Patents
Literature
38 results about "Brassica carinata" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Brassica carinata (Ethiopian rape, Ethiopian mustard, Abyssinian mustard) is a member of the genus Brassica. It is believed to be a hybrid between Brassica nigra and Brassica oleracea. Although Brassica carinata is cultivated as an oilseed crop in Ethiopia, it has high levels of undesirable glucosinolates and erucic acid. The closely related Brassica napus (Rapeseed) is considered a better oilseed crop in comparison.
Method for rapidly detecting expression of ANS (Anthocyanidin Synthetase) genes from different sources in rape seed capsule and application thereof
InactiveCN102433379AEasy to detectQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyHeterologous
The invention discloses a method for rapidly detecting expression of ANS (Anthocyanidin Synthetase) genes from different sources in rape seed capsules. In the method, a specific primer capable of distinguishing ANS genes from chromosome sets A, B and C by cloning and analyzing sequences of ANS genes in three elementary species of rape (cabbage: the chromosome set is AA, and 2n=20; brassica oleracea: the chromosome set is CC, and 2n=18; and brown mustard: the chromosome set is BB, and 2n=16) and three allotetraploids (mustard type rape: the chromosome set is AABBA, and 2n=36; cabbage type rape: the chromosome set is AACC, and 2n=38; brassica carinata: the chromosome set is BBCC, and 2n=34) according to the nucleotide polymorphic loci of ANS genes from the chromosome sets A, B and C, and the ANS gene types expressed in the seed capsules of rape of different chromosome set types are identified in combination with an RT-PCR (Reverse Transcriptase-Polymerase Chain Reaction). The method plays a role in further researching the molecular adjusting mechanism for the color formation of rapeseed capsules and accelerating the variety breeding of yellow seed rape; and meanwhile, a novel methodfor detecting the source of a rape ANS gene is provided.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Brassica plants comprising mutant fad3 alleles
ActiveUS20120246755A1Lower Level RequirementsReduce contentSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAlpha-Linolenic acidNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention relates to Brassica plants comprising mutant FAD3 alleles, FAD3 nucleic acid sequences and proteins, as well as methods for generating and identifying said plants and alleles, which can be used to obtain seed oil with a reduced alpha-linolenic acid content.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
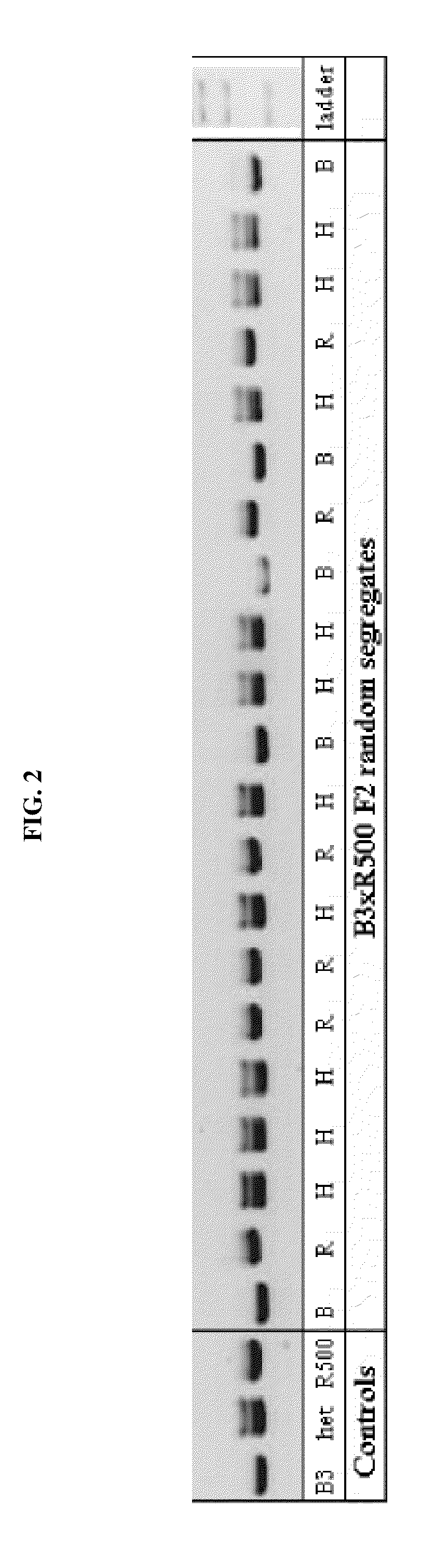
Self-compatible, rapid-cycling brassica rapa plants lacking inbreeding depression
The invention provides Brassica rapa plants and seeds thereof that are self-compatible, rapid-cycling and lack inbreeding depression. For instance, the invention provides plants and seeds of the Brassica rapa line designated B3. The invention thus relates to plants, seeds and tissue cultures of Brassica rapa plants that are self-compatible, rapid-cycling and lack inbreeding depression, such as Brassica rapa line B3, and methods to produce and propagate said plants by crossing such a Brassica rapa plant with itself, or another Brassica rapa plant. The invention further relates to seeds and plants produced by such crossing. Educational materials, such as a kit comprising said Brassica rapa plants are also provided by the invention.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Brassica Rapa Transparent Testa Genes for Controlling Seed Colour in Brassica Species
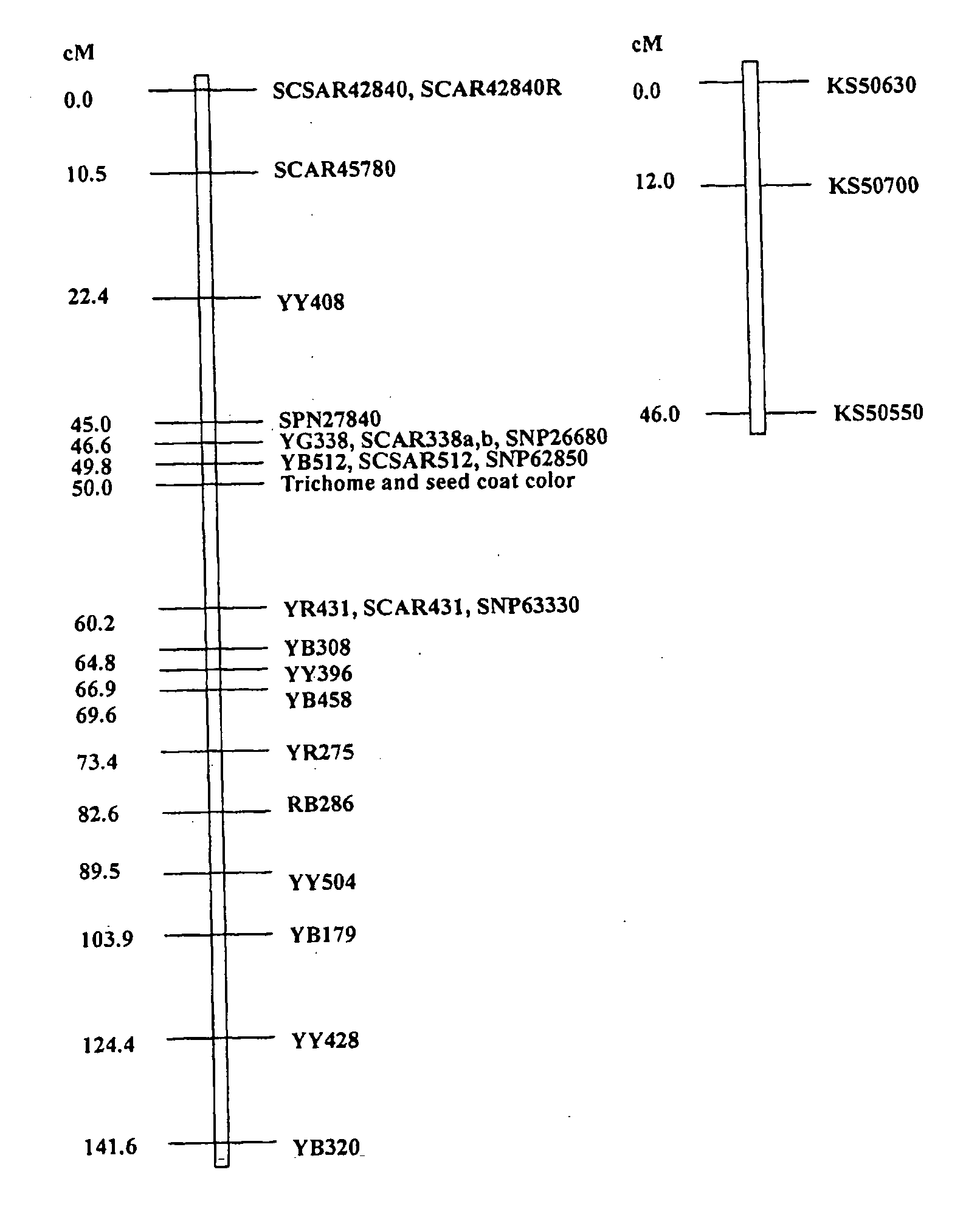
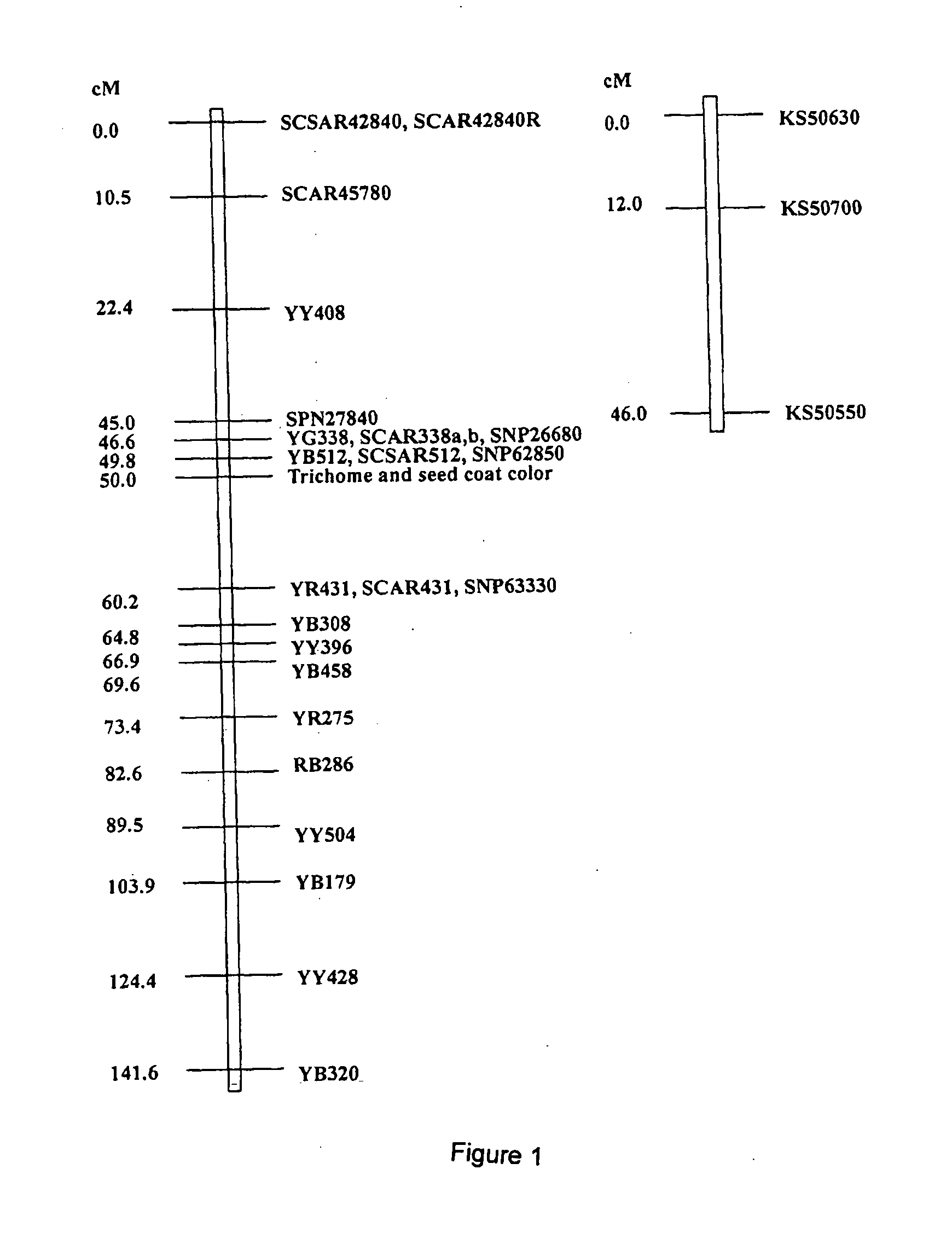
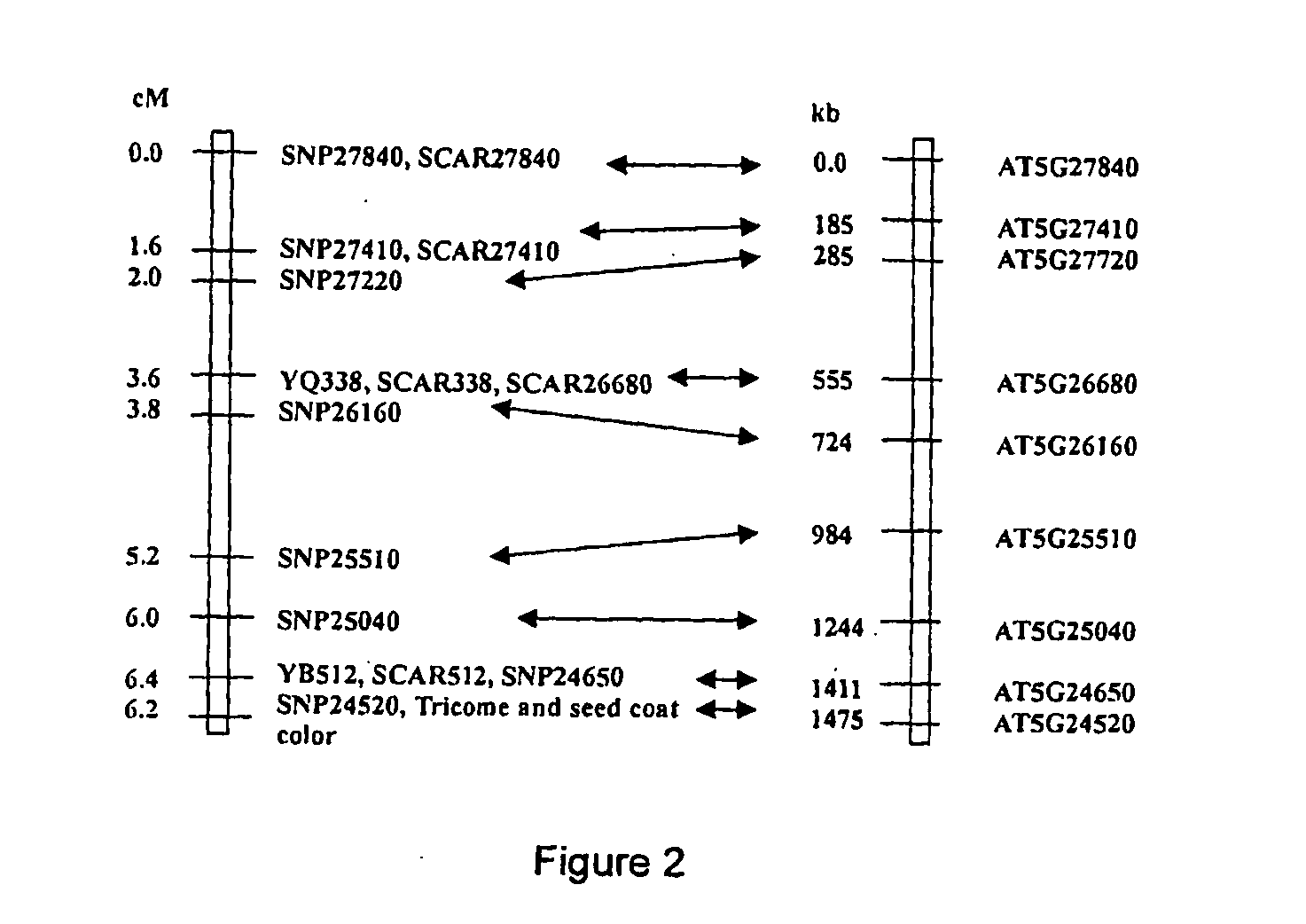
Seed coat color is a very important trait in oilseed type Brassica crops. Identification of the genes controlling the seed coat color is essential to the manipulation of these genes to develop new yellow-seeded germplasm for oilseed breeding The Brassica rapa Transparent Testa Glabra (TTG1) and Transparent Testa (TT1) genes may be used to control seed coat color in Brassica plants.
Owner:ZHANG JIEFU +5
Novel brassica plants
ActiveUS20060277637A1Low production costImprove efficiencyAngiosperms/flowering plantsOvuleBrassica carinata
The present invention relates to novel brassica plants, in particular to novel cauliflower plants. In one embodiment, the novel cauliflower plants provided herein comprise a long stem and are suitable for mechanical harvesting. The application also further discloses seeds the cauliflower plants of the present invention and parts thereof, for example pollen, ovules and curds. The application also further discloses methods of using a plant of instant invention, such as methods of producing a cauliflower curd of the instant invention, and methods of harvesting the curds of plants of the instant invention.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Brassica carinata varieties producing seed with reduced glucosinolate content
ActiveUS20190364779A1Fine grainOptimized oil compositionAngiosperms/flowering plantsBrassica carinataAgronomy
The invention is in the field of Brassica carinata breeding (i.e. Ethiopian mustard breeding), specifically to Brassica carinata varieties producing seed having reduced total glucosinolate content relative to seed from existing Brassica carinata commercial varieties when grown in the same location under the same conditions. The present invention relates to seeds, plants or parts thereof, cells, methods of making, and uses of such Brassica carinata varieties and their progeny.
Owner:NUSEED GLOBAL INNOVATION LTD
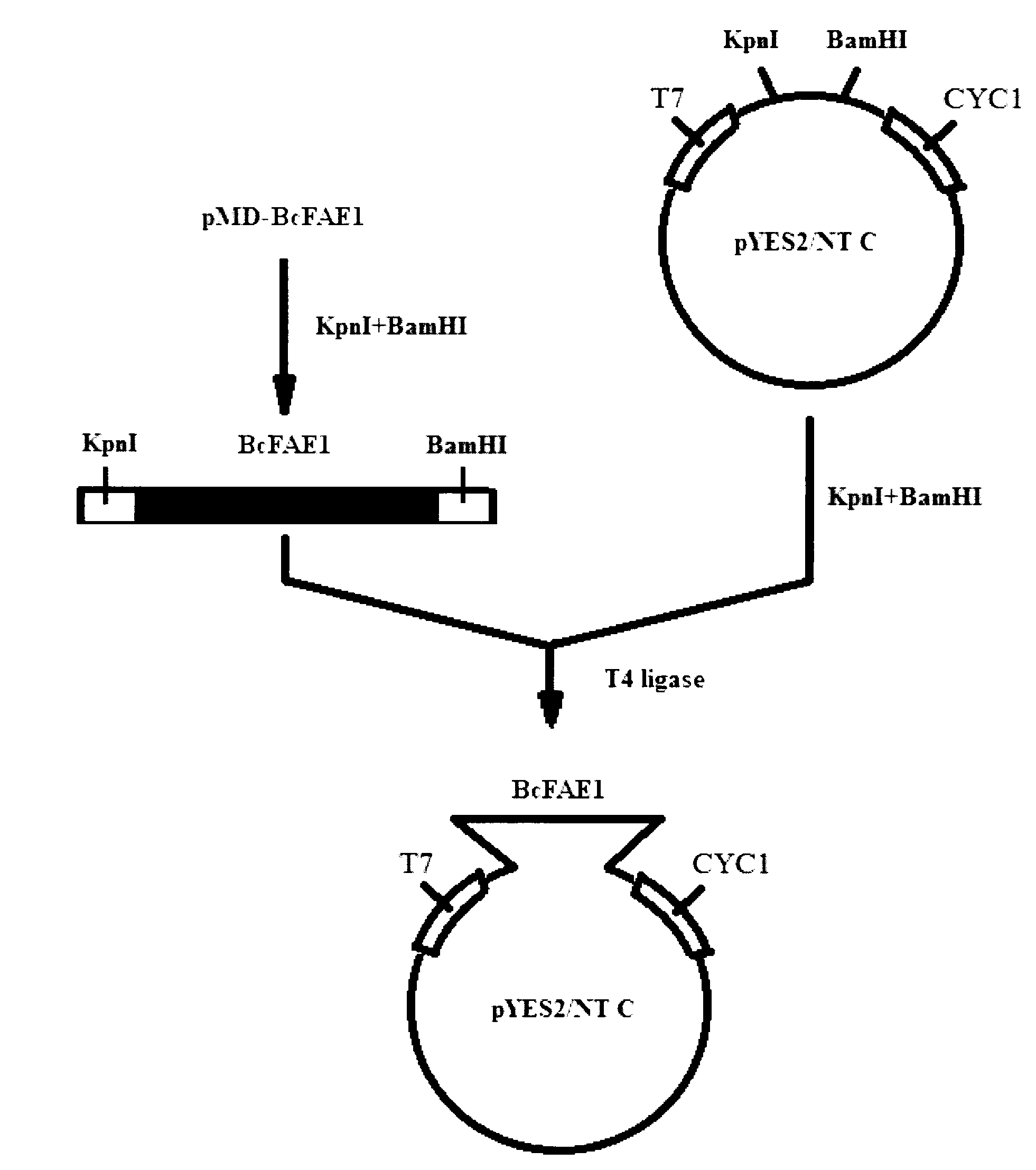
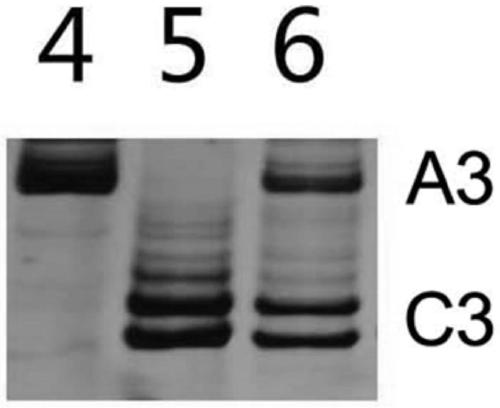
Brassica carinata A. braun fatty acid elongase and coding gene thereof
The invention provides a Brassica carinata A. braun fatty acid elongase and a coding gene thereof (BcFAE1). The gene is introduced in to yeast; and the erucic acid content in the recombinant yeast reaches 0.27+ / -0.24%. The protein and the coding gene thereof have important theoretical and practical significance for the research of a genetic control mechanism of plant erucic acids, the increasement of the erucic acid content and the improvement of related traits, can play an important role in the genetic engineering improvement of the plant erucic acid genes, and have wide application prospects.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY JIANGSU PROVINCE & CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Plants and seeds of brassica carinata variety dh-153.113
InactiveUS20190373836A1Reduce accumulationEasy constructionAngiosperms/flowering plantsBiotechnologyBrassica carinata
Owner:AGRISOMA BIOSCI
Methods of agricultural production of brassica carinata oilseed crops
ActiveCN111405846ASustainable farmingQuality improvementExcrement fertilisersWaste based fuelCarbon creditCarbon sequestration
The present invention relates to the agricultural practices for maximizing carbon sequestration, enhanced productivity, sustainable farming and minimizing greenhouse gas emissions. In one embodiment,there is provided a method comprising planting a Brassica carinata variety as a second crop in rotation with a first crop or to replace fallow; implementing the land management practices to reduce theuse of fossil fuel inputs and to maximize the capture of atmospheric carbon by the plant material of Brassica carinata; harvesting the Brassica carinata variety to obtain the grain; and returning about 70% to about 90% of all plant material from the Brassica carinata variety aside from the grain to the soil, so that the overall greenhouse gas emissions associated with agriculture are reduced. Insome embodiments, the method further comprises producing grain for use in the production of a plant-based feedstock, and the plant-based feedstock is used for producing low carbon intensity fuels, adding carbon in soil, and / or acquiring a carbon credit.
Owner:纽希得全球创新有限公司
Method for increasing proanthocyanidin content in escherichia coli by cotransformation of brassica juncea gene ANS and brassica carinata BAN
InactiveCN102827861AIncrease proanthocyanidin contentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyLiquid medium
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for increasing proanthocyanidin content in escherichia coli by cotransformation of brassica juncea gene ANS and brassica carinata BAN
InactiveCN102827861BIncrease proanthocyanidin contentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyLiquid medium
The invention discloses a method for increasing proanthocyanidin content in escherichia coli by cotransformation of brassica juncea gene ANS and brassica carinata BAN. According to the invention, an anthocyanidin synthetase ANS gene is cloned from cDNA of brassica juncea seeds, and an anthocyanidin reductase BAN gene is cloned from cDNA of brassica carinata seeds; a prokaryotic expression vector pET-ANS-BAN containing the ANS and BAN genes is constructed; and the ANS and the BAN genes are introduced into a BL21 escherichia coli strain simultaneously. The transformed strain is cultured in an LB liquid medium at 28-38 DEG C at 150-250 rpm for 6-12 hours, transferred into an LB liquid medium containing grape skin extracts (0.2-0.8 g / L), and cultured under shaking at 28-38 DEG C at 150-250 rpm for 36-54 hours; the strain is collected by centrifugation; and the proanthocyanidin content in escherichia coli is determined by a DMACA-HCl method. The transgenic escherichia coli obtained in the invention has significantly increased proanthocyanidin content, and the maximum content can be 24.2 times higher than that of a non-transformed control strain.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
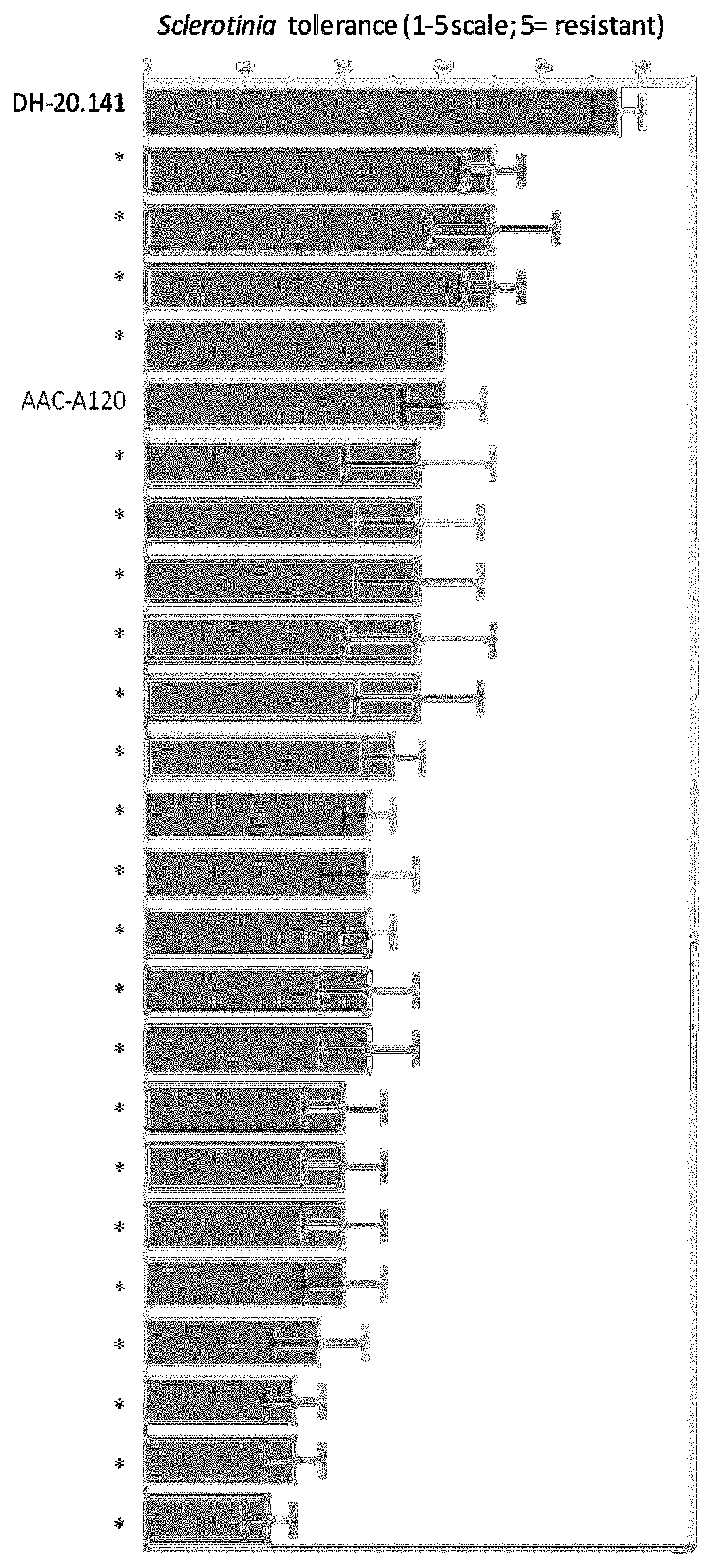
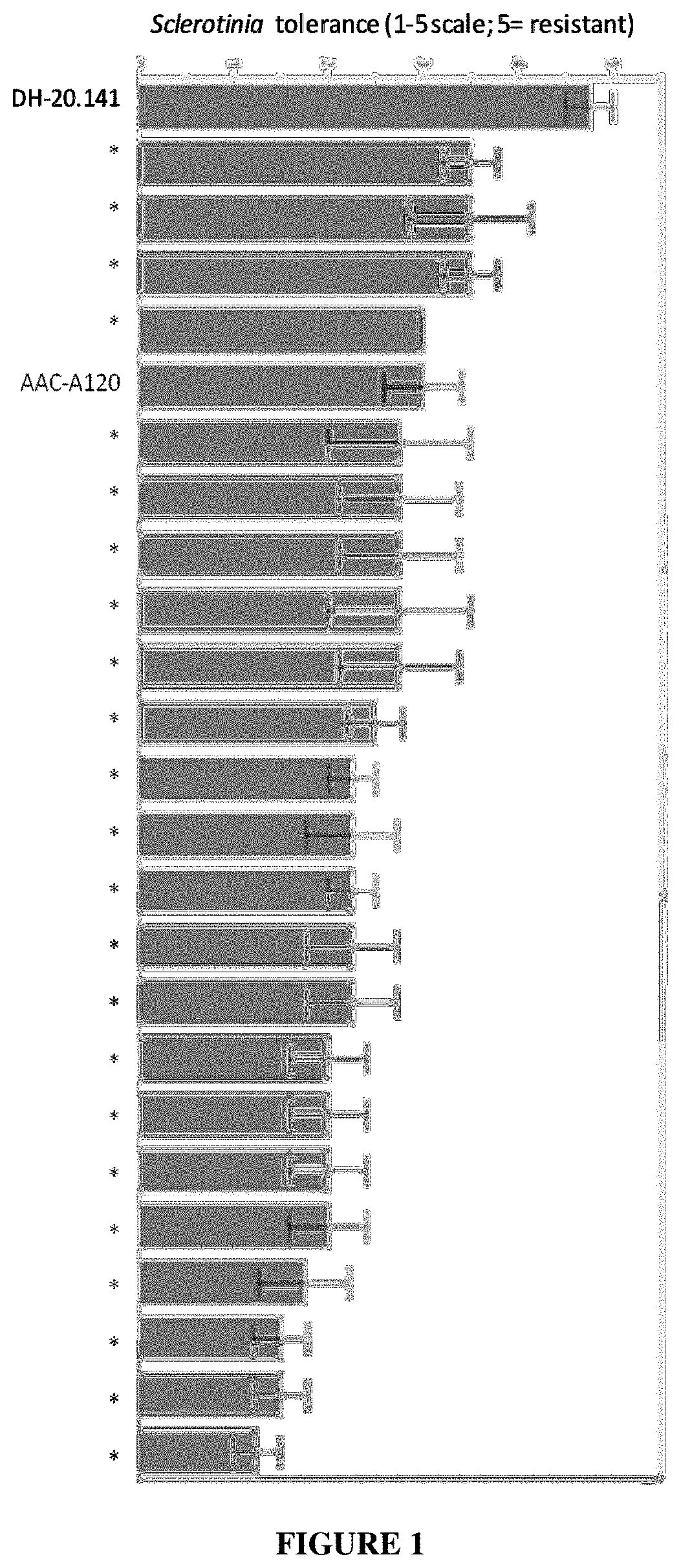
Plants and seeds of Brassica carinata variety DH-20.141
Owner:NUSEED GLOBAL INNOVATION LTD
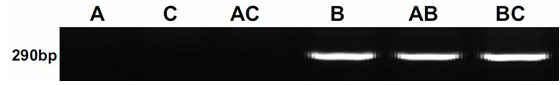
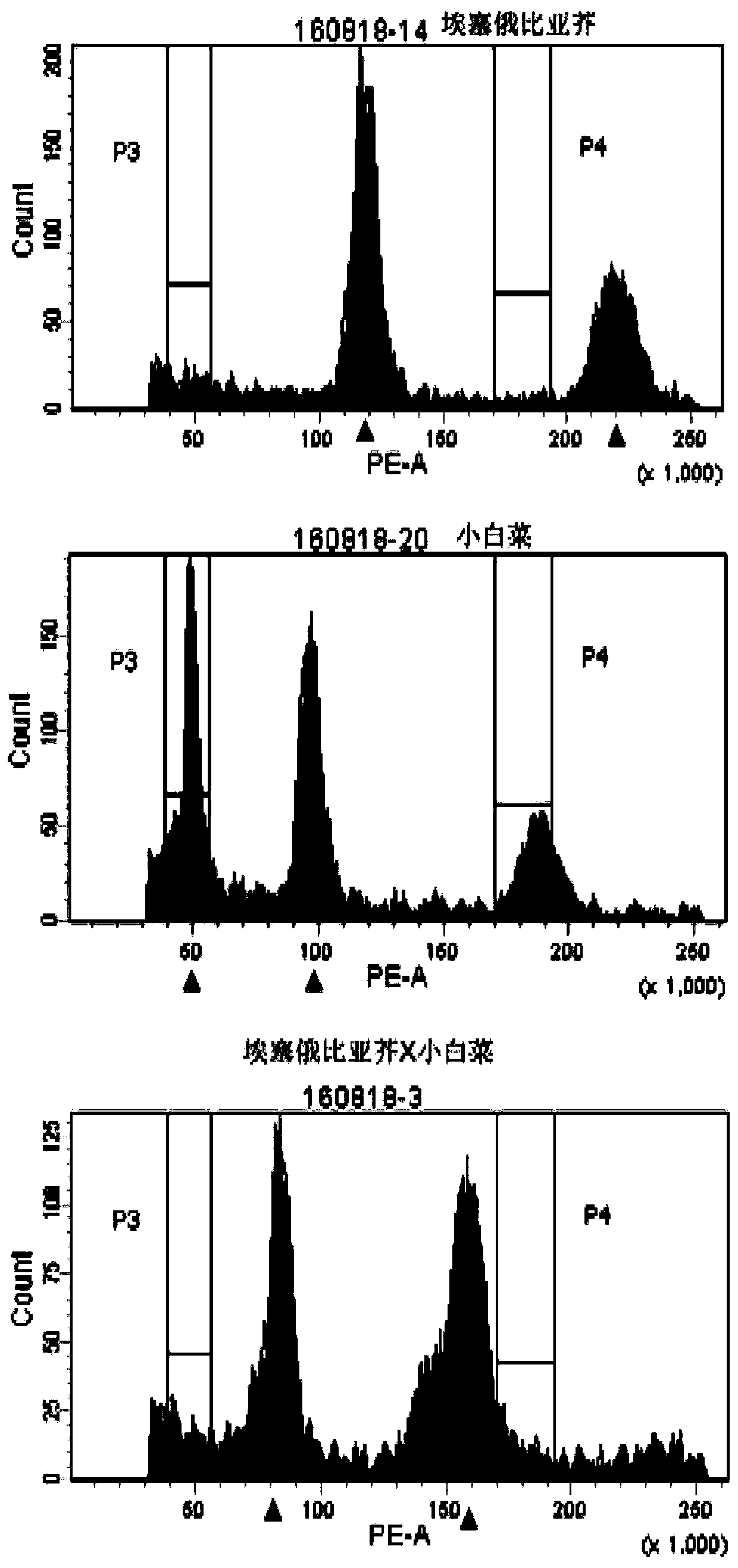
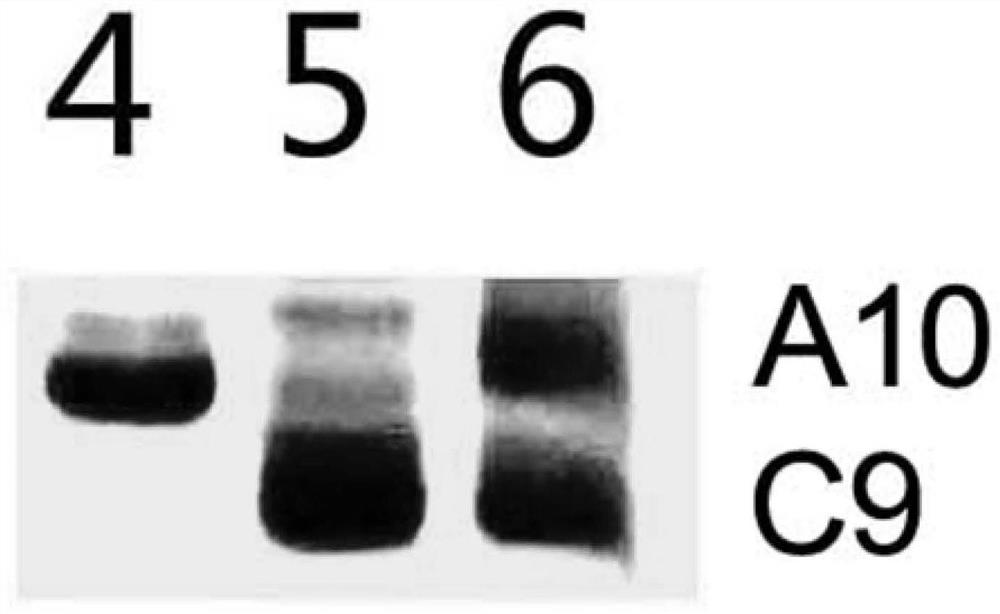
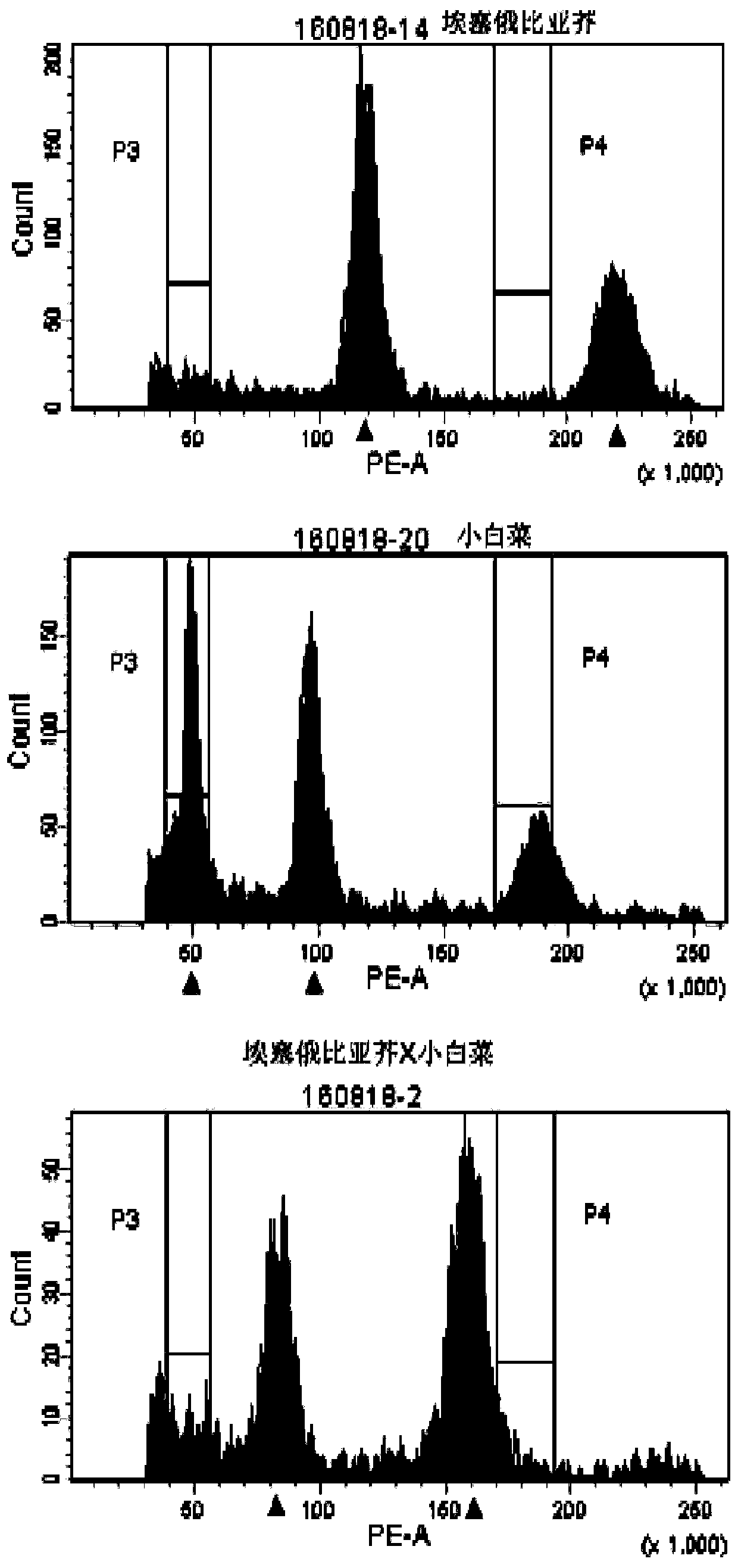
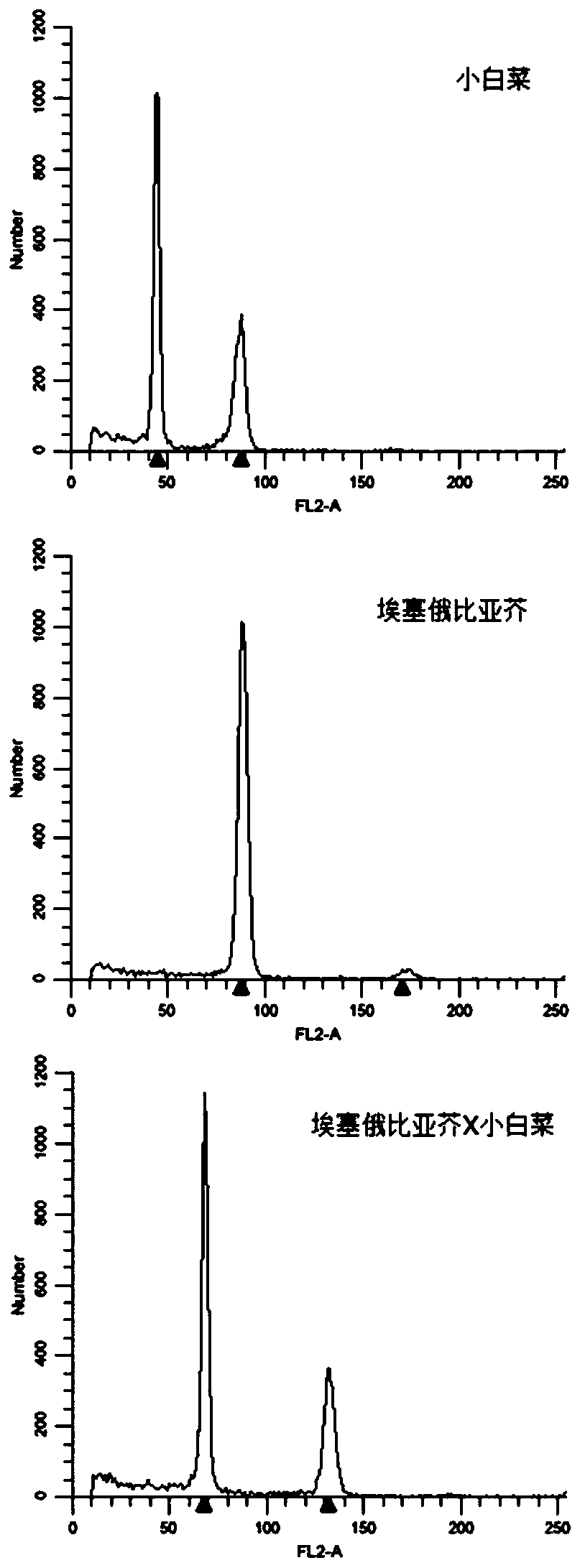
Molecular marker for identifying interspecific hybrids of Chinese cabbage and brassica carinata and separation conditions of A10 and C09 chromosomes of progeny materials
ActiveCN110423841AExpand genetic resourcesRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGeneticsHeterodea muelleri
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Molecular markers for identification of a10 and c09 chromosome segregation in hybrids between Chinese cabbage and Ethiopian mustard and their progeny
ActiveCN110423841BExpand genetic resourcesRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyGenetics
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Molecular markers for identification of a03 and c03 chromosome segregation in hybrids between Chinese cabbage and Ethiopian mustard and their progeny
ActiveCN110387432BExpand genetic resourcesRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyGenetics
The invention discloses a molecular marker and a method for identifying hybrids between Chinese cabbage and Ethiopian mustard and tracking the chromosomal separation of A03 and C03 offspring materials, belonging to the field of plant genetics and breeding. This marker is a pair of co-dominant molecular markers, which can be used to identify the authenticity of hybrids between Chinese cabbage and Ethiopian mustard, and can also be used to identify and track self-crossed offspring, backcrossed offspring, chromosome addition lines, and recombination of distant hybrids Chromosomal segregation of A03 and C03 in segregating populations and plants.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Plants and seeds of brassica carinata variety dh-20.141
ActiveUS20200037559A1Improve toleranceIncrease resistanceAngiosperms/flowering plantsBiotechnologyBrassica carinata
Owner:NUSEED GLOBAL INNOVATION LTD
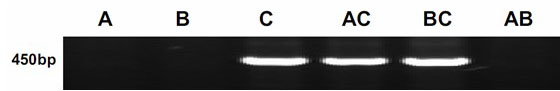
Molecular marker for identifying interspecific hybrid between Chinese cabbage and Ethiopian mustard and for tracking chromosome separation of progeny materials A03 and C03
ActiveCN110387433AExpand genetic resourcesEnrich daily dietary nutritionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationCO-DOMINANTBirdsrape Mustard
The invention discloses a molecular marker and method for identifying interspecific hybrid between Chinese cabbage and Ethiopian mustard and for tracking the chromosome separation of progeny materialsA03 and C03, and belongs to the field of plant heredity and breeding. The marker is a pair of co-dominant molecular markers which can be used for identifying the true and false of the interspecific hybrid between the Chinese cabbage and the Ethiopian mustard, and can also be used for identifying and tracking self cross progeny, backcross progeny, and chromosome addition lines of distant hybrid, and the A03 and C03 chromosomal segregation of recombinant isolated population and plants.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Plants and seeds of Brassica carinata variety DH-156.090D
ActiveUS10842100B2Maximizes captureEmission minimizationAngiosperms/flowering plantsBiotechnologyBrassica carinata
Owner:NUSEED GLOBAL INNOVATION LTD
Plants and seeds of brassica carinata variety dh-156.090d
ActiveUS20190373840A1Maximizes captureMinimizing greenhouse gas emissionAngiosperms/flowering plantsLomentBiology
Owner:NUSEED GLOBAL INNOVATION LTD
Plants and seeds of Brassica carinata variety AGR044-312E
Owner:NUSEED GLOBAL INNOVATION LTD
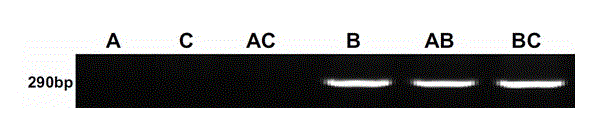
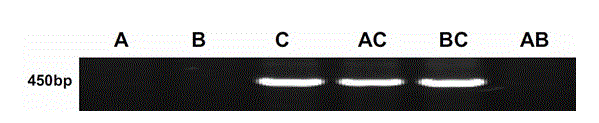
Molecular marker and method for identifying interspecific hybrids between Chinese cabbages and Brassica carinata and tracking segregation of A02 chromosomes and C02 chromosomes in offspring materials of interspecific hybrids
ActiveCN110499383AExpand genetic resourcesRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBirdsrape MustardBiology
The invention discloses a molecular marker and method for identifying interspecific hybrids between Chinese cabbages and Brassica carinata and tracking segregation of A02 chromosomes and C02 chromosomes in offspring materials of the interspecific hybrids, and belongs to the field of plant genetic breeding. The marker comprises a pair of codominant molecular marker bodies, and can be used for identifying the authenticity of the interspecific hybrids between Chinese cabbages and Brassica carinata, and can also be used for identifying and tracking selfing offsprings, backcross offsprings, chromosome addition lines and recombined segregation populations of distant hybrids and segregation of A02 chromosomes and C02 chromosomes in plants.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for rapidly detecting expression of ANS (Anthocyanidin Synthetase) genes from different sources in rape seed capsule and application thereof
InactiveCN102433379BEasy to detectQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyHeterologous
The invention discloses a method for rapidly detecting expression of ANS (Anthocyanidin Synthetase) genes from different sources in rape seed capsules. In the method, a specific primer capable of distinguishing ANS genes from chromosome sets A, B and C by cloning and analyzing sequences of ANS genes in three elementary species of rape (cabbage: the chromosome set is AA, and 2n=20; brassica oleracea: the chromosome set is CC, and 2n=18; and brown mustard: the chromosome set is BB, and 2n=16) and three allotetraploids (mustard type rape: the chromosome set is AABBA, and 2n=36; cabbage type rape: the chromosome set is AACC, and 2n=38; brassica carinata: the chromosome set is BBCC, and 2n=34) according to the nucleotide polymorphic loci of ANS genes from the chromosome sets A, B and C, and the ANS gene types expressed in the seed capsules of rape of different chromosome set types are identified in combination with an RT-PCR (Reverse Transcriptase-Polymerase Chain Reaction). The method plays a role in further researching the molecular adjusting mechanism for the color formation of rapeseed capsules and accelerating the variety breeding of yellow seed rape; and meanwhile, a novel methodfor detecting the source of a rape ANS gene is provided.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Plants and seeds of brassica carinata variety dh-069.485
ActiveUS20190373839A1Reduce accumulationEasy constructionAngiosperms/flowering plantsAgronomyOffspring
Owner:NUSEED GLOBAL INNOVATION LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com