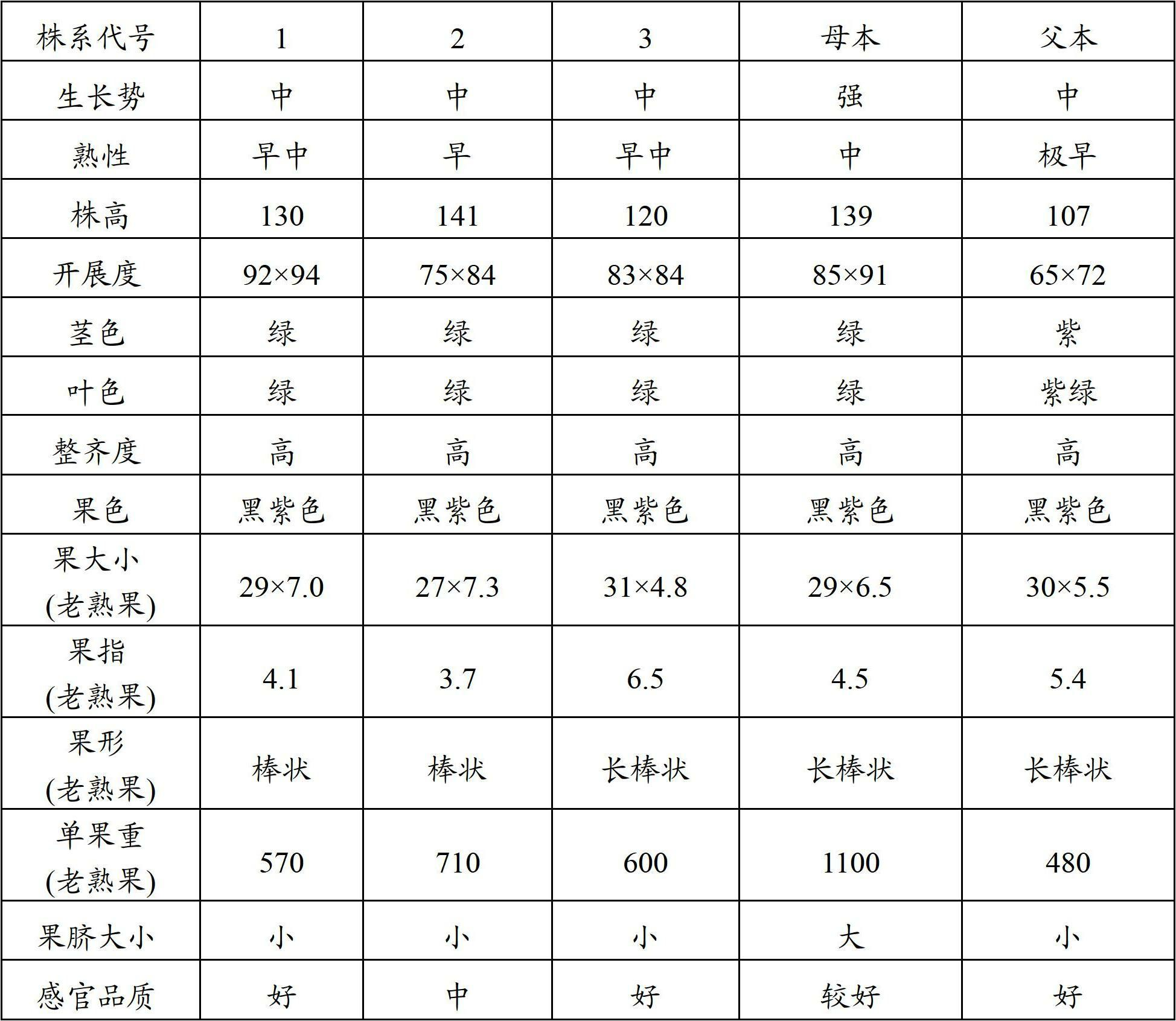
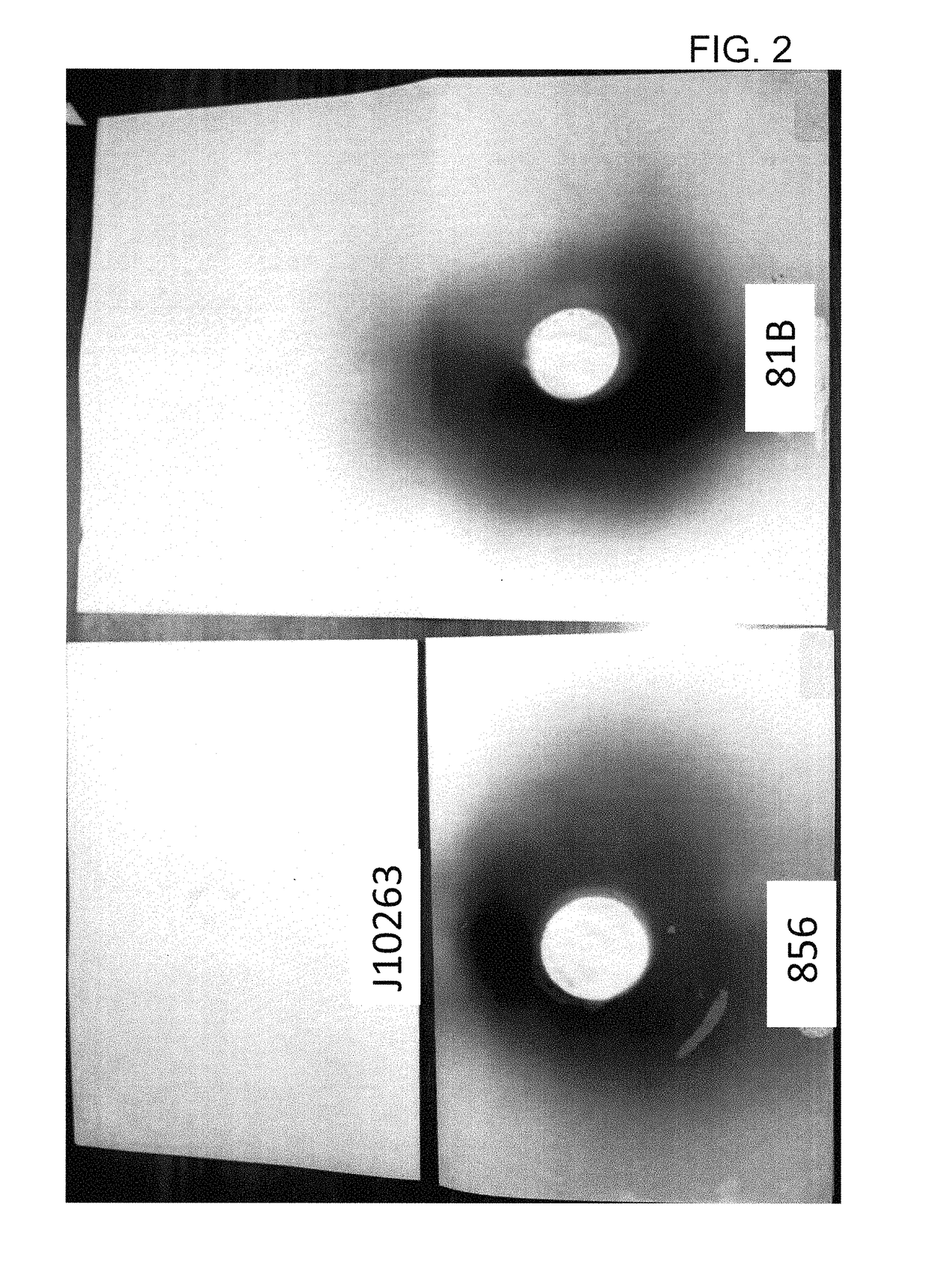
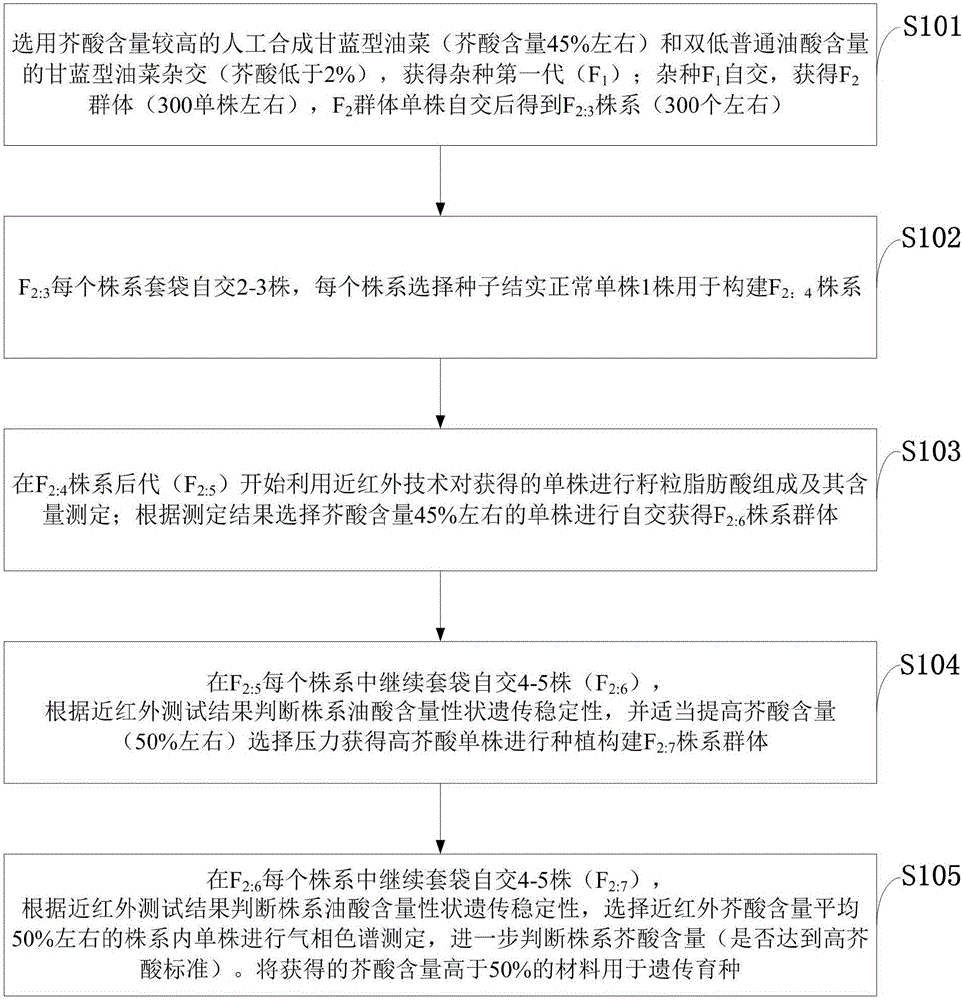
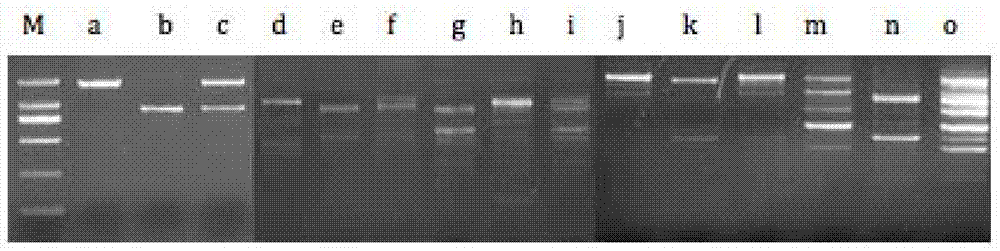
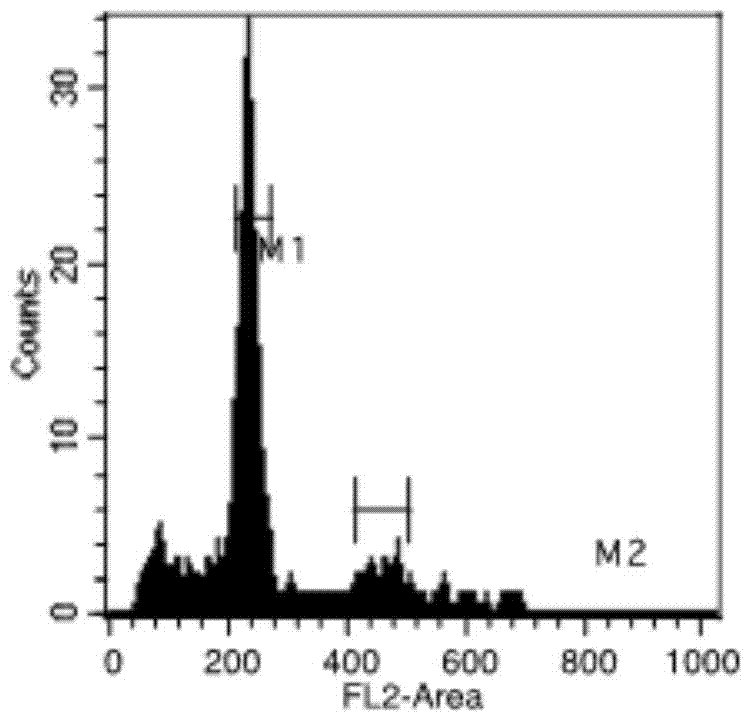
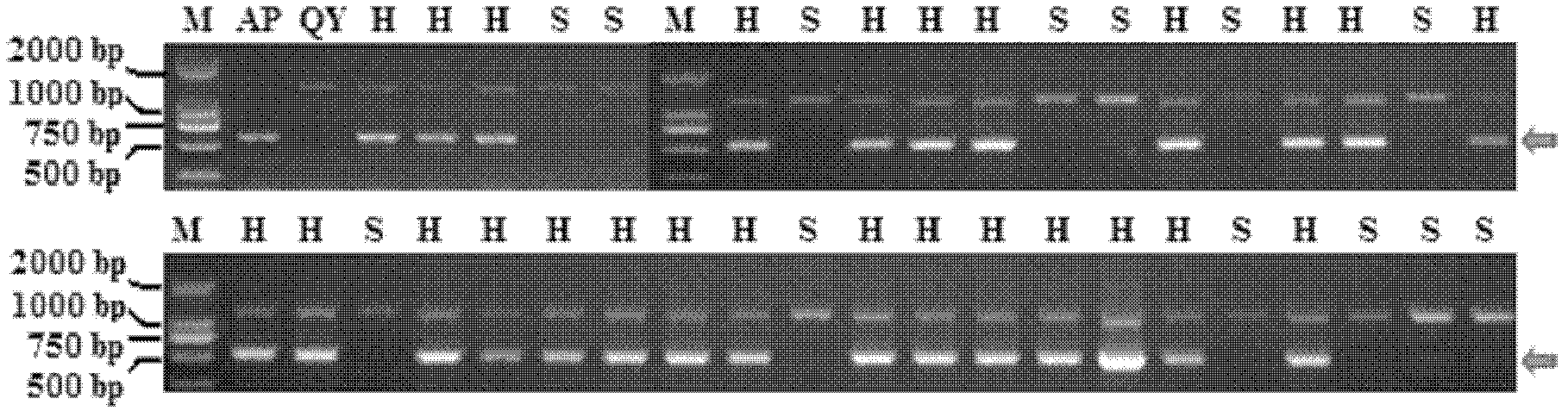Patents
Literature
51 results about "Heterodea muelleri" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Heterodea muelleri (Hampe) Nyl. Heterodea is a genus of lichenized fungi in the family Cladoniaceae. References External links. Index Fungorum; This Lecanoromycetes-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it ...
Method for cultivating aneuploid perennial forage grass variety by using corn heterologous polyploidy
ActiveCN103548674AOvercoming the Difficulty of Distant HybridizationNo resistancePlant genotype modificationHorticultureHeterologousNutritive values
The invention discloses a method for cultivating an aneuploid perennial forage grass variety by using a corn heterologous polyploidy and belongs to the field of corn distant hybridization. According to the method, MTF-1 (Tripsazea creammaize T.2n=76) cultivated by Sichuan Agricultural University is used as a female parent and teosinte is used as a male parent to be hybridized; a filial generation is selected from perennials, a wintering habit, a tiller number, a chromosome number and chromosome constitution to select the perennial heterologous aneuploid forage grass variety. According to the method, firstly, a heterologous aneuploid is used as the forage grass variety to be applied so as to creatively expand an application range of corn affinis species and explore a novel way for utilizing corn affinis specie materials; secondly, a material cultivated by the method is used as a bridge material and has a very great application value; furthermore, a vegetative propagation manner can be used for fixing a hybrid vigor and the variety is perennial, so that the production cost is very low, the yield and the nutritive value are high, and the economic benefit is great.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
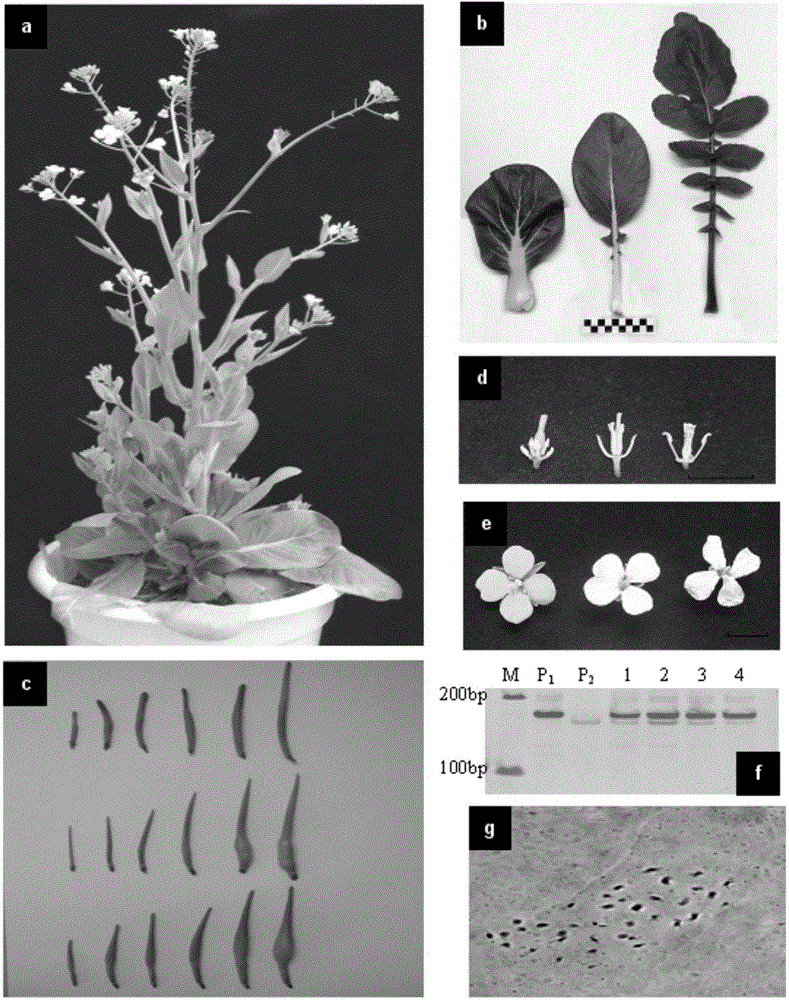
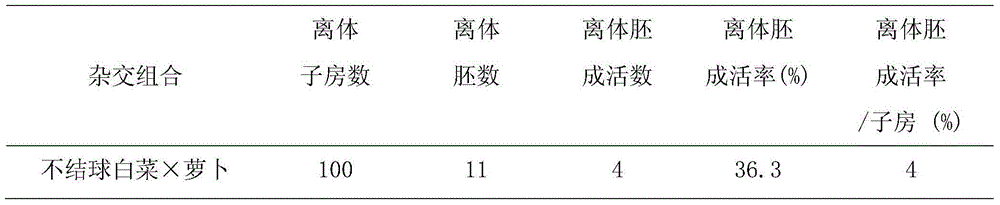
Novel germplasm creating method by distant hybridization of Brassica campestris ssp. chinensis Makino and Raphanus sativus
InactiveCN103947536AGenetic stabilityShorten breeding timePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsBrassicaGenetic diversity
The invention discloses a novel germplasm creating method by distant hybridization of Brassica campestris ssp. chinensis Makino and Raphanus sativus. The method uses autotetraploid Brassica campestris ssp. chinensis Makino as a female parent and autotetraploid Raphanus sativus as a male parent to conduct artificial sexual crossbreeding; and repeated pollination and in vitro embryo rescue techniques are employed to obtain distant hybridization novel germplasm of autotetraploid Brassica campestris ssp. chinensis Makino and autotetraploid Raphanus sativus. The invention for the first time adopts sexual crossbreeding of the autotetraploid Brassica campestris ssp. Chinensis Makino and autotetraploid Raphanus sativus and in vitro embryo rescue technique to obtain new germplasm of distant hybridization. Compared with traditional diploid hybridization, which obtains zygotic embryo for ploidy reduplication, the method does not require chromosome doubling operation, and can significantly shorten the breeding time; and the hybrid F1 can reach stable inheritance. The novel germplasm created by the invention creation has the genetic materials of Brassica campestris ssp. chinensis Makino and Raphanus sativus, and a wider genetic diversity.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
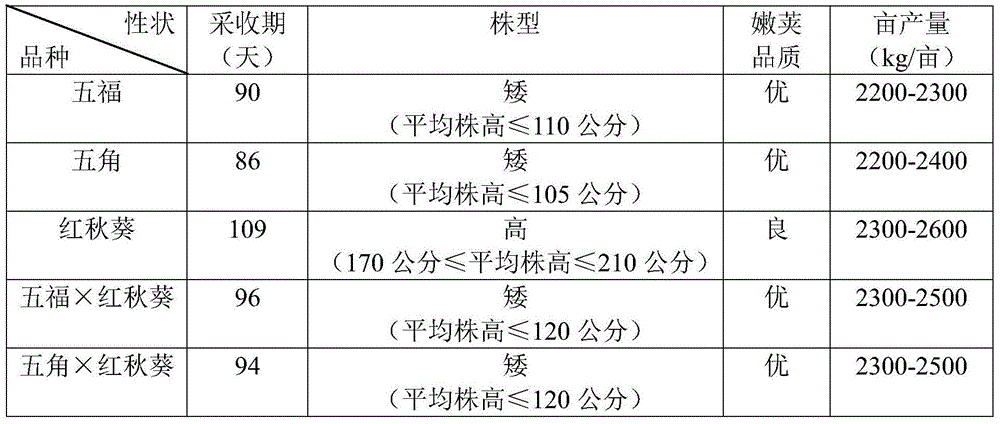
Cultivation method for new okra varieties
ActiveCN104472157ALodging resistanceFull of nutritionPlant genotype modificationHorticultureAnthesisHeterodea muelleri
The invention discloses a cultivation method for new okra varieties. The cultivation method includes seeding and planting management and sexual hybridization of okra parents, pollen activity of the okra parents is tested, the okra parents are assisted in sexual hybridization by means of manual castration and pollination when the pollen activity of the okra parents reaches more than 30%, seeds are collected, hybrid progenies are screened and purified, expressed characters of the parents and the hybrid progenies are compared in the same planting environment, the hybrid progenies with excellent characters are screened out and inbred, and the excellent characters are purified and stabilized. The okra varieties 'Wu Fu' and 'pentagon' are used as female parents, red okra is used as a male parent, sexual hybridization is performed by means of manual pollination, and the obtained new okra varieties have the advantages of nutrient-rich pods, long collecting period, high yield per mu and the like as compared with the female parents 'Wu Fu' and 'pentagon', have the advantages of excellent pod quality, short plant form, lodging resistance and the like as compared with the male parent red okra, and are novel healthcare new vegetable varieties with excellent quality.
Owner:中节能(汉川)光伏农业科技有限公司
Pickle and purple cabbage trigenomic species allohexaploid vegetable germplasm and acquisition method
ActiveCN103651111AShorten the timeEasy to operateHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureGermplasmOperability
The invention discloses a pickle and purple cabbage tri-genome species allohexaploid vegetable germplasm and an acquisition method, which fill in the blank of lack of brassica trigenomic species allohexaploid vegetable germplasm. The acquisition method comprises the steps that pickle and purple cabbages of brassica vegetable germplasm are cross-fertilized; an ovary is picked at the seventh day after pollination; mature seeds are obtained by embryo rescue; a large quantity of propagated progenies are obtained through subculture and propagation after seed germination; duplication treatment is carried out on a haploid by a liquid culture medium with colchicine to obtain the multi-genome allohexaploid vegetable germplasm. The pickle and purple cabbage tri-genome species allohexaploid vegetable germplasm and the acquisition method, disclosed by the invention, have the advantages of strong operability, simpleness and practicality, save the time for obtaining multi-genome polyploidy material, can be widely used for embryo rescue for interspecies cross of cruciferous brassica vegetable germplasm, and have great significance to cultivation and breeding of new species of special plants.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for cultivating seedless eggplant variety
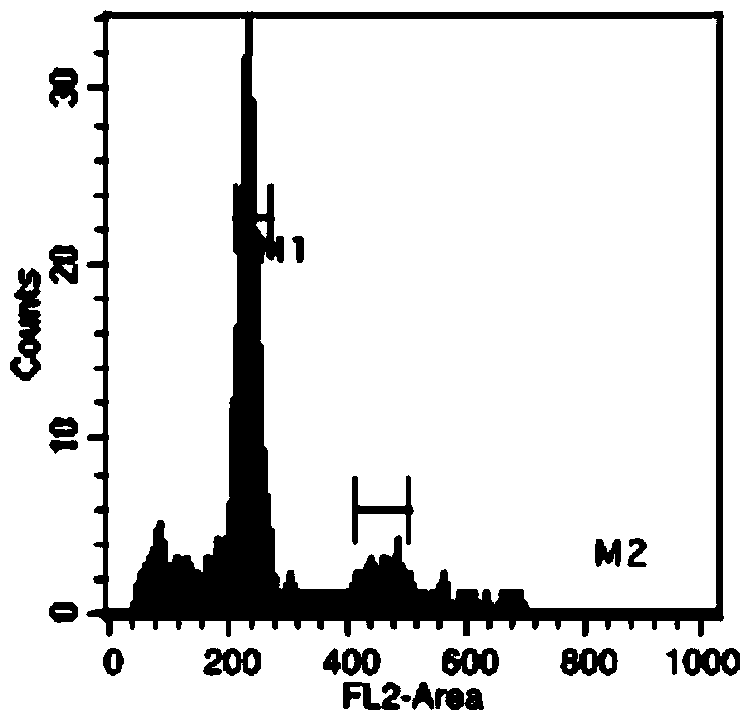
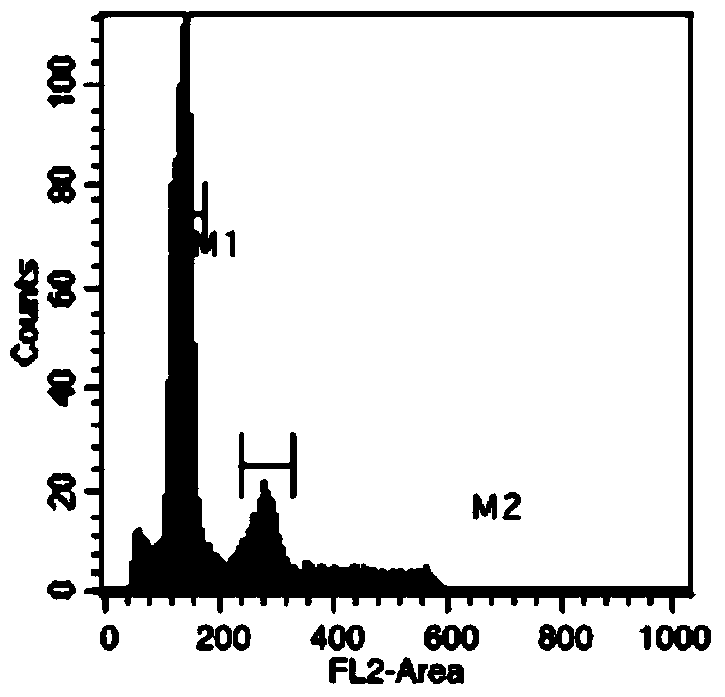
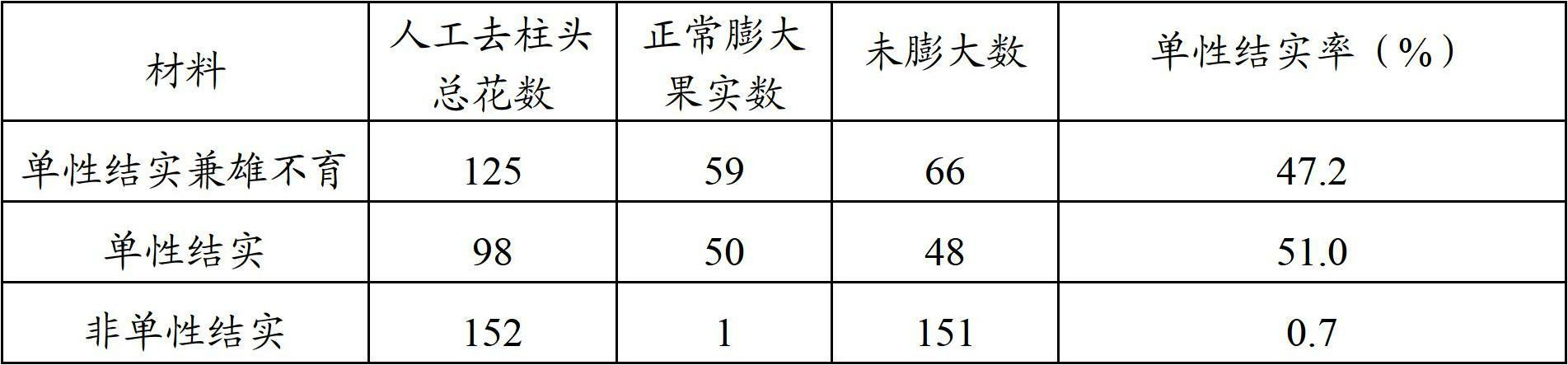
The invention relates to the technical field of agriculture, in particular to a method for cultivating a seedless eggplant variety. According to the method, two characters, namely parthenocarpy and male sterility of eggplants are integrated on the same strain to obtain a novel male sterility breeding material with parthenocarpy performance; and the parthenocarpic rate of the material is about 50 percent, and the sterile plant rate and the sterility degree are over 99 percent. Fruits of the variety are seedless or have few seeds in the whole harvest period, and the character can be stably inherited. The hybrid eggplant variety which is naturally seedless or has few seeds in the whole harvest period can be cultivated by using the eggplant breeding material by a heterosis breeding method; and the natural seedless fruit rate of the variety is about 76 percent generally. Eggplant fruits which are seedless or have few seeds can be produced by using the variety.
Owner:CHONGQING ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for cultivating Lilium oriental hybrid embryos
InactiveCN102599053APrevent premature agingAddressing Post Fertilization BarriersPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsGermplasmPollination
The invention relates to a method for cultivating Lilium oriental hybrid embryos, which is effective in breeding effect and short in breeding period. The method includes: pollinating a Lilium oriental hybrid line; sectioning and peeling small embryos, ovules or ovaries; and performing isolated culture. By cross pollination of the ovaries and young embryos and isolated culture, the embryos can be taken out for culturing before abortion to avoid premature senility of distant hybrid embryos, and accordingly Lilium post-fertilization barrier can be overcome effectively, a great amount of distant hybrid embryos are allowed to continue growing into normal seeds, a breeding procedure is drawn close as soon as possible, and the breeding cycle is shortened. In addition, a great amount of distant hybrids are obtained, Lilium interspecific distant hybridization is achieved, and a batch of novel germplasm is created. The embryo rescue technology and the technology of within-bottle Lilium bulbing are combined, so that culture cycle of Lilium hybrids is shortened effectively, and hybrid survival rate is increased.
Owner:赵兴华
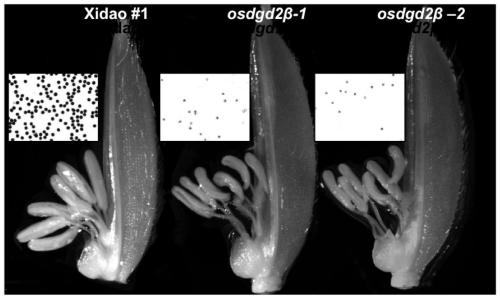
Application of OsDGD2beta gene in cultivating male sterile rice varieties
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Cultivation method for reserving seeds of globe artichoke
Disclosed is a cultivation method for reserving seeds of globe artichoke. The cultivation method includes greenhouse selection, seedling culturing, transplantation, field management, seed collection and the like. The field management specifically includes managements of transplanting time, winter management technology of seedling earlier stage, spring management technology of seedling later period, bud stage, flowering period and grain filling stage. The cultivation method for reserving seeds of globe artichoke has the advantages that the costs are reduced, each seed from foreign countries is 0.5 yuan, and each seed obtained by the scheme is 0.1 yuan; the supply is timely, the seeds from the foreign countries are ripe basically in August but sowing is required in September in China so that season connection is not timely, and the seeds obtained by the scheme can be completely ripe in July without delay of sowing of the next season; the seeds obtained by the scheme are produced in local area, advantages exist in terms of area adaptability, and the number of hybrid seeds and hybrid plants is small.
Owner:爱可道生物科技有限公司
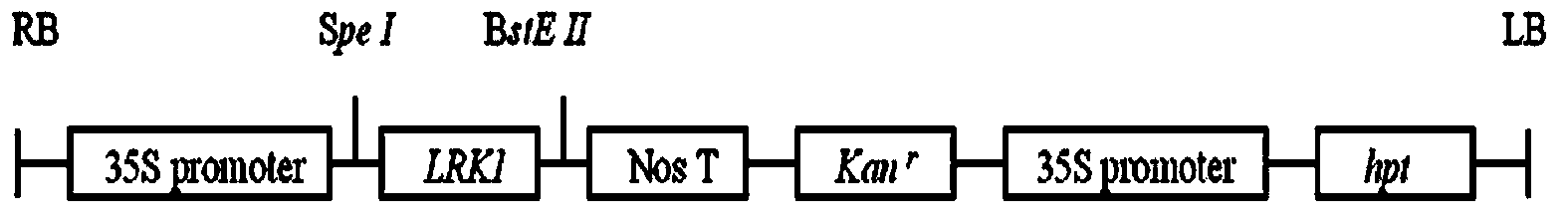
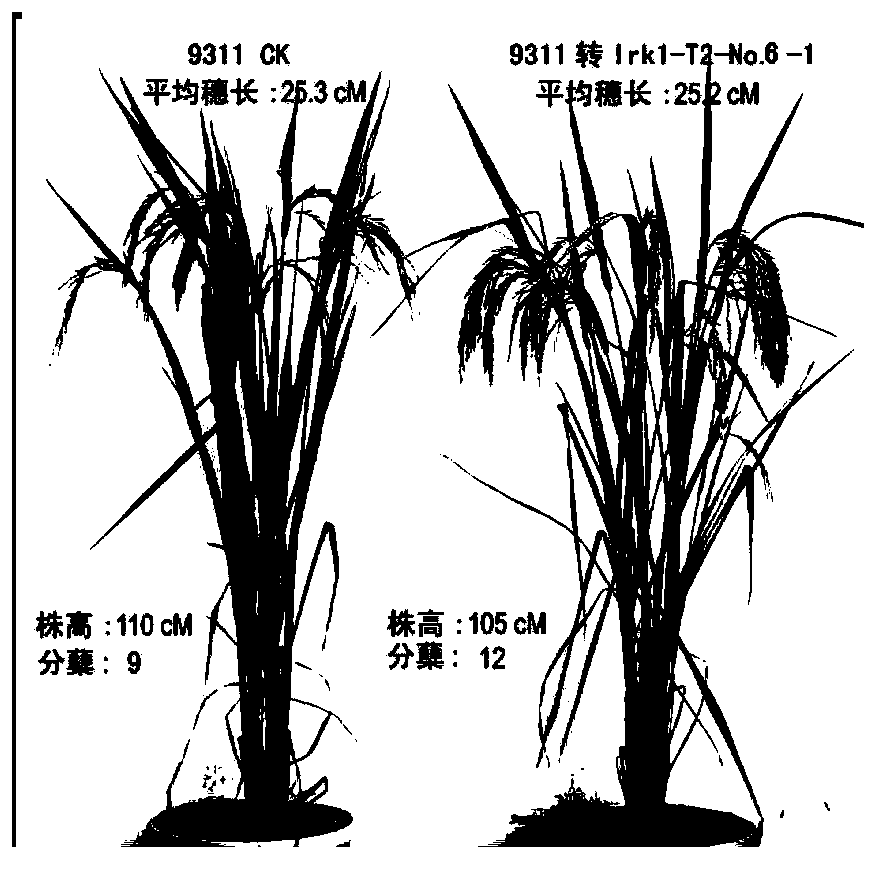
Method for improving fertility of indica-japonica rice hybrids by virtue of LRK1 gene transformation
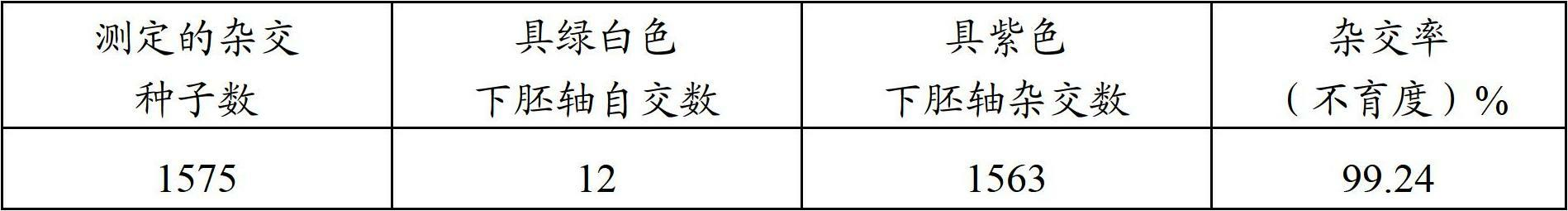
InactiveCN103571869AOvercoming sterilityBroad affinityPlant peptidesFermentationF1 generationHeterodea muelleri
The invention belongs to the field of transgenic technologies, and relates to a method for improving the fertility of indica-japonica rice hybrids by virtue of LRK1 gene transformation. According to the method, rice LRK1 genes are transformed into indica calluses by virtue of a gene gun microprojectile bombardment method, and rice plants for expressing the LRK1 genes are obtained through recovery culture. Experimental results show that the LRK1 genes can be used for successfully transforming rice and hybridizing rice with japonica rice varieties such as Nipponbare and Akihikari respectively, and the F1-generation seed setting rates are greatly higher than the control so as to achieve the seed setting rate level of regular varieties. Rice is provided with wide compatibility and can overcome the infertility characteristic of indica-japonica hybrids after being transformed by the rice LRK1 genes provided by the invention and the homologous genes thereof. The invention provides a low-cost and high-benefit novel method for utilization for the advantages of indica-japonica rice intersubspecific hybrids.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
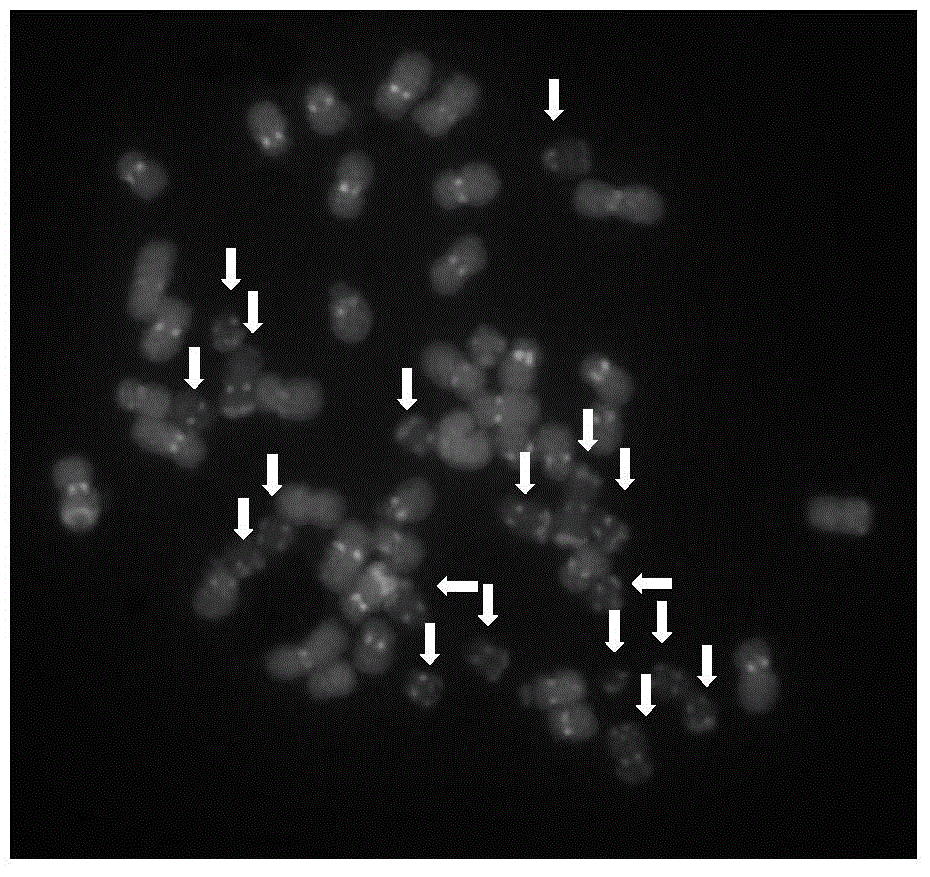
Method for interspecific hybrid genome in-situ hybridization of crambe cordifolia
InactiveCN104745695AEasy to shapeGood dispersionMicrobiological testing/measurementDispersityConcentration ratio
The invention belongs to the technical field of crop molecular breeding, and in particular relates to a method for interspecific hybrid genome in-situ hybridization of crambe cordifolia. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a probe marker, preparing a slide, performing in-situ hybridization, performing signal detection and the like. In the slide preparation process, a chromosome slide which is good in morphology and good in dispersity in the meiosis period of crambe cordifolia can be obtained under appropriate enzymolysis conditions by using an acetic acid extension flame drying method. When probes and chromosomes are modified, appropriate temperature and time can be selected, appropriate blocking DNA and a probe concentration ratio can be confirmed, fluorescent in-situ hybridization images with clear signals can be obtained, and different interspecific chromosomes of hybrid crambe cordifolia species can be clearly identified, so that genome in-situ hybridization can be well applied to cytological detection of crambe cordifolia species with characteristics of a large number of chromosomes, small morphology and the like, and novel techniques and methods are provided for identification and structural research on crambe cordifolia chromosomes, evolution research on crambe cordifolia, and the like.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Method for cultivating apple hybrid seedlings
ActiveCN107047187ASimple and fast operationImprove germination rateCultivating equipmentsHybrid seedGreenhouse
The invention discloses a method for cultivating apple hybrid seedlings. The method includes the following steps: picking up ripe apple hybrid fruits, and storing the ripe apple hybrid fruits in a refrigeration house at the temperature of 1-4 DEG C; acquiring hybrid seeds from the apple hybrid fruits stored in the refrigeration house, and using clean water to clean the hybrid seeds; preparing a bed with the width of about 1 meter in a greenhouse, putting a medium in nutriment pots, straightening the medium in the bed, watering the medium thoroughly, and allowing the medium to stand for 2-3 days; sowing the cleaned hybrid seeds in the nutriment pots, covering the hybrid seeds with wet nutriment soil with the thickness of 1 cm, and controlling the temperature of the greenhouse at 25-30 DEG C; changing the temperature of the greenhouse to 20-25 DEG C when the height of hybrid seedlings is 5-10 cm, keeping the relative humidity at 50-70%, performing ventilation at suitable time, transplanting the hybrid seedlings to a nursery garden after the hybrid seedlings are cultivated for 15-20 days, watering the hybrid seedlings once after transplanting, and performing management after planting. The method can avoid sand storage and germination accelerating in an apple hybrid seedling cultivation process, is easy to operate, and can improve the rate of emergence by about 25%.
Owner:CHANGLI INST OF POMOLOGY HEBEI ACADEMY OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI
Cultivation method for high-oleic-acid peanuts with spotted seeds and peels
InactiveCN109156340AEfficient use ofGuaranteed qualityPlant genotype modificationHeterodea muelleriHigh oleic acid
The invention discloses a cultivation method for high-oleic-acid peanuts with spotted seeds and peels. The cultivation method for high-oleic-acid peanuts with spotted seeds and peels comprises the following steps: separately selecting a pink-peel high-oleic-acid peanut and a spotted common peanut as a female parent and a male parent, carrying out hybridization to obtain F1, erasing false hybrid from the generation F1 and then carrying out selfing to obtain F2, screening a single strain with spotted seeds and peels from F2 by using a KASP label, screening F3 again to obtain a stable good-performance single strain with spotted seeds and peels, carrying out variety test on F4 line, and screening a candidate variety to finally obtain a F5 formation variety. The appearance of the cultivated high-oleic-acid peanuts with spotted seeds and peels is different from that of common pink-peel peanuts, the cultivated high-oleic-acid peanuts with spotted seeds and peels are conveniently distinguishedfrom common peanuts, and thus, the high-oleic-acid peanuts can be utilized well.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
Cucumber hybrid corinto
ActiveUS8399740B2Improve featuresImprove nutritional qualityPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsGenetic MaterialsHeterodea muelleri
A hybrid cucumber designated ‘Corinto’ is disclosed having resistance to powdery mildew (Sphaerotheca fuliginea), cucumber mosaic virus and cucumber vein yellowing virus. The invention relates to the seeds of hybrid cucumber ‘Corinto,’ to the plants of hybrid cucumber ‘Corinto’ and to methods for producing a cucumber plant, either inbred or hybrid, by crossing the hybrid ‘Corinto’ with itself or another cucumber plant. The invention further relates to methods for producing a cucumber plant containing in its genetic material one or more transgenes and to the transgenic plants produced by that method and to methods for producing other cucumber lines, cultivars or hybrids derived from the hybrid cucumber ‘Corinto.’
Owner:ENZA ZADEN BEHEER BV
Pentas clone 99/280-6
ActiveUS7880073B2Increase the number ofImprove performanceTissue cultureOther foreign material introduction processesStage iibGenetic Materials
A Pentas variety designated 99 / 280-6 is disclosed. The invention relates to the tissue of Pentas clone 99 / 280-6, to the plants of Pentas 99 / 280-6, to plant parts of Pentas clone 99 / 280-6 and to methods for producing a Pentas plant produced by crossing Pentas clone 99 / 280-6 with itself or with another Pentas variety. The invention also related to the vegetative propagation of Pentas clone 99 / 280-6. The invention also relates to methods for producing a Pentas plant containing in its genetic material one or more transgenes and to the transgenic Pentas plants and plant parts produced by those methods. This invention also relates to Pentas varieties or breeding varieties and plant parts derived from Pentas clone 99 / 280-6, to methods for producing other Pentas varieties, lines or plant parts derived from Pentas clone 99 / 280-6 and to the Pentas plants, varieties, and their parts derived from use of those methods. The invention further relates to hybrid Pentas seeds, plants and plant parts produced by crossing the clone 99 / 280-6 with another Pentas variety.
Owner:ERNST BENARY SAMENZUCHT
Cucumber hybrid Menfis
InactiveUS8445753B2Improve featuresImprove nutritional qualityPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsGenetic MaterialsHeterodea muelleri
A hybrid cucumber designated Menfis is disclosed having resistance to powdery mildew (Sphaerotheca fuliginea), cucumber mosaic virus, and cucumber vein yellowing virus. The invention relates to the seeds of hybrid cucumber Menfis, to the plants of hybrid cucumber Menfis, and to methods for producing a cucumber plant, either inbred or hybrid, by crossing the hybrid Menfis with itself or another cucumber plant. The invention further relates to methods for producing a cucumber plant containing in its genetic material one or more transgenes and to the transgenic plants produced by that method and to methods for producing other cucumber lines, cultivars, or hybrids derived from the hybrid cucumber Menfis.
Owner:ENZA ZADEN BEHEER BV
Method for breeding cucumis allotriploid cucumbers
InactiveCN102210264AImprove germination rateStrong growthPlant genotype modificationHeterologousProcessing type
The invention relates to a method for breeding cucumis allotriploid cucumbers, belonging to the field of biotechnological breeding. The method is special for chromosome engineering and ploidy breeding of cucumbers. Cucumis diploid new species are positively and negatively hybridized with diploid cucumbers; and the seeds harvested from the hybridized fruit are the seeds of the allotriploid cucumbers. The seedling allotriploid cucumbers have strong growth potential and excellent economic characteristic, and can serve as low-temperature-resistant, weak-light-resistant and Meloidogyne incognita Chitwood-resistant processing type greenhouse culture cucumber new species to be popularized and applied. The seedling allotriploid cucumbers provide precious materials for researching scientific problems such as cucumber cotyledon genetic development law, fruit development, parthenocarpy mechanism, heterosis mechanism and the like, facilitates utilization of the allotriploid cucumbers, and contributes to transducing wild type excellent genes to culture the cucumber new species.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Breeding method for selfing prior to hybridizing of whiteleg shrimp populations
InactiveCN102524138AGuaranteed low temperature resistanceStrong low-salt abilityClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaWhiteleg shrimpShrimp
The invention provides a breeding method for selfing prior to hybridizing of whiteleg shrimp groups, which is characterized by including: selecting whiteleg shrimp populations with excellent seed sources, clear genetic background and close relation between individuals in the same population; selecting the individuals from the same population, and performing close inbreeding to produce self-bred offspring; selecting the self-bred offspring generated by close inbreeding based on merit, and establishing fundamental breeding populations subjected to inbreeding purification; selecting the fundamental breeding populations with character complementation for inter-population hybridization so as to obtain offspring seeds with heterosis. The method has the advantages that the fundamental breeding populations are established by selfing passage and selection, young shrimps produced by inter-population combined hybrid breeding are higher in resistance to low temperature and low saline, and the production speed in the cultivation period is faster.
Owner:FISHERIES RES INST OF FUJIAN +2
Identification method of interspecific hybrids of Brassica campestris and Brassica napus
InactiveCN102768210AImprove accuracyAccurate identificationInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsStomaCuticle
The invention discloses an identification method of interspecific hybrids of Brassica campestris and Brassica napus, falling into the technical field of plant cytology. The method includes collecting the 4th-7th leaves of a plant in the seedling stage, tearing to collect hypoderm tissues of lower parts of the leaves, staining with iodine-potassium iodide solution, observing stomata under an optical microscope, measuring major / minor axis values of guard cells, calculating perimeter values of the guard cells with an ellipse model while observing and counting chloroplasts, recording 15 data per leaf, and identifying with parents as controls. For Brassica campestris, stoma guard cells have perimeter smaller than 58.90 micrometer and chloroplast count of 9-11; for Brassica napus, stoma guard cells have perimeter greater than 75.83 micrometer and chloroplast count of 19-20; while, for the to-be-identified material, if more than ten stomata simultaneously satisfy that guard cells have perimeter of 58.90-75.83 micrometer and chloroplast count of 14-16, it is determined that the plant is interspecific hybrids F1 of Brassica campestris and Brassica napus, otherwise it is false hybrid.
Owner:GANSU AGRI UNIV
Method for quickly obtaining interspecific hybrids of incompatible wide species and cultivated species of peanuts
InactiveCN102577930AEfficiently obtainedEasy to getPlant genotype modificationMolecular identificationPollination
The invention relates to a plant distant hybridization technology, in particular to a method for quickly obtaining a large amount of interspecific hybrids of an incompatible wide species and a cultivated species of peanuts through medicine induction after pollination. The method for quickly obtaining the interspecific hybrids of the incompatibility wide species and the cultivated species of the peanuts comprises the following steps of: (1) preparing a hormone mixed solution; (2) collecting incompatible peanut wide species pollen and pollinating a peanut cultivated species female parent; (3) dipping the hormone mixed solution and applying on a base of each pollinated cultivated species female parent flower; and (4) carrying out molecular identification on the harvested seeds. According to the invention, the method can be operated in the field and a large amount of interspecific hybrids can be effectively obtained, a long-winded complicated tissue cultivation step is omitted, and the incompatible hybrids of the peanuts can be simply and easily obtained.
Owner:SHANDONG PEANUT RES INST
Method of obtaining primula forbesii and primula saxatilis interspecific hybrid by utilizing immature embryo rescue technology
ActiveCN103563749AImproved germplasmFacilitate genetic exchangeHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureInterspecific hybridizationPrimula
The invention provides a method of obtaining a primula forbesii and primula saxatilis interspecific hybrid by utilizing an immature embryo rescue technology. The method comprises the following steps: selecting primula primula forbesii and primula saxatilis which are originated in China to carry out hybridization; carrying out immature embryo rescue by adopting an ovary culture means; carrying out hybrid morphological identification on obtained progeny materials; selecting the progeny material which has morphological characteristics, such as stems, leaves, flowering phase and inflorescence, similar to parents at the same time, and has novel properties not owned by the parents as a interspecific crossing new variety. The method disclosed by the invention realizes the interspecific distant hybridization of the primula, and obtains a batch of new hybrid germplasms.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Method for creating intergeneric hybridization of radish and turnip
ActiveCN105993912AImprove developmentHigh affinityHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureGlycineBrassica
The invention relates to a method for creating intergeneric hybridization of radish and turnip and belongs to the technical field of biotechnology breeding. The method specifically includes: sowing parent materials; performing cross pollination during the flowering stage; checking seeds; performing tissue culture to obtain hybrid seedlings; domesticating aseptic seedlings; performing hybrid morphological identification; performing hybrid cytological identification. The method has the advantages that according to the features that the distant hybridization of the radish and Brassica is severe in pre-fertilization barrier and minor in barrier after pollination, bud pollination is used and glycine of certain concentration is smeared to female parent stigmas before pollination to improve the compatibility of the intergeneric hybridization, natural pod bearing is used after the pollination, seed sterile culture is performed by the aid of the tissue culture technology, and the morphological and cytological identification of the obtained hybrid seedlings shows that the hybrid seedlings are actual intergeneric triploid hybrids.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Method for culturing orchid new variety through hybridization between sword-leaved cymbidium and renanthera coccinea
InactiveCN109122302ASolve mildewSolve the bottleneck problem of hybrid floweringPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsPollenBud
The invention discloses a method for quickly and efficiently cultivating a new orchid variety through hybridization between sword-leaved cymbidium and renanthera coccinea. The method comprises the steps of pollen collection and preservation, artificial pollination and hybrid fruit cultivation, hybrid embryo culture development into rhizomes, rhizome proliferation culture, rhizome differentiation culture, adventitious bud rooting and seedling culture, seedling transplanting and culture, and the like. According to the method provided by the invention, the infrequent bottleneck problem in a flowering period of interspecific hybridization of orchids is solved by using low-temperature preserved, sterile and vigorous pollen, the key problem of dysplasia of interspecific distant hybridization hybrid embryos is solved by using an embryo rescue culture technology, and corresponding rhizome clone proliferation culture is carried out after a single hybrid embryo is developed into a rhizome through sterile culture, so that the defect of long years of traditional hybridization breeding is avoided, and a new orchid variety can be rapidly cultivated.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
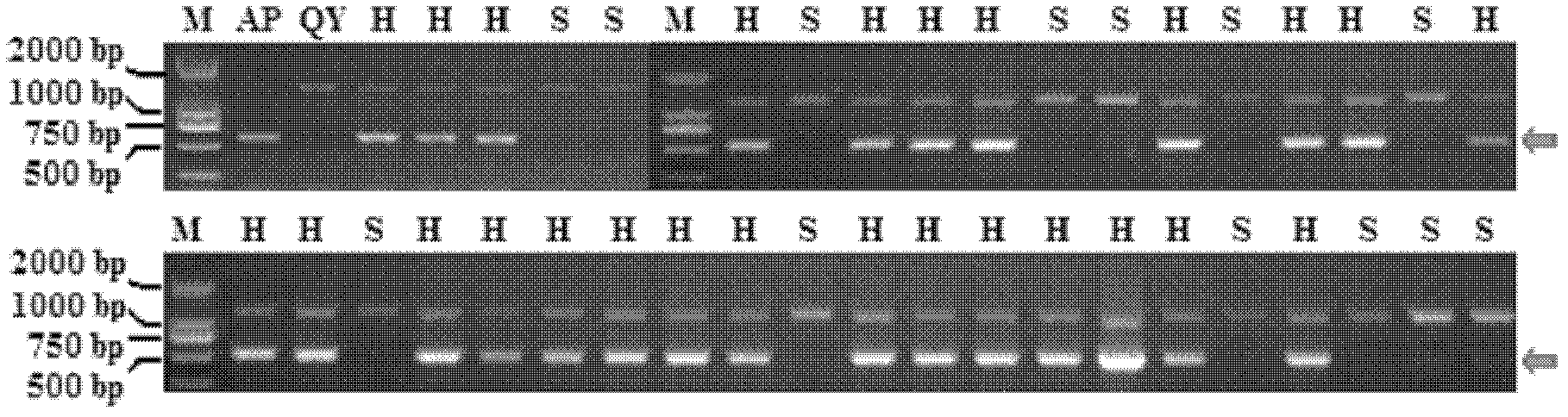
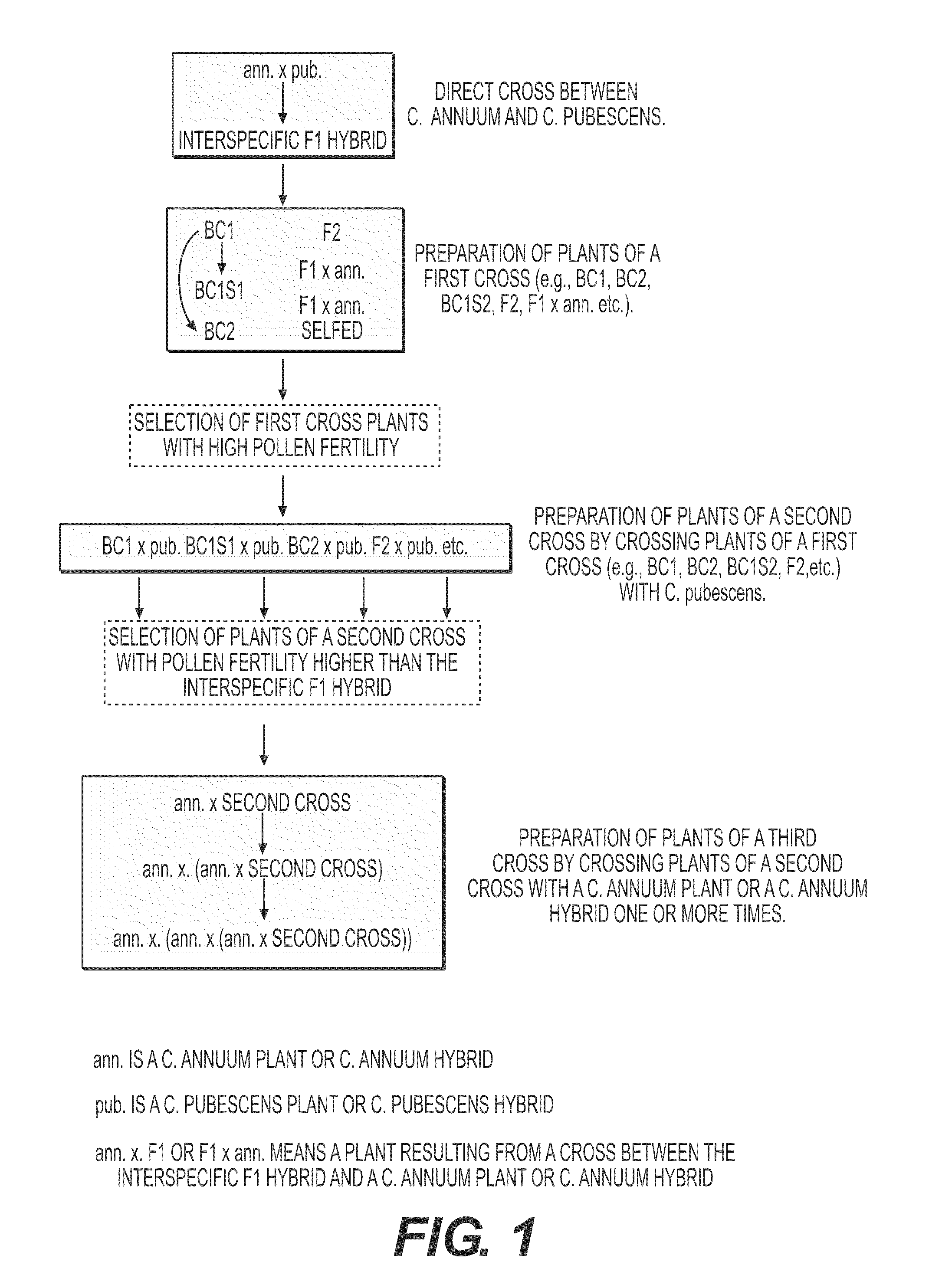
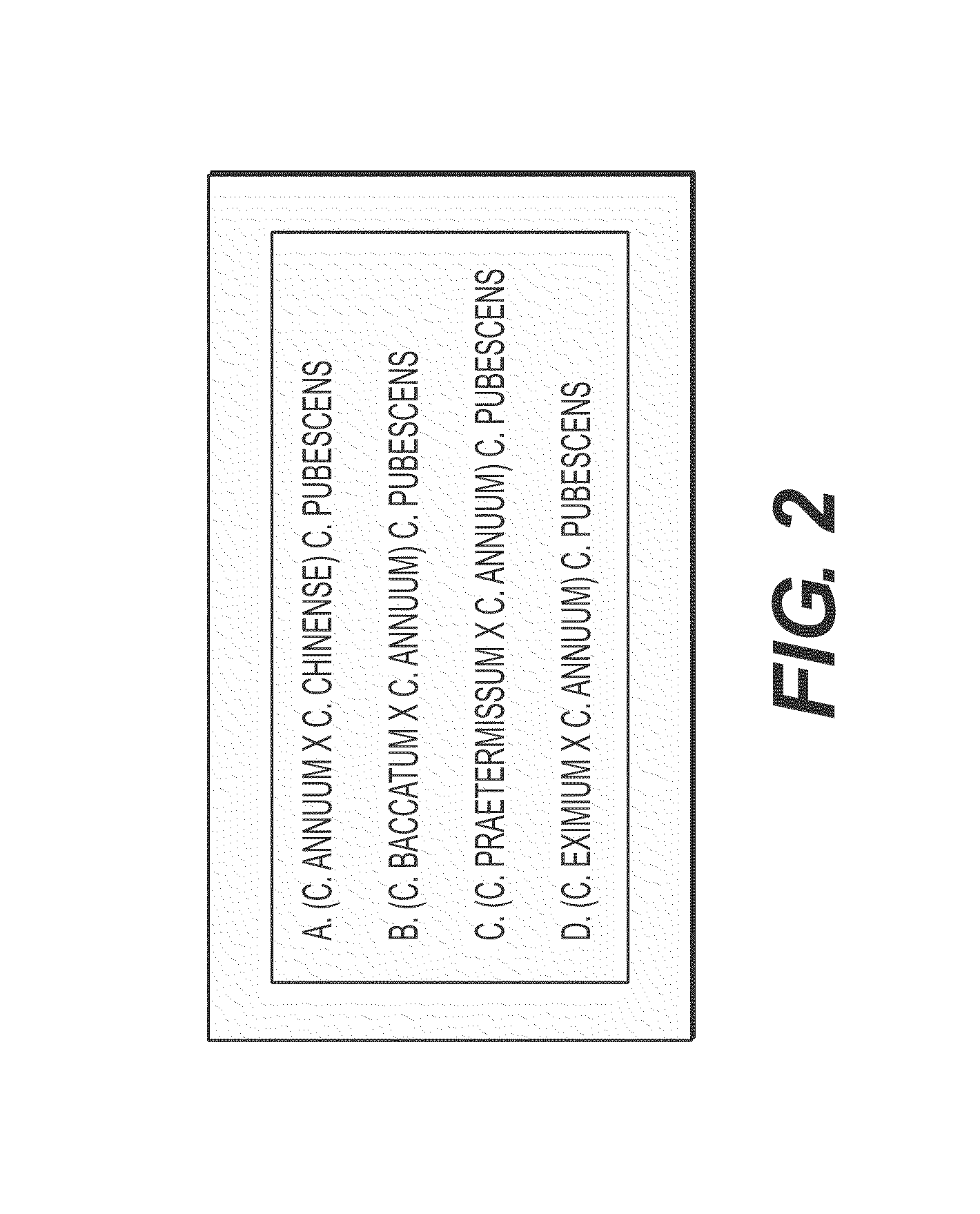
Hybrid pepper plants resulting from a cross between C. annuum and C. pubescens
InactiveUS8802939B2Improve abilitiesAbility to introgress traitsTissue culturePlant tissue cultureXanthomonas campestrisGenetic Materials
Owner:SEMINIS VEGETABLE SEEDS
Efficient cross breeding method for E. pungens var. variegata
The invention provides a method for increasing the cross pollination efficiency of E. pungens var. variegata and belongs to the technical field of artificial cross breeding of woody plants. The method comprises the steps: (1) disease and insect pest control; (2) pollen collection; (3) flower thinning; (4) castration, bagging and artificial pollination; (5) crossbreed collection and stratifcation; and (6) sowing, wherein castration is carried out in the full-bloom stage of the E. pungens var. variegata, flower buds which are consistent in growth on each flowering branch of the E. pungens var. variegata are retained, and the rest flower buds are trimmed and removed. The method provided by the invention is not only simple in operation, but also capable of effectively keeping the complete natural structures of flowers and effectively increasing the fruit setting rate of natural crossing from 8% to 65% and high in success rate of cross pollination. By using the method, the castration efficiency of the E. pungens var. variegata is effectively increased, false crossbreeds are avoided, and the purity and fruit setting rate of the crossbreeds are effectively increased.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY JIANGSU PROVINCE & CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
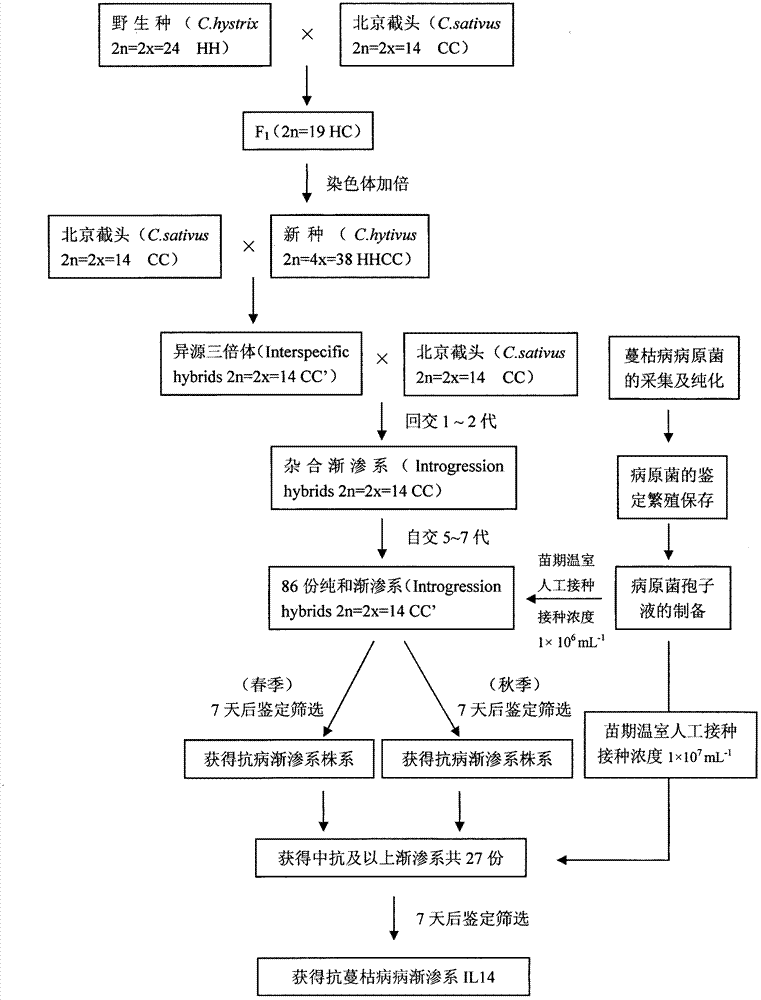
Method for screening mycosphaerella melonis resistance IL14 of cucumber-pickled cucumber introgression line
InactiveCN104737901ASolve the problem of narrow backgroundImprove disease and stress resistancePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsWild speciesChromosome fragment
The invention relates to a method for screening mycosphaerella melonis-resistant IL 14 of cucumber-pickled cucumber introgression line. According to batch treatment of different concentrations, plants with good resistance are screened, and the method belongs to the field of biotechnology breeding. The method comprises the following steps: by taking wild species pickled cucumber as a female parent, cultivating cucumber 'Beijing jietou' as a male parent, and hybridizing to obtain hybrid F1; combining the hybrid F1 with a somaclone variation chromosome reduplication technology by virtue of embryo rescue, thereby obtaining a fertile inter-specific heterologous tetraploid new species which is named as Cucumis hytivus; and by taking the heterologous tetraploid new species Cucumis hytivus as a female parent, performing system backcrossing and self-cross selective breeding with the cultivated variety 'Beijing jietou', thereby obtaining 86 parts of cucumber inter-specific introgression line materials carried with wild species chromosome segments, and respectively numbering as IL1-IL86. The 86 parts of introgression line groups are screened by adopting the greenhouse seedling stage artificial inoculation identification technology, stable moderate resistance or more strains are obtained by virtue of inoculation treatment in spring and autumn, the inoculation treatment is performed by increasing the concentration of bacterium, and the mycosphaerella melonis resistance strain IL14 is screened.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Methods for production of sporeless Agaricus bisporus mushrooms
Owner:SYLVAN AMERICA
Method for preparing high-erucic acid brassica napus by utilizing artificially synthesized brassica napus
InactiveCN106718824ABroaden the range of variationBroaden germplasm resourcesPlant genotype modificationMutation AccumulationGermplasm
The invention discloses a method for preparing high-erucic acid brassica napus by utilizing artificially synthesized brassica napus. The method comprises the following steps: hybridizing the artificially synthesized brassica napus and natural brassica napus to expand the mutation range of compositions of fatty acid of rape seeds; obtaining a large amount of mutations to affect the metabolic pathway of the brassica napus by utilizing a large amount of exchange and recombination among chromosomes of a hybrid progeny of the artificially synthesized brassica napus and the natural brassica napus, and the missing, inserting, transposition and inactivation of a gene sequence, and obtaining a high-erucic acid material by utilizing mutation accumulation. According to the method, the breeding period is shortened through a generation-adding technology; only the materials with the erucic acid content of greater than 45 percent are selected, so that the workload is small; through directional selecting, the selecting pressure is increased generation by generation, so that the frequency of obtaining different types of high-erucic acid materials is improved; the obtained materials contain the compositions of the artificially synthesized brassica napus, so that the germplasm resources are expanded, and strong hybrid vigour is beneficially achieved in later breeding.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIV
Pickle and purple cabbage trigenomic species allohexaploid vegetable germplasm and acquisition method
ActiveCN103651111BShorten the timeEasy to operateHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureGermplasmColchicine
The invention discloses a pickle and purple cabbage tri-genome species allohexaploid vegetable germplasm and an acquisition method, which fill in the blank of lack of brassica trigenomic species allohexaploid vegetable germplasm. The acquisition method comprises the steps that pickle and purple cabbages of brassica vegetable germplasm are cross-fertilized; an ovary is picked at the seventh day after pollination; mature seeds are obtained by embryo rescue; a large quantity of propagated progenies are obtained through subculture and propagation after seed germination; duplication treatment is carried out on a haploid by a liquid culture medium with colchicine to obtain the multi-genome allohexaploid vegetable germplasm. The pickle and purple cabbage tri-genome species allohexaploid vegetable germplasm and the acquisition method, disclosed by the invention, have the advantages of strong operability, simpleness and practicality, save the time for obtaining multi-genome polyploidy material, can be widely used for embryo rescue for interspecies cross of cruciferous brassica vegetable germplasm, and have great significance to cultivation and breeding of new species of special plants.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for cultivating triploid dendrobium officinale
ActiveCN102257964BAchieve innovationIncrease productionPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsGermplasmHeterodea muelleri
The invention relates to a method for cultivating triploid dendrobium candidum. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) firstly widely collecting dendrobium candidum seed resources in which good dendrobium candbium is selected; (2) carrying out artificial mutagenesis on the selected dendrobium candbium to obtain autotetraploid dendrobium candbium; (3) carrying out sexual hybridization based on the autotetraploid dendrobium candbium as a female parent and diploid dendrobium candbium as a male parent to obtain triploid dendrobium candbium seeds; (4) carrying out non symbiosis germination culture on the triploid dendrobium candbium seeds; (5) carrying out induction and differentiation culture on the protocorms (PLBs) of the triploid dendrobium candbium seeds; (6) carrying out differentiation on triploid dendrobium candbium mature seedling; (7) transplanting triploid dendrobium candbium seedlings in bottles; and (8) carrying out cultivation management on the triploid dendrobium candbium mature seedling. In the invention, a triploid having the advantages of a polyploid and a hybrid cultivar can be obtained through genome triplication, and the triploid is giant and non substitutable; the yield of dendrobium candbium medicinal material can be greatly improved; and meanwhile, the triploid dendrobium candbium is a permanent hybrid, and hybrid vigor can be fixed.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Molecular marker for identifying interspecific hybrids of Chinese cabbage and brassica carinata and separation conditions of A10 and C09 chromosomes of progeny materials
ActiveCN110423841AExpand genetic resourcesRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGeneticsHeterodea muelleri
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com