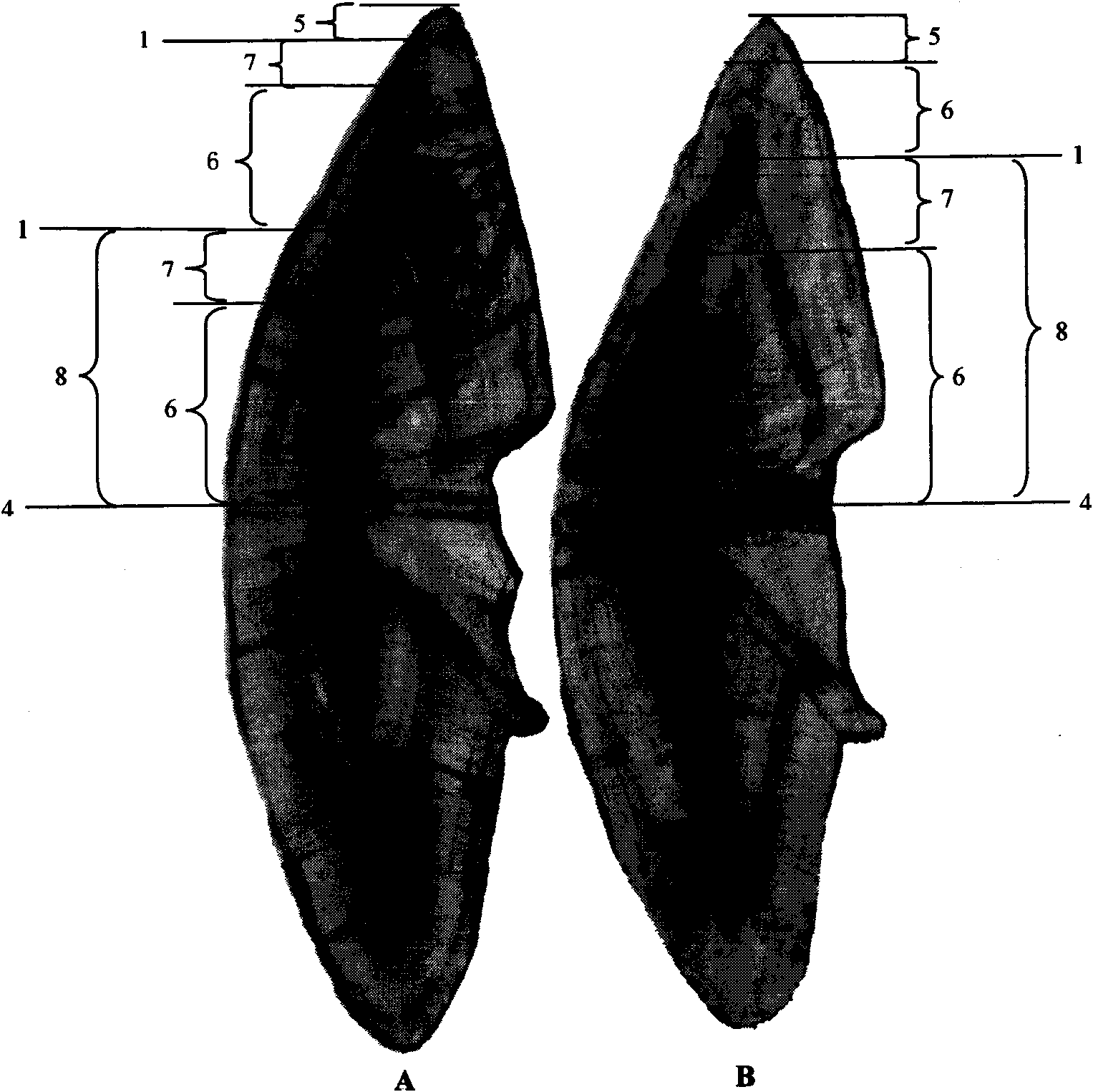
Patents
Literature
80 results about "Life history" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Life history may refer to: Life history theory, a theory of biological evolution that seeks to explain aspects of organisms' anatomy and behavior by reference to the way that their life histories have been shaped by natural selection; Life history (sociology), the overall picture of an informant's or interviewee's life
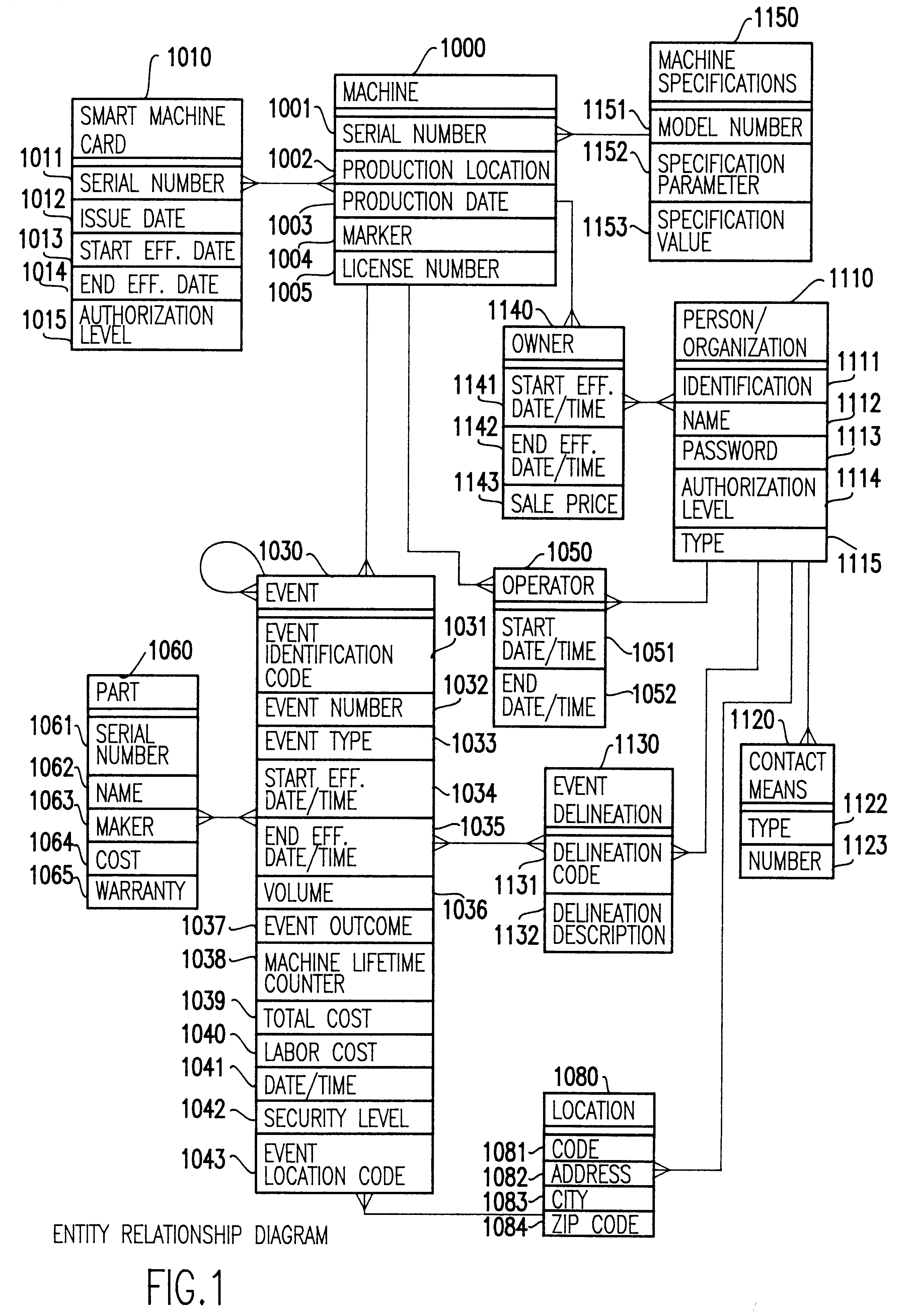
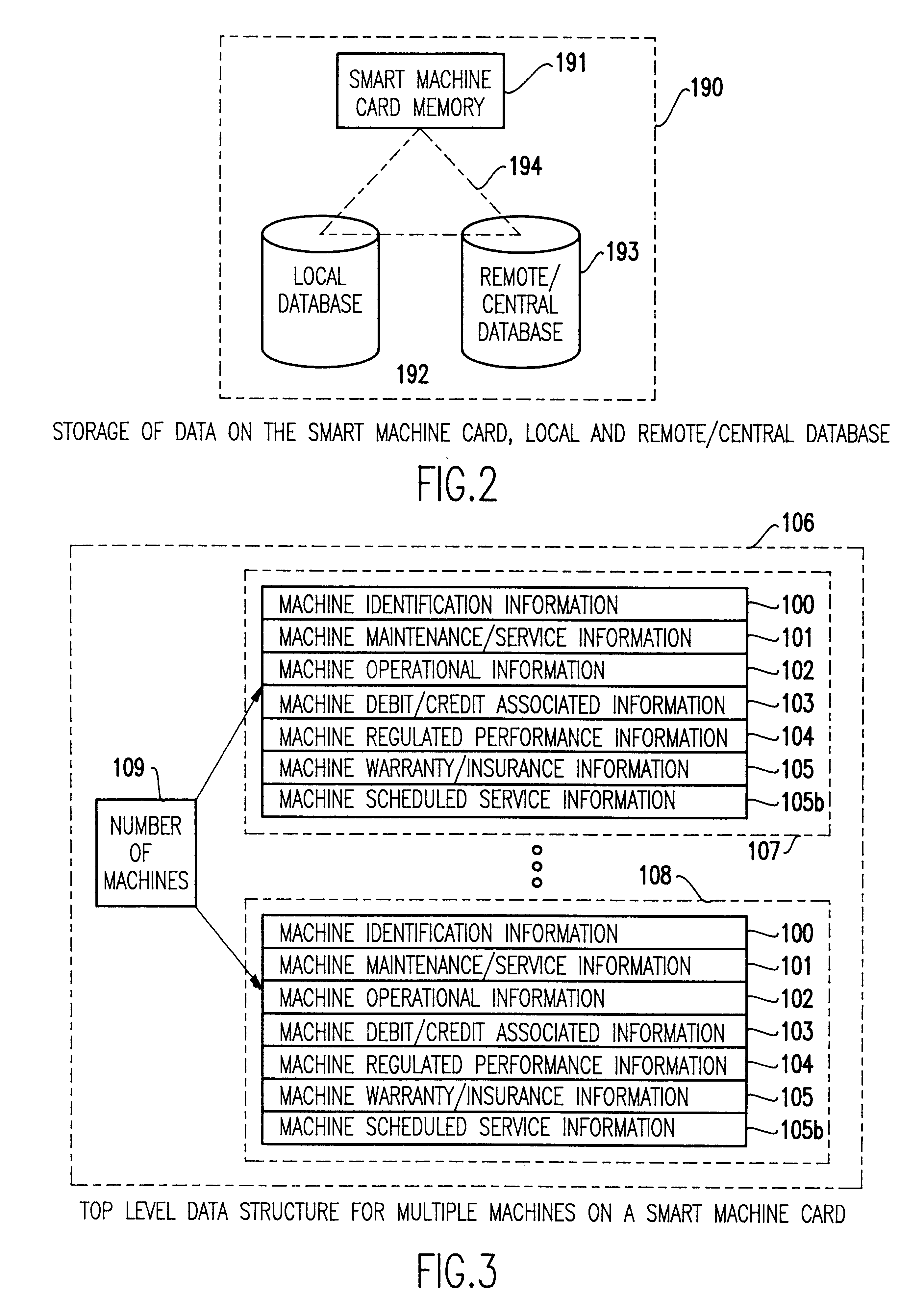
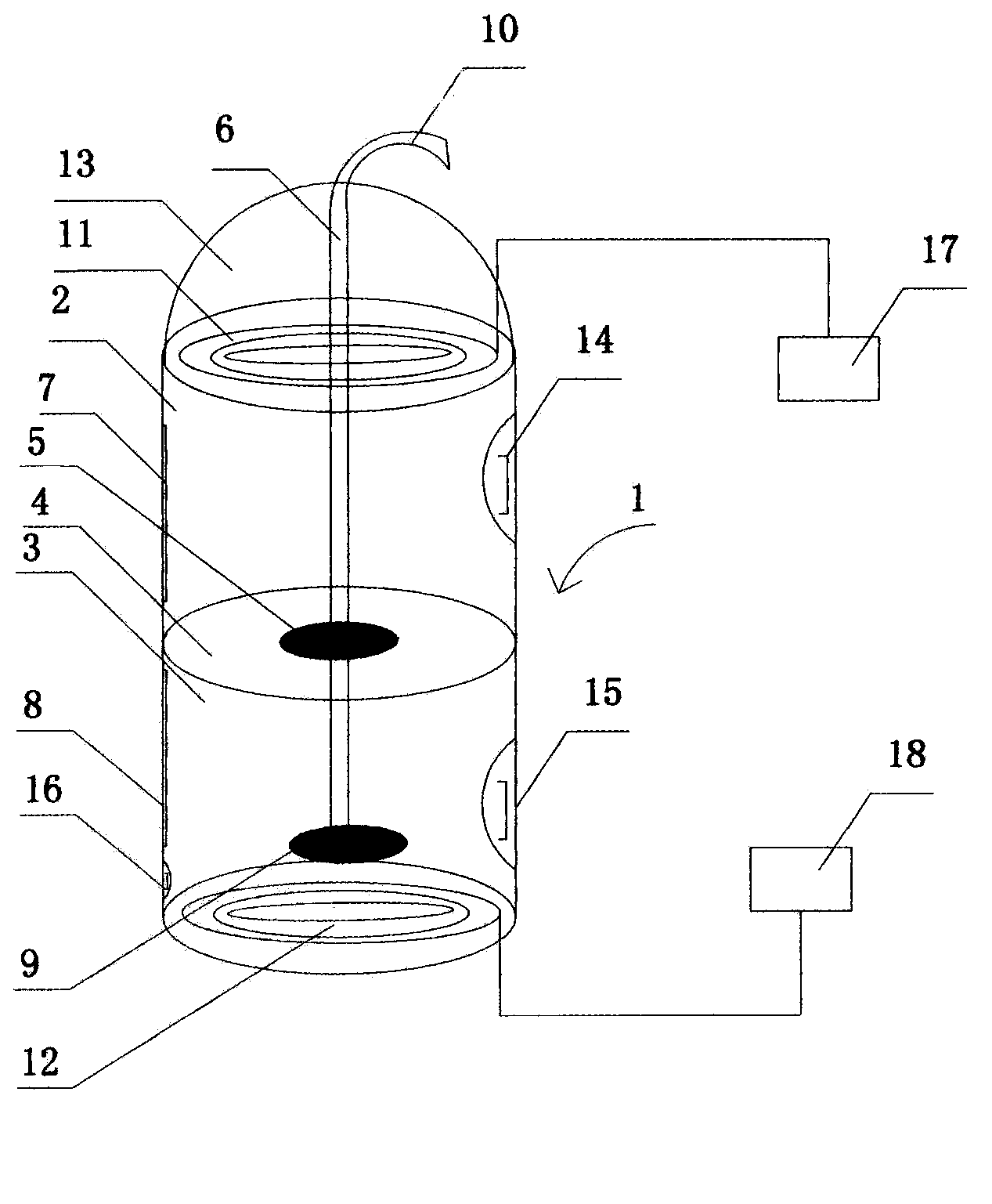
Smart card for recording identification, and operational, service and maintenance transactions
InactiveUS6557752B1Registering/indicating working of vehiclesRegistering/indicating working of machinesTelecommunications linkCommunication link
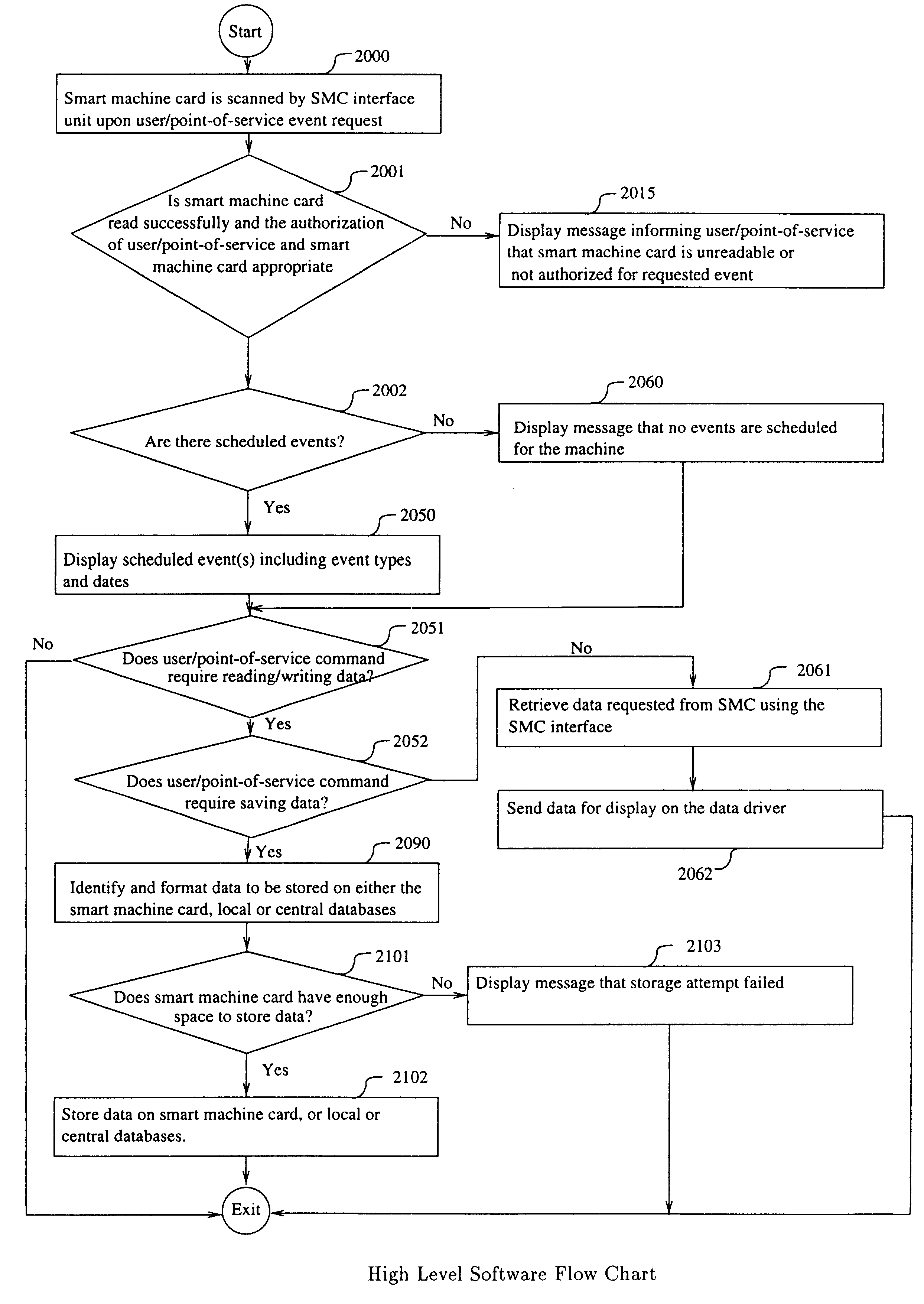
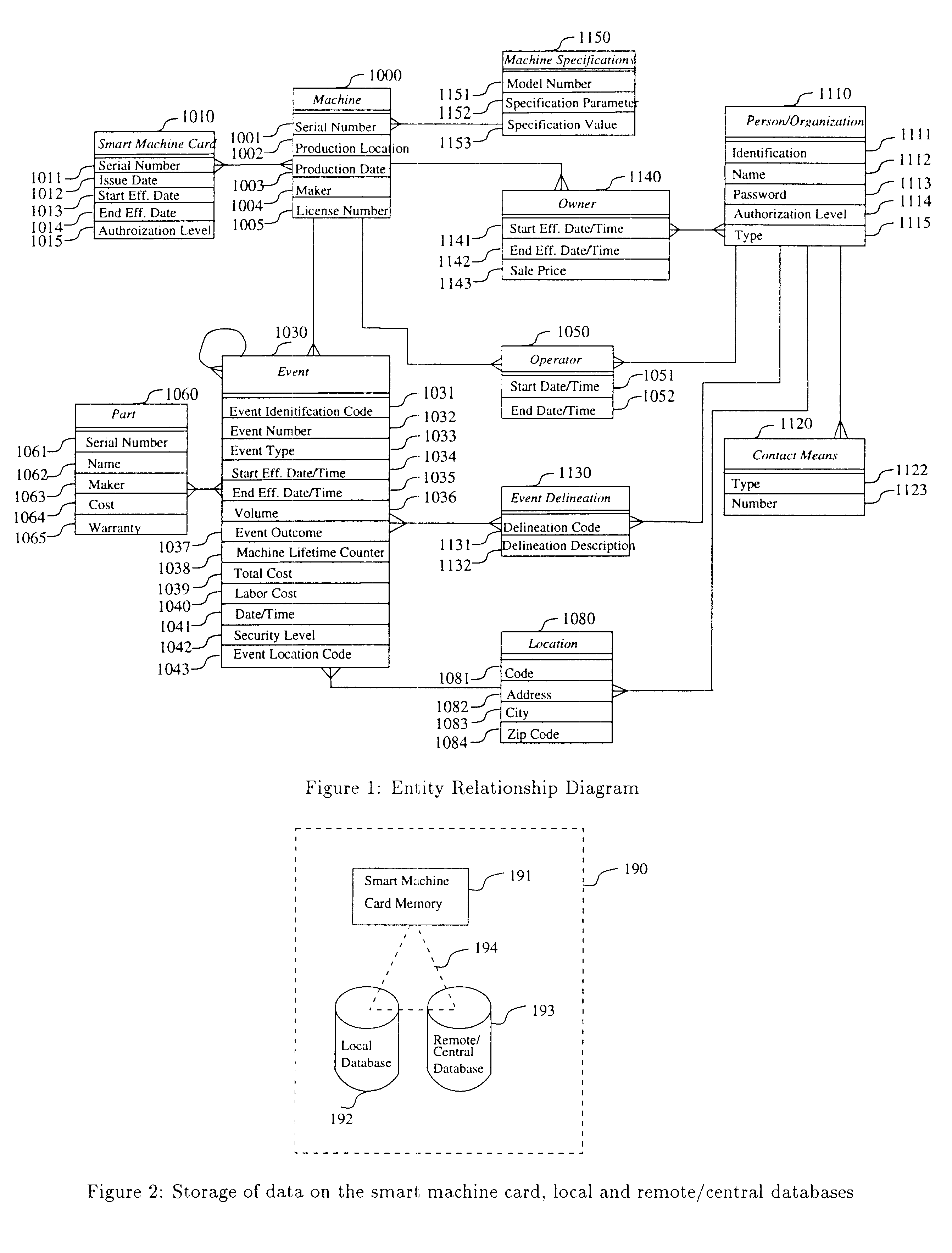
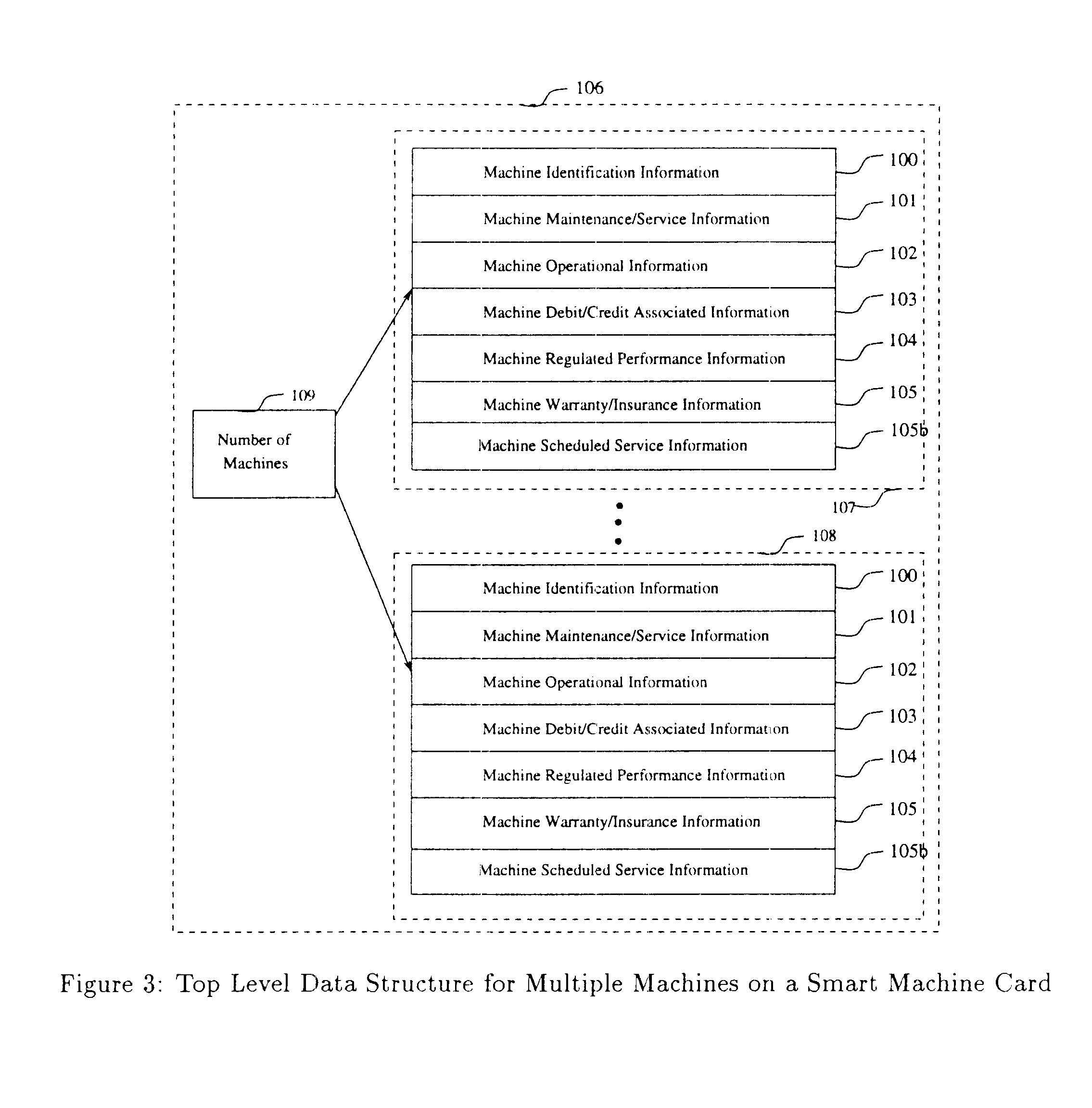
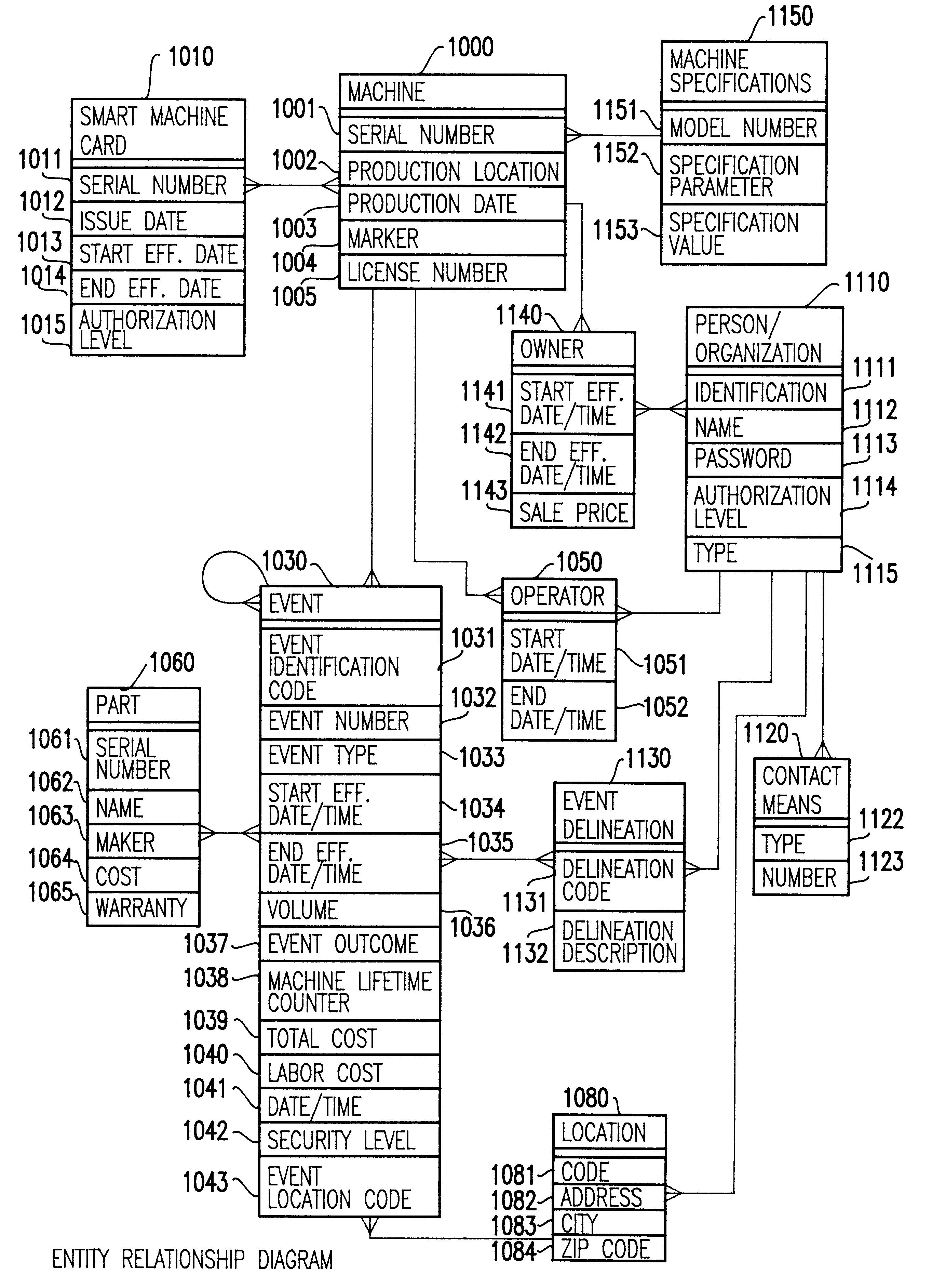
A computerized "smart card" which has a read / write memory and formatted data storage blocks is used to track the life history of one or more associated machine(s) (e.g., vehicles, medical instrumentation and apparatus, business and copying machines, etc.). The smart card can store a variety of information including machine identification, hardware / software specifications, debit / credit, regulated performance, warranty / insurance, maintenance / service and operational transactions that might impact the hardware, software or the intended operation or performance of the machine. The smart card will be equipped to interact with any of a plurality of autonomous reader / writer smart card units and computer-based reader / writer smart card units that may be equipped to interact with any of the plurality of computer databases through the utilization of land or wireless communications links. Preferably, each smart card will be associated with one or more specific machines at the time of sale of the machines, and will be periodically updated at each transaction (e.g., repair, scheduled maintenance, transfer of title, etc.) using reader / writer units operated by service technicians, repair shops, insurance agents, or the like. Thus, upon transfer of title of the machine, the smart card will also be transferred to provide the new owner with a complete life history for the machine. The stored life history can be used for valuation, maintenance scheduling, problem trouble shooting, and other applications. In the case of a single card being associated with a group of machines (e.g., a company with a fleet of cars, trucks or buses, or a company with several photocopiers, etc.), the card can also be used to track the scheduled replacement of individual machines within the group. Provisions are also made to associate new cards with existing machines to track the future life history of a particular machine.
Owner:Q INT
Method for using a smart card for recording operations, service and maintenance transactions and determining compliance of regulatory and other scheduled events
InactiveUS6170742B1Specific performanceRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesRegistering/indicating working of machinesTelecommunications linkSmart card
A computerized "smart card" which has a read / write memory and formatted data storage blocks is used to track the life history of one or more associated machine(s) (e.g., vehicles, medical instrumentation and apparatus, business and copying machines, etc.). The smart card can store a variety of information including machine identification, hardware / software specifications, debit / credit, regulated performance, warranty / insurance, maintenance / service and operational transactions that might impact the hardware, software or the intended operation or performance of the machine. The smart card will be equipped to interact with any of a plurality of autonomous reader / writer smart card units and computer-based reader / writer smart card units that may be equipped to interact with any of the plurality of computer databases through the utilization of land or wireless communications links. Preferably, each smart card will be associated with one or more specific machines at the time of sale of the machines, and will be periodically updated at each transaction (e.g., repair, scheduled maintenance, transfer of title, etc.) using reader / writer units operated by service technicians, repair shops, insurance agents, or the like. The stored life history can be used for valuation, maintenance scheduling, problem trouble shooting, and other applications.
Owner:Q INT
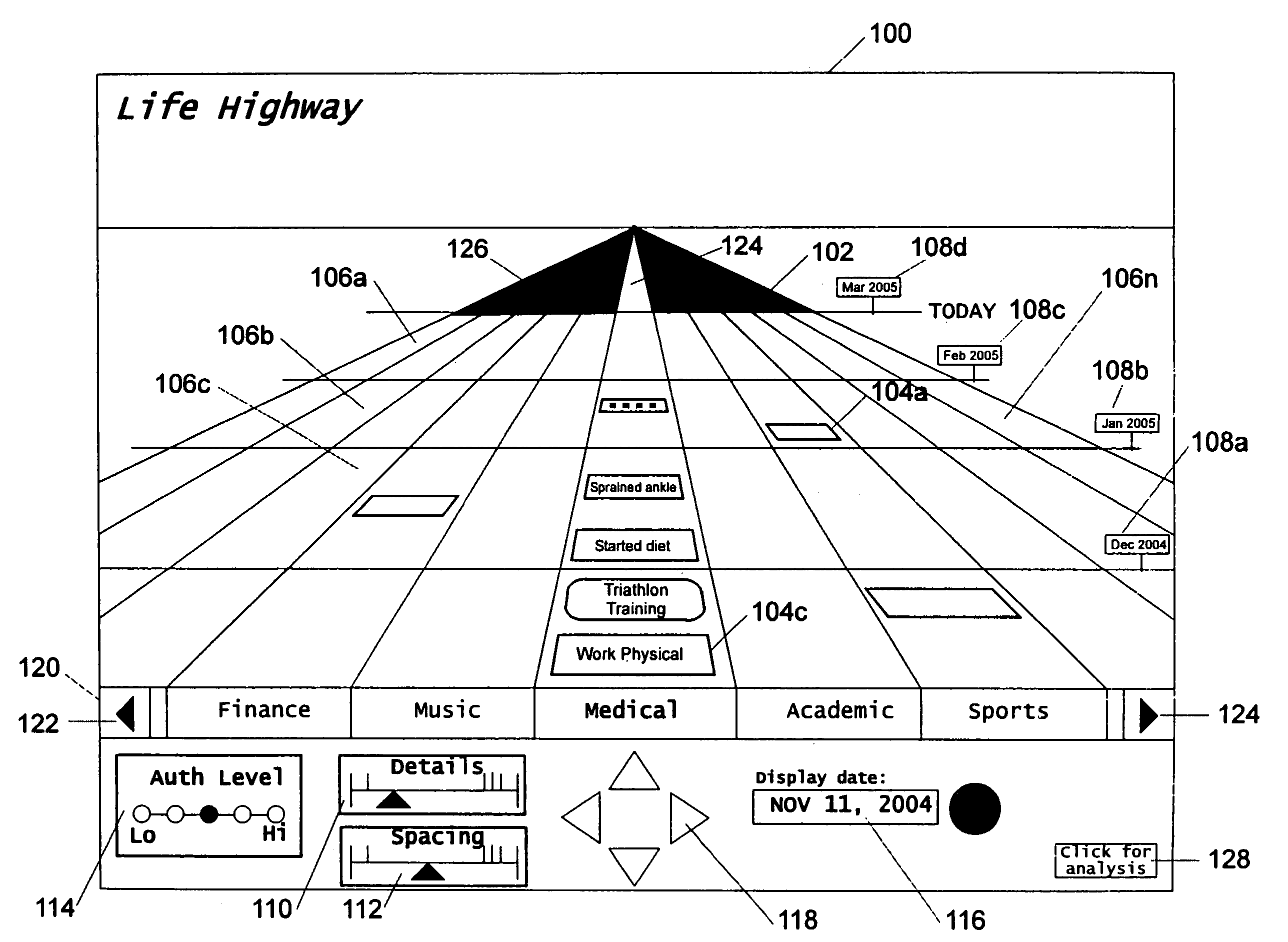
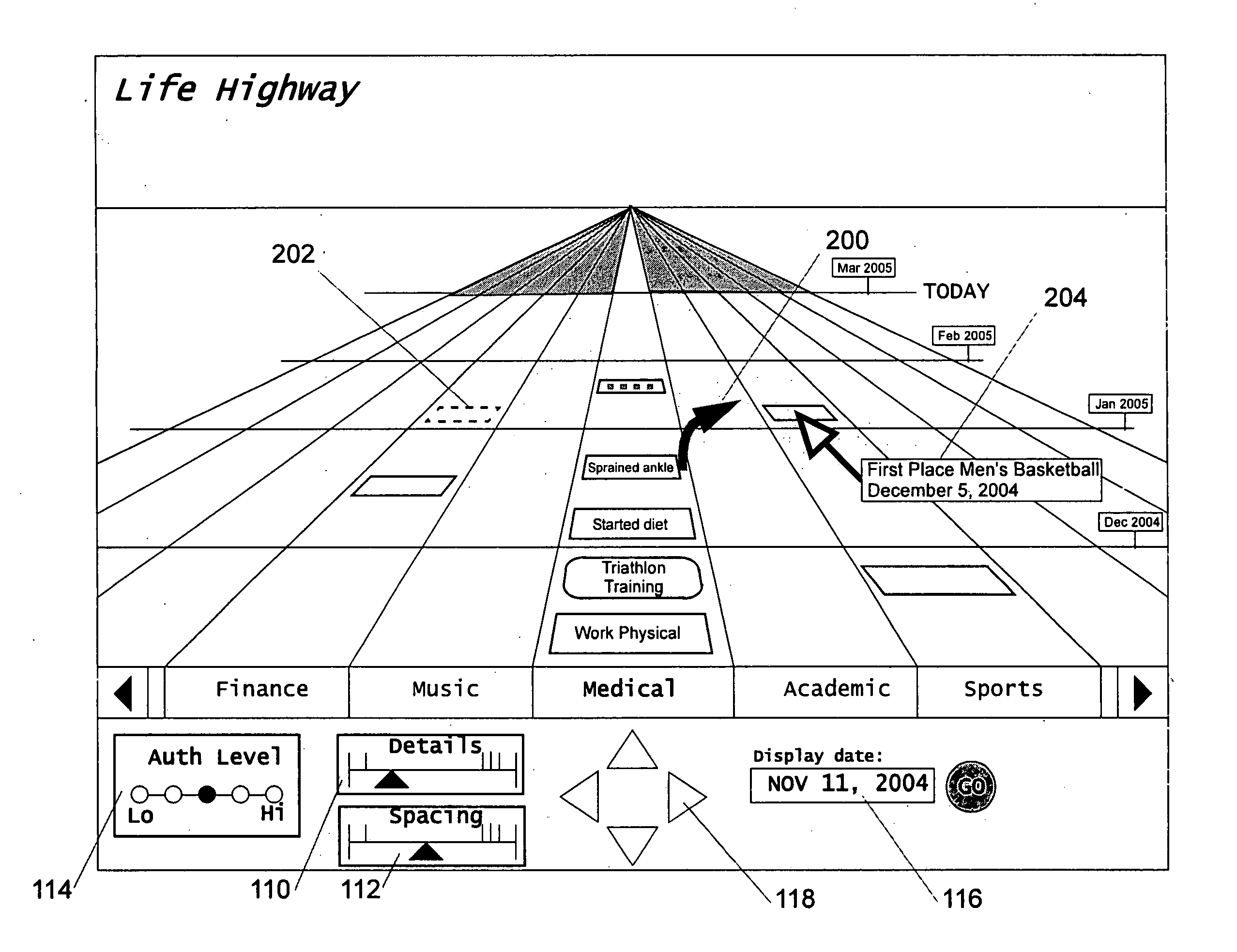
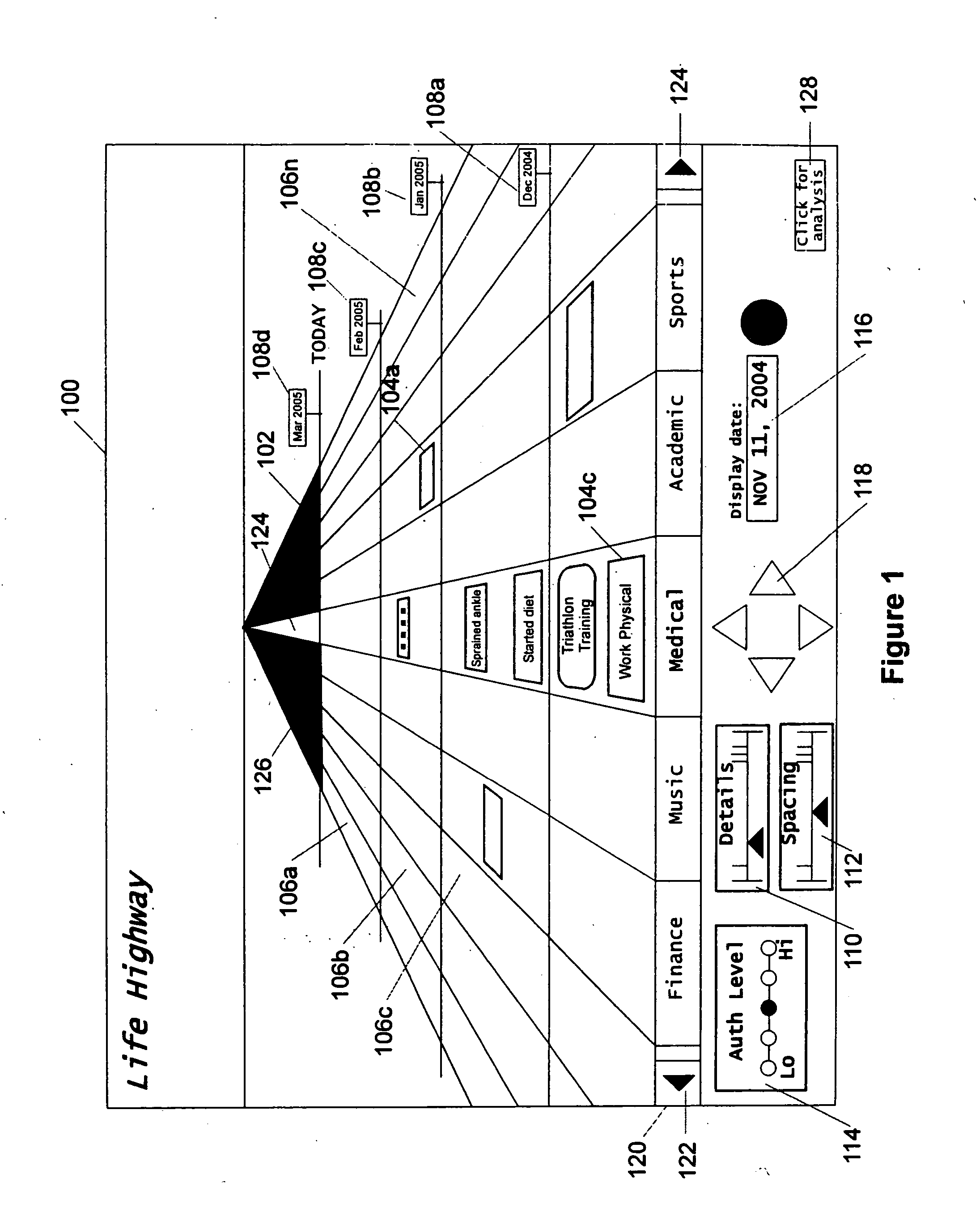
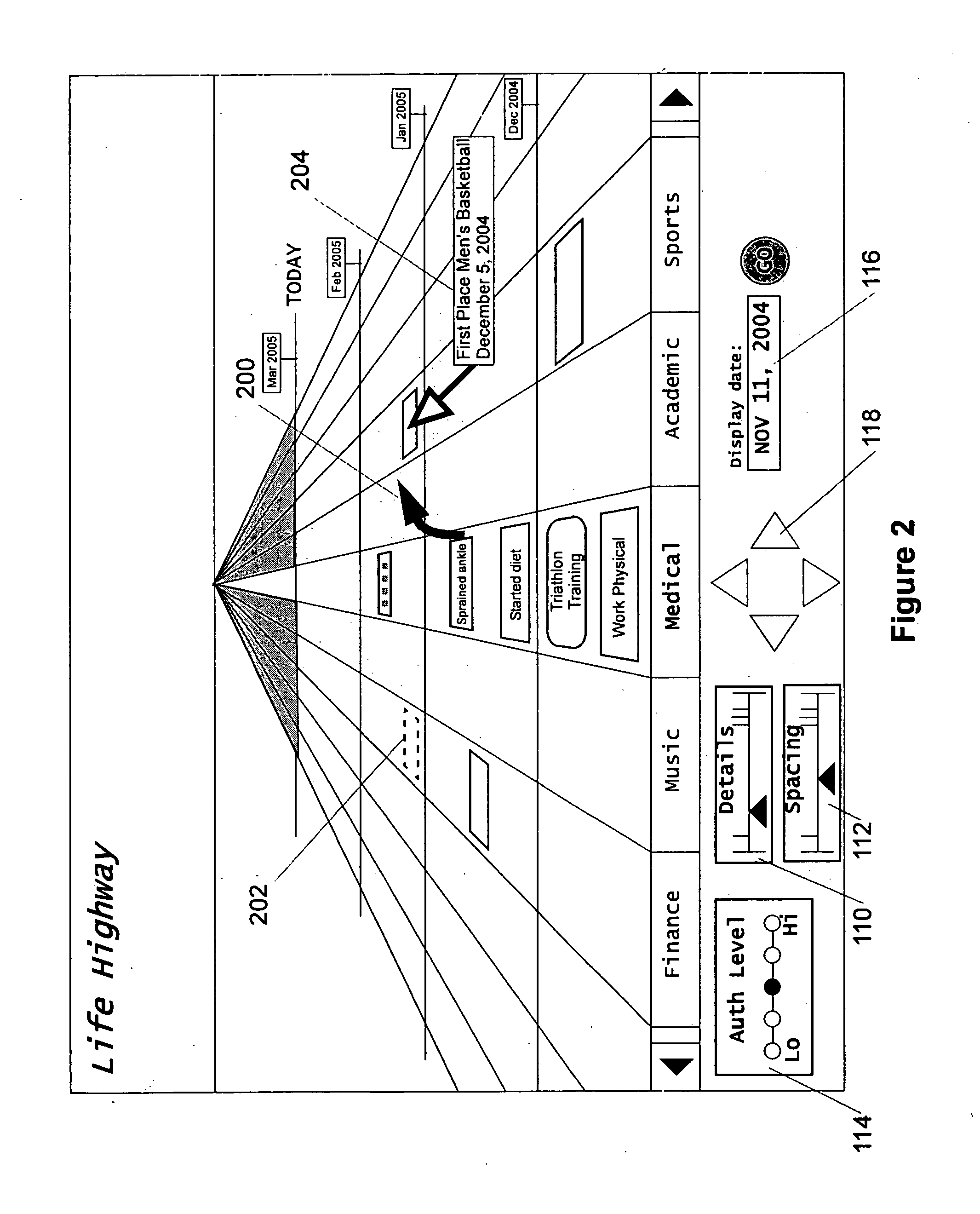
Graphical chronological path presentation
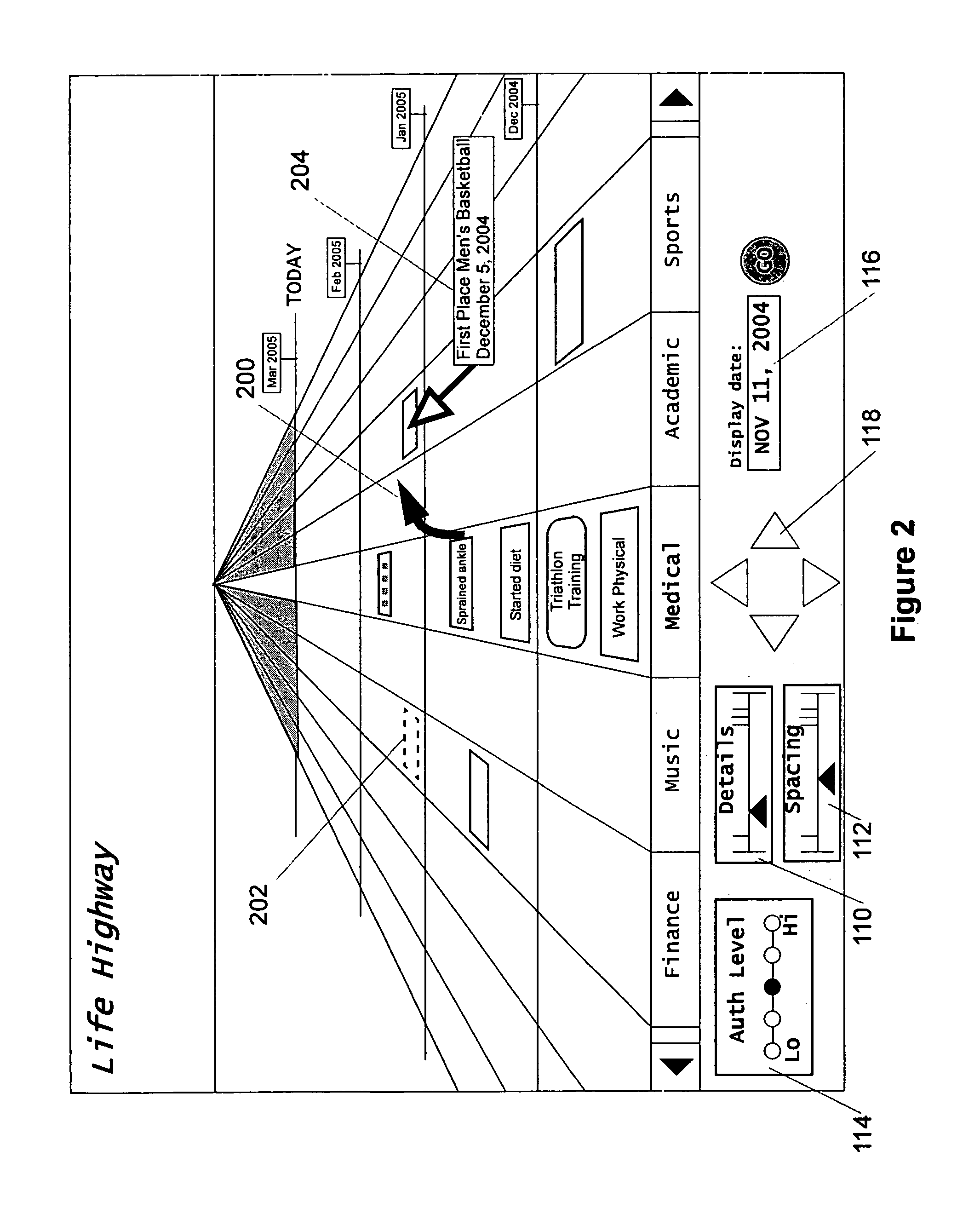
The life history of a person or entity can be presented in a graphical representation of a highway. Life events may be represented by simple data strings, or by files such as photographs, dissertations, job offers, and love-letters, among others. For ease in viewing, the information representing the life history is categorized according to type (medical, educational, photographic, etc.) and placed in lanes corresponding to the type of information. The information is also organized by date, being placed between mile corresponding to temporal periods, for instance, years. Other graphical arrangements of stored information are also included.
Owner:BELLSOUTH INTPROP COR
Device and Method For Monitoring Life History and Controlling Maintenance of Industrial Batteries
ActiveUS20080186028A1Batteries circuit arrangementsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansLife historyLife expectancy
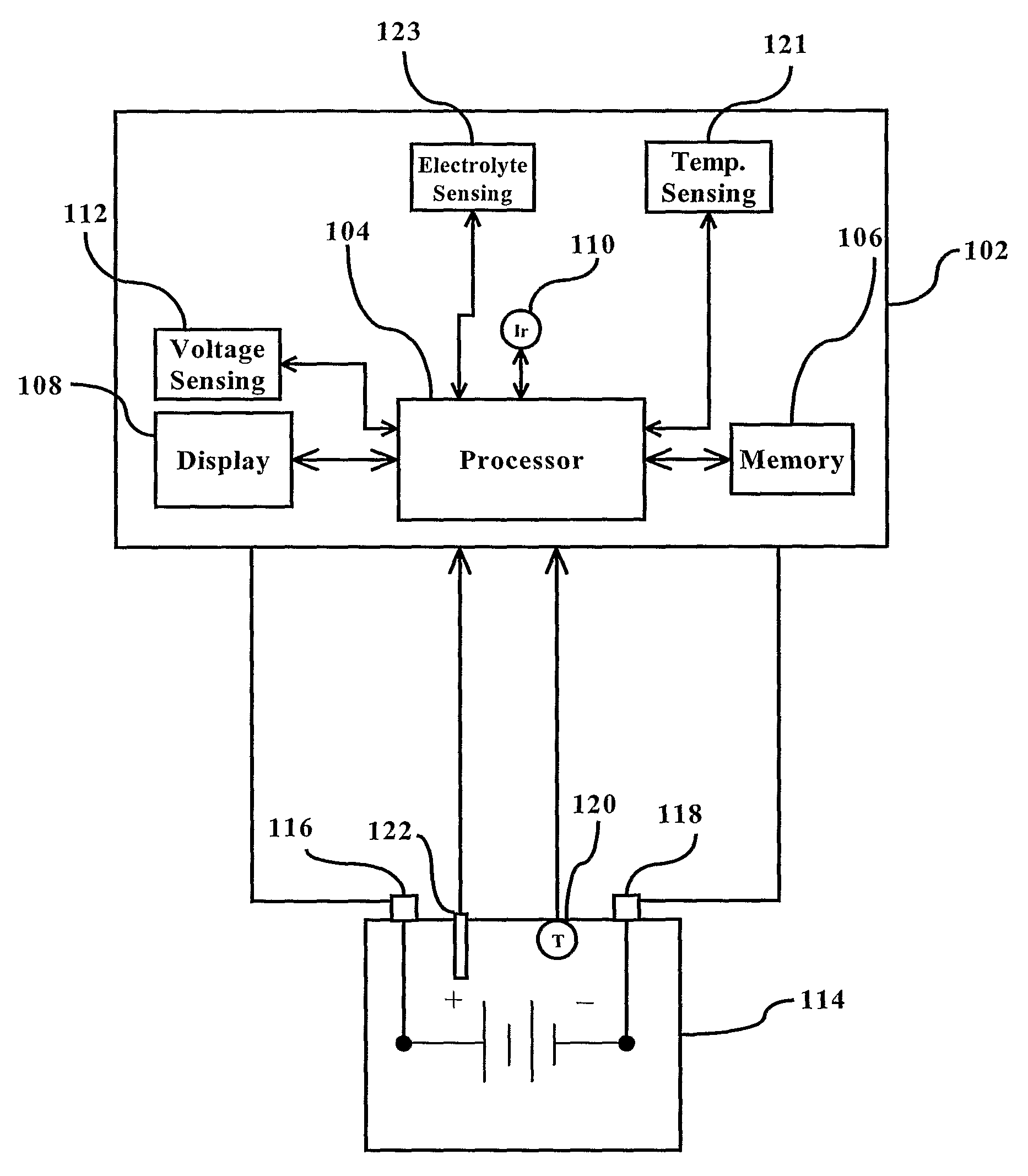
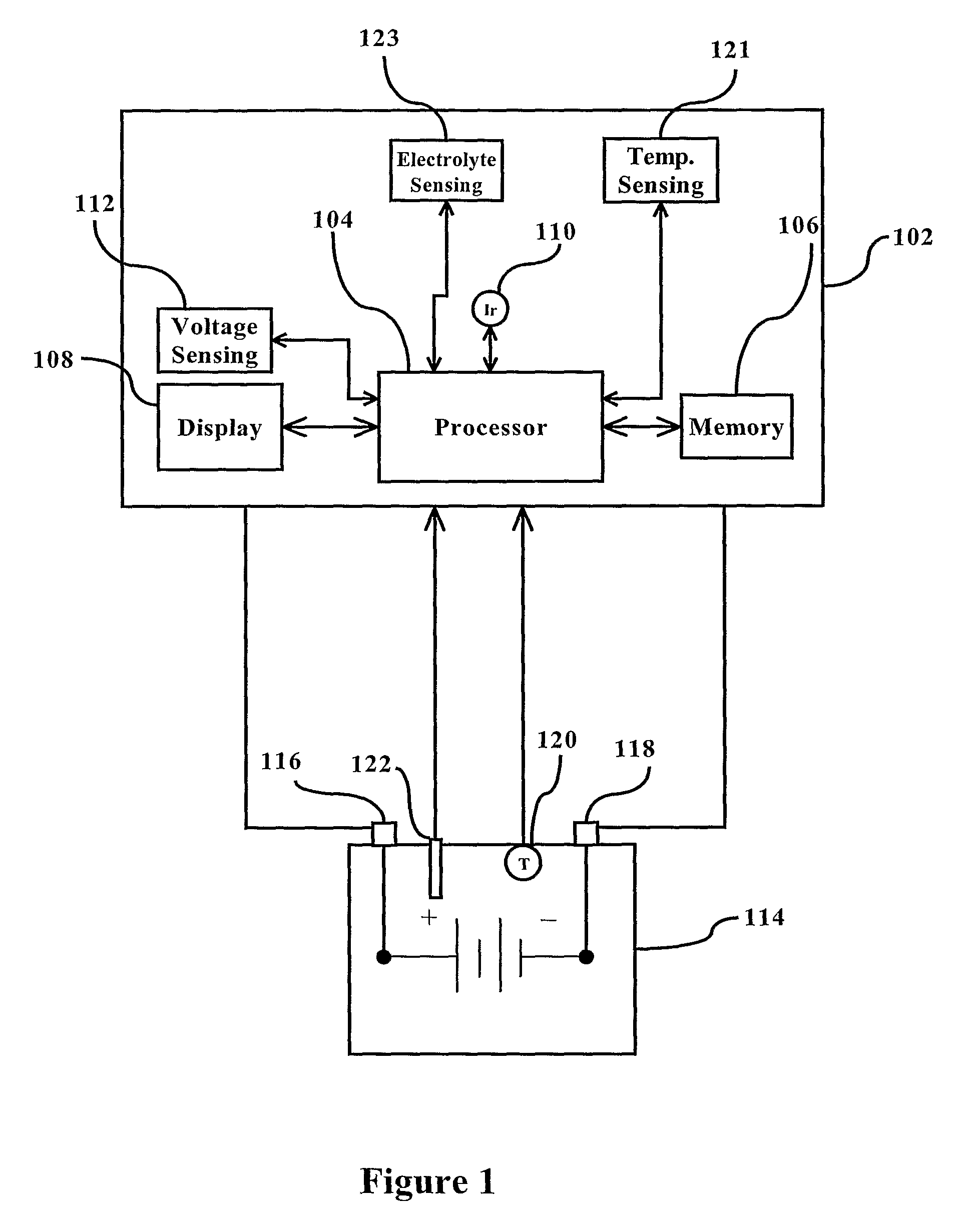
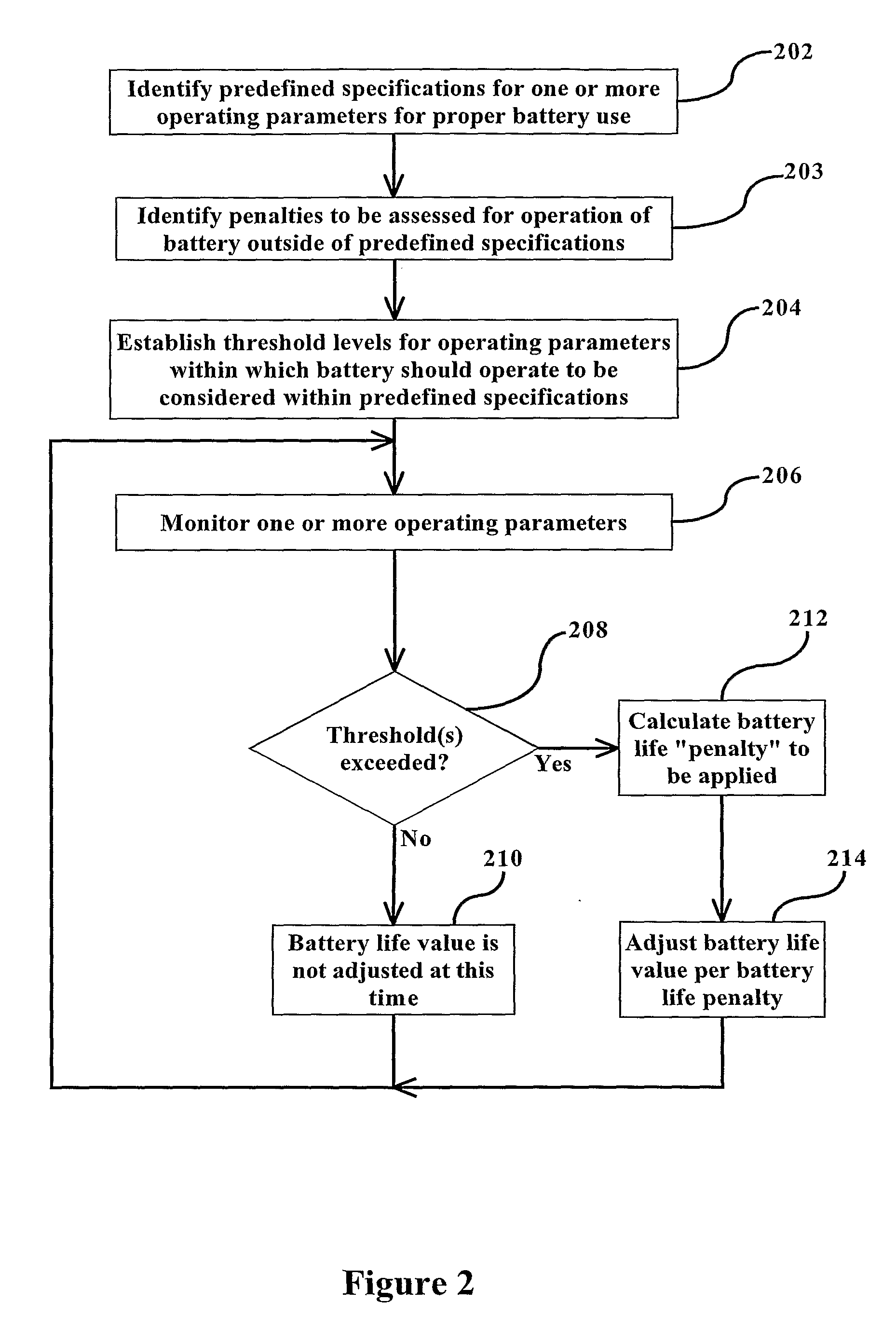
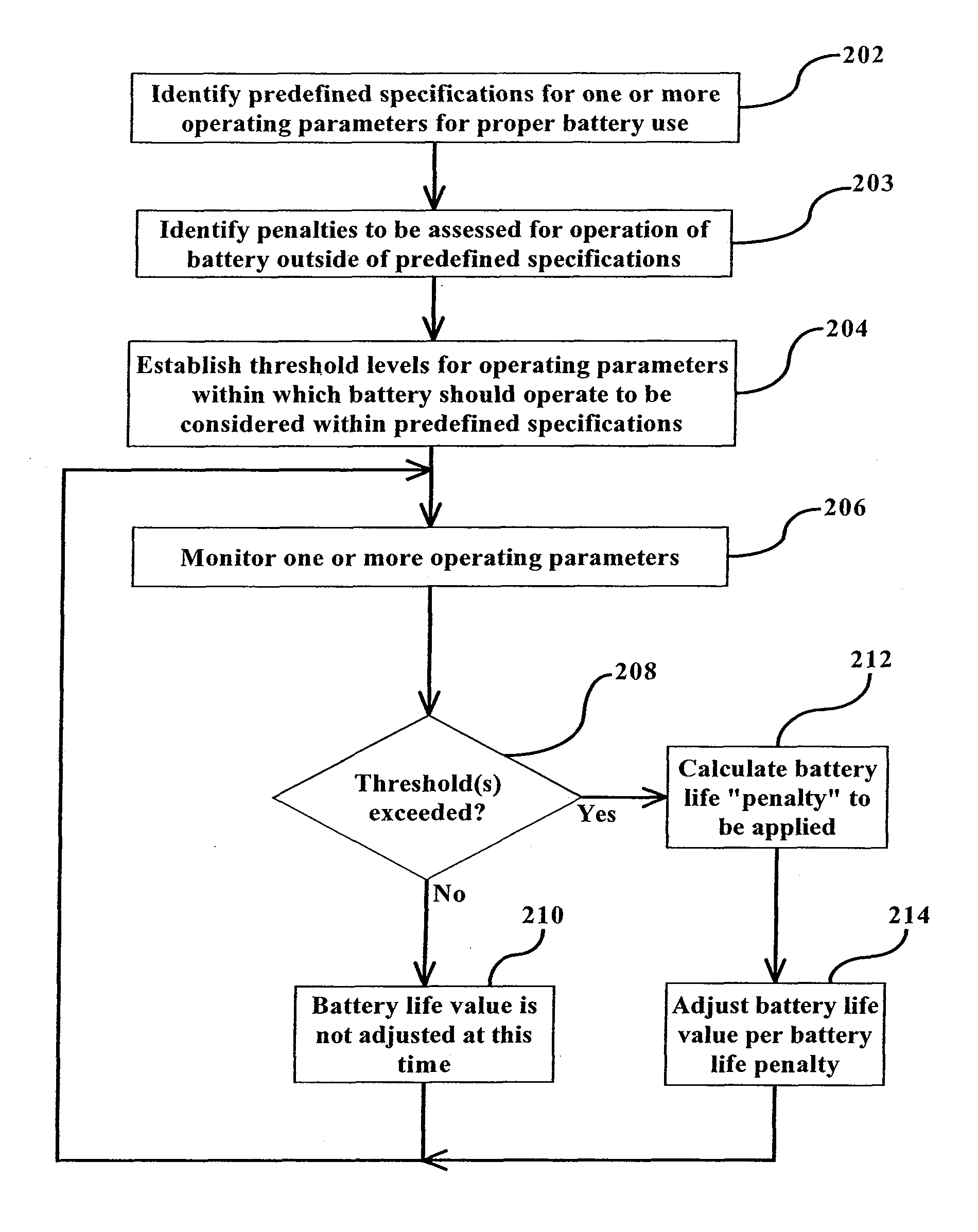
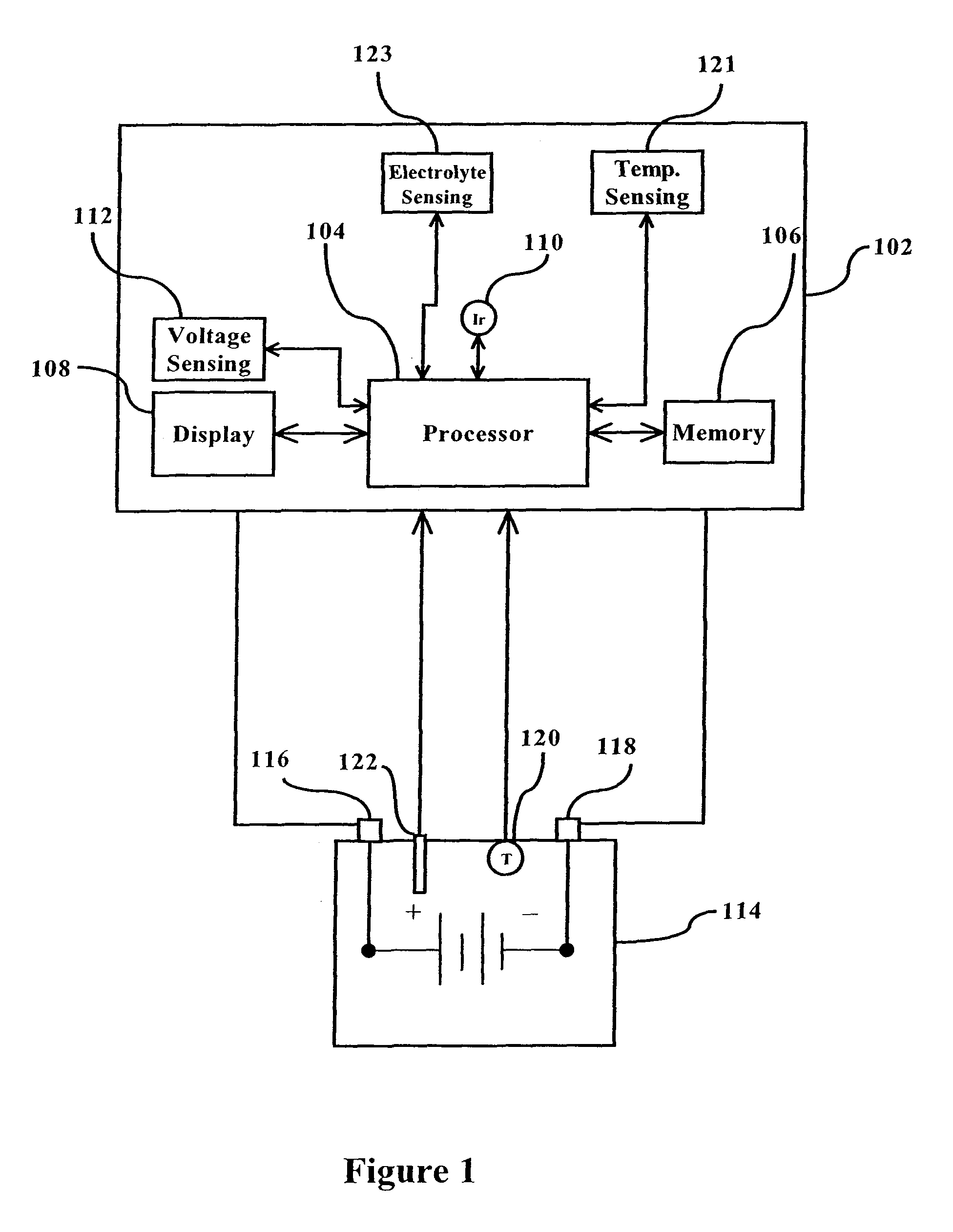
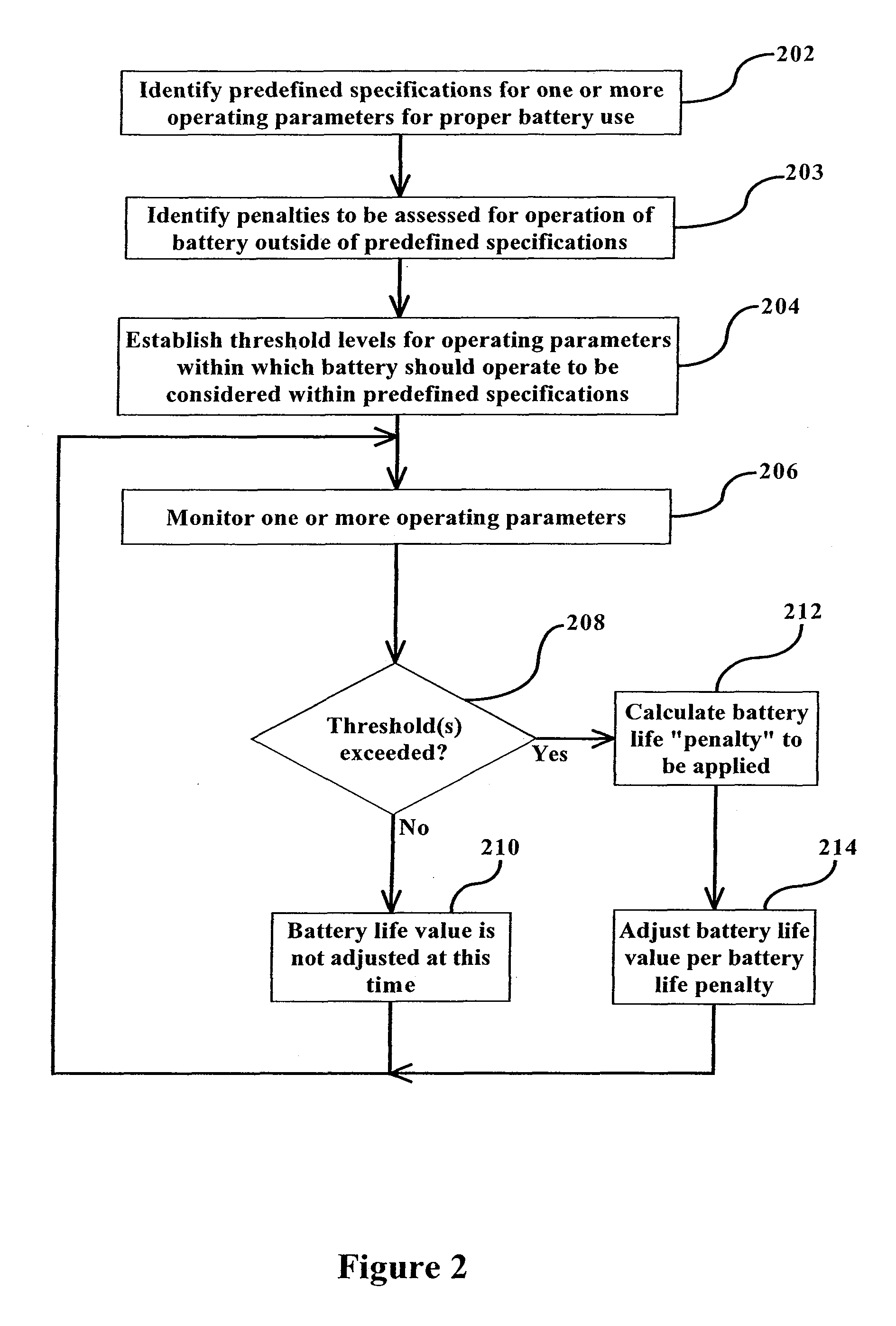
This invention is a method and device for monitoring and storing data regarding the “life history” of a battery with which it is associated and interpreting the data to create an accurate record of use and abuse patterns. A manufacturer's specified life expectancy, measured in battery cycles, is established for the battery under normal use, and then the actual use of the battery is monitored and stored. Complete cycles, partial cycles, and operation of the battery outside of acceptable specifications are automatically derived into a value in units equivalent to a number of battery cycles, and this derivation is compared with the manufacturers life expectancy, and adjustments to the manufacturers life expectancy are made so that a more accurate and up-to-date estimation of battery life can be evolved over the life of the battery. The monitoring device is mounted on the battery for the lifetime of the battery, with certain information regarding the battery being displayed to all persons having access to the battery. Additional information may be made available to an authorized person or entity. This enables a lessor of the battery, for example, to identify abuse of the battery by a lessee and adjust fees, lease terms, etc. accordingly.
Owner:PHILADELPHIA SCI
Computer implemented methods and systems for storing product history and/or failure data and/or analyzing causes of component and/or system failure
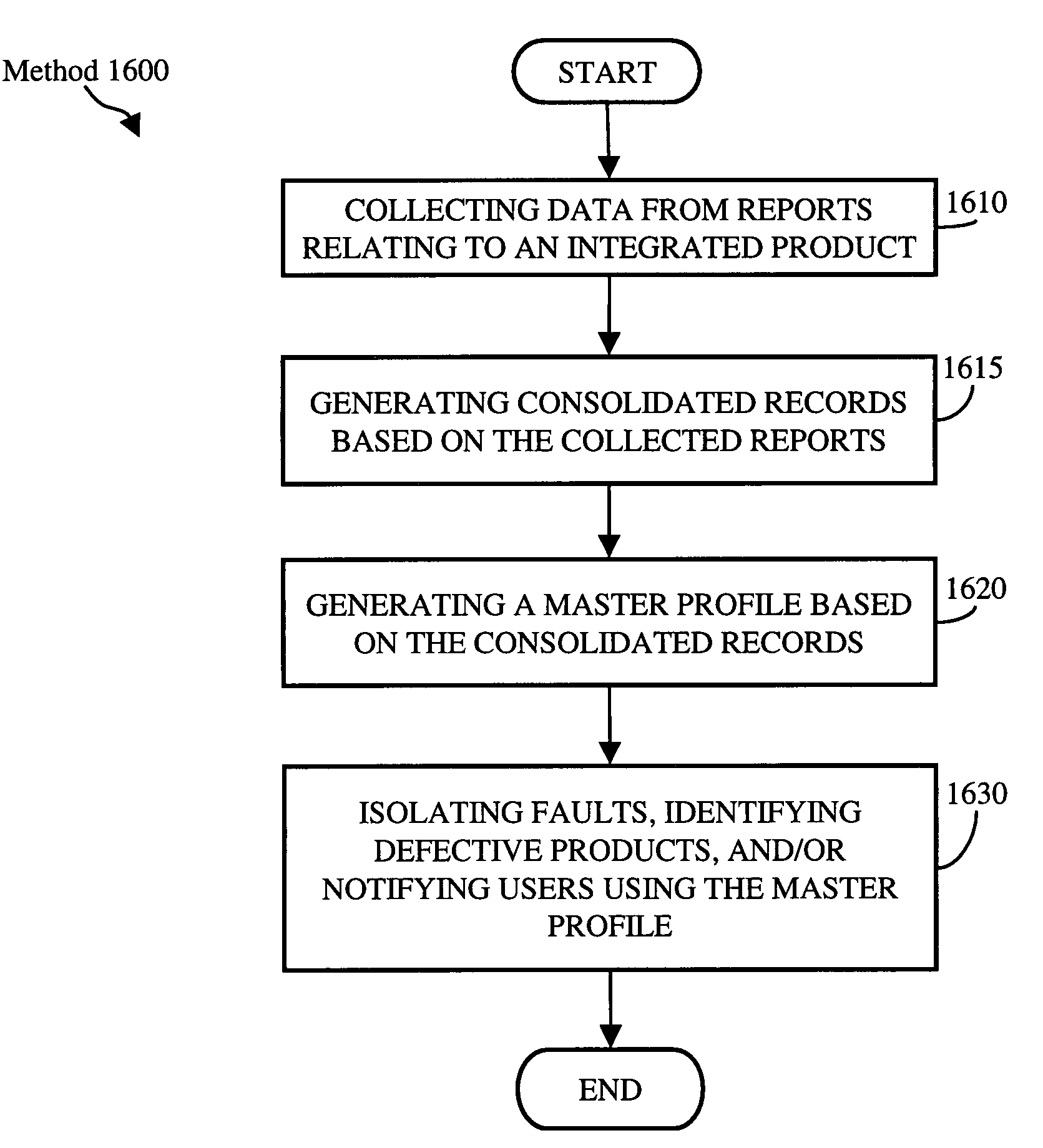
Methods and systems are provided for storing and analyzing product history data to determine root causes of performance anomalies and / or field failures. In accordance with some embodiments of the present invention, the life history of an integrated product and its constituent components may be consolidated into a master profile. The master profile may include one or more product profiles and behavior profiles that may be generated from data collected over the product's life history. In response to receiving an indication that an integrated product is defective, the master profile may be analyzed to isolate the component of the integrated product that caused the product to be defective.
Owner:TRACEABILITY SYST ARCHITECTS
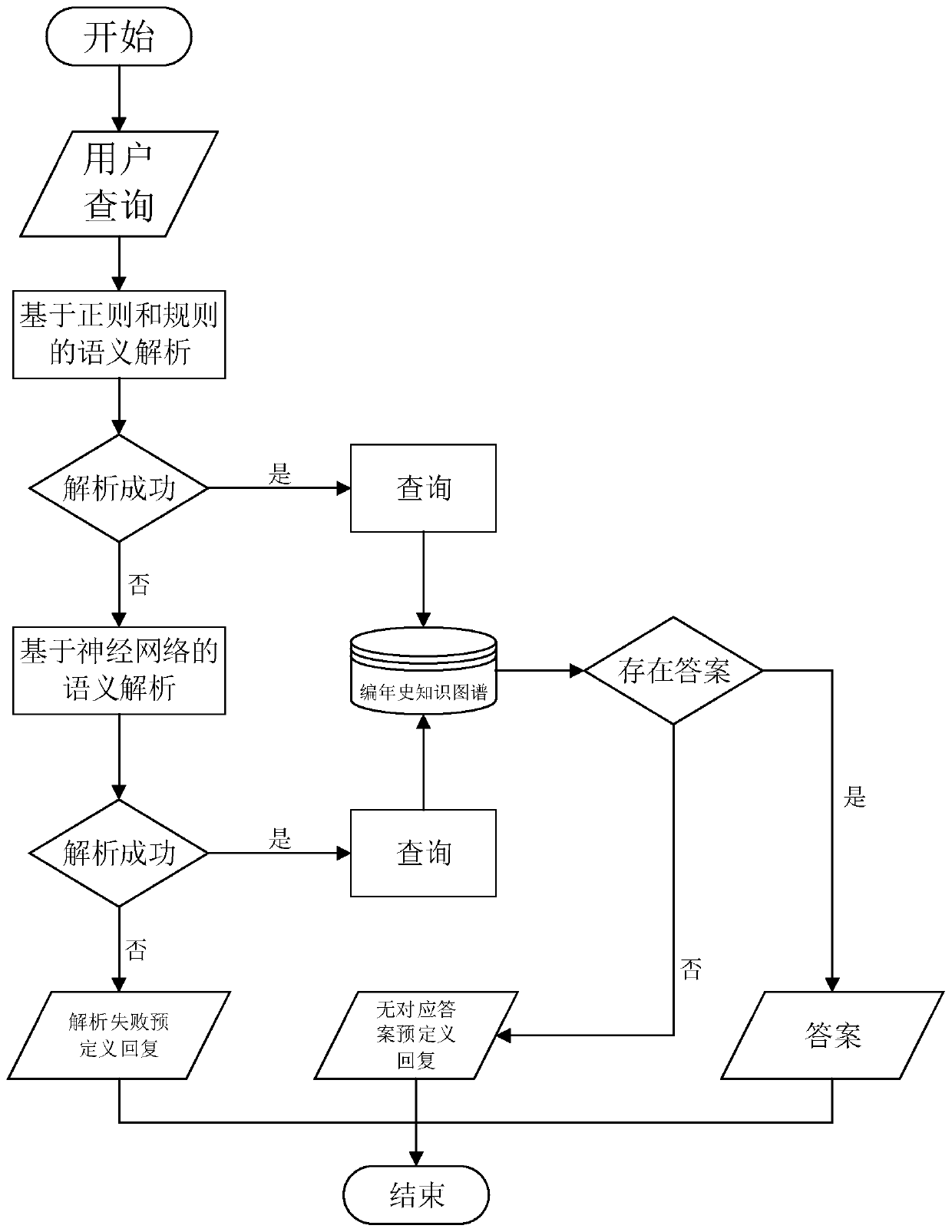
A construction method of a literature compilation life history question and answer system based on a knowledge graph
ActiveCN109766417AImprove the efficiency of acquiring specific knowledgeAccurate analysisNeural architecturesSpecial data processing applicationsQuestion analysisTight frame
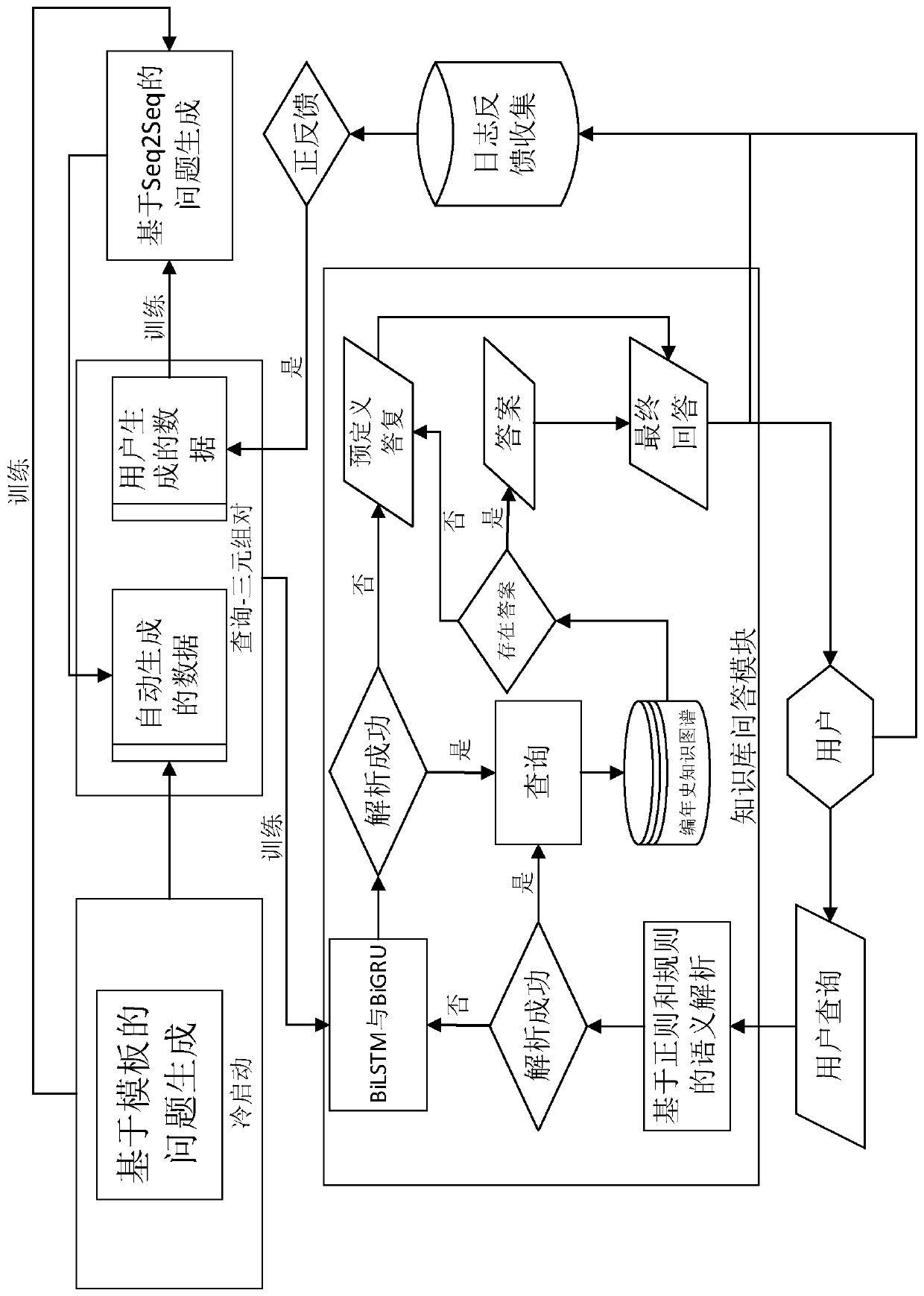
The invention discloses a construction method of a literature history question and answer system based on a knowledge graph, which comprises the following steps of constructing the knowledge graph ofa literature history vertical field by taking structural data related to Chinese literature history as a basis and combining a literature history ontology structure created from top to bottom; designing a semantic analysis framework which comprises two user question analysis modules characterized in that one module is based on regularization and rules, and the other module is based on a neural network; organizing the results obtained through problem analysis into corresponding SPARQL query statements, and searching the corresponding results for in the constructed knowledge graph; organizing the result as a reply, and returning the reply to the user; designing a webpage side and a WeChat official account service as a window for interaction between the system and a user; designing a user uses a log and feedback collection module, wherein the related data is used for iteratively training a neural network model, and the generalization capability of the model is enhanced. According to the present invention, the natural language query of a user can be directly processed, an accurate result is returned, and the method plays an important role in improving the knowledge acquisition efficiency, promoting Chinese culture research and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
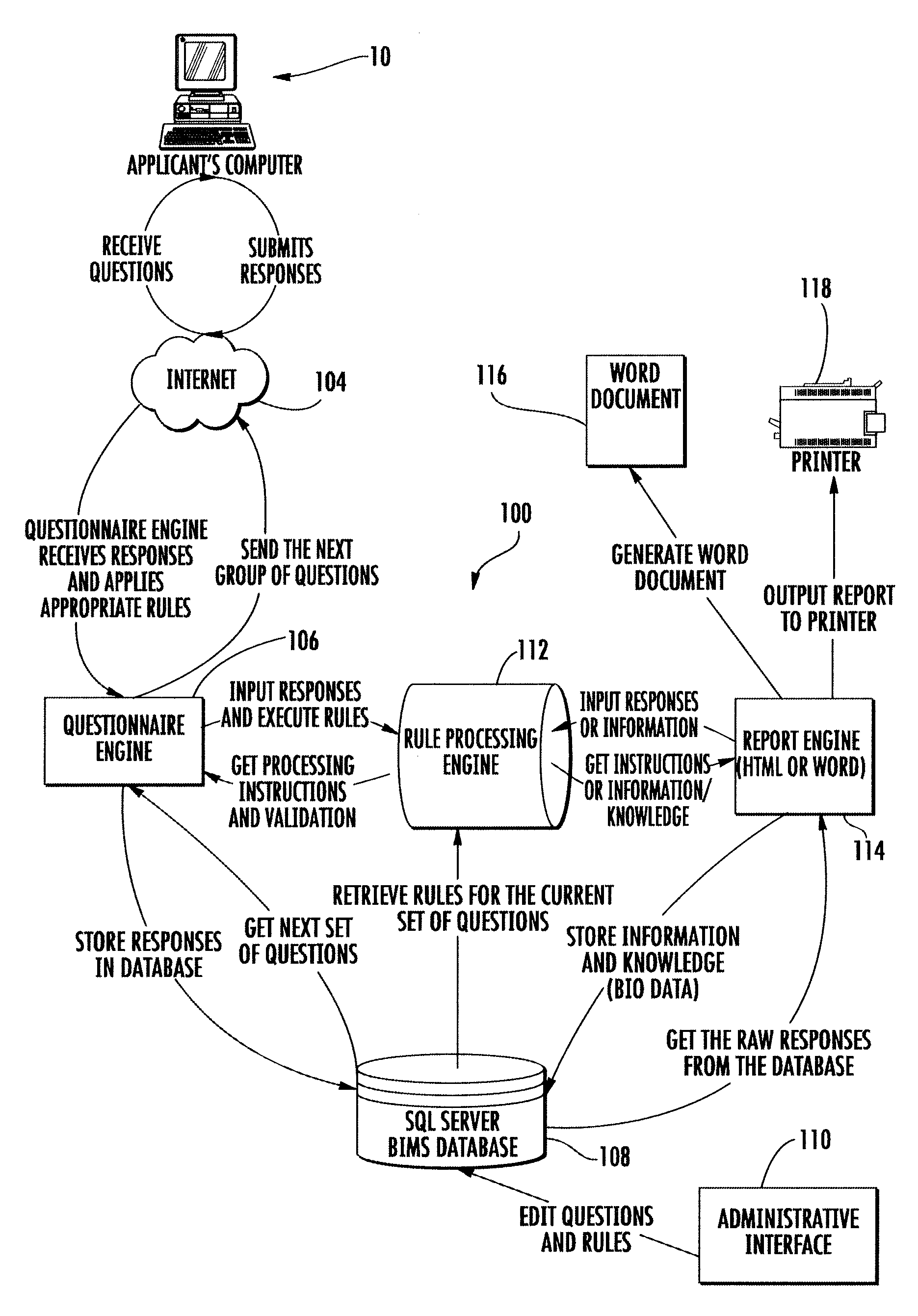
System, method and computer readable medium for acquiring and analyzing personal history information
InactiveUS7346541B1Minimize positive response biasIncrease authenticitySpecial service for subscribersHardware monitoringPositive responseLife events
A computer based method for acquiring life history information from an applicant for employment to minimize positive response bias and enhance the veracity of the acquired life history information. A question collection related to at least one life event is presented to the applicant. The question collection is comprised of a revealed stem question and at least one hidden branch question, the hidden branch question being related to the stem question. Based on the stem question response, the method automatically determines whether to present at least one hidden branch question to the applicant. If a hidden branch question is presented to the applicant, the applicant's response is received and stored in the computer database. The response to the stem question and the response to the hidden branch question are predictive of a predefined negative outcome for the applicant.
Owner:CUTTLER MICHAEL J +1
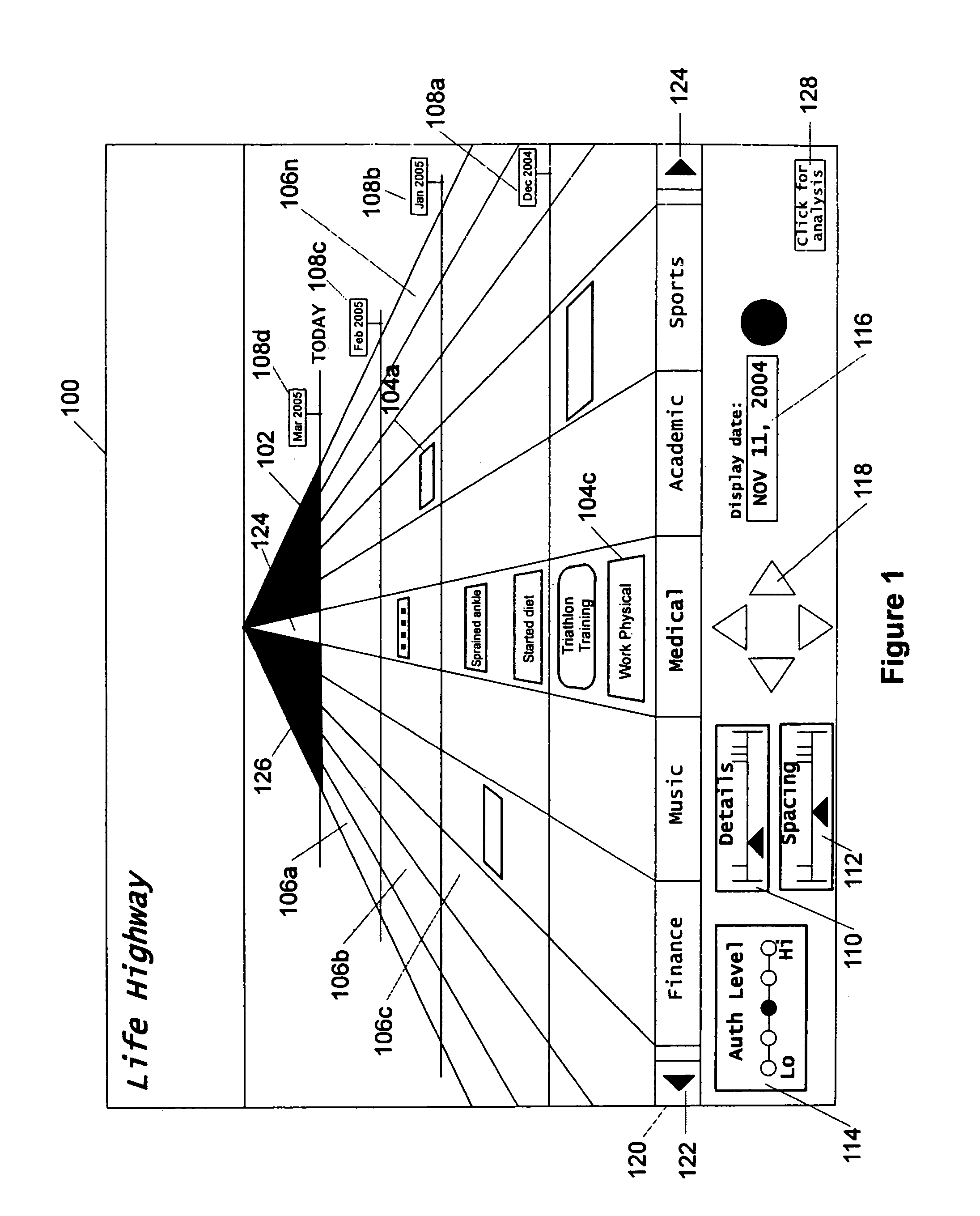
Graphical chronological path presentation
The life history of a person or entity can be presented in a graphical representation of a highway. Life events may be represented by simple data strings, or by files such as photographs, dissertations, job offers, and love-letters, among others. For ease in viewing, the information representing the life history is categorized according to type (medical, educational, photographic, etc.) and placed in lanes corresponding to the type of information. The information is also organized by date, being placed between mile corresponding to temporal periods, for instance, years. Other graphical arrangements of stored information are also included.
Owner:BELLSOUTH INTPROP COR
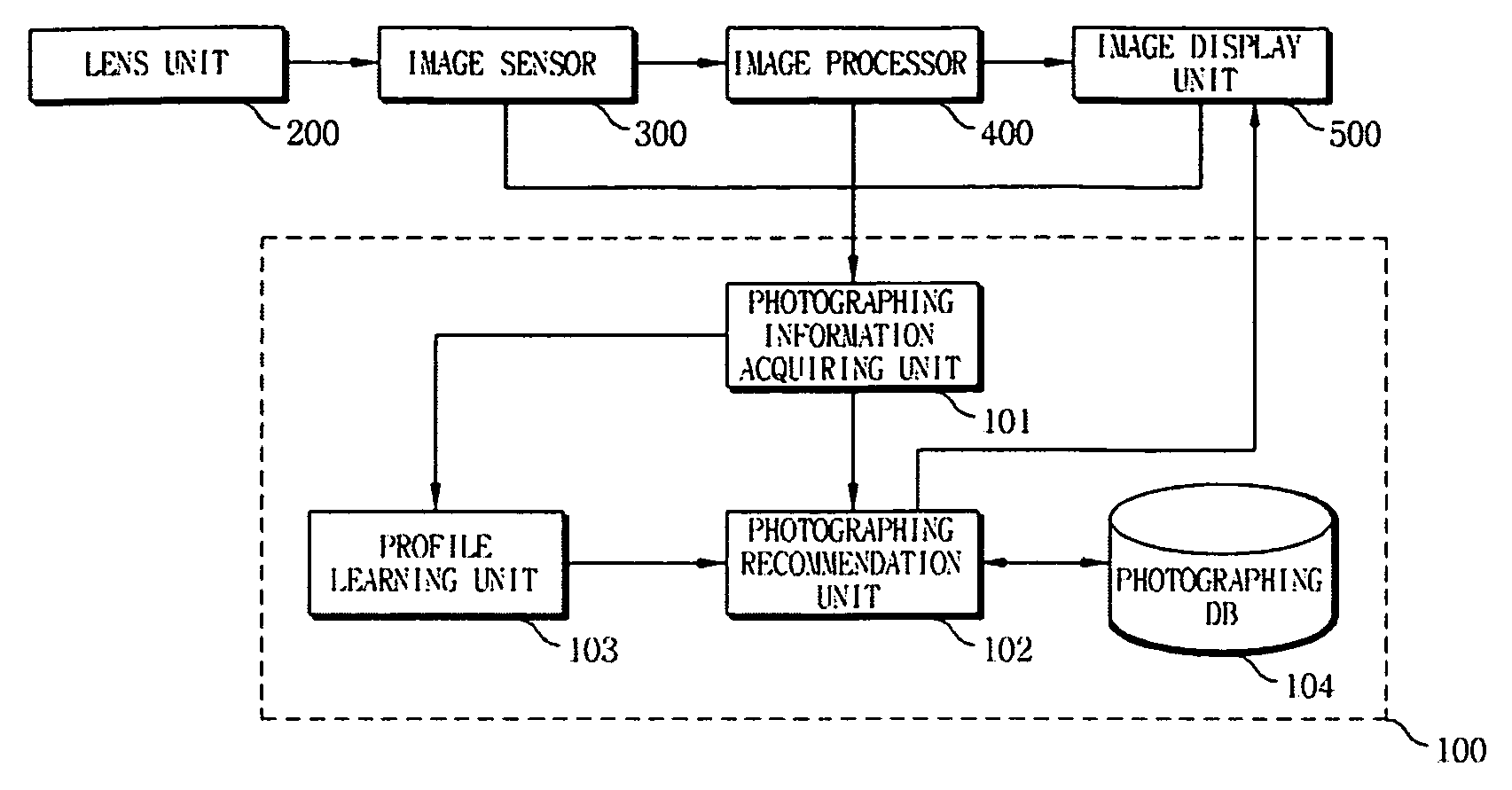
Apparatus and method for learning photographing profiles of digital imaging device for recording personal life history
Provided are a photographing profile learning apparatus and method of a digital imaging device for recording a personal life history. The photographing profile learning method learns a user's photographing patterns by recommending at least one previous picture consistent with a user's photographing tendencies, using a recommendation function and a user profile based on a user feedback value and a compensation value, receiving user feedback regarding the recommended previous picture, and updating the user profile and the recommendation function according to the user feedback. Therefore, since photographing settings are performed according to a user's tendency and conditions, it is possible to maintain consistency between a currently photographed picture and previously photographed pictures and systematically produce a visual diary.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Trunk insect device
InactiveCN101053321AEasy to collectCollect practicalInsect catchers and killersFruit treeEngineering
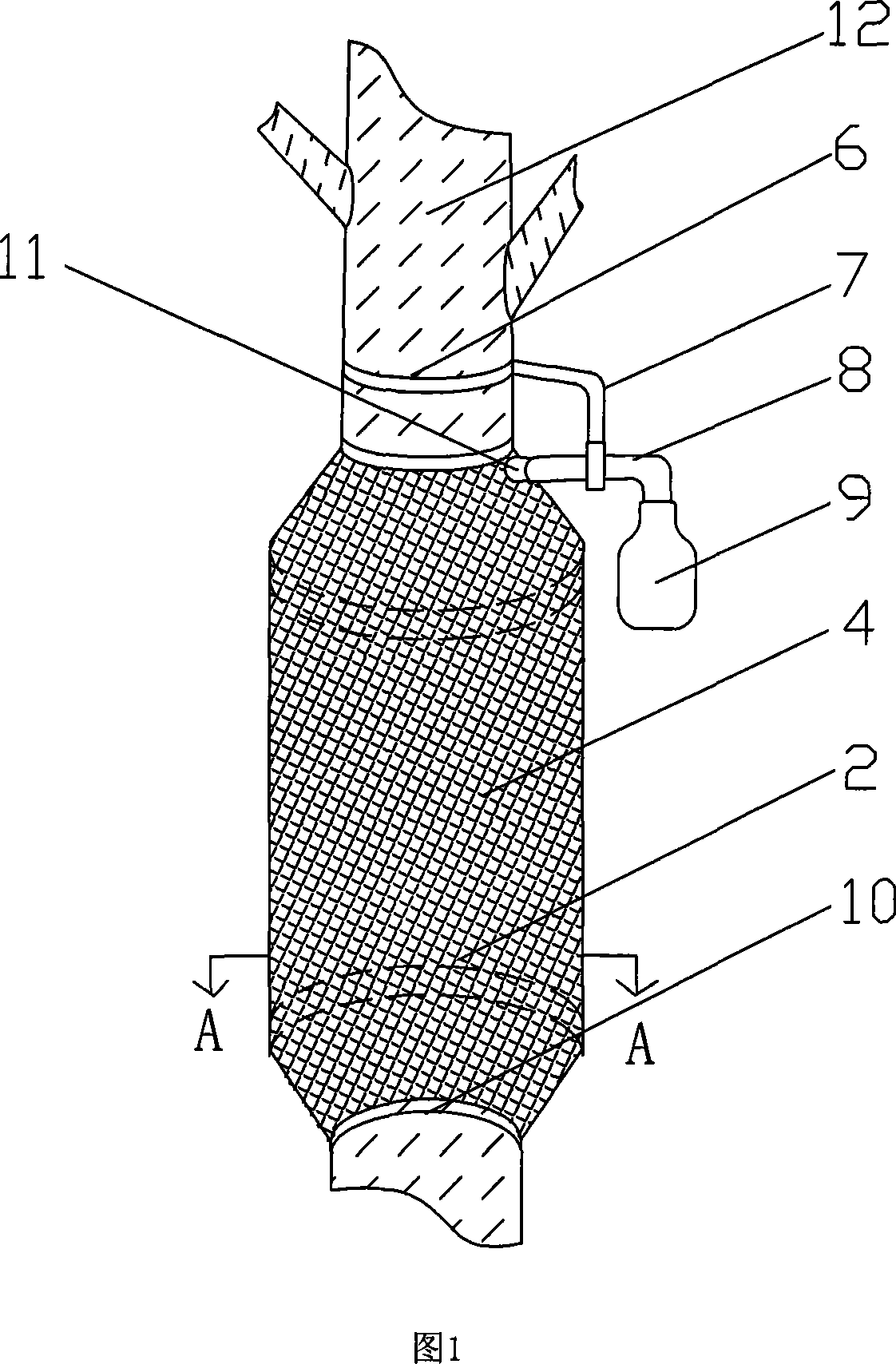
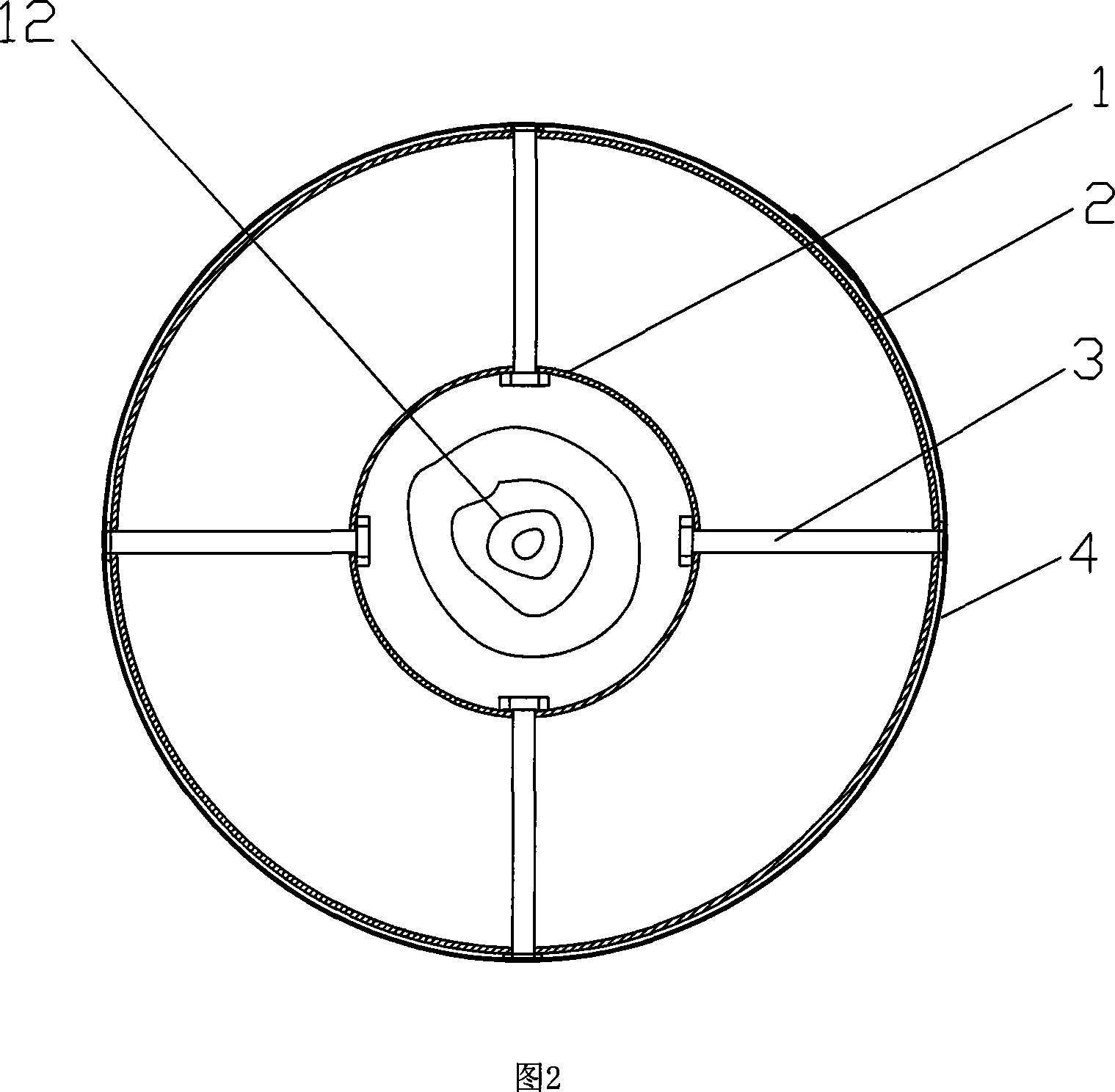
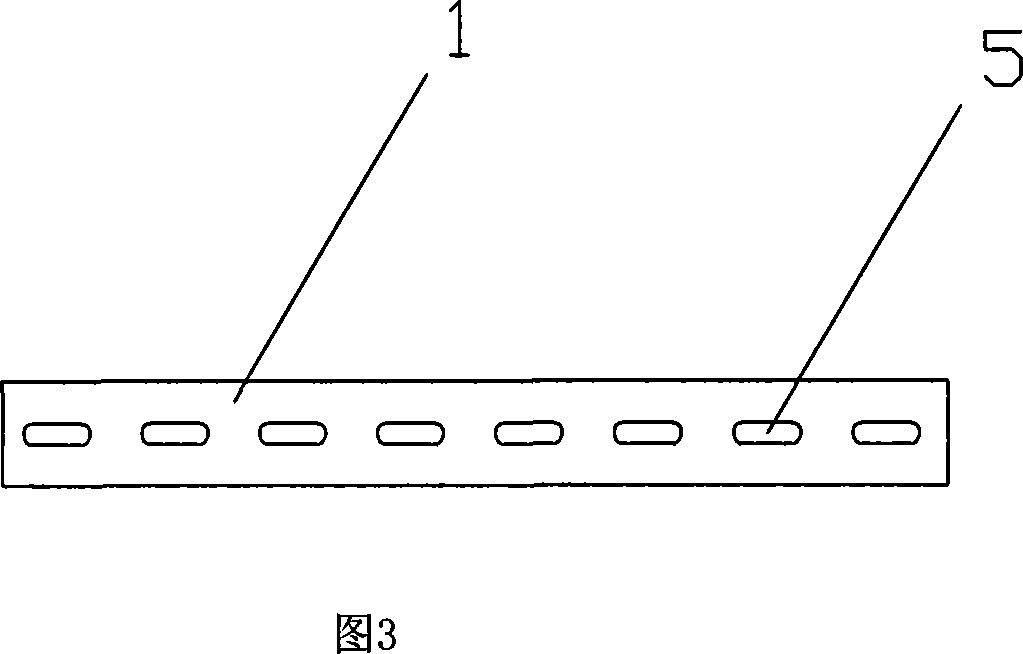
The present invention relates to a trunk insect device sitting a nylon net cover (4) surrounding covering the trunk (12), left end and right end of the nylon net cover (4) are linked together flexible, upper end and lower end of nylon net cover surround the trunk closely, above the nylon net cover (4) setting a fixation ring (6) used for surrounding the trunk, fixation bending rod (7) connects on the fixation ring, there is a via hole on the nylon net cover (4), joint tube (11) through the via hole connects with one end of bending tube (8), the other end of bending tube (8) connects with collecting bottle (9), the bending tube (8) is fixed by the fixation bending rod (7). The present invention is simple to use, it can be fixed on the trunk insect device on the forest land trunks, gardens trunks, courtyard trunks, fruit trunks. It can not only obtain target insect adult specimens and life history specimens of insect different stages, but also obtain parasitic natural enemy for the insects at the same time. The present invention also suits for observing and studying biological, ethology etc. of trunk boring insects and its parasitic natural enemies.
Owner:盛茂领 +1
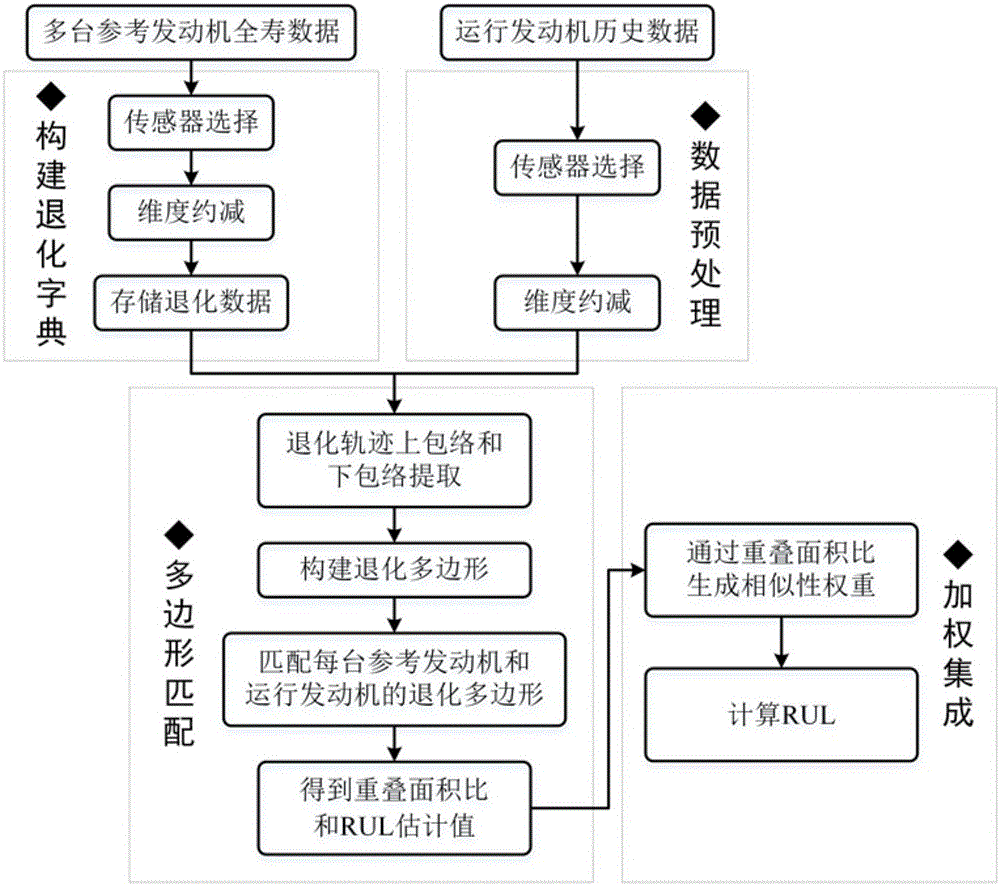
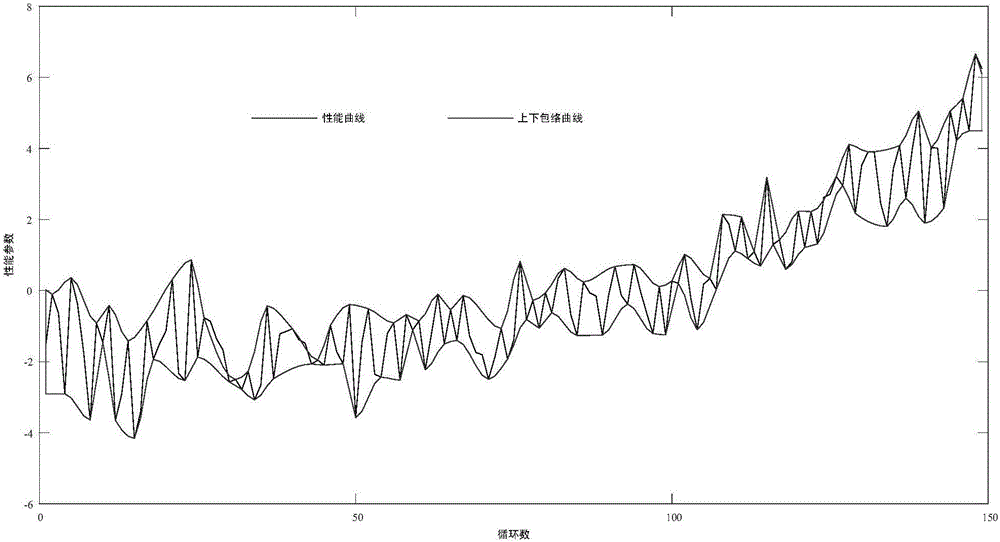
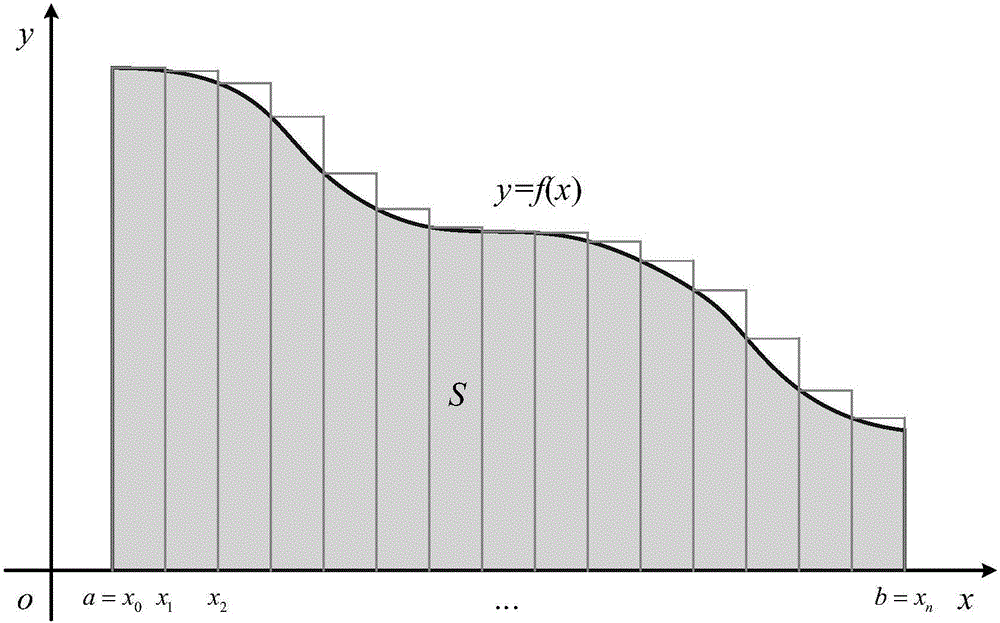
Aero-engine complete machine residual life prediction method based on gas path performance parameter graphic matching
ActiveCN106169001AImprove forecast accuracyImprove robustnessGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationAviationGraphics
The present invention provides an aero-engine complete machine residual life prediction method based on gas path performance parameter graphic matching to solve the problem that an aero-engine complete machine residual life is difficult to predict accurately. First, a degradation mode dictionary is constructed by using full-life history degradation data of engines of the same type. Secondly, sensor selection and state parameter dimensionality reduction are performed on data of a to-be-predicted engine. Then, graphic matching is performed on a recession trajectory of the to-be-predicted engine and recession trajectories of reference engines in the degradation dictionary, and life estimation of the to-be-predicted engine and similarity with the reference engines are obtained. Finally, the residual service life of the to-be-predicted engine is obtained via a similarity weighting strategy. According to the method, the residual service life of the aero-engine can be accurately predicted, and life prediction has a great significance for maintenance of the engine.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method for researching age and migration life history of coilia by eardust
InactiveCN101548653AFilling in the gaps in unclear fish age studiesImprove efficiencyClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaMicro structureBones fish
The present invention discloses a method for researching age and migration life history of coilia by eardust which belongs to the ichthyological ecology field. The method selects the eardust as researching material, processes grinding to an intersecting surface of the eardust, observes a micro-structure of the eardust for researching age, growth and life history of the coilia. Compared with traditional method, the method provides a new method for researching fish type annual zone, fills blank of unclear bright band and dark lane on the eardust to research fish type age; the eardust grinding has high efficiency, each eardust can be ground only five minutes, and the result is more reliable than other hard bone tissue analyzing; a nail enamel has transparent function to the eardust in embedding and enveloping simultaneity which is more safety and has better transparent effect than using dimethylbenzene. The method is suitable for researching relative age and migration life history of all hard bone fish type with eardust back and belly morphology curve.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA
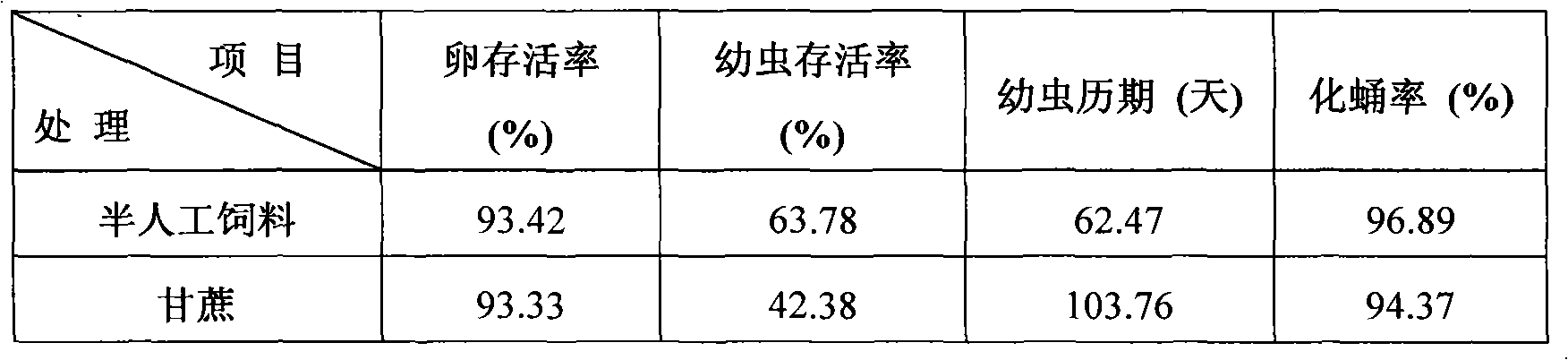
Conogethes punctiferalis artificial forage, preparation method and secondary culture method
InactiveCN104304694AImprove stress resistanceImprove toleranceAnimal feeding stuffArtificial rearingConogethes punctiferalis
The invention discloses a conogethes punctiferalis artificial forage, a preparation method and a secondary culture method, and belongs to the technical field of insect forages and breeding. The technical schemes help to solve the following three problems: (1) indoor manual secondary culture of conogethes punctiferalis with a complete life history is realized; (2) under the premise of indoor manual breeding is realized, the decline problem of bred populations is solved by continuously optimizing the forage formula and improving breeding operations; and (3) an excellent forage formula special for indoor manual secondary culture of conogethes punctiferalis is obtained, and satisfies demands on standardized health insect resource of conogethes punctiferalis imago and all-age larvas for sensitive population selective breeding and other various tests.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Indoor feeding and life history observation method of bark beetle
An indoor feeding and life history observation method of a bark beetle belongs to the technical field of insect feeding and control and solves the problem that observers cannot observe life habits such as gallery building, mating, oviposition, feeding and growth of larvas and life history of the bark beetle by means of an existing indoor bark beetle feeding technology. The method comprises the following steps: (1) preparation of a host wood section, (2) preparation of an insect feeding cage, (3) collection of imagoes, (4) insect receiving and feeding, (5) observation of the characteristics of imago intruding holes and mother galleries and observation statistics of oviposition quantity, (6) inoculation of eggs and observation of incubation behaviors, (7) observation of feeding behaviors and characteristics of son galleries, (8) inoculation of pupas and observation of pupation behaviors and (9) inoculation of imago eclosion. The method enables the observers to conveniently track and observe life habits and states of an imago stage, an egg stage, a larva stage and a pupal stage of the bark beetle, and provides scientific evidence for comprehensive control of the bark beetle.
Owner:THE RES INST OF RESOURCES INSECTS RIRI OF THE CHINESE ACADEMY OF FORESTRY
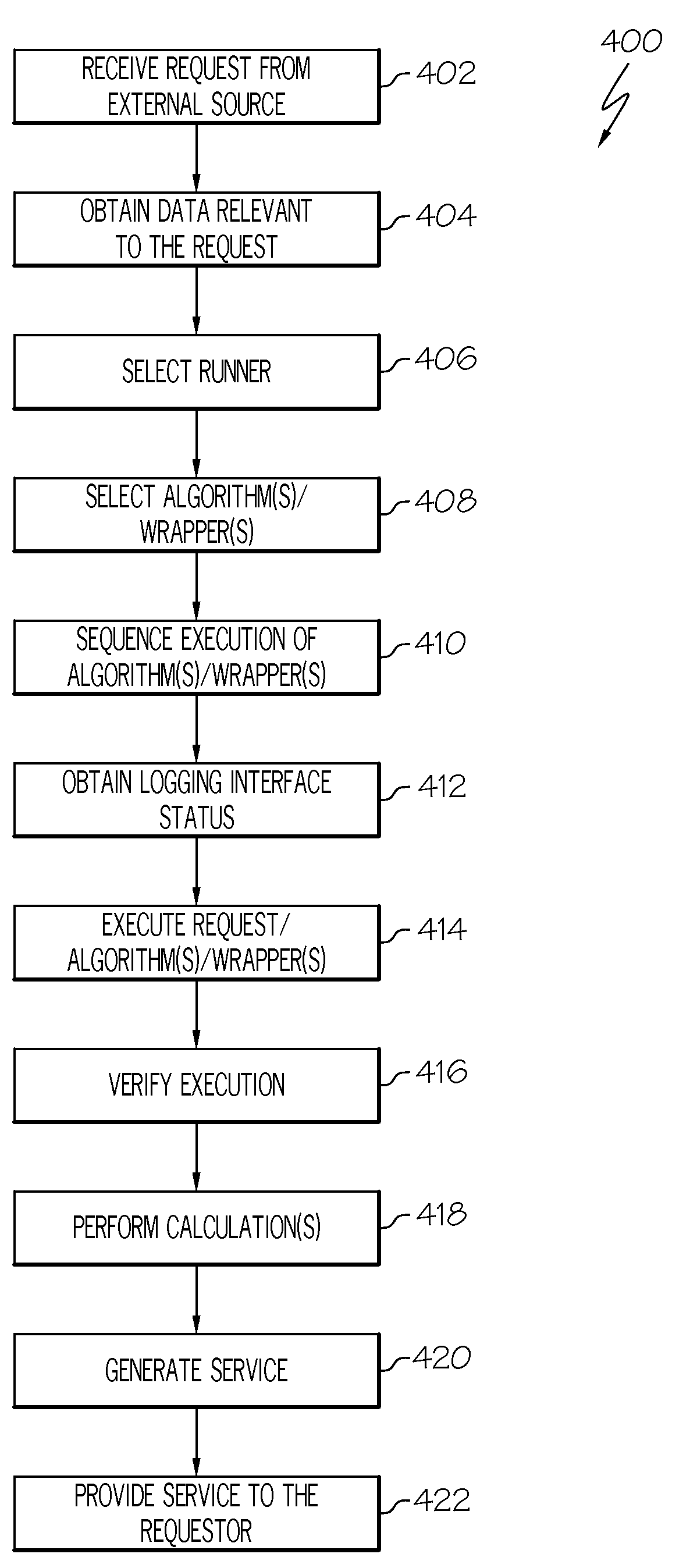
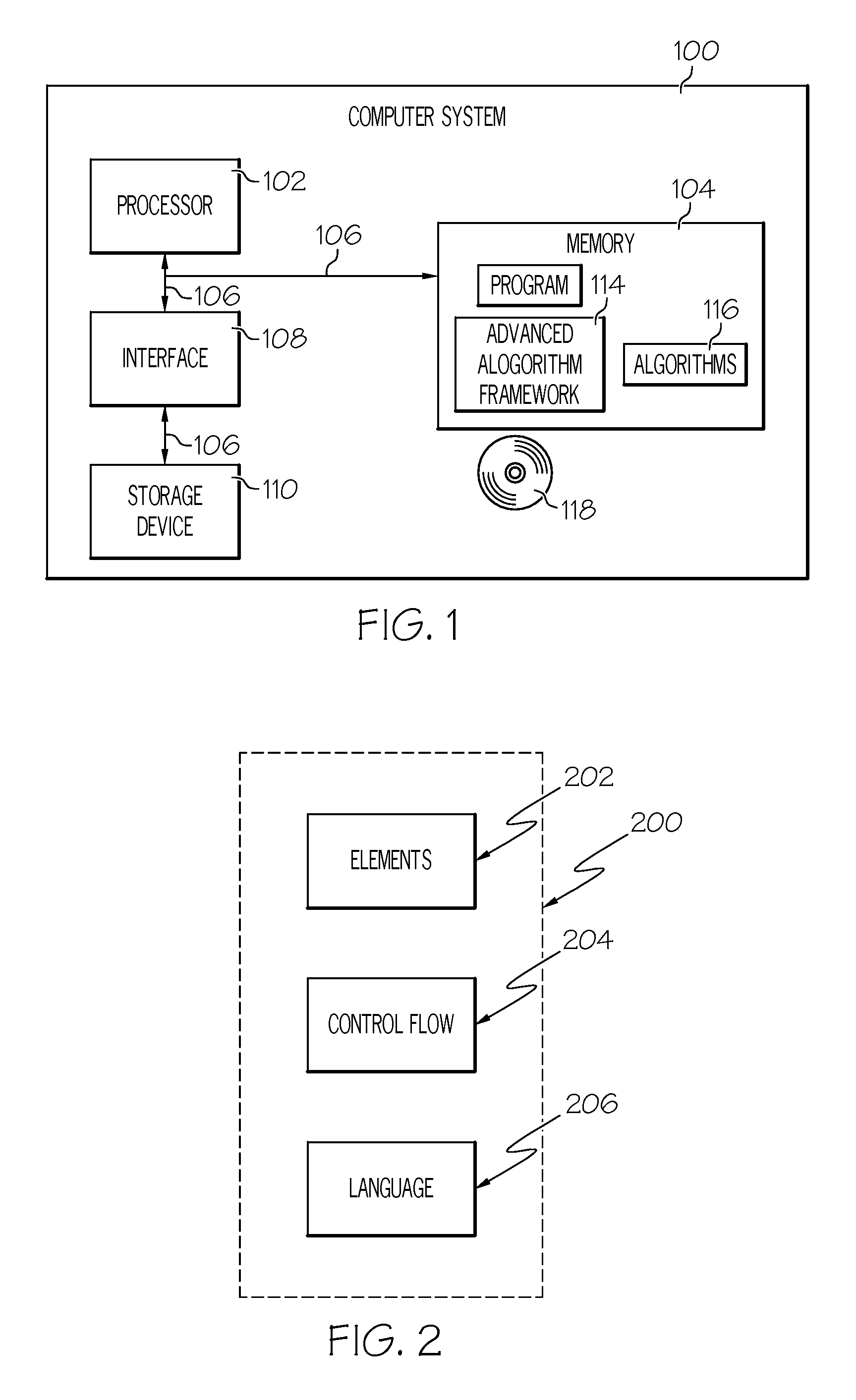
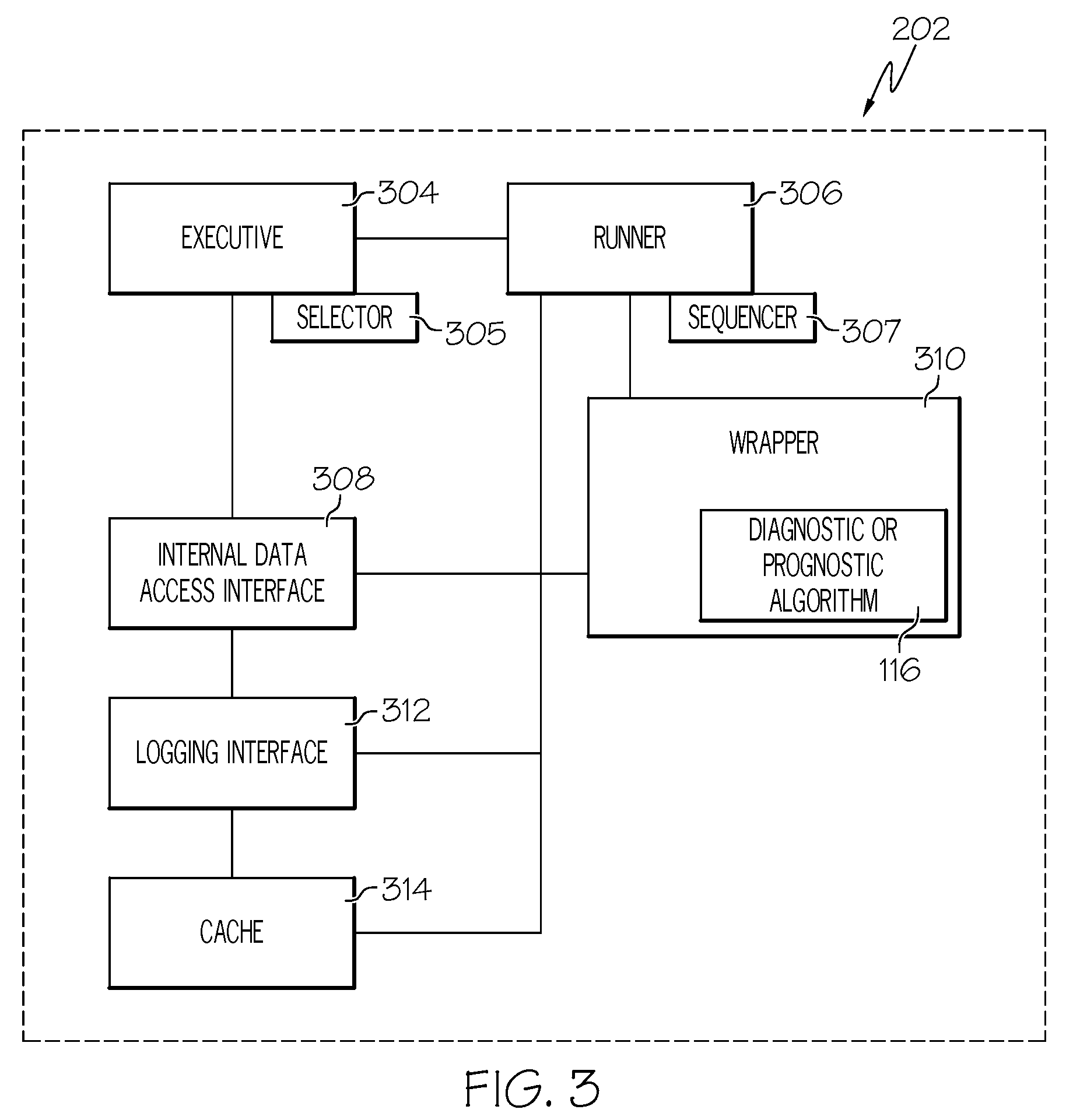
Advanced algorithm framework
InactiveUS20090138153A1Easy access to dataProgramme controlVehicle testingDiagnostic informationData mining
A method for performing diagnostics on a system of a vehicle includes the steps of receiving a request form an external source, obtaining data relevant to the request, processing the request using the data, and generating a report based at least in part on the processing of the request. The report comprises a diagnostic vector and a life usage vector. The diagnostic vector comprises diagnostic information for the system based at least in part on the processing of the request. The life usage vector comprises information as to usage of the system throughout a life history of the system, based at least in part on the processing of the request.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
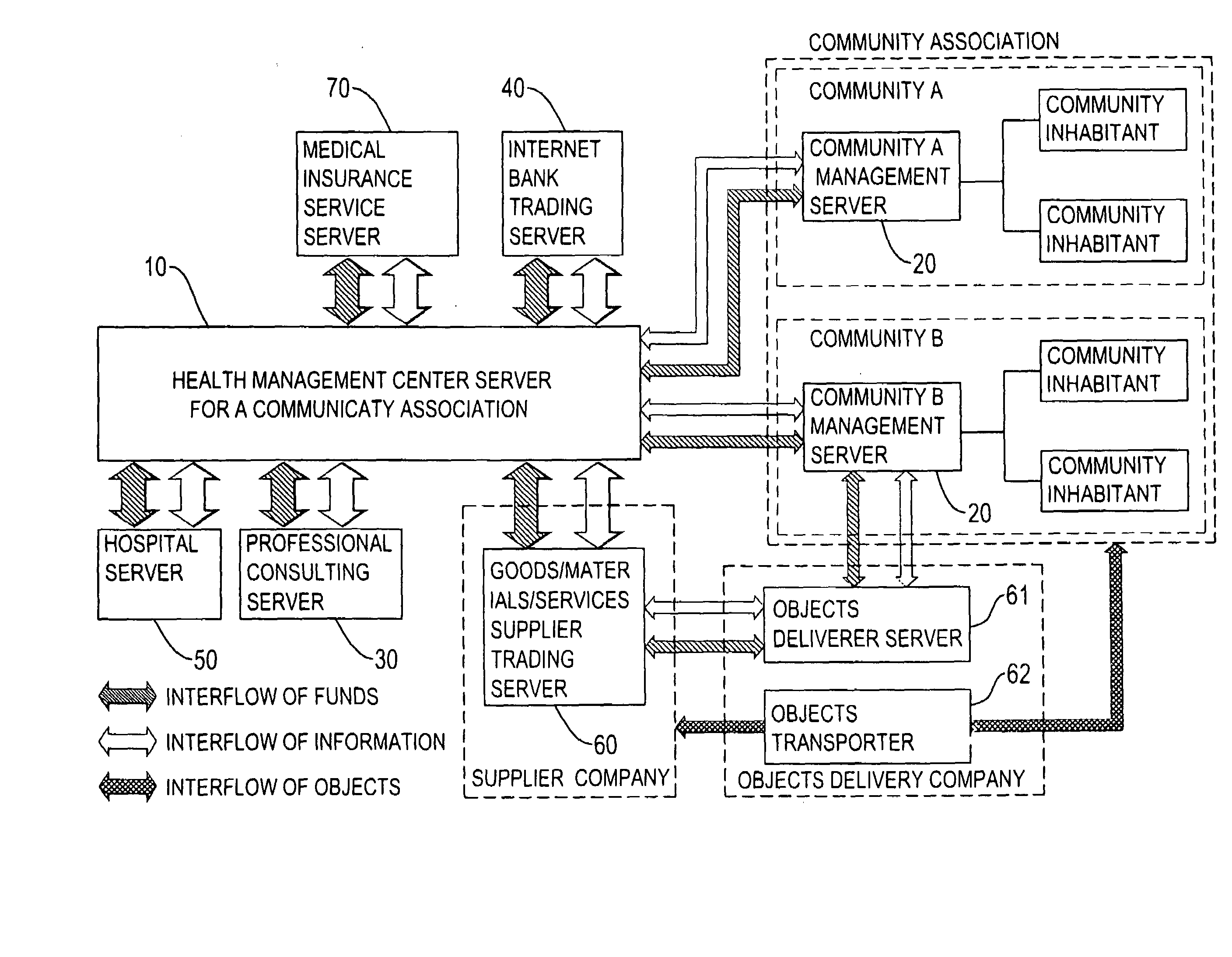
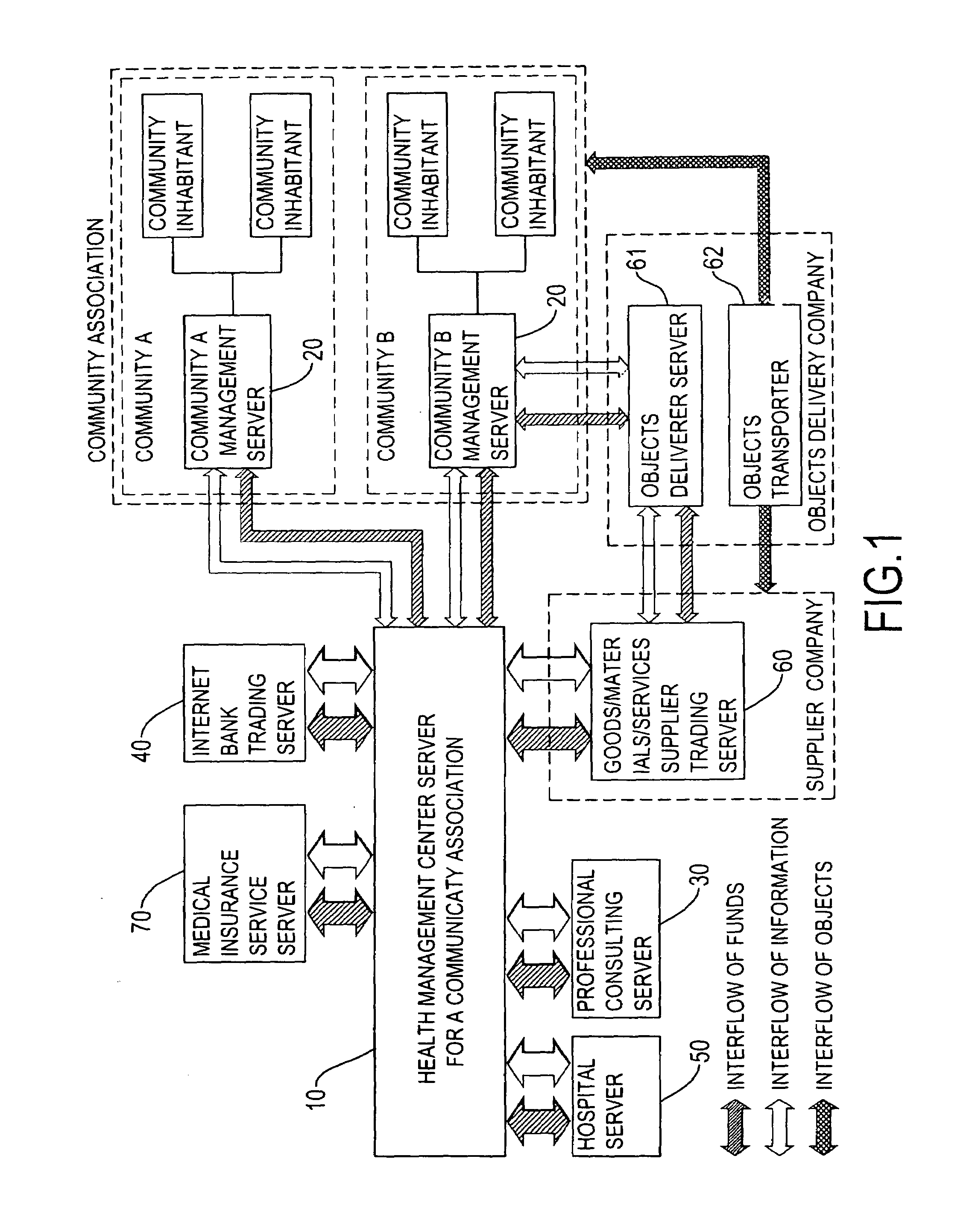
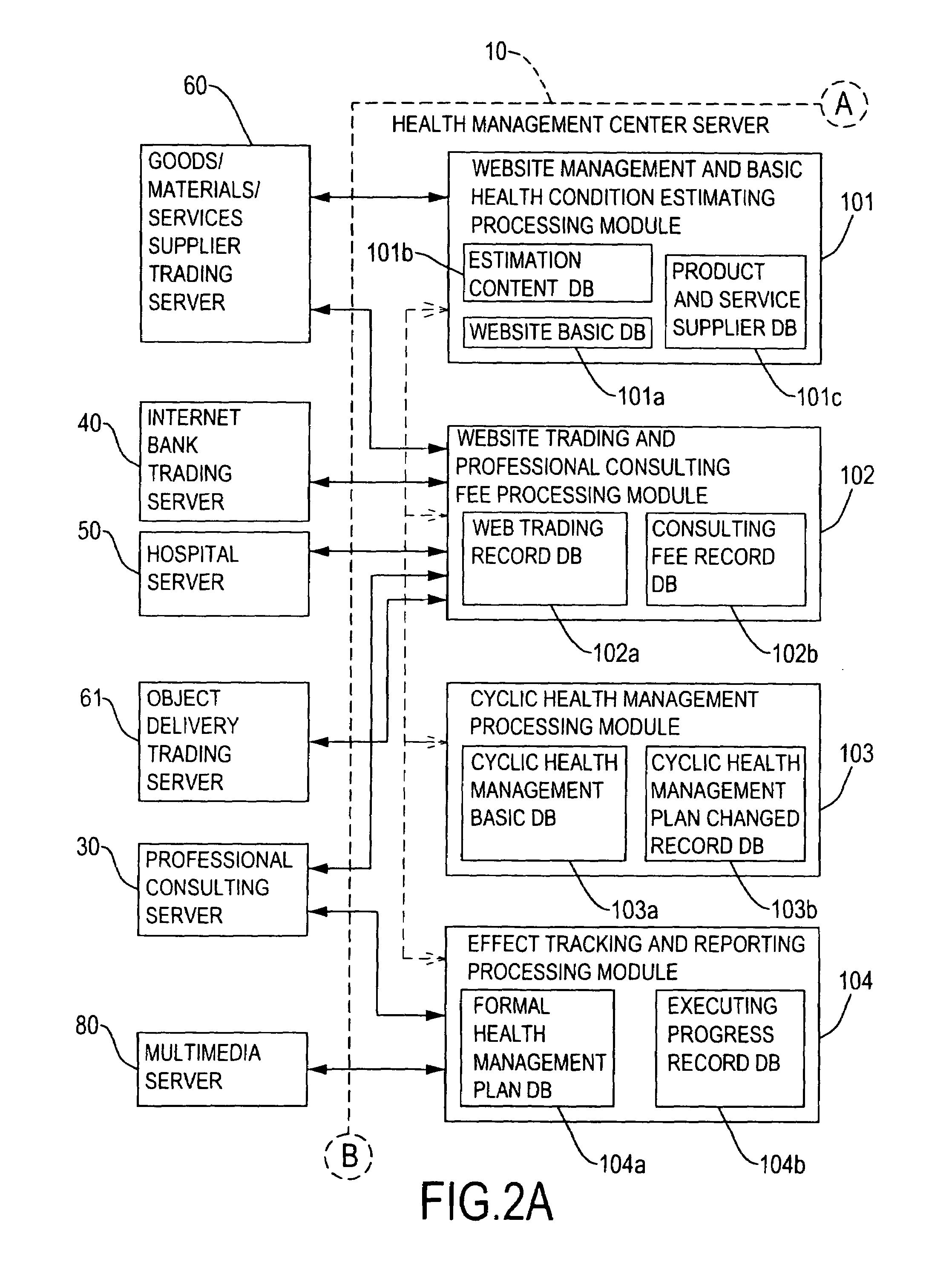
Health management cyclic service method of a community association and system of using the same
InactiveUS20080059225A1Improve management effectReduce in quantityData processing applicationsTherapiesEngineeringLiving environment
A health management cycling service method and system for a community association has five steps to scheme a personal health management plan according to each inhabitant's conditions of the life history, living environment, and the situations of body and mind. In addition, the business actively monitors and records the progresses of executing his or her personal health management plan to obtain a better management effect. The inhabitant can repeats the five steps to progressively and effectively reduce the number and the level of any abnormal health problem and finally reaching the best healthy situation.
Owner:CHANG FONG CHYI
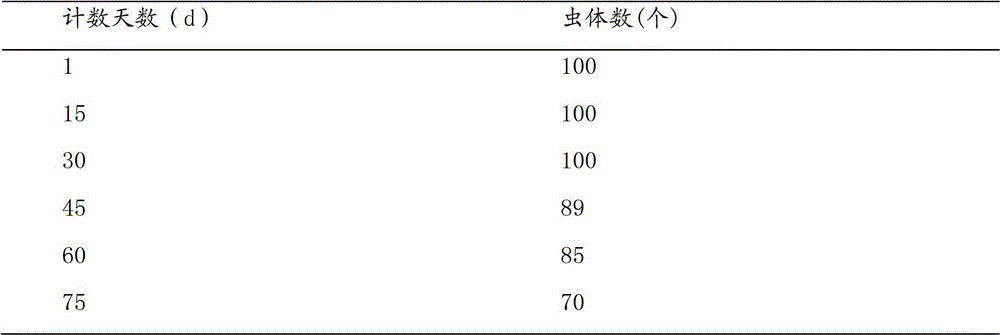
Method for raising experimental population of Rhynchophorus ferrugineus
InactiveCN102124999ASimple processShort developmental durationFood processingAnimal feeding stuffAdult wormHigh survival rate
The invention relates to a method for raising an experimental population of Rhynchophorus ferrugineus. The method comprises the following steps of: performing eclosion on pupae of Rhynchophorus ferrugineus to be raised into worms, then putting each pair of adult worms which are taken as a group into a container with hydromel for mating and oviposition, routinely disinfecting eggs and then hatching to obtain larvae, inoculating the larvae into a Rhynchophorus ferrugineus larvae raising container loaded with a semi-artificial feed of the Rhynchophorus ferrugineus larvae, and putting into a healthy worm raising room for raising until the larvae are pupated. The method is simple, the life history of the Rhynchophorus ferrugineus is finished indoors by adopting the semi-artificial feed, and a large quantity of intact eggs, accurate larvae at various ages and pupae are obtained under the condition of not hurting the eggs and the larvae; and the method has the characteristics of short development duration, high survival rate and the like, effectively and greatly shortens the generation cycle, and provides adequate experiment populations for completing the deep and systemic research on the Rhynchophorus ferrugineus in the fields such as biology, ecology and control technologies and the like.
Owner:COCONUT RES INST OF CHINESE ACAD OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Preparation and cultivation methods of fluid nutrient medium of stichopus japonicus in-vivo parasitic deuterostomia
The invention discloses a preparation method of a fluid nutrient medium of stichopus japonicus in-vivo parasitic deuterostomia, and belongs to the field of disease prevention and control of mariculture animals. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: adding EDTA (ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid) with the final concentration of 10<-7>-10<-5>mol / L into seawater; boiling and sterilizing the seawater for 15-30min, wherein the EDTA is added into the seawater; and cooling to 3-10 DEG C, and then adding fresh stichopus japonicus body cavity liquid, wherein the volume ratio of the body cavity liquid to the sterilized seawater is equal to 1:500 to 1:1000. By using the preparation method, the in-vitro cultivation time of the stichopus japonicus in-vivo parasitic deuterostomia in the nutrient medium can be up to 60 days, and the technical problems of short in-vitro survival time of the deuterostomia, difficultly in studying the life history of the deuterostomia and difficultly in choosing prevention and treatment medicines are solved.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
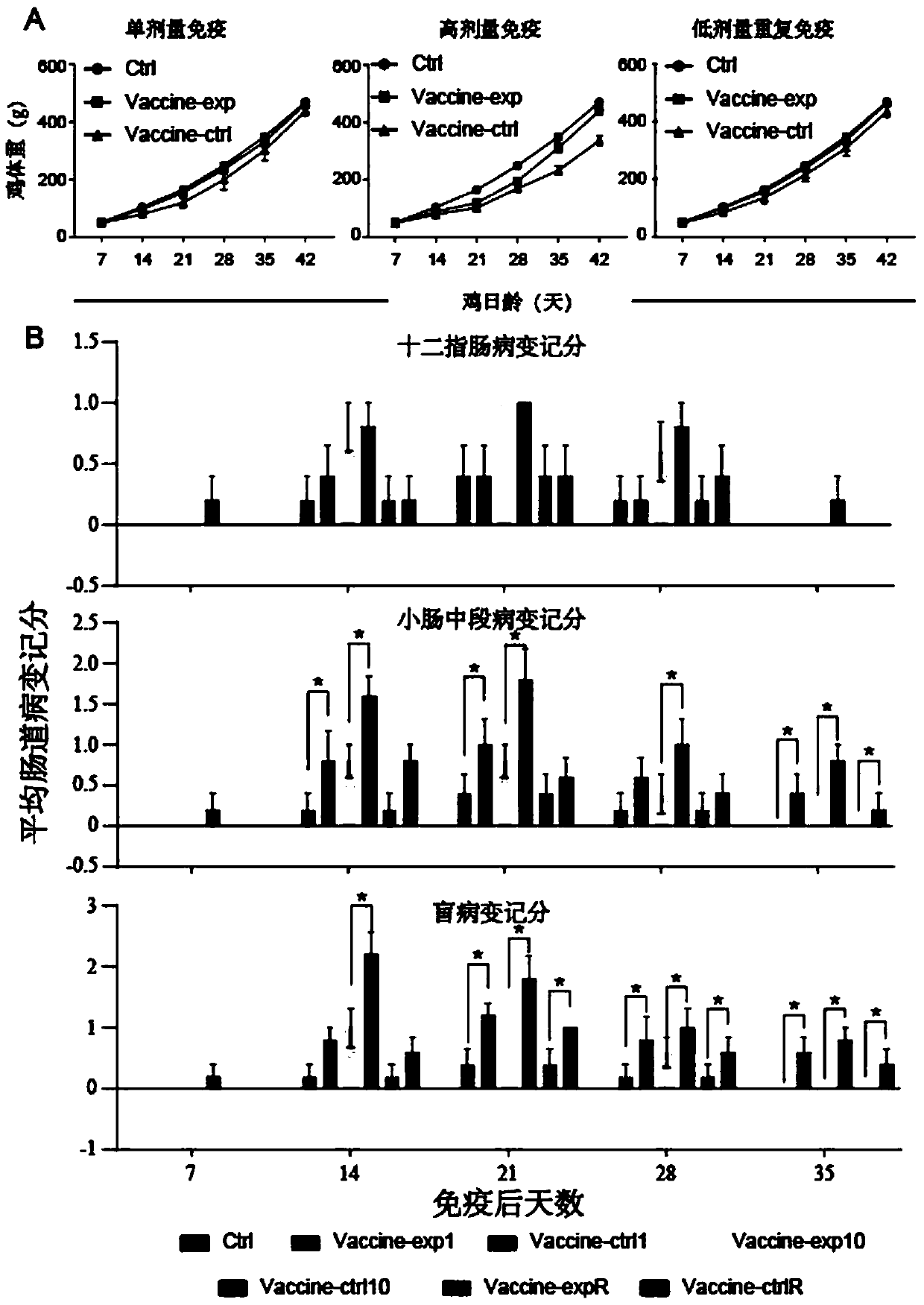
Live coccidiosis vaccine and application thereof
ActiveCN109646674AImprove securityWithout compromising securityAntiparasitic agentsAntibody medical ingredientsPoultry diseaseHighly pathogenic
The invention relates to the technical field of prevention and control of livestock and poultry diseases, in particular to a live coccidiosis vaccine and application thereof. The vaccine comprises a coccidiosis virulent strain and a coccidiosis attenuating strain having the same parasitic site or having the same parasitic site at any one or more stages of the parasitic life history; in the vaccine, the oocysts number ratio of the coccidiosis attenuated strain to the coccidiosis virulent strain is 50:1-3:1. A high dose of the weakly pathogenic coccidiosis strain is used for producing a competitive occupying advantage for a highly pathogenic strain having the same parasitic site, a occupying effect of the symbiotic pathogen in vaccine components is established, and the fertility, pathogenicity and damage to a host caused by over-intake are reduced after the highly pathogenic strain is immunized as the vaccine components. The coccidiosis vaccine can effectively improve the safety of the vaccine, reduce the cost of drug prevention and control, and have a good application potential while ensuring the immune efficacy of the vaccine.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Green branch insect breading device for observing forest tree seed insect life history
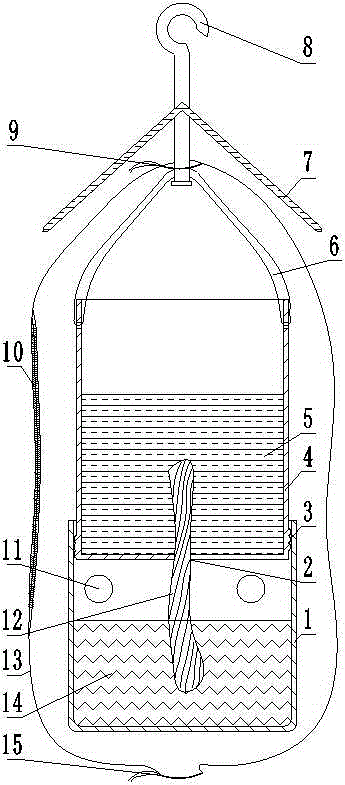
InactiveCN105265398AWill not affect the law of lifeRealize quantitative feedingAnimal husbandryInsect diseaseEnvironment of Albania
The invention discloses a green branch insect breading device for observing forest tree seed insect life history and belongs to the forestry insect disease research technology field. The green branch insect breading device comprises a hook, an awning, a water box, a soil box and a gauze and is characterized in that, the soil box is a cylinder, the upper end of the soil box is a rope, the upper end of the rope is provided with the awning, the upper end of the awning is provided with the hook, the lower end of the soil box is provided with a through hole in the cylinder, the through hole is internally equipped with a cotton core, the soil box is internally filled with forest soil, the lower end outer side of the soil box is provided with thread, the upper end of the water box is provided with thread in matching with the soil box, the middle and upper end is provided with a ventilation hole, the water box is internally filled with cleaning water, the water box and the soil box are in thread connection, the outer side of the water box and the soil box is equipped with the gauze, a side end of the gauge is provided with a pull lock, the upper end of the gauze is provided with an upper cable sleeve, and the lower end of the gauze is provided with a lower cable sleeve. According to the green branch insect breading device, and the soil box and the water box are manufactured by a transparent material which can be transparent plastic, or glass and a synthetic glass material. Seed insects are placed in the green branch insect breading device having a survival environment similar to the environment of the seed insects in the wild, quantitative breeding of the seed insects on a tree can be realized, and regular observation about life history can be realized.
Owner:黑龙江省森林与环境科学研究院
Sterile cultivation method of mealworms
InactiveCN103098762ASimple and fast operationGood effectAnimal husbandryBiotechnologyEarly generation
The invention relates to a sterile cultivation method of mealworms. The operation steps mainly comprise processing of early generation mealworm materials, preparation of sterile bran culture media, sterile cultivation of the mealworms, and detection of sterile imagoes and quantity statistics. Through using of the provided sterile cultivation method of the mealworms, purposes that imago bodies do not carry germs, and the mealworms grow healthily and strongly are achieved. The sterile cultivation method of the mealworms is easy and convenient to operate, good in effects, and capable of being applied to material drawing experiments of sterile materials each stage of the life history of the mealworms.
Owner:BAOSHAN UNIV
Cyst removal method for controlling fish cryptocaryon irritans
The invention discloses a cyst removal method for controlling fish cryptocaryon irritans. A cloth liner with the strong attaching effect on cryptocaryon irritans brown cysts is screened out mainly and laid on a water bottom of fish infected with the cryptocaryon irritans, the cryptocaryon irritans brown is nourished, falls down and is attached to the cloth liner, the cryptocaryon irritans brown cysts are removed by removing the cloth liner, the life history of the cryptocaryon irritans brown is cut off, and deaths caused when fish is repeatedly infected with the cryptocaryon irritans brown are reduced. By screening the materials, the cloth liner which is resistant to corrosion and free of toxicity and has the strong attaching effect on the cryptocaryon irritans brown cysts is obtained, the method for removing the cryptocaryon irritans brown cysts is used for treating plectorhinchus cinctus infected with cryptocaryon irritans, and the relative protection rate can reach 98%.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Cyst inactivation method for controlling cryptocaryon irritans disease of fishes
The present invention discloses a cyst inactivation method for controlling the cryptocaryon irritans disease of fishes. Mainly through screening a cloth liner having a strong adhesion effect on cryptocaryon irritans cysts, laying the cloth liner to the water bottom of the fishes infected by the cryptocaryon irritans disease so as to enable trophozoites of the cryptocaryon irritans to be adhered on the cloth liner after falling off, and removing the cloth liner to remove the cryptocaryon irritans cysts, life history of the cryptocaryon irritans is cut off, and death of the fishes caused by repeated infection of the cryptocaryon irritans is reduced. According to the method, the cloth liner which is corrosion resisting and nontoxic and has a strong adhesion effect on the cysts is obtained through screening materials, plectorhinchus cinctus infected by the cryptocaryon irritans disease is treated by using the method of removing the cryptocaryon irritans cysts, and relative protection ratio can reach 98%. Drying treatment and heat treatment are carried out on the cysts, and the results show that the cysts can be 100% inactivated when the cysts are dried for 120 min, and the cysts can be 100% inactivated when the cysts are processed for 3 min at 43 DEG C or processed for 1 min at 48 DEG C.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Method for researching migratory behaviour of anguilla japonica by employing otolith microchemistry
InactiveCN102687693AReduce measurement errorHigh detection sensitivityClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaRiver mouthSr element
The invention discloses a method for researching migratory behaviour of anguilla japonica by employing otolith microchemistry, wherein the migratory behaviour of anguilla japonica is determined by analyzing the microchemical constitution of the cross section of otolith life history of anguilla japonica by using a proton scanning microprobe technique, and the process comprises otolith excavating, embedding, flaking, film bonding, otolith centering, life history cross section scanning, guide sample correction and life history analysis. The invention provides a method which is capable of accurately positioning the center of otolith, sensitive in detection and quick in analyzing Sr / Ca ratio change in the cross section of the otolith life history, so that the following problems are solved: low Sr element content in otolith, long detection time, big errors, difficulty in accurate positioning because the center of an otolith ground slice of anguilla japonica is not at the geometric center, easiness in loss of information of partial stages of the life history caused by the use of a quick line scanning manner, and the like; and in combination with the annual ring marks of the otolith, the migratory behaviour of anguilla japonica at habitats such as fresh water, river mouths, oceans and the like can be effectively analyzed.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
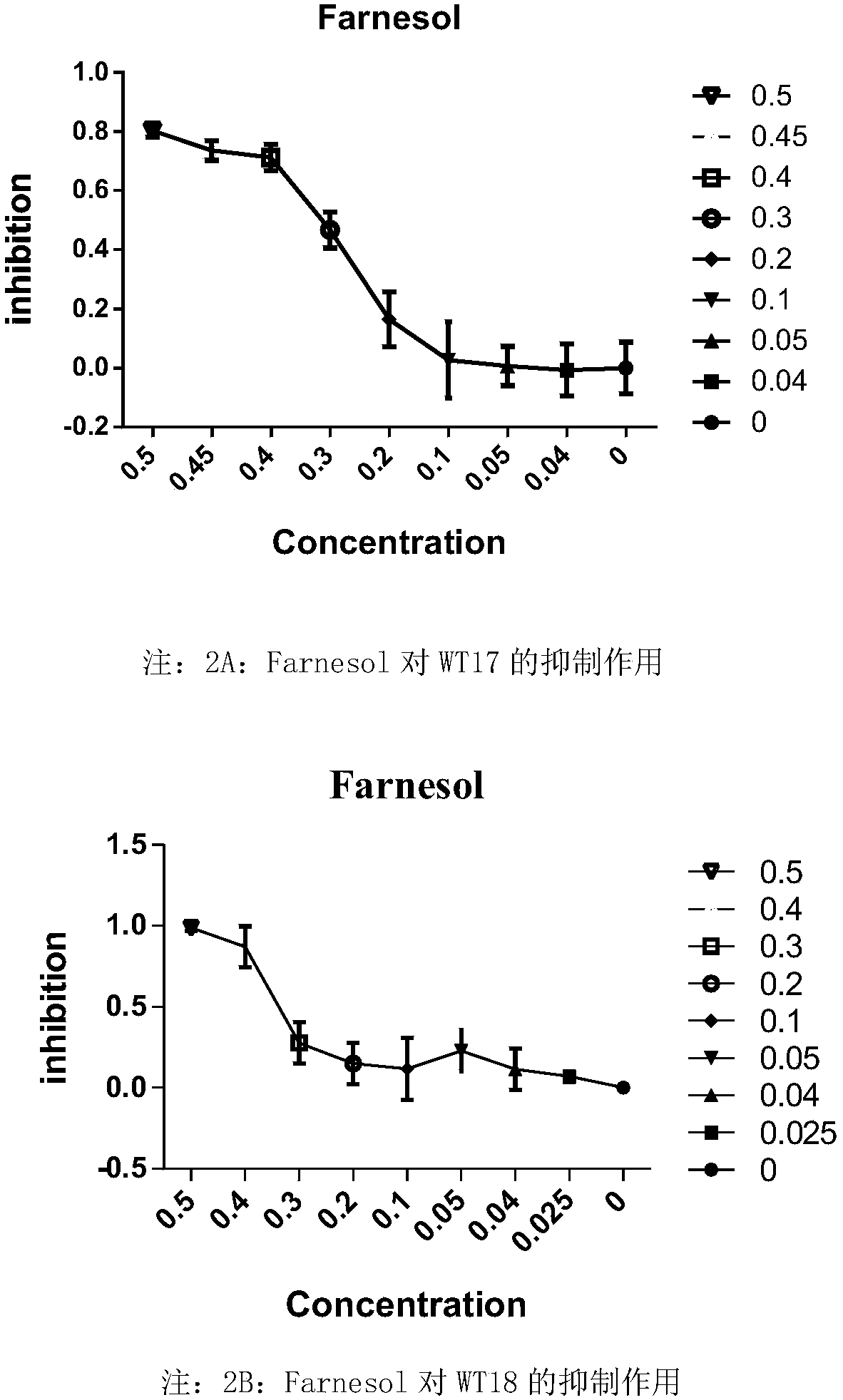
Application of farnesol in preventing and treating smut disease
ActiveCN108552205ARealize green and sustainable developmentReaching the goal of zero growthBiocideFungicidesDiseaseBasidiospore
The invention discloses an application of farnesol in preventing and treating the smut disease of sugarcane and corn. According to the application of farnesol in preventing and treating smut disease,the life history of sugarcane smut can be affected. Farnesol has better inhibiting effect on the germination of teliospore, the proliferation and growth of basidiospore and the sexual cooperation. Theformation of the binuclear mycelium can be effectively blocked, the sugarcane can not be normally infected with sugarcane smut, and the occurrence of the smut disease of the sugarcane can be effectively inhibited; the proliferation and growth of corn smut can be affected and the occurrence of corn smut can be inhibited.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Device and method for monitoring life history and controlling maintenance of industrial batteries
ActiveUS8482258B2Batteries circuit arrangementsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansLife historyLife expectancy
This invention is a method and device for monitoring and storing data regarding the “life history” of a battery with which it is associated and interpreting the data to create an accurate record of use and abuse patterns. A manufacturer's specified life expectancy, measured in battery cycles, is established for the battery under normal use, and then the actual use of the battery is monitored and stored. Complete cycles, partial cycles, and operation of the battery outside of acceptable specifications are automatically derived into a value in units equivalent to a number of battery cycles, and this derivation is compared with the manufacturers life expectancy, and adjustments to the manufacturers life expectancy are made so that a more accurate and up-to-date estimation of battery life can be evolved over the life of the battery. The monitoring device is mounted on the battery for the lifetime of the battery, with certain information regarding the battery being displayed to all persons having access to the battery. Additional information may be made available to an authorized person or entity. This enables a lessor of the battery, for example, to identify abuse of the battery by a lessee and adjust fees, lease terms, etc. accordingly.
Owner:PHILADELPHIA SCI
Eimeria tenella invasion-related protein Et CHP559 gene and application thereof
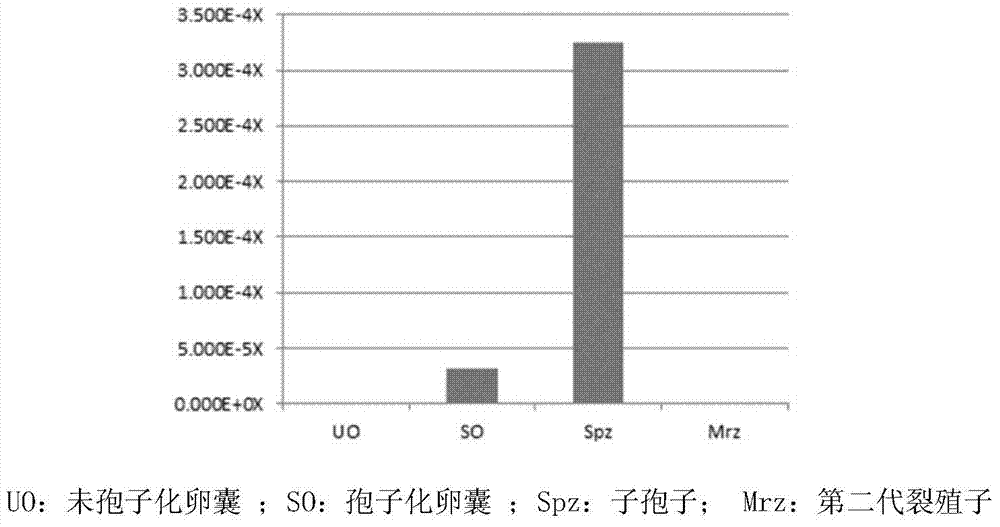
InactiveCN104328130AImproving immunogenicityInhibitionGenetic material ingredientsDepsipeptidesSporeOpen reading frame
The invention discloses an eimeria tenella Et CHP559 gene. The Et CHP559 gene includes an open reading frame nucleotide sequence represented as the SEQ ID No.1. The eimeria tenella conserved protein Et CHP559 gene is a new gene of the eimeria tenella and is relative to sporozoite invaded host cells. The eimeria tenella conserved protein Et CHP559 gene has quite high application value in development of a new vaccine or a new medicine capable of inhibiting the sporozoite invaded host cells and blocking a life history of the eimeria tenella.
Owner:SHANGHAI VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for constructing chronic transfection model of hepatitis B virus
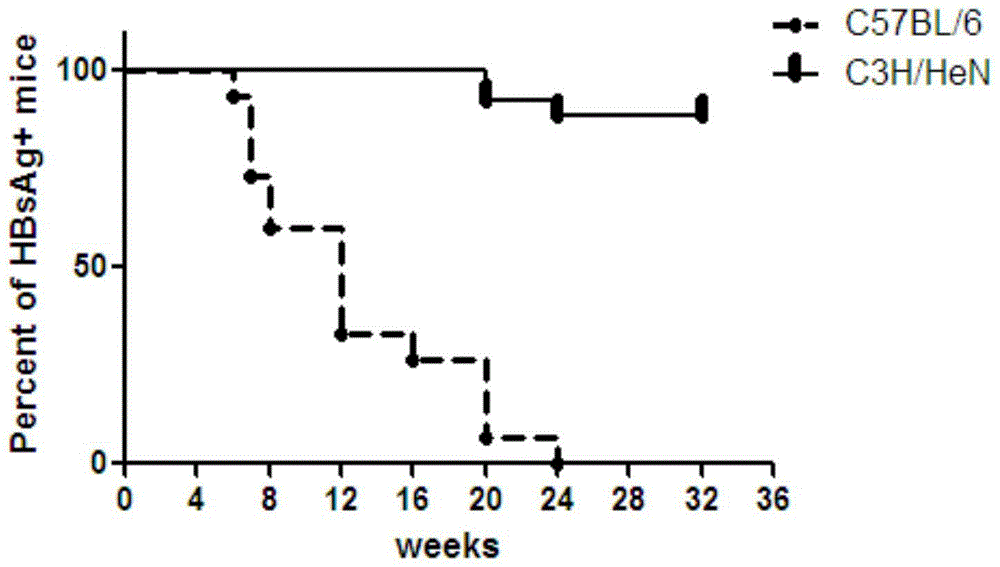
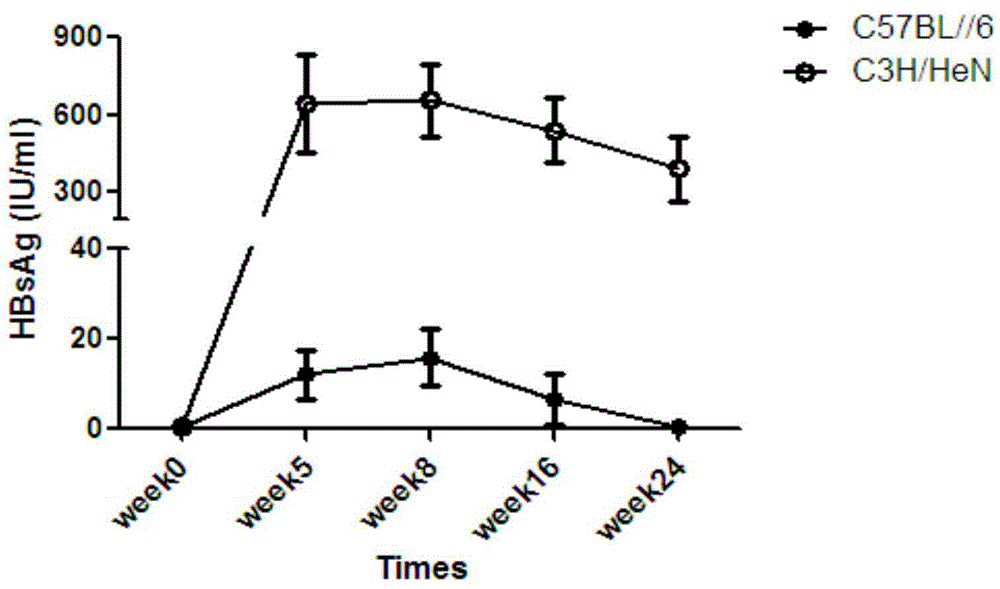
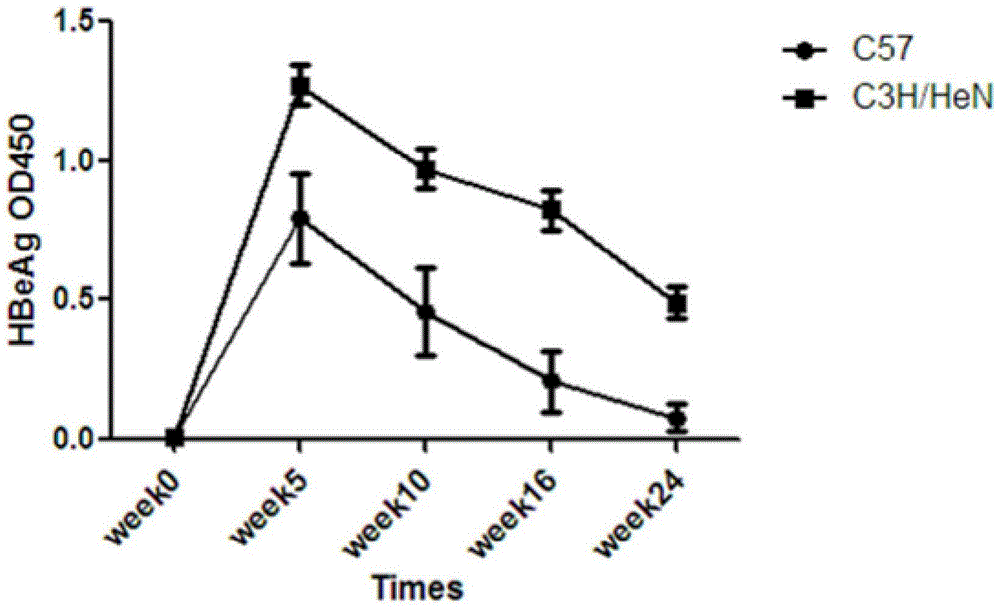
ActiveCN104673834AIncreased rate of chronic moldingFermentationGenetic engineeringMechanism of actionHepatitis B virus
The invention belongs to the field of biomedicine, and particularly relates to a method for constructing a chronic transfection model of a hepatitis B virus. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: transfecting HBV (hepatitis B virus) plasmids into a model-preparing experimental mouse (preferably adopting male C3H / HeN of 4-8-week old), and constructing the chronic transfection model of the HBV. The chronic transfection model of the hepatitis B virus constructed by the method can be used for researching specific action mechanism of single or multiple genes in an HBV pathogenic process; transgenic modification of the mouse is not needed; the method is free of limitations such as immunologic tolerance, easy to obtain, and low in cost; the problem of long-term shortage of an animal model suitable for the HBV in related technical fields can be solved; and a good animal model is provided for further research on life history and chronic mechanism of the HBV and screening of vaccines and new medicines.
Owner:SHANGHAI PUBLIC HEALTH CLINICAL CENT
Device for studying animal hibernation
InactiveCN103907565ASimple structureWide range of raw materialsAnimal husbandryCold winterNatural state
The invention discloses a device for studying animal hibernation. The device is mainly applied to scientific research of hibernating animals such as insects in cold winter. The studying device for the hibernating animals in winter comprises an observation chamber which is barrel-shaped and used for preserving an egg or a body of a hibernating animal; the observation chamber is divided into upper and low parts which are a growing living box and a cryopreservation box, respectively; the growing living box and the cryopreservation box are separated by thermal insulating glass, a round hole is formed in the middle part of the thermal insulating glass and the round hole can be closed by openable rubber; the studying device further comprises a lifting shaft penetrating through the rubber; the observation chamber is made of glass convenient for observation. The device for studying the animal hibernation has the advantages of simple structure, abundant raw materials, health care and environmental protection, low price and the like; the observing experimental device is capable of quickly and clearly reflecting the life history of the animal in hibernation and the temperature selectivity of the animal under different temperature conditions or in the natural state, and thus is worthy of popularization in laboratories.
Owner:林建斌
Method for controlling curculio chinensis chevrolat as camellia oleifera old forest pest
InactiveCN109566241AHealthy growth environmentIncrease productionCultivating equipmentsHorticulture methodsEcological environmentHabit
The invention discloses a method for controlling curculio chinensis chevrolat as a camellia oleifera old forest pest. The method includes the following steps of biological control, physical control and field management. On the basis of the life history and habits of camellia oleifera, different control measures are adopted in different harmful periods of curculio chinensis chevrolat, and curculiochinensis chevrolat larva and imagoes can be effectively killed; through biological control, physical control and a field management method, the land and the ecological environment are protected, andthe production safety of camellia oleifera, the quality safety of camellia oleifera seeds and the ecological environment of cultivation areas are effectively prevented. At the same time, the method greatly reduces the damage of curculio chinensis chevrolat to camellia oleifera fruits, a healthy growth environment is provided for camellia oleifera, and the yield and quality of camellia oleifera canbe effectively improved.
Owner:湖南省林大生物科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com