Specific primer pair, allele and molecular marker for screening thea section with low caffeine trait and screening method
A specific primer pair and allele technology, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of long time consumption and low efficiency, and achieve the effect of accelerating the pace of breeding
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Discovery of TCS1 allele differential sequence, primer pair and development of functional marker InDel-TCS1:
[0039] 1. Test materials
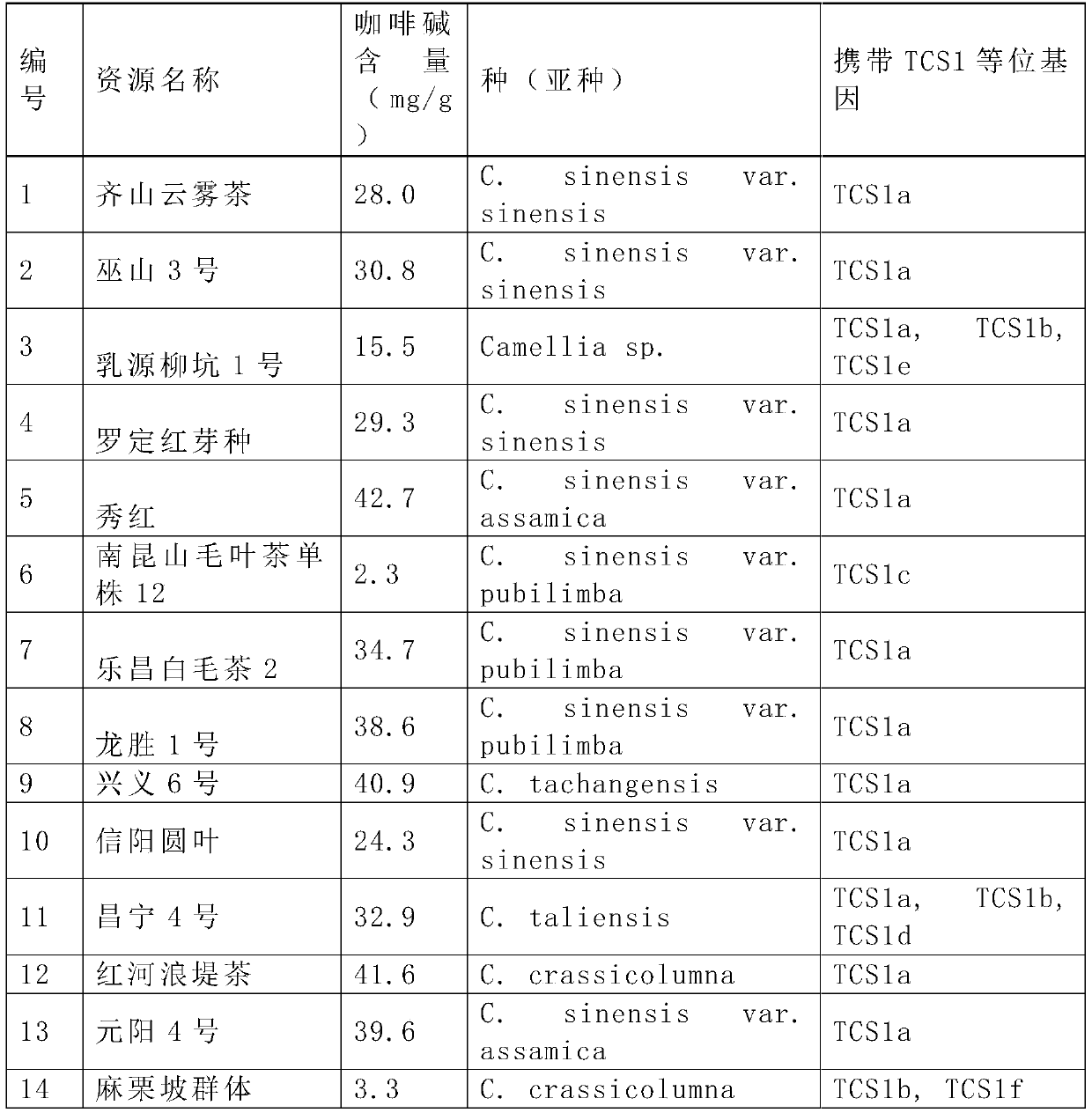
[0040] Select 5 parts of tea (C.sinensisvar.sinensis), 2 parts of Assam tea (C.sinensisvar.assamica), 3 parts of white hair tea (C.sinensisvar.pubilimba), 2 parts of thick shaft tea (C.crassicolumna), 1 15 tea group plant resources with large genetic background differences, including one Dali tea (C.taliensis), one Dachang tea (C.tachangensis) and one unclassified wild tea tree (Camellia sp.), were studied. The specific names are shown in the table 1.
[0041] Table 1 The 15 tea group plant resources studied in this experiment
[0042]
[0043]
[0044] 2. Genomic DNA extraction:
[0045] Take 1g of fresh young shoots, add liquid nitrogen and grind to powder. Put 0.2g of the powder into a 1.5mL centrifuge tube, add 700 μL CTAB extract, mix well, put in a water bath at 65°C for 1 hour, and stir once every 20 minutes. Add an ...
Embodiment 2
[0056]Genotype Analysis of Tea Plant Resources by Functional Marker InDel-TCS1
[0057] 1. Test materials
[0058] The materials studied in this experiment are listed in Table 2, including 10 decaffeinated (caffeine content less than 10 mg / g) and 17 conventional caffeine resources (caffeine content greater than 10 mg / g).
[0059] Table 2 The 10 low caffeine and 17 conventional caffeine resources studied in this experiment
[0060]
[0061]
[0062] 2. Identification of caffeine content in 27 materials
[0063] Caffeine identification method high-performance liquid chromatography is the same as described in Example 1. The results showed that 10 were decaffeinated resources and 17 were regular resources.
[0064] 3. Genotype detection of different tea group plant resources by functional markers
[0065] DNA extraction, PCR amplification system and procedures are the same as in Example 1. Amplified products were separated by 2% agarose gel electrophoresis. Such as f...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com