Patents
Literature
44 results about "Macrophyte" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
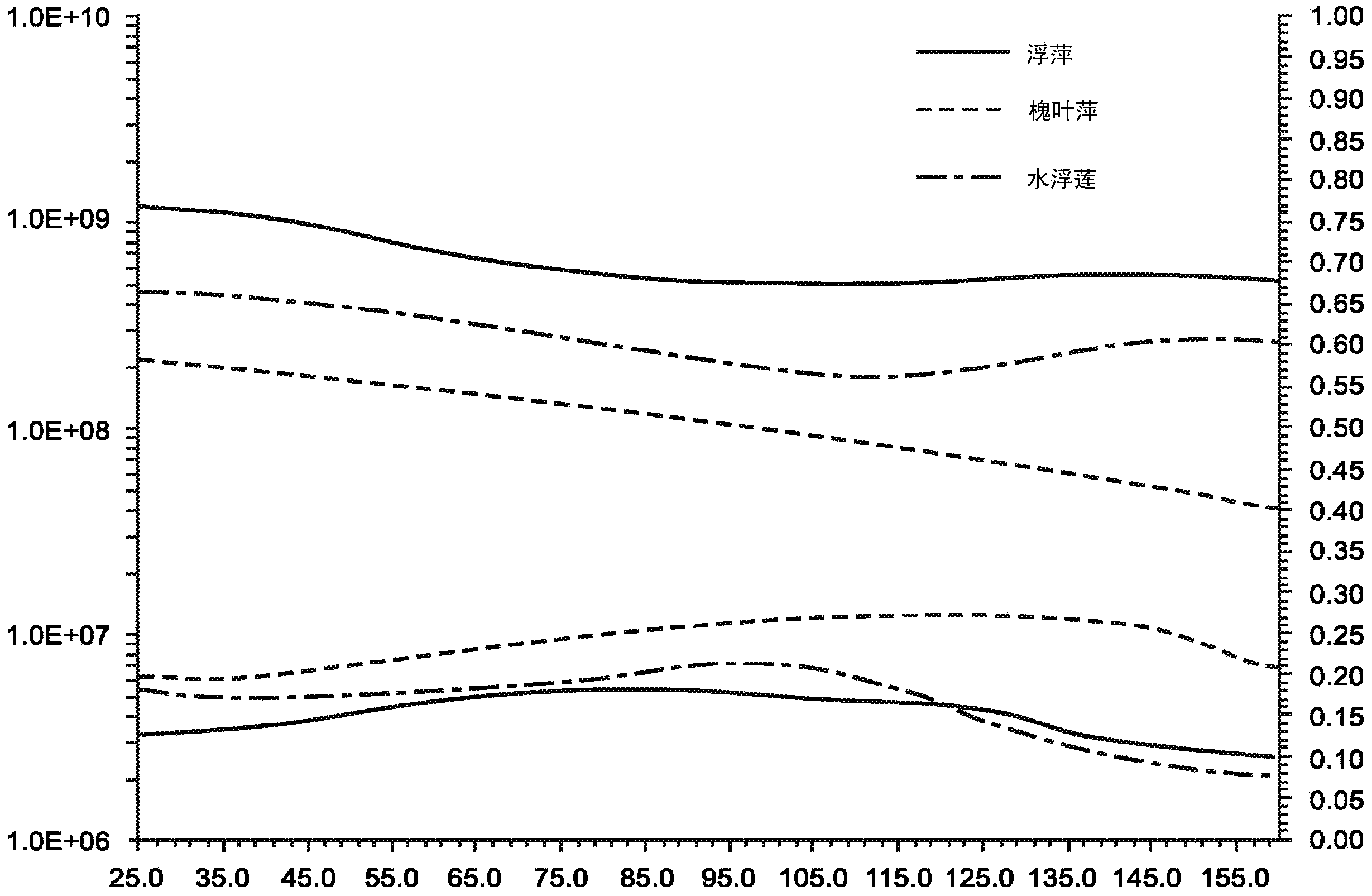
A macrophyte is an aquatic plant that grows in or near water and is either emergent, submergent, or floating. In lakes and rivers macrophytes provide cover for fish and substrate for aquatic invertebrates, produce oxygen, and act as food for some fish and wildlife.
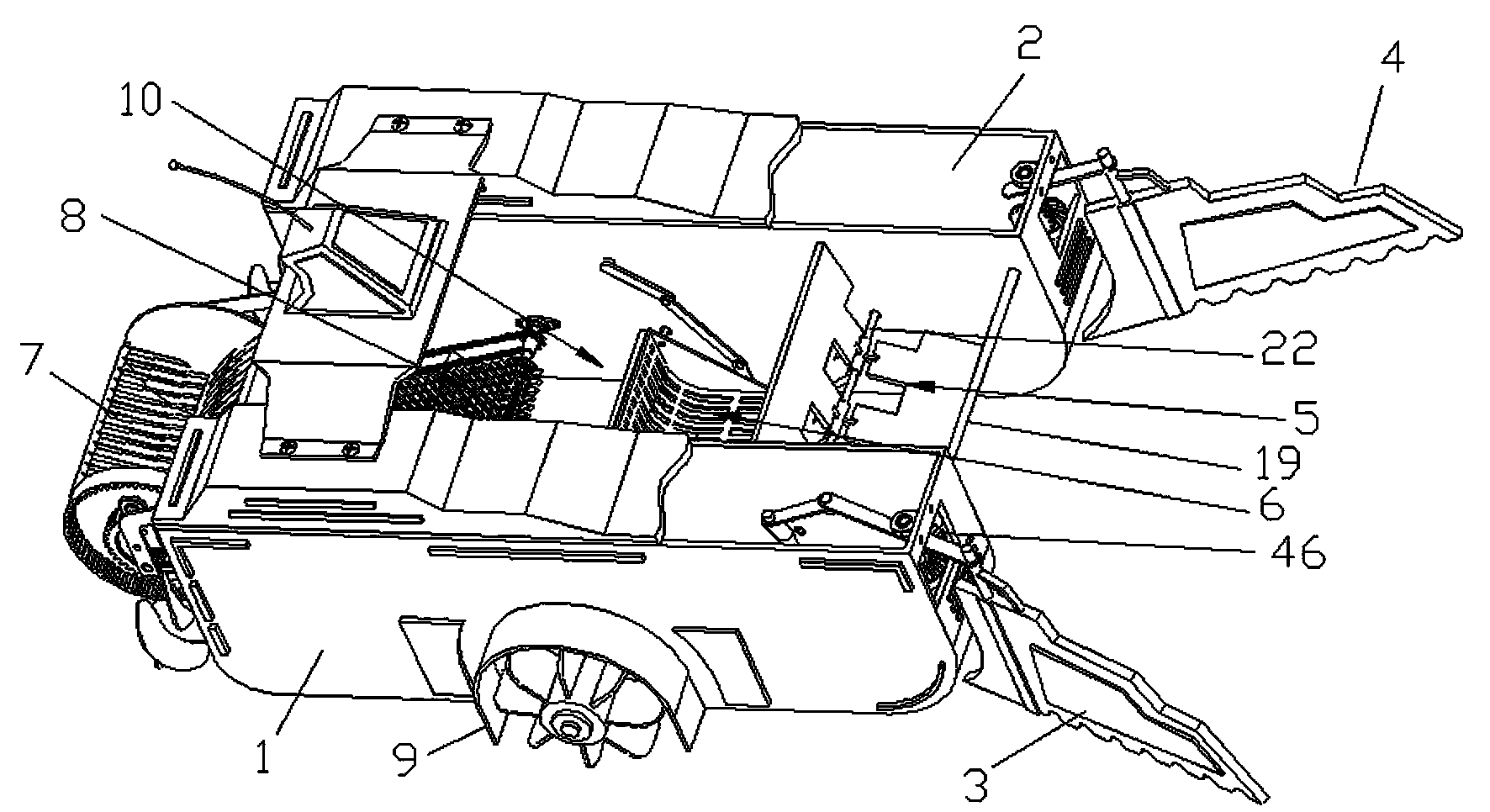
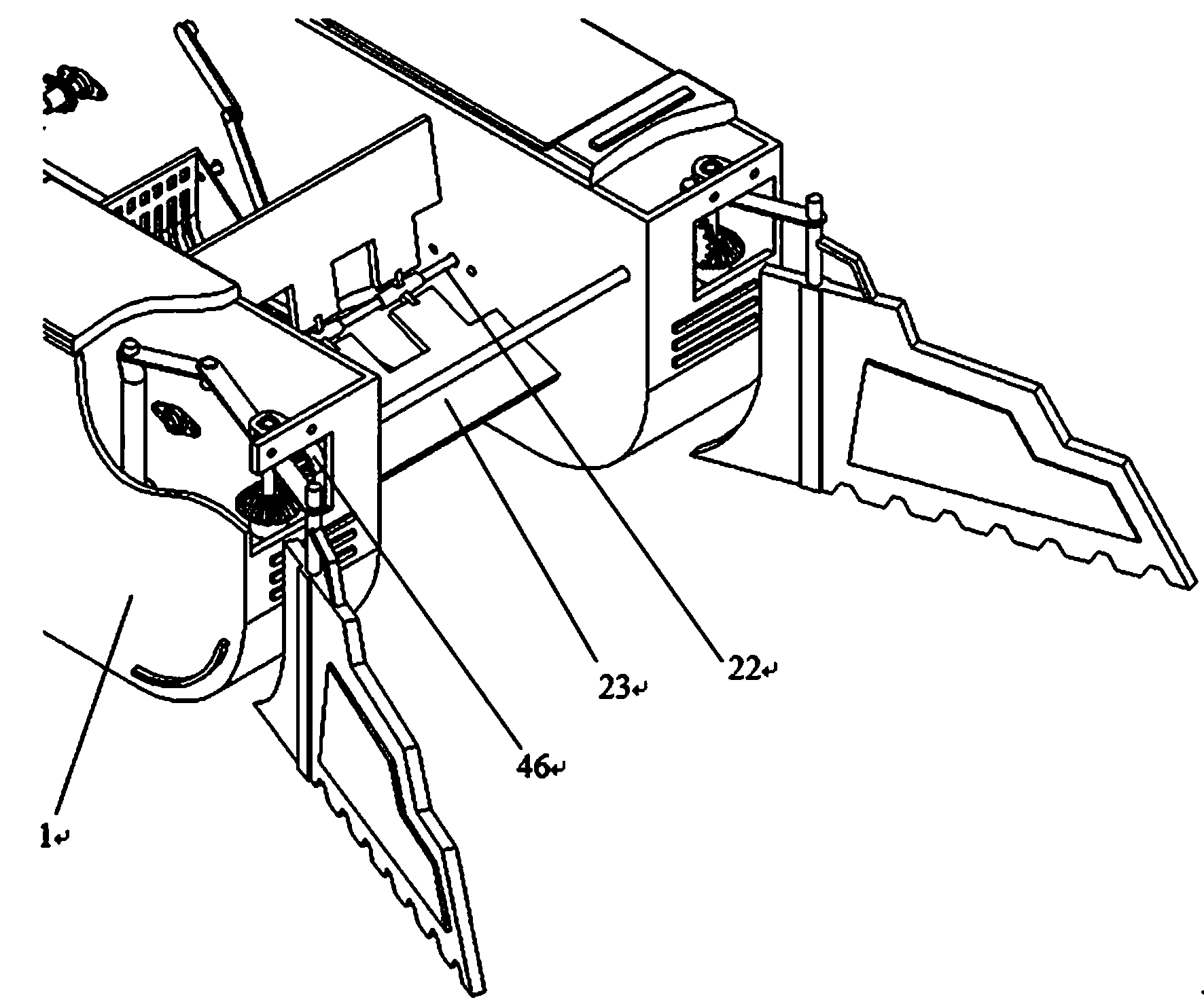
Refuse on water surface and cleaning ship for phytoplankton
InactiveCN104071309AOvercoming the disadvantage of being difficult to synchronizeAvoid knife entanglementWater cleaningWaterborne vesselsHull structureRefuse collection
The invention discloses a cleaning ship for phytoplankton. The cleaning ship is in a double ship structure and is composed of a driving wheel, a refuse guide mechanism, an impeller water distributor, a refuse tipping mechanism, a refuse cabin, a water plant cutting and collecting mechanism, a drive control system and other parts. When the ship works, the refuse in front of the ship is sucked into a tipping bucket refuse collecting area through a refuse guide mechanism and an impeller distributor, and then the refuse collected by the refuse tipping mechanism is poured into the refuse cabin on the ship; meanwhile, the phytoplankton and macrophyte are cut by an aquatic plant cutting mechanism, and then are transported to the refuse cabin through a water plant collecting mechanism (i.e. a rake type conveying crawler), after the refuse is full of the refuse cabin, a ship body docks, and the refuse is hung to a transfer trolley through a hoist. The cleaning ship is fast in speed of clearing away the refuse and phytoplankton on the water surface, and is capable of preventing the phenomenon that a cutter is twisted by the water plants.
Owner:SHENYANG LIGONG UNIV
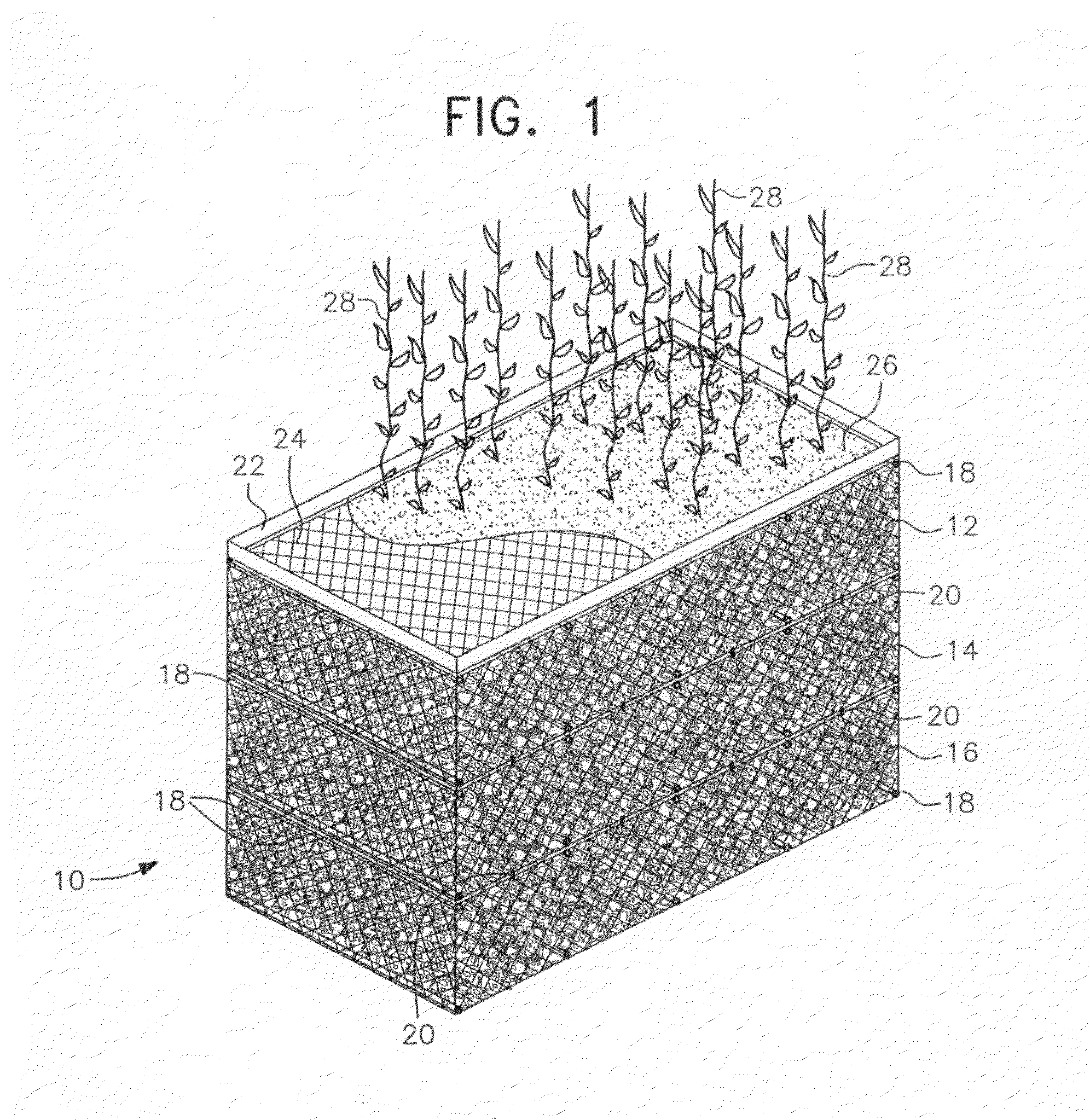
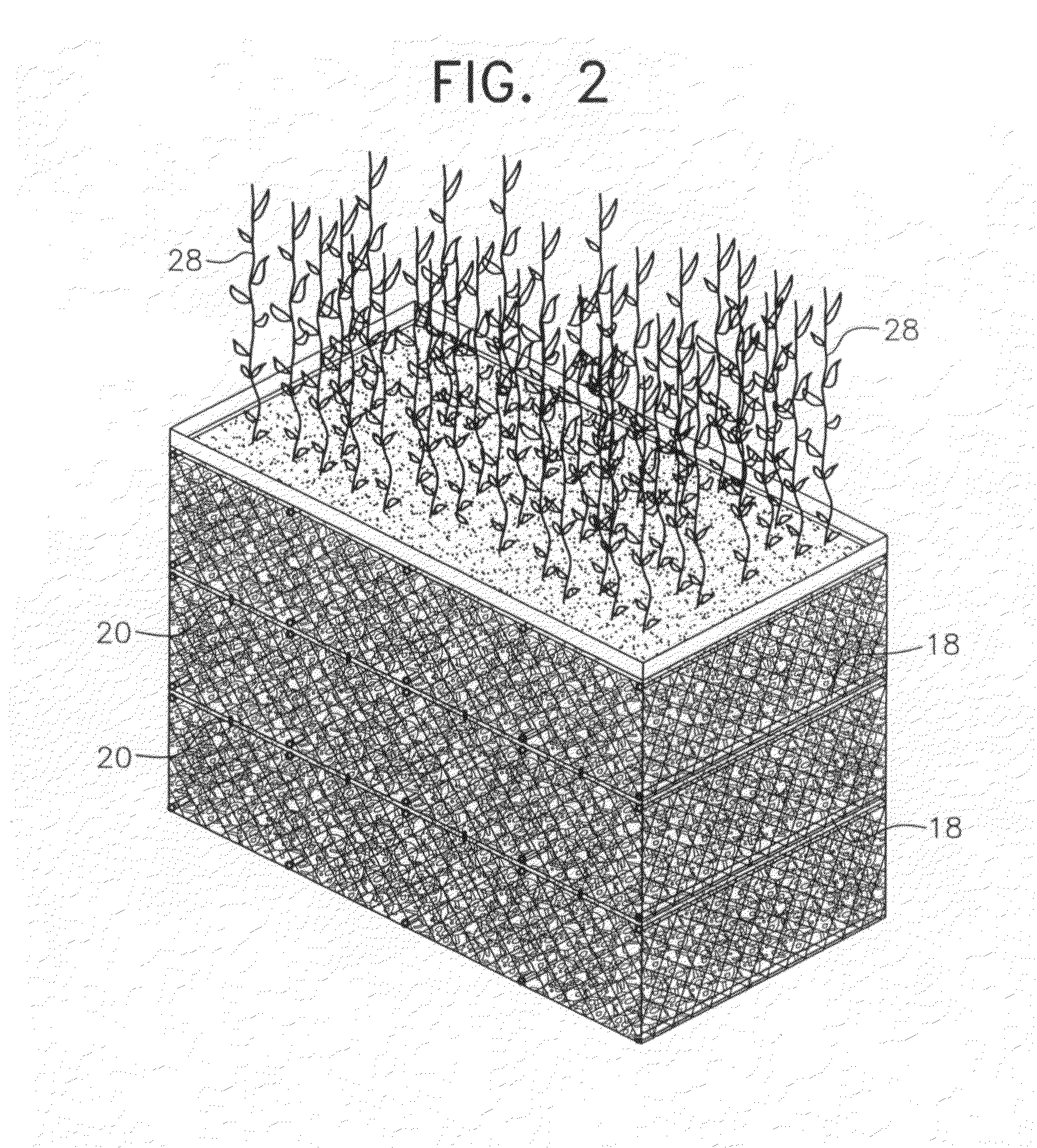
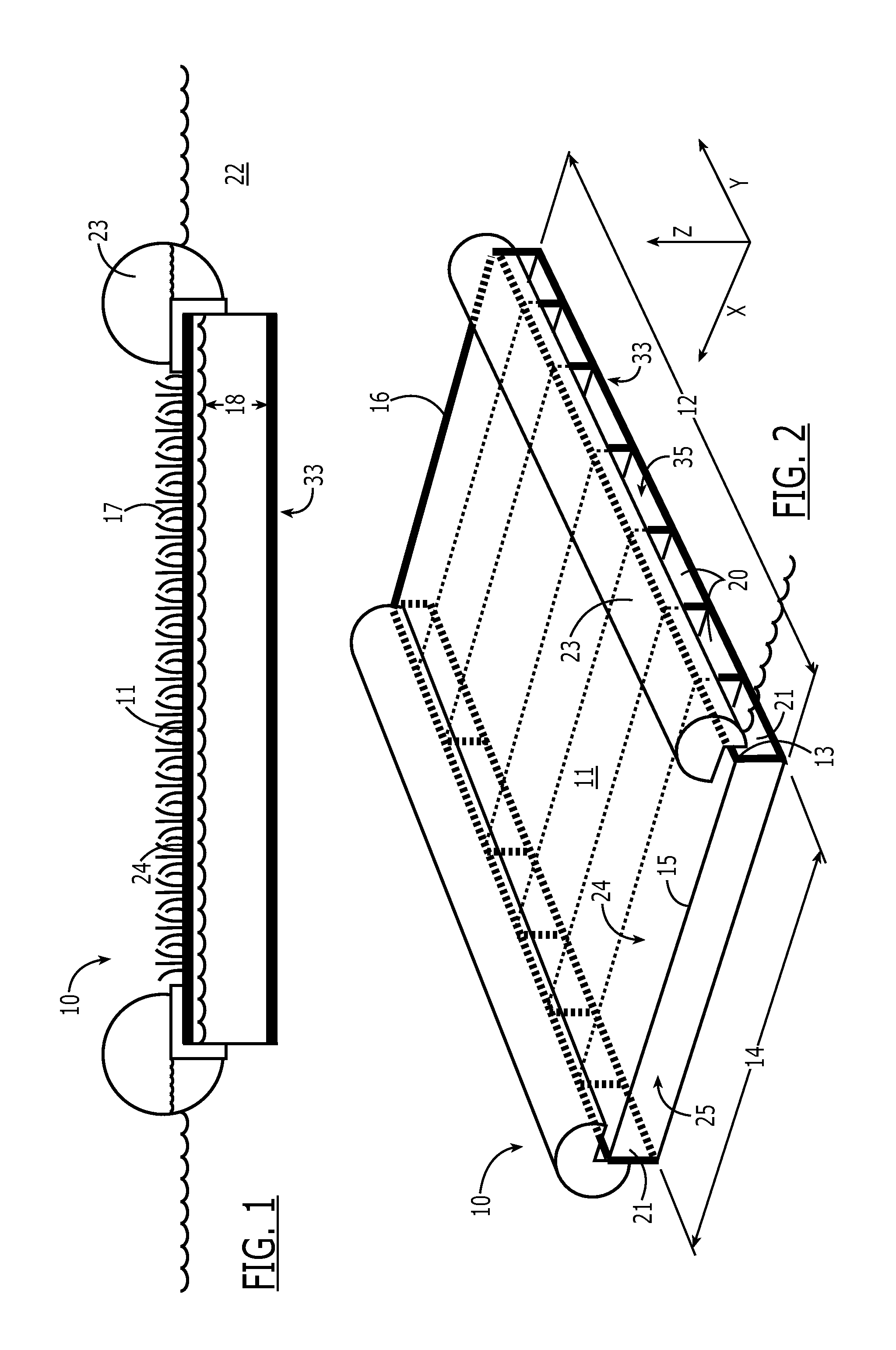
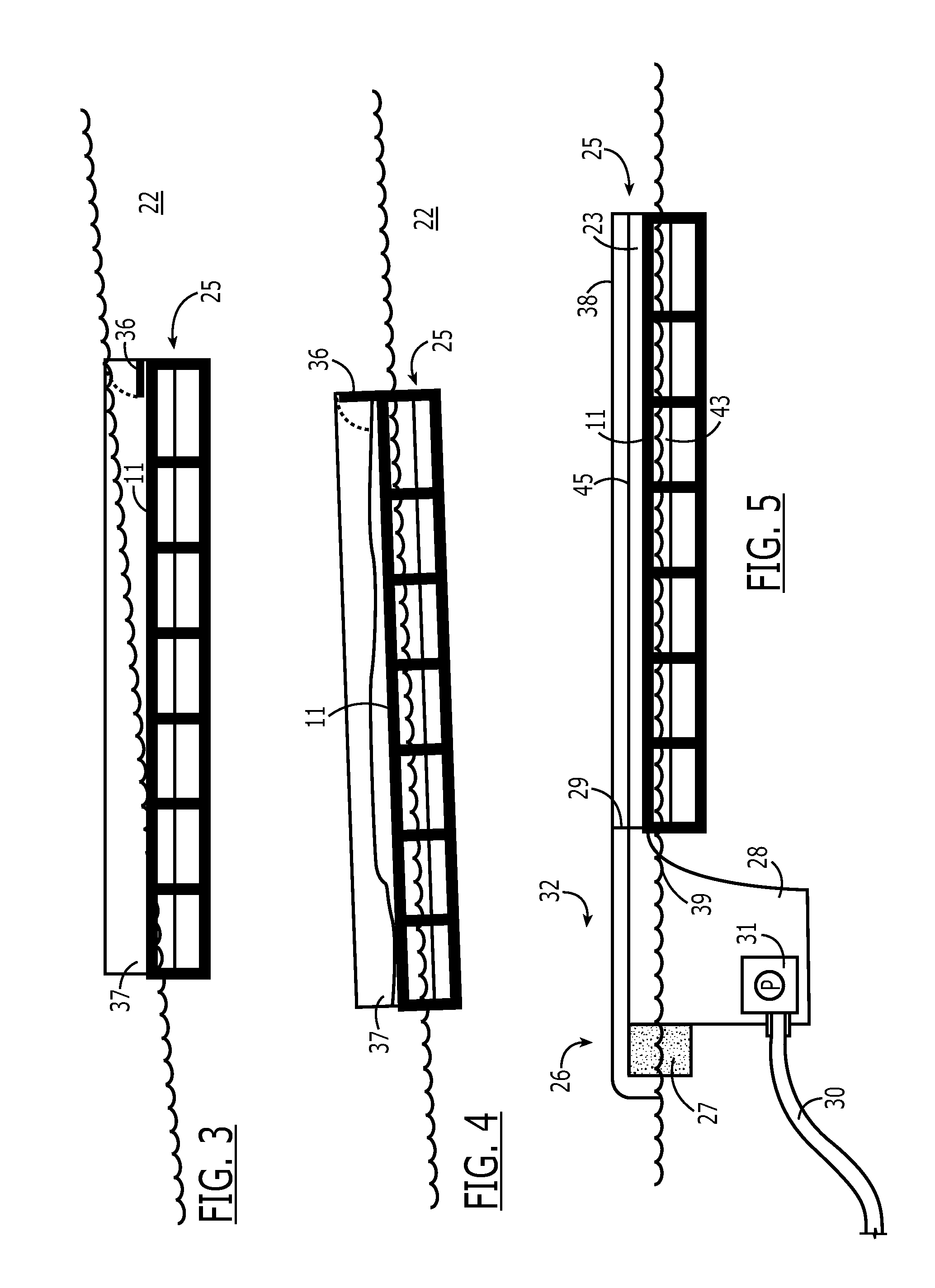
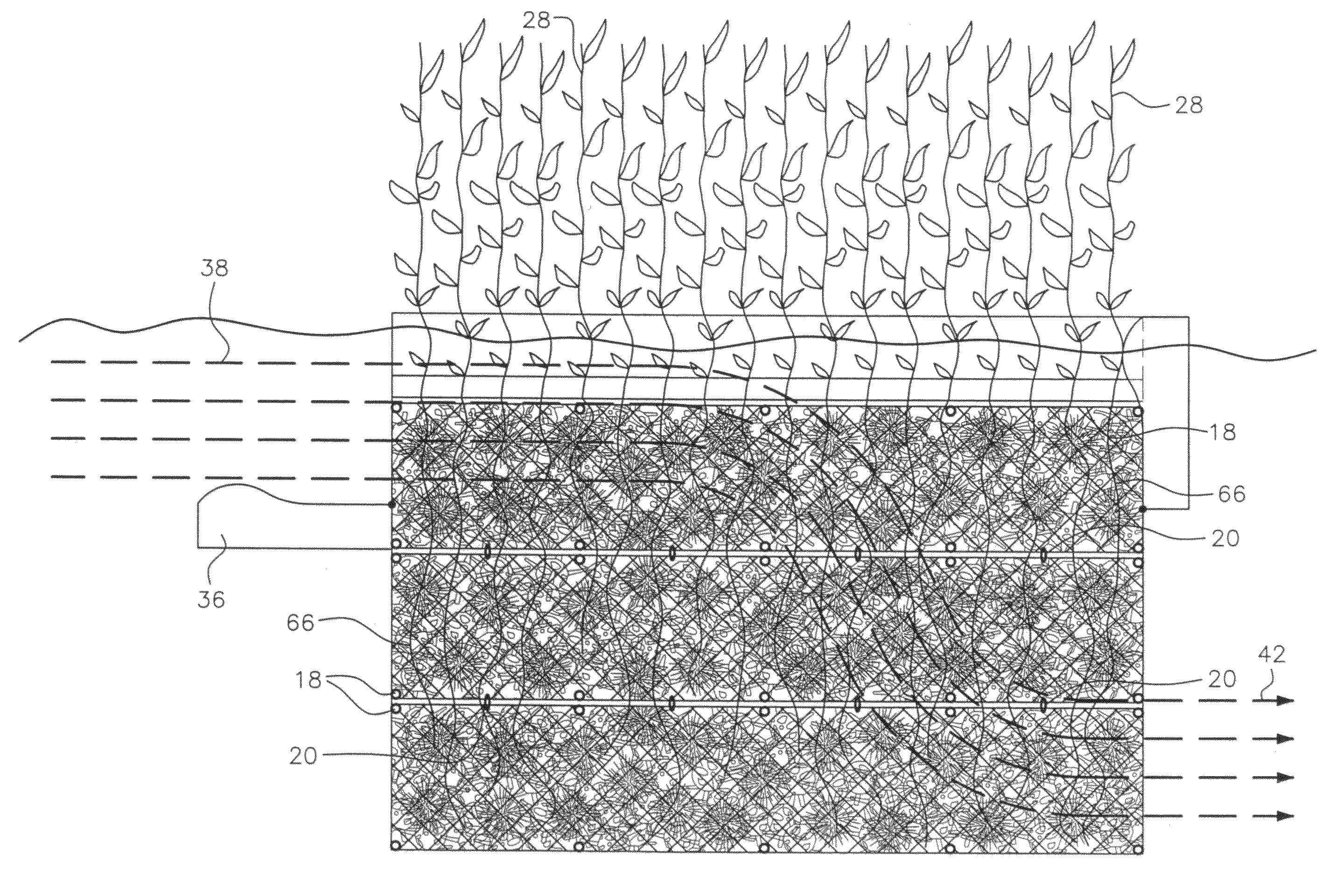
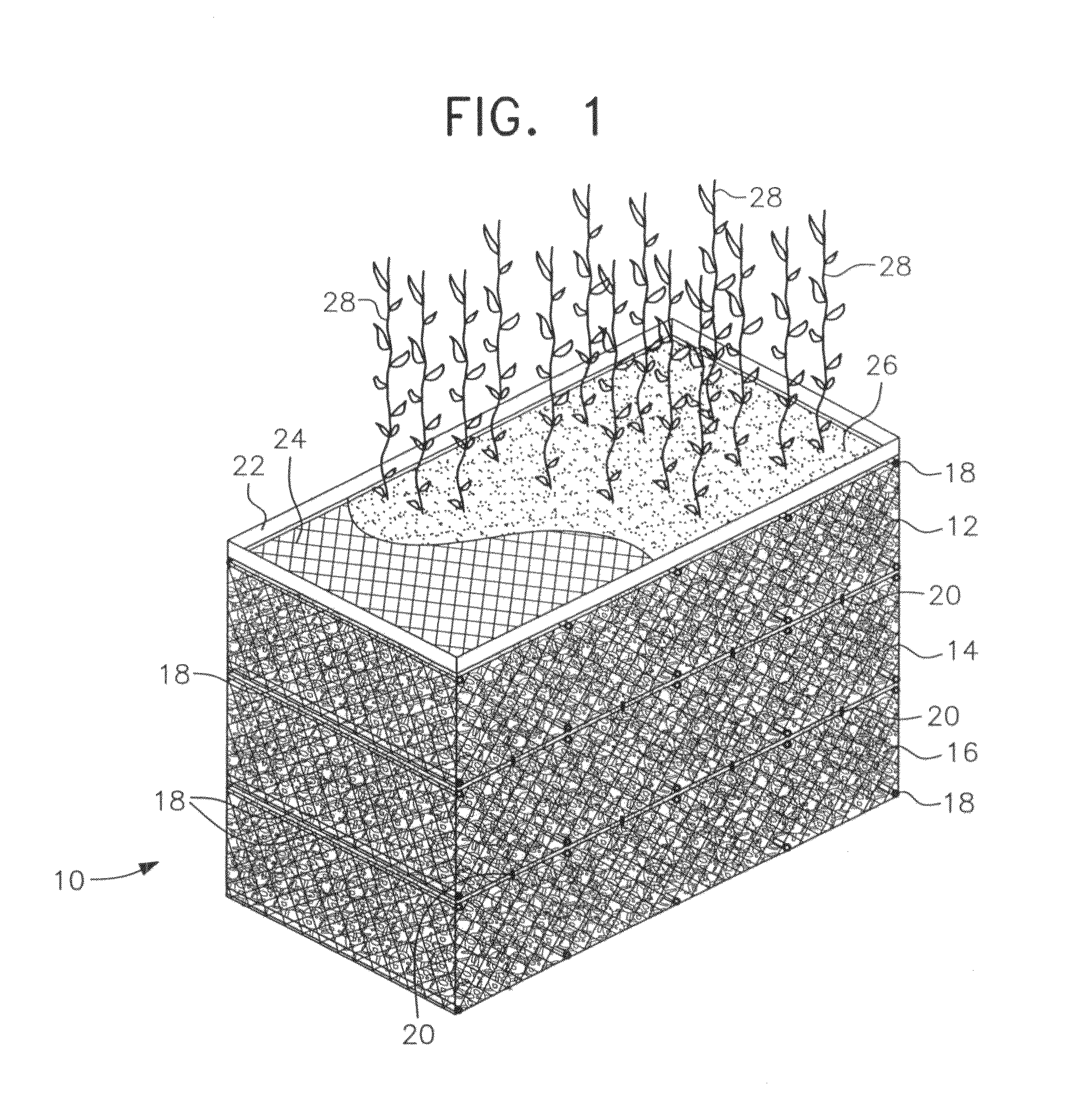
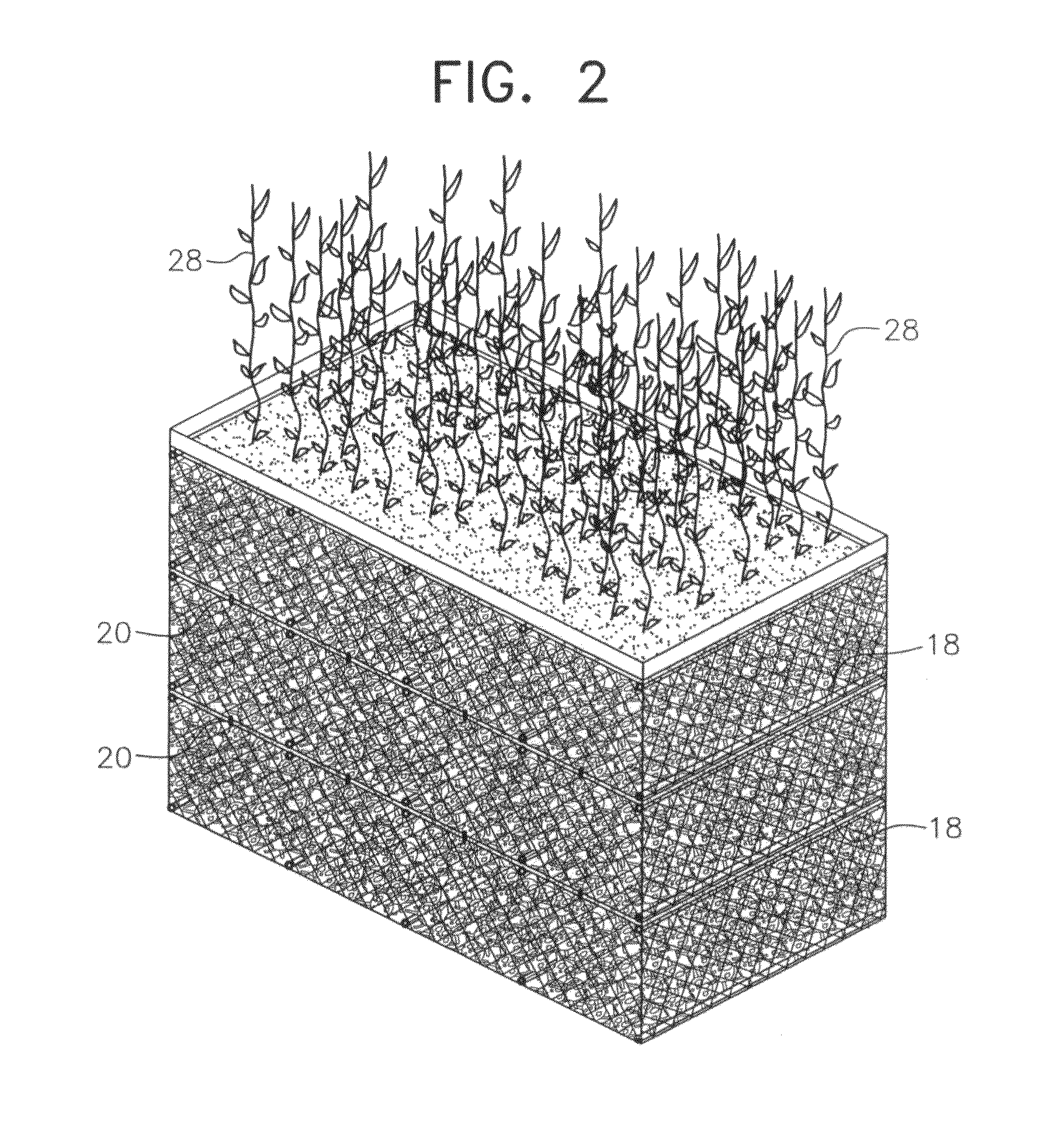
Apparatus merging wetland plants with a floating substrate to treat pollution in any river, lake or body of water
ActiveUS20110297596A1Extended stayOxidize-reduce organic, inorganic pollutantsWater cleaningTreatment using aerobic processesMacrophyteFluvial
Apparatus to treat pollution in rivers, streams, lakes, bays, ports and all bodies of water, employing as methodology wetland plants or macrophytes growing atop a wire or rigid frame basket filled with polygons or other irregular shaped objects of various configurations. The root system of the macrophytes are merged with and grow down amid the substrate composed of small polygons, other irregular shaped hollow, plastic, ceramic objects or other materials. The substrate provides nutrients, oxygen and sanctuary to bacteria, thereby reducing and eliminating pollutants in all bodies of water.
Owner:HONDULAS JOHN L
Macrophyte-based bioplastic
A bioplastic composition may contain certain biodegradable and renewable components. In some examples, the bioplastic composition includes at least one kind of aquatic macrophyte biomass, which may contain a native composition of protein and carbohydrates, in a blend with one or more types of biodegradable or durable thermoplastic polymers. The aquatic macrophyte composition may provide a balance of both polymeric and reinforcing properties to the blended bioplastic not typically exhibited by terrestrial feedstock such as soy meal or corn starch. Such a bioplastic composition may be formed into molded articles using extrusion, injection molding, compression molding, or the like.
Owner:ALGISYS
Floating aquatic plant culture systems and associated methods
A floating plant culture system has improved strength and durability and includes a substantially planar platform having a length along opposed sides thereof and a width along front and back thereof generally perpendicular to the sides. The platform is adapted for growing a culture of attached plants including micro- and macrophytes thereon. Beneath the platform are affixed a plurality of cells extending in bridging relation to the sides and open at each end adjacent the sides. The cells are placeable in fluid communication with a body of water desired to be remediated. Affixed along at least a portion of the sides extend a pair of opposed hollow beams, for providing flotation to the platform. The beams are also placeable in fluid communication with the body of water, and an upper surface of the platform is floodable by the body of water from beneath for submerging plants attached thereto.
Owner:AQUAFIBER TECH CORP
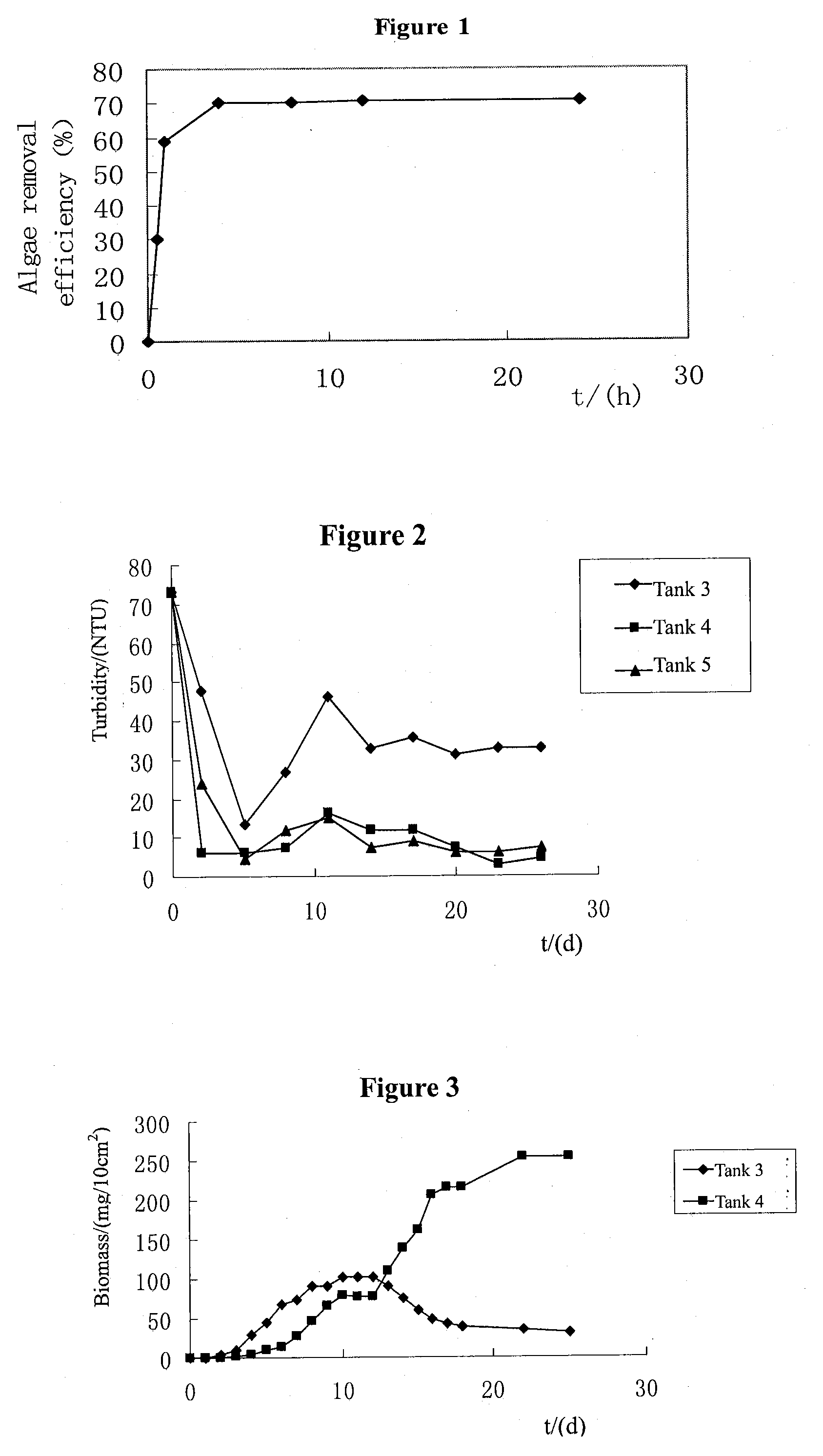
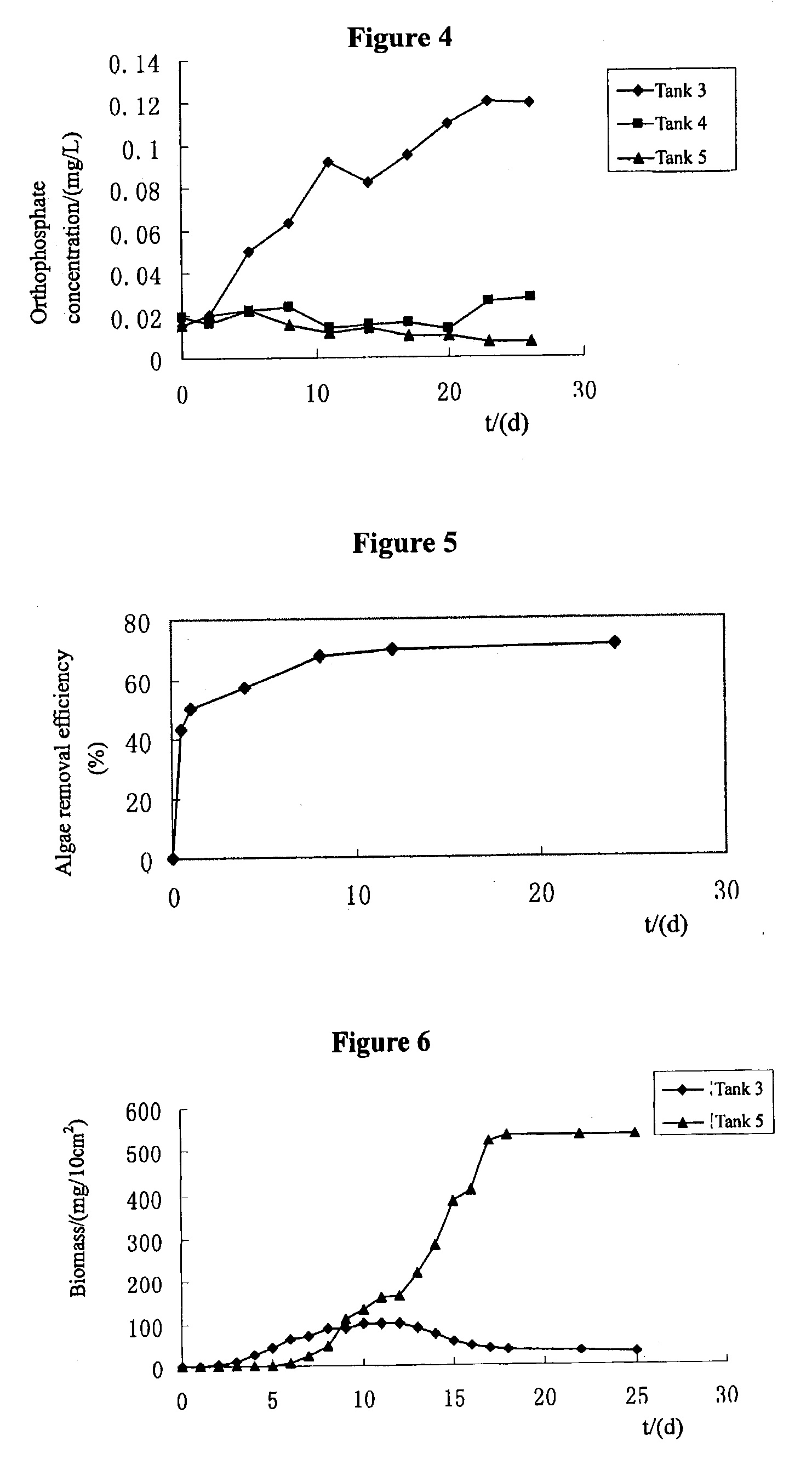
Composite material and method for removing harmful algal blooms and turning them into submerged macrophytes
InactiveUS7758752B2Enhancing ecological restorationEasy to removeScale removal and water softeningEnergy based wastewater treatmentEutrophicationCombined method
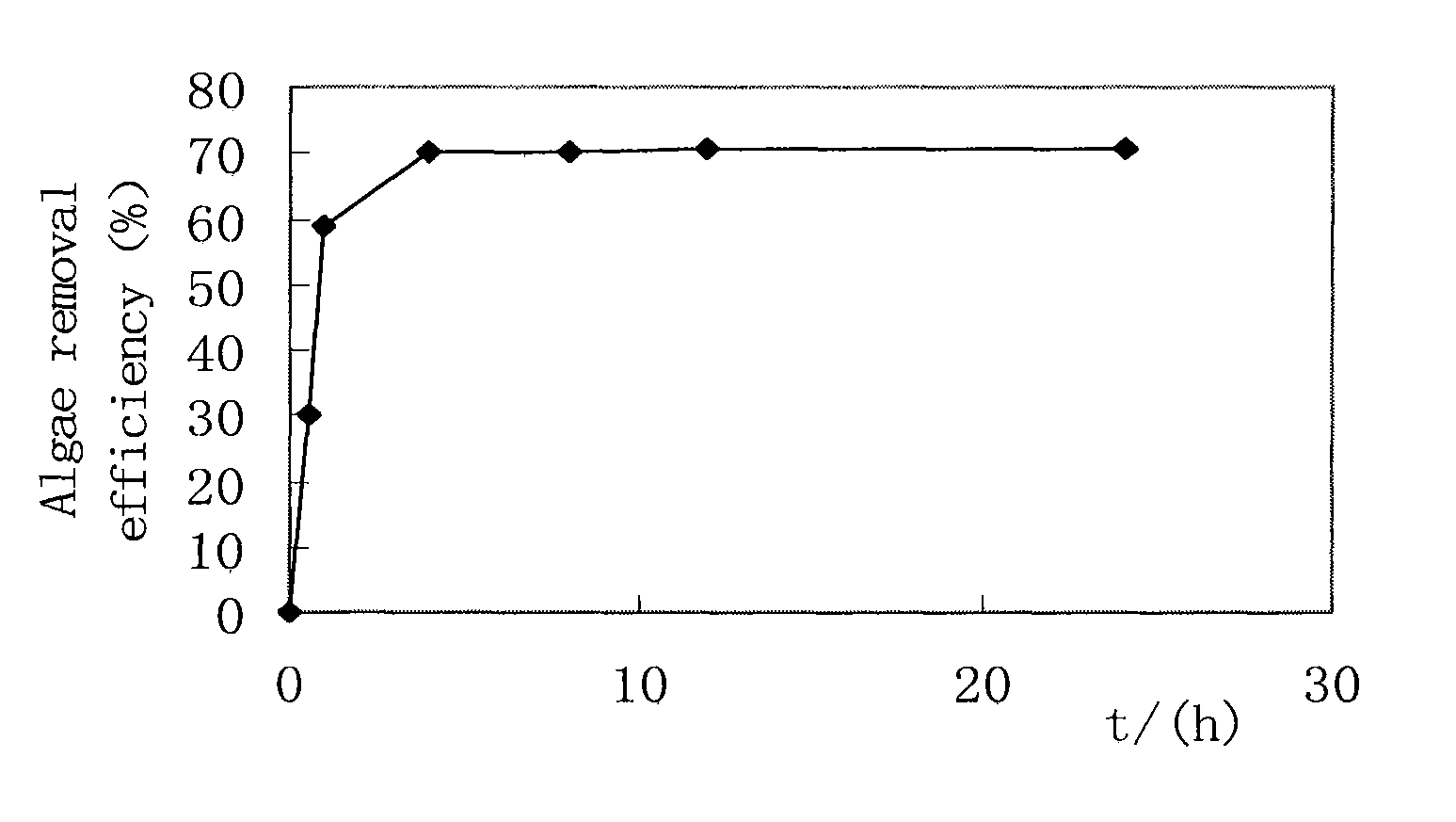
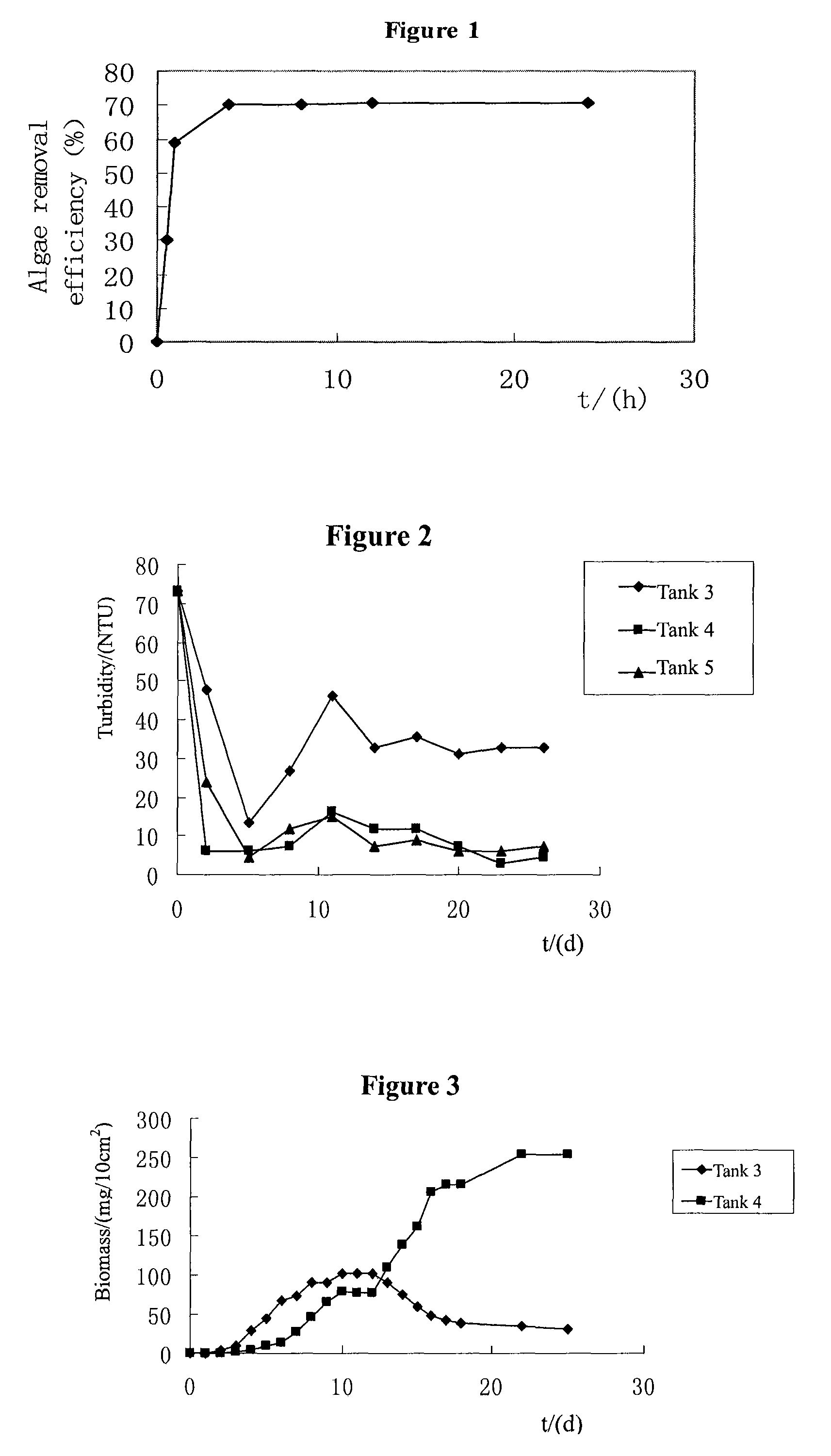
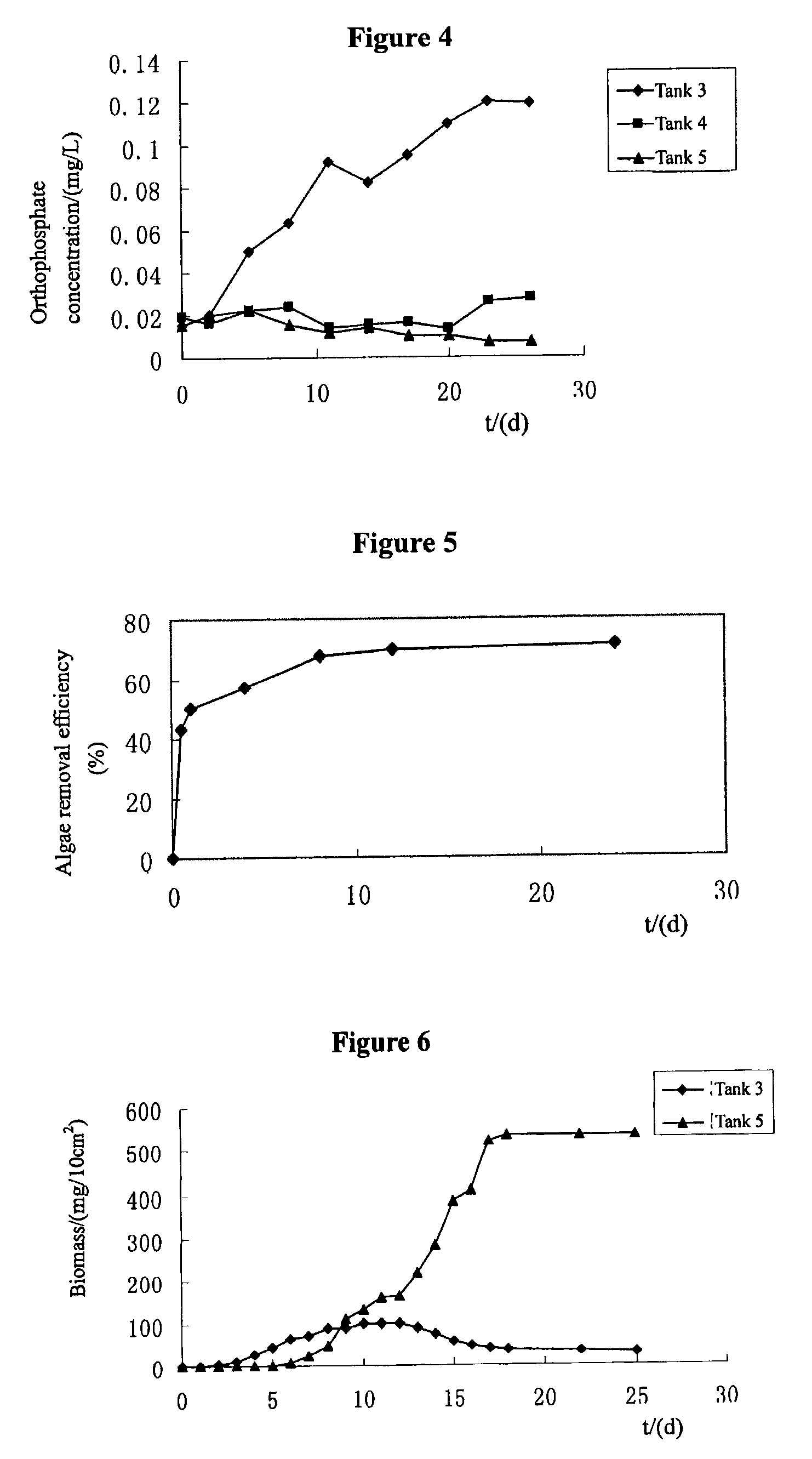
The present invention proposes a composite material which can rapidly and effectively remove algae and transform them into submerged macrophytes. The composite material is a mixture of two functional materials: one can grow into submerged macrophytes, and the other is clays or modified local soil particles which can flocculate algae, inhibit phosphorus release from sediments and act as the carrier of the above-mentioned seeds, earthnuts, buds, and roots of submerged macrophytes. In addition, the present invention proposes a physical-chemical-ecological combined method for improving water quality and enhancing the ecological restoration of eutrophic lakes using the above-mentioned material. By spraying the composite material to the lake surface, the new method can remove algae and turbidity through flocculation and complete the planting process simultaneously so that HABs and eutrophication are effectively controlled.
Owner:BEIJING GREEN ECO ENVIRONMENTAL TECH
Ecosystem model and biomanipulation technology based eutrophic water body remediation method
InactiveCN108793410AEasy to operateIncrease the number of cyclesBiological water/sewage treatmentEnergeticsCommunity structure
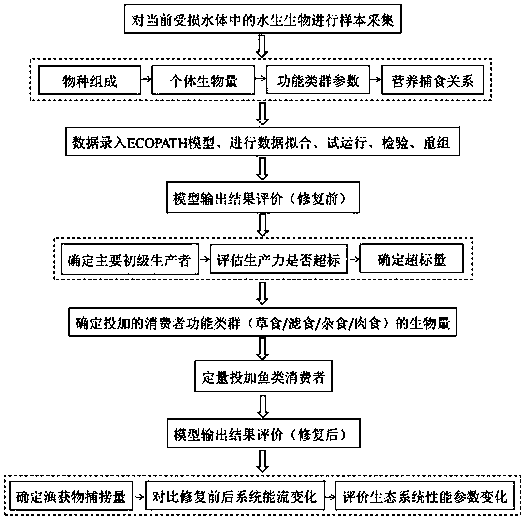
The invention discloses an ecosystem model and biomanipulation technology based eutrophic water body remediation method. Firstly, an ECOPATH model is used to fit the energy flowing mode of the currentecosystem, when the annual production of phytoplankton or aquatic macrophyte in a water body is too high, the minimum primary production requiring for maintaining the operation of the system is takenas the baseline according to the output result of the model, the consumption of the extra primary production in the system is increased through the predation action of fish by using a method of quantitatively adding a fish consumer, and meanwhile, the top-down effect is produced to control the biomass and the community structure of a primary producer. After finishing remediation, the ECOPATH model is used to access the fish catch, the commercial fish species added in the same year are harvested according to the assessment result, so that the balance of energy of the ecosystem is maintained, the fishing catch directly takes away a large quantity of nutritive salts in the water body, and certain economic value is produced. The novel thinking for reference and the technical support are provided for the remediation method taking the scientific experiment as the method from the perspectives of ecology, quantity and energetics, and the method has a very important application value for the ecological remediation of the damaged water body.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Composite Material and Method for Removing Harmful Algal Blooms and Turning Them into Submerged Macrophytes
InactiveUS20090107912A1Enhancing ecological restorationEasy to removeScale removal and water softeningEnergy based wastewater treatmentEutrophicationCombined method
The present invention proposes a composite material which can rapidly and effectively remove algae and transform them into submerged macrophytes. The composite material is a mixture of two functional materials: one can grow into submerged macrophytes, and the other is clays or modified local soil particles which can flocculate algae, inhibit phosphorus release from sediments and act as the carrier of the above-mentioned seeds, earthnuts, buds, and roots of submerged macrophytes. In addition, the present invention proposes a physical-chemical-ecological combined method for improving water quality and enhancing the ecological restoration of eutrophic lakes using the above-mentioned material. By spraying the composite material to the lake surface, the new method can remove algae and turbidity through flocculation and complete the planting process simultaneously so that HABs and eutrophication are effectively controlled.
Owner:BEIJING GREEN ECO ENVIRONMENTAL TECH
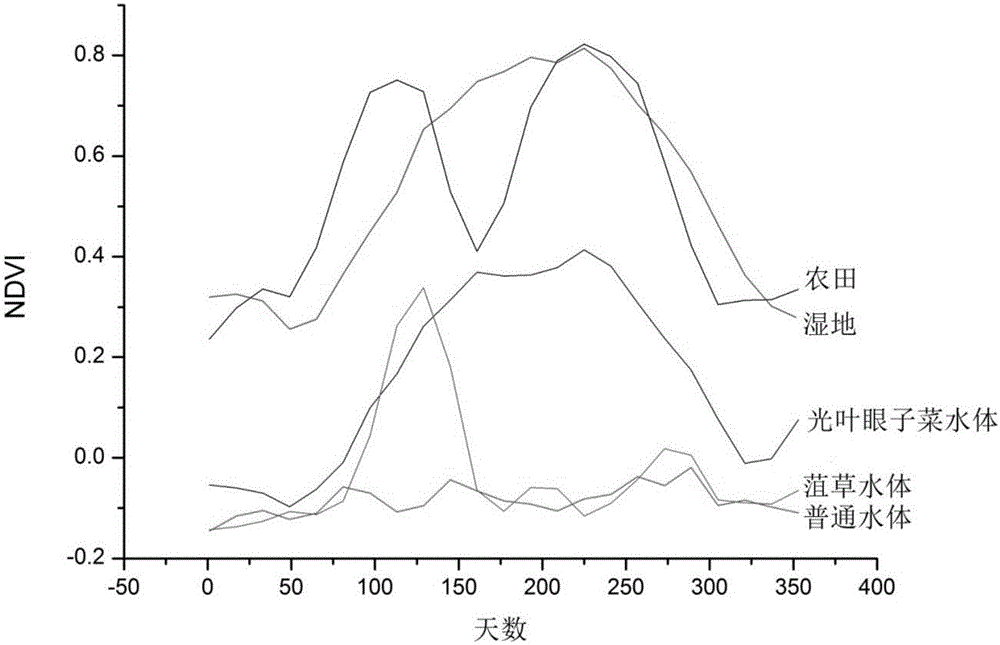
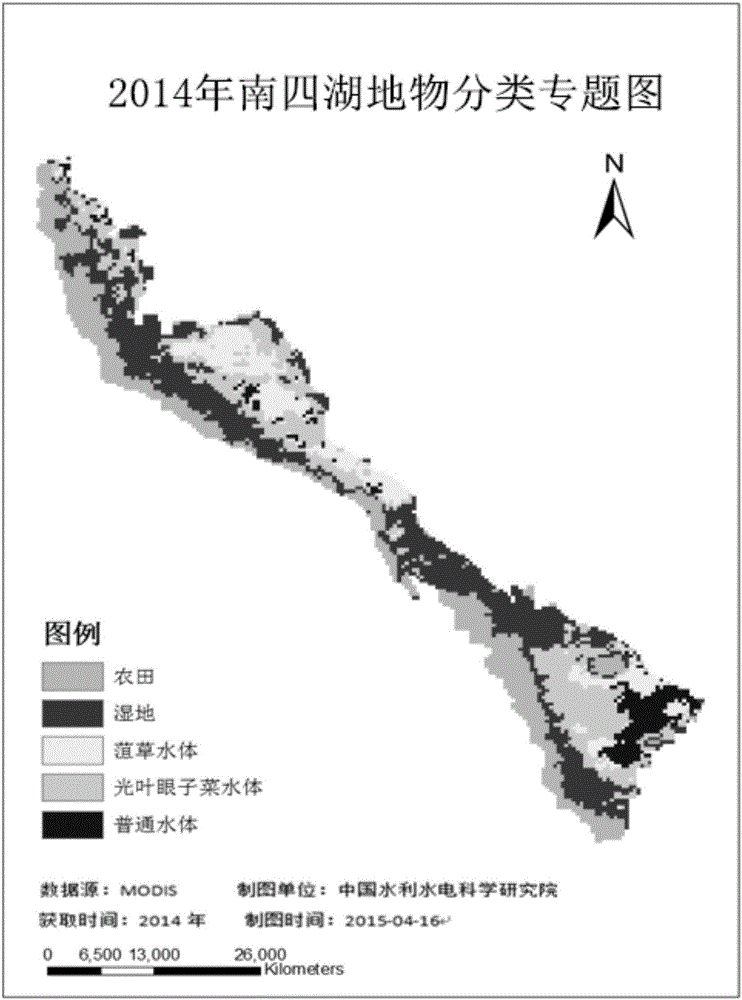
Method for indirect remote-sensing monitoring of water quality of macrophytic regions of macrophytic lakes
InactiveCN106442422AOvercome the difficulty of remote sensing inversion of water quality in aquatic grass areasMaterial analysis by optical meansVegetation IndexMacrophyte
The invention relates to the field of remote-sensing monitoring of water quality, in particular to a method for remote-sensing monitoring of water quality of macrophytic regions of macrophytic lakes. The method has the advantages that types and phonological characteristics of macrophytes are acquired through acquisition of a normalized differential vegetation index curve of the macrophytes in a research area, the macrophytes in the research area are recognized by combination of mono-temporal hyperspectral and multispectral images, and the problem that a traditional remote-sensing means performs remote-sensing retrieval on the water quality of the macrophytic regions difficultly due to the hindrance effect of the macrophytes is solved with the help of indicative effect of the macrophytes on the water quality.
Owner:CHINA INST OF WATER RESOURCES & HYDROPOWER RES
Ecology reparation method of eutrophication barricaded sea area using gracilaria marine macroalgae
ActiveCN101331849AHigh transparencyAvoid elevationClimate change adaptationEnergy based wastewater treatmentOpen seaMacrocystis pyrifera
The invention relates to an ecological method for restoring eutrophication enclosure sea area by Gracilaria Greville macrophyte. The ecological method for restoring eutrophication enclosure sea area mainly comprises the following steps: collecting the seedlings of Gracilaria, Gracilaria seedling transportation, domestication in sea area, building a dam and enclosing sea in eutrophication sea area, cutting off the tide of the open sea and carrying out ecological restoration. After the Gracilaria which is cultivated in a large scale in the eutrophication sea area is introduced and cultivated, the Gracilaria can absorb the superfluous dissolution-typed nutrient salt with a great deal for supplying for self-growth, can restrain the explosible growth of monoplast algae meanwhile and can also absorb mud and sand; the Gracilaria can be gained again so as to transfer the nutrient matters in water body out of a pollution system, improve the water quantity and restore the ecology of the sea area; the water body after ecological restoration is exchanged with the environment again, thus achieving the purpose of relieving and eliminating eutrophication of the sea area, eliminating eutrophication can be realized gradually, meanwhile higher economic value can be produced. The method is applicable to carrying out ecological restoration for the eutrophication enclosure sea area.
Owner:SHANGHAI FISHERIES UNIV
Submerged macrophytes restoring process guided by water conservation fishery
InactiveCN101960951ARestrict growthImprove water qualityClimate change adaptationCultivating equipmentsChemical oxygen demandFood chain
The invention discloses a submerged macrophytes restoring process guided by water conservation fishery. By stocking silver carp and bighead carp and reducing COD (chemical oxygen demand), TP (total phosphor), chlorophyll and other chemical indexes of the water body, the process effectively reduces the algae biomass in the water body, improves the water body transparency, and achieves the aim of preventing algal bloom and improving the water quality, so an excellent growing condition is provided for aquatic macrophytes (in particular, the submerged macrophytes); and by adding fish and other key organisms eating attaching organisms, which is a key link in a food chain, the attaching organisms growing vigorously on the surface of the submerged macrophytes can be removed in time, and the aim of restoring the submerged macrophytes can be achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Method for implanting and cultivating Gracilaria bursa-pastoris in north pond
InactiveCN101779595AHigh economic valueGood purification effectClimate change adaptationCultivating equipmentsMacrocystis pyriferaEutrophication
The invention provides a method for implanting and cultivating Gracilaria bursa-pastoris in a north pond. By using the method, the problems of water eutrophication and the like, caused by the ecological imbalance owning to using the prior art for signal animal breeding in the north pond, can be solved. The cultivation process of the invention can be divided to a sprout proliferation phase, a bottom sowing propagation phase, an increasing interharvesting phase and an overwintering seedling protection phase. By using the invention, the problem that owning to the change of factors such as climate, growing environment and the like in the north, the transplanting of south macrophyte fails, can be solved; the method has effects of low input and high output, and the ratio of the fresh weight input to fresh weight output of the algae is 1:1500. The yield per mu is 1500kg. The method of the invention can be used to fill the gap of cultivating macrophyte in aestival pond of northern areas and the diversity of algae resources in northern China is enriched.
Owner:MARICULTURE INST OF SHANDONG PROVINCE
Biological and ecological sectional method for purifying and treating domestic sewage
InactiveCN101602563AMaintain ecological balanceImprove purification effectTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentFood chainWater quality
The invention discloses a biological and ecological sectional method for purifying and treating domestic sewage, comprising the following steps: sending the sewage into a first treatment system, comprising a hydrolysis acidification pool, a contact oxidation pond and a anaerobic settling tank, then sending the sewage into a second treatment system, comprising a biofilm belt aeration pipe oxidation pond; finally sending the sewage into a third treatment system, comprising a biofilm belt deep processing oxidation pond. The organisms for purifying and treating domestic sewage in three stage continuously comprises bacteria, algae, protozoa, metazoan, large-scale plants, fish, benthic animals and the like which form complete food chains and ecosystems and the organisms can deeply treat domestic sewage and has high nitrogen and phosphorus removal rate. By using the invention, the degradation function of natural organisms can be fully achieved, thus the water quality purification and improvement can be realized. The method has the advantages that the system has stable running, strong impact resistant and load resistant ability, high safety and high system controlling and regulating, the systematic upgrading of water quantity and water quality can be easily realized and a park-like sewage treatment plant can be established by combine the system with landscapes.
Owner:袁伟刚
Facility for treating and recycling animal waste comprising methanisation, cultivation of microalgae and macrophytes, and vermiculture
ActiveUS20160264484A1No wasteAvoid disadvantagesFlowers cultivationBio-organic fraction processingElectricitySludge
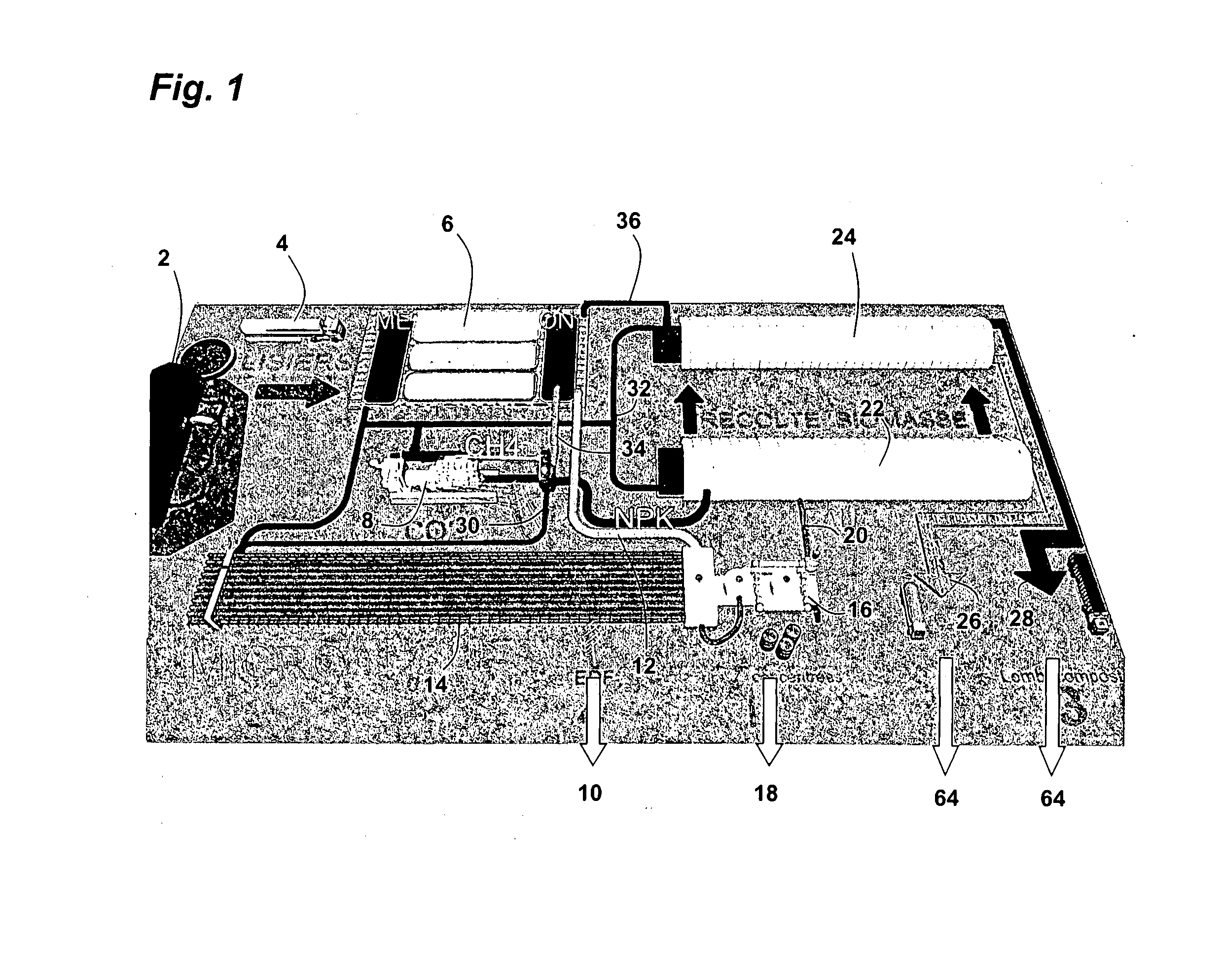
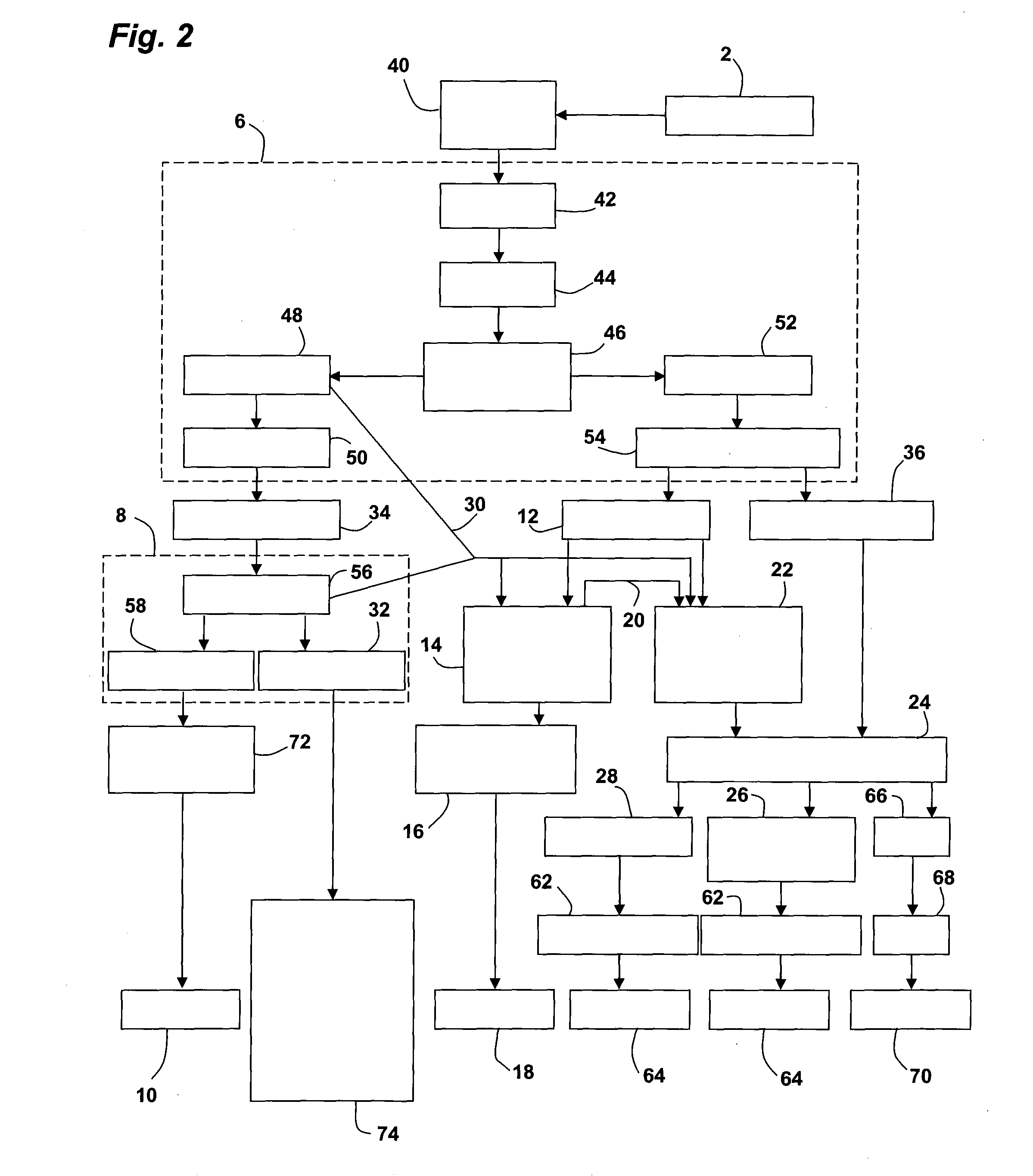
A facility for treating and recycling animal waste (2), including a unit (6) for methanizing the waste including treatment of the obtained biogases, a cogeneration unit (8) delivering electricity and heat (32) from the biogases, and a unit for hydroponically cultivating microalgae (14) in photo-bioreactors supplied by the liquid phase (12) of the organic residues from the methanization. The facility further includes a unit for cultivating macrophytes (22) supplied with water (20) leaving the unit for cultivating microalgae, and a vermiculture unit (24) fed by harvesting the macrophytes (22) and by the sludge (36) coming from the raw digestate from the methanization.
Owner:SKYWORLD INT OVERSEAS
Takifugu obscurus parent and scatophagus argus pond greenhouse overwintering mixed culture method
ActiveCN106665427AImprove water qualityReduce construction investmentClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaMixed cultureGreenhouse
A takifugu obscurus parent and scatophagus argus pond greenhouse overwintering mixed culture method is characterized in that a land with a flat floor is selected, the depth of a pond is more than 2m, a steel wire rope flexible plastic film greenhouse is built above the pond, takifugu obscurus parents are transferred into the pond greenhouse for overwintering when the water temperature of an external pond is reduced to 13 DEG C in November, scatophagus argus overwintering stocking time is similar to takifugu obscurus overwintering stocking time, a takifugu obscurus feedstuff feeding method is as same as an external pond conventional culture method, feeding of commercial feedstuff is omitted if aquatic macrophytes are placed in the scatophagus argus pond, water change is avoided when the water temperature of the pond in the greenhouse is lower than 12 DEG C, water is changed once every three weeks when the water temperature of the pond in the greenhouse is higher than 12 DEG C to 15 DEG C, the water temperature of the external pond is kept higher than 15 DEG C in April every year, takifugu obscurus and scatophagus argus are dragged out of the greenhouse through a net and cultured in the external pond, the scatophagus argus is firstly picked out and placed into another net cage when the net is dragged, the takifugu obscurus parents are directly transported, and the scatophagus argus is dragged out of the greenhouse or cultured in the pond after the takifugu obscurus is dragged out of the pond through the net.
Owner:SHANGHAI FISHERIES RES INST
Construction method for water body self-cleaning ecological chain
InactiveCN105417709AImprove MicroecologyImprove water qualitySustainable biological treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentEutrophicationWater source
The present invention relates to a construction method for a water body self-cleaning ecological chain. The method comprises the following steps: feeding parent bacteria of common beneficial compound bacteria in water, wherein the feeding frequency is 1 time / month, and the feeding density of the parent bacteria of the common beneficial compound bacteria is 300 g / km(3); domesticating cladocera zooplankton, and enabling the cladocera zooplankton to eat cyanobacteria in a polluted water body; according to polluted indexes of the water body, feeding beneficial microorganisms in the water body, wherein the beneficial microorganisms can live together with the cladocera zooplankton; and planting submerged macrophytes on the water bottom, planting emergent macrophytes at shoreside of the water body, and planting floating macrophytes on the surface of the water body. The water body ecological restoration effects can ensure that water is crystal clear, main eutrophication indexes of water can reach a national surface water third-class water quality standard (a drinking water resource basic standard), and wherein data can be measured by a a water quality monitoring authority.
Owner:NINGBO QINGQUANSHUI ECOLOGICAL TECH
Process for biostabilization and humification of biological sludge in planted filtering beds
InactiveCN101687675AReduce visual impactSludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningBio-organic fraction processingSludgeMacrophyte
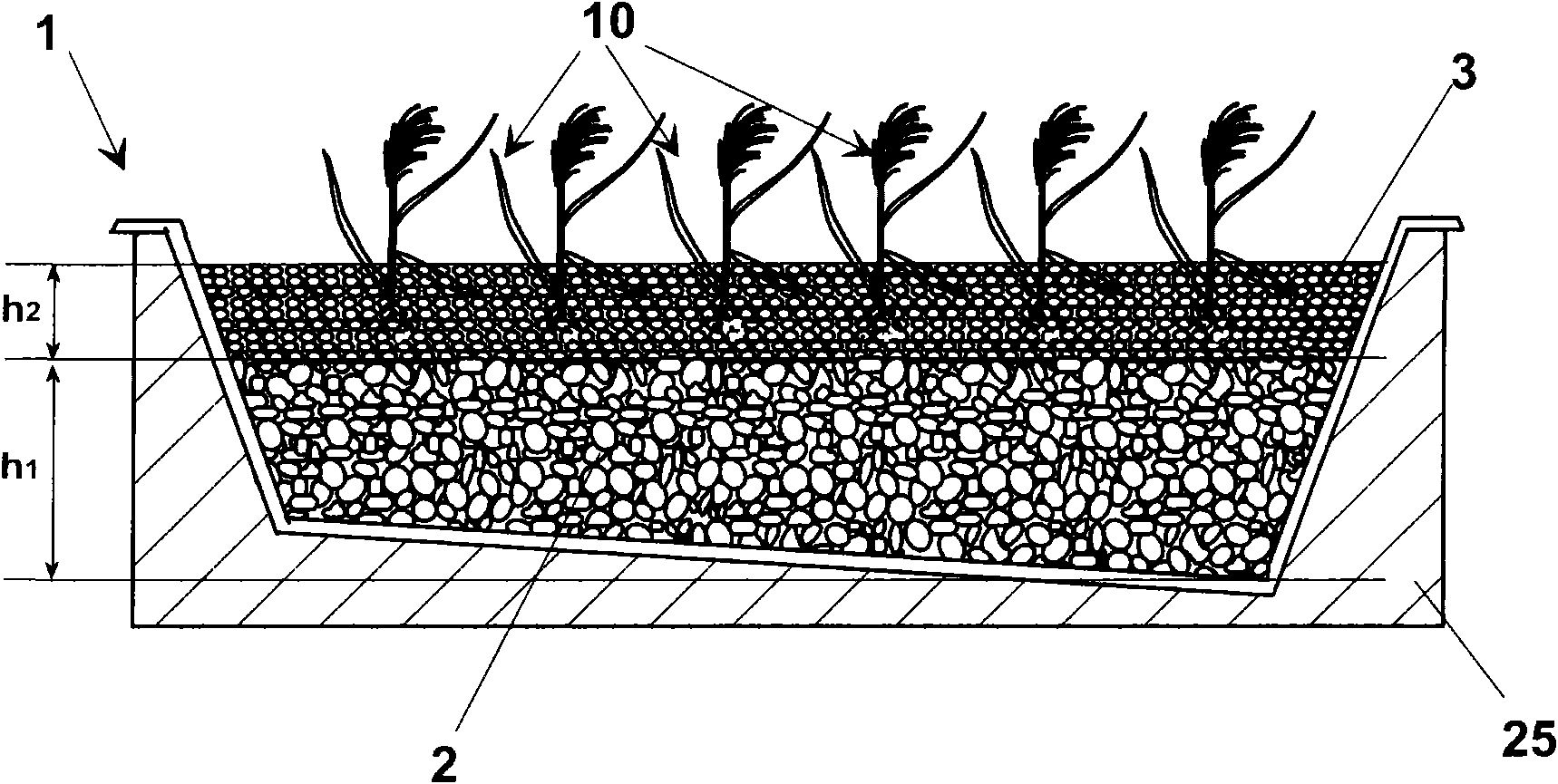
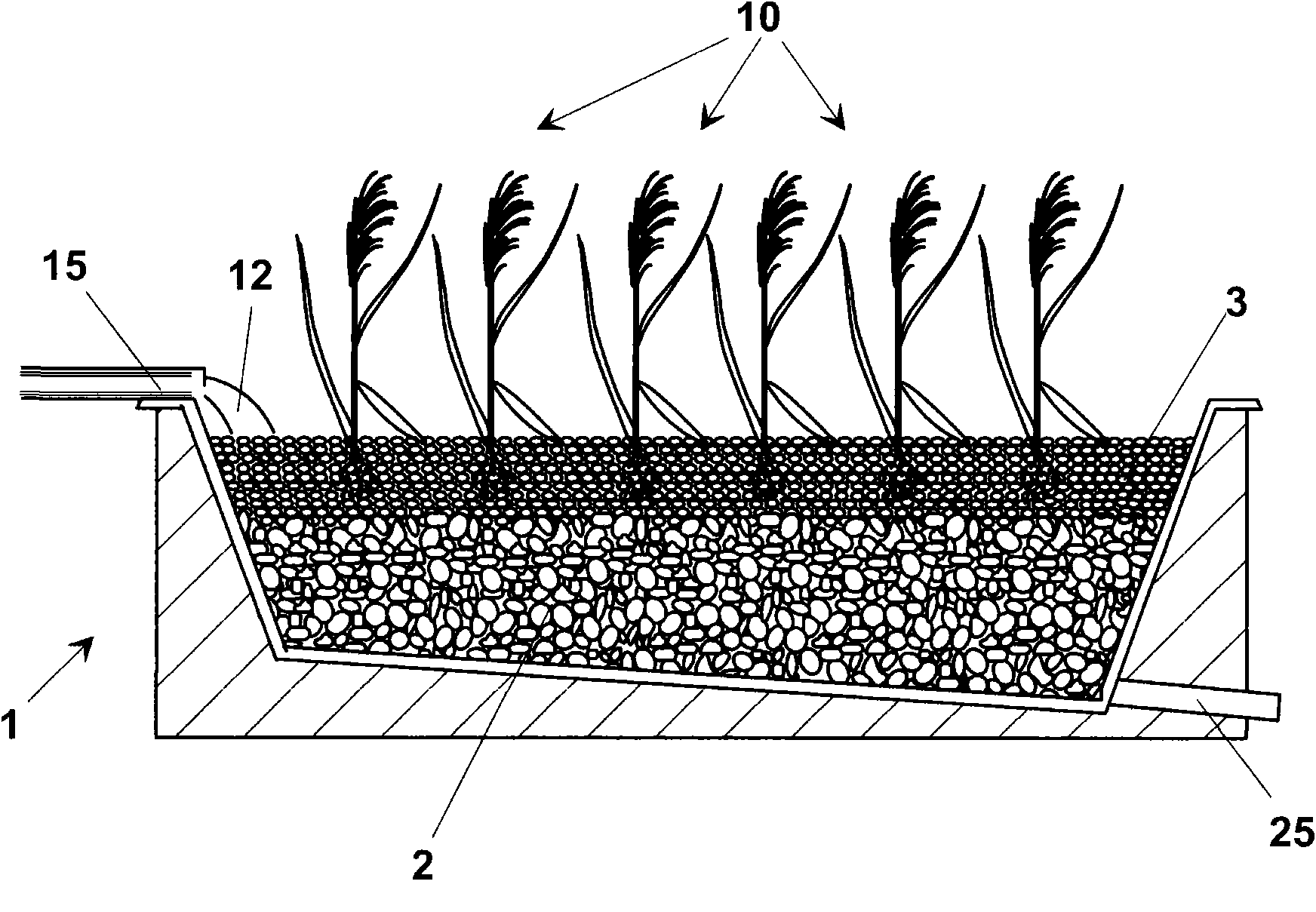
A process for stabilization of biological sludge provides the step of laying in a containing volume, or basin (1), a draining material (2). In particular, the layer of draining material (2) can be a layer of gravel having granulometry set between 40 and 70 mm and a height (hi) about 25 cm. On the first layer (2) a second draining layer (3) can be laid comprising a material, for example gravel having granulometry less than the first layer (2), set between 4 and 6 mm. The second layer (3) has preferably a height (h2) about 15 cm. Once made the draining layers (2, 3) a planting step is made in the second layer (3) of a plurality of seedlings of an aquatic macrophyte, preferably Phragmites australis (10). The base granular filtering gravel layer has also the function of supporting the root ofthe seedlings. To ensure a high efficiency of the process a measured density of plants is chosen, corresponding to a relative distance between two seedlings of Phragmites australis set between 40 and60 cm. once achieved a measured vegetative growth, a first spilling in the containing volume (1) is carried out of an amount of biological sludge (12). The amount of sludge (12) fed in the containingvolume (1) corresponds to a predetermined height, set between 2 and 4 cm, of the layer of sludge (12) on the draining layer (3).
Owner:ACQUE +1
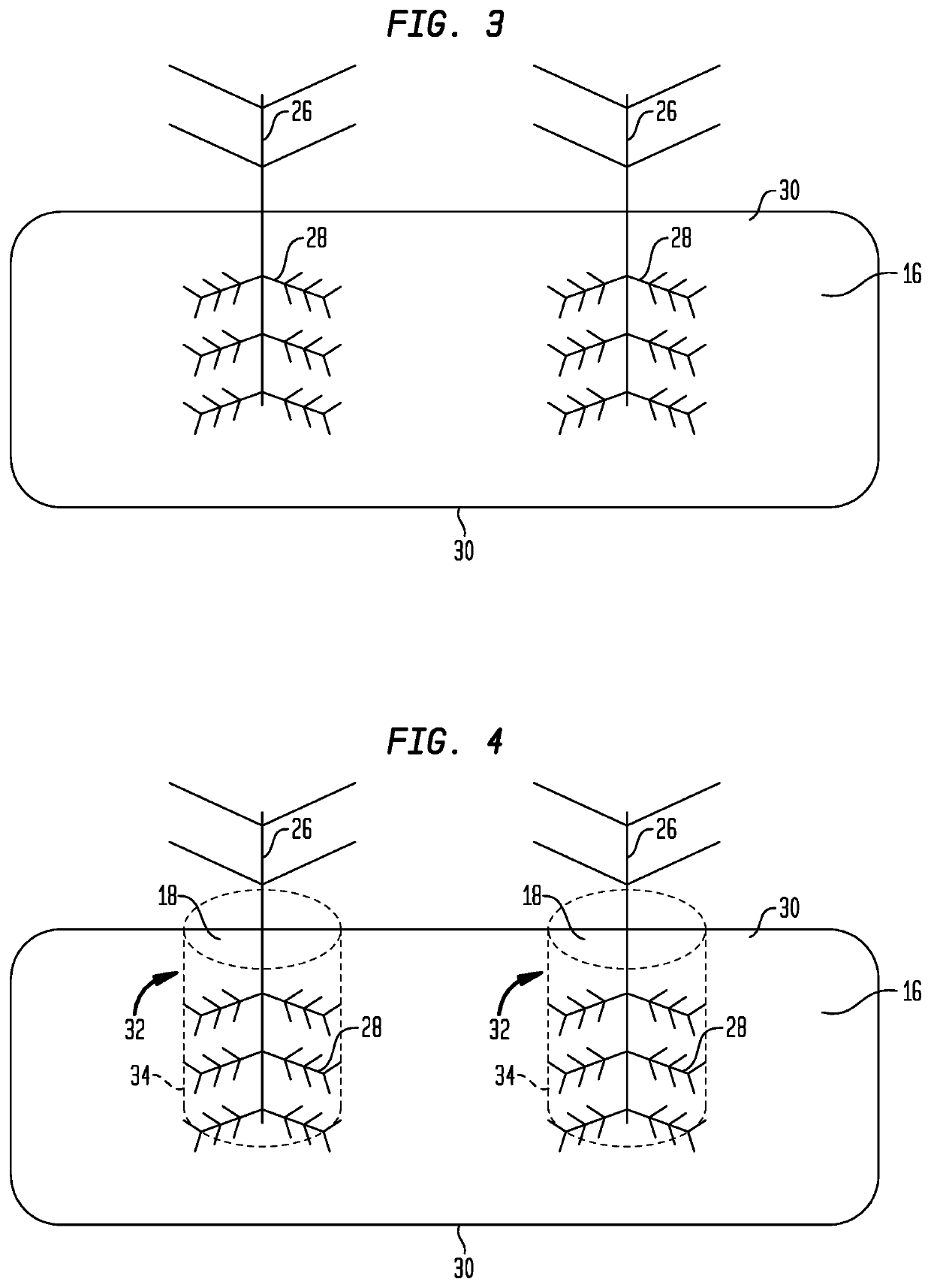
Plant biomass management system and method
A method for managing plant biomass in a wetland containing floating macrophytes includes the steps of draining a body of water having wetland plants growing thereon and permitting the plants to dry. The dried plant matter is then tilled into the bed of the water body, along with a coagulant. The body of water is then re-flooded, and another remediation cycle begun. In a particular embodiment the bed of the body of water has a first depth over a first area of the bed and a second depth greater than the first depth over a second area of the bed. Drainage is to a depth sufficient to expose the first area and leave depressions above the second area at least partially filled, plants in the depressions serving to re-inoculate the wetland upon reflooding.
Owner:DEBUSK THOMAS A
Floating aquatic plant culture systems and associated methods
A floating plant culture system has improved strength and durability and includes a substantially planar platform having a length along opposed sides thereof and a width along front and back thereof generally perpendicular to the sides. The platform is adapted for growing a culture of attached plants including micro- and macrophytes thereon. Beneath the platform are affixed a plurality of cells extending in bridging relation to the sides and open at each end adjacent the sides. The cells are placeable in fluid communication with a body of water desired to be remediated. Affixed along at least a portion of the sides extend a pair of opposed hollow beams, for providing flotation to the platform. The beams are also placeable in fluid communication with the body of water, and an upper surface of the platform is floodable by the body of water from beneath for submerging plants attached thereto.
Owner:AQUAFIBER TECH CORP
Apparatus merging wetland plants with a floating substrate to treat pollution in any river, lake or body of water
ActiveUS8382982B2Extended stayOxidize-reduce organic, inorganic pollutantsWater cleaningWater contaminantsMacrophyteEnvironmental engineering
Apparatus to treat pollution in rivers, streams, lakes, bays, ports and all bodies of water, employing as methodology wetland plants or macrophytes growing atop a wire or rigid frame basket filled with polygons or other irregular shaped objects of various configurations. The root system of the macrophytes are merged with and grow down amid the substrate composed of small polygons, other irregular shaped hollow, plastic, ceramic objects or other materials. The substrate provides nutrients, oxygen and sanctuary to bacteria, thereby reducing and eliminating pollutants in all bodies of water.
Owner:HONDULAS JOHN L
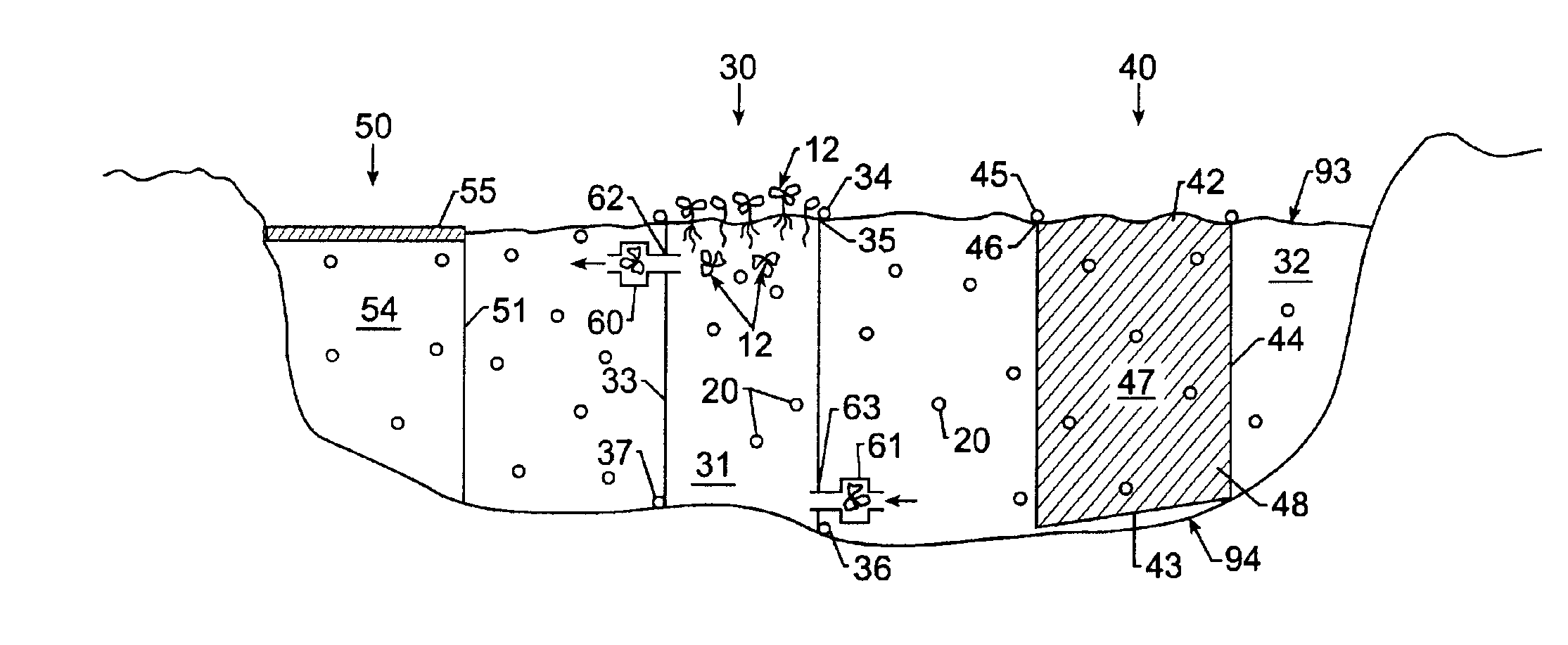
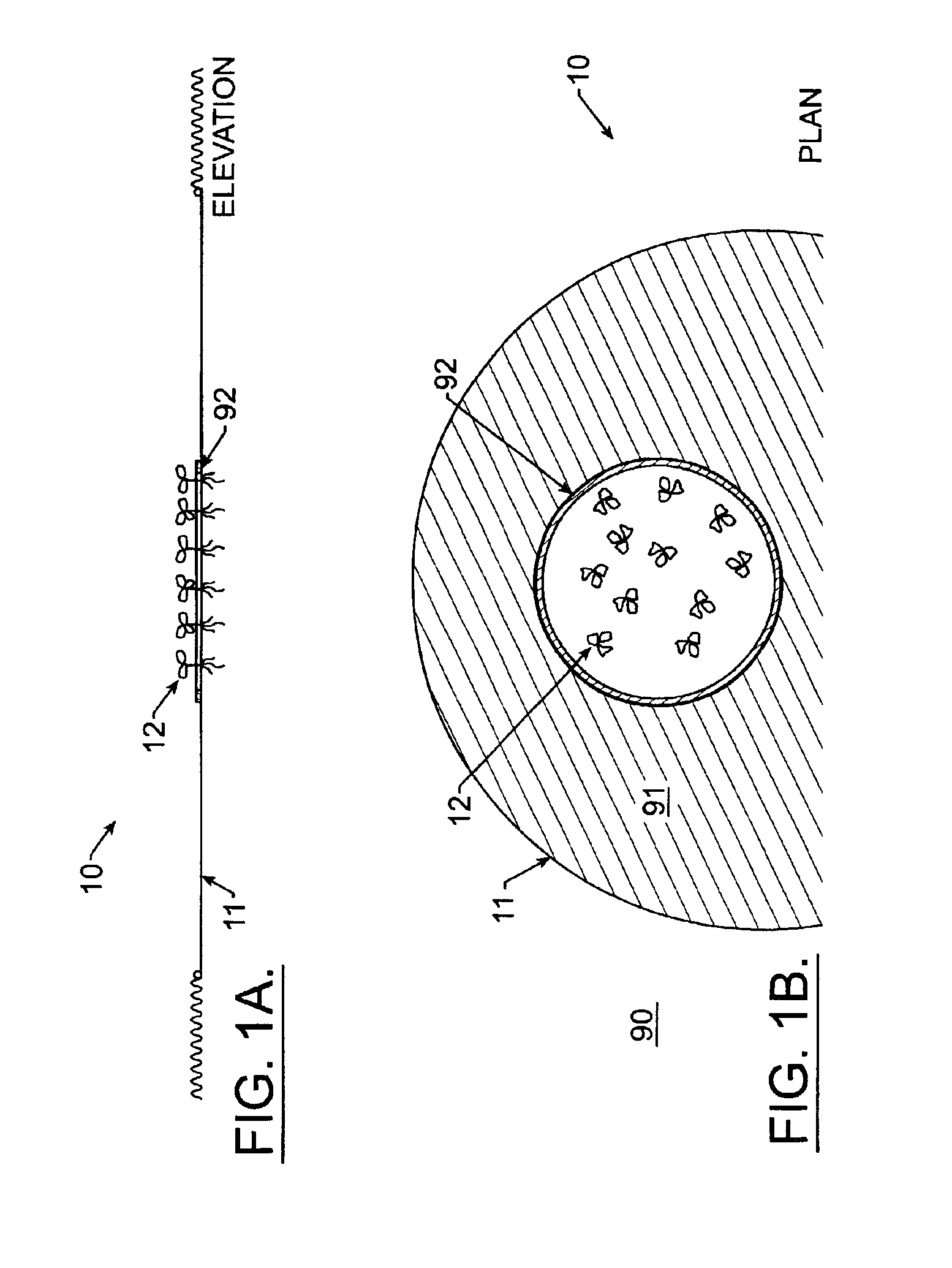
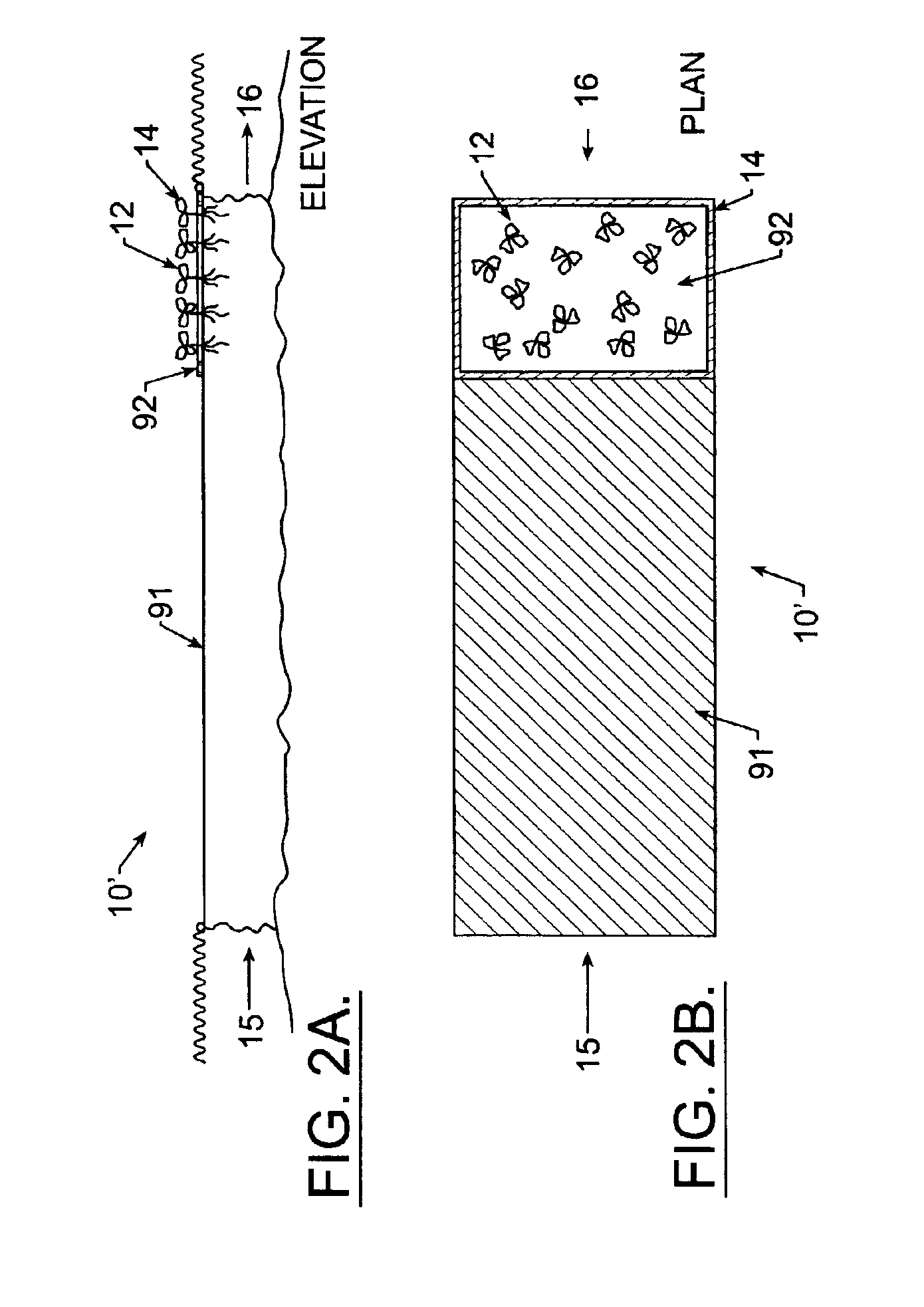
Algal and nutrient control system and method for a body of water
InactiveUS6986845B2Reduce usageTreatment using aerobic processesSpecific water treatment objectivesToxic algaeWater Hyacinths
A system to control nutrients, suspended algae, and filamentous algae in lakes, ponds, and estuaries includes a structure for containing macrophytic vegetation. One embodiment segregates a column of water within a body of water desired for remediation and shields the water column from sunlight sufficiently to kill phytoplankton therein, the lysis thereof releasing nutrients. The released nutrients are sequestered, and remediated water is replaced in the water column with water from the body of water. Floating or submerged macrophytes can be introduced in combination with shading and induced water movement to optimize nutrient uptake by the macrophytes. Water column shading may also be achieved by the macrophytes themselves, or by other means. The macrophytes can include floating aquatic plants, such as water hyacinths, submerged aquatic plants, and terrestrial or aquatic plants caused to float artificially. The invention also deals with toxic algae in a safe and sequestered way.
Owner:DEBUSK THOMAS A +1
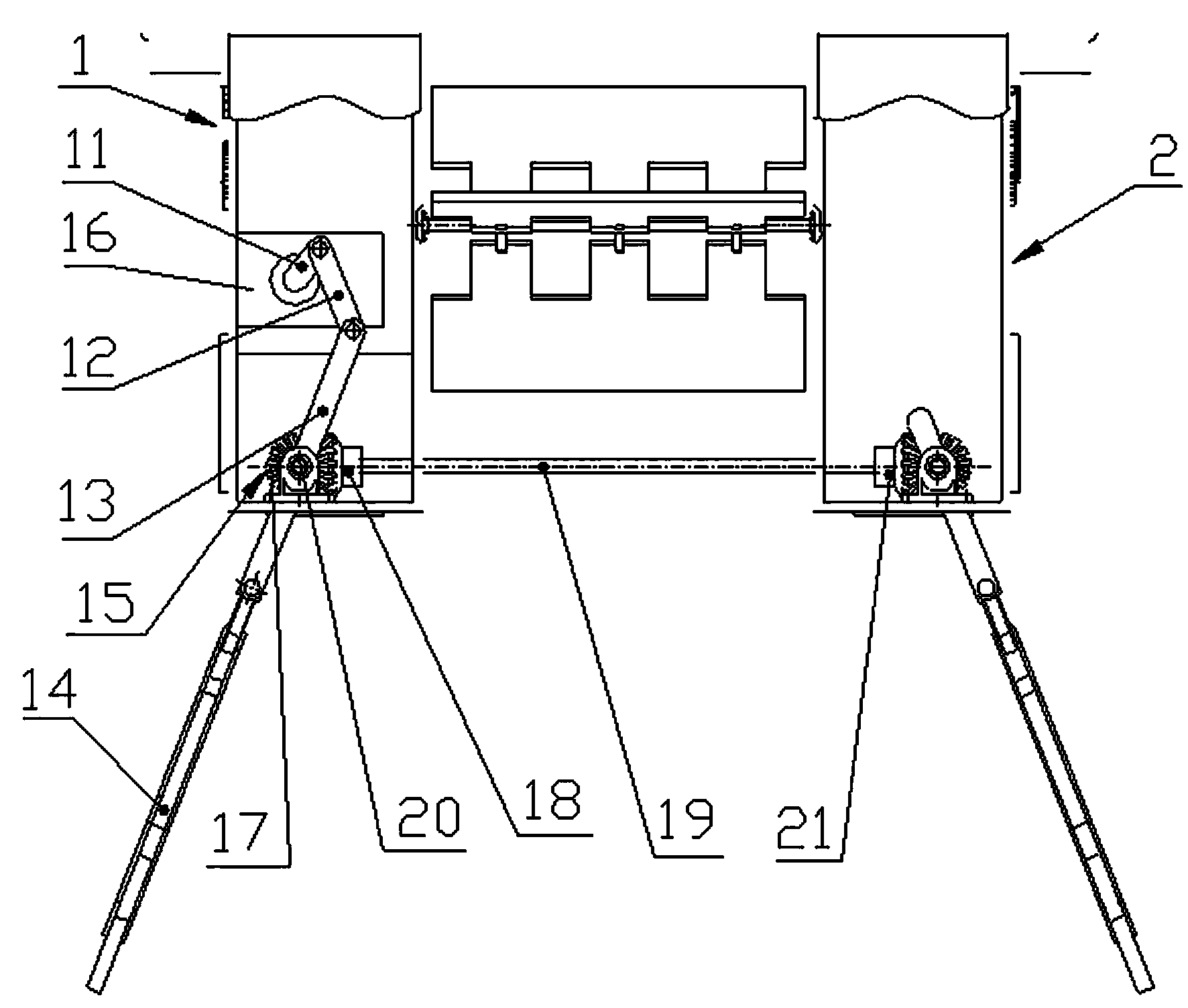
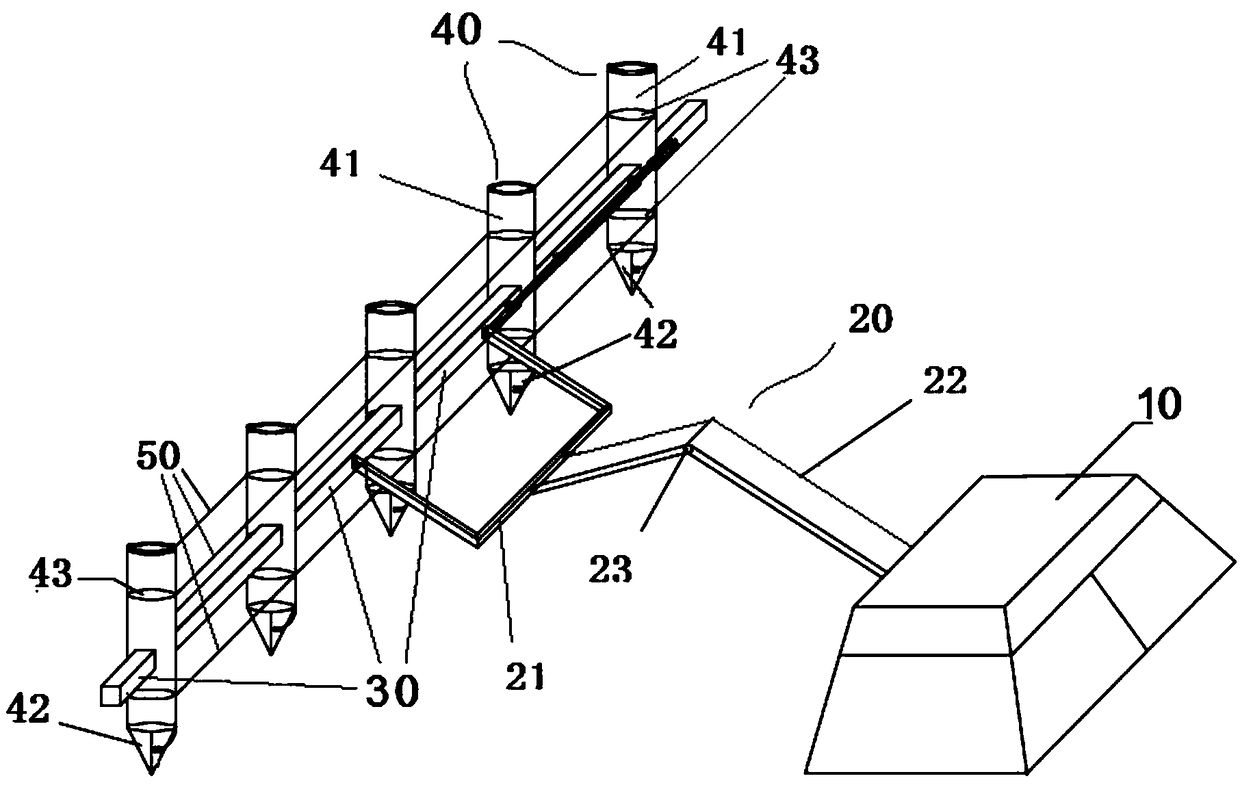
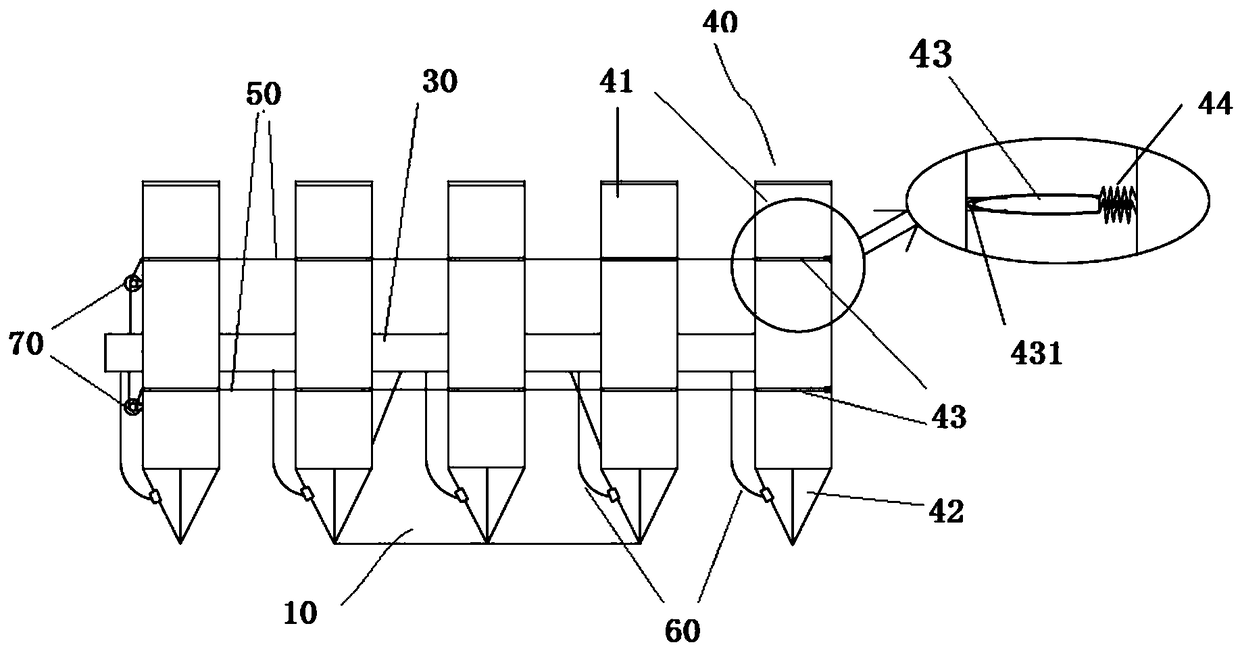
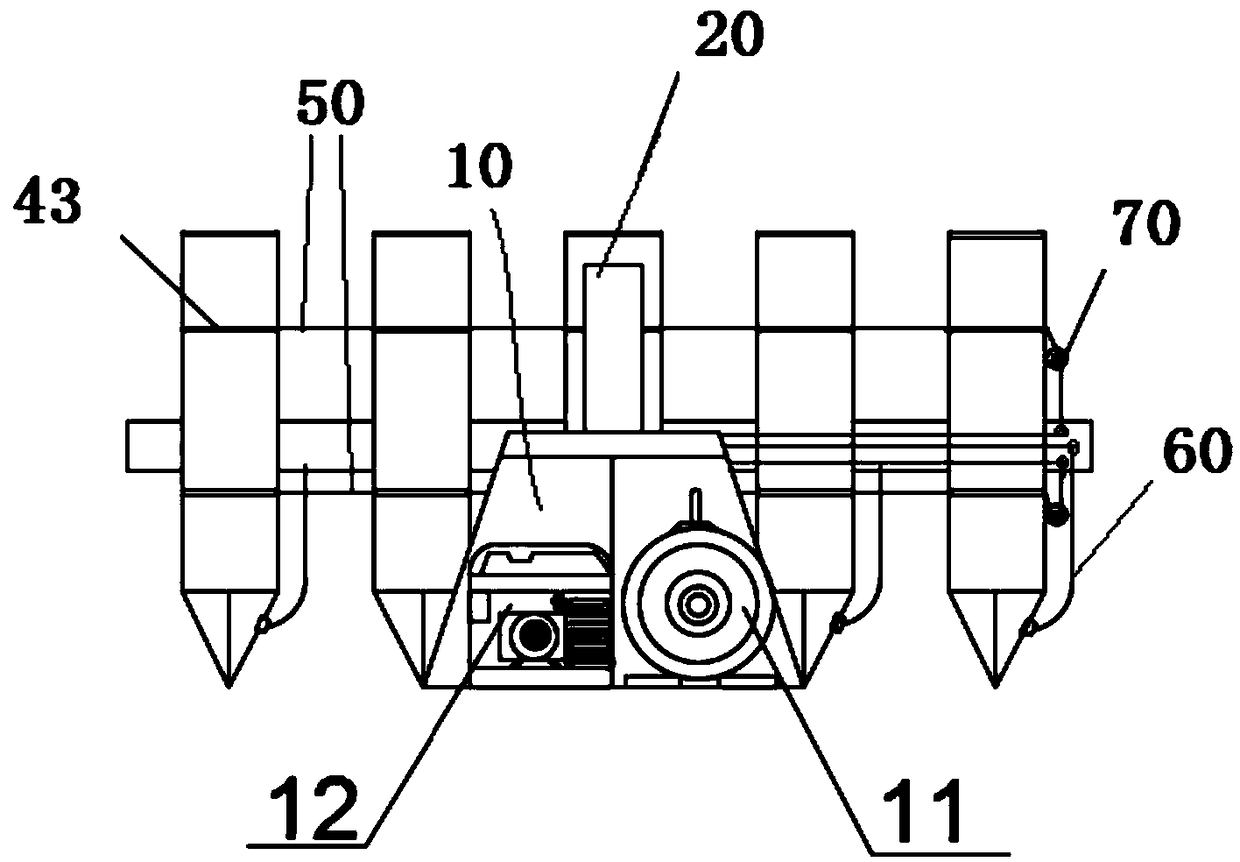
Mechanized submerged macrophyte planting device
InactiveCN108901801AFast plantingHigh degree of mechanizationAgriculture gas emission reductionCultivating equipmentsMacrophyteEngineering
The invention relates to a mechanized submerged macrophyte planting device comprising a console, a mechanical arm connected with the console, a plurality of planters arranged at intervals and connecting pieces for connecting the plurality of planters; each planter comprises a columnar main part, a cone part located at the lower end of the columnar main part and at least one placing tray arranged in the columnar main part, an opening is formed in the side wall of the columnar main part, and the placing tray can enter and exit from the columnar main part through the opening; the planting devicefurther comprises lines for connecting the placing trays of all the planters in series, and the console is capable of applying a force to the lines, so that all the placing trays are pulled to outwards move through a gap; the cone part comprises a fixed part and a movable part; and the planting device further comprises connecting lines, one end of each connecting line is connected with the movablepart of the cone part of the corresponding planter, the other end of each connecting line is connected to the console, and the console is capable of applying a force to the connecting lines, so thateach movable part is pulled and opened.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
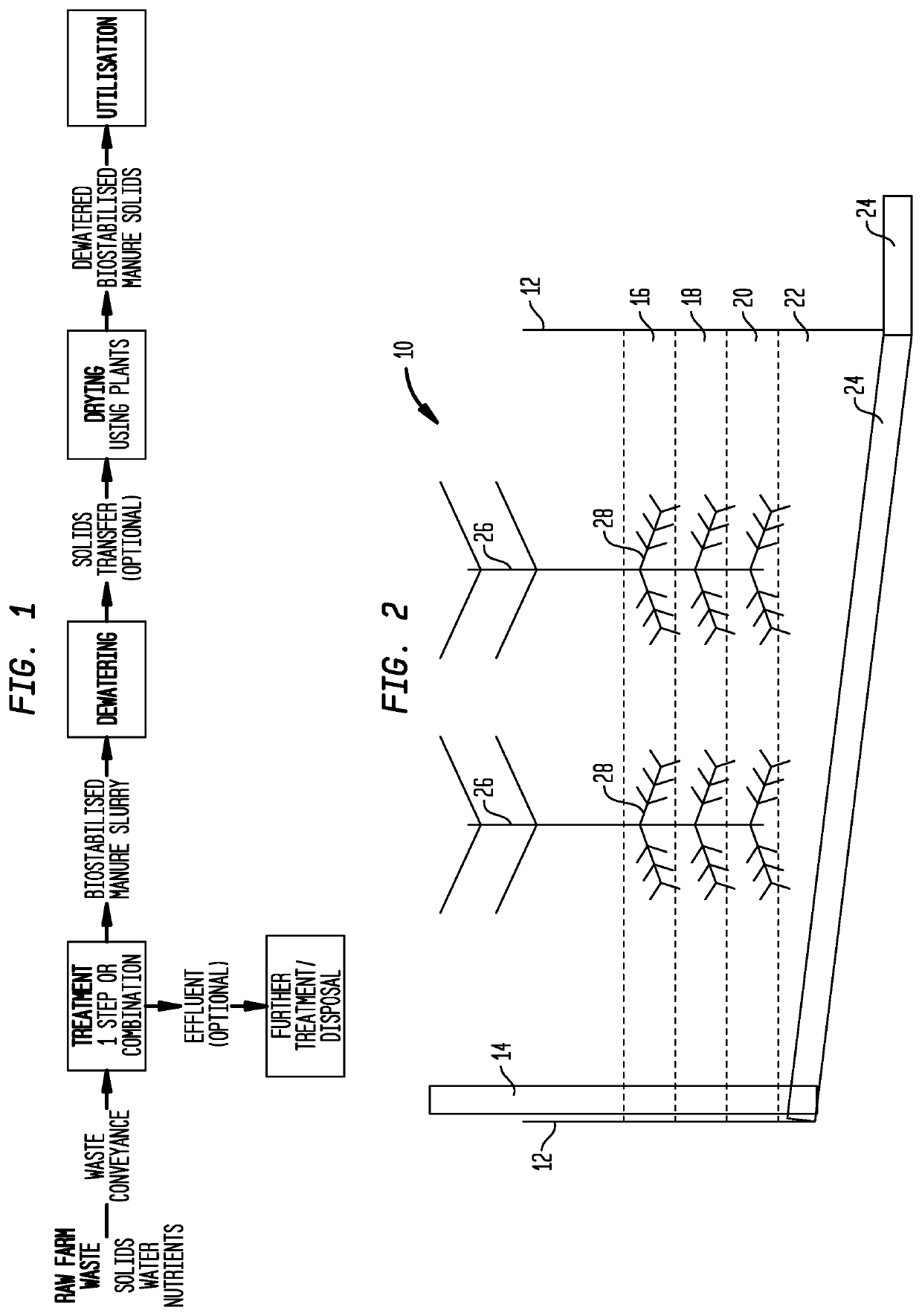
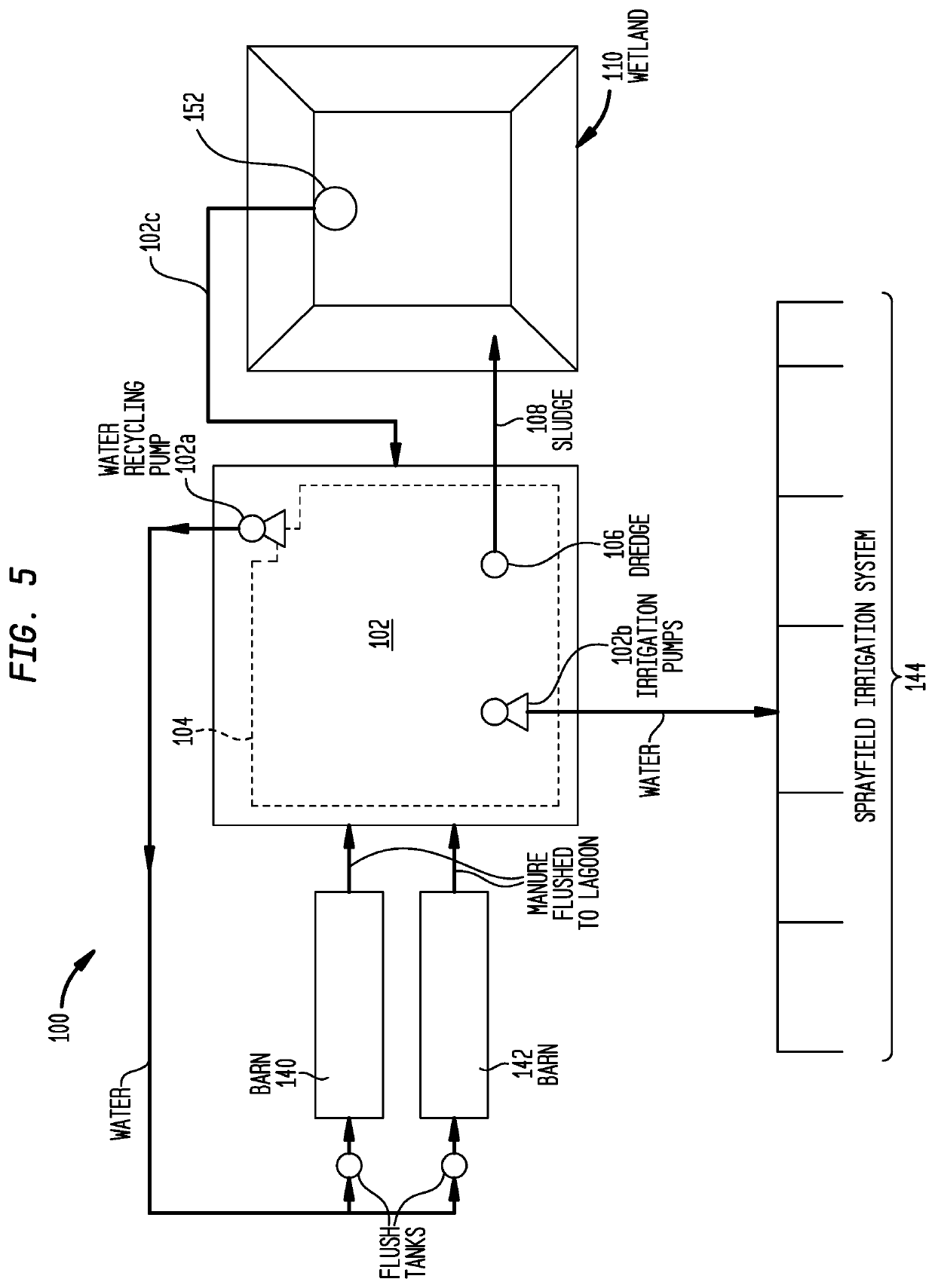
Method to Improve the Dewatering of Farm Waste Sludges
InactiveUS20200223731A1Sludge treatment by de-watering/drying/thickeningSettling tank with pumpMacrophyteEngineering
A system for processing a manure sludge includes in a preferred embodiment: (a) an anaerobic digester; (b) a drying bed planted with a plurality of macrophytes, said macrophytes being nurtured so they are growing and engaging in evapotranspiration bed; and (c) a transfer assembly adapted to deliver a manure sludge from the anaerobic digester to the drying bed so that the roots of the plants contact manure sludge transferred to the drying bed so that the sludge is dried by evapotranspiration. The anaerobic digester and transfer assembly are adapted to: (i) treat raw farm waste slurry to provide a biostabilized manure sludge composition; and (ii) deliver the biostabilized manure sludge composition to the drying bed at a solids content of at least about 1% by weight.
Owner:PHINITE INC
Ecology reparation method of eutrophication barricaded sea area using gracilaria marine macroalgae
ActiveCN101331849BHigh transparencyAvoid elevationClimate change adaptationEnergy based wastewater treatmentOpen seaMacrocystis pyrifera
The invention relates to an ecological method for restoring eutrophication enclosure sea area by Gracilaria Greville macrophyte. The ecological method for restoring eutrophication enclosure sea area mainly comprises the following steps: collecting the seedlings of Gracilaria, Gracilaria seedling transportation, domestication in sea area, building a dam and enclosing sea in eutrophication sea area, cutting off the tide of the open sea and carrying out ecological restoration. After the Gracilaria which is cultivated in a large scale in the eutrophication sea area is introduced and cultivated, the Gracilaria can absorb the superfluous dissolution-typed nutrient salt with a great deal for supplying for self-growth, can restrain the explosible growth of monoplast algae meanwhile and can also absorb mud and sand; the Gracilaria can be gained again so as to transfer the nutrient matters in water body out of a pollution system, improve the water quantity and restore the ecology of the sea area; the water body after ecological restoration is exchanged with the environment again, thus achieving the purpose of relieving and eliminating eutrophication of the sea area, eliminating eutrophication can be realized gradually, meanwhile higher economic value can be produced. The method is applicable to carrying out ecological restoration for the eutrophication enclosure sea area.
Owner:SHANGHAI FISHERIES UNIV
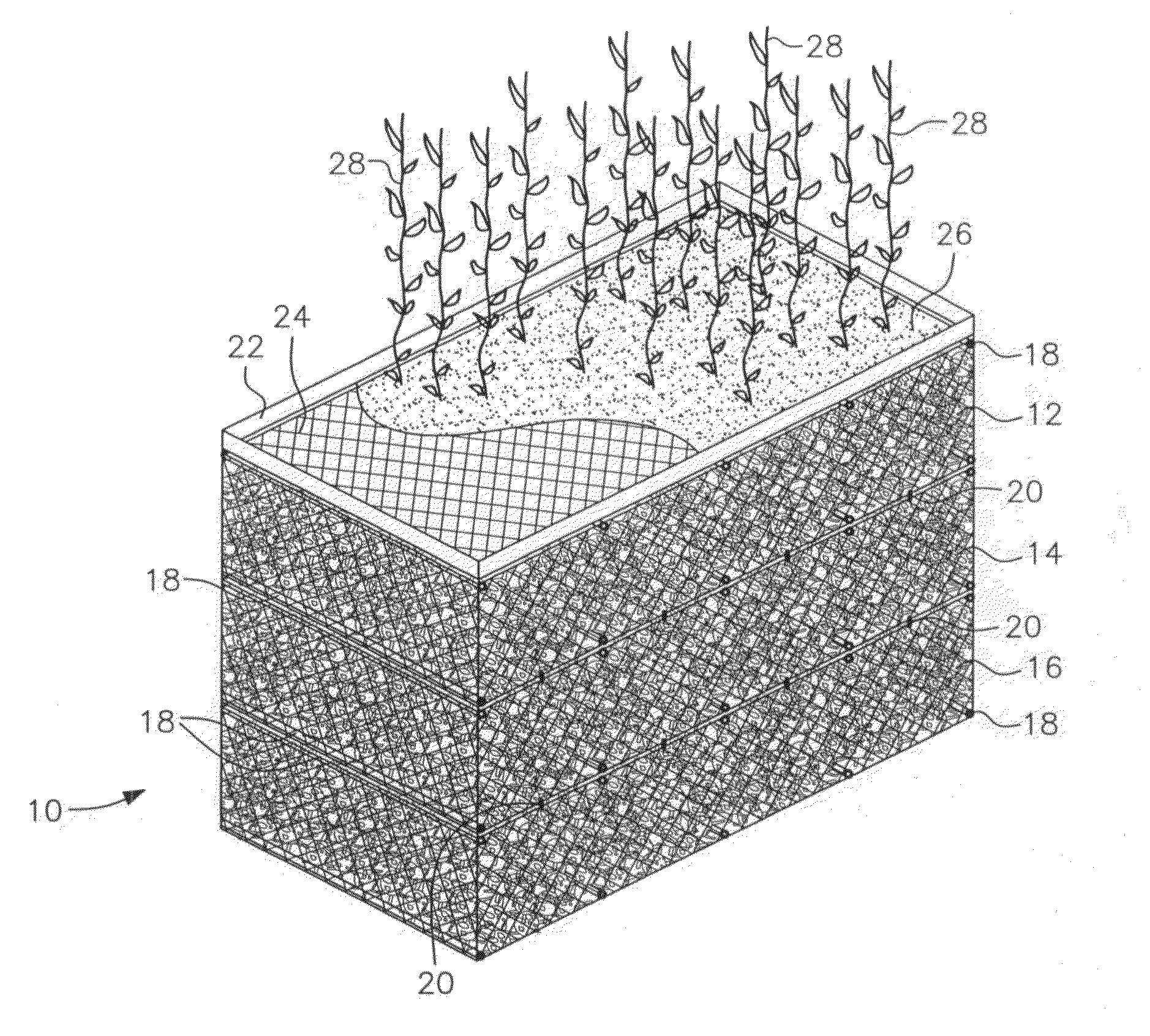
System and devices for assisting in the planting and growth of floating macrophyte plant species in water purification
InactiveUS20130091767A1Climate change adaptationSustainable biological treatmentCross-linkPlanar polygon
A system and device for assisting in planting and growing floating macrophyte-type plant species in uses for the purification of water. The system comprises the use of three devices preferably formed from low-density plastic materials: a plane polygonal floating structure with elements for connecting to other floating structures, provided with at least one inner coupling bar connected to the contour of the floating structure or to another inner bar by a flexible arc; a plane cross-linked structure with elements for anchoring to the floating structure and at least one central circular housing; and a basket or cone consisting of a flexible plastic material and for receiving a macrophyte plant, a root cutting or rhizome with a troncoconical form.
Owner:MACROFITAS
Construction method of foamed concrete vegetation nutrition enclosed cave
The invention discloses a construction method of a foamed concrete vegetation nutrition enclosed cave. The construction method comprises the following steps that the position and the size of the enclosed cave are determined on a side slope; anchor nails are driven into a rock mass of the side slope from the periphery of the enclosed cave; a degradable fiber cushion layer is laid along the anchor nails to form a pocket-shaped structure; a first nutrient medium is sprayed and seeded into a configuration, and the spraying thickness is 6-10 cm; subarbor or arbor seedlings are transplanted into the configuration with soil balls; and a second nutrient medium containing seeds is sprayed and seeded into the configuration, so that the second nutrient medium covers the soil balls. A structure for bearing medium and large plants such as subarbor or arbor seedlings can be formed through rivets, the degradable fiber cushion layer and the first nutrient medium, the subarbor or arbor seedlings can be limited through the second nutrient medium, and both the first nutrient medium and the second nutrient medium can provide survival conditions for plants; and by means of the construction method, the enclosed cave can be formed in the side slope, the medium and large plants can be planted, and necessary growth conditions are created for landscape layering sense and biological diversity.
Owner:江苏绿之源生态建设有限公司
Outdoor device for simulating pond ecosystem
ActiveUS20210267178A1Evaluating effectPisciculture and aquariaGymnasiumChemical contaminantsTransfer station
The disclosure provides an outdoor device for simulating a pond ecosystem comprising a plurality of simulated ponds connected together by pipelines and including an adjusting pool, a plurality of control groups and a plurality of treatment groups with different concentrations; the plurality of control groups and the treatment groups are randomly distributed in the ponds according to a random draw method or a random allocation method, and the adjusting pool is a transfer station for water inlets and outlets of the ponds. According to the device, the plurality of control groups and treatment groups are arranged in a system, achieving a scale of a middle-scale pond ecological simulation system, which can stimulate an actual complex hydrostatic ecological system including a plurality of aquatic macrophytes, algae, zooplankton, benthos and microorganisms, and evaluate the effects of the complex ecological efficiency caused by chemical pollutants entering an actual water body.
Owner:NANJING INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI MINIST OF ECOLOGY & ENVIRONMENT
Comprehensive treatment system for river
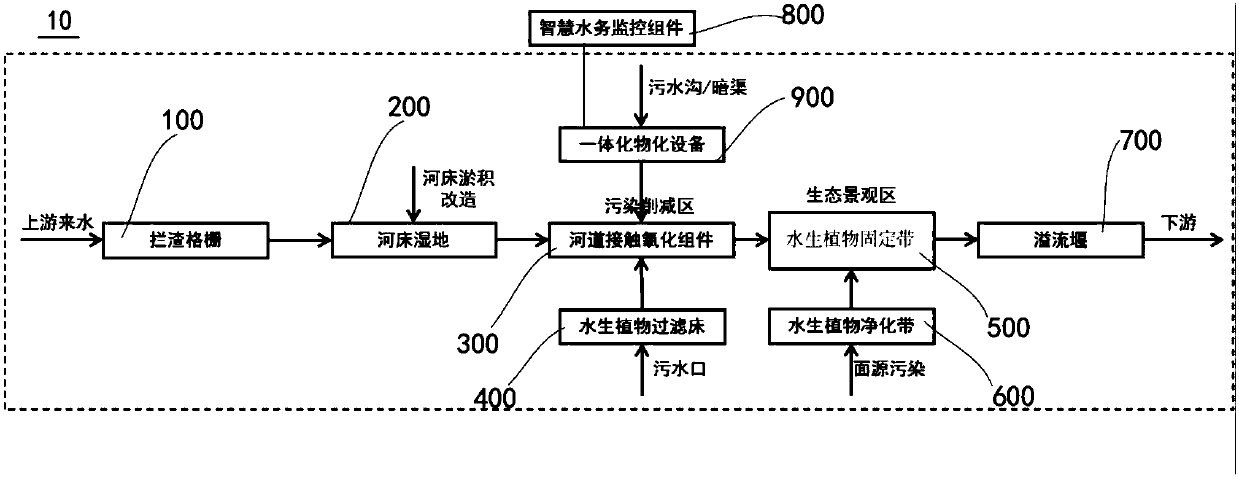
PendingCN107892448ATreatment using aerobic processesTreatment involving filtrationTreatment costsMacrophyte
The invention discloses a comprehensive treatment system for a river. The comprehensive treatment system comprises a slag retaining grid, riverbed wetland, a riverway contact oxidation component, an aquatic-plant filter bed, an aquatic-plant fixing zone and an aquatic-plant purification zone; wherein two ends of the slag retaining grid are erected on river banks located at sides of a riverway, andthe slag retaining grid is used for intercepting foreign matters on the surface of the river; the riverbed wetland is distributed on the river banks located at both sides of the river; the riverway contact oxidation component comprises an aeration and oxygenation part and a biofilm, the aeration and oxygenation part is arranged in the riverway for aeration and aeration, and the biofilm is fixed in the riverway; the aquatic-plant filter bed is arranged at a mixed water outlet of the riverway; and the aquatic-plant fixing zone and the aquatic-plant purification zone are arranged in the riverway. The comprehensive treatment system for the river has the advantages of a wide application scope and low treatment cost.
Owner:广州太和水生态科技有限公司
Landscaping method indoors through large plants without soil
InactiveCN1759659AAbsorb moreBright colorCultivating equipmentsSoilless cultivationEnvironmental designMacrophyte
Owner:郭晓来
Epidemic prevention method of macrophytes with soil on the root
InactiveCN101371654AReduce dosageLow costForestryInsect catchers and killersMacrophyteUltimate tensile strength
The invention relates to an epidemic prevention method for macrophyte with mud on roots, which comprises the flowing steps: 1. perforate position is marked on a parcel bag which wraps the mud on the roots; 2. a plurality of openings are opened on the perforate position marked on the parcel bag; 3. holes are drilled on the roots of the macrophyte from every opening; 4. insecticide is injected into the holes of the macrophyte roots. The good technical effect is as follows: low cost, high efficiency, simple site; good insecticidal effect, no pollution to environment; simple operation and reducing damage to tree as well as labor intensity.
Owner:SHENZHEN AUDAQUE DATA TECH
Method for preparing ultramicro living body bait from macrophyte
InactiveCN101869179AHigh nutritional valueWidely distributedAnimal feeding stuffMacrocystis pyriferaMacrophyte
The invention discloses a method for preparing an ultramicro living body bait from macrophyte, which can obviously improve the culture efficiency, reduce the production cost and provide a stable ad reliable food source for seeds of marine economic animals. The method comprises the following steps of: cleaning the macrophyte with pure water, soaking in seawater for 20 minutes, and drying by using a screen; adding sea snail pulp into the macrophyte for digestion reaction for 60 to 120 minutes, wherein 10ml of sea snail pulp is added into each 100g of macrophyte; mixing the digested macrophyte and clean seawater in a ratio of 1g:1ml, and crushing in a crusher for 5 minutes; centrifuging macrophyte-crushed liquid in a centrifugal machine at a speed of 2,000 turns / 10minutes, and taking supernate; and filtering the supernate by using a 20 mu m filter membrane to obtain filtrate.
Owner:DALIAN FISHERIES UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com