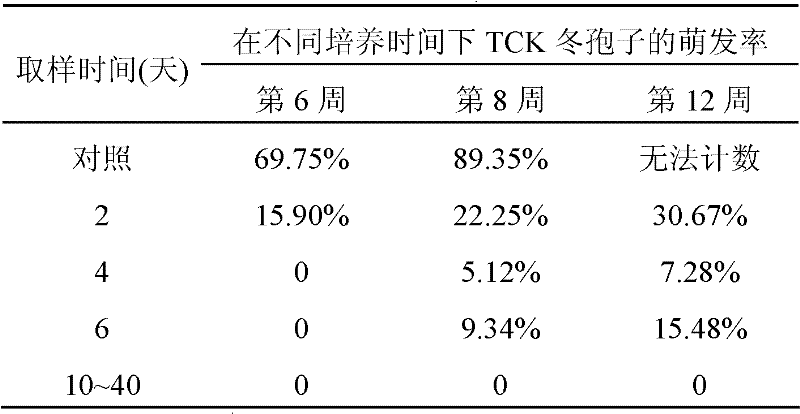
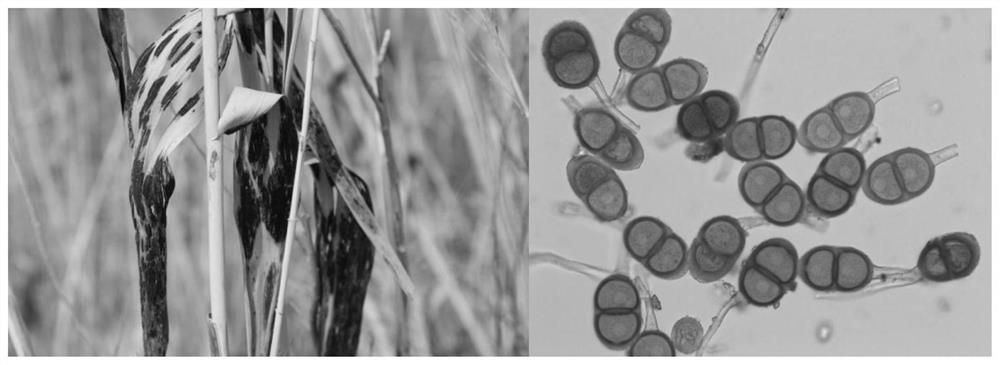
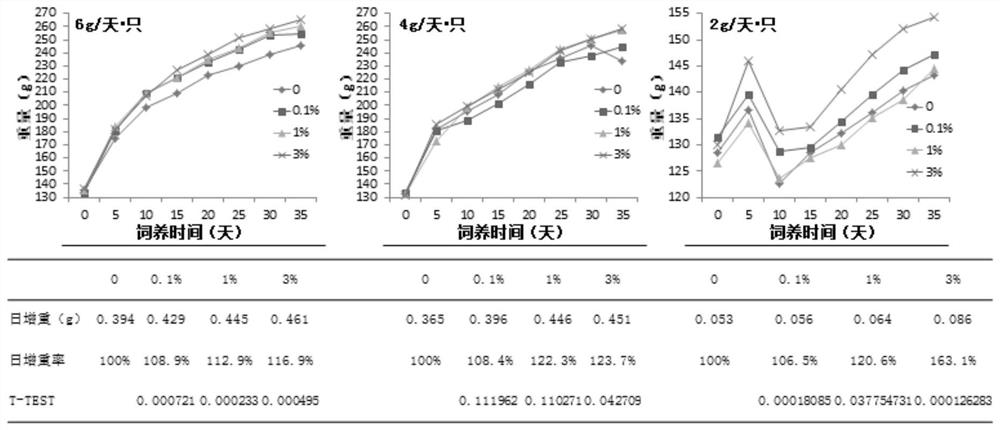
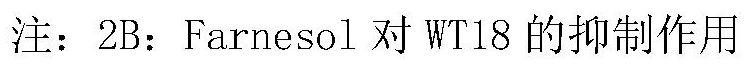Patents
Literature
48 results about "Teliospore" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Teliospore (sometimes called teleutospore) is the thick-walled resting spore of some fungi (rusts and smuts), from which the basidium arises.
Method for identifying sugarcane smut resistance
InactiveCN102204465AEffectively guide reasonable allocationMeet vaccination needsHorticulture methodsDiseaseTeliospore
The invention relates to the technical field of plant disease resistance, and discloses a method for identifying sugarcane smut resistance. The method for identifying sugarcane smut resistance comprises the steps of: firstly carrying out separate culture to obtain sugarcane smut alien mating type (+or -) haplospores by using a trace amount of fresh sugarcane smut teliospore; and then carrying out the steps of culture enlargement of strains, inoculation, investigation of disease incidence, resistance evaluation and the like. The method for identifying sugarcane smut resistance has the outstanding substantial characteristics and is improved remarkably as follows: 1. the inoculation need can be met by separate culture of only an extremely trace amount of sugarcane smut teliospore, and the working amount is low; 2. the alien mating type strains can be stored at an ultra-low temperature and can be used as the inoculation source after subjected to activation and enlarge culture without repeated taking of strains and separate culture for each time; 3. in the method for identifying sugarcane smut resistance, the resistance identifying period is short, and the sensitivity is high; and 4. the method for identifying sugarcane smut resistance can also be used for identifying the type of smut biological strains resisted by the tested varieties, and effectively guiding smut-resisting seed breeding of sugarcane and reasonable collocation of varieties in a sugarcane area.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SUGARCANE IND RES INST +1
Method for optimal seedling selection and breeding of novel carassius auratus gibelio series
InactiveCN101796932AMeet the breeding goalsGenetically stableClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaCarassius auratus gibelioBiology
The invention relates to a method for optimal seedling selection and breeding of novel carassius auratus gibelio series, which comprises the following steps: (1) extracting an egg of a Fangzheng crucian carp; (2) extracting a sperm of a Xingguo red carp; (3) stimulating the female nucleus of the egg of the crucian carps for development to generate an offspring through the sperm of the Xingguo red carp; (3) extracting a sperm of a grass carp and a sperm of a megalobrama amblycephala, and extracting an egg of the offspring generated in the previous step; (5) stimulating the female nucleus of the egg of the offspring generated Step (3) for development with the sperm of the grass carp and the sperm of the megalobrama amblycephala; and (6) breeding the improved seedling. The invention has the following technical effects that: 1) the novel carassius auratus gibelio series with genetic stability can be obtained; 2) the sporozoon resistance of the bred novel carassius auratus gibelio series can be significantly improved; 3) the growth speed of the bred novel carassius auratus gibelio series is high, and the intestinal length / full length is increased, thereby facilitating the improvement of the digestibility; and 4) the thickness of the dorsal muscles and the tightness of the scales of the bred novel carassius auratus gibelio series are improved, the survival rate in the long-distance transport is more than 95 percent, the visceral mass is reduced, the body length is increased, and the intramuscular bones are decreased.
Owner:江苏海辰科技集团有限公司
Sporozoan cleaning fish medicine
InactiveCN101156940ANo pollutionNo drug resistanceAntiparasitic agentsPlant ingredientsDiseaseSophora Root
The invention relates to a medicine for preventing and curing the fish diseases, in particular to an ichthyosporidiumhoferi removal medicine. The invention is characterized in that the medicine is formed by preparing omphalias, flavescent sophora roots, roor of sessile stemonas, carpeium fruits, arecas, chinaberry fruits, abtipyretic dichroas, belamcandas, capillary artemisias, dyers woad roots, and peppers. The medicine consists of Chinese herbal medicines, the environment can not be polluted, the drug resistance is not caused, and the medicine accords with the requirements of environment-friendly food. The invention has the advantages that the cost is low and the curative effect is remarkable, the cost of the medicine added in the one ton feeding stuff is about 400 RMB, but the cost of the medicine which adopts the prior art and is added in the one ton feeding stuff in the market is about 800 RMB. Through the trial and verification, after the diseased fishes takes the medicines, the diseases caused by a variety of sporozoons are radically and effectively cured, and the recurrence does not exist after the speedy recovery. The invention has the universal use and promotion values.
Owner:严必福
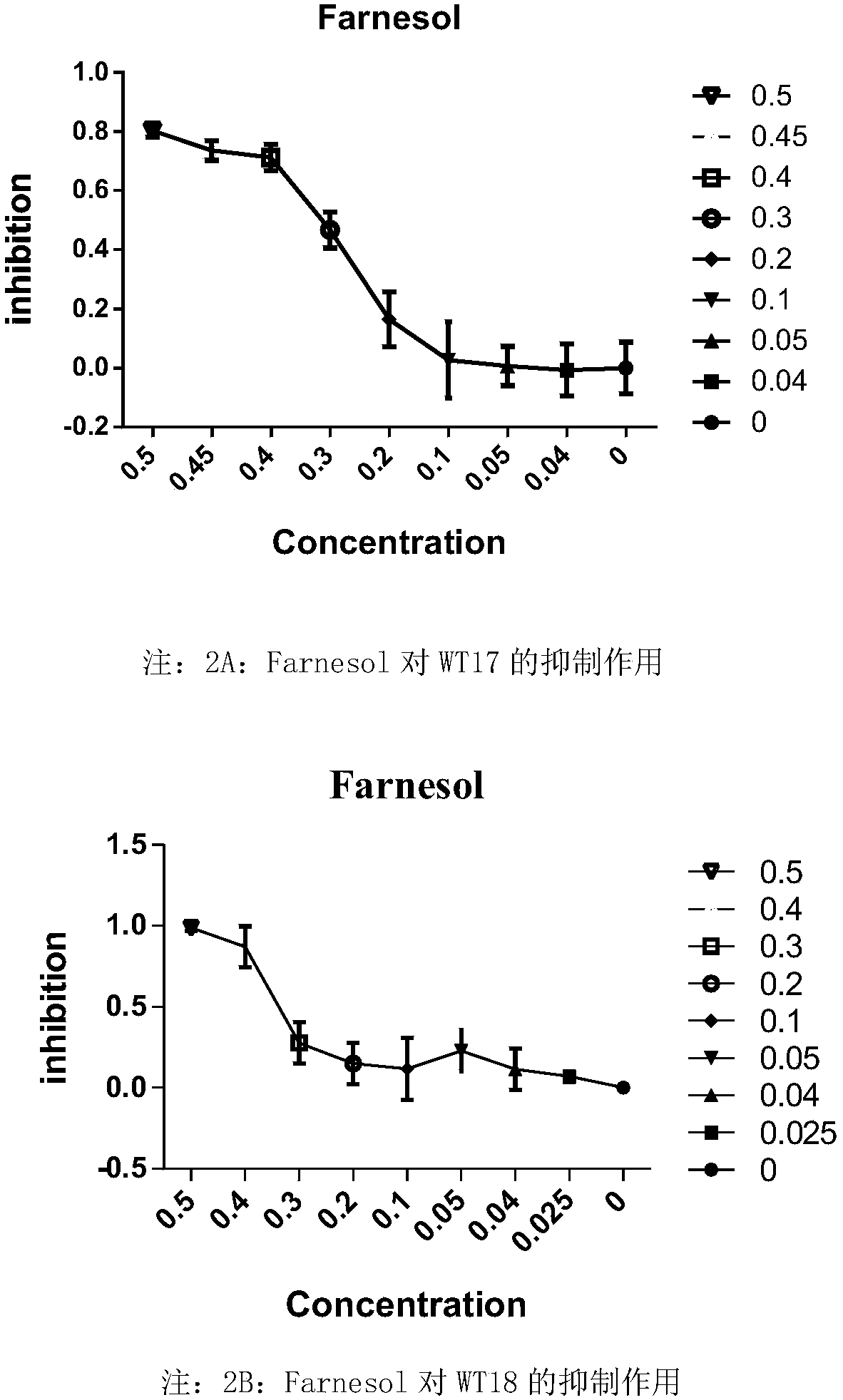
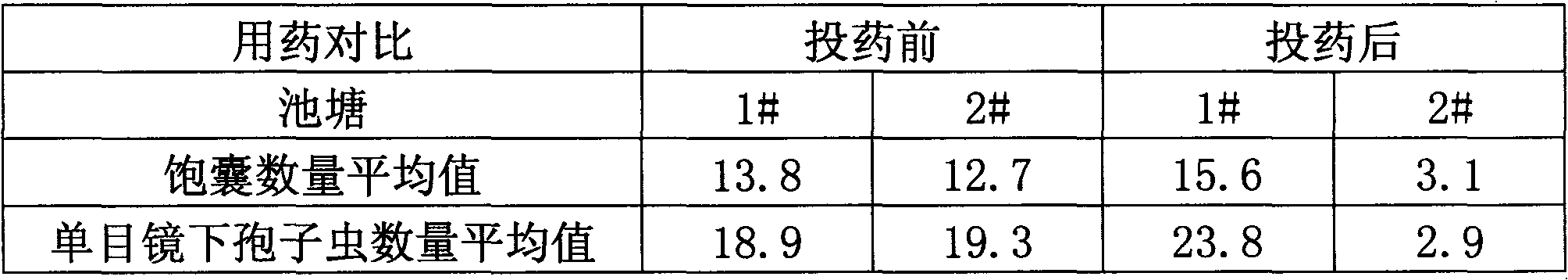
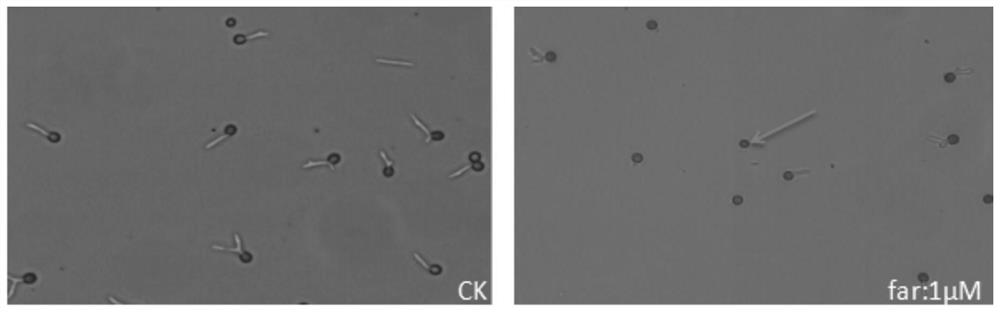
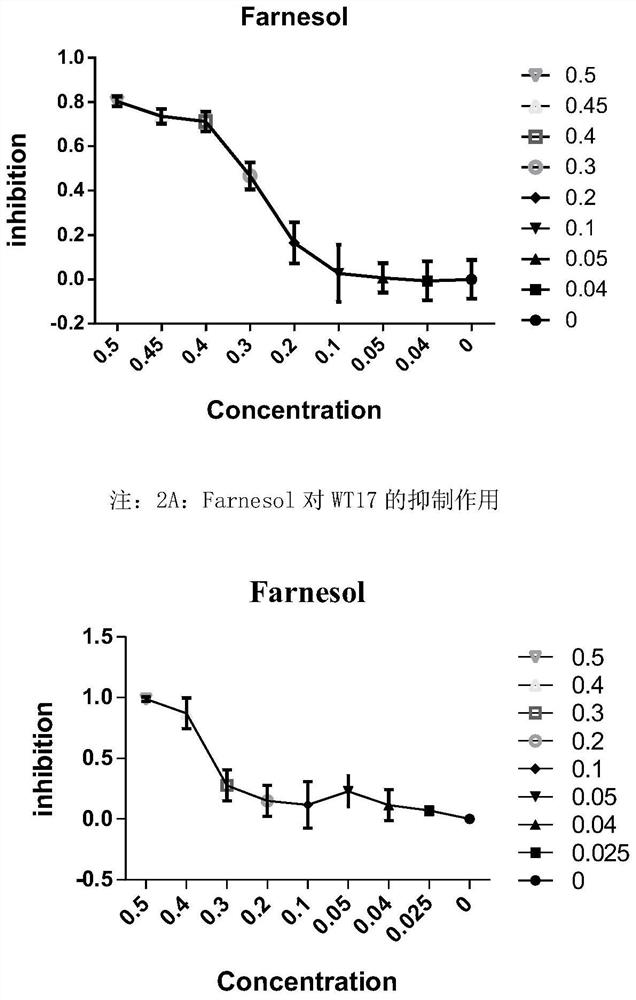
Application of farnesol in preventing and treating smut disease
ActiveCN108552205ARealize green and sustainable developmentReaching the goal of zero growthBiocideFungicidesDiseaseBasidiospore
The invention discloses an application of farnesol in preventing and treating the smut disease of sugarcane and corn. According to the application of farnesol in preventing and treating smut disease,the life history of sugarcane smut can be affected. Farnesol has better inhibiting effect on the germination of teliospore, the proliferation and growth of basidiospore and the sexual cooperation. Theformation of the binuclear mycelium can be effectively blocked, the sugarcane can not be normally infected with sugarcane smut, and the occurrence of the smut disease of the sugarcane can be effectively inhibited; the proliferation and growth of corn smut can be affected and the occurrence of corn smut can be inhibited.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating encephalitozoon intestinalis of freshwater fish and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103656020ABlock developmentBlock formationAntiparasitic agentsAgainst vector-borne diseasesSide effectPumpkin seed
The invention relates to a traditional Chinese medicine composition for treating encephalitozoon intestinalis of freshwater fish. The traditional Chinese medicine composition comprises the following components in parts by weight: 15 to 25 parts of betel nut, 7 to 12 parts of pumpkin seed, 3 to 5 parts of peking euphorbia root, 4 to 8 parts of sargent gloryvine, 4 to 8 parts of fructus chaenomelis lagenariae, and 5 to 10 parts of szechwan chinaberry fruit. The traditional Chinese medicine composition is used for exterminating encephalitozoon intestinalis of freshwater fish based on the penetrability of special components as well as the paralysis and etermination promoting effect of the Chinese herbal medicines. The preparation method comprises the following steps: naturally drying the natural Chinese herbal medicines; crushing the natural Chinese herbal medicines until the granularity is more than 65 meshes. The traditional Chinese medicine composition can be uniformly mixed with a fish feed for use, and is convenient to use and free from toxic and side effects.
Owner:TIANJIN REBATE SCI & TECH DEV
Method for identifying teliospores of Tilletia controversa Kuhn and Tilletia foetida
PendingCN105039491AMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesTriticeaeTriticum turgidum
The invention provides a method for identifying teliospores of Tilletia controversa Kuhn and Tilletia foetida and relates to the technical field of cell biology. The method includes the steps of 1, making slides, to be specific, smearing the teliospores of Tilletia controversa Kuhn and Tilletia foetida, respectively, after drying, dropwise adding oil camera oil to a microscopic portion, and covering the smears with cover slips; 2, performing observation, to be specific, placing the made slides under a laser confocal scanning microscope, selecting a proper scanning mode and scanning parameters to perform scan-observation and photographing, with the scanning mode being an xyz scanning mode and the scanning parameters including excitation wavelength and emission wavelength, the excitation wavelength of Tilletia controversa Kuhn being 488nm, the emission wavelength of Tilletia controversa Kuhn being 510 to 550nm, the excitation wavelength of Tilletia foetida being 488nm, and the emission wavelength of Tilletia foetida being 510 to 550nm. The method enables quick identification of the teliospores of Tilletia controversa Kuhn and Tilletia foetida.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Neospora caninum isolate
Owner:UNIV OF TECH SYDNEY
Method for artificial inoculation insolated identification of white rust resistance of chrysanthemum
InactiveCN101889549AIdentification safe and effectiveAvoid safety hazardsMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant tissue cultureCataphyllWide mouth
The invention provides a method for artificial inoculation insolated identification of resistance of chrysanthemum to white rust of chrysanthemum. The method comprises the following steps: A, using a 500ml wide-mouth glass bottle as an insolated culture container; B, preparing a liquid culture medium and a solid culture medium respectively and combining the culture media by putting the liquid culture medium above the solid culture medium; C, cutting chrysanthemum stems which are healthy and not infected with pathogenic bacteria of chrysanthemum white rust; D, picking up chrysanthemum leaves with telia; E, rubbing teliospores on telia of infected leaves by hands, and inoculating the teliospores onto the chrysanthemum leaves to be detected; F, performing cottage of the chrysanthemum stems inoculated with the pathogenic bacteria in the culture bottle filled with the solid-liquid combined culture medium for culture by placing the chrysanthemum stems in the dark at 17 to 21 DEG C for 24 hours and then placing the chrysanthemum stems in light of which the intensity is 1,000 Lx for 16 hours and then in the dark in a culture room for 8 hours; and G, after 15 days, observing whether the telia is on the chrysanthemum leaves by eyes. The method for artificial inoculation insolated identification of white rust resistance of chrysanthemum provided by the invention has the advantages of eliminating potential safety hazards in identification of white rust resistance of chrysanthemum and realizing safe and effective identification of the resistance of different chrysanthemum varieties on white rust resistance of chrysanthemum under controlled conditions.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
Preparation method of tilletia controversa protoplasts
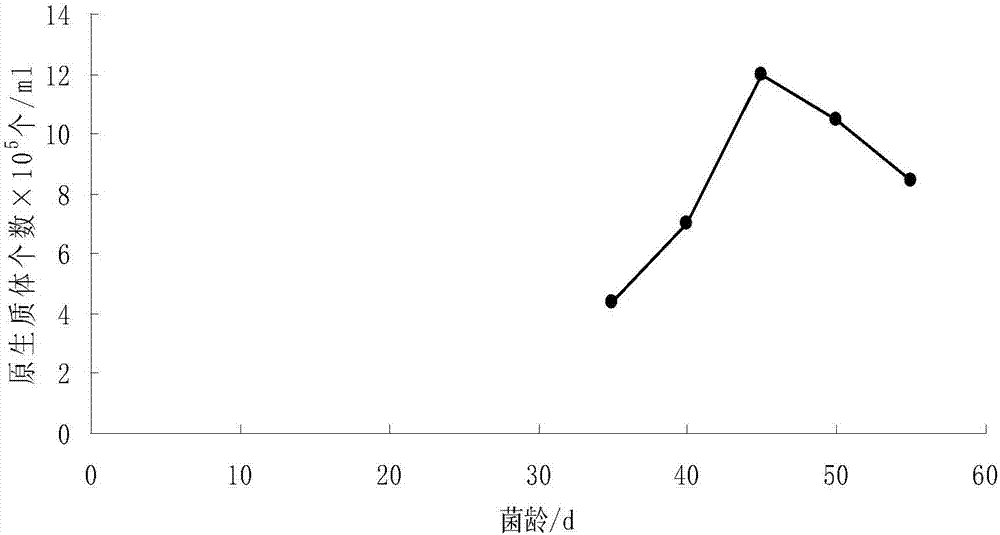
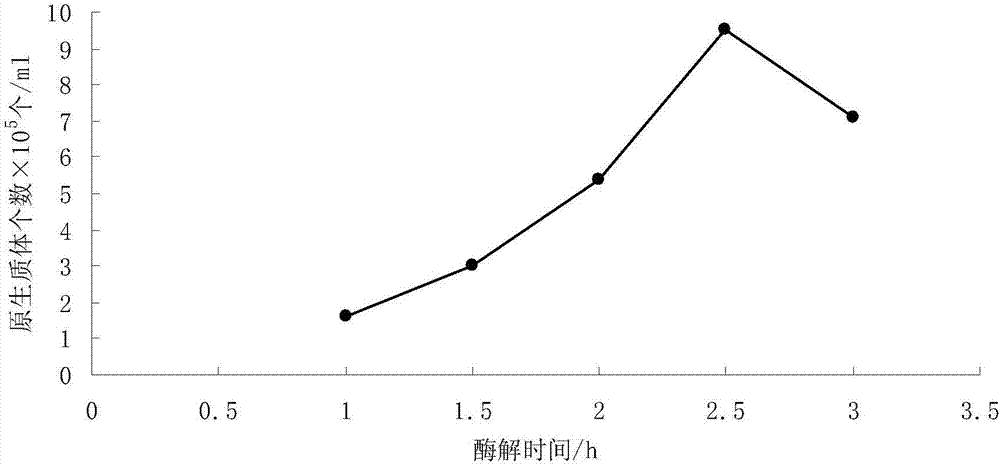
PendingCN107058132AUniform scattered distributionIncrease productionFungiMicroorganism based processesSpore germinationTilletia ayresii
The invention relates to a preparation method of tilletia controversa protoplasts. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) mycelium culture: culturing tilletia controversa teliospore on a soil aqueous extract culture medium, after the teliospore sprouts, transferring the teliospore to a T19 liquid culture medium and carrying out shaking culture, and collecting mycelium, wherein the sum of the number of culture days on the soil aqueous extract culture medium and the number of shaking culture days on the T19 liquid culture medium is 40-50 days; and (2) cell wall cracking: taking a KCl solution as an osmotic pressure stabilizer, preparing mixed enzyme liquid, adding the mixed enzyme liquid in the mycelium, and carrying out shaking enzymolysis for 2-3 hours at the temperature of 28 DEG C to obtain the tilletia controversa protoplasts. The mixed enzyme liquid comprises the following components in percentages by mass: 1.5% of driselase, 1.5% of lywallzyme and 1.5% of helicase. The yield of the tilletia controversa protoplasts prepared by the method reaches up to 12.0* 105 per mL, and the released protoplasts are uniformly distributed in a scattered manner and cannot be accumulated or piled.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for detecting brome Tilletia foetida on broome by using PCR primer
InactiveCN101328495AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSporelingMedical mycology
The invention relates to a method for detecting Tilletia bromi of (Bromus spp.L) by adopting PCR primers, belonging to the Gramineae grass seed medical mycology detection field. The method designs and synthesizes four sets of primers which comprise: a common outer primer, a common inner primer, an outer primer of the T.bromi and a special primer of the T.bromi, wherein, the common outer primer is used for the shell type amplification of the Tilletia hypha genome DNA or teliospore; the common inner primer is used for the shell type amplification of the Tilletia hypha; the two sets of primers are used for the quality monitoring in the amplification process to avoid false negative in the detection process. The T.bromi special primer different from T.controversa, T.caries and T.fusca is designed and is used for the shell type PCR special amplification of the hypha genome DNA conventional PCR and the teliospore, and the outer primer and the special primer perform the shell type amplification on the teliospore DNA. The molecule detection method, which is applied to the T.bromi, is rapid and convenient, has strong specificity and high sensitivity and is accurate and reliable, is established, and the whole detection process can be finished within one working day.
Owner:ANIMAL & PLANT & FOOD INSPECTION CENT OF TIANJIN ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
Method for controlling ambrosia trifida by using rust fungus
InactiveCN103229785AWill not infectSimple and fast operationBiocideAnimal repellantsTeliosporeLactose
The invention relates to a method for controlling ambrosia trifida by using rust fungus. According to the invention, ambrosia trifida seeds are soaked by using concentrated sulfuric acid, and are soaked by using gibberellins; the seeds are sowed in a sunlight greenhouse; when 4-6 pairs of leaves are grown, the ambrosia trifida is preserved for later use; dried ambrosia trifida leaves with teliospores are crushed by using a small crusher, such that teliospore coarse powder is obtained; the teliospore coarse powder is added into a water solution, xylose or lactose, such that a teliospore suspension liquid is prepared; the prepared teliospore suspension liquid is added into a small sprayer, and is uniformly shaken and uniformly sprayed on the leaves of the ambrosia trifida seedlings; in 7-15 days after inoculation, ambrosia trifida leaves are attacked; the teliospores are brushed off by using a stiff brush, and are prepared into a teliospore suspension liquid; water is added into the teliospore suspension liquid according to a certain ratio, and the solution is sprayed on the leaves of ambrosia trifida by using a small sprayer. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of simple operation, low cost, no residue, no pollution, no infection on other crops, and environment safety.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
Wheat stripe rust teliospore germination technology system
The invention relates to a wheat stripe rust teliospore germination technology system, which comprises the following steps: conducting low-temperature treatment on a wheat stripe rust teliospore material for one week or longer time, treating wheat tissues (leaves or sheathes) containing wheat stripe rust teliospore with sterile water, spraying water, soaking and placing in the low-temperature environment for 24 hours, then moving out and placing in a 16DEG C incubator and naturally drying for 24 hours; and repeating the above drying-wetting operation for 2-4 cycles, then soaking the wheat tissues containing wheat stripe rust teliospore for 24 hours with sterile water, placing the wheat stripe rust teliospore-containing tissue on a 2-4% water agar medium, placing in the 16DEG C incubator for culturing, and thus observing the germination of the wheat stripe rust teliospore. The wheat stripe rust teliospore germination technology system discloses that the wheat stripe rust in China has a perfect stage, and provides technological guarantee for disclosing the action of sexual propagation of the wheat stripe rust in China in the toxicity variation.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Novel method for rapidly identifying resistance level of sugarcane smut
PendingCN114231589ASave cuttingSave plantingMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologySporeling
The invention discloses a novel method for rapidly identifying the resistance level of sugarcane smut, which comprises the following steps: selecting a mature plant which grows vigorously, cutting off sugarcane tips, and binding the tail ends of stems with a plastic film; the smut fungus teliospore suspension with the concentration of 5 * 10 < 6 > spores / m L is prepared from smut fungus teliospore with the germination rate of 90% or above. A medical injector is adopted to inject about 25 microliters of smut fungus teliospore (the concentration is 5 * 10 < 6 > spores / mL) suspension into each sugarcane bud of a plant, and about 90 buds are inoculated to each sugarcane material. After inoculation, the sugarcane material is still planted in a greenhouse and normally managed, the morbidity condition of sugarcane smut is investigated regularly, the total morbidity plant number is counted, and the final morbidity of each treatment is calculated. Positive control is set in the test, and resistance evaluation is carried out by meeting sugarcane smut resistance grading standards.
Owner:SUGARCANE RES INST OF YUNNAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Detection kit for Neosporiasis
InactiveCN105219878APromote healthy developmentTo achieve the purpose of purifying the herdMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesPositive controlPolypide
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular biological detection and relates to a (Real-Time PCR) detection kit for Neosporiasis. The detection kit is established based on 3D digital PCR scalar positive control and is applied to the clinical diagnosis and the daily monitoring of animals infected with the Neosporiasis. The detection kit comprises Neospora specific primers and a probe, wherein the Neospora specific primers are used for detecting; nucleotide sequences of the probe are represented by SEQ ID NO.1-3; a detected Neospora NcSRS2 gene is represented by SEQ ID NO.4. The detection kit has the characteristics of accurate detection, high sensitivity, strong specificity, simplty, convenience and rapidity, and is used for detecting DNA of polypides in an early infection stage and a recessive 'Neospora attached' period, thereby providing scientific technical supports for the clinical diagnosis and the daily monitoring of the Neosporiasis.
Owner:XINJIANG AGRI UNIV
Ustilago esculenta haploid strain UeTSP and application thereof
The invention relates to an ustilago esculenta haploid strain UeTSP and application thereof and belongs to the field of a biotechnology. On one hand, the ustilago esculenta haploid strain UeTSP is provided; on the other hand, the application of the ustilago esculenta haploid strain UeTSP in impregnation is provided. The ustilago esculenta haploid strain UeTSP and the application thereof have the advantages that the ustilago esculenta haploid strain UeTSP can directly infect zizania aquatica plants to make zizania aquatica pregnant without producing teliospores, that is to say that an unfavorable grey angle expression type is not formed, and a new idea is provided for artificial impregnation of zizania aquatica.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Sporozoan cleaning fish medicine
InactiveCN101156940BNo pollutionNo drug resistanceFungi medical ingredientsAntiparasitic agentsDiseaseSophora Root
The invention relates to a medicine for preventing and curing the fish diseases, in particular to an ichthyosporidiumhoferi removal medicine. The invention is characterized in that the medicine is formed by preparing omphalias, flavescent sophora roots, roor of sessile stemonas, carpeium fruits, arecas, chinaberry fruits, abtipyretic dichroas, belamcandas, capillary artemisias, dyers woad roots, and peppers. The medicine consists of Chinese herbal medicines, the environment can not be polluted, the drug resistance is not caused, and the medicine accords with the requirements of environment-friendly food. The invention has the advantages that the cost is low and the curative effect is remarkable, the cost of the medicine added in the one ton feeding stuff is about 400 RMB, but the cost of the medicine which adopts the prior art and is added in one ton feeding stuff in the market is about 800 RMB. Through the trial and the verification, after the diseased fishes take the medicine, the diseases caused by a variety of sporozoons are radically and effectively cured, and the recurrence does not exist after the speedy recovery. The invention has universal use and promotion values.
Owner:严必福
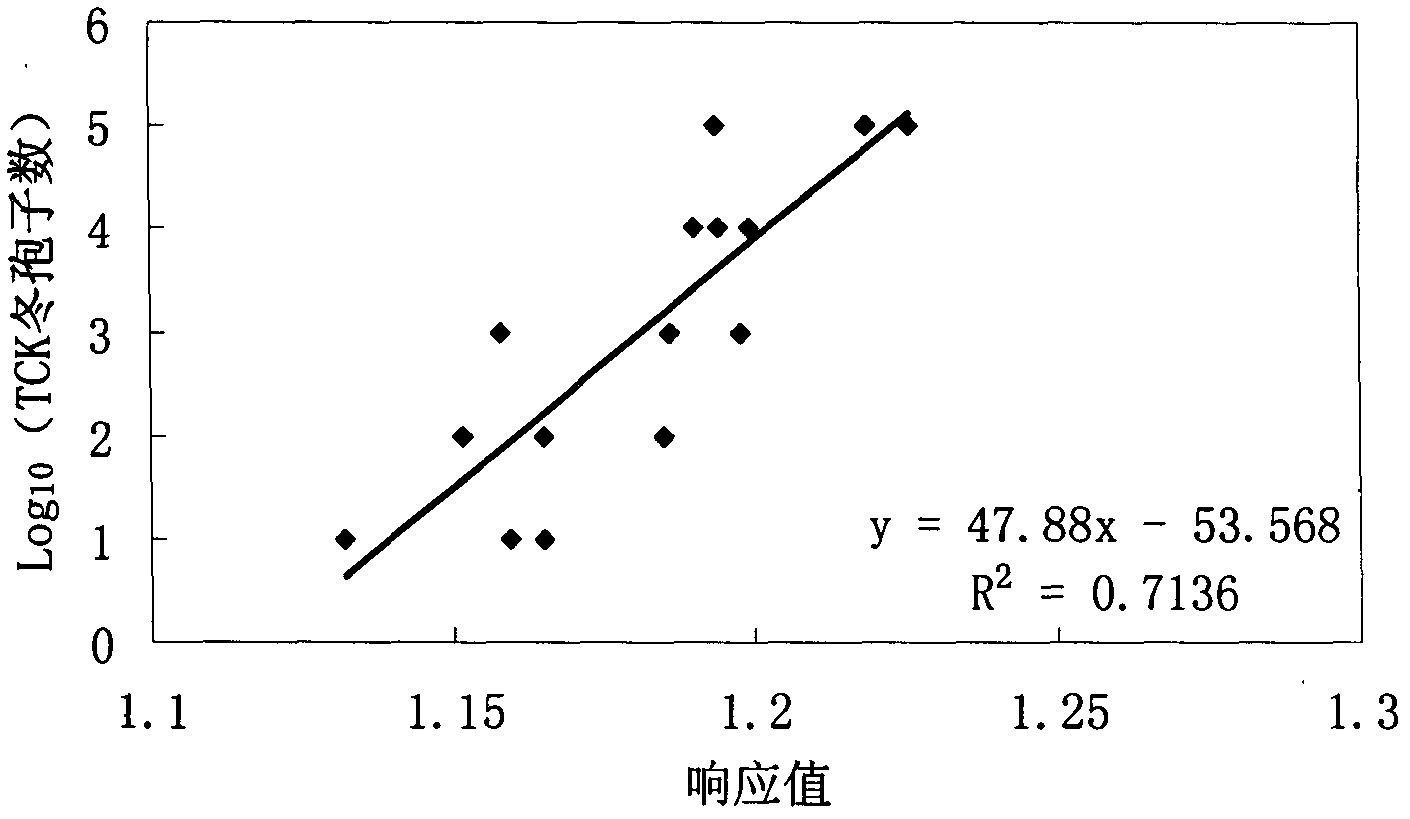
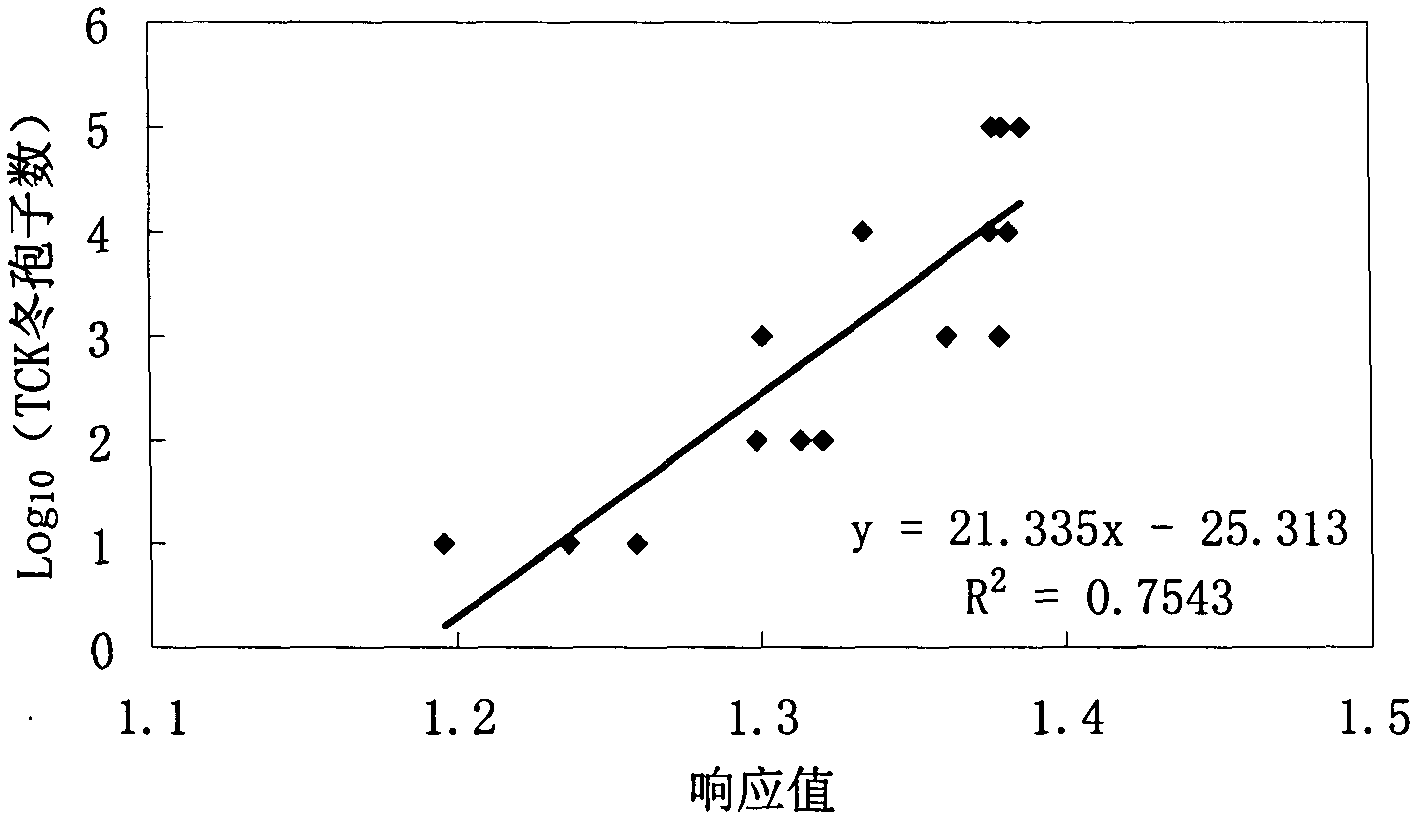
Method for rapidly and quantitatively detecting Tilletia controversa Kuhn in wheat based on electronic nose
InactiveCN103257155AEasy to operateEasy to separateMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansTeliosporePlant disease
The invention relates to a method for rapidly and quantitatively detecting Tilletia controversa Kuhn (TCK) in wheat based on an electronic nose, and belongs to the technical field of crop disease control and plant quarantine. In the invention, the quantitative detection of the content of TCK teliospores in an unknown wheat sample is realized through respectively establishing models of relations between the response values of ten sensors in the electronic nose and different TCK teliospore contents in fumigated or unfumigated wheat. The method shortens the time required by the quantitative detection, does not damage a sample for detecting, and can save the quantitative detection cost because no other reagents are basically needed in the detection process. The method can be massively popularized in the TCK quarantine in the ports in China.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Parasitic protozoan isolate
InactiveUS20030185852A1Avoid abortionReduce the possibilityBiocideProtozoaNeospora speciesTeliospore
Owner:UNIV OF TECH SYDNEY
Serological assay for Neospora caninum
InactiveUS20050112567A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingNeospora speciesWestern blot
The present invention relates to the serological detection of Neospora caninum-vaccinated animals by means of reaction of a subject serum with a protein reactive with N. caninum. The protein may be a full-length native or recombinant N. caninum or Toxoplasma gondii bradyzoite fusion protein or a truncated fusion protein or fragment thereof. The protein may be used in any of a number of assays including enzyme linked immunosorbant assays (ELISA), a radioimmunoassay (RIA), a Western Blot and other suitable forms of immunoassay.
Owner:PFIZER INC +1
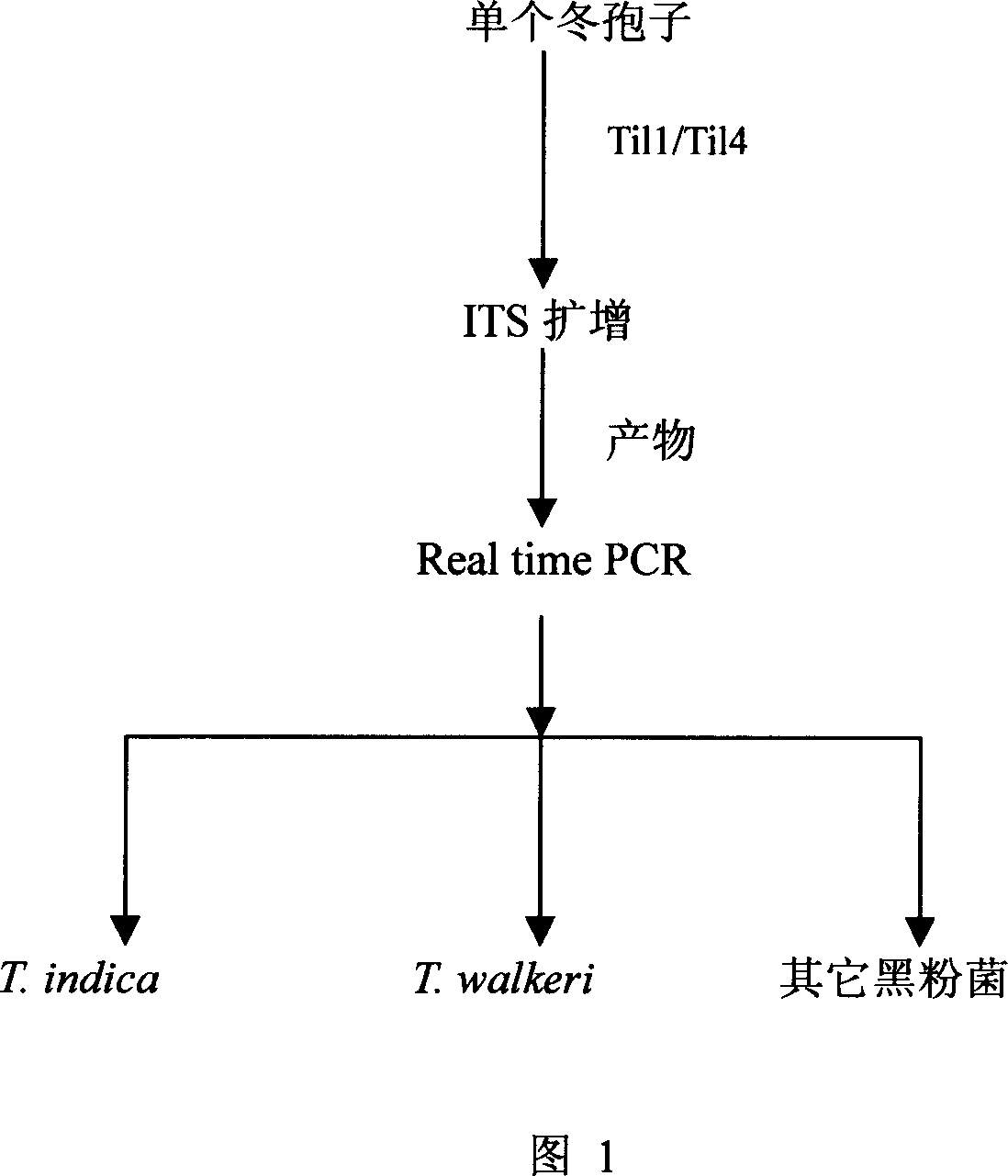
Primer, probe and method for detecting tilletia walkeri
InactiveCN101054600AShorten detection timeHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationTeliosporeBiology
The present invention discloses specific primer and probe for detecting Tilletia walkeri and method for detecting Tilletia walkeri using the primer and probe. The inventive method can shorten greatly the detection time and promote the sensitivity. Single teliospore can be detected. Two kinds of pathogen teliospore can be simultaneously detected in the invention so detection efficiency is promoted.
Owner:上海出入境检验检疫局
A kind of wild rice smut haploid bacterial strain uetsp and application thereof
The invention relates to a haploid strain of Ustilago smut UeTSP and an application thereof, belonging to the field of biotechnology. On the one hand, the present invention provides a new Ustilago smut haploid strain UeTSP, and on the other hand provides the use of the Ustilago smut haploid strain UeTSP in pregnant bamboo. Beneficial effects of the present invention: the smut fungus of the present invention ( Ustilago esculenta ) The haploid strain UeTSP can directly infect Zizania japonica plants and make Zizania zizania gestation without producing teliospores, that is, without the unfavorable phenotype of gray horns, which provides a new idea for zizania zizania artificial pregnancy.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Tilletia controversa teliospore composting harmless treatment method
InactiveCN102358707AImprove fertilityImprove water holding capacityBio-organic fraction processingOrganic fertiliser preparationCelluloseBiology
The invention discloses a Tilletia controversa teliospore composting harmless treatment method. The method is as follows: composting the raw material to be treated for more than six days, wherein the water content of the raw material is 60-70wt%, the C / N is 30-40 and the internal temperature of a pile body is 50-60 DEG C. The technical scheme provided by the invention utilizes the high temperature generated in the composting process to kill pathogenic bacteria, weed seeds, worm eggs and the like. In addition, the soil microorganisms in the pile body can be used for degrading the important components of plants, such as cellulose and lignin and the converted product can be used as the fertilizer, thus the environment can be protected, the soil fertility can be increased, the soil water retention capacity can be increased, the volume and smell of an organic material and the pathogenic bacteria can be reduced and the recycling of resources can be realized.
Owner:曹际娟
Method for artificial inoculation of insolated identification of white rust resistance of chrysanthemum
InactiveCN101889549BIdentification safe and effectiveAvoid safety hazardsMicrobiological testing/measurementHorticulture methodsWide mouthTeliospore
The invention provides a method for artificial inoculation insolated identification of resistance of chrysanthemum to white rust of chrysanthemum. The method comprises the following steps: A, using a 500ml wide-mouth glass bottle as an insolated culture container; B, preparing a liquid culture medium and a solid culture medium respectively and combining the culture media by putting the liquid culture medium above the solid culture medium; C, cutting chrysanthemum stems which are healthy and not infected with pathogenic bacteria of chrysanthemum white rust; D, picking up chrysanthemum leaves with telia; E, rubbing teliospores on telia of infected leaves by hands, and inoculating the teliospores onto the chrysanthemum leaves to be detected; F, performing cottage of the chrysanthemum stems inoculated with the pathogenic bacteria in the culture bottle filled with the solid-liquid combined culture medium for culture by placing the chrysanthemum stems in the dark at 17 to 21 DEG C for 24 hours and then placing the chrysanthemum stems in light of which the intensity is 1,000 Lx for 16 hours and then in the dark in a culture room for 8 hours; and G, after 15 days, observing whether the telia is on the chrysanthemum leaves by eyes. The method for artificial inoculation insolated identification of white rust resistance of chrysanthemum provided by the invention has the advantages of eliminating potential safety hazards in identification of white rust resistance of chrysanthemum and realizing safe and effective identification of the resistance of different chrysanthemum varieties on white rust resistance of chrysanthemum under controlled conditions.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
A kind of animal growth promoter containing Puccinia reedi and its preparation method
ActiveCN110012965BWidely distributedIncrease contentBacteriaAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologySporeling
The invention belongs to the technical field of development and research of feed additives, and specifically discloses an animal growth promoter containing Puccinia reedi, which contains Puccinia reedi with the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1. Preparation method: 1. collection of teliospores of Puccinia reed; 2. drying; 3. crushing of reed leaves; 4. crushing of teliospores of Puccinia reed; In the invention, the teliospores of Puccinia reedi are broken and fed to animals in the form of feed additives, which can significantly promote the growth of animals in practice.
Owner:VETERINARY INST XINJINAG ACADEMY OF ANIMAL SCI CLINIC MEDICAL SCI RES CENT XINJIANG ACADEMY OF ANIMAL HUSBANDRY SCI
Germination Technology System of Teliospores of Wheat Stripe Rust
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
A kind of wild rice smut haploid strain uemtsp and its application
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Novel field testing method and device for detection of equine protozoal myeloencephalitis
InactiveUS20060199175A1Minimize false positives and false negativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingProtozoaNematode
The present invention discloses a quick, simple, qualitative and semi-quantitative immunologic method and device in a field test kit format for the detection and the stage of infection of certain protozoal, viral, bacterial, or nematodal pathogens in body fluids, using vaccines specific to such pathogens as antigens. The method comprises immobilizing an antigen specific to a selected protozoal, bacterial, viral or nematodal pathogen on a support membrane, obtaining a sample of a body fluid from a human or animal suspected of harboring the pathogen, thus containing antibodies thereto, contacting the antigen with the sample of body fluid and detecting the binding of the antigen with the antibodies by any suitable means. The device comprises a rigid member, an absorbent layer, a foam layer and a support member on which the antigen is immobilized, glued together to form a compact assembly. The field test kit comprises the device enclosed in a casing and vials containing additional reagents such as washing and dilution buffers, a chromogenic label for the detection of the antigen-antibody complex and positive and negative control solutions to verify the accuracy of the tests, instructions for use and the like. All the components are packaged in a small plastic container or box for easy transportation and use. While this invention is particularly adaptable to the detection of S. neurona using its vaccine as an antigen, other pathogens can also be detected by the method of this invention. These include but are not limited to Neospora hughesi, Neospora Canninum, Leishmania, Leptospira, West Nile virus, and other similar organisms.
Owner:KRISTIPATI RAMA SHARMA +3
The use of farnesol in the prevention and treatment of smut
ActiveCN108552205BRealize green and sustainable developmentReaching the goal of zero growthBiocideFungicidesBiotechnologyBasidiospore
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for identifying loose smut resistance of highland barley
ActiveCN113424720AHigh identification accuracyResistance identification, accurate reflection of the resistance level of different highland barley varietiesCereal cultivationHorticulture methodsBiotechnologyDiseased plant
The invention provides a method for identifying loose smut resistance of highland barley, and belongs to the technical field of plant disease resistance. The pathogenic bacteria of the loose smut of the highland barley enable seeds to carry bacteria by embryo infecting, after sowing, the seeds germinate and are systematically infected along with growing points, and finally floral organs are infected to form teliospore powder. According to the method, teliospores of sick ears are separated and extracted, a teliospore suspension is prepared, highland barley florets is accurately inoculated with the suspension by an injection inoculation method to cause embryo infecting and bacterium carrying of seeds, and highland barley seeds inoculated with pathogenic bacteria are harvested after the highland barley is mature; and the highland barley seeds are sown, the diseased plant rate is counted in the heading period, the highland barley material resistance is determined according to the loose smut resistance grading standard, and the resistance level of the highland barley variety (line) is obtained. The identification method has the characteristics of high identification accuracy and simplicity and convenience in operation, and can accurately reflect the resistance level of the highland barley variety. Compared with resistance identification of natural disease attacking in the field, the method can more objectively reflect the line resistance level of the variety.
Owner:AGRI RES INST TIBET ACADEMY OF AGRI & ANIMAL HUSBANDRY SCI
Agrobacterium-mediated Transformation Method of Tilletia glabris
The invention relates to the genetic transformation of Tilletia tritici, in particular to an Agrobacterium-mediated transformation method for Tilletia tritici. Including: cultivating TFL teliospores, collecting mycelium when the germination rate is ≥60%, and preparing 1×10 6 Mycelia liquid per ml; inoculate Agrobacterium in LB medium, shake culture at 28°C for 2‑3d, dilute to OD with IM medium 600 0.5, continue to cultivate for 7‑8h, dilute to OD with IM medium 600 0.45-0.5; spread a layer of sterile cellophane on the CM medium, mix the Agrobacterium bacterial liquid and mycelia liquid in equal volumes, add AS to 200 μmol / l, spread on the cellophane, and incubate in the dark at 22°C for 24 hours; Transfer the cellophane to a new CM medium, make the side coated with the bacterial solution stick to the medium, and cultivate at 16°C until colonies grow out. The method can successfully transfer the exogenous gene into the genome of Tilletia tritici and stably inherit it.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com