Macrophyte-based bioplastic
A technology of bioplastics, aquatic plants, applied in the field of polymeric materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
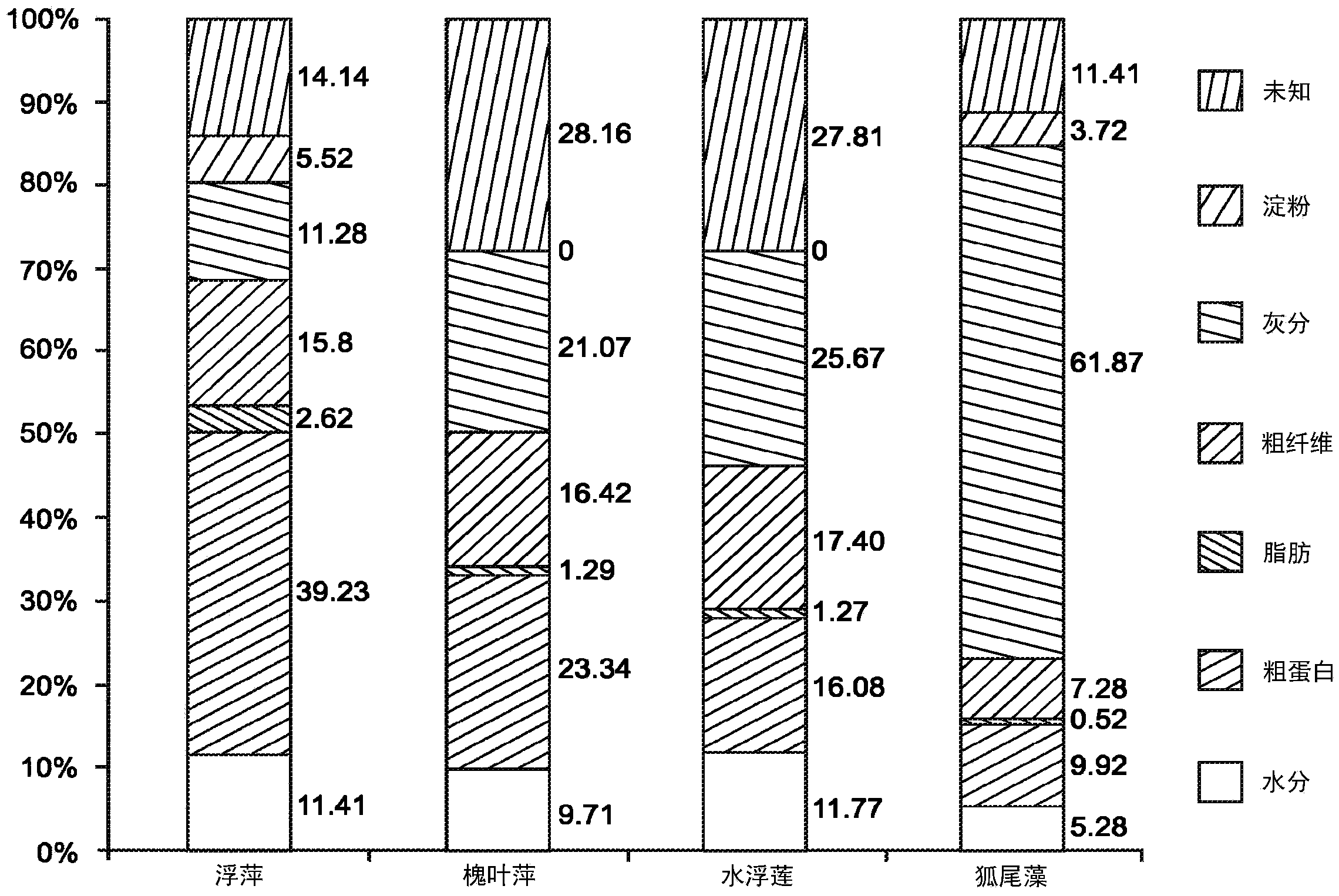
[0019] The present disclosure provides, in some embodiments, macrophyte-based compositions that exhibit thermoplastic properties. The composition may include macrophyte biomass material mixed with a thermoplastic polymer and other additives to define a bioplastic composition. Natural compounds in macrophyte biomass materials such as natural proteins and carbohydrate polymers in macrophyte biomass materials can be combined with thermoplastic polymers and other additives to produce plastic materials that appear to be acceptable for most plastic material applications. Balanced composite composition of polymeric and reinforcing properties.
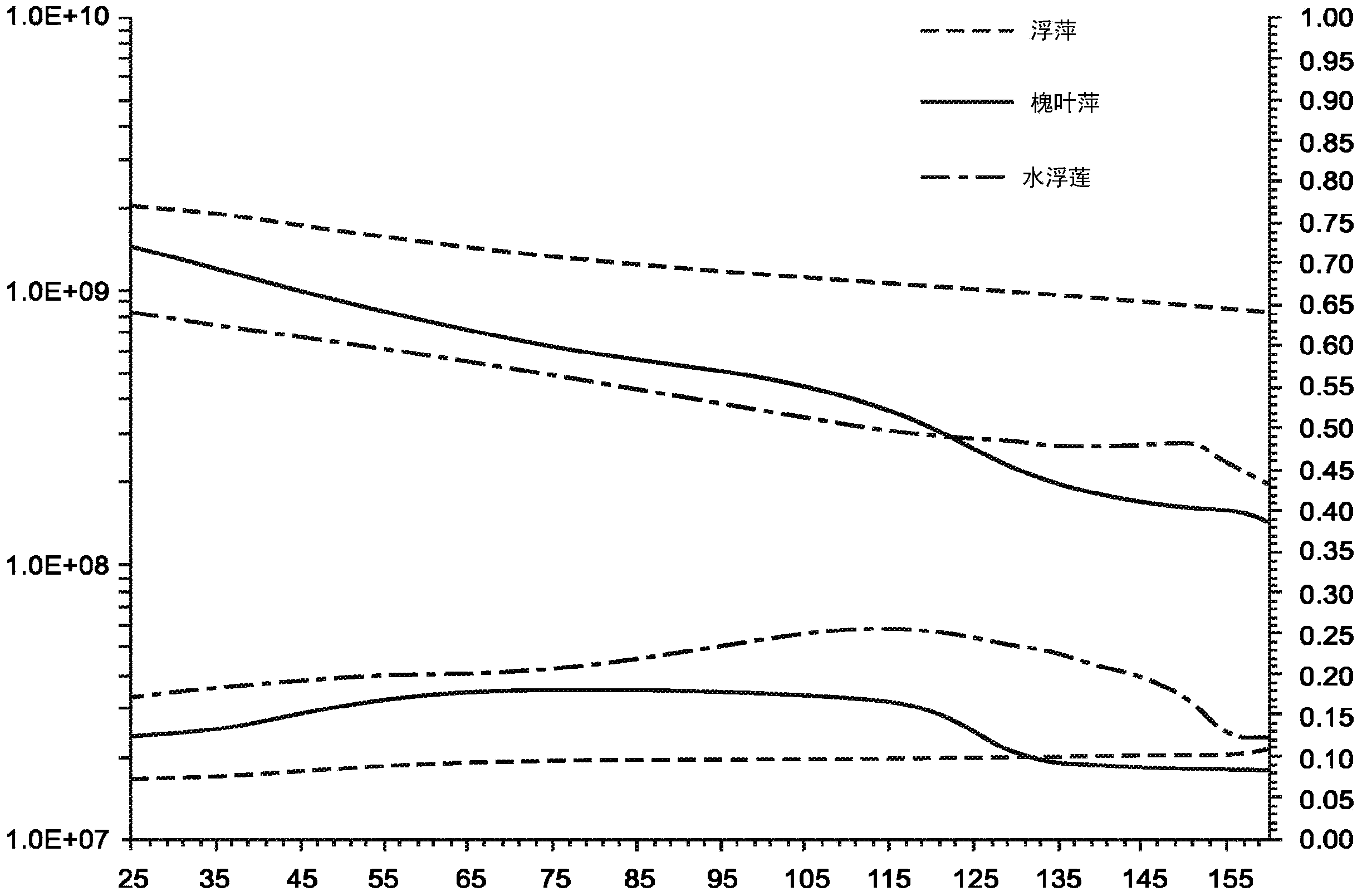
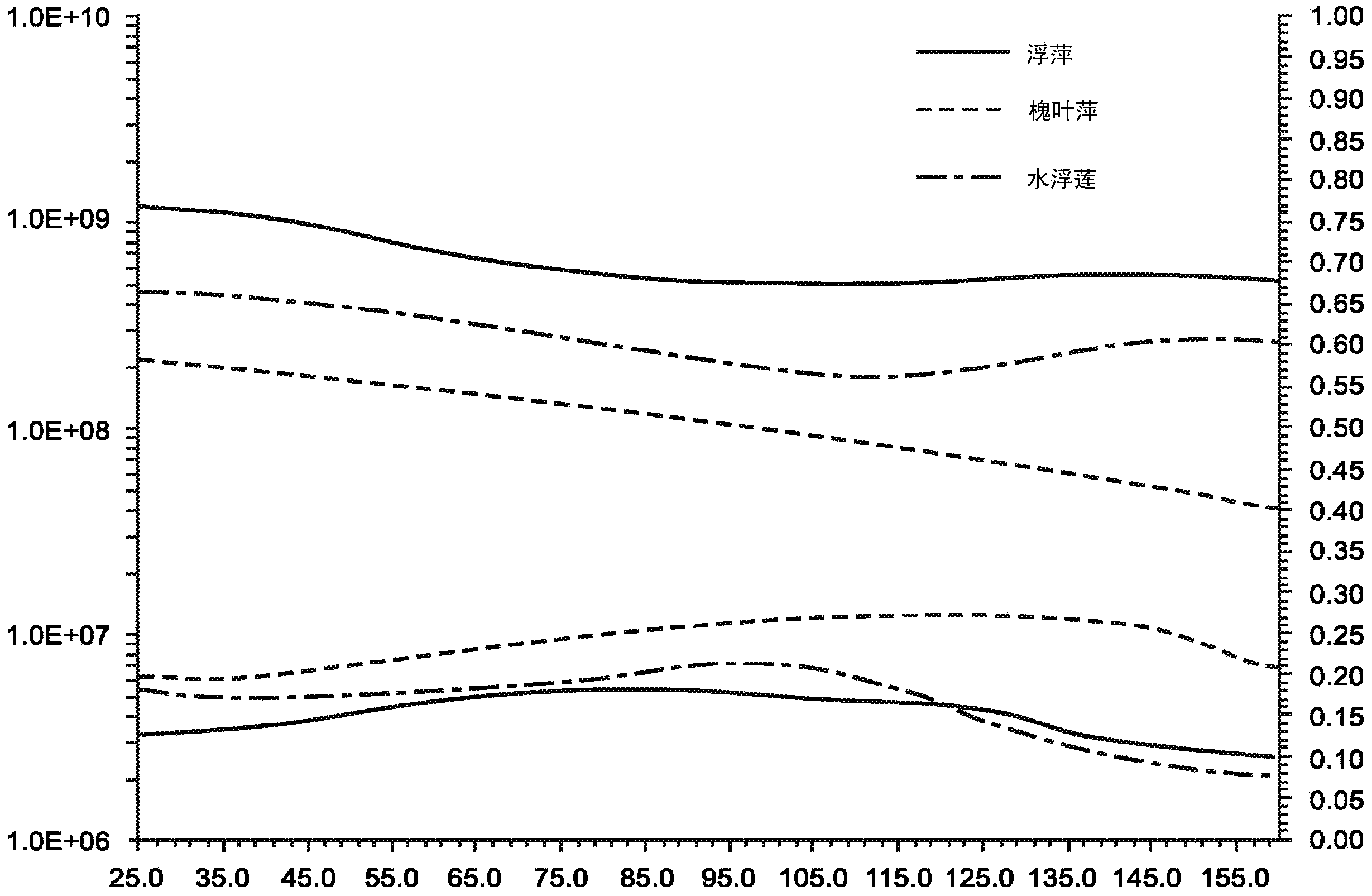
[0020] Unlike plastic compositions made from non-renewable raw materials and renewable raw materials derived from edible food sources, macrophyte biomass in macrophyte-based compositions can be readily obtained from environmentally sustainable sources regeneration. For example, macrophyte biomass material can be harvested from wastewater col...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com