Fertilisation independent fruit formation in tomato
a fertilisation independent, tomato technology, applied in the field of plants and plant parts, can solve the problems of fragmentary knowledge of physiological and molecular events which play a role in the initial steps of fruit formation, poor fruit set, yield loss, etc., and achieve the effect of improving fertilisation independent fruit formation without negative pleiotropic effects on the growth and development of the plan
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0094]Genetic Modification of Tomato by Ethyl Methane Sulfonate (ems)
[0095]Seeds of the tomato breeding line TR306 were treated with ems by submergence of approximately 10,000 seeds into an aerated solution of 0.5% (w / v) ems during 24 hours at room temperature.
[0096]The treated seeds were germinated and the resulting plants were grown in a greenhouse to produce M2 seeds.
[0097]After maturation, M2 seeds were harvested and bulked in one pool. The resulting pool of M2 seeds was used as starting material to identify the individual M2 plants containing fertilisation independent fruit formation.
[0098]The efficacy of the genetic modification procedure was assessed by determining the occurrence of bleached plants, which is indicative for chlorophyll loss due to modifications in genes directly or indirectly involved in the formation or accumulation of chlorophyll.
example 2
[0099]Identification of Tomato Plants which have Obtained the Trait of Fertilisation Independent Fruit Formation
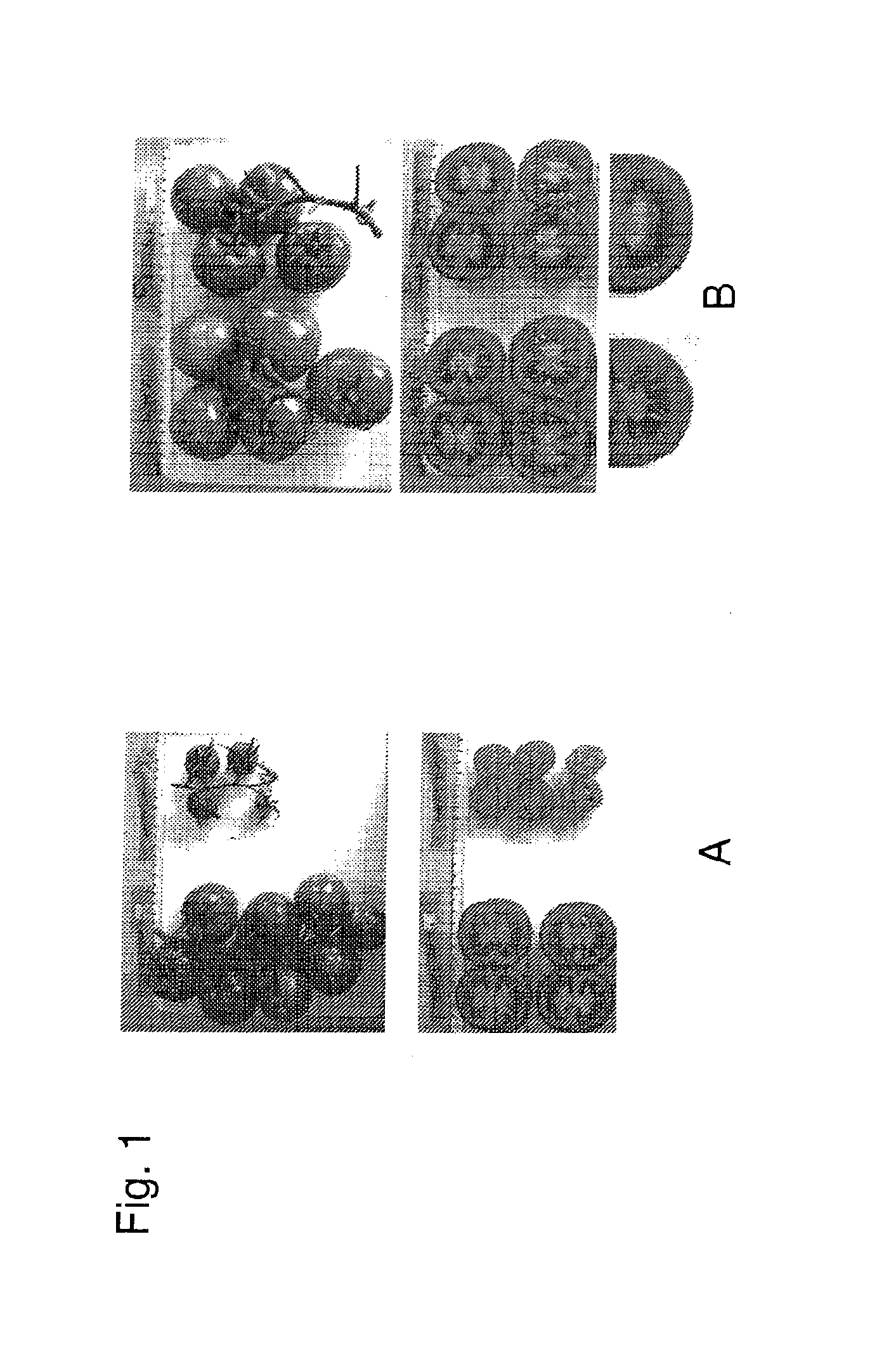
[0100]M2 tomato seeds were germinated in soil and grown to small plantlets. Subsequently, approximately 7000 randomly chosen plants were transferred to a greenhouse in which they were raised according to common tomato cultivation practice. After the first two trusses of each plant have set fruit, all flowers of the third truss were emasculated by hand in order to prevent pollination. The plants were monitored on a regular basis in order to determine which mutants show fertilisation independent fruit formation. The first criterion was the formation of a fruit of a size similar to a normal seeded fruit growing on the same plant as a consequence of pollination and fertilisation. As a second criterion, the fruits were selected which contained no seeds and which were normally filled with jelly. On the basis of these criteria 3 parthenocarpic mutants numbered 3475, 5364 and 5879...
example 3
[0101]Confirmation of the Fertilisation Independent Fruit Formation in Progeny
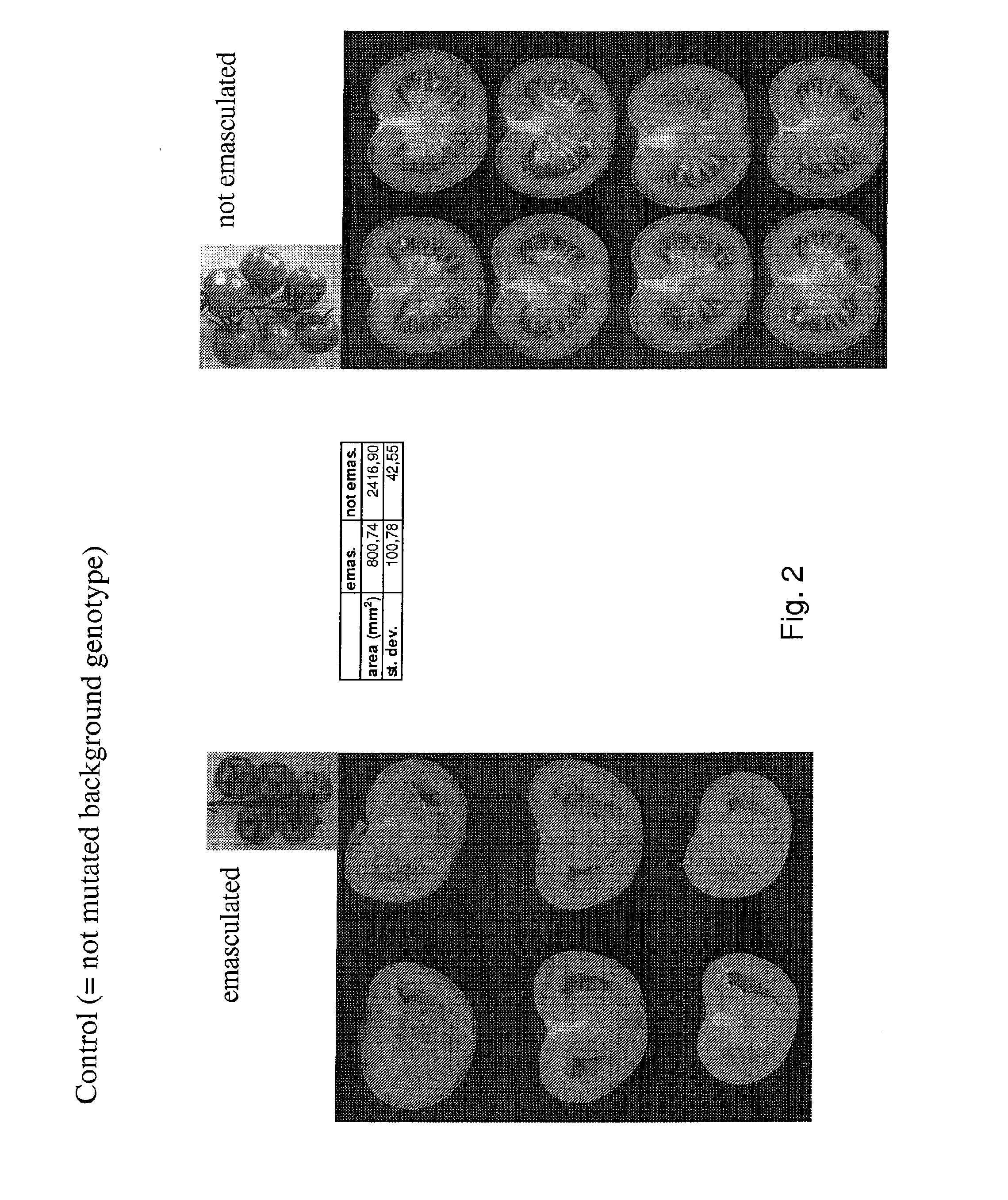
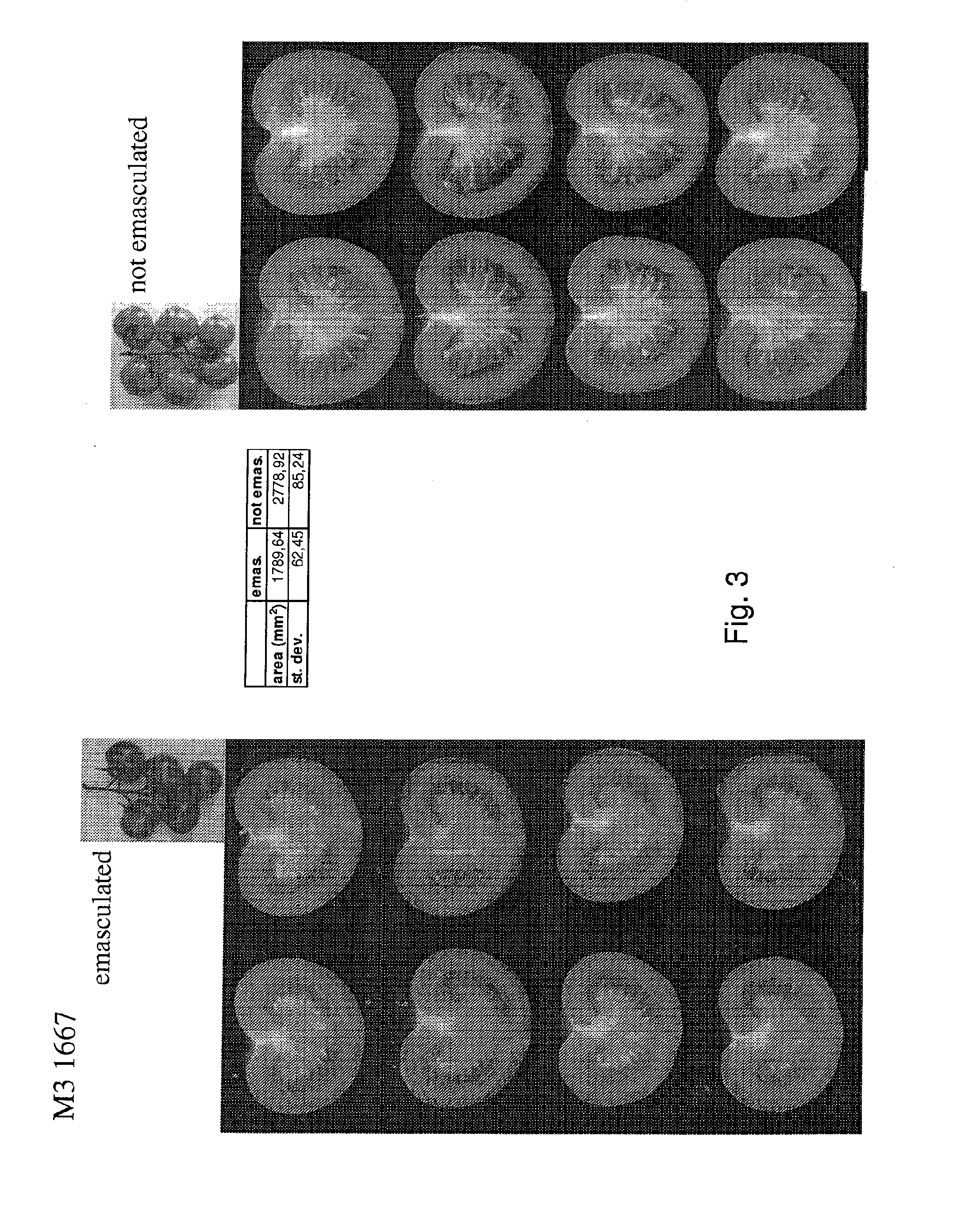
[0102]M3 seeds were produced through self pollination of selected parthenocarpic mutants numbered 1667, 2019, 3475, 5364, 5879 and 6162. A total of 7 or 12 plants per M3 population were grown in the greenhouse according to common tomato cultivation practice. As a negative control progeny of M2 plants which were not showing parthenocarpic fruit formation was included in this experiment (FIG. 2). On each plant the flowers of the third truss were emasculated by hand and fruit formation was monitored. It was observed that for each plant of the M3 population derived from mutants 1667 (FIG. 3), 2019 (FIG. 4), 3475 (FIG. 5), 5364 (FIG. 7), 5879 (FIG. 9) and 6162 (FIG. 11) the emasculated truss showed parthenocarpic fruit formation, i.e. the fruits showed a normal size, contained no seeds, were normally filled with jelly and showed a normal ripening. This shows that the parthenocarpic trait identified by the metho...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com