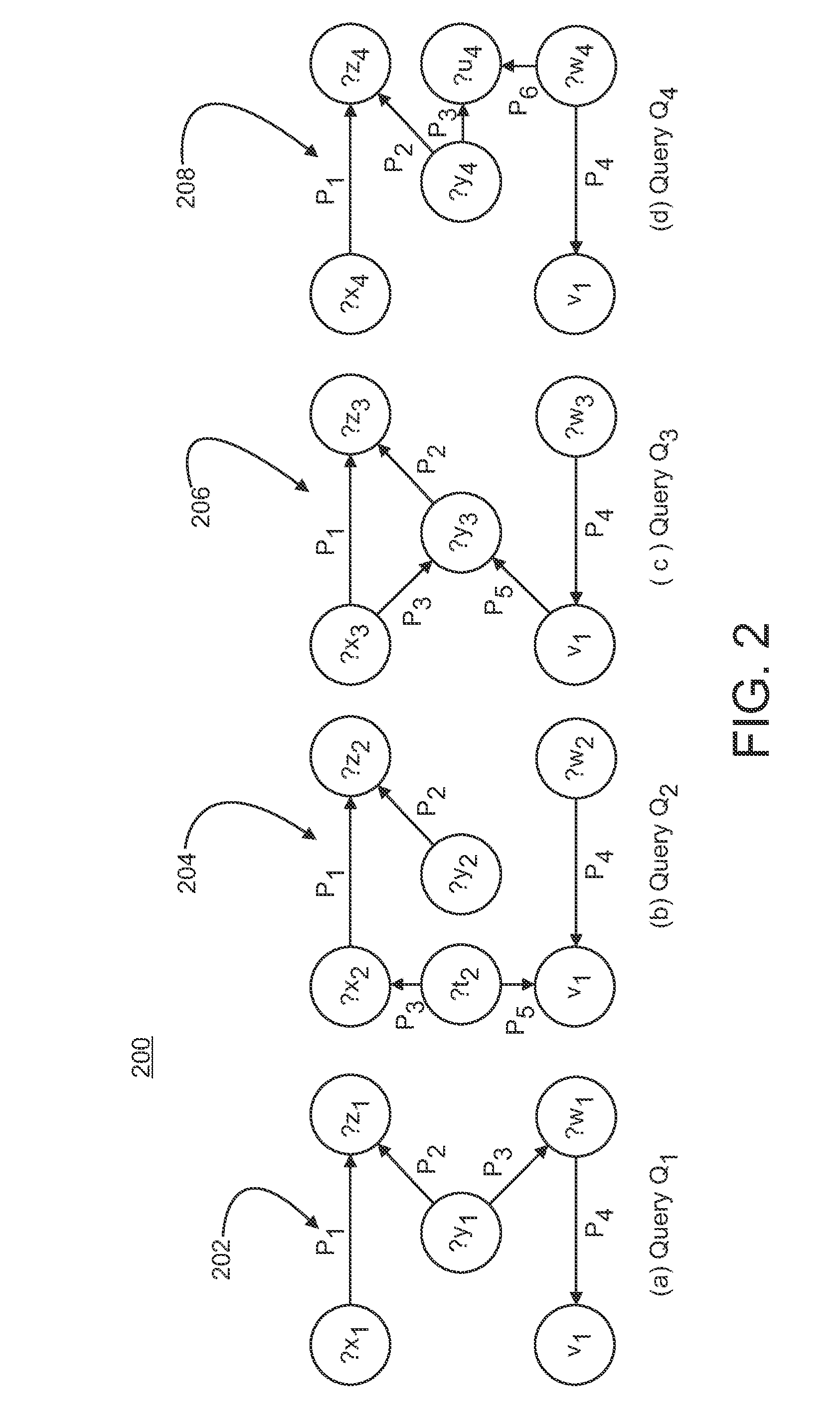
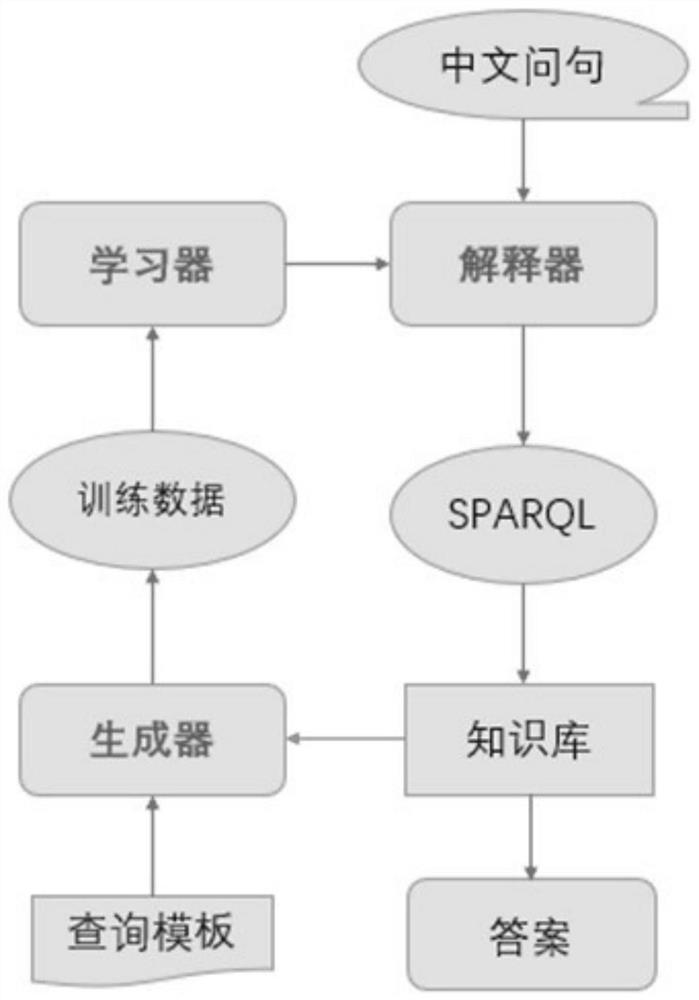
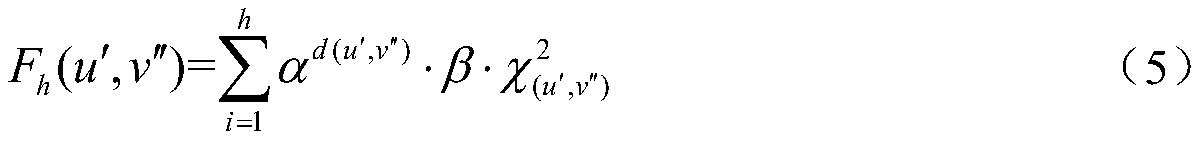Patents
Literature
51 results about "SPARQL" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
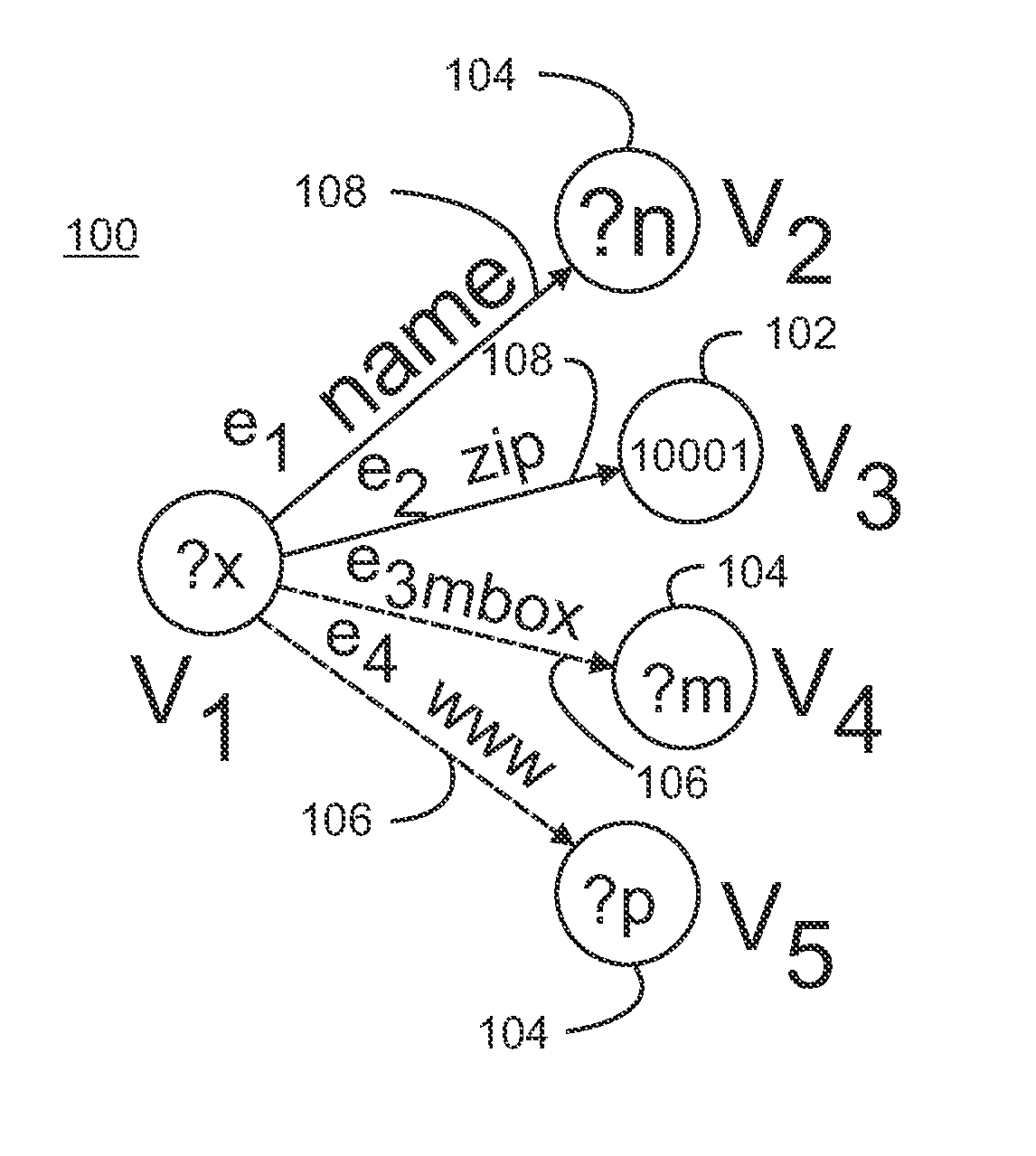
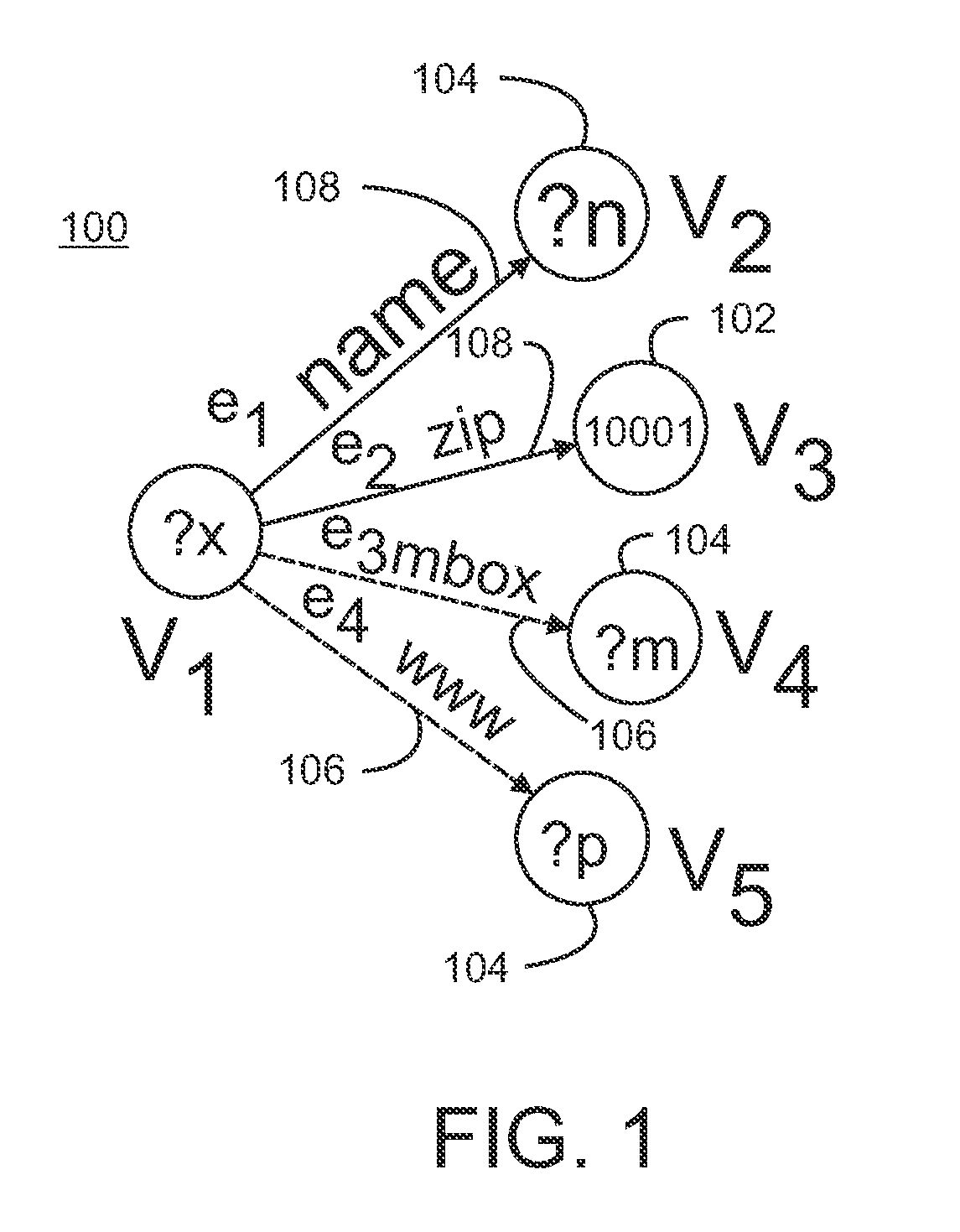
SPARQL (pronounced "sparkle", a recursive acronym for SPARQL Protocol and RDF Query Language) is an RDF query language—that is, a semantic query language for databases—able to retrieve and manipulate data stored in Resource Description Framework (RDF) format. It was made a standard by the RDF Data Access Working Group (DAWG) of the World Wide Web Consortium, and is recognized as one of the key technologies of the semantic web. On 15 January 2008, SPARQL 1.0 became an official W3C Recommendation, and SPARQL 1.1 in March, 2013.
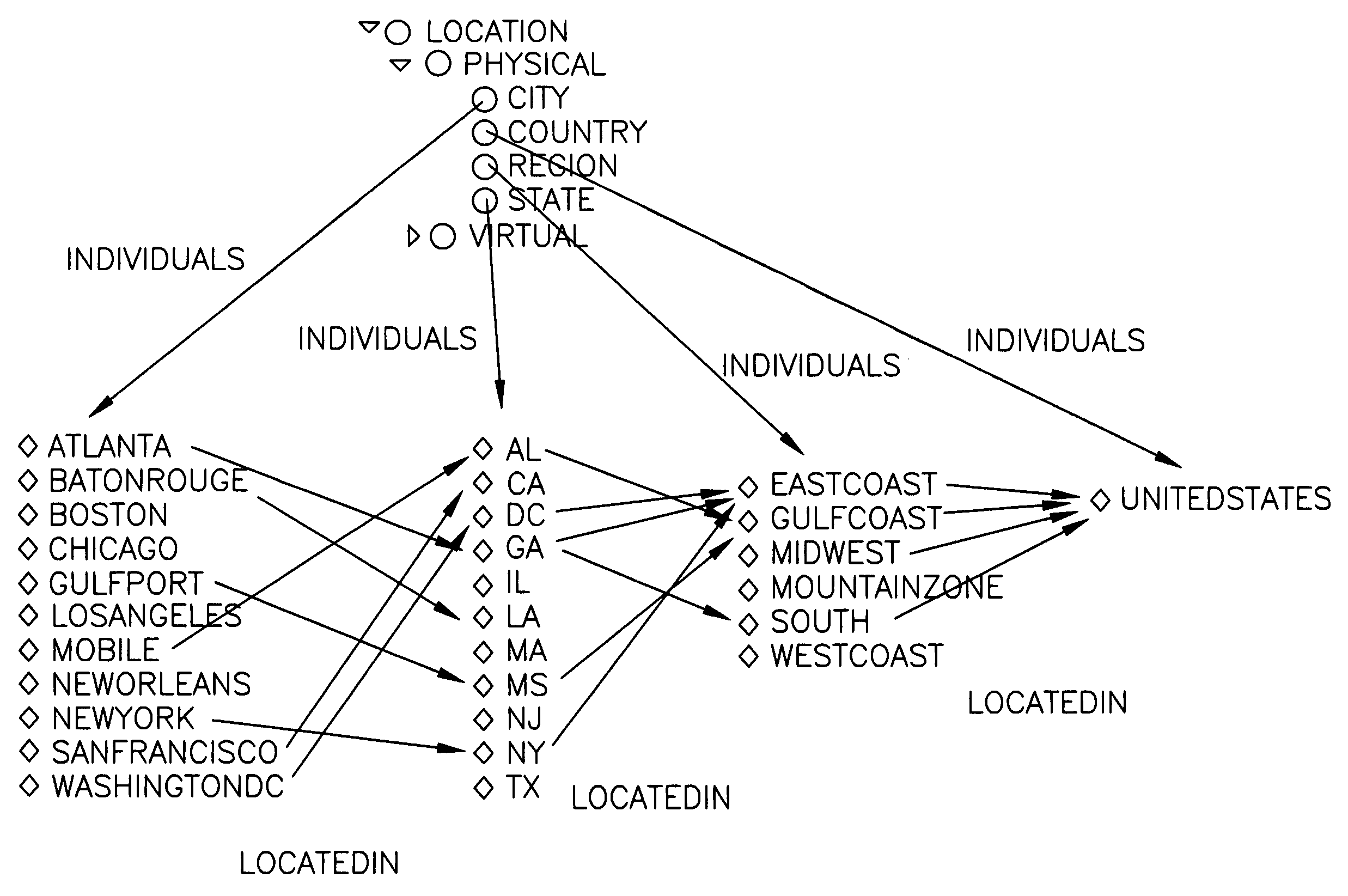
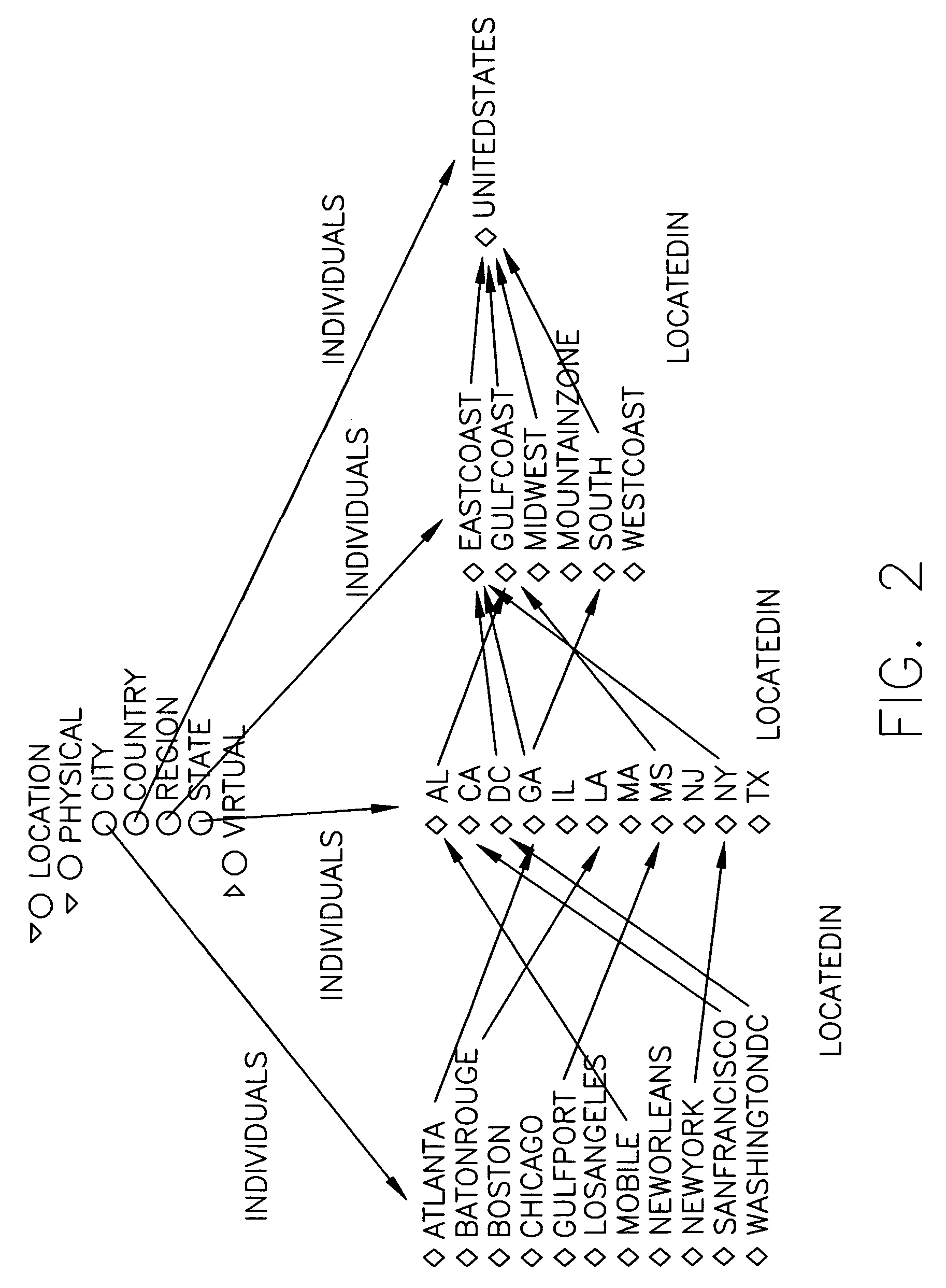
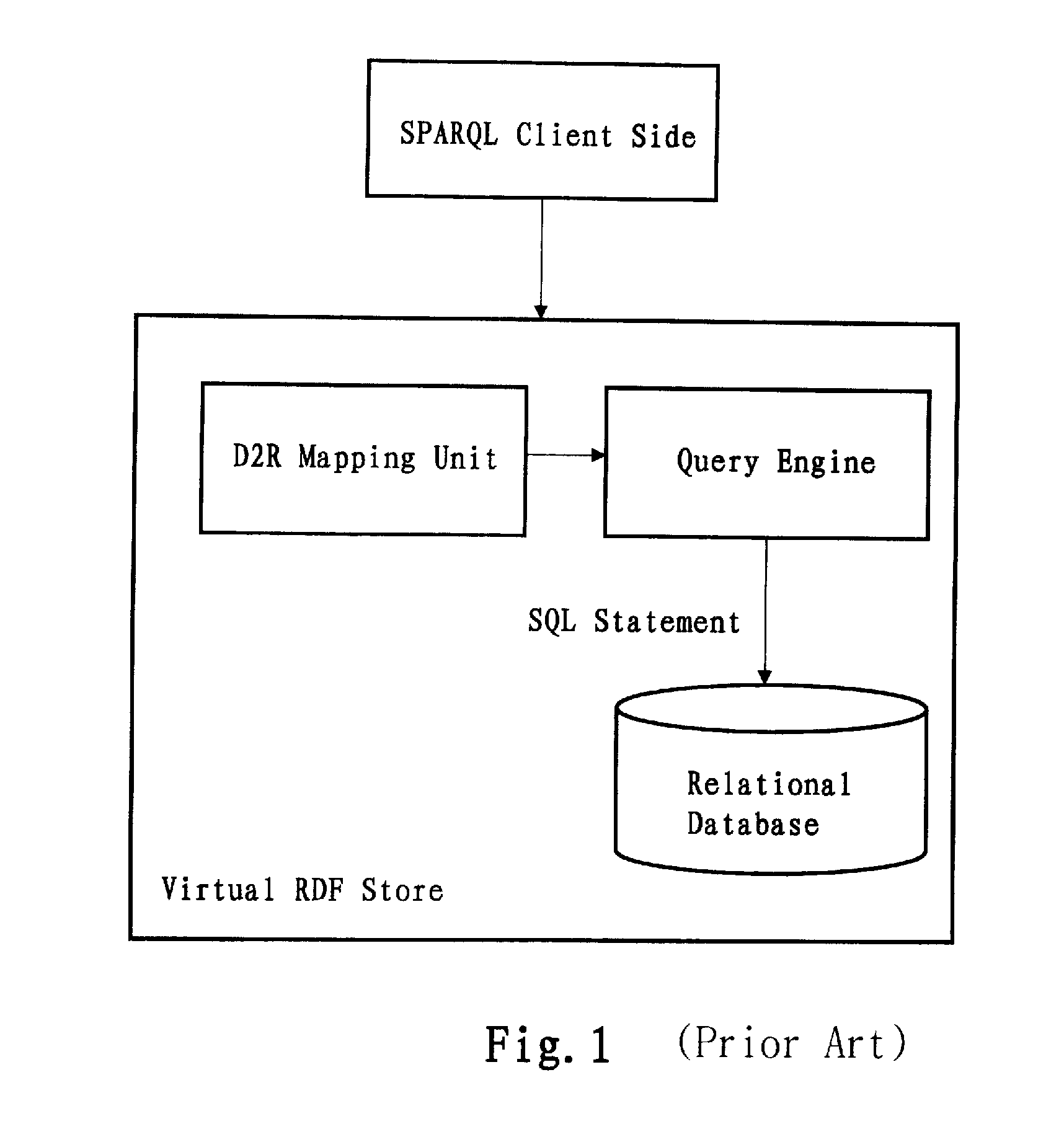
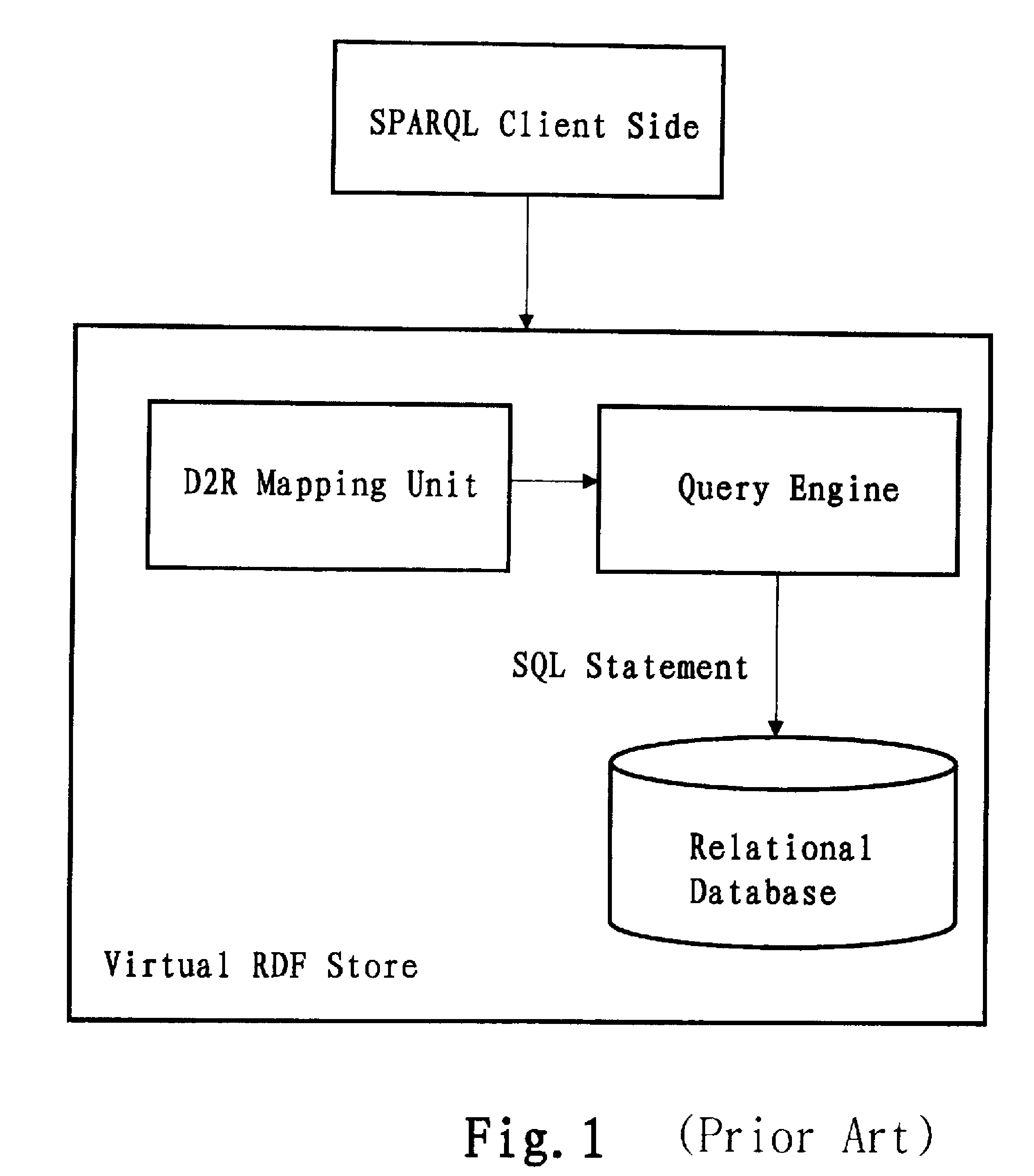
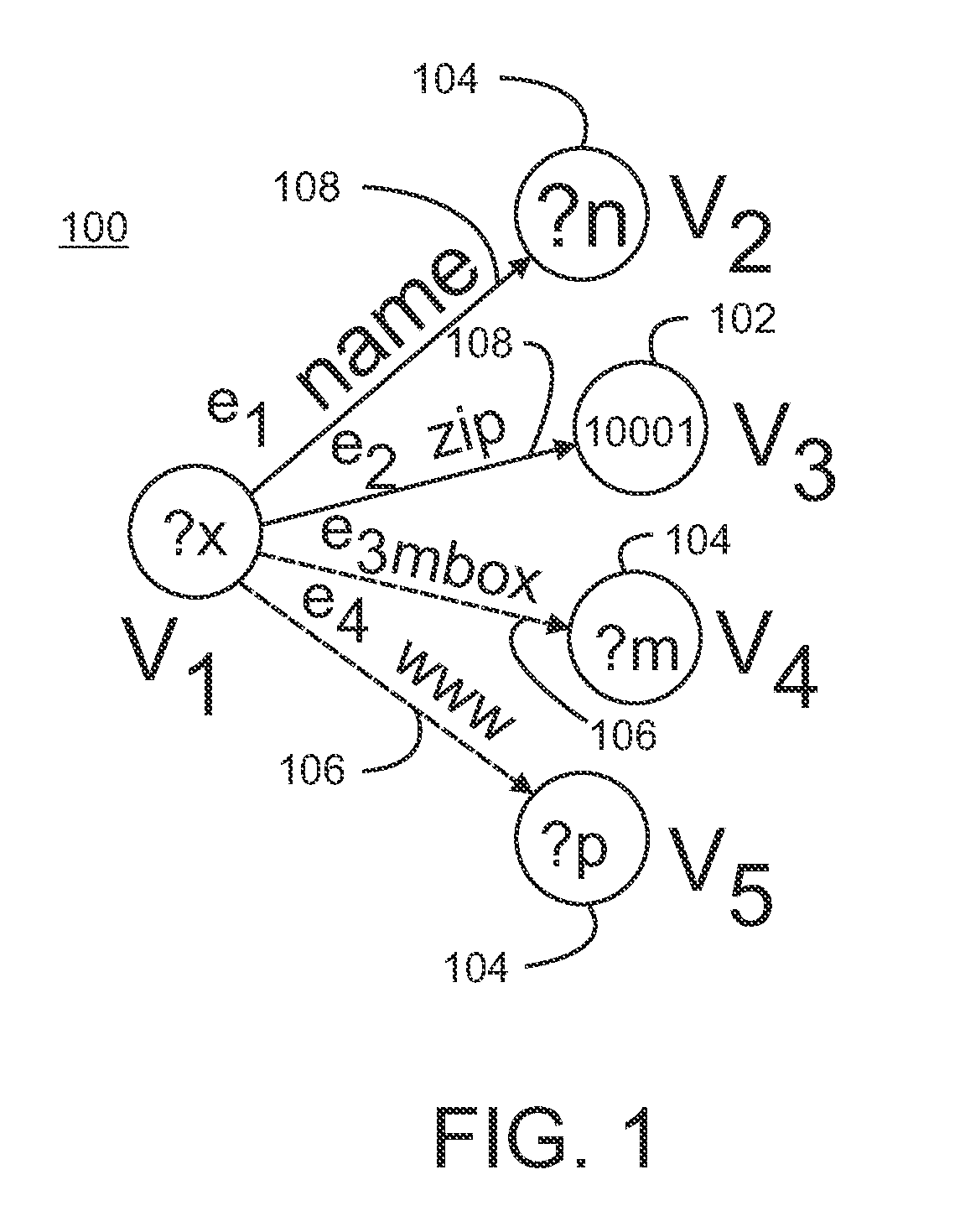
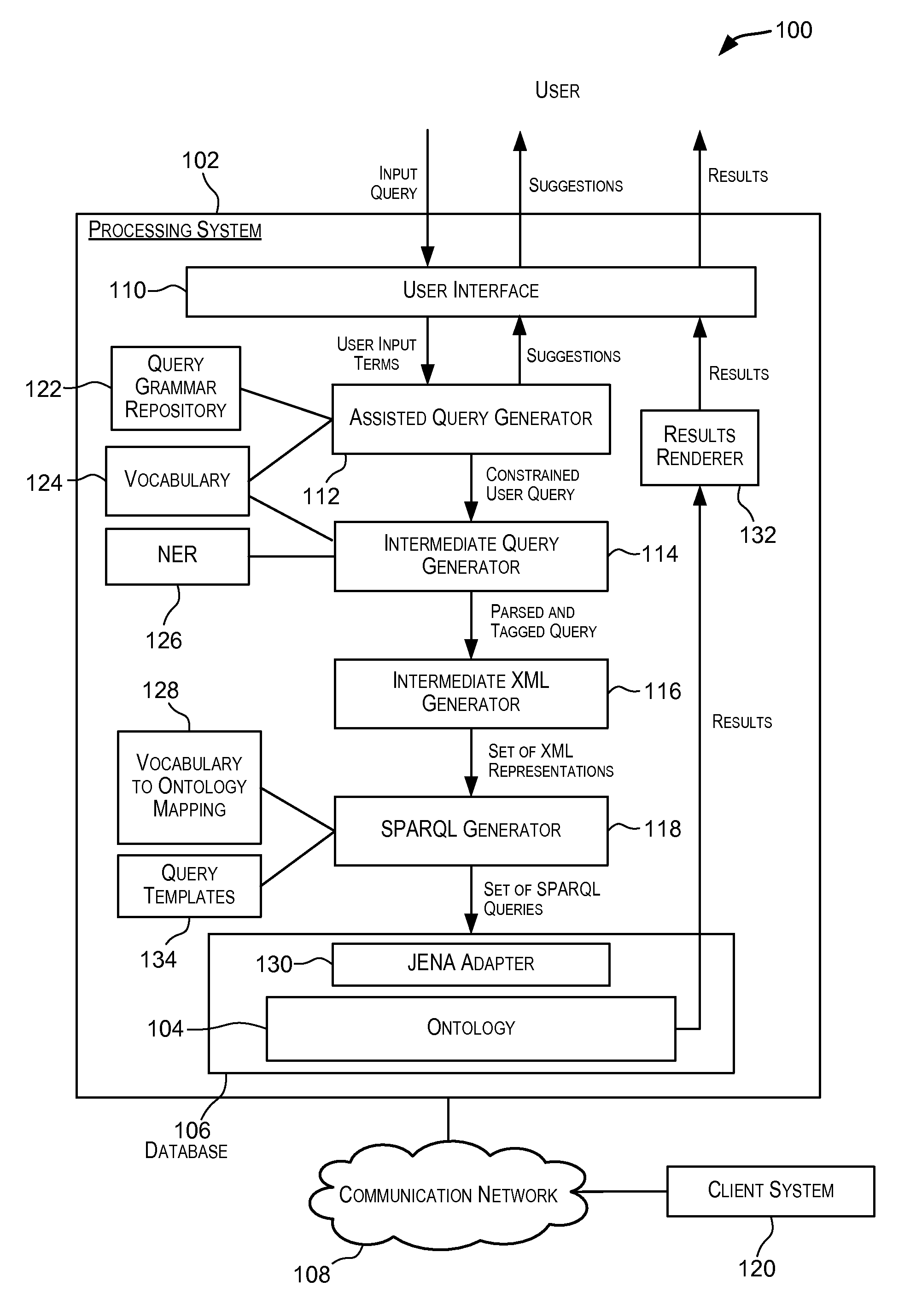
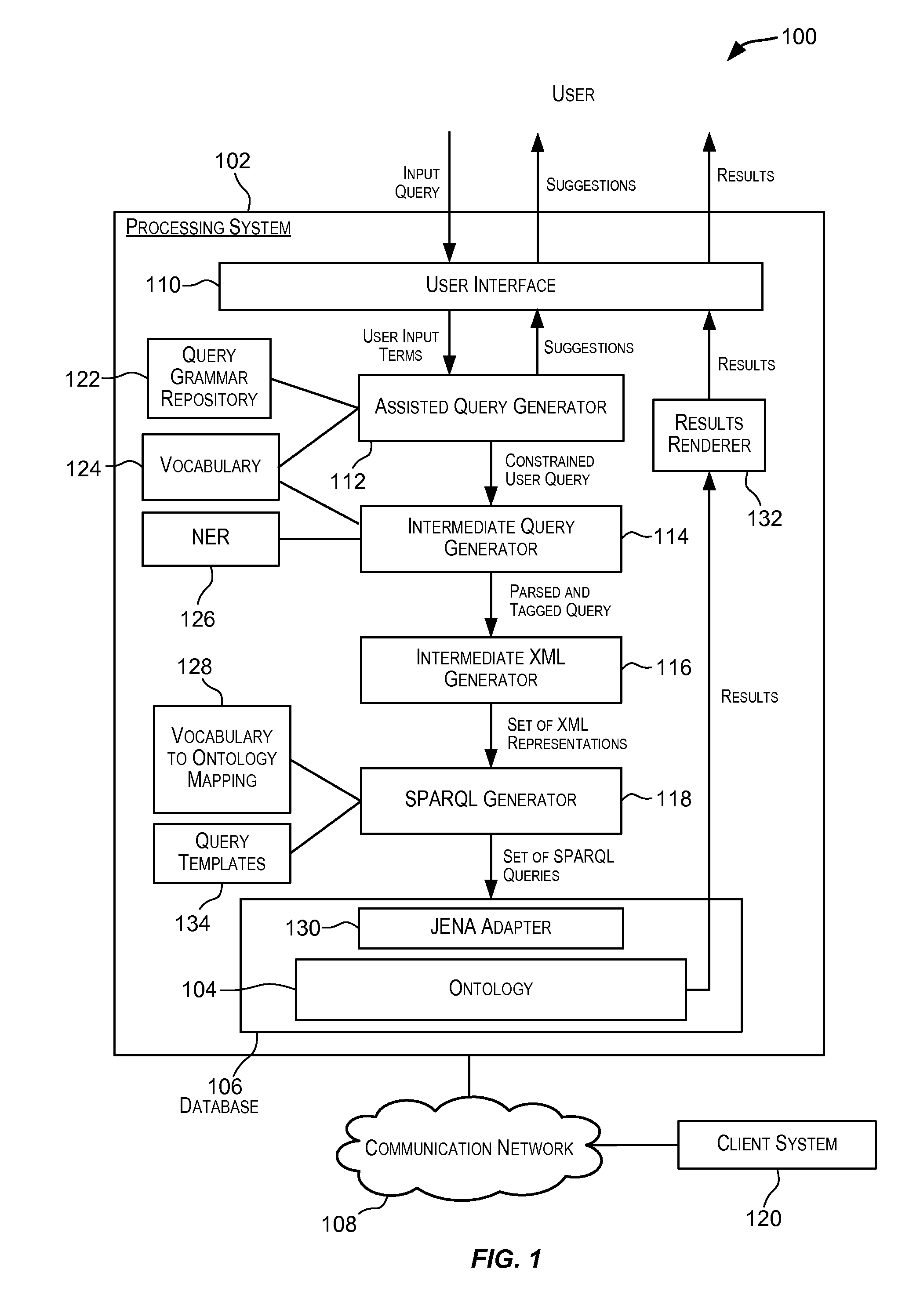
Information retrieval from relational databases using semantic queries
ActiveUS20080040308A1Digital data processing detailsRelational databasesSemantic gapRelational database
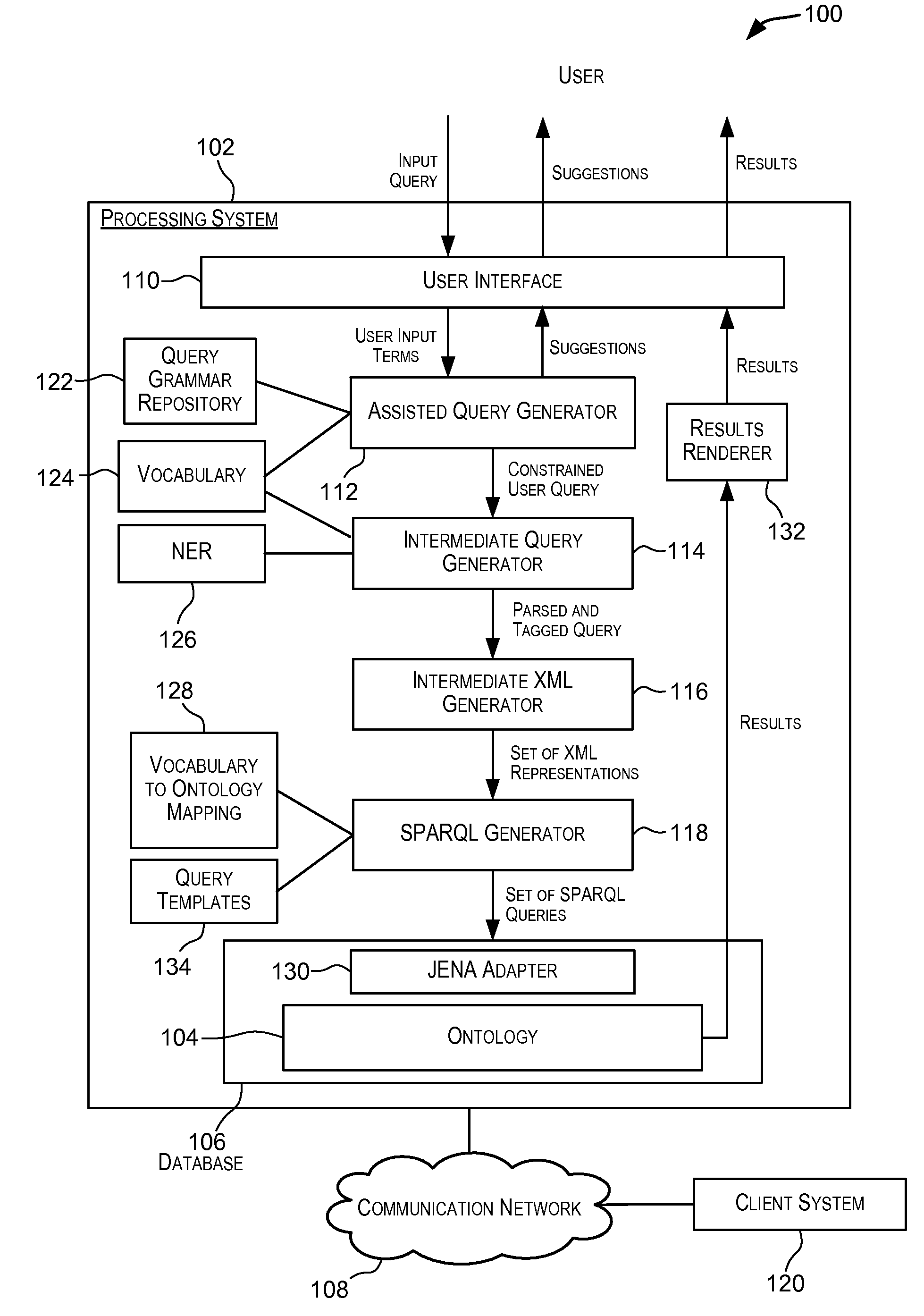
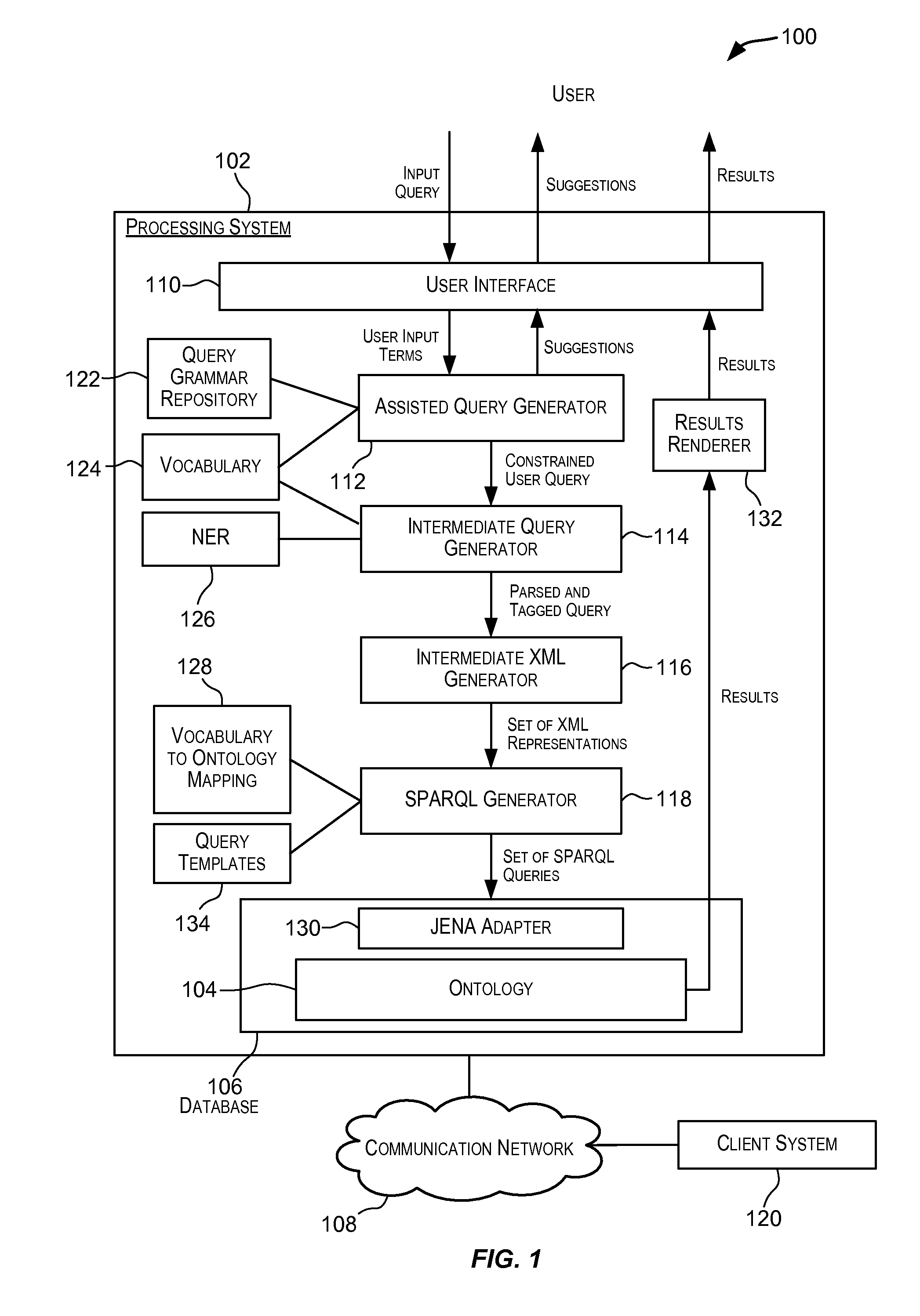
In the realm of managing relational databases, a system that uses both the data in a relational database and domain knowledge in ontologies to return semantically relevant results to a user's query. Broadly contemplated herein, in essence, is a system that bridges a semantic gap between queries users want to express and queries that can be answered by the database using domain knowledge contained in ontologies. In accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention, such a system extends relational databases with the ability to answer semantic queries that are represented in SPARQL, an emerging Semantic Web query language. Particularly, users may express their queries in SPARQL, based on a semantic model of the data, and they get back semantically relevant results. Also broadly contemplated herein is the definition of different categories of results that are semantically relevant to a user's query and an effective retrieval of such results.
Owner:IBM CORP
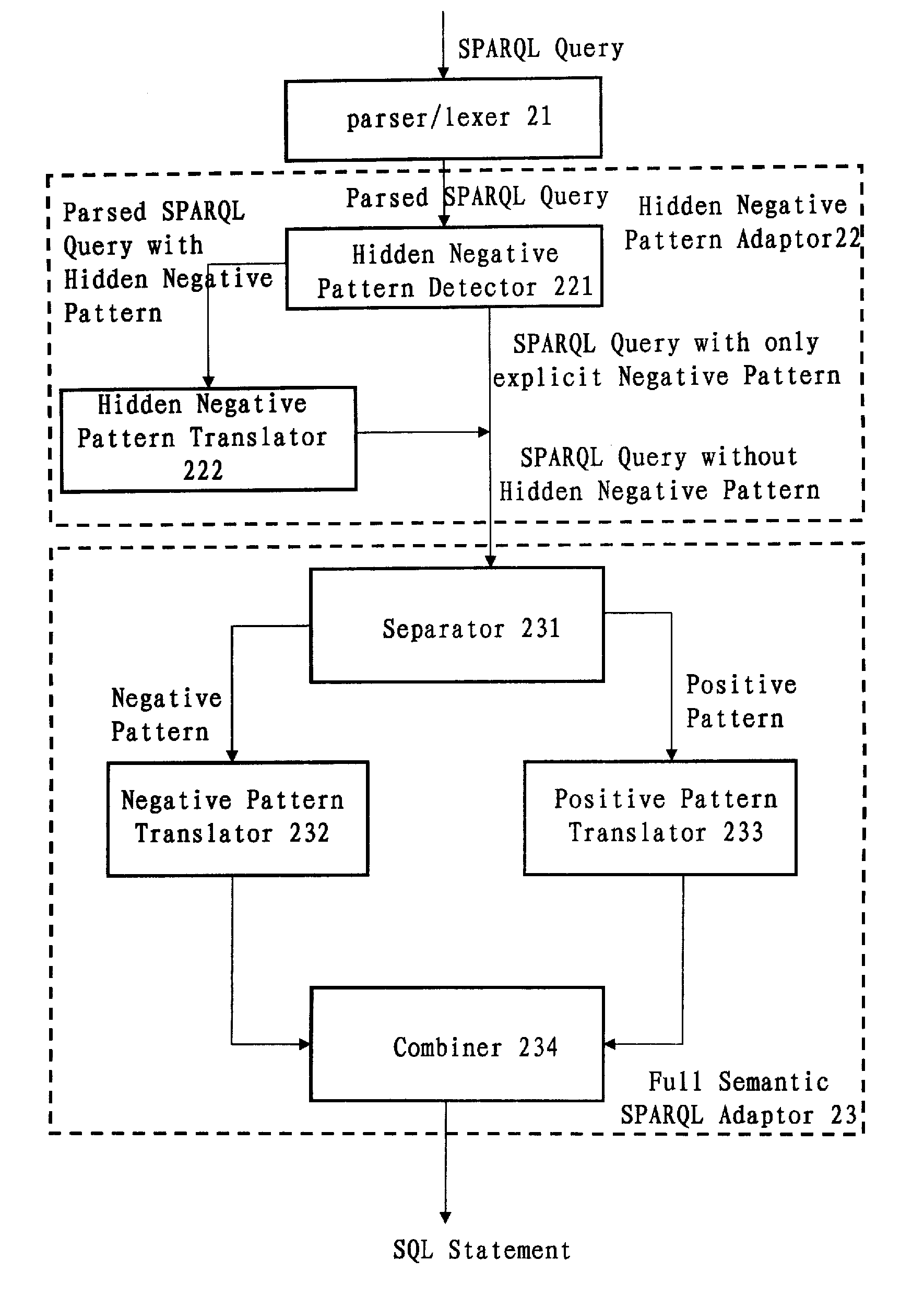
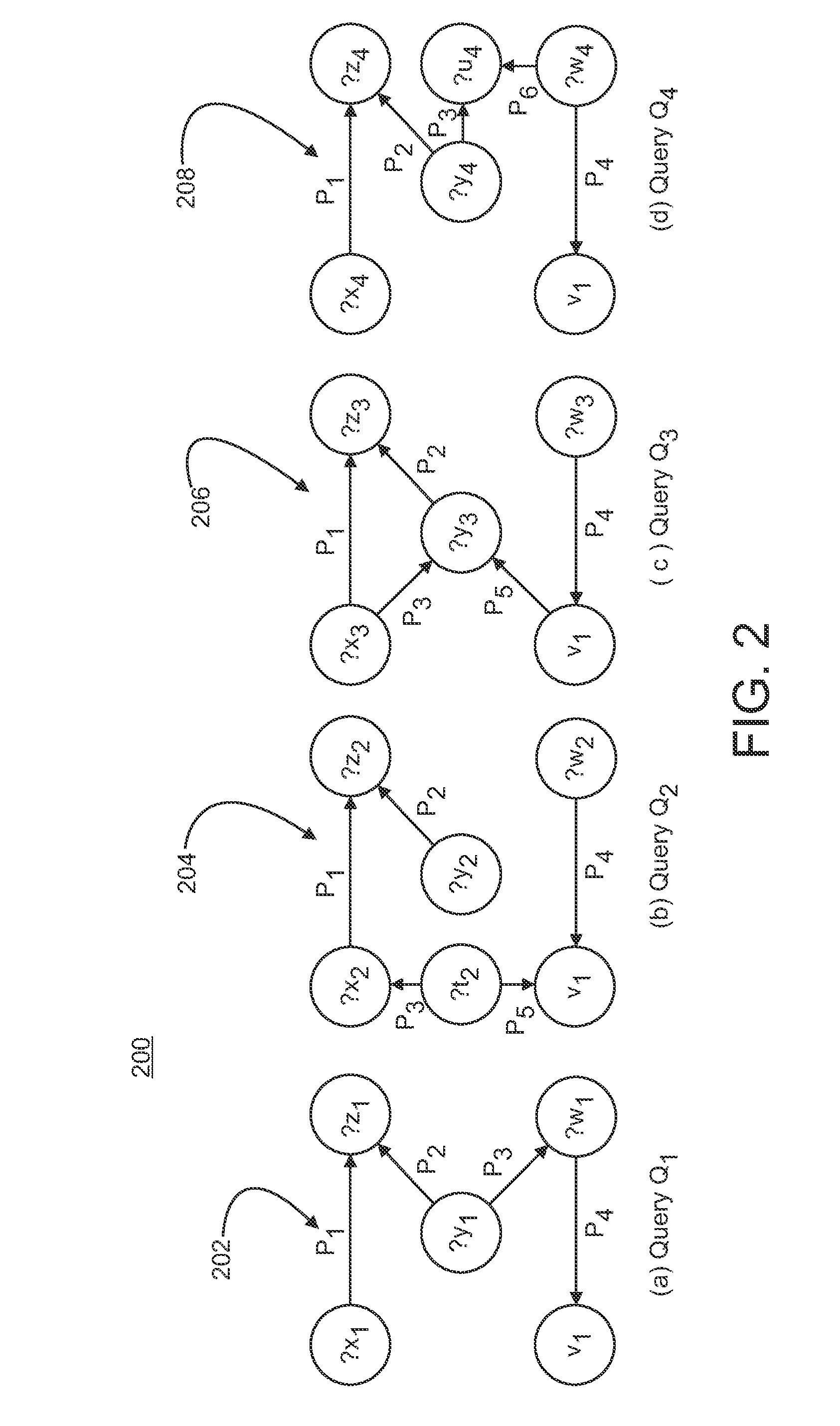
Translation system and method for sparql queries
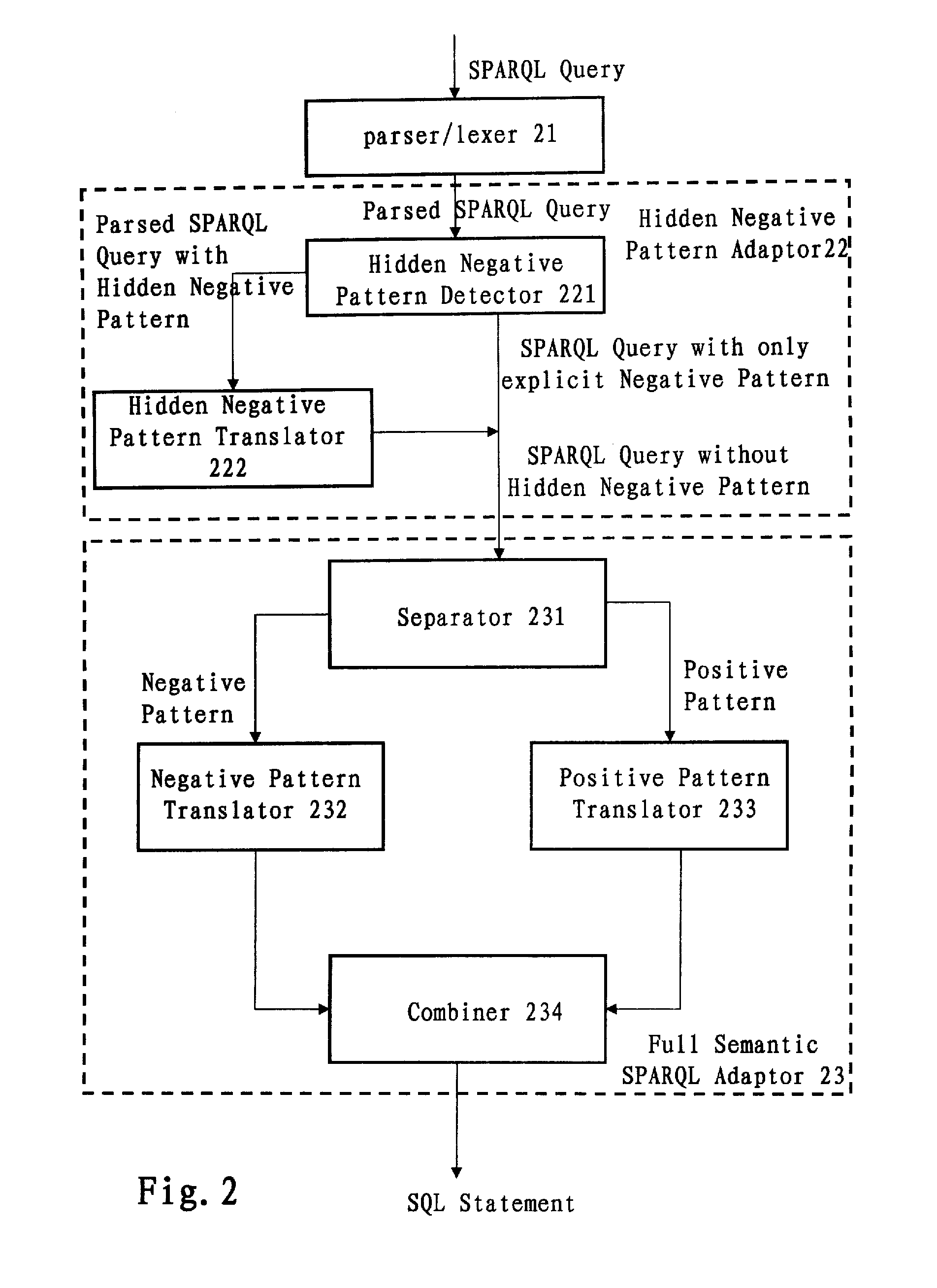
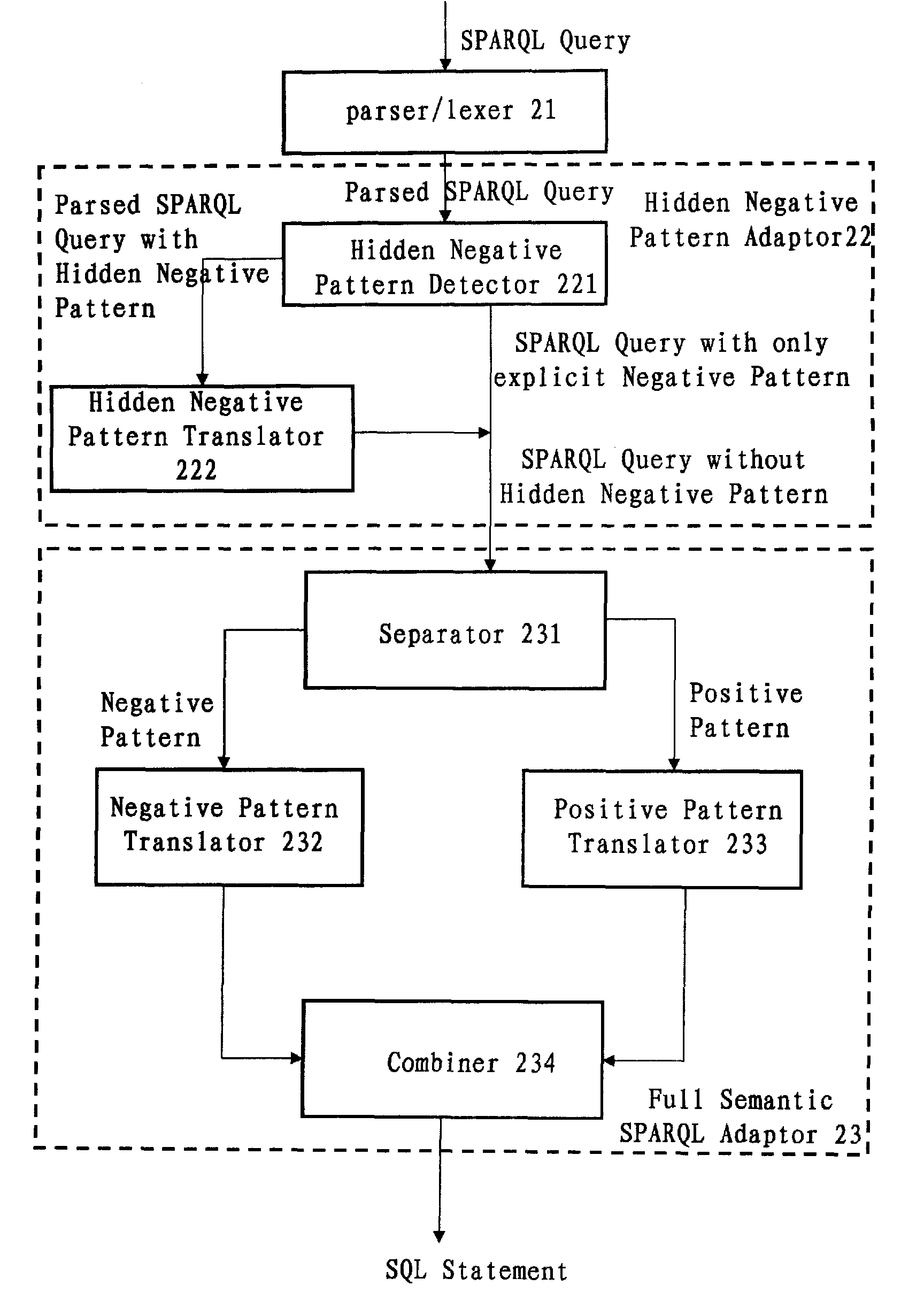
InactiveUS20100250577A1Efficiently translatedDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsLexical analysisPattern detection
A computer-implemented system and method for translating a SPARQL query. The system includes: a parser / lexer for parsing the SPARQL query; a hidden negative pattern detector for detecting a hidden negative pattern in the parsed SPARQL query; a hidden negative pattern translator for translating the detected hidden negative pattern into an explicit negative pattern; a separator for separating the explicit negative pattern from a positive pattern in the parsed SPARQL query; a negative pattern translator for translating the explicit negative pattern into a negative portion of an SQL statement; a positive pattern translator for translating the positive pattern into a positive portion of the SQL statement; and an SQL statement combiner for combining the negative portion of the SQL statement with the positive portion of the SQL statement.
Owner:IBM CORP
Translation system and method for SPARQL queries
InactiveUS8275784B2Efficiently translatedDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsLexical analysisTheoretical computer science
A computer-implemented system and method for translating a SPARQL query. The system includes: a parser / lexer for parsing the SPARQL query; a hidden negative pattern detector for detecting a hidden negative pattern in the parsed SPARQL query; a hidden negative pattern translator for translating the detected hidden negative pattern into an explicit negative pattern; a separator for separating the explicit negative pattern from a positive pattern in the parsed SPARQL query; a negative pattern translator for translating the explicit negative pattern into a negative portion of an SQL statement; a positive pattern translator for translating the positive pattern into a positive portion of the SQL statement; and an SQL statement combiner for combining the negative portion of the SQL statement with the positive portion of the SQL statement.
Owner:IBM CORP
Techniques for automated generation of queries for querying ontologies
ActiveUS20100185643A1Simple queryDigital data processing detailsSpecial data processing applicationsSimple languageSPARQL
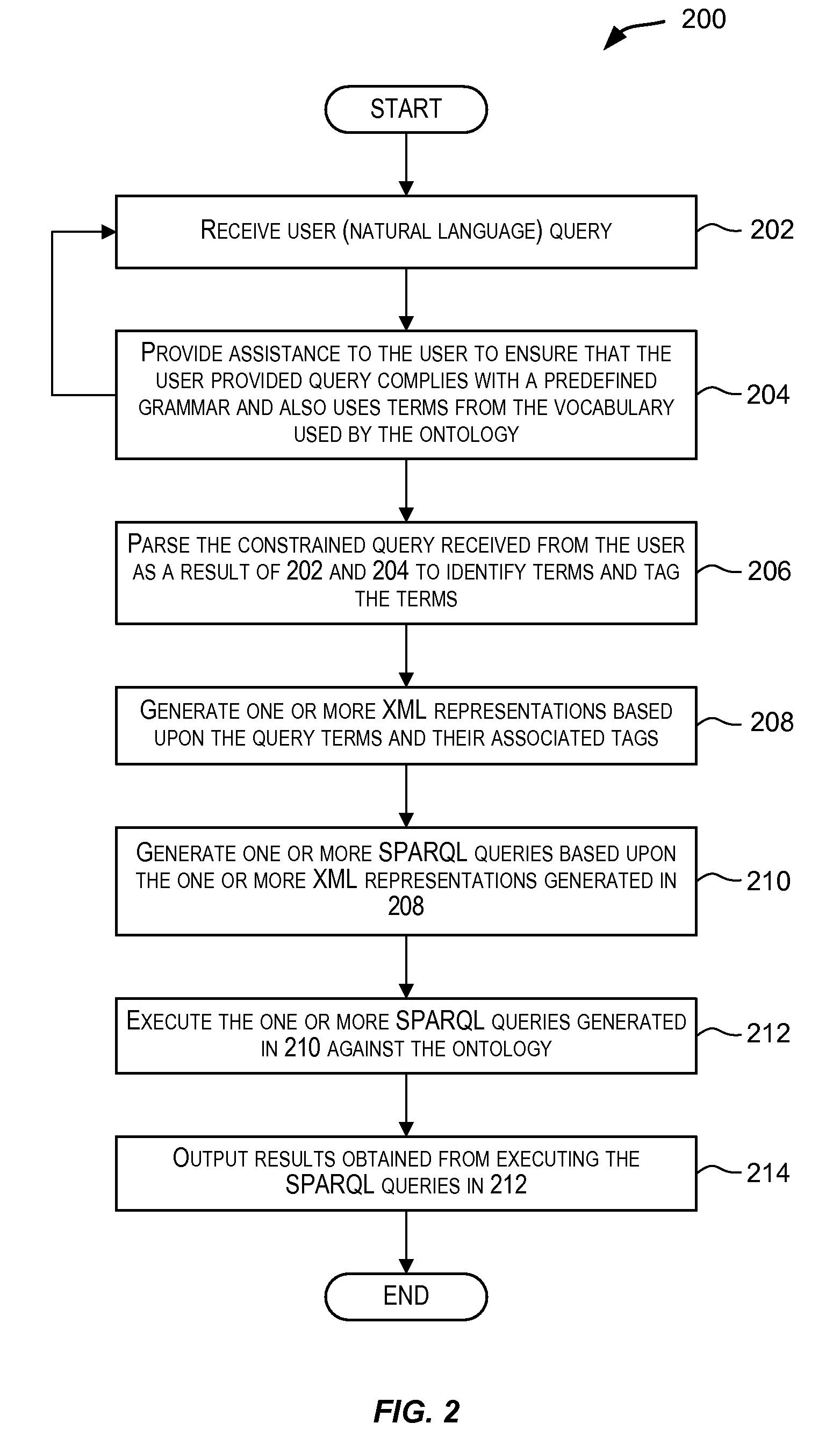
Techniques for simplifying querying of ontologies. In one embodiment, one or more queries for querying an ontology are automatically generated in a language suitable for querying the ontology. A user may enter a query in a simple language such as a natural language query. In response, one or more queries capable of querying the ontology are automatically generated in a second language. The automatically generated queries may, for example, be in SPARQL or PL / SQL. The one or more automatically generated queries may then be used to query one or more ontologies.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Scalable Multi-Query Optimization for SPARQL
ActiveUS20140156633A1Minimize timeHigh expressionDigital data processing detailsRelational databasesExecution planQuery optimization
Multiquery optimization is performed in the context of RDF / SPARQL. Heuristic algorithms partition an input batch of queries into groups such that each group of queries can be optimized together. The optimization incorporates an efficient algorithm to discover the common sub-structures of multiple SPARQL queries and an effective cost model to compare candidate execution plans. No assumptions are made about the underlying SPARQL query engine. This provides portability across different RDF stores.
Owner:IBM CORP
Techniques for automated generation of queries for querying ontologies
ActiveUS8140556B2Simple queryDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsSimple languageSPARQL
Techniques for simplifying querying of ontologies. In one embodiment, one or more queries for querying an ontology are automatically generated in a language suitable for querying the ontology. A user may enter a query in a simple language such as a natural language query. In response, one or more queries capable of querying the ontology are automatically generated in a second language. The automatically generated queries may, for example, be in SPARQL or PL / SQL. The one or more automatically generated queries may then be used to query one or more ontologies.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
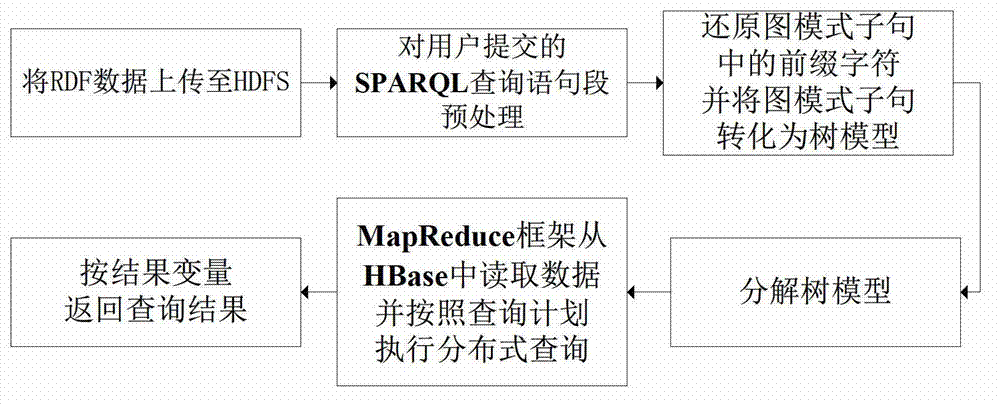
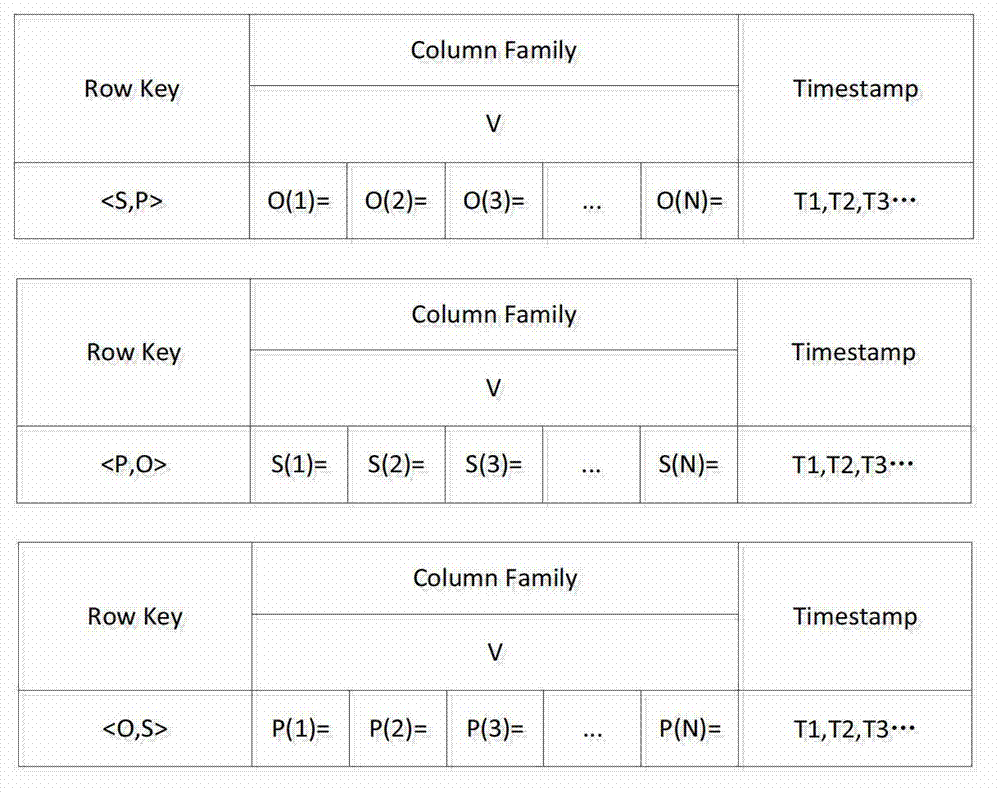
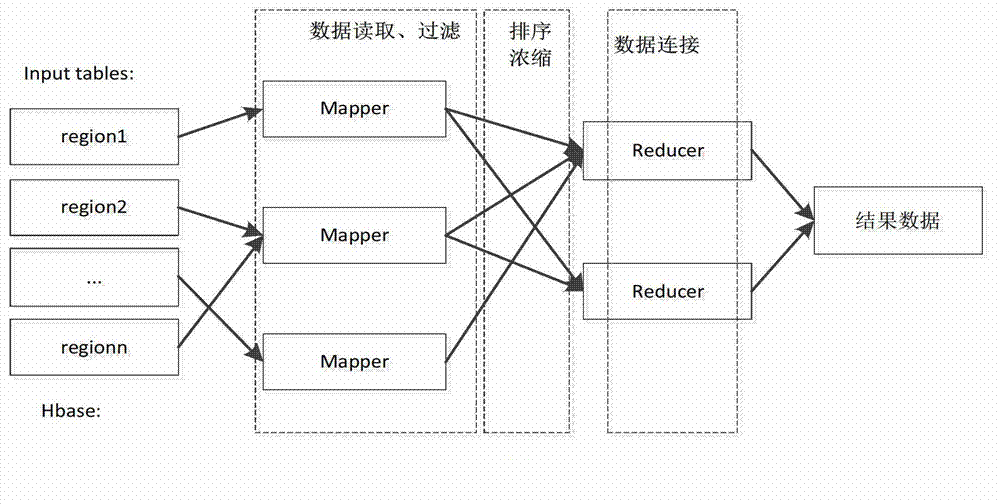
Volume radio direction finde (RDF) data distribution type query processing method based on Hadoop
InactiveCN103116625AImprove query efficiencyRelieve stressSpecial data processing applicationsDistributed File SystemRDF query language
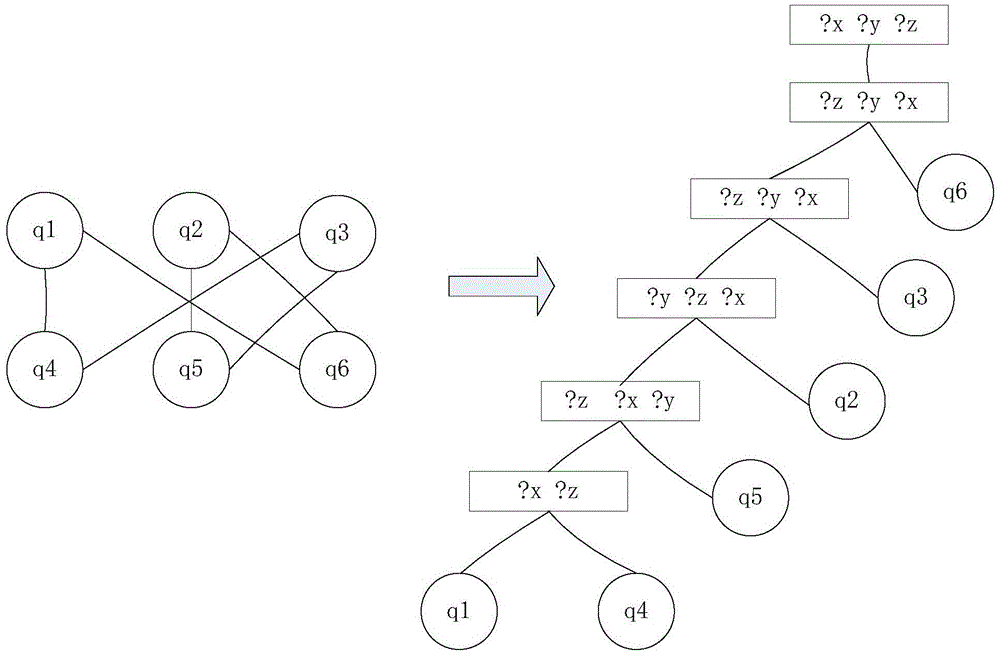
The invention discloses a volume radio direction finde (RDF) data distribution type query processing method based on a Hadoop platform and belongs to the field of the computers. The method mainly comprises the following steps. Step a, RDF data can be uploaded to a hadoop distributed file system (HDFS), data can be read by a MapReduce frame of the Hadoop platform and stored in a distributed database HBase. Step b, a simple protocol and RDF query language (SPARQL) inquiry statement section which is provided by a user can be preprocessed. Statements can be analyzed and extracted a prefix statement, an outcome variable and a picture-model sub sentence. Step c, prefix characters of the picture-model sub sentence can be restored, and the restored picture-model sub sentence can be converted into a tree model. Step d, the tree model can be resolved. Tree joints can be traversed in a bottom-up method and a left-to-right method and inquiry plans can be generated, wherein the inquiry plans are matched with each joints. The final inquiry plans can be sent to the Hadoop platform. Step e, data can be read form the HBase through the MapReduce frame. Distributed query can be implemented according to the inquiry plans. Eventually, the outcome variable can be returned to an inquiry result.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
RDF data storage and query method combined with star figure coding
InactiveCN104462609AReduce the number of query tasksReduce the number of intermediate resultsSemi-structured data indexingSpecial data processing applicationsRelevant informationMap reduce
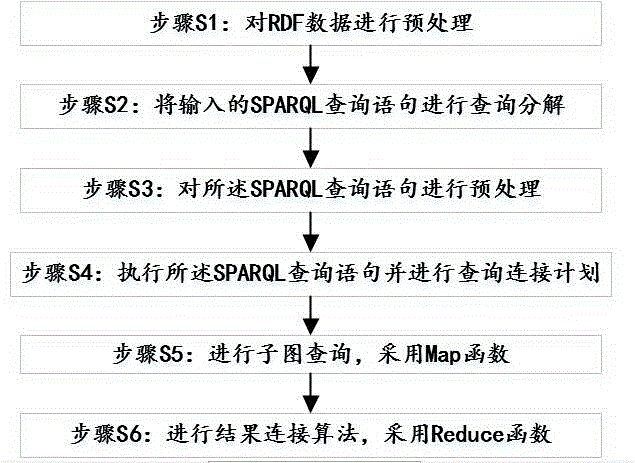
The invention relates to an RDF data storage and query method combined with star figure coding. The RDF data storage and query method comprises the steps that S1, RDF data are preprocessed, and the RDF data are presented in an RDF data map mode; S2, an input SPARQL query statement is presented in an SPARQL query graph mode, and query decomposition is carried out; S3, the SPARQL query statement is preprocessed, and the task number of whole query, the connecting sequence of query star sub-nodes and relevant information of the query star sub-nodes are obtained; S4, the SPARQL query statement is executed, query connection planning is carried out, a Map Reduce parallel computation frame of Hadoop is adopted, and the number of times of starting a query task Job is decided according to the relevance of the SPARQL query statement; S5, subgraph query is carried out, and a Map function is adopted; S6, a result connecting algorithm is carried out, and a Reduce function is adopted. Due to the fact that a Hash coding index query strategy based on star configuration is adopted, stored data redundancy and the number of query tasks are reduced, and query efficiency is improved.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
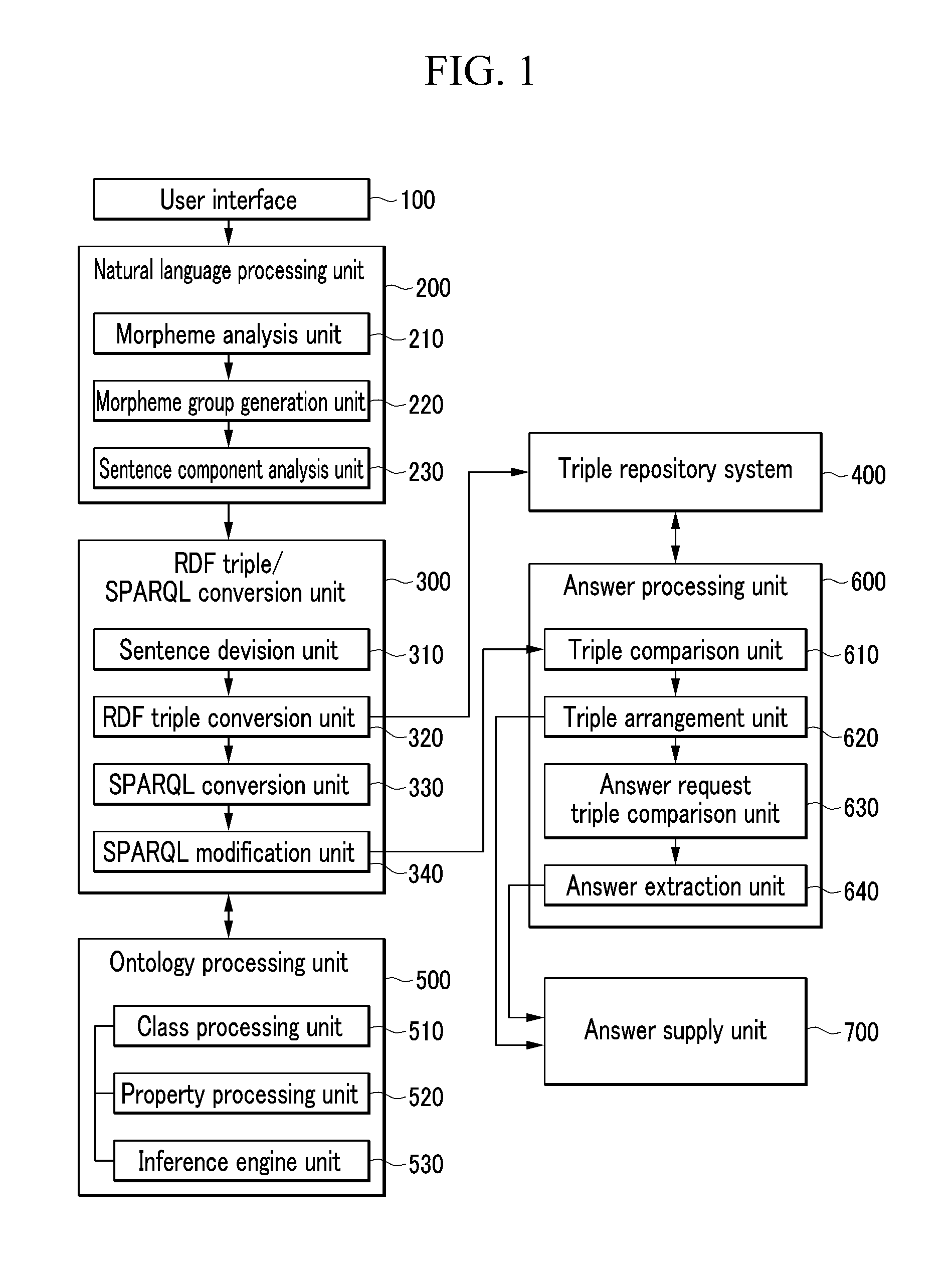
System and method for searching and question-answering
InactiveUS20110047178A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsQuestion answerSPARQL
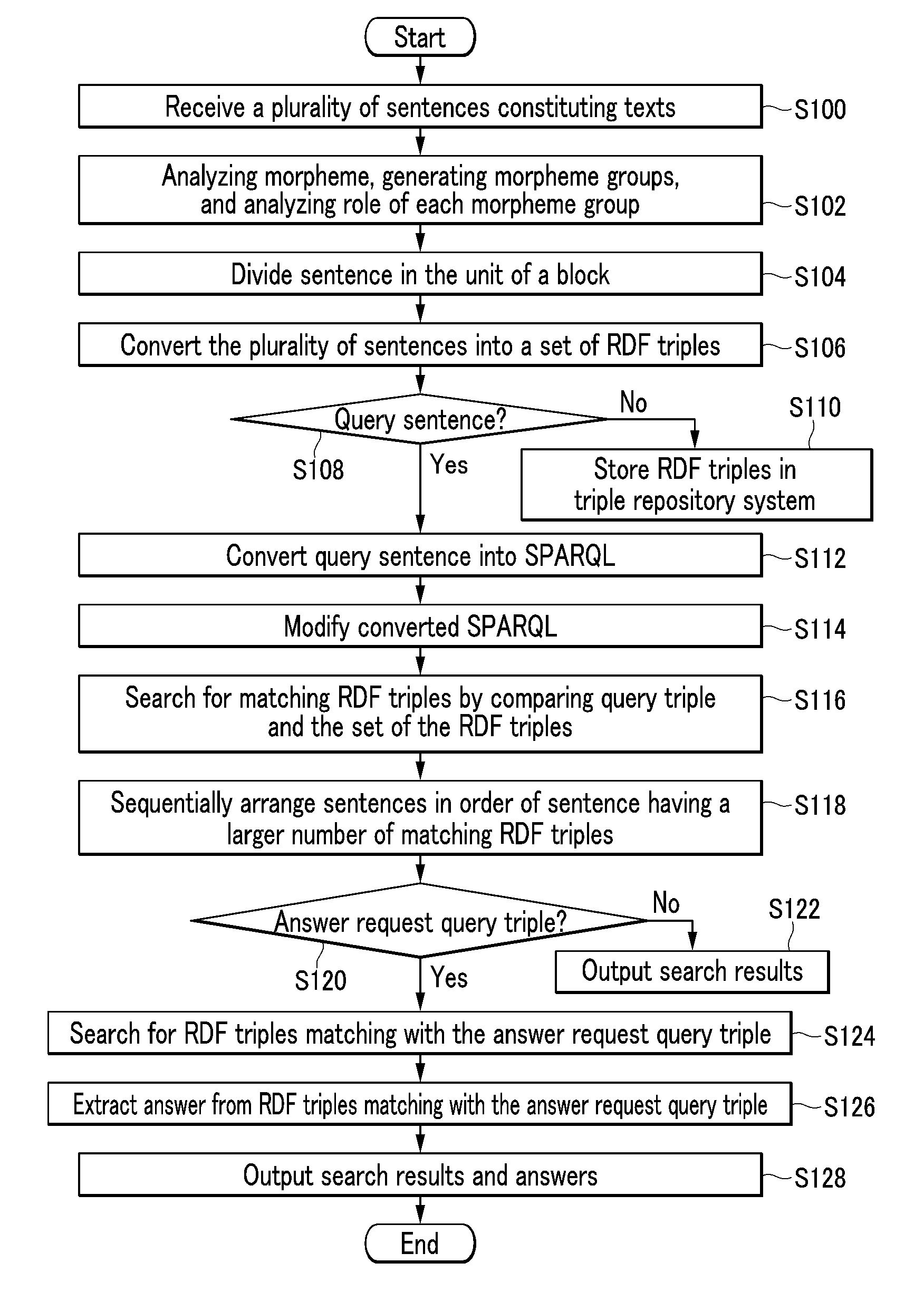
A method of searching for answers to a query in a question-answering search system based on Resource Description Framework (RDF) triples is provided. A plurality of sentences constituting texts are converted into a set of RDF triples, and a query sentence is converted into a SPARQL including query triples. Triples matching with the query triples are searched for among the set of RDF triples stored in a triple repository, sentences having those triples are arranged in order of the larger number of matching triples, and the arranged sentences are provided as a search result.
Owner:SENSOLOGY
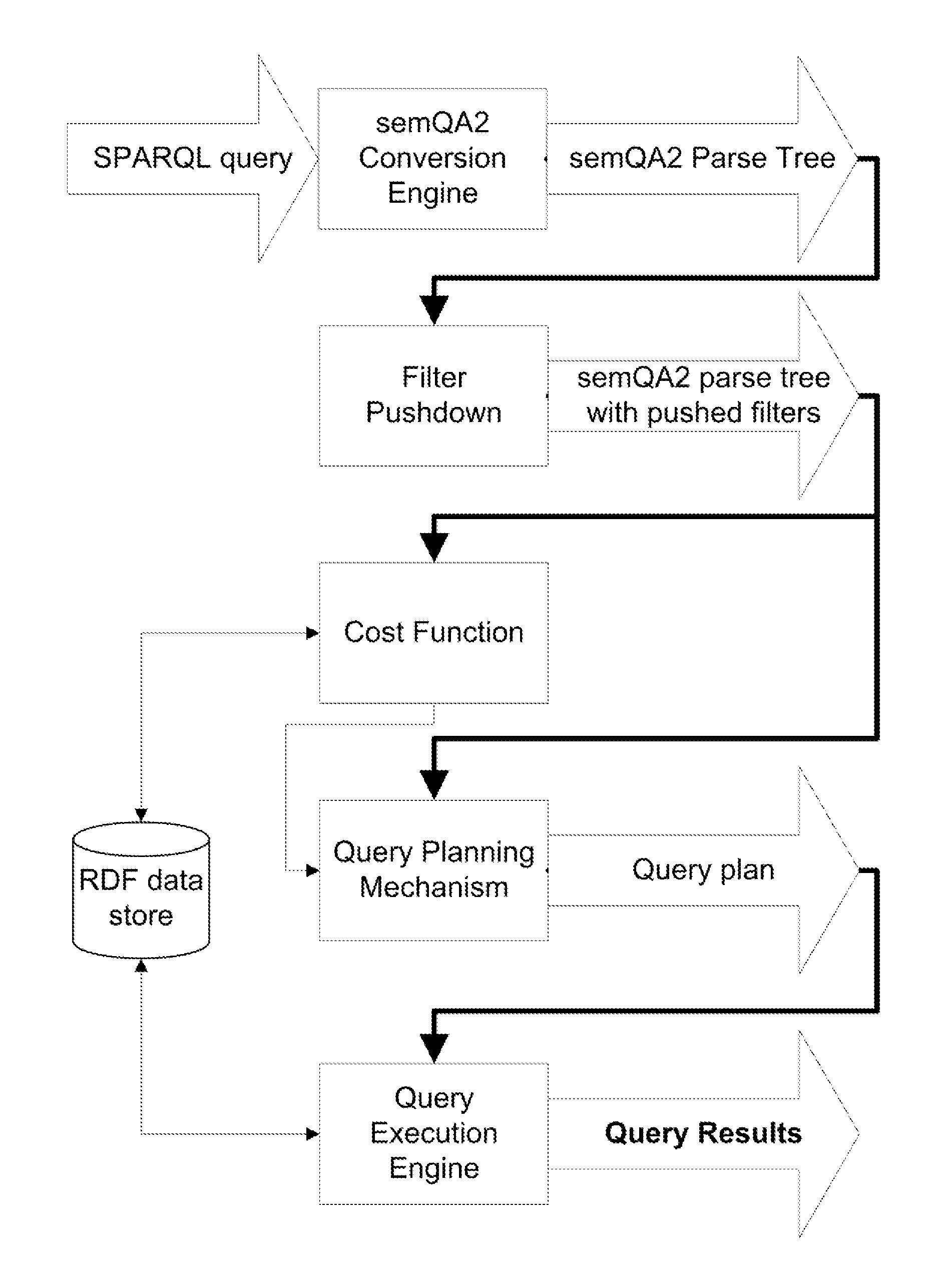
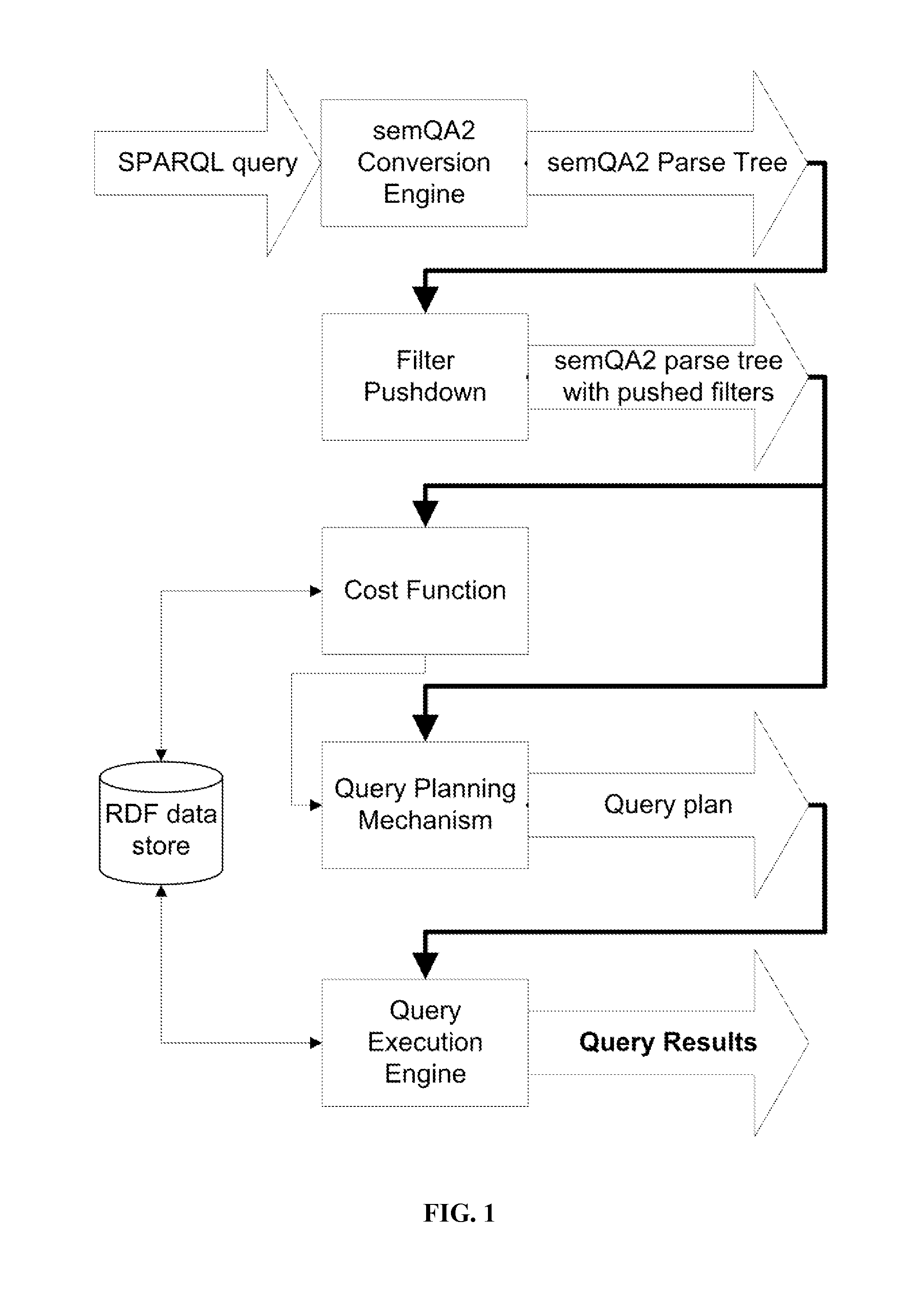
Query Optimization for SPARQL
ActiveUS20140067793A1Efficient retrievalEfficiently retrieving resultDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsQuery planDatasource
The present invention relates to computer implemented methods and system for creating and executing an query plan for SPARQL Protocol And Query Language (SPARQL) queries. The methods and systems are designed to accept as input a query in SPARQL syntax, convert this query to semQA2 and generate a parse tree, perform filter pushdown, generate an efficient query plan potentially using a cost function, and execute this query plan against data sources complying to or modeled as Resource Description Framework (RDF). The result of these methods and of the systems implementing these methods is a set of triples contained in the data sources that comprise a solution of the SPARQL query provided.
Owner:INFOTECH SOFT
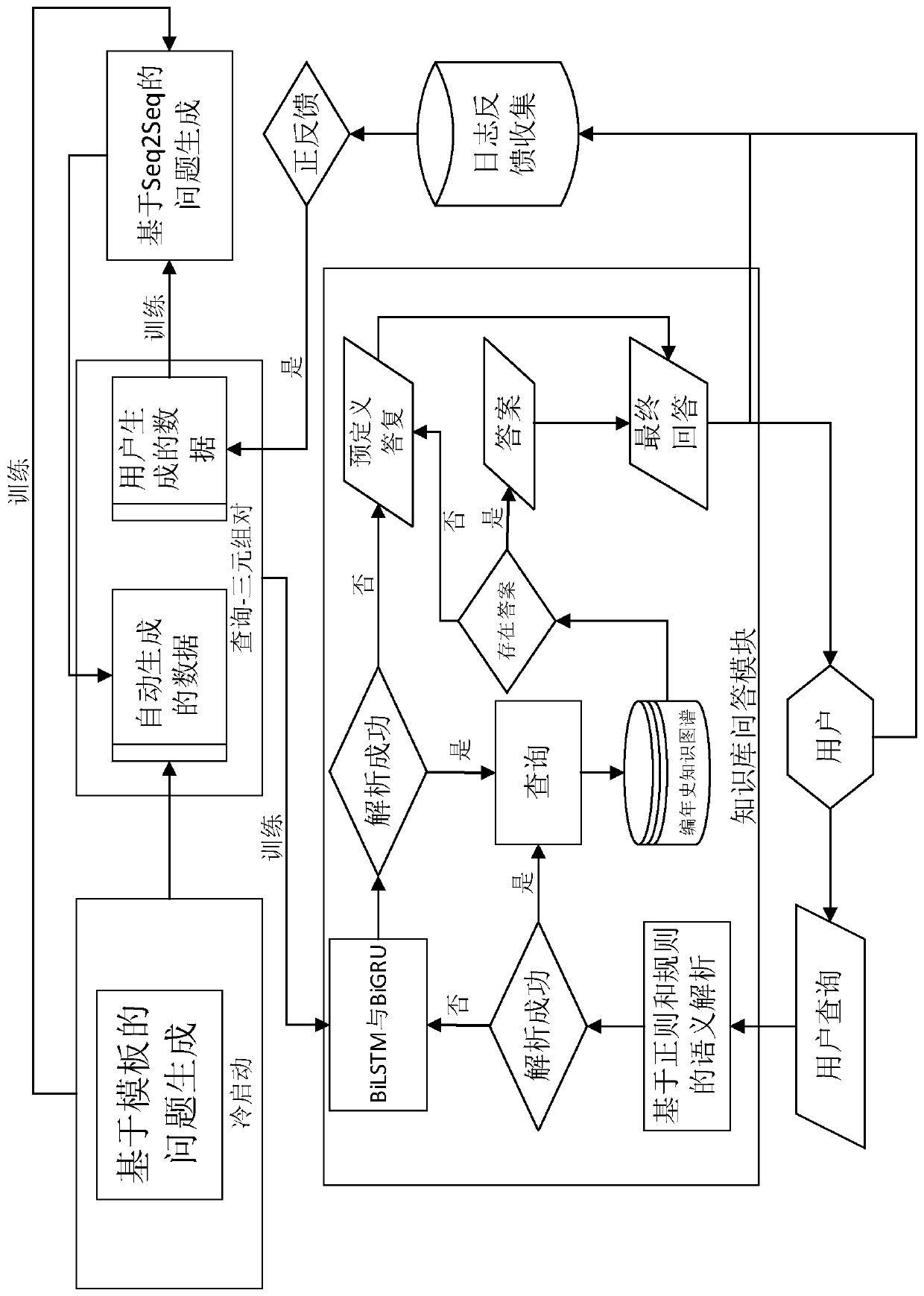
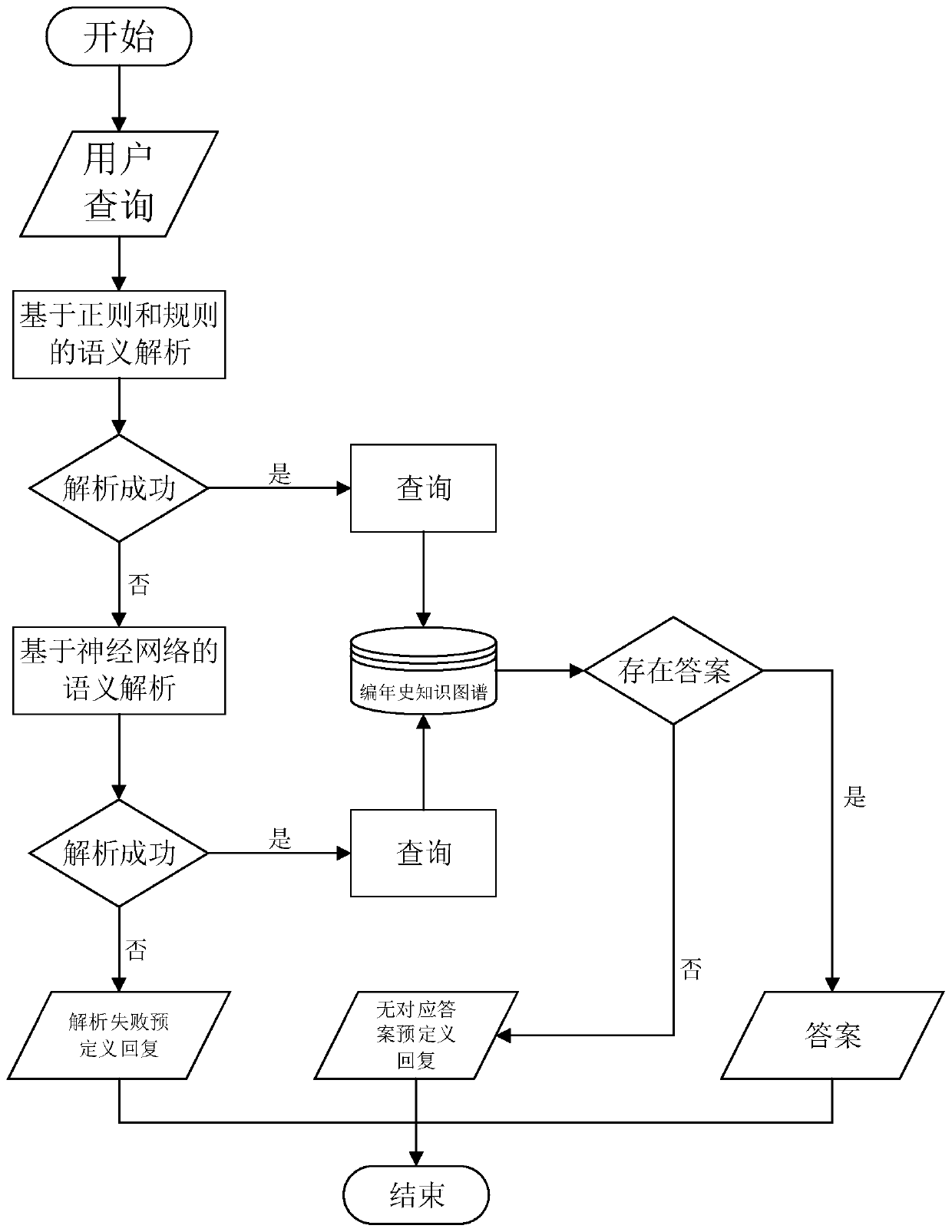
A construction method of a literature compilation life history question and answer system based on a knowledge graph
ActiveCN109766417AImprove the efficiency of acquiring specific knowledgeAccurate analysisNeural architecturesSpecial data processing applicationsQuestion analysisTight frame
The invention discloses a construction method of a literature history question and answer system based on a knowledge graph, which comprises the following steps of constructing the knowledge graph ofa literature history vertical field by taking structural data related to Chinese literature history as a basis and combining a literature history ontology structure created from top to bottom; designing a semantic analysis framework which comprises two user question analysis modules characterized in that one module is based on regularization and rules, and the other module is based on a neural network; organizing the results obtained through problem analysis into corresponding SPARQL query statements, and searching the corresponding results for in the constructed knowledge graph; organizing the result as a reply, and returning the reply to the user; designing a webpage side and a WeChat official account service as a window for interaction between the system and a user; designing a user uses a log and feedback collection module, wherein the related data is used for iteratively training a neural network model, and the generalization capability of the model is enhanced. According to the present invention, the natural language query of a user can be directly processed, an accurate result is returned, and the method plays an important role in improving the knowledge acquisition efficiency, promoting Chinese culture research and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
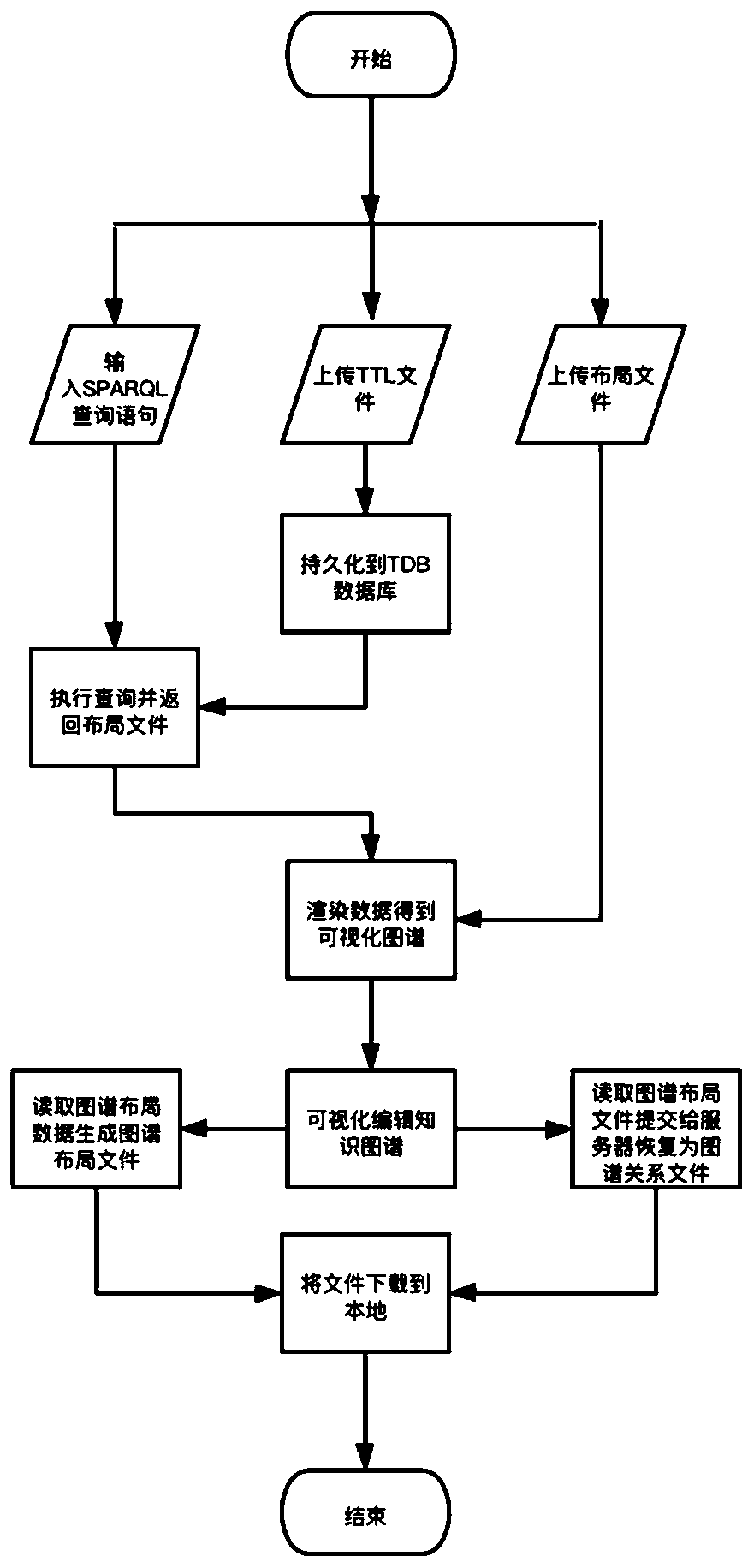
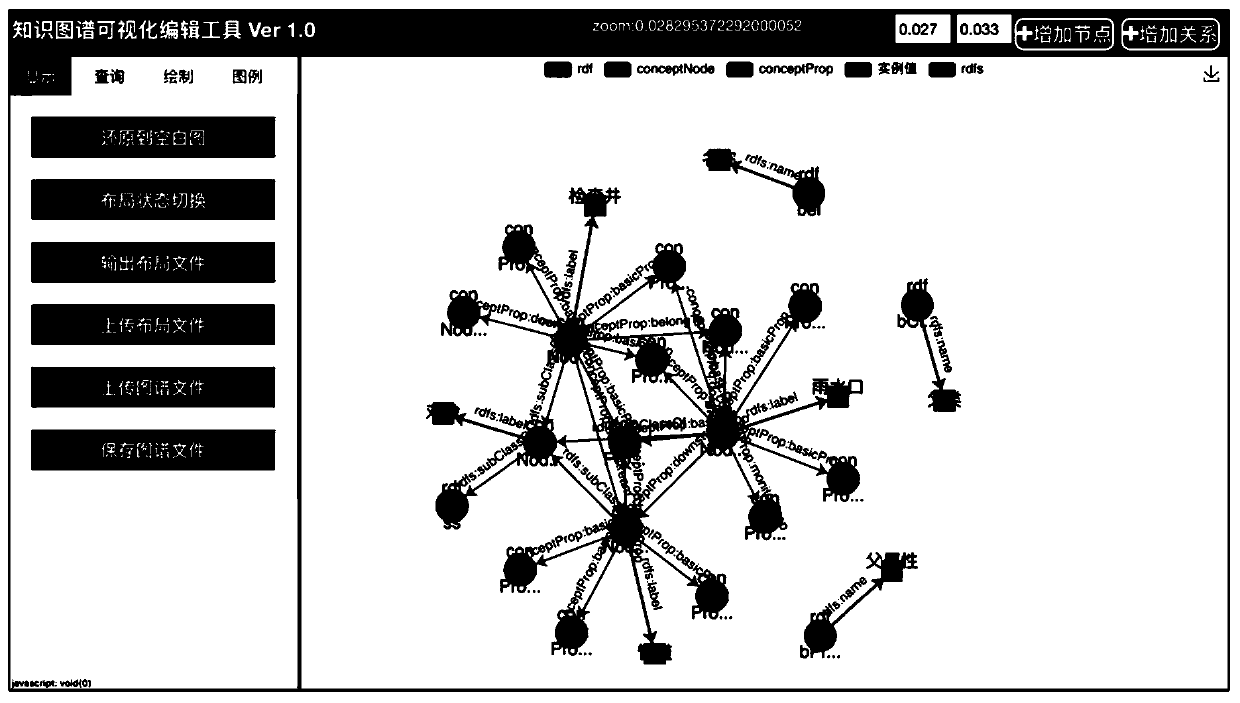
Knowledge graph visual editing and persistence implementation method and system architecture
PendingCN111339316AEasy to storePromote recoverySpecial data processing applicationsText database browsing/visualisationInteractive editingTheoretical computer science
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
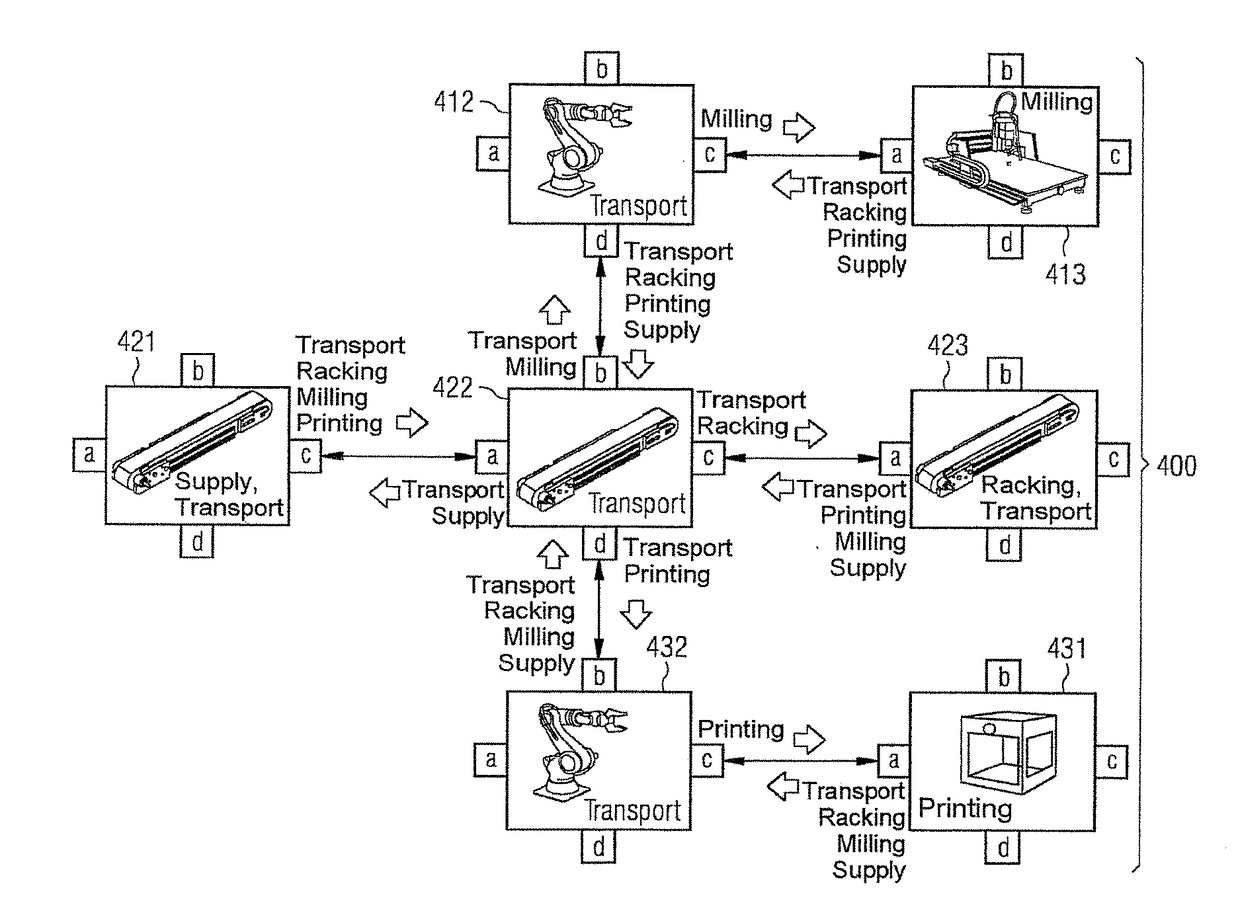
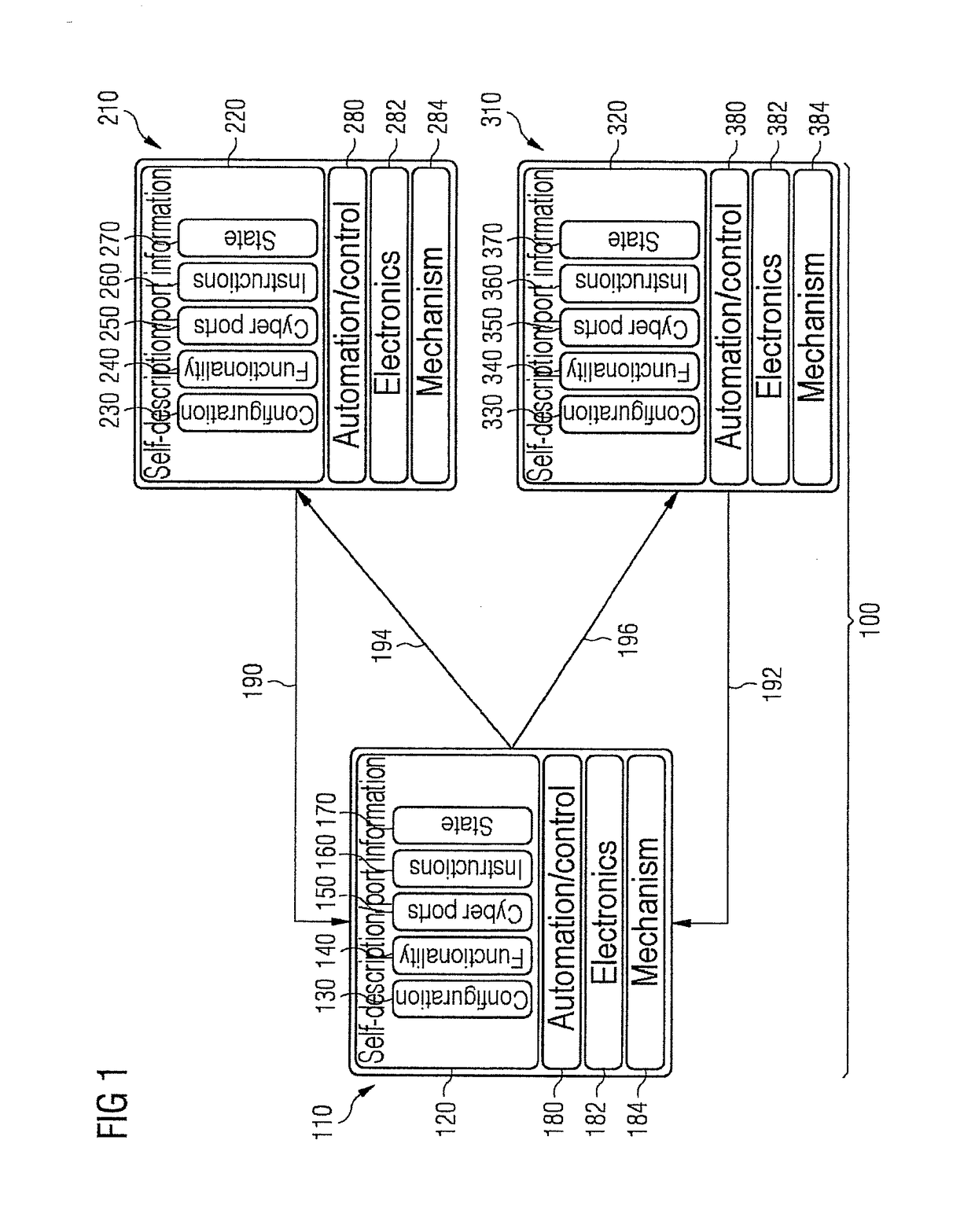
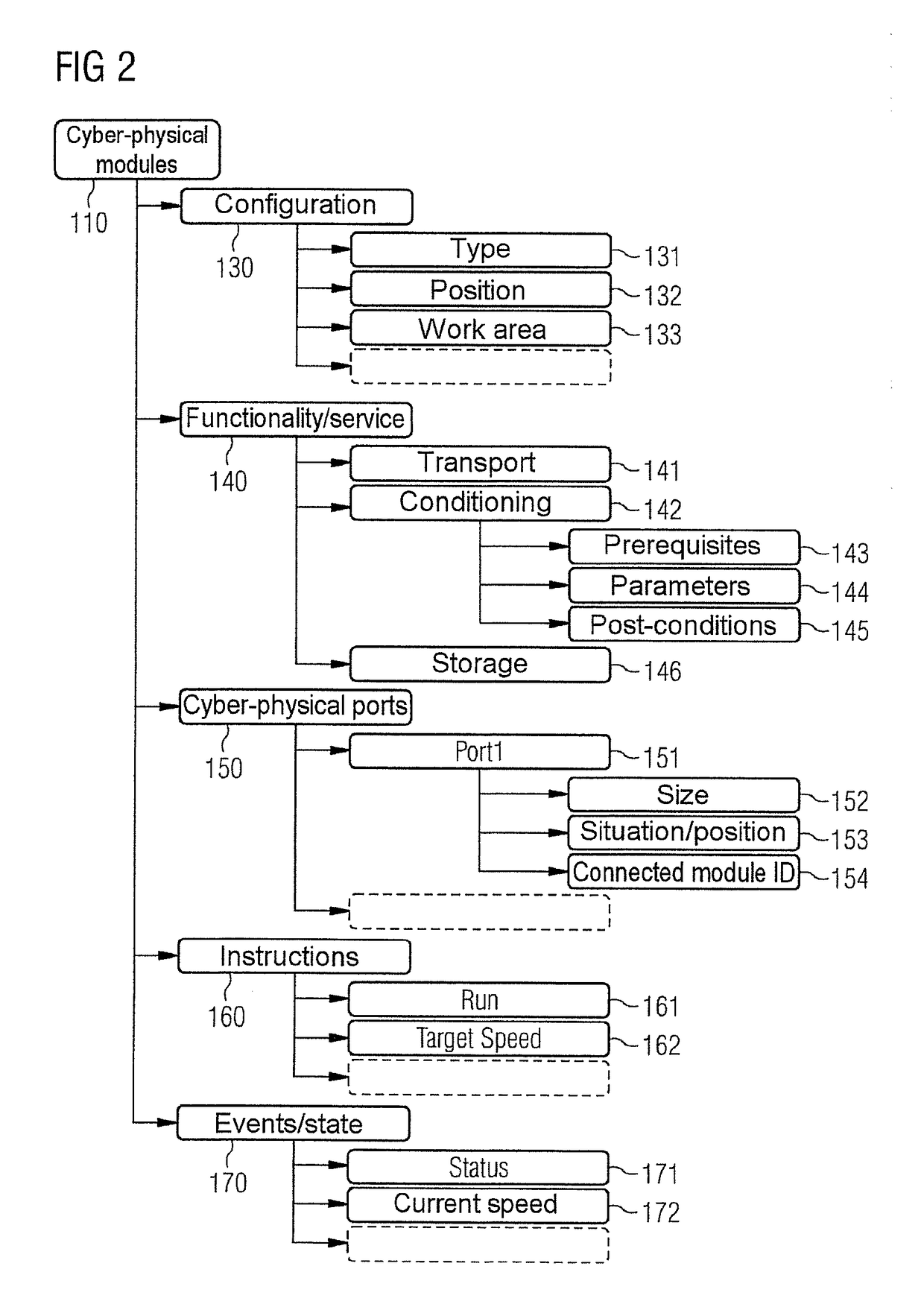
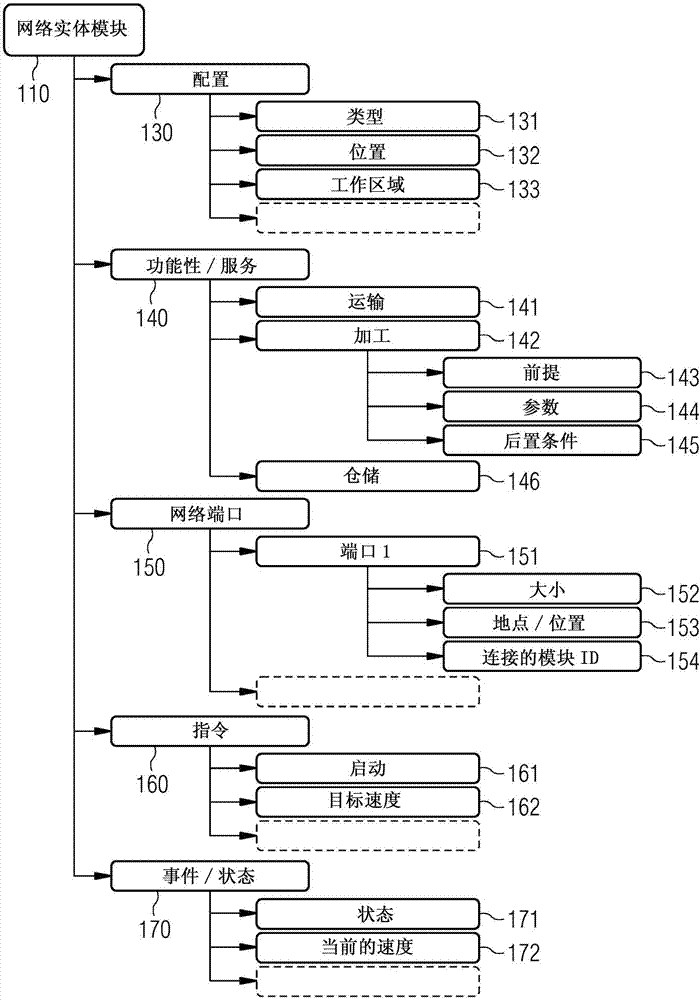
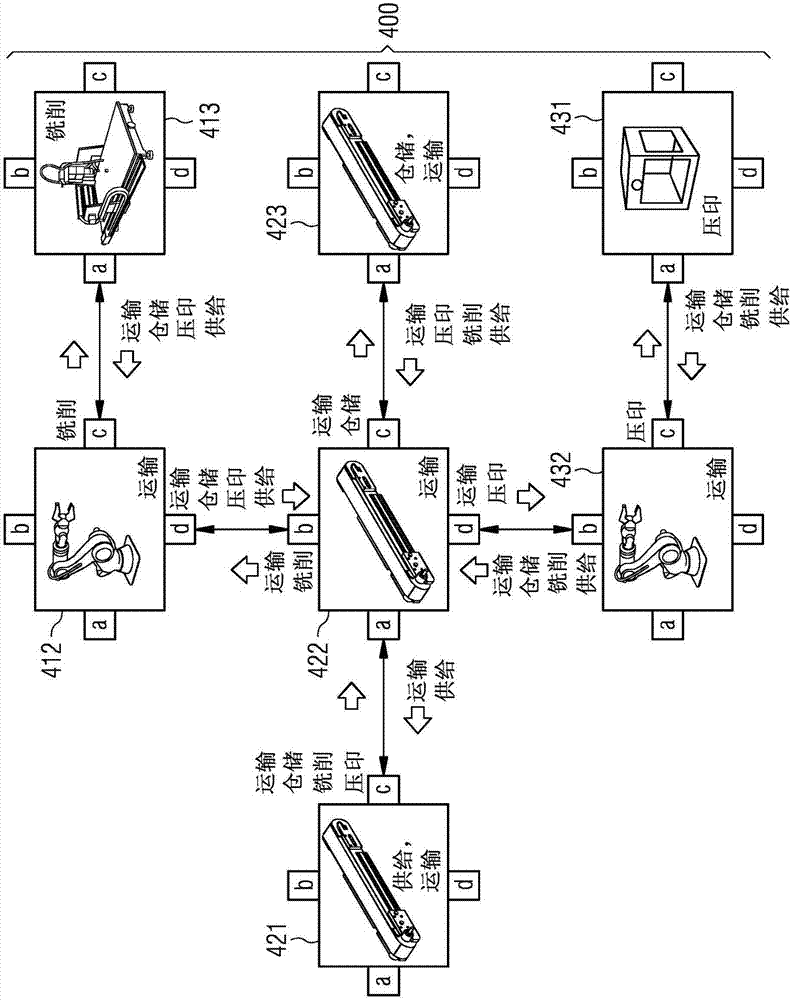
Method for Planning the Manufacture of A Product and Production Module Having Self-Description Information
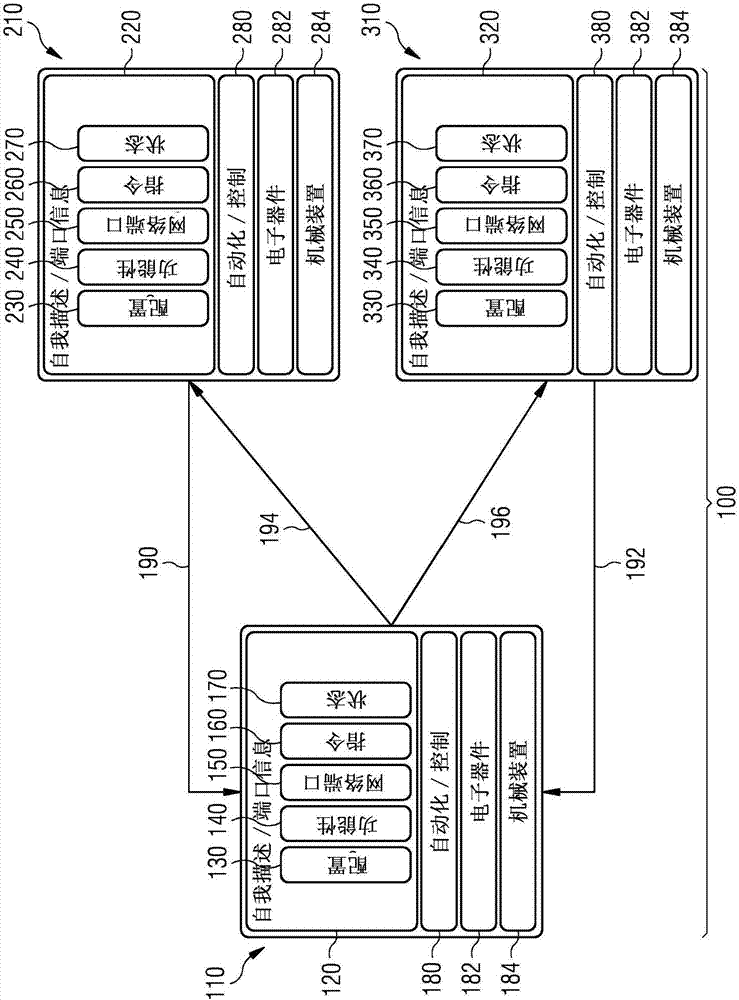
ActiveUS20170308067A1Simple configuration and operationTotal factory controlProgramme total factory controlComputer moduleSPARQL
A production module for performing a production function on a product, production system, production planning device, and method for planning the production of the product, wherein a plurality of production modules are intercoupled, where a self-description information set is stored within each production module as a database, e.g., NoSQL, OWL, ontology, SPARQL, which comprises properties of the production module, where if a production information set comprising the production steps required to produce the product is present, then the production information set and the self-description information sets or parts thereof are transmitted to a production planning device to plan production of the product and a production procedure plan for a product to be processed is determined, and where the production procedure plan comprises an information set about a sequence of production modules of the production system, which sequence a product should pass through to produce an intermediate product or end product.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Data storage method and query method for RDF (Resource Description Framework)
ActiveCN105630881AImprove comparison speedSave storage spaceSemi-structured data indexingSpecial data processing applicationsData setLeast cost
The invention relates to a data storage method and query method for an RDF (Resource Description Framework). The data storage method comprises the steps of designing entity-oriented RDF data storage structure and storage mapping; converting a URI (Uniform Resource Identifier) and a literal amount of RDF data into 64-bit binary data; and storing the 64-bit binary data according to the designed storage structure. The data query method comprises the steps of analyzing and converting an SPARQL query statement; estimating single query cost according to an analysis result of the whole data set and a connection relationship among queries by a plurality of query triples in the SPARQL statement; and finally generating a least-cost query process. According to the data storage method and query method, the data comparison speed can be greatly increased and the storage space can be reduced; and compared with a conventional method for directly converting SPARQL into SQL to perform query, the query method provided by the invention has the advantages that the query efficiency is greatly improved and the query method can be used in the fields of Web data management, Web semantic retrieval and the like.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
SPARQL parallel query method facing large-scale RDF graph data
ActiveCN103778251AImprove query speedHelp to take advantage ofSpecial data processing applicationsData setRDF query language
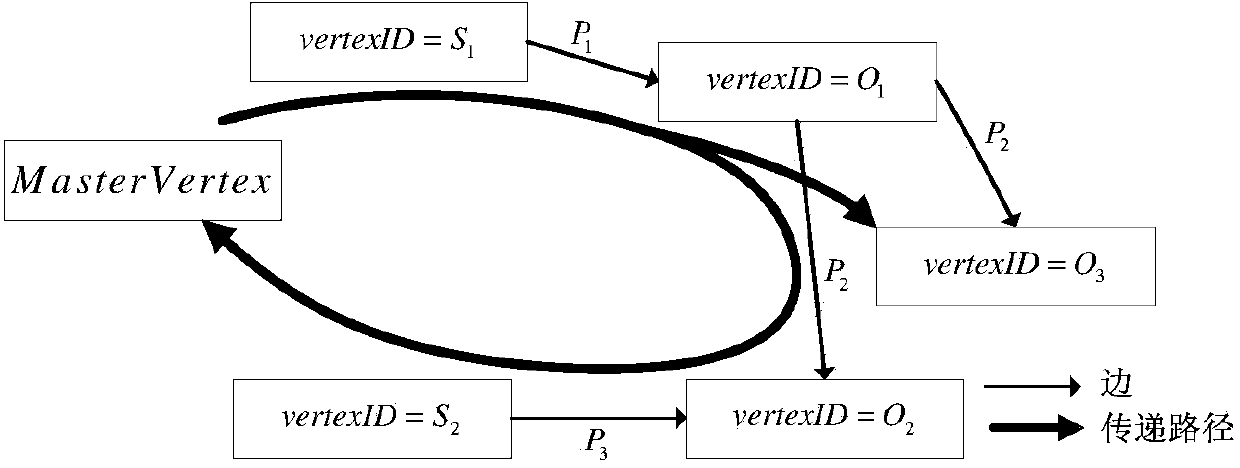
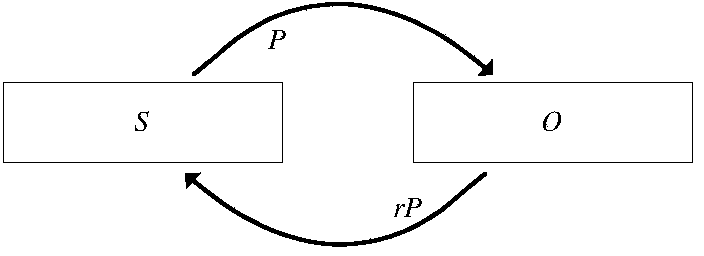
The invention relates to RDF (Resource Description Framework) graph data processing. In order to provide a high-efficiency parallel query processing method for the large-scale RDF graph data, reduce read-write times of disks and improve query efficiency, the invention adopts the technical scheme that an SPARQL (Simple Protocol And Rdf Query Language) parallel query method facing the large-scale RDF graph data comprises the following steps: 1, describing the RDF graph data by using a bulk synchronous parallel (BSP) model; 2, marking by using URIs (Uniform Resource Identifiers) of resources; 3, for each triple in an RDF graph data set, i.e. a subject calculating unit S, a predicate P and an object calculating unit O, establishing a directed edge e from the subject calculating unit S to the object calculating unit O, using an URI of the predicate P as a mark of the e and storing related information of the e in a local data field of the subject calculating unit S; 4, for each edge e in the step 3, using an URIr as a mark of an er; 5, acquiring an query request q0 submitted by a user; 6, selecting different propagation paths to carry out propagation; 7, estimating a quantity of information contained in each clause in the qi-1 by utilizing a greedy algorithm; 8, repeatedly carrying out the steps 6 and 7 until all the clauses are bound. The SPARQL parallel query method is mainly applied to graph data processing.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
SPARQL query optimization method based on graph traversal
ActiveCN107291807AReduce generationAvoid expensiveSpecial data processing applicationsGraph traversalQuery optimization
The invention discloses an SPARQL query optimization method based on graph traversal. The method comprises the steps of 1), expressing triples in RDF (Resource Description Framework) data through utilization of an attribute graph and storing the RDF data through utilization of a Bigtable model, thereby obtaining Bigtable data corresponding to the RDF data; 2), converting SPARQL query into traversal for the RDF attribute graph; and 3), traversing all nodes satisfying conditions in the Bigtable data according to a traversing sequence obtained in the step 2), thereby finishing the SPARQL query. According to the method,
Owner:COMP NETWORK INFORMATION CENT CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Information retrieval from relational databases using semantic queries
In the realm of managing relational databases, a system that uses both the data in a relational database and domain knowledge in ontologies to return semantically relevant results to a user's query. Broadly contemplated herein, in essence, is a system that bridges a semantic gap between queries users want to express and queries that can be answered by the database using domain knowledge contained in ontologies. In accordance with a preferred embodiment of the present invention, such a system extends relational databases with the ability to answer semantic queries that are represented in SPARQL, an emerging Semantic Web query language. Particularly, users may express their queries in SPARQL, based on a semantic model of the data, and they get back semantically relevant results. Also broadly contemplated herein is the definition of different categories of results that are semantically relevant to a user's query and an effective retrieval of such results.
Owner:IBM CORP
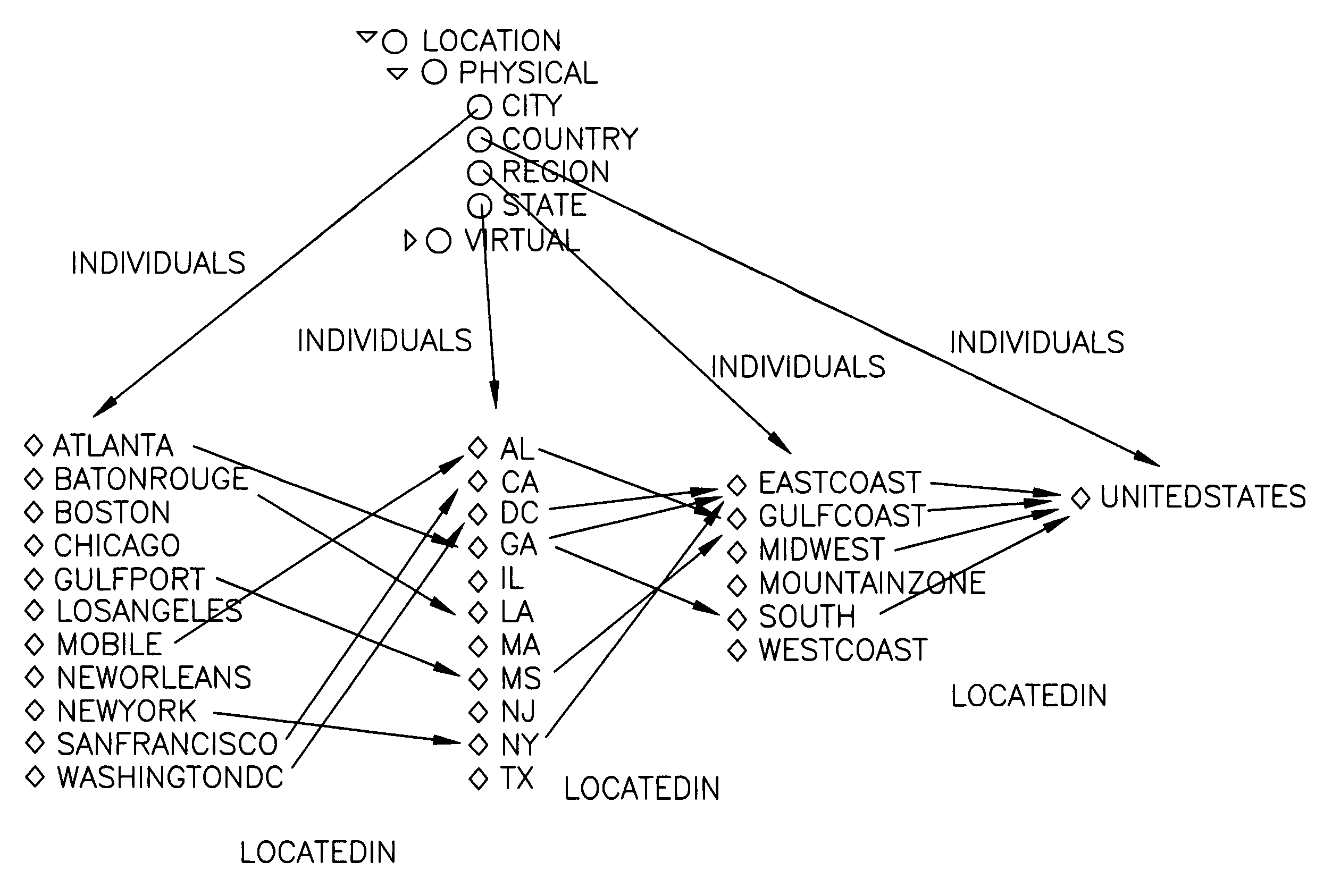
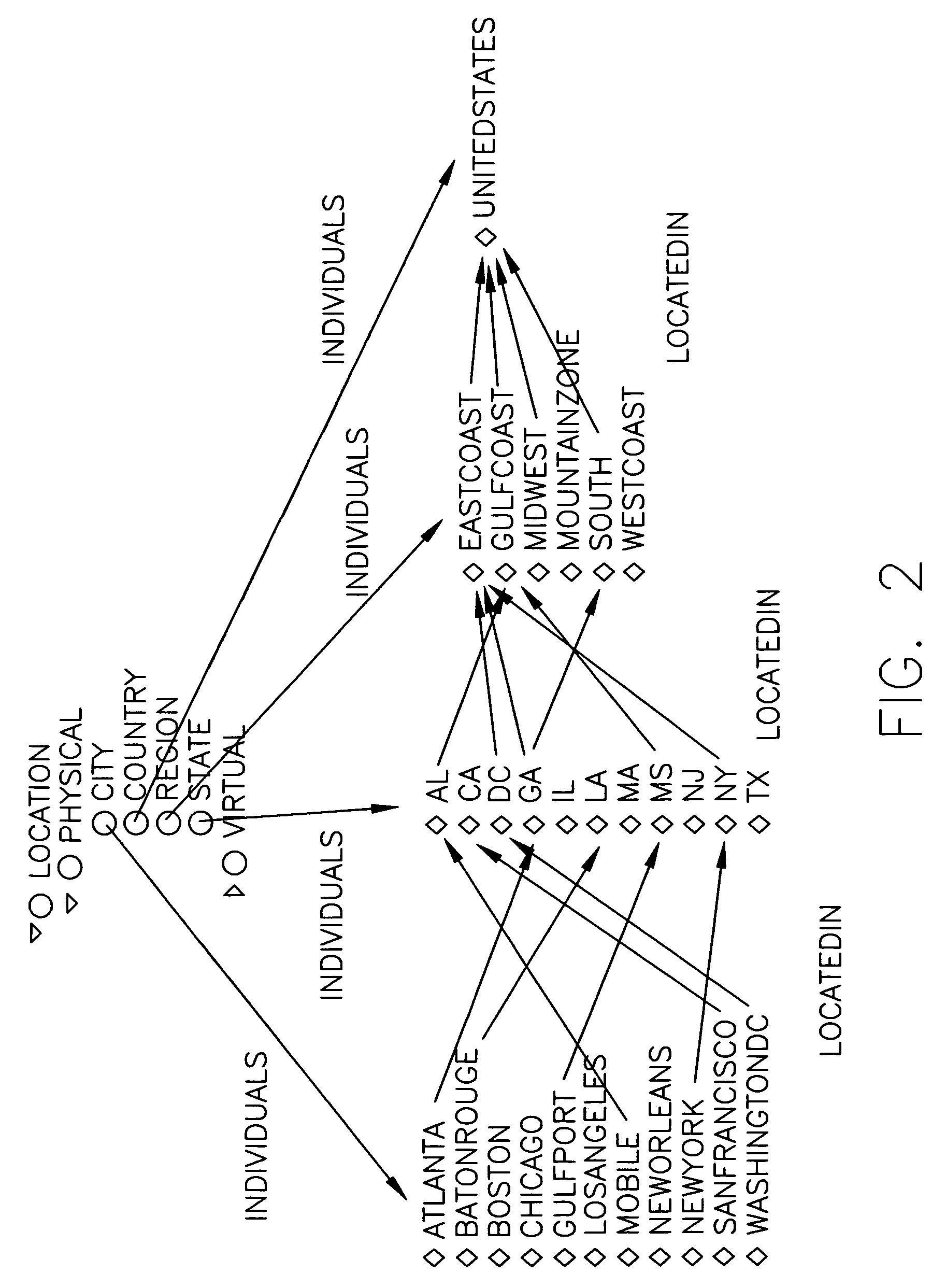
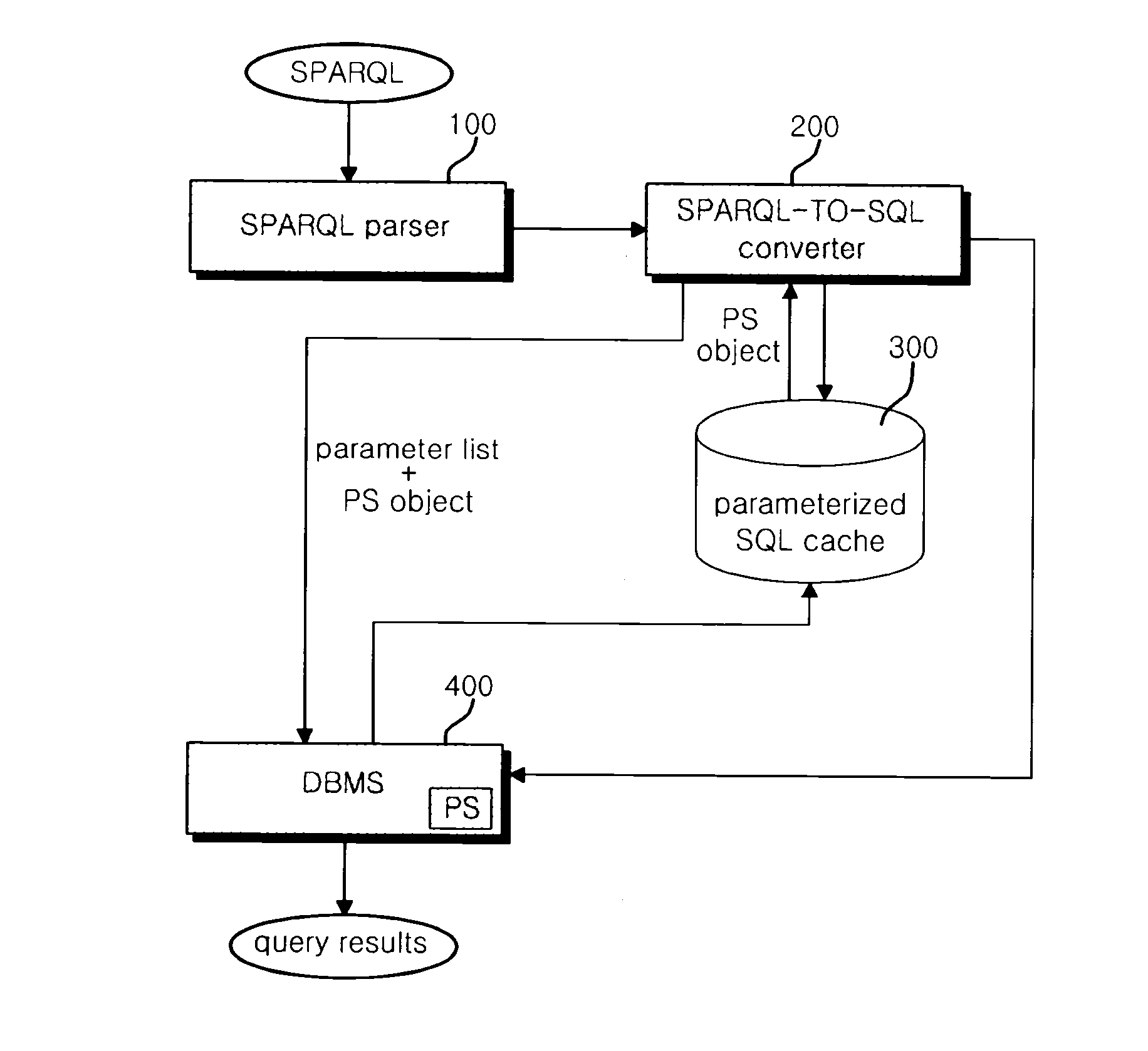
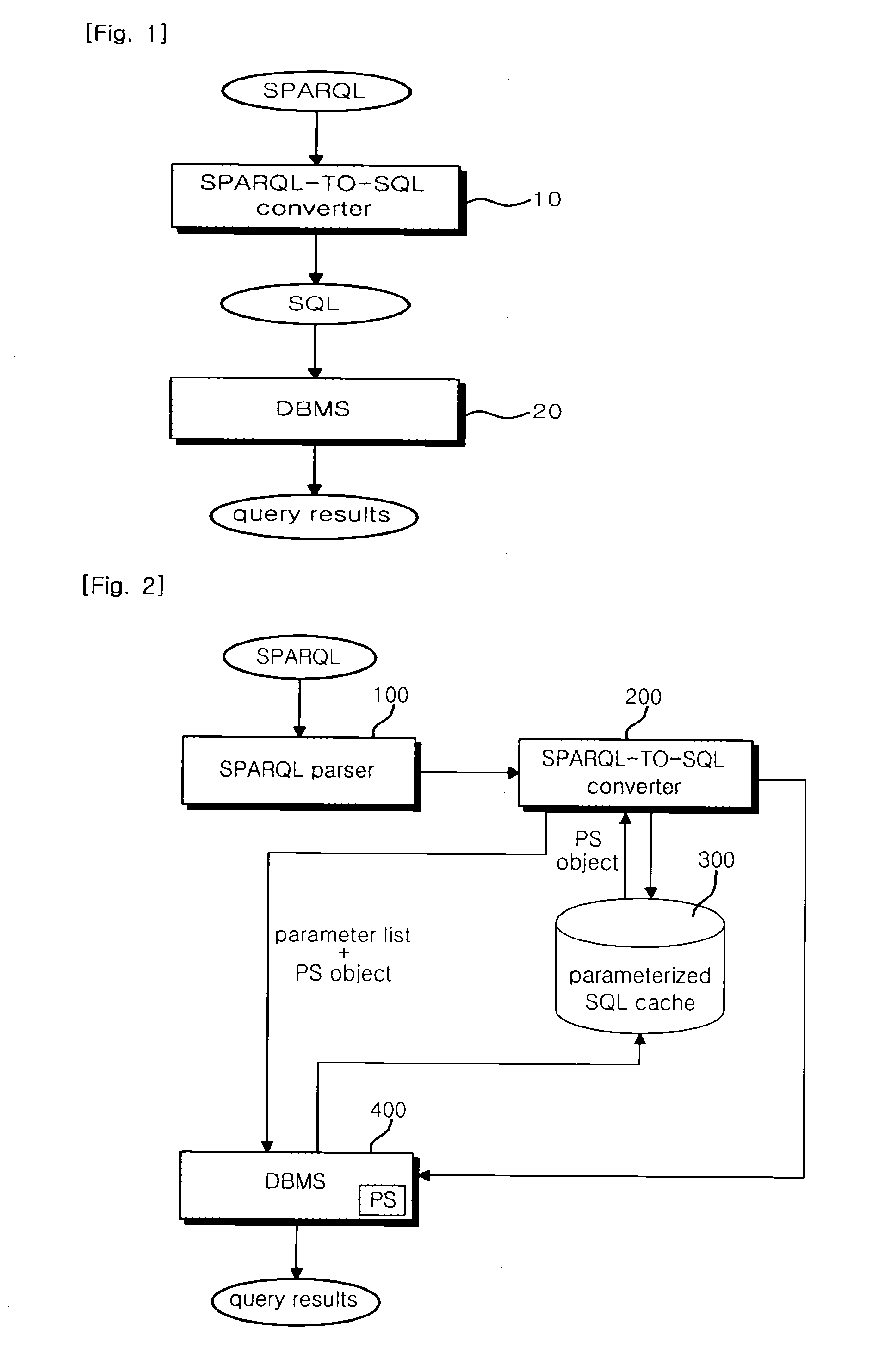
System and method for sparql-query processing using the parametrized-sparql-query in based dbms
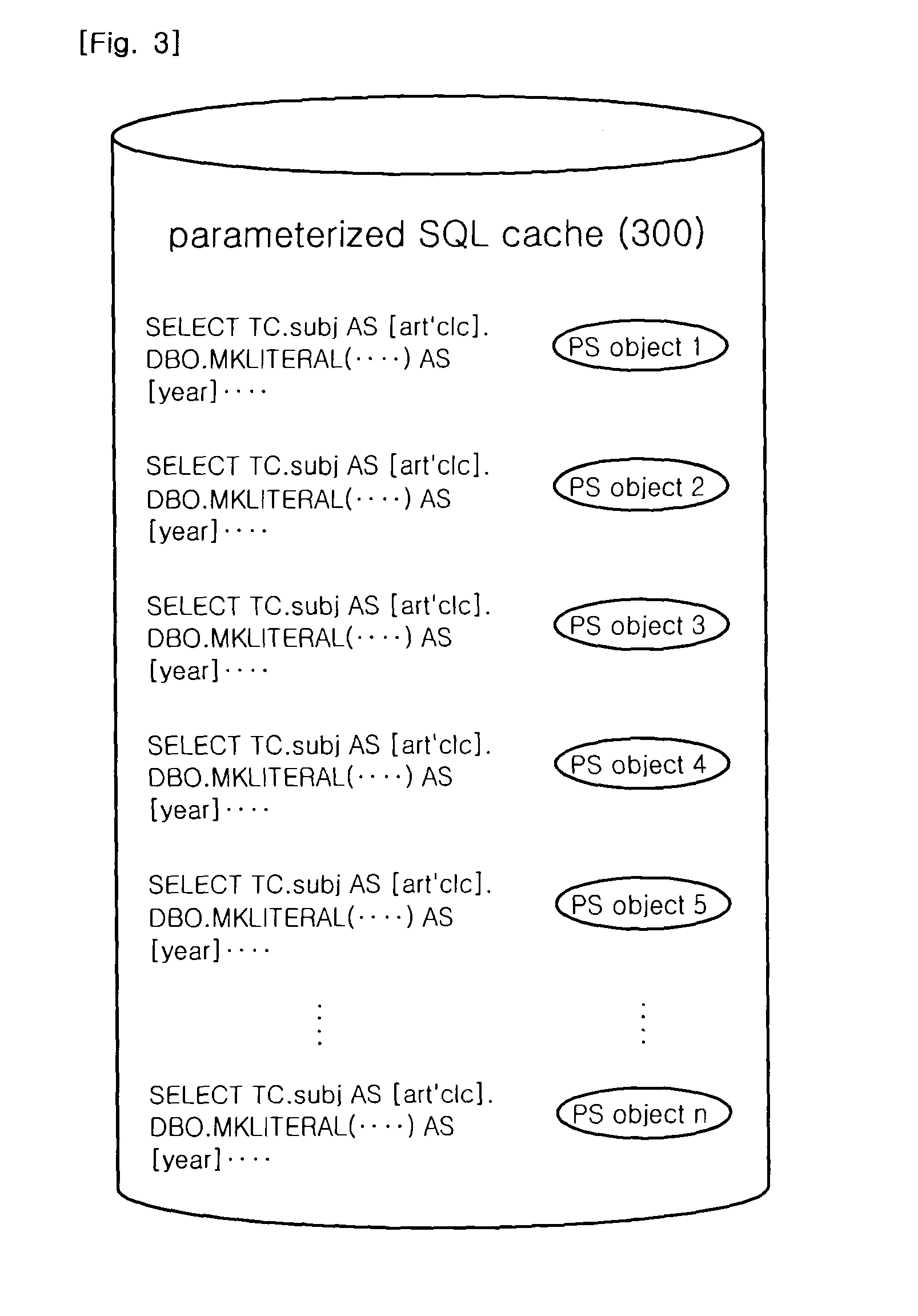
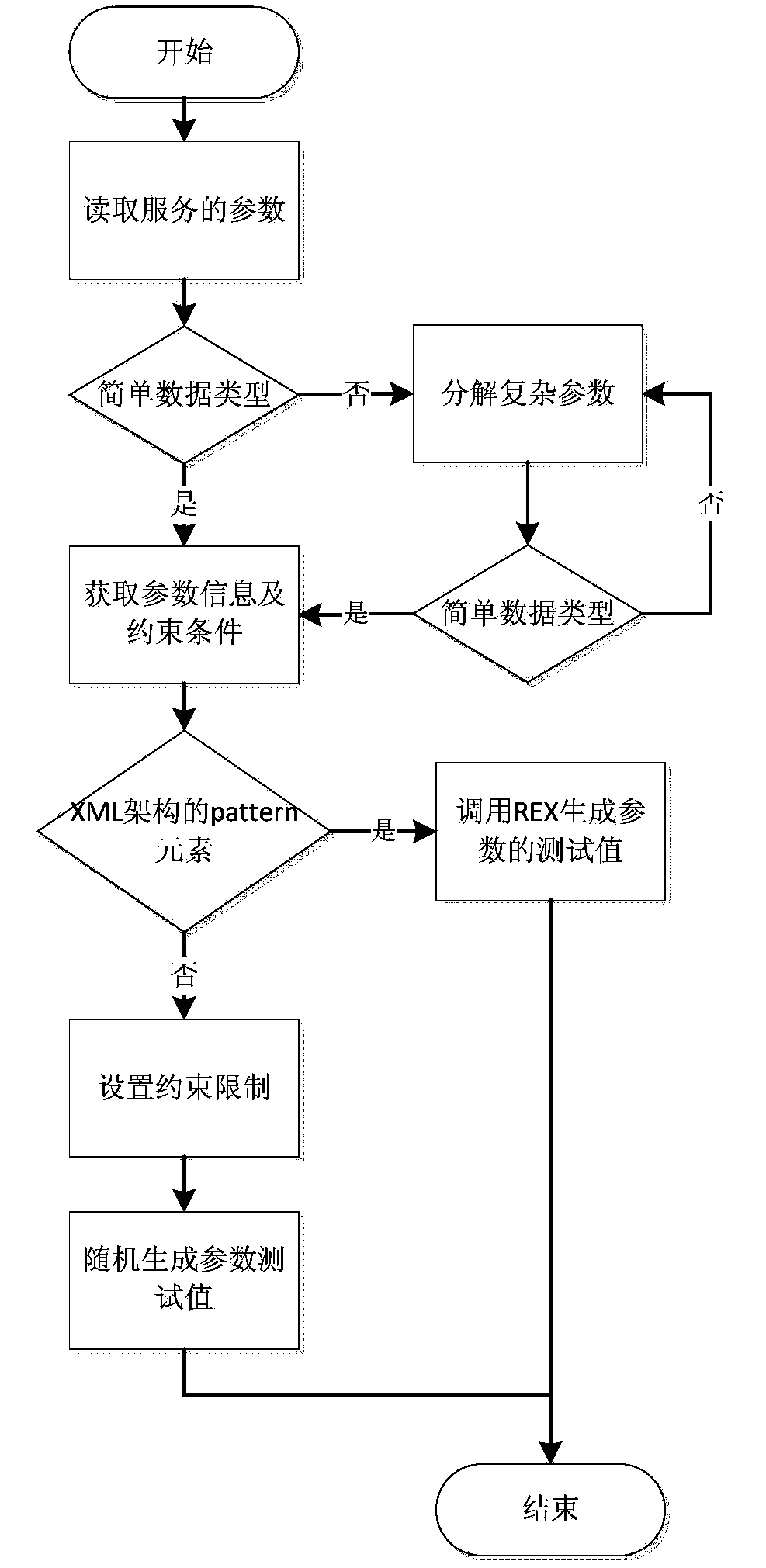
InactiveUS20110238683A1Quality improvementReduce query timeDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsSemantic web servicesWeb service
A Database Management System (DBMS)-based Semantic Web query system and method using parameterized SPARQL queries are provided. The present invention is configured to include output means that creates a parameter list from a SPARQL query statement, converts the query statement into an SQL statement and stores a PREPARED STATEMENT (PS) object in association with the SQL statement, thereby outputting query results. Accordingly, the query time of a Semantic Web service can be reduced, thereby improving QoS.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH INFORMATION
BIM (Building Information Model) specification detection device and detection method based on semantic retrieval
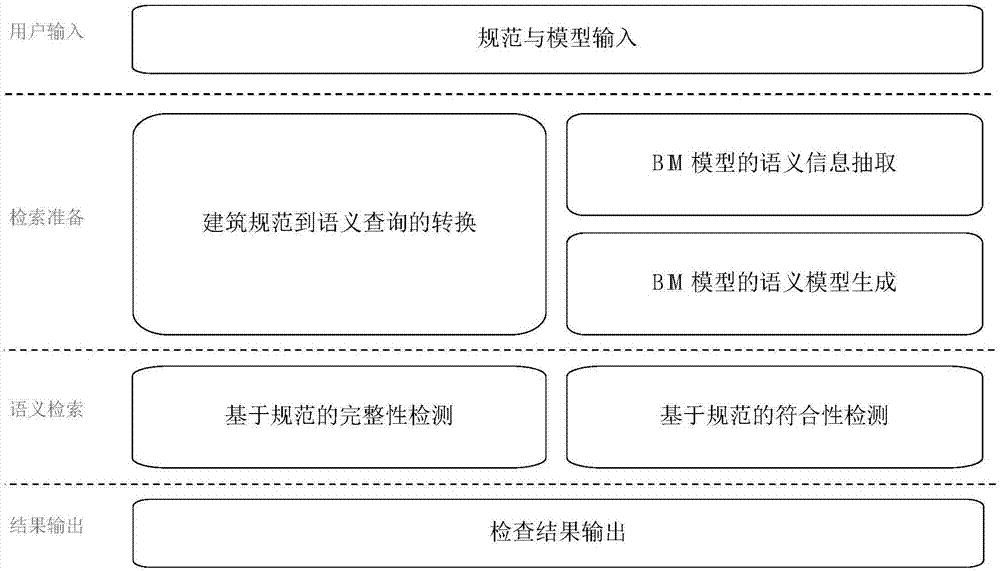
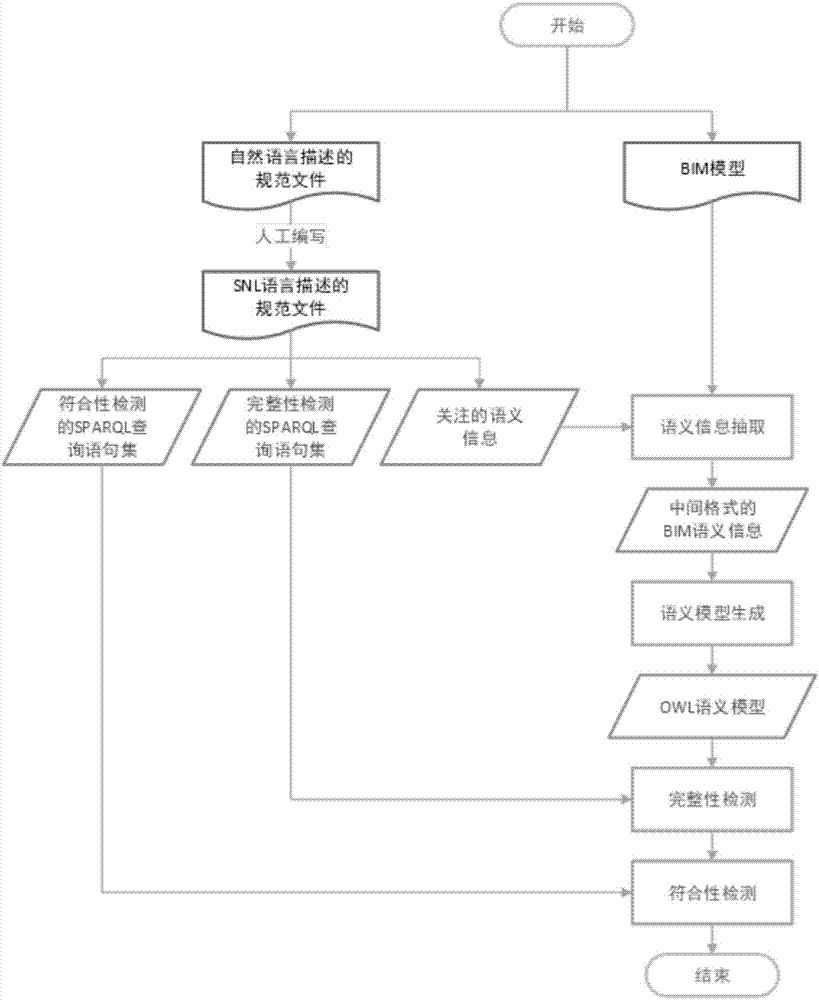
ActiveCN107341209ASolve incomprehensible problemsSolve problems that are difficult to retrieve efficientlySpecial data processing applicationsRDF query languageSemantic search
The invention discloses a BIM (Building Information Model) specification detection device based on semantic retrieval. The detection device includes a specification and model input module, a conversion module from building specification to semantic query, a semantic information extraction module of a BIM, a semantic model generation module of the BIM, a specification integrity detection module and a specification conformity detection module. According to the detection device, extraction is carried out on the BIM on the basis of specification requirements, detection space is reduced, and the query efficiency of semantic detection is improved; and an SPARQL (SPARQL Protocol and RDF Query Language) and OWL (Web Ontology Language) ontology technology are introduced, and the problem that a storage format of the BIM is hard to be efficiently retrieved is solved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
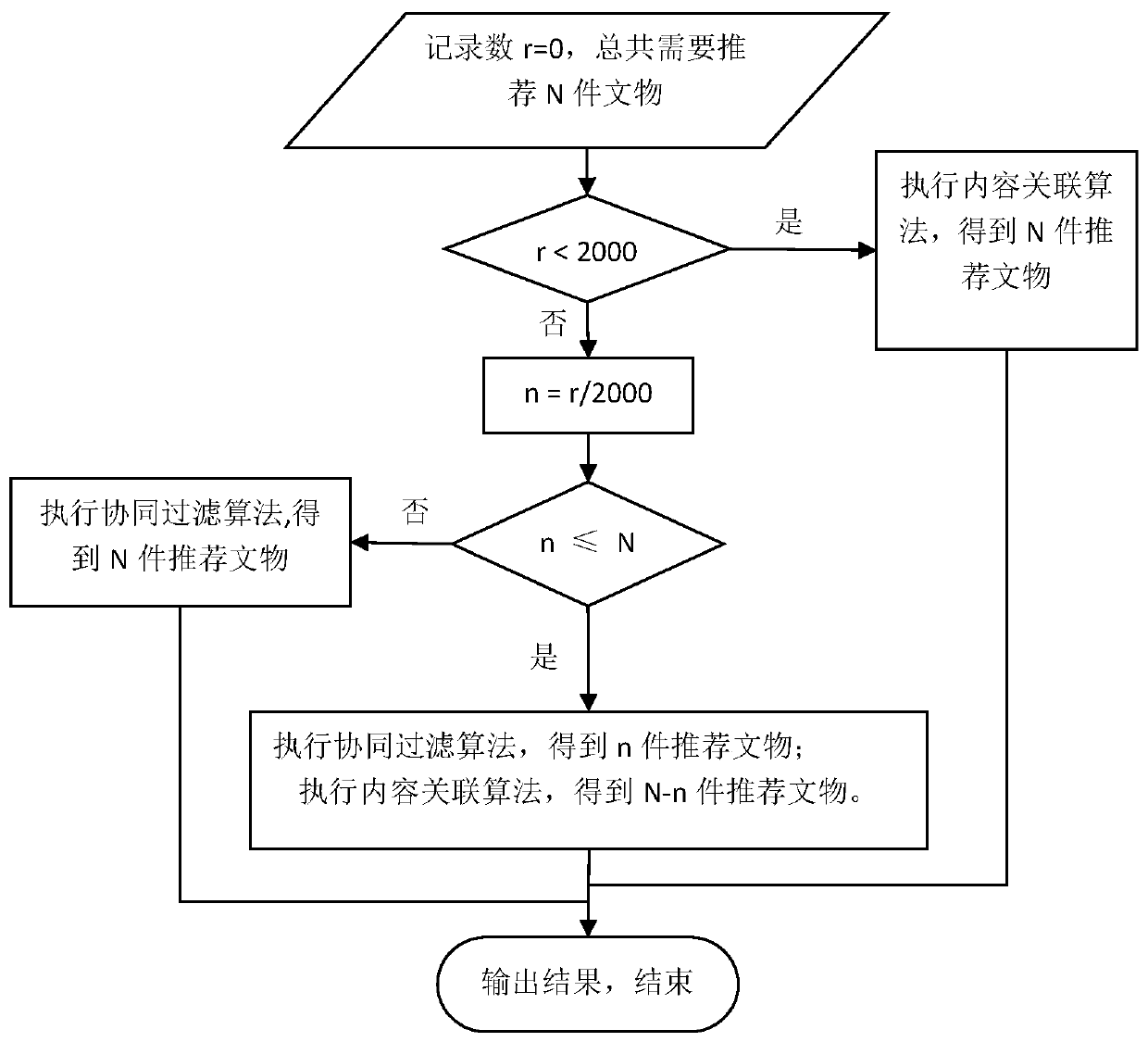
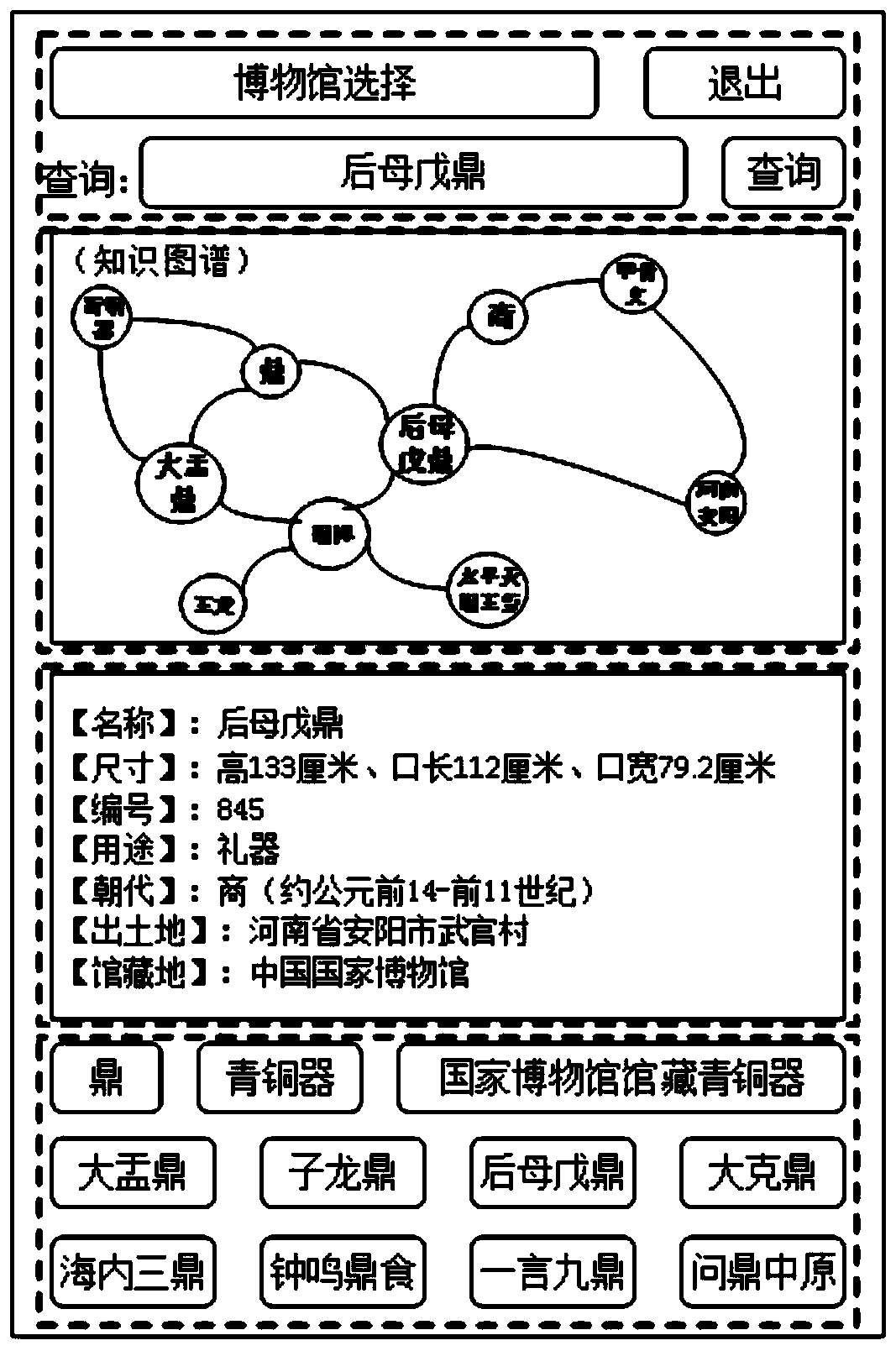
A museum guide and knowledge recommendation method based on a cultural relic knowledge map
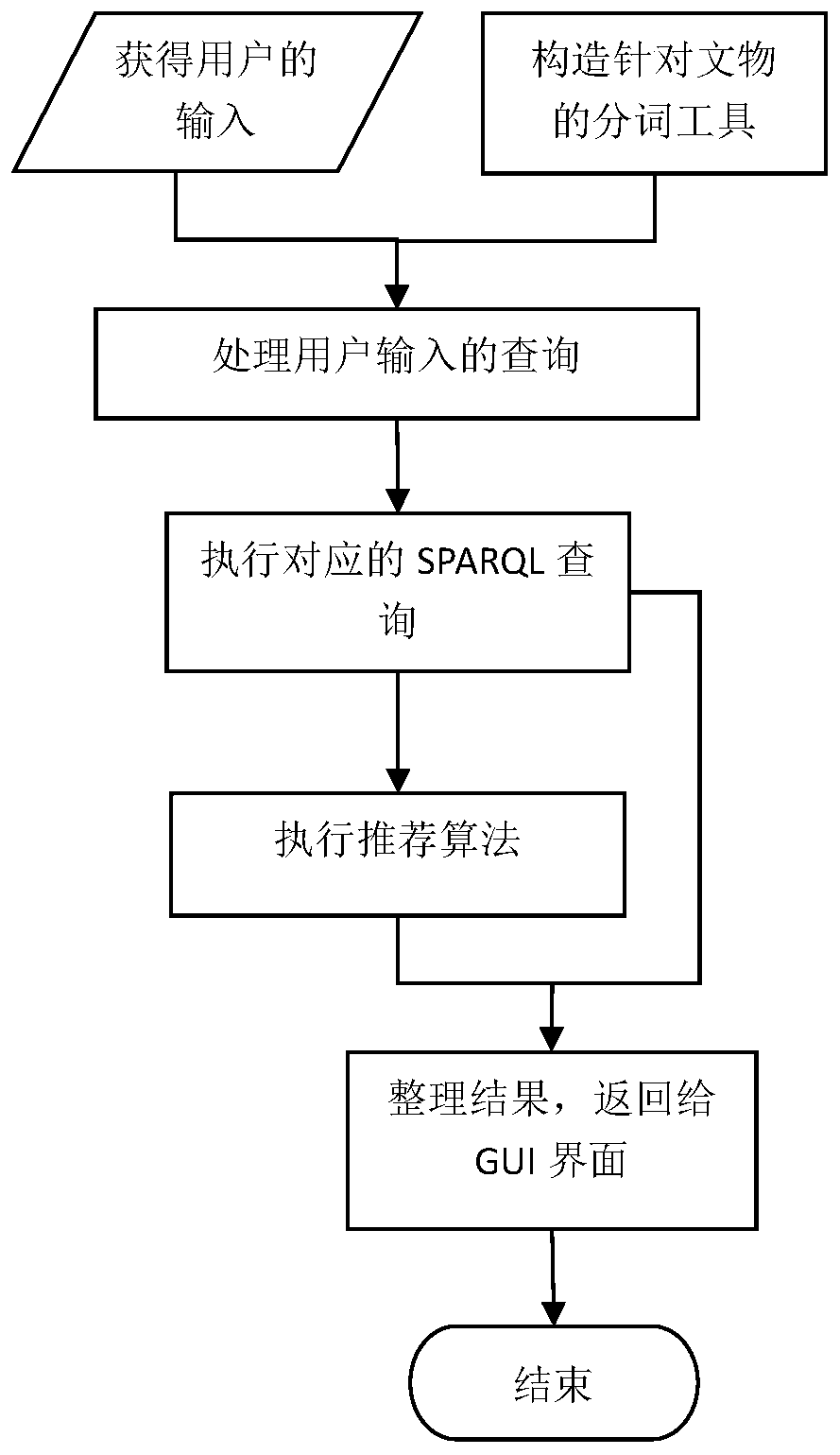
ActiveCN109710935AEasy to understandShorten study timeSpeech recognitionSpecial data processing applicationsGraph spectraUser input
The invention discloses a museum cultural relic guide and knowledge recommendation method based on a knowledge graph. The method comprises the steps that firstly, a word segmentation tool and a regular expression conversion rule are used for converting natural language query input by a user into SPARQL query statements, cultural relic knowledge query and reasoning are carried out in a SPARQL language mode, and the queried cultural relics are visually presented to the user in a knowledge graph mode; meanwhile, through recommendation algorithms such as cultural relic attribute association and collaborative filtering, cultural relics or cultural relic background knowledge related to currently inquired cultural relics are recommended to the user for the interested user to select and browse ina knowledge graph mode. The method can interact with the user through the natural language based on the constructed cultural relic knowledge map, recommend other cultural relics related to the currentcultural relic or possibly interested by the user to the user, guide the user to better browse cultural relic information and understand related cultural relic knowledge.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Scalable multi-query optimization for SPARQL
ActiveUS9280583B2Minimize timeHigh expressionRelational databasesSpecial data processing applicationsExecution planQuery optimization
Multiquery optimization is performed in the context of RDF / SPARQL. Heuristic algorithms partition an input batch of queries into groups such that each group of queries can be optimized together. The optimization incorporates an efficient algorithm to discover the common sub-structures of multiple SPARQL queries and an effective cost model to compare candidate execution plans. No assumptions are made about the underlying SPARQL query engine. This provides portability across different RDF stores.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
System and method for generating SPARQL query statements in field of medical treatment
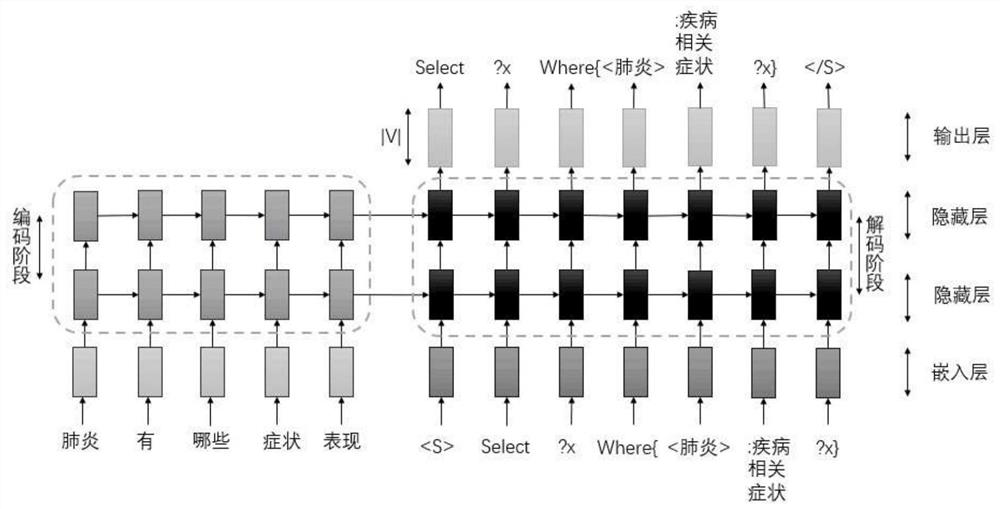
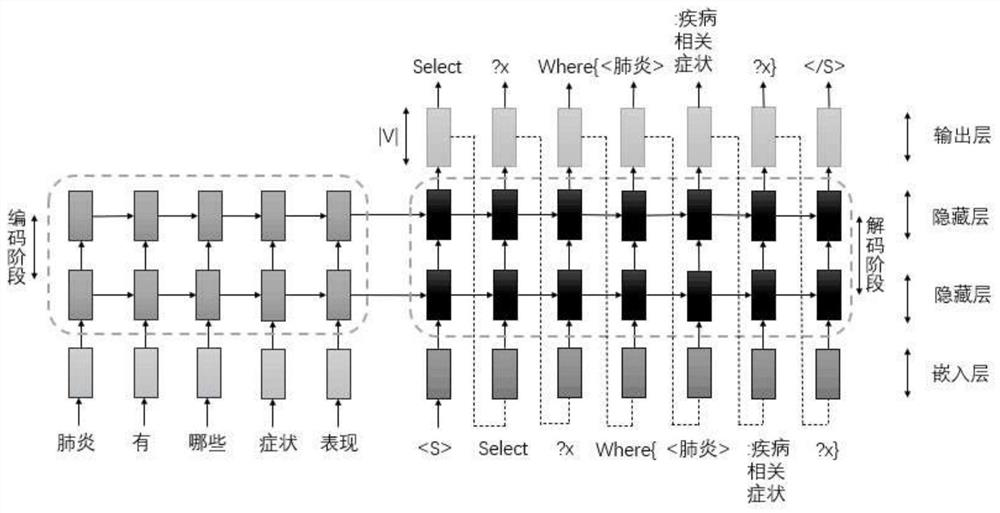
PendingCN111639254ASolving Mismatch ProblemsText database queryingSpecial data processing applicationsNetwork modelMachine translation
The invention discloses a system and method for generating SPARQL query statements in the medical field, and belongs to the field of machine translation. The system comprises a generator which takes aquery template library and a knowledge base as input and is used for extracting entities and attributes from the knowledge base and filling the entities and attributes into a Chinese question template and an SPARQL query template to generate a training set; the word segmentation module is used for carrying out word segmentation processing on the Chinese questions in the training set and forwarding a word segmentation result to the learner; performing word segmentation processing on the target Chinese question, and forwarding a word segmentation result to an interpreter; the learner is used for training the neural network model according to the Chinese training set after word segmentation to obtain a trained model; and the interpreter is used for predicting the target Chinese questions after word segmentation by using the trained neural network model to obtain predicted SPARQL query statements, so that complex statistical and manual models are not used any more, and the medical healthquery Chinese questions are directly converted into the SPARQL query statements.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
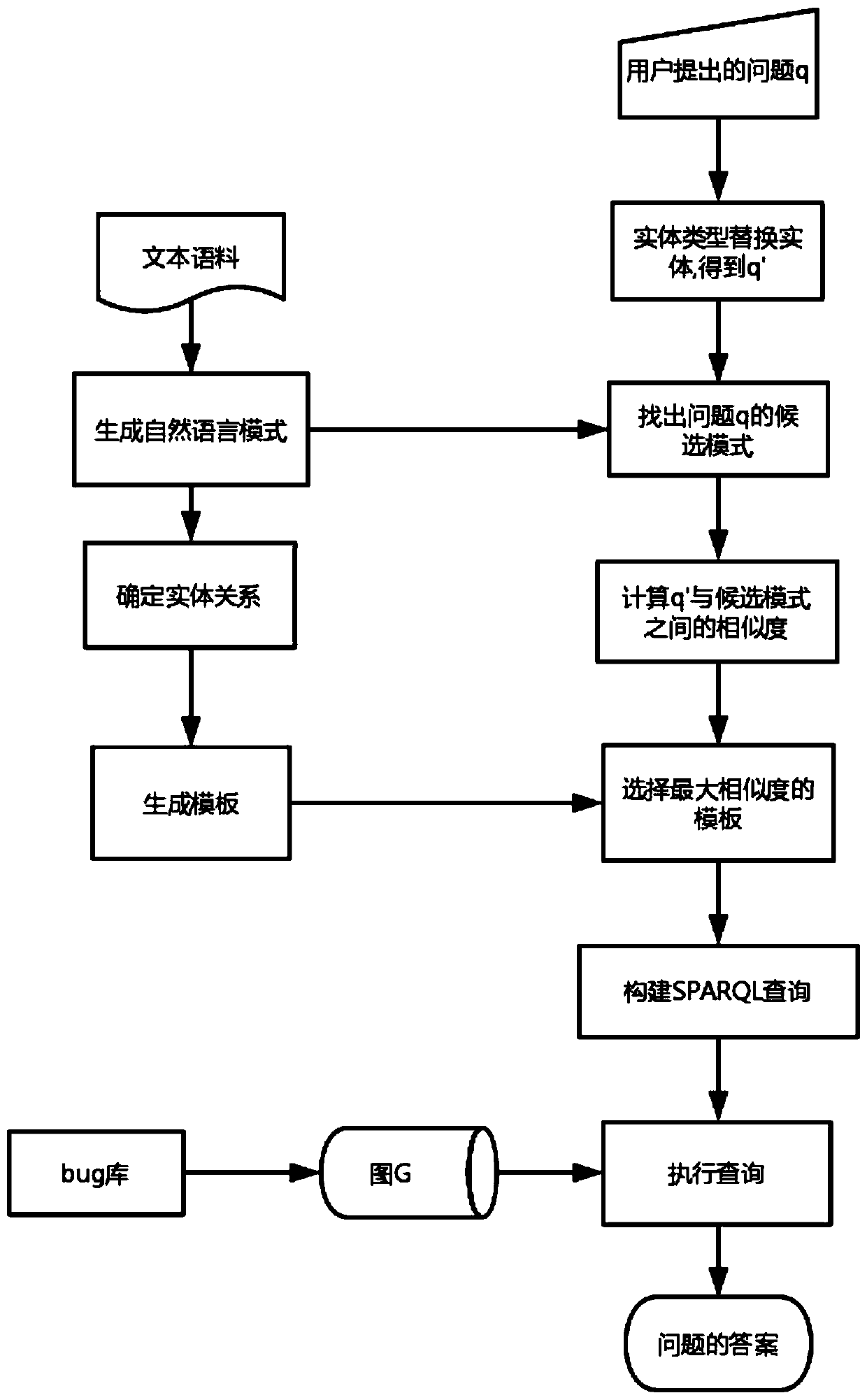
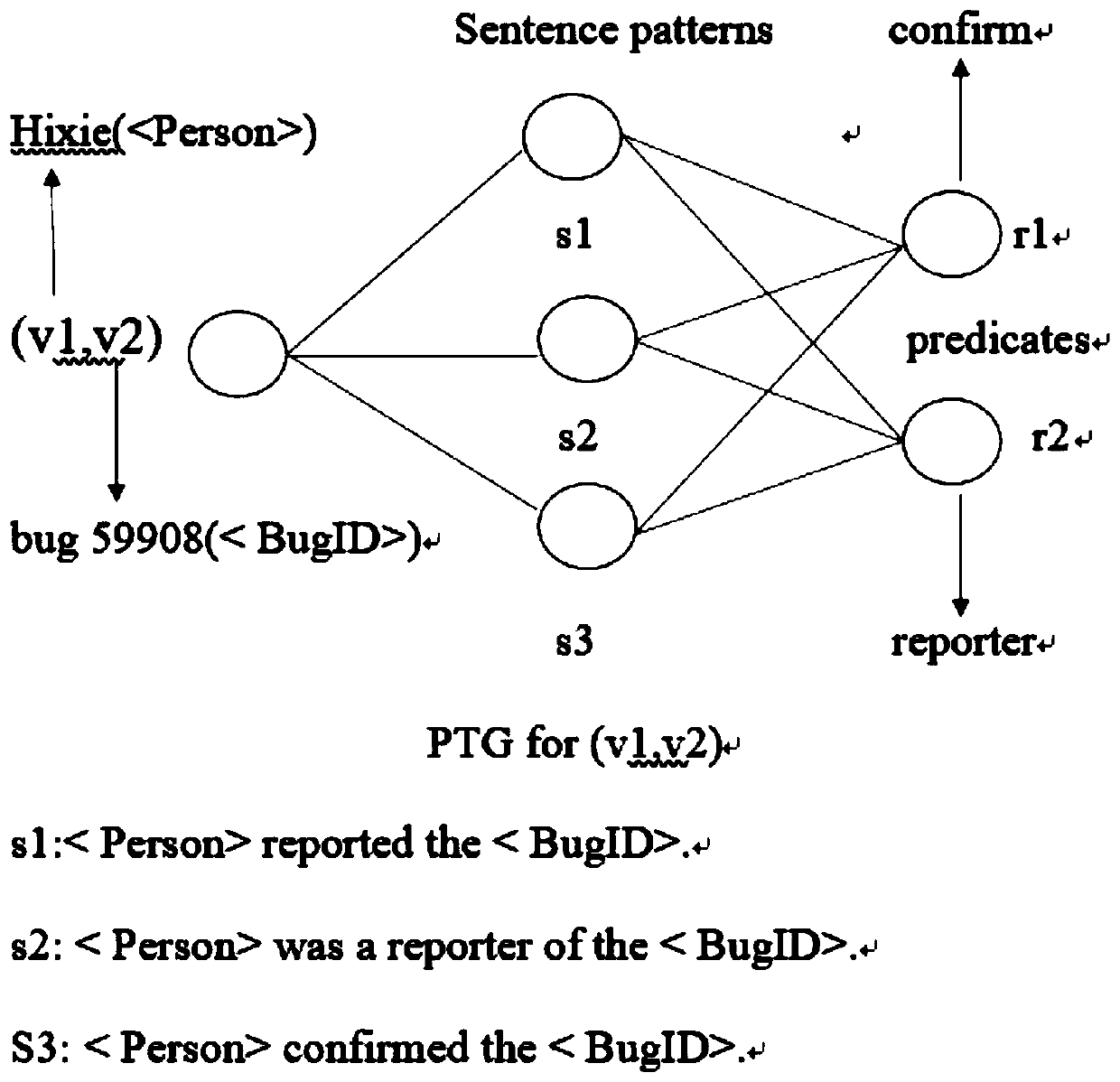
A template-based software defect automatic question and answer method
ActiveCN109947914AImprove accuracyHigh feasibilityDigital data information retrievalSemantic analysisTemplate matchingEntity type
The invention discloses a template-based software defect automatic question and answer method, and belongs to the field of software maintenance, and the method comprises the steps: firstly, extractingan entity relationship triple from a bug corpus, and obtaining a natural language mode; Then determining an entity relationship in the triple; Acquiring a query template corresponding to the naturallanguage mode; Replacing an entity in the question q proposed by the user with an entity type to obtain a question q '; Comparing and searching the entity type in the q'with the entity type in the natural language mode, and calculating the similarity; Obtaining an SPARQL query mode of the question q according to the similarity and the entity in the question q; And finally, searching and executingthe SPARQL query mode of the question q on the entity relation graph constructed by the bug report, thereby obtaining the answer of the question q. According to the method, natural language semantic understanding is carried out through the template, the understanding effect is good, template matching is carried out based on the entity type, the search space is greatly reduced, and the efficiency of software defect automatic question answering is improved.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
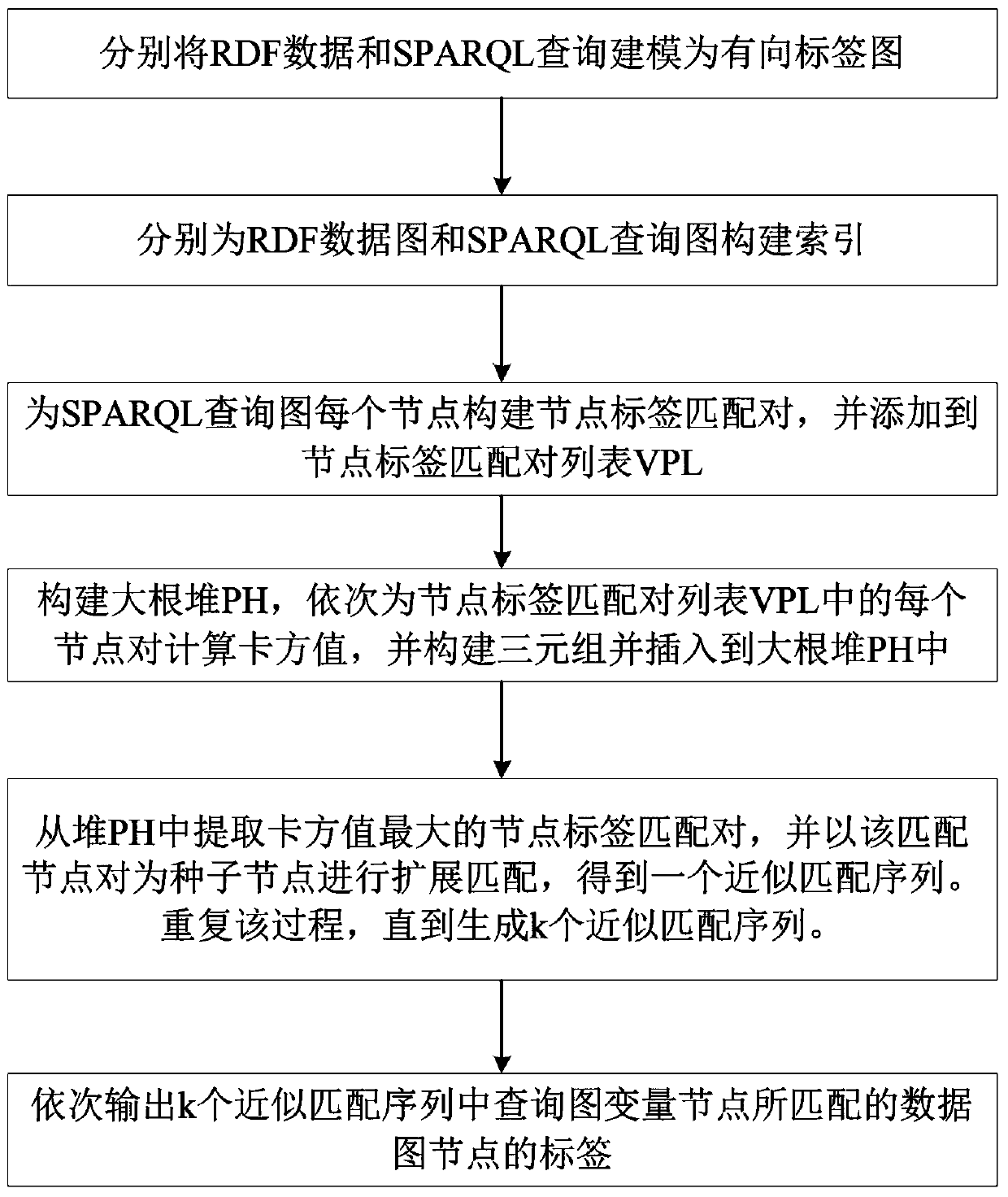
RDF Top-k query method based on neighbor vectors
ActiveCN111309979AAnswer accurately and efficientlyImprove robustnessOther databases indexingOther databases queryingData graphTheoretical computer science
The invention discloses an RDF Top-k query method based on neighbor vectors. According to the method, in an offline stage, RDF data and SPARQL query are modeled into an RDF data graph and an SPARQL query graph respectively, and indexes such as an adjacency list, an inverse adjacency list, a label node reverse list index, a node neighbor node label list index, a node h-hop neighbor node set, P-In and P-Out are constructed; in the matching stage, similarity measurement is conducted on the structure of neighbor nodes of candidate nodes and labels of the neighbor nodes based on the chi-square statistics technology, and extension matching is conducted in a spanning tree mode; and finally, obtaining Top-k sequences approximately matched with the SPARQL query graph, and outputting labels of datagraph nodes matched with variable nodes in the SPARQL query graph in each sequence. According to the method, expensive graph isomorphism and editing distance calculation are avoided, high robustness is achieved under the condition that labels and structures are not matched, and SPARQL approximate query questions can be accurately and efficiently answered.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Knowledge-driven SPARQL query construction method
ActiveCN109992658AExecute the result correctlyNarrow down the search spaceEnergy efficient computingSpecial data processing applicationsData miningQuery statement
The invention discloses a knowledge-driven SPARQL query construction method, and belongs to the technical field of data query. The method comprises the following steps of obtaining an SPARQL query statement submitted by a user, and extracting an entity set and a predicate set in the SPARQL query statement; analyzing and judging respectively, entity numbers and predicate numbers in an entity set and a predicate set, classifying query statements into simple questions, fact questions and complex questions respectively, dividing the complex questions into display entity questions and implicit entity questions, constructing query processes for different categories of questions respectively, and corresponding query answers are obtained. According to different problems, a corresponding knowledgegraph is constructed, and correct SPARQL query statements are screened out. The search space of a traditional method is reduced, and the operation time is shortened. When a complex problem is processed, if the implicit entity does not appear, the implicit entity is limited through an intermediate product, so that a correct SPARQL query statement is found out, and a result is executed accurately and quickly.
Owner:智言科技(深圳)有限公司
Semanteme-based Web service automatic calling and QoS information monitoring method
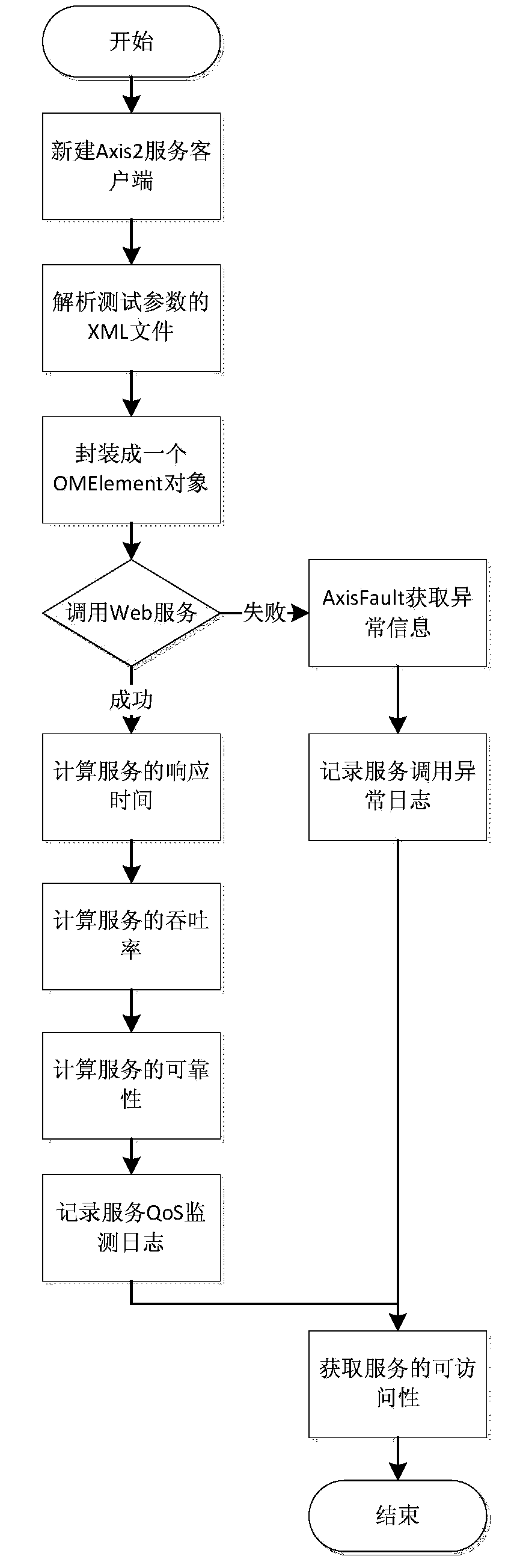
ActiveCN104268070AAvailability monitoringResponse Time MonitoringHardware monitoringSpecific program execution arrangementsTime efficientRDF query language
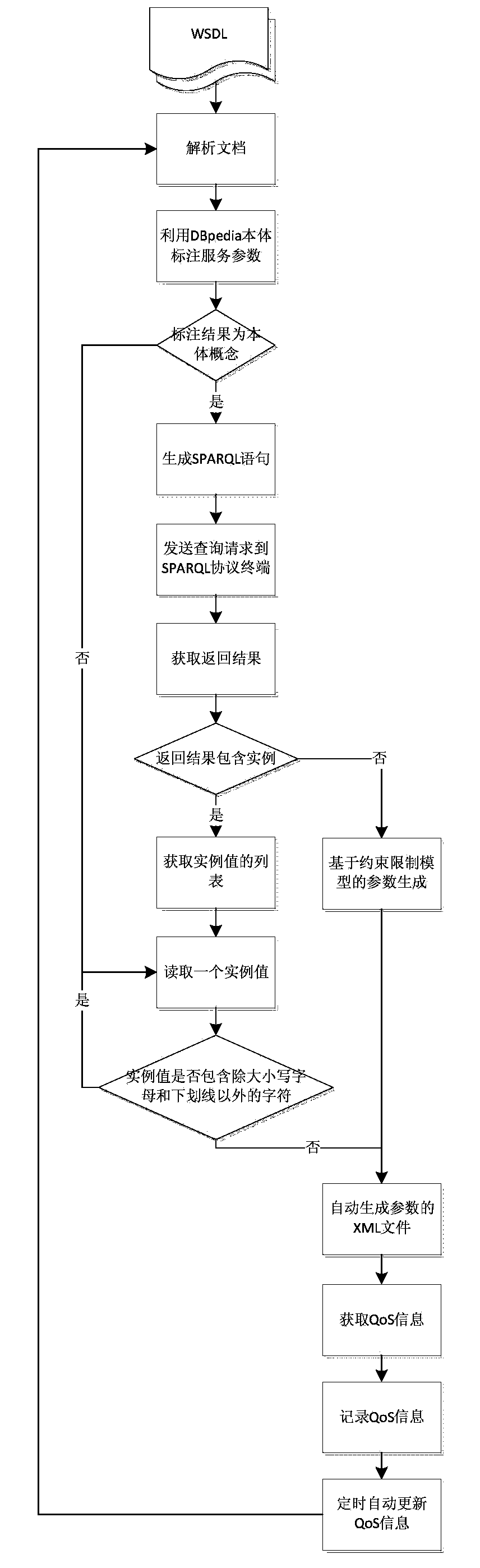
The invention relates to the technical field of Web service and aims to achieve monitoring on the availability and response time of Web service and other QoS information, greatly relieve the load of manual parameter input, save time and expense and ensure QoS accuracy and timeliness. The technical scheme includes that a semanteme-based Web service automatic calling and QoS information monitoring method includes steps of: (1) parsing a WSDL (Web Services Description Language) document of Web service; (2) building a Web service tagging model based on DBpedia associated data; (3) judging whether the tagging result is an ontology concept; (4) making the tagged ontology concept to be the object; (5) sending a request with an SPARQL (Simple Protocol And Rdf Query Language) packaged in to a DBpedia SPARQL protocol terminal http: / / dbpedia.org / sparql by aid of Java Script. The semanteme-based Web service automatic calling and QoS information monitoring method is mainly applied to Web service.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Predicate association-based SPARQL query optimization method and system
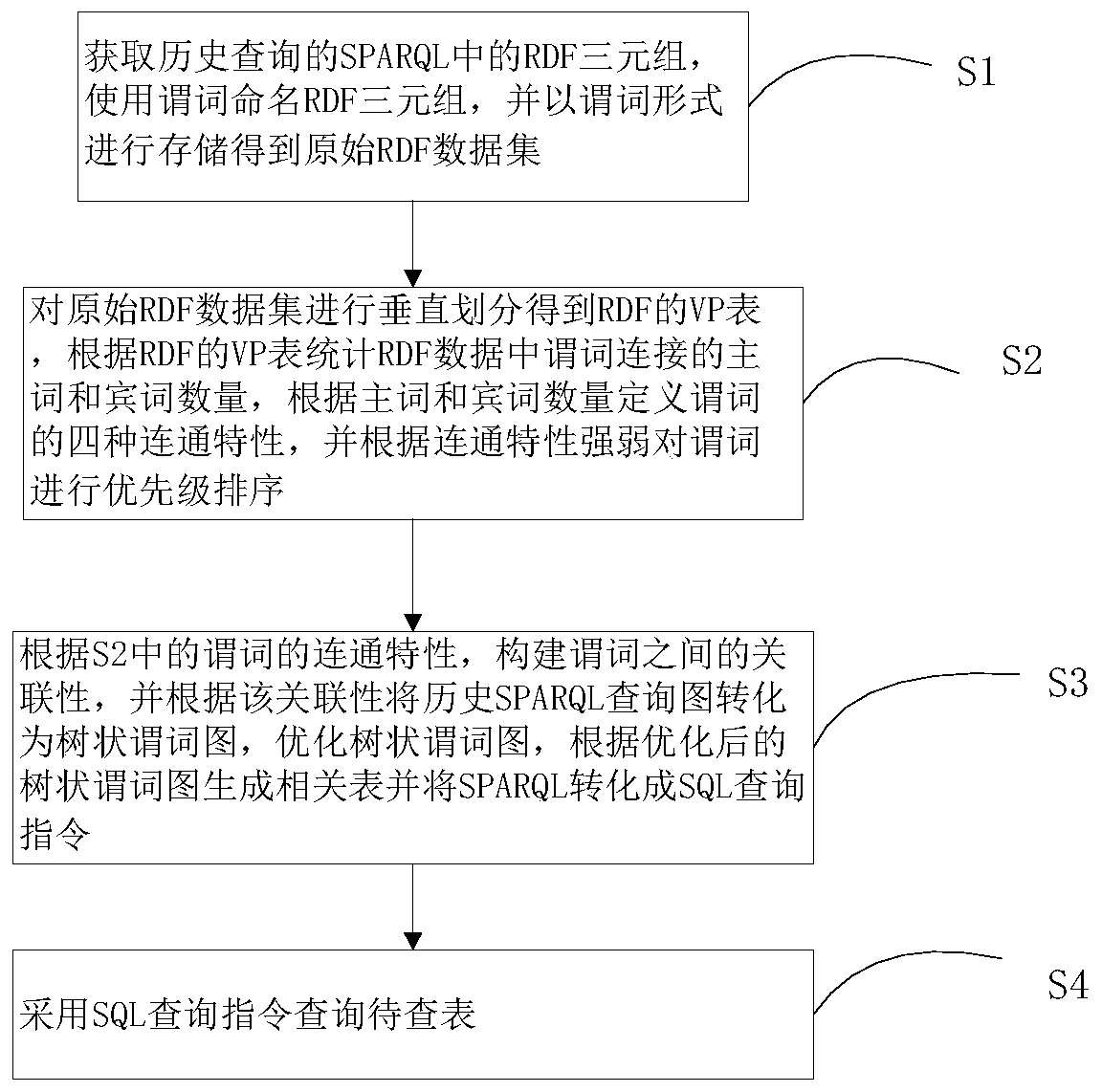
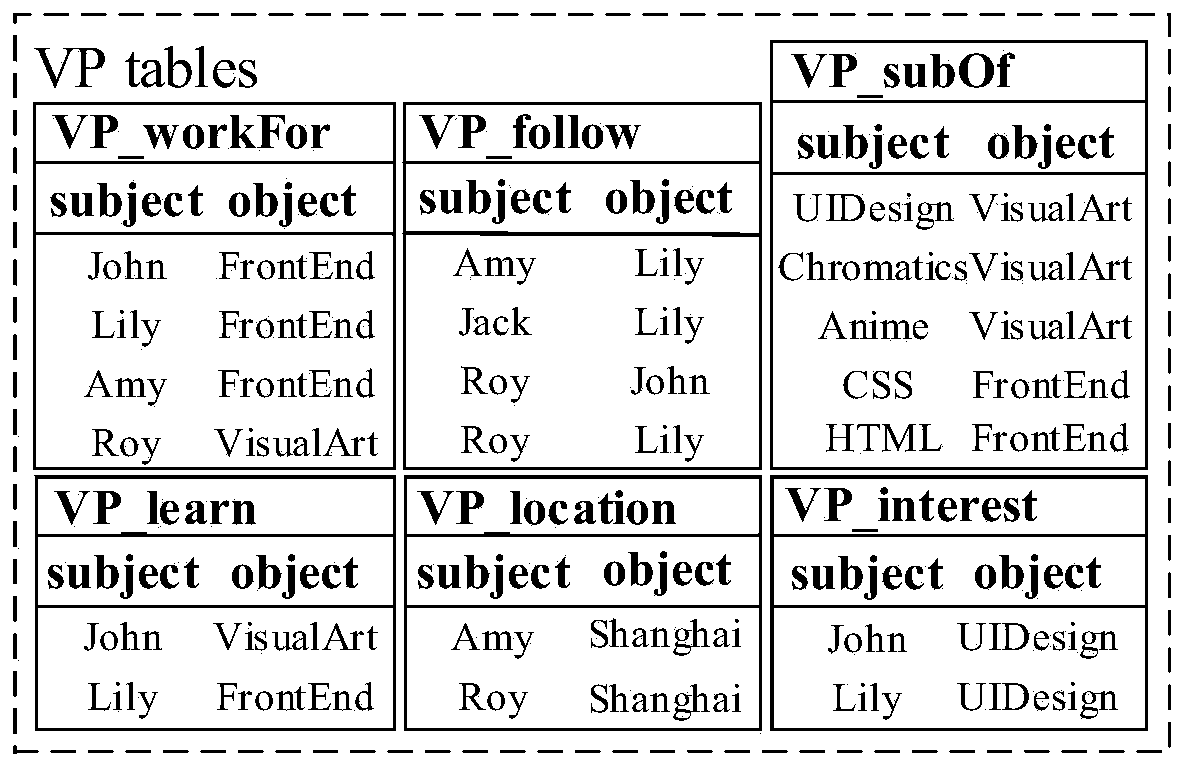
ActiveCN110032676AQueries are quickly and efficiently implementedImplement queryDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsData setQuery optimization
The invention relates to the technical field of big data association-oriented storage and query, and discloses a predicate association-based SPARQL query optimization method and system which is used for more quickly and effectively realizing the distributed SPARQL query. The method comprises the following steps of obtaining the RDF triplets in the SPARQL of the historical query, and naming the RDFtriplets by using predicates to obtain an original RDF data set; dividing the RDF data set to obtain a VP table, counting the number of subjects and guests connected with predicates in the RDF data according to the VP table, defining four connection characteristics of the predicates, and carrying out priority ranking on the predicates according to the strength of the connection characteristics; constructing relevance between predicates, converting the historical SPARQL query graph into a tree-shaped predicate graph according to the relevance, optimizing the tree-shaped predicate graph, generating a correlation table according to the optimized tree-shaped predicate graph, and converting the SPARQL into a query instruction; and querying the to-be-queried table by adopting the query instruction.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for planning the production of a product and production module having self-description information
The invention relates to a production module (412, 413, 421, 422) for performing a production function on a product, to a production system (400), to a production planning device, and to a method for planning the production of product. A plurality of production modules are coupled to each other. In each production module, a self-description information set (130, 230, 330) is stored as a database, e.g., NoSQL, OWL, ontology, SPARQL, which comprises properties of the production module. If a production information set comprising the production steps required to produce the product is present, the production information set and the self-description information sets or parts thereof are transmitted to a production planning device for planning the production of the product and a production procedure plan (460) for a product to be processed is determined, wherein the production procedure plan (460) comprises an information set about a sequence of production modules of the production system, which sequence a product should pass through in order for an intermediate product or end product to be produced.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
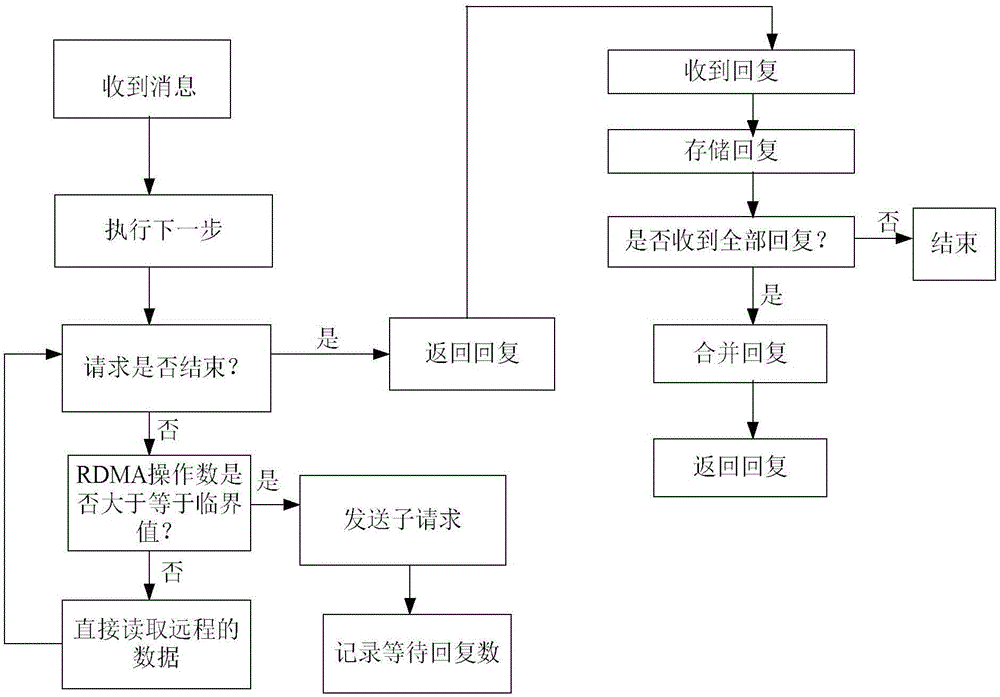
RDMA-friendly SPARQL query method based on multi-mode switching
ActiveCN106776815AImprove parallelismReduce the latency of query requestsSpecial data processing applicationsInformation typeGraph traversal
The invention discloses an RDMA-friendly SPARQL query method based on multi-mode switching. The method comprises the following steps: 1, receiving information and judging the information type; 2, executing one-step query, finding a new node by using the graph traversal method; 3, determining whether the request is executed or not; 4, determining whether the RDMA operation number in the next step is equal to or bigger than a critical value or not; 5, generating a new sub request, sending the new sub request to other machines, recording the number of waiting replies; 6, when the needed RDMA operation number is smaller than the critical value, reading long-distance data directly, finishing the next request, and repeating the third step. The method can utilize a long-distance direct memory access mode provided by high-performance network connected devices, more reasonably select the query execution model, reduce the communication cost of a system and improve the parallelism of complex queries.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Graph-based efficient SPARQL query response method and device and equipment
ActiveCN113220820AImprove accuracyImprove the response rate of implicit acknowledgmentSemantic analysisText database indexingData setAlgorithm
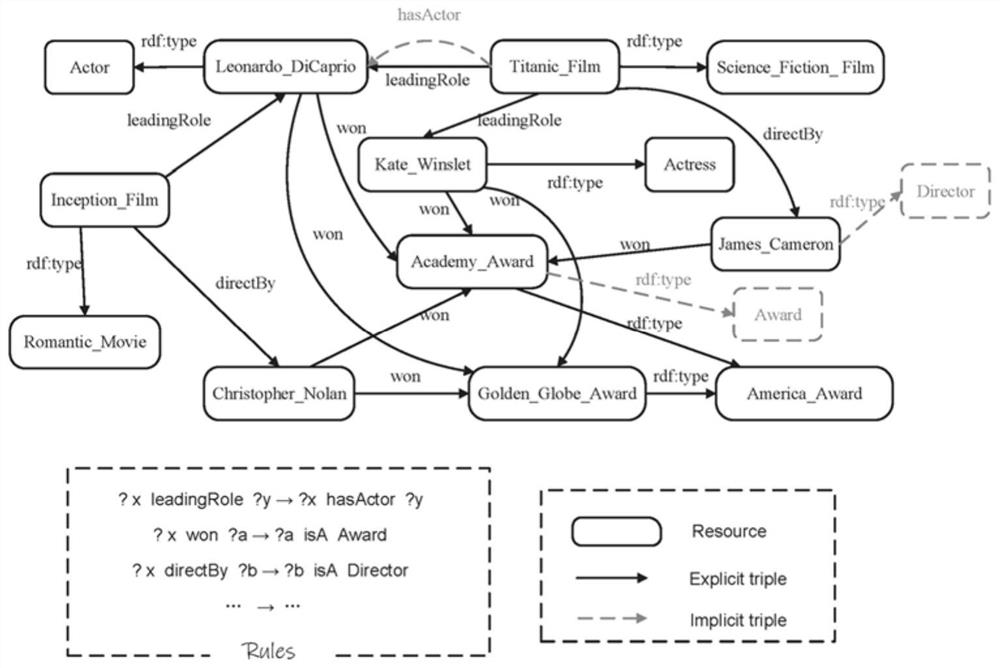
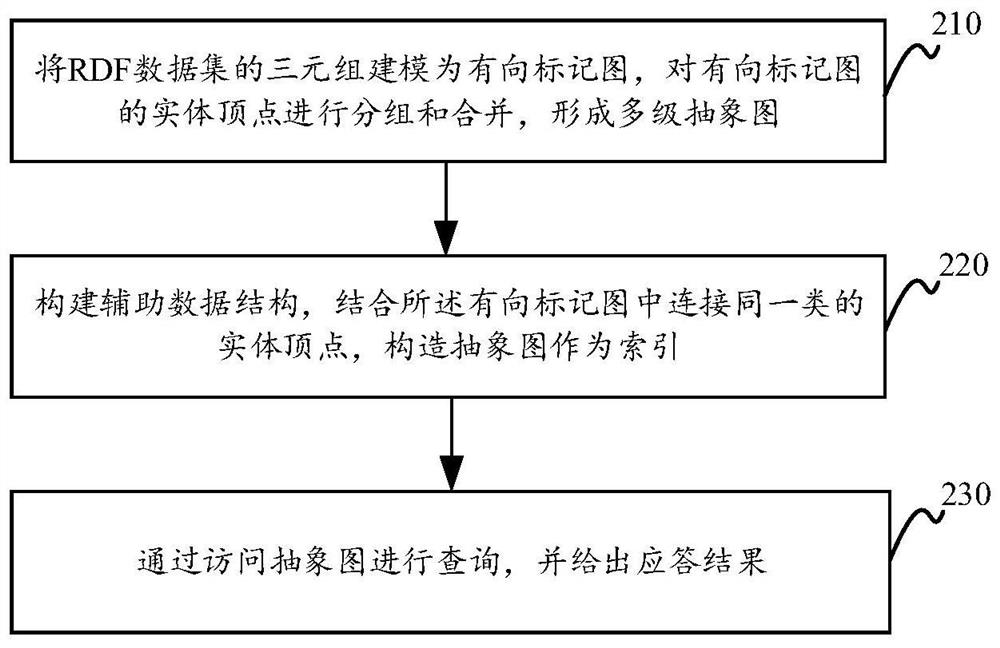
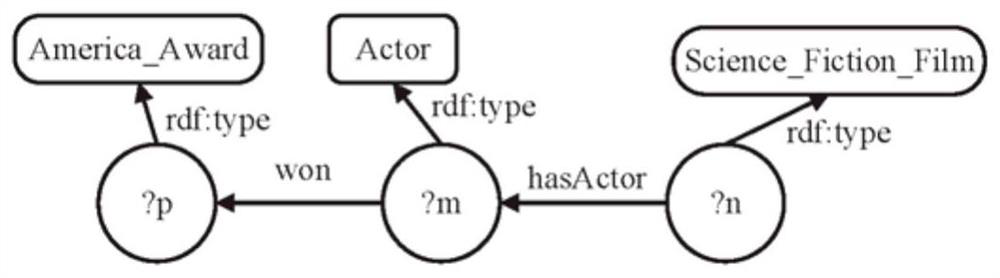
The embodiment of the invention provides a graph-based efficient SPARQL query response method and device and equipment, and the method comprises the steps of: modeling a triple of an RDF data set into a directed marked graph, grouping and merging entity vertexes of the directed marked graph, and forming a multi-level abstract graph, wherein an object and a main body in the triple are the entity vertexes of the directed marked graph; constructing an auxiliary data structure, and constructing an abstract graph as an index in combination with entity vertexes connected with the same class in the directed marked graph, wherein the auxiliary data structure comprises a set of semantic inclusion relationships in a directed marked graph mode, and the directed marked graph mode is used for describing features of the directed marked graph; querying by accessing the abstract graph, and giving a response result. The query response effect of the method is far better than that of an existing query method.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com