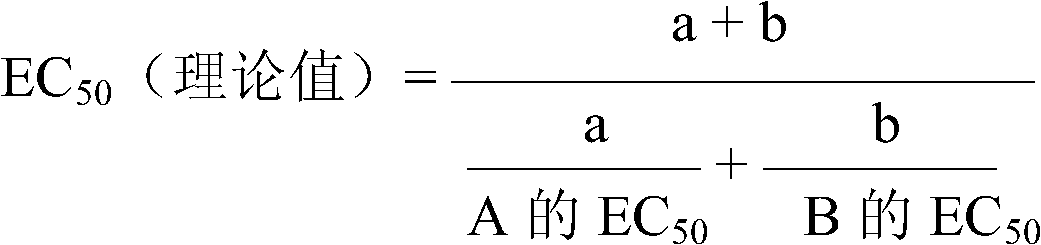
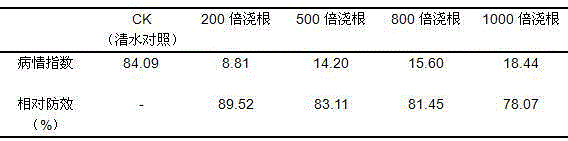
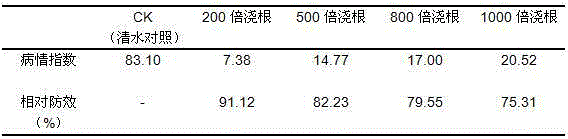
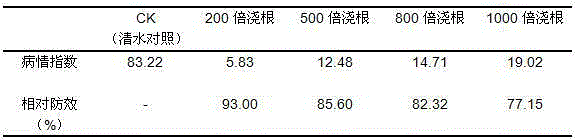
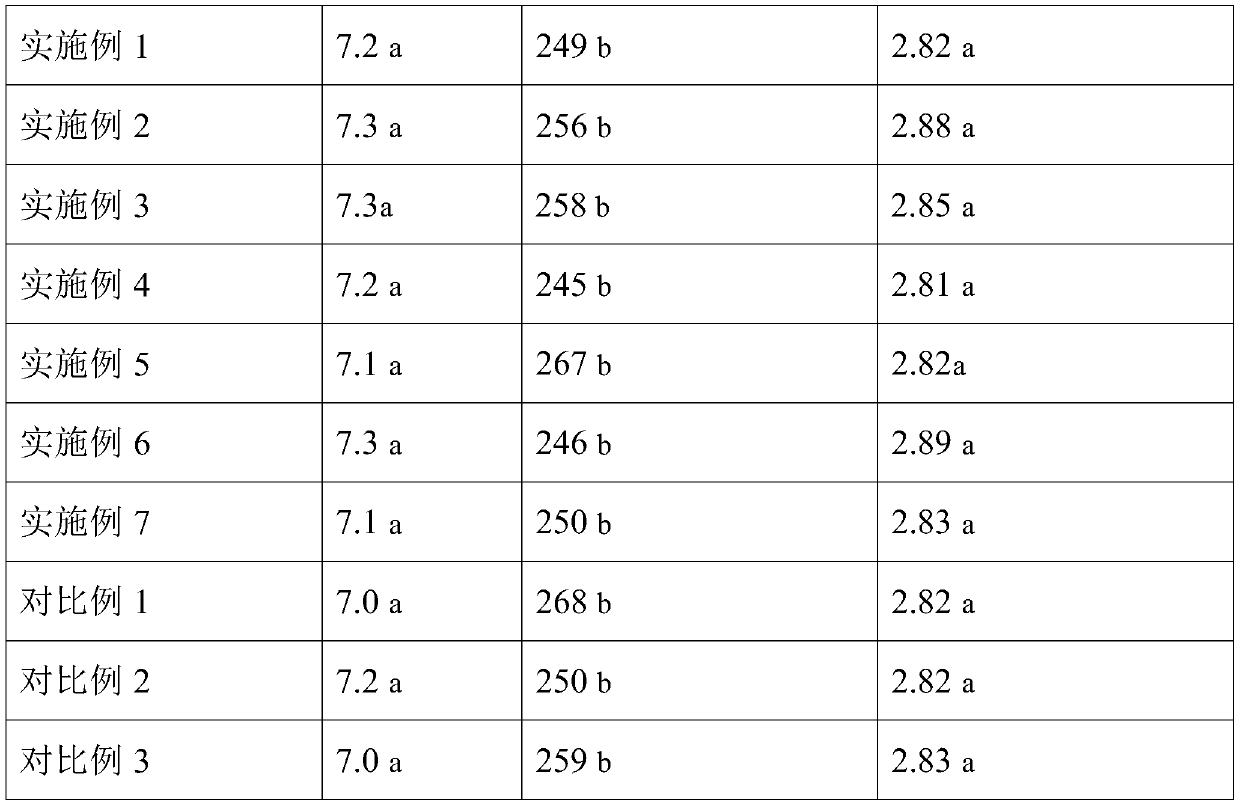
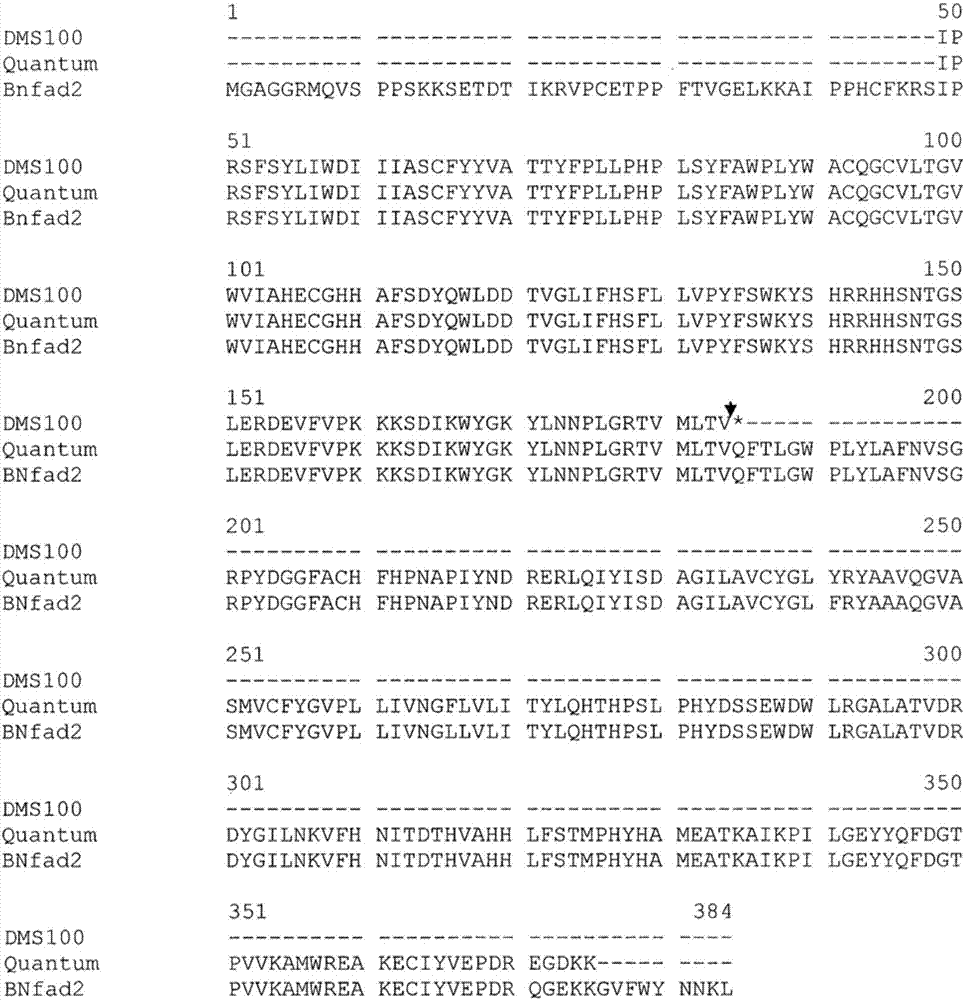
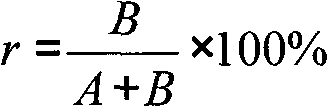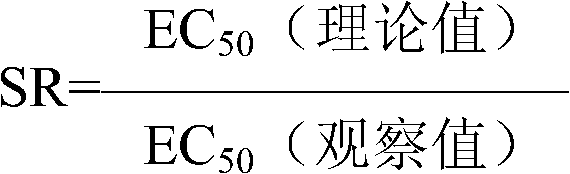Patents
Literature
64 results about "Plasmodiophora brassicae" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Clubroot is a common disease of cabbages, broccoli, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts, radishes, turnips, stocks, wallflowers and other plants belonging to the family Brassicaceae (Cruciferae). It is caused by Plasmodiophora brassicae, which was once considered a slime mold but is now put in the group Phytomyxea.
Ho/ll canola with resistance to clubroot disease
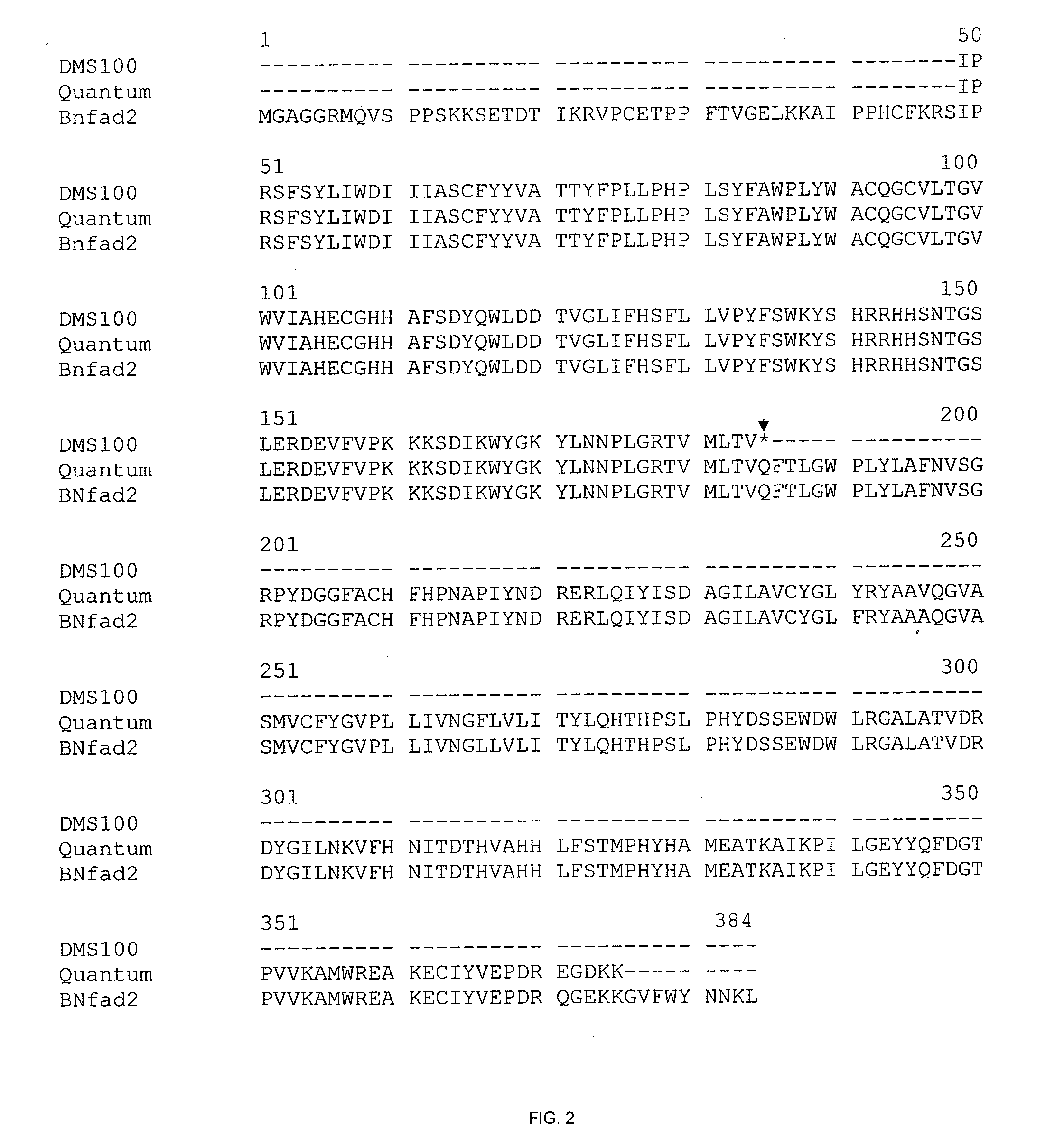
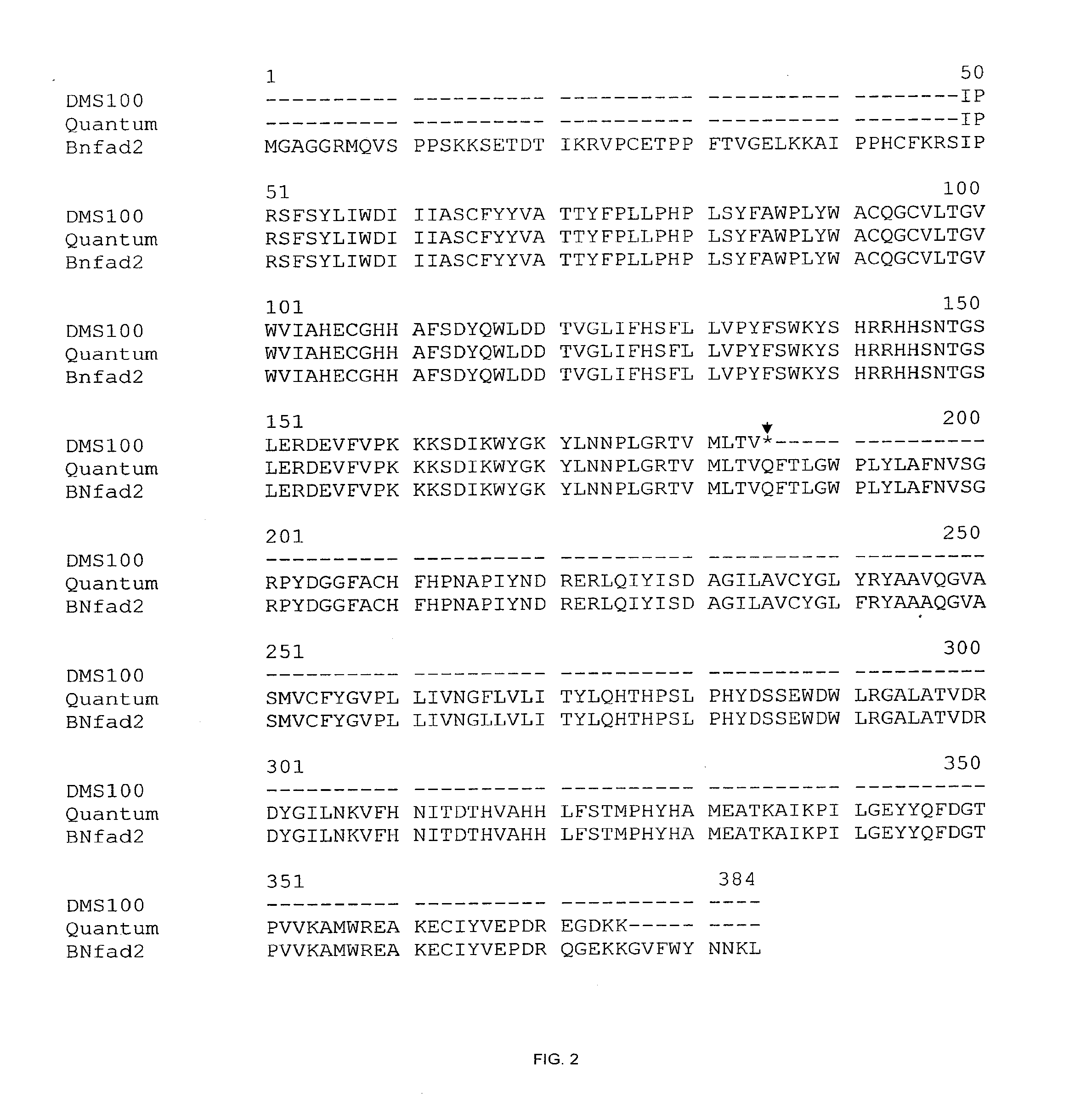
This disclosure concerns a plant of the genus, Brassica, or parts thereof, which comprise one or more traits selected from the group consisting of high oleic acid content, low linolenic acid content, increased herbicide resistance, restorer of cytoplasmic male sterility, and increased clubroot disease (Plasmodiophora brassicae) resistance, compared to a wild-type plant of the same species. This disclosure further relates to wild-type and mutant alleles of genes involved in these traits, molecular markers linked thereto, and methods of their use.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Ho/ll canola with resistance to clubroot disease
ActiveUS20130298279A1Microbiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyMutant allele
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
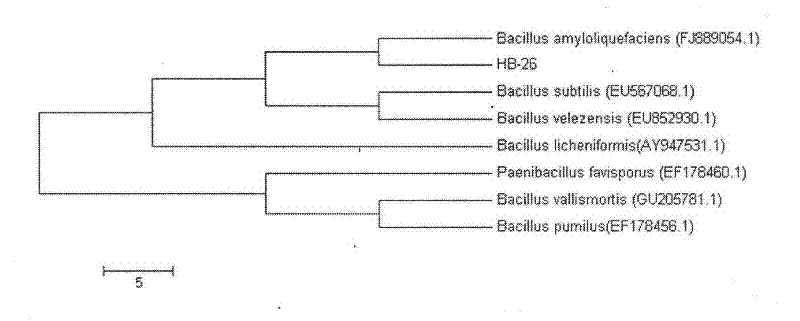
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens for inhibiting bird rape plasmodiophora brassicae and separation and application of active substances thereof
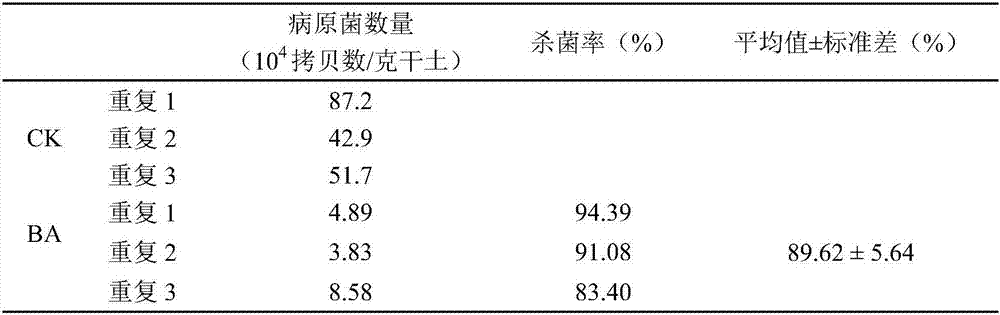
The invention relates to a bacillus amyloliquefaciens for inhibiting bird rape plasmodiophora brassicae and separation, application and purposes of active substances thereof. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens HB-26 is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC), the preserving number is CCTCCNO: M2011259. A culture method is as follows: inoculating biogas slurry separated bacterial strain in an LB liquid nutrient medium, preserving the biogas slurry separated bacterial strain at 30 DEG C for one night, pouring fermentation liquor at the root of Chinese cabbage and finding the bacterial strains with bacteriostatic activity on plasmodiophora brassicae. The separated active substance is characterized in that the HB-26 is inoculated in the LB liquid nutrient medium, the fermentation liquor is dried by freezing, the frozen strain powder is added with ethyl acetate for extraction, is vibrated, rotated and evaporated, is dissolved by methyl alcohol, and then subjected to HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatrography) separation, the components are collected, the mass spectrum identification is conducted, and the component of the active substance can be judged according to the condition of the generation of plasmodiophora brassicae disease of the Chinese cabbage. The molecular weight of the bacteriostatic activity substance BA20 is 1494.0, and the nuclear magnetic resonance hydrogen spectrum shows that the chemical nature of the bacteriostatic activity substance is carbohydrate bacteriocin. The active substance is used for preparing a microbial agent for preventing the plasmodiophora brassicae disease of the Chinese cabbage.
Owner:HUBEI BIOPESTICIDE ENG RES CENT
Cyazofamid aqueous emulsion and preparation method thereof
Cyazofamid belongs to sulfanilamide imidazole bactericide and has high bioactivity on oomycete fungi such as phytophthora capsici, downy mildew, pseudo downy mildew and pythium and brassica plasmodiophora brassicae of plasmodiophoromycetes. A preparation method for cyazofamid aqueous emulsion has a formulation comprising 1 to 30 percent of the cyazofamid, 2 to 15 percent of emulsifying agent, 0.2 to 5 percent of co-emulsifying agent, 10 to 20 percent of solvent, 10 to 20 percent of latent solvent, 0.1 to 5 percent of anti-freezing agent, 2 to 10 percent of stabilizing agent, 0.1 to 2 percent of defoaming agent, 0.1 to 5 percent of thickening agent, 0.1 to 4 percent of pH value conditioner and the balance of deionized water, and comprises the following steps: adding the latent solvent into the deionized water according to a ratio; dispersing the latent solvent in a high-shear preparation kettle and stirring the solution evenly; adding cyazofamid raw powder and solvent as well as latent solvent mother solution into the solution; shearing the mixed solution at high speed; and finally adding the thickening agent into the mixed and stirring the resulting solution evenly to obtain the cyazofamid aqueous emulsion. The cyazofamid aqueous emulsion is a new environment-friendly water-based dosage form of agricultural bactericide, uses water as a dispersive medium to replace an expensive organic solvent, reduces environment and dust pollution, and is a new dosage form with development prospect.
Owner:SHAANXI BIAOZHENG CROP SCIENCE CO LTD
Bacillus velezensis and application thereof in preventing and treating clubroot of cruciferae
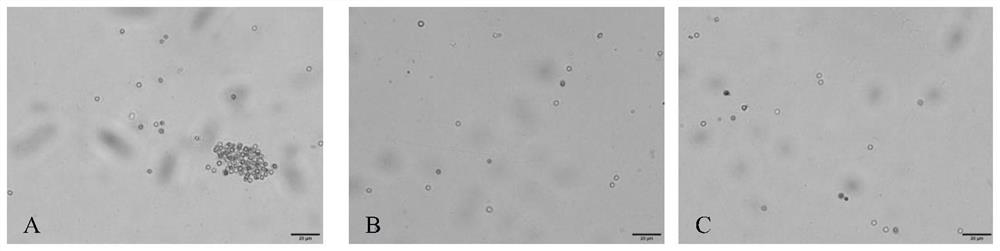
The invention discloses bacillus velezensis ZF481 and application thereof. The strain number of the bacillus velezensis is ZF481, the bacillus velezensis is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on July 8, 2020, and the registration number of the bacillus velezensis is CGMCC No.20320. The bacillus velezensis ZF481 or / and the metabolite of the bacillus velezensis ZF481 can be used for preventing and / or treating the plant clubroot, or preparing a product for preventing and / or treating the plant clubroot. The strain has an inhibiting effect on the activity and germination of plasmodiophora brassicae resting spores, has a good growth promoting effect on brassicaceous crops such as Chinese cabbage and the like, and also has a good antibacterial effect on phytophthora capsici, stemphylium solani, fusarium oxysporum, alternaria solani, corynespora, Botryis cinerea, rhizoctonia solani and the like.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Organic preparation for controlling cruciferous vegetable club root and application thereof
InactiveCN107987838AHigh incidenceReduce morbidityBiocideAgriculture tools and machinesContinuous croppingDecomposition
The invention belongs to the technical field of agricultural sustainable development, relates to preparation of organic preparations and in particular relates to an organic preparation for controllingcruciferous vegetable club root and application thereof. The organic preparation is composed of organic raw materials and decomposition-promoting ingredients, wherein the organic materials include but not limited to one or more of crop straws, saw dust and other solid organic materials and molasses, alcoholic fermentation liquor and other liquid organic materials; the decomposition-promoting ingredients include but not limited to one or more of special microbes and organic catalysts; and a ratio (mass) of the organic raw materials to the decomposition-promoting ingredients is (95-100):(5-0).The invention further discloses a preparation method and application of the organic preparation. The organic preparation disclosed by the invention is ecologically environment-friendly and is applicable to soil with high incidence of club root after continuous cropping of various cruciferous vegetables. The quantity of plasmodiophora brassicae woron in soil and the incidence rate of the club rootof crops can be effectively reduced after treatment, the sterilization rate and the club root control rate respectively reach 60-90%, and the yield of the crops is obviously increased.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIV CHANGZHOU INST OF INNOVATION & DEV
Method for evaluating resistance of brassica plants on club root
InactiveCN102511368ASave landAccurate and reliable identification resultsCultivating equipmentsHorticulture methodsBiotechnologyBrassica cretica
Owner:云南省农业科学院园艺作物研究所
Cyprodinil-containing germicide composition
InactiveCN102007912ASynergistic effect is obviousImprove the effect of disease preventionBiocideFungicidesBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENTPythium
Owner:SHAANXI MEIBANG PHARMA GRP CO LTD
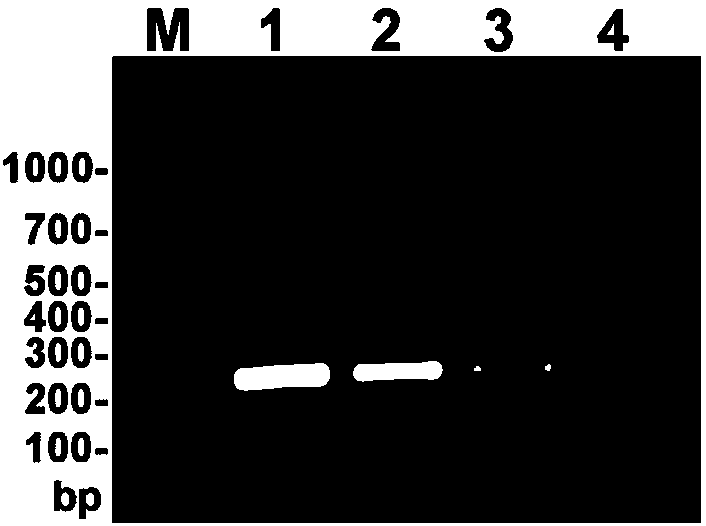
Specific pcr detection method of clubroot pathogen in soil
ActiveCN102296120ASensitive PCR detection methodQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationPlasmodiophora brassicaeClubroot
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Application of bacillus amyloliquefaciens Bamm22 for preventing and treating plasmodiophora brassicae
ActiveCN105230664ALow application concentrationReduce doseBiocideFungicidesBiotechnologyBrassicaceae
The invention provides an application method of bacillus amyloliquefaciens Bamm22 for preventing and treating plasmodiophora brassicae. The method comprises the following two methods: the method I comprises: carrying out root-irrigation treatment on a cruciferae crop by a bacillus amyloliquefaciens Bamm22 bacterial liquid with the amount of 80-100 ml per time per strain, and carrying out treatment for at least three times, wherein the treatment times are the first day, the seventh day and the fifteenth day after transplanting; the method II comprises: carrying out spraying treatment on the cruciferae crop by a bacillus amyloliquefaciens Bamm22 bacterial liquid with the amount of 150-200 ml per square meter, and carrying out treatment for at least three times, wherein the treatment times are the first day, the seventh day and the fourteenth day after seeding. The bacillus amyloliquefaciens Bamm22 provided by the invention is simple in using method, the application concentration of the bacterial liquid is less and the application dosage of the bacterial liquid is less.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION SICHUAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for detecting plasmodiophora brassicae in Chinese cabbages
InactiveCN103115891AQuick checkNon-destructive testingColor/spectral properties measurementsFourier transform infrared spectroscopyRepeatability
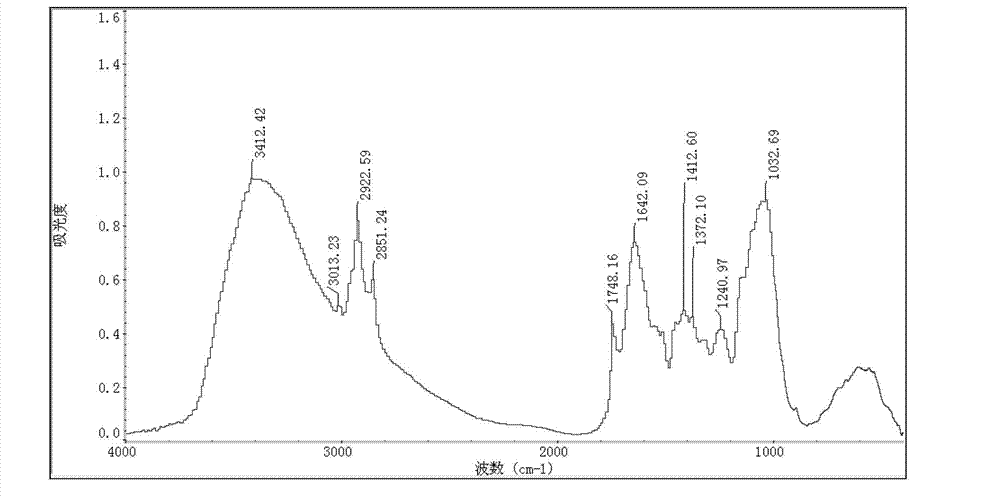
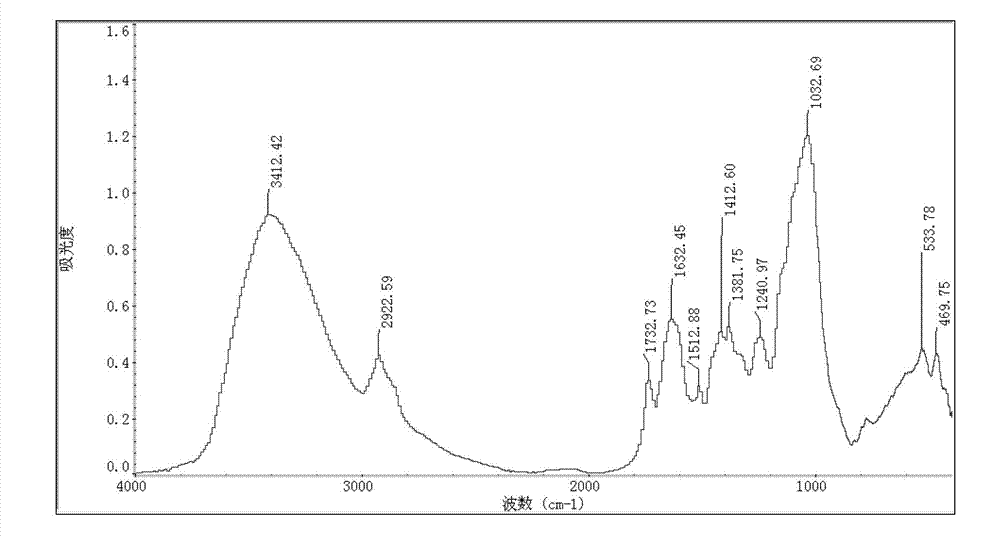
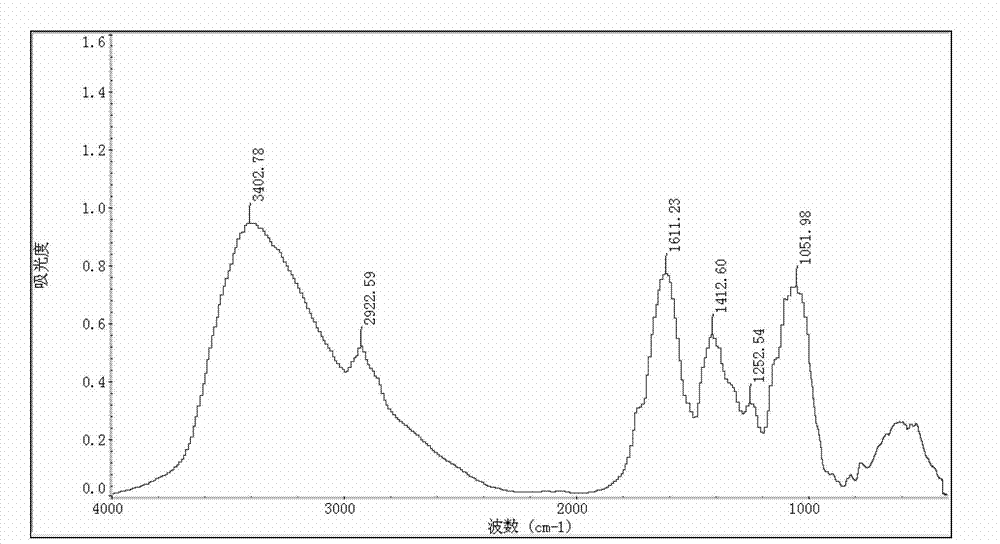
The invention discloses a method for detecting plasmodiophora brassicae in Chinese cabbages. The method comprises the following steps of: making roots and leaves of the Chinese cabbages into tablets; acquiring infrared spectrograms of the tablets; and analyzing the infrared spectrograms, wherein if the tablets made from the roots have a characteristic peak in at least one part in the ranges of 1748.16+ / -0.75cm<-1>, 2851.24+ / -0.05cm<-1> and 3013.23+ / -0.28cm<-1>, the roots of the Chinese cabbages are infected with the plasmodiophora brassicae; and if the tablets made from the leaves have a characteristic peak in at least one part in the ranges of 1252.54+ / -0.50cm<-1> and 1051.98+ / -4.23cm<-1>, the leaves of the Chinese cabbages are infected with the plasmodiophora brassicae. According to the method, the plasmodiophora brassicae in the Chinese cabbages can be rapidly and accurately detected in a lossless manner by virtue of a Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy technique, and the detection is convenient to implement, does not depend on skills of people and is high in security and repeatability.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for detecting activity of spores of plant pathogenic fungi and plasmodiophora brassicae
InactiveCN103674906AEffectively distinguish between life and deathGood repeatabilityFluorescence/phosphorescenceSpore germinationFluorescence microscope
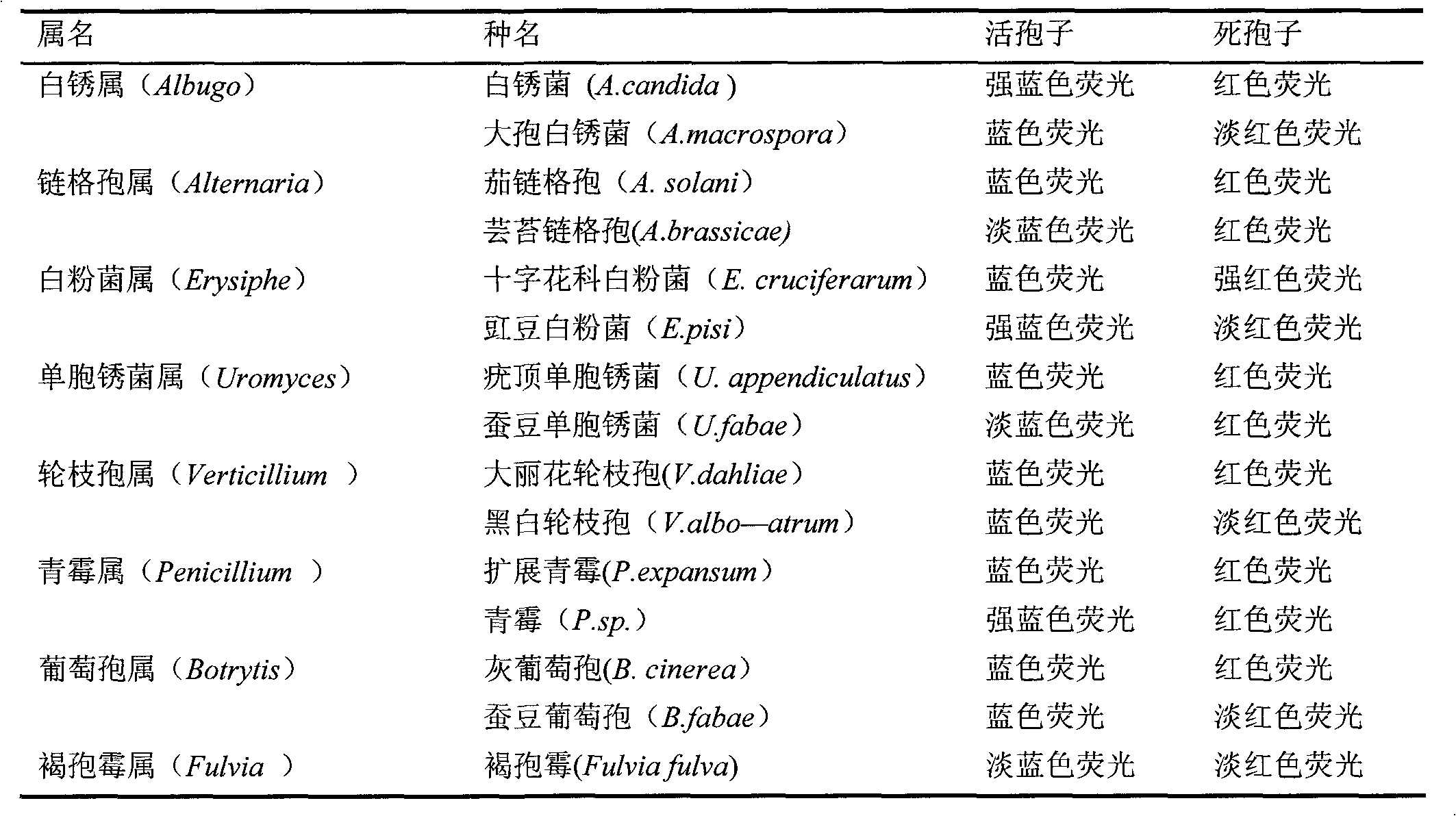
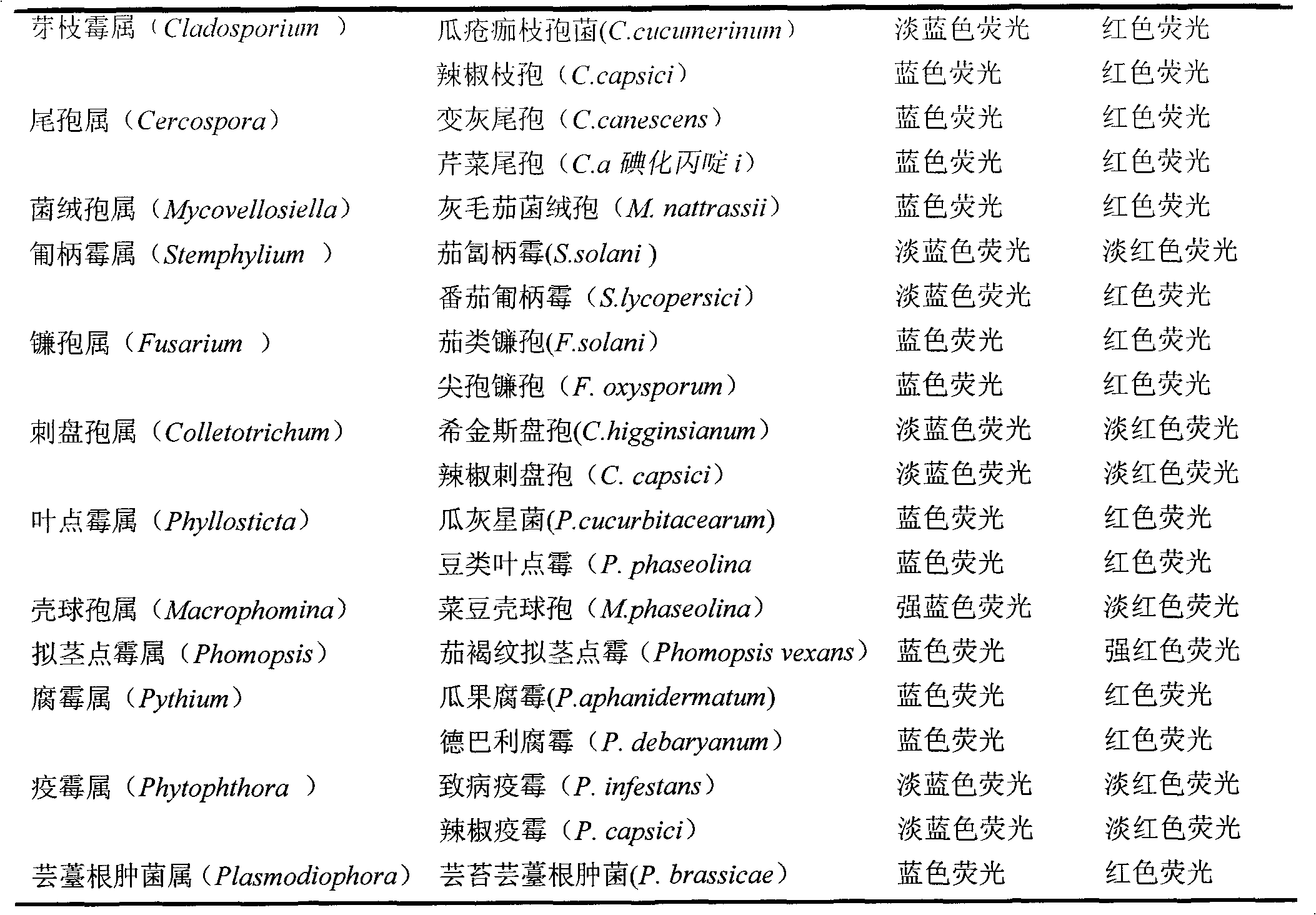
The invention discloses a method for detecting the activity of the spores of plant pathogenic fungi and plasmodiophora brassicae woronin. According to the method, a Hochest 33342 / PI double-staining method is adopted, and a fluorescence microscope is used for detection, so that life or death of the spores of the plant pathogenic fungi and the plasmodiophora brassicae woronin can be rapidly, accurately and sensitively distinguished; a spore germination method is also used for identifying the activity of the spores of the plant pathogenic fungi and the plasmodiophora brassicae woronin, but according to the spore germination method, time-consuming and labor-consuming effects are adopted; the method can be used for replacing the traditional spore germination method and is suitable for departments such as agricultural production, plant protection, etc.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Fermentation method of bacillus amyloliquefaciens Bam22 for preventing and treating cruciferae plasmodiophora brassicae
ActiveCN105296392AHigh activityEasy to carry out prevention workBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesMicroorganism
The invention provides a fermentation method of bacillus amyloliquefaciens Bam22 for preventing and treating cruciferae plasmodiophora brassicae. The method comprises the following steps: (1) picking up a bacillus amyloliquefaciens Bam22 colony cultivated on a solid culture medium, and carrying out shake culture in a liquid culture medium at 30-32 DEG C for 10-12 hours, wherein the rotating speed is 200-220rpm; and the product is taken as a seed solution; (2) fermenting the seed solution obtained in the step (1) in a fermentation tank for 40-50 hours, wherein the access amount of the seed solution is 8%-10%; the temperature of the tank is 27-30 DEG C; the stirring speed of the fermentation tank is 220-250rpm; the air flow is 0.8:1 to 1:1 (V / V.m); the efficient bacillus amyloliquefaciens Bam22 for cruciferae plasmodiophora brassicae is preserved at the General Microbiology Center of the China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms on September 6, 2015; and the preservation number is CGMCC No.11329. The fermentation method provided by the invention is very favorable to cultivation of the bacillus amyloliquefaciens Bam22; and multiple bacteria are obtained and have good activity.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION SICHUAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Bactericidal composition containing mandipropamid and cyazofamid
The invention relates to a bactericidal composition with a synergistic effect, which has an effective active component containing mandipropamid and cyazofamid, wherein the weight ratio of the mandipropamid to the cyazofamid is (1-85) : (85-1). The effective active component is added with auxiliaries and polybutene so as to be prepared into wettable powder, water dispersible granules and suspending agent, and has very high biological activity for oomycetes fungus such as phytophthora, plasmopara viticola, pseudoperonospora cubensis, pythiumuhtimum, and plasmodiophora brassicae woron of plasmodiophoromycetes.
Owner:陕西汤普森生物科技有限公司
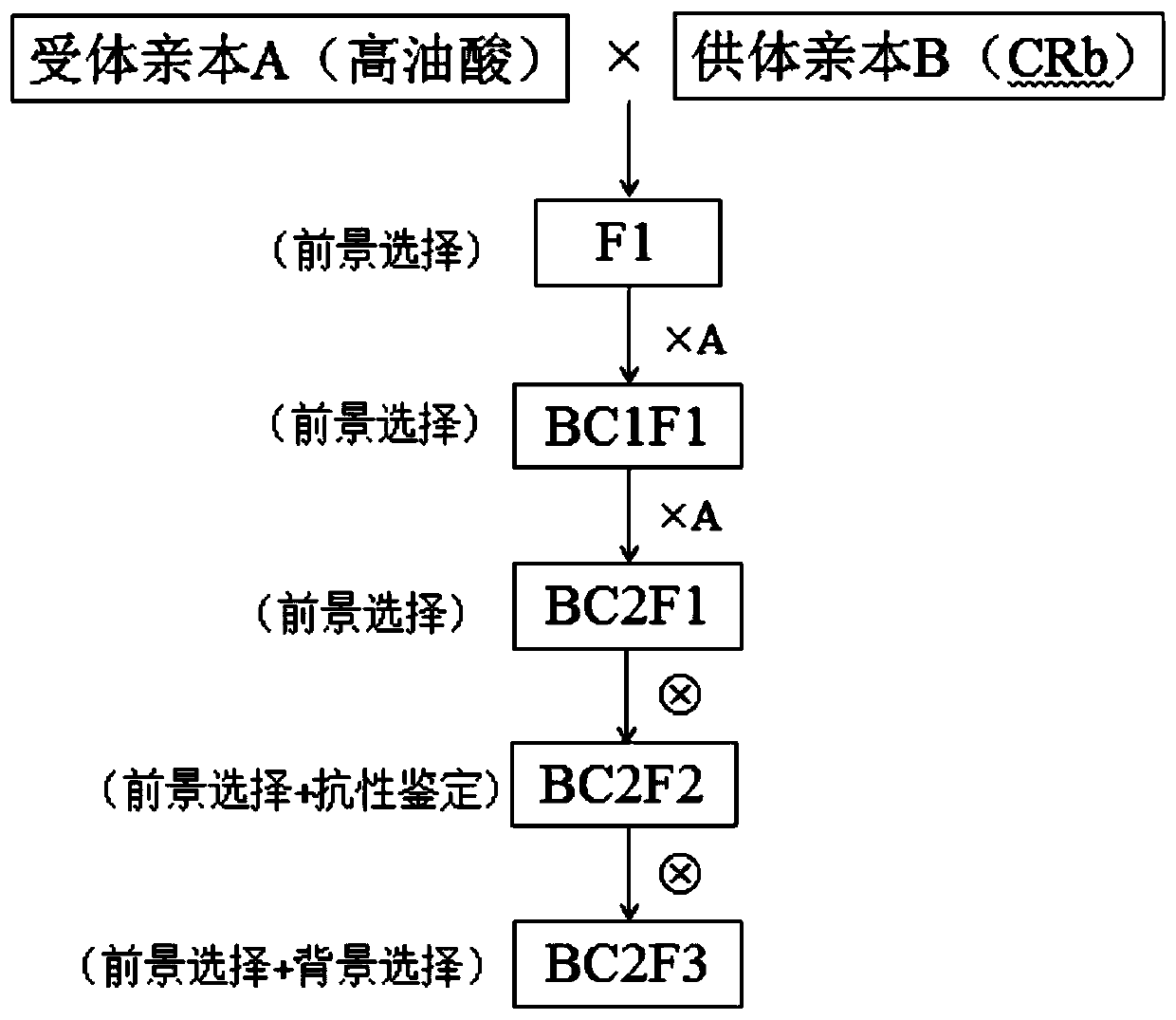
Breeding method for high oleic acid rape for resisting plasmodiophora brassicae and application of breeding method
ActiveCN110305980AReduce breeding workloadImprove qualityMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationAgricultural scienceHigh oleic acid
The invention belongs to the technical field of rape breeding, and particularly relates to a breeding method for high oleic acid rape for resisting plasmodiophora brassicae and an application of the breeding method. The breeding method is characterized by comprising the following steps of enabling a high oleic acid plant and a plasmodiophora brassicae-resisting gene containing plant to be hybridized to obtain composite F1 rape seeds containing high oleic acid and CRb disease-resistant sites; planting the composite F1 rape seeds, identifying the relevant gene sites with high oleic acid and a plasmodiophora brassicae resisting molecular marker, and selecting individuals containing the sites and recurrent parents for hybridizing; performing high oleic acid and plasmodiophora brassicae resisting molecular marker analysis on backcross and selfed progeny groups, performing screening, and performing homozygosis to obtain the high oleic acid plasmodiophora brassicae resisting plant. The invention provides a simple, quick and effective method for breeding good disease-resistant high oleic acid rape kinds. The breeding method can selectively select a single plant according to the genotype atany stage in the breeding process, so that the selection efficiency is improved, and the breeding age limit is shortened.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Anti-plasmodiophoa-brassicae-woron inbred line breeding method
ActiveCN106489723AImprove breeding efficiencySave spaceMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationPollinationDisease resistant
The invention discloses an anti-plasmodiophoa-brassicae-woron inbred line breeding method which comprises the steps of seed soaking for germination hastening, vernalization, inoculation and identification, and inbred pollination. The method specifically comprises the following steps: in spring, carrying out carrying out seed soaking for germination hastening and vernalization on an F2-generation anti-plasmodiophora-brassicae breeding material, carrying out inoculationand identification by a bacterium soil process, permanently growing a disease-resistant individual plant into a flowerpot, and carrying out normal culture and management; after the plant bolts and blooms, carrying out inbred pollination, and collecting the seeds; and in next spring, continuing seed soaking for germination hastening, vernalization, inoculation and identification and inbred pollination, and after 3-5 generations of selection, breeding the anti-plasmodiophoa-brassicae Chinese cabbage inbred line with regular characters. The method can enhance the selection efficiency and accelerate the breeding progress.
Owner:LIAONING ACAD OF AGRI SCI
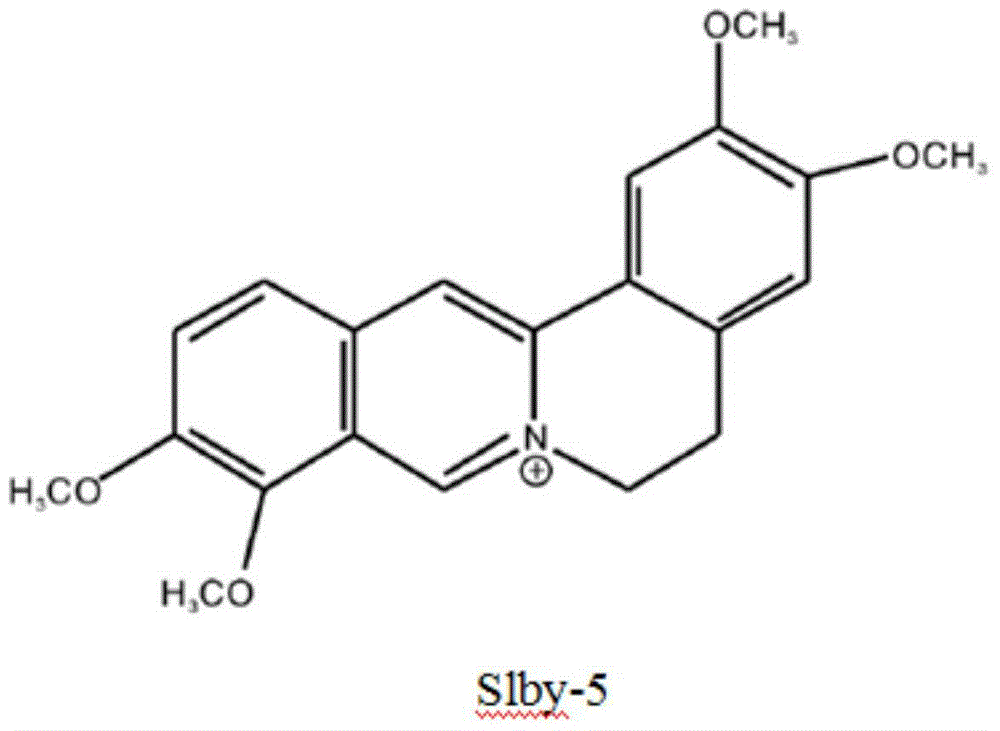
Microbial secondary metabolite palmatine hydrochloride and application thereof
InactiveCN104561179AGood characterEase of industrial productionBiocideMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyLysobacter antibioticus
The invention relates to a microbial secondary metabolite palmatine hydrochloride and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of biological pesticides. The secondary metabolite is prepared by the following steps: (a), producing a strain of L.antibioticus YFY02 with the collection number of CGMCC NO.2403; (b) culturing the strain YFY02 for two days by utilizing a KB culture medium, performing enlarged culture by adopting a conventional fermentation method, extracting the fermentation liquor by using ethyl acetate, and performing rotary evaporation, thereby obtaining a crude metabolite extract; (c) by utilizing liquid chromatography, Sephadex LH-20 gel column chromatography, mass spectrometry, nuclear magnetic resonance and other spectroscopic techniques, and separating, purifying and identifying the crude extract of the secondary metabolite; and (d) identifying to obtain the effective secondary metabolite palmatine hydrochloride. The invention also discloses application of the microbial secondary metabolite palmatine hydrochloride in the preparation of agents for preventing and controlling bacterial blight of rice, bacterial leaf streak and plasmodiophora brassicae woronin. The microbial secondary metabolite disclosed by the invention has the advantages of environment friendliness, low cost and excellent effects of preventing and controlling the rice bacterial diseases and plasmodiophora brassicae woronin.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Streptomyces cuspidosporus and application thereof in prevention and treatment of plasmodiophora brassicae
The invention discloses streptomyces cuspidosporus and an application thereof in prevention and treatment of plasmodiophora brassicae. The preservation number of the streptomyces cuspidosporus WS-29246 is CCTCC (China Center For Type Culture Collection) NO: M2012413. The streptomyces cuspidosporus fermented generates a fermented liquid with a strong bacteriostatic action. The fermented liquid can be used for preparing a biocontrol suspension and a biocontrol slow release capsule for resisting plasmodiophora brassicae for biologically preventing and treating plasmodiophora brassicae.
Owner:HUBEI BIOPESTICIDE ENG RES CENT
Genetic transformation method of PEG/LiAc mediated plasmodiophora brassicae woronin
InactiveCN104480138AHigh fluorescence intensityFungiMicroorganism based processesUnit massTransformation efficiency
The invention discloses a genetic transformation method of PEG / LiAc mediated plasmodiophora brassicae woronin. The genetic transformation method comprises the following specific steps: (a) preparing root secretion; (b) collecting hypnospore liquid; (c) preparing competent hypnospore liquid; (d) carrying out genetic transformation on plasmodiophora brassicae woronin; (e) carrying out resistance screening on bleomycin, repeatedly inoculating and screening for three generations, thus obtaining stable genetic transformation spores. The genetic transformation method disclosed by the invention realizes the genetic transformation of PEG / LiAc mediated plasmodiophora brassicae woronin and obtains stably genetic transformation strain capable of expressing green fluorescent proteins with a high intensity, and the transformation efficiency reaches 1000 transformants / mg of DNA (by DAN in a unit mass); in addition, a carrier used for the transformation in the genetic transformation method disclosed by the invention has enhanced green fluorescent protein genes and strong promoter RP27 in fungus, thus effectively increasing the fluorescent intensity of the transformation strain.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Carbon-based complex microbial inoculant and application thereof
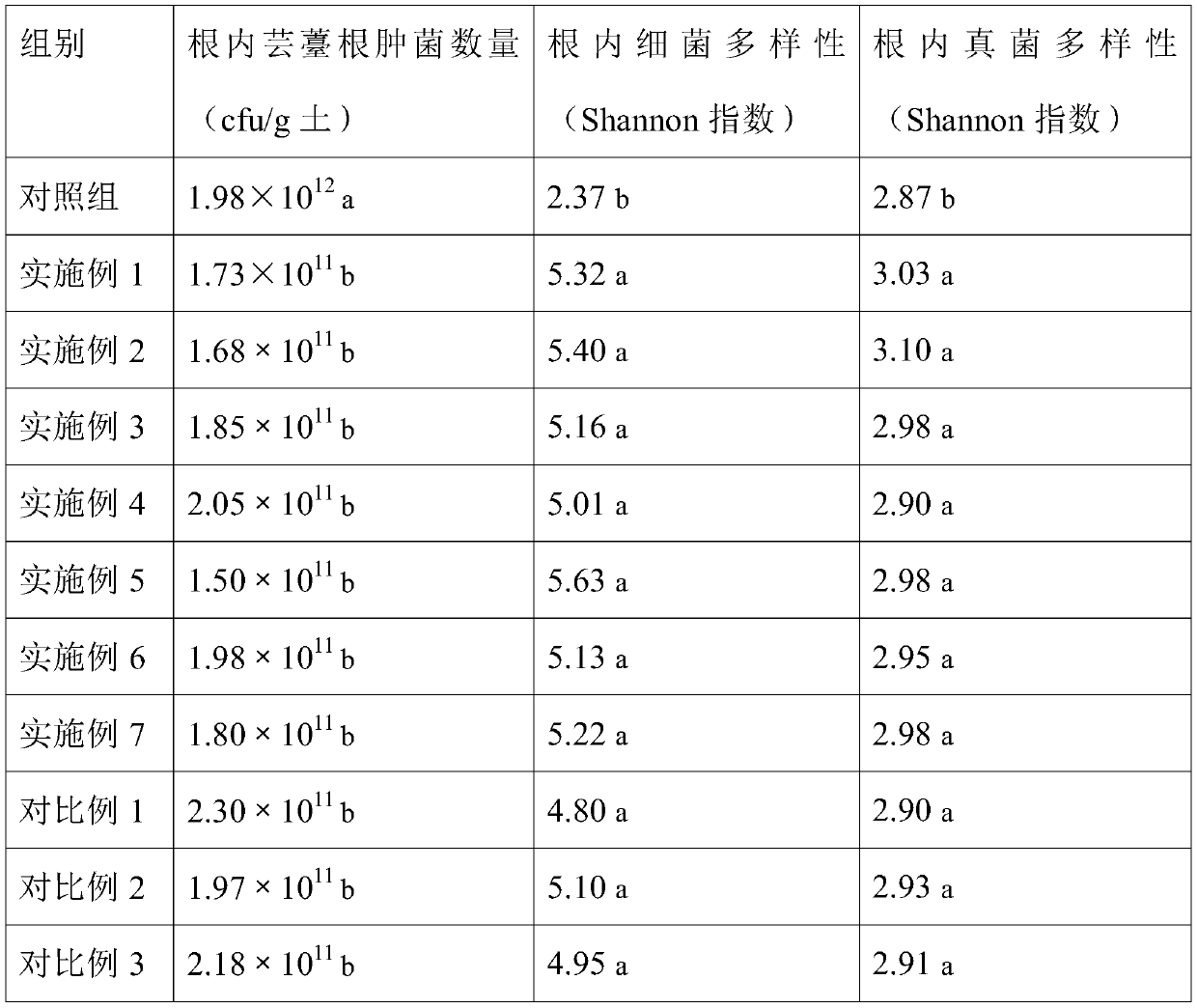
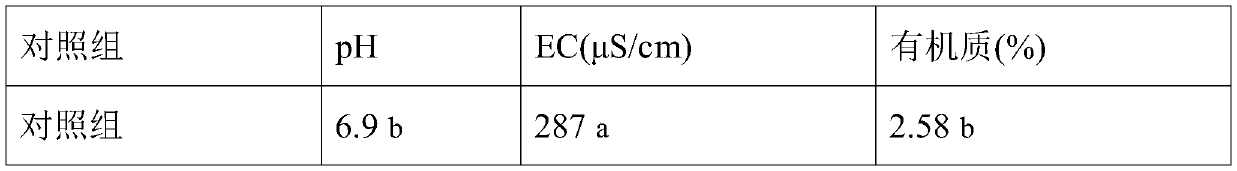
The invention relates to a carbon-based complex microbial inoculant and an application thereof. The carbon-based complex microbial inoculant comprises an aspergillus oryzae solid fermentation product,a zygosaccharomyces rouxii liquid fermentation product, a bacillus velezensis liquid fermentation product and biomass charcoal. According to the carbon-based complex microbial inoculant, the three fermentation products and the biomass charcoal are creatively compounded, the multiple components have a synergistic interaction effect, the carbon-based complex microbial inoculant is used in a soil remediation agent, and under the condition that no pesticide is introduced, the pH value of soil can be adjusted to be 7, so that the salt content of the soil is reduced, the content of organic mattersis increased, and the incidence rate of clubroot of green vegetables in the continuous cropping soil is reduced. The number of plasmodiophora brassicae woron in the continuous cropping soil treated with the soil remediation agent is remarkably reduced, the number of plasmodiophora brassicae woron in the root systems of the green vegetables in a harvesting period is remarkably reduced, and the diversity of microbial community species in the soil and the plant root systems is remarkably increased.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
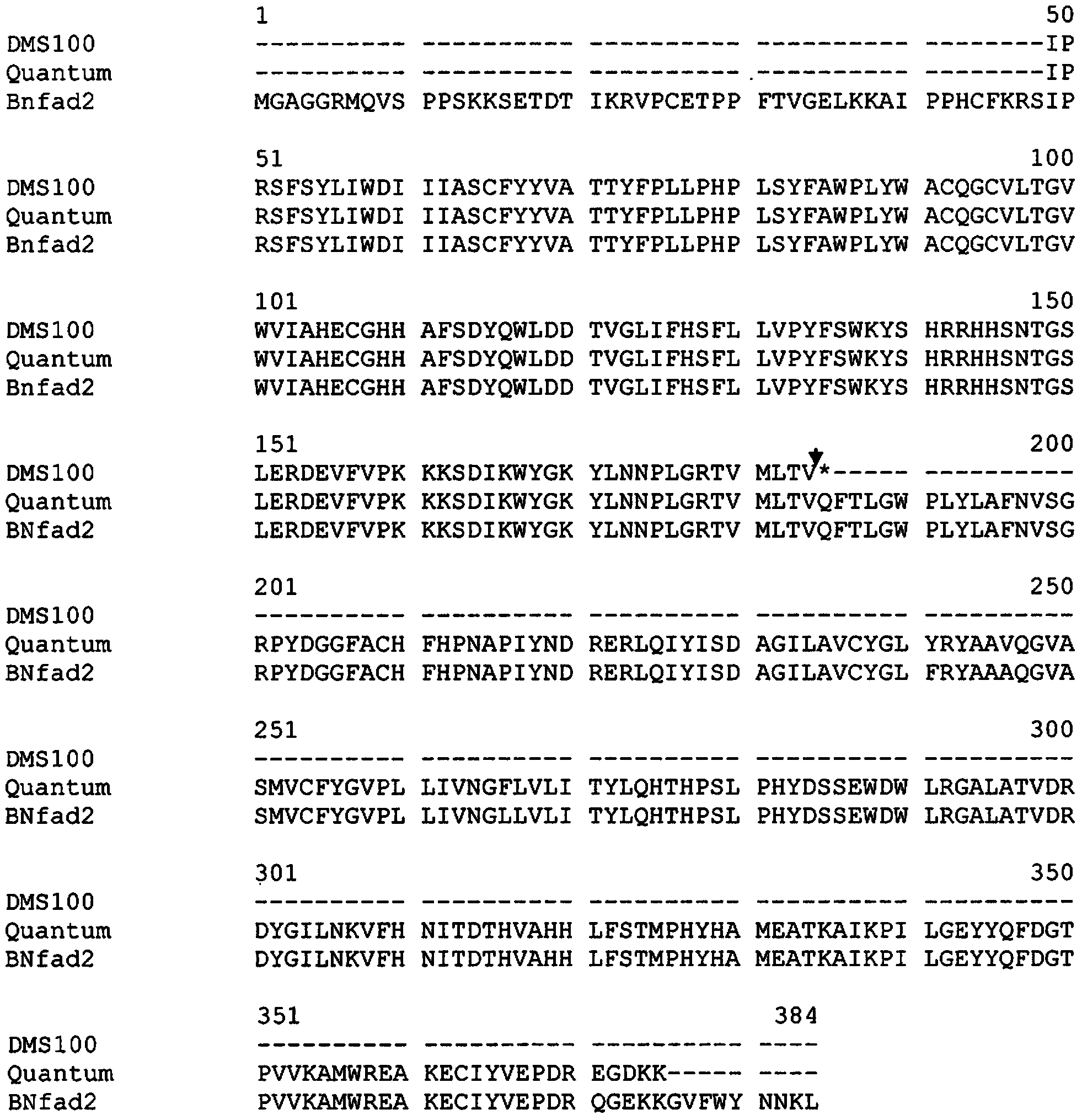
Brassicaceae plants resistant to plasmodiophora brassicae (clubroot)
ActiveUS20190241904A1Microbiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationBrassicaceaeResistant genes
The present invention relates to the identification of clubroot resistance genes from Brassica. Clubroot resistant Brassicaceae plants are provided, as well as clubroot resistance genes and methods and means to increase clubroot resistance in Brassicaceae.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Pyrimorph and cyazofamid-containing bactericidal composition
InactiveCN101953349AGood synergyImprove efficiencyBiocideFungicidesSuspending AgentsBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The invention relates to a bactericidal composition with synergy. The bactericidal composition comprises the following effective active ingredients of pyrimorph and cyazofamid, wherein the weight ratio of the pyrimorph to the cyazofamid is 1-80:60:1. By adding aids and excipients into the effective active ingredients to prepare wettable powder, water dispersible granules and suspending agents, the bactericidal composition has the advantage of high bioactivity on oomycetes fungi, such as phytophthora, downy mildews, pseudoperonospora, pythium and plasmodiophora brassicae in plasmodiophoramycetes.
Owner:陕西汤普森生物科技有限公司
HO/LL canola with resistance to clubroot disease
This disclosure concerns a plant of the genus, Brassica, or parts thereof, which comprise one or more traits selected from the group consisting of high oleic acid content, low linolenic acid content, increased herbicide resistance, restorer of cytoplasmic male sterility, and increased clubroot disease (Plasmodiophora brassicae) resistance, compared to a wild-type plant of the same species. This disclosure further relates to wild-type and mutant alleles of genes involved in these traits, molecular markers linked thereto, and methods of their use.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
HO/LL canola with resistance to clubroot disease
The disclosure concerns a plant of the genus, Brassica, or parts thereof, which comprise one or more traits selected from the group consisting of high oleic acid content, low linolenic acid content, increased herbicide resistance, restorer of cytoplasmic male sterility, and increased clubroot disease (Plasmodiophora brassicae) resistance, compared to a wild-type plant of the same species. This disclosure further relates to wild-type and mutant alleles of genes involved in these traits, molecular markers linked thereto, and methods of their use.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
Streptomyces luteogriseus YAAS0018 strain, and plasmodiophora brassicae resistant microbial preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN103289943ALow costSimple production processBiocideBacteriaStreptomyces luteogriseusMicrobial pesticide
The invention discloses a streptomyces luteogriseus YAAS0018 strain, and a plasmodiophora brassicae resistant microbial preparation and an application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of microbial pesticides. The strain is the streptomyces luteogriseus YAAS0018 CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No.7628. The plasmodiophora brassicae resistant microbial preparation of the strain is prepared by strain tube seed culture, liquid seed culture and liquid fermentation culture. The strain and the plasmodiophora brassicae resistant microbial preparation which contains the strain have an obvious prevention effect on the plasmodiophora brassicae; and the average prevention and treatment effect is up to 91.71 percent.
Owner:INST OF AGRI ENVIRONMENT & RESOURCES YUNNAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Compound fertilizer special for pakchoi, preparation method and application thereof
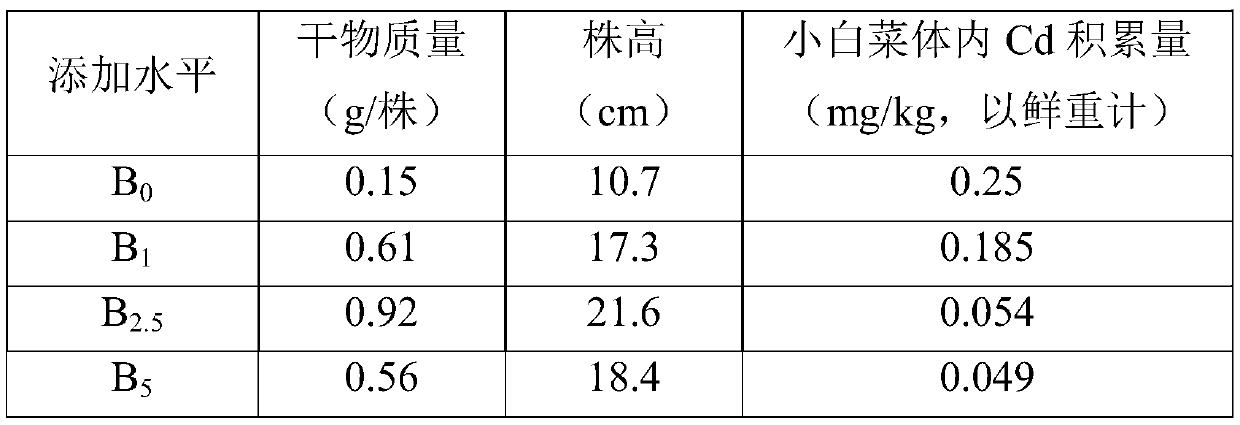
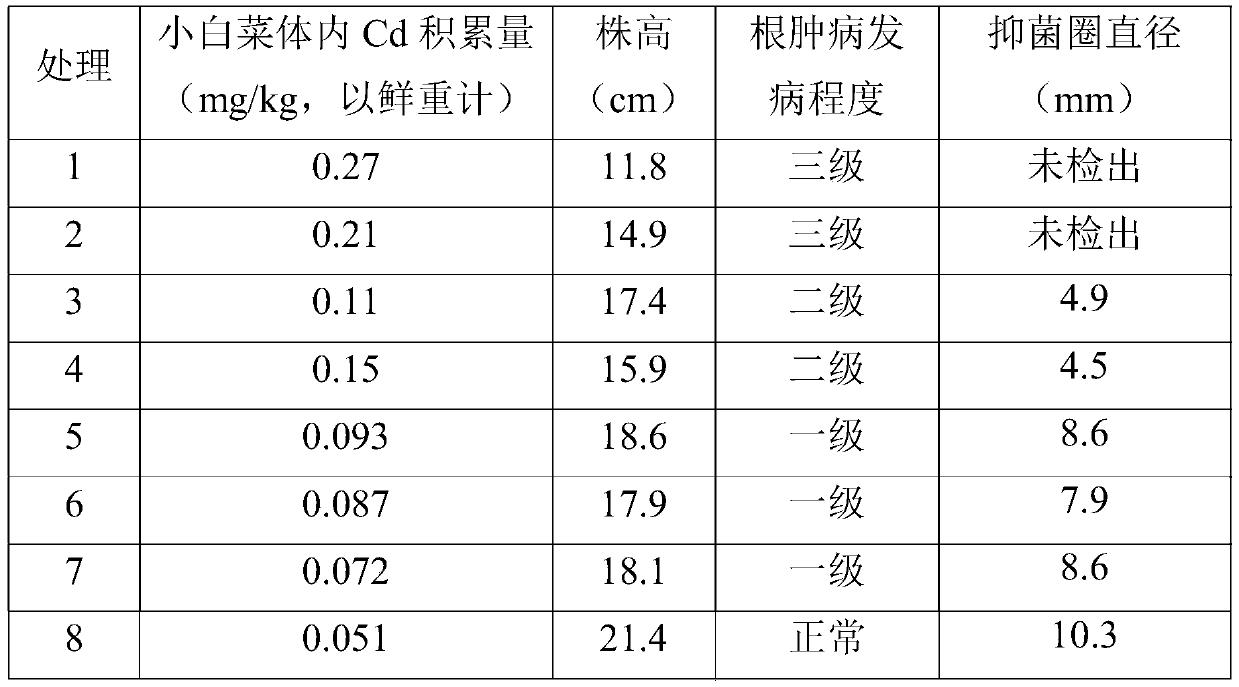
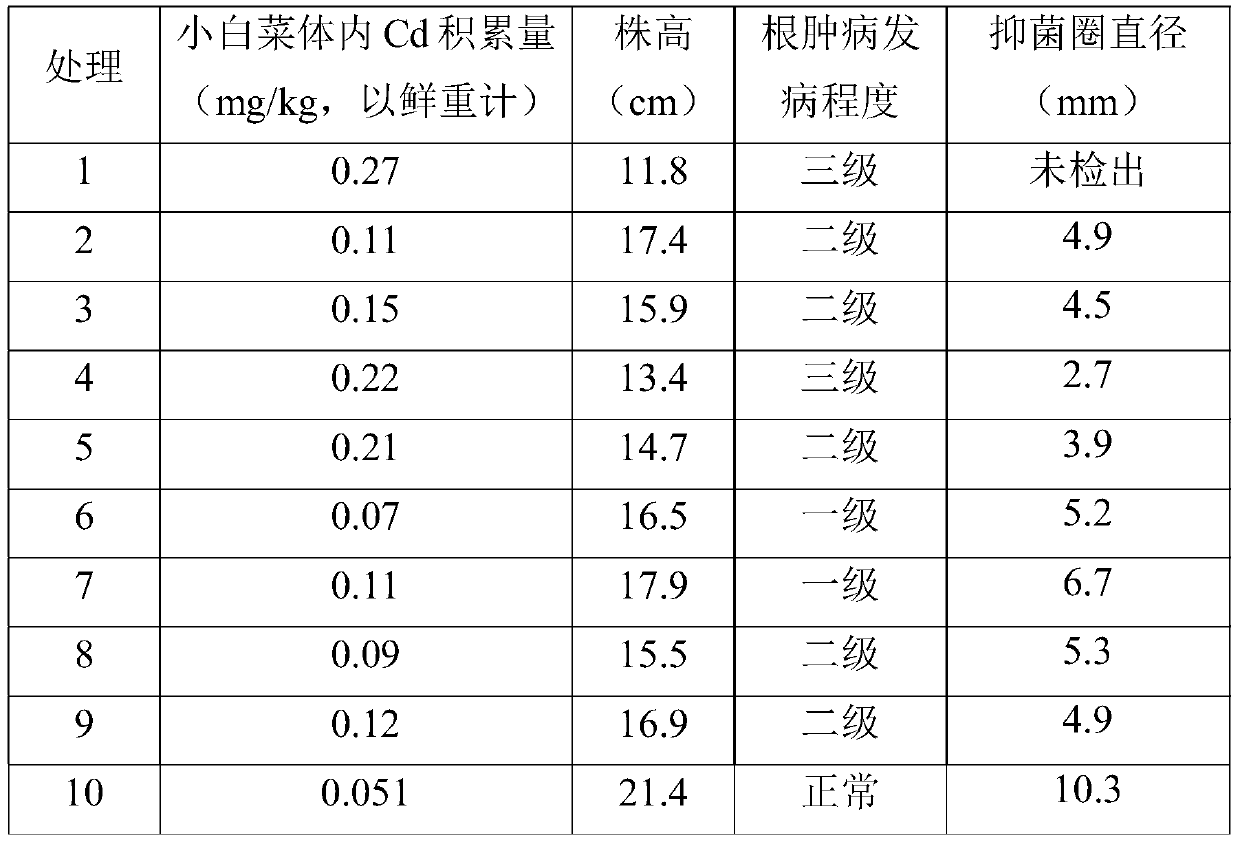
InactiveCN109721423AInhibition of ClubrootReduce accumulationFertilizer mixturesDecompositionSoil heavy metals
The invention discloses a compound fertilizer special for pakchoi and application thereof. The compound fertilizer includes an organic fertilizer, an inorganic fertilizer and improved biochar in a weight ratio of 65-75:8-12:15-23, and the pH value of the compound fertilizer is 6-9, wherein the improved biochar is mainly prepared by: standing 2 parts of peanut shell charcoal and 1 part of corn straw charcoal in an LB medium of bacillus subtilis for 24-48h. The application amount of the compound fertilizer is 50-100kg / mu. The invention adopts a special compound fertilizer of appropriate dosage proportion directed at cadmium polluted pakchoi cultivated land having plasmodiophora brassicae. The compound fertilizer is not added with improved biochar, but also is introduced with bacillus subtilis having bacteriostatic effect, and is added with the organic fertilizer and inorganic fertilizer obtained by thorough decomposition of livestock and poultry excrement. Therefore, the special fertilizer not only can effectively reduce the accumulation of heavy metal cadmium in pakchoi, improve the in-situ remediation efficiency of heavy metal contaminated soil, promote the growth of pakchoi, but also can inhibit the growth ofplasmodiophora brassicae woron, and achieves the technical effect of inhibiting the plasmodiophora brassicae of pakchoi.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY UNIVERSITY +1
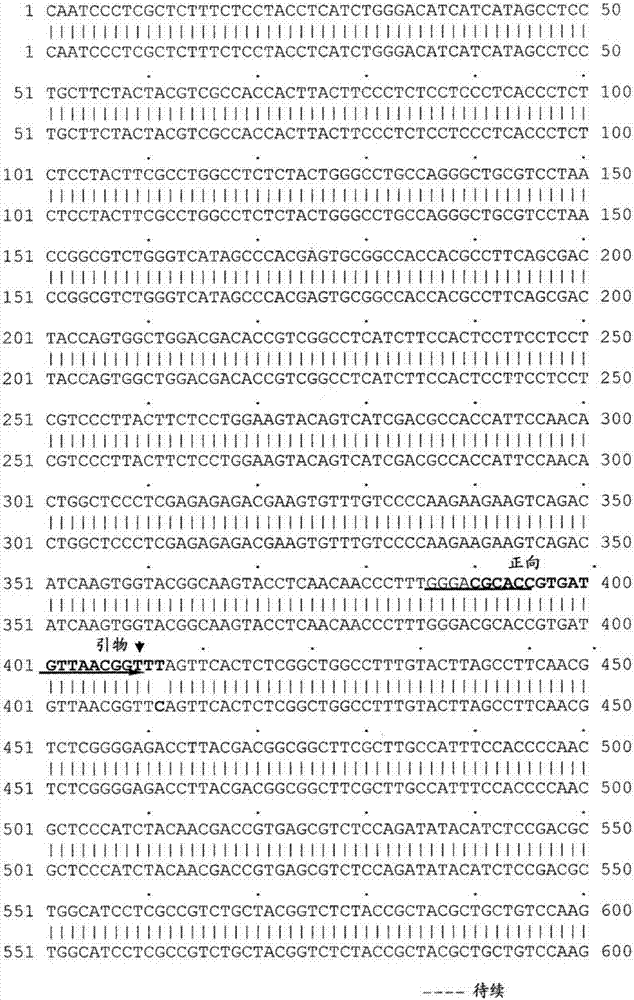
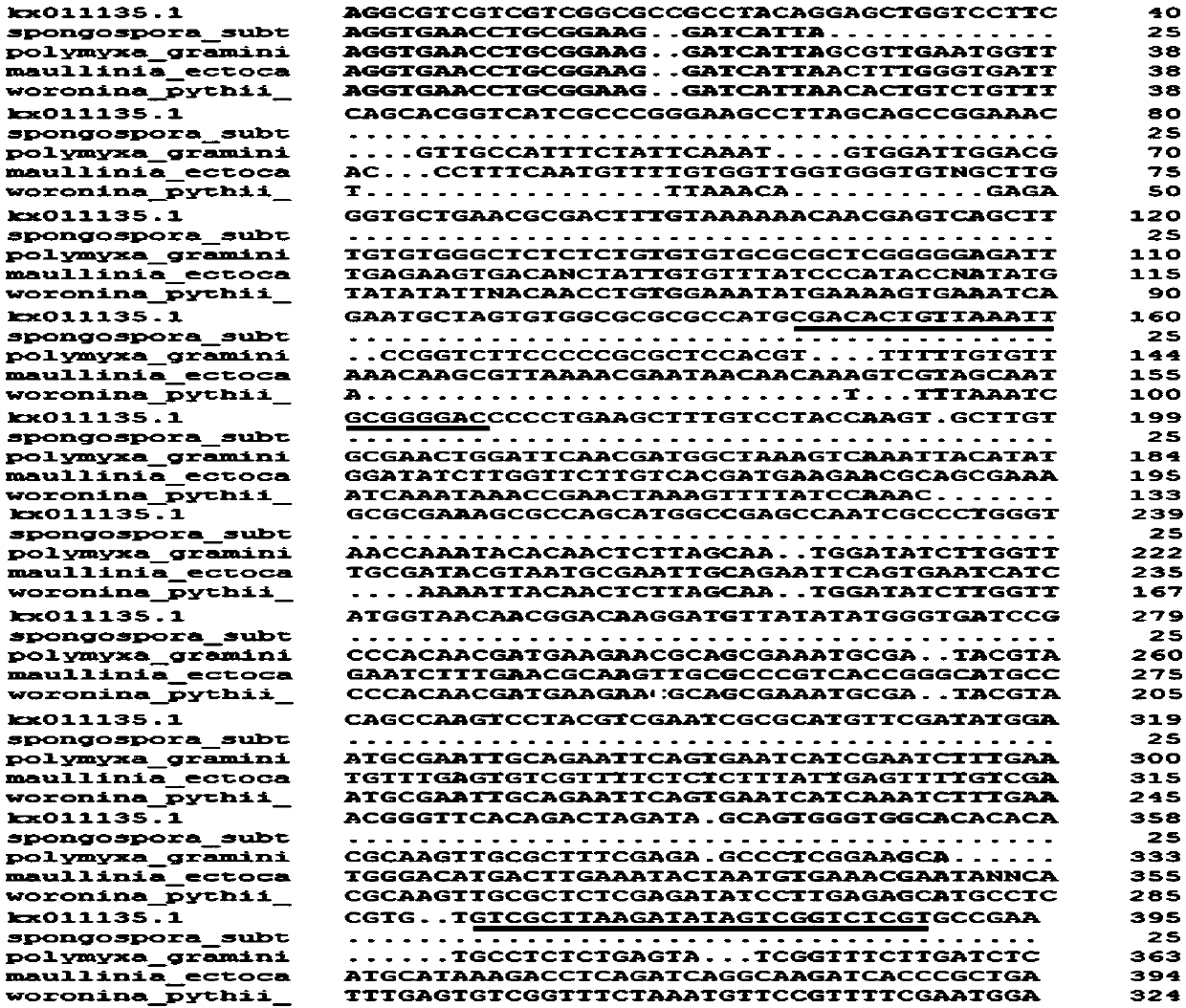
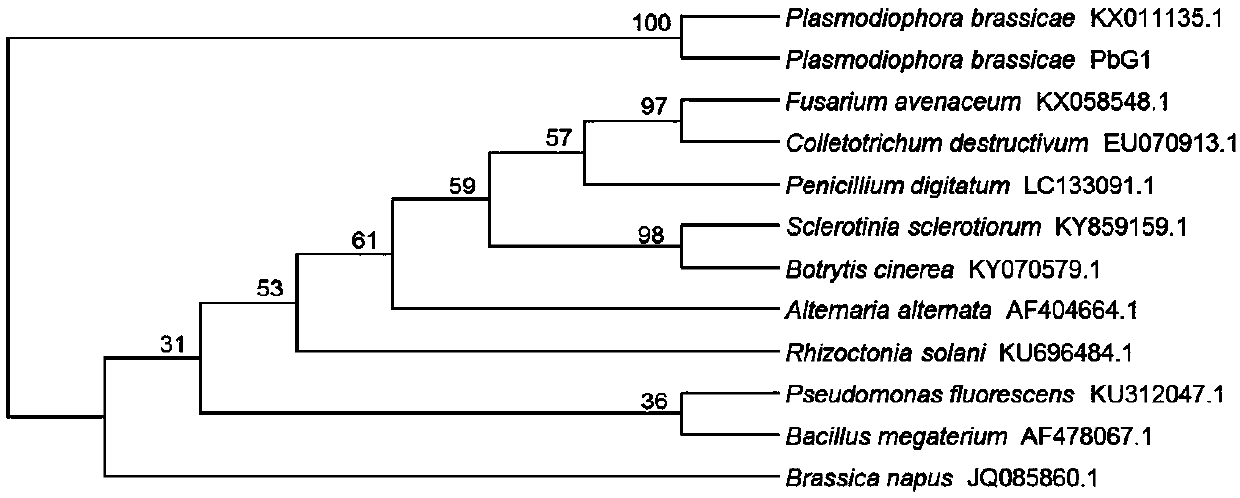
Specific PCR primers for Plasmodiophora brassicae Woron and detection method
PendingCN107937593AQuick checkAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMolecular identificationDynamic monitoring
The present invention provides specific PCR primers for Plasmodiophora brassicae Woron and a detection method. The specific PCR primers Pb4871F and Pb4871R (SEQ ID NO: 1-2) are designed based on conserved internal transcribed spacer sequences in the whole genomic sequence of the Plasmodiophora brassicae. The pair of primers can be used for molecular identification and disease epidemic dynamic monitoring of the Plasmodiophora brassicae. A rapid, accurate, simple and effective method for the early diagnosis and bacteria detection of clubroot of crucifers is provided, and an important tool and technical support are provided for effective monitoring of development and progression of the Plasmodiophora brassicae in a field and prediction and forecast of the clubroot of crucifers.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
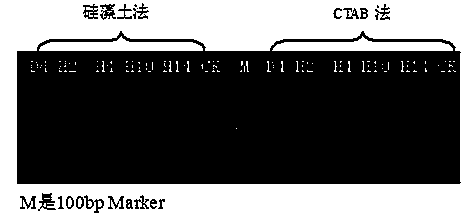
Method for extracting plasmodiophora brassicae DNA of cruciferae vegetables and application of method
InactiveCN104212794AEasy extractionQuick extractionMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicrobiology
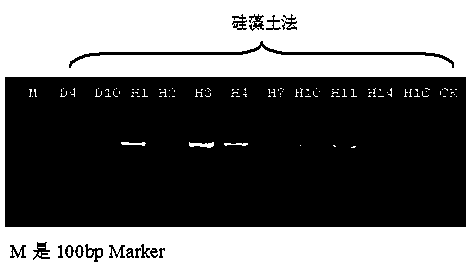
The invention provides a method for extracting plasmodiophora brassicae DNA of cruciferae vegetables and application of the method. A diatomite method is adopted to extract the DNA of a plasmodiophora brassicae sample of the cruciferae vegetables, the DNA of a plasmodiophora brassicae host is isolated, and a basis is laid for molecular studies of plasmodiophora brassicae. The method can be used for separating and detecting physiological strains of the plasmodiophora brassicae of the cruciferae vegetables, a specific molecular marker of the plasmodiophora brassicae is simultaneously used in a process of plant disease resistance identification, and the accuracy of specific disease resistance identification of the physiological strains can reach 100%. The method for extracting the plasmodiophora brassicae DNA of the cruciferae vegetables by using the diatomite method has good repeatability, high reliability and low detection cost and is time-saving and labor-saving.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
Quantitative detection method of plasmodiophora brassicae in different kinds of samples
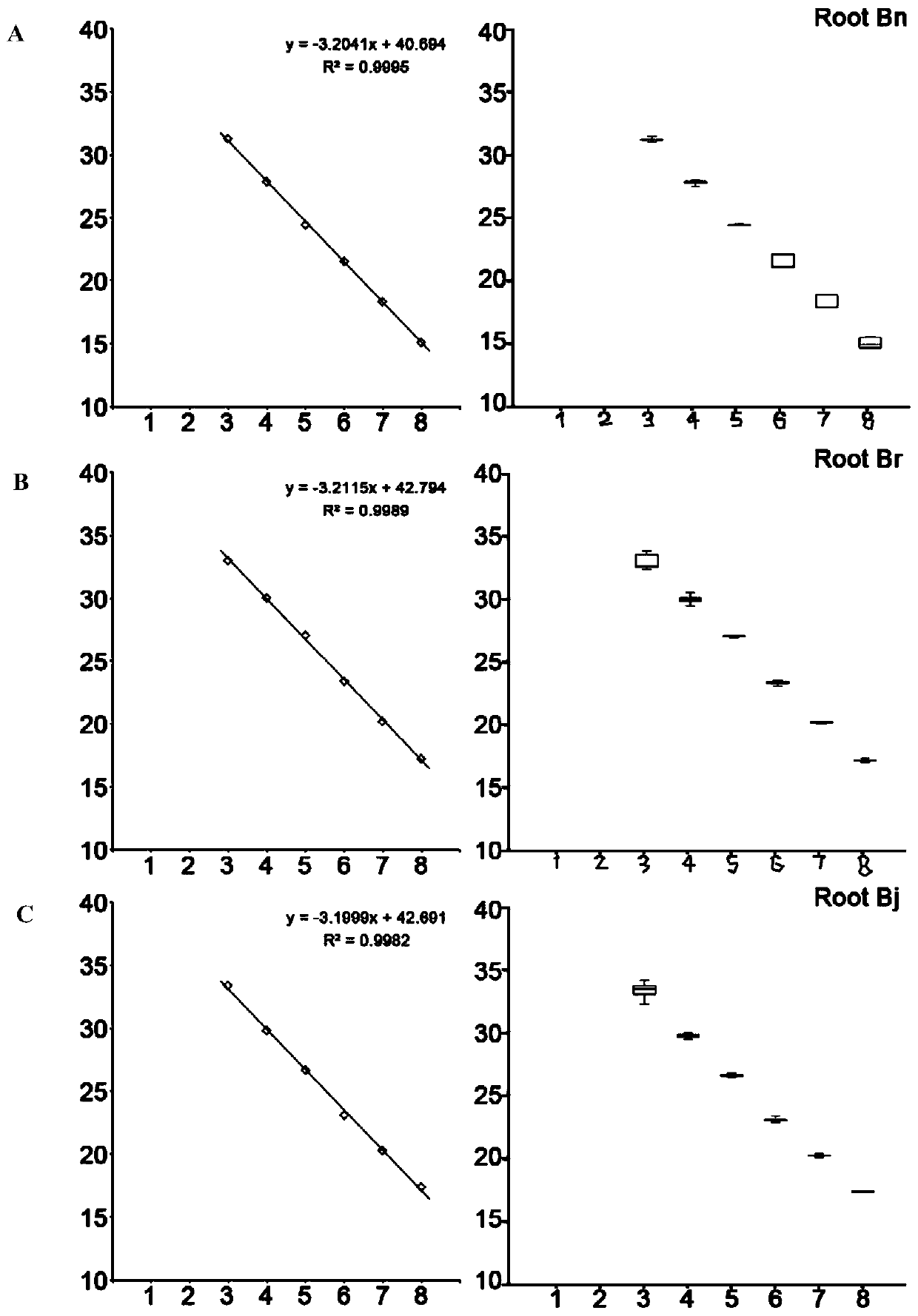
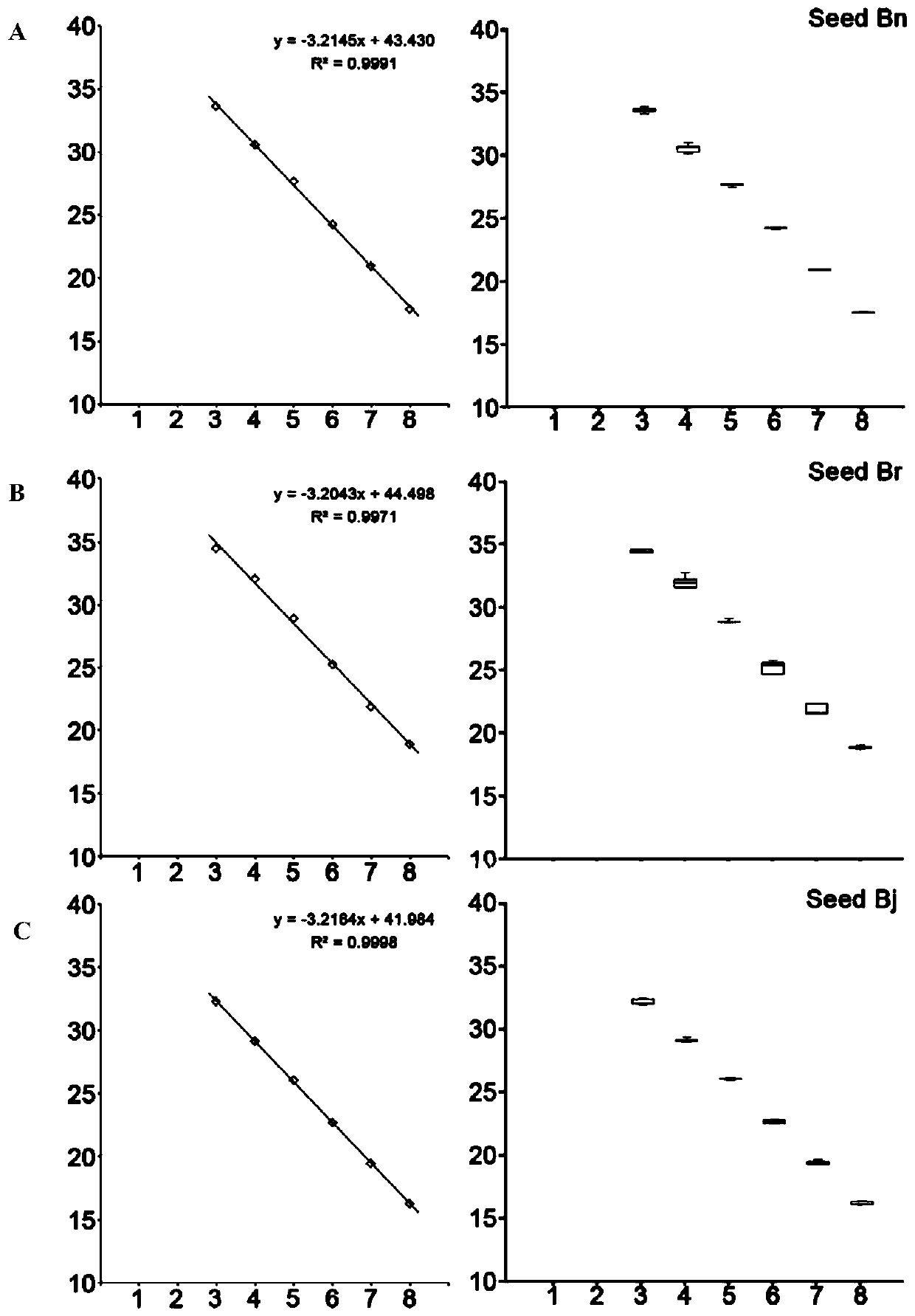
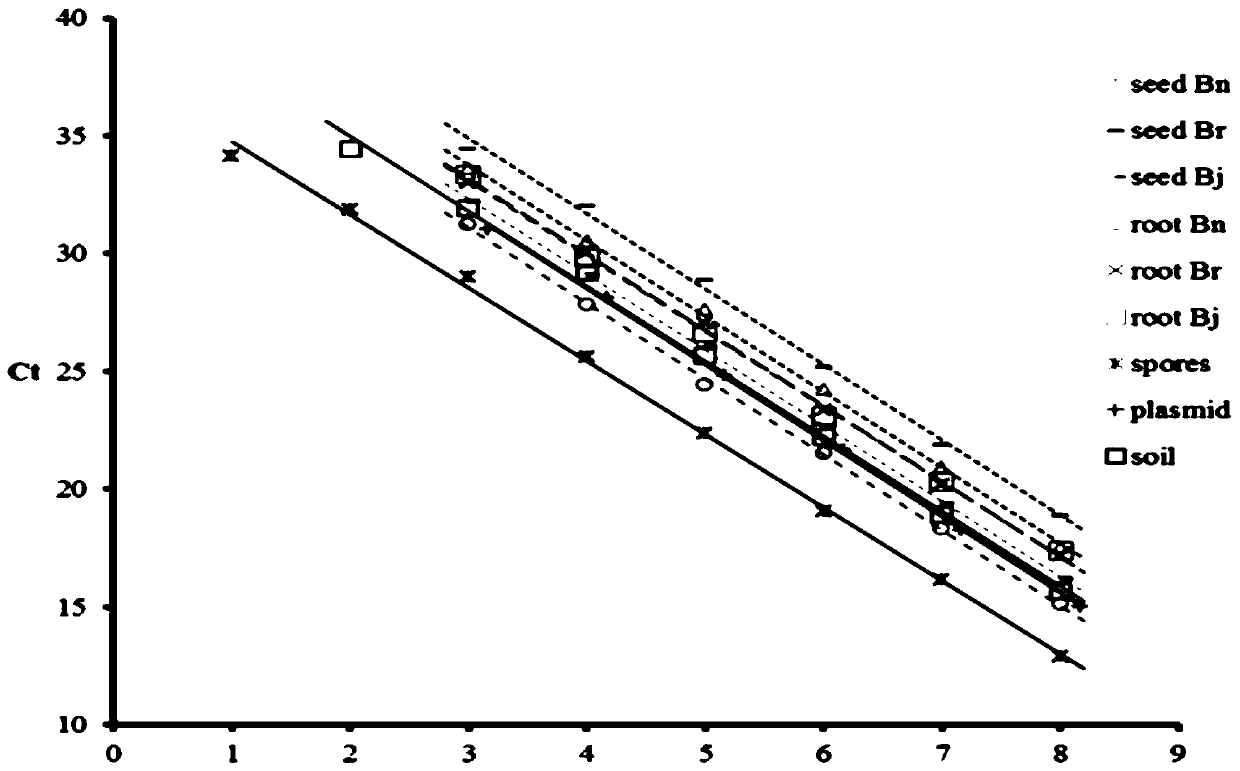
InactiveCN110241242ARealize quantitative detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesStatistical analysisIts region
The invention provides a quantitative detection method of plasmodiophora brassicae in different kinds of samples. The method comprises the steps of extracting DNA including plasmids, resting spores, germ carrying soil, crucifer germ carrying root tissue and seeds. ITS region gene fragments of the plasmodiophora brassicae in different samples are detected through a fluorescent quantitation PCR technique, and a regression equation between the number of the plasmodiophora brassicae in the samples and Ct value is established. The regression equations of different samples are fitted through statistics software, a universal model and an equation suitable for different samples are obtained, and quantitative detection for assessing the plasmodiophora brassicae in different samples through the universal model is realized. According to the quantitative detection method disclosed by the invention, a molecular biology technique is used, a mathematics and statistics analysis method is combined for use, the universal models for quantitative detection are fitted, the purpose of accurately assessing the quantity of the plasmodiophora brassicae in different samples is achieved, the quantitative detection method has the characteristics of saving test cost, shortening detection time and the like, and technical means and theory reference are provided for the respects of early diagnosis, epidemic early warning, prevention and control and the like of cruciferae club roots.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
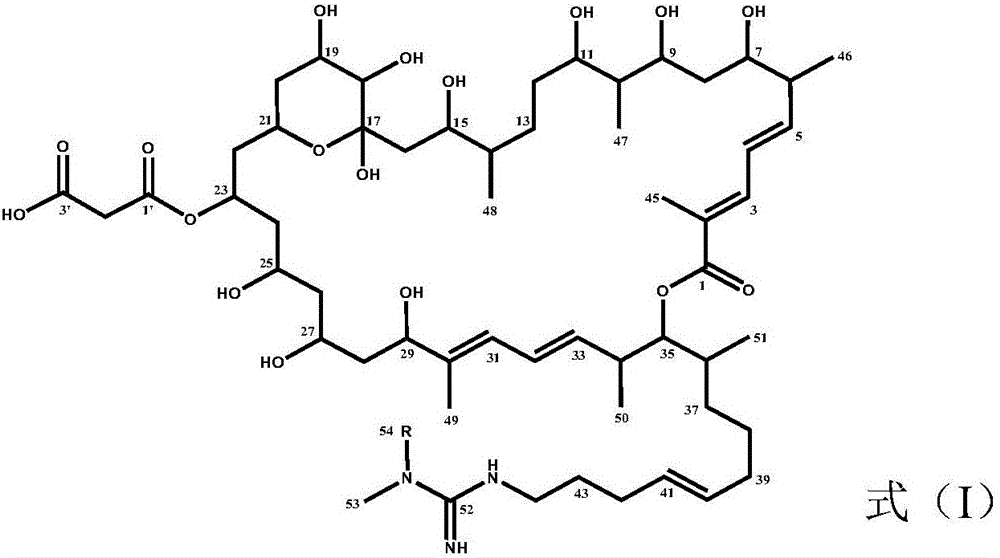
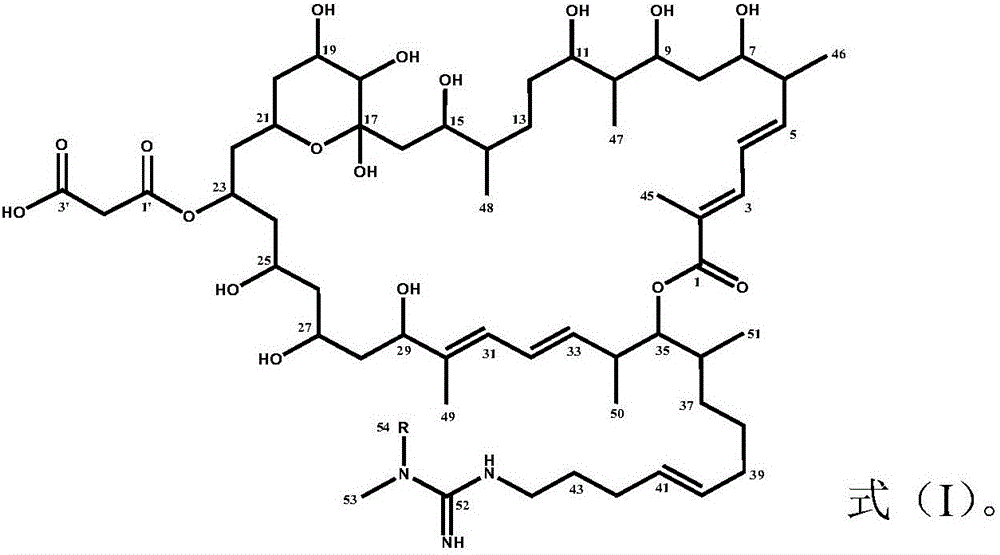
Method for inhibiting growth of plasmodiophora brassicae woronin, method for preventing and treating club roots of cruciferae crops and application of azalomycin
ActiveCN106719770APrevention and treatment of clubrootEnvironmentally safeBiocideFungicidesMicroorganismPlasmodiophora brassicae
The invention relates to a method for inhibiting growth of plasmodiophora brassicae woronin, a method for preventing and treating club roots of cruciferae crops and application of azalomycin. Specifically, the invention provides the method for inhibiting the growth of the plasmodiophora brassicae woronin; the method comprises the steps of enabling the azalomycin to be in contact with the plasmodiophora brassicae woronin. The invention further provides the method for preventing and treating the club roots of the cruciferae crops and the method comprises the step of applying the azalomycin to the cruciferae crops. The invention further provides the application of the azalomycin to prevention and treatment of the club roots of the cruciferae crops. According to the method for inhibiting the growth of the plasmodiophora brassicae woronin, the method for preventing and treating the club roots of the cruciferae crops and the application of the azalomycin, the club roots of the cruciferae crops can be effectively prevented and treated; the azalomycin can be obtained through a microorganism manner so that the azalomycin has the advantage of safety to environment and the application prospect is wide.
Owner:INST OF AGRI ENVIRONMENT & RESOURCES YUNNAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com