Patents
Literature
58 results about "Brassica cretica" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Process for preparing brassica vegetable seedling powder chewable tablets and brassica vegetable seedling powder chewable tablet product
InactiveCN102511753ASmooth appearanceEmerald green colorFood shapingFood preparationBrassica creticaBroccoli raab
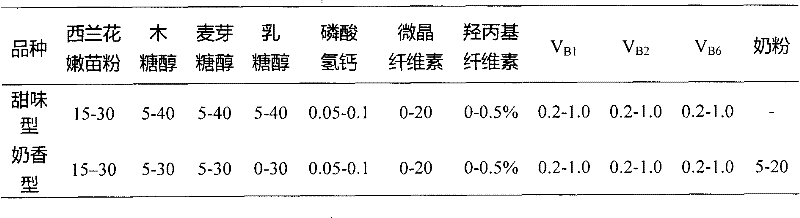
The invention relates to a process for preparing brassica vegetable seedling powder chewable tablets and a brassica vegetable seedling powder chewable tablet product, belonging to the technical field of deep processing of agricultural products. The process is characterized by comprising the following steps of: with brassica vegetable seedling powder, such as broccoli and the like as a main basic stock, compounding, preparing a soft material, granulating, drying, tabletting, sterilizing and packing to prepare the brassica vegetable seedling powder chewable tablet with the advantages of clean appearance, green color and crispness. The process for preparing the brassica vegetable seedling powder chewable tablet, disclosed by the invention, is simple, has high industrial degree and can realize complete utilization on the brassica vegetable seedling, such as broccoli and the like, thereby increasing the additional value of the brassica vegetable seedling. The brassica vegetable seedling powder chewable tablets, including the broccoli and the like, prepared by the process disclosed by the invention have functions of resisting oxidation, slowing aging and resisting inflammation and cancer and the like of human bodies, and is a kind of casual healthcare food. According to the product of the process for preparing the brassica vegetable seedling powder chewable tablets, disclosed by the invention, the content of 4-methylsulfinylglucosinolate is up to 185.0-413.0mg / 100g, and the content of sulforaphane provided by each chewable tablet is equal to that provided by 30-75g of fresh brassica vegetable, such as broccoli and the like.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for enriching and extracting sulforaphane from brassica vegetable seeds
InactiveCN102586352AReduce manufacturing costSimple production processOrganic chemistryFermentationVitamin CSulforaphane
The invention relates to a method for enriching and extracting sulforaphane from brassica vegetable seeds and belongs to the technical field of food biological technology. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: taking the sulforaphane brassica vegetable seeds with germinating ability as raw materials; crushing the raw materials and adding a Tris-HCl buffer solution according to the ratio of the materials to liquid being (w / v) 1:(3-5); adjusting the pH value to 6.0-8.0 to form an incubation buffer; adding vitamin C and Zn<2+>, activating endogenous myrosinase in the vegetable seeds and hydrolyzing glucosinolate to form the sulforaphane with an anti-cancer effect; and extracting the sulforaphane from the incubation buffer with ethyl acetate and carrying out filtering, vacuum concentration, ultrasonic extraction and vacuum condensation to obtain a sulforaphane product. The method disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of wide application range of the raw material, low production cost, high enrichment quantity of the sulforaphane and the like. The method is suitable for health-care food sulforaphane products.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for evaluating resistance of brassica plants on club root
InactiveCN102511368ASave landAccurate and reliable identification resultsCultivating equipmentsHorticulture methodsBiotechnologyBrassica cretica
Owner:云南省农业科学院园艺作物研究所
Core primer composition for Brassica SSR (simple sequence repeats)
InactiveCN102154277AIncrease profitImprove efficiencyDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyBrassica cretica
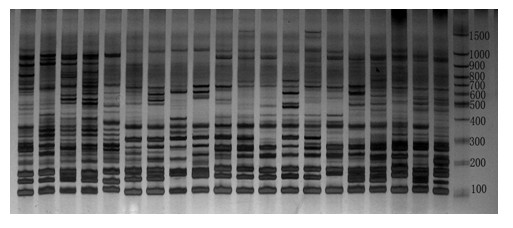
The invention discloses a core primer composition for Brassica SSR (simple sequence repeats) and belongs to the technical field of molecular inheritance. The core primer composition comprises 190 core SSR primer pairs for 19 chromosomes in Brassica A and C genomes; and 10 SSR primer pairs are uniformly distributed on each chromosome, which have high polymorphism levels, substantially consistent annealing temperature and clear amplification band patterns. The core SSR primer composition is applied to increasing the molecular marking efficiency by 3 to 5 times without increasing the working costs, and is particularly suitable for the identification, the genetic diversity analysis, the nullisome and abnormal chromosome individual identification and the seed purity determination of the Brassica germplasm resources. The core SSR primer composition has the advantages of simpleness in operation, high stability and good reproducibility.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Agrobacterium-mediated flowering cabbage genetic transformation method
InactiveCN111893133ASimple and fast operationImprove performancePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsBrassica creticaPlant genetic engineering
The invention relates to the field of plant genetic engineering application, in particular to an agrobacterium-mediated flowering cabbage genetic transformation method. The method comprises the following steps: performing surface disinfection on flowering cabbage seeds, culturing the seeds on a sowing culture medium, and performing pre-culture, infection, co-culture, recovery culture and subculture by taking cotyledons with petiole of aseptic seedlings with the seedling age of 3 days as explants; transferring adventitious buds subjected to subculture into a rooting culture medium for rooting culture to obtain tissue culture seedlings, opening bottles for hardening the tissue culture seedlings in one step, and performing normal management to obtain transgenic plants. According to the method, flowering cabbages are taken as materials, a flowering cabbage genetic transformation system is constructed, the transgenic plants are obtained, the operation is simple and efficient, the pollutionrate is low, the comprehensive performance is high, and a foundation is laid for genetic function research and molecular breeding of brassica plants.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
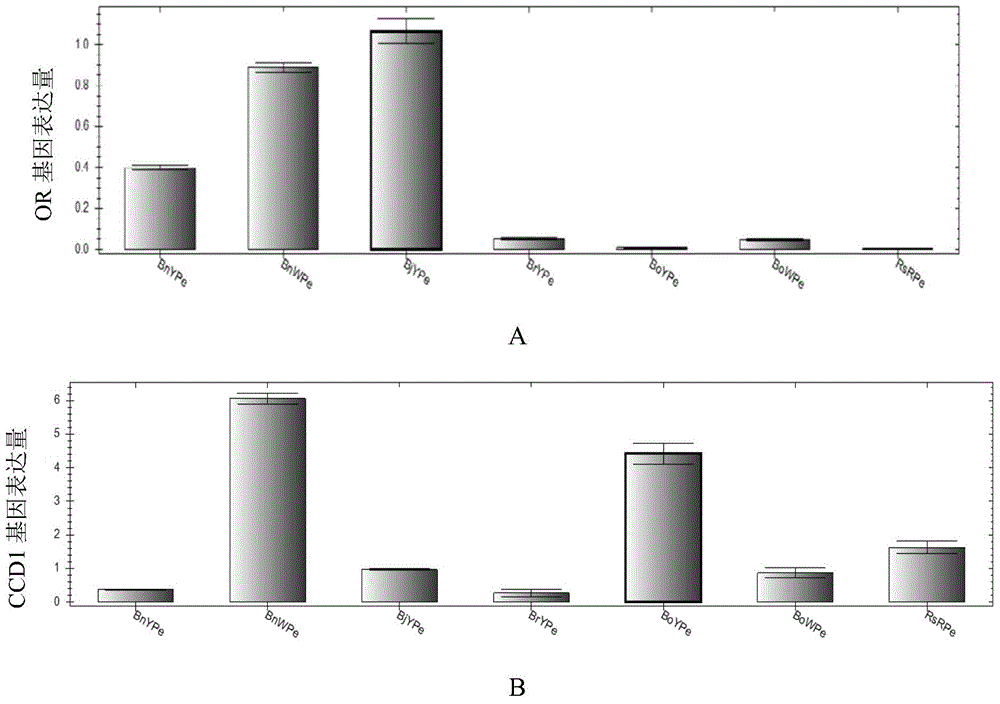
Application of inhibiting accumulation of xantheins and accumulating lycopene and anthocyanin in preparation of Brassica plants with red pedals
InactiveCN104480128AIdentify key differentially expressed gene lociBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBrassicaLycopene
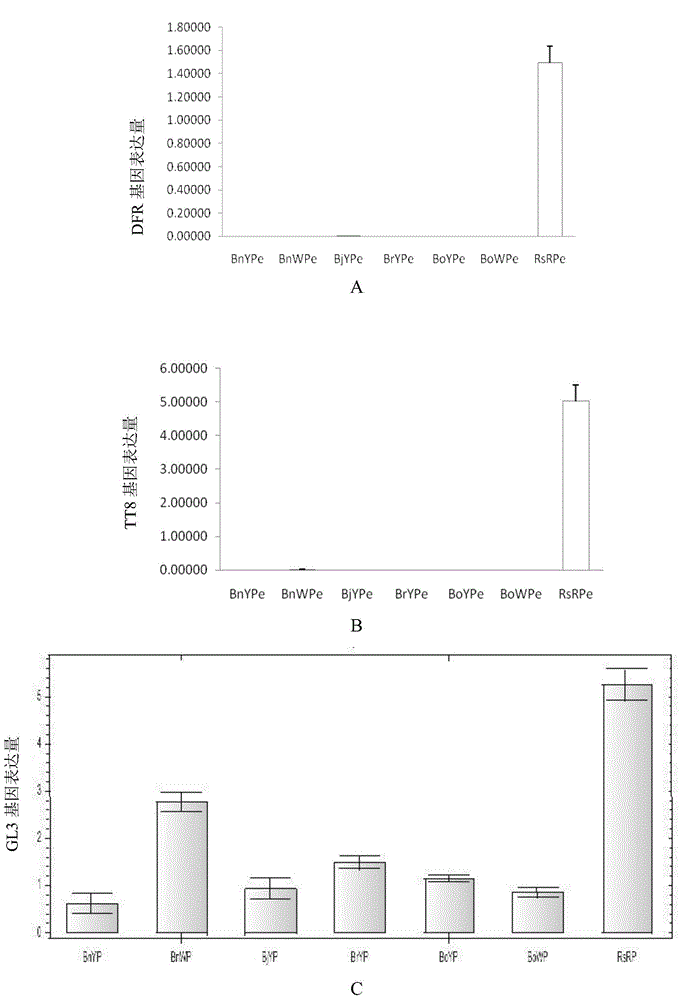
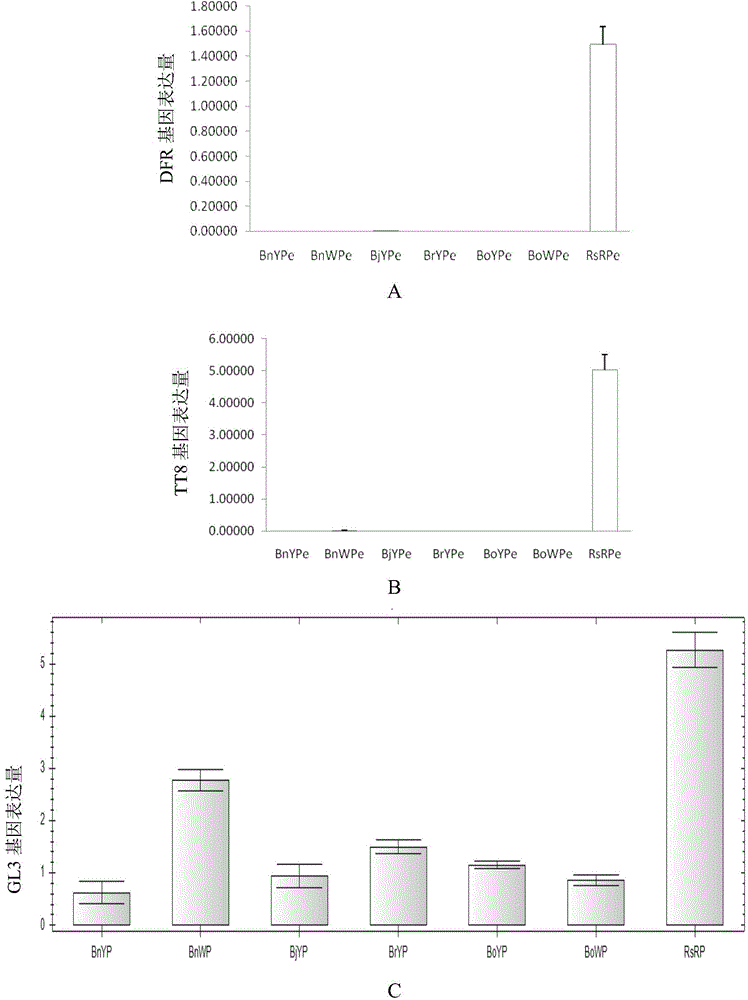
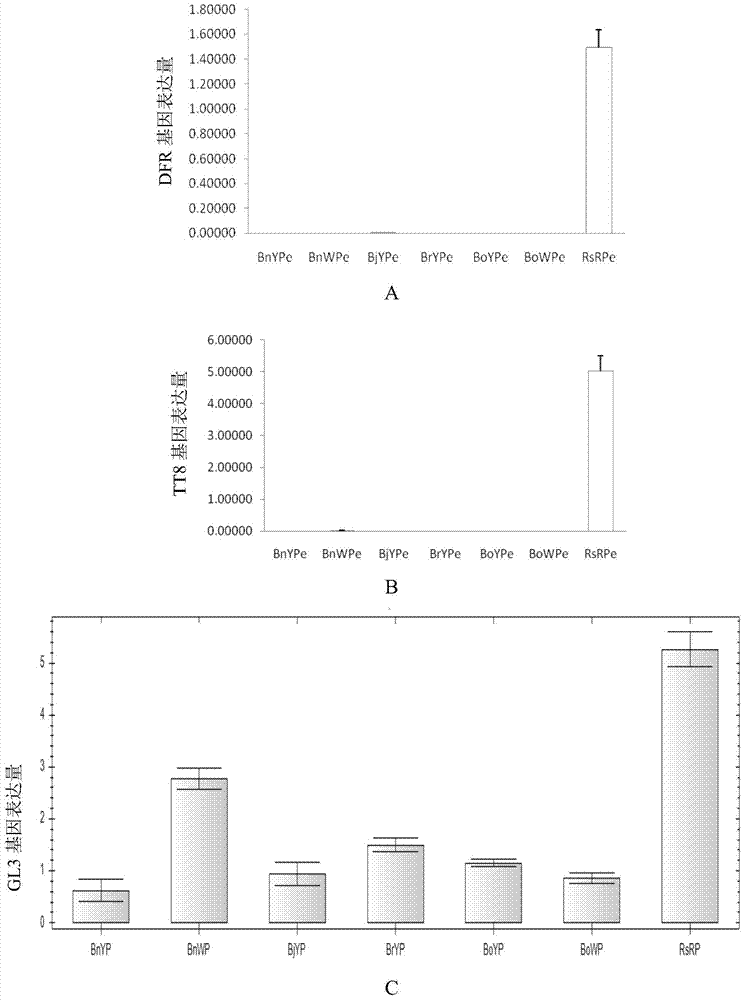
The invention discloses application of inhibiting accumulation of xantheins while accumulating lycopene and anthocyanin in preparation of Brassica plants with red pedals. The application is specifically as follows: interfering with the gene expression of LCYB, LCYE, MYB12 and MYB111 and simultaneously performing ectopic expression of TT8 genes. The invention further discloses a preparation expression vector for interfering with the gene expression of LCYB, LCYE, MYB12 and MYB111 and simultaneously performing ectopic expression of the TT8 genes and a preparation method of the vector. By interfering with the gene expression of LCYB, LCYE, MYB12 and MYB111, the xantheins, namely carotenoid and flavonol are inhibited; and by performing the ectopic expression of the TT8 genes, the accumulation of lycopene and anthocyanin can be promoted, so that the pedals are red, the Brassica plants with the red pedals are successfully prepared, and the flower colors of the Brassica plants are enriched.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
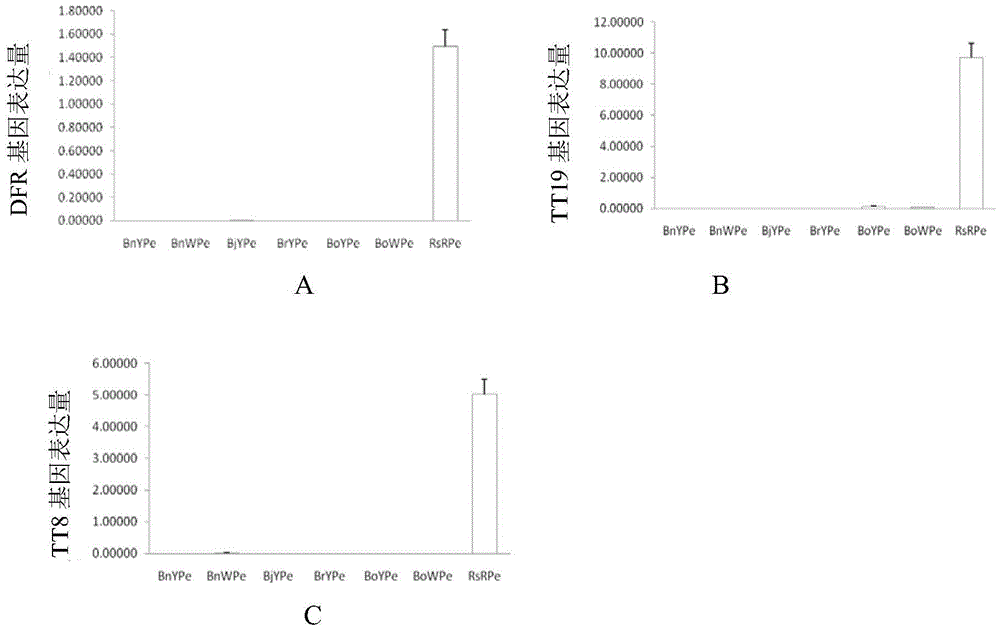
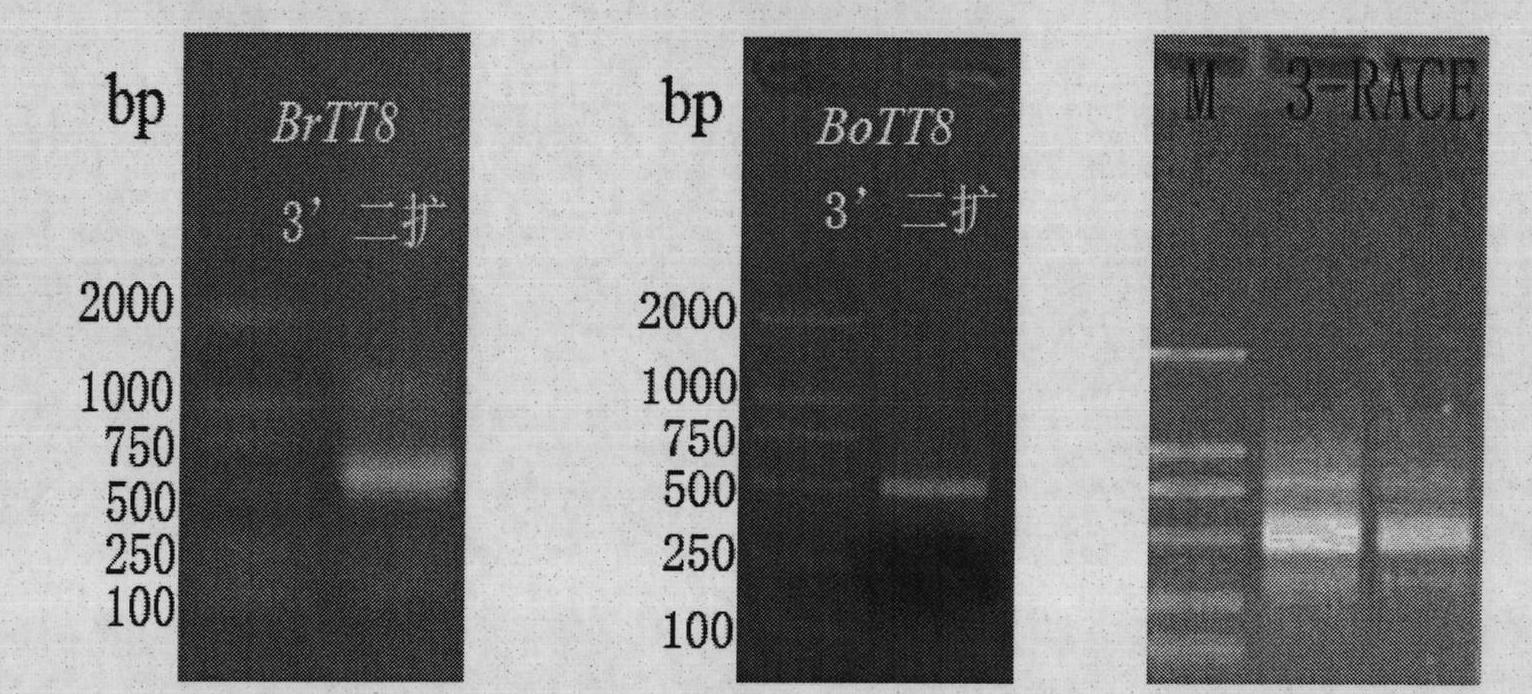
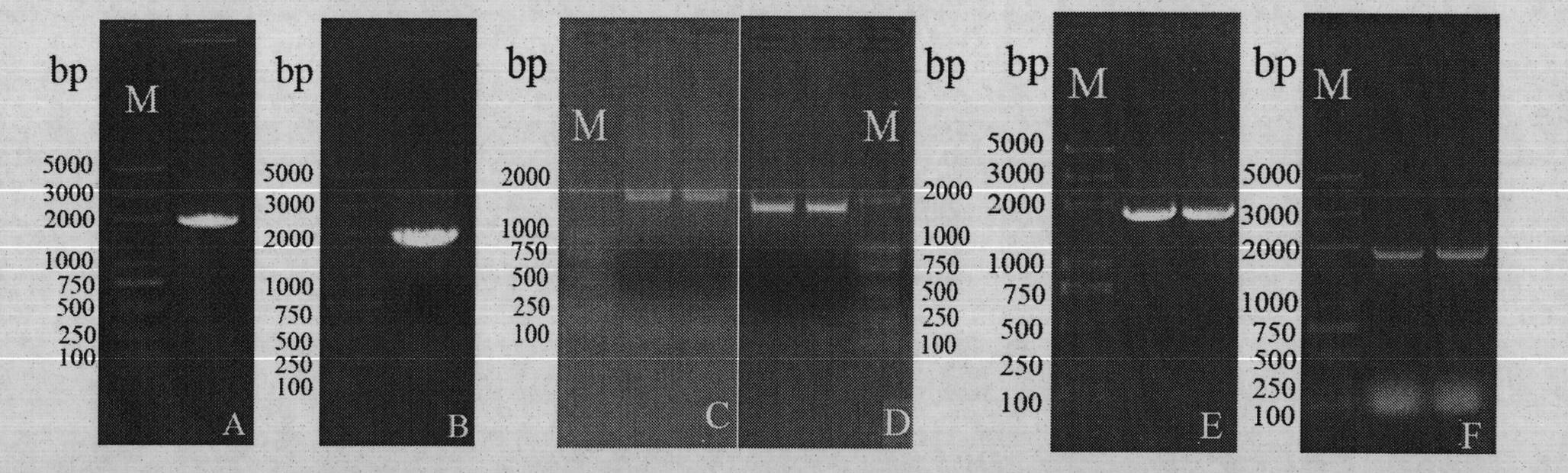
Cabbage-type rape as well as parent species Chinese cabbage and cabbage TT8 gene families and applications thereof
InactiveCN101942457AFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBrassicaMolecular breeding
The invention discloses cabbage-type rape as well as parent species Chinese cabbage and cabbage TT8 gene families and applications thereof, wherein, the Chinese cabbage TT8 gene family comprises a BrTT8-1 gene (SEQ ID No.1-2) and a Br TT8-2 gene (SEQ ID No.3-4); the cabbage TT8 gene family comprises a BoTT8-1 gene (SEQ ID No.5-6) and a BoTT8-2 gene (SEQ ID No.7-8); the cabbage-type rape TT8 gene family comprises a BnTT8-1 gene (SEQ ID No.9-10) and a BnTT8-2 gene (SEQ ID No.11-12). The above gene families can be used for molecule breeding of the brassica crop seed properties.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Novel selective breeding method for male sterile line of Sichuan preserved pickle cytoplasm brasica napus
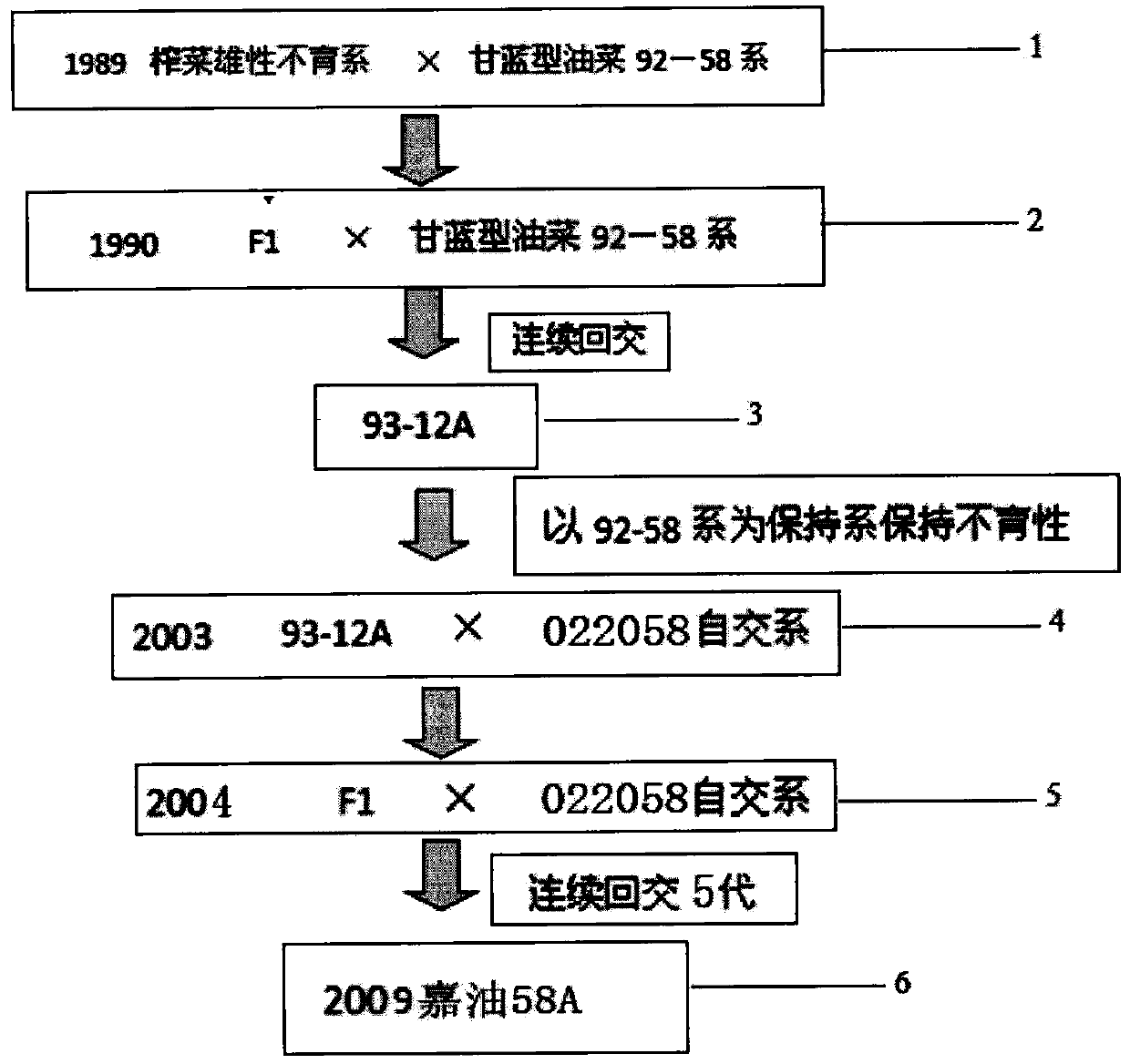
The invention discloses a novel selective breeding method for a male sterile line of Sichuan preserved pickle cytoplasm brasica napus. According to the method, a sterile source of the Sichuan preserved pickle is transferred into the brasica napus through distant hybridization and continuous backcrossing between different inter-species in brassica, so as to obtain Sichuan preserved pickle cytoplasm brasica napus CMS '93-12A'. The Sichuan preserved pickle cytoplasm brasica napus CMS '93-12A' is improved by hybridization and continuous backcrossing, so as to obtain a novel, stable, and double low sterile line material 'Jia rapeseed 58A'; the identification of the restoring and maintaining relationship of the Sichuan preserved pickle cytoplasm CMS shows that the restoring and maintaining relationship of the 'Jia rapeseed 58A' is different from the restoring and maintaining relationships of Pol CMS and Shaan 2A CMS, and meanwhile, one part of restorer material is screened out, and is improved to obtain five parts of double haploid restorer materials; the PCR identification with a specific primer shows that sterile sources of the '93-12A', the 'Jia rapeseed 58A' and mustard CMS are the same; an identification result of hybridization mating group yield of the 'Jia rapeseed 58A' and different restorer materials shows that a part of the combinations have a good yield-increasing potential, and the 'Jia rapeseed 58A' has a good combining ability. The method provided by the invention can be applied to the selective breeding of rapeseed varieties and the planting of the rapeseed in production.
Owner:ZHEJIANG JIAXING AGRI SCI ACADEMY INST
Culture medium prescription of regenerated plant from isolated microspore of brassica
InactiveCN101433184AWide adaptabilityRich breeding resourcesPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsSporeBrassica
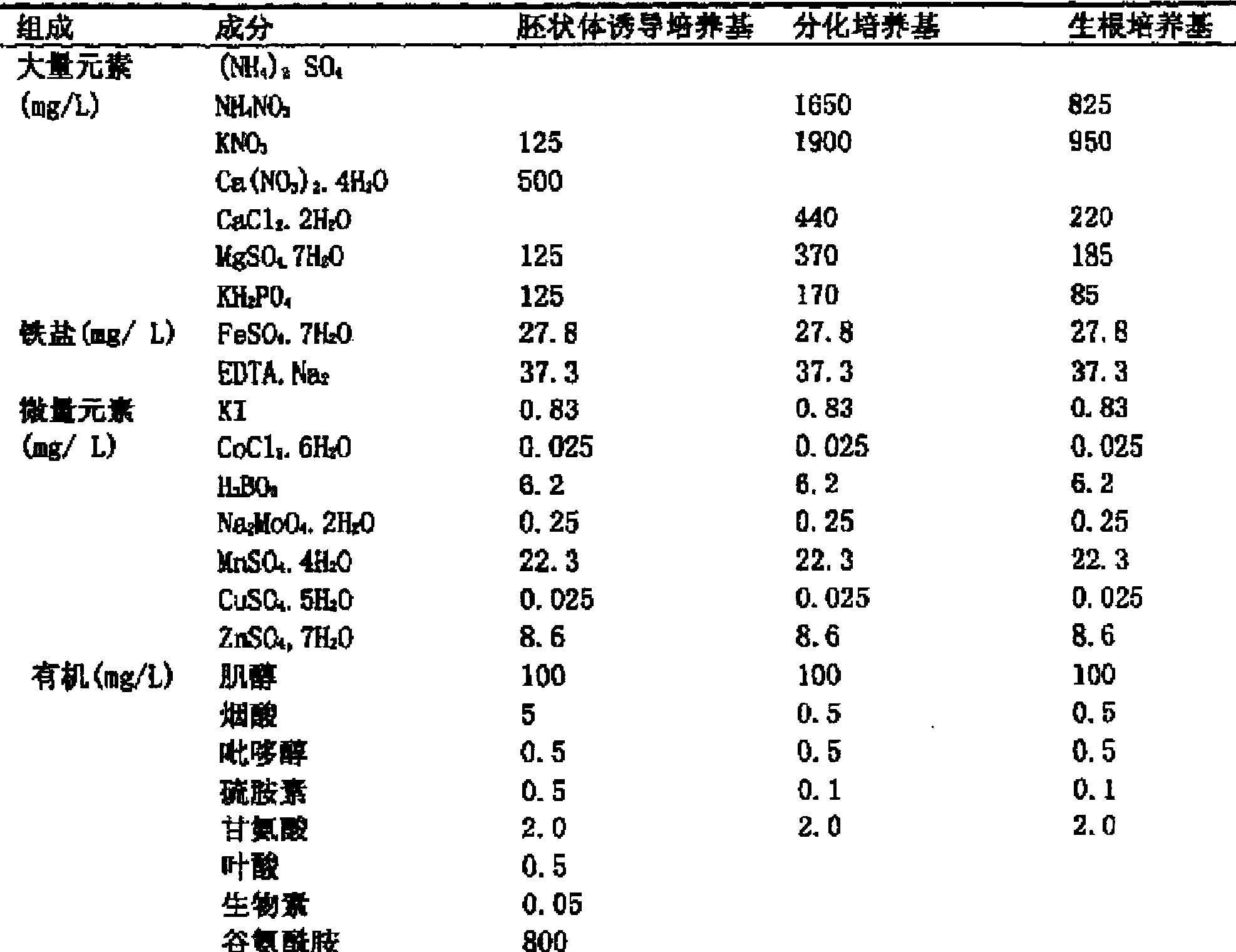
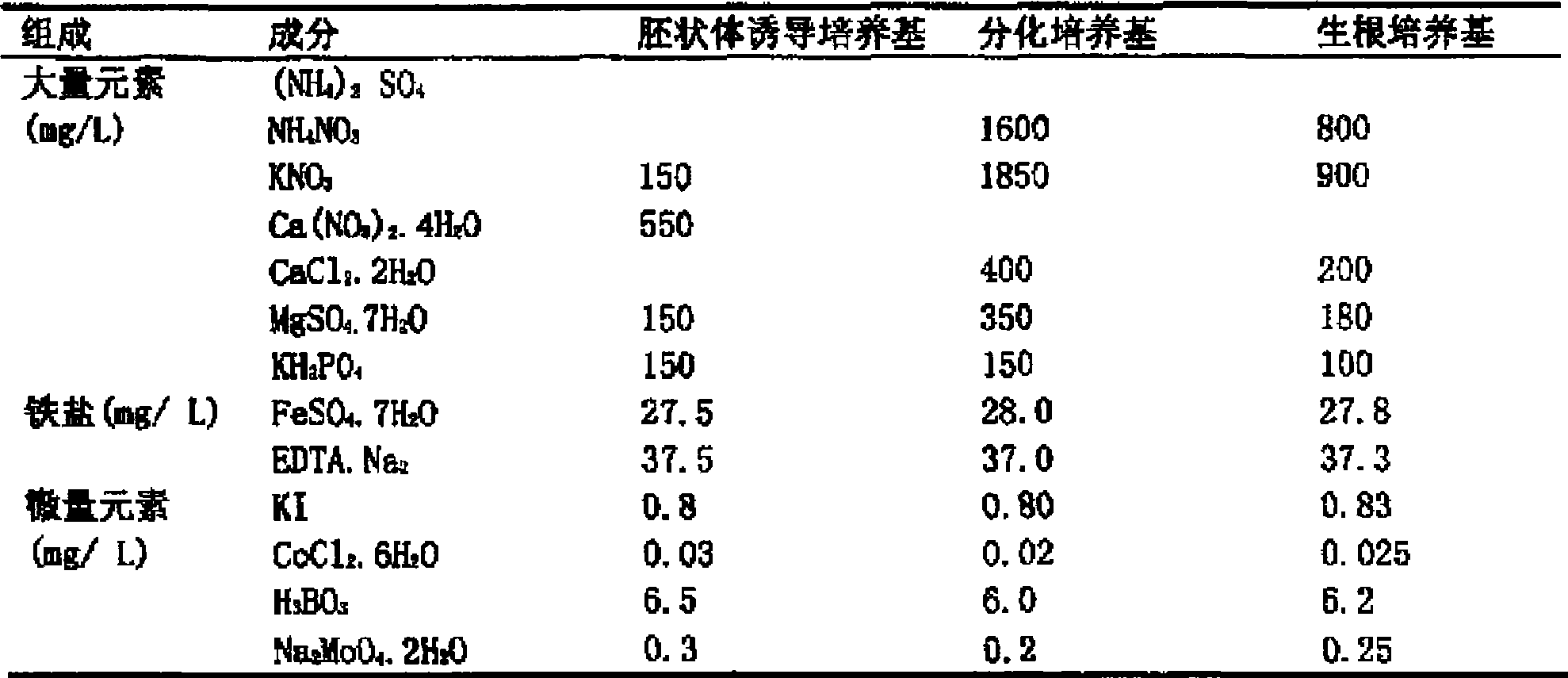
The invention provides a culture medium formulation for regenerated plantlets of Brassica isolated microspores, which relates to improvement of a culture medium formulation for regenerated plantlets of Brassica microspores as horticultural crops, and belongs to the field of bioengineering. The invention provides the culture medium formulation for regenerated plantlets of Brassica isolated microspores, which is high in induced embryo formation rate and differentiation rate. A culture medium of the invention comprises an embryoid induction culture medium, a differentiation culture medium and a rooting culture medium, wherein the embryoid induction culture medium, the differentiation culture medium and the rooting culture medium all comprise macroelements, trace elements and organic elements. The formulation has the advantages of providing a large number of new genotype pure lines for breeding and greatly enriching breeding resources of Brassica.
Owner:刘祥军
Method for preventing root-knot nematode by taking brassica crop rapes as raw materials
InactiveCN103250525AGood control effectSimple structurePlant protectionBrassica creticaRoot-knot nematode
The invention relates to a method for biologically preventing root-knot nematode by taking brassica crop rapes as raw materials. The rapes are taken as the raw materials and are uniformly turned over to a plowing layer after crushed on site during growth, and plastic films for covering are used for high-temperature treatment for 15-20 days, so that the root-knot nematode is killed. The rapes internally contain a large quantity of thioglycosides, the thioglycosides can be decomposed into isothiocyanate substances under the action of self-contained myrosinase under the condition of a certain temperature and humidity, and the root-knot nematode is effectively killed. Besides, the ground temperature can be increased by the aid of the covering films, decomposition of straws is promoted, and the root-knot nematode can also be directly killed. Compared with an existing prevention method, the method has the advantages that natural plants are completely taken as the raw materials, chemical pesticides are completely omitted, energy consumption is low, the method conforms to the low-carbon concept and is applicable to wide area, simple in operation, low in service cost and remarkable in comprehensive benefit, the root-knot nematode can be effectively prevented, soil fertility and a soil structure can be improved, and high economic, social and ecological benefits are achieved.
Owner:卢志军
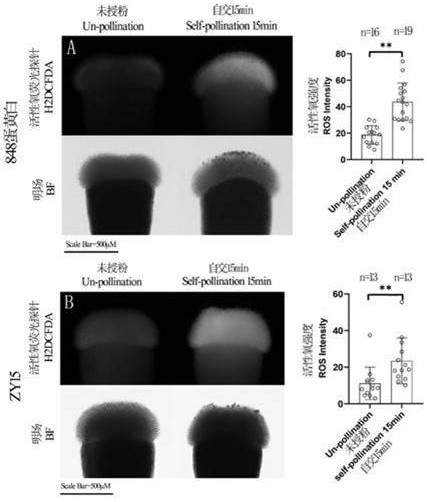
Reagent for overcoming self-incompatibility of brassica and raphanus and use method and application of reagent
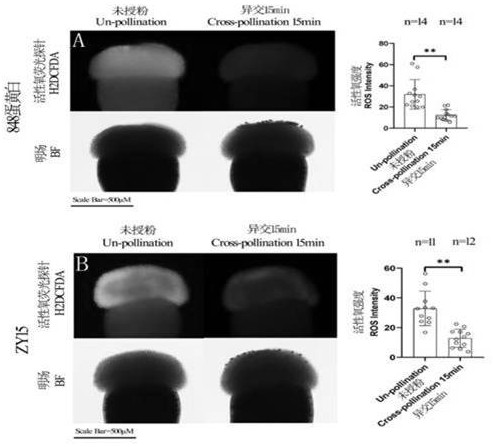
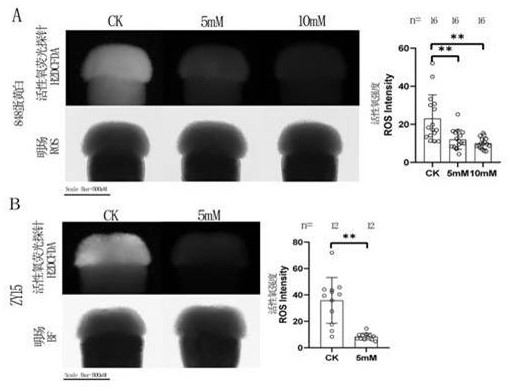
ActiveCN112042670AActive oxygen reductionReduce inhibitionBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBrassica creticaBrassica rapa
The invention relates to the technical field of brassica and raphanus plant breeding, self-incompatible Chinese cabbages and self-incompatible radishes are taken as examples, when the Chinese cabbagesand the radishes enter an initial flowering stage and bloom in quantity, a potassium iodide solution of 1-10mM mixed with 0.025% Tween20 (for increasing the adhesiveness of the solution) is sprayed by a sprayer at 8: 00-10: 00 in sunny morning; the solution is sprayed on a cross-shaped stigma which is just unfolded until the surface of the stigma is stained with water drops. Spraying is performedfor the second time and the third time at an interval of 15 minutes. After spraying for the third time and the fog drops on the stigmas are completely dried, pollinating with fresh pollen, pinching off redundant unexpanded inflorescences, and sleeving with a seed collecting bag. The method is suitable for self-incompatible lines of brassica and raphanus plants. The potassium iodide solution is sprayed on stigmas, which are just developed into cross flowers, of inflorescences of self-incompatible Chinese cabbages (Brassica rapa L. Sp. Pekinensis) and self-incompatible radishes (Raphanus sativus) so that the self-affinity index can be increased to different degrees.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Gene families of cabbage type rape, parental species Chinese cabbage and cabbage AHA10 thereof and applications thereof
InactiveCN101942458AFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBrassicaMolecular breeding
The invention discloses gene families of cabbage type rape, parental species Chinese cabbage and cabbage AHA10 and applications thereof, wherein the Chinese cabbage AHA10 gene family comprises a BrAHA10-1 gene (SEQ ID No.1-2) and a BrAHA10-2 gene (SEQ ID No.3-4); the cabbage AHA10 gene family comprises a BoAHA10-1 gene (SEQ ID No.5-6) and a BoAHA10-2 gene (SEQ ID No.7-8); the cabbage type rape AHA10 gene family comprises a BnAHA10-1 gene (SEQ ID No.9-10) and a BnAHA10-2 gene (SEQ ID No.11-12); and the gene families can be applied to the molecular breeding of the seed properties of brassica plants.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
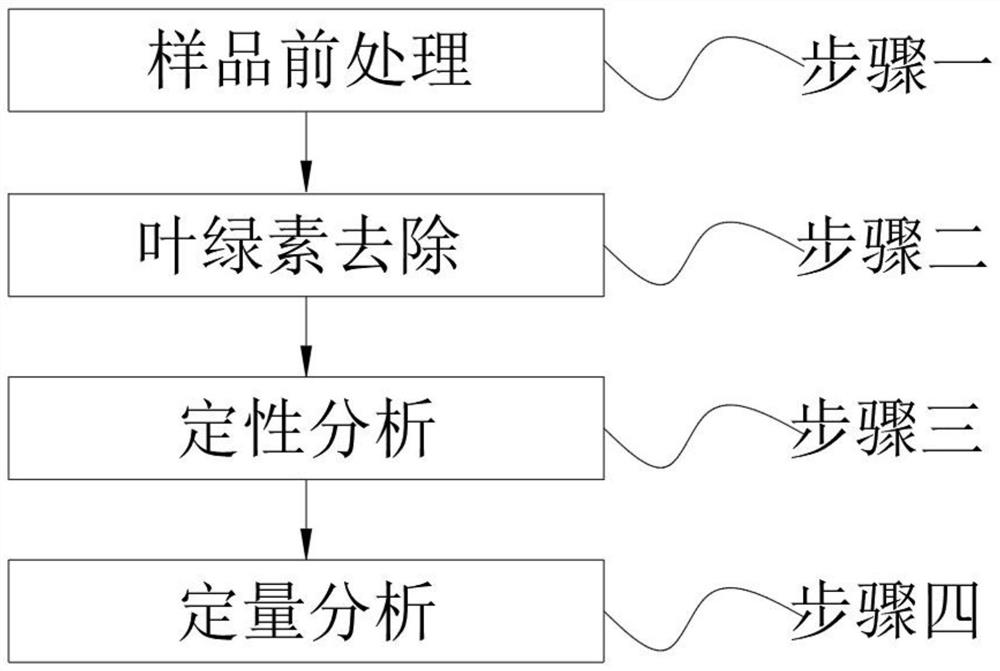
Method for rapidly screening farm chemical residues in vegetables
The invention discloses a method for rapidly screening farm chemical residues in vegetables. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, sample pretreatment; step 2, chlorophyll removal; step 3, qualitative analysis; step 4, quantitative analysis. In the first step, firstly, vegetable leaves of leaf vegetables are cut into pieces and put into a homogenizer to be ground uniformly, and part of pulp with skins of solanaceous vegetables, bulbs, brassica vegetables, melons and legume vegetables is put into the homogenizer to be ground uniformly, so that a sample is prepared. The method is safe and reliable, the screening method is high in screening speed and convenient to use, chlorophyll can be conveniently removed before screening by adding the step of removing chlorophyll in vegetables, sensitivity is improved, screening is convenient, and by using the screening method, 83 farm chemicals with high toxicity, common use and high residual risk and metabolite parameters thereof can be conveniently screened out, the types of the farm chemicals capable of being screened out are more comprehensive, and the method is convenient to popularize and use.
Owner:耿春辉 +1
Application of gene for interfering expression of LCYB and LCYE and simultaneously over-expressing PAP in preparation of brassica plant having red petals
InactiveCN104531754AIdentify key differentially expressed gene lociFermentationHorticulture methodsBrassicaLycopene
The invention discloses application of a gene for interfering expression of LCYB and LCYE genes and simultaneously over-expressing a PAP gene in preparation of a brassica plant having red petals. The invention further discloses an expression vector for interfering expression of the LCYB and LCYE genes and simultaneously over-expressing the PAP gene and a preparation method of the expression vector. Yellow carotenoid is inhibited and red lycopene is accumulated by interfering expression of the LCYB and LCYE genes; accumulation of cyanin can be promoted through over-expression of the PAP gene; therefore, the petals are red; the brassica plant having red petals is successfully prepared; and colours of the brassica plants are enriched.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
Method for simultaneously increasing sulforaphane content and selenium content in edible organs of brassica vegetables
InactiveCN110668858AIncreased sulforaphane contentMagnesium fertilisersFertilising methodsBrassica creticaBrassica sinapis
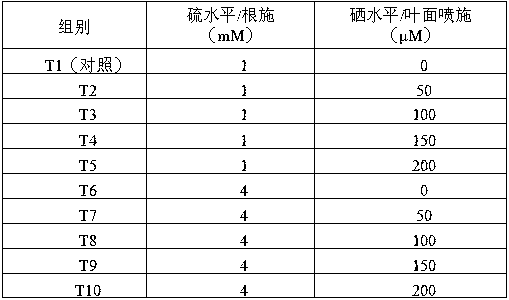
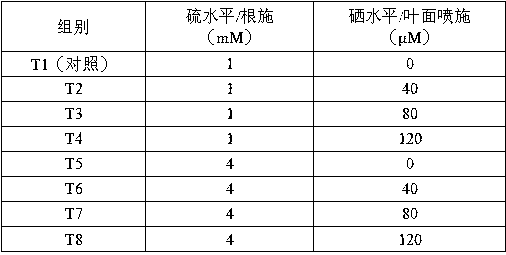
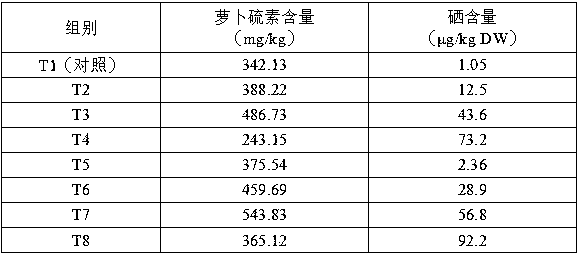
The invention discloses a method for simultaneously increasing the sulforaphane content and the selenium content in the edible organs of brassica vegetables. According to the method, in the squaring stage of Brassica oleracea or the bolting stage of Brassica alboglabra, 1-4 mM of a sulfur fertilizer is subjected to root application, and 40-150 [mu]M of a selenium fertilizer is sprayed to leaf surfaces. According to the invention, by using the method, the sulforaphane content in the edible organs of brassica vegetables can be effectively increased by 13.5-59%, and the content of organic selenium can be effectively increased by 11.9-99.5 times.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
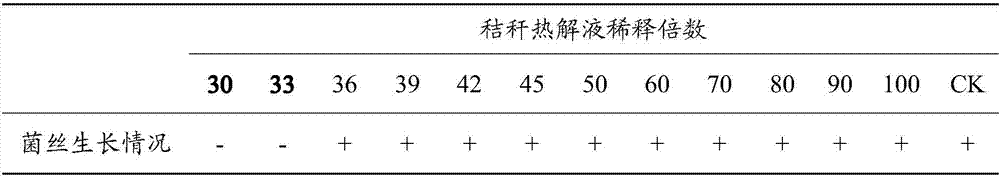
Biological agent for controlling sclerotinia blight of Chinese cabbage
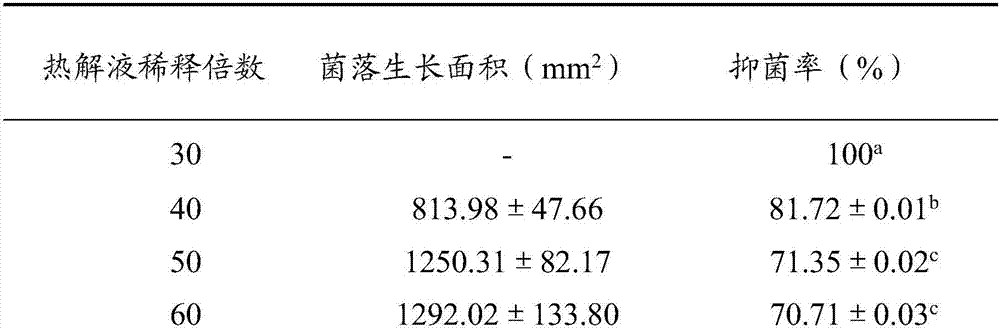
The invention relates to the technical field of bactericides, and especially relates to a biological agent for controlling sclerotinia blight of Chinese cabbage. The biological agent comprises, by volume, 33.3-66.7 parts of a straw pyrolysis liquid and 66.7-33.3 parts of chitosan, or comprises, by volume, 33.3-75 parts of the straw pyrolysis liquid and 66.7-25 parts of a Bacillus spp fermentation broth. The biological agent has a significant bacteriostatic effect on the sclerotinia blight of Chinese cabbage, can effectively control the sclerotinia blight of Chinese cabbage and other diseases caused by the sclerotinia blight of Chinese cabbage, and is a nontoxic and non-residual biological agent.
Owner:YANBIAN UNIV
Method for detecting cadmium pollution through variation of genetic expression of brassica plant
InactiveCN102912023AImprove identification efficiencyFast wayMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyBrassica cretica
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Chinese cabbage TT8 gene family and application thereof
The invention discloses a Chinese cabbage TT8 gene family comprising two members, namely a BrTT8-1 gene with a full-length cDNA sequence shown as SEQ ID No.2 and a BrTT8-2 gene with a full-length cDNA sequence shown as SEQ ID No.4. The gene family can be applied to the molecular breeding based on seed traits such as seed coat color, seed size and the like of a brassica plant.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
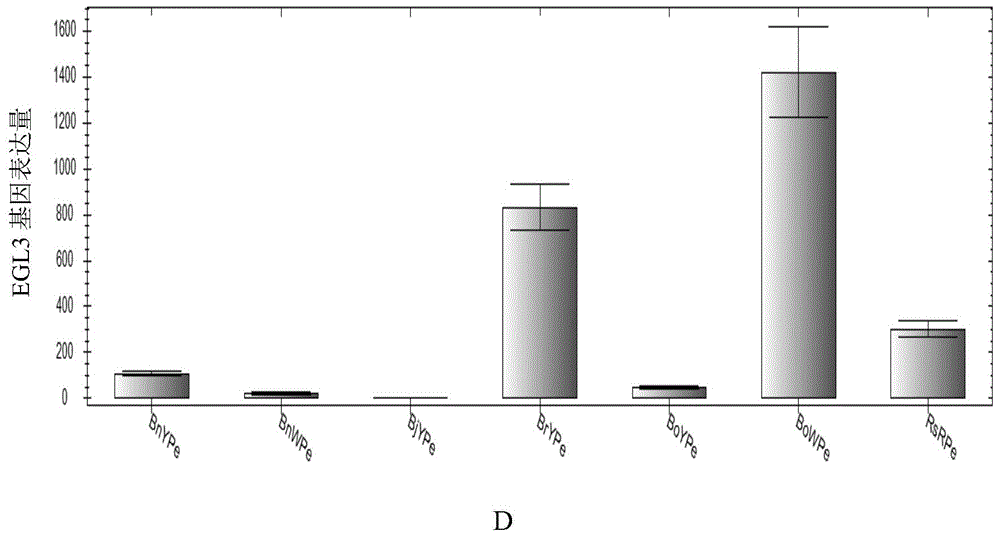
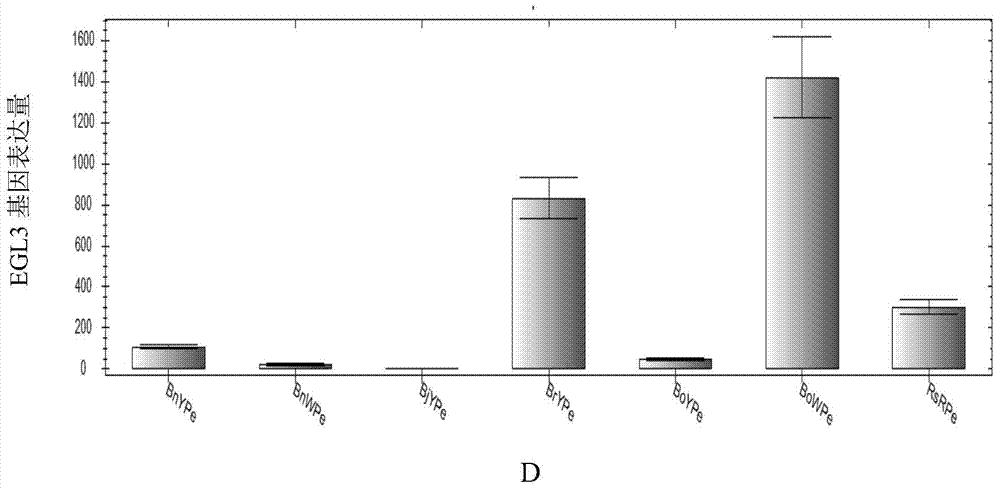
Application of LCYB (lycopene-beta-cyclase) and LCYE (lycopene-epsilon-cyclase) expression interference and EGL3 excessive expression in preparation of brassica plants with red petals
InactiveCN104404080AIdentify key differentially expressed gene lociFermentationGenetic engineeringLycopene beta-cyclaseCarotene
The invention discloses an application of LCYB (lycopene-beta-cyclase) and LCYE (lycopene-epsilon-cyclase) expression interference and EGL3 excessive expression in preparation of brassica plants with red petals, and further discloses an expression vector for interfering LCYB and LCYE gene expression and simultaneously excessively expressing EGL3 genes and a preparation method of the expression vector. Yellow carotenoid is inhibited and red lycopene is accumulated through interference for LCYB and LCYE gene expression, accumulation of anthocyanin is promoted through excessive expression of EGL3 genes, so that petals are red, the brassica plants with the red petals are prepared successfully, and the flower colors of the brassica plants are enriched.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Molecular marker for identifying separation conditions of interspecific hybrid and descendant materials A06 and C07 chromosome of brassica vegetables and method
ActiveCN110438254AExpand genetic resourcesBreeding new traitsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenetic resourcesInterspecific hybrids
The invention provides a molecular marker for identifying separation conditions of interspecific hybrid and descendant materials A06 and C07 chromosome of brassica vegetables and a method and belongsto the field of plant genetic breeding. The molecular marker can rapidly and accurately identify interspecific hybrid and descendant materials of brassica A genome (such as Chinese cabbage and red brassica campestris) and C genome (such as cabbage mustard and brassica carinata) (containing C genome) plants. The method can identify distant hybridization and backcross descendants of brassica A genome and C genome plants, broaden genetic resources of brassica vegetables, transform new traits, enrich vegetable types and enrich daily dietary nutrients of people.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
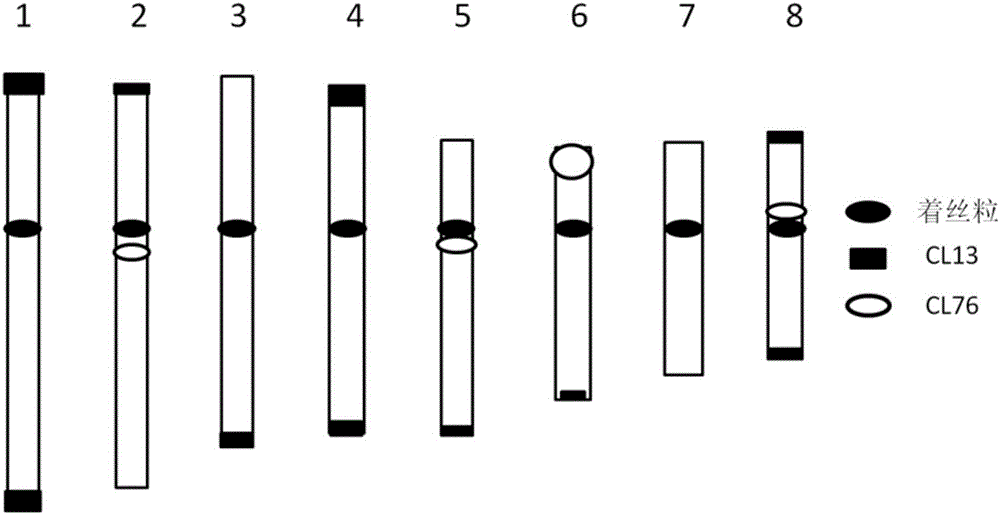
Two black mustard repeated DNA sequences and application thereof
ActiveCN106916895AEasy to identifyAccurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionA-DNASingle strand dna
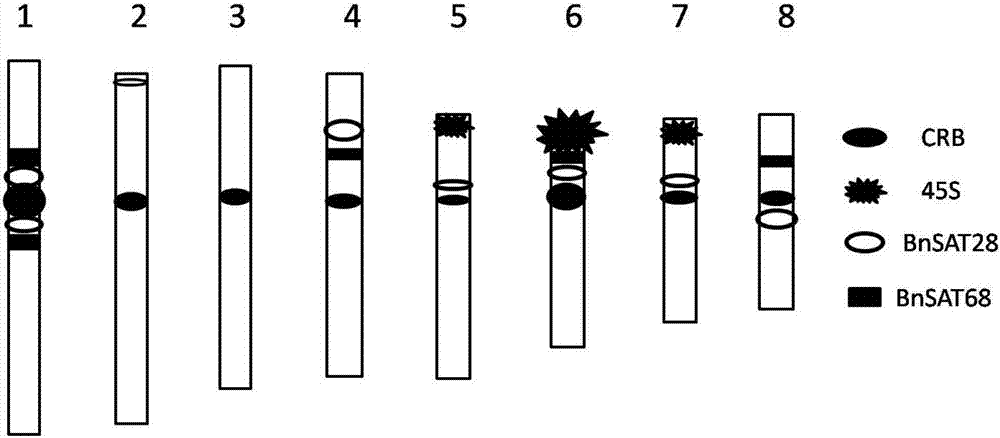
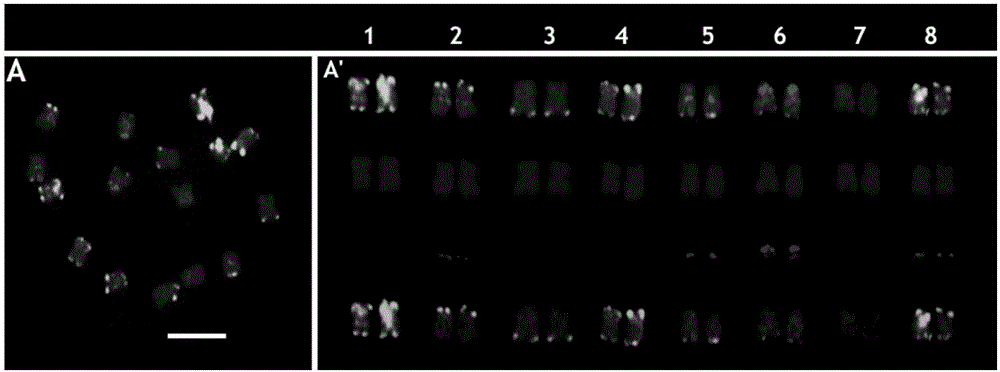
The invention discloses two black mustard genome DNA sequences and application thereof, and provides a DNA molecule set used for identifying a B genome of brassica plants. The DNA molecule set is composed of a single stranded DNA molecule as shown in sequence 1 in a sequence table and a single stranded DNA molecule as shown in sequence 2 in the sequence table. Experiments prove that by obtaining BNSAT28 and BNSAT68, chromosomes of brassica plants can be identified more easily and more accurately, and the problem that no ideal probe is available for identification of chromosomes of brassica plants is solved.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Thrips resistant cabbage
ActiveUS9765357B2Easy to mergeMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesBrassica creticaPepino mosaic virus
The present invention relates to a tomato plant (Solanum lycopersicum L.) which may comprise a genetic determinant that confers resistance to Pepino Mosaic Virus (PepMV), wherein the resistance is characterised by the presence of at least QTL1 and / or QTL2. The invention also relates to sources for obtaining said genetic determinant, representative seed of which were deposited with the NCIMB under accession numbers NCIMB 41927, NCIMB 41928, NCIMB 42068, and NCIMB 42069. The invention further relates to seeds and progeny of the plant and to its fruits and processed fruits. In addition the invention relates to molecular markers linked to PepMV resistance conferring QTLs and the use thereof.
Owner:RIJK ZWAAN ZAADTEELT & ZAADHANDEL BV
Milk-fragrance Chinese cabbage juice
InactiveCN106578059ALow priceNutritional balanceMilk preparationMilk preservationBrassica creticaBirdsrape Mustard
The invention mainly relates to the technical field of foods, and discloses milk-fragrance Chinese cabbage juice. The milk-fragrance Chinese cabbage juice is made from the following raw materials of Chinese cabbages, milk, soybean oligosaccharides, table salt, konjak starch, lactic acid bacteria, complex enzymes, a yeast extract and a purple perilla extract. The milk-fragrance Chinese cabbage juice is rich in milk fragrance, moderate in sour and sweet degrees, balanced in nutrients, extensive in raw materials and low in price; the deep processing ways of the Chinese cabbages are increased, and economic returns are increased by 10.3%; the Chinese cabbages are subjected to enzymolysis through complex enzymes, so that the juice yield rate is increased by 8.7%, the utilization rate of the Chinese cabbages is increased, and production cost is saved; the raw materials are subjected to fermentation twice, so that the milk-fragrance Chinese cabbage juice is sour and sweet in mouth feel and rich in nutrition, the growth of infectious microbes is restrained, and the shelf life of the milk-fragrance Chinese cabbage juice is prolonged; the konjak starch is added, so that the nutrients of the milk-fragrance Chinese cabbage juice are rich, the functions of the stomach and the intestines are promoted, the product state is stable, and the milk-fragrance Chinese cabbage juice is not layered; and various nutrient extraction agents are added, so that nutrients are increased, absorption is promoted, the infectious microbes can also be restrained, health-care functions are improved, additives are not contained, and the milk-fragrance Chinese cabbage juice can enhance immunity, beautify faces, protect skin, reduce weight, enable bodies to be slim, prevent dental caries and resist and restrain cancers.
Owner:ANHUI FUNAN CHANGHUI FOOD
Two black mustard genomes DNA sequence and application thereof
InactiveCN106048057AEasy to identifyAccurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSingle strand dnaGenome
The invention discloses two black mustard genomes DNA sequence and application thereof. A set of DNA molecules used for identifying brassica plant B genome are composed of single-stranded DNA molecules as shown in the sequence of the sequence table and single-stranded DNA molecules as shown in the sequence 2 of the sequence table. It is proved through experiments that it is easier and more accurate to identify chromosome of brassica plants by the acquisition of CL13 and CL76. The gap that there is no ideal probe for identification of chromosome of brassica plants is filled.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
Method for utilizing stamen petalody to mark male sterility genes of Brassica campestris ssp.chinensis
InactiveCN102978287AEasy to operateLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementBrassica creticaMarker-assisted selection
The invention relates to a method for utilizing stamen petalody to mark male sterility genes of Brassica campestris ssp.chinensis, belongs to the field of a biotechnology and is used for marker-assisted selection breeding of a Brassica campestris ssp.chinensis male sterility line. The method comprises the following step of: amplifying DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) synthesized by RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) inverse transcription of a stamen petalody line and a maintainer line thereof by utilizing a mark primer AFLP17 (Amplified Fragment Length Polymorphism 17) or a mark primer SCAR33, wherein if a 300bp segment can be amplified, the male sterility genes of the Brassica campestris ssp.chinensis do not exist. The method can be used for carrying out cDNA-AFLP and SCAR molecular marker sieving on the DNA synthesized by the RNA inverse transcription of the Brassica campestris ssp.chinensis stamen petalody line W053 and the maintainer line W052 thereof, can effectively expand the marker-assisted selection breeding of the Brassica campestris ssp.chinensis male sterility line, and greatly improves the selection efficiency, so that the breeding progress is accelerated.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
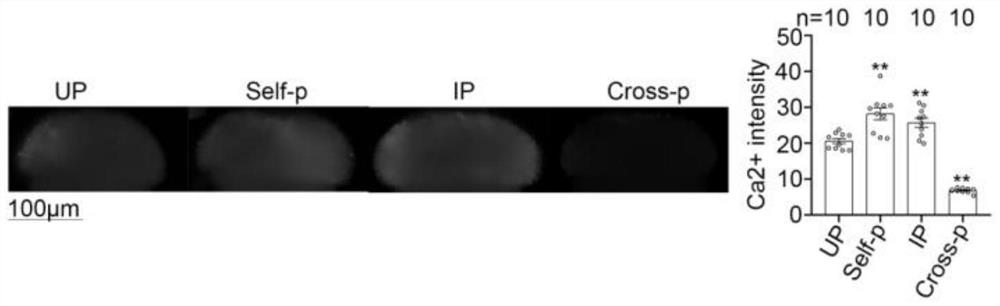
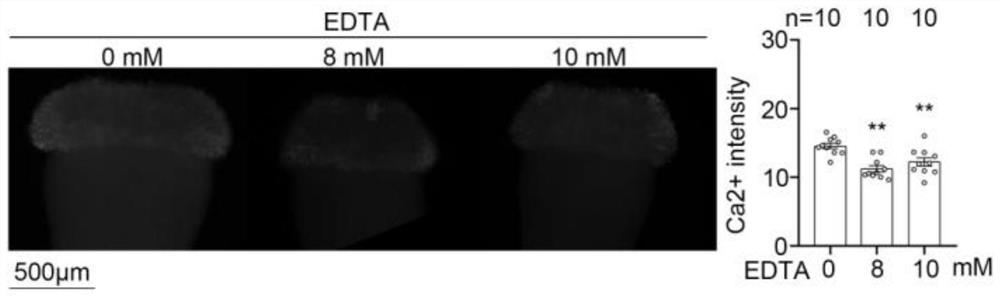
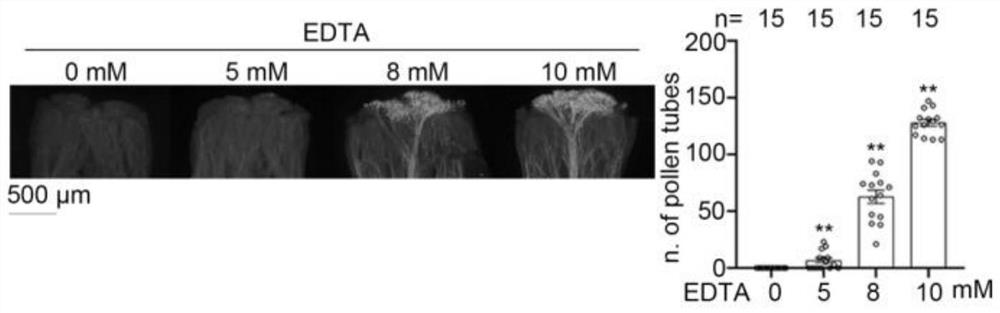
Application method and application of reagent for eliminating content of calcium ions in stigmas in overcoming selective fertilization of cruciferous plants
PendingCN113906998AOvercoming interspecies hybrid incompatibilityPromote germinationPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyBrassica cretica
The invention provides an application method and application of a reagent for eliminating the content of calcium ions in stigmas in selective fertilization of cruciferous plants, and relates to the technical field of cruciferous plant breeding. The application or the reagent is suitable for a self-incompatible line or a male sterile line with self-incompatibility of brassica crops. The method is easy and convenient to operate, easy to popularize, small in damage to plants, remarkable in effect of overcoming self-incompatibility, wide in application range and capable of being applied to brassica crops such as Chinese cabbages and cabbages and various radish crops; and in addition, the method can be further used for overcoming self-incompatibility of other cruciferous crops, and has important value for breeding and seed production of the cruciferous crops.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY +1
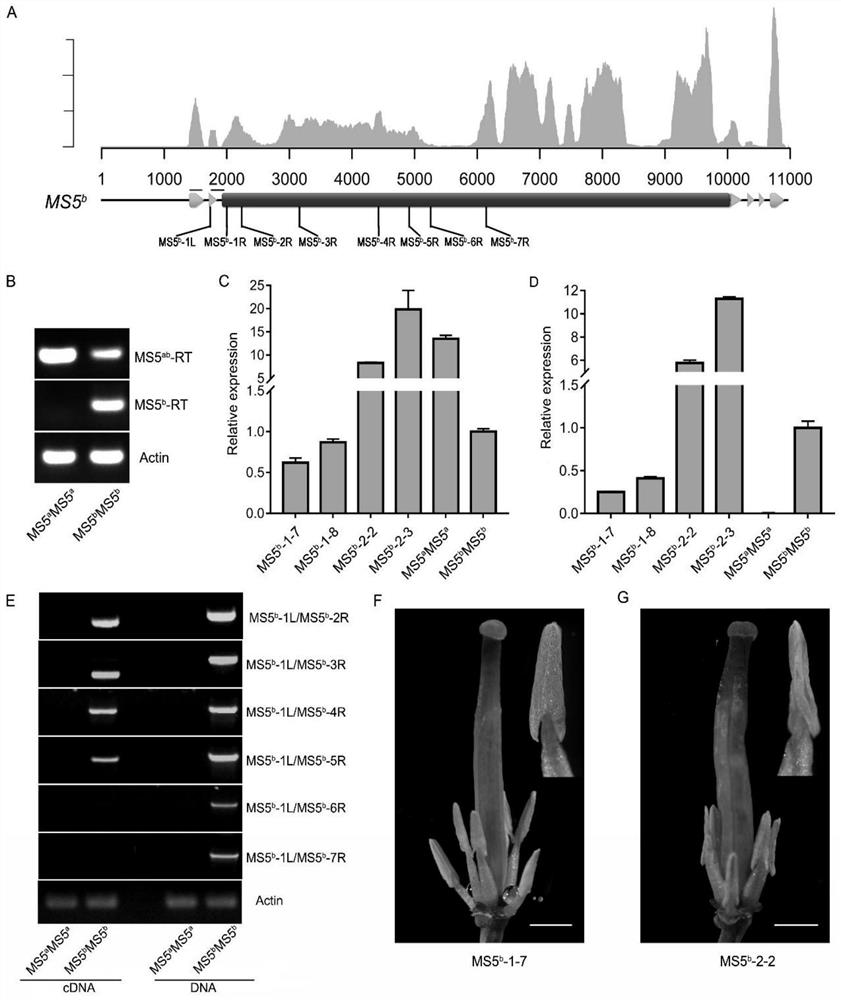
Dominant nuclear male sterility gene ms5 in Brassica napus b and its application
ActiveCN110452292BExcellent artificial sterile systemPlant peptidesFermentationBrassica creticaAnimal science
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Cabbage-type rape TT8 gene families and applications thereof
InactiveCN101942457BFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyBrassica cretica
The invention discloses cabbage-type rape as well as parent species Chinese cabbage and cabbage TT8 gene families and applications thereof, wherein, the Chinese cabbage TT8 gene family comprises a BrTT8-1 gene (SEQ ID No.1-2) and a Br TT8-2 gene (SEQ ID No.3-4); the cabbage TT8 gene family comprises a BoTT8-1 gene (SEQ ID No.5-6) and a BoTT8-2 gene (SEQ ID No.7-8); the cabbage-type rape TT8 gene family comprises a BnTT8-1 gene (SEQ ID No.9-10) and a BnTT8-2 gene (SEQ ID No.11-12). The above gene families can be used for molecule breeding of the brassica crop seed properties.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
Application of interfering lcyb and lcye expression and overexpressing egl3 in preparing Brassica plants with red petals
InactiveCN104404080BIdentify key differentially expressed gene lociGenetic engineeringFermentationBiotechnologyLycopersene
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
Reagent for overcoming self-incompatibility between Brassica and Radish and its usage and application
ActiveCN112042670BActive oxygen reductionReduce inhibitionPlant growth regulatorsBiocideBrassica creticaBrassica rapa
The invention relates to the technical field of plant breeding of the genus Brassica and the genus Radish. Taking self-incompatible Chinese cabbage and self-incompatible radish as examples, when the Chinese cabbage and radish enter the initial flowering stage and bloom in large quantities, the radishes are planted at 8 am on a sunny day. : 00-10:00 time period, 1 mM-10 mM potassium iodide solution mixed with 0.025% Tween-20 (increasing the adhesion of the solution), using a sprayer, sprayed on the stigma that has just expanded into a cross, until the stigma Water beads on the surface. Spray the second and third times at intervals of 15 minutes. After spraying for the third time, the mist droplets on the stigma are all dry, and then fresh pollen is given, and the excess unexpanded inflorescences are pinched off, and the seed collection bag is put on. The method of the invention is applicable to the self-incompatibility lines of plants of the genus Brassica and the genus Radish. To self-incompatibility Chinese cabbage ( Brassica rapa L. ssp. pekinensis ) and self-incompatible radish ( Raphanus sativus ) Potassium iodide solution was sprayed on the stigma of the cruciferous inflorescence just unfolded, which can improve the self-compatibility index to varying degrees.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com