Method for culturing non-heading Chinese cabbage microspore plantlets
A technique for headed cabbage and microspores is applied in the field of cultivating non-headed cabbage microspore plants, which can solve the problems of cumbersomeness, pollution, and low embryo rate.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] 1. Selection of flower buds: Collect samples from 9 am to 11 am, select flower buds with a ratio of petals to anthers close to 1:1, add a small amount of distilled water and store in a refrigerator at 4°C.
[0031] 2. Cultivate microspore embryos: Put the collected samples into a 2ml centrifuge tube, add 1% sodium hypochlorite directly to disinfect for 10-15 minutes, wash with sterilized water twice, and moisten with NLN-13 for the last time wash. Transfer the cleaned sample to the test tube of the sample grinding machine (Germany LKA control type test tube disperser S025), add a small amount of NLN-13, and grind the sample to make the sample fully ground. Prepare a 50mL centrifuge tube, place a 40μm cell filter plug on top of it to filter, centrifuge, pour off the supernatant, then add NLN-13 to shake well, then centrifuge, pour off the supernatant, leaving a yellow-green precipitate. Then add a small amount of NLN-13 to the test tube and dilute to 10 cells 5 per mL....
Embodiment 2
[0038] Embodiment 2: the cultivation of microspores of non-heading Chinese cabbage of different varieties
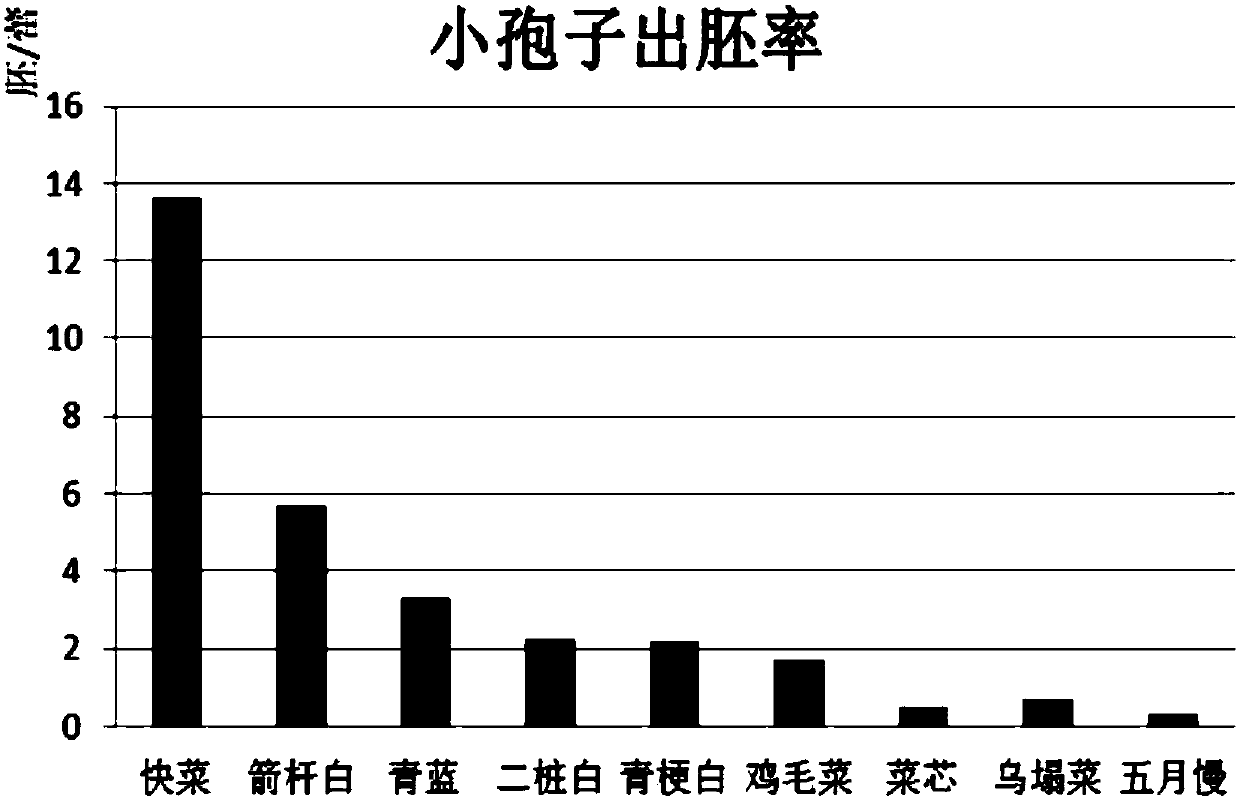
[0039] Choose 9 different varieties (Kaicai Jianshan white, Qinglan, Erzhuangbai, Qinggengbai, chicken feathers, cabbage core, Wutaicai, Wuyueman) and adopt the method described in Example 1 to carry out the microspore culture test, Count their embryonic rate, compare the impact of this invention on the microspore embryonic rate. Among them, Jianshabai, Qinglan, and Erzhuangbai are easy-to-germ varieties; Qinggengbai, Chimaera, and Caixin are varieties that can produce embryos; Caixin, Wutaicai, and Wuyuemanan are difficult-to-embryo varieties. Such as figure 1 , such as comparing the results of embryo emergence, among the 9 selected varieties, the embryo emergence rate reached 100%, of which 3 difficult-to-embryo varieties all produced embryos, and the easy-to-embryo variety Kuaicai reached 13.62 embryos / bud.
[0040] Such as Figure 4 to Figure 7 Respectively are th...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Example 3: Effects of Boron Element and Activated Carbon on Microspore Germination Rate of Non-heading Cabbage of Different Varieties
[0042] Two varieties with high embryo emergence rate were selected, and the research on the microspore embryo emergence rate of boron element and activated carbon was carried out. Image 6 , divided into four groups, control (NLN-13), only adding activated carbon, only adding boron, and adding boron and activated carbon at the same time. The comparison results show that when nothing is added, the embryo emergence rate of the two varieties is very high. Low, after adding activated carbon and boron respectively, the germination rate has been improved to varying degrees, and after adding activated carbon and boron at the same time, compared with adding boron and activated carbon alone, both varieties have significantly improved, higher than the control out 4-5 times Figure 7 It is a graph comparing the emergence of embryos after adding a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com