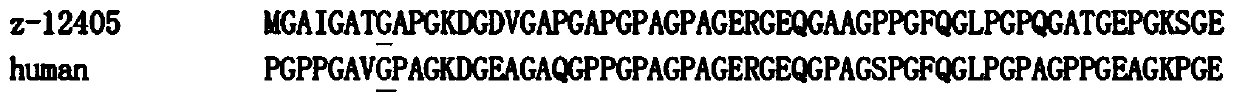Patents
Literature
111 results about "Amino acid change" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Jump to navigation Jump to search. Amino acid replacement is a change from one amino acid to a different amino acid due to point mutation in DNA sequence. It is caused by nonsynonymous missense mutation which alters the codon sequence to code other amino acid instead of the originals.
Reducing the immunogenicity of fusion proteins
InactiveUS6992174B2Low immunogenicityHigh expressionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMHC class IIVaccine Immunogenicity
Disclosed are compositions and methods for producing fusion proteins with reduced immunogenicity. Fusion proteins of the invention include a junction region having an amino acid change that reduces the ability of a junctional epitope to bind to MHC Class II, thereby reducing its interaction with a T-cell receptor. Methods of the invention involve analyzing, changing, or modifying one or more amino acids in the junction region of a fusion protein in order to identify a T-cell epitope and reduce its ability to interact with a T cell receptor. Compositions and methods of the invention are useful in therapy.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
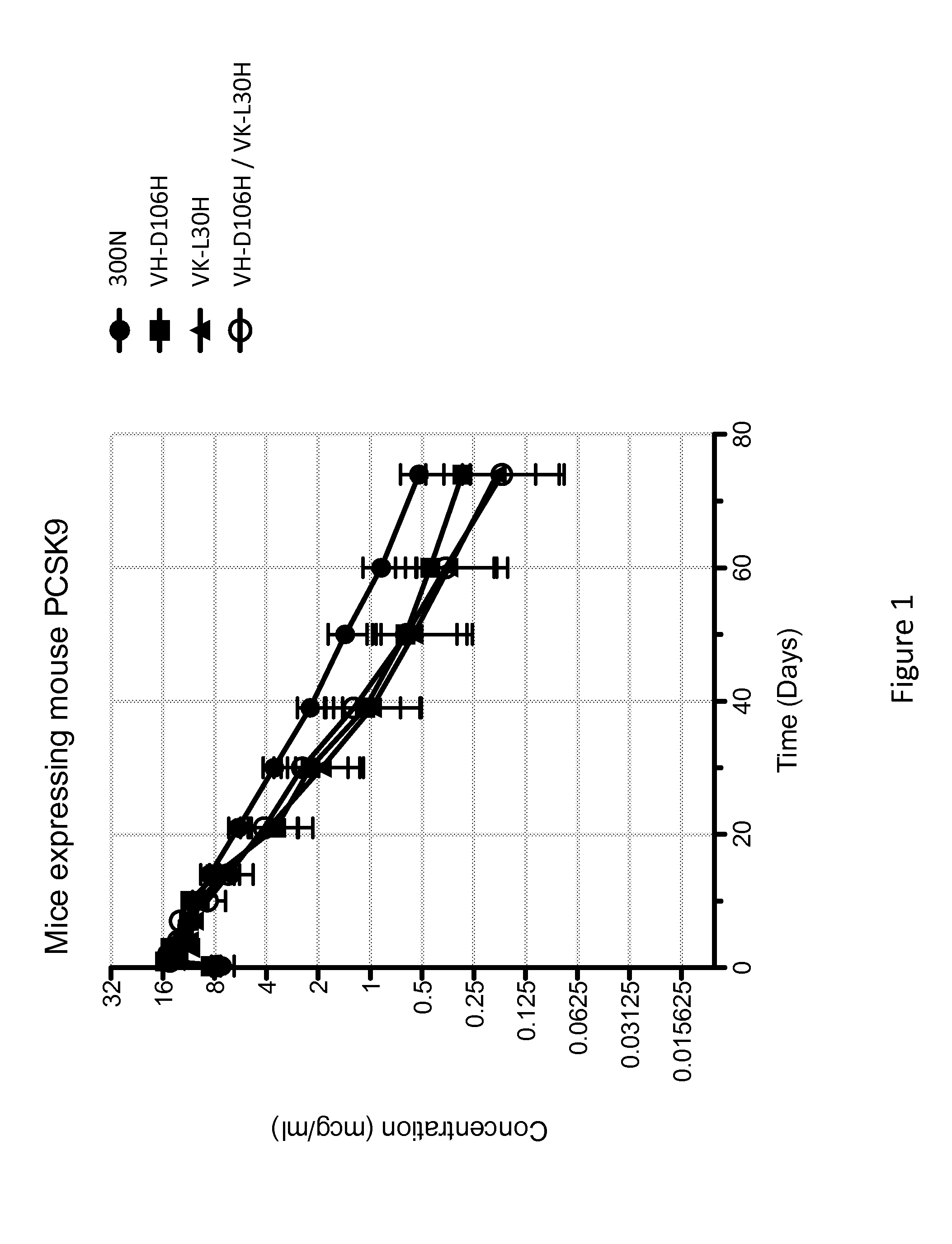
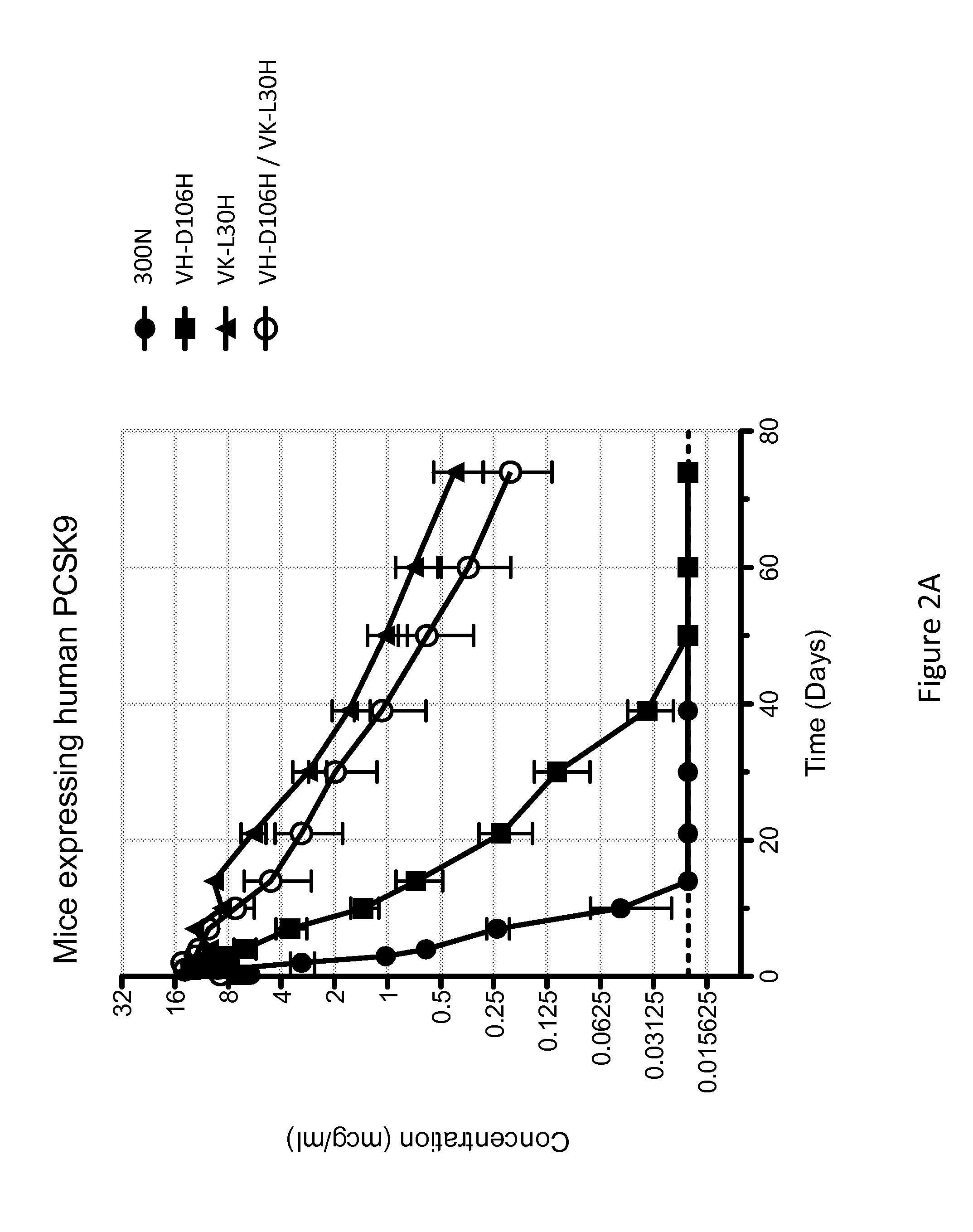
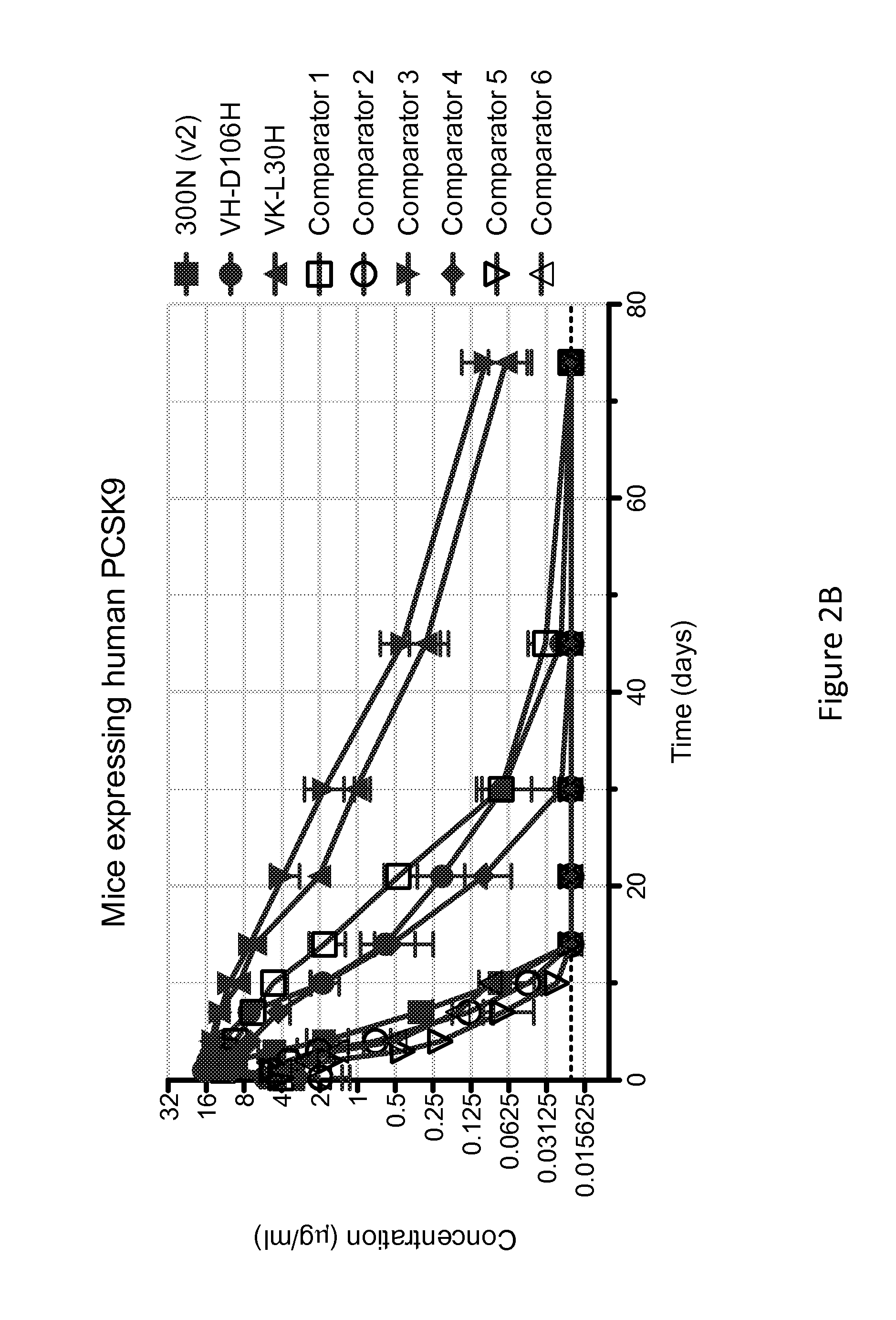
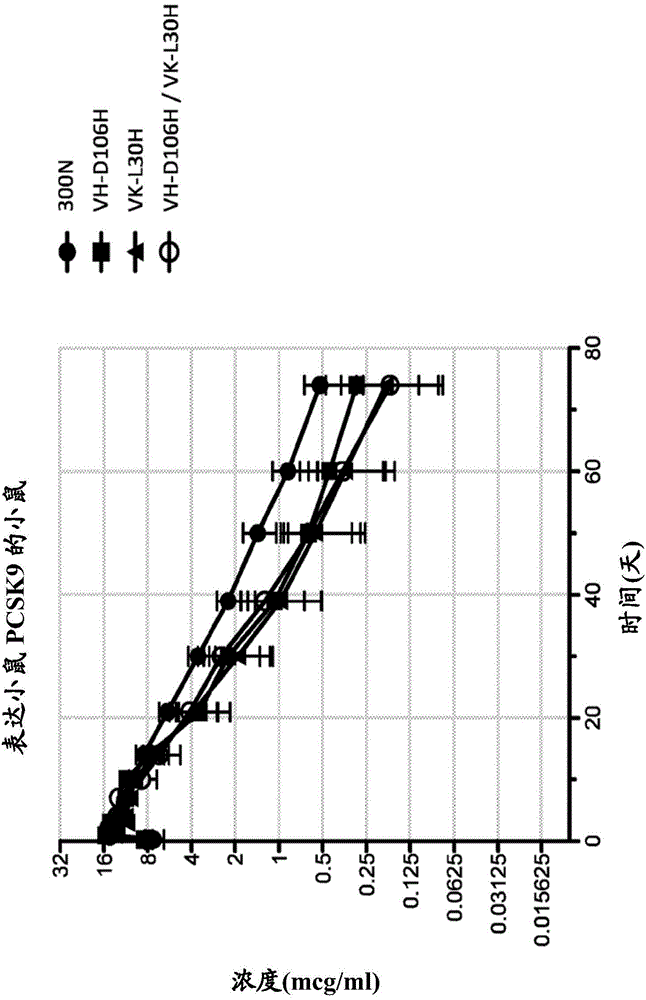
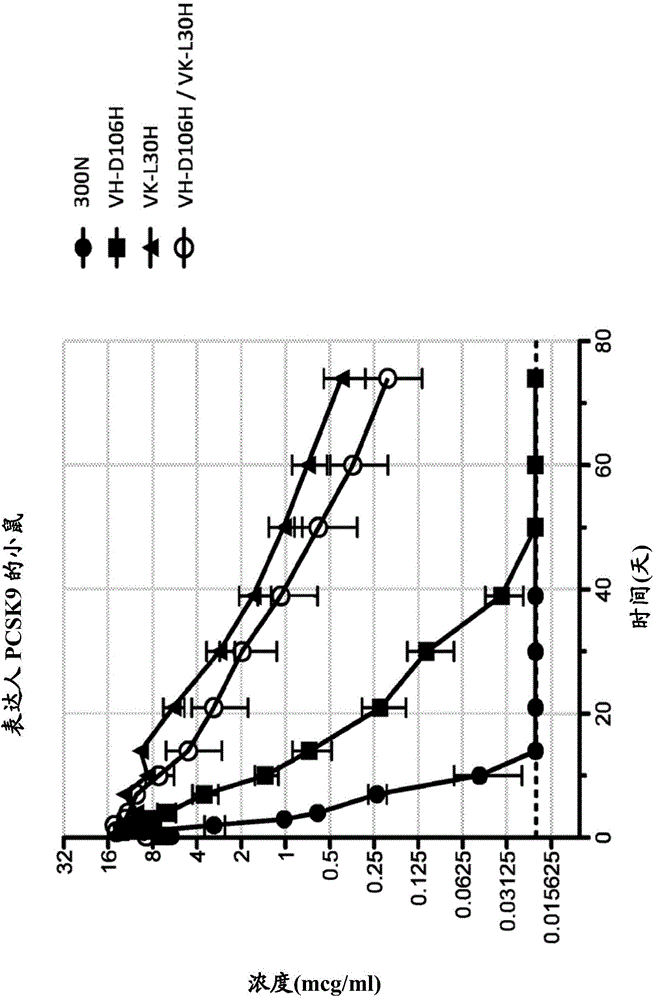
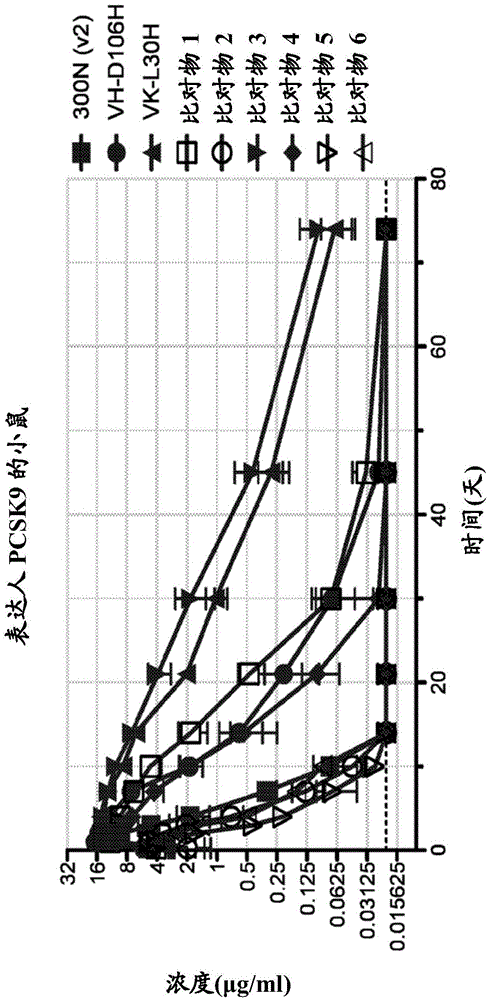
ANTI-PCSK9 ANTIBODIES WITH pH-DEPENDENT BINDING CHARACTERISTICS
ActiveUS20140044730A1High affinityReduced binding affinityMetabolism disorderAntibody ingredientsDiseaseKexin
The present invention provides antibodies and antigen-binding fragments thereof that specifically bind proprotein convertase subtilisin / kexin-9 (PCSK9) with greater affinity at neutral pH than at acidic pH. The antibodies of the invention may possess one or more amino acid changes as compared to antibodies that do not exhibit pH-dependent binding properties. For example, the present invention includes anti-PCSK9 antibodies which possess one or more histidine substitutions in one or more complementarity determining regions. The antibodies of the invention, with pH-dependent binding properties, remain in circulation and exhibit cholesterol lowering activity for prolonged periods of time in animal subjects as compared to anti-PCSK9 antibodies that do not exhibit pH-dependent binding properties. The antibodies of the invention are therefore useful for treating diseases and disorders related to elevated HDL cholesterol, wherein the antibodies of the invention can be administered to a patient at a lower dose and / or with less frequent dosing as compared to antibodies that do not exhibit pH-dependent binding properties.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Reducing the immunogenicity of fusion proteins
InactiveUS20060025573A1Improve clinical efficacyExtended half-lifePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMHC class IICellular receptor
Disclosed are compositions and methods for producing fusion proteins with reduced immunogenicity. Fusion proteins of the invention include a junction region having an amino acid change that reduces the ability of a junctional epitope to bind to MHC Class II, thereby reducing its interaction with a T-cell receptor. Methods of the invention involve analyzing, changing, or modifying one or more amino acids in the junction region of a fusion protein in order to identify a T-cell epitope and reduce its ability to interact with a T cell receptor. Compositions and methods of the invention are useful in therapy.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
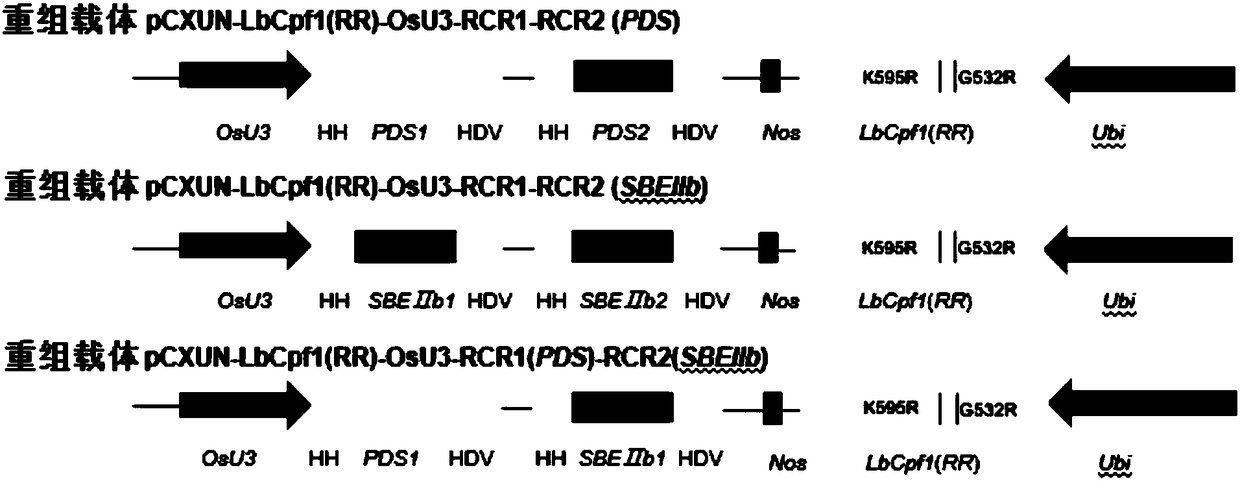
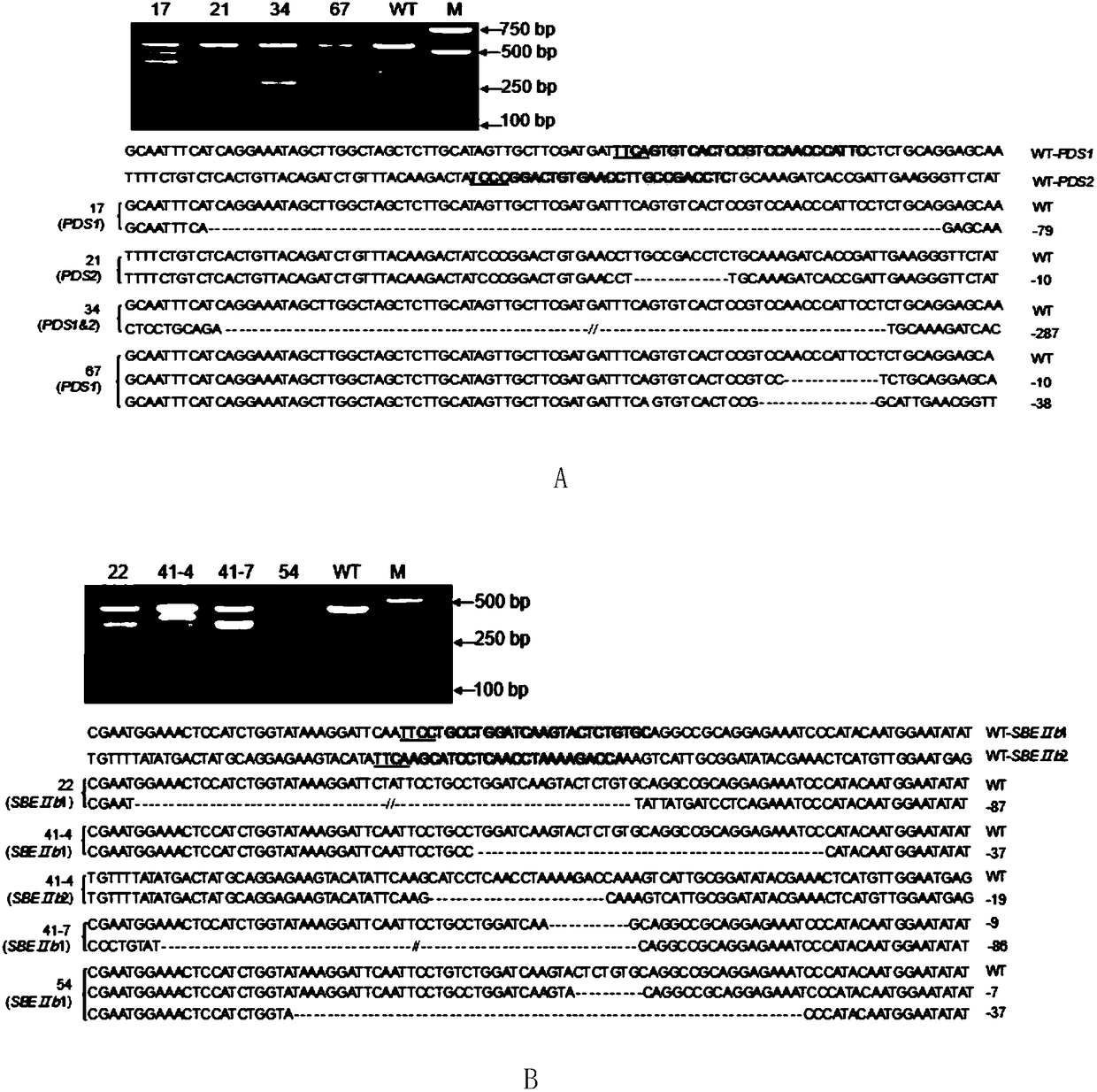
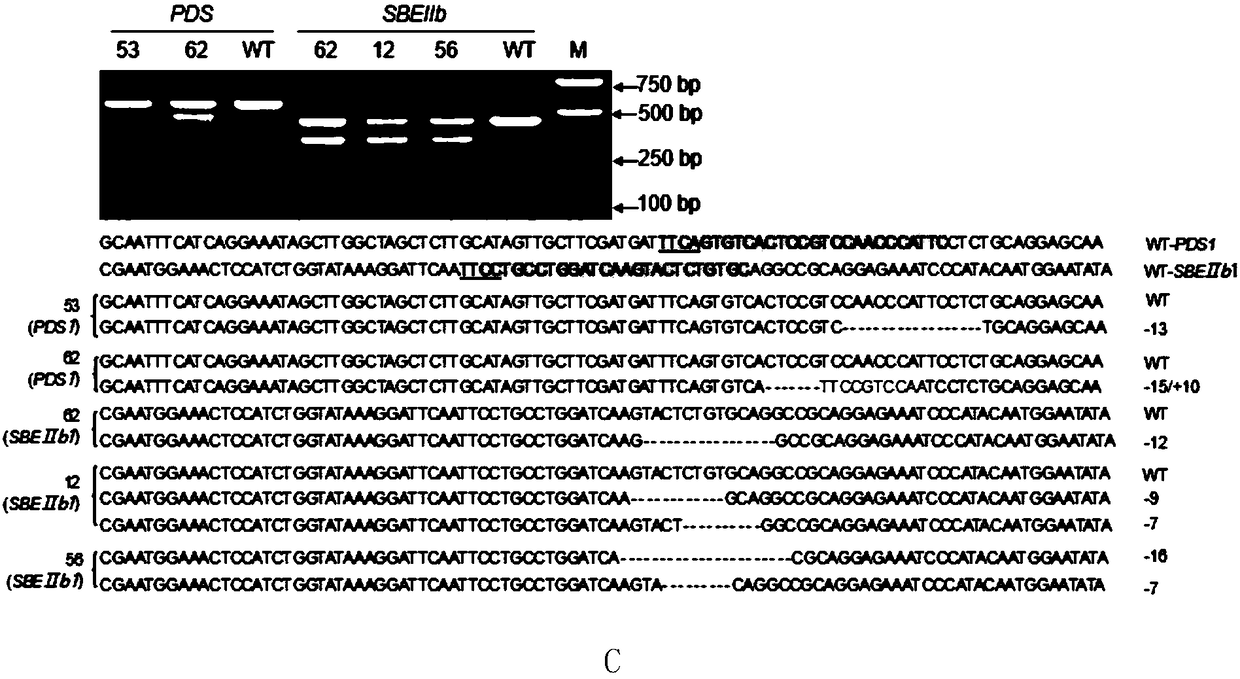
Application for using LbCpf1-RR mutant in CRISPR/Cpf1 system in plant gene editing
ActiveCN108486146AExpand the scope of editingAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNucleic acid vectorRice plantsMutant
The invention discloses application for using an LbCpf1 - RR mutant in a CRISPR / Cpf1 system in plant gene editing. The application for using the LbCpf1 - RR mutant in the CRISPR / Cpf1 system in plant gene editing uses an OsPDS gene and an OsSBEIIb gene as target genes, constructs a target double loci of one gene and a series of vectors of two genes, and utilizes an agrobacterium-mediated transformation method to import the vectors into rice callus, and rice plants with the target gene knockout are successfully obtained by using the LbCpf1-RR mutant. The only difference between the LbCpf1-RR mutant and the protein LbCpf1 is that the 532nd amino acid changes from G to R, and the 595th amino acid changes from K to R. The LbCpf1-RR mutant provided by the application for using the LbCpf1 - RR mutant in the CRISPR / Cpf1 system in plant gene editing expands the PAM site sequence identified by the LbCpf1-RR mutant, so that the editing range of the CRISPR / Cpf1 system in rice genome is expanded, great significance for promoting the application of the system in the field of plant genome editing is achieved. The application for using the LbCpf1 - RR mutant in the CRISPR / Cpf1 system in plant geneediting has great application value.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
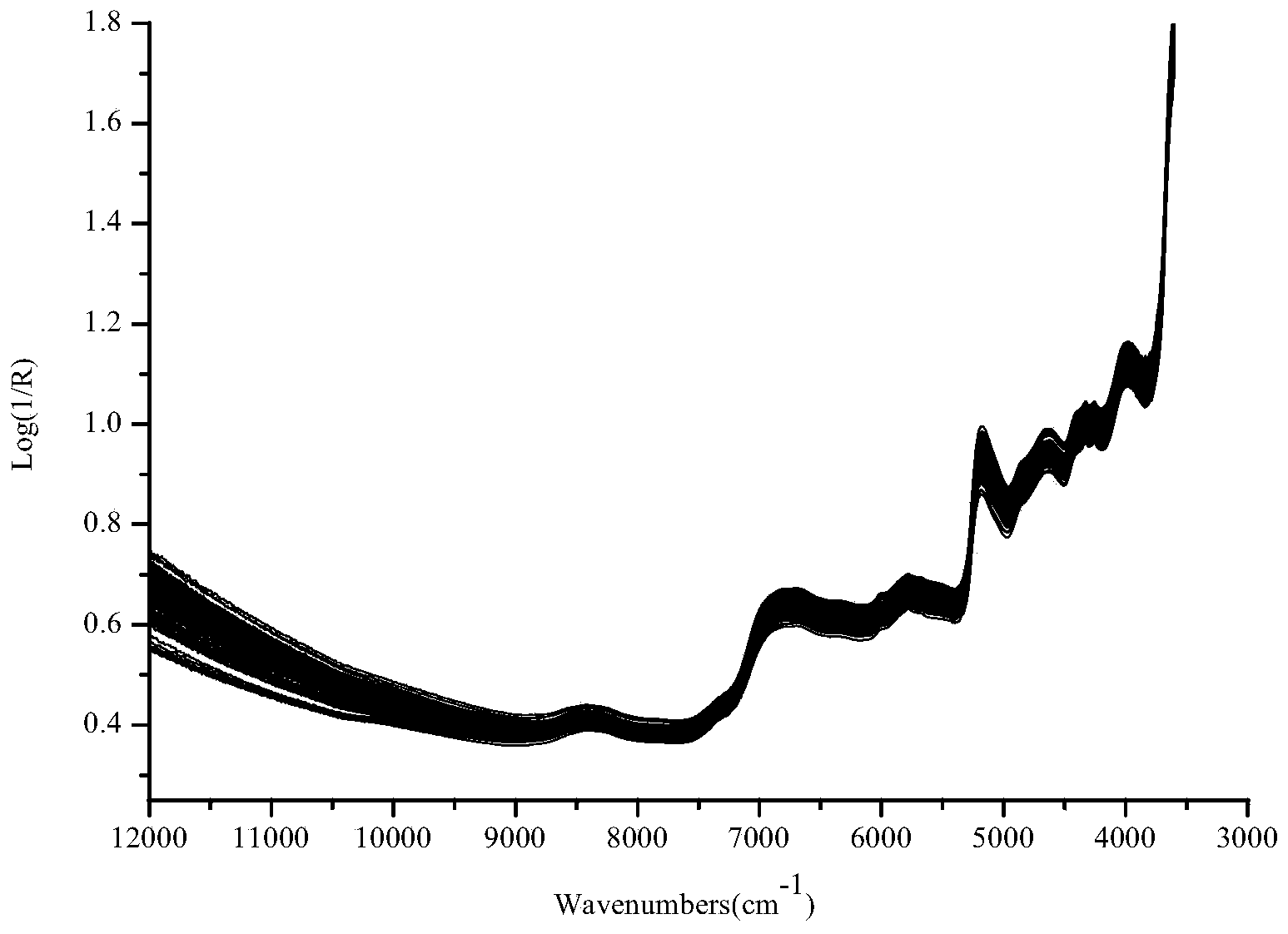
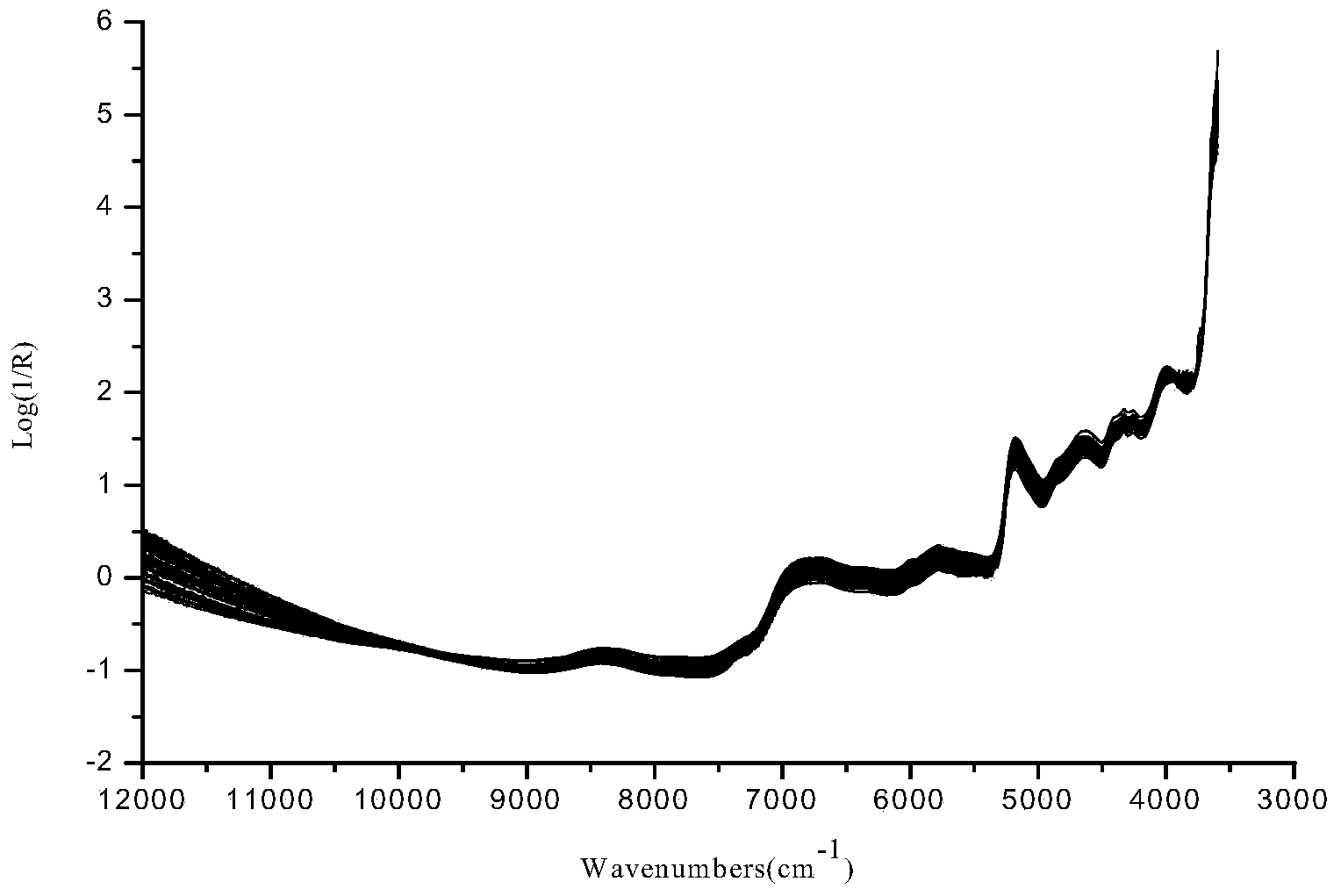
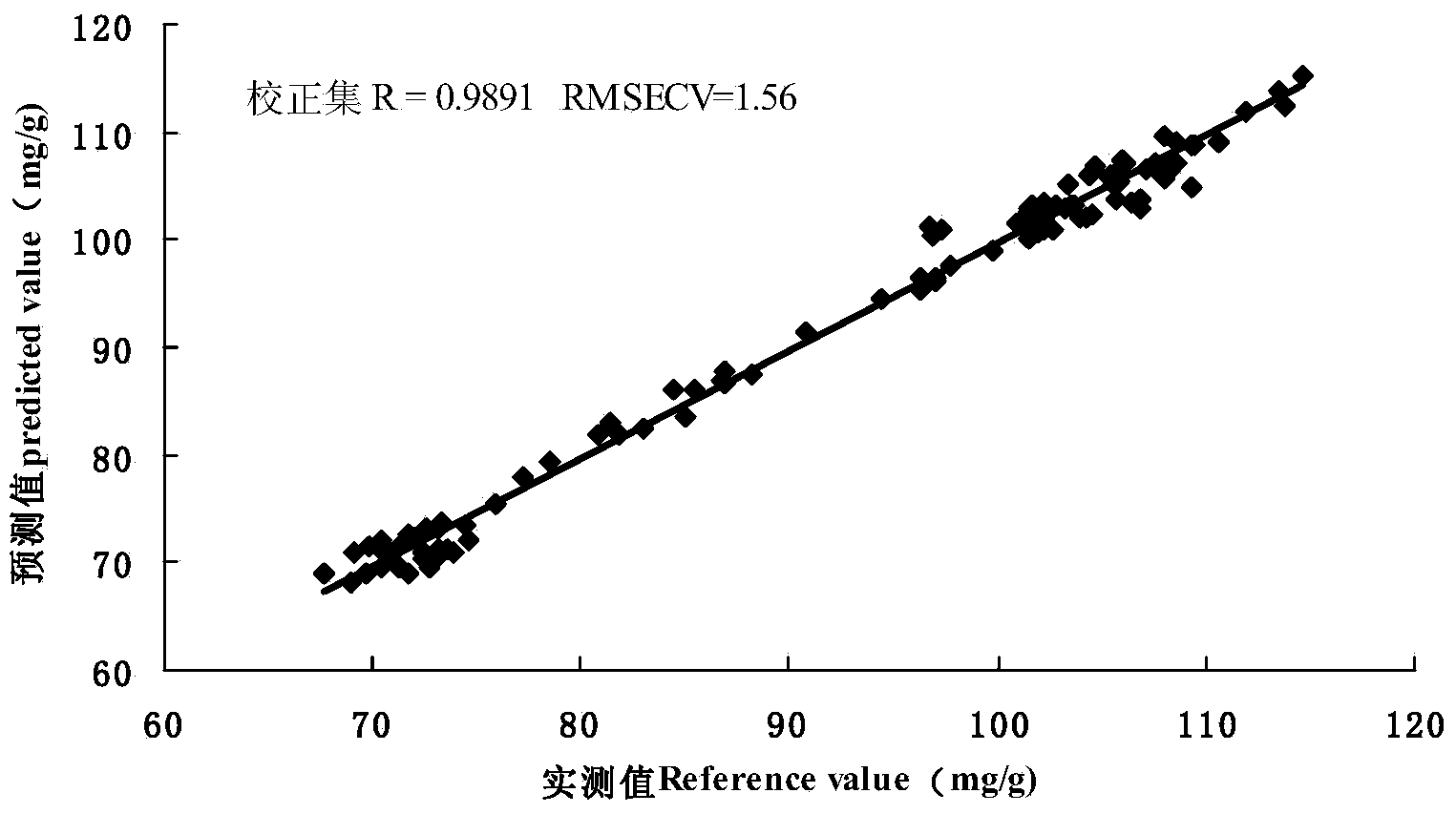
Method for discriminating fermentation quality of congou black tea based on near-infrared-spectroscopy-combined amino acid analysis technology
InactiveCN104020129ADiscrimination scienceAccurate discriminationMaterial analysis by optical meansBlack teaAmino acid content
The invention discloses a method for discriminating fermentation quality of congou black tea based on a near-infrared-spectroscopy-combined amino acid analysis technology. The method comprises: selecting a sample and performing pre-processing; using high performance liquid chromatograph to determine the content of amino acids in the sample; acquiring the spectrum of the sample, utilizing synergy interval partial least square to establish a near-infrared-spectroscopy quantitative discrimination model for amino acids, finding amino acid variation distribution, and discriminating the fermentation quality of congou black tea. According to the method for discriminating the fermentation quality of congou black tea based on the near-infrared-spectroscopy-combined amino acid analysis technology, pretreatment is performed on an acquired original spectrum by utilizing standard normal variable transformation (SNVT), and the amino acid near-infrared discrimination model is constructed by employing synergy interval partial least square (SiPLS). The invention provides the quantitative determining method for scientifically accurately discriminating the fermentation quality congou black tea.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
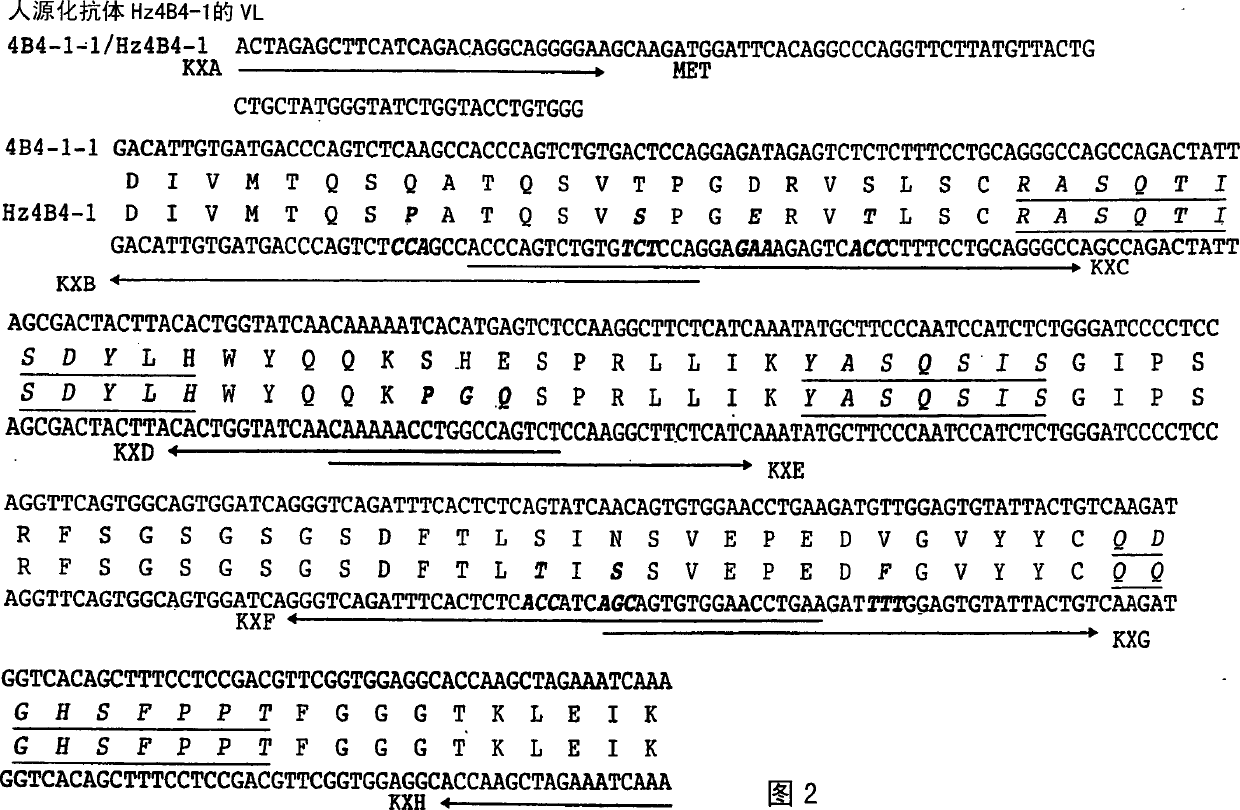
Humanized antibody specific for human 4-1BB and pharmaceutical compsn comprising same
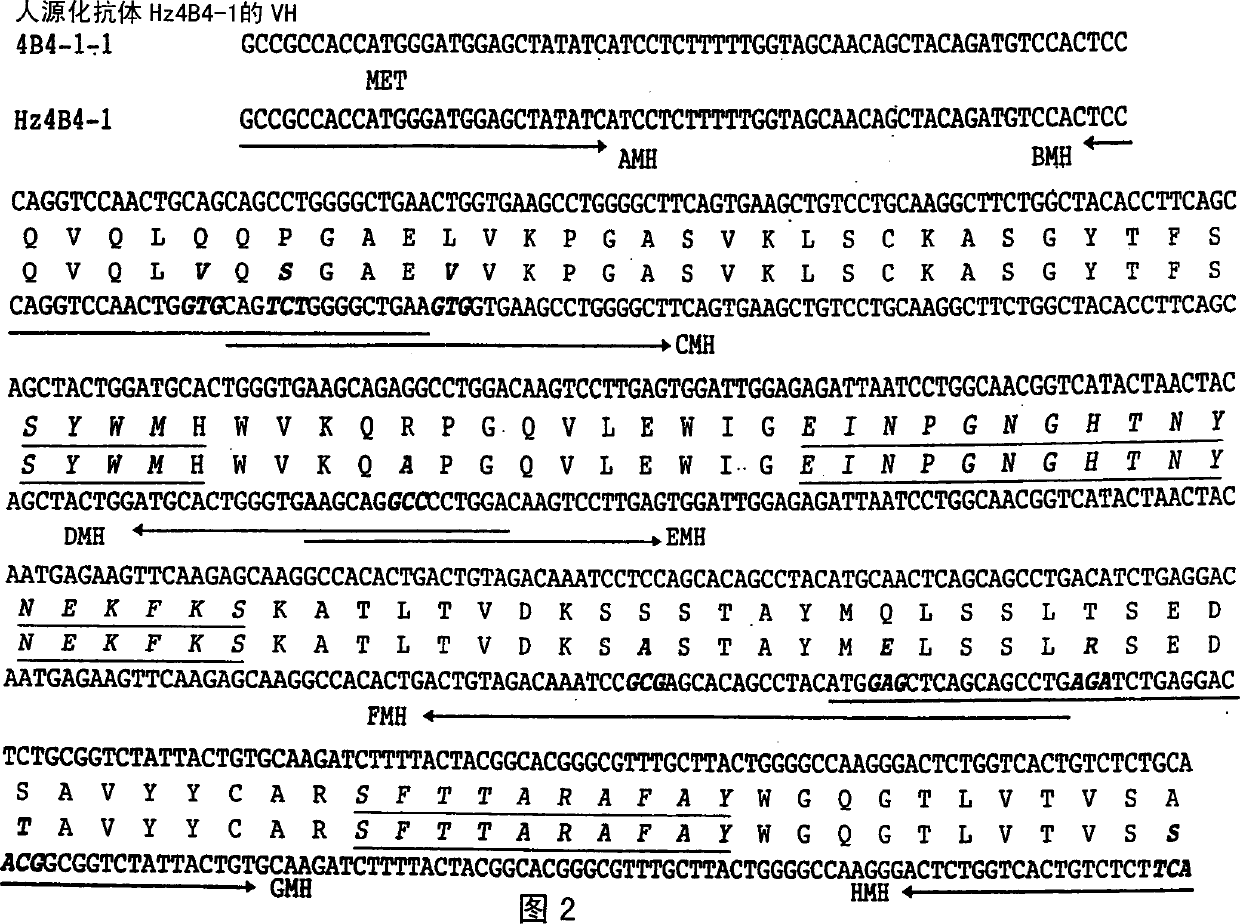
The present invention is directed to humanized antibodies that specifically bind the protein 4-1BB. The antibodies can be made by grafting of the complementarity determining regions (CDR's) of mouse monoclonal antibody to human 4-1BB to the remaining portions of a human antibody and by making further amino acid replacements. In addition, a pharmaceutical composition that includes the humanized antibody can be made and can be used to treat autoimmune diseases to suppress an immune response. The humanized antibody of the invention has high affinity for human 4-1BB, and exhibits sequence similarity to human antibody. As a result, the pharmaceutical composition of the present invention can be used to treat autoimmune disease and act as an immunosuppressant in humans without much side-effect.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
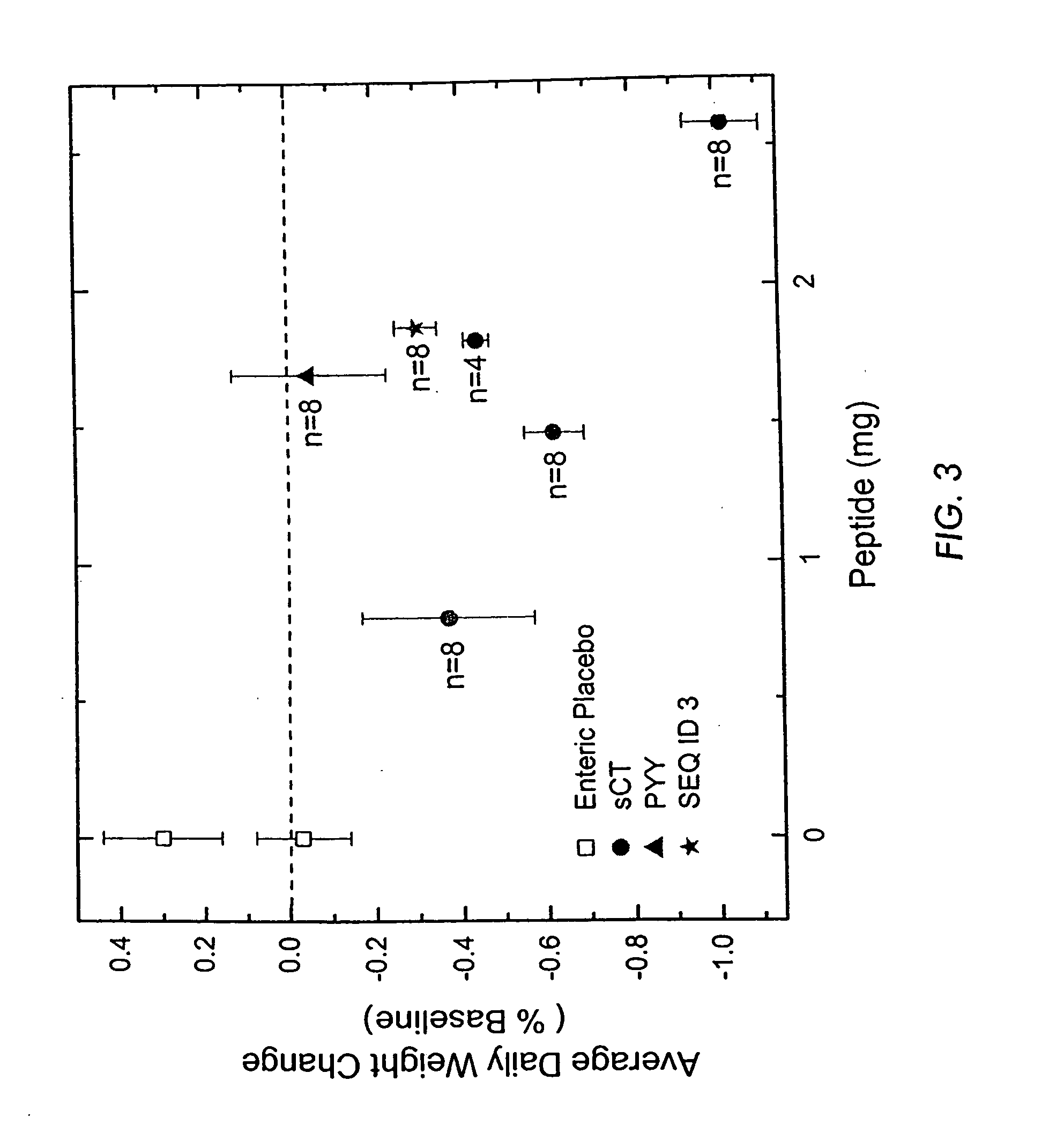
Treatment for obesity
ActiveUS20100311650A1Treating or preventing an overweight conditionAppetite suppressantPeptide/protein ingredientsCalcitoninsMedicineAmylin
The present invention provides peptides and pharmaceutical compositions thereof for appetite suppression and weight control. Preferred peptides are calcitonin analogs, preferably with specific amino acid changes to make the peptide more amylin-like.
Owner:KEYBIOSCI
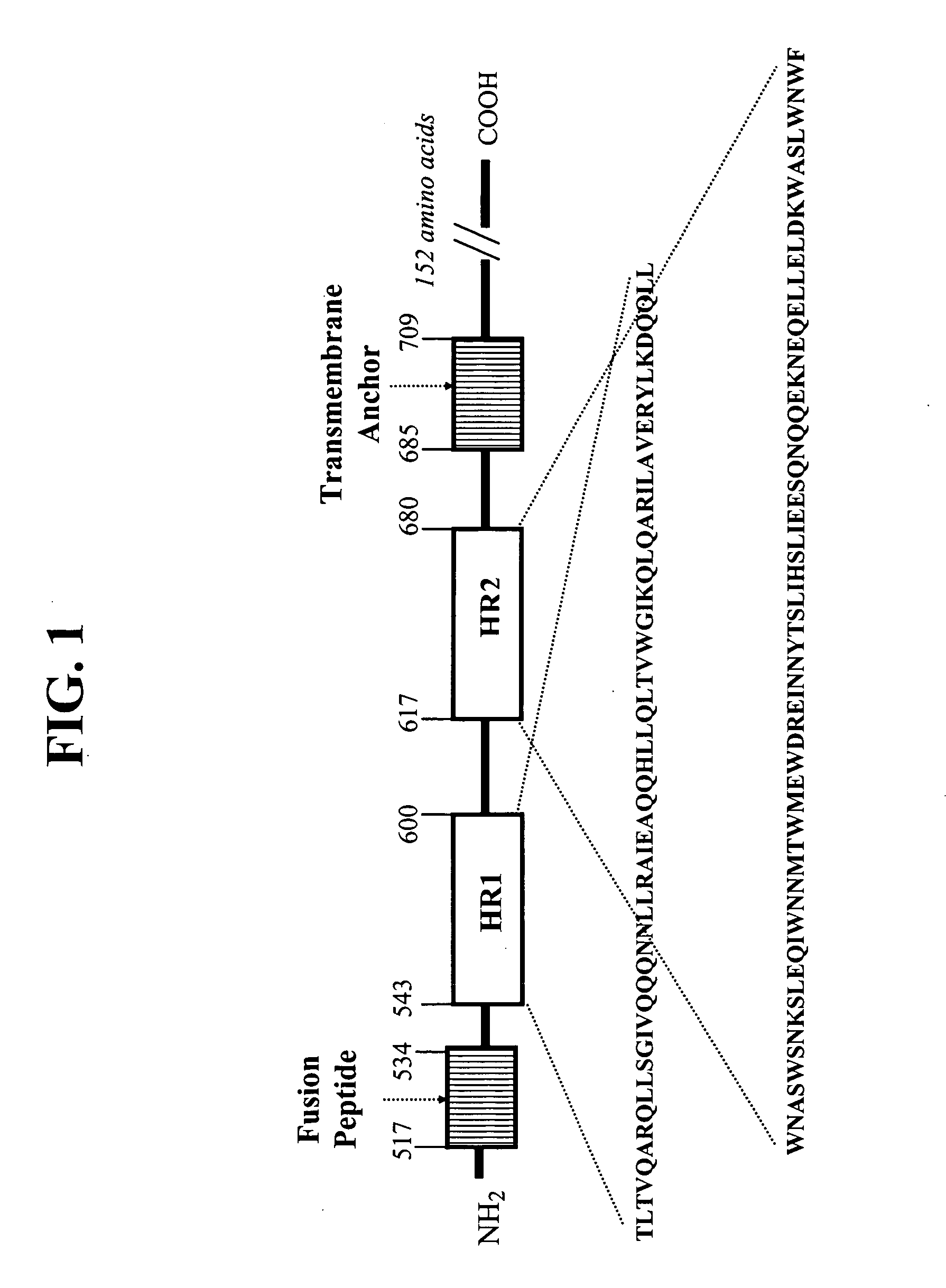
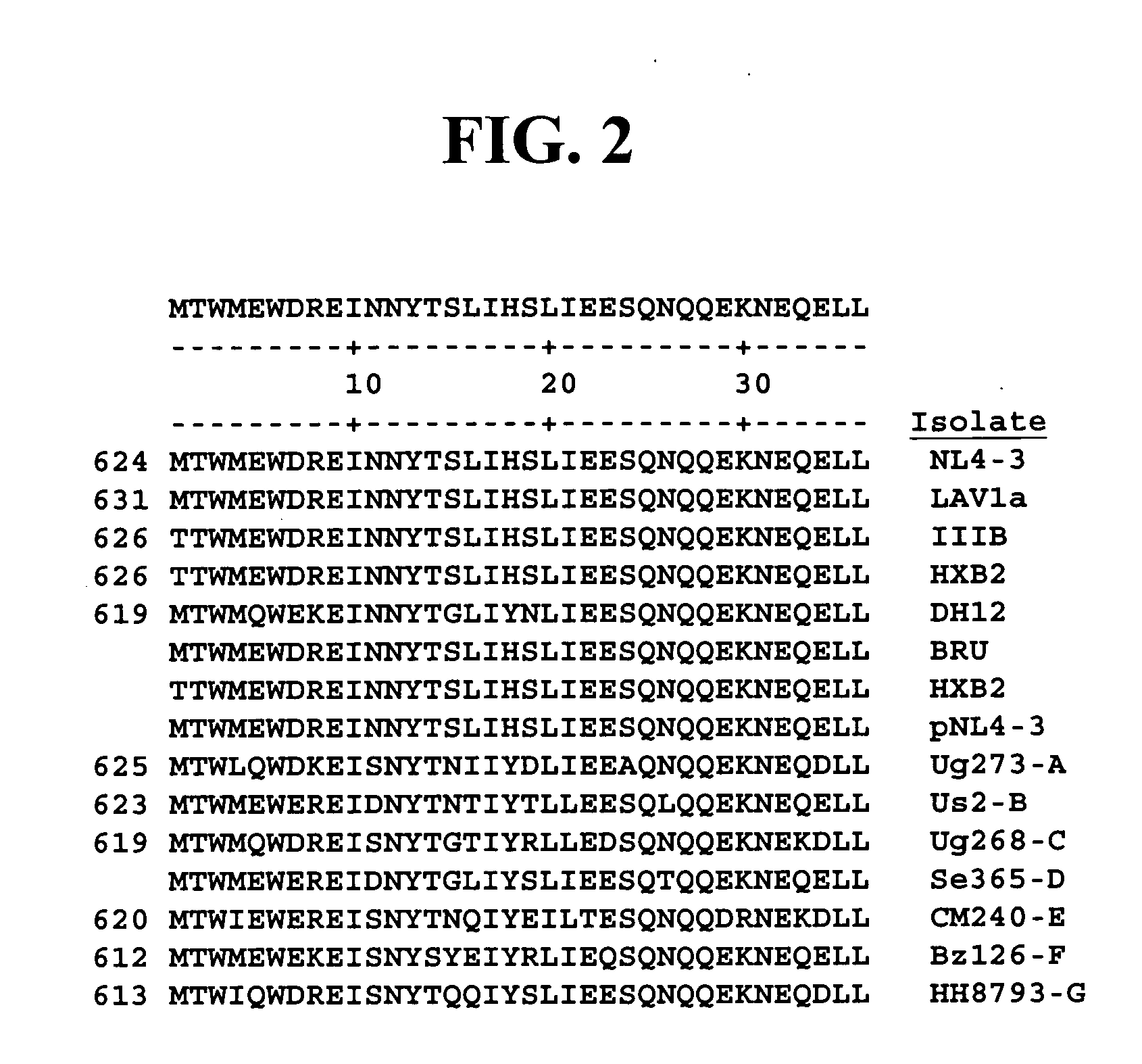
HIV gp41 HR2-derived synthetic peptides, and their use in therapy to inhibit transmission of human immunodeficiency virus
InactiveUS20060247416A1Improve biological activityStrong antiviral activityPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSugar derivativesImmunodeficiency virusAmino acid substitution
Provided are synthetic peptides based on a native sequence of HIV gp41 HR2 except that the synthetic peptides have a plurality of amino acid replacements comprising (a) a helix-promoting amino acid, or (b) a combination of helix-promoting amino acids, and charged amino acids introduced to form ion pairs in the synthetic peptide; wherein the synthetic peptides demonstrate an unexpected, improved biological activity, as compared to a peptide having an amino acid sequence without the plurality of amino acid substitutions. Also provided are polynucleotides encoding synthetic peptide, and methods of using these synthetic peptides in inhibition of, or as compositions to inhibit, transmission of HIV to a target cell.
Owner:TRIMERIS
Superluminescent luciferase variant with prolonged bioluminescence
InactiveUS20120034672A1High activityHigh luminous intensityFungiSugar derivativesOptical propertyAmino acid replacement
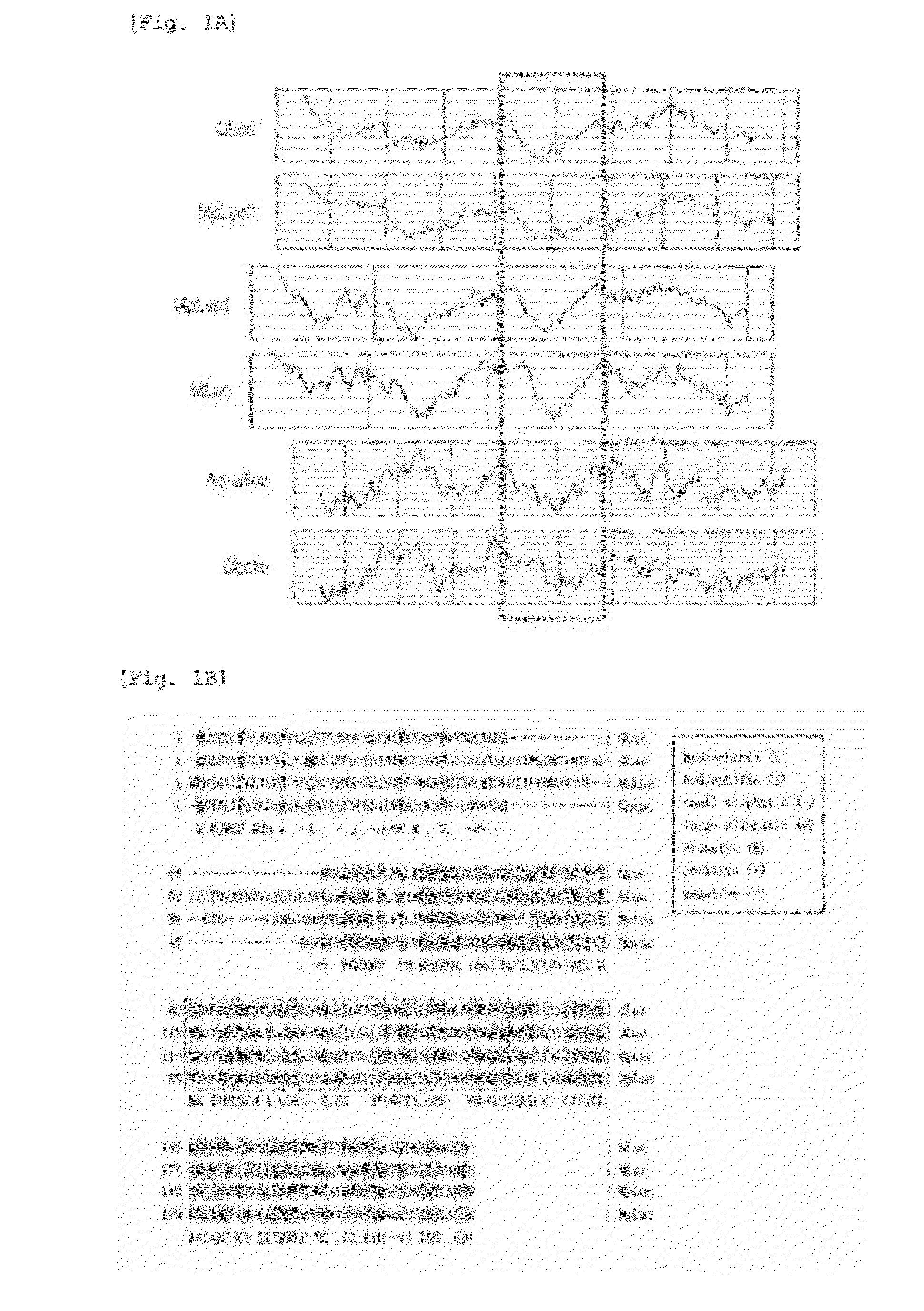
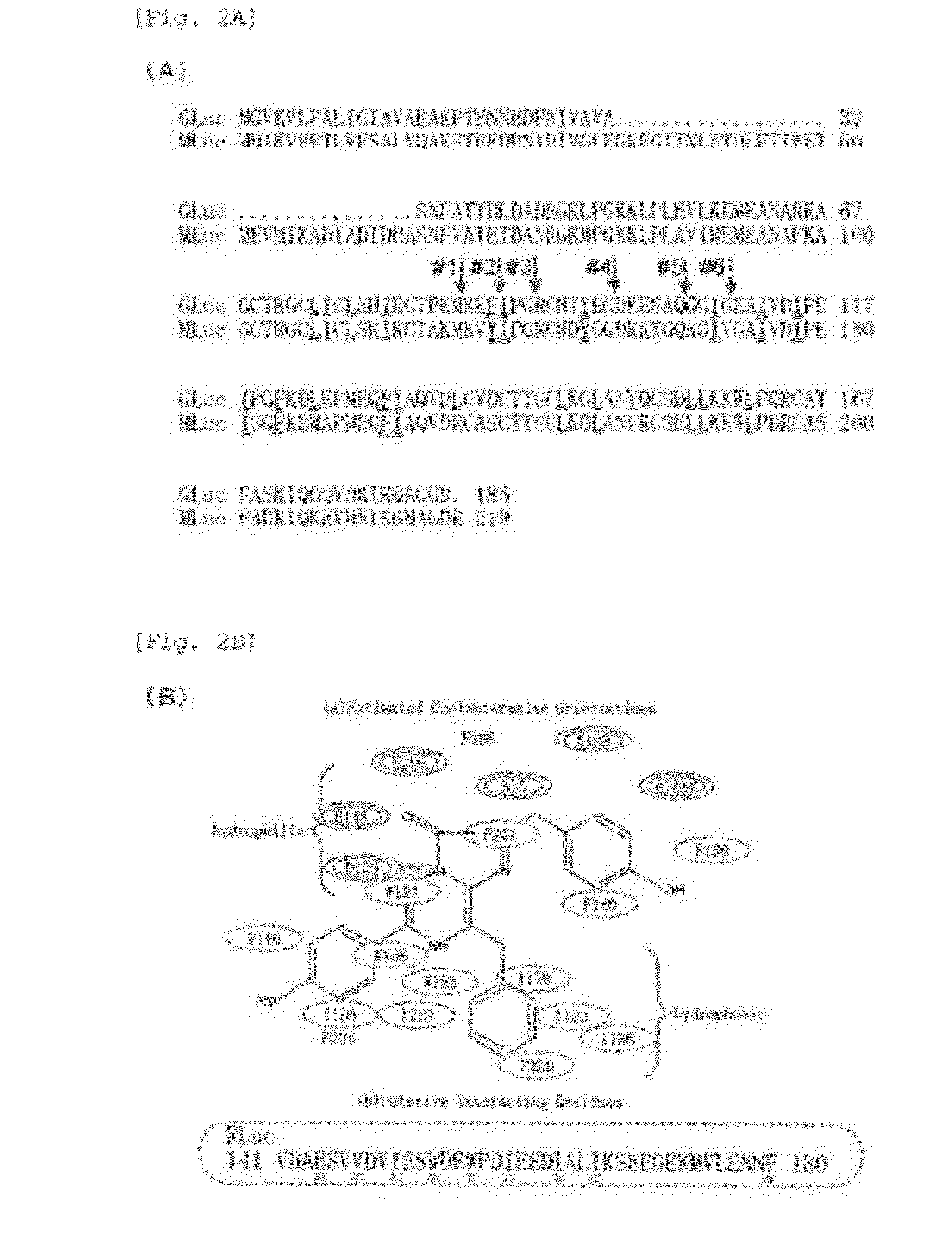
This invention provides a genetically modified marine luciferase such as Gaussia luciferase, which has high bioluminescence intensity, and has high bioluminescence stability and / or red-shifted wavelength. Specifically disclosed is a luciferase variant with improved optical property obtained by replacing at least one amino acid residue among the amino acid sequence of a marine luciferase at positions corresponding to positions 89 to 118 in the amino acid sequence of Gaussia luciferase (GLuc), wherein an amino acid residue at a position corresponding to at least one selected from positions 89, 90, 95, 97, 100, 108, 112, 115, and 118 in the amino acid sequence of GLuc is replaced by way of conservative amino acid replacement. The above-mentioned replacement in a marine luciferase improves enzymatic activity of the luciferase. Also disclosed is a bioluminescent probe having an improved optical property, which is produced using the luciferase variant of the present invention.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
High affinity sirp-alpha reagents
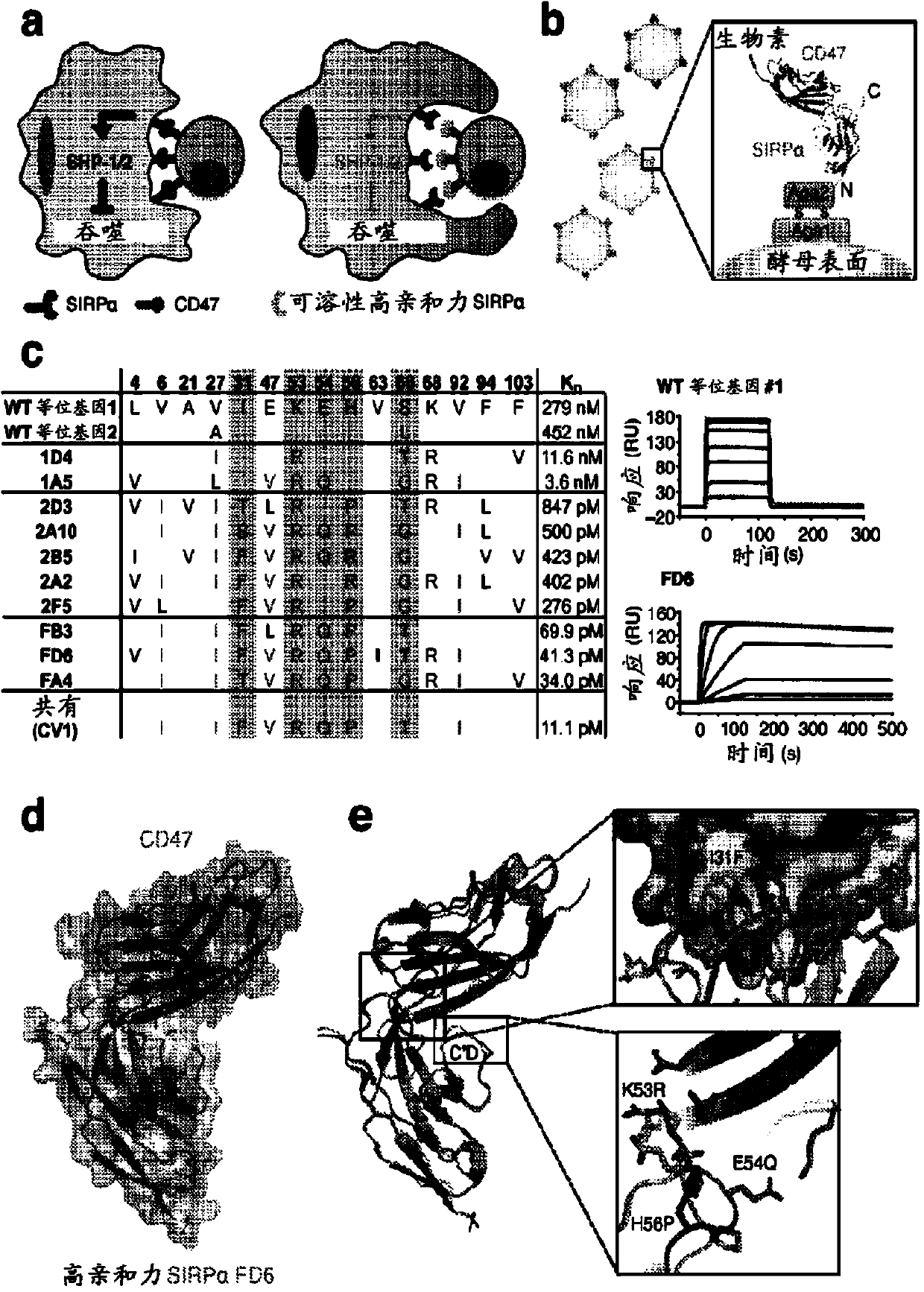
High affinity SIRP-alpha reagent are provided, which (i) comprise at least one amino acid change relative to the wild-type protein; and (ii) have an increased affinity for CD47 relative to the wild-type protein. Compositions and methods are provided for modulating phagocytosis in a mammal by administering a therapeutic dose of a pharmaceutical composition comprising a high affinity SIRPalpha reagent, which blocks the physiological binding interaction between SIRPalpha and its ligand CD47.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
NY-ESO-1 tumour antigen mimic epitope and use thereof
InactiveCN101381402AImproving immunogenicityStrong specificityPeptidesAntibody medical ingredientsCtl epitopePredictive methods
The invention discloses epitope for an NY-ESO-1 tumor antigen. The amino acid sequence of the mimic epitope is Ser-Leu-Leu- Met-Phe-Ile-Thr-Trp-Cys, namely SLLMFITWC; the mimic epitope can raise a CTL immunity response, can undergo a cross reaction with a natural epitope, has the characteristics of strong immunogenicity, immune tolerance breaking, strong specificity, safety, low cost, and easy synthesis and storage, and can be used to prepare tumor-therapeutic polypeptide vaccine. The invention also discloses a method for predicting the mimic epitope, which comprises steps of the establishment of a structural model of a TCR-pMHC complex, the analysis of TCR binding sites of the epitope, and the analysis of amino acid replacement of the TCR binding sites of the epitope. The method is also applicable to the computer-aided modification of CTL epitopes of other antigens, and can provide a useful tool for the design and research of therapeutic polypeptide vaccine.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Modified gene resulting in parthenocarpic fruit set
ActiveUS20170335339A1Good effectMicrobiological testing/measurementCis-trans-isomerasesFruit setWild type
The invention relates to a modified PIN4 gene, the wild type of which is as identified in SEQ ID No. 1, encoding the protein of SEQ ID No. 5, or the wild type of which encodes a protein that has a sequence similarity of at least 80% to SEQ ID No. 5, which modified PIN4 gene encodes a protein that comprises an amino acid change as a result of the modification, and which modified protein is capable of inducing parthenocarpic fruit set when present in a plant. The invention also relates to plants and fruits that carry the gene. Such plants are capable of parthenocarpic fruit set and the fruits do not contain seeds. The invention further relates to use of the gene in breeding and producing plants capable of parthenocarpic fruit set.
Owner:RIJK ZWAAN ZAADTEELT & ZAADHANDEL BV
Mutants of Streptococcal toxin A and methods of use
This invention is directed to mutant SPE-A toxins or fragments thereof, vaccine and pharmaceutical compositions, and methods of using the vaccine and pharmaceutical compositions. The preferred SPE-A toxin has at least one amino acid change and is substantially non-lethal compared with the wild type SPE-A toxin. The mutant SPE-A toxins can form vaccine compositions useful to protect animals against the biological activities of wild type SPE-A toxin.
Owner:MINNESOTA UNIV OF REGENTS THE +1
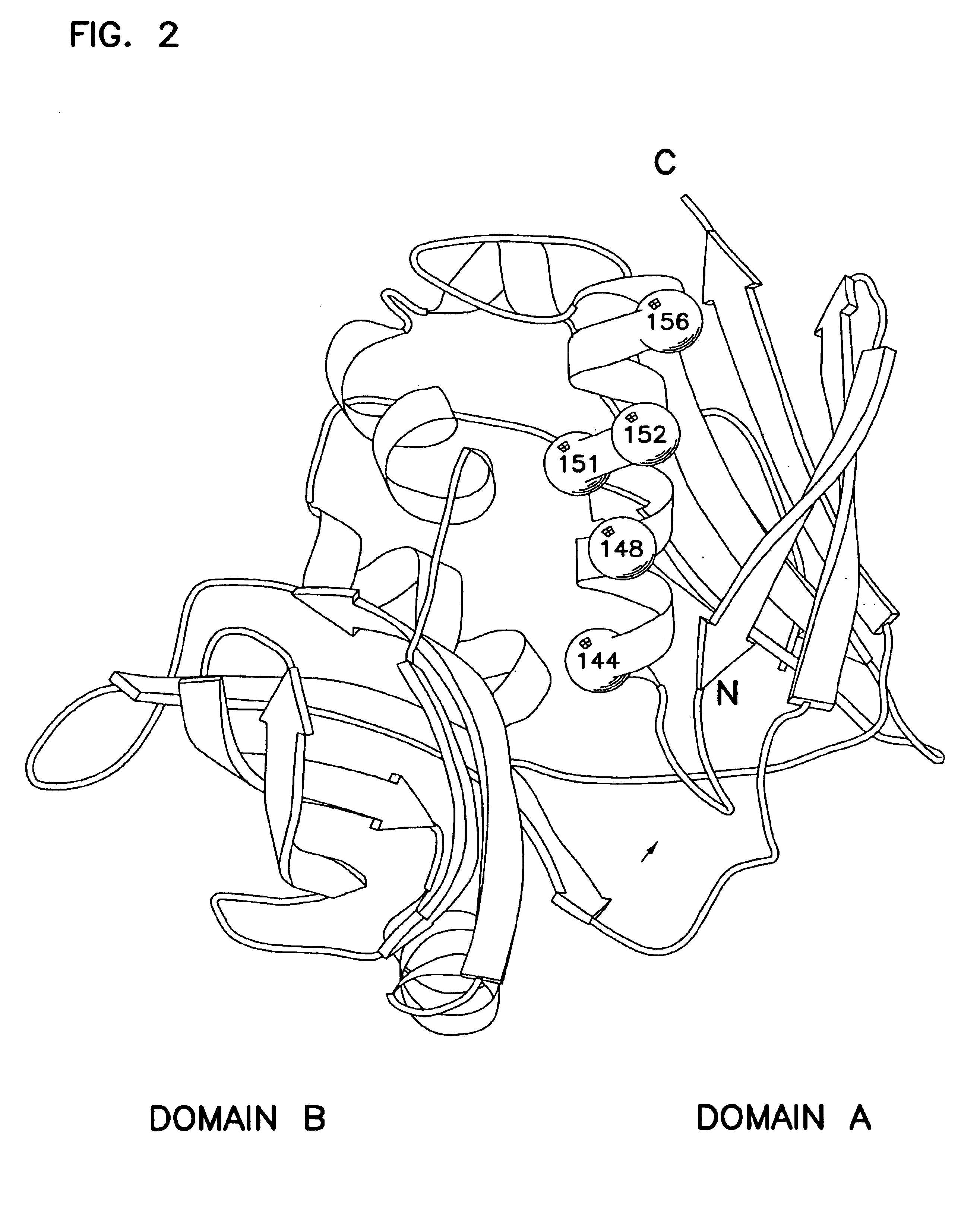
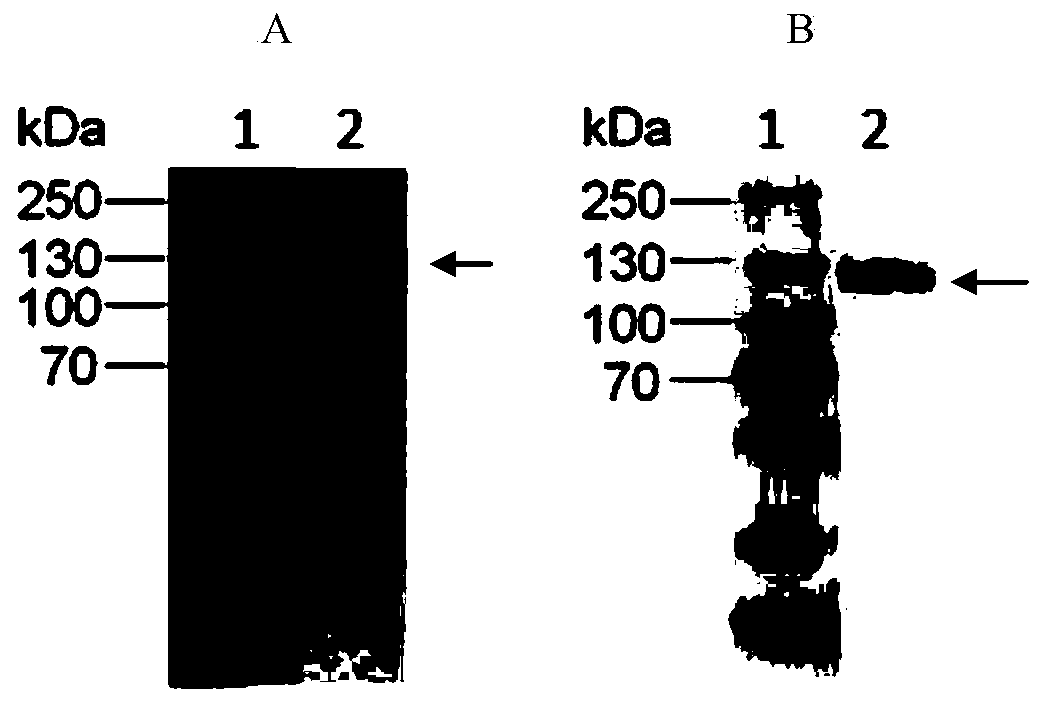
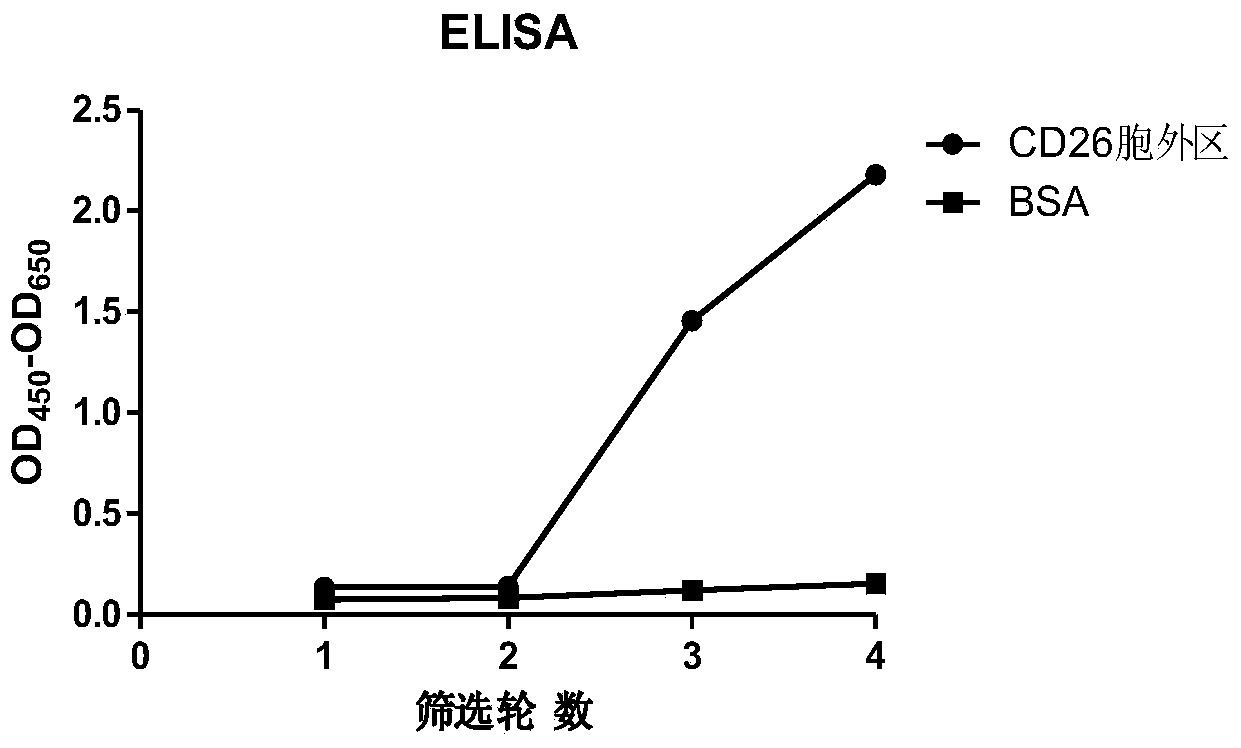
Humanized anti-CD26 antibody and application thereof
ActiveCN103724431APrevent proliferationPrevent invasionFungiBacteriaSingle-Chain AntibodiesComplementarity determining region
The invention provides a novel high-affinity completely humanized antibody which can specifically bind with CD26 as well as a preparation method and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering antibodies. The CD26 is a ubiquitous multifunctional II type transmembrane glycoprotein, has various biological functions and can be interacted with various proteins such as ADA, CD45, FAP-alpha and the like. The invention provides the humanized antibody or a fragment thereof, wherein the antibody or the fragment thereof is capable of specifically binding with the human CD26, preferably the CD26 extracellular domain; the amino acid sequence of the antibody or the fragment thereof comprises an amino acid sequence containing a monoclonal antibody or a fragment thereof or a conjugate of the fragment in any one of 6 complementary determining regions in one of SED ID NO: 2, SED ID NO: 3, SED ID NO: 4, SED ID NO: 6, SED ID NO: 7, and SED ID NO: 8, or an amino acid sequence obtained through amino acid replacement or modification. The obtained anti-CD26 single-chain antibody provided by the invention can highly specifically bind with the CD26 and is simultaneously capable of obviously inhibiting the proliferation, the invasion and the metastasis of tumor cells.
Owner:ZONHON BIOPHARMA INST
Firefly luciferase and gene thereof, and process for production of firefly luciferase
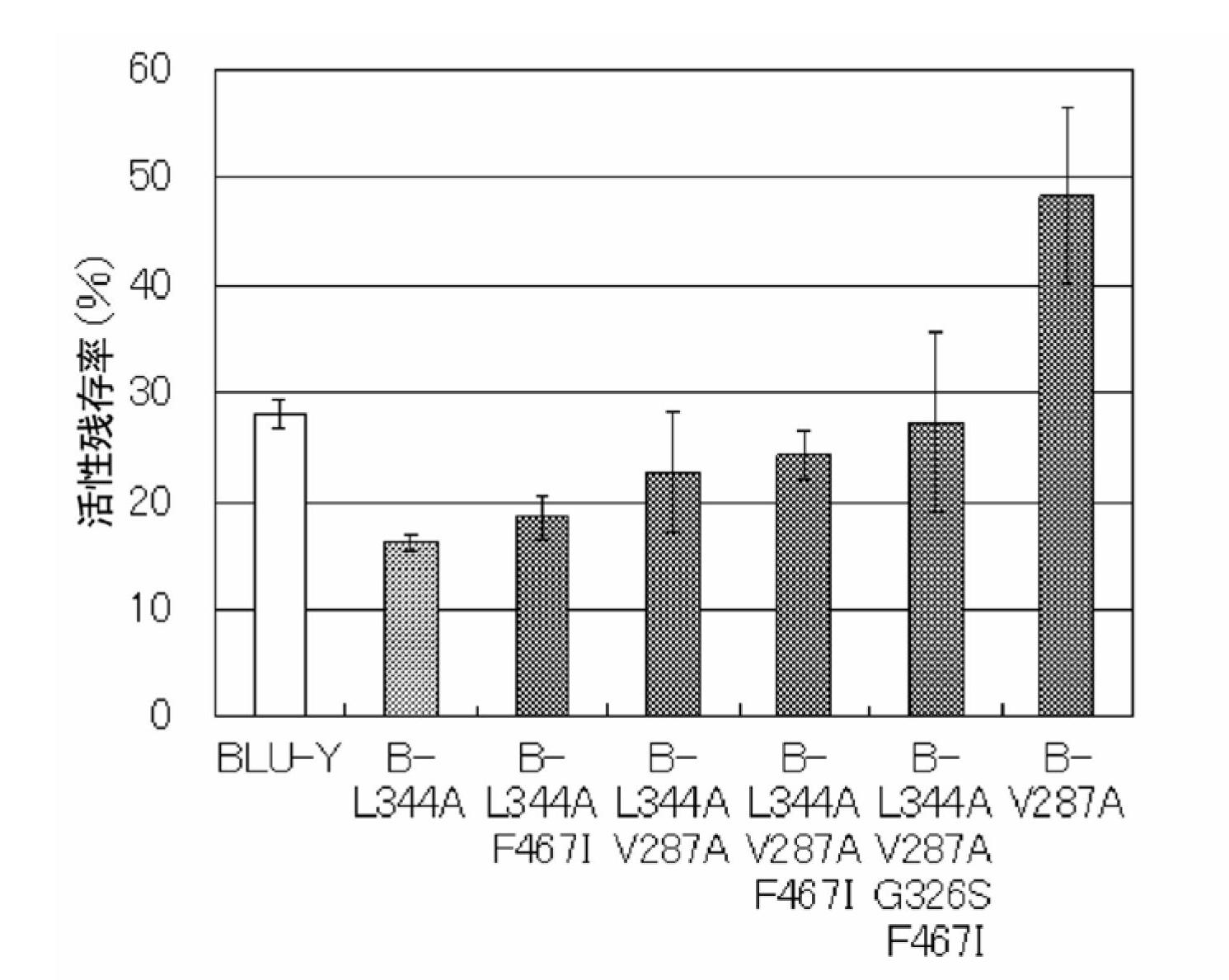
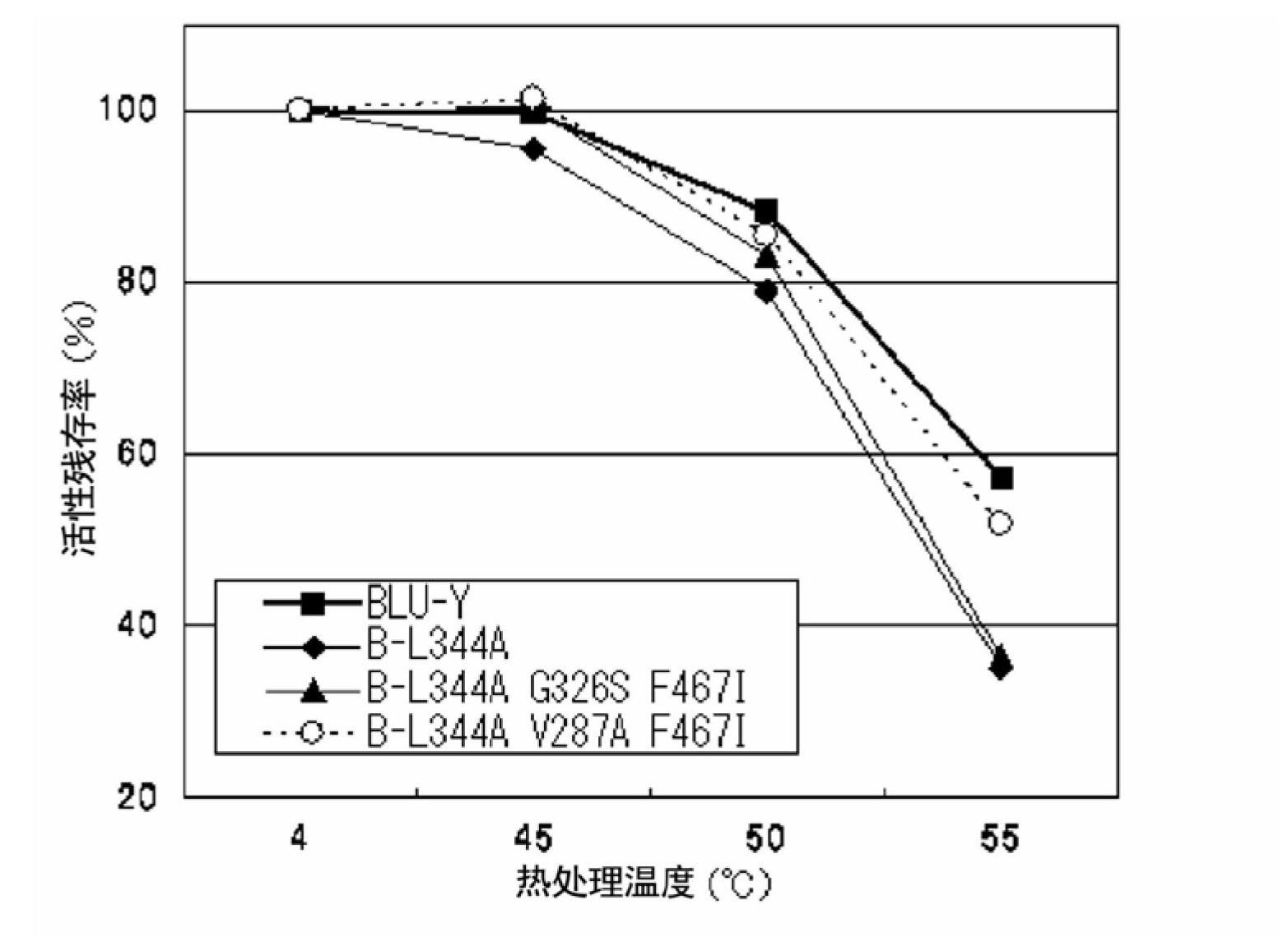
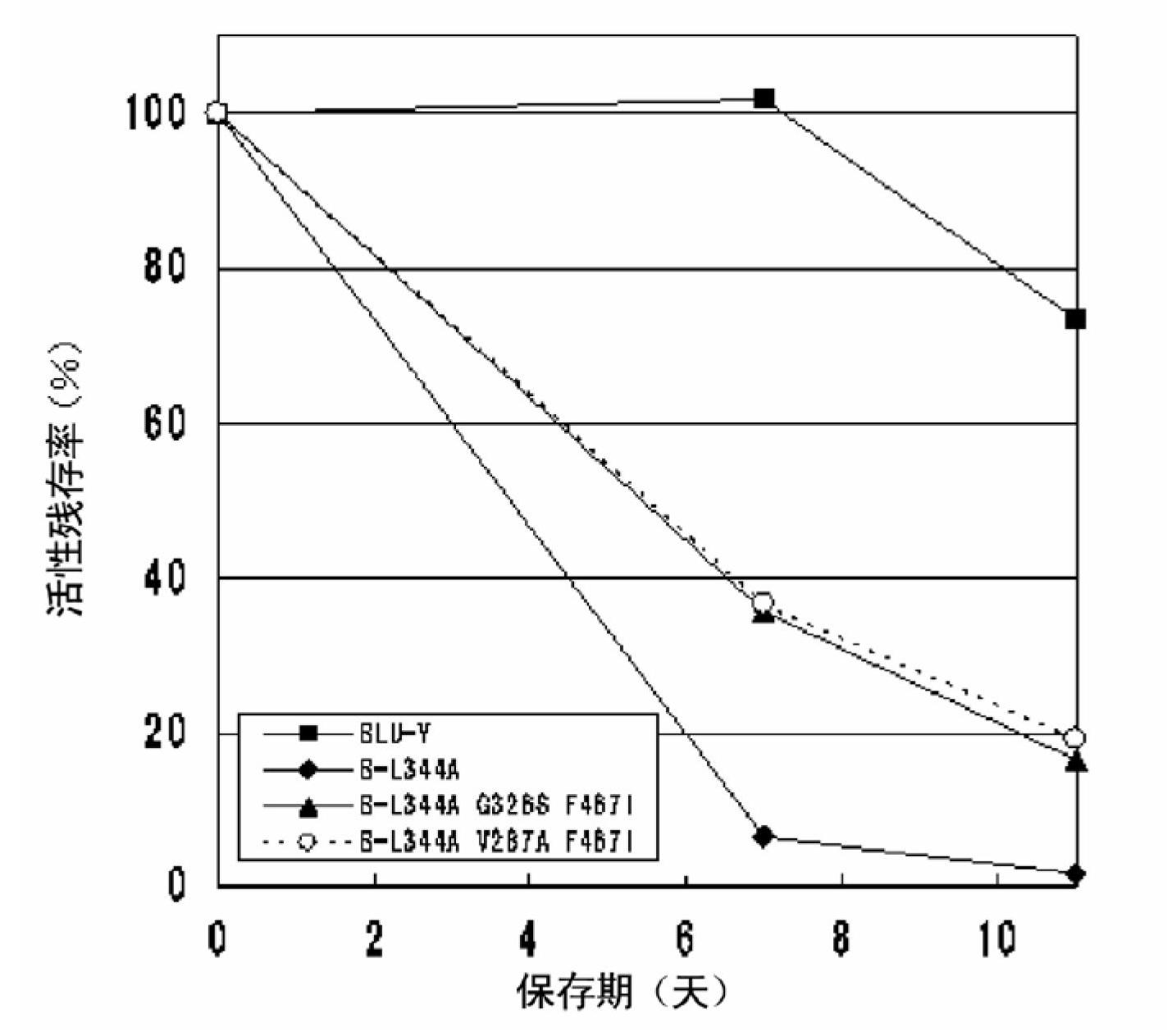
Disclosed are: a firefly luciferase having excellent thermal stability and / or storage stability; and a process for producing the firefly luciferase. Specifically disclosed are: a firefly luciferase characterized by comprising an amino acid sequence that is produced by substituting an amino acid residue located at position-287 by an alanine residue or mutating an amino acid residue located at position-392 by an isoleucine residue in the amino acid sequencer for a Japanese firefly Luciola lateralis; and a gene for the firefly luciferase. The use of the gene enables the efficient production of a firefly luciferase having improved stability. The above-mentioned mutation may be combined with a mutation produced by substituting an amino acid residue located at position-326 by a serine residue and / or a mutation produced by substituting an amino acid residue located at position-467 by an isoleucine residue in the same amino acid sequence, thereby producing a firefly luciferase having further improved stability.
Owner:KIKKOMAN CORP
Anti-CD26 antibody and application thereof
ActiveCN103641917AGrowth inhibitionPrevent proliferationFungiBacteriaSingle-Chain AntibodiesComplementarity determining region
The invention provides a novel full-humanized antibody which is high in affinity and can be specifically combined with CD26, and a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of a genetically engineered antibody. CD26 is a ubiquitous multifunctional II-type transmembrane glycoprotein, has a plurality of biological functions, and can interact with a plurality of proteins, such as ADA, CD45, FAP-alpha and the like. The invention provides an antibody from a human source or a segment thereof. The antibody or the segment thereof is specifically combined with human CD26, and preferably specifically combined with a CD26 extracellular region; an amino acid sequence of the antibody or the segment thereof comprises a monoclonal antibody which is selected from any region of six complementary determining regions containing a group of sequences of SEQ ID NO:2, SEQ ID NO:3, SEQ ID NO:4, SEQ ID NO:6, SEQ ID NO:7 and SEQ ID NO:8, or a segment thereof or a conjugate of the segment thereof, or an amino acid sequence which is obtained by amino acid replacement or modification. The anti-CD26 single-chain antibody obtained by the method is highly specifically combined with the CD26, and meanwhile, multiplication of tumor cells can also be obviously inhibited.
Owner:ZONHON BIOPHARMA INST
MHC completion database, and establishment method and application thereof
ActiveCN105512514AImprove accuracyReduce usageMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecial data processing applicationsData setTyping
The invention discloses a MHC completion database, and an establishment method and application thereof. The MHC completion database comprises a genotype dataset, a HLA typing type dataset, an amino acid changing information dataset, and a HLA haplotype dataset combined together. In the establishment process of the database, LD and HWE are used for the first time for filtering a variation result, and data accuracy is improved. A simple method which is easy to operate is used to obtain SNP distinguishing datasets in least number, and MHC haplotype information is obtained through phasing analysis. Compared with using the whole SNP dataset to perform phasing, the establishment method saves more time, and reduces CPU and memory use, and obtained haplotype information is more accurate. The MHC completion database comprises various datasets in a MHC region, and can effectively complete sites, and lays foundation for deep research of the MHC region.
Owner:BGI GENOMICS CO LTD +1
DNA polymerase, nucleic acid test method and nucleic acid test kit
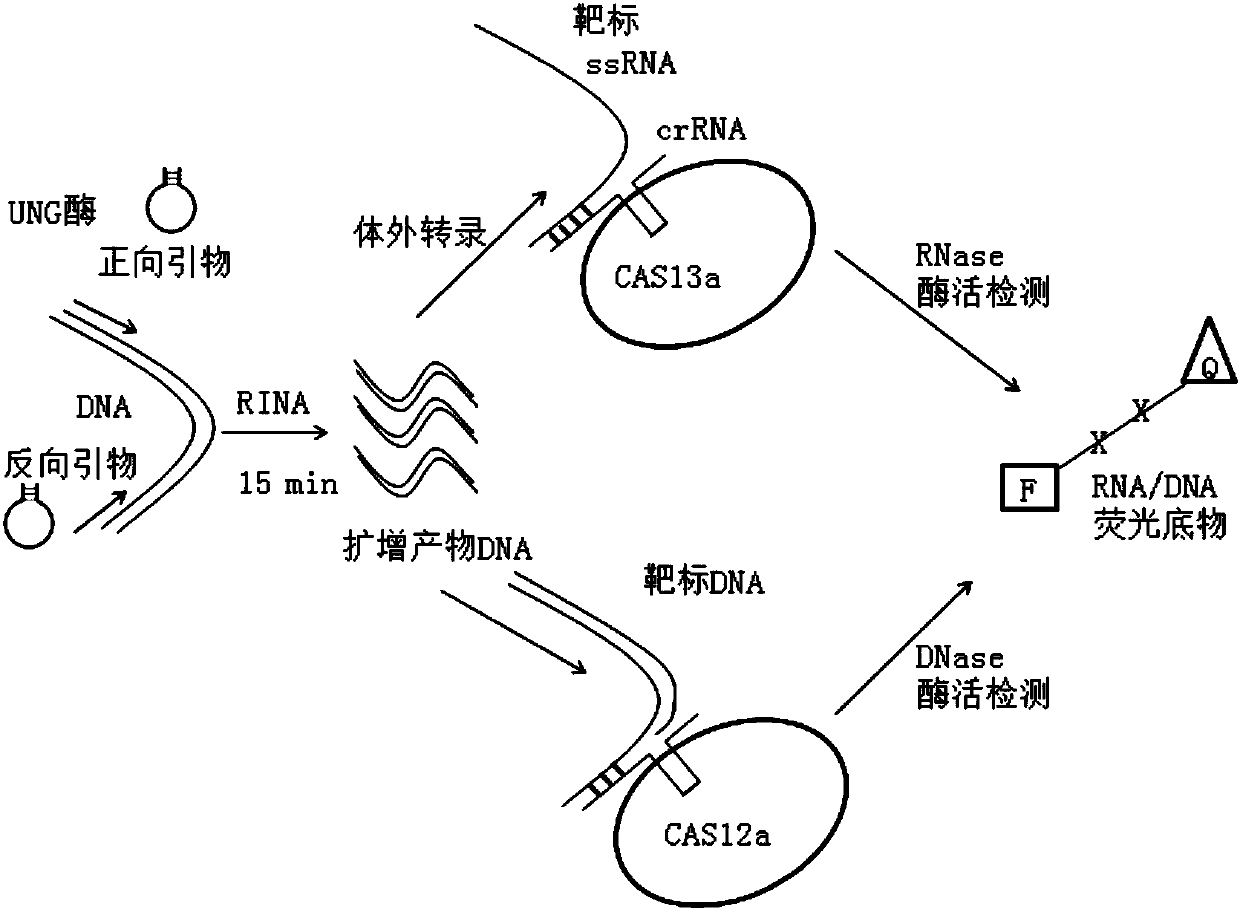
ActiveCN108588050ALow costShort detection timeMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesEscherichia coliPolymerase L
The invention provides a DNA polymerase with DNA or RNA as a template. The DNA polymerase is obtained through amino acid replacement, including G198W, V222I, E306K, Q354E, A381E and E582K, of klenow fragments of escherichia coli polymerases I. The invention also provides a primer with a stem loop structure and used for constant-temperature nucleic acid amplification. The invention further providesa nucleic acid test technique and a test kit both based on combination between rapid constant-temperature nucleic acid amplification and a Cas test system. The DNA polymerase, the nucleic acid test technique and the test kit can be used for testing nucleic acid targets in test samples at a constant temperature, have the advantages of low cost, short test time, simplicity and convenience in operation, high specificity, high sensitivity and the like, and are particularly applied to POCT (point-of-care testing).
Owner:BEIJING EXELLON MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Reverse transcriptase having improved thermostability
ActiveCN103348004AImprove thermal stabilityStabilized reverse transcription activityBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementReverse transcriptaseThreonine
The present invention relates to a reverse transcriptase having improved thermostability, more precisely a mutant reverse transcriptase with improved thermostability by substitution of one or more amino acids selected from the group consisting of the 63rd glutamine (Q63), the 264th lysine (K264), the 295th lysine (K295), the 306th threonine (T306), the 346th glutamic acid (E346), the 408th proline (P408), the 438th histidine (H438), and the 454th asparagin (N454) of the amino acid sequence of M-MLV originated reverse transcriptase represented by SEQ. ID. NO: 1 with other amino acids. The mutant reverse transcriptase of the present invention demonstrates excellent thermostability, compared with the wild type reverse transcriptase. Therefore, it is advantageous to obtain the target cDNA with stable reverse transcription activity even in the presence of RNA that can form the stable secondary structure at a high temperature.
Owner:BIONEER
Recombinant expression vectors comprising a human codon-optimized marburg virus (MARV) angola glycoprotein gene insert and method of immunization employing said vector
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
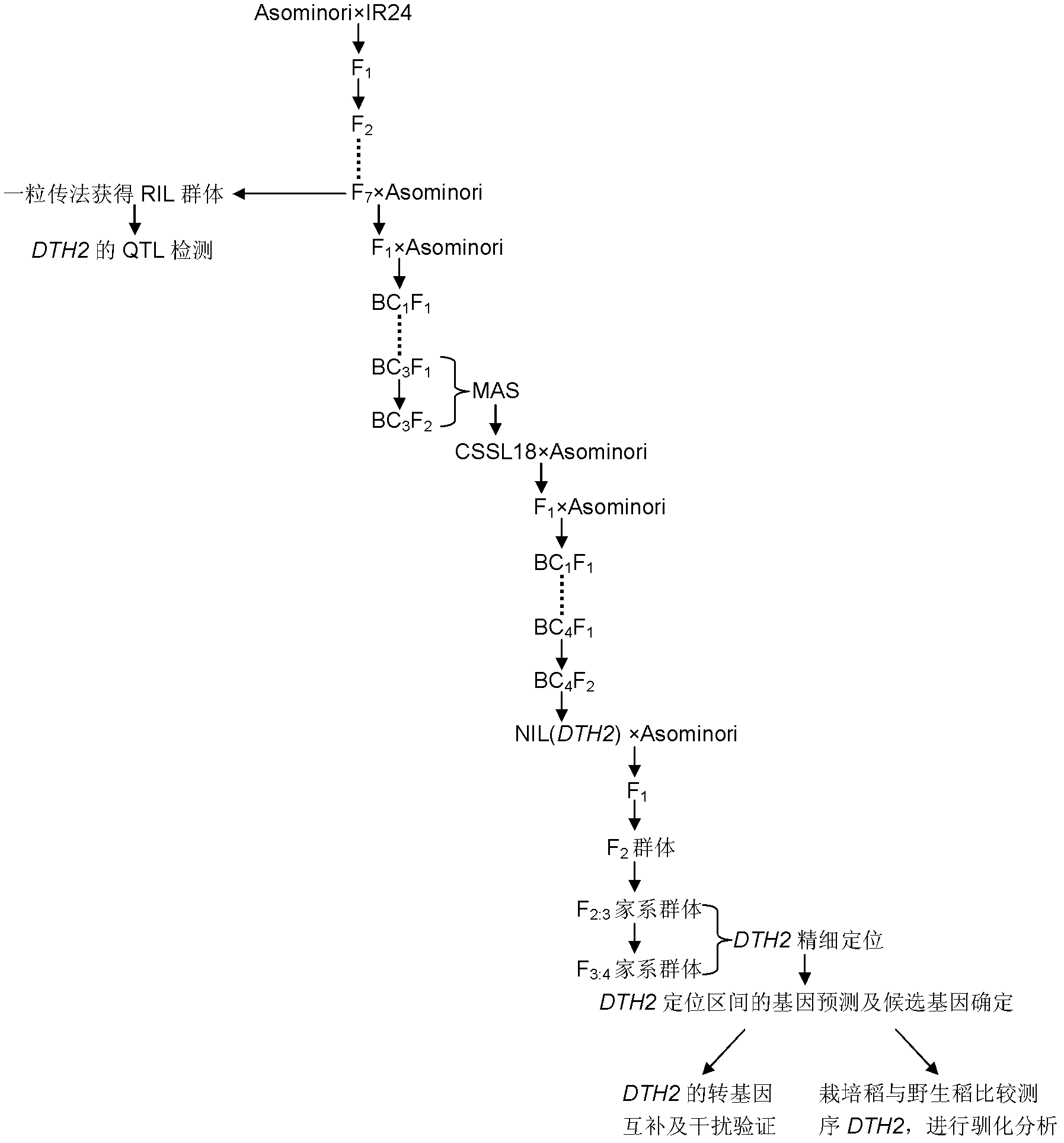
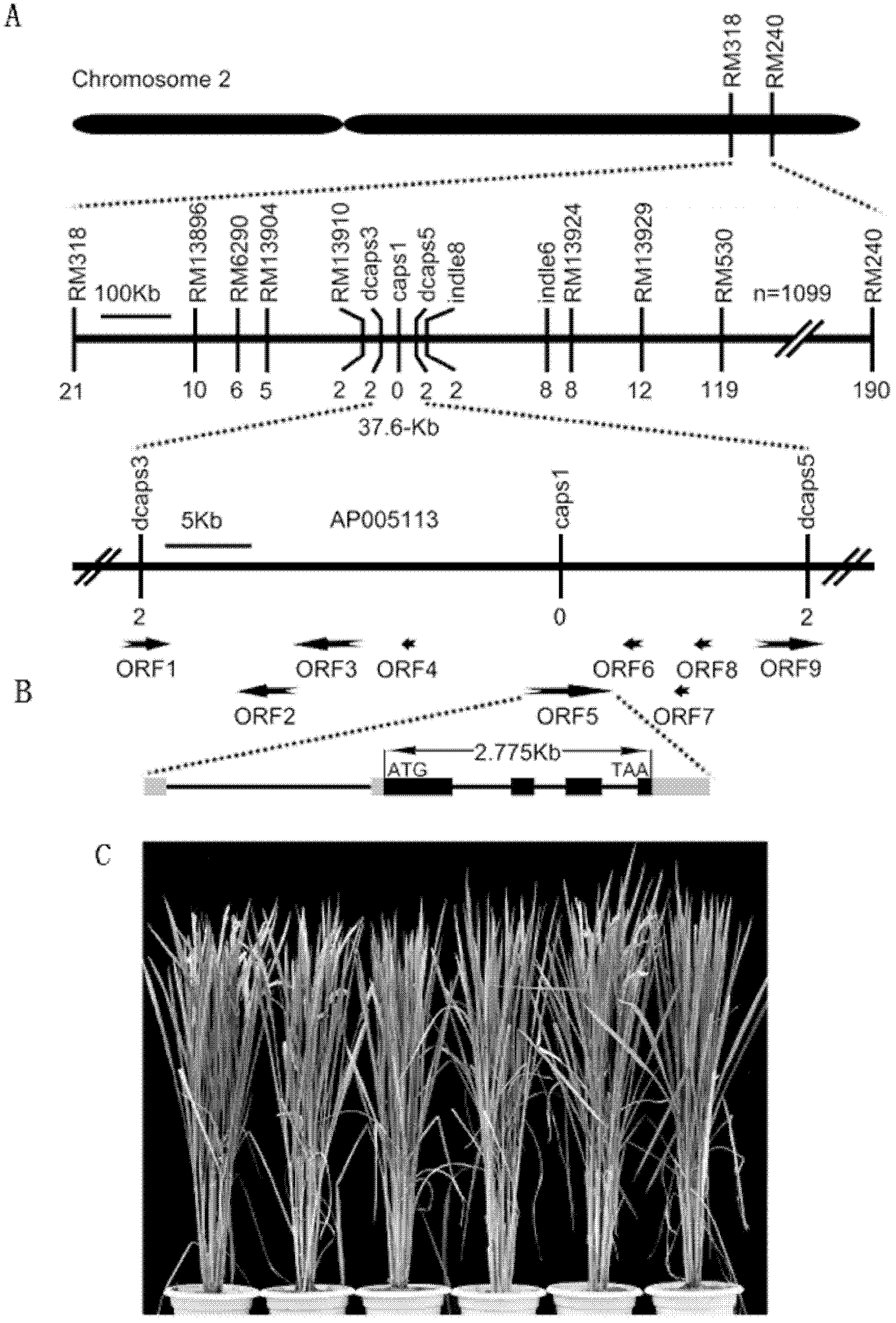
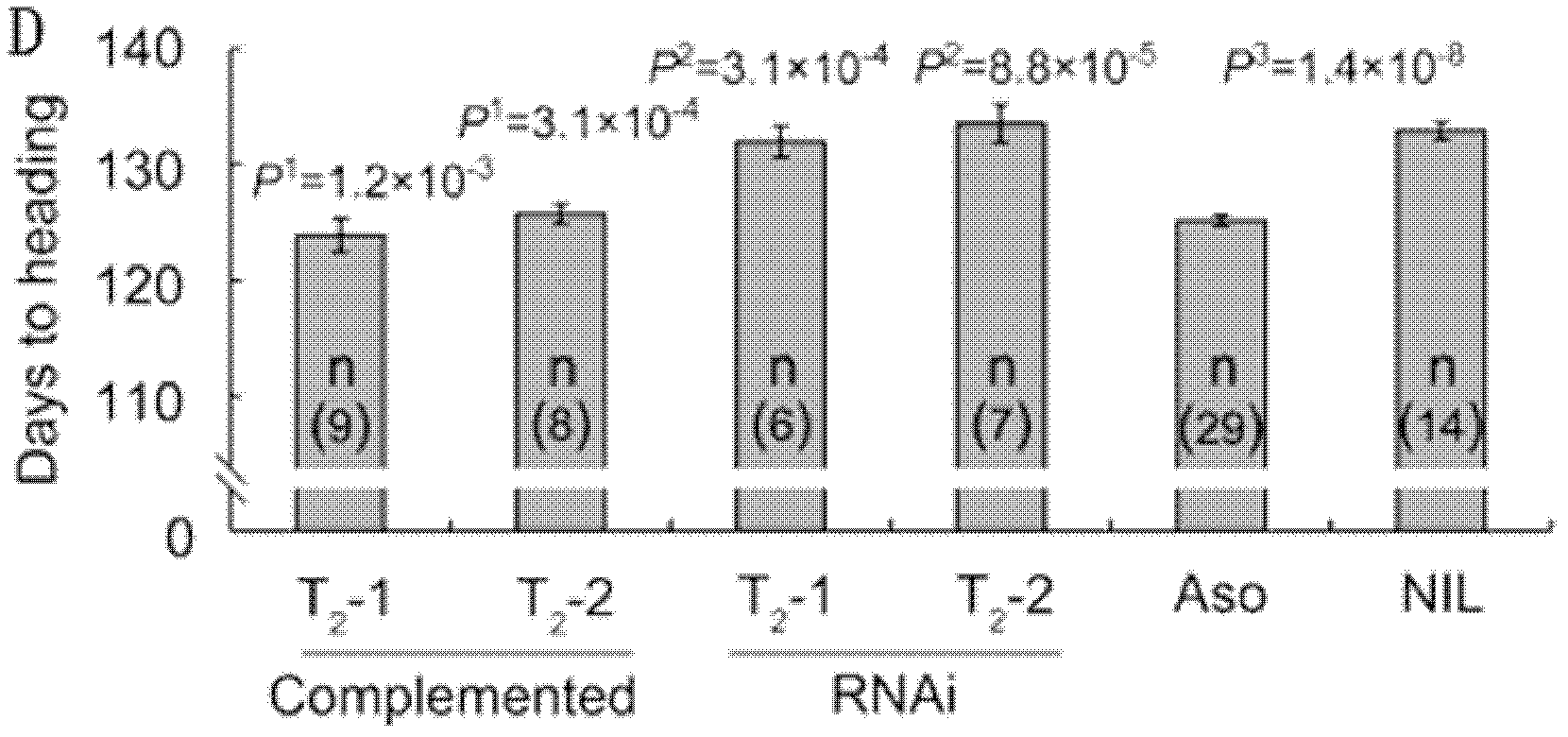
Set of DTH2 genes for controlling heading stage of paddy rice and haplotypes and application thereof
InactiveCN102586277AHeading promotionEarly heading datePlant peptidesFermentationHaplotypeGenetic engineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering, and relates to a set of DTH2 genes for controlling the heading stage of paddy rice and haplotypes and application thereof. The gene is coded with a CCT / B-box zinc finger protein, and belongs to the CONSTANS-Like transcription factor gene family, the dominant allele sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO.1, and flowering is promoted only under the long sunshine condition. The DNA sequence of the recessive allele is shown as SEQ ID NO.3. A transgenosis experiment proves that the gene has the function of advancing the heading stage of paddy rice. By sequencing 79 pieces of cultivated rice and 48 pieces of wild rice, five-base difference is discovered in the DTH2 coding region, as a result, three amino acids change, and five types of haplotypes are generated. Moreover, the transgenosis experiment proves that the gene is selected in domestication and originated in China.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
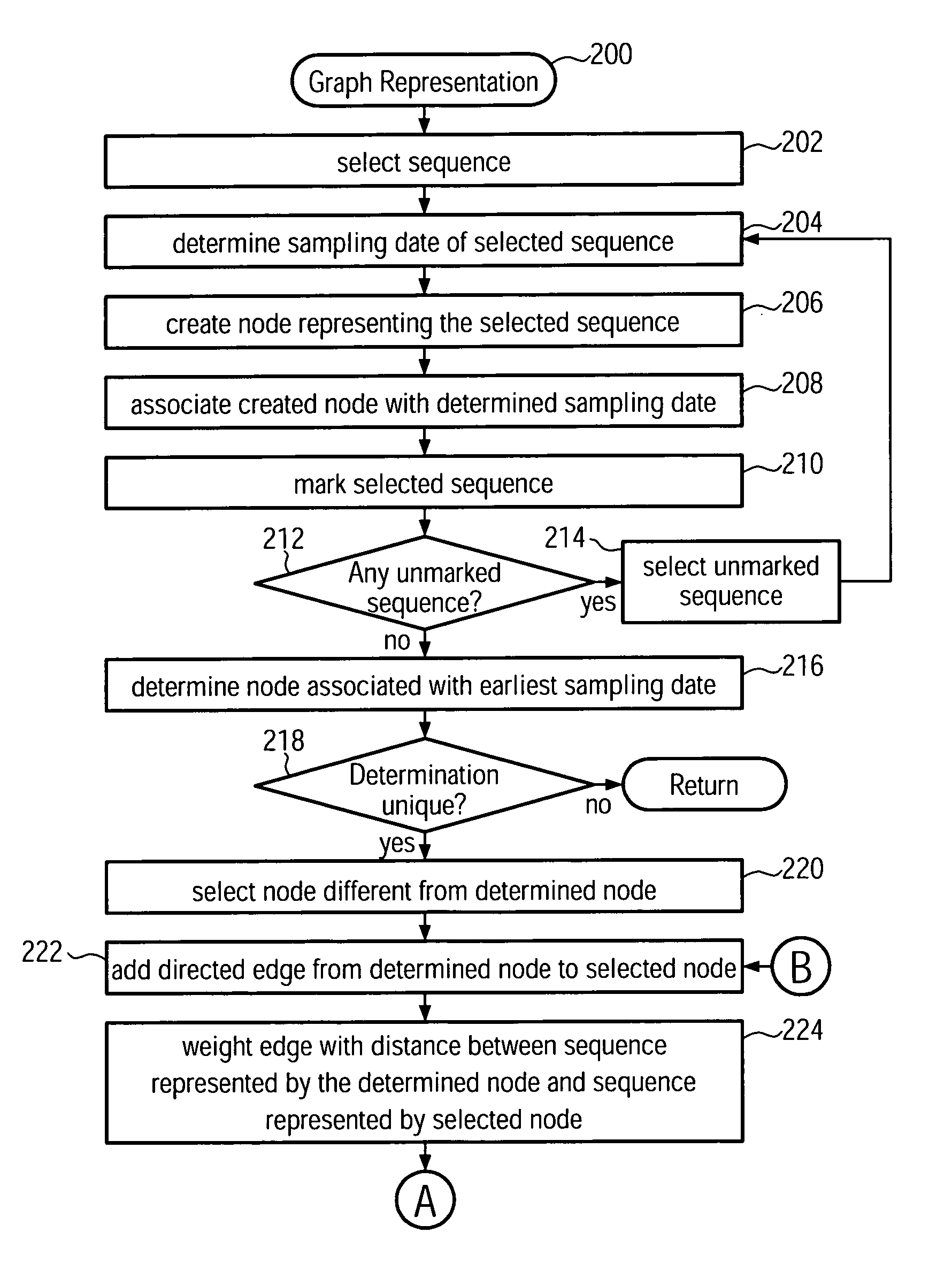
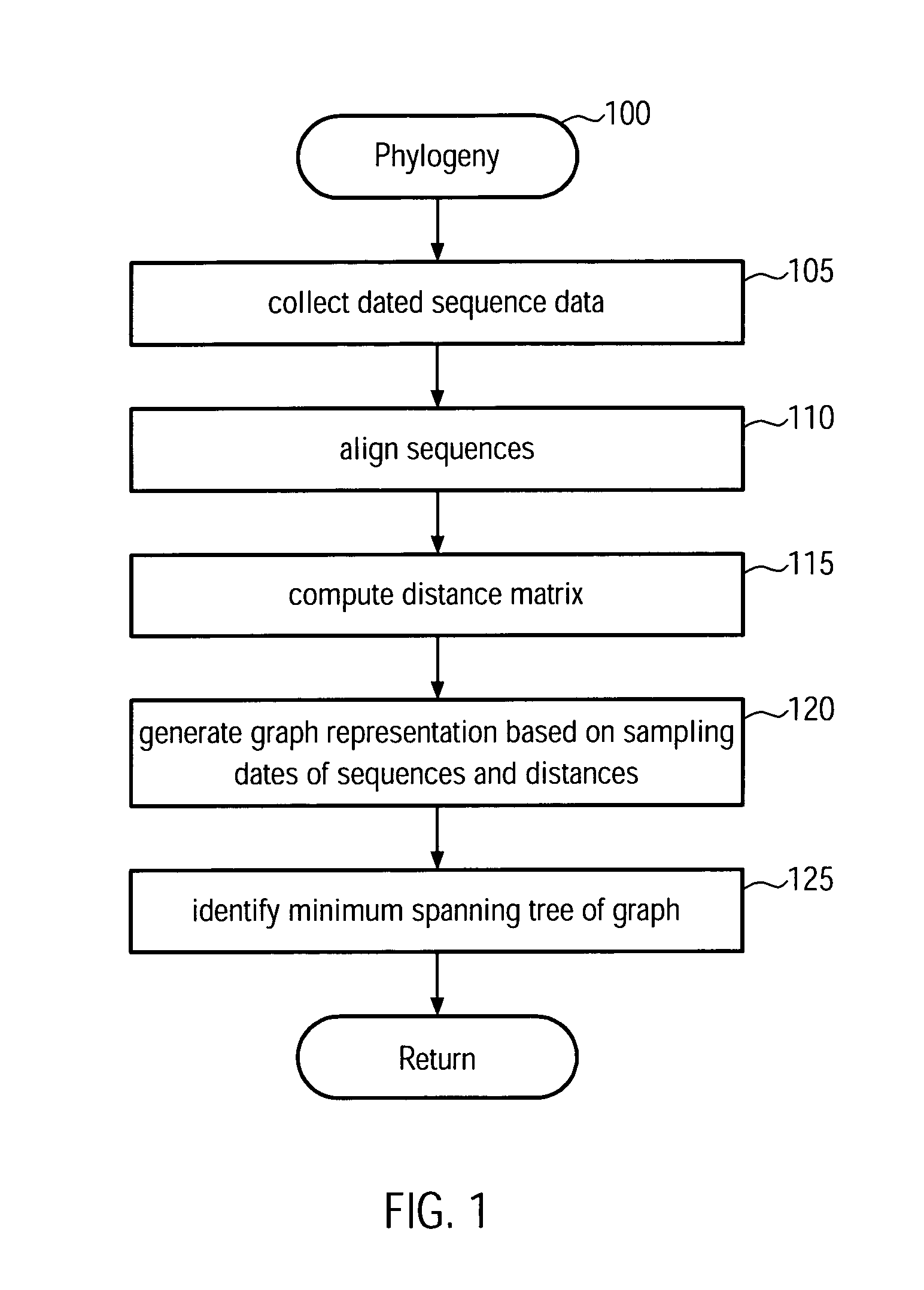
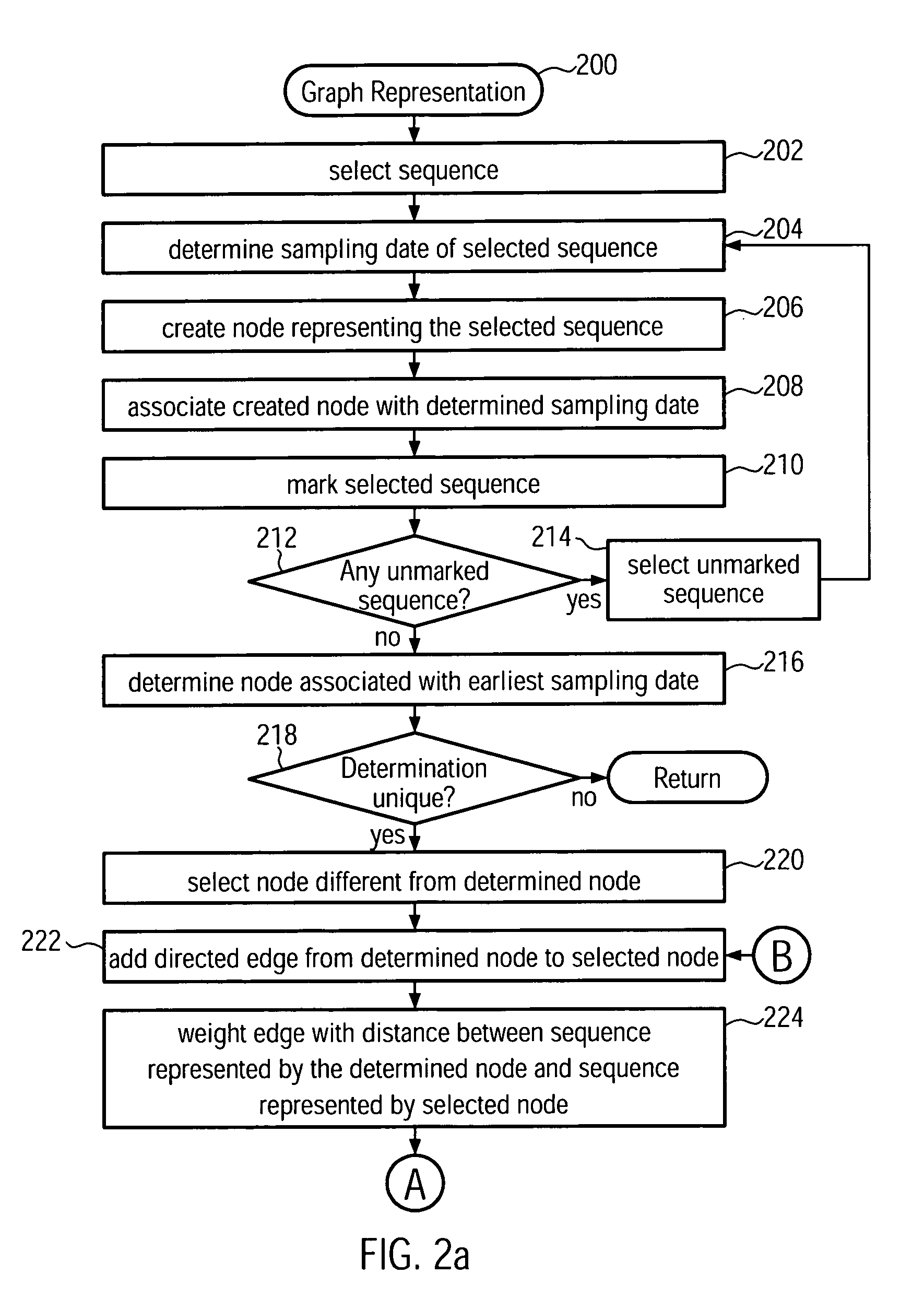
Method and system for building a phylogeny from genetic sequences and using the same for recommendation of vaccine strain candidates for the influenza virus
A computer-implemented method and a computer system for identifying a phylogenetic tree from a plurality of biological sequences is provided. Each biological sequence is associated with a sampling date. First, the plurality of biological sequences is aligned and a distance matrix is obtained. Then, a subset of these sequences without any duplicated sequences is selected and a directed graph representation of the subset of biological sequences is generated based the associated sampling dates. Then, a minimum spanning tree is computed from the weighted directed graph representation. Then, in an iterative procedure, the sequences of unsampled evolutionary intermediates are inferred from mutation patterns that reflect the difference in sequence between the nodes in the minimum spanning tree. The new sequences are added with associated time stamps to the sequence set. Then, sets of identical sequences are removed. Then, an optimum branching is recomputed. This step is repeated until no new intermediates are found. In the final step, the sequences that have been set aside in the initializing step are added to the plurality of sequences derived in the update step. From this plurality of sequences an optimum branching is computed and identified as the phylogenetic tree. Amino acid changes repeatedly occurring on the internal branches of the obtained tree can be used to identify sequences and associated viral isolates suitable as vaccine strains for the following influenza season.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
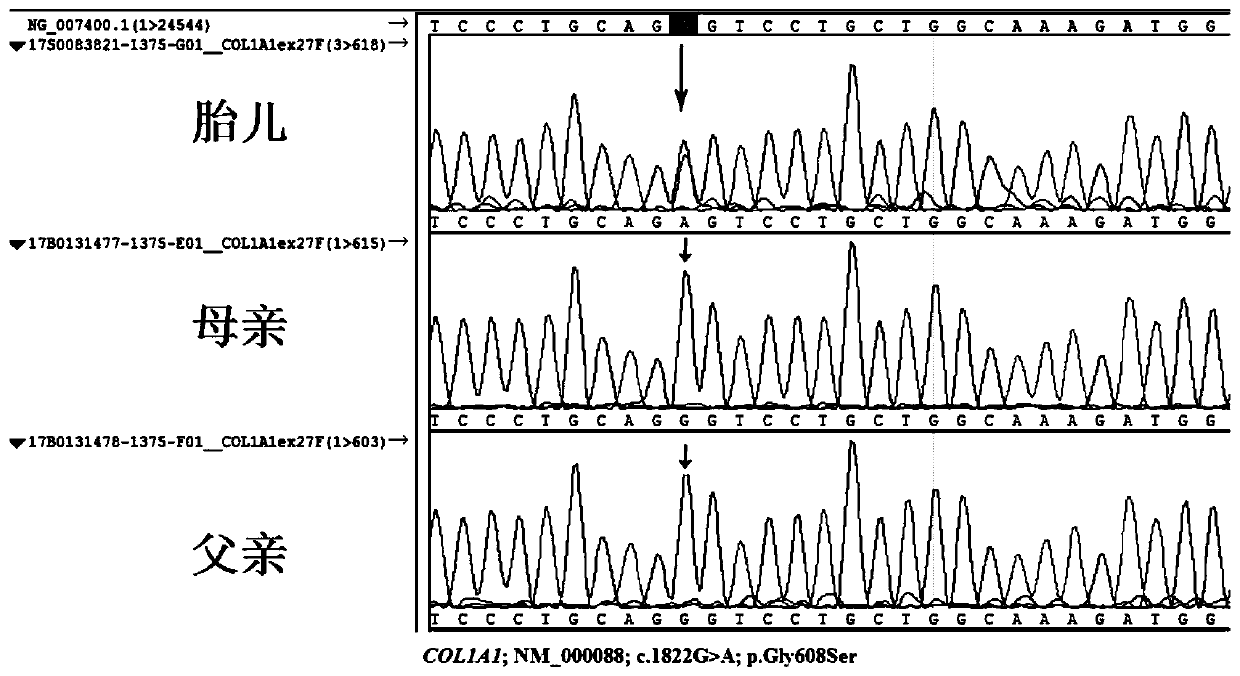
Pathogenic mutation of osteogenesis imperfecta disease and detection reagent of pathogenic mutation
ActiveCN109897894ASignificant genetic heterogeneityBirth preventionMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic engineeringCol1a1 geneAmino acid change
The invention discloses a pathogenic mutation of osteogenesis imperfecta and a detection reagent of the pathogenic mutation. According to a novel mutant COL1A1 gene, the mutated COL1A1 gene is a single point mutation c.1822G>A (chr17:48270211), a heterozygous mutation is pathogenic and in a mode of dominant heredity, the amino acid change is p.Gly608Ser, dyssynthesis of I-type collagen in connective tissue is caused by locus mutation of the p.Gly608Ser, and a lesion is formed. A kit for detection of osteogenesis imperfecta includes a reagent for detection of the 1822bpth locus of a COL1A1 geneCDS or a reagent for detection of the 608th amino acid locus of a COL1A1 protein. The pathogenic mutation (c.1822G>A on the COL1A1 gene) of the osteogenesis imperfecta disease is obtained, and the osteogenesis imperfecta disease can be diagnosed by detecting the mutation.
Owner:黄欢
Anti-pcsk9 antibodies with ph-dependent binding characteristics
The present invention provides antibodies and antigen-binding fragments thereof that specifically bind proprotein convertase subtilisin / kexin-9 (PCSK9) with greater affinity at neutral pH than at acidic pH. The antibodies of the invention may possess one or more amino acid changes as compared to antibodies that do not exhibit pH-dependent binding properties. For example, the present invention includes anti-PCSK9 antibodies which possess one or more histidine substitutions in one or more complementarity determining regions. The antibodies of the invention, with pH-dependent binding properties, remain in circulation and exhibit cholesterol lowering activity for prolonged periods of time in animal subjects as compared to anti-PCSK9 antibodies that do not exhibit pH-dependent binding properties. The antibodies of the invention are therefore useful for treating diseases and disorders related to elevated HDL cholesterol, wherein the antibodies of the invention can be administered to a patient at a lower dose and / or with less frequent dosing as compared to antibodies that do not exhibit pH-dependent binding properties.
Owner:REGENERON PHARM INC
Mutation penicillin ring enlargement enzyme and process preparing 7-ADCA using same
The present invention is mutant expandase with even higher activity to benzyl penicillin used for preparing phenylacetyl-7-aminodeacetoxy cephalosporanic acid (7-ADCA). The mutant expandase has one or several amino acid substitutes selected from M73T, S79E, V275I, L277K, C281Y, G300V, N304K, I305L and I305M.
Owner:骏翰生化股份有限公司
Anti-hbs monoclonal antibodies
ActiveCN1896102AImmunoglobulins against animals/humansBiological material analysisWild typeMonoclonal antibody
An anti-HBs monoclonal antibody is described herein. This antibody can bind to the following: a wild type HBsAg; at least one mutant HBsAg selected from the group consisting of a first mutant HBsAg and a second mutant HBsAg; and at least one mutant HBsAg selected from the group consisting of a third mutant HBsAg and a fourth mutant HBsAg. The first mutant HBsAg has a mutation at position 120. The second mutant HBsAg has a mutation at position 141. The third mutant HBsAg has a substitution to a lysine at position 118. The fourth mutant HBsAg has only one mutation at position 144 and an amino acid at the position 144 is substituted by a glutamic acid.
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
Transgenic animal model for catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (CPVT) and use thereof
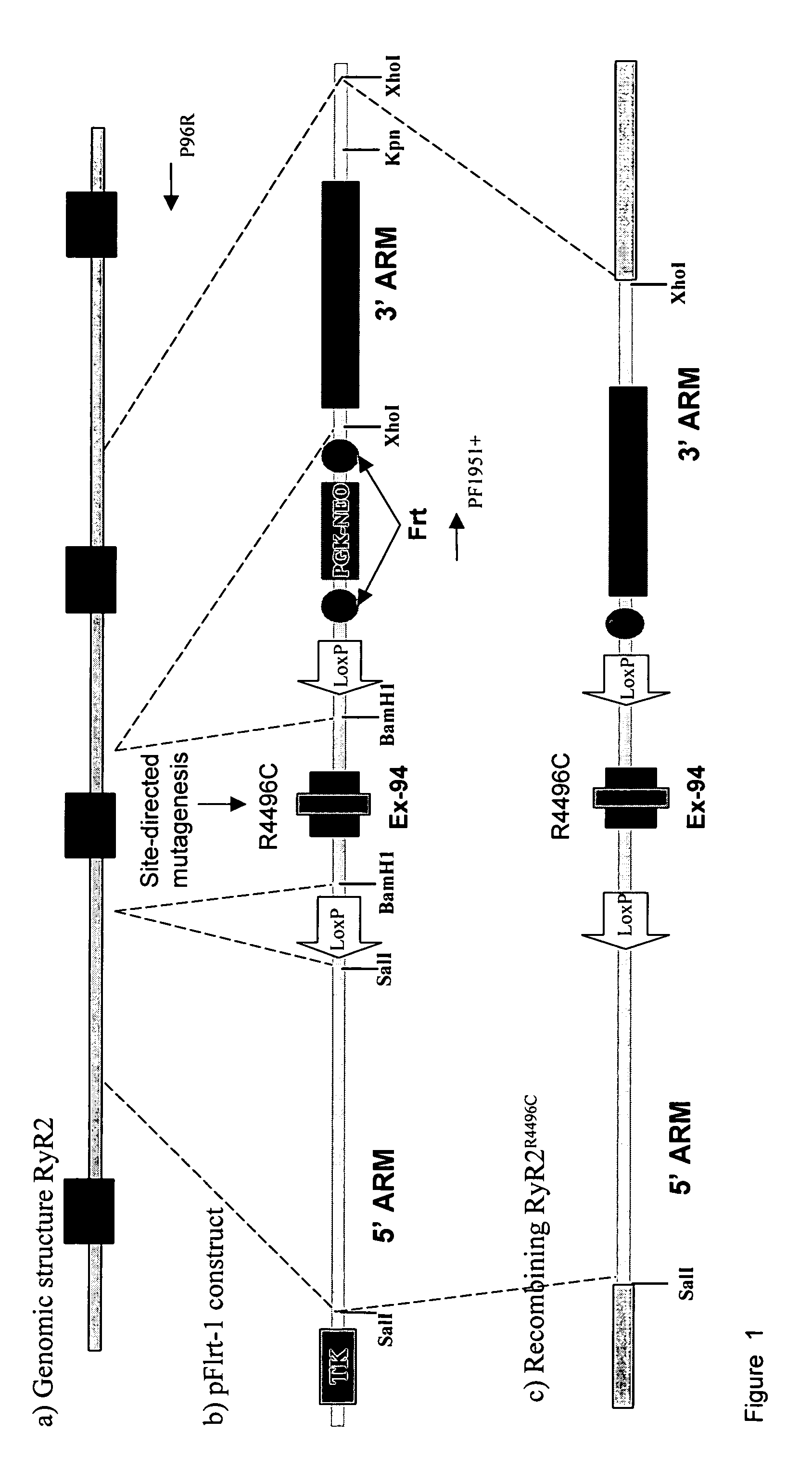
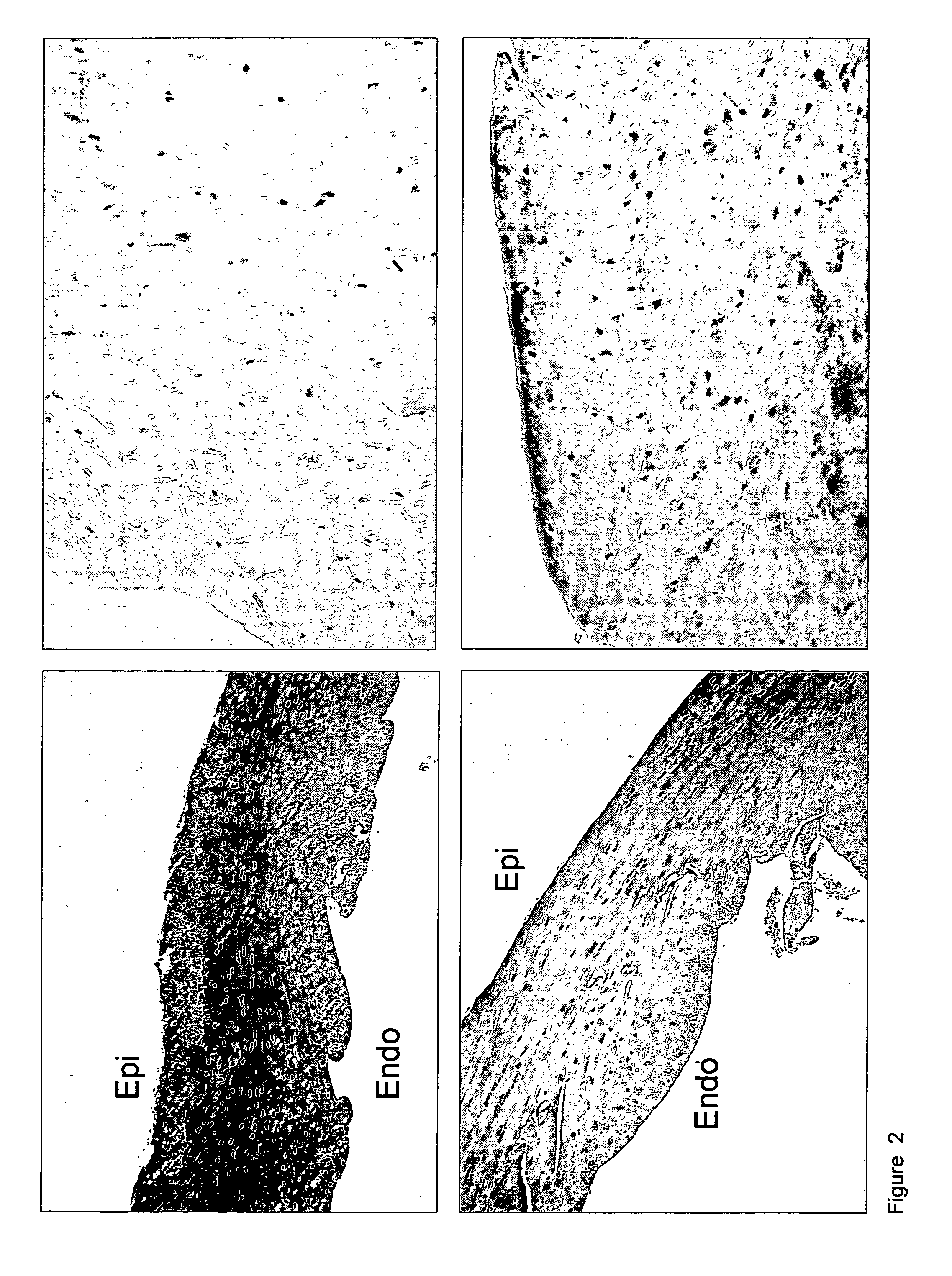
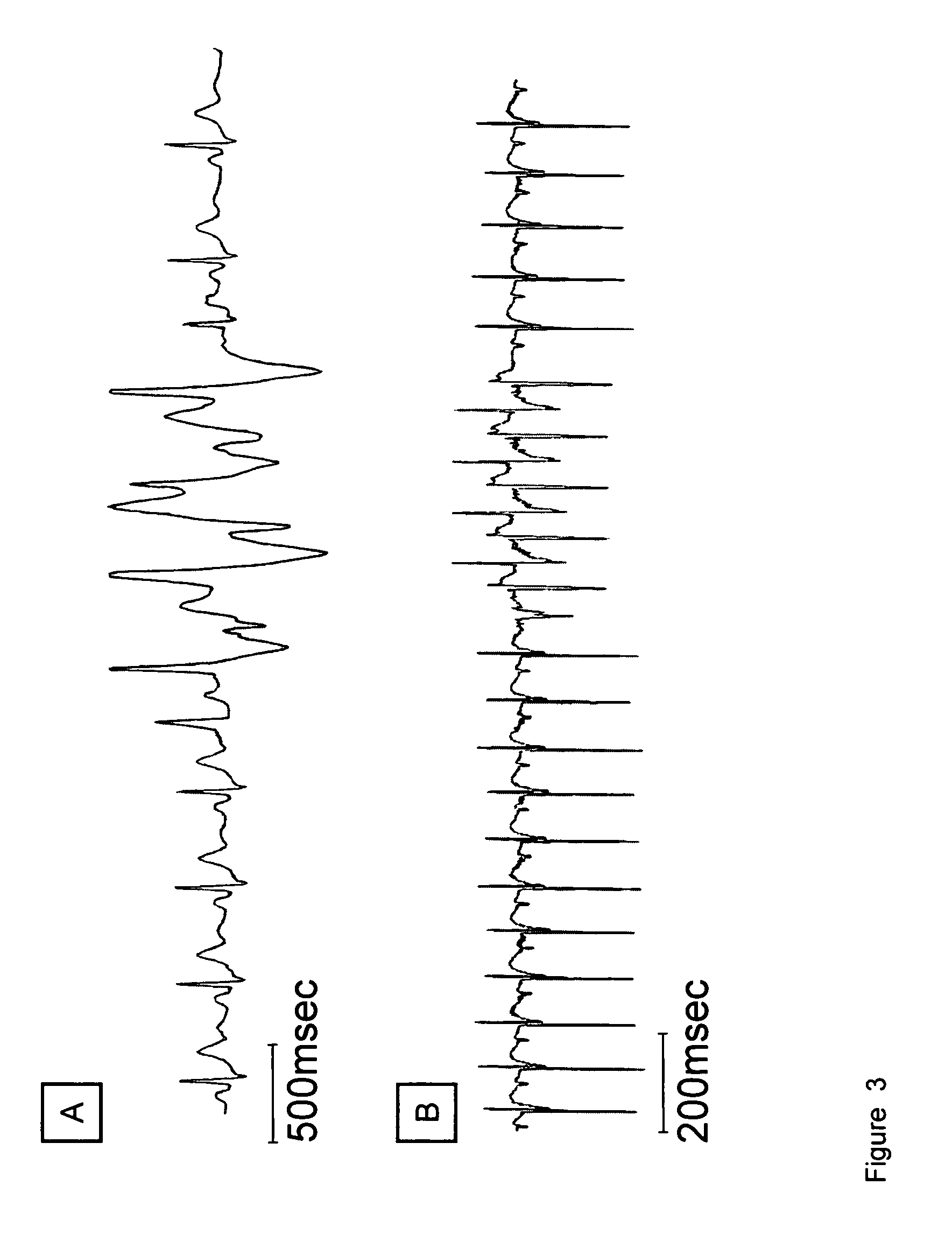
The present invention refers to non-human transgenic mammals, preferably rodents, or mice, which comprise a mutation in the gene encoding for the cardiac ryanodine receptor (RyR2).Transgenic animals carrying the amino acid change R4496C in the RyR2 protein show a phenotype similar to that of Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia (CPVT) (OMIM: 604772). Further provided are methods for using these animals as in vivo model of Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia and RyR2 dependent arrhythmias, in drug screening and for understanding the molecular basis of RyR2 dependent arrhythmias.
Owner:PRIORI SILVIA G +1
Application of obese receptor (OB) as goose fat character genetic marker
InactiveCN102911942ALess abdominal fatSignificant application valueMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationEconomic benefitsAmino acid change
The invention discloses an obese receptor (OB) gene and application thereof as a goose fat character genetic marker. Genetic markers in the OB gene relevant to goose abdominal fat weight and abdominal fat rate are determined, and the polymorphism in the OB gene in a nucleic acid sample obtained from a goose is determined and causes that the coded amino acid changes and is relevant to the abdominal fat weight and the abdominal fat rate. According to the single nucleotide polymorphism of the OB gene, animals containing the OB genes in a genome DNA are subjected to fatty breeding, and protogene types reducing the abdominal fat weight and abdominal fat rate of the goose are screened, thus the OB gene has important application value and economic benefit.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV +1
Cloning and application of major gene GS5 capable of controlling width and weight of rice grain
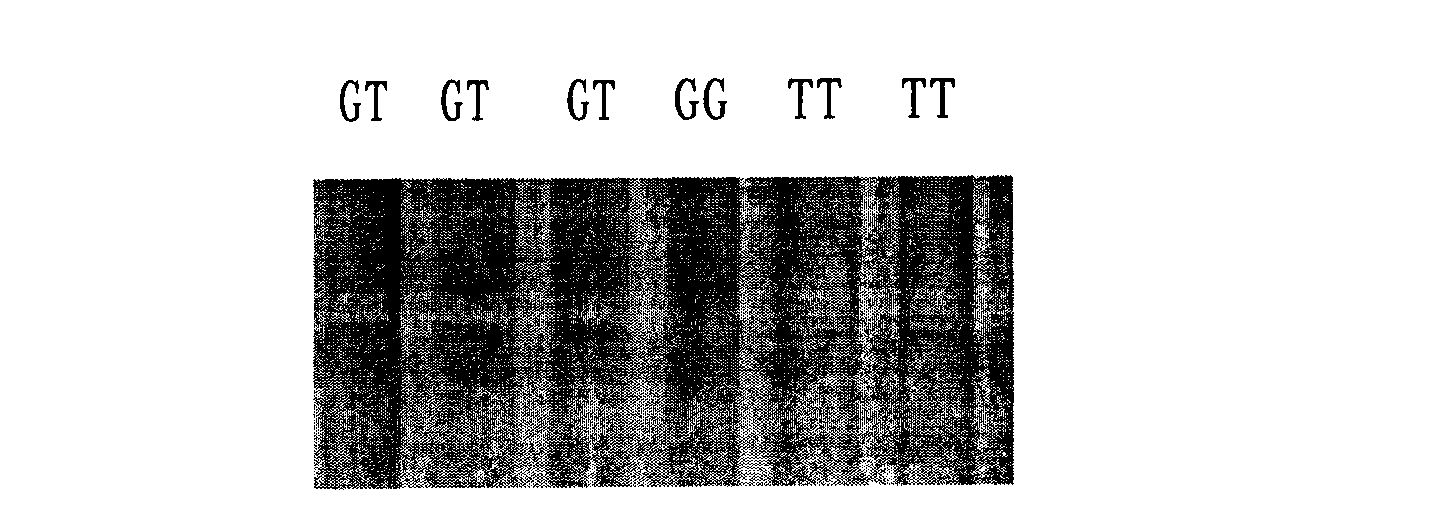
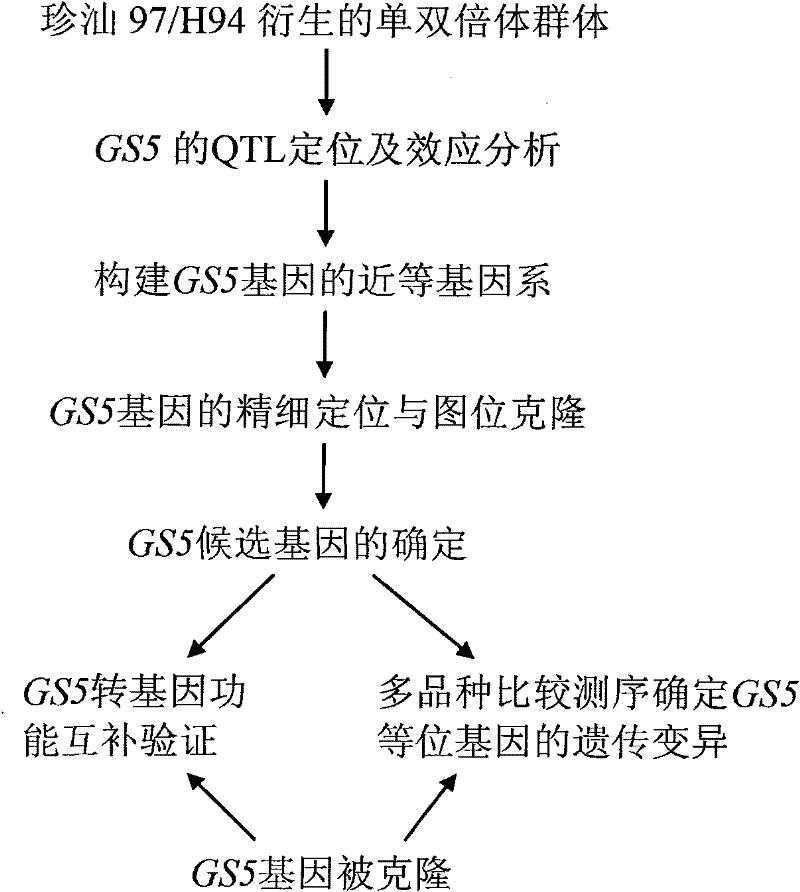
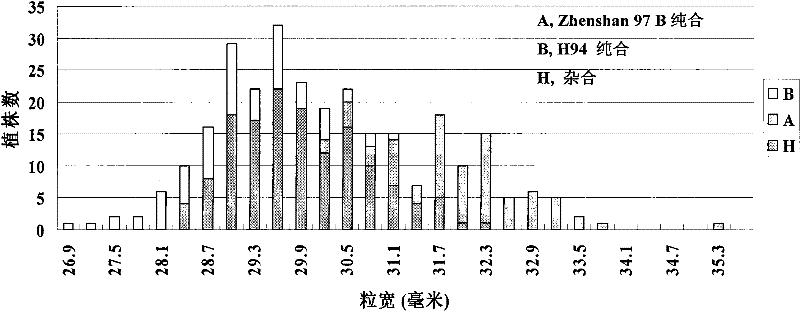
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant gene engineering, disclosing a separated and cloned major gene GS5 capable of controlling the width and the weight of a rice grain and the DNA sequence of the allelic gene of the major gene GS5. The DNA sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO.1 (Zhenshan 97B) and SEQ ID NO.3 (H94) and contains 10 exons. The amino acid sequence of the major gene and the amino acid sequence of the allelic gene are shown as SEQ ID NO.2 and SEQ ID NO.4. By using two large-grain rice varieties and two small-grain rice varieties for comparative sequencing, in an approximately 6.1kb range, 22 common base differences exist between the large-grain variety and the small-grain variety, wherein 18 mutations are in a promoter area, 4 mutations are in a code area and 5 aminoacids are caused to be changed. By using a transgenic technology, GS5 transgenic rice plants are obtained and express that the width and the weight of the rice grain are obviously improved when being compared with the control width and the control weight of the rice grain. The character changes are quite coincident with the two genotype expressions of a Zhenshan 97 near-isogenic line and a GS5 near-isogenic line. The invention additionally discloses a method of near-isogenic line breeding, gene cloning and gene transfer and application thereof.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
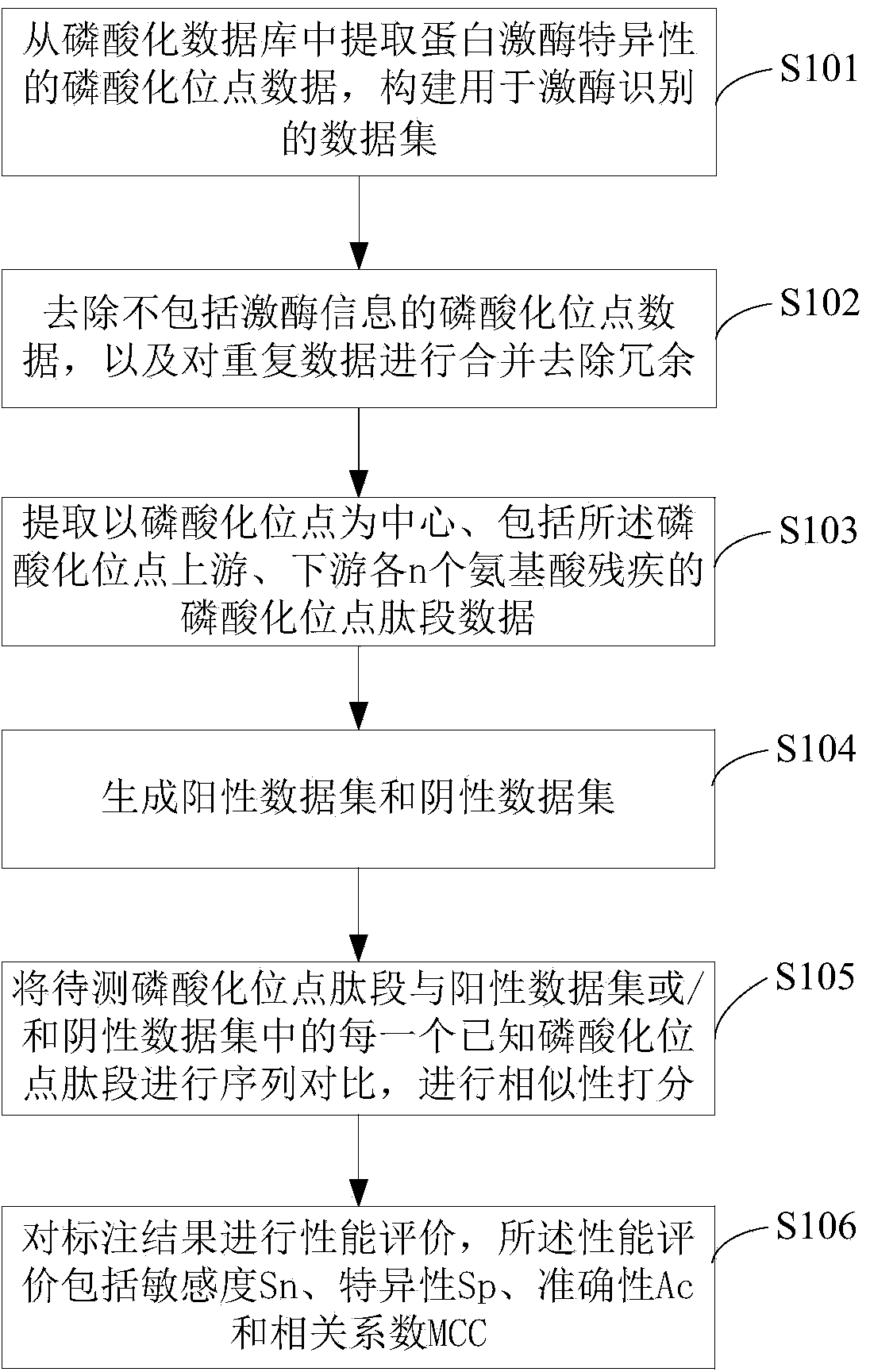
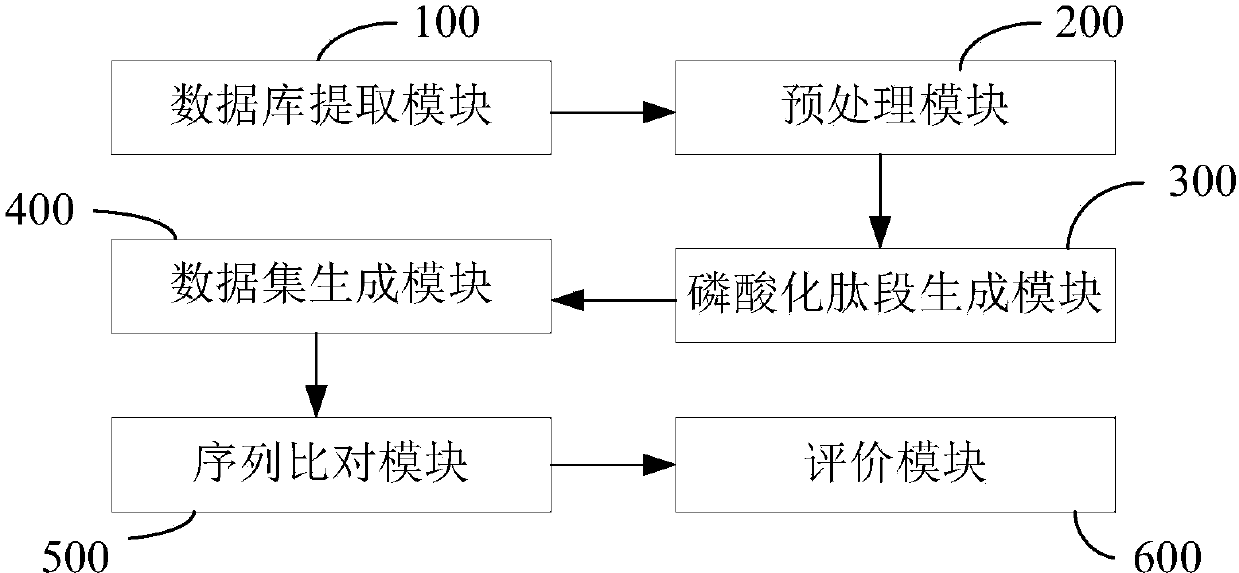
Protein kinase specificity prediction method and device based on nearest neighbor algorithm
InactiveCN103745135AImprove accuracyHigh sensitivitySpecial data processing applicationsNear neighborTrue positive rate
The invention relates to the technical field of protein modification site identification, in particular to a protein kinase specificity prediction method and device based on a nearest neighbor algorithm. According to the prediction method, amino acid information on the upstream and the downstream of a phosphorylation site is fully utilized, and the accuracy of prediction is increased. According to the protein kinase specificity prediction method, an amino acid permutation matrix is used for scoring the similarity of a phosphorylation site peptide fragment to be detected and a known phosphorylation site peptide fragment, the phosphorylation site peptide fragment to be detected is marked to be the highest scored known phosphorylation site peptide fragment, and the sensitivity and the specificity of prediction are improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com