Patents
Literature
102 results about "CD31" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
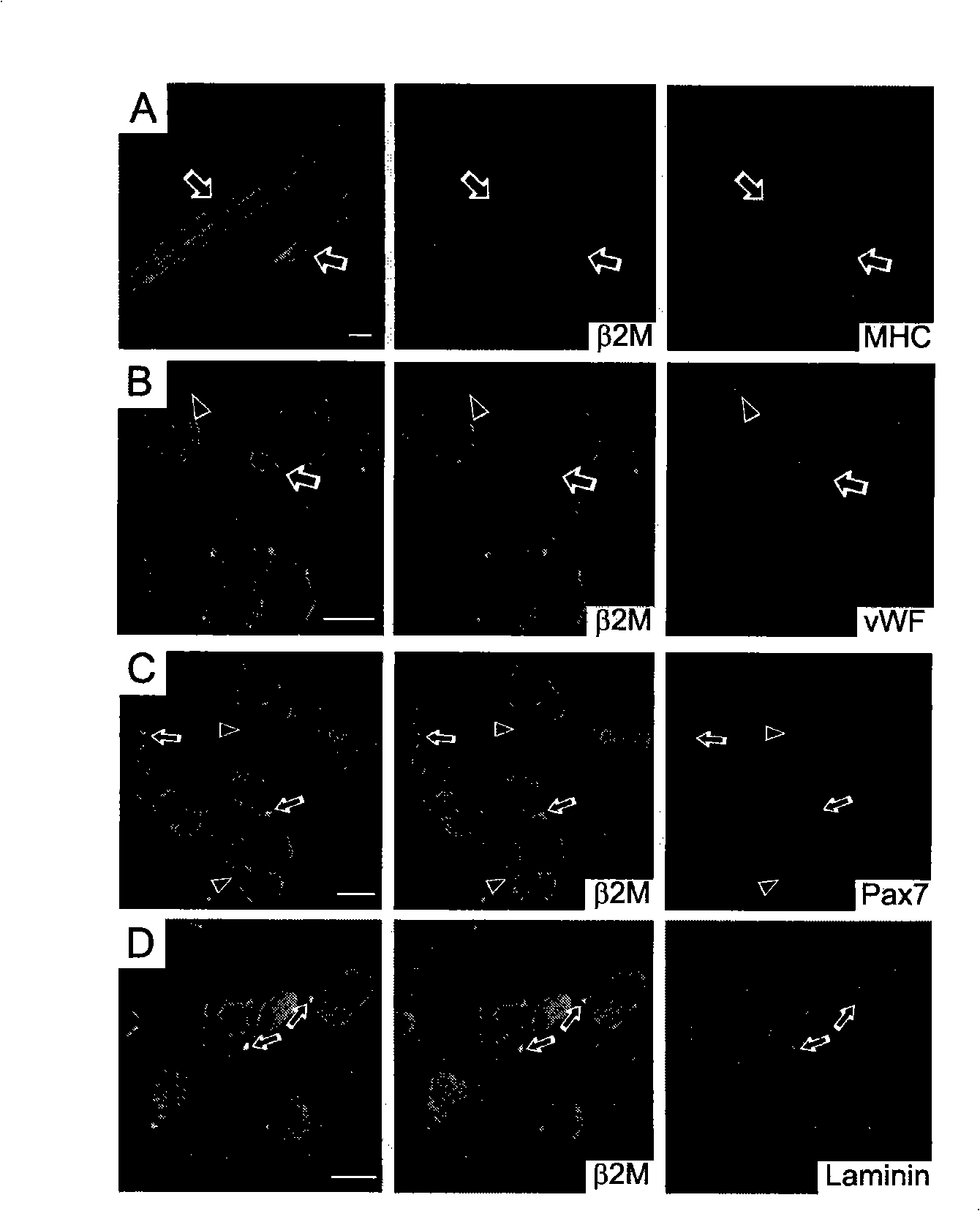
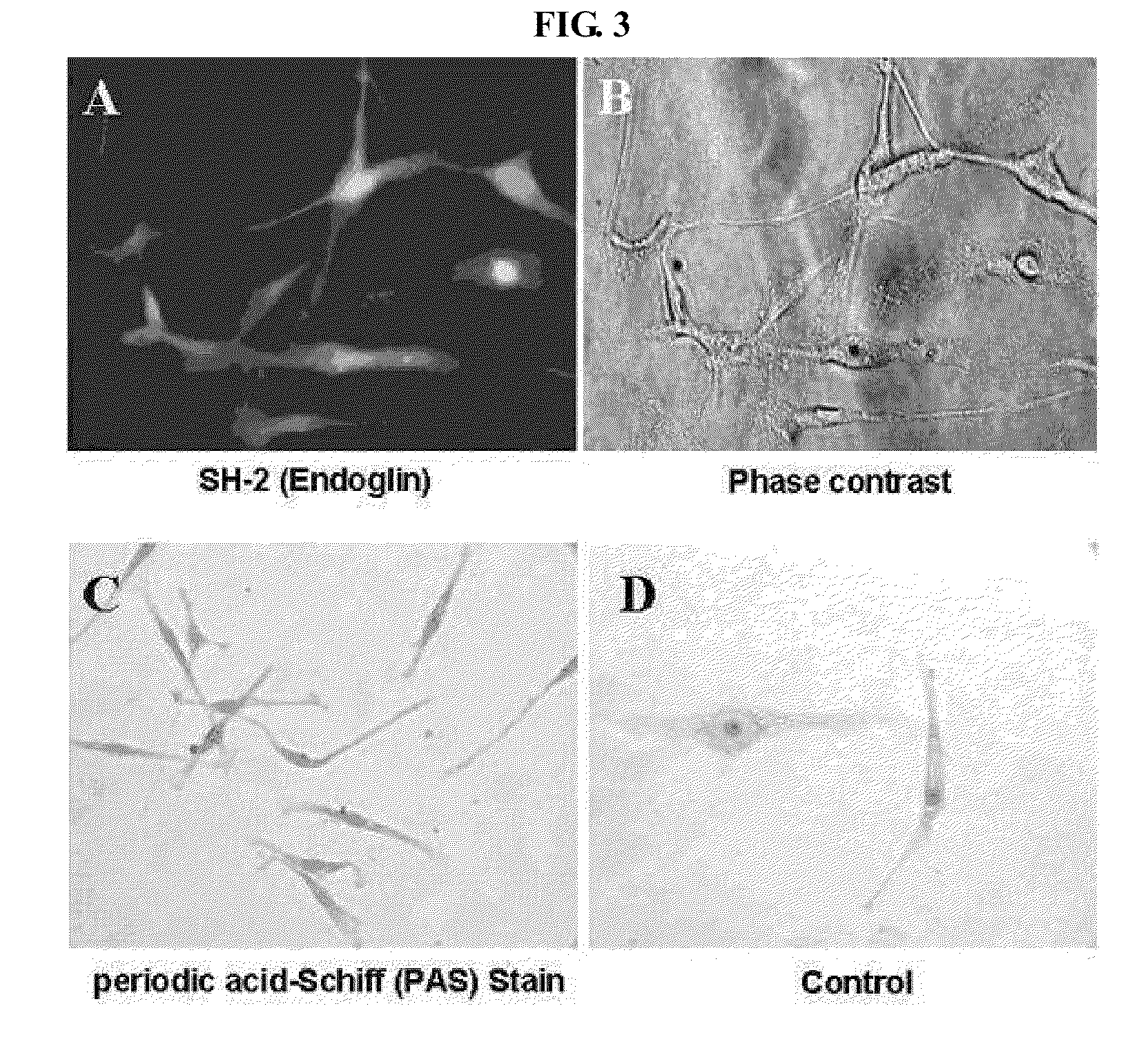
Platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule (PECAM-1) also known as cluster of differentiation 31 (CD31) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PECAM1 gene found on chromosome 17. PECAM-1 plays a key role in removing aged neutrophils from the body.
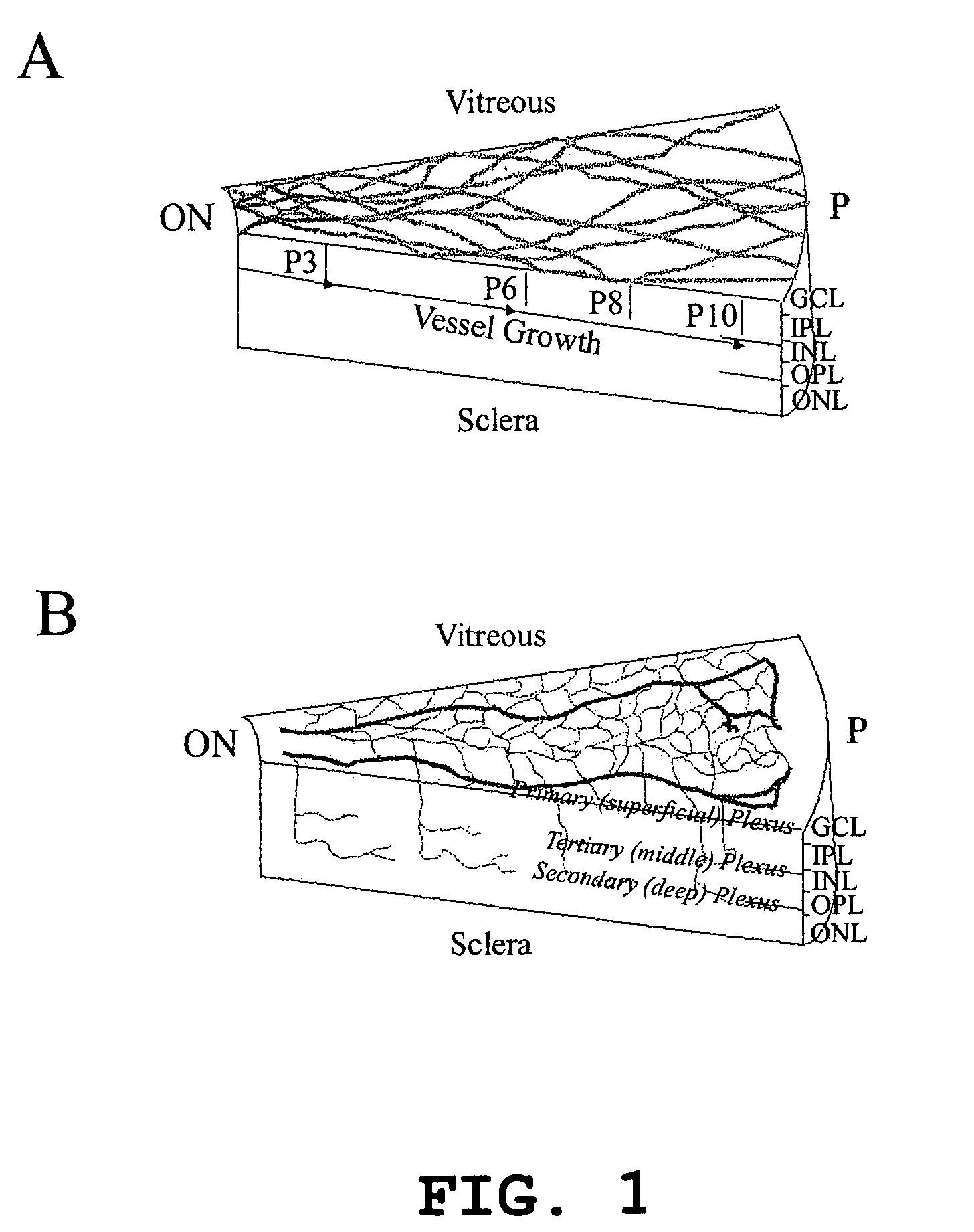
Hematopoietic stem cells and methods of treatment of neovascular eye diseases therewith
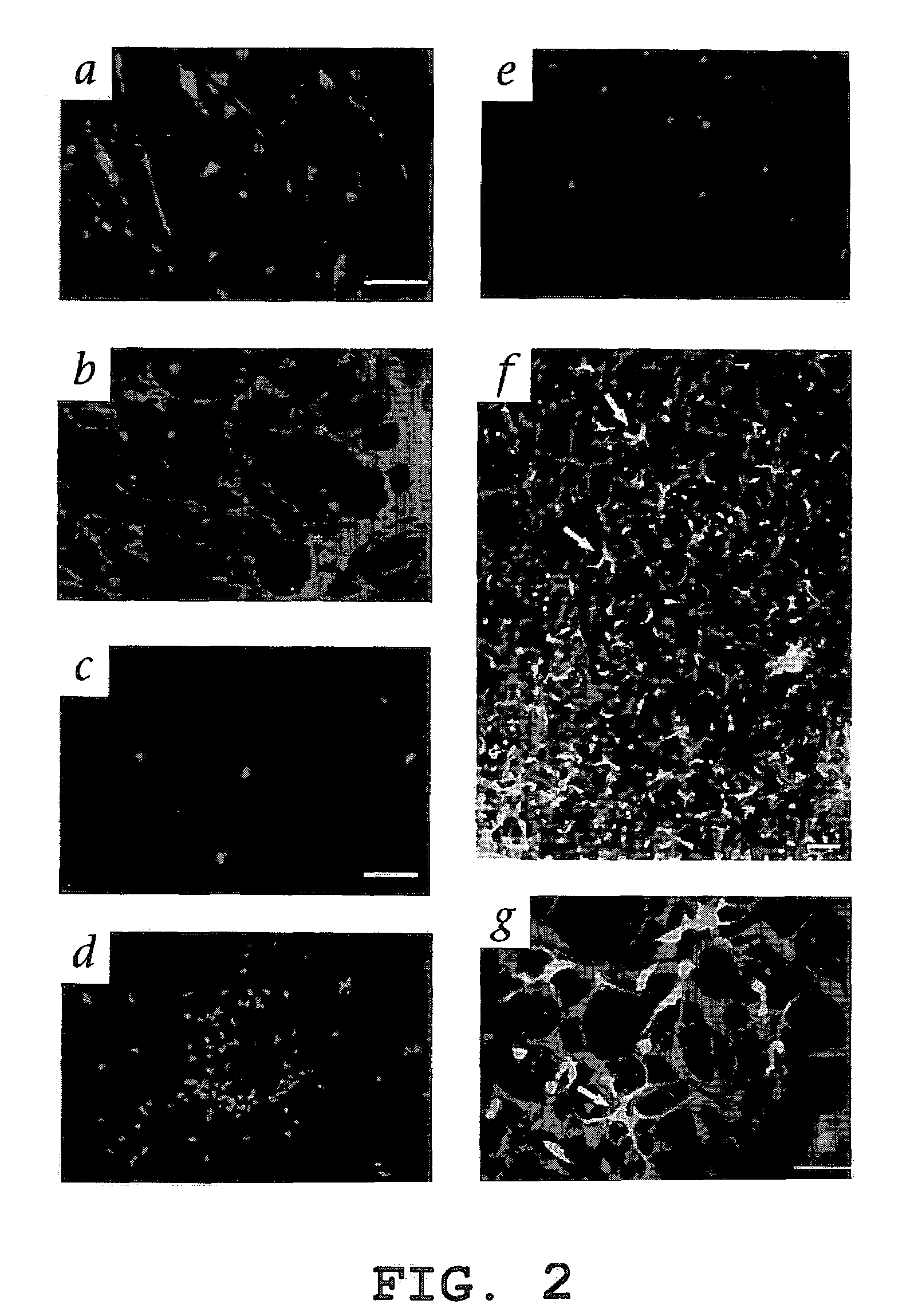
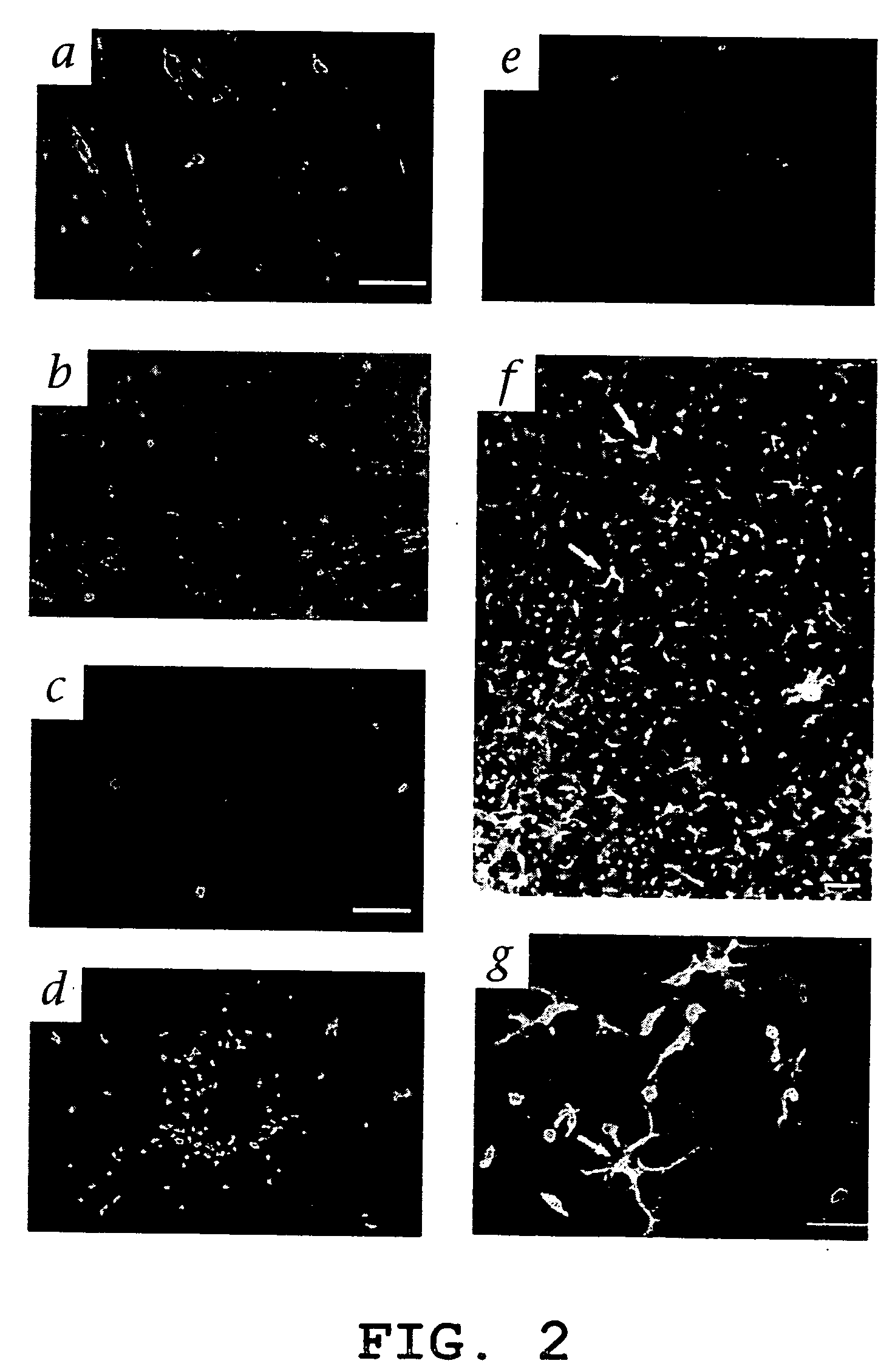
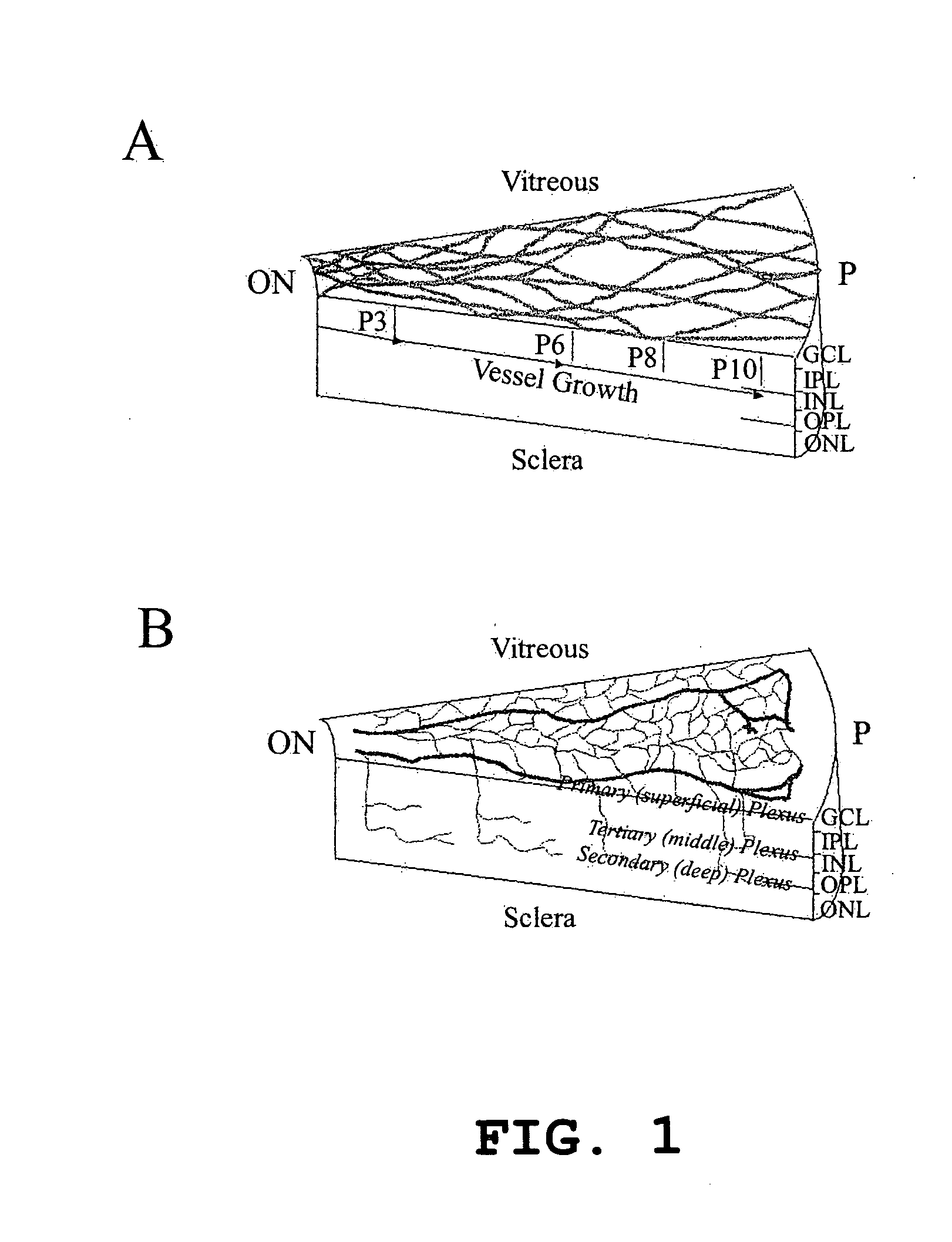
InactiveUS20050063961A1Stably incorporated into neovasculature of the eyePromote repairBiocideSenses disorderDiseaseProgenitor
Isolated, mammalian, adult bone marrow-derived, lineage negative hematopoietic stem cell populations (Lin− HSCs) contain endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) capable of rescuing retinal blood vessels and neuronal networks in the eye. Preferably at least about 20% of the cells in the isolated Lin− HSCs express the cell surface antigen CD31. The isolated Lin− HSC populations are useful for treatment of ocular vascular diseases. In a preferred embodiment, the Lin− HSCs are isolated by extracting bone marrow from an adult mammal; separating a plurality of monocytes from the bone marrow; labeling the monocytes with biotin-conjugated lineage panel antibodies to one or more lineage surface antigens; removing of monocytes that are positive for the lineage surface antigens from the plurality of monocytes, and recovering a Lin− HSC population containing EPCs. Isolated Lin− HSCs that have been transfected with therapeutically useful genes are also provided, and are useful for delivering genes to the eye for cell-based gene therapy. Methods of preparing isolated stem cell populations of the invention, and methods of treating ocular diseases and injury are also described.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Isolation of pericytes
In one embodiment, the invention provides a pericyte having a marker pattern comprising CD146+, CD34−, and CD45−, wherein said pericyte is substantially isolated from cells that are CD146− or CD31+ or CD34+ or CD45+ or CD56+ or NG2− or CD133−. The invention also provides populations of such pericytes. In another embodiment, the invention provides a method for isolating a pericyte. In another embodiment, the invention provides a method for modeling tissue in vivo.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Multipotent stem cells derived from placenta tissue and cellular therapeutic agents comprising the same
InactiveUS20070243172A1Negative immunological responseBiocideArtificial cell constructsGerm layerDisease
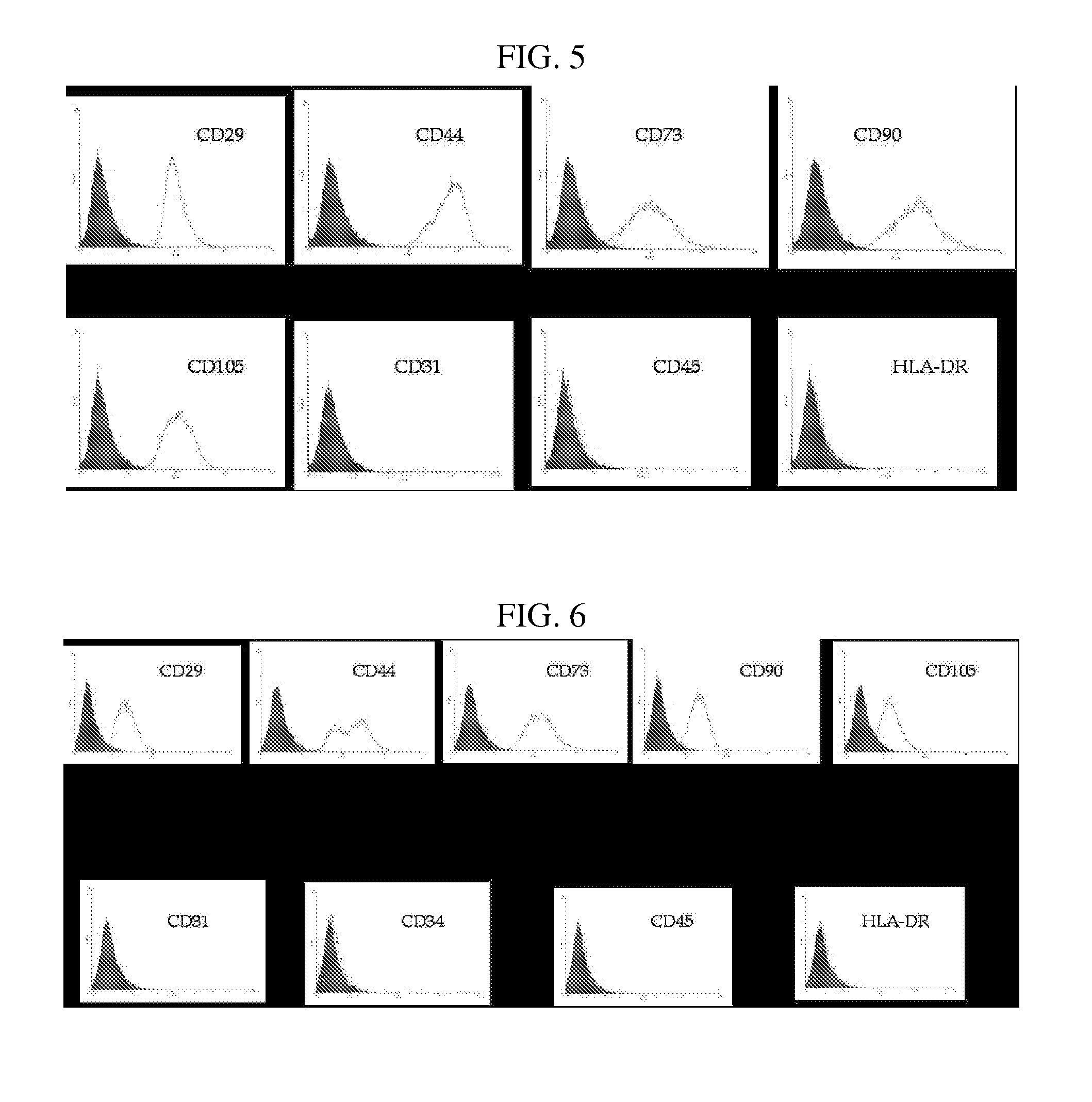
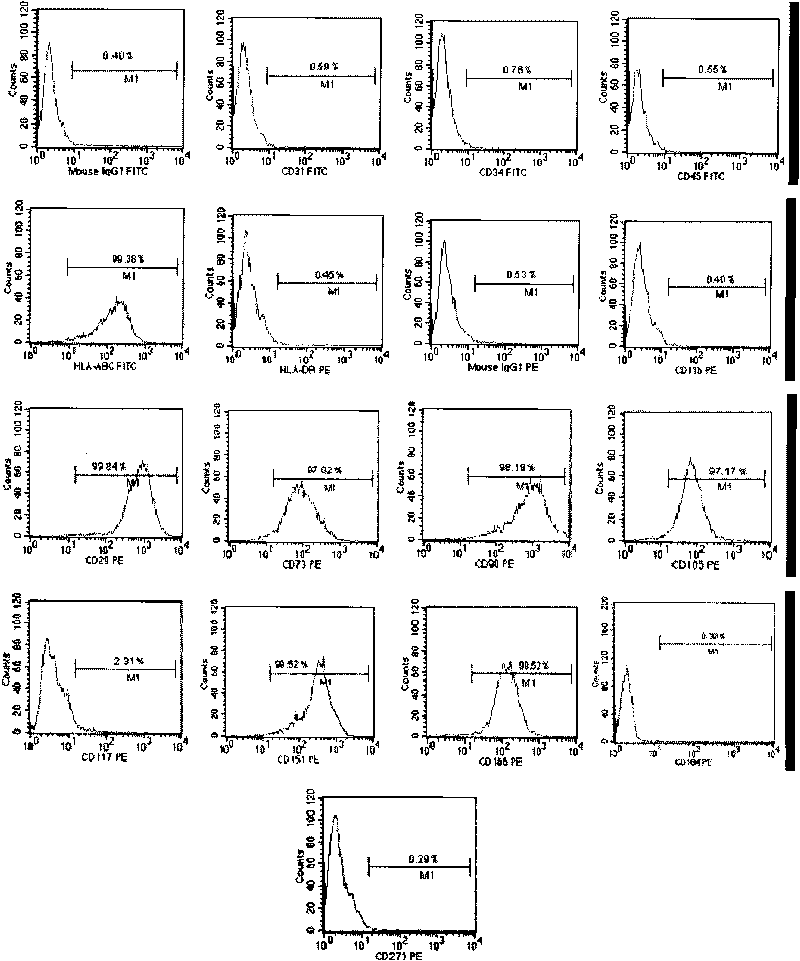
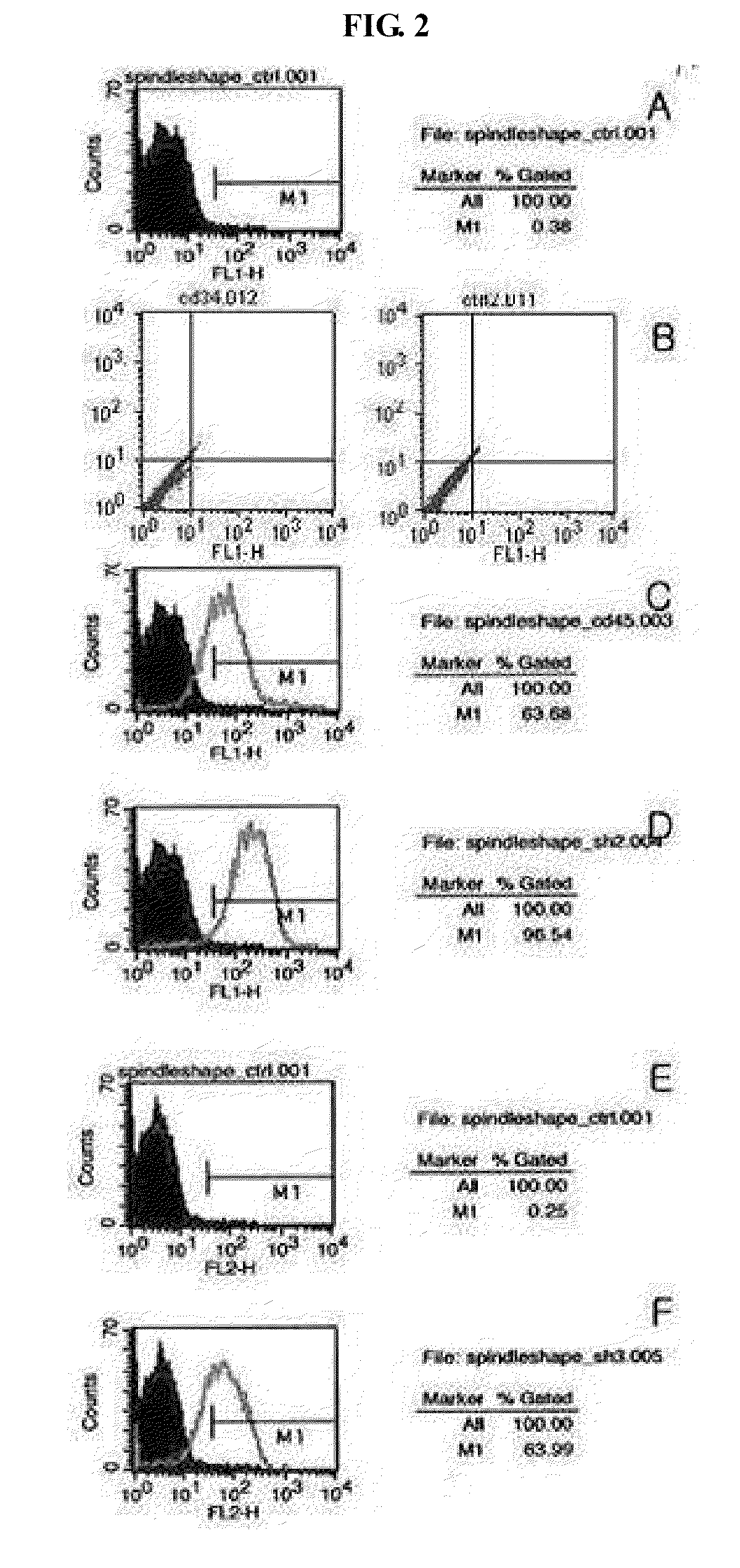
The present invention relates to placenta tissue-derived multipotent stem cells and cell therapeutic agents containing the same. More specifically, to a method for producing placenta stem cells having the following characteristics, the method comprising culturing amnion, chorion, decidua or placenta tissue in a medium containing collagenase and bFGF and collecting the cultured cells: (a) showing a positive immunological response to CD29, CD44, CD73, CD90 and CD105, and showing a negative immunological response to CD31, CD34, CD45 and HLA-DR; (b) showing a positive immunological response to Oct4 and SSEA4; (c) growing attached to plastic, showing a round-shaped or spindle-shaped morphology, and forming spheres in an SFM medium so as to be able to be maintained in an undifferentiated state for a long period of time; and (d) having the ability to differentiate into mesoderm-, endoderm- and ectoderm-derived cells. Also the present invention relates to placenta stem cells obtained using the production method. The inventive multipotent stem cells have the ability to differentiate into muscle cells, vascular endothelial cells, osteogenic cells, nerve cells, satellite cells, fat cells, cartilage-forming cells, osteogenic cells, or insuline-secreting pancreatic β-cells, and thus are effective for the treatment of muscular diseases, osteoporosis, osteoarthritis, nervous diseases, diabetes and the like, and are useful for the formation of breast tissue.
Owner:RNL BIO
Identification and Isolation of Multipotent Cells From Non-Osteochondral Mesenchymal Tissue
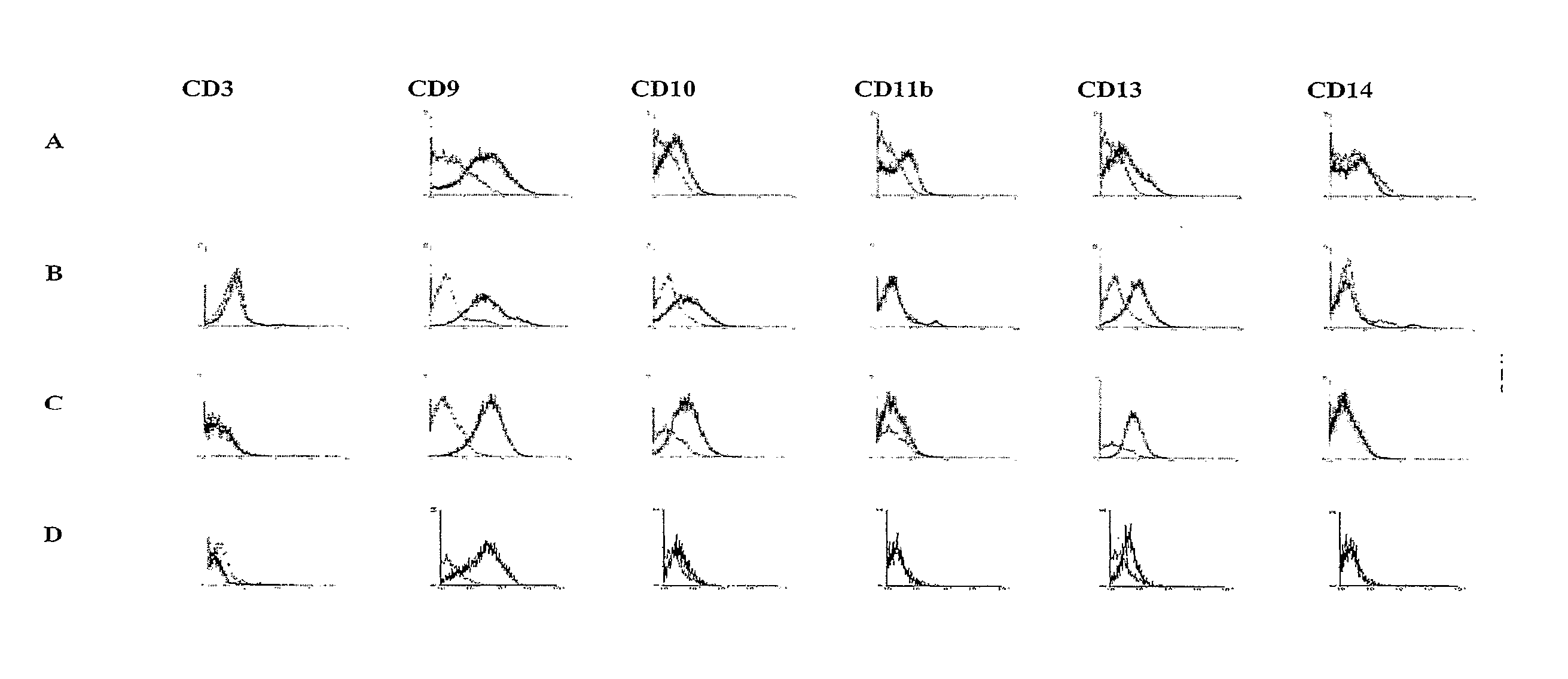
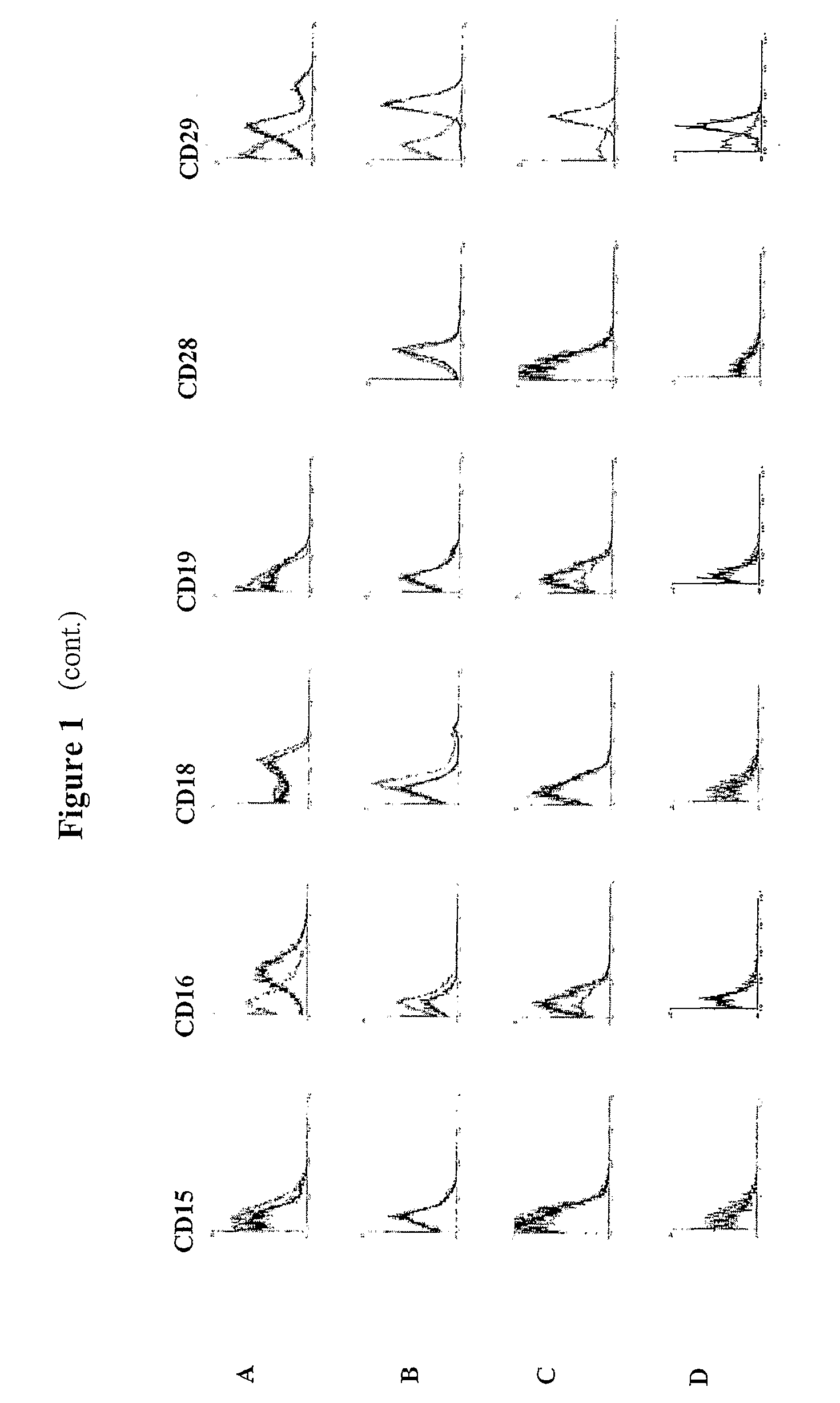
Identification and isolation of multipotent cells from non-osteochondral mesenchymal tissue. This invention relates to the identification and isolation of multipotent cells from non-osteochondral mesenchymal tissue. Specifically, it relates to an adult multipotent cell or a cell population or composition comprising said cell, isolated from non-osteochondral mesenchymal tissue, characterized in that it is positive for the following markers: CD9, CD10, CD13, CD29, CD44, CD49A, CD51, CD54, CD55, CD58, CD59, CD90 and CD105 and because it lacks expression of the following markers: CD11b, CD14, CD15, CD16, CD31, CD34, CD45, CD49f, CD102, CD104, CD106 and CD133.
Owner:AUTONOMOUS UNIVERSITY OF MADRID +1
Hemangioblast progenitor cells
InactiveUS20040052771A1Reduce bleedingAvoid adjustmentBiocideArtificial cell constructsP-selectinProgenitor
The invention relates to isolated hemangioblast cells. Hematopoietic and endothelial cells are postulated to be derived from a common progenitor, hemangioblast. While hemangioblast has been isolated retrospectively during embryonic stem cell differentiation, it has not been isolated from embryos or from bone marrow. Prospectively stable clonal cell lines have been isolated from mammalian embryos, from embryonic stem cells and from mammalian bone marrow that can differentiate in vitro into tubular structures with both endothelial and hematopoietic markers such as CD34, CD31, Flk-1, TIE2, P-selectin, Sca-1, thy-1, CD45, and smooth muscle actin. Gene expression profiles in the undifferentiated and differentiated cells were consistent with endothelial and hematopoietic differentiation potential. Transplantation studies in isogenic or immunodeficient mice demonstrated that these cells were not tumorigenic. In an appropriate microenvironment, the cells incorporate into the vasculature and participate in hematopoiesis.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE +1
N2S2 chelate-targeting ligand conjugates
ActiveUS20050129619A1Sufficient amountHybrid immunoglobulinsRadioactive preparation carriersAngiostatinAbnormal tissue growth
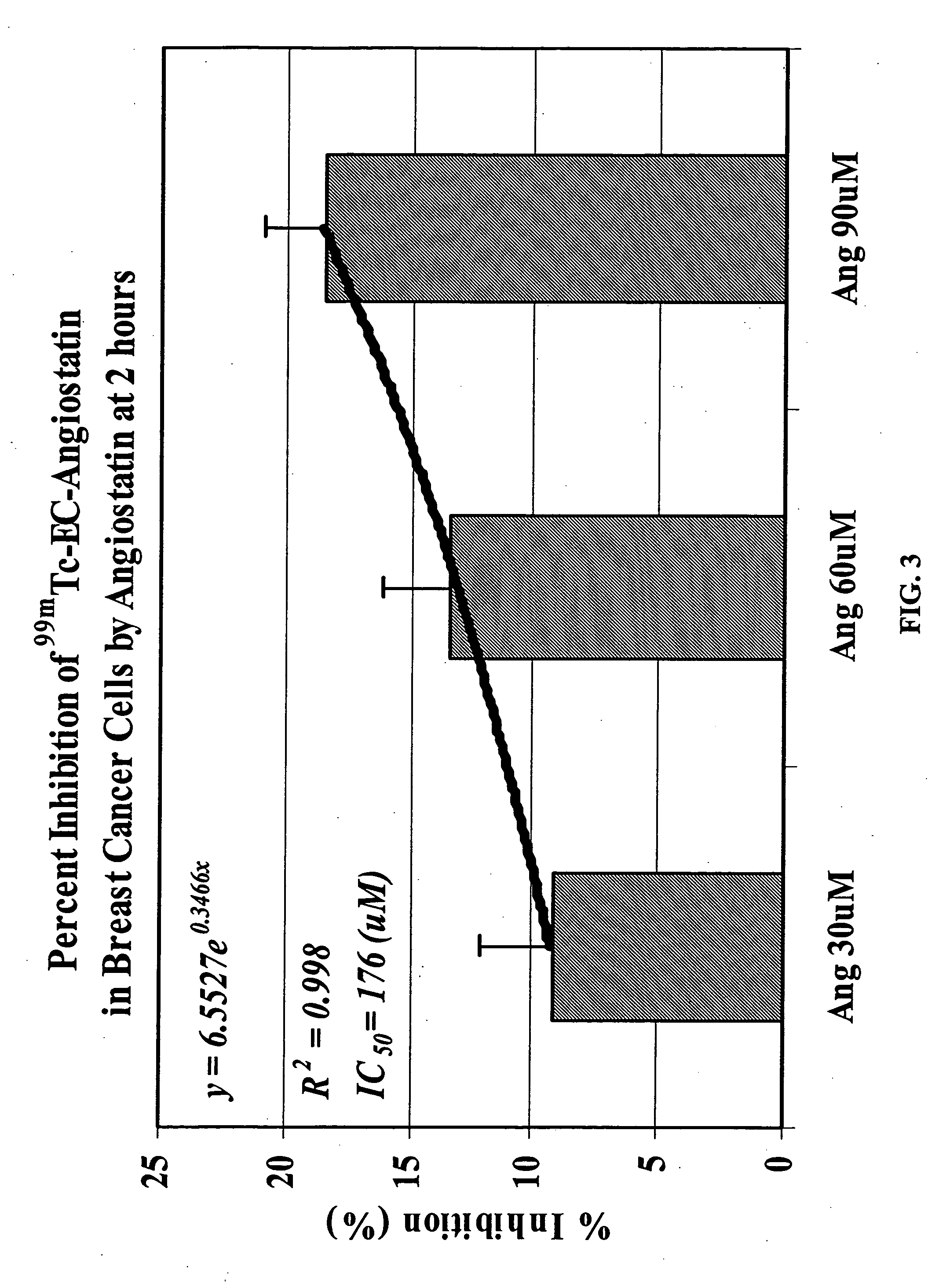
The invention provides, in a general sense, a new labeling strategy employing compounds that are are N2S2 chelates conjugated to a targeting ligand, wherein the targeting ligand is a disease cell cycle targeting compound, a tumor angiogenesis targeting ligand, a tumor apoptosis targeting ligand, a disease receptor targeting ligand, amifostine, angiostatin, monoclonal antibody C225, monoclonal antibody CD31, monoclonal antibody CD40, capecitabine, a COX-2 inhibitor, deoxycytidine, fullerene, herceptin, human serum albumin, lactose, leuteinizing hormone, pyridoxal, quinazoline, thalidomide, transferrin, or trimethyl lysine. The present invention also pertains to kits employing the compounds of interest, and methods of assessing the pharmacology of an agent of interest using the present compounds.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Root canal filler and dental tissue regeneration method
ActiveUS20110020310A1Improve regenerative abilityIncrease differentiationBiocideDigestive systemPulpectomyCell-Extracellular Matrix
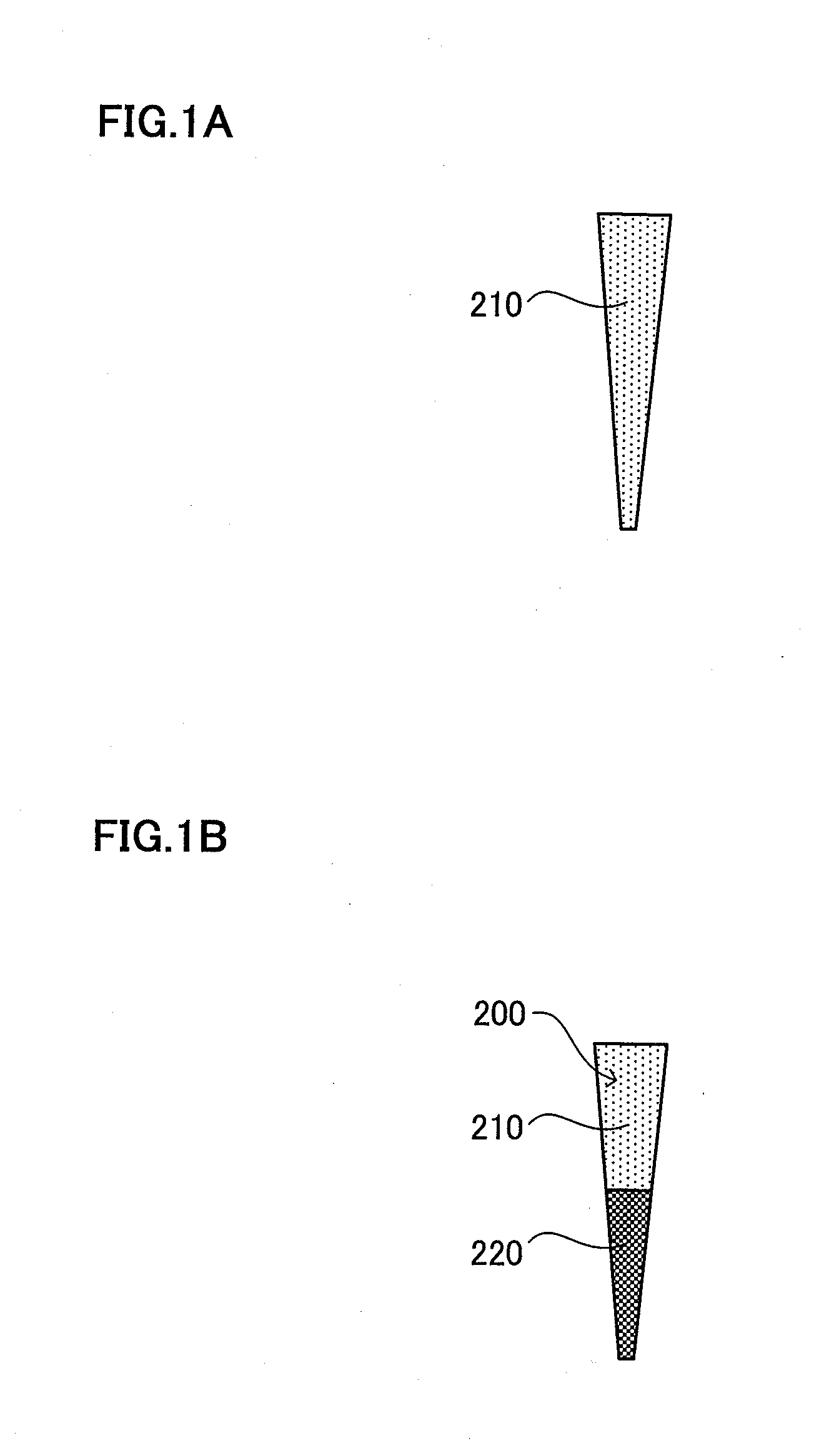
Provided is a novel and creative dental tissue regeneration method for regenerating dental tissue after pulpectomy or the enlargement and cleaning of an infected root canal. After pulpectomy or the enlargement and cleaning of an infected root canal, a root canal filler (200) having an extracellular matrix (210) containing the cells (220) enriched for dental pulp stem cells, is inserted into the apical side of the root canal of a target tooth (100). The cells including dental pulp stem cells include at least one of the following: dental pulp SP cells, CD31-negative and CD146-negative cells, CD24-positive cells, CD105-positive cells, and CD150-positive cells. For instance, dental pulp SP cells are CD31− and CD146− negative. Even if pulpitis due to deep caries occurs, appropriate dental pulp regeneration and recovery of dental pulp function are possible.
Owner:NAT CENT FOR GERIATRICS & GERONTOLOGY
Sub totipotential stem cell and preparation method and application thereof
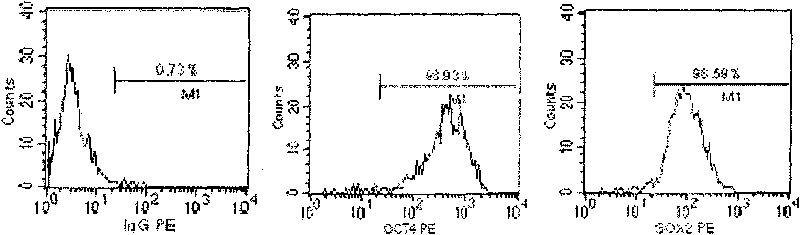
The invention discloses a method for preparing a population of?human pluripotent stem cells and the application thereof. The preparation of stem cells is characterized by comprising the following steps: CD151<+>, CD31<->, Sox<2+> pluripotent stem cells are separated and collected from human umbilical cord and or placenta tissues; the cells adhere to grow in a culture vessel under a predetermined condition and expand through passage 20 or above to be still stable in gene expression. The population of cells of this invention do not form teratoma after injection into animals. The human pluripotent stem cells highly express CD151, OCT4 and Sox-2 as specific markers of embryonic stem cells, as well as specific markers of epidermic cells, endothelial cells, thrombocytes, dendritic cells, while lack expression of CD31, CD34, CD45 and HLA-II. The pluripotent stem cells are also characterized as being able to adhere to tissue culture plastic and having the potential to differentiate into three germ layers: endoderm, mesoderm and ectoderm. These pluripotent stem cells are able to be used as carrier cells of gene therapy and for the treatment of diseases caused by cell damage or cell aging. The present invention provides a method of isolating, purifying and culturally expanding of a population of human pluripotent stem cell for preparing the high purity injection preparation. The preparation of stem cells has a good therapeutic effect on the treatment of diseases caused by cell damage or cell aging in animal and human clinical trials. The preparation also has no toxic side effect and no immune rejection.
Owner:BEIJING HEALTH & BIOTECH (H&B) CO LTD
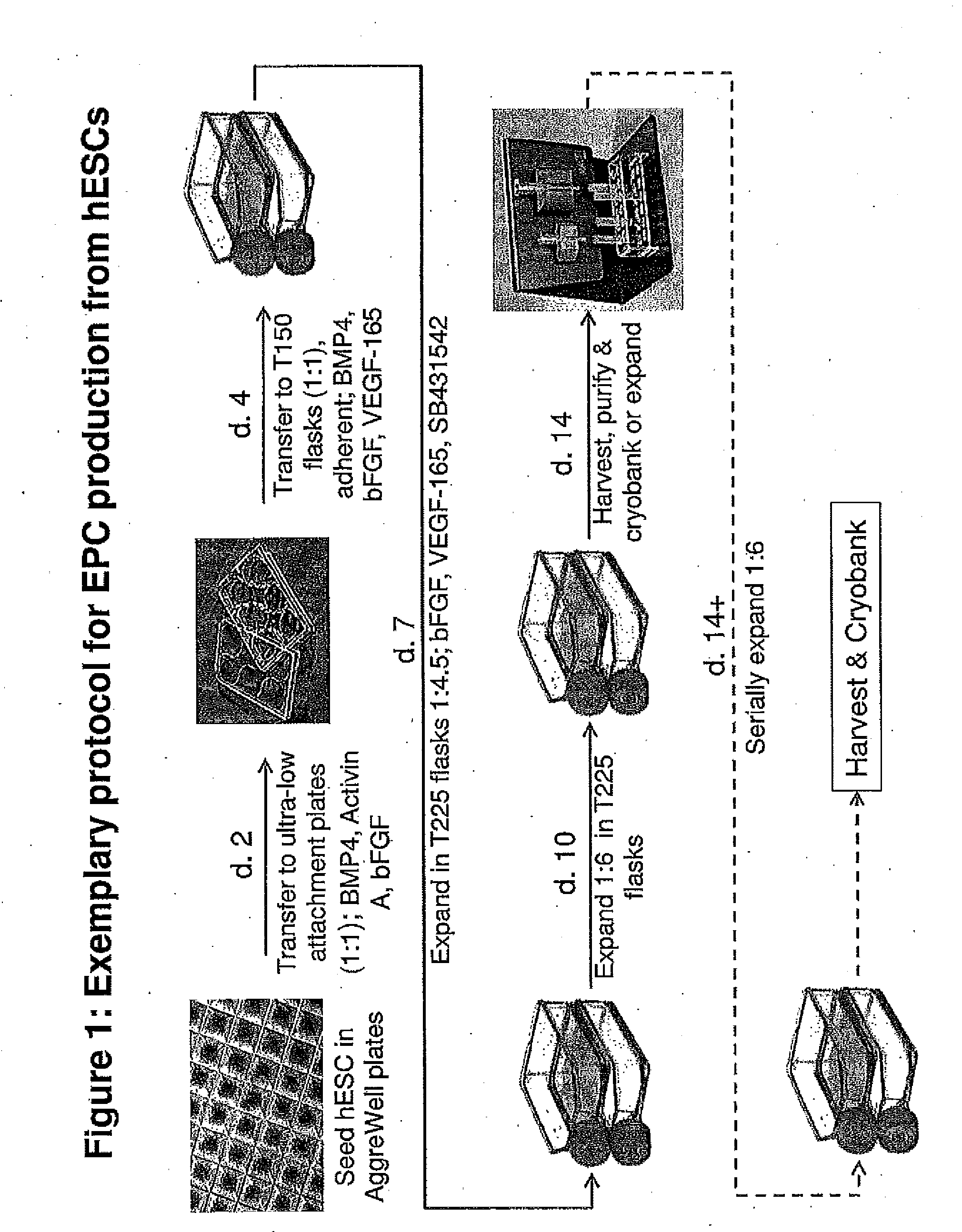
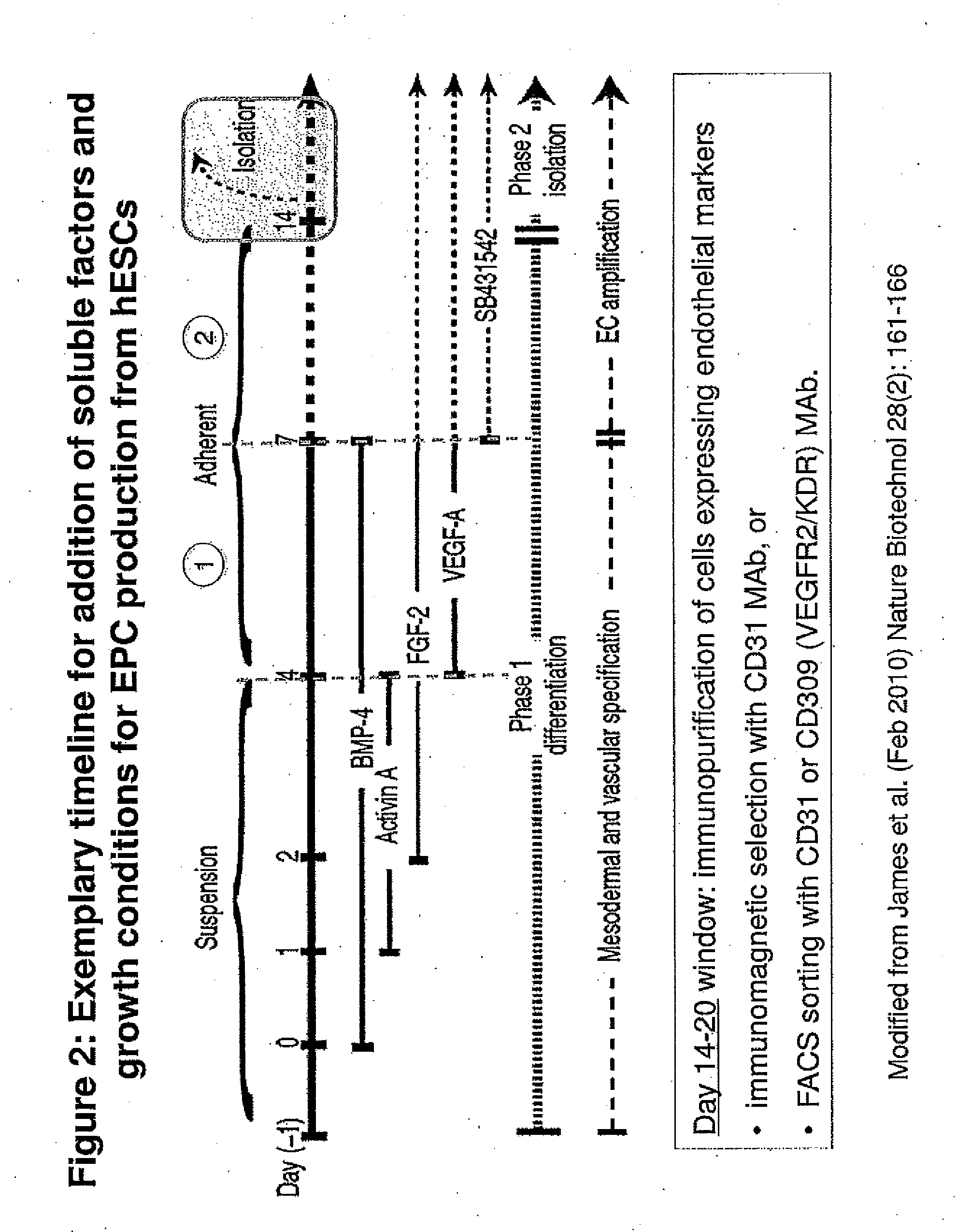
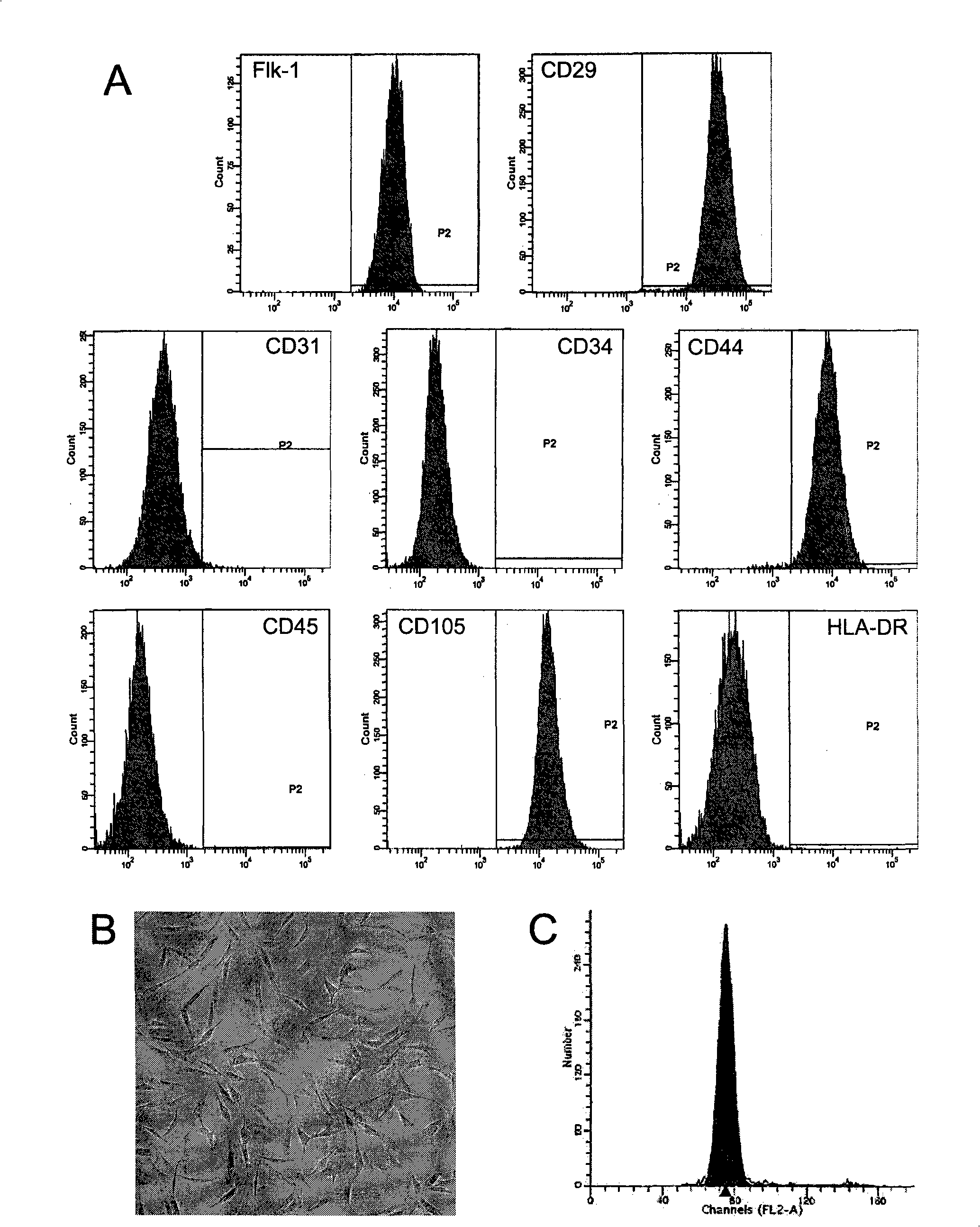
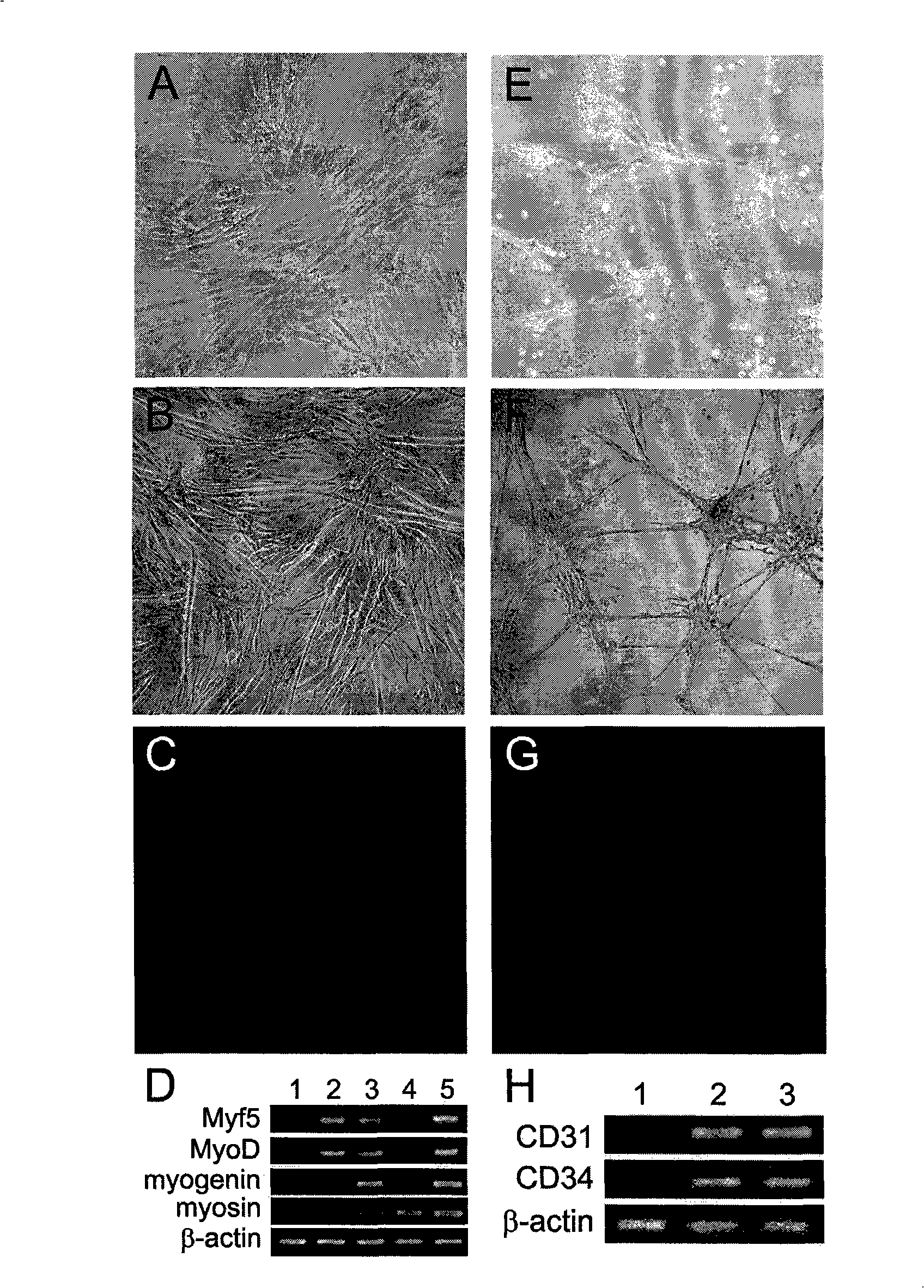
Methods and Compositions for Producing Endothelial Progenitor Cells from Pluripotent Stem Cells
InactiveUS20120295347A1Artificial cell constructsCell culture supports/coatingProgenitorLymphatic vessel
Aspects of the present invention are drawn to methods and compositions for producing endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) in vitro from pluripotent stem cells and compositions containing such EPCs. The methods produce sufficient EPCs to use in therapeutic applications. In certain embodiments the EPCs are bipotent, giving rise to both vascular and lymphatic endothelial cells. In certain embodiments, EPCs express one or more of the following gene products: LYVE-1, PV-1 / PAL-E, CD31, and CD34.
Owner:RECYTE THERAPEUITCS
Method for isolated culture of human fat mesenchyma stem cell and special culture medium thereof
ActiveCN101314766AThe method of isolation and culture is simpleImprove efficiencySkeletal/connective tissue cellsAntigenMuscle injury
The invention discloses a method for separately culturing a human adipose mesenchymal stem cell and a dedicated culture medium thereof. The culture medium used for separately culturing the human adipose mesenchymal stem cell comprises an animal cell basic culture medium, fetal calf serum, an epidermal growth factor and a platelet-derived growth factor. The final concentration of the fetal calf serum is 1-200 mL / L, the final concentration of the epidermal growth factor is 1-100 ng / ml, and the final concentration of the platelet-derived growth factor is 1-100 ng / ml. The adipose mesenchymal stem cell of the invention has CD31-, CD34-, CD45- and HLA-DR-, as well as the phenotype of CD29+, CD44+, CD105+ and Flk-1+. The specificity cell surface marker and the relevant antihelion molecule of a skeletal muscle cell and a vascular endothelia cell can be expressed after inducement is performed in vitro. Muscle fiber, vascular endothelin and functional muscle satellite cells can be differentiated in a muscle injury model mouse body caused by medicine and the expression of dystrophin protein on the ducheme muscular dystrophy (DMD) model mouse (mdx) myolemma can be partially recovered, so as to release the pathological symptom of the model mouse.
Owner:微能生命科技集团有限公司
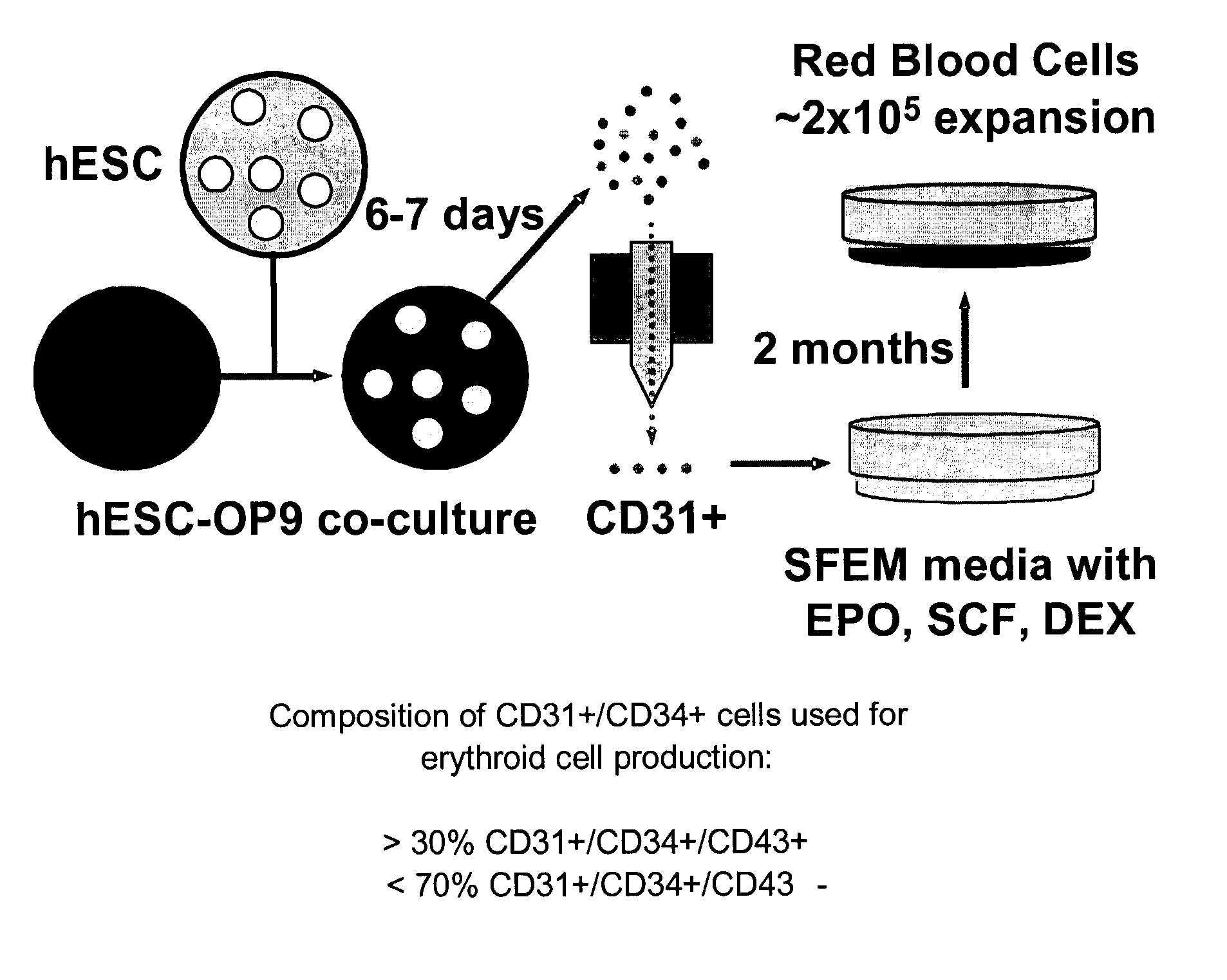
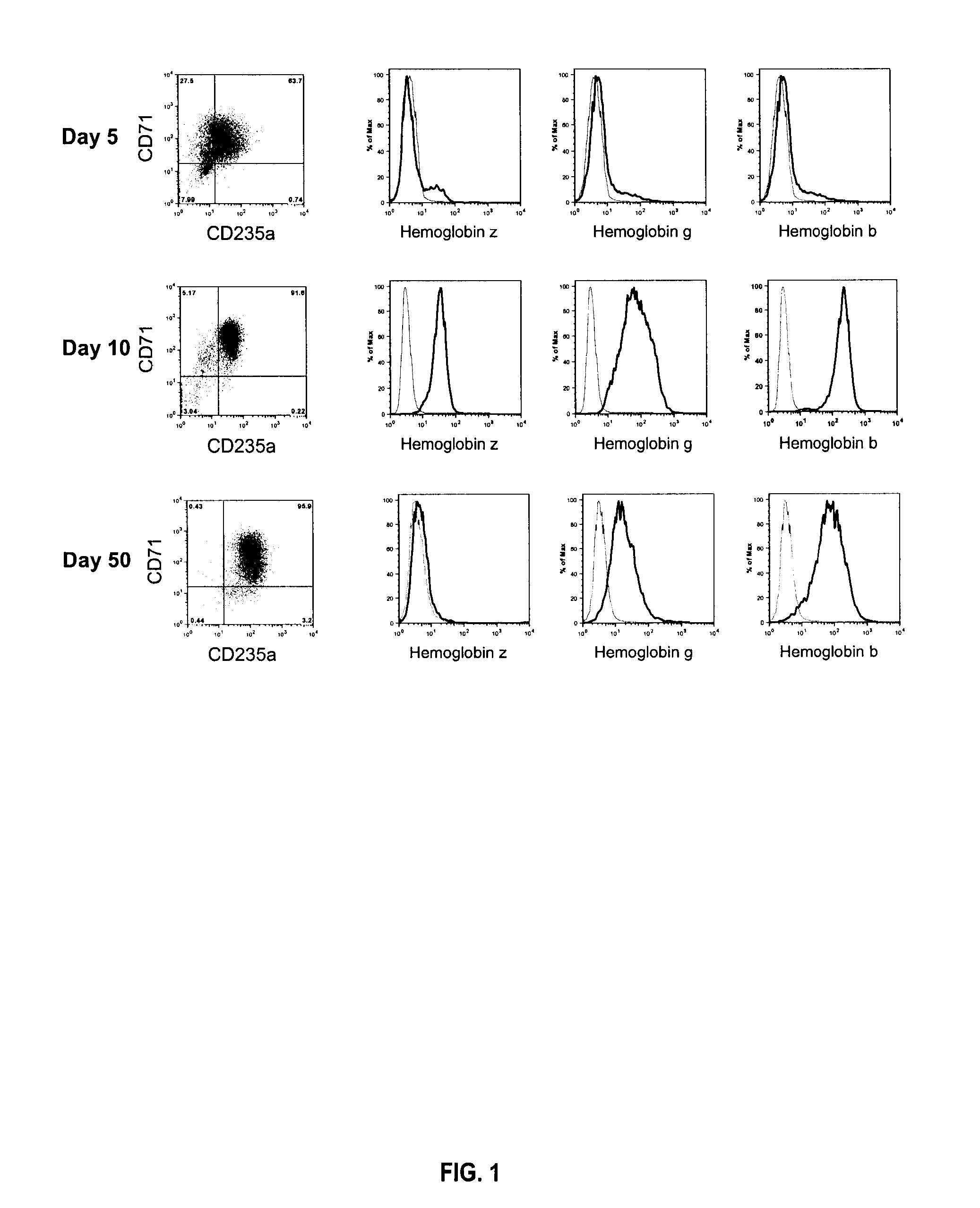
ERYTHROID CELLS PRODUCING ADULT-TYPE Beta-HEMOGLOBIN GENERATED FROM HUMAN EMBRYONIC STEM CELLS
Methods and compositions of erythroid cells that produce adult β-hemoglobin, generated by culturing CD31+, CD31+ / CD34+ or CD34+ cells from embryonic stem cells under serum-free culture conditions.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
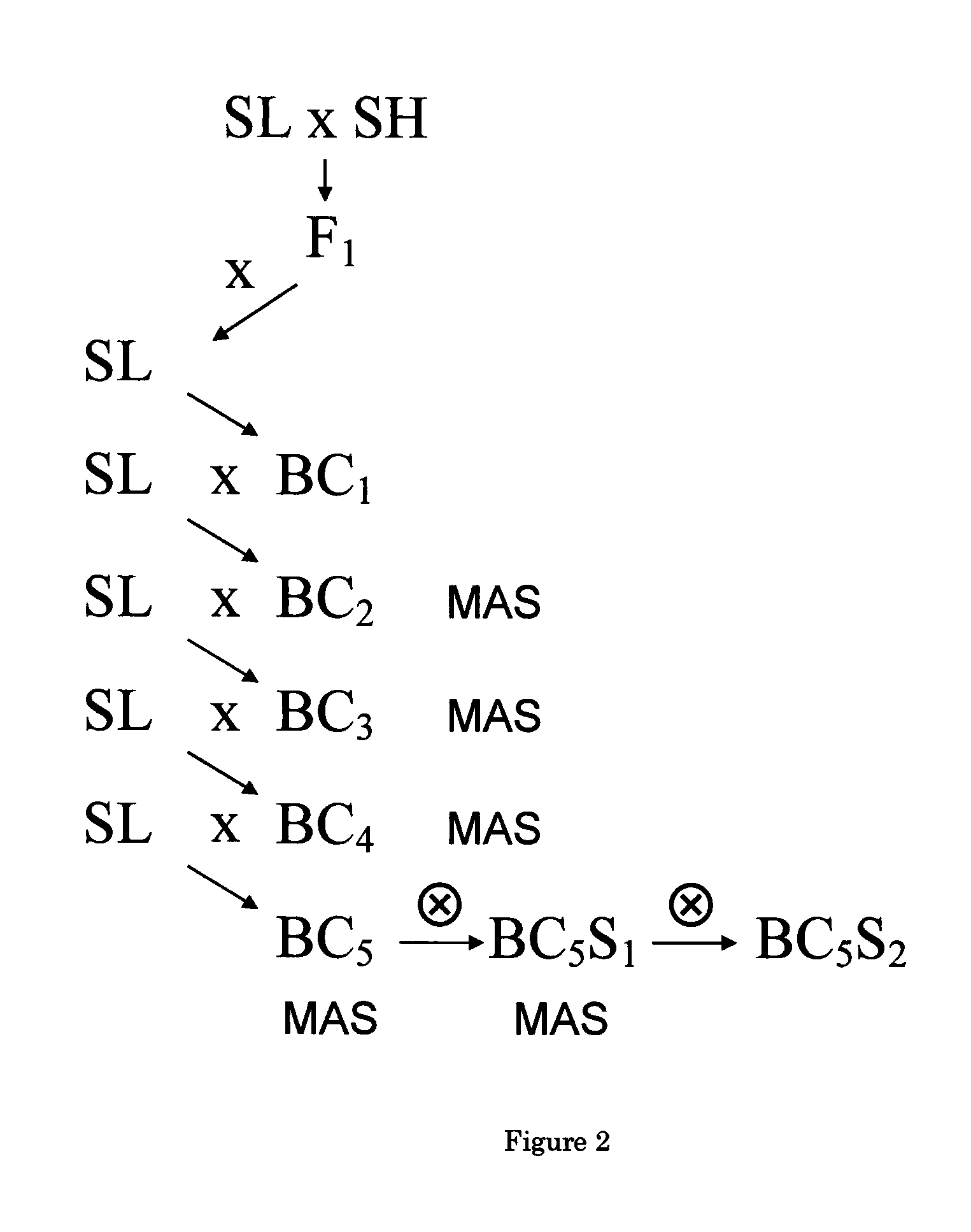
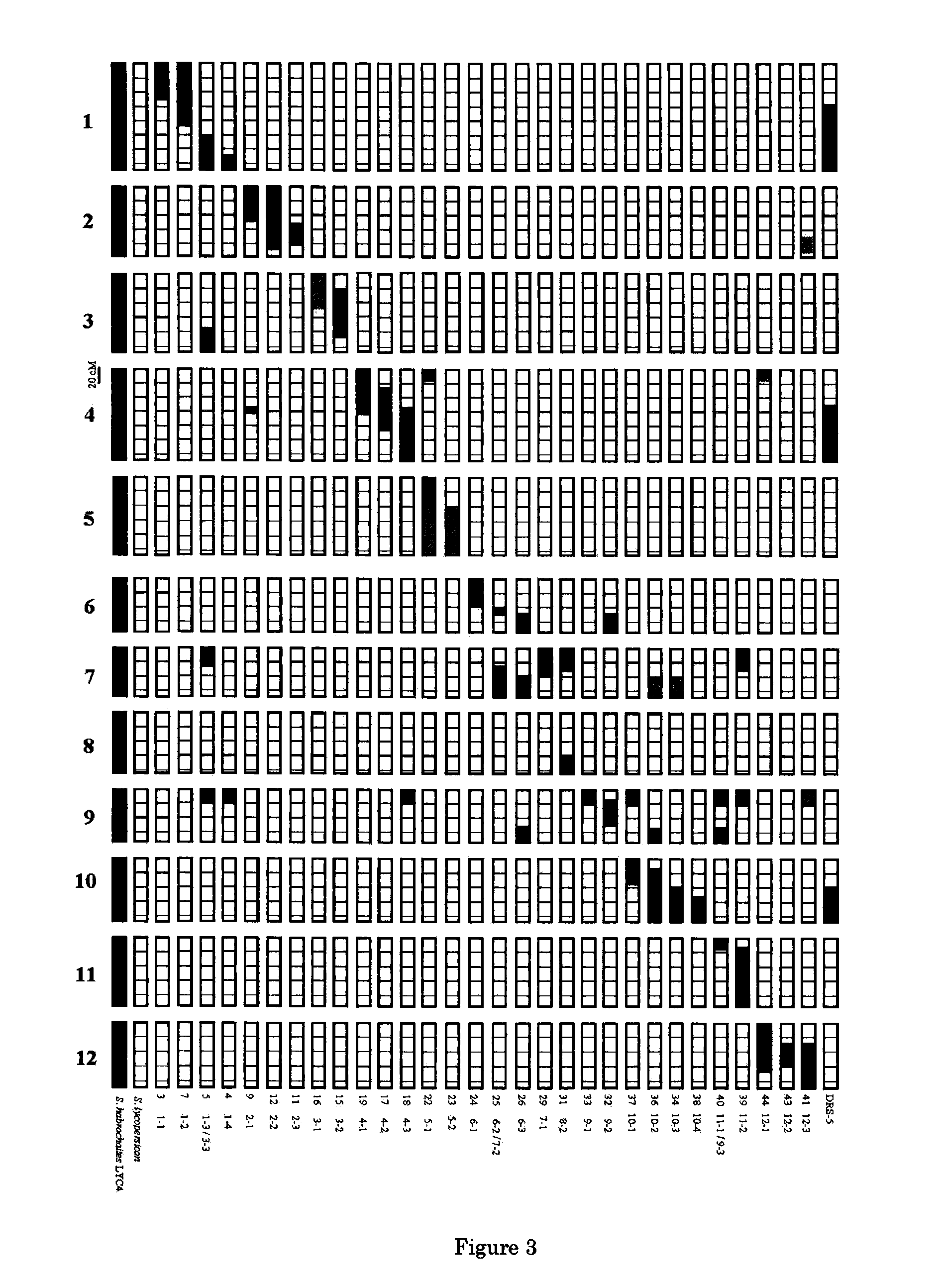
Parthenocarpic genetic elements derived from S. habrochaites
The present invention relates to a method of producing a parthenocarpic, and optionally male sterile, tomato plant comprising introgressing into said plant a genetic region from Chromosome 4, 5 and / or 12 of S. habrochaites LYC4 / 78, a representative sample of seed of which was deposited on 13 Nov. 2007 with the NCIMB under Accession number 41517, wherein the genetic region from Chromosome 4 of S. habrochaites LYC4 / 78 includes at least one marker selected from Marker CD59, RFLP Marker CT229, and COS Marker T1068, and wherein the genetic region from Chromosome 5 of S. habrochaites LYC4 / 78 includes at least one marker selected from COS Marker T1181, RFLP Marker TG441 and / or RFLP Marker CD31(A).
Owner:MONSANTO INVEST BV
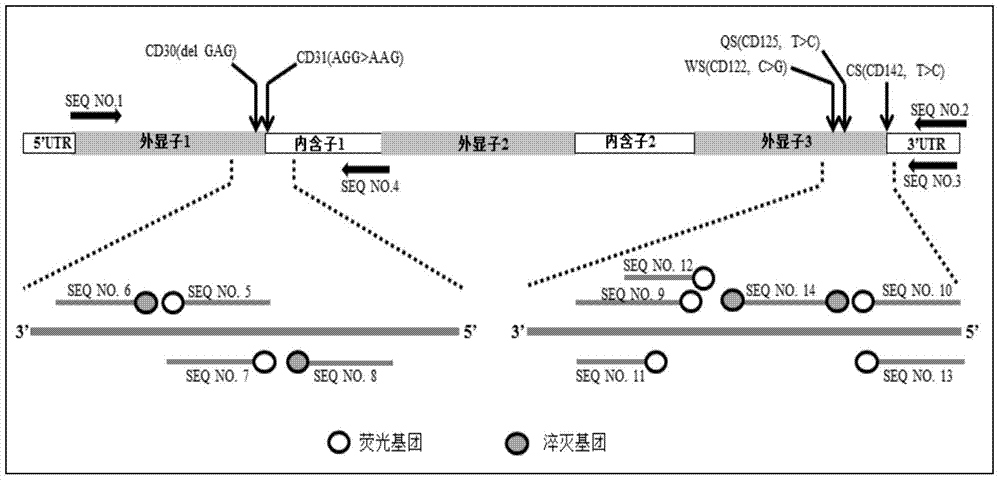
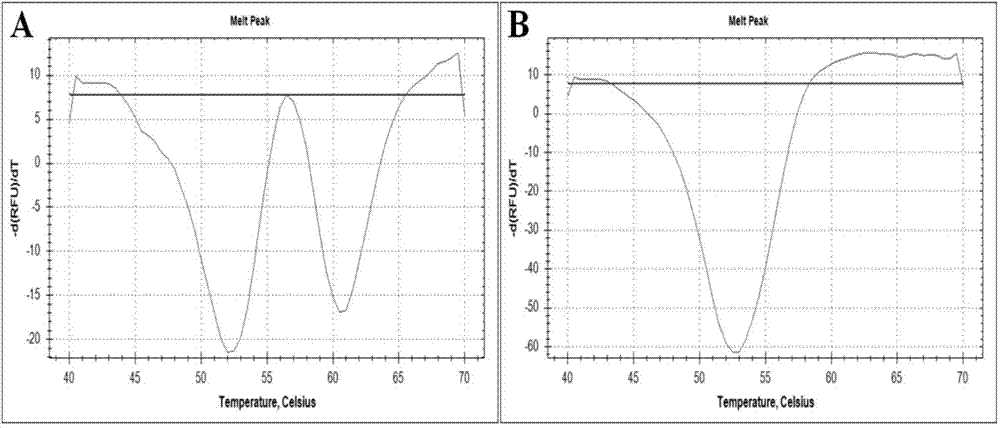
Nested asymmetric PCR reagent kit for detecting alpha 2 globin gene point mutation
ActiveCN103898213AImprove featuresGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceWild type
The invention discloses a nested asymmetric PCR reagent kit for detecting alpha 2 globin gene point mutation. The reagent kit comprises a nested asymmetric PCR amplification primer, a fluorescent probe, a quenching probe, an LADNA polymerase and the like. The alpha-thalassemia point mutation genotype of a detected sample is detected by virtue of specific amplification of five point mutation destination fragments WS, QS, CS, CD30 and CD31 of the human alpha 2 globin gene and molecular hybridization and unwinding analysis of a specific fluorescent probe. The reagent kit has good sensitivity and accuracy to wild type and mutation type of alpha-thalassemia five point mutation positions WS, QS, CS, CD30 and CD31, has good repeatability and stability, and is totally suitable for clinical detection of alpha-thalassemia point mutation.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Method for separating and purifying mouse lung microvascular endothelial cell
A method for separating and purifying mouse lung microvascular endothelial cell is characterized by comprising using an enzyme to perform digestive treatment on subpleural lung marginal tissue to obtain a single-cell suspension, and performing CD31 immunomagnetic bead sorting to obtain the target cell. Concretely, the method comprises getting subpleural lung marginal tissue of a large suckling mouse, firstly using a mixed solution of collagenase II and neutral protease for digestion to prepare the single-cell suspension, then performing incubation combination with CD31 immunomagnetic bead, then utilizing a magnetic bead sorting purification system to screen CD31+ cell, and removing magnetic beads combined with CD31+ cell by using a magnetic-bead release solution, so as to obtain high-purity mouse lung microvascular endothelial cell. The advantages comprise that the high-purity mouse lung microvascular endothelial cell can be obtained from mouse lung tissue through separation extraction by using enzyme digestion to prepare the single-cell suspension and performing CD31 immunomagnetic bead sorting.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF AGRI
Animal model establishment method of human primary skin squamous epithelial cell cancer stem cell
ActiveCN103239479APromote growthPromote differentiationUnknown materialsSolution deliveryMatrigelSingle cell suspension
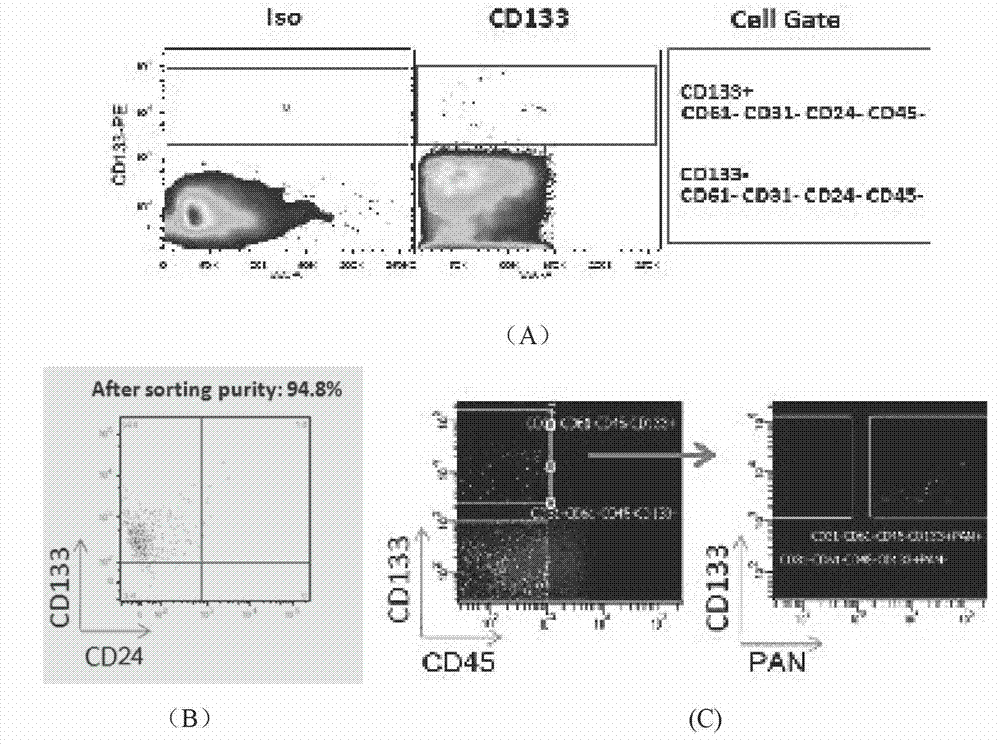
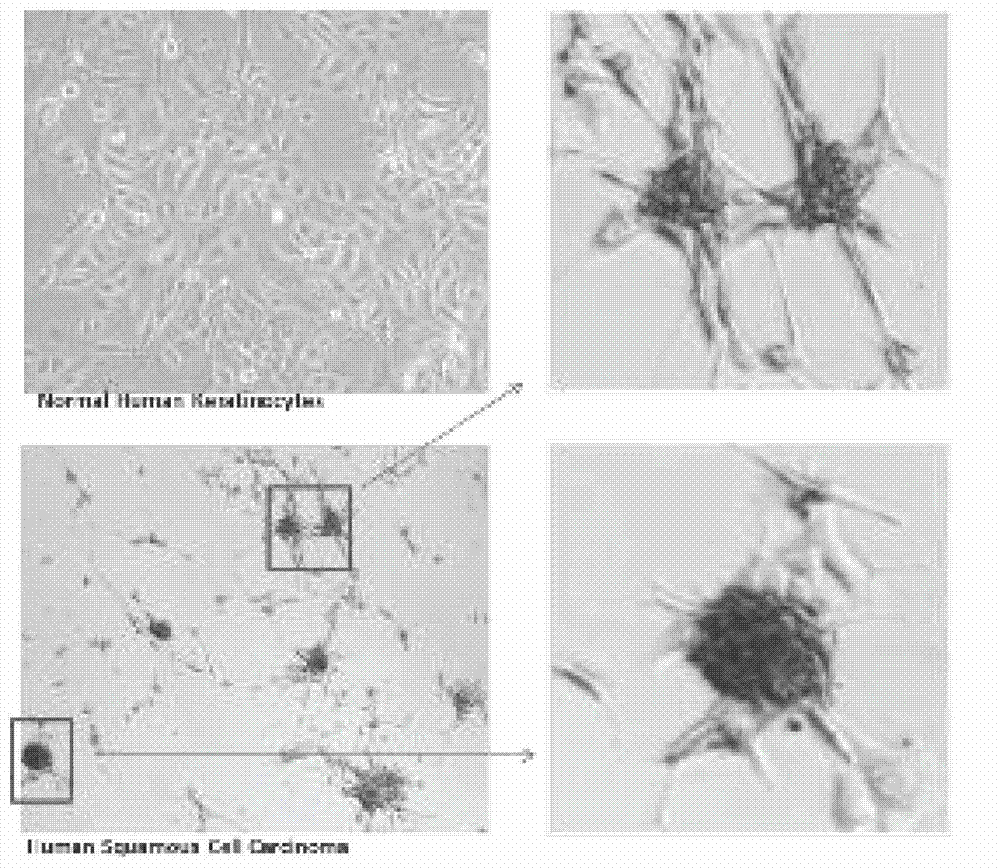
The invention relates to an animal model establishment method of human primary skin squamous epithelial cell cancer stem cell. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing collected skin squamous epithelial cell cancer tissue in a clinical case into a single-cell suspension, separating CD31-CD24-CD45-CD61-CD133+tumor stem cell population, suspending and mixing with 1*10<6> human primary mouse embroy fibroblasts and 1*10<6> human primary endothelial cells in matrigel, and then injecting the obtained product into microenvironment through humanized nude mouse subcutaneous tumorigenesis parts. The invention makes further research on molecular biological mechanisms of human skin primary SCC tumour possible.
Owner:WUHAN DENUOMEI BIOLOGY MEDICINE TECH
Method for inducing and differentiating human multipotent stem cells into aged blood cells
InactiveCN106834224ASimplified induction procedureShorten induction timeBlood/immune system cellsCell culture active agentsRed blood cellCD31
The invention belongs to the field of induced differentiation of blood cells, and provides a method for inducing and differentiating human multipotent stem cells into aged blood cells. The method comprises the following steps of A, inducing and differentiating the human multipotent stem cells into hematopoietic progenitor cells CD31 and CD34; B, inducing and differentiating the hematopoietic progenitor cells CD31 and CD34 into human aged cells. The method has the advantages that by adopting the two-step inducing type of single-layer cell culture and suspension cell culture, the inducing procedure is simplified, the inducting time is shortened, the operation is simple, the efficiency is high, and the stability is realized; by adopting the inducing and differentiating system without feed layer cells, the induced blood cell has biological safety guarantee, the requirements of clinical conversion and clinical experiment can be met, and the medical conversion value is high.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Endothelial cell culture medium and endothelial cell culture method
ActiveCN104974978AImprove proliferative abilityImprove angiogenesisArtificial cell constructsVertebrate cellsCell phenotypeVitamin C
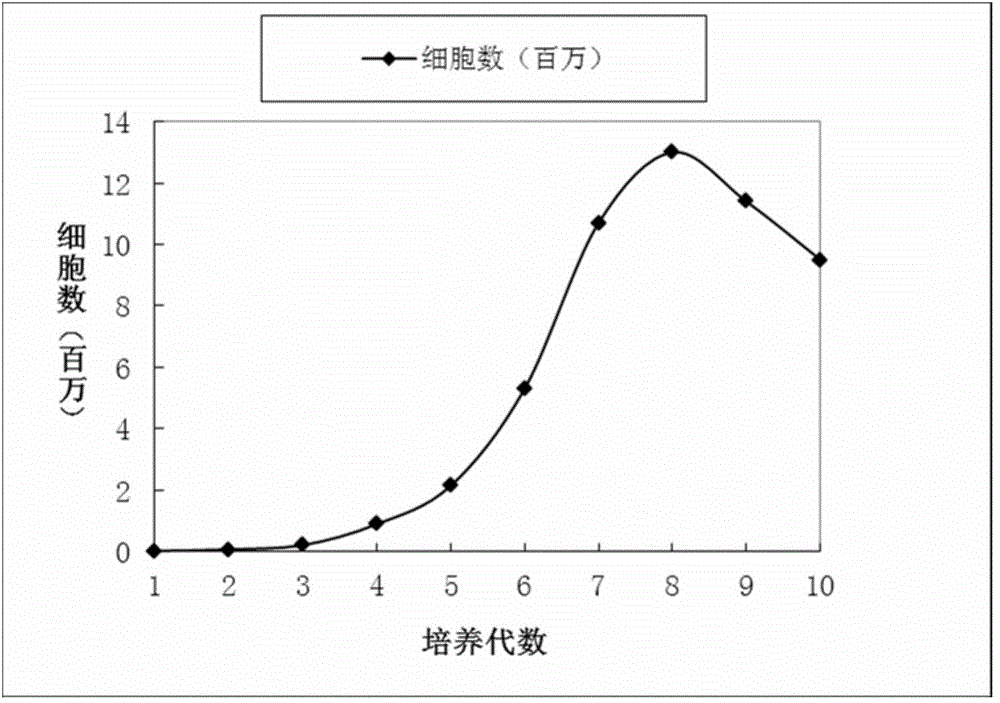
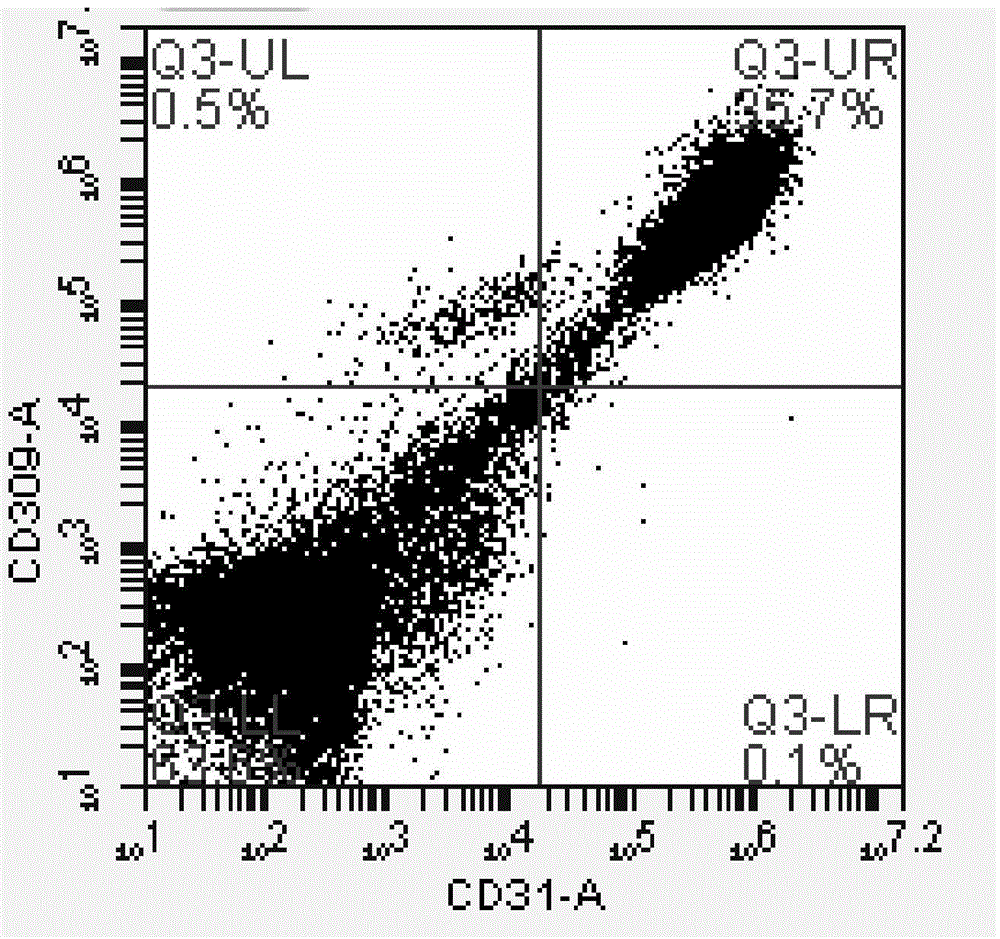
The invention provides an endothelial cell culture medium and an endothelial cell culture method, wherein the endothelial cell culture medium comprises a serum-free basal culture medium, insulin, transferin, vitamin C, bovine serum albumin, a basic fibroblast growth factor, a blood vessel endothelium growth factor, a stem cell growth factor, laminin, an epidermal growth factor, non-essential amino acid and melbinum hydrochloride. By virtue of compatibility of ingredients, the endothelial cell culture medium provided by the invention is capable of improving the endothelial cell multiplication capacity. In addition, the endothelial cell culture medium provided by the invention is further capable of improving the blood vessel formation capability of endothelial cells. The experimental result indicates that when endothelial cells are cultured to the P10 generation by virtue of the endothelial cell culture medium provided by the invention, the cells still grow vigorously; the P10-generation endothelial cell phenotype CD309 and CD31 double-positive expression is as high as 97.2%.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SALIAI STEMCELL SCI & TECH CO LTD
Parthenocarpic Genetic Elements Derived From S. Habrochaites
InactiveUS20100146656A1Microbiological testing/measurementOther foreign material introduction processesGenetic elementCD31
The present invention relates to a method of producing a parthenocarpic, and optionally male sterile, tomato plant comprising introgressing into said plant a genetic region from Chromosome 4, 5 and / or 12 of S. habrochaites LYC4 / 78, a representative sample of seed of which was deposited on 13 Nov. 2007 with the NCIMB under Accession number 41517, wherein the genetic region from Chromosome 4 of S. habrochaites LYC4 / 78 includes at least one marker selected from Marker CD59, RFLP Marker CT229, and COS Marker T1068, and wherein the genetic region from Chromosome 5 of S. habrochaites LYC4 / 78 includes at least one marker selected from COS Marker T1181, RFLP Marker TG441 and / or RFLP Marker CD31(A).
Owner:MONSANTO INVEST BV
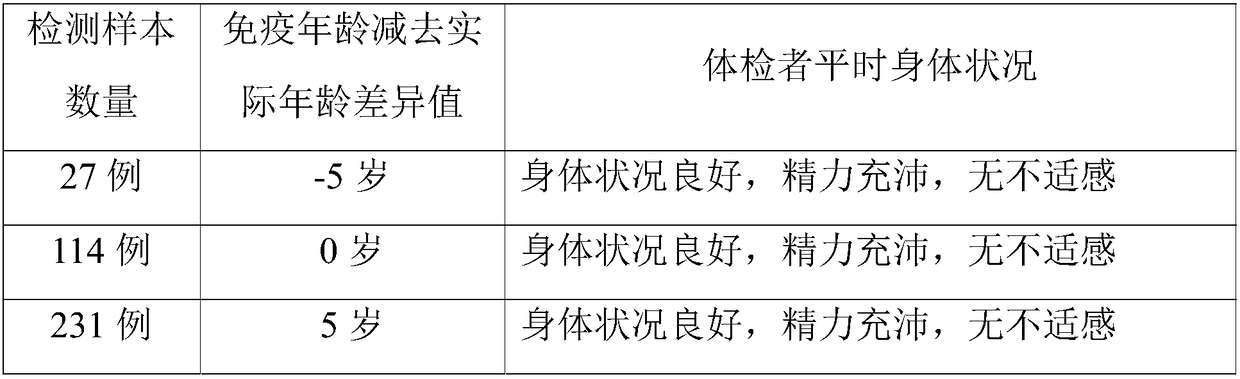
Kit for detecting human immune ages and application of kit
InactiveCN109490544AEvaluate immunityRapid Quantitative AnalysisIndividual particle analysisBiological testingFluoresceinMonoclonal antibody
The invention provides a kit for detecting human immune ages and an application of the kit. Reagents in the kit comprise CD3, CD4, CD31 and CD45RA monoclonal antibodies which are four fluoresceins applicable to flow cytometers, and the colors of the four fluoresceins are different. The reagents in the kit comprise, in weight percent, 0.66-94.34% of fluorescent labeled CD3, 0.66-94.34% of fluorescent labeled CD4, 0.66-94.34% of fluorescent labeled CD31 and 0.66-94.34% of fluorescent labeled CD345RA. The kit is used for detecting recently outputted cell number of human thymuses, the immune agesof people are determined according to detection results of the recently outputted cell number of the human thymuses, and the immune ability of a human body is evaluated.
Owner:ZHEJIANG BOZHEN BIOTECH CO LTD
Hematopoietic stem cells and methods of treatment of neovascular eye diseases therewith
InactiveUS7153501B2Rescue and stabilize degenerating retinal vasculatureStably incorporated into neovasculature of the eyeBiocideSenses disorderGene deliveryProgenitor
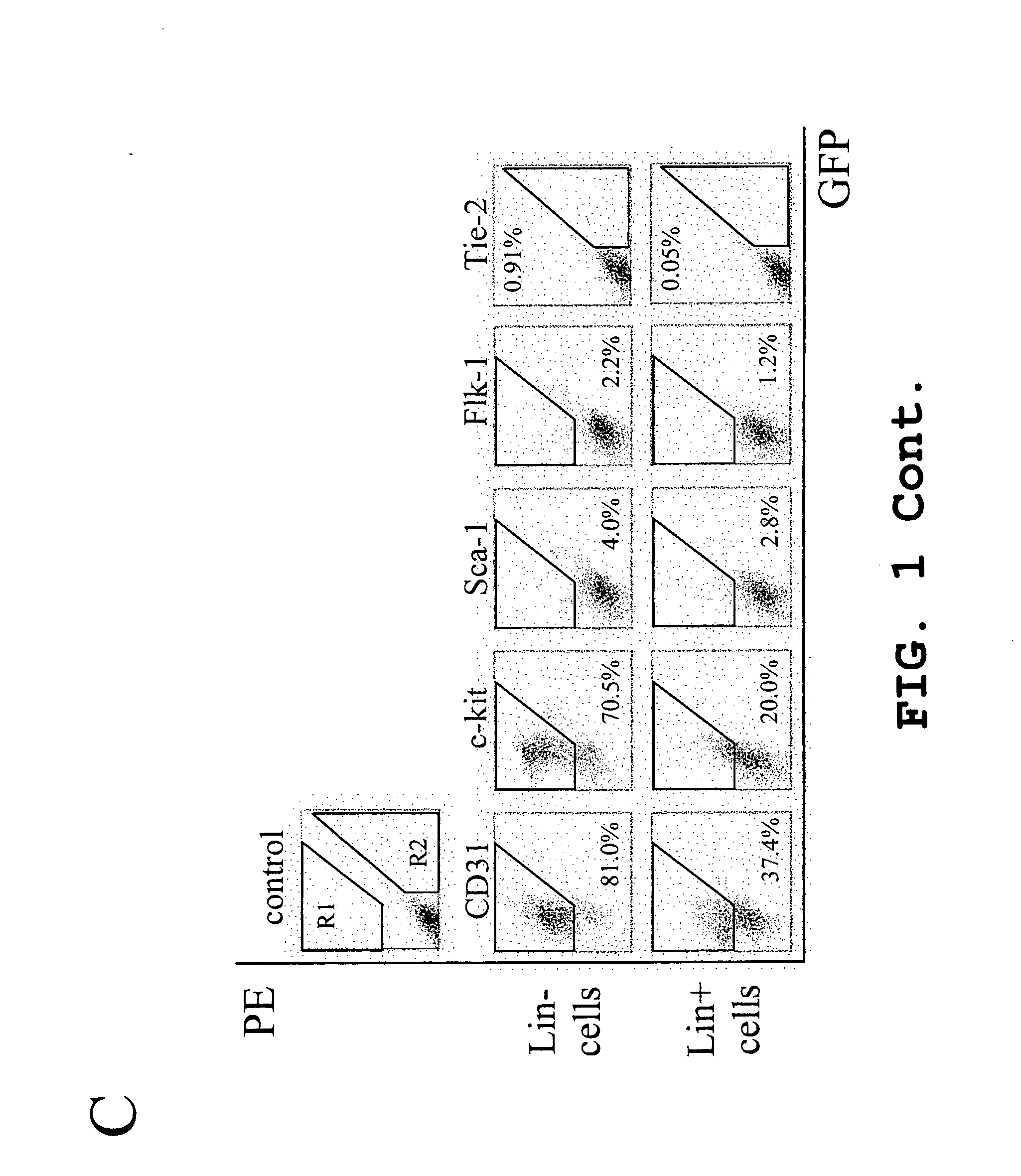
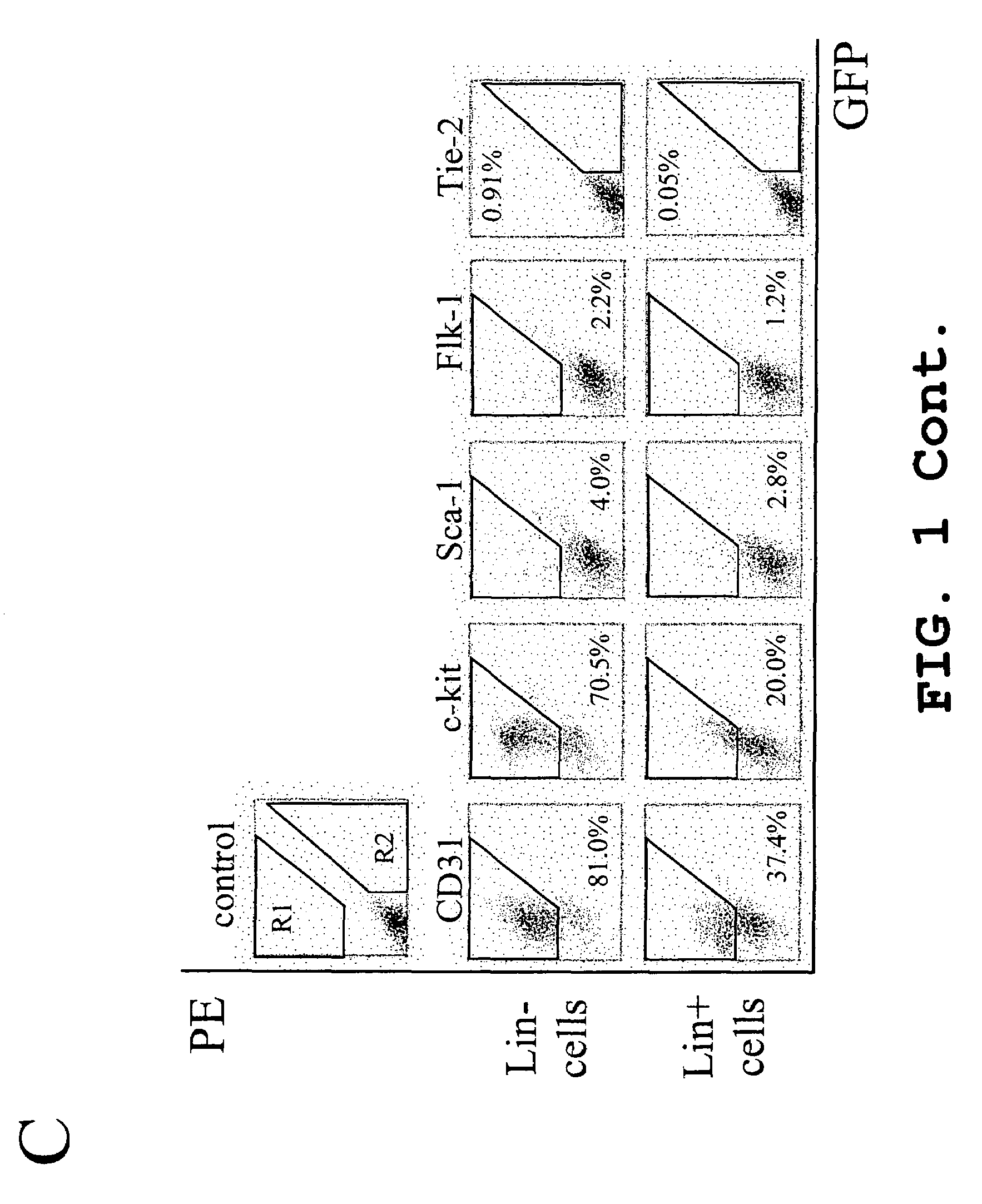
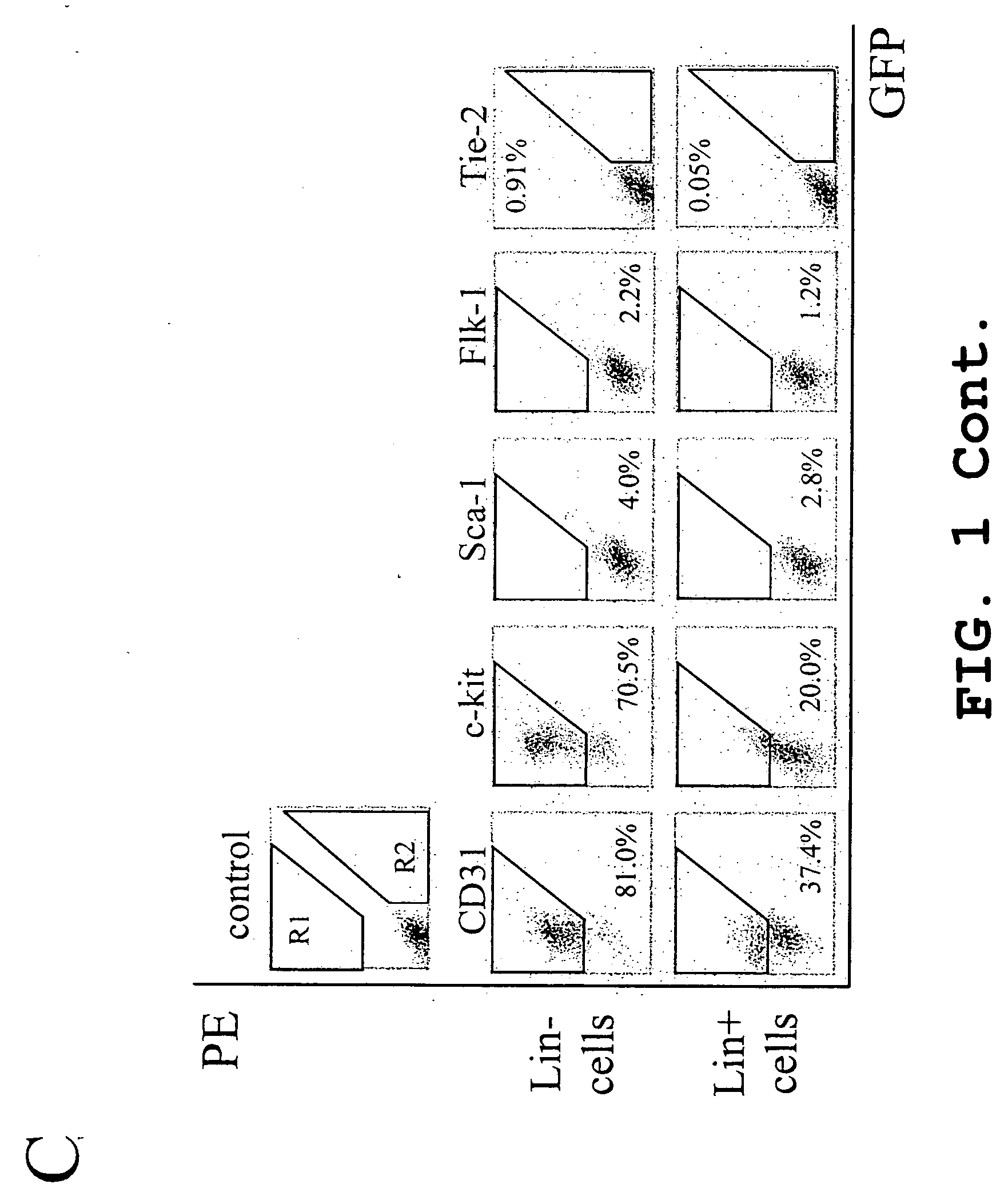
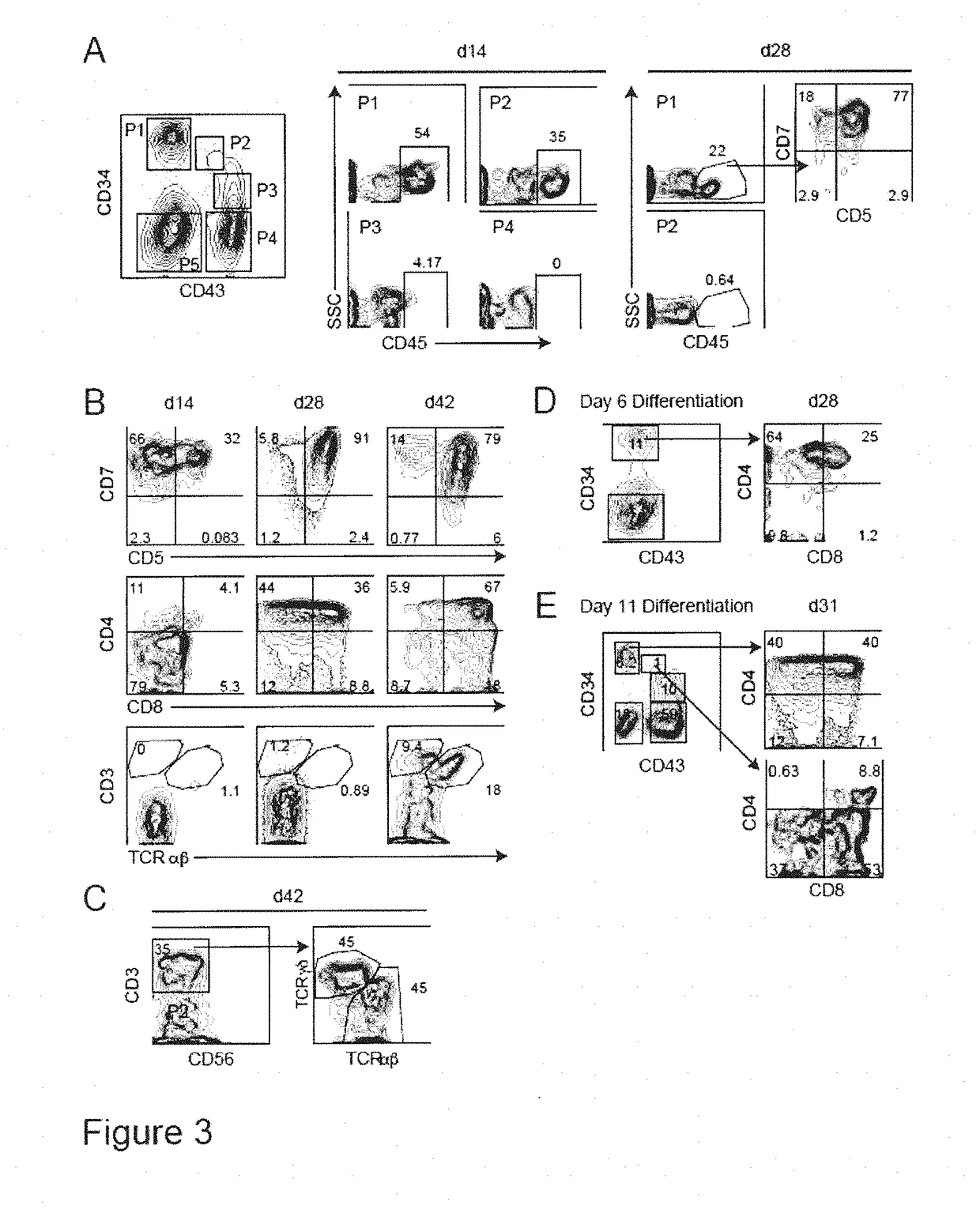
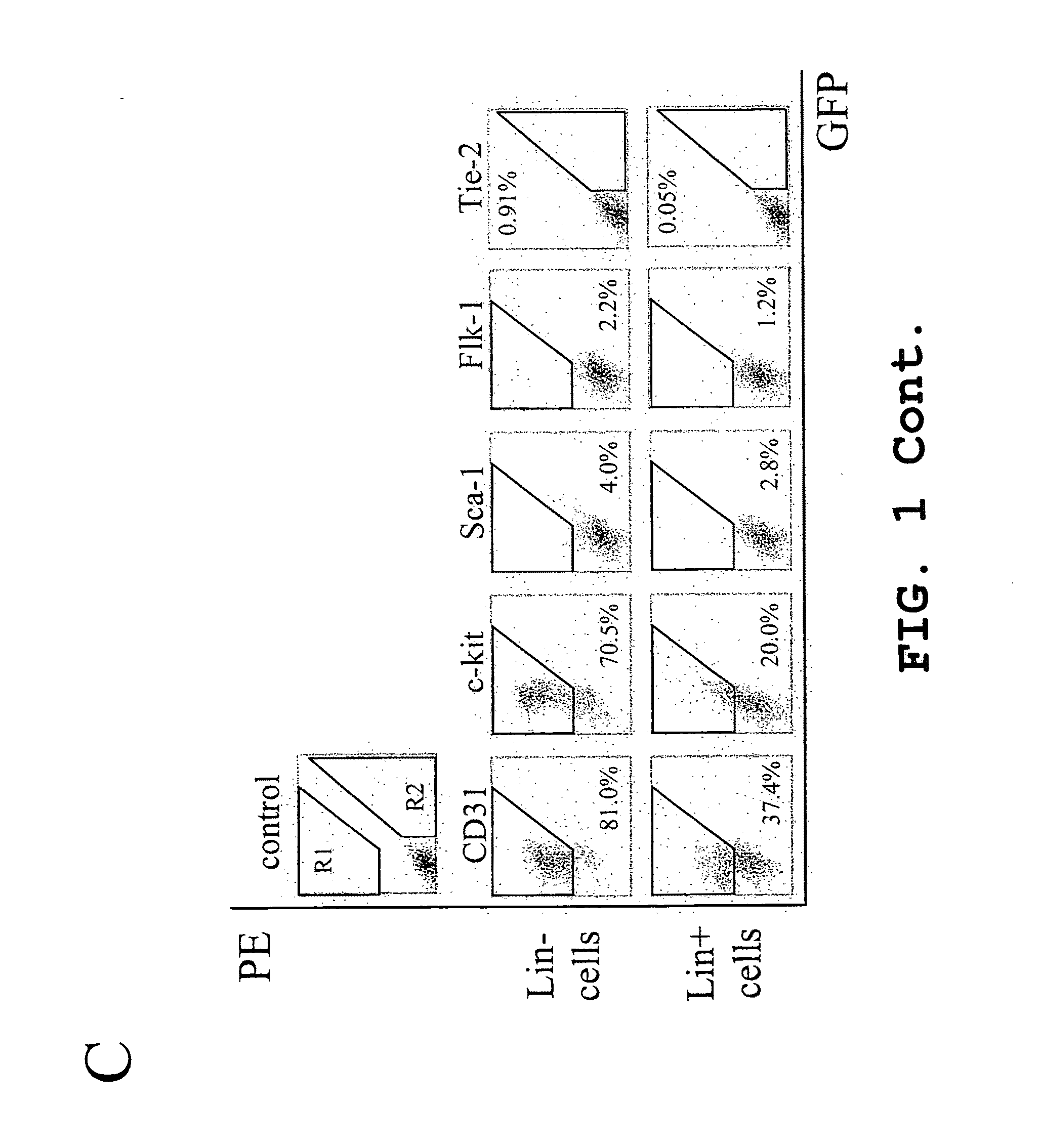
Isolated, mammalian, bone marrow-derived, lineage negative hematopoietic stem cell populations (Lin− HSC) contain endothelial progenitor cells (EPC) capable of forming retinal blood vessels. At least about 50% of the cells in the isolated Lin− HSC population include cell surface markers for CD31 and c-kit. Up to about 8% of the cells can include the Sca-1 cell marker, and up to about 4% of the cells can include the Flk-1 / KDR marker. The isolated Lin− HSC populations of the present invention are useful for treatment of ocular vascular diseases. The isolated Lin− HSC populations that have been transfected with therapeutically useful genes are also provided, which are useful for delivering genes to the eye for cell-based gene therapy.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Isolated lineage negative hematopoietic stem cells and methods of treatment therewith
Isolated, mammalian, adult bone marrow-derived, lineage negative hematopoietic stem cell populations (Lin− HSCs) contain endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) capable of rescuing retinal blood vessels and neuronal networks in the eye. Preferably at least about 20% of the cells in the isolated Lini HSCs express the cell surface antigen CD31. The isolated Lin− HSC populations are useful for treatment of ocular vascular diseases and to ameliorate cone cell degeneration in the retina. In a preferred embodiment, the Lin− HSCs are isolated by extracting bone marrow from an adult mammal; separating a plurality of monocytes from the bone marrow; labeling the monocytes with biotin-conjugated lineage panel antibodies to one or more lineage surface antigens; removing of monocytes that are positive for the lineage surface antigens from the plurality of monocytes, and recovering a Lin− HSC population containing EPCs. The isolated Lin− HSCs also can be transfected with therapeutically useful genes. The treatment may be enhanced by stimulating proliferation of activated astrocytes in the retina using a laser.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Populations of hematopoietic progenitors and methods of enriching stem cells therefor
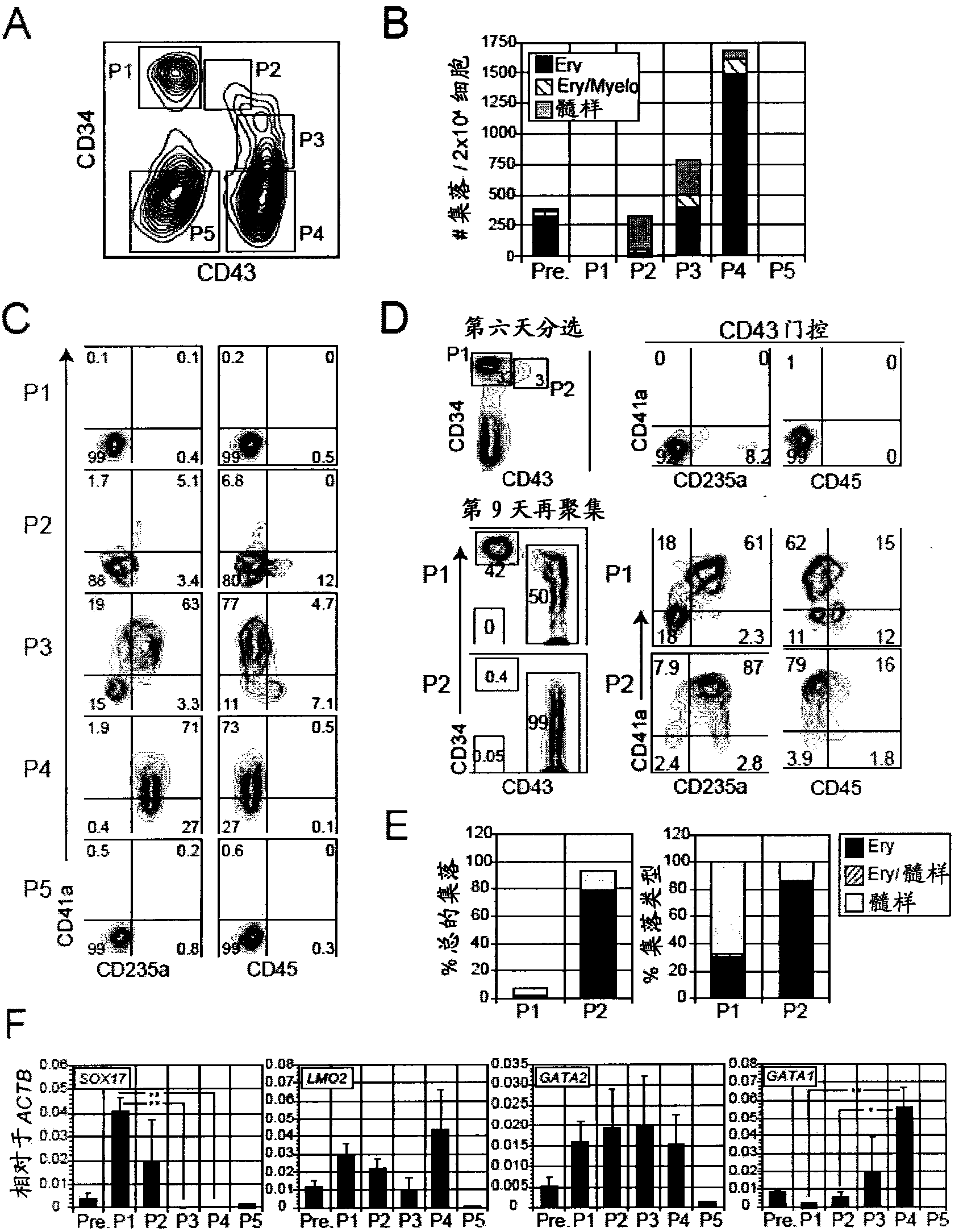
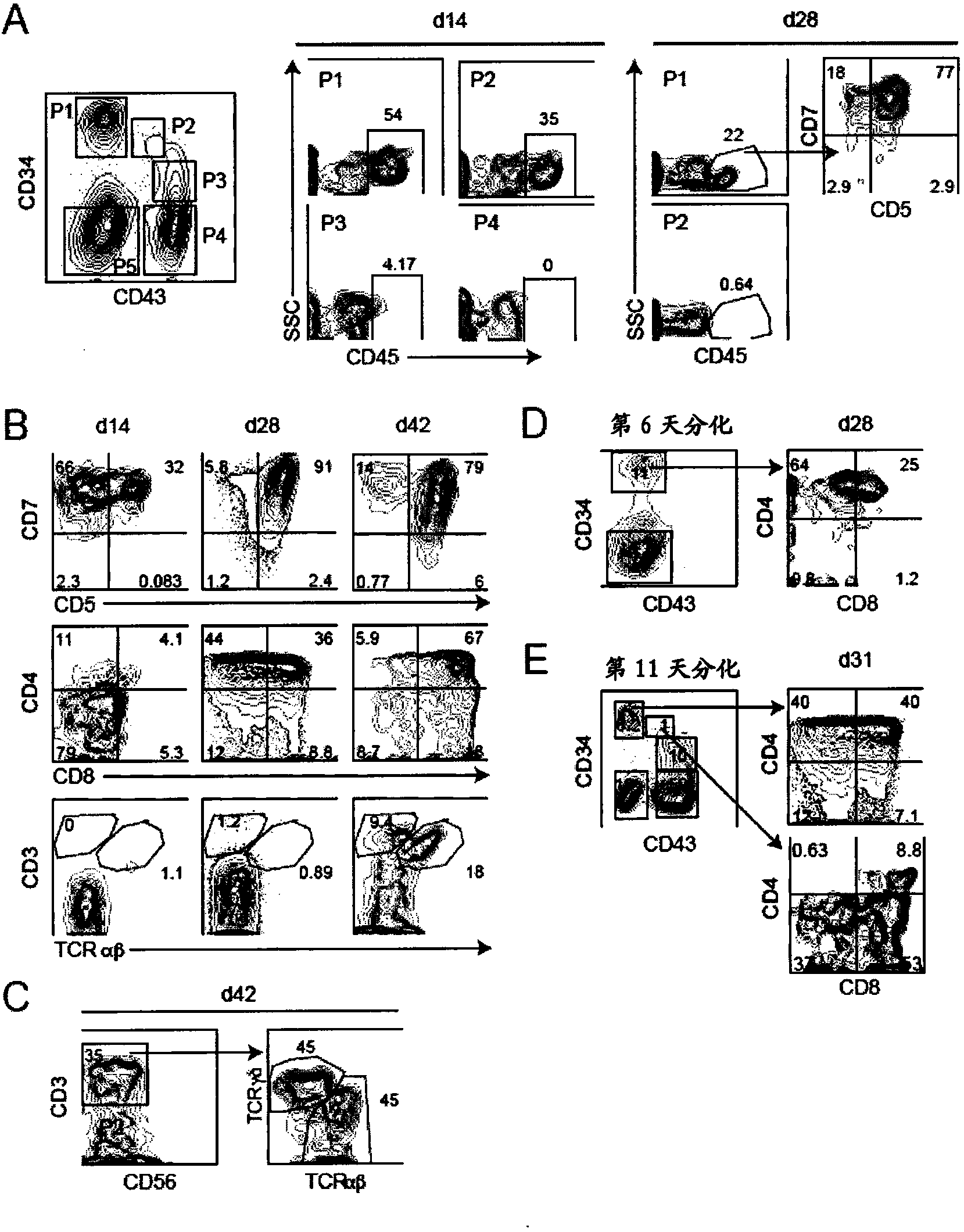
InactiveCN104053769AMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisCD43Hematopoietic progenitor
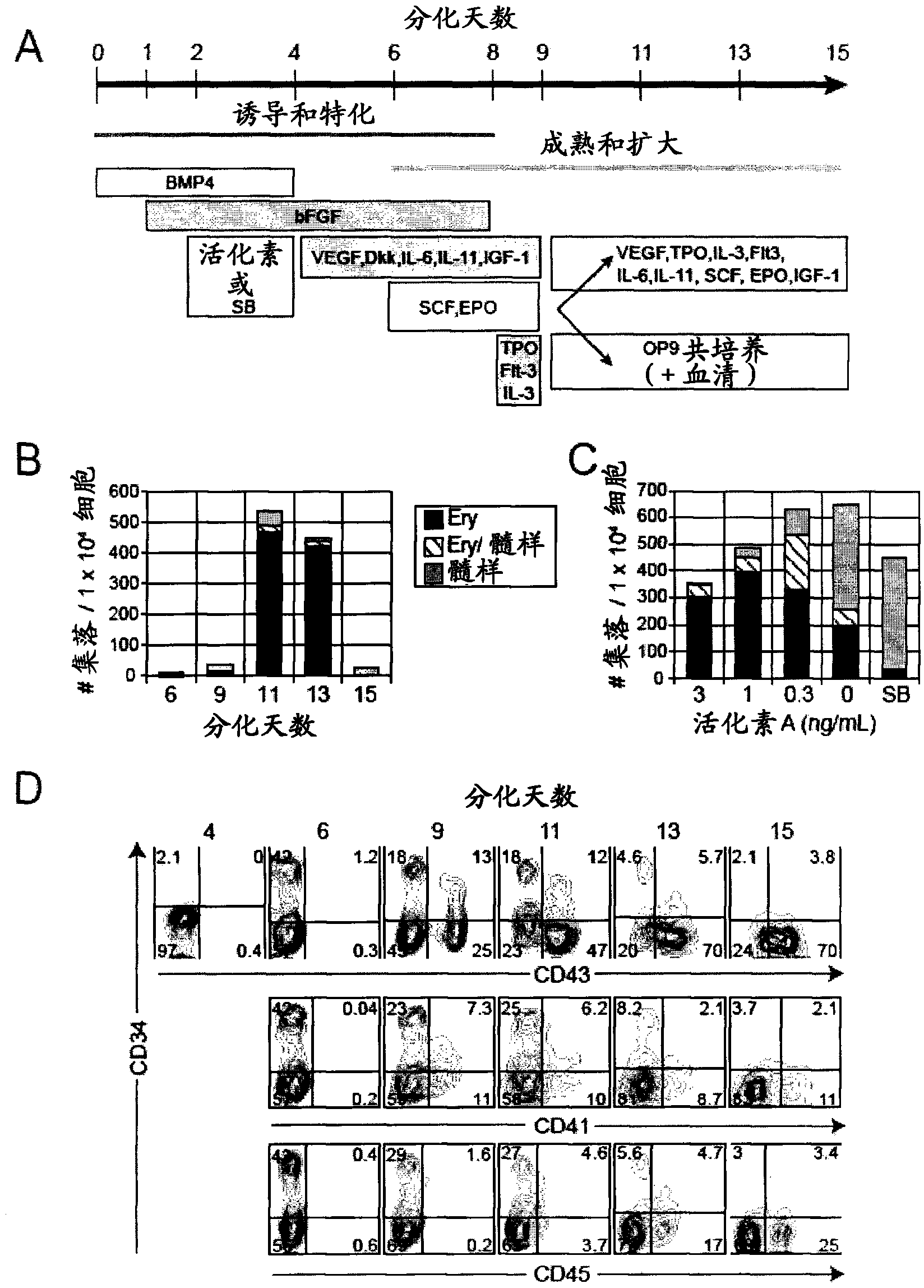
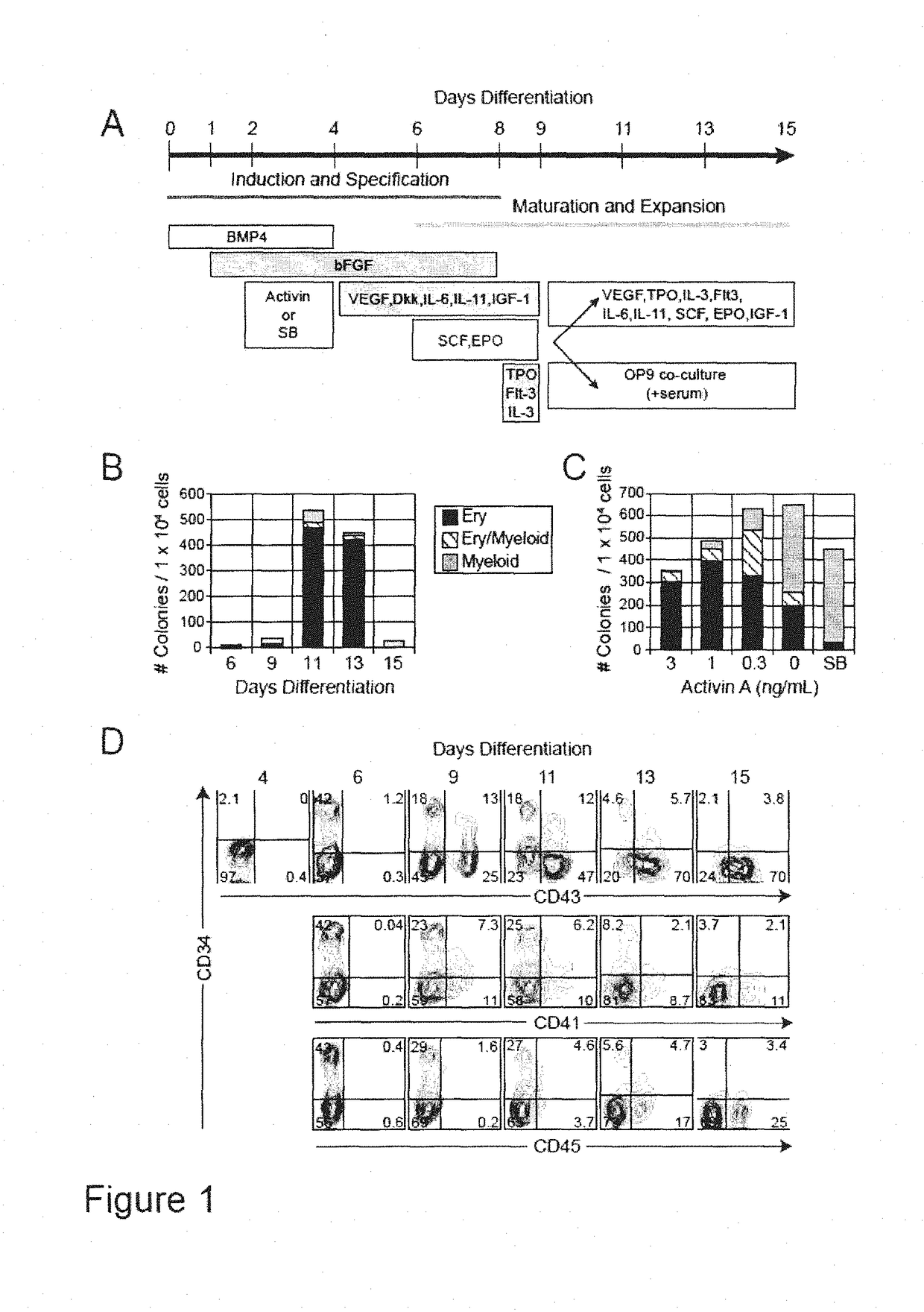
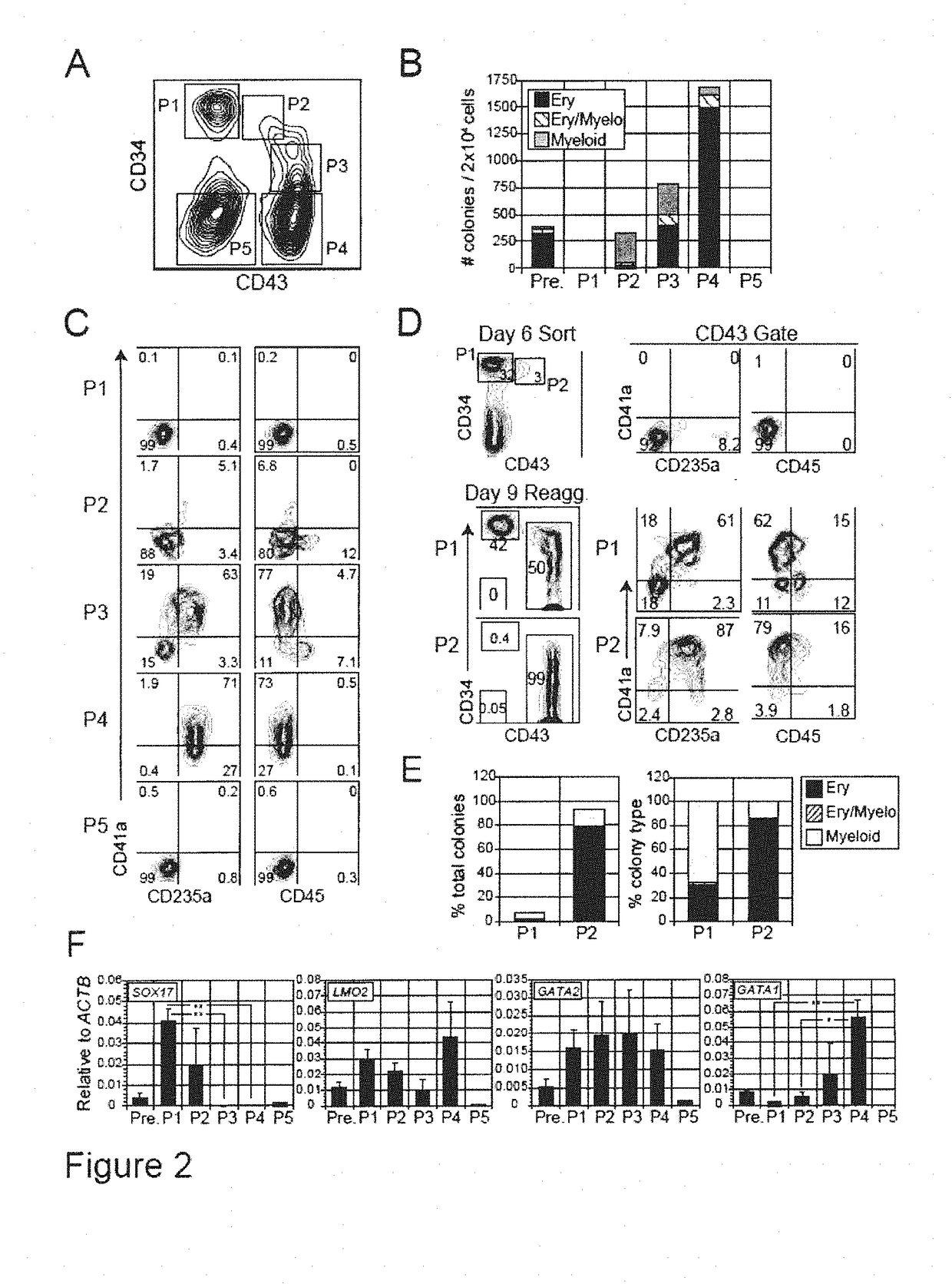
There is described herein a method of enriching a population of stem cells for hematopoietic progenitors. The method comprises inducing hematopoietic differentiation in a population of human embryonic stem cells or human induced pluripotent stem cells; sorting the population based on expression of CD43 and at least one of CD34, CD31 and CD144; and selecting a fraction that is at least one of CD34+CD43-, CD31+CD43- and CD144+CD43-. Also provided are populations of hematopoietic progenitors obtained by the methods described herein.
Owner:UNIV HEALTH NETWORK +1
Multipotent adult stem cells having an ability of oct4 expression derived from umbilical cord blood and method for preparing the same
InactiveUS20090305413A1Negative immunological responseBlood/immune system cellsCell culture active agentsGerm layerDisease
The present invention relates to multipotent adult stem cells expressing Oct4, derived from umbilical cord blood (UCB) and also these cell are expressing CD29, CD31, CD44, simultaneously, a method for preparing the same, and more specifically to multipotent adult stem cells which are obtained by culturing umbilical cord blood-derived monocytes in a medium containing bFGF (basic fibroblast growth factor) and human serum or plasma. In addition, multipotent adult stem cells expressing Oct-4 from UCB are morphologically spindle or round shaped cells Although the stem cells according to the present invention are adult stem cells, they are multipotent and capable of differentiating into ectodermal-, messodermal-, endodermal-originated tissue or cells including osteogenic cells or nerve cells etc, thus they can be effectively used in the treatment of intractable diseases and incurable diseases.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
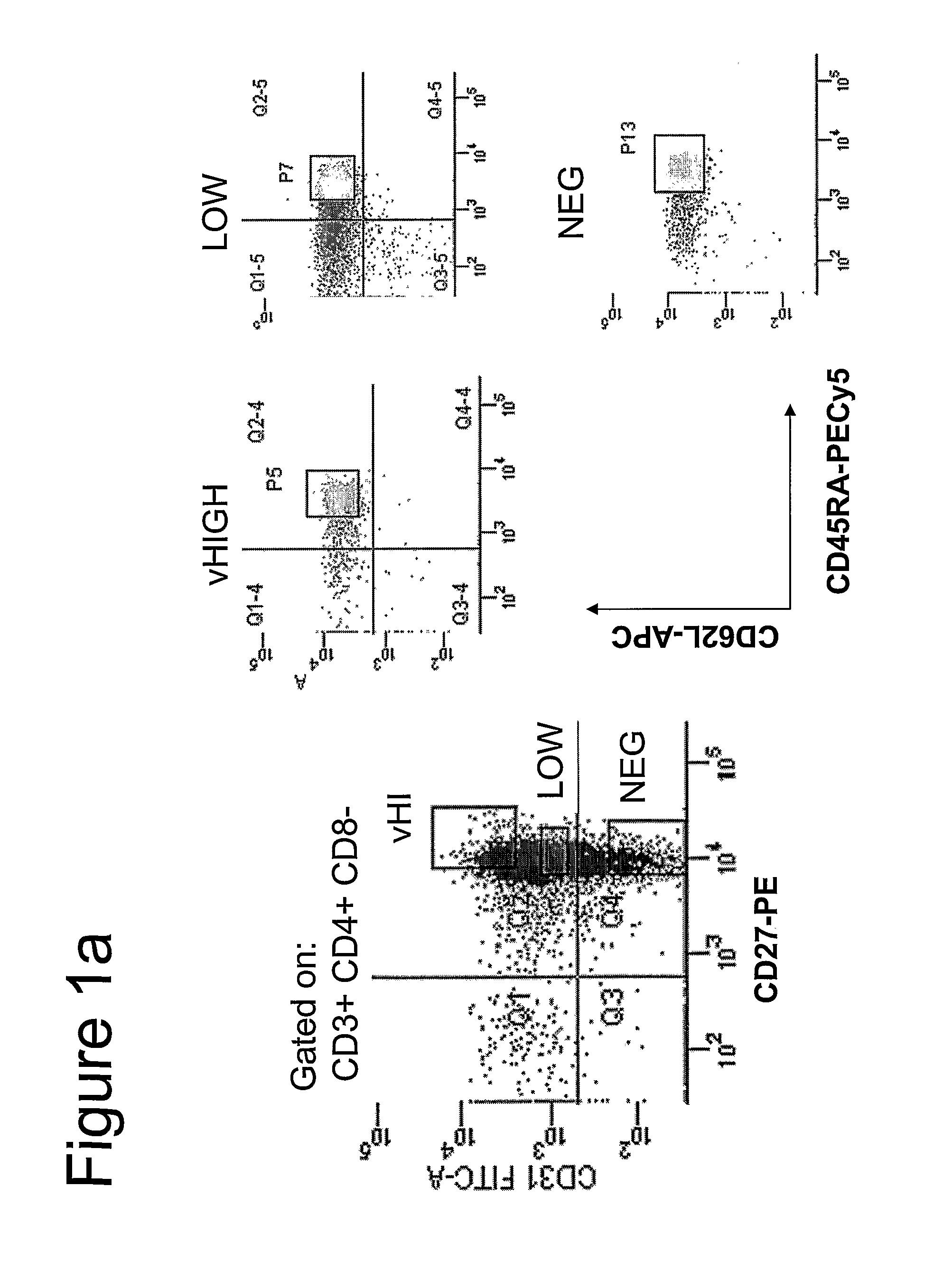
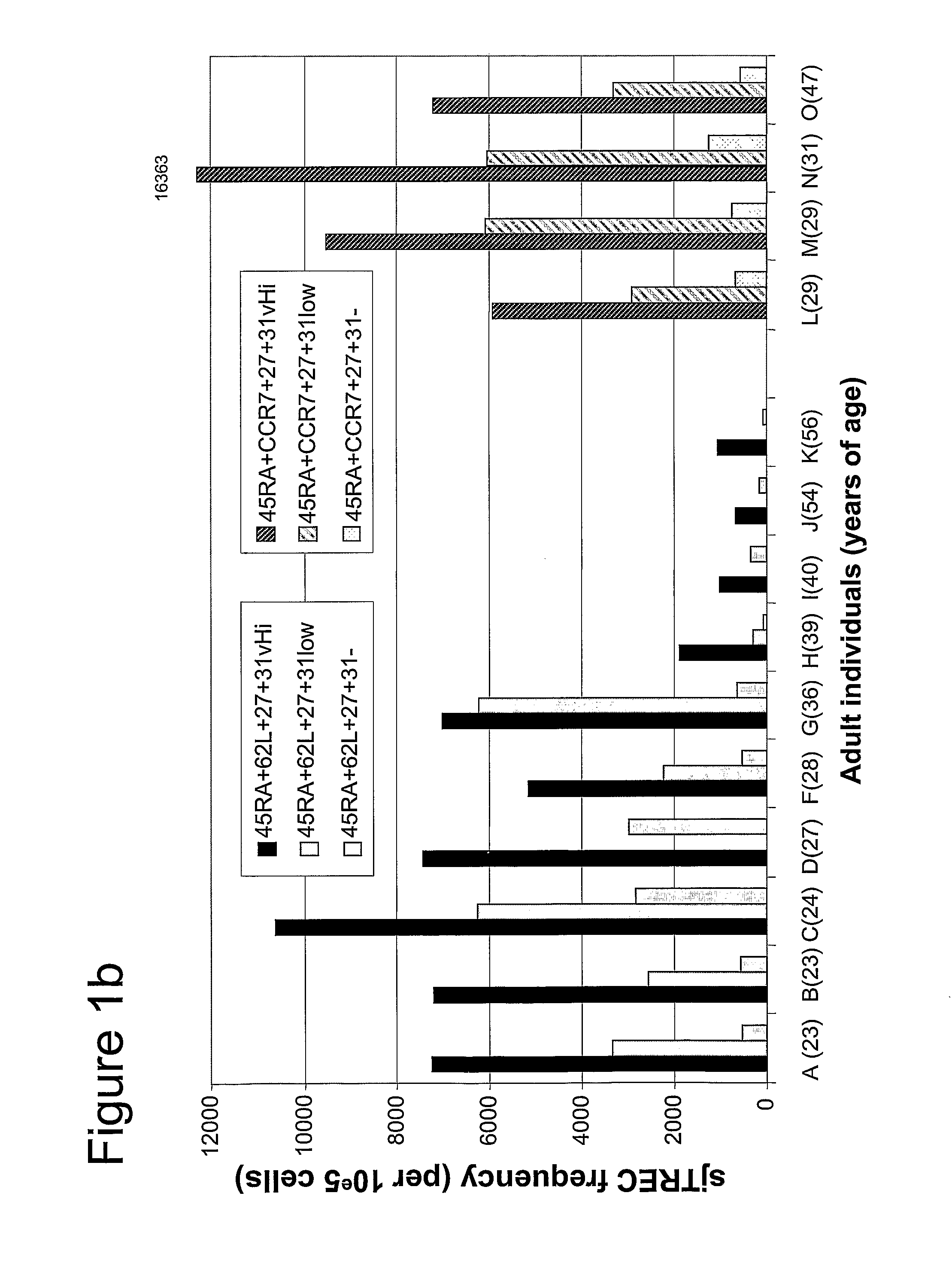
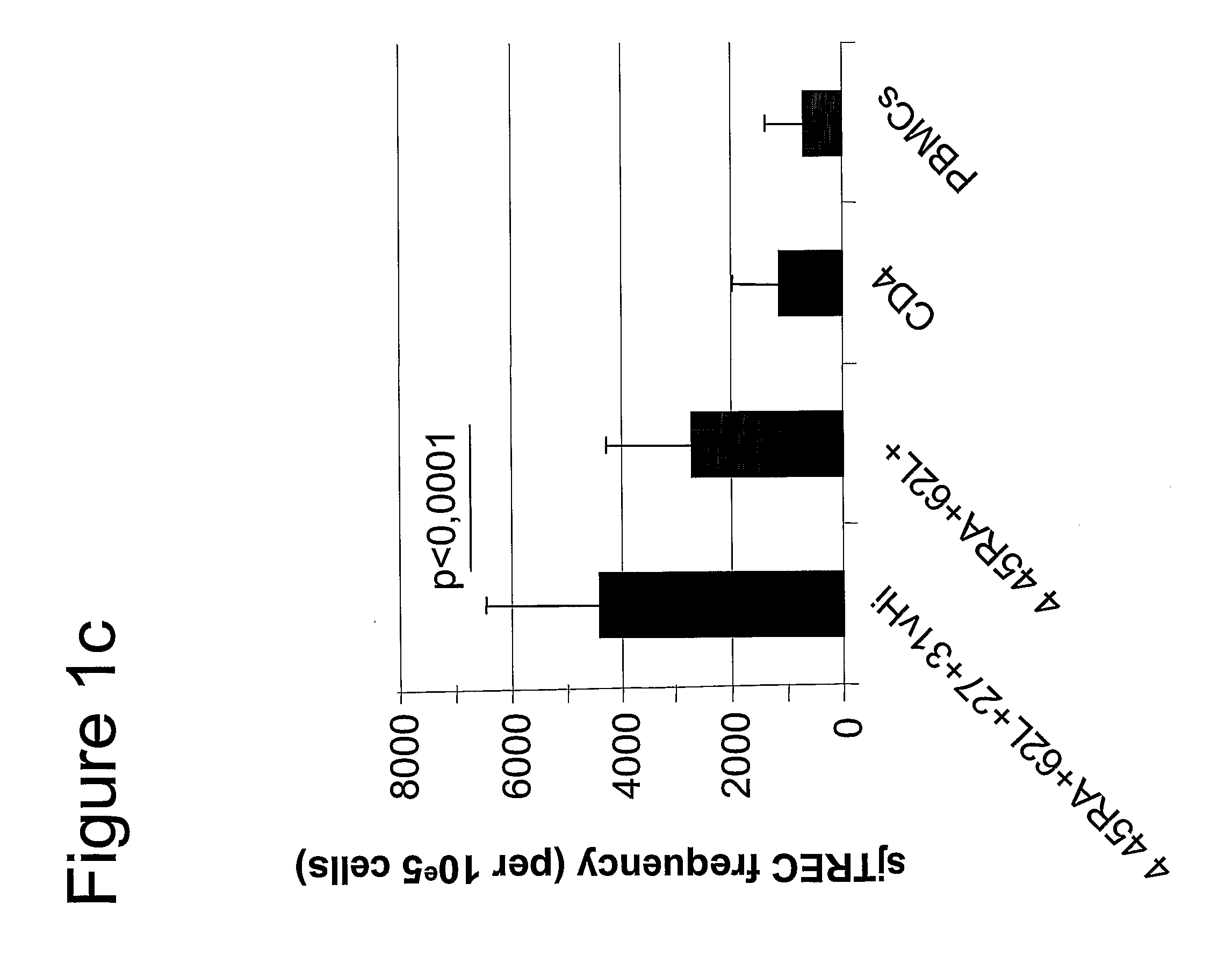
Methods To Identify, Prepare, And Use Naive T Cell Recent Thymic Emigrants
A method of purifying a subpopulation of naive T cells that have recently emigrated from the thymus, comprising (a) contacting a biological sample susceptible of containing T cells with at least four different ligands, namely ligands directed to the markers CD3, CD4, CD45RA, and CD31; (b) sorting the cells so as to recover T cells having a phenotype comprising at least the following four markers CD3+, CD4+, CD45RA+ and CD31hi, whereby a subpopulation of naive T cells is purified.
Owner:SEKALY RAFICK PIERRE +4
Method for inducing differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells into endothelial progenitor cells
ActiveCN110438065AImprove efficiencyArtificial cell constructsArtificially induced pluripotent cellsProgenitorSurface marker
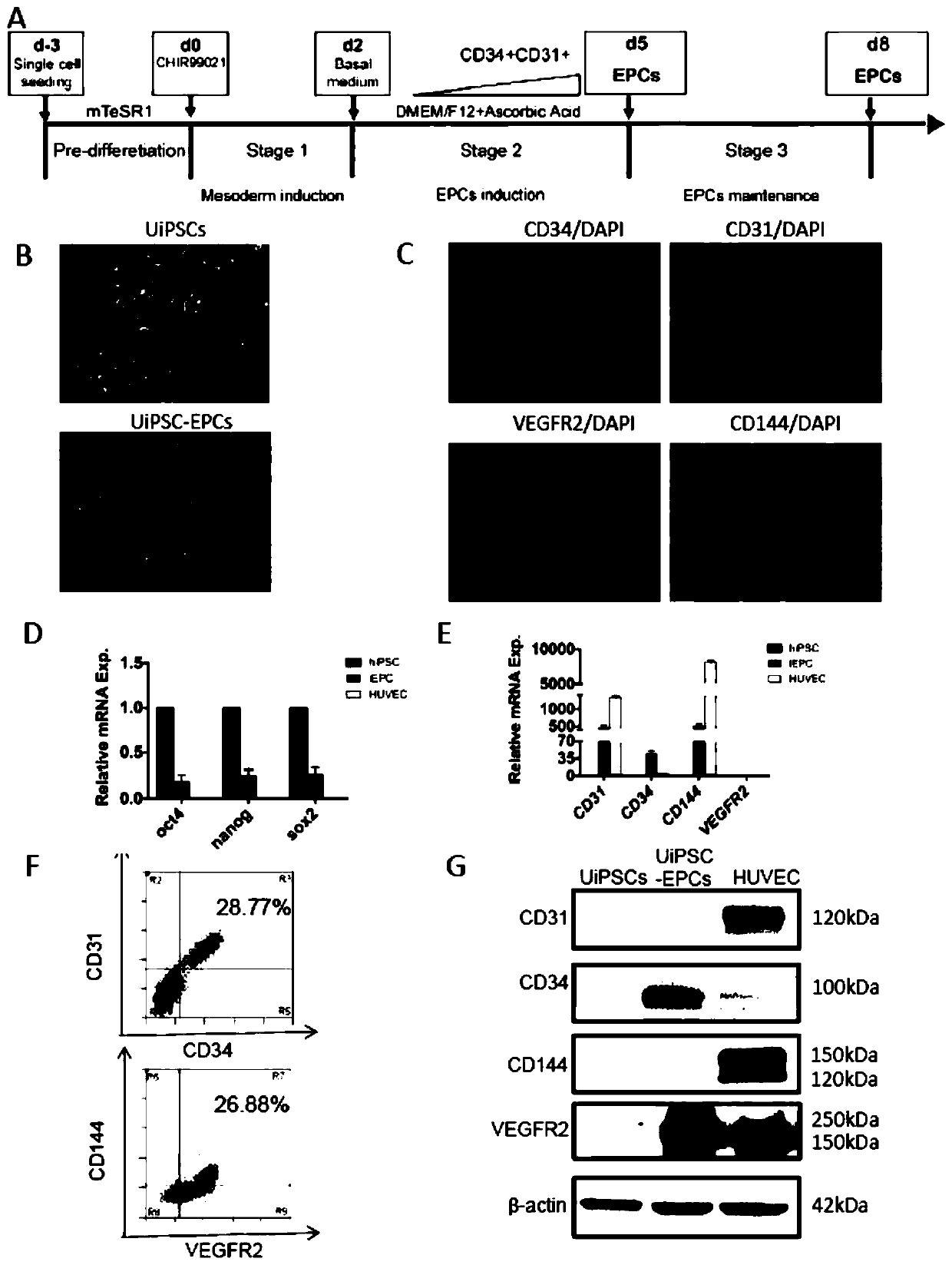
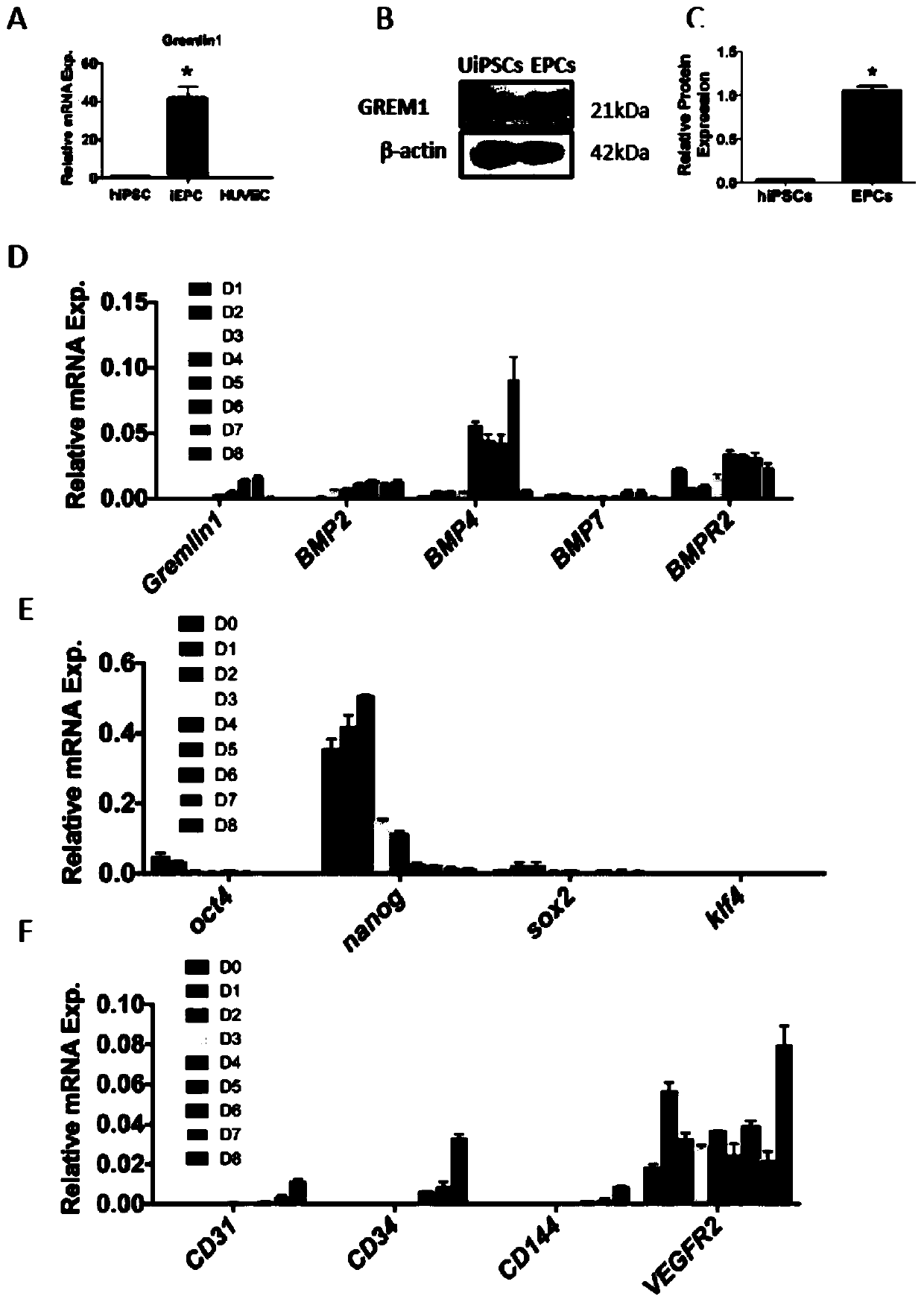
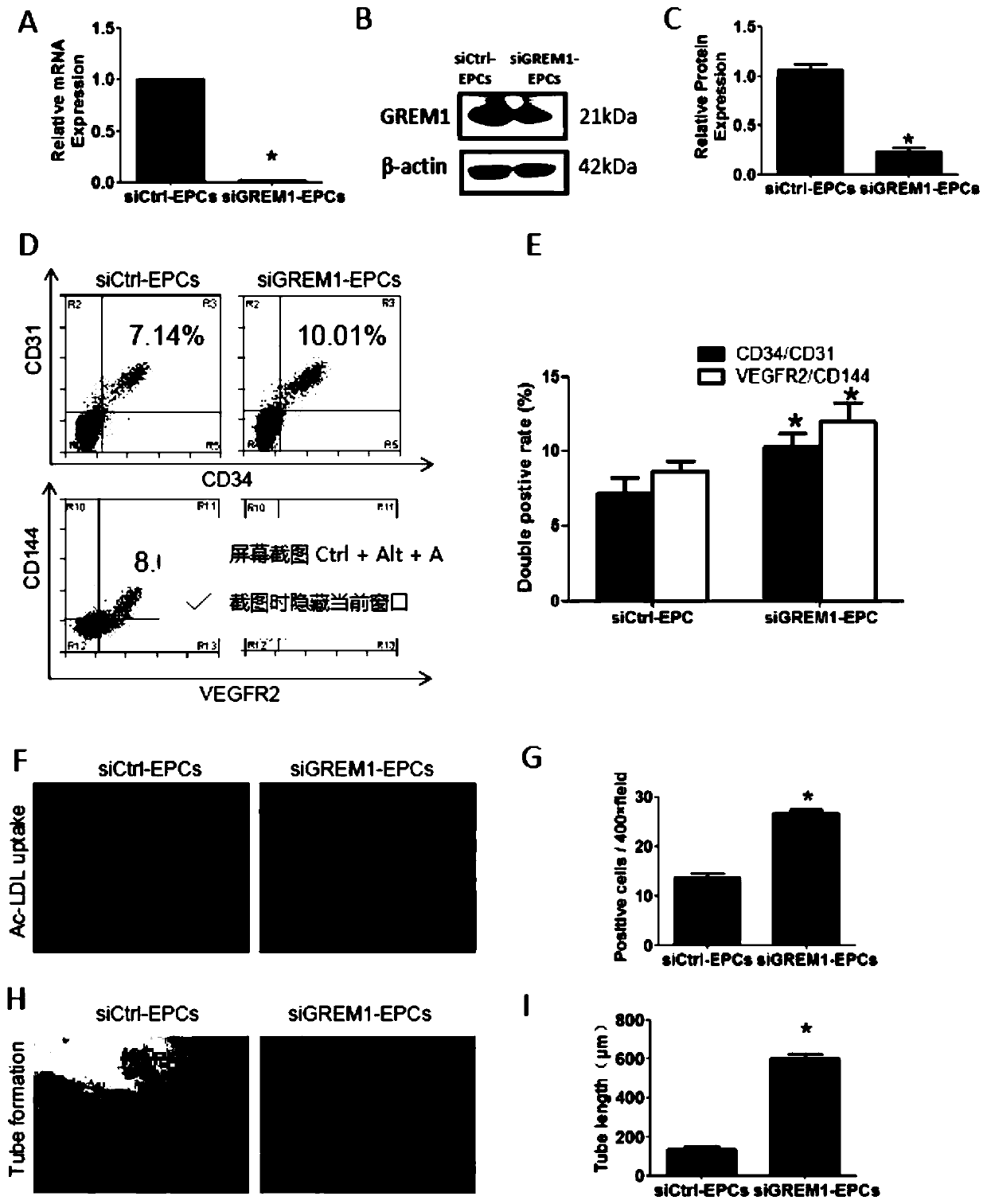
The invention discloses a method for inducing differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells into endothelial progenitor cells. The method for inducing differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells into endothelial progenitor cells comprises the following steps: 1) maintaining culture of human induced pluripotent stem cells in an mTeSR1 culture medium, carrying out inoculation at a density of 80-90% on a six-well plate coated with matrix adhesive, and adding the mTeSR1 culture broth into Y27632; 2) after 24 hours of inoculation, starting induction of differentiation with a DMEM / F12 medium added into the culture broth at the beginning of the induction of differentiation; and 3) sucking the medium on day 2 of differentiation, adding DMEM / F12 medium, changing DMEM / F12medium every day so as to allow maintenance of cells, adding recombinant protein GREM1 on days 0-2, days 3-5 or days 5-8 of differentiation, and then, detecting cell surface markers so as to obtain CD34+ and CD31+ endothelial progenitor cells. Being adopted, the method for inducing differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells into endothelial progenitor cells disclosed by the inventionis capable of efficiently obtaining double-positive (namely CD34+ and CD31+) endothelial progenitor cells; and the differentiation efficiency is up to 22.4-34.7%.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Method for separating and purifying rat dermal microvascular endothelium cells
InactiveCN104877955AFully exposedHigh purityArtificial cell constructsVertebrate cellsNeutral proteaseParenchyma
The invention discloses a method for separating and purifying rat dermal microvascular endothelium cells. The method for separating and purifying the rat dermal microvascular endothelium cells relates to the technical field of animal blood vessel endothelium cell culture in vitro, in particular to a method for culturing the rat dermal microvascular endothelium cells in vitro. The method is characterized by the following steps of digesting rat skin through neutral protease II, separating to obtain a dermal layer, digesting through collagenase I and II, obtaining single-cell suspension, and utilizing a CD31 immunomagnetic beads sorting technology to obtain purified target cells. Through the method, the pollution of parenchyma cells in microvascular endothelium cell culture can be simply, conveniently and effectively solved, the rat dermal microvascular endothelium cells with high purity can be obtained through separating, and no obvious morphological feature change occurred after continuous cell culture for 20 times.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF AGRI
Populations of hematopoietic progenitors and methods of enriching stem cells therefor
ActiveUS9834754B2Avoid signalingCulture processBiological material analysisPluripotential stem cellHematopoietic progenitor
There is described herein a method of enriching a population of stem cells for hematopoietic progenitors. The method comprises inducing hematopoietic differentiation in a population of human embryonic stem cells or human induced pluripotent stem cells; sorting the population based on expression of CD43 and at least one of CD34, CD31 and CD144; and selecting a fraction that is at least one of CD34+CD43−, CD31+CD43− and CD144+CD43−. Also provided are populations of hematopoietic progenitors obtained by the methods described herein.
Owner:SUNNYBROOK RES INST +1
Isolated lineage negative hematopoietic stem cells and methods of treatment therewith
Isolated, mammalian, adult bone marrow-derived, lineage negative hematopoietic stem cell populations (Lin− HSCs) contain endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) capable of rescuing retinal blood vessels and neuronal networks in the eye. Preferably at least about 20% of the cells in the isolated Lin− HSCs express the cell surface antigen CD31. The isolated Lin− HSC populations are useful for treatment of ocular vascular diseases and to ameliorate cone cell degeneration in the retina. In a preferred embodiment, the Lin− HSCs are isolated by extracting bone marrow from an adult mammal; separating a plurality of monocytes from the bone marrow; labeling the monocytes with biotin-conjugated lineage panel antibodies to one or more lineage surface antigens; removing of monocytes that are positive for the lineage surface antigens from the plurality of monocytes, and recovering a Lin− HSC population containing EPCs. The isolated Lin− HSCs also can be transfected with therapeutically useful genes. The treatment may be enhanced by stimulating proliferation of activated astrocytes in the retina using a laser.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
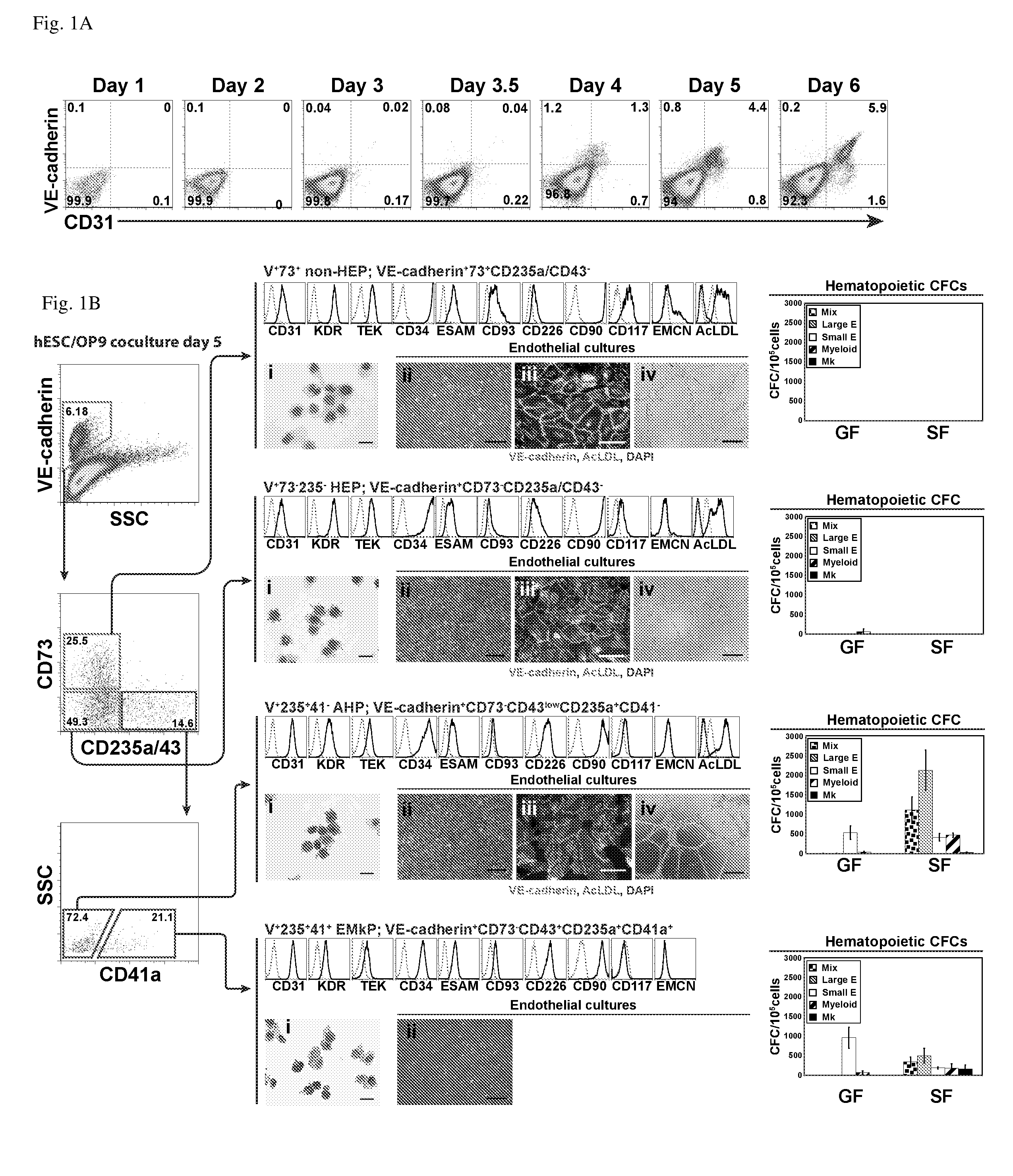
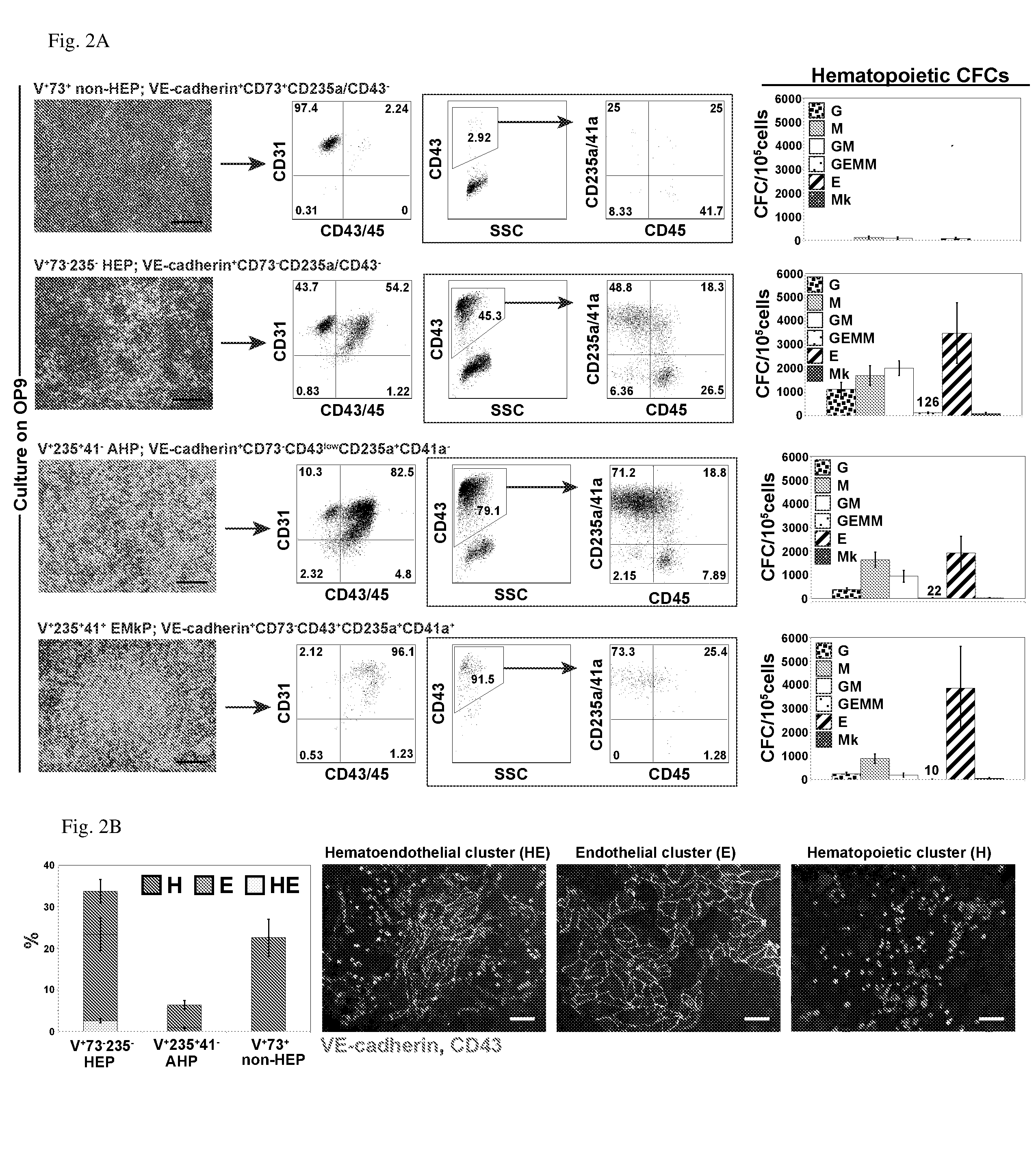
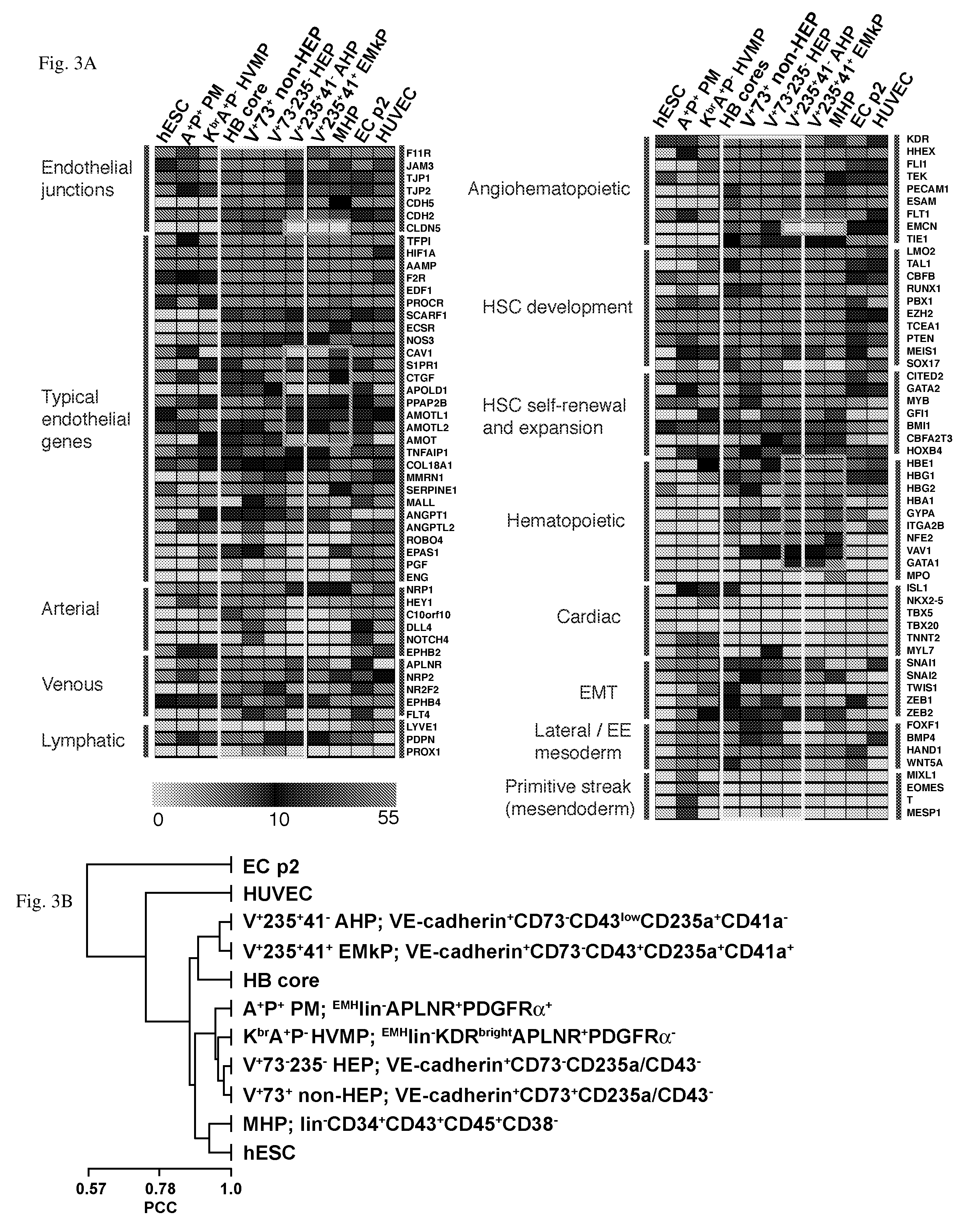
Angiohematopoietic Progenitor Cells
A purified human cell population of subsets of angiohematopoietic progenitor cells, wherein the population is at least 94% pure and wherein the cells are selected with cell markers selected from the group of KDR, APLNR, VE-cadherin, PDGFRα, CD31, CD235a, CD73, CD43, and CD41a.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Method for isolating stem cells and their use in cell therapy
The invention relates to a method for isolating muscle-derived stem cells that can be used in cell therapy, said method comprising the steps of (i) dissociating cells from at least one muscle sample, (ii) plating the cells obtained at the end of step (i) on a non-coated cell container, (iii) isolating the cells present in the supernatant of the non-coated cell container obtained at the end of step (ii), (iv) plating the cells obtained at the end of step (iii) on a coated cell container, (v) isolating the cells present in the supernatant of the coated cell container obtained at the end of step (iv), (vi) repeating, or not, the steps (iii) and (iv) at least one or two times, (vii) plating and culturing the cells isolated from the supernatant of the coated cell container obtained at the end of step (vi) until said cells have reached a confluence level of at least 50%, (viii) isolating, at the end of step (vii), the stem cells which can be used in cell therapy, wherein after expansion (a) at least 95% of said cells express CD44, CD73, (b) at least 95% of said cells express CD29, (c) at least 70% of said cells express CD90, and (d) said cells do not express CD4, CD8, CD34, CD45, CD31, CD1 17, CD144 and CD133. The invention also relates to said isolated stem cells and pharmaceutical compositions containing them.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL DE LA RECHERCHE AGRONOMIQUE +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com