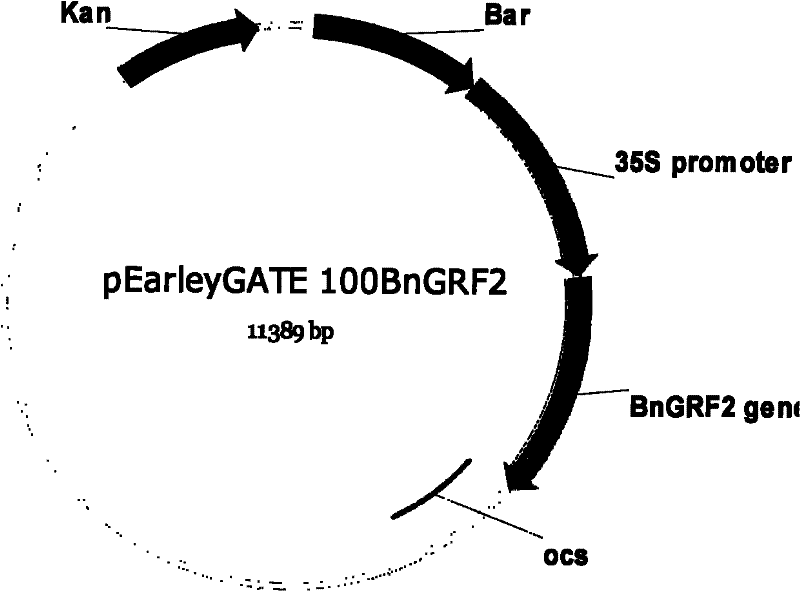
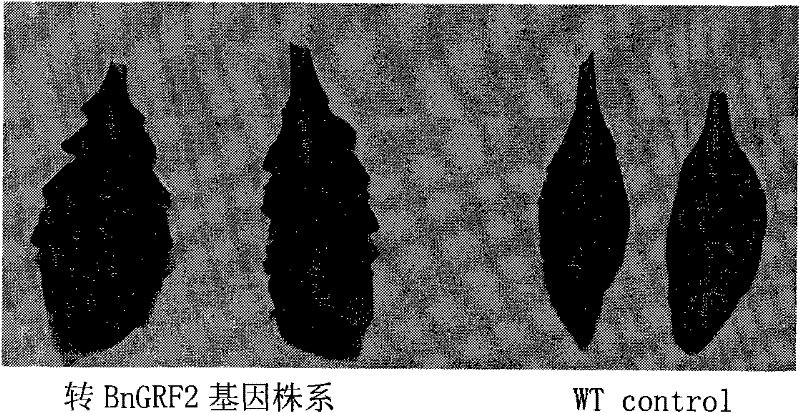
Rape growth regulator gene grf2 and its application
InactiveCN102268441AAccelerate the pace of breedingHigh oil contentPlant peptidesFermentationGrowth Factor GeneNucleotide
The invention discloses a brassica napobrassica growth regulatory factor gene GRF2 and an application thereof. A base sequence of the gene is a nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ ID NO:1; or a gene sequence of another crop, wherein the gene sequence has no less than 70% homology with that represented by SEQ ID NO:1; or a mutant allele or a derivative obtained after one or more nucleotides areprocessed through addition, substitution, insertion or deletion. As a result of researches, the expression level of the gene in brassica napobrassica high-oil parents and high-oil mixture crops is higher than that in low-oil parents and low-oil mixture crops. A transgene result obtained by using arabidopsis thaliana as an acceptor verified that, with the over-expression of the gene, arabidopsis thaliana oil content is improved, and a 1000-seed weight of arabidopsis thaliana is increased. The invention also provides an application of brassica napobrassica growth regulatory factor gene BnGRF2 in improving the 1000-seed weight and oil content of plants such as arabidopsis thaliana. Therefore, the gene has good application prospect in oil-yield seed breeding of brassica napobrassica and otheroil crops.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for appraising salinity tolerance potential by using stress resistance of isolated leaves
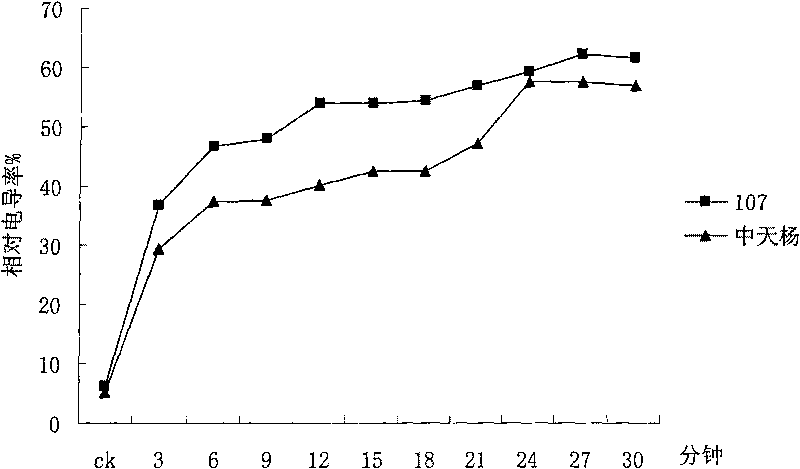
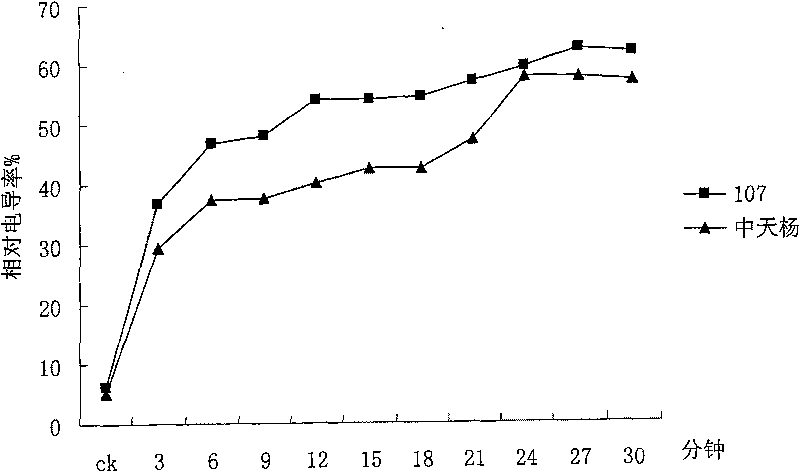
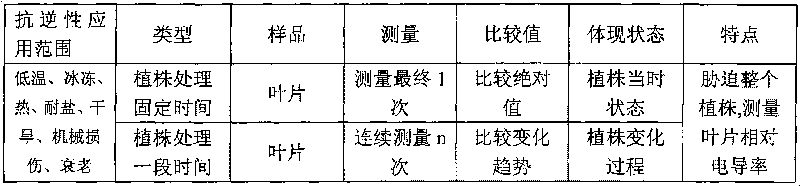
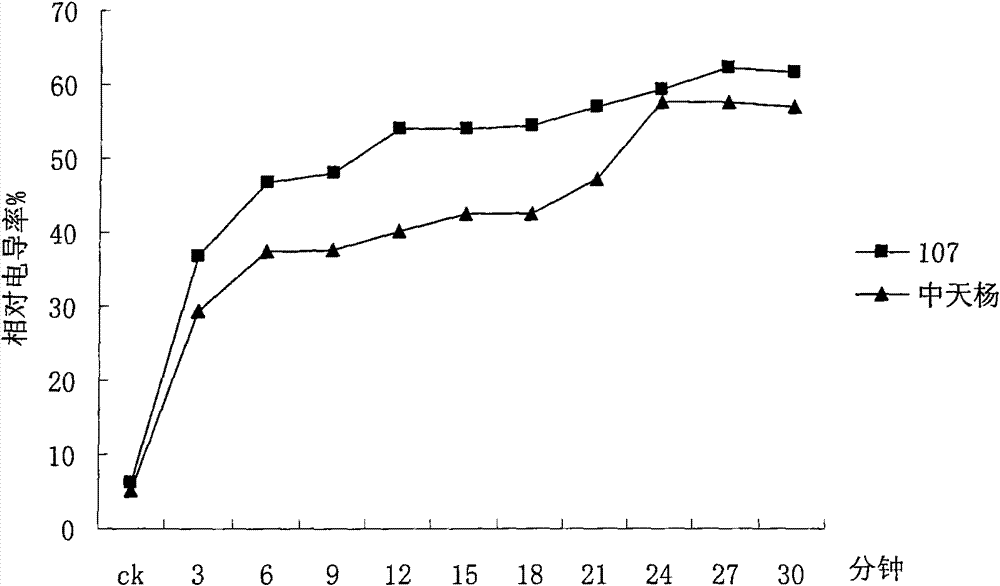
InactiveCN101706465ASmall scaleImprove screening efficiencyMaterial resistanceMembrane permeabilityLeaf cell
The invention discloses a method for appraising salinity tolerance potential by using stress resistance of isolated leaves. In the method, the leaves directly absorb NaCl, membrane permeability of leaf cells can be destroyed, and the magnitude of relative conductivity can precisely reflect the salinity tolerance of different poplar leaf cells. The membranes of poplar leaf cells are destroyed in high-salt condition, destruction degrees of cell membranes with different salinity tolerance are different, the more serious the destruction degree, the more the exudate in the cells; the destruction degrees of leaf cell membranes are judged on the basis of the relative conductivity of the isolated leaves in saline solution, thus judging genetypes of poplar with different salinity tolerance. The relative conductivity of the isolated leaves which are processed a certain time in high saline solution can rapidly and precisely reflect the salinity tolerance of the genetypes. By using the appraising technology, the salinity tolerance potential of the genetypes can be precisely judged by processing the leaves under certain salt concentration for 6-12min, thus saving labor and time, and having extremely high working efficiency and very wide application prospect.
Owner:TIANJIN CITY AGRI BIO TECH RES CENT
Scientific and effective peanut planting method
InactiveCN106489639AAccelerate the pace of breedingImprove qualitySeed and root treatmentCultivating equipmentsComing outEconomic benefits
The invention discloses a scientific and effective peanut planting method. The method comprises the steps of accelerating germination and breeding, grafting, fertilizer and moisture management and field management. According to the method, an improved peanut variety is bred quickly, new breakthrough of seeding in the same year, grafting in the same year and outplanting in the same year in peanut reproduction is achieved, seedlings come out of the nursery and a garden is established 1-2 years ahead of conventional grafting reproduction, the problem that a conventional peanut tree planting production cost is too high is solved, the pace of peanut variety improvement can be accelerated, planted peanuts are high in quality, the yield is increased, and the economic benefit is improved.
Owner:三台县建设镇大油家沟核桃种植专业合作社
Functional molecular marker of related genes of cell nuclear male sterility of peppers and application thereof
ActiveCN108148920AQuick filterAccelerate the pace of breedingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceSingle strand dna
The invention discloses a functional molecular marker of related genes of cell nuclear male sterility of peppers and application thereof. A specific primer pair provided by the invention consists of two primers for amplifying specific DNA fragments; the specific DNA fragments have target sequences of the primer pairs formed by primers InDel-12F and primers InDel-12R in a pepper genome; the primersInDel-12F is single-chain DNA molecules shown in a sequence 3 of a sequence table, and the primers InDel-12R is single-chain DNA molecules shown in a sequence 4 of the sequence table. By applicationof the molecular marker InDel-12 provided by the invention, the varieties of pepper with cell nuclear male sterility can be rapidly screened. The functional molecular marker and the application have important theoretical significance and economic value.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Application of hydrogen ion transport inorganic pyrophosphatase gene expression difference on salt tolerance of tomatoes
InactiveCN104450906ASensitive detectionSmall scaleMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyDistilled water
The invention discloses application of hydrogen ion transport inorganic pyrophosphatase gene expression difference on salt tolerance of tomatoes. The application method comprises the following steps: taking 5-6 tomato seedlings as materials, and taking the first mature leaf of each tomato plant; washing the detached leaves three times by using distilled water, washing once by using deionized water, shearing the leaves to be rectangles by using a shear, washing three times by using deionized water, and absorbing the moisture by using absorbent paper; and selecting chemically pure 5 percent of NaCl, and treating for 6 minutes. The RNA of the detached leaves subjected to salt stress within 2 minutes is extracted, the gene expression amount of tomato genotype H+-PPase with high salt tolerance is enhanced by virtue of real-time quantitative PCR, and the expression amount of the tomato genotype with low salt tolerance is extremely small. According to the gene expression difference of H+-PPase, the salt tolerance of tomatoes is compared. According to the method, the salt tolerance potential is indicated on the gene level, and the method has important theoretical and practical significances on cultivation tomatoes of which the stress resistance is improved and other new varieties of plants.
Owner:TIANJIN CITY AGRI BIO TECH RES CENT
Method of quickly stabilizing spinach strong female line parent and improving hybrid seed purity
ActiveCN106718844ARapid Breeding PaceFast and stable purificationPlant genotype modificationAnimal scienceHybrid seed
The invention provides a method of quickly stabilizing a spinach strong female line parent and improving hybrid seed purity. Particularly, according to the method, a female line material is stabilized and purified quickly in a short period by using the characteristic that a strong female line is sensitive to a high temperature; a seed breeding course is accelerated; a bottleneck problem in spinach seed breeding is quickly solved; the hybrid seed purity is improved; the seed breeding pace of spinach hybrid seeds is quickened; and a blank in the existing spinach breeding technology is filled in.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for auxiliary identification of drought resistance of wheat to be detected and special molecular marker thereof
ActiveCN113652423ADrought resistantQuick filterMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention discloses a method for auxiliary identification of drought resistance of wheat to be detected and a special molecular marker thereof. The method comprises the following steps: by taking genome DNA of wheat to be detected as a template, carrying out PCR amplification by adopting a primer pair consisting of a primer F and a primer R to obtain a DNA fragment; the DNA fragment being the molecular marker related to wheat drought resistance. The molecular marker specifically can be a DNA segment A or a DNA segment B. The nucleotide sequences of the primer F, the primer R, the DNA segment A and the DNA segment B are shown as SEQ ID NO: 12, SEQ ID NO: 13, SEQ ID NO: 14 and SEQ ID NO: 15 in sequence. The wheat variety of which the genome contains the DNA segment B and does not contain the DNA segment A has drought resistance. By applying the molecular marker provided by the invention, the wheat variety with drought resistance can be quickly screened out, so that the breeding pace of the wheat variety is accelerated. The method has an important application value.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
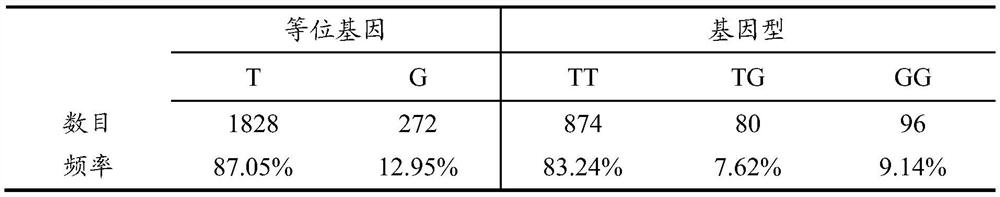
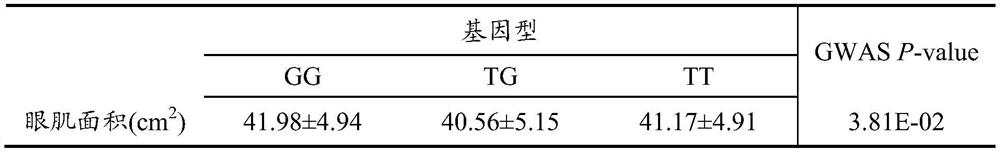
SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) marker for detecting pig eye muscle area and application thereof
ActiveCN112941198ASpeed up breedingAccelerate the pace of breedingFood processingMicrobiological testing/measurementLarge eyesPhysiology
The invention discloses an SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) marker related to pig eye muscle area as well as a detection method and application thereof, the SNP marker is located at the 134th, 993rd and 242nd positions of chromosome 4 of a reference sequence of version 10.2 of international pig genome and has T / G polymorphism; compared with pigs with genotypes of TT and TG, pigs with genotypes of GG of the SNP marker have a larger eye muscle area. The determination of the SNP marker related to the pig eye muscle area provided by the invention can assist in selecting pig dominant varieties with large eye muscle areas, shortens the breeding period, and improves the breeding efficiency and the breeding precision.
Owner:AGRI GENOME INST OF SHENZHEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
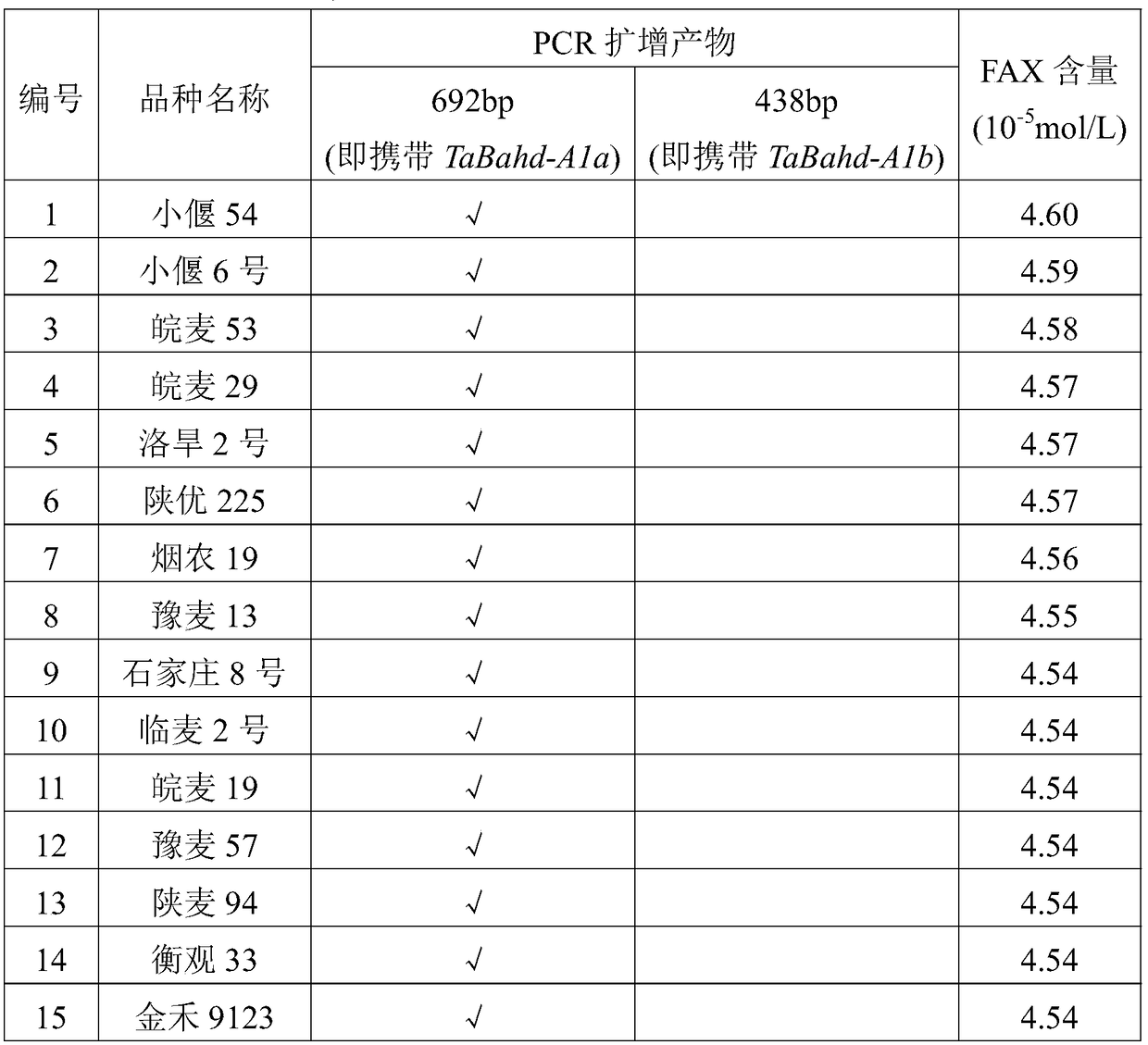
Molecular marker relevant to wheat grain ferulic acid arabiaxylan (FAX) content
ActiveCN108486274AHigh FAX contentAccelerate the pace of breedingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceArabinoxylan
The invention discloses a molecular marker relevant to the wheat grain ferulic acid arabiaxylan (FAX) content. The invention provides a set primer for identifying the content of the wheat grain ferulic acid arabiaxylan content. The molecular marker consists of a primer pair 1 and a primer pair 2, wherein the primer pair 1 consists of single-chain DNA shown as SEQ ID No. 1 and SEQ ID No. 2; the primer pair 2 consists of single-chain DNA shown as SEQ ID No. 3 and SEQ ID No. 4. The molecular marker can be used for fast identifying TaBahd-A1a and TaBahd-A1b allelic variation and the relevant relationship between the allelic variation and the wheat FAX content; the wheat variety with high FAX content is screened out; the culture step of the new variety of the high-quality wheat is accelerated;in addition, the important theoretical significance and economic values are realized on the auxiliary selection of high-FAX-content wheat variety by using the molecular marker.
Owner:XINJIANG AGRI UNIV +1
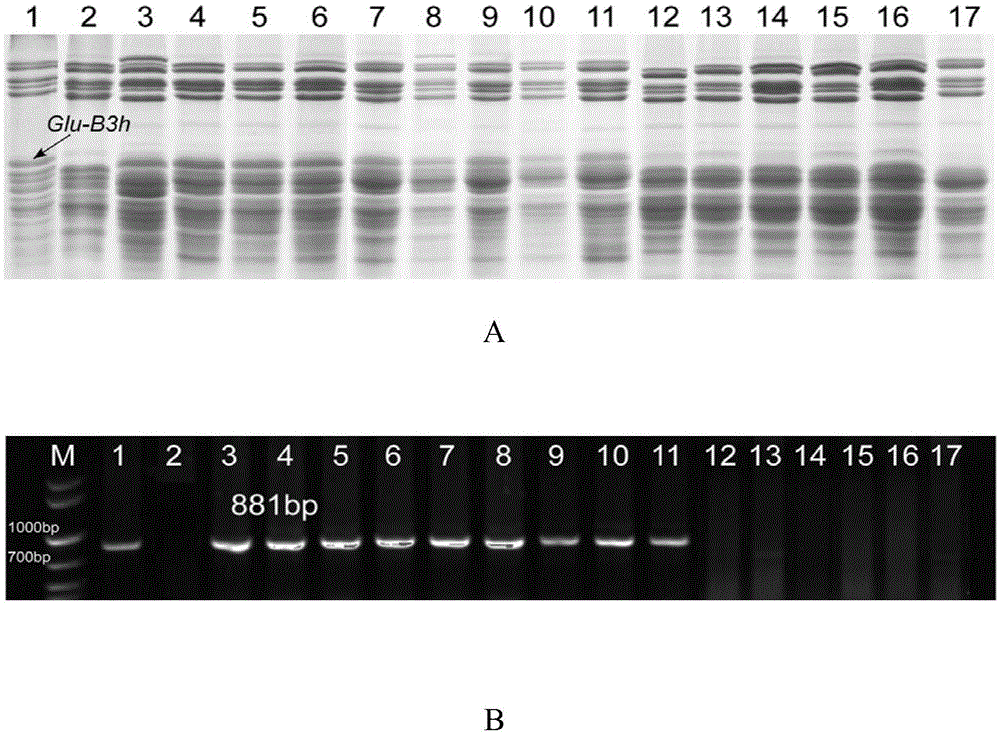
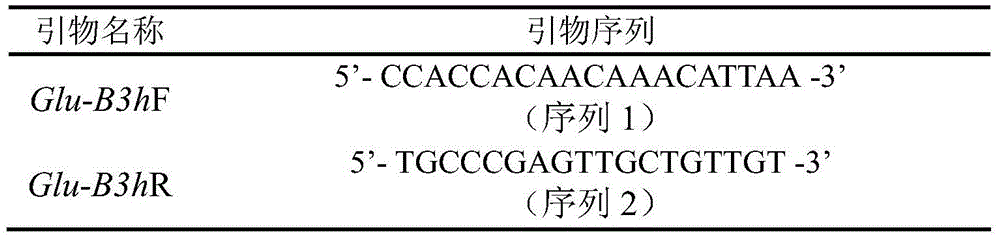
Molecular marker and application of common wheat low-molecular-weight glutelin Glu-B3h gene
ActiveCN105567824AImprove qualityAccelerate the pace of breedingMicrobiological testing/measurementAgricultural scienceSingle strand dna
The invention discloses a molecular marker and application of a common wheat low-molecular-weight glutelin Glu-B3h gene. The molecular marker is composed of single-chain DNA molecules as shown in sequence 1 and single-chain DNA molecules as shown in sequence 2. Experiments prove that by means of the molecular marker, wheat species with the Glu-B3h gene can be fast screened out, correspondingly, the flour quality will be improved, and therefore the breeding pace of new wheat species containing high-quality genes is accelerated.
Owner:CAPITAL NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for evaluating back fat thickness and eye muscle area of pig and application thereof
ActiveCN112941199AIncrease breeding speedSpeed upFood processingMicrobiological testing/measurementEye musclesBreed
The invention discloses an SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) marker for evaluating the back fat thickness and the eye muscle area of a pig as well as an recognition method and application of the SNP marker, and the SNP marker is located on an ENSSSCG00000004081 gene, is located at reference sequences Chromosome1: 16, 077 and 935 of an international pig genome version 10.2, and has T / C polymorphism. The determination of the SNP marker related to evaluation of pig backfat thickness and 100kg ocular muscle area can assist in selection of pig dominant varieties with low backfat thickness and high ocular muscle area, shortens the breeding period, and improves the breeding efficiency and breeding precision.
Owner:AGRI GENOMICS INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
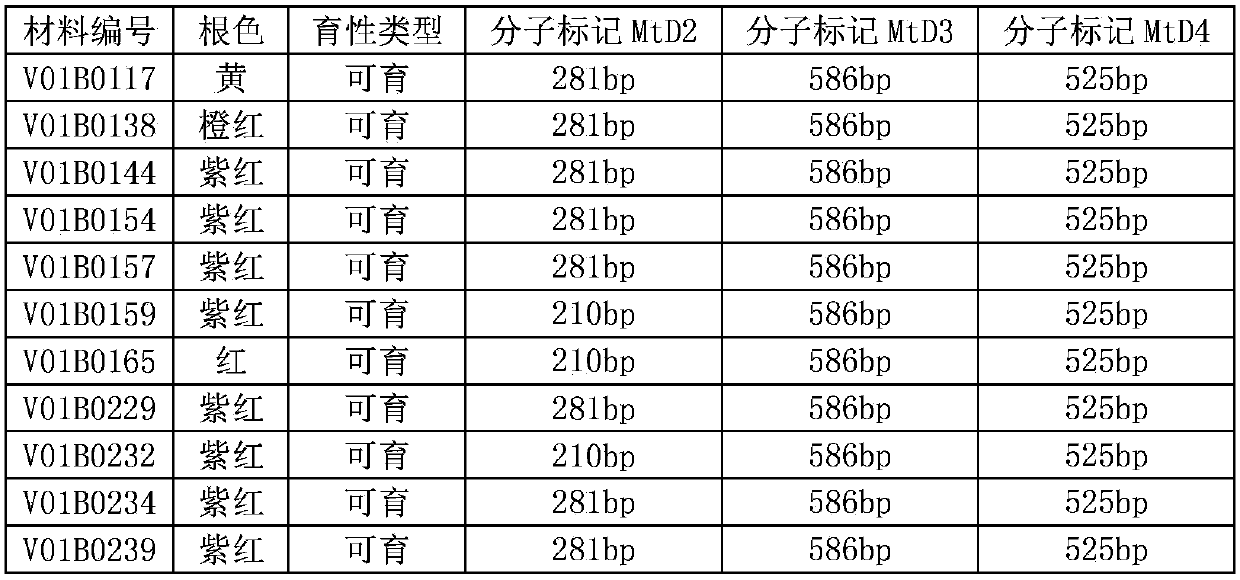
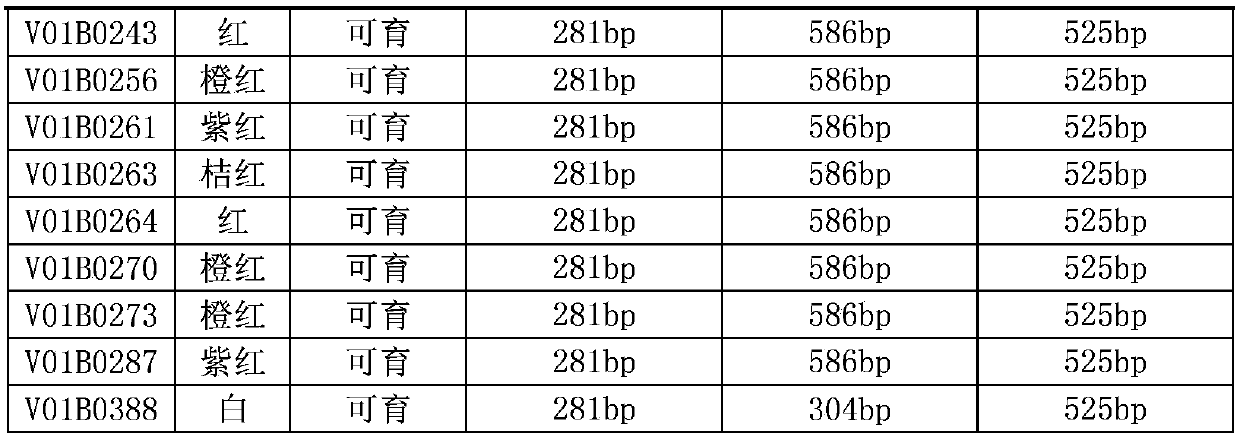
Application of molecular marker MtD4 in identifying carrot petal male sterility
ActiveCN109628634AQuick filterAccelerate the pace of breedingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceNucleotide
The invention discloses application of a molecular marker MtD4 in identifying carrot petal male sterility. Genomic DNA of a carrot to be tested is used as a template, and a primer pair consisting of aprimer F and a primer R is used for PCR amplification to obtain a DNA fragment. The DNA fragment is the molecular marker MtD4 related to the carrot petal male sterility. The nucleotide sequences of the primer F and the primer R are sequentially shown as the sequence 8 and the sequence 9 in the sequence listing. The molecular marker MtD4 may specifically be a DNA fragment 1 or a DNA fragment 2. The nucleotide sequences of the DNA fragment 1 and the DNA fragment 2 are sequentially shown as the sequence 14 and the sequence 15 in the sequence listing. The carrot variety carrying the DNA fragment1 and not carrying the DNA fragment 2 has the petal male sterility. By using the molecular marker MtD4, the carrot variety with the petal male sterility can be rapidly screened out. The application has important application value.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Scientific effective juglans regia planting method
InactiveCN108293540ASpeed upHigh quality walnutsGraftingCultivating equipmentsFertilizerSite management
The invention discloses a scientific effective juglans regia planting method. The method mainly comprises the following steps of: sprouting and seed breeding, grafting, fertilizer and water managementand field management. Fine seeds of juglans regia are propagated rapidly, so that a new break that seed sowing, grafting and harvest for propagating juglans regia are performed in a same year is achieved, and harvest and garden construction are 1-2 years earlier than conventional grafting propagation; in addition, the problem of too high cost of planting production of juglans regia trees in the past is solved, the pace of seed improvement of juglans regia can be quickened, and the planted juglans regia has good quality, increased yield and improved economic benefits.
Owner:颜家钦
Method for appraising salinity tolerance potential by using stress resistance of isolated leaves
InactiveCN101706465BSmall scaleImprove screening efficiencyMaterial resistanceMembrane permeabilityCell membrane
Owner:TIANJIN CITY AGRI BIO TECH RES CENT
SNP marker related to pig backfat thickness and utilization method thereof
ActiveCN113355427ASpeed up breedingAccelerate the pace of breedingFood processingMicrobiological testing/measurementMolecular breedingReference genome
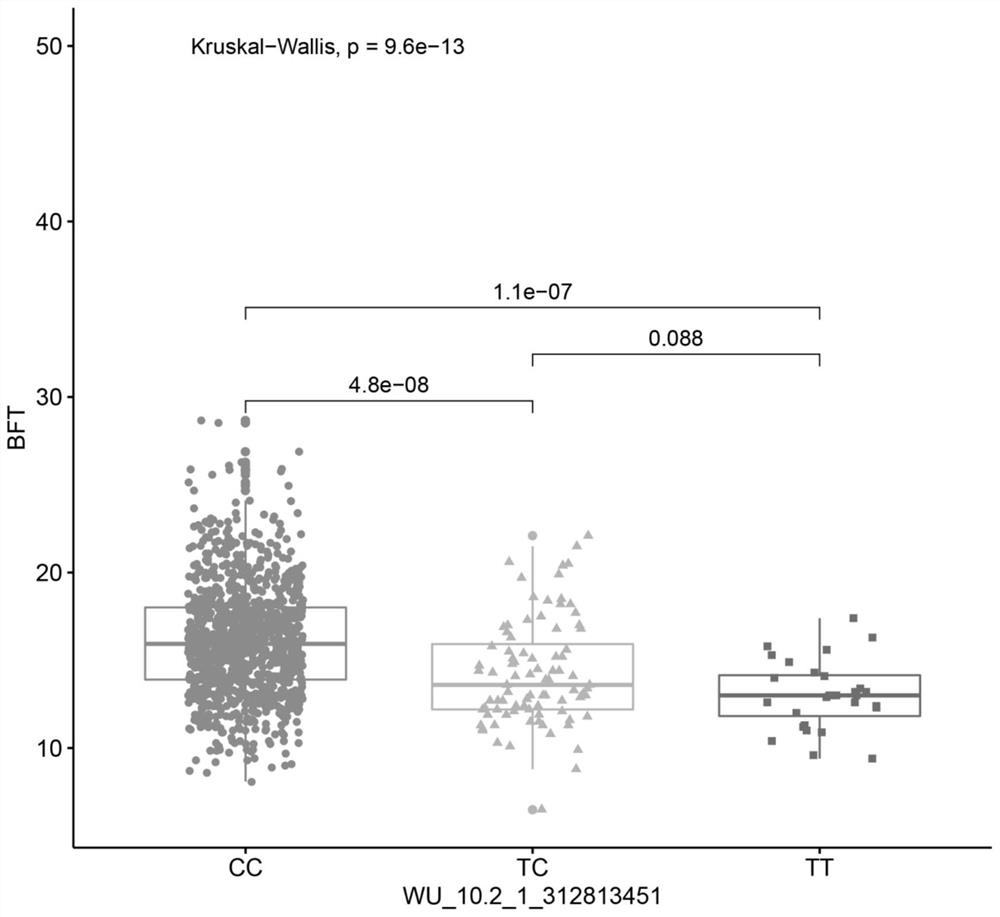
The invention discloses an SNP marker significantly related to pig backfat thickness and a utilization method thereof. The SNP marker is located at 312bp, 813bp and 451bp positions of chromosome No.1 of a pig reference genome Sscrofa10.2 version sequence, and the SNP marker has specific C / T polymorphism; and compared with pigs with genotypes of TC and CC, the pig with the genotype of TT has lower backfat thickness. The SNP marker obviously related to the pig backfat thickness can be used for identifying or assisting in identifying individuals with low pig backfat thickness, molecular markers for assisting breeding are enriched, the breeding speed of good pig breeds is increased, the steps of pig molecular breeding are accelerated, meanwhile, a feasible scheme is provided for breeding of pigs with low backfat thickness, the method is suitable for popularization and application, and the economic benefits of pig production enterprises are improved.
Owner:AGRI GENOMICS INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com