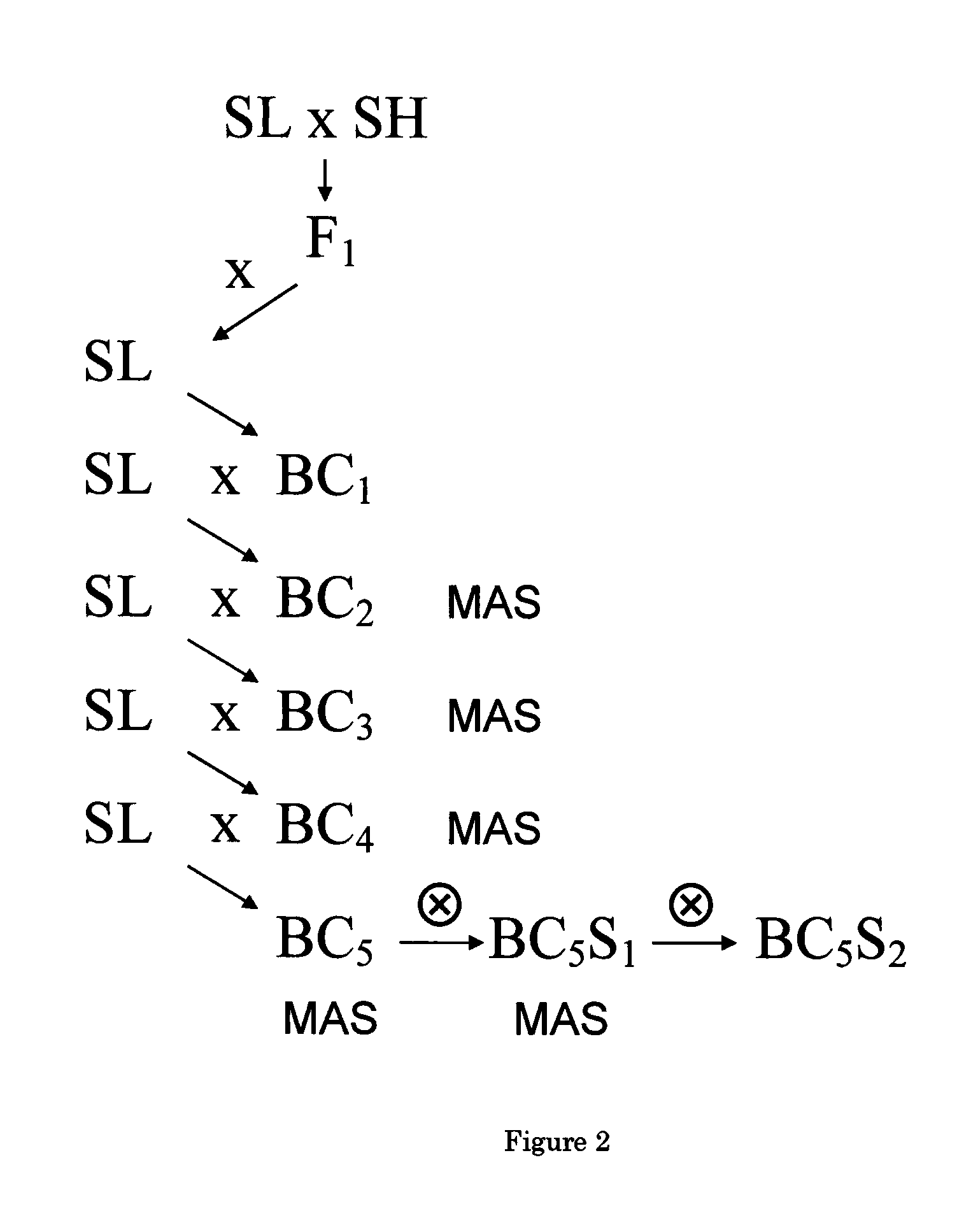
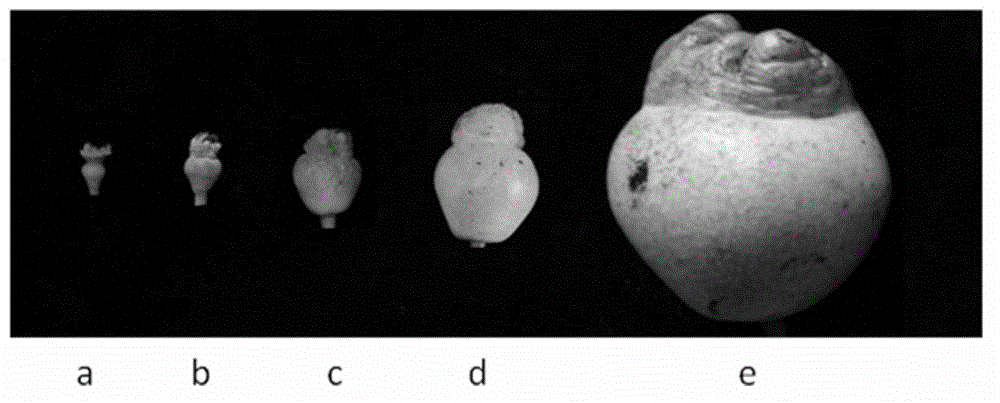
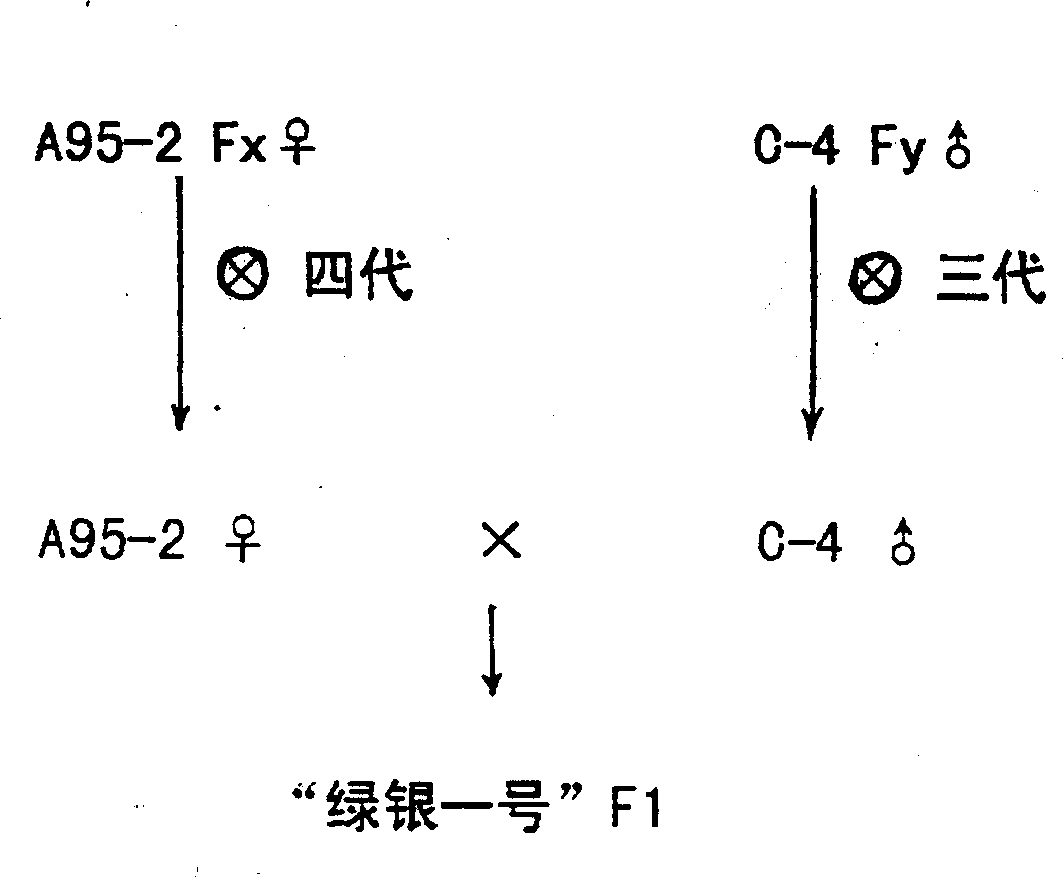
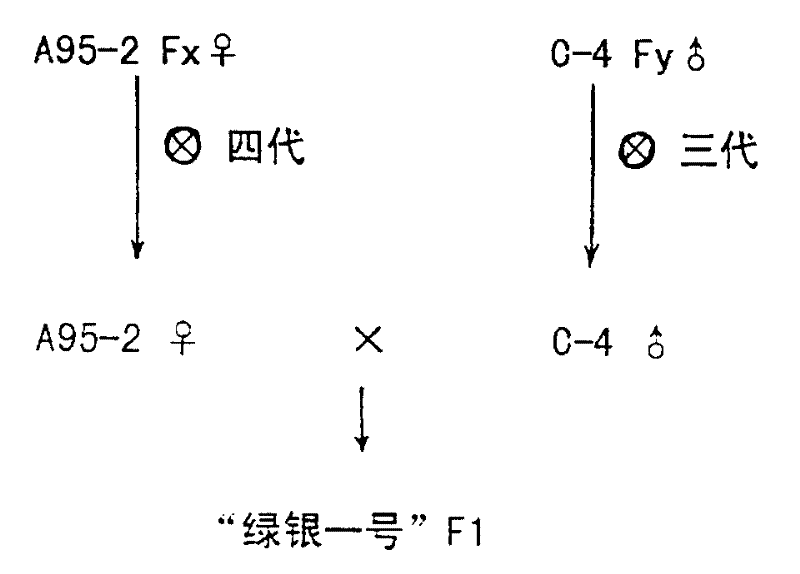
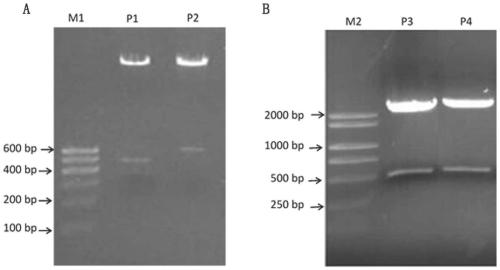
Patents
Literature
66 results about "Parthenocarpy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In botany and horticulture, parthenocarpy is the natural or artificially induced production of fruit without fertilisation of ovules, which makes the fruit seedless. Stenospermocarpy may also produce apparently seedless fruit, but the seeds are actually aborted while they are still small. Parthenocarpy (or stenospermocarpy) occasionally occurs as a mutation in nature; if it affects every flower the plant can no longer sexually reproduce but might be able to propagate by apomixis or by vegetative means.
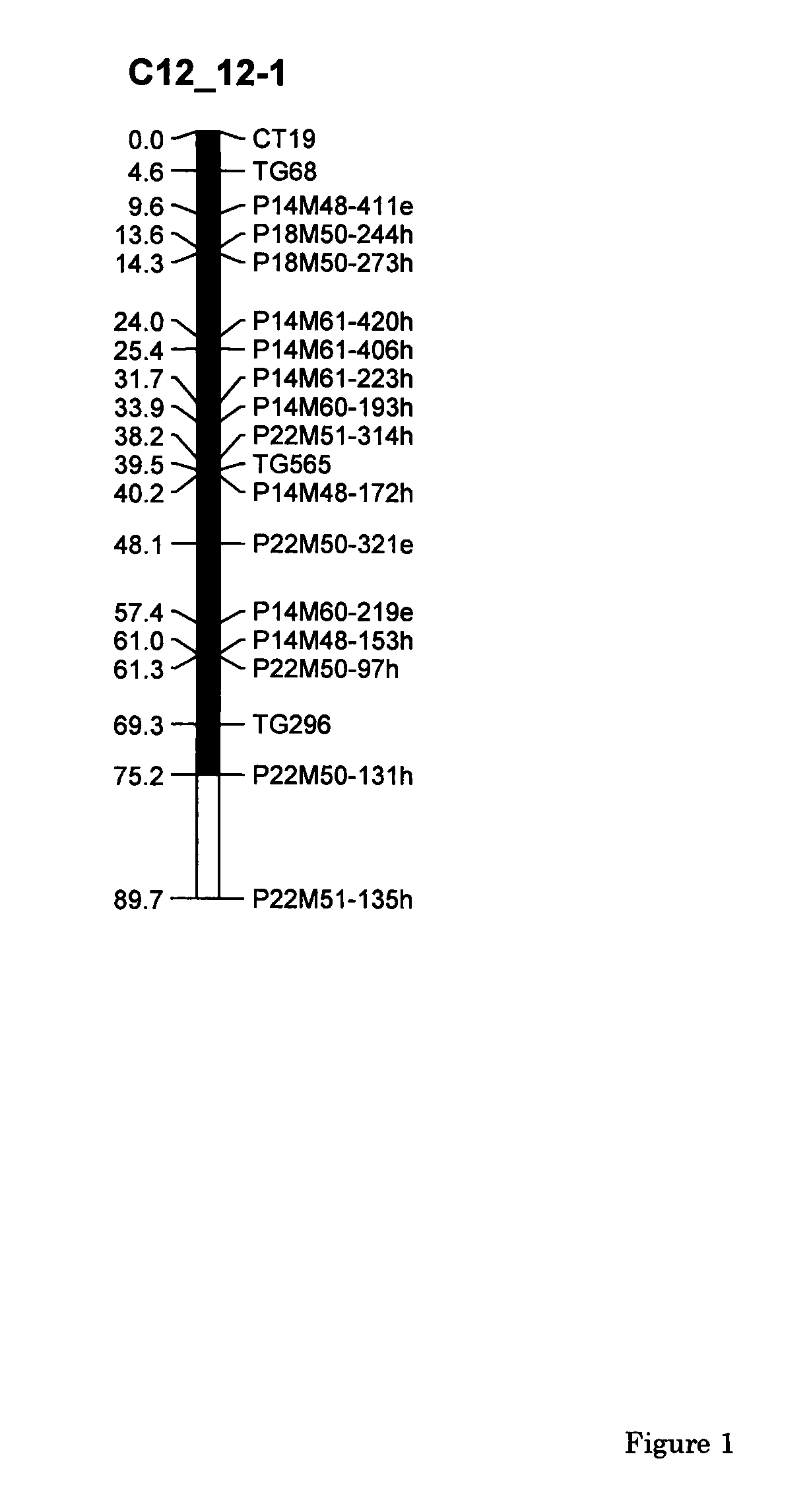
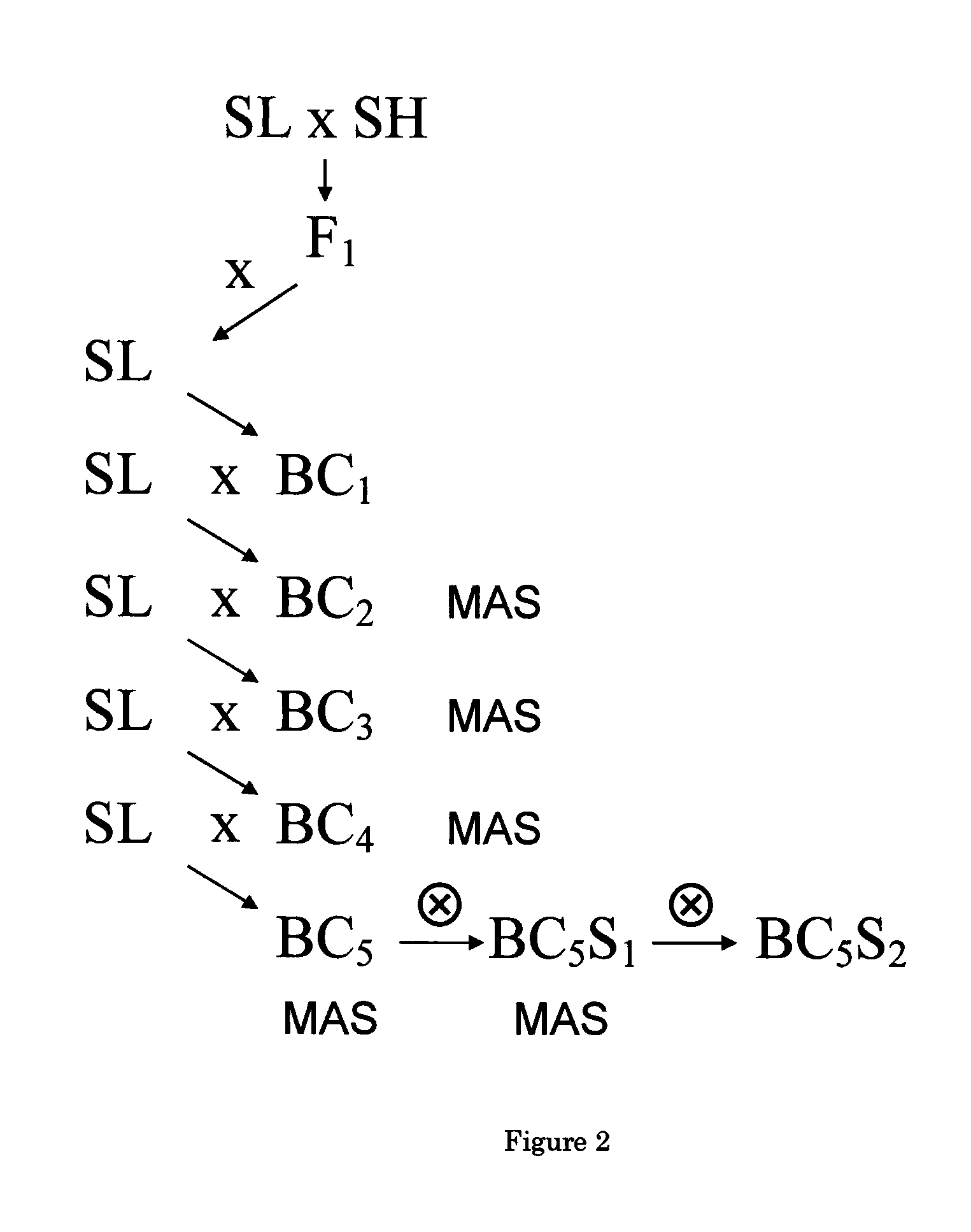
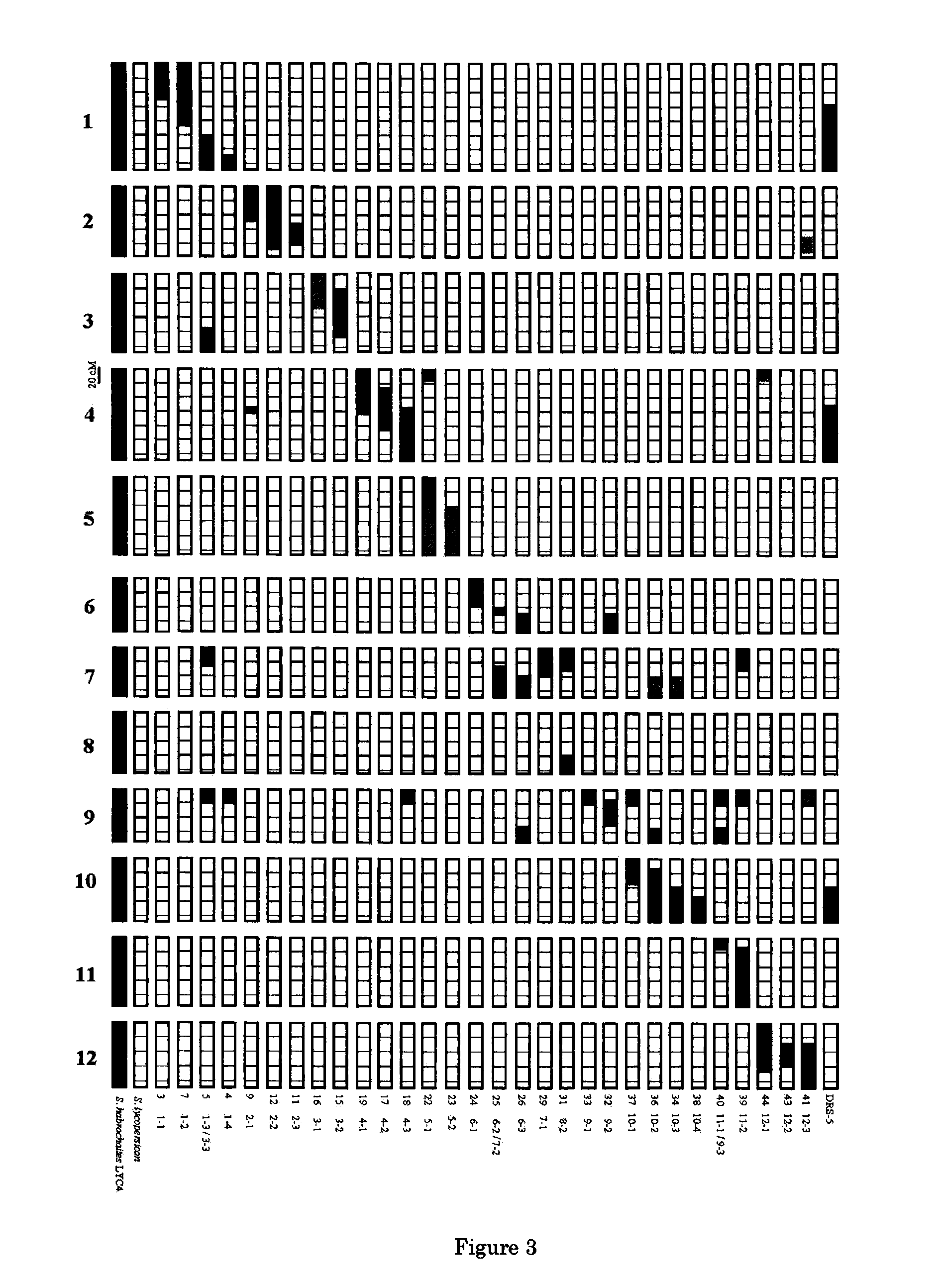
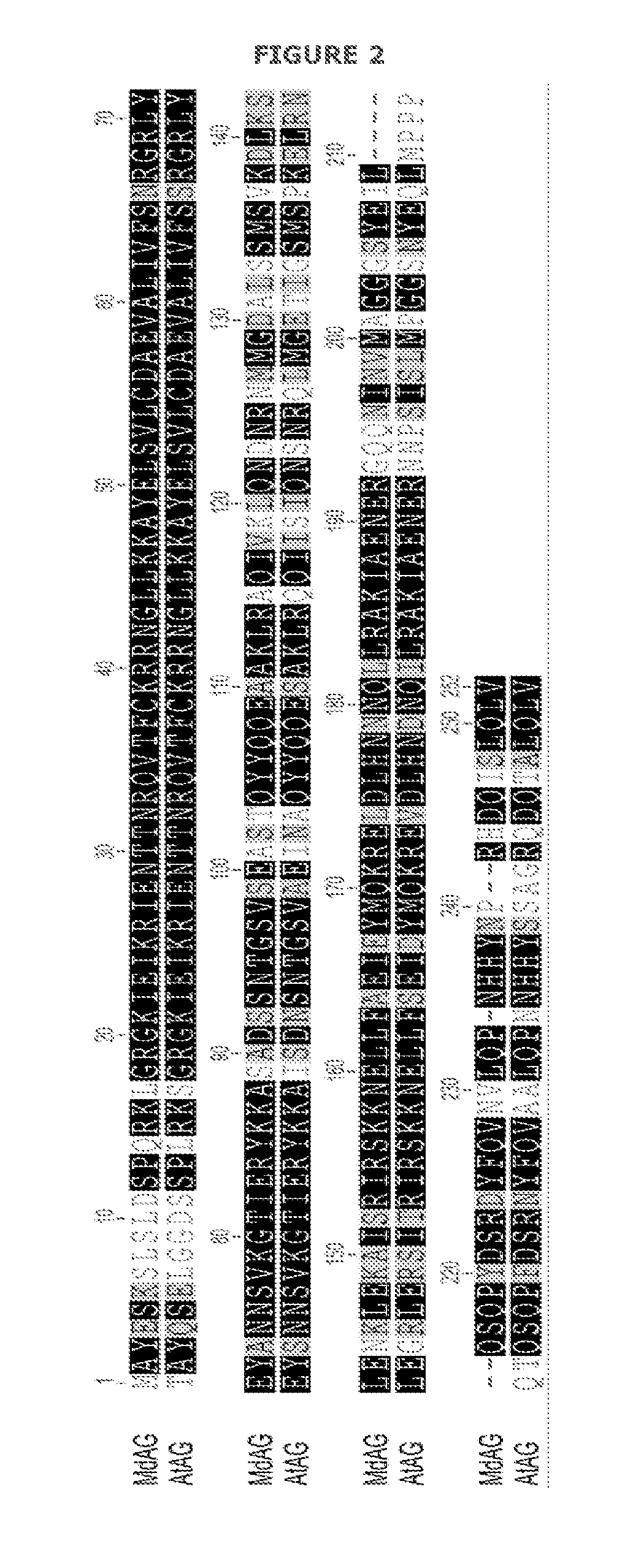
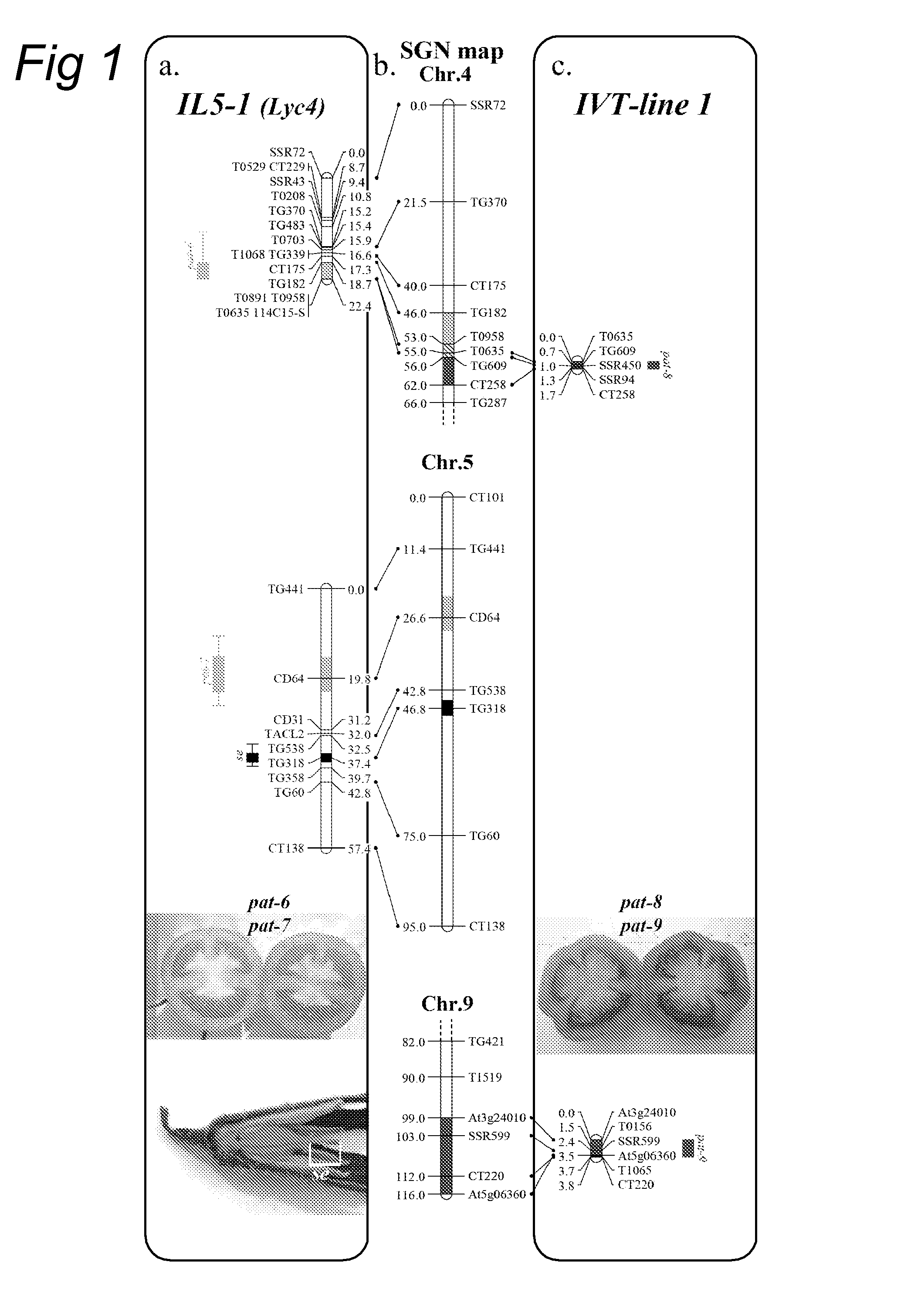
Parthenocarpic genetic elements derived from S. habrochaites
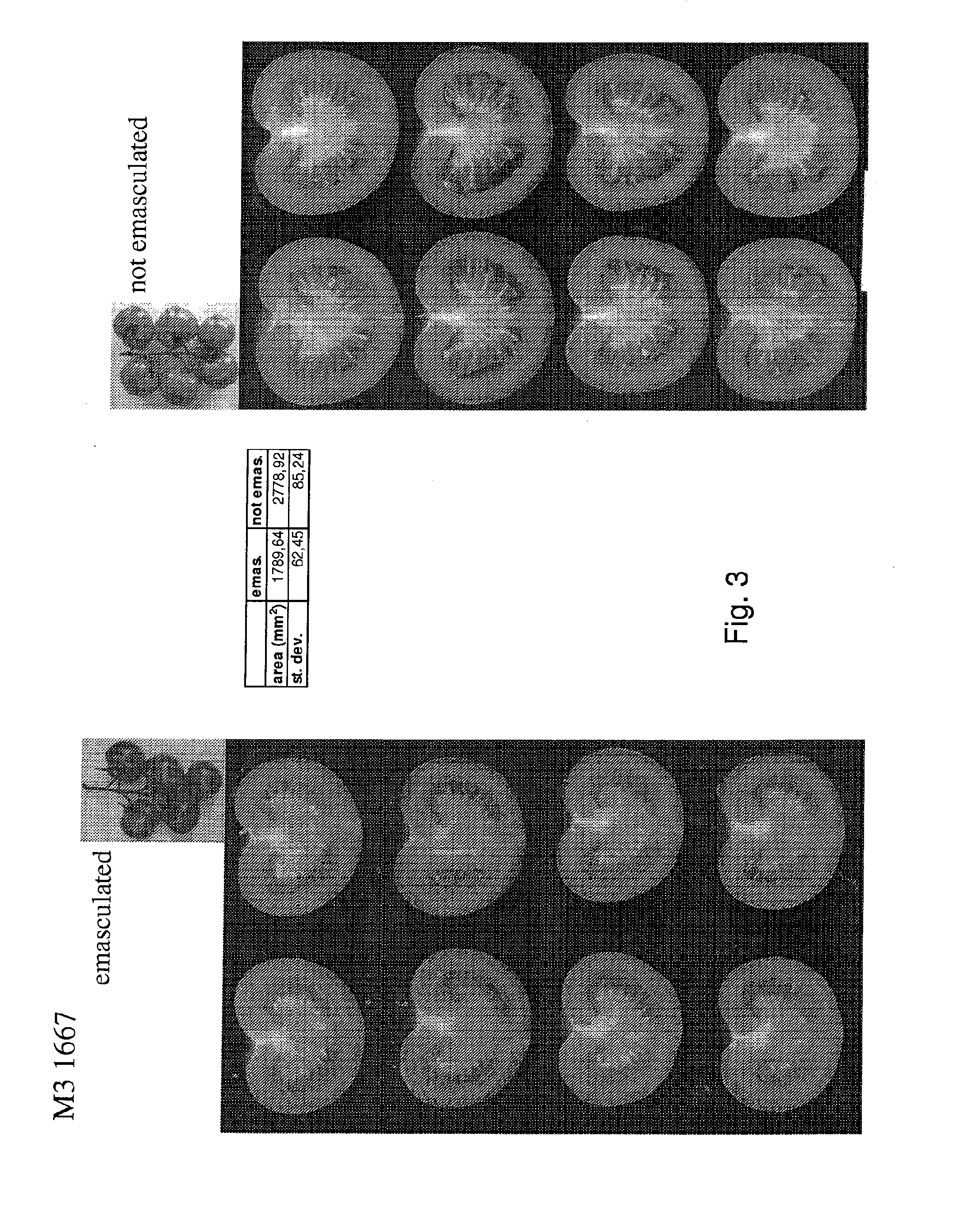
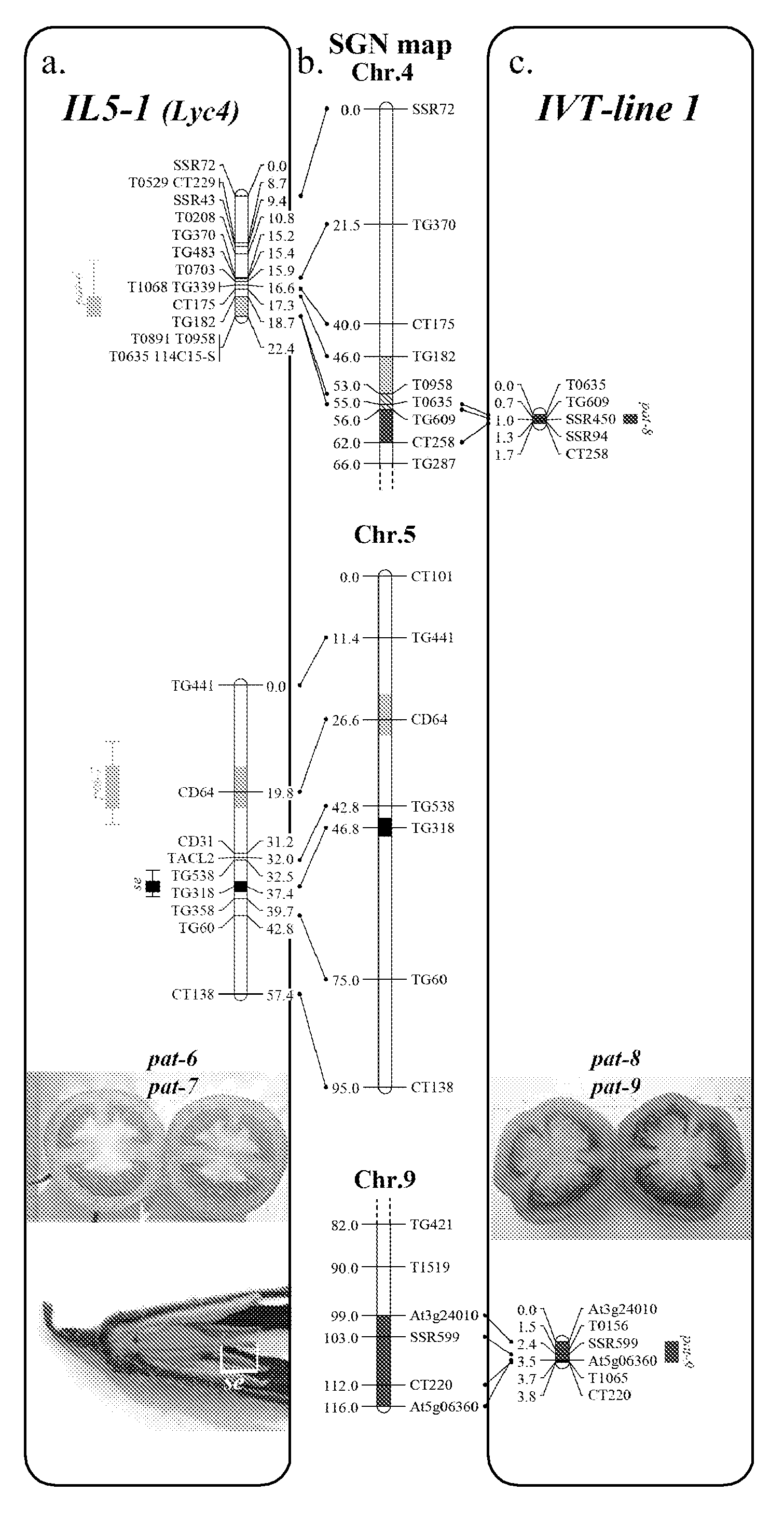
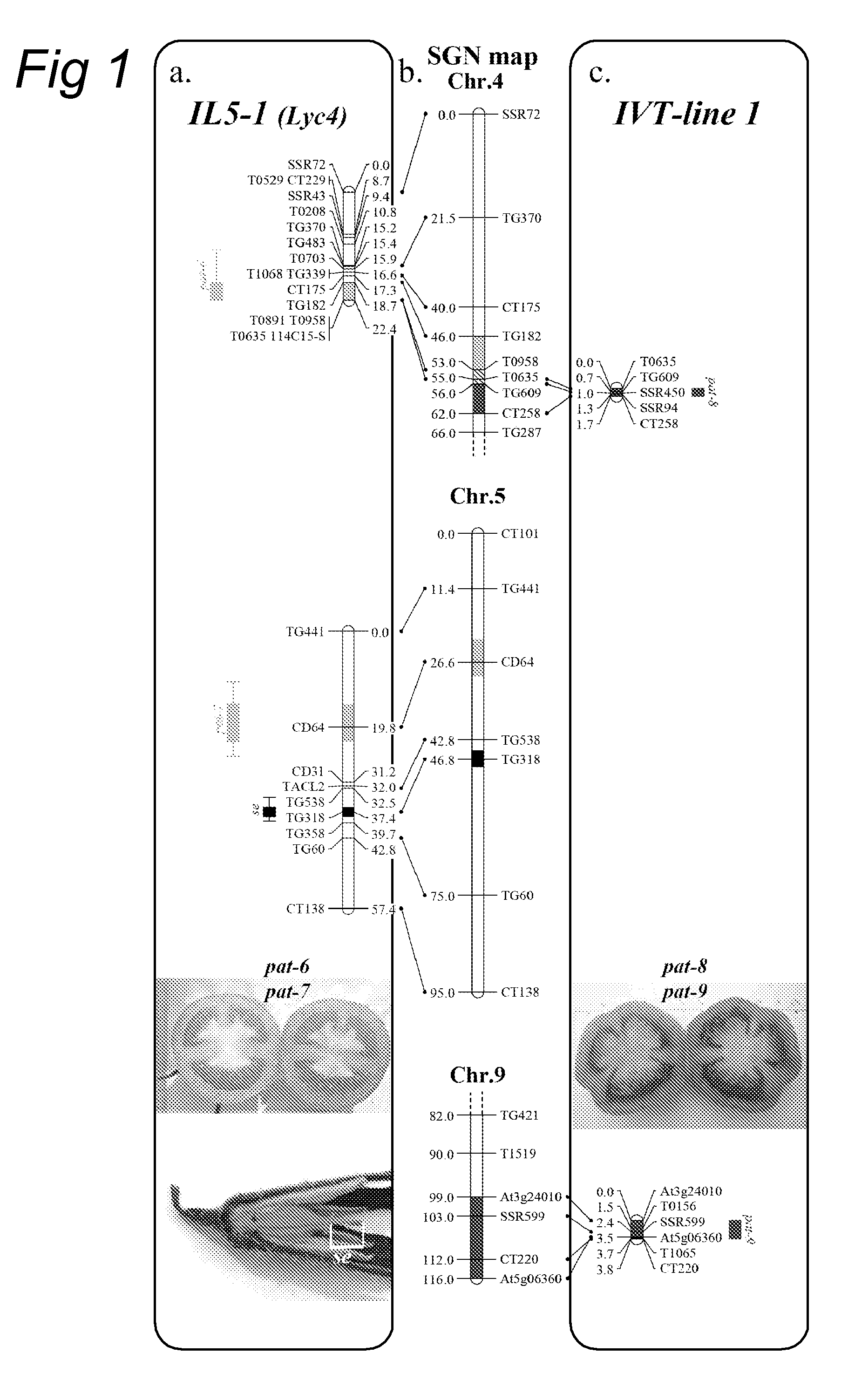
The present invention relates to a method of producing a parthenocarpic, and optionally male sterile, tomato plant comprising introgressing into said plant a genetic region from Chromosome 4, 5 and / or 12 of S. habrochaites LYC4 / 78, a representative sample of seed of which was deposited on 13 Nov. 2007 with the NCIMB under Accession number 41517, wherein the genetic region from Chromosome 4 of S. habrochaites LYC4 / 78 includes at least one marker selected from Marker CD59, RFLP Marker CT229, and COS Marker T1068, and wherein the genetic region from Chromosome 5 of S. habrochaites LYC4 / 78 includes at least one marker selected from COS Marker T1181, RFLP Marker TG441 and / or RFLP Marker CD31(A).
Owner:MONSANTO INVEST BV
Modified gene resulting in parthenocarpic fruit set
ActiveUS20170335339A1Good effectMicrobiological testing/measurementCis-trans-isomerasesFruit setWild type
The invention relates to a modified PIN4 gene, the wild type of which is as identified in SEQ ID No. 1, encoding the protein of SEQ ID No. 5, or the wild type of which encodes a protein that has a sequence similarity of at least 80% to SEQ ID No. 5, which modified PIN4 gene encodes a protein that comprises an amino acid change as a result of the modification, and which modified protein is capable of inducing parthenocarpic fruit set when present in a plant. The invention also relates to plants and fruits that carry the gene. Such plants are capable of parthenocarpic fruit set and the fruits do not contain seeds. The invention further relates to use of the gene in breeding and producing plants capable of parthenocarpic fruit set.
Owner:RIJK ZWAAN ZAADTEELT & ZAADHANDEL BV
Methods and Materials for Producing Coreless Fruit
InactiveUS20170240913A1High sensitivityFast and accurate multiple sequence alignmentMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesBiotechnologyProviding material
The invention provides materials and methods for producing coreless fruit, or plants that produce coreless fruit. The invention involves combining reduced expression of AGAMOUS (AG) with parthenocarpy. Parthenocarpy can be induced by hormone treatment, or can be provided by reduced or eliminated expression of PISTILATA (PI) or APETALA3 (AP3). The invention provides methods and materials for producing the plants and coreless fruit by genetic modification (GM) and non-GM means. The invention also provides the plants and coreless fruit.
Owner:THE NEW ZEALAND INST FOR PLANT & FOOD RES LTD
Plant parthenocarpy regulation gene and use thereof
InactiveCN101451138AFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionAuxin response factorTransgene
The invention discloses a gene related to plant parthenocarpy and particularly relates to an auxin response factor SmARF8 for regulating and controlling the parthenocarpy of an eggplant, wherein the full length of a cDNA sequence of the gene is 3,750bp. The invention also relates to a method for interference expression of the gene related to the parthenocarpy in the eggplant. The gene can ensure that a transgenic plant produces the parthenocarpy, thereby improving the quality, prolonging the preservation storage period, and having a simple operation method.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Parthenocarpic Genetic Elements Derived From S. Habrochaites
InactiveUS20100146656A1Microbiological testing/measurementOther foreign material introduction processesGenetic elementCD31
The present invention relates to a method of producing a parthenocarpic, and optionally male sterile, tomato plant comprising introgressing into said plant a genetic region from Chromosome 4, 5 and / or 12 of S. habrochaites LYC4 / 78, a representative sample of seed of which was deposited on 13 Nov. 2007 with the NCIMB under Accession number 41517, wherein the genetic region from Chromosome 4 of S. habrochaites LYC4 / 78 includes at least one marker selected from Marker CD59, RFLP Marker CT229, and COS Marker T1068, and wherein the genetic region from Chromosome 5 of S. habrochaites LYC4 / 78 includes at least one marker selected from COS Marker T1181, RFLP Marker TG441 and / or RFLP Marker CD31(A).
Owner:MONSANTO INVEST BV
Loquat unisexual fruiting induction agent and its use technology
A parthenocarpy inducing agent of loquat tree for bearing the non-kernel loquat fruit is prepared proportionally from gibberellin (GA3) and 1-(2-Cl-4-pyridyl)-3-phenylurea (CPPU) through mixing and dissolving it in water. Its application features that it is used to treat the flower buds, flower, or fruit every 29+ / -4 days before fertilization.
Owner:福州市农业科学研究所
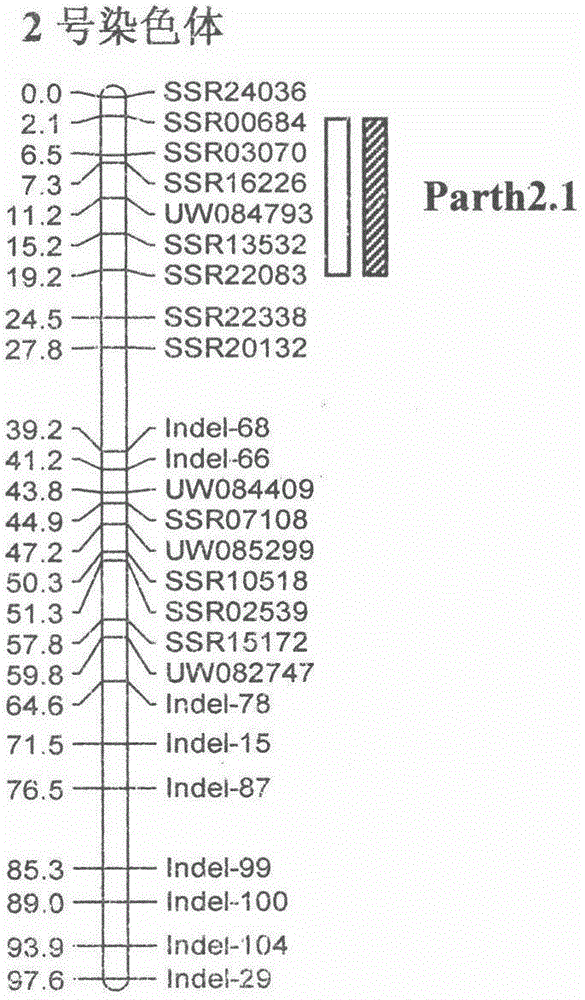
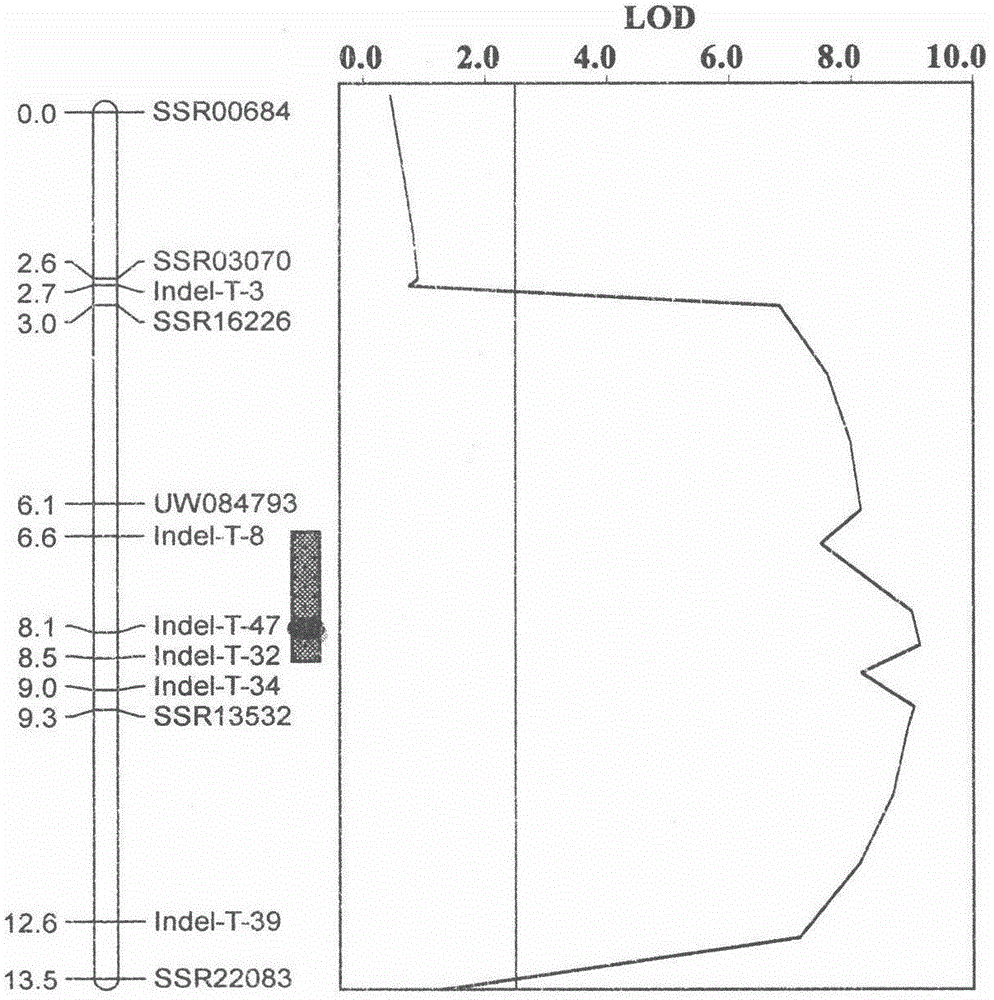
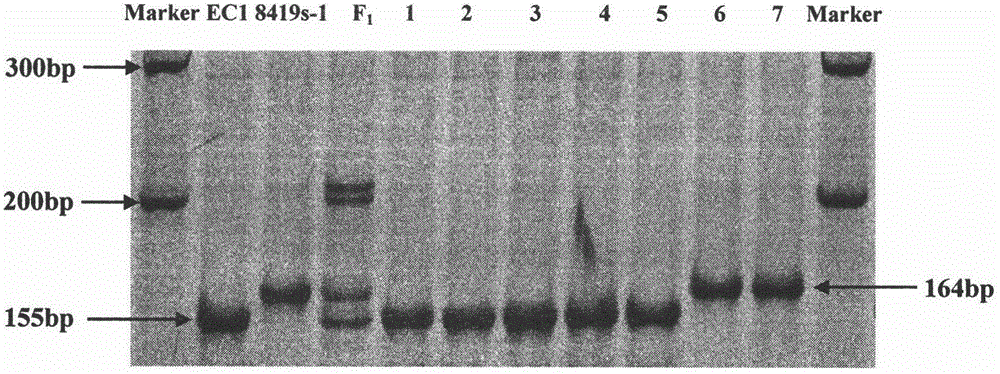
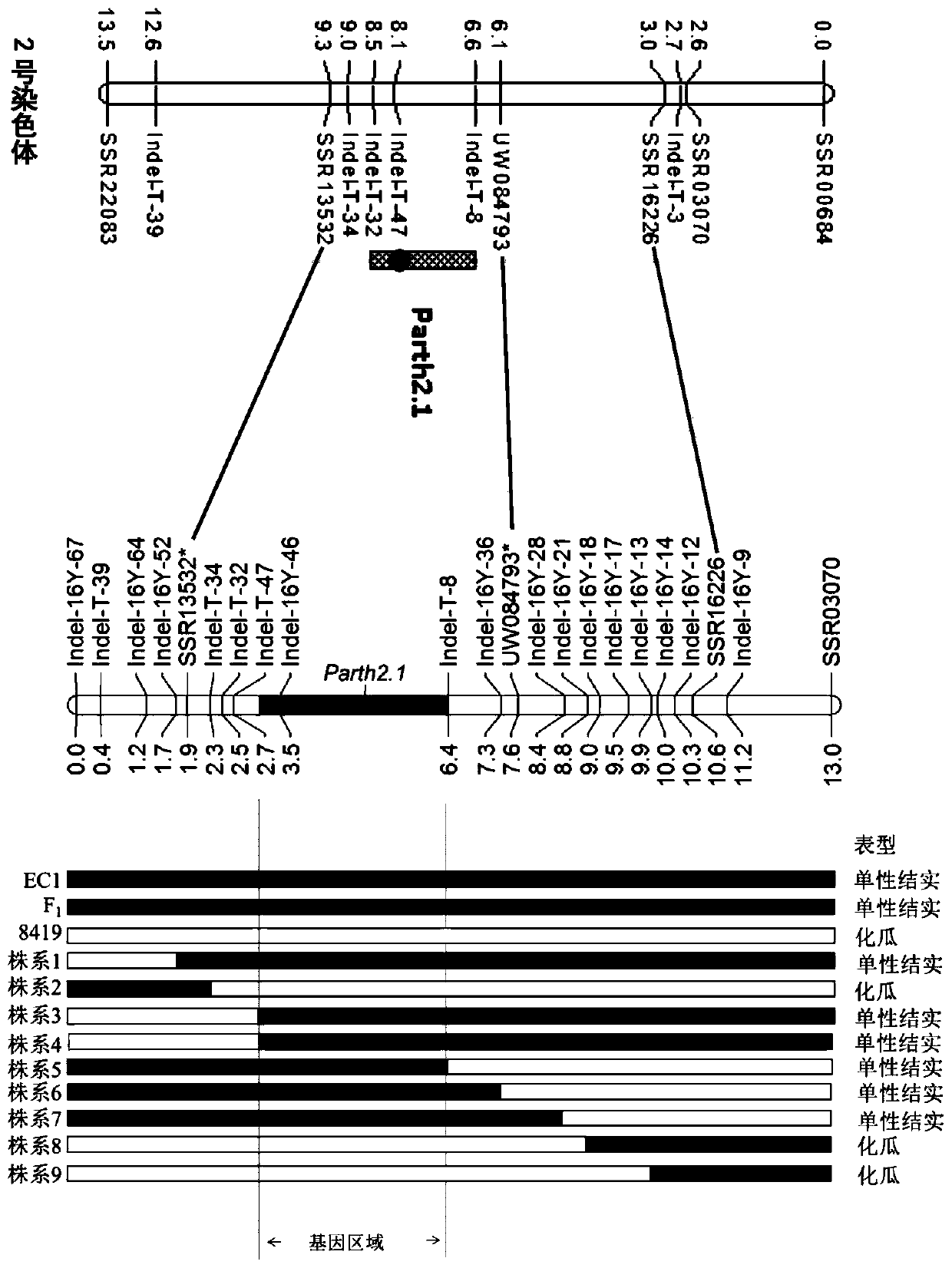
Molecular marker Indel-T-47 for close linkage with cucumber parthenocarpic main-effect QTL (quantitative trait loci)
InactiveCN104789562ASimple methodStable amplificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceQuantitative trait locus
The invention discloses a molecular marker Indel-T-47 for close linkage with cucumber parthenocarpic main-effect QTL (quantitative trait loci), and belongs to the technical field of biology. The invention firstly discloses a molecular marker Indel-T-47 for close linkage with QTL Parth2.1, and further discloses a primer Indexl-T-47F / Indel-T-47R of the marker. In a segregating population containing Parth2.1, the marker is significantly related to parthenocarpy; in an all-female selfing line material containing the Parth2.1, a 155bp product can be amplified from a strong parthenocarpy strain by the marker primer Index-T-47F / Index-T-47R; the marker primer Index-T-47F / Index-T-47R is a peak marker of the Parth2.1, and is closely linked with the Parth2.1. The molecular marker for close linkage with the Parth2.1 disclosed by the invention can be applied to assistant breeding of an all-female cucumber parthenocarpy molecular marker.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Breeding method of high-quality high-output pumpkin new variety
InactiveCN107912295APlant type short vine erectStrong growthPlant genotype modificationAgricultural scienceFruit set
The invention discloses a breeding method of a high-quality high-output pumpkin new variety, comprising the following steps: selecting a parent source, a sowing time, a pollination and fruit setting time, and a seed collecting and seed taking time, wherein American pumpkin material is used as a female parent, Indian pumpkin material is used as a male parent, the American pumpkin material and the Indian pumpkin material are hybridized, selfing separation and screening are performed on the filial generation, the filial generation with different plant types, stem and vine colors, fruit colors andfruit types are selected as the F1 generation, selfing breeding is performed until reaching F5 generation, so as to obtain a strain with steady and consistent phenotype and excellent comprehensive characters, and then variety identification is performed, so as to obtain the pumpkin new variety. According to the breeding method provided by the invention, the bred pumpkin new variety not only has the characteristics of being straight in short vines, easy in maturing and moderate in pumpkin type of American pumpkin material, but also has the characteristics of powdery, glutinous and sweet flavorquality of the Indian pumpkin material, and can resist weak light and has the characteristics of parthenocarpy, high fruit setting rate, good fruit quality, strong growth vigor, high output, and excellent appearance quality and eating quality in comparison with general American pumpkin varies.
Owner:衢州市农业科学研究院
Modifier for increasing production of corns and rice
The invention discloses a modifier for increasing production of corns and rice, which contains forchlorfenuron, gibberellin and salicylic acid and the like. The medicaments are uniformly mixed according to a certain ratio under a room temperature drying environment. An increasing agent solution is sprayed in a later stage of flowering of rice and corns or a filling stage. The modifier can promote cell growth and division and the synthesis of nucleic acid and protein, and delay the organ abscission, crop senescence and chlorophyll synthesis. The photosynthetic rate is improved and the stress resistance is enhanced. The apical dominance is broken, the fruit setting is promoted and the fruits are amplified, and the parthenocarpy is induced, so that the crops are matured for 7-10 days in advance. The yields of rice and corns are increased by above 10%. The modifier is nontoxic and harmless, safe and reliable, low in cost, convenient to use and easy to operate.
Owner:NORTHEAST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Storing method of pollens subjected to soft x ray irradiation
InactiveCN104872111AEffective maintenance of activityKeep aliveDead plant preservationSoft x rayPollen
The invention discloses a storing method of pollens subjected to soft x ray irradiation. The storing method particularly comprises the following steps: subpacking the pollens subjected to soft x ray irradiation in a packing bag or a vessel, then vacuumizing the packing bag or the vessel, filling the packing bag or the vessel with inert gas, and storing at the temperature of lower than or equal to -5 DEG C. The pollens subjected to soft x ray irradiation, which is stored according to the storing method, are long in storing time, and after the pollens are stored for 1 year, the activity of the pollens is more than 75% of that of pollens which are not stored. The applicant experiment shows that even if the pollens after being stored for 1 year are subjected to pollinating and induced parthenocarpy according to the existing conventional technology, seedless watermelons can be still obtained, wherein the fruit setting rate is more than 75%, and the occupancy of the seedless watermelons in the obtained commodity fruit is more than 80%.
Owner:桂林嘉佰农农业科技有限公司
Method for inducing parthenocarpy of pears
The invention discloses a method for inducing parthenocarpy of pears. The method comprises the following steps of: at 1-2 days before a full-bloom stage, using inductive agent to process flower buds; and at the 5-7th day of the full-bloom stage, using the inductive agent to process flowers again, wherein the inductive agent is GA4+7 aqueous solution with the concentration being 200-500mg / L. According to the method, the parthenocarpy of the pears can be effectively induced, the parthenocarpy fruits have better appearance, no malformed fruits, high edible rate, small kernel, small core, no seeds, small fruit-to-core ratio, better flavor and high yield. In addition, the method has reasonable design, simplicity and convenience in operation, lower requirement on equipment, less cost, and large-scale operability, and can be demonstrated to be popularized and applied in commercial orchards.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Corn yield improvement accelerant
The invention discloses corn yield improvement accelerant. The corn yield improvement accelerant is composed of zhongshengmycin, cyprosulfamide, cysteine, plant growth regulator agents, zeatin, 2,4-dichlorobenzene oxygen butyl acetate, nanometer titania, abamectin and alginic acid. The corn yield improvement accelerant is a compound and efficient type accelerant, the proportion is reasonable, the accelerant has the great functions of promoting cell enlargement and division, promoting synthesis of nucleic acid and protein, suspending organ abscission, crop aging and chlorophyll synthesis, improving photosynthetic rate, enhancing the stress resistance, breaking apical dominance, promoting fruit setting, enlarging the fruits and inducing parthenocarpy, the cob rate is high, cobs are big, the grains are starlatine, and under the normal growth environment, the yield per mu is increased by 250 kilograms at the minimum. The corn yield improvement accelerant has a great effect for preventing and treating field diseases caused by bacteria and fungus, the chemical dosage is reduced, the chemical cost is reduced, no residues exist, the accelerant is convenient to use, the operation and implementation are easy, the dosage is little, and the cost is low.
Owner:许彦计 +3
Method for breeding protection field special-purpose Hua'nan type cucumber hybrid species
InactiveCN1366809AGood yieldStrong disease resistancePlant genotype modificationDiseaseHybrid species
Owner:YANBIAN INST OF VEGETABLES FLOWERS & PLANTS
Eggplant fruit gene silencing system and construction method thereof
ActiveCN109810988AFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionFruit developmentGene silencing
The invention discloses an eggplant fruit gene silencing system and a construction method thereof and in particular discloses application of CDS sequences of eggplant anthocyanin anabolism related genes including SmANS and SmMYB1 genes to construction of an eggplant fruit VIGS system; the CDS sequences are shown as SEQ ID NO. 1 and SEQ ID NO. 2. The invention establishes an efficient and rapid eggplant fruit virus mediated gene silencing system which can be used for verifying and analyzing fruit important property regulation and control gene functions including eggplant fruit peel pigment metabolism, peel color and luster, parthenocarpy and the like. Influences, caused by environment temperature, sizes of fruits for injection, sizes of target gene insert segments and injection amount, on the eggplant fruit VIGS system are defined. The gene silencing system disclosed by the invention is simple, rapid and efficient and can be applied to eggplant fruit development and functional verification of other tissue genes containing anthocyanin.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLES GUANGDONG PROV ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
Parthenocarpic tomatoes and production method thereof
InactiveUS20090089900A1Other foreign material introduction processesFermentationBiotechnologyDNA construct
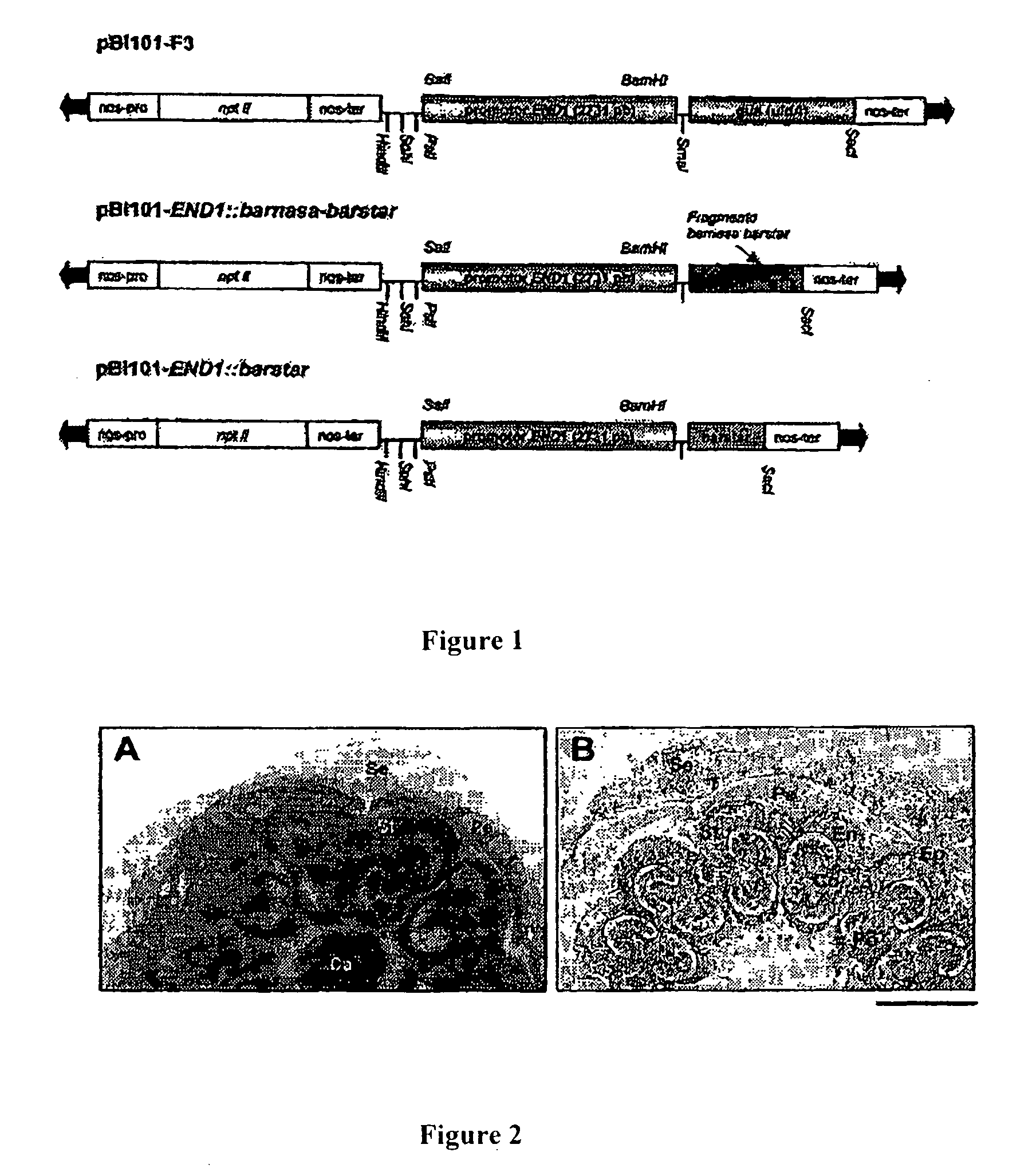
The invention relates to parthenocarpic tomatoes (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.) which are grown from seeds, which are smaller than wild tomatoes and which, when ripe, display a more intense red colour than wild tomatoes. The tomatoes are obtained by cultivating a transgenic tomato plant which produces said parthenocarpic tomatoes and which is obtained using a method consisting in: (a) introducing a DNA construction into a cell or tissue of a tomato plant, said construction comprising (i) the pea END1 gene promoter or a functional fragment of same and (ii) a cytotoxic gene which is functionally bound to the aforementioned promoter or fragment of same; and (b) regenerating the tomato plant cell or tissue transformed in step (a) in order to produce a transgenic tomato plant that produces parthenocarpic tomatoes. The invention is suitable for use in food and agrifood industries.
Owner:CONSEJO SUPERIOR DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS (CSIC) +1
Application of tomato SlMPK20 gene in creating tomato genic male sterile line
ActiveCN108588112AFast transferVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsComplete abortionAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses an application of a tomato SlMPK20 gene in creating a tomato genic male sterile line. The tomato SlMPK20 is subjected to fixed-point knockout via a CRISPR / Cas9 knockout system,so that a tomato transgenic line undergoing SlMPK20 gene specific knockout is obtained; by implementing the SlMPK20 knockout, complete abortion of pollen grains is caused, and just a few of parthenocarpic fruits are formed; however, the SlMPK20 knockout has no obvious influence to vegetative growth of plants and development of female reproductive organs; and the SlMPK20 can specially act to a development process of tomato anthers. The tomato genic male sterile line, which is created through the SlMPK20 knockout, can achieve an infertility rate of 100%; and based upon genetic analysis, it is indicated that the tomato genic male sterile line belongs to recessive genic male sterility, and the genic male sterile line can be propagated by taking corresponding wild-type tomatoes as a maintainerline. The sterile line, which is free from transgenic ingredients, can be obtained through offspring screening. The sterile line can hybridize with a great amount of tomato breeding materials (a restorer line), so that the first generation of hybrid can be obtained. With the application of the method provided by the invention, sterile traits can be rapidly led into normal tomato breeding materials; therefore, a broad application prospect is achieved in tomato cross-breeding.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for inducing Corsvenor Momordica Fruit parthenocarpy by using hormone
InactiveCN105123492AEffective in inducing parthenocarpyEasy to shapePlant genotype modificationMomordicaPollination
The invention relates to a method for inducing Corsvenor Momordica Fruit parthenocarpy by using hormone. The method is characterized in that a combination of different hormones is applied to Corsvenor Momordica Fruit in different flowering phases in order to obtain the stable and effective parthenocarpy inducing method. The method omits tedious pollination work, and allows seedless Corsvenor Momordica Fruit convenient to process to be obtained. Compared with traditional triploid seedless Corsvenor Momordica Fruit preparation methods, the method has the advantages of no need of chromosome doubling or hybridization, short production cycle, simplicity, easy operation, and suitableness for large-area application.
Owner:怀化兴科创生物技术有限公司
Hybrid gherkin variety 12-107 rz
InactiveUS20150189845A1Early floweringEasy to set upMicrobiological testing/measurementTissue cultureFruit setCultivar
The present invention relates to a gherkin (Cucumis sativus) seed designated 12-107 RZ, whereby a plant grown from such seed may exhibit early flowering, gynoecious sex expression, good parthenocarpic fruit set, a small to very small fruit diameter, a small to medium L / D fruit ratio, a prickled skin, resistance to Cladosporium cucumerinum, and intermediate resistance to Podosphaera xanthii. The present invention also relates to a gherkin (Cucumis sativus) plant produced by growing the 12-107 RZ seed. The invention further relates to methods for producing the gherkin (Cucumis sativus) cultivar, represented by gherkin (Cucumis sativus) variety 12-107 RZ.
Owner:RIJK ZWAAN ZAADTEELT & ZAADHANDEL BV
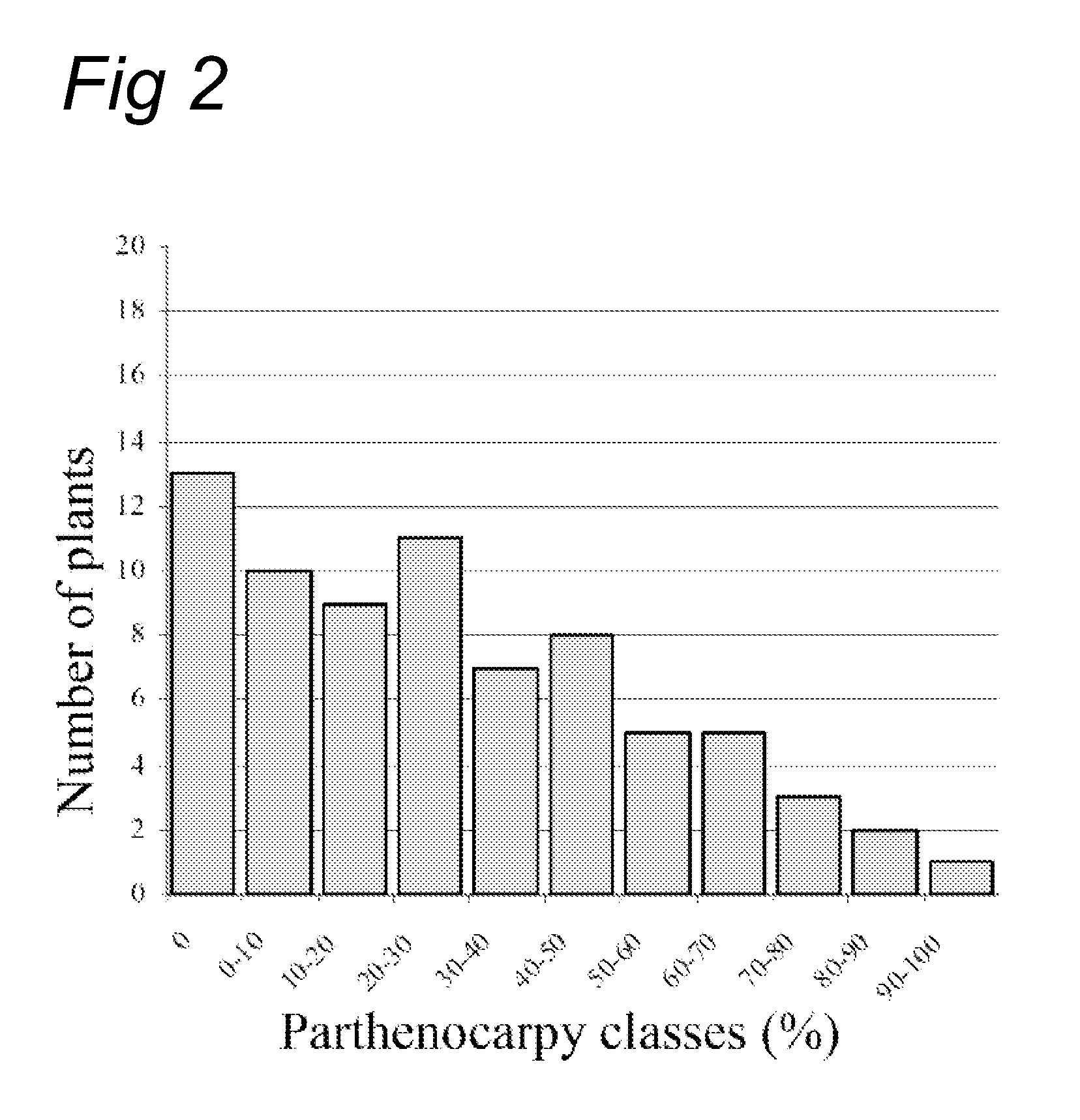
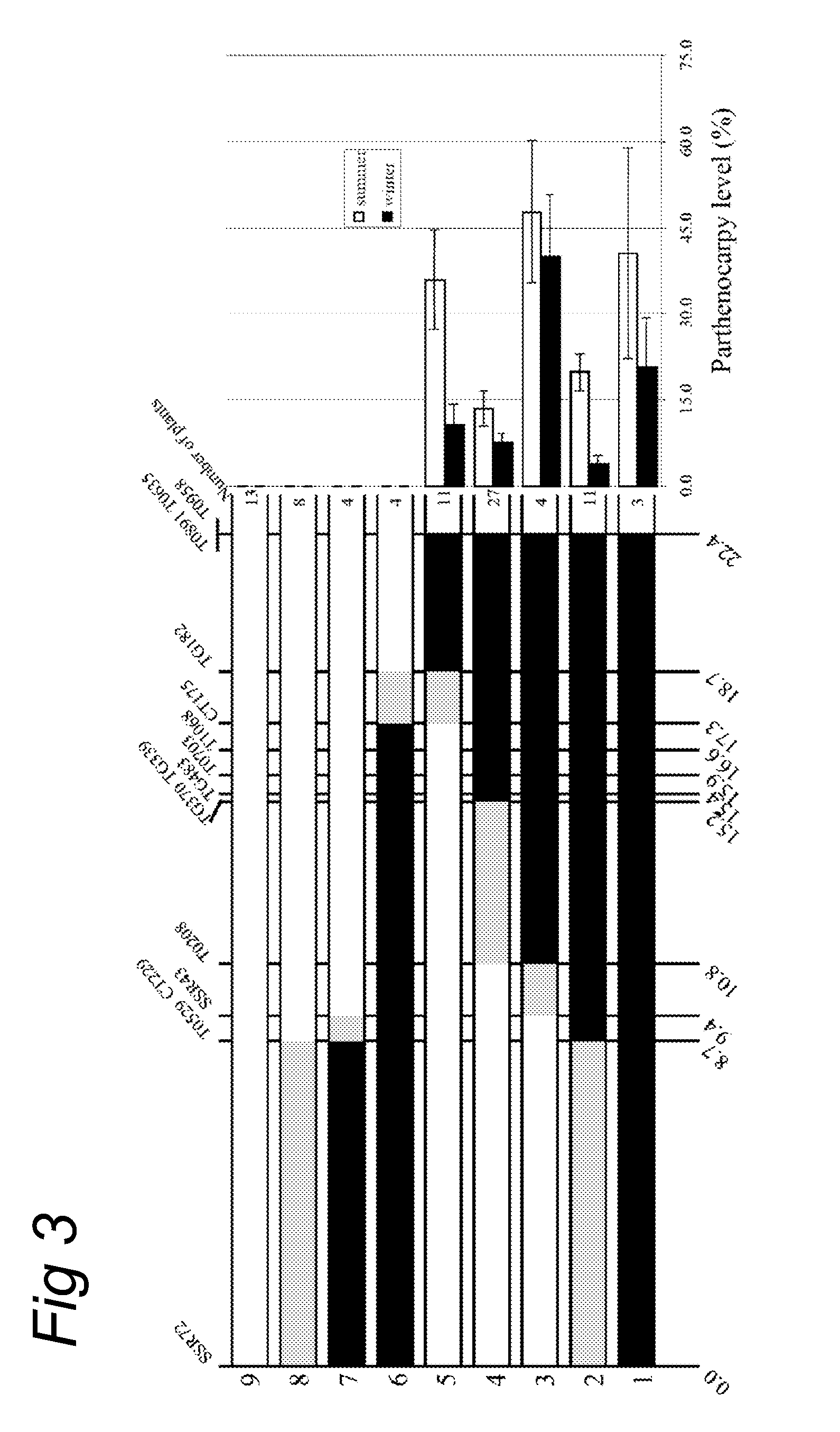
Parthenocarpy genes in tomato
InactiveUS9474222B2Excellent for hybridisationEasily cross-bredPlant genotype modificationAngiosperms/flowering plantsGeneSolanum
The present invention relates to Solanum lycopersicum plants carrying one or more of the pat-6, pat-7, pat-8 and pat-9 parthenocarpy genes. Preferred plants comprise a pair of pat-6 and pat-7 genes or a pair of pat-8 and pat-9 genes, whereby preferably the plant is homozygous for at least one of the two genes in the pair, more preferably the plant is homozygous for both genes in the pair. Such plants are capable of producing seedless tomatoes. The invention further relates to methods for producing plants carrying one or more of the pat-6, pat-7, pat-8 and pat-9 parthenocarpy genes using marker-assisted breeding.
Owner:MONSANTO HOLLAND
Genetic basis for cucumber fruit having small seed cavity
The present invention relates to a parthenocarpic cucumber fruit (Cucumis sativus L.) having a small seed cavity. A parthenocarpic cucumber fruit (Cucumis sativus L.) having a small seed cavity has a lower total moisture content. Two QTLs have been identified that either alone or in combination lead to the phenotype of having a small seed cavity. The invention further relates to a cucumber plant comprising one of the QTLs or a combination of both QTLs, which cucumber plant is capable of producing parthenocarpic fruits that have a small seed cavity. The invention also relates to markers for identifying the QTLs.
Owner:RIJK ZWAAN ZAADTEELT & ZAADHANDEL BV
Method for breeding cucumis allotriploid cucumbers
InactiveCN102210264AImprove germination rateStrong growthPlant genotype modificationHeterologousProcessing type
The invention relates to a method for breeding cucumis allotriploid cucumbers, belonging to the field of biotechnological breeding. The method is special for chromosome engineering and ploidy breeding of cucumbers. Cucumis diploid new species are positively and negatively hybridized with diploid cucumbers; and the seeds harvested from the hybridized fruit are the seeds of the allotriploid cucumbers. The seedling allotriploid cucumbers have strong growth potential and excellent economic characteristic, and can serve as low-temperature-resistant, weak-light-resistant and Meloidogyne incognita Chitwood-resistant processing type greenhouse culture cucumber new species to be popularized and applied. The seedling allotriploid cucumbers provide precious materials for researching scientific problems such as cucumber cotyledon genetic development law, fruit development, parthenocarpy mechanism, heterosis mechanism and the like, facilitates utilization of the allotriploid cucumbers, and contributes to transducing wild type excellent genes to culture the cucumber new species.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Parthenocarpy breeding method of industrial hemp and application of parthenocarpy breeding method
InactiveCN112841023AEliminate distractionsGood characterPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyHemp plant
The invention relates to the technical field of breeding, in particular to a parthenocarpy breeding method of industrial hemp and application of the parthenocarpy breeding method. The breeding method of the industrial hemp comprises the following steps: firstly inducing female plants to generate male flowers, carrying out cross seed set on the female plants of different varieties of hemp once, and mixing genetic materials of two parents; and then screening female single plants integrating excellent characters of the two parents in the filial generation, inducing male flowers to be subjected to selfing or backcross fruiting, and then repeatedly conducting multi-generation screening and selfing or backcross till the hemp variety uniform in character and stable in heredity is obtained. According to the method, a key technology for inducing female hemp plants to generate fertile male flowers and disperse pollen is developed, normal seeds capable of germinating are generated after unisexual selfing of the female plants, female plant selfing breeding and seed reproduction of the hemp are achieved, all progenies are female plants, all genetic materials of single-plant maternal female plants are kept, and the bottleneck problems of variety shortage and difficult breeding in industrial hemp production are fundamentally solved.
Owner:北大荒垦丰种业股份有限公司
Cucumber variety Paraiso
ActiveUS7714197B2Improve featuresImprove nutritional qualityOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationCucumber yellow stunting disorder virusGenetic Materials
A hybrid cucumber cultivar designated ‘Paraiso’ is disclosed which is the first parthenocarpic slicing cucumber that also has intermediate resistance to powdery mildew, cucumber mosaic virus, cucumber vein yellowing virus and cucumber yellow stunting disorder virus. The invention relates to the seeds of hybrid cucumber cultivar ‘Paraiso’, to the plants of hybrid cucumber cultivar ‘Paraiso’ and to methods for producing a cucumber plant, either inbred or hybrid, by crossing the hybrid cultivar ‘Paraiso’ with itself or another cucumber cultivar. The invention further relates to methods for producing a cucumber plant containing in its genetic material one or more transgenes and to the transgenic plants produced by that method and to methods for producing other cucumber cultivars derived from the hybrid ‘Paraiso’.
Owner:ENZA ZADEN BEHEER BV
Linkage molecular marker of main effect QTL Parth2.1 of cucumber parthenocarpy and application thereof
ActiveCN110195125AImprove breeding efficiencyIncrease productionMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationAgricultural scienceGreenhouse
The invention discloses a linkage molecular marker of a main effect QTL Parth2.1 of cucumber parthenocarpy and an application thereof. The linkage molecular marker Indel-16Y-46 of the main effect QTLParth2.1 of cucumber parthenocarpy has an upstream primer of SEQ ID NO.1 and a downstream primer of SEQ ID NO.2. Provided is the application of the molecular marker in molecular marker assisted breeding of a new full-female strong parthenocarpic cucumber variety. The selection efficiency of the molecular marker on a Parth2.1 locus is 100%. Based on the molecular marker, a method for molecular marker assisted breeding of the new full-female strong parthenocarpic cucumber variety is developed. The obtained new full-female strong parthenocarpic cucumber variety is a greenhouse cucumber selfing line variety in Europe, has high yield and good fruit quality, and can be directly used for improving the parthenocarpy and full-female primal parents of other varieties.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for modifying plant morphology, biochemistry and physiology
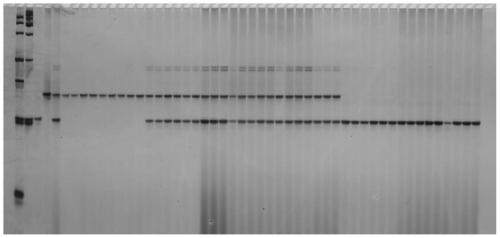
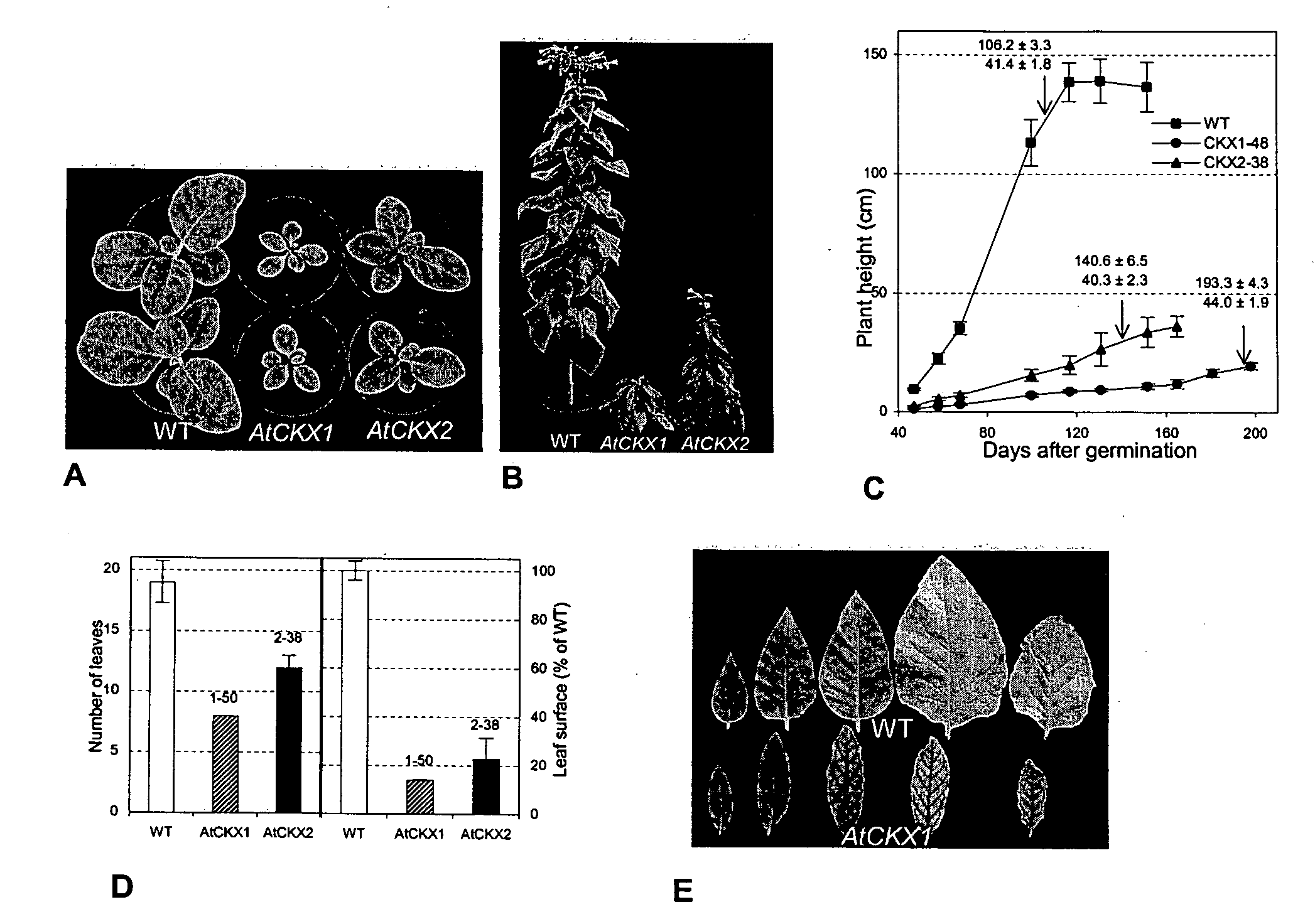
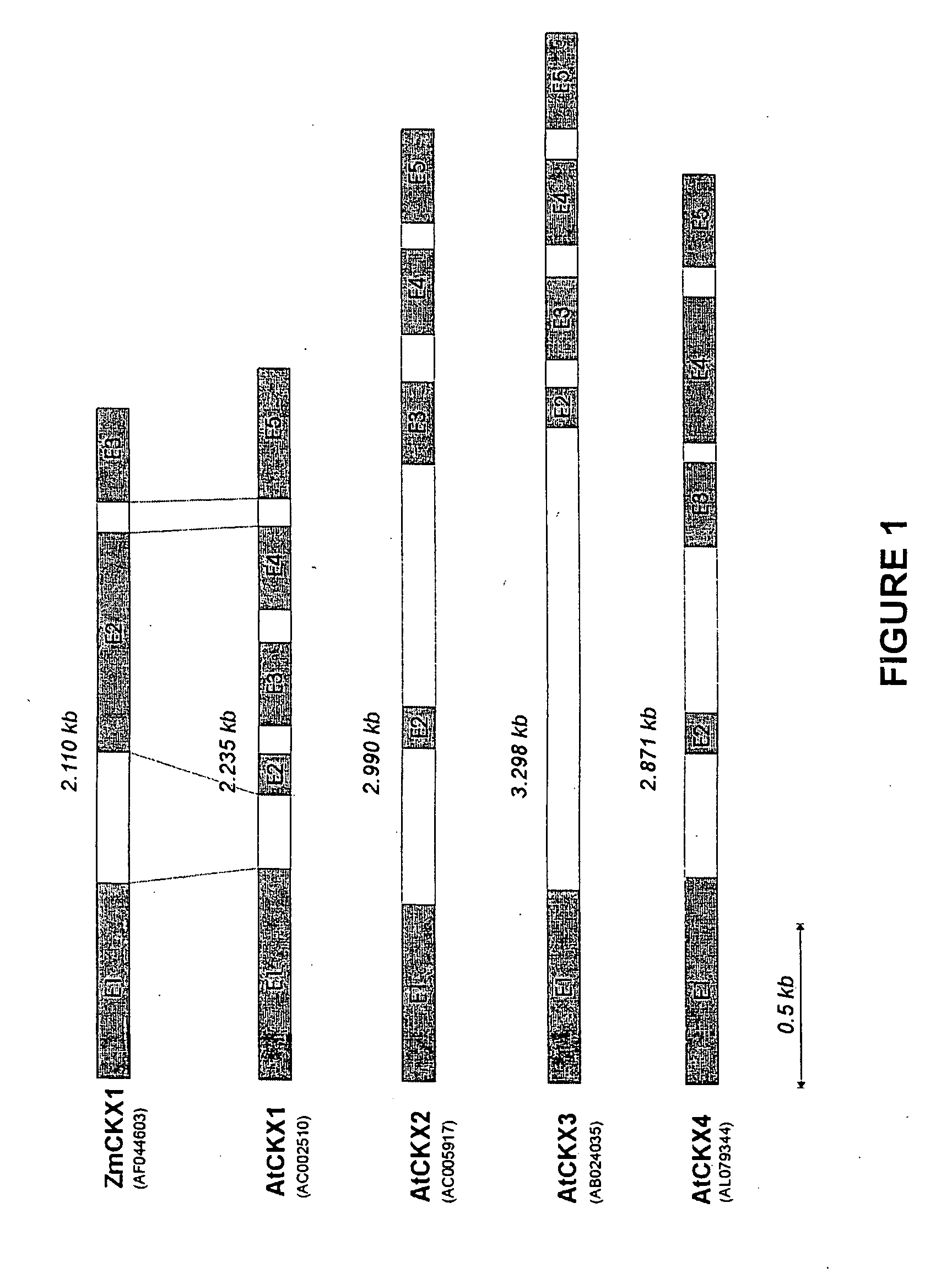
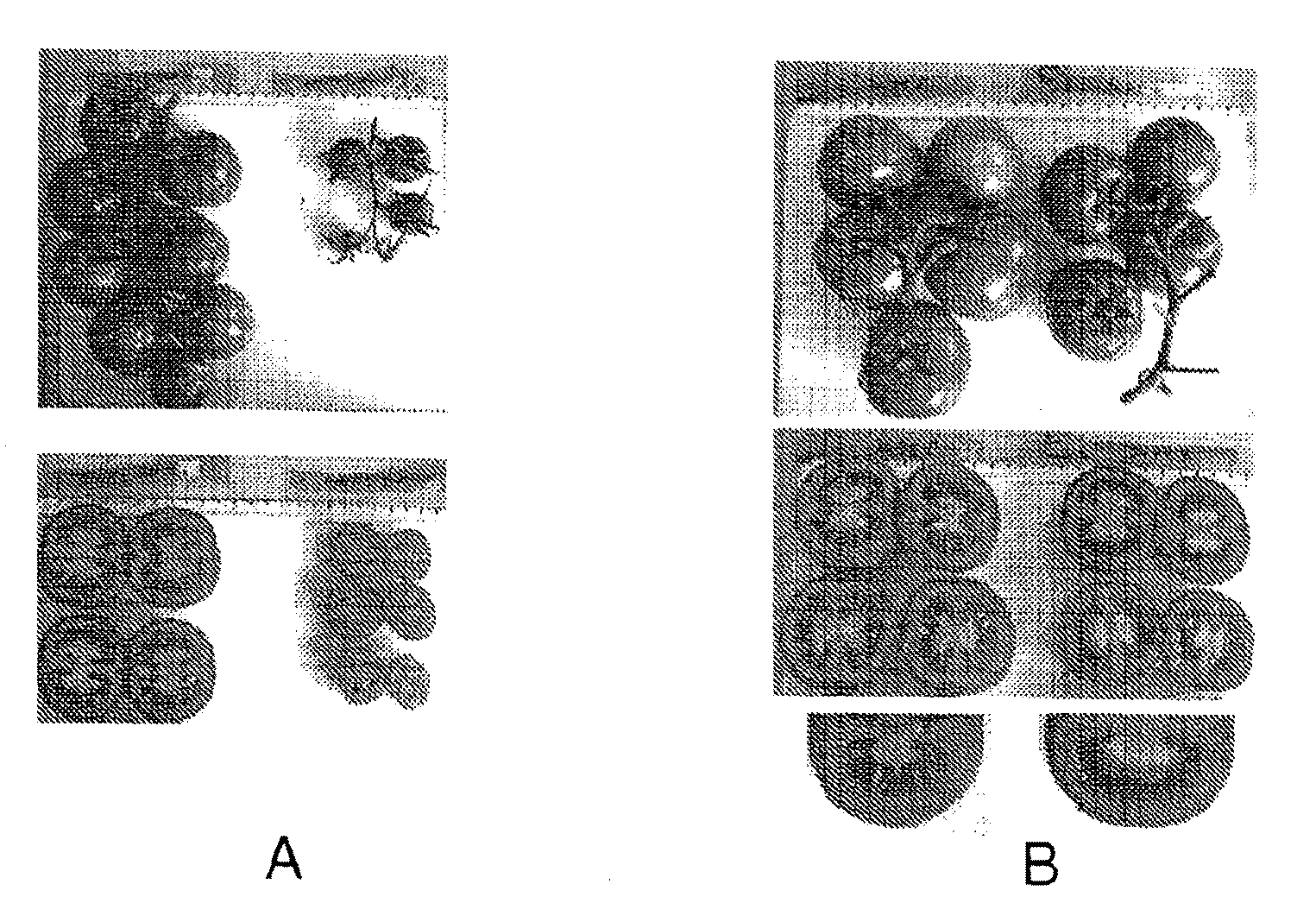
The present invention provides nucleotide sequences and corresponding amino acid sequences for plant cytokinin oxidase proteins. In addition, vectors, host cells, and transgenic plants comprising such sequences as well as methods for stimulating root growth and / or enhancing the formation of lateral or adventitious roots and / or altering root geotropism using such sequences are provided by the present invention. Also provided by the present invention are methods for altering various plant phenotypes including delaying onset to flowering, increasing leaf thickness, reducing vessel size, inducing parthenocarpy, increasing branching, increasing seed size and / or weight, embryo size and / or weight, and cotyledon size and / or weight using cytokinin oxidase proteins and / or nucleic acid molecules encoding cytokinin oxidase.
Owner:SCHMULLING THOMAS +1
Loquat unisexual fruiting induction agent and its use method
InactiveCN100376159CHigh and stable non-nuclear rateBroad spectrum of actionBiocidePlant growth regulatorsGibberellic acidLoquat Tree
A parthenocarpy inducing agent of loquat tree for bearing the non-kernel loquat fruit is prepared proportionally from gibberellin (GA3) and 1-(2-Cl-4-pyridyl)-3-phenylurea (CPPU) through mixing and dissolving it in water. Its application features that it is used to treat the flower buds, flower, or fruit every 29+ / -4 days before fertilization.
Owner:福州市农业科学研究所
Fertilisation independent fruit formation in tomato
ActiveUS20120164303A1Improve developmentPromote growthAnimal feeding stuffPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyPollination
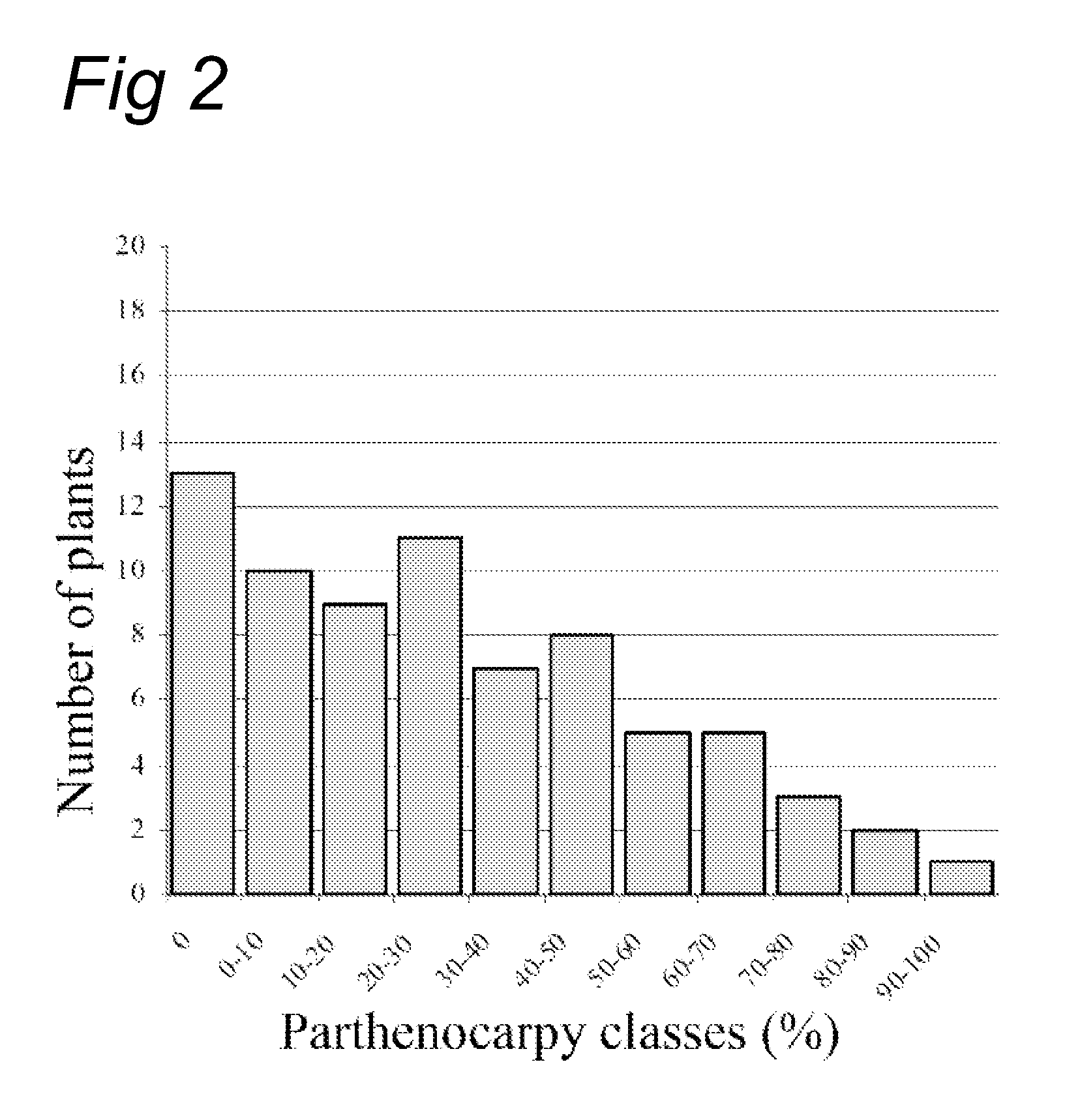
The invention relates to tomato plants which may comprise the trait fertilization independent fruit formation, which may be obtainable by introgression from a plant, representative seed of which was deposited with the NCIMB under accession number NCIMB 41626, NCIMB 41627, NCIMB 41628, NCIMB 41629, NCIMB 41630 or NCIMB 41631. Such tomato plant may be obtainable by crossing plants, representative seed of which was deposited with the NCIMB under accession number NCIMB 41626, NCIMB 41627, NCIMB 41628, NCIMB 41629, NCIMB 41630 or NCIMB 41631, with a plant not showing the trait to obtain an F1 population; selfing plants from the F1 population to obtain an F2 population; preventing pollination of the F2 plants and allowing fruit formation to occur; and selecting plants producing fruits as plants showing fertilization independent fruit formation. The invention further relates to parthenocarpic fruits, seeds of the plants and propagation material of the plant.
Owner:RIJK ZWAAN ZAADTEELT & ZAADHANDEL BV
Fertilisation independent fruit formation in tomato
InactiveUS20130189419A1Improve the fertilisation independent fruit formation without negative pleiotropic effects on the growth and development of the plantAnimal feeding stuffPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyPollination
Owner:RIJK ZWAAN ZAADTEELT & ZAADHANDEL BV
Parthenocarpy Genes in Tomato
InactiveUS20110016549A1Excellent for hybridisationEasily cross-bredPlant genotype modificationAngiosperms/flowering plantsGeneParthenocarpy
The present invention relates to Solanum lycopersicum plants carrying one or more of the pat-6, pat-7, pat-8 and pat-9 parthenocarpy genes. Preferred plants comprise a pair of pat-6 and pat-7 genes or a pair of pat-8 and pat-9 genes, whereby preferably the plant is homozygous for at least one of the two genes in the pair, more preferably the plant is homozygous for both genes in the pair. Such plants are capable of producing seedless tomatoes. The invention further relates to methods for producing plants carrying one or more of the pat-6, pat-7, pat-8 and pat-9 parthenocarpy genes using marker-assisted breeding.
Owner:MONSANTO HOLLAND
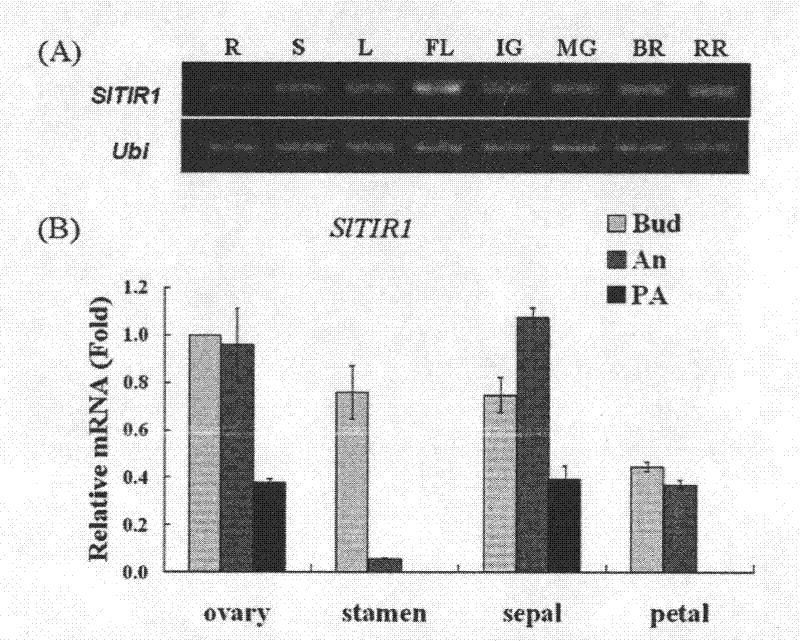
Application of tomato growth hormone receptor homologous gene S1TIR1 in fruit parthenocarpy
InactiveCN102533779AParthenocarpicFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyFrame sequence
The invention discloses a tomato growth hormone receptor homologous gene S1TIR1. The gene has a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:1; and transgenic crops obtained by transformation with the cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) encoding frame sequence of the gene can generate parthenocarpy fruits. The invention also discloses DNA plasma which contains the tomato growth hormone receptor S1TIR1 gene or an ultra-expression frame constructed by the encoding frame sequence in the S1TIR1 gene. According to the invention, the encoding sequence of the gene is led into plant tissues, cells or organs through a recombinant expression vector and then transformed plant cells, tissues or organs are cultured to a plant, thus a parthenocarpy transgenic plant is obtained. The gene disclosed by the invention has important theoretical and actual significance to research on a parthenocarpy mechanism, improvement of plant parthenocarpy and modification of related characters of a plant, and has good application prospect in modification work of crops.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com