Method for increasing barley microspore culture callus yield and green seedling yield
A microspore culture and barley technology, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve problems such as the limitation of the area of an artificial climate chamber, the limitation of the number of planted barley seedlings, etc., and achieve the effects of increasing the number of green seedlings, increasing the yield of callus, and optimizing the cultivation process.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
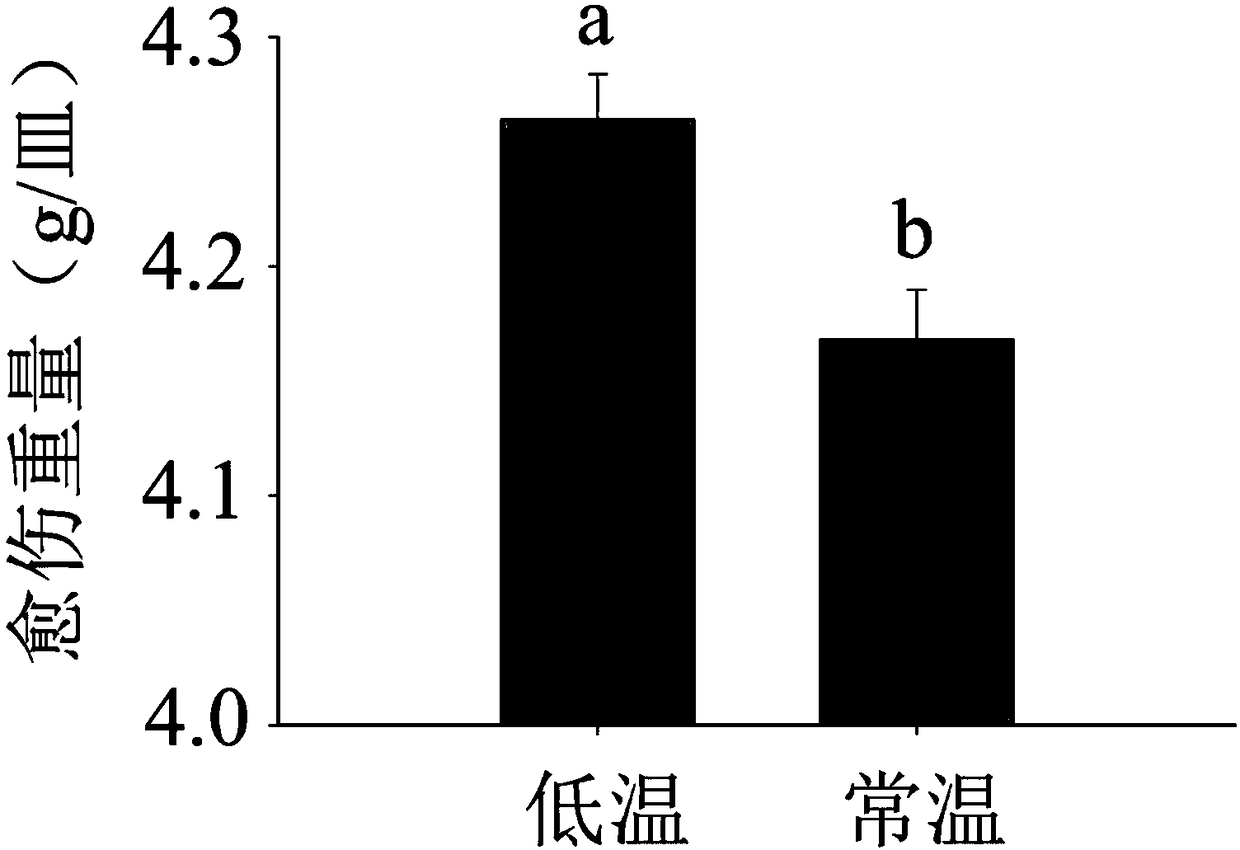
[0019] Embodiment 1 low temperature treatment barley material flower 30 seedlings
[0020] Plant barley material flower 30 in the pot (barley variety flower 30 is an excellent barley variety cultivated by the cell engineering laboratory of Shanghai Academy of Agricultural Sciences Institute of Biotechnology, the domestic planting area is relatively wide, the seeds are provided by the cell engineering laboratory of Shanghai Academy of Agricultural Sciences Preservation), when the seedlings grow to the stage of two leaves and one heart, they are moved to the intelligent incubator for low temperature treatment. The plant cultivation conditions are: temperature 4°C at night and 4°C during the day; humidity 65%; 12 hours of light and 12 hours of darkness. After 30 days of low temperature treatment, they were transplanted into the artificial climate chamber, and the plants without low temperature treatment were planted as the control group at the same time. The plant culture conditio...
Embodiment 2
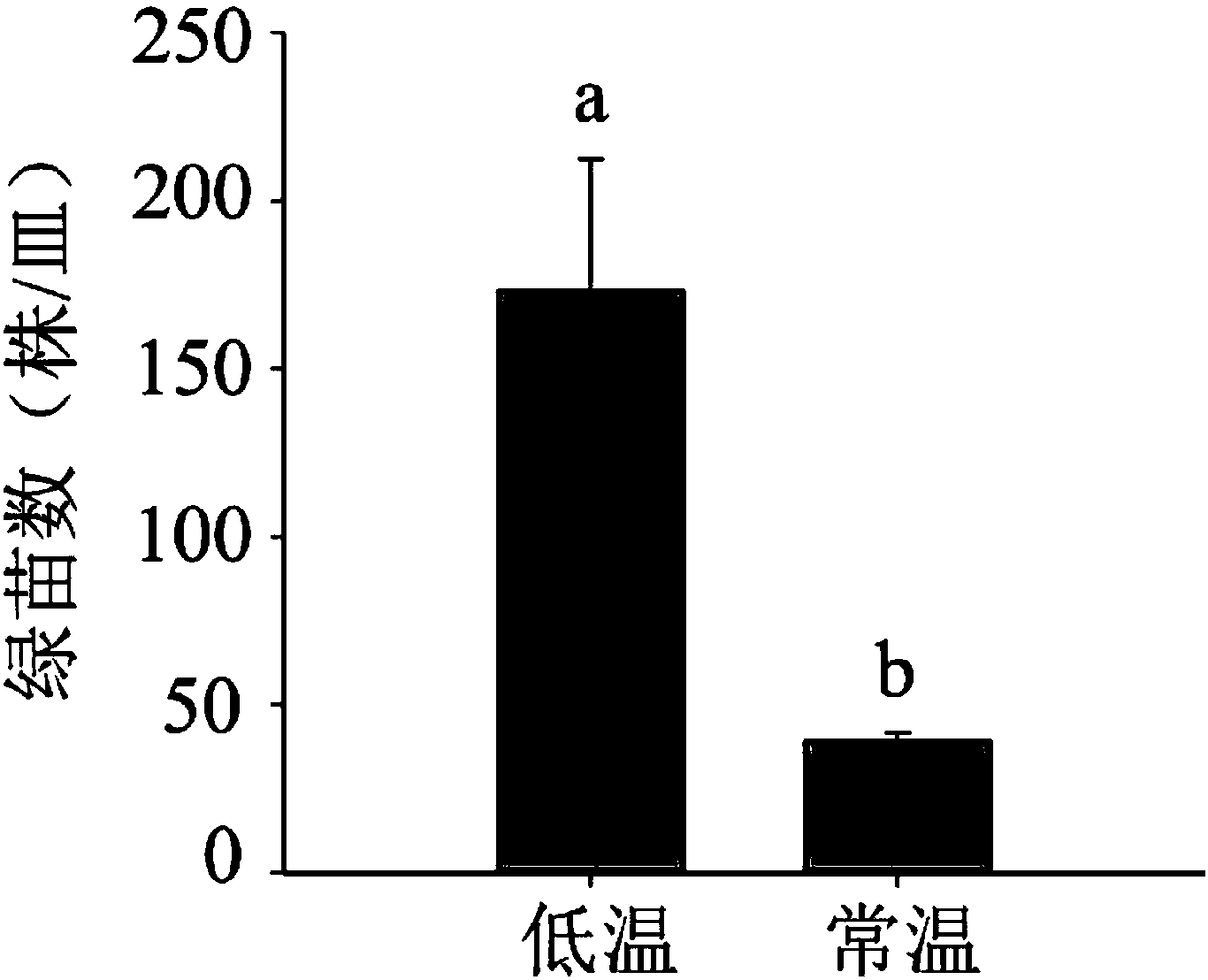
[0021] Embodiment 2 barley material flower 30 microspore culture
[0022] Select low-temperature treatment and control barley ears whose florets and microspores in the middle of the young ears of the control plants are in the early-middle stage of uninucleation, cut off the leaves (keep the base of the upper two leaves about 1.5 cm), wrap the young ears with clean wet gauze, and put them in Moisturize in a fresh-keeping bag, mark the date and quantity of the material, and put it in a 4°C refrigerator for 2 to 4 weeks of low-temperature pretreatment. Free microspores from flower buds were taken from low-temperature-treated materials, and the microspores were freed with reference to methods such as Lu Ruiju (references: Lu Ruiju, Huang Jianhua, etc., the impact of colchicine on the survival and seedling formation of barley in vitro cultured microspores. Journal of Plant Physiology, 2001 , 27(2): 135-140). Each test tube connects the flower buds of 4 spikes, and adds 12ml extrac...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com