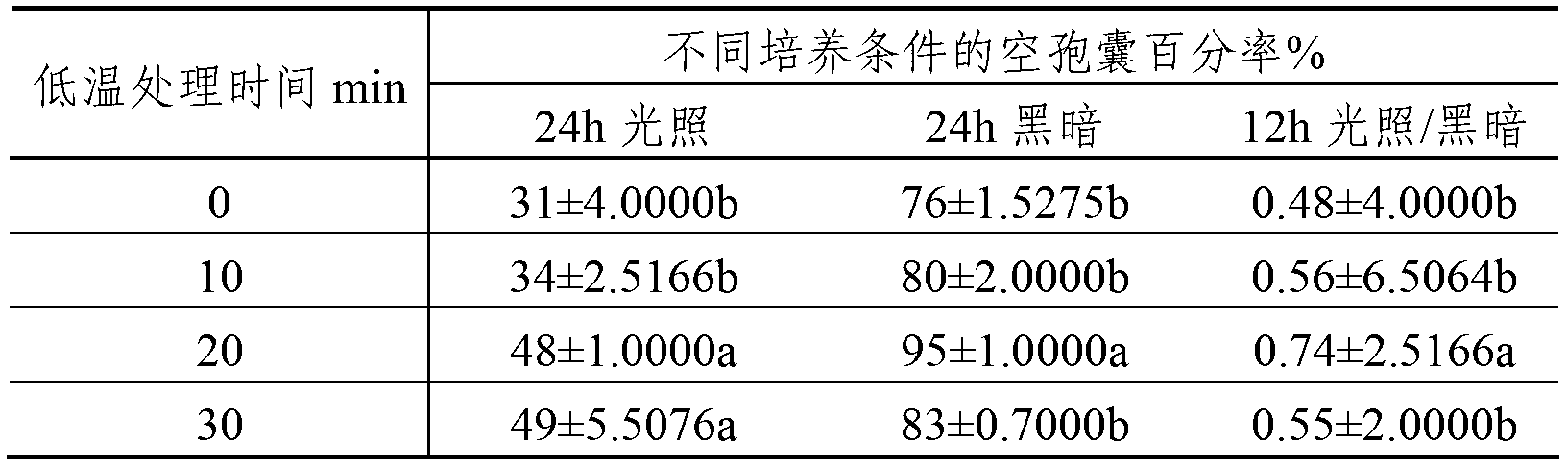
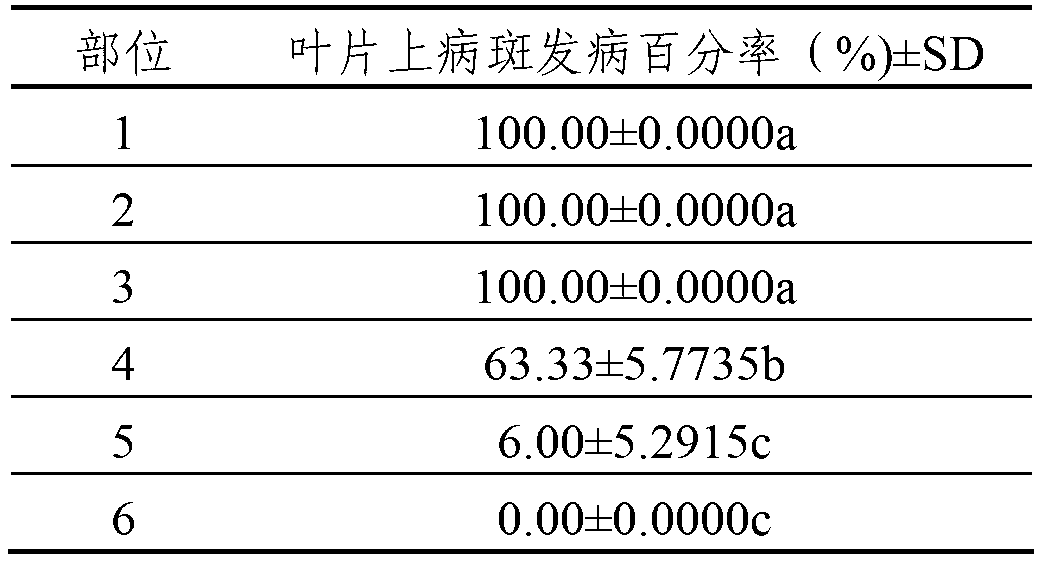
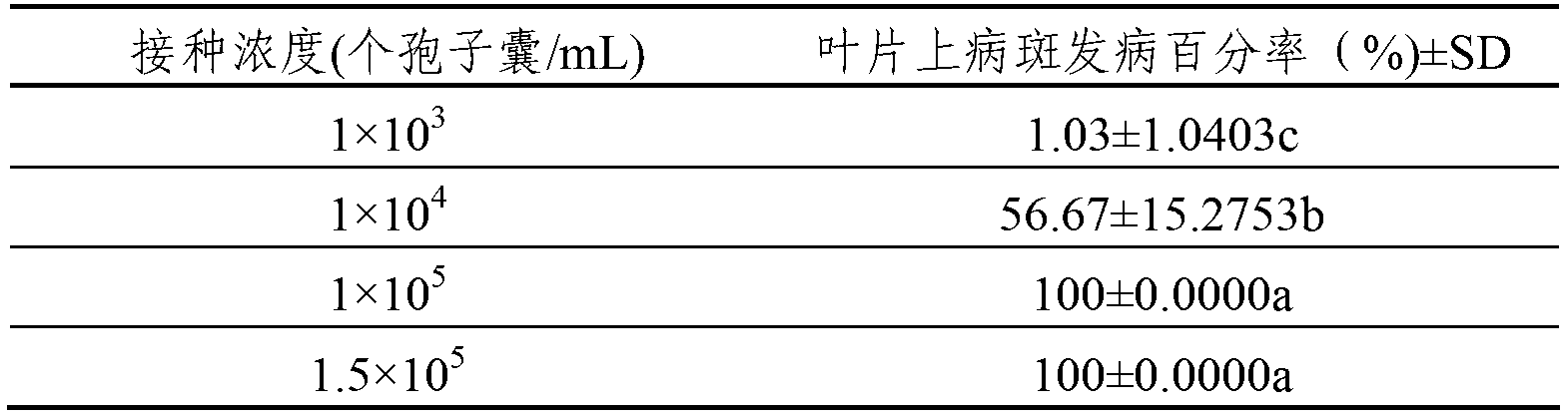
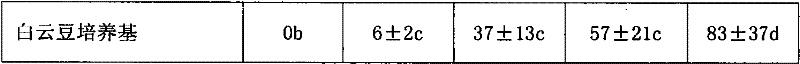Patents
Literature
129 results about "Sporangium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
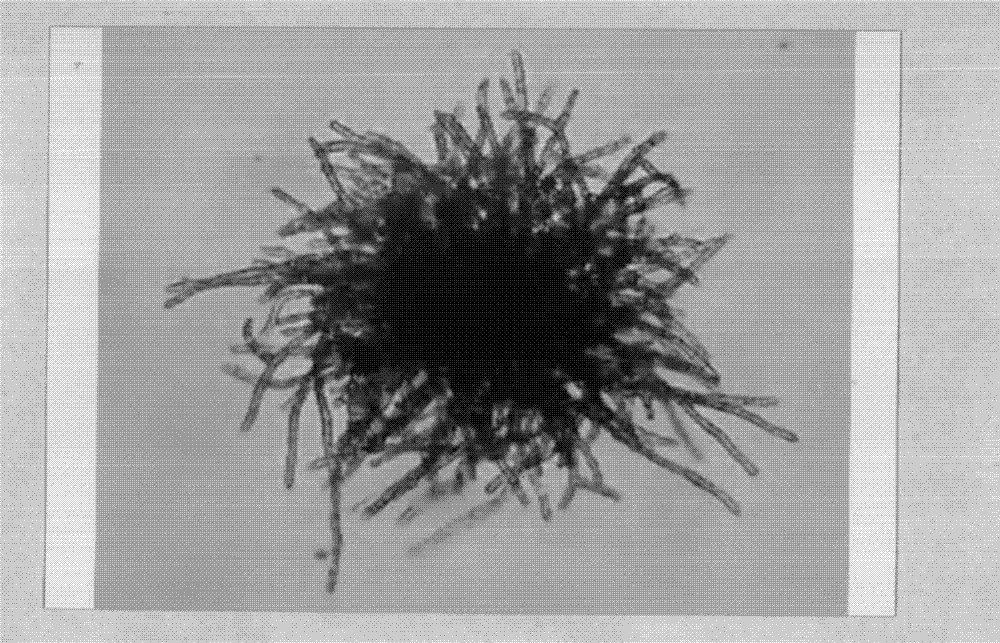
A sporangium (pl., sporangia) (modern Latin, from Greek σπόρος (sporos) ‘spore’ + ἀγγεῖον (angeion) ‘vessel’) is an enclosure in which spores are formed. It can be composed of a single cell or can be multicellular. All plants, fungi, and many other lineages form sporangia at some point in their life cycle. Sporangia can produce spores by mitosis, but in nearly all land plants and many fungi, sporangia are the site of meiosis and produce genetically distinct haploid spores.
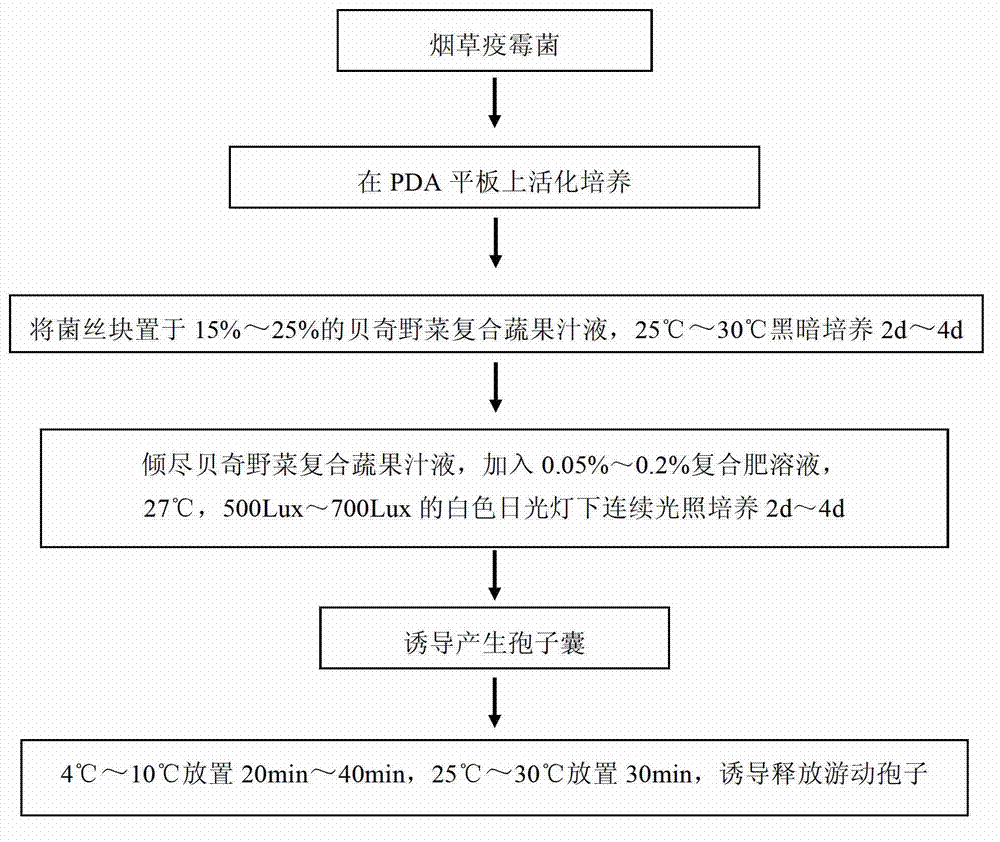
Method for generating sporangia and releasing zoospore by inducing phytophthora capsici
ActiveCN105441375AShort induction periodNo pollution in the processMicroorganism based processesSpore processesContinuous lightSporangium
The invention discloses a method for generating sporangia and releasing zoospore by inducing phytophthora capsici. The method includes the steps that phytophthora capsici is activated, an inducing solution for generating sporangia is prepared, sporangia are induced to be generated, and zoospore is induced to be released. The inducing solution used in the method is originally imported V8 vegetable juice with the volume concentration being 10-15% and a CaCO3 solution with the volume concentration being 0.2-0.3 g / L. When phytophthora capsici is induced to generate the sporangia, continuous light culture is carried out under a white fluorescent lamp. The method is simple, convenient to use, quick, free of pollution and capable of being used in phytophthora capsici pathogenicity measurement and biological activity measurement, achieved through an antibacterial agent, of phytophthora capsici.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION FAAS
A kind of Melaleuca prothallus induction and propagation method
InactiveCN102283129AEasy to sterilizeSimplify the build processPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsSporangiumTower
The invention discloses a method for inducing and multiplying a prothallium of Huperzia serrata. The method comprises the following steps of taking a sporangium or a spore as an explant, performing in vitro tissue culturing on the explant; establishing an induced system of the prothallium of the Huperzia serrata, wherein the induction frequency of the prothallium reaches 15 percent; and under an artificial regulation, performing multiplication culturing for the prothallium until the month multiplication time reaches 5 times. The method is easy, has high efficiency, and can be used for establishing an import technical base for artificial propagation for the Huperzia serrata.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
Introduction method for sea-tangle
InactiveCN101120650AHigh ability to withstand harsh environmentsIncrease success rateCultivating equipmentsPlant cellsFrondCataphyll
The present invention provides an introduction method of the laminaria japonica, which can resolve the problems of the prior art that the selected frond section having the mature sporangia is easy to decay and the spore is easy to release, thereby leading to the failure of the introduction. The introduction method adopted by the present invention is to firstly dry and incite the mature sporangia leaf of the laminaria japonica in a temperature-controllable laboratory, then put the mature sporangia leaf of the laminaria japonica into a water tank that is provided with the fresh sterilized sea water and the temperature of the water is controlled between eight cent degrees and twelve cent degrees to release the spores, then cultivate the spore to form the gametophyte, to put the seedling curtain attached with the gametophyte into a low-temperature enclosed bag and finally transport in low-temperature storage to the destination. The shape of all gametophytes on the laminaria japonica seedling curtain is normal, which has high successful rate and the survival rate is nearly one hundred percentages.
Owner:MARICULTURE INST OF SHANDONG PROVINCE
Method of inducing phytophthora nicotianae breda de haan bacteria to generate sporangiums and release zoospores
ActiveCN103045529AShort induction periodNo pollution in the processSpore processesSnow moldNicotiana tabacum
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant protection, and discloses a method of inducing phytophthora nicotianae breda de haan bacteria to generate sporangiums and release zoospores. The method comprises the following steps: activating the phytophthora nicotianae breda de haan bacteria, preparing the induction liquid generating sporangiums and inducing to generate sporangiums and release zoospores. According to the invention, the used induction liquid is the Bache wild vegetable composite fruit and vegetable juice with the volume concentration of 15-25 percent and the compound fertilizer solution with the mass concentration of 0.05-0.20 percent, and when the phytophthora nicotianae breda de haan is induced to generate the sporangiums, the continuous illumination culture is performed under the white fluorescent lamp. The method provided by the invention is simple, convenient, rapid and pollution-free, and can be used for the researches on virulence determination of the phytophthora nicotianae breda de haan bacteria, the biological activity assay of the phytophthora nicotianae breda de haan bacteria by the sterilizing agent, the evaluation of disease resistance of an epidemic disease by the luffa varieties and the like.
Owner:PLANT PROTECTION RES INST OF GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Semi-leaf laver seedling cultivating method
ActiveCN103798123ARapid seedlingEfficient seedling cultivationCultivating equipmentsSeaweed cultivationCulture fluidPorphyra
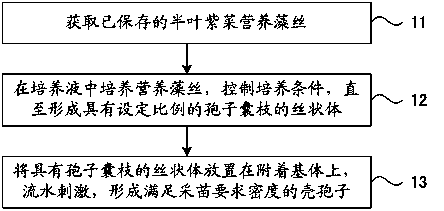
The invention discloses a semi-leaf laver seedling cultivating method. The method includes the following steps that semi-leaf laver nutritious trichome is obtained; the semi-leaf laver nutritious trichome is cultivated in nutritious liquid until a protonema of a sporangium branch with the set proportion is formed and the cultivating conditions include that the temperature ranges from 20 DEG C and 30 DEG C, the light intensity ranges from 1000 lx and 2600 lx, the lighting period is 10 hours to 16 hours and the nutritious liquid sea water ratio ranges from 1.026 to 1.031. The protonema of the sporangium branch with the set proportion is placed on an attachment basal body and stimulated by water currents until conchospores of which the density reaches the seedling collecting requirement are formed and seedling cultivating of the semi-leaf laver is finished. Thus, the problem that the seedlings of the semi-leaf laver can not be rapidly and efficiently cultivated with the prior art is solved.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Method for cloning and culturing seaweed gametophytes
InactiveCN102771394ANormal growthNormal statusClimate change adaptationCultivating equipmentsStainingFiltration
The invention discloses a method for cloning and culturing seaweed gametophytes, which comprises the following steps of: cutting seed seaweed pieces with mature sporangia; using sterilized absorbent cotton to dip the boiled seawater for cleaning the seed seaweed pieces; respectively soaking the pretreated seed seaweed pieces with sterilized double-resistant seawater for 30 minutes, sterilized seawater solution with the potassium iodide concentration being 1.5% for 10 minutes, and sterilized seawater for 20 minutes; carrying out free spore diffusion and filtration in a serum bottle; and pouring the filtered spore water into a vertical staining jar which is provided with a glass slide, after the free spores are attached to the glass slide to form embryo spores, pouring the spore water out, filling sterilized double-resistant seawater, using a micropipette to separate single male and female gametophytes to the serum bottle, then using sterilized double-resistant seawater to culture, and thus obtaining the unicellular seaweed gametophyte clone group. The seaweed gametophyte which is cultured by the method has stable clone characteristics and high survival rate, can be effectively prevented from being contaminated, and is suitable for long-term storage.
Owner:SHANDONG ORIENTAL OCEAN SCI TECH
Total artificial scytosiphon lomentaria breeding technology
InactiveCN103858745ARelieve the pressure of expansionIncrease the number ofClimate change adaptationCultivating equipmentsBiotechnologySporeling
The invention relates to a total artificial scytosiphon lomentaria breeding technology. The total artificial scytosiphon lomentaria breeding technology comprises the following steps: (1) performing germplasm preparation, namely preparing germplasm from scytosiphon lomentaria collected in the current year, or preparing the germplasm by the recovery of the germplasm stored in the previous years; (2) performing germplasm amplification, namely amplifying the germplasm of the scytosiphon lomentaria by using an airlift photo-bioreactor; (3) performing germplasm induction, namely inducing the germplasm of the scytosiphon lomentaria to generate a mature unilocular sporangium; (4) performing spore seedling collection, namely stimulating the unilocular sporangium to diffuse spores, and collecting the spores on a net curtain formed by blending vinylon and polyvinyl chloride; (5) performing indoor seedling breeding; (6) performing mariculture, namely performing mariculture in a raft culture manner for 60-80 days to breed commercial scytosiphon lomentaria of which the body length is 60-100cm, wherein 80-120 seedlings exist on a seedling rope which is 1cm long. According to the total artificial scytosiphon lomentaria breeding technology, the scytosiphon lomentaria breeding efficiency can be improved, and the stable yield of commercial seedlings is ensured. The technology has the advantages of high germplasm utilization rate, firm seedling adhesion, low breeding cost, good production benefit and the like, and can be widely applied to large-scale industrial breeding and artificial culture of the scytosiphon lomentaria.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Harmine compound and applications of harmine compound in prevention and control of peronophthora litchi chen disease
ActiveCN105037350AEnhanced inhibitory effectGood control effectBiocideOrganic chemistryChemical structureHarmine
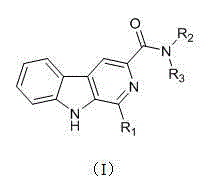
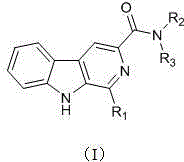
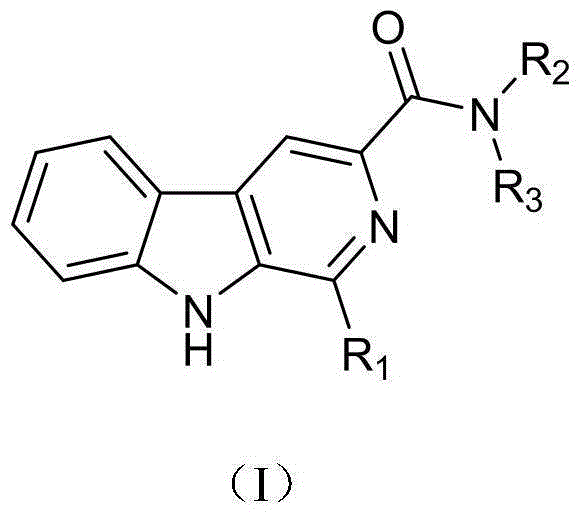
The present invention discloses a harmine compound, wherein the chemical structure formula is represented by a formula (I), R1 is selected from phenyl, p-nitrophenyl, p-methoxyphenyl, 3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl, p-trifluoromethylphenyl and p-chlorophenyl, R2 is selected from ethyl, isopropyl, 2-pyridyl and 2-chlorophenyl, and R3 is selected from hydrogen and ethyl. According to the present invention, the compound provides good inhibition effects on multiple pathogenic bacteria, especially provides good inhibition and prevention and control effects on peronophthora litchi chen, has advantages of small molecular weight, simple structure, easy synthesis and the like, can effectively inhibit hypha growth, sporangium production and sporangium germination of peronophthora litchi chen, has good potential in prevention and control of peronophthora litchi chen disease, and is expected to become a new pesticide fungicide, such that the small molecule compound of the present invention can be used as the new pesticide for prevention and control of the peronophthora litchi chen disease so as to be developed and can provide the new way and means for prevention and control of the peronophthora litchi chen disease.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for collecting seedlings from scytosiphon filaments
InactiveCN101946683ASolve the limitation of algae breeding seasonResolution timeClimate change adaptationCultivating equipmentsSporangiumBiology
Owner:DALIAN OCEAN UNIV
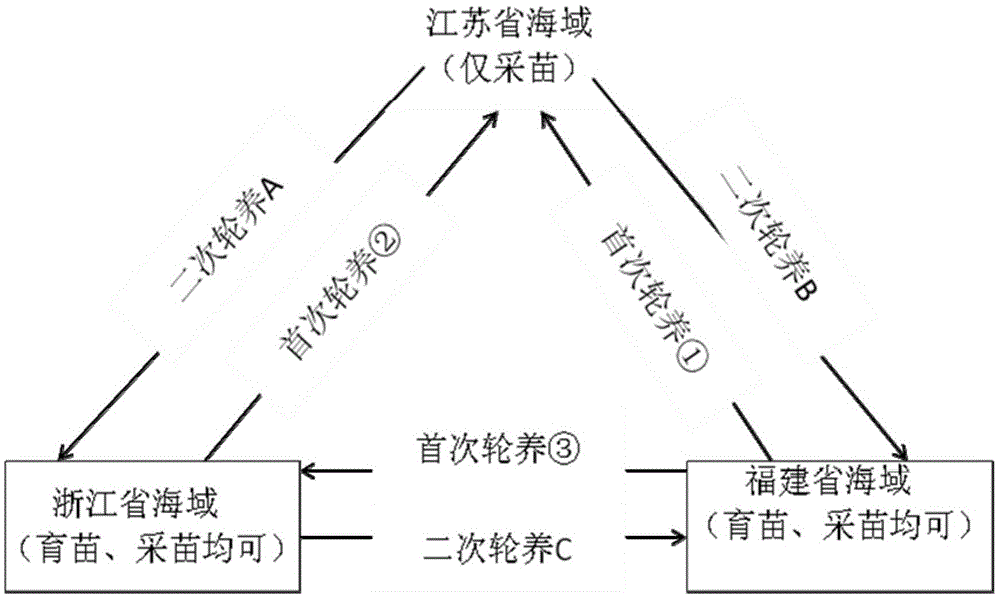
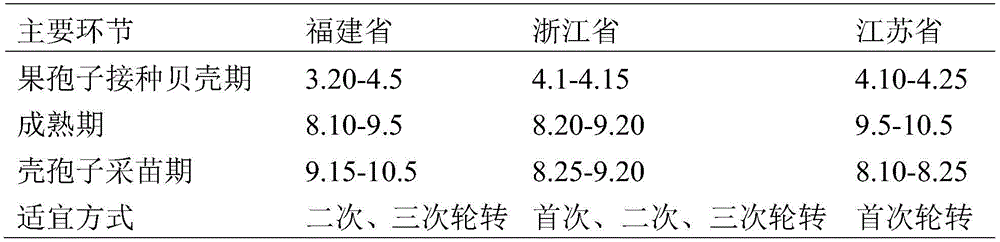
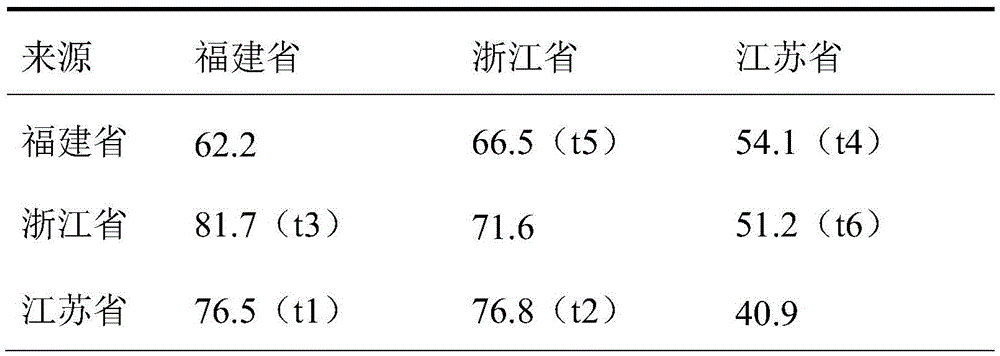
Trans-regional relay seedling method for porphyra haitanensis
ActiveCN105409755AEasy to shrinkImprove efficiencyCultivating equipmentsSeaweed cultivationSporangiumPorphyra
The present invention discloses a trans-regional relay seedling method for porphyra haitanensis. The method comprises: inoculating protonema or carposporophyte of porphyra haitanensis on shell strings in southern part of Zhejiang and sea area of Fujian; after the protonema of shells is cultivated to conchosporangium by adopting a three-dimensional seedling method, promoting maturity by way of shortening the illuminating time, reducing the illuminating intensity and adjusting the adding proportion of a nutritive salt; and transporting mature shells with sporangia to the north of Jiangsu, releasing conchospore by virtue of the thermal expansion principle, and culturing the conchospores attached to a net cord into a sea area. The seedling method disclosed by the present invention has the advantages that shell protonema is cultured rapidly in the south, and is transported to the north if being mature to perform spore dispersion and seedling collection for the first time. The seedling method disclosed by the present invention is suitable for large-scaled porphyra haitanensis cultivation in the north in advance, or performing efficient cultivation by transporting the seedling nets back to the south. Furthermore, the collected seedling shells can be transported back to the south for continuous secondary cultivation, secondary seedling collection is performed in shells in the same batch and are cultured in the south. The method is suitable for being widely applied in porphyra haitanensis seedling fields.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Sporolactobacillaceae and produced preparation of living fungus thereof
InactiveCN1687400AReduce diarrhea rateAdd lessBacteriaAnimal feeding stuffEscherichia coliStaphylococcus cohnii
The present invention provides a kind of bacterium and its procreation of living bacterium reagent, which can reduce the rate of piglet diarrhea. The used of bacterium is gelanshi pigmentation feedback electropositive bacterium S1, according to appraisal, it is Sporolactobacillus sp..Its main biological character is G+, the shape of bacterium is slim, divided burl, elliptical sporangium, after malachite pigmentation pigmentation is obvious, concurrently, exclude oxygen development, endure lower pH(pH2.5) and higher saline chroma(0.2%), not sensetive to pepsin, endure high temperature, it can restrain coliform and golden ball bacterium well. It indicated from the track of molecule biological technology, this bacterium can propagated in alvine of piglet. The flow chart is bevel bacterium--- rocky bottle seed liquid--- ferment jar---freez dryness--- production. The animal test indicates, this bacterium can be used directly and widely in reduce alvine of piglet, enhance the growth rate of piglet, reduce the use of antibiotics in piglet feedstuff.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for establishing in-vitro regeneration system of Osmunda vachellii
InactiveCN105230483AAchieve heightIncrease production capacityPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsBiotechnologySporeling
The invention discloses a method for establishing an in-vitro regeneration system of Osmunda vachellii, which belongs to the field of agricultural biotechnology. According to the method, sporangiorus is used as explant; after surface disinfection, the explant is inoculated into a variety of mediums containing an improved Beneck basal medium; prothallus is obtained through in-vitro germination of spores in sporangium; a part of the prothallus can further undergo enrichment culture, while the other part of the prothallus can be used for induced production of juvenile sporophyte (a sapling); and the sapling is transplanted into a matrix after rooting culture, and the seedling of Osmunda vachellii is formed eventually. The method provided by the invention can realize rapid and continuous obtainment of a great number of high-quality seedlings.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Polysiphonia urceolata tetraspore seedling formation method
InactiveCN101167439ALarge biomassUltrasonic cleaning time is shortCultivating equipmentsSeaweed cultivationSpore germinationPolysiphonia urceolata
A method for forming seedlings of polytubule tetraspores, which is characterized in that mature tetraspores are collected from wild populations, and are first washed several times with clean sea water until there are no obvious miscellaneous algae; then ultrasonic cleaning is performed for 3- 5 times, until there is no miscellaneous algae; cut out the part with more sporangia near the end of the algae body and cultivate it at a temperature of 15-20°C, a light intensity of 2000-3000lux, and a light time of 10-12 hours; wait until the spores are released to meet the demand Finally, take away the algae, and continue to cultivate the tetraspores in the water until they germinate into gametophyte algae. Advantages of the present invention: 1. tetrasporocytes germinate into gametophytes of different sexes, which are important materials for related genetics research; 2. ultrasonic cleaning time is short and effective; 3. tetrasporocytes exist in nature for a long time, and biological The quantity is large, which ensures sufficient provenance; 4. The germination rate of tetraspores is high, and offspring algae can be obtained directly without sexual process.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Cucumber downy mildew sporangium in vitro conservation method
InactiveCN1966669ASolve the problem of severe reduction in pathogenicity in vitro storageHigh pathogenicityFungiDiseaseSporangium
The invention provides a in vitro conservation method for Pseudoperonospora cubensissporangium. It includes process of: the treatment and conservation method and conditions ofPseudoperonospora cubensissporangium, the detection of sporangium germination rate and pathogenicity. The invention is to conserve thePseudoperonospora cubensissporangium in a mixed liquid containing 10% dimethyl sulfoxide and 5% skimmed milk, at -20DEG C, -70DEG C, or pretreat at -20DEG C for 24h, and conserve at -70DEG C. The best conservation method is pretreating at -20DEG C for 24h, and conserving at -70DEG C, after 12 months conservation, the sporangium germination rate is 46%, disease incidence and pathogenetic condition index are 50% and 40 respectively after inoculate to cucumber seminal leaves, high pathogenicity is preserved. The invention is fit for the long term in vitro conservation of Pseudoperonospora cubensis, and can solve the problem of serious pathogenicity descent in vitro conservation fundamentally.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for indoor culture breeding of Plasmopara viticola
InactiveCN103173365AEasy to monitorImprove pathogenicity assayFungiMicroorganism based processesSporangiumPathogenicity
The invention provides a method for the indoor culture breeding of Plasmopara viticola. The method comprises the following steps: 1, acquiring a Plasmopara viticola sample; 2, preparing a sporangium suspension; 3, selecting the grape variety and blade; 4, inoculating the sporangium suspension; and 5, carrying out blade moisturizing culture. The method has the advantages of simplicity, easy learning, low requirements on a tester, and culturing for 7-10 days under a same environment condition after blade morbidity, overcomes the defects comprising difficult survival, no indoor mass propagation of the Plasmopara viticola sample, and sporangium suspension insufficiency after the previous inoculation of the Plasmopara viticola, can be used for monitoring the Plasmopara viticola and determining the pathogenicity, and has very high practical application values.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION HEBEI ACAD OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
Method for diagnosing sporangium and egg capsule molecules of sarcocyst
This invention relates to a method for detecting sporangium and oocyst of Sarcocystis. The method comprises: (1) mixing a small amount of feces with 37% ZnSO4 solution, centrifuging and standing; (2) detecting floating feces with a microscope, collecting sporangium and oocyst, placing in centrifugal tube, and storing at a low temperature; (3) performing PCR with the primers to amplify 18SrRNA in sporangium and oocyst of Sarcocystis; (4) digesting PCR product with restriction endonuclease, and detecting through gel electrophoresis, or detecting the nucleotide sequence with the primers used before. The primers can also be used as probes in hybridization reactions, or for manufacturing gene chips or microarrays. The method can be used for identifying Sarcocystis with high sensitivity and high specificity.
Owner:KUNMING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Artificial sexual propagation method for dicranopteris pedata
InactiveCN104663186AEasy to operateShort cultivation periodPlant cultivationCultivating equipmentsSurface layerSporangium
An artificial sexual propagation method for dicranopteris pedata belongs to the technical field of agricultural production. Particularly, the invention relates to the artificial sexual propagation method for the dicranopteris pedata. The artificial sexual propagation method for the dicranopteris pedata, provided by the invention, is simple, and the survival rate is high. The artificial sexual propagation method for the dicranopteris pedata is characterized by comprising the following steps: at the end of autumn and at the beginning of winter, selecting pinnule with more sporangium groups when sporangia on the back surfaces of the pinnule of the dicranopteris pedata are about to grow up, covering the pinnule by a plastic bag; collecting the plastic bag after several days to obtain a lot of sporangia of the dicranopteris pedata from the plastic bag; intensively storing the sporangia of the dicranopteris pedata; at the early spring of the next year, selecting a more shady and cool place and digging a land furrow; paving one layer of yellow soil with the thickness of 10cm on the land furrow; mixing the treated sporangia with sand and scattering; and hanging one layer of sunshade net above the furrow, and frequently spraying water to guarantee that the surface layer of the soil is not dry.
Owner:陈忠敬
Embedding-dehydrating ultralow temperature storage method for scytosiphon lomentaria mitoplast
ActiveCN103621395AFor long-term storageEffective preservationDead plant preservationCultivating equipmentsSucroseSporangium
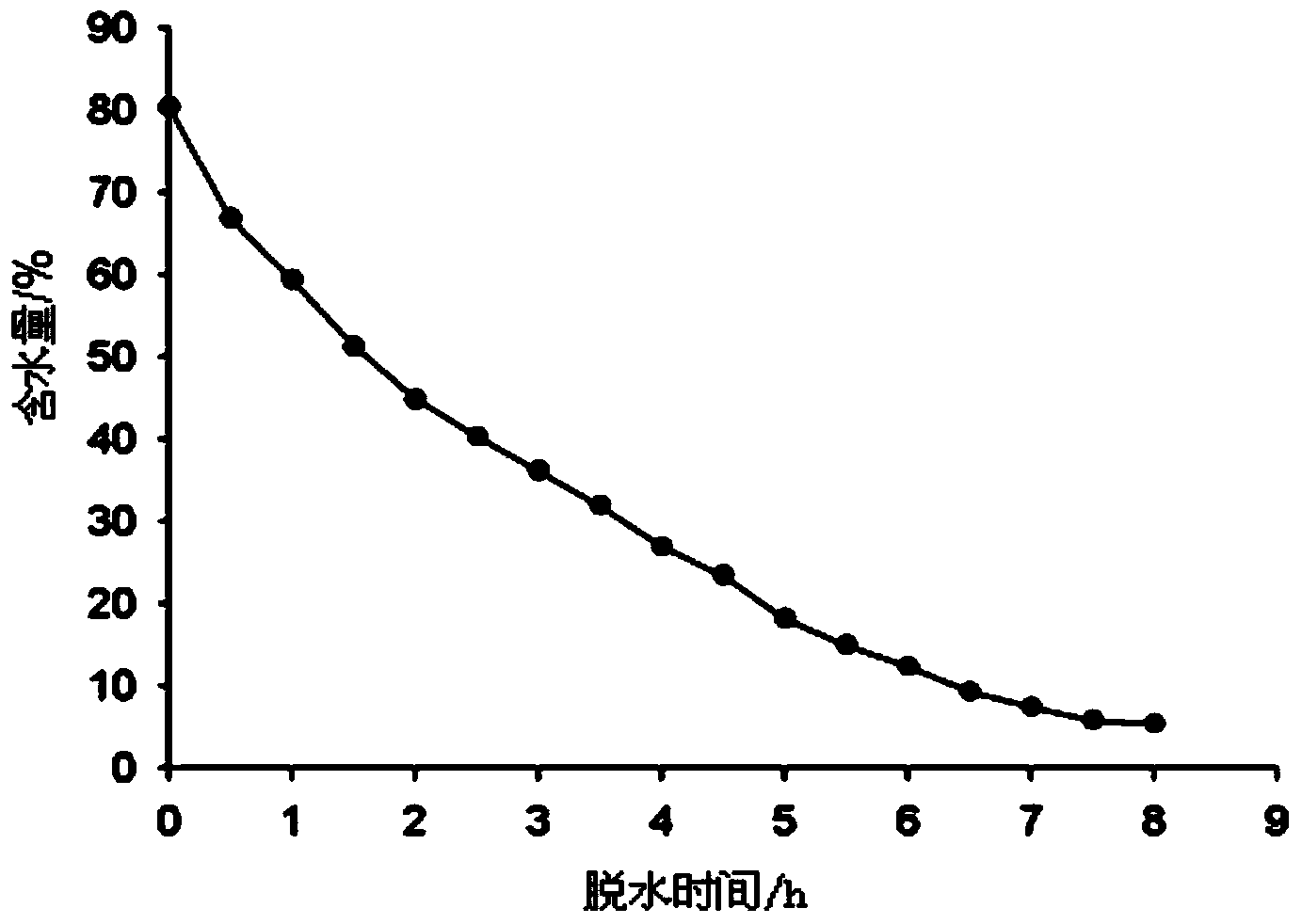
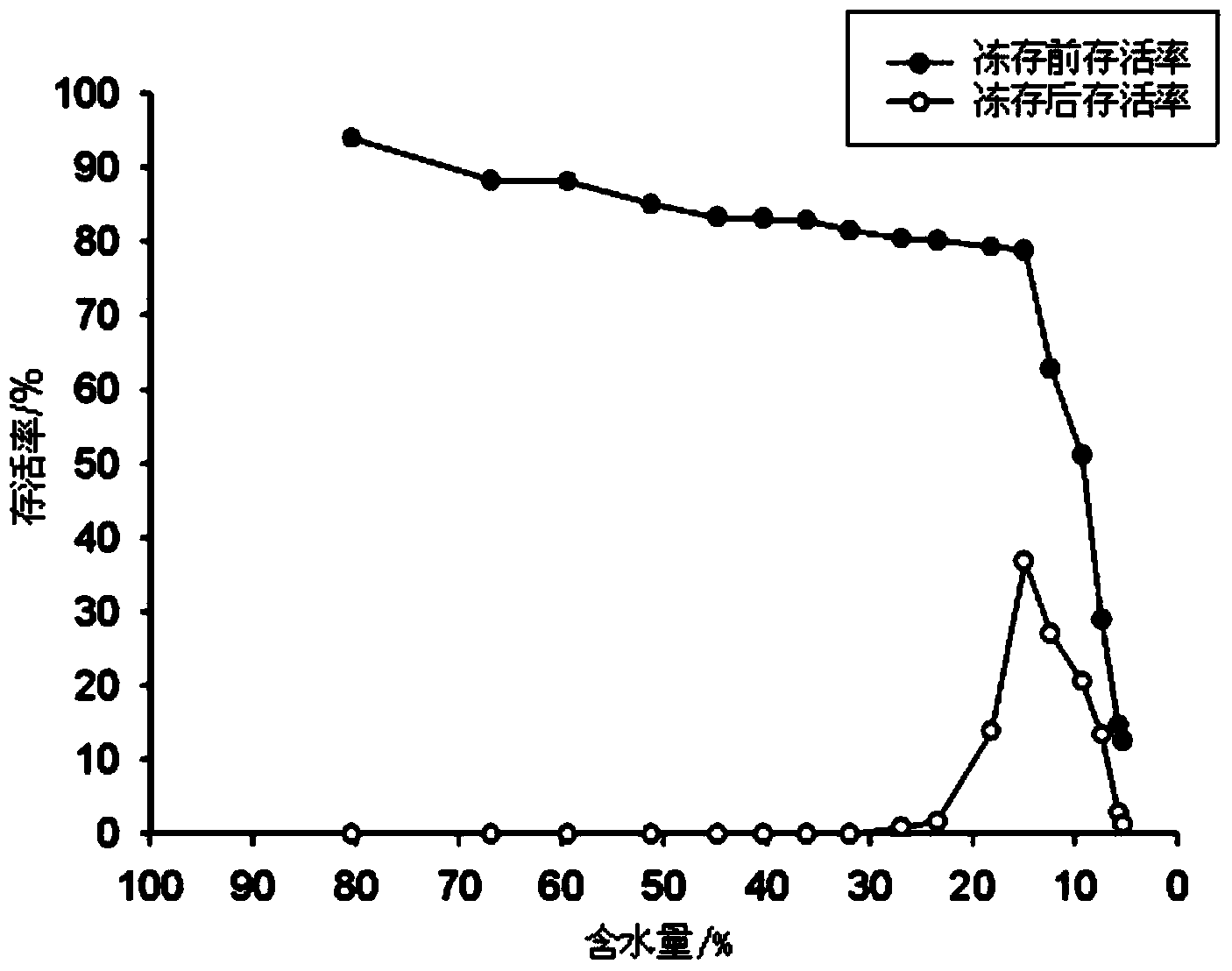
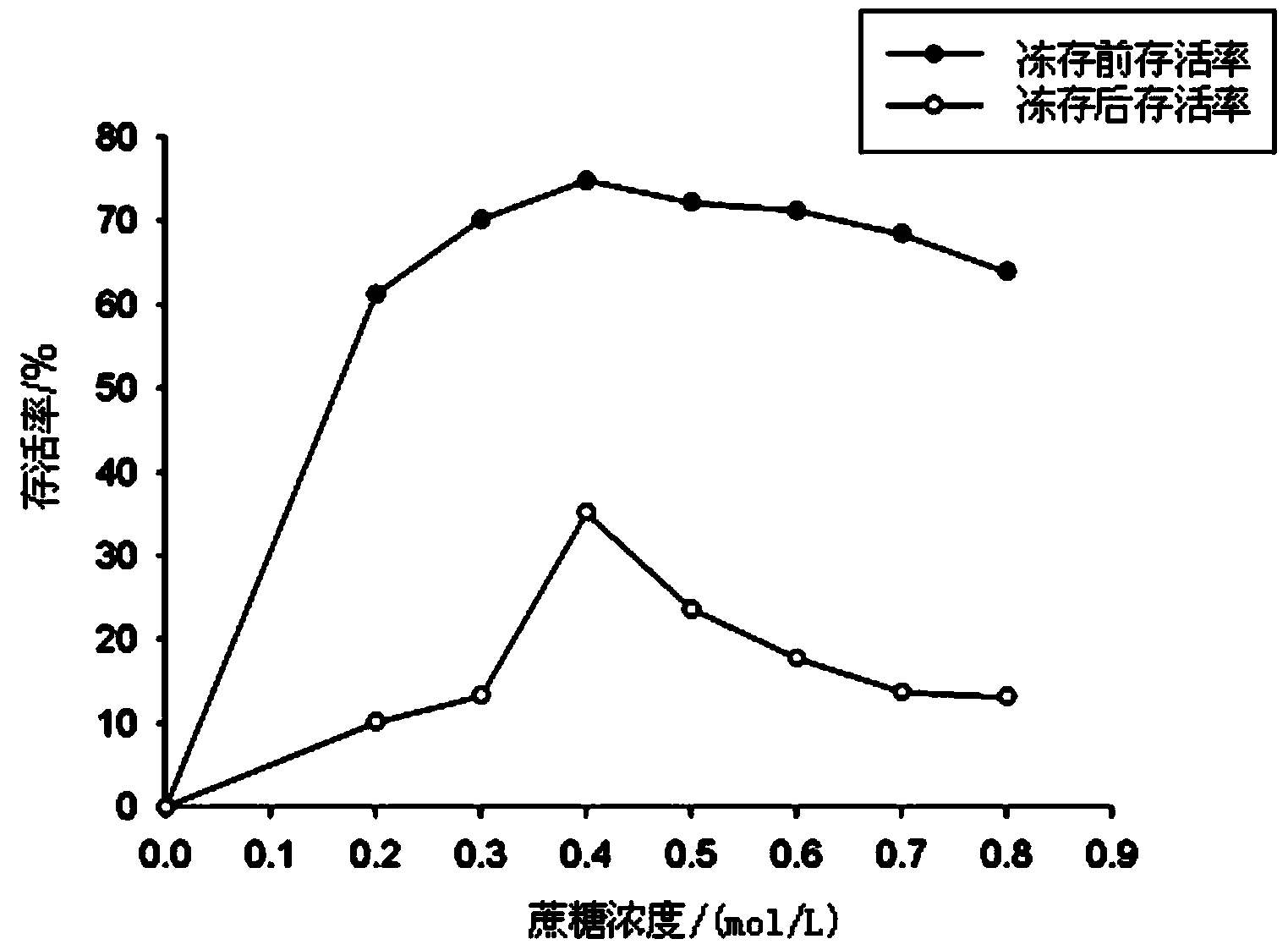
The invention discloses an embedding-dehydrating ultralow temperature storage method for scytosiphon lomentaria mitoplast. The embedding-dehydrating ultralow temperature storage method comprises the following steps of: collecting mature thallus of the scytosiphon lomentaria, and culturing until brown mitoplast is used as an embedding material; crushing the mitoplast to uniformly mix with sodium alginate liquor containing sucrose and glycerol; dropping NaCl liquor to form rubber balls, and hardening to complete an embedding process; pre-culturing the immobilized rubber balls; placing the rubber balls in a culture dish, placing the culture dish in a large culture dish paved with drying silica gel on bottom, sealing, and immediately placing in an incubator of 21 DEG C for drying and dehydrating under a dark condition; placing the dehydrated rubber balls into a freezing tube, and immediately adding into liquid nitrogen for storage after sealing. The embedding-dehydrating ultralow temperature storage method for scytosiphon lomentaria mitoplast disclosed by the invention effectively solves problems such as variation and pollution in a scytosiphon lomentaria seed storage process; the scytosiphon lomentaria mitoplast has complete growth and development ability and amplification ability after being recovered from freezing, and can form normal sporangium and release spores, so that thallus is developed, a dear apparatus is not needed, and an anti-freezing protective agent with toxic action to the stored material is also not needed to be used. Therefore, popularization and application of the method are facilitated.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Fiddlehead spore seedling nursing technology
The invention relates to a fiddlehead spore seedling nursing technology. Uncracked sporangium groups in a dark brown color are selected; leaves having spores are cut down and placed in a ventilating position for natural drying; scattered spores are collected and refrigerated at the temperature of 4 DEG C; reed powder, urea formaldehyde foamed plastic, pine needle soil, bone meal, silicate bacterial fertilizer, kinetin, betaine, spermidine, inositol, vitamin B1 and vitamin B2 are mixed to form culturing substrate; the fiddlehead spores are fully flushed via sterile water, and then immersed into a mixed solution formed by zeatin and naphthylacetic acid with growth humidity remained around 82% to 85%, growth temperature of 26 to 26.5 DEG C and illumination strength of 1800 to 20001x; and when the spore infant seedling grows to 6cm, the fiddlehead spore infant seedlings on the culturing substrate are thinned. The fiddlehead spore seedling nursing technology is advantaged by high stability, strong controllability and great operability; seedling nursing period of the fiddlehead spores can be shortened; and seedling rate and rooting rate can be enhanced.
Owner:HEFEI YUANZHENG AFE SCI TECH
Breeding method of cibotium barometz spores
InactiveCN107646697ADoes not affect growthGrow neatlyHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureSporangiumTwo step
The invention discloses a method for breeding golden-haired dog ridge spores. Pick pinnae with sporangia clusters on wild golden-haired dog plants, collect the sporangia, disinfect and wash them, then dry them, collect them in a sterile bag, and then put the aseptic After 340-380 days of low-temperature storage in the bag, sterilize the sporangia with 70%-75% alcohol, and then inoculate them into the spore germination medium for germination culture; when the prothallus grows, inoculate the prothallus into the conventional culture medium Carry out gametophyte transformation and culture; when the gametophyte grows the third leaf, transfer the culture tank to the room, open the lid of the culture tank for seedling cultivation, then add nutrient soil for field transplant adaptation, and finally carry out field transplant. The method for cultivating the golden-haired dog's spores of the present invention has a simple operation process, the two-step method cultivates the golden-haired dog's ridge seedlings, saves costs, the seedlings grow neatly, and are suitable for large-scale cultivation.
Owner:傅明尧
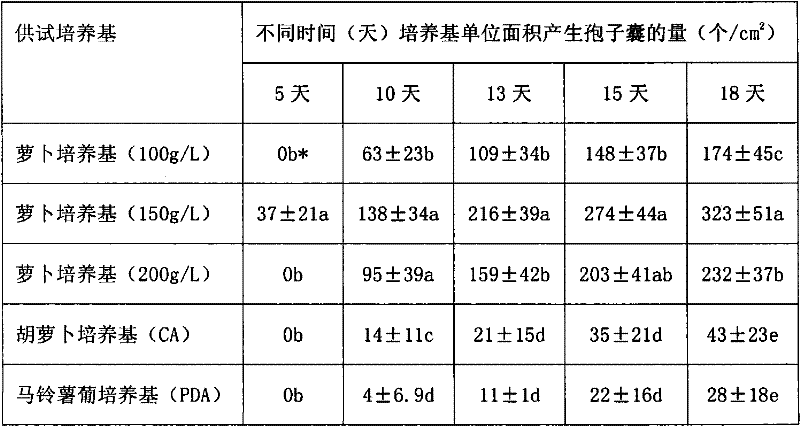
Method for preparing culture medium appropriate for phytophthotacactorum to produce sporangiums by taking radish as raw material
InactiveCN102643776AEasy to manufactureThe resulting program is simple and easy to learnFungiMicroorganism based processesSporangiumHigh pressure
The invention discloses a method for preparing a culture medium appropriate for phytophthotacactorum to produce sporangiums by taking radish as a raw material. The concrete preparation method comprises the following steps of: taking 100-200g of radish; chopping and boiling in 0.5 L of water for 30 minutes; filtering; adding 15g of agar in filtrate, heating to melt the agar with the constant volume to be 1 L; split charging; carrying out steam sterilization at high pressure of 0.103MPa and 121 DEG C for 20 minutes; putting the sterilized culture medium into a sterilized culture dish with the diameter of 9cm so as to form a surface plate; after cooling, punching the edge of a bacterial colony cultured for 3 days through a puncher with the diameter being 5mm to obtain bacterial blocks; inoculating the bacterial blocks on the culture medium; and culturing the inoculated culture dish in darkness for 10 days at 25 DEG C so as to produce a large number of sporangiums. The probability of pollution in an operation process that a water culture method is utilized for inducing to produce the sporangiums is reduced. The raw material of the culture medium is low in cost and is easy to obtain, and the processes of preparing the culture medium and producing the sporangiums are simple and easy to learn.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Alternate utilization method of porphyra haitanensis shell conchocelis
ActiveCN105660358ASolve the problem of seed sourcePrevents premature aging as a problemCultivating equipmentsSeaweed cultivationSporangiumEngineering
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Fluid medium made from celery and suitable for phytophthotacactorum to generate sporangium
InactiveCN102839148AEasy accessLow costMicroorganism based processesSpore processesCELERY JUICESporangium
The invention discloses a fluid medium made from celery and suitable for phytophthotacactorum to generate sporangium. A preparation method of the fluid medium particularly comprises the following steps: removing leaves, washing and cutting up celery, adding deionized water to celery in a w / v ratio being 1:1, and juicing by using a juicer; filtering the obtained celery juice by using four layers of gauze, diluting with deionized water containing 0.02% (w / v) CaCO3 till the celery juice is 10%-50%(v / v); and subpackaging and autoclaving for 20min at 121 DEG C under 0.103MPa; pouring autoclaved fluid medium into culture dishes with diameter being 9cm, wherein 15ml of autoclaved fluid medium into each culture dish. The raw material of the fluid medium are low in cost and can be acquired easily, the steps for making the fluid medium and generating sporangium are simple and easy to learn, and the sporangium generation efficiency of phytophthotacactorum is improved greatly, so great convenience is provided for preparation of pathogenic bacteria inoculants.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Culture method of helminthosporium sporangium spores
InactiveCN101886058ASimple compositionLow costMicroorganism based processesSpore processesMicroorganismGram
The invention relates to a culture method of helminthosporium sporangium spores, belonging to the technical field of microorganisms. The culture method of helminthosporium sporangium spores comprises the following steps of: (1) preparing an inoculum; (2) preparing a production culture medium of helminthosporium sporangium spores; and (3) culturing the helminthosporium sporangium spores. The culture method of the helminthosporium sporangium spores has reasonable design, the production culture medium in the invention has simple composition and low cost, the spore culture and production method is simple and practical, can reach the yield of 0.0213 + / - 0.00145 billion spores on each gram of substrate medium and is possible to develop helminthosporium sporangium spore preparations.
Owner:CHINA NAT RICE RES INST
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens GN03 and application thereof
ActiveCN107099486AImprove nitrogen fixationPromoting effect is goodBiocidePlant growth regulatorsSporeGram
The invention relates to a bacillus amyloliquefaciens GN03 strain and application thereof. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens GN03 is separated from purple soil with high yield and quality of vegetables, a bacterial colony is white and semitransparent, is smooth and moist, and has circular tiny projections and neat edges, gram stain thallus is positive, spores are oval, sporangia are not expanded and grown in the middle, and capsules are plump. After the bacillus amyloliquefaciens GN03 cultures for 1-2 days, the diameter of the bacterial colony is 2-3 mm; after the bacillus amyloliquefaciens GN03 cultures for 3-5 days, the diameter of the bacterial colony is 6-8 mm. On an ashby nitrogen-free medium, when the concentration of the thallus is 1.5* 106 cfu / ml, after the bacillus amyloliquefaciens GN03 cultures for 7 days at the temperature of 28 DEG C and at the speed of 120 r / min, the nitrogen fixation quantity of fermentation liquor reaches up to 91.5+ / - 2.69 mg / L, and the free living nitrogen fixation ability is high.
Owner:重庆千明农业发展有限公司
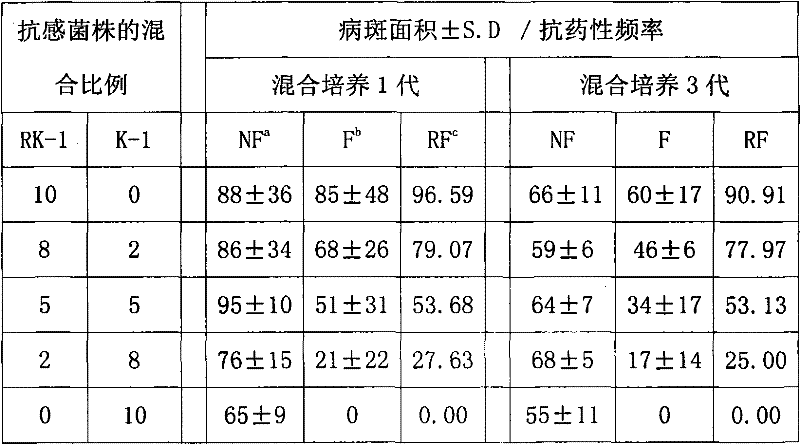
Method for monitoring drug resistance frequency of peronospora parasitica
InactiveCN102643892ASolve the difficulties that cannot be separated and cultivatedEasy to solveMicrobiological testing/measurementSporangiumSterile water
The invention discloses a method for monitoring the drug resistance frequency of peronospora parasitica of a plant. The method comprises the following steps of: A1, collecting a peronospora tabacina sample in an area to be monitored and carrying the peronospora tabacina sample back to a room; and cultivating and inducing under a dark condition to generate new sporangiums at a temperature of 19 DEG C; A2, eluting and mixing the all newly borne sporangiums collected on a diseased leaf to obtain a sporangium suspension; A3, respectively vaccinating the sporangium suspension with a back face of a leaf disc, which is manufactured by a health separated plant leaf by using a sessile drop method, wherein the leaf disc is soaked with sterile water for 30 minutes and is soaked with two liquid medicines (with a minimum inhibition concentration of a bactericide to be detected) for 30 min in advance; A4, arranging the vaccinated leaf disc in a culture dish for moisturizing absorbent paper so as to culture in a moisturized manner; and A5, measuring and calculating a frequency of a drug resistance strain. The method is simple and easy to learn and is easy to operate, and has low requirements on an experiment instrument. Furthermore, the method can be used for more accurately reflecting the drug resistance condition of a field drug resistance group and has higher actual application values.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Application of litsea cubeba essential oil in controlling pepper phytophthora blight
ActiveCN107232238AImprove protectionGood treatment effectBiocideDead animal preservationPhytophthora sp.Sporangium
The invention discloses an application of litsea cubeba essential oil in controlling pepper phytophthora blight. The litsea cubeba essential oil is dissolved in an organic solvent, and then a Tween emulsifying agent is added and lastly the mixture is diluted with sterile water and is uniformly mixed, so that the liquor in the required litsea cubeba essential oil concentration is acquired; the liquor is applied in the manner of spraying or root irrigation; the litsea cubeba essential oil is prepared from the following steps: drying, grinding and screening the litsea cubeba fruits, thereby acquiring the litsea cubeba powder, and then adopting supercritical CO2 extraction for the litsea cubeba powder, thereby acquiring the litsea cubeba essential oil. The liquor prepared from the litsea cubeba essential oil according to the invention is an efficient inhibitor for pepper phytophthora blight, has an excellent field control effect for pepper phytophthora blight and can be used for comprehensively treating pepper phytophthora blight. The litsea cubeba essential oil can be used for preventing and controlling in different stages of the diseases. The drug, especially applied before the forming of sporangia, can effectively restrain the secondary infection of the pathogenic bacteria and the development and propagation of the diseases.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for separating monosporangiums of potato late blight pathogens
InactiveCN105483032AShorten the timeImprove operational efficiencyFungiSpore processesMicroorganismGenetic Materials
The invention belongs to the field of microorganisms, and particularly relates to a method for separating monosporangiums of potato late blight pathogens. On the basis of an existing suspension liquid separating method, the monosporangiums are separated through the characteristic that each monosporangium contains a plurality of zoospores, and genetic materials of the zoospores are the same; the monosporangiums are stimulated at the low temperature to release the zoospores, and the new method for separating the monosporangiums is formed. The success rate of the improved method is nearly 6 times that of the original method, and operation time is halved; meanwhile, operative difficulty is greatly reduced, and the method is an effective method for rapidly separating a large mass of monosporangiums in a pathogeny-group researching test.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Method capable of promoting formation of sporangial branchlets of shell conchocelis of pyropia katadae
ActiveCN111066648AImprove the success rate of artificial breedingGrow fastCultivating equipmentsLiquid fertilisersSporelingPyropia katadae
The invention relates to a method capable of promoting formation of sporangial branchlets of shell conchocelis of pyropia katadae, and belongs to the field of marine algae cultivation. The method capable of promoting the formation of the sporangial branchlets of the shell conchocelis of the pyropia katadae comprises the following steps: 1) collecting carpospores of the pyropia katadae; 2) inoculating shells with the carpospores of the pyropia katadae; 3) impelling fast algal filament growth of the shell conchocelis in a vegetative growth stage of algal filaments; and 4) increasing concentration of iron ions so as to induce transformation of the algal filaments from the vegetative growth stage to a developmental state when the shells are fully covered with vegetative algal filaments of theshell conchocelis of most of the pyropia katadae and the sporangial branchlets begin to appear, thereby allowing rapid formation of the sporangial branchlets. The method capable of promoting the formation of the sporangial branchlets of the shell conchocelis of the pyropia katadae is capable of promoting fast growth of the vegetative algal filaments of the shell conchocelis of the pyropia katadae,as well as allowing synchronous formation of the sporangial branchlets by the vegetative algal filaments without heating; and moreover, the risk of diseases, such as bacterial infection, large amountof heteroalgae attachment and the like, can be reduced in environment with relatively low water temperature, thereby improving success rate of artificial seedling-raising of the shell conchocelis ofthe pyropia katadae.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Solid-phase preservation method for kelp gametophytes
ActiveCN103555649AUniform densitySimplify aseptic processingMicroorganism based processesPlant cellsCulture fluidSporangium
The invention discloses a solid-phase preservation method for kelp gametophytes. The solid-phase preservation method comprises the following steps of scrubbing obtained sporangium kelp blocks; performing germfree treatment on the sporangium kelp blocks; spreading, attaching and germinating kelp spores; separating and inoculating single kelp gametophytes; cultivating the kelp gametophytes in a solid culture medium and performing later-stage preserving. According to the solid-phase preservation method for the kelp gametophytes, the germfree collection and the solid-phase preservation are combined, so that the pollution of germs is inhibited from the sources, the opportunity that the kelp gametophytes pollute the germs is reduced, the germfree treatment flow in the early-stage solid-phase preservation of the kelp gametophytes is greatly simplified, the difficulty in treating the germs on the kelp gametophytes through solid-phase cultivation is alleviated, and the kelp gametophytes with low pollution or even no pollution can be easily obtained; furthermore, the working amount of later replacement of culture liquid during the liquid-phase preservation of the kelp gametophytes is reduced, and a limited preservation space is saved; moreover, the solid-phase preservation method is convenient to popularize and apply.
Owner:SHANDONG ORIENTAL OCEAN SCI TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com