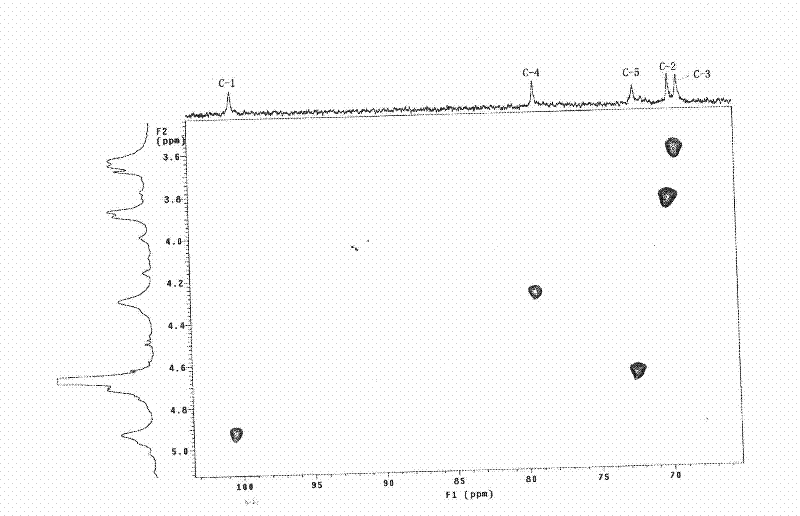
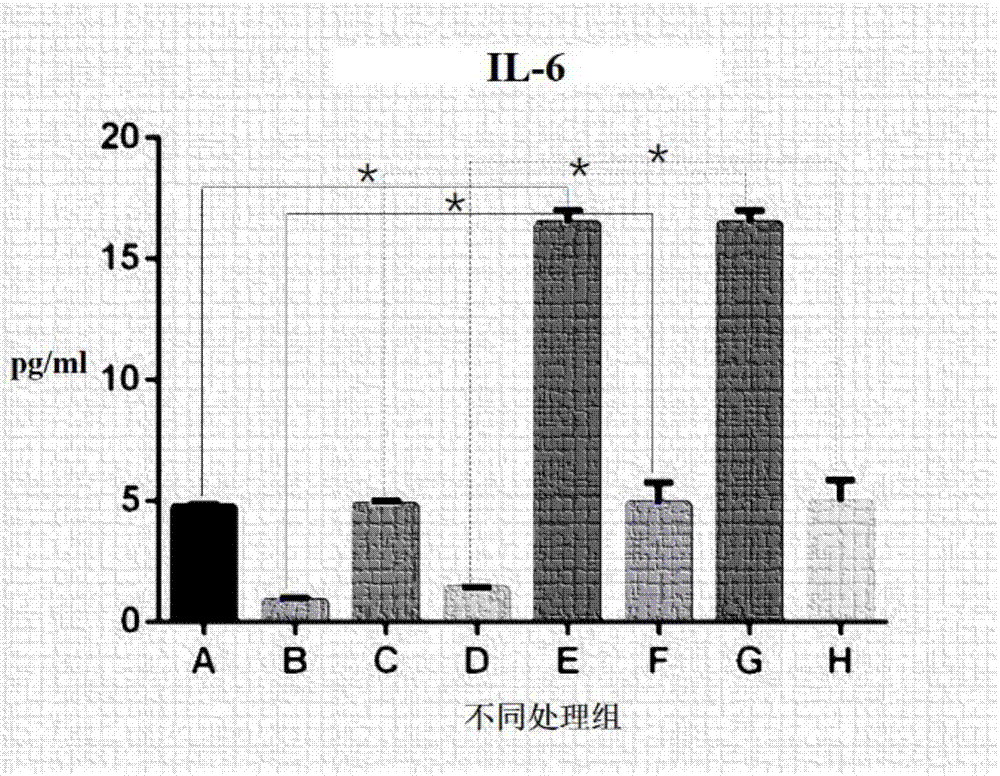
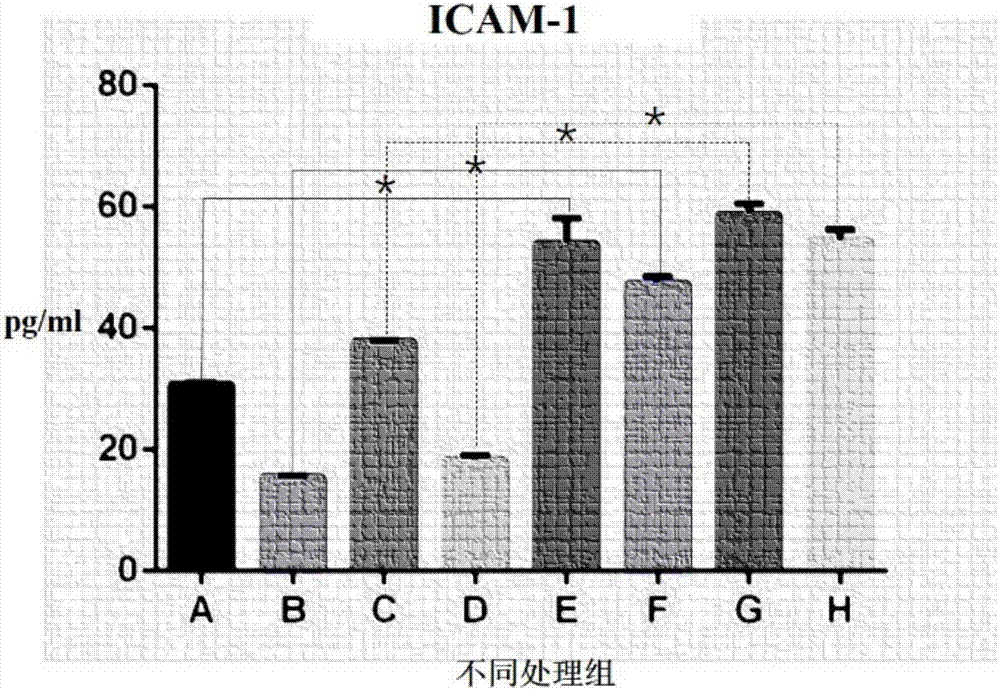
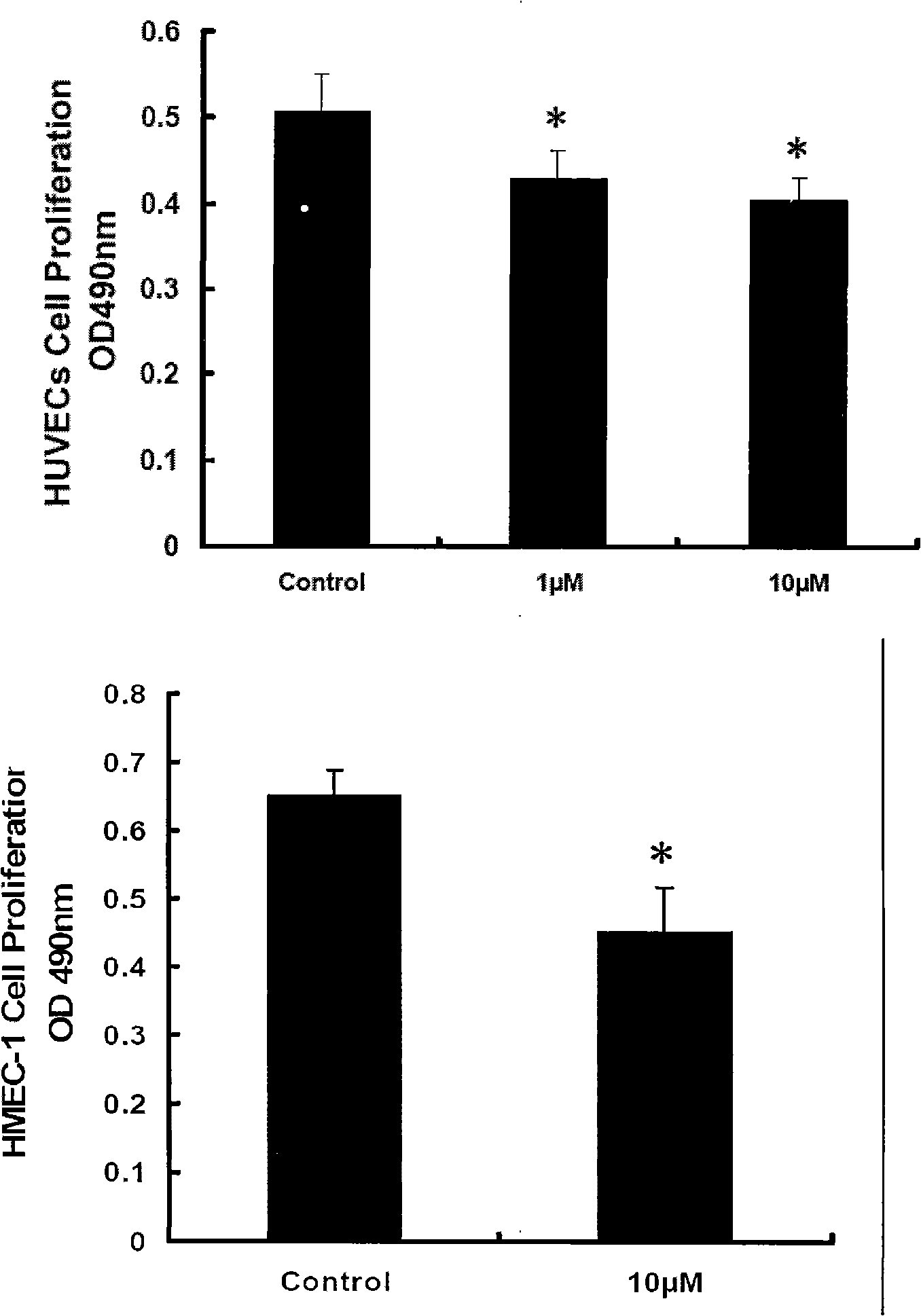
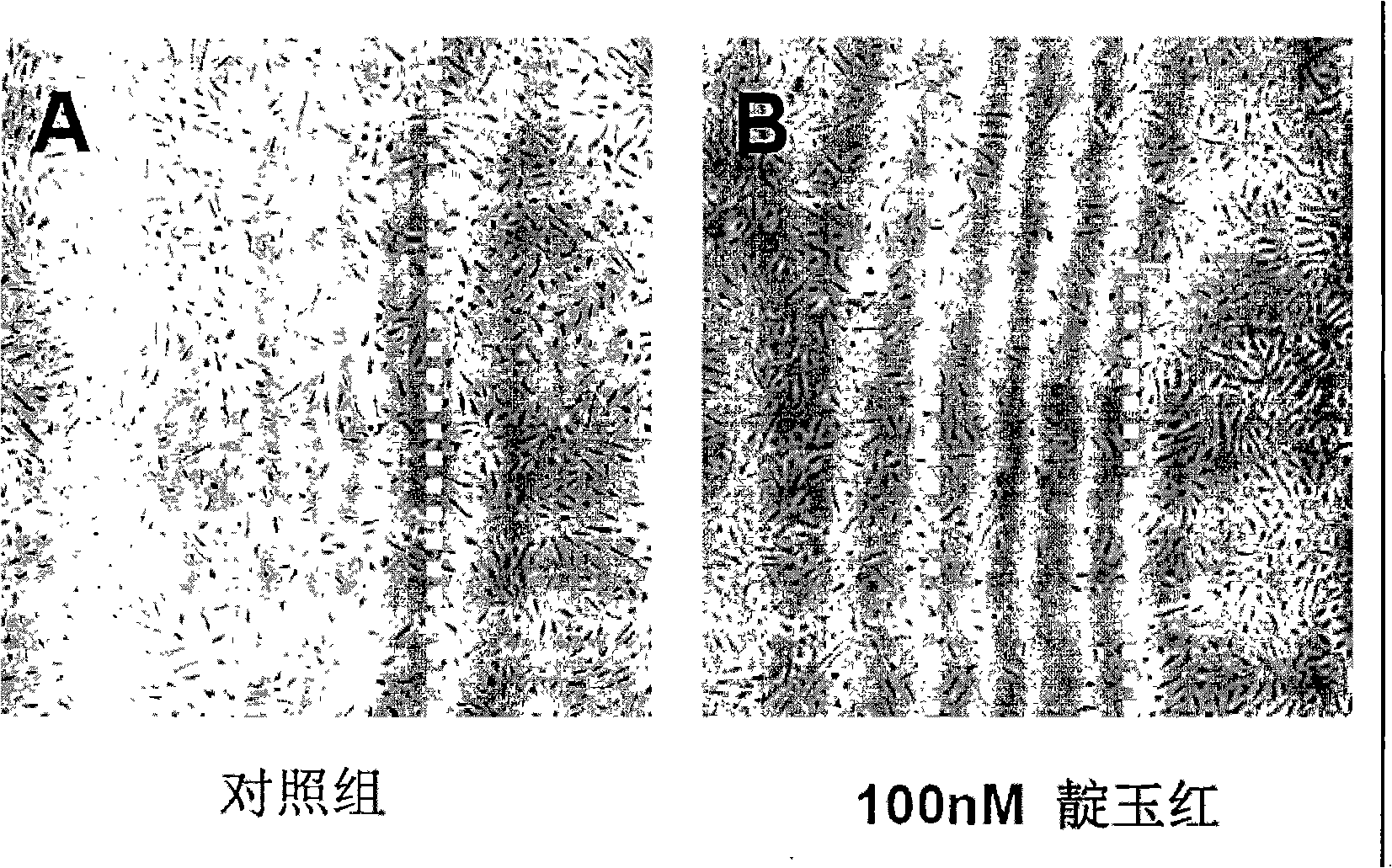
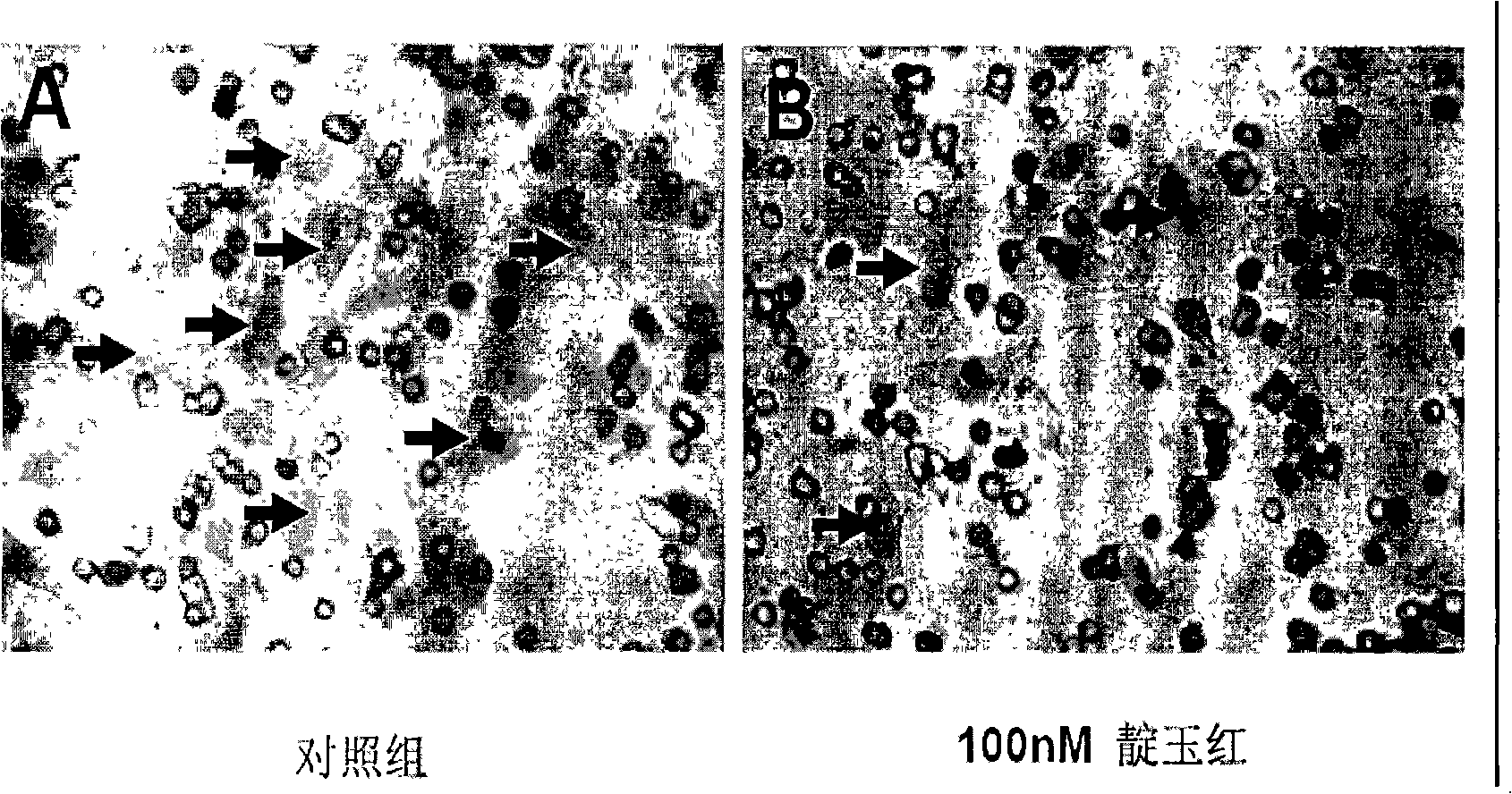
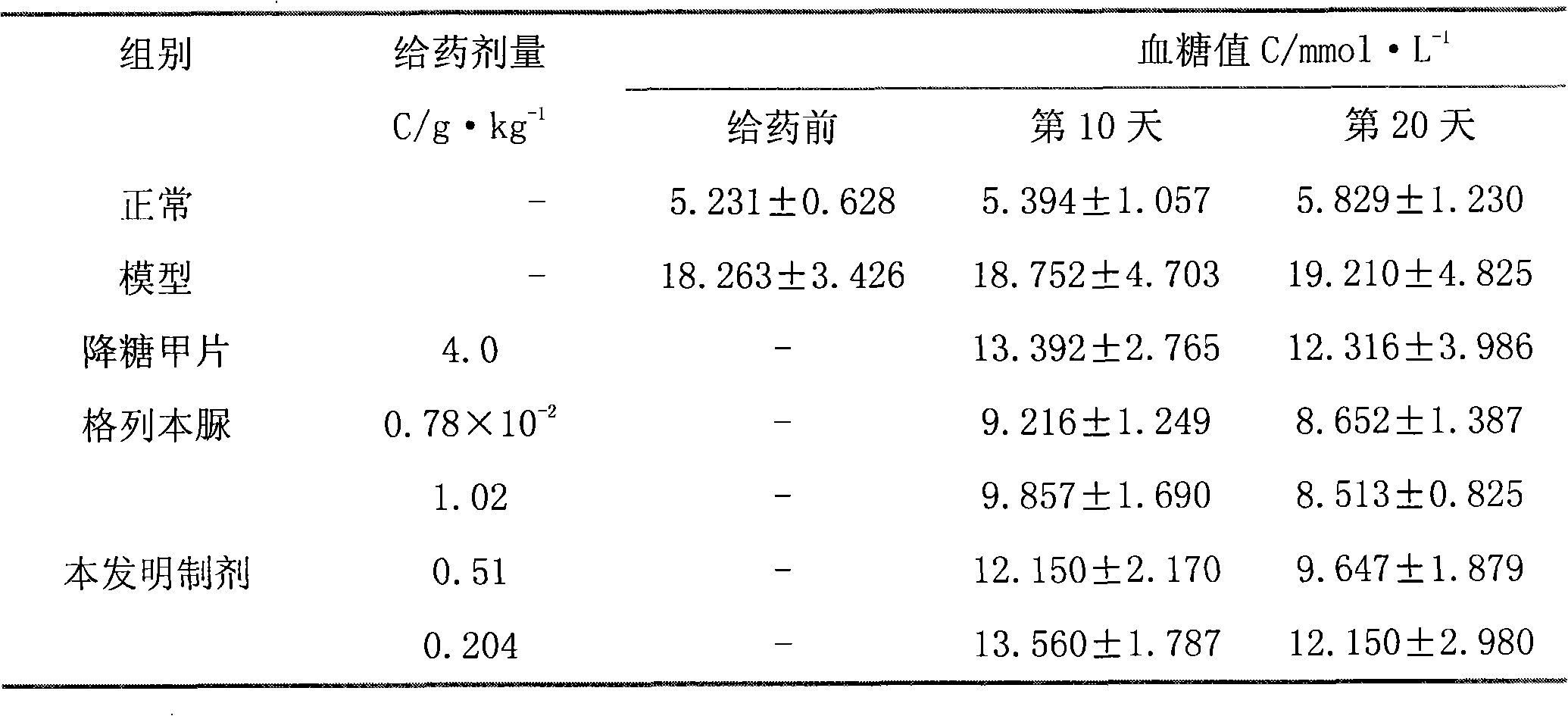
Patents
Literature
87 results about "Microvascular endothelium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
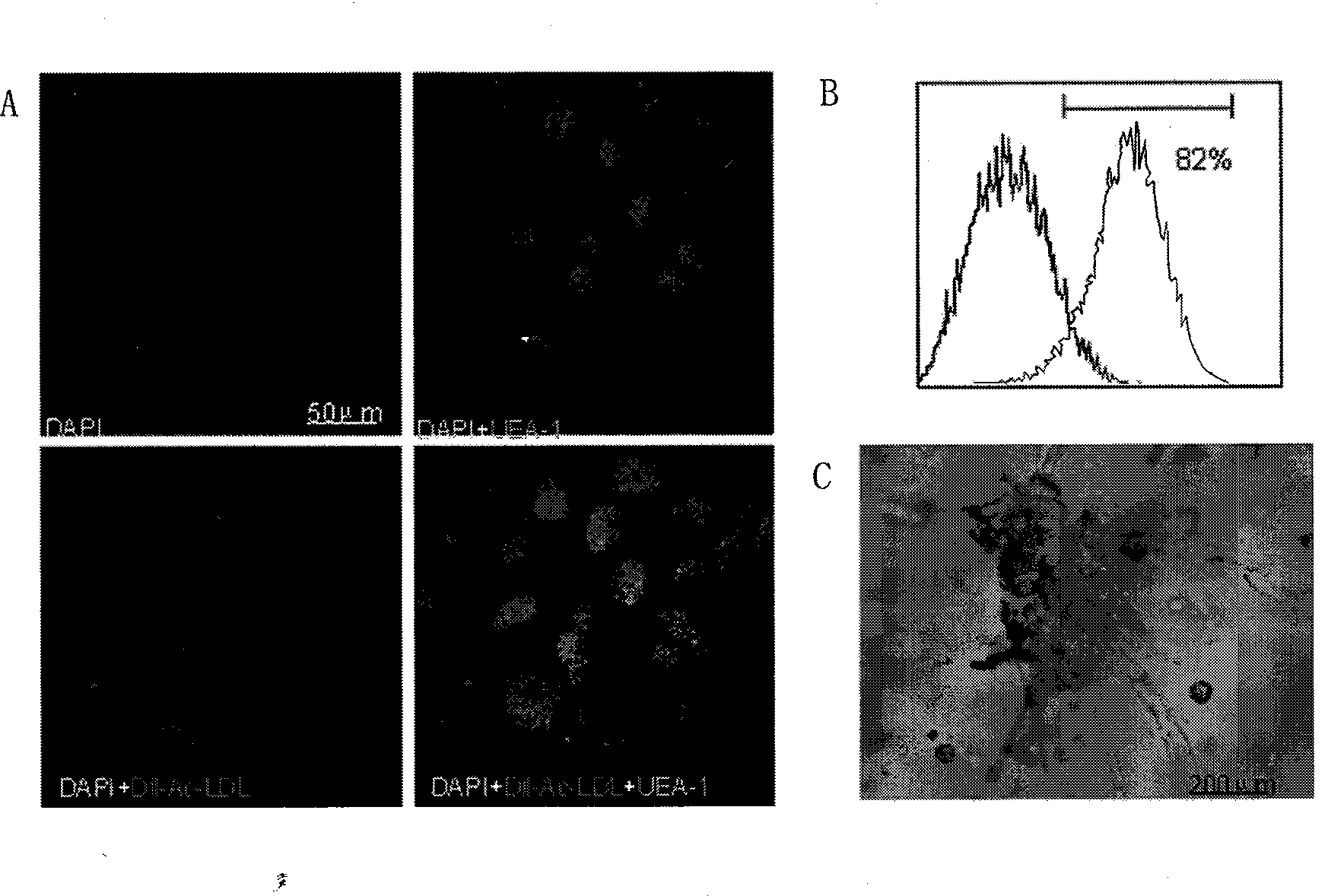
The endothelium of the brain microvasculature represents the interface between blood and the central nervous system. Due to its unique location, it has specific protective properties that strictly regulate the infiltration of plasma components and circulating cells into the brain.
Devices for harvesting and homogenizing adipose tissue containing autologous endothelial cells
InactiveUS6020196AExpand the populationEasy to operateBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrotherapyAmbient pressureWhite adipose tissue
Disclosed herein are methods for harvesting adipose tissue so as to preserve an increased population of viable microvascular endothelial cells. Adipose tissue containing microvascular endothelial cells is harvested using a collection apparatus incorporating an elongate cannula having apertures with tissue cutting edges. A sub-ambient pressure is applied to a lumen in the cannula to draw the adipose tissue through the aperture where it is then severed using the cutting edge to disrupt the connective adipose matrix. This harvesting provides a cleaner, more homogeneous sample of adipose tissue, thereby increasing the population of viable microvascular endothelial cells obtained through further processing. Rapid and easy methods for the further homogenization of the harvested adipose tissue are also disclosed.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Novel small molecules with selective cytotoxicity against human microvascular endothelial cell proliferation
InactiveUS20070254894A1Little and no harmful effectMinor side effectsBiocideOrganic chemistryAngiogenesis growth factorAngiogenic inhibitors
Disclosed herein are angiogenesis inhibitors represented by formula (I) or formula (II): The variables for formulas (I) and (II) are defined herein.
Owner:KANE JOHN L JR +5
Microfluidic chip and method for establishing in-vitro co-culture model of three kinds of cells
ActiveCN104630059AScientific reproductionNervous system cellsArtificial cell constructsDiseaseBasic research
The invention relates to the field of micromachining technology and tissue engineering technology, and particularly relates to a microfluidic chip and method for establishing an in-vitro co-culture model of three kinds of cells. The microfluidic chip is used for establishing a co-culture model of three kinds of cells; different cells are located in different areas through connected micro-channels in the microfluidic chip; and two kinds of cells can conduct cell communication through the connected micro-channels. Therefore, through the scheme, a new model capable of connecting astrocyte as a middle bridge in a neurovascular unit with the neuron and microvascular endothelial cell in a three-dimensional or plane space is established in vitro, a neurovascular network in the brain can be reproduced in vitro more scientifically and really, and a better platform is provided for clinical basic research on the central nervous system diseases and particularly the blood vessels of brain; and meanwhile, as an emerging biochip, the microfluidic chip is used for establishing the neurovascular in vitro, and thus the application range of the microfluidic chip is further widened.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for culturing cells
InactiveUS20020039787A1Enhance microvascular endothelial cell growthHigh purityDiagnosticsCulture processCulture cellIn vitro growth
Owner:MONASH UNIV
Method for separating and purifying mouse lung microvascular endothelial cell
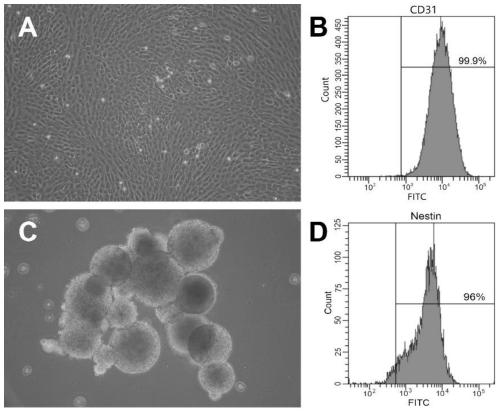
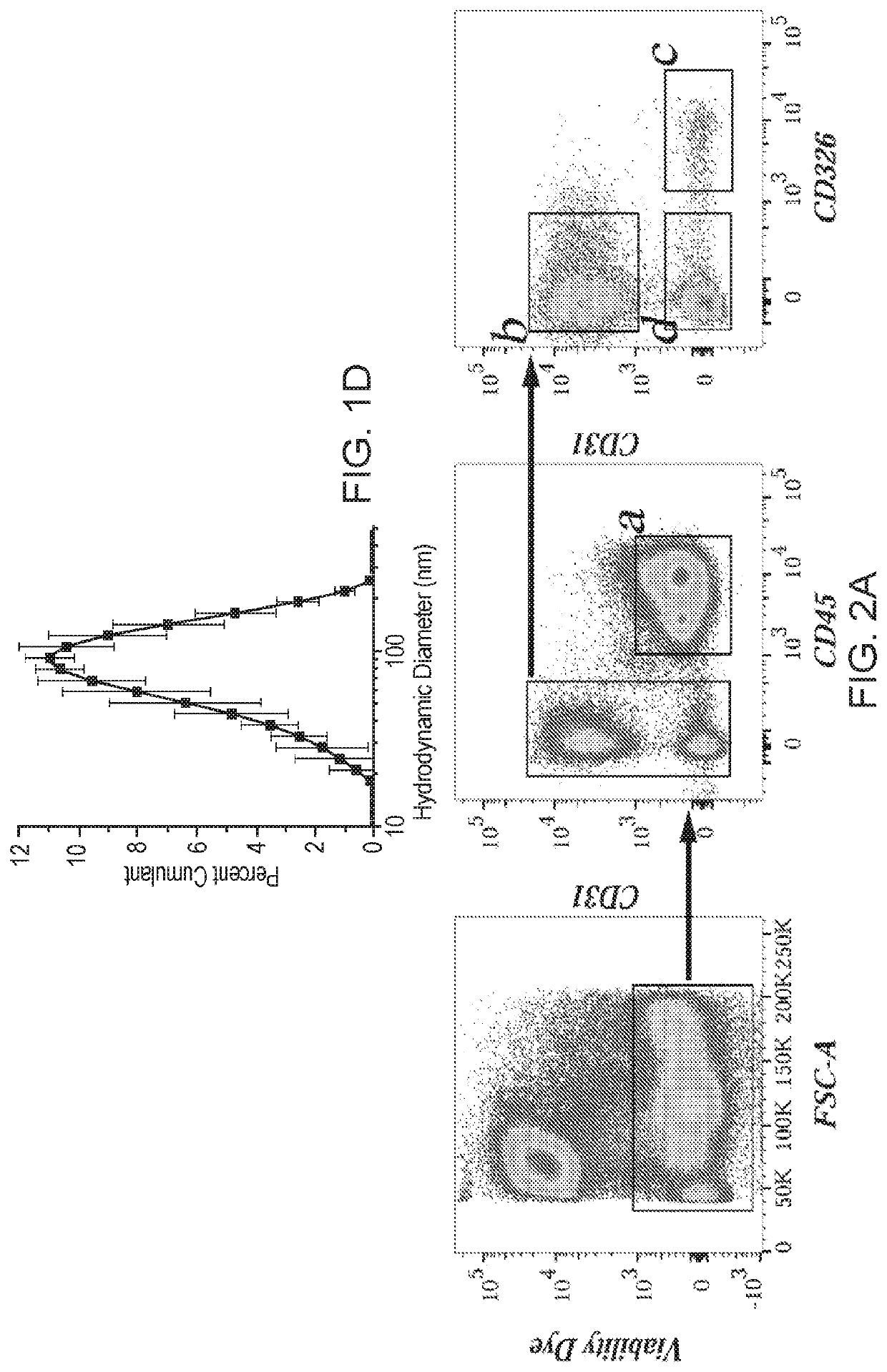
A method for separating and purifying mouse lung microvascular endothelial cell is characterized by comprising using an enzyme to perform digestive treatment on subpleural lung marginal tissue to obtain a single-cell suspension, and performing CD31 immunomagnetic bead sorting to obtain the target cell. Concretely, the method comprises getting subpleural lung marginal tissue of a large suckling mouse, firstly using a mixed solution of collagenase II and neutral protease for digestion to prepare the single-cell suspension, then performing incubation combination with CD31 immunomagnetic bead, then utilizing a magnetic bead sorting purification system to screen CD31+ cell, and removing magnetic beads combined with CD31+ cell by using a magnetic-bead release solution, so as to obtain high-purity mouse lung microvascular endothelial cell. The advantages comprise that the high-purity mouse lung microvascular endothelial cell can be obtained from mouse lung tissue through separation extraction by using enzyme digestion to prepare the single-cell suspension and performing CD31 immunomagnetic bead sorting.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF AGRI
Anti-tumor medicine
InactiveCN101103973AOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsAbnormal tissue growthProstate cancer cell
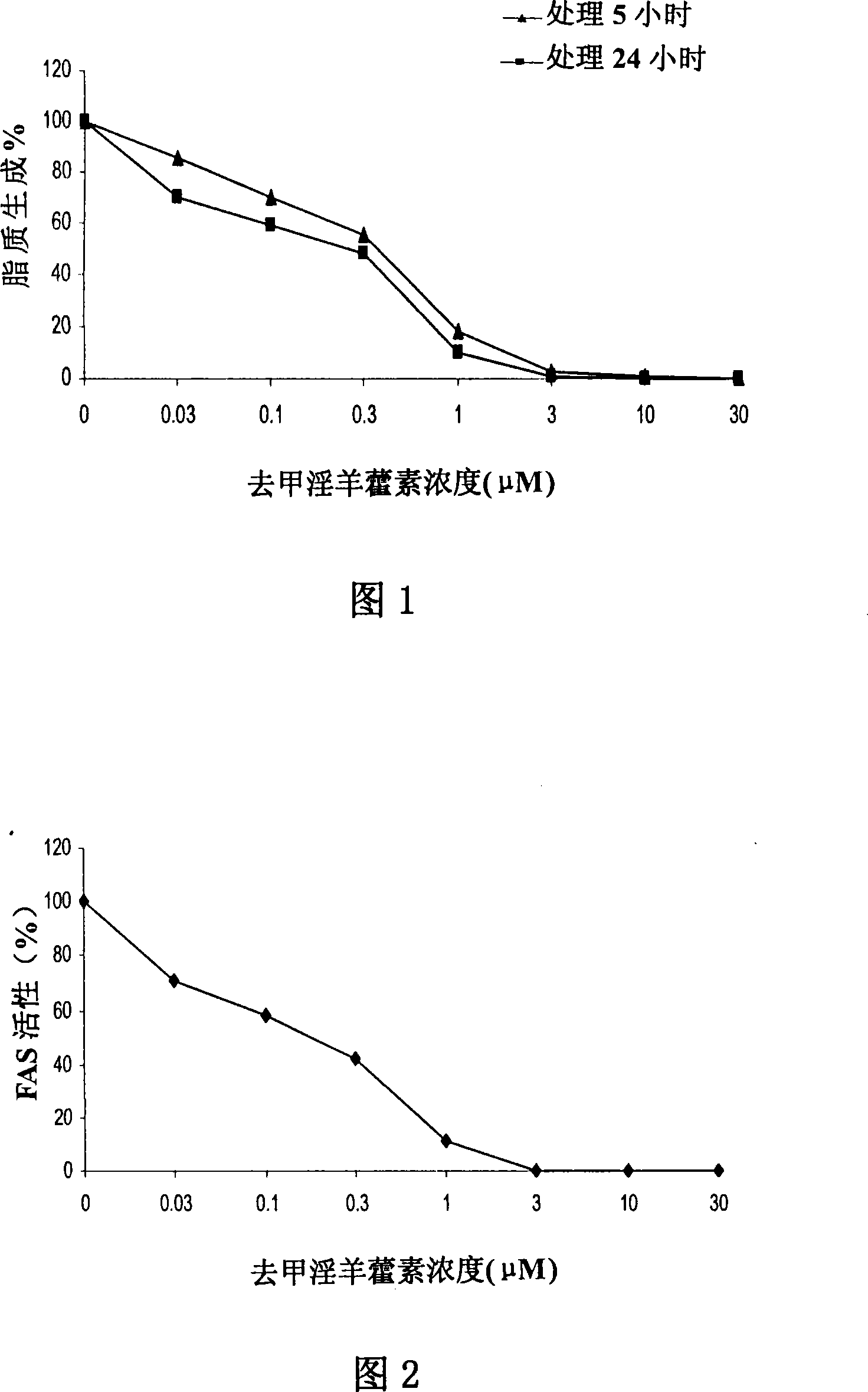
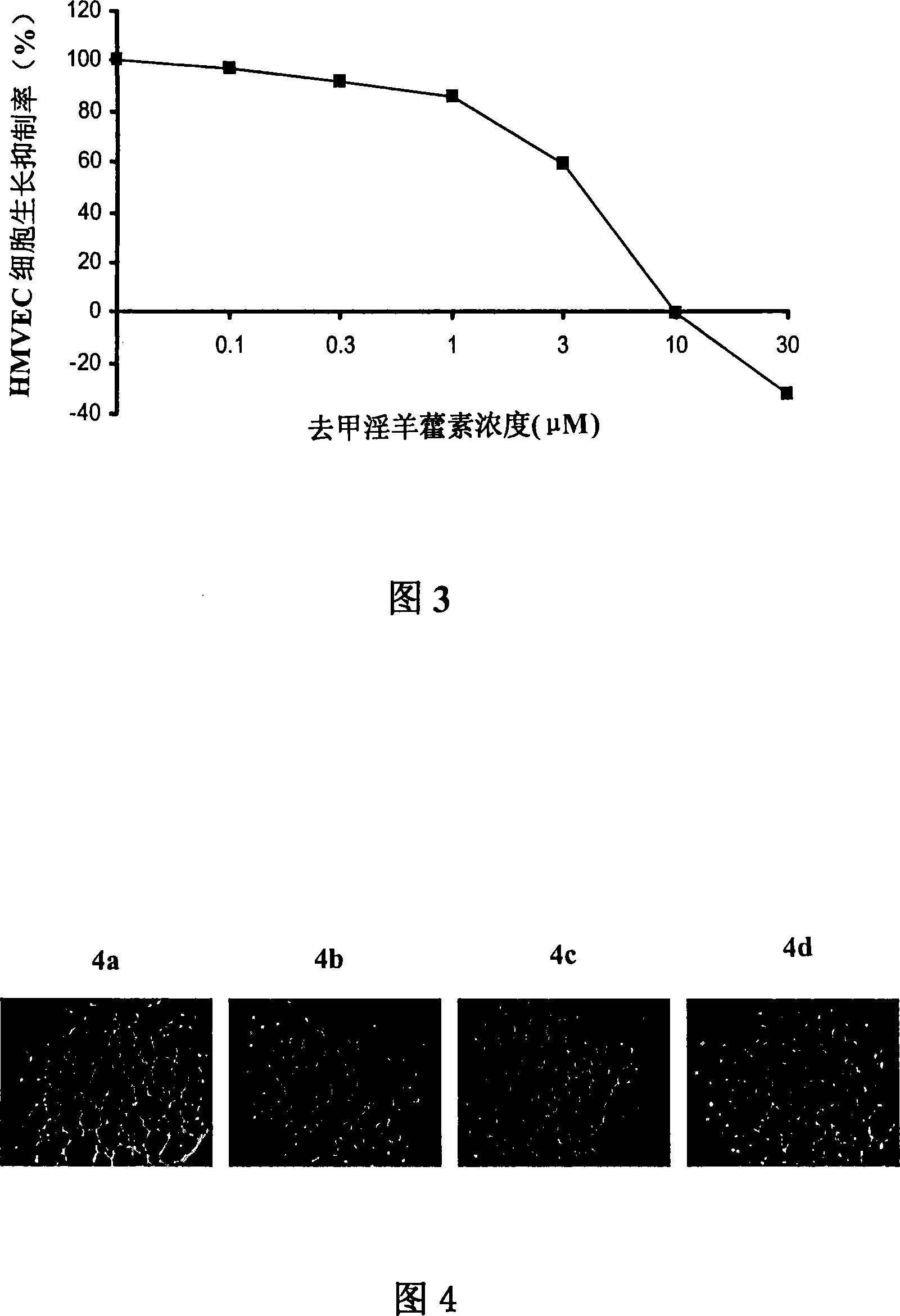
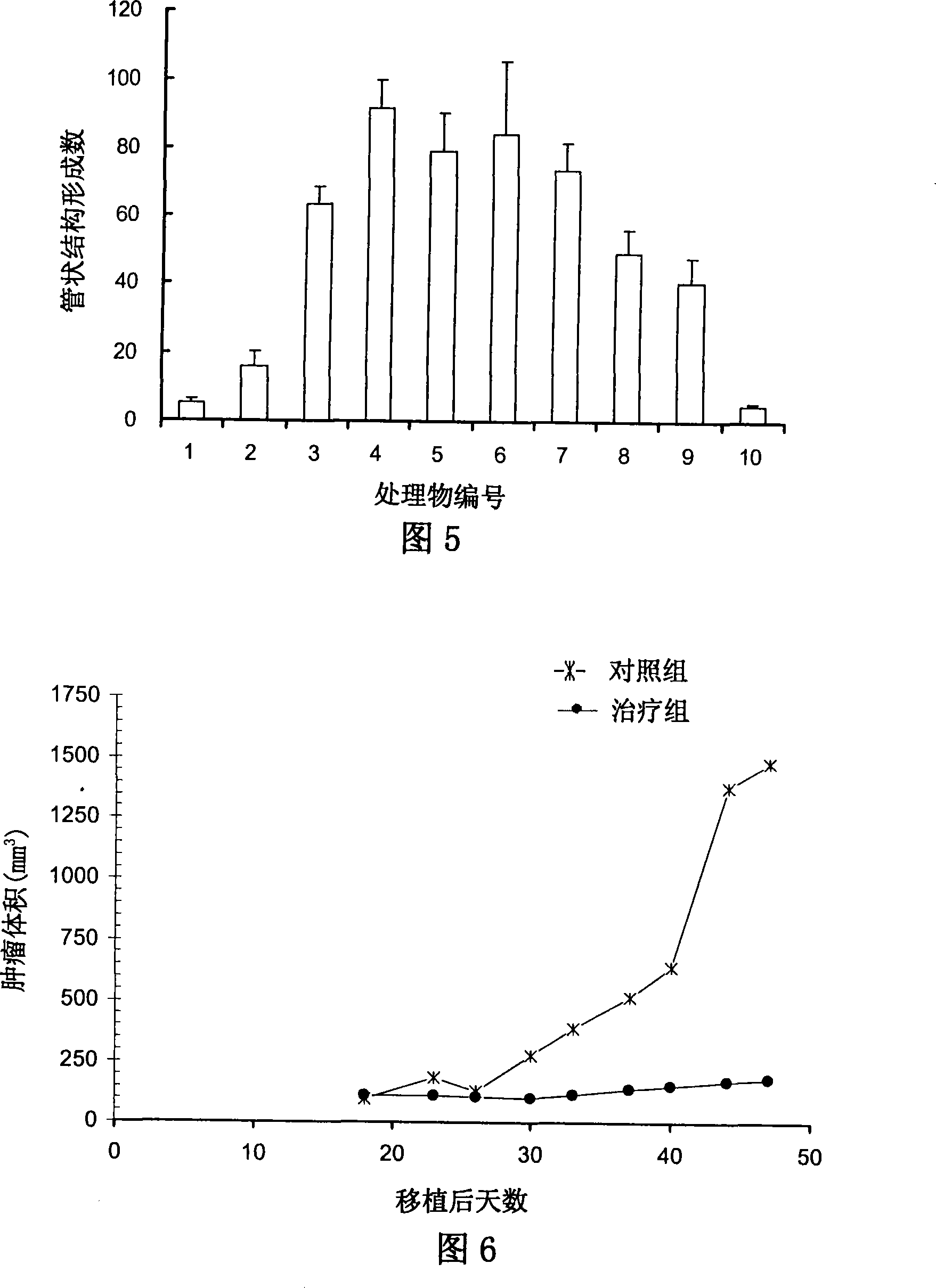
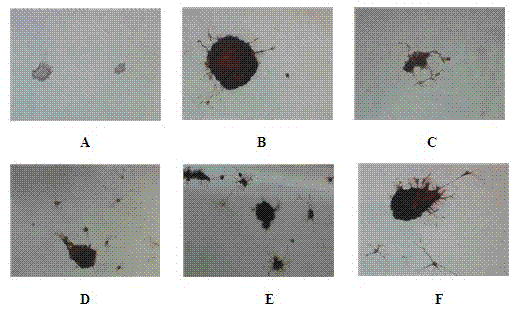
Disclosed is an anti-tumor drug with nor-icariin as the effective ingredient. Pharmacological test effect proves that the nor-icariin has the activity to inhibit the production of cellular lipid, can reduce the production of cellular fatty acid by inhibiting the activity of FAS, has a function of inhibiting the production and causing withering of microvascular endothelial cells, shows a broad-spectrum anti-tumor function in a cytotoxicity test of thirty-three tumor cell strains of a human body, and shows a function in strongly inhibiting the production of tumor, such as prostate cancer cells LnCAP, lung cancer cells NCI-H23 and colon cancer cells HCT-116 of a human body in a tumor transplantation nude mice model test. A pharmacokinetics test of the nor-icariin in the body of a little mouse proves that the nor-icariin can be kept with a certain concentration, good for better anti-humor effect. The acute toxicity test of the nor-icariin in the body of the mouse shows nontoxicity; therefore the nor-icariin is proved to be a newly-developed broad spectrum anti-humor drug with broad development prospect.
Owner:殷正丰 +1
Application of daucosterol in preparing medicines for promoting proliferation of neural stem cells
The invention relates to a new application of daucosterol in medicine and health care product preparation, in particular to application of daucosterol in preparing medicines and health care products for promoting proliferation of neural stem cells. The daucosterol is a phytosterol derivative and is sitosterol-3-O-glucoside which widely exists in plants, and the processes of extracting, separation and content detection are simple and convenient. According to research, the medicines can promote proliferation of osteoblastlike cells, protect endothelial cells of human capillaries and further can reduce blood sugar activity. By means of the application, primarily-cultured neural stem cells and aged mice serve as the materials, and users can observe the effect of daucosterol on the neutral stem cells. In-vitro experiments and integral experiments prove that the daucosterol has the effect of promoting proliferation of the neutral stem cells. In the in-vitro experiments, the daucosterol with the dose ranging from 10 mu mol / L to 100 mu mol / L can promote proliferation of the neutral stem cells, and in the integral experiments, the daucosterol with the dose of 10mg / kg can promote proliferation of the neutral stem cells of the aged mice.
Owner:NANJING UNIVERSITY OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE +1
Vivo assay for anti angiogenic compounds
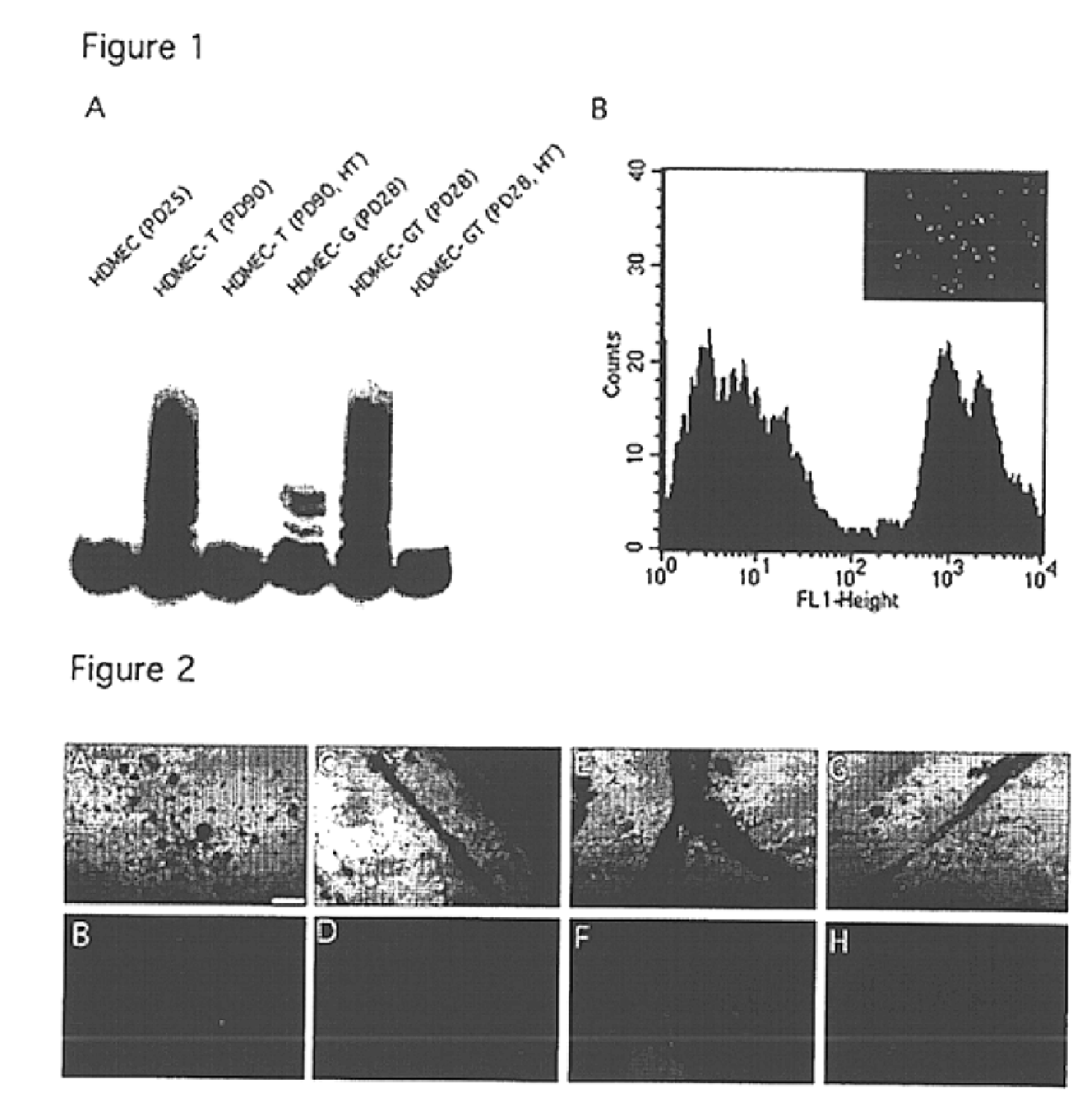
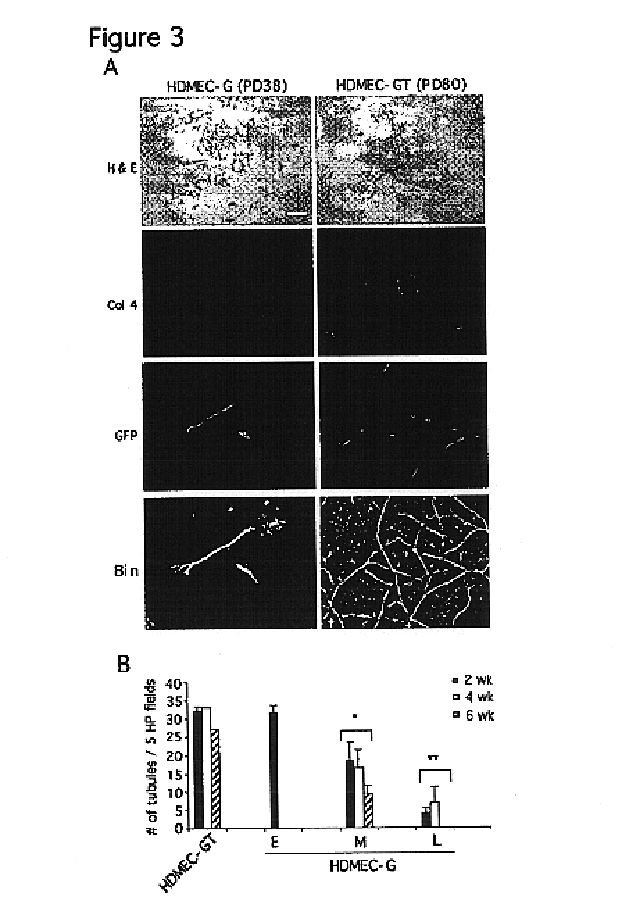
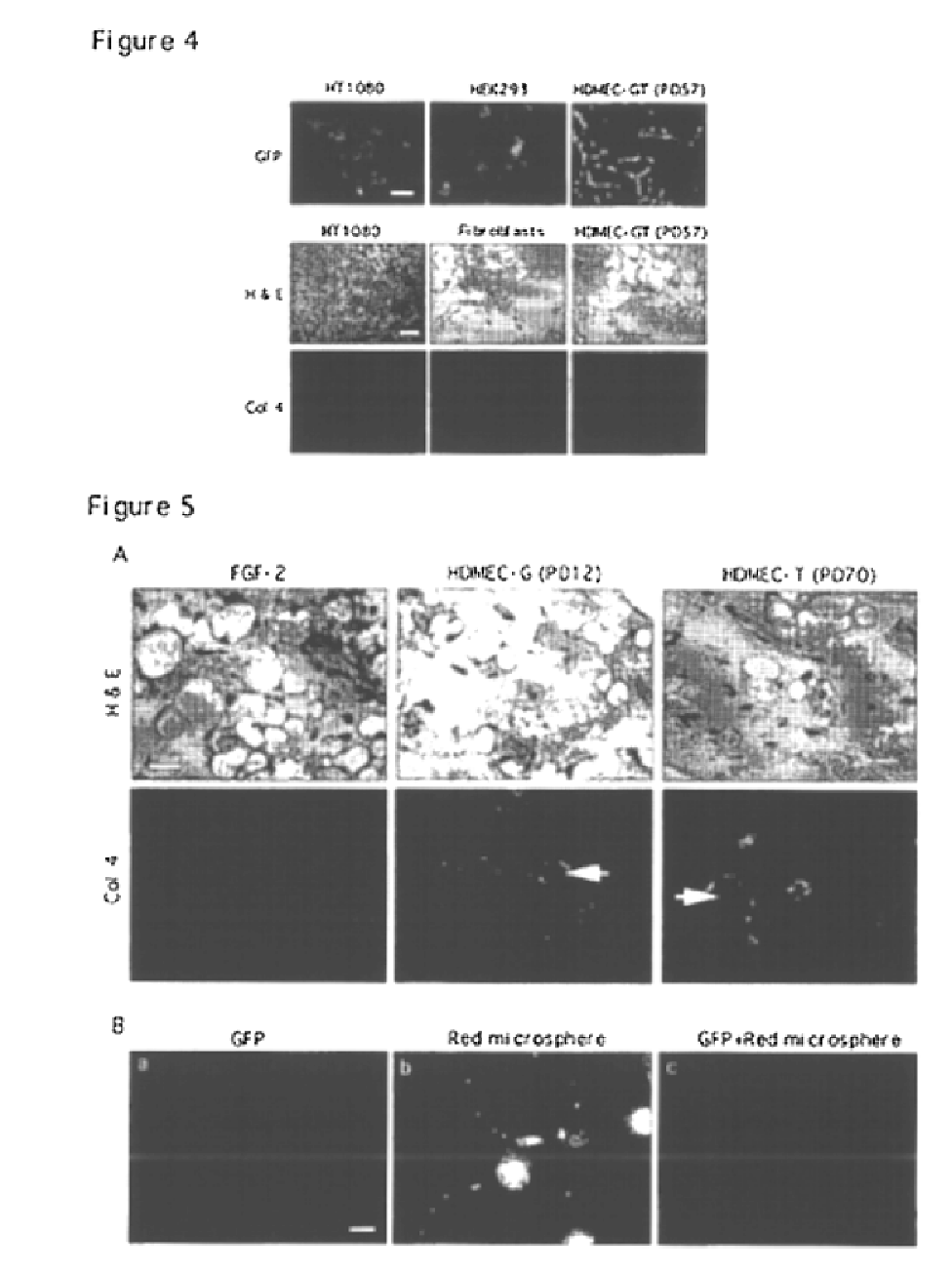
We report the use of telomerase-immortalized human microvascular endothelial cells in the formation of functional capillary blood vessels in vivo. Previously we showed the superior in vitro survival of human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT)-transduced human endothelial cells. Here we show that retroviral-mediated transduction of hTERT in human dermal microvascular endothelial cells (HDMEC) results in cell lines that form microvascular structures when subcutaneously implanted in severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) mice. The human origin of xenografted microvaculature was confirmed both by basement membrane immunoreactivity with anti-human type IV collagen staining and visualization of fluorescent vessels containing HDMEC that were co-transduced with hTERT and green fluorescent protein (eGFP). The lack of human vascular structures after implantation of HT1080 fibrosarcoma cells, 293 human embryonic kidney cells or human skin fibroblasts demonstrated the specificity of HDMEC at forming capillaries. Intravascular red fluorescent microspheres injected into the host circulation were found within green “telomerized” microvessels indicating functional murine-human vessel anastamoses. Whereas primary HDMEC-derived vessel density decreased steadily with time, telomerized HDMEC maintained durable vessels 6 weeks after xenografting. Modulation of implant vessel density by exposure to different angiogenic and angiostatic factors demonstrated the utility of this system for the study of human microvascular remodeling in vivo.
Owner:HERRON G SCOTT
Platycodon grandiflorum polysaccharide, and degradation product, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102477103ASignificant anti-angiogenic effectOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesPyranoseDisease
The invention relates to platycodon grandiflorum polysaccharide extracted from rhizome of platycodon grandiflorum, a degradation product of the polysaccharide, a method for extracting the platycodon grandiflorum polysaccharide from the rhizome of the platycodon grandiflorum, a method for preparing the degradation product of the platycodon grandiflorum polysaccharide, and application of the platycodon grandiflorum polysaccharide and the degradation product thereof to preparing a medicine for treating anti-tumour cell angiogenesis diseases. The structure of the platycodon grandiflorum polysaccharide disclosed by the invention is (1->4)-alpha-D- pyranose homogalacturonan, has the polymerization degree of 15-100, the corresponding molecular weight of 2.0-18.0 kD, and the specific rotation of [alpha]D19+125 DEG (c0.05, H2O), and is represented by the following structural formula described in the specification. The molecular weight range of a degradation product obtained by partial acid hydrolysis of the platycodon grandiflorum pectin polysaccharide is 1.4-3.0 kDa. Vivo experiments prove that the platycodon grandiflorum polysaccharide can obviously inhibit lumen generation function of a human microvascular endothelial cell (HMEC-1) and is hopefully used as a novel anti-tumour medicine for inhibiting the growth of a solid tumour by inhibiting angiogenesis.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for establishing in-vitro model capable of simulating barrier functions of pulmonary epithelial cells and capillary endothelial cells during acute lung injury
InactiveCN107988144APresents a barrier effectPromotes adhesion and infiltrationEpidermal cells/skin cellsArtificial cell constructsInflammatory factorsVascular endothelium
The invention discloses a method for establishing an in-vitro model capable of simulating barrier functions of pulmonary epithelial cells and capillary endothelial cells during acute lung injury. Themethod comprises the following steps: (1) inoculating endotoxin-infected mouse C3H / 10T1 / 2 microvascular endothelial cell strains into lower culture of a cell by using a Transwell co-culture system; inoculating mouse-derived TC-1 pulmonary epithelial cells into the upper layer of the cell, co-culturing for a period of time, and collecting the cell culture supernatant; and (2) detecting conditions of barrier synthesis of pulmonary epithelial cells / capillary endothelial cells in the cell culture supernatant and expressions of inflammatory factor and inflammatory cell infiltration associated proteins, and establishing a pulmonary epithelial cell / capillary endothelial cell co-culture model applicable to endotoxic acute lung injury study. The model established by the method disclosed by the invention is close to a cell barrier function during in-vivo endotoxic acute lung injury, and can provide a reliable model basis for clinical acute lung injury study.
Owner:KUNMING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Application of TTR (transthyretin) to angiogenesis inhibition
InactiveCN109432403AInhibitionInhibition formationSenses disorderNervous disorderAngiogenesis InhibitionMammal
The invention discloses application of TTR (transthyretin) to angiogenesis inhibition, and belongs to the fields of biochemistry, molecular biology and medicine. After the TTR is given to mammals, inSTZ induced diabetes rat and mouse models, the new vessels of eyes are obviously reduced. Tumor new vessel, diabetes new vessel, eye new vessel and brain new vessel in vitro experiment models verify that the TTR has the effect of inhibiting the angiogenesis; the result shows that the TTR can act on an in vitro cell model in anoxic environment of brain and can continuously and efficiently inhibit the generation of new vessels. When the TTR acts on endothelial cells of umbilical veins, the formation of 90 percent of vessels can be obviously inhibited; when the TTR acts on endothelial cells of cerebral microvessel, the formation of 95 percent of vessels can be effectively inhibited; when the TTR acts on the endothelial cells of eye microvessel, the formation of 90 percent of vessels can be effectively inhibited; when the TTR acts on rat and mouse models, the as high as generation of 90 percent of new vessels can be effectively inhibited.
Owner:SHANGHAI CUTSEQ BIOMEDICAL TECH CO LTD
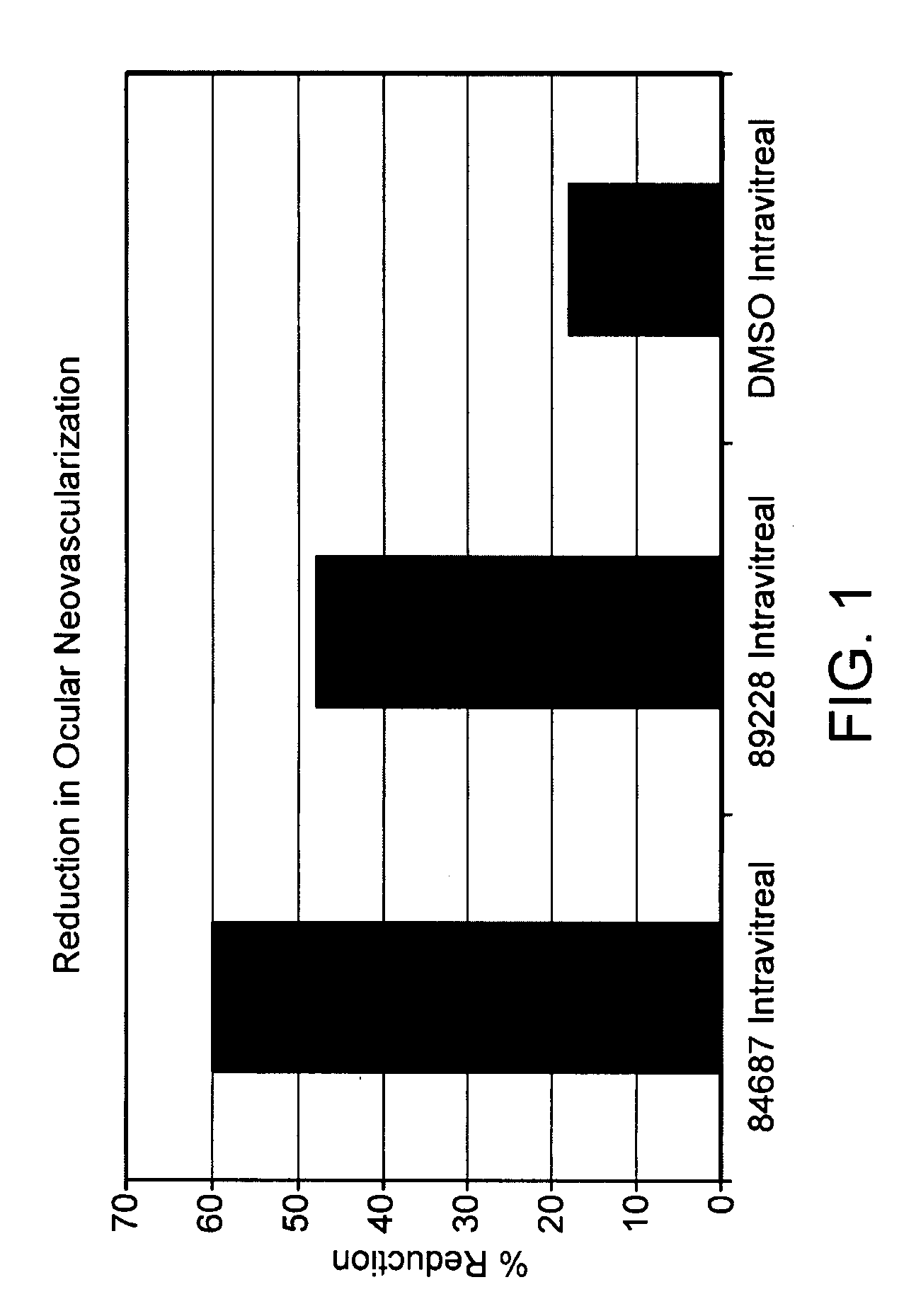
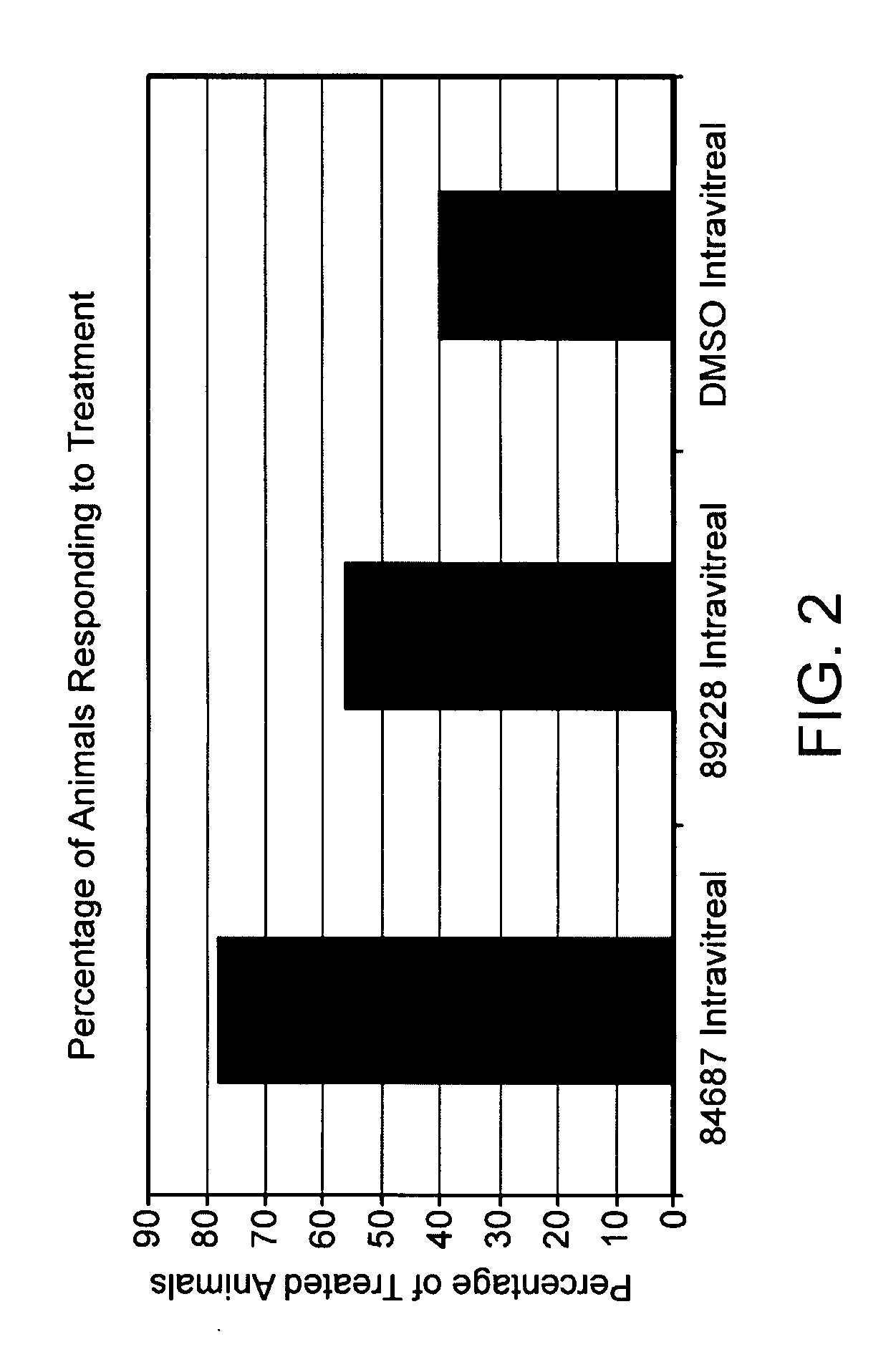
Application of transthyretin to inhibition of ocular neovascularization
InactiveCN109481668AInhibitionInhibition of neogenesisAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderDiabetes mellitusOcular neovascularization
The invention discloses application of transthyretin (TTR) to the inhibition of ocular neovascularization and belongs to the field of biochemistry, molecular biology and medical science. The application finds out that mammal TTR is given and ocular new blood vessels in STZ (Streptozocin)-induced diabetes mellitus rat and mouse models are obviously reduced. An in-vivo experiment model of ocular neovascularization and brain neovascularization verifies that the TTR has the effect of inhibiting the neovascularization and a result shows that the TTR acts on ocular capillary endothelial cells and can be used for effectively inhibiting the formation of 90 percent of the blood vessels; and when the TTR acts in the rat and mouse models, high up to 90% of neovascularization can be effectively inhibited.
Owner:SHANGHAI CUTSEQ BIOMEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Micro-fluidic chip for constructing brain function unit model and construction method
ActiveCN110106081AImprove general performanceEasy to operateNervous system cellsArtificial cell constructsDiseasePerfusion Culture
The invention provides a micro-fluidic chip for constructing a brain function unit model and a construction method thereof. The micro-fluidic chip includes a first elastic layer, a second elastic layer, a middle layer and a substrate, wherein the first elastic layer is provided with a first culture chamber, a liquid inlet and a liquid outlet, the second elastic layer is provided with a second culture chamber, a liquid inlet and a liquid outlet, the middle layer is located between the first elastic layer and the second elastic layer, and the substrate fits the bottom of the second elastic layer. First cells such as microvascular endothelial cells attached to the middle layer are cultured in the first culture chamber, second cells such as primary neural stem cells are cultured in the secondculture chamber, the liquid inlets and the liquid outlets are connected with the corresponding culture chambers through micro-channels to form a perfusion culture channel, and thus the purpose of using a relatively simple method and least cell types for simulating and constructing a relatively complex brain structure functional unit is achieved. The micro-fluidic chip for constructing the brain function unit model and the construction method thereof can be used for constructing models of various neural system diseases, evaluating the safety and efficacy of drugs and conducting dosage screeningand the like, so that a good carrier and technical support are provided for clinical drug screening.
Owner:FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF DALIAN MEDICAL UNIV
Method for separating and purifying rat dermal microvascular endothelium cells
InactiveCN104877955AFully exposedHigh purityArtificial cell constructsVertebrate cellsNeutral proteaseParenchyma
The invention discloses a method for separating and purifying rat dermal microvascular endothelium cells. The method for separating and purifying the rat dermal microvascular endothelium cells relates to the technical field of animal blood vessel endothelium cell culture in vitro, in particular to a method for culturing the rat dermal microvascular endothelium cells in vitro. The method is characterized by the following steps of digesting rat skin through neutral protease II, separating to obtain a dermal layer, digesting through collagenase I and II, obtaining single-cell suspension, and utilizing a CD31 immunomagnetic beads sorting technology to obtain purified target cells. Through the method, the pollution of parenchyma cells in microvascular endothelium cell culture can be simply, conveniently and effectively solved, the rat dermal microvascular endothelium cells with high purity can be obtained through separating, and no obvious morphological feature change occurred after continuous cell culture for 20 times.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF AGRI
Application of circRNA in field of angiogenesis inhibition
ActiveCN109432119AChange structureInhibition formationOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderDiseaseVascular endothelium
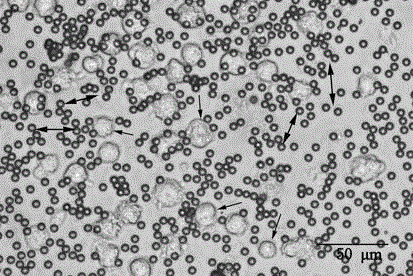
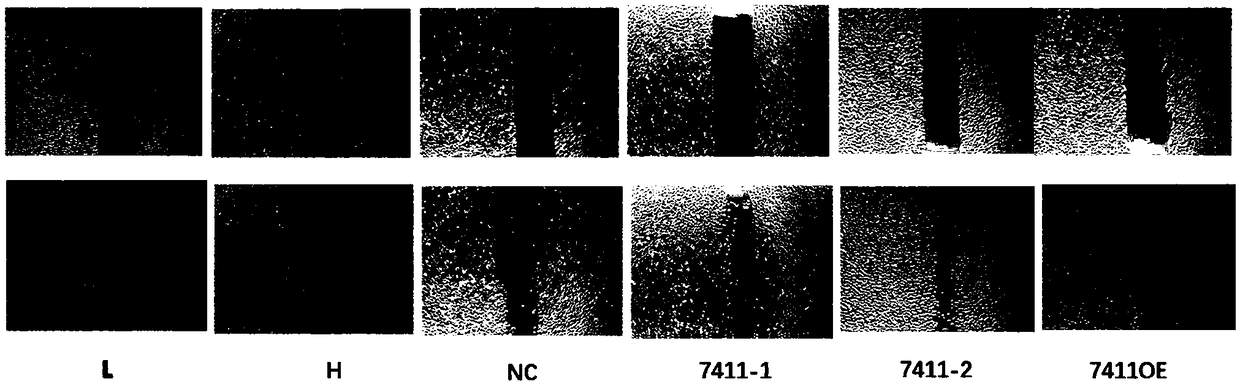
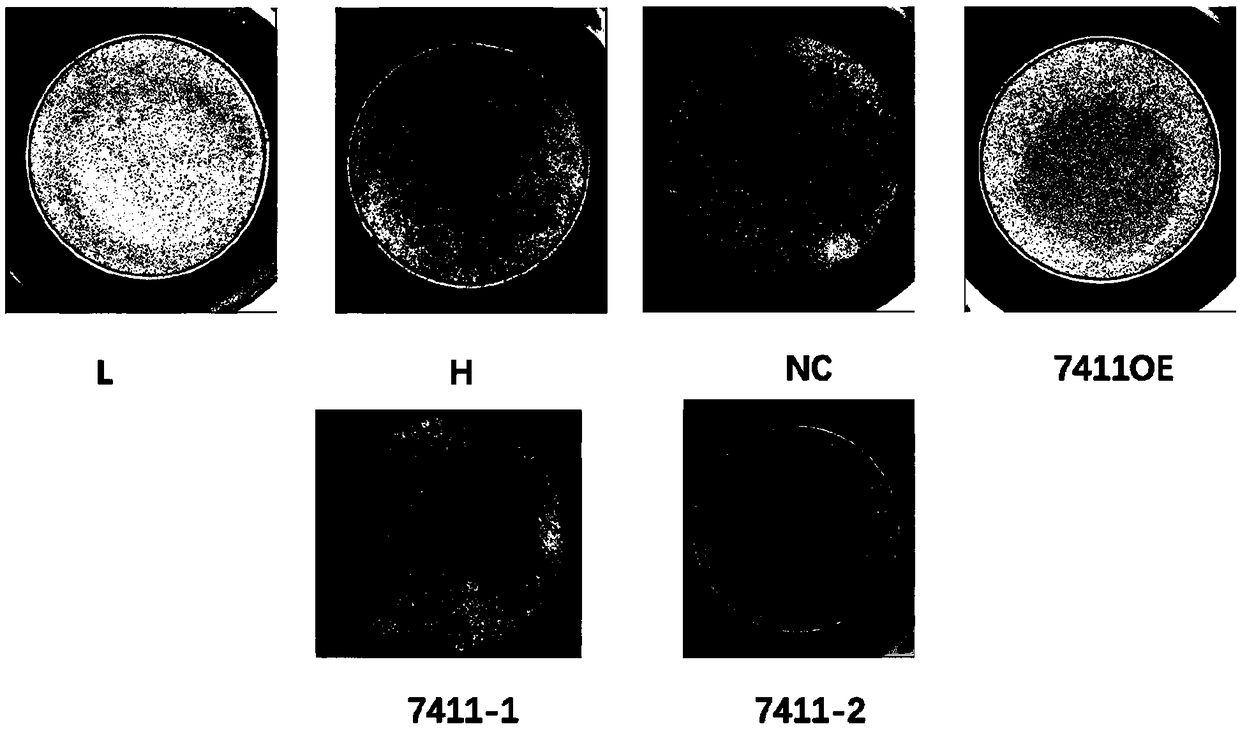
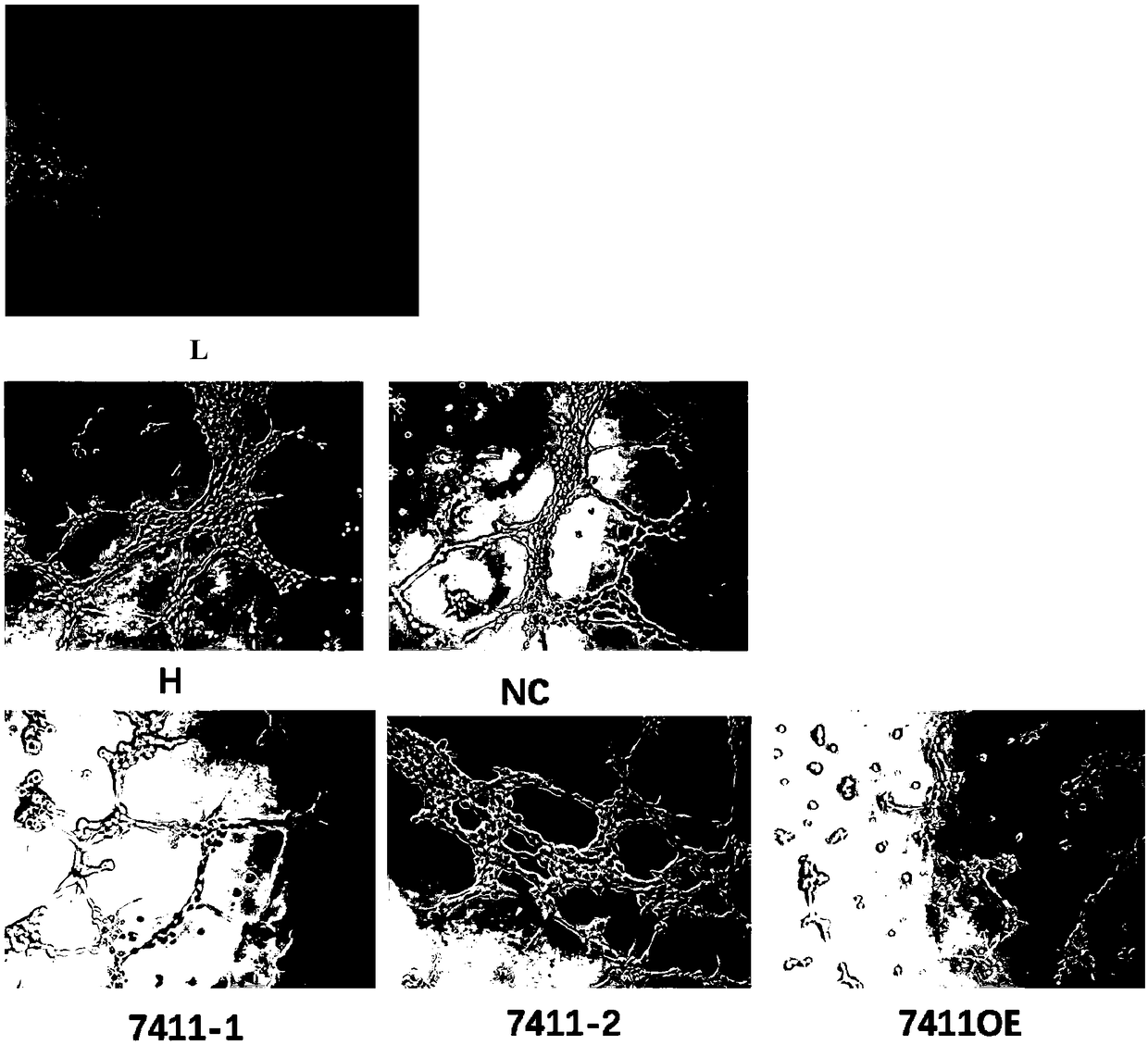
The invention discloses application of circRNA in the field of angiogenesis inhibition, and belongs to the fields of biochemistry, molecular biology and medicine. The invention discovers that hsa_circ_0007411 can continuously act on eye vascular endothelial cells, change the structure of angiogenesis and inhibit angiogenesis. By applying the hsa_circ_0007411 to the eye microvascular endothelial cells, 90 percent of angiogenesis can be effectively inhibited, and angiogenesis of neovascularization-related diseases can be effectively inhibited. The effect of hsa_circ_0007411 on cell proliferationand migration is verified, thereby proving that hsa_circ_0007411 can remarkably inhibit cell proliferation and migration, has a remarkable inhibition effect on the proliferation of endothelial cells,and has important guiding significance for diseases related to the proliferation of vascular endothelial cells.
Owner:易舟(上海)生物医药有限公司
Process for obtaining a sprinkling compound of microvascular endothelial skin cells and mesenchymal stem cells and method of application for tissue regeneration
ActiveUS20190046573A1Promote rapid formationRapid re-epithelization and regenerationArtificial cell constructsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsRe-epithelializationTherapeutic treatment
The invention relates to a process for obtaining a cellular sprinkling compound and to the respective method of application to provide a therapeutic treatment for skin injuries, based on the implantation, by sprinkling and / or spraying, of human mesenchymal stem cells and microvascular endothelial cells that have been pre-expanded in vitro and resuspended in a regenerative solution for cellular implantation of biocompatible biomaterials. The solution is formed by blood plasma rich in growth factors obtained from the patient to be treated and, in some cases, by medical-grade type I collagen and by medical-grade hyaluronic acid, which potentiates the regeneration, re-epithelialization, and reconstruction of skin tissue.
Owner:ALVARO GALUE EDUARDO
Application of preclinical pharmacokinetic key technology and research system in cefoperazone sodium and sulbactam sodium
The invention provides application of a preclinical pharmacokinetic key technology and research system in cefoperazone sodium and sulbactam sodium, comprising the steps of (1) after the cefoperazone sodium and sulbactam sodium with a certain concentration is administrated to an experimental animal for a certain time, collecting one or more biological samples in blood, urine and faeces; (2) treating the biological samples obtained in step (1) by adopting liquid-liquid extraction, albumen precipitation, and solid phase extraction technologies to obtain corresponding solutions; (3) analyzing the prepared solutions in step (2) by adopting an LC-MS(liquid chromatography-mass spectrography) and an LC-MS / MS((liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry). According to the application provided by the invention, the Caco-2 cell can also be adopted to detect the membrane permeability of the medicine and cell absorptive capacity; or the medicine with a certain concentration treats primary culture cerebral microvascular endothelial cells to detect the blood-brain barrier permeability of the medicine; or by adopting a whole animal, S9, human intestinal microsome and monoclonal purified enzyme, in vitro metabolism stability of the medicine is detected and a metabolite is identified.
Owner:刘晓东 +1
Application of embellin in preparation of medicament for inhibiting angiogenesis
InactiveCN101278925AEnhanced inhibitory effectOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderDiseaseEmbryo
The invention relates to a novel use of Chinese herbal medicine monomer embelin, in particular to an application of the embelin in a preparation of a drug for inhibiting angiogenesis. The embelin is applied in the inhibition of angiogenesis dependent disease such as mammary cancer, colon cancer, lymphoma, acute myelocytic leukemia, rheumatoidarthritis, psoriasis, diabetic syndrome, hemangioma, etc. Experiments show that the embelin has remarkable inhibitory action in proliferation experiment, migration experiment, invasion experiment, cell tabulation experiment, the angiogenesis of chick embryo allantois, etc. in the human microvascular endothelial cells (HMEC-1), thereby being used for preparing the drug for inhibiting the angiogenesis.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Chronic inflammation and transplantation
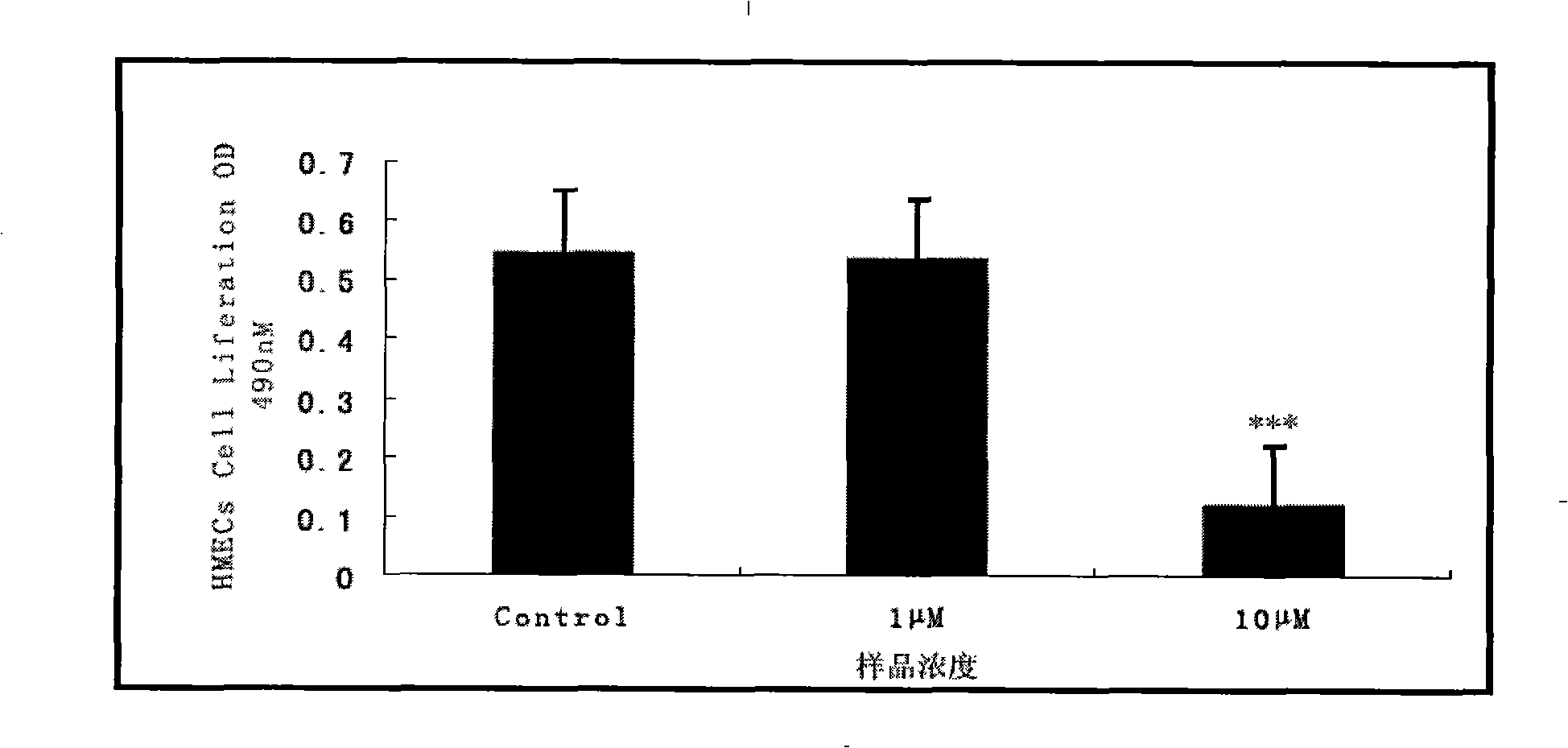
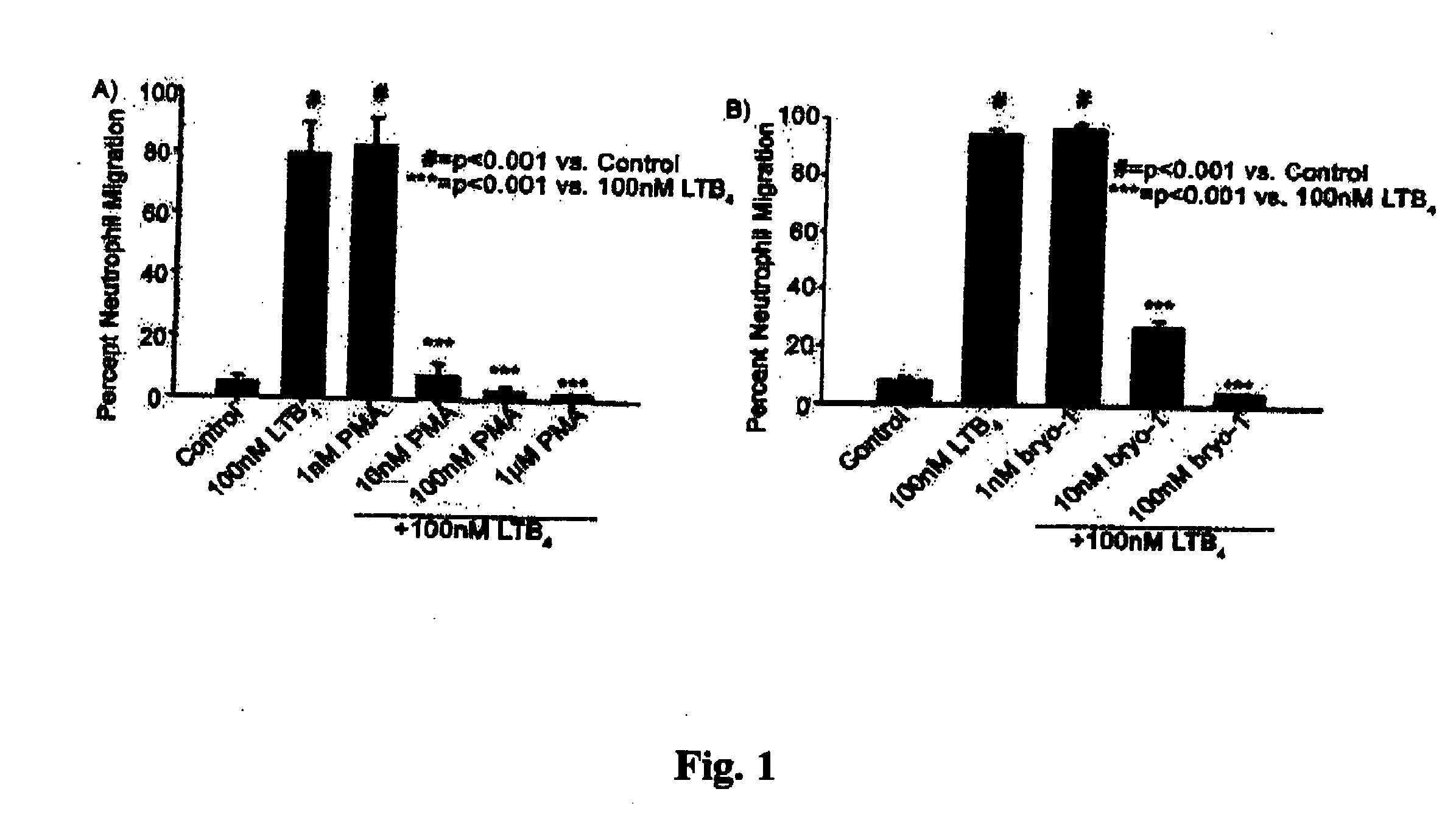
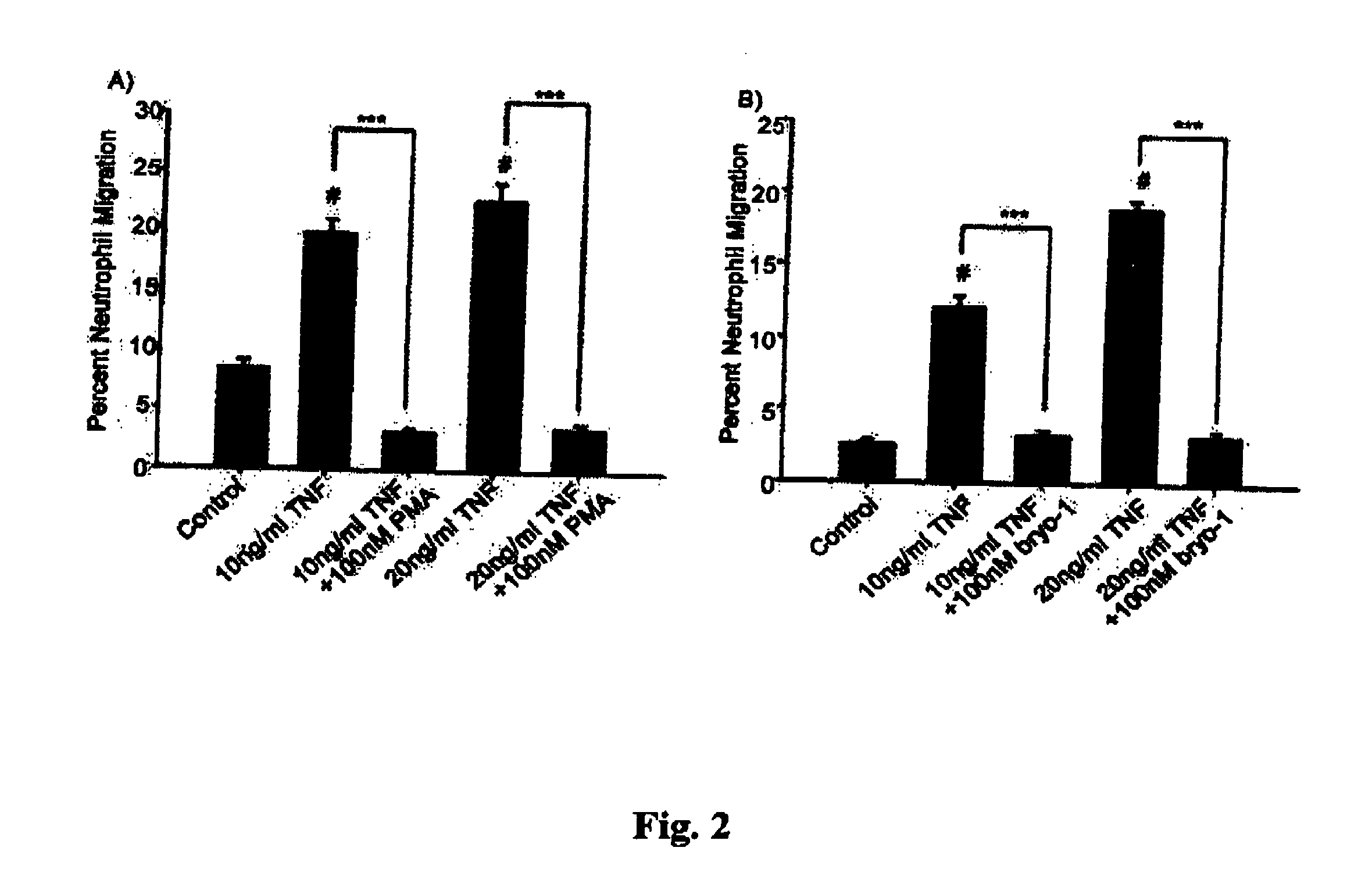
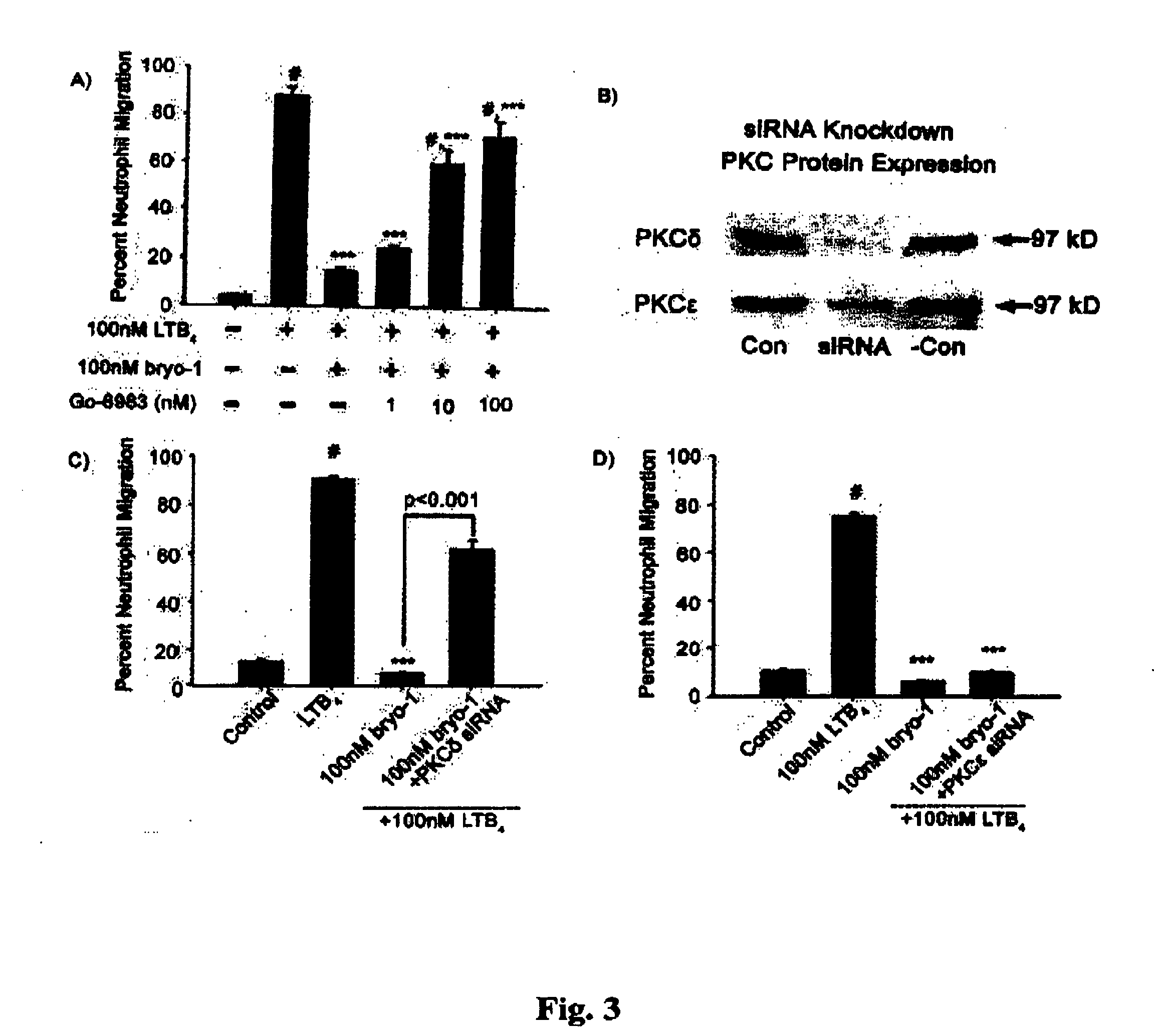
Neutrophils (PMN) can migrate along gradients of chemoattractants across endothelial monolayers to sites of inflammation and infection. This chemotaxis through endothelial cell borders is involved in several acute and chronic inflammatory diseases, however our understanding of the role of endothelial second messengers in the regulation of leukocyte emigration is still incomplete. We investigated this using an in vitro model of neutrophil migration across human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and human microvascular endothelial cells (HMECs) on cell culture inserts. We report that activation of endothelial protein kinase C (PKC) by both phorbol myristate acetate (PMA) and Bryostatin-1 (a potent PKCδ and c activator) can completely abolish neutrophil migration mediated by both endothelial TNF-α stimulation and a leukotriene B4 (LTB4) gradient. PMA protected against LTB4 induced PMN transmigration for at least 24 hours in HMECs and HUVECs. Bryostatin-1 protected PMN migration for at least 24 hours in HMECs and at least 48 hours in HUVECs. Pretreatment with Go-6983 (PKCα, β, and δ inhibitor) before the addition of Bryostatin-1 restored the loss of LTB4 induced neutrophil migration, while pretreatment with GO-6976 (PKCα and β inhibitor) did not. In addition using PKCδ and ε specific small interfering RNA, we were able to show that PKCδ, but not ε was at least mostly responsible for the loss of neutrophil migration in response to LTB4. Taken together, these observations suggest that activation of endothelial PKCδ could be therapeutic in the treatment of various inflammatory disorders characterized by enhanced neutrophil infiltration.This invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions, particularly pharmaceutical compositions comprising bryostatin-1 and substituted derivatives of bryostatin-1, thereof as pharmaceuticals for inhibition of inflammation, and for use in combating arteriosclerosis, diseases of the cardiovascular system, of the central nervous system and prior to / following organ transplantation, ischemia. The invention relates to methods for treating leukocyte dependent injury in chronic inflammatory diseases, and injury from transplantation mediated organ stress. The method involves injecting bryostatin-1 into patients with the inflammatory condition, treating the skin with bryostatin-1, or perfusing organs with bryostatin-1 prior to transplantation / cold storage. Activation of protein kinase Cd (PKCd) results in a near complete blockade of leukocyte infiltration which is the result of stabilization of the microvascular (endothelial) barrier.
Owner:LOUSNA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE
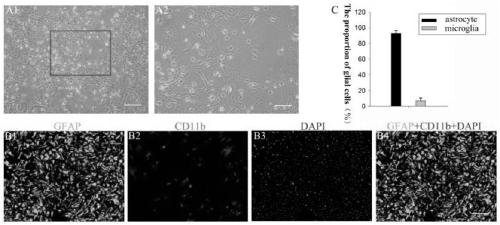
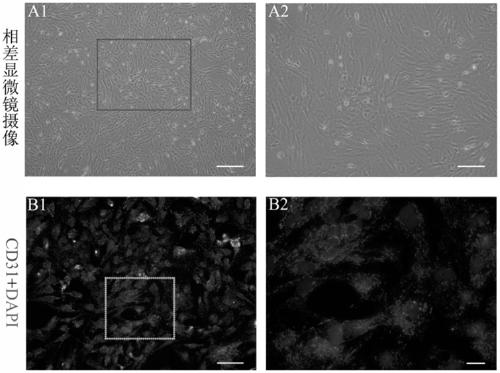
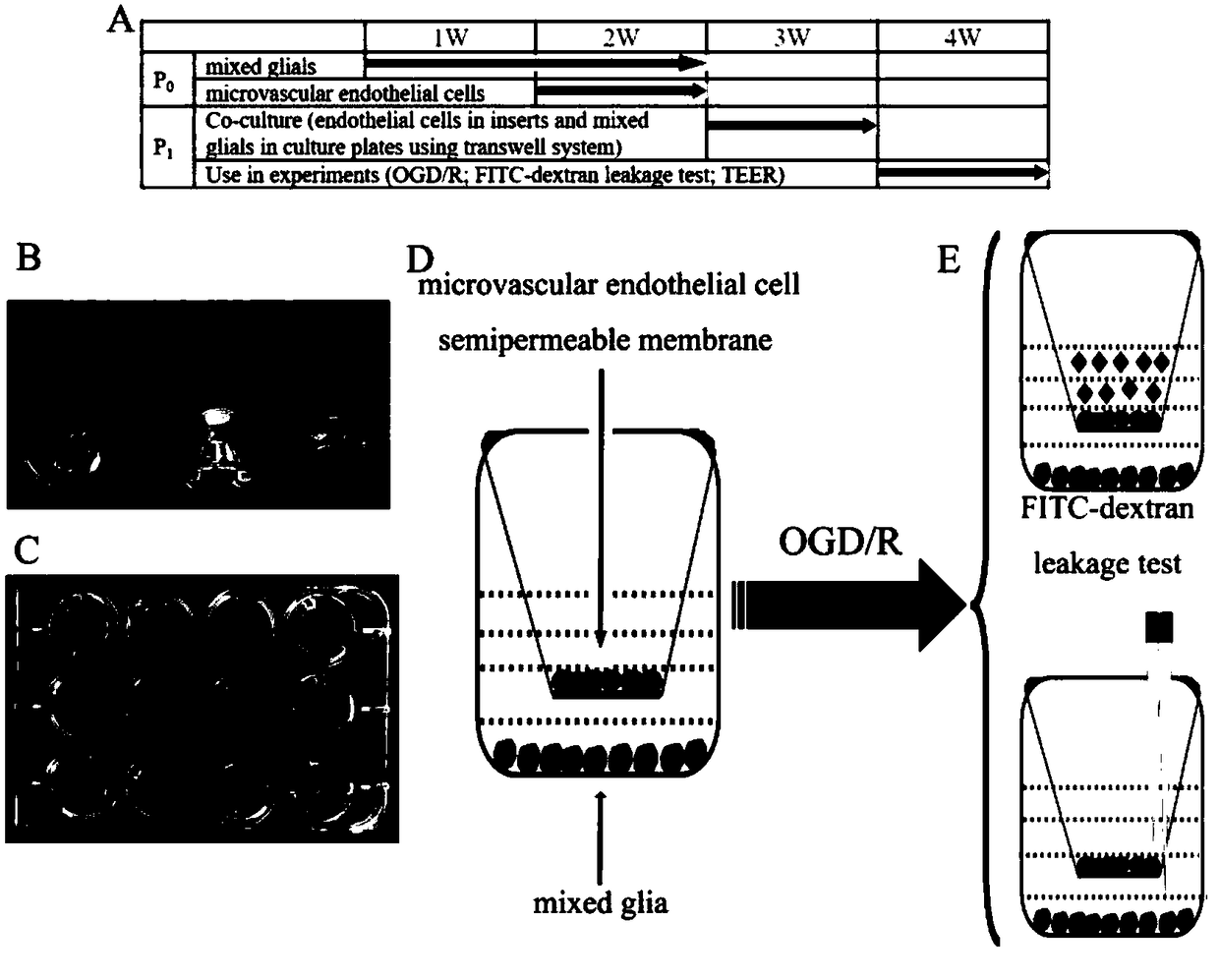
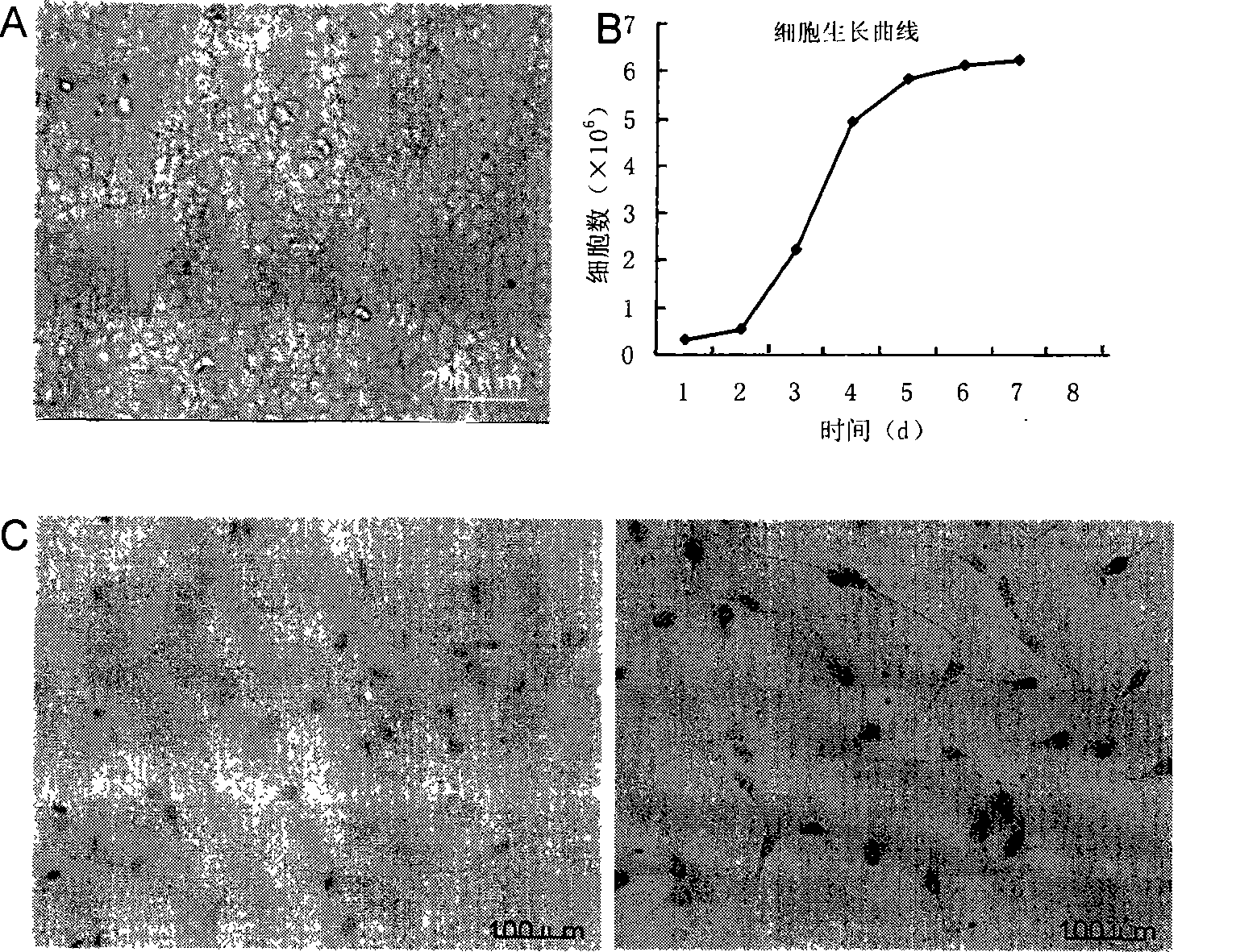
Blood-spinal cord barrier OGD/R injury model and construction method and application thereof
PendingCN109234233ASimple and fast operationGood repeatabilityCompound screeningApoptosis detectionReperfusion injuryClinical study
The invention discloses a method for constructing a blood-spinal cord barrier (BSCB) oxygen-glucose deprivation / reoxygenation (OGD / R) injury model and an application thereof. Spinal cord derived microvascular endothelial cells were cultured in the upper chamber and mixed glial cells were cultured in the bottom chamber of the transwell culture system to construct the in vitro BSCB model. Microvascular endothelial cells in the upper chamber of transwell and mixed glial cells in the lower chamber of transwell interact with each other by secreting cytokines to form molecular membranes with good barrier function. OGD / R can effectively simulate the injury of BSCB induced by ischemia / reperfusion in vivo, and can more directly and accurately understand the changes of structure and function of BSCBafter ischemia / reperfusion injury. The results of the study have a high reference value, thus providing an effective basis for clinical study of BSCB.
Owner:WUXI PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Isolation in vitro and amplification method for adult rat heart microvascular endothelial cell
InactiveCN101463341AArtificial cell constructsVertebrate cellsVascular endotheliumCorrelational study
The invention relates to a method for separating and expanding cardiac microvascular endothelial cells of adult rat vitro, which provides an ideal cell model for the correlational studies of cardiac endothelial function and a complementary source of vascular neogenesis treatment and tissue engineering cells after myocardial infarction, and lays foundation for deeply studying the clinical treatment of myocardial infarction, angiocarpy endothelial dysfunction, etc. The method adopts the technical proposal that (1) by utilizing the biological characteristics of the cardiac microvascular endothelial cells, the cardiac microvascular endothelial cells of the adult rat are separated and enriched by adopting a method of enzymic digestion, and are expanded by utilizing the self-renewing and proliferation characteristics of the endothelial cells, thus obtaining a great deal of cardiac microvascular endothelial cells; (2) the separated cells are separated and purified vitro; (3) the separated cells are purified and expanded vitro.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
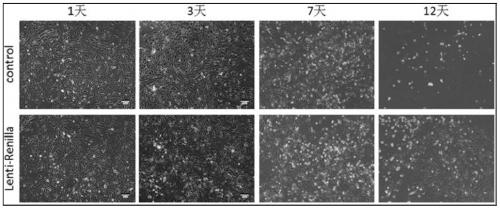
Brain blood vessel endothelial cell line for quickly detecting activity of classical Wnt signal channel
PendingCN110218740AImprove screening efficiencyImprove accuracyCompound screeningApoptosis detectionVirusSlow virus
The invention provides a preparing method of a brain blood vessel endothelial cell line for stably expressing TOP-Flash / Renilla dual-luciferase reporter genes. The preparing method comprises the following steps of 1, selecting cerebral microvascular endothelial cells, infecting the cerebral microvascular endothelial cells with a slow virus carrying a Renilla gene, and conducting screening to obtain a cell line for stably expressing Renilla; 2, infecting the cell line obtained in step 1 with a slow virus carrying a TOP-Flash gene, and conducting screening to obtain the brain blood vessel endothelial cell line for simultaneously stably expressing the Renilla and TOP-Flash dual-luciferase reporter genes. The brain blood vessel endothelial cell line can be used for screening active substancesfor activating the activity of a Wnt signal channel in the brain blood vessel endothelial cells, the screening efficiency and accuracy are improved, and the preparing method is simple.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Aftosa vaccine immunopotentiator
InactiveCN101554477AFree from harmEliminate side effectsAntiviralsAntibody medical ingredientsSide effectAdditive ingredient
The invention belongs to the field of traditional Chinese medicine preparations and particularly relates to an aftosa vaccine immunopotentiator. The immunopotentiator contains astragalus polyose, chondroitin sulfate, ginsenoside Rb1 and Salvianic acid A and the weight ratio of all the components is 4-40:4-40:1-20:1-20. The immunopotentiator has the function of inducing the increase of microvascular endothelial cell interferons. Proved by experimental animals, the immunopotentiator has the function of remarkably improving the titer of aftosa vaccines after first immunization, and can lead the titer of more than 80 percent of immune animal antibodies to meet standards after the existing aftosa vaccines are first used for immunization. Being a compound of traditional Chinese medicine ingredients, the immunopotentiator can eliminate the toxic and side effects of the existing aftosa vaccines and is also convenient for use.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF AGRI +1
Antisense inhibition of laminin-8 expression to inhibit human gliomas
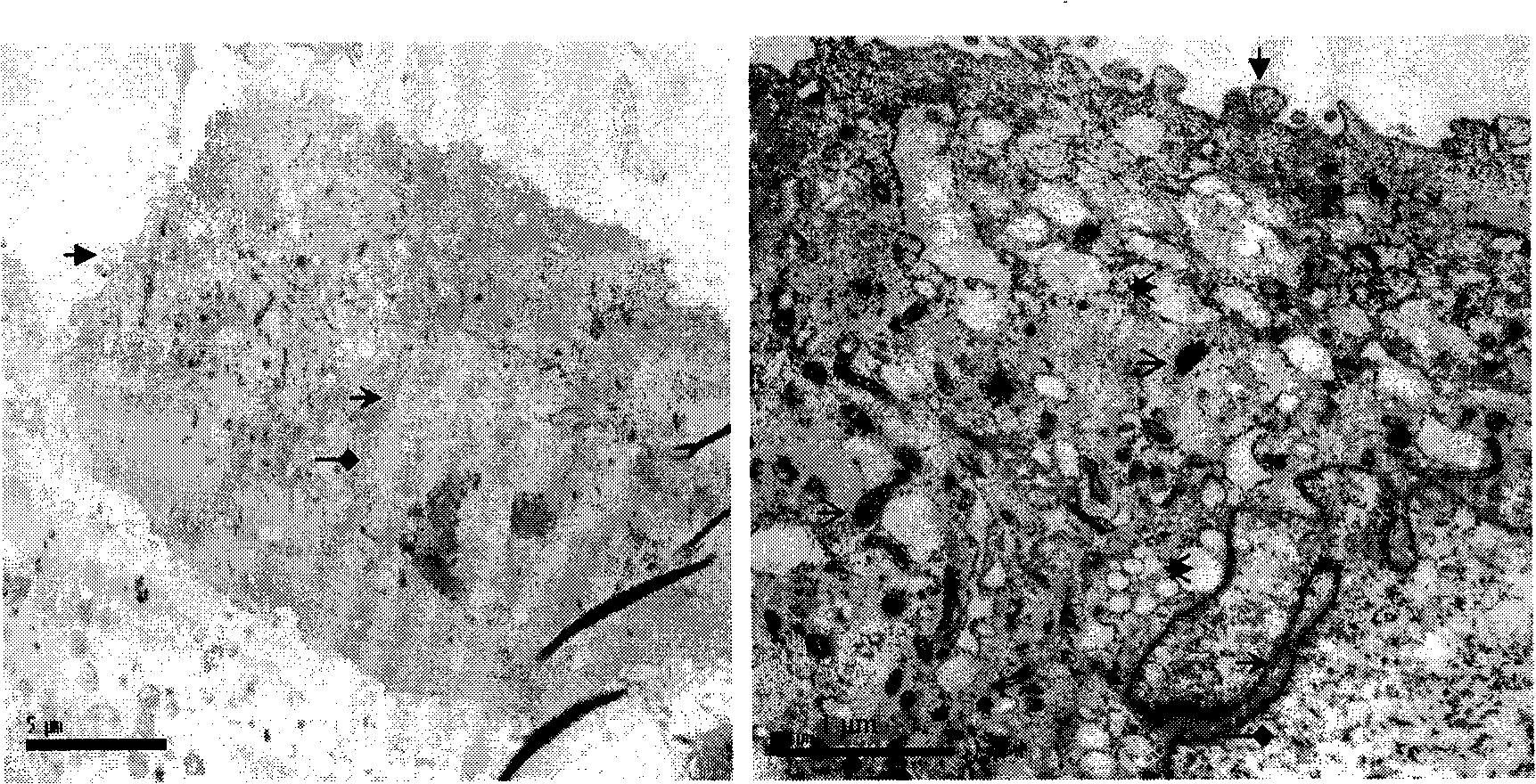
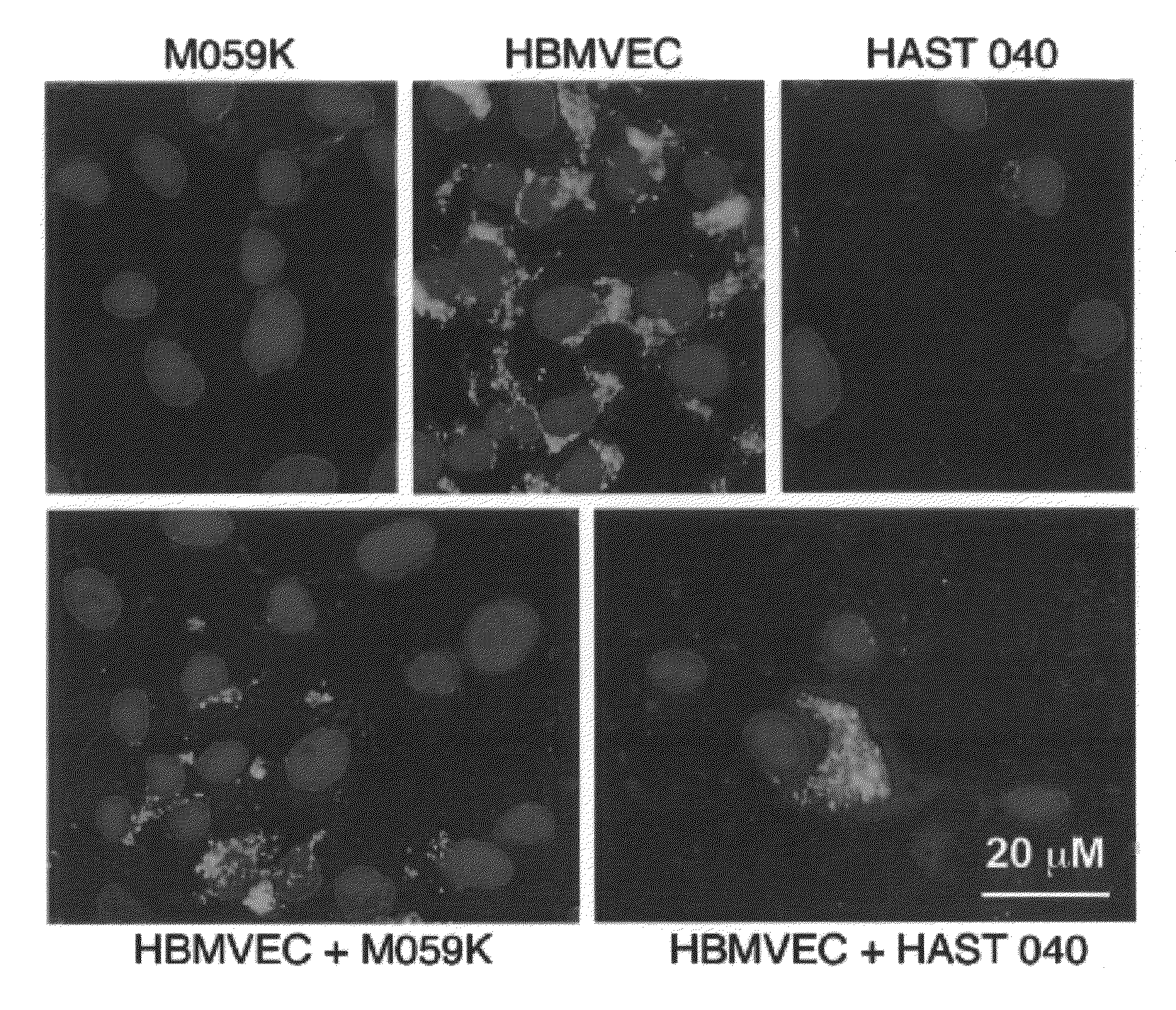
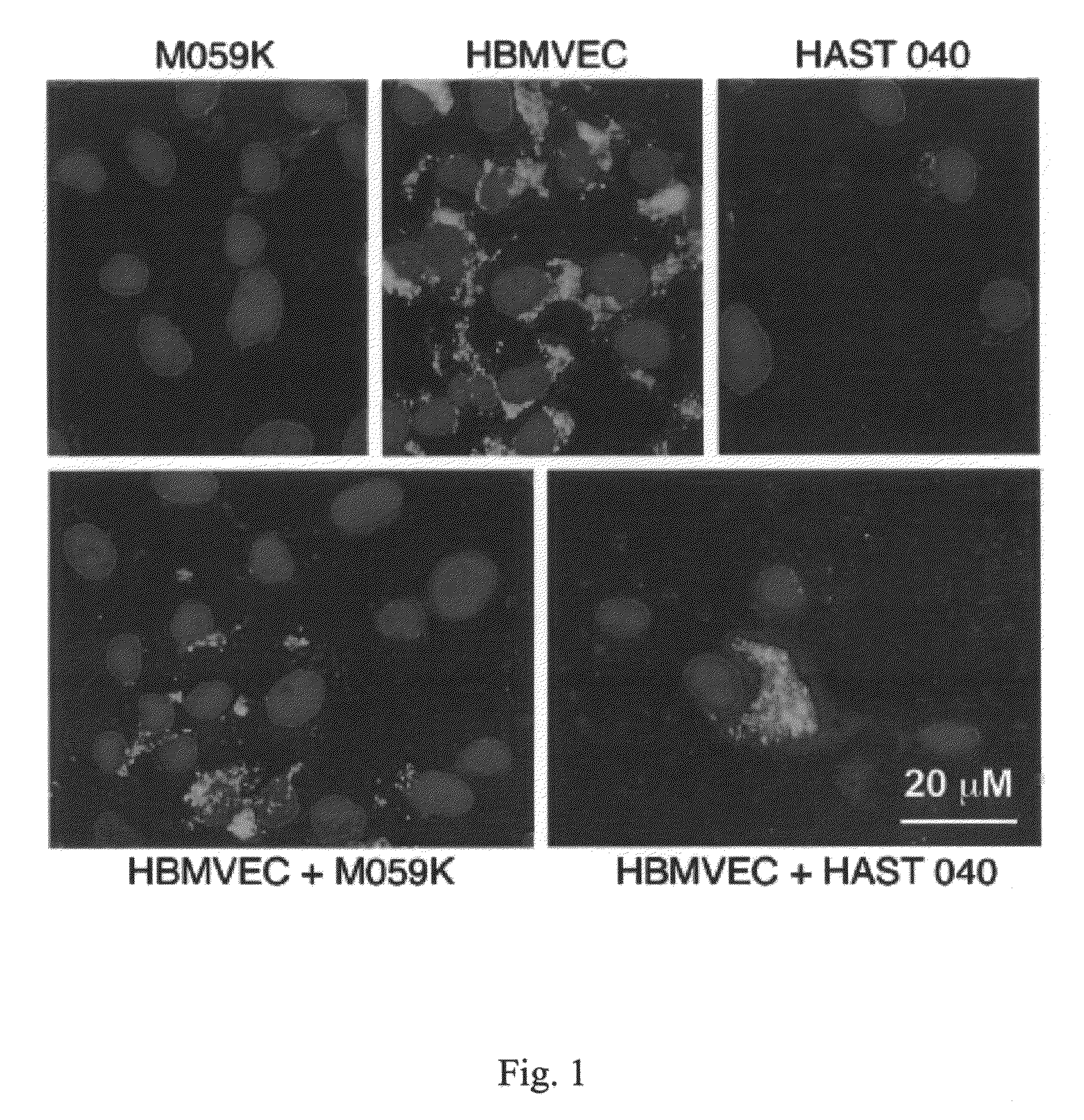
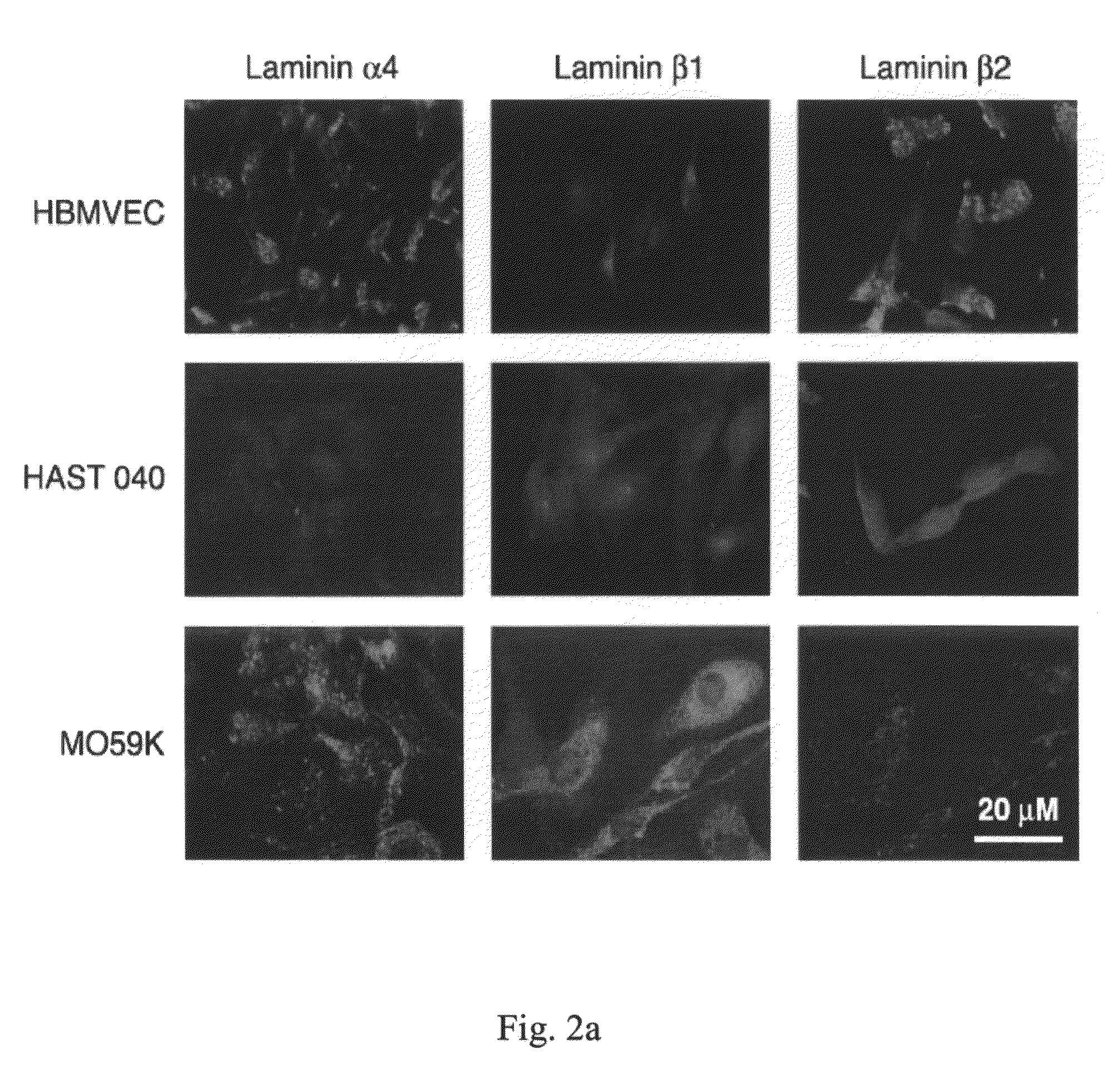
Using gene array technology, we observed that an increase of the α4 chain-containing Laminin-8 correlated with poor prognosis for patients with brain gliomas. We established that inhibition of Laminin-8 expression by a new generation of highly specific and stable antisense oligonucleotides (Morpholino™) against chains of Laminin-8 could slow or stop the spread of glioma. This was demonstrated in an in vitro model using human glioblastoma multiforme cell lines M059K and U-87MG co-cultured with normal human brain microvascular endothelial cells (HBMVEC). Using Western blot analysis and immunohistochemistry, we con-firmed that antisense treatment effectively blocked laminin-8 protein synthesis. Antisense oligonucleotides against both α4 and β1 chains of laminin-8 blocked significantly the invasion of co-cultures through Matrigel. The results show that Laminin-8 may not only contribute to glioma progression and recurrence as part of the neovascularization process but also by directly increasing the invasive potential of tumor cells.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Polyethylenimine nanoparticles and methods of using same
InactiveUS20200206134A1Strong specificityOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsPolyethylene glycolFatty acid
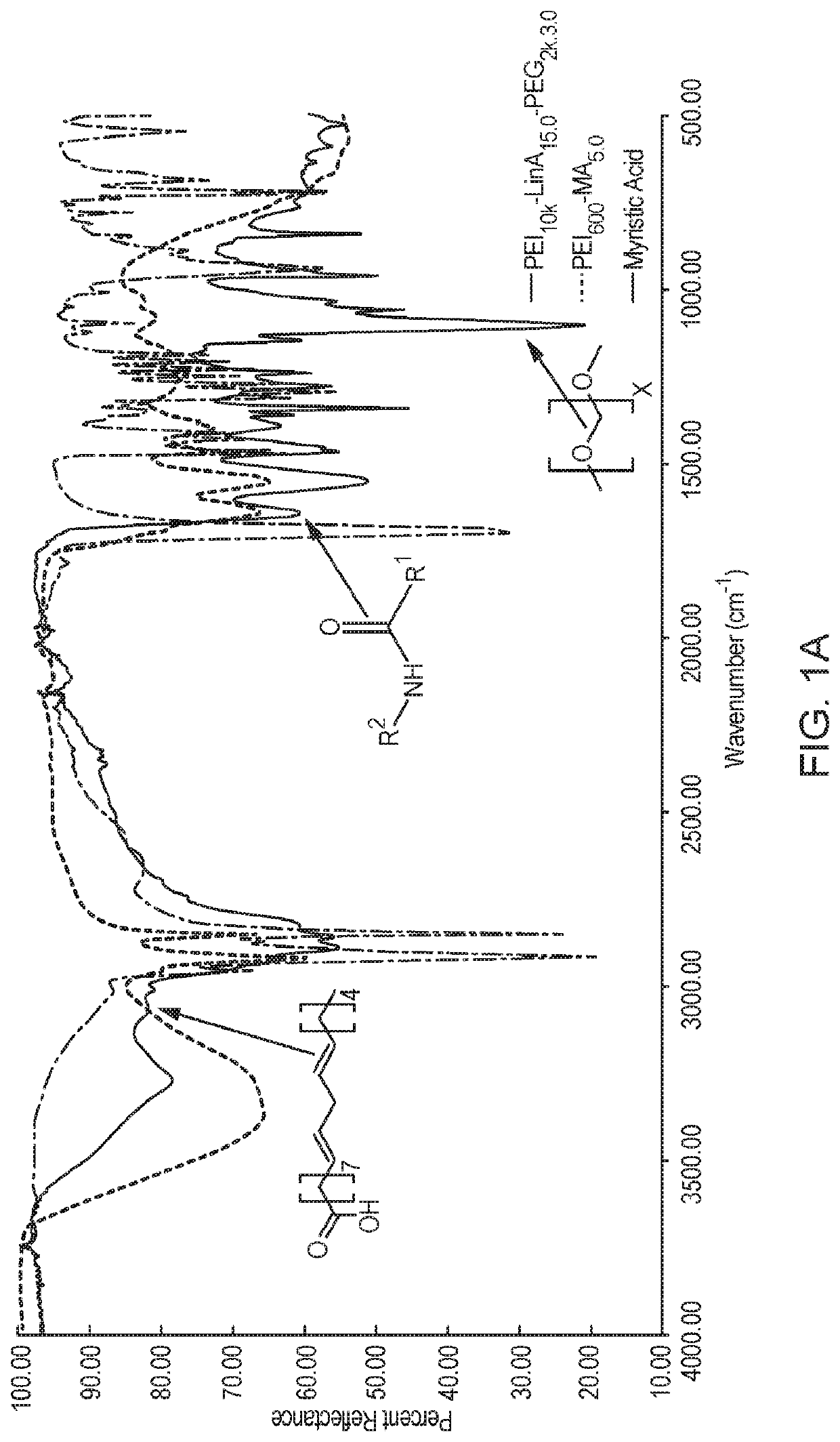
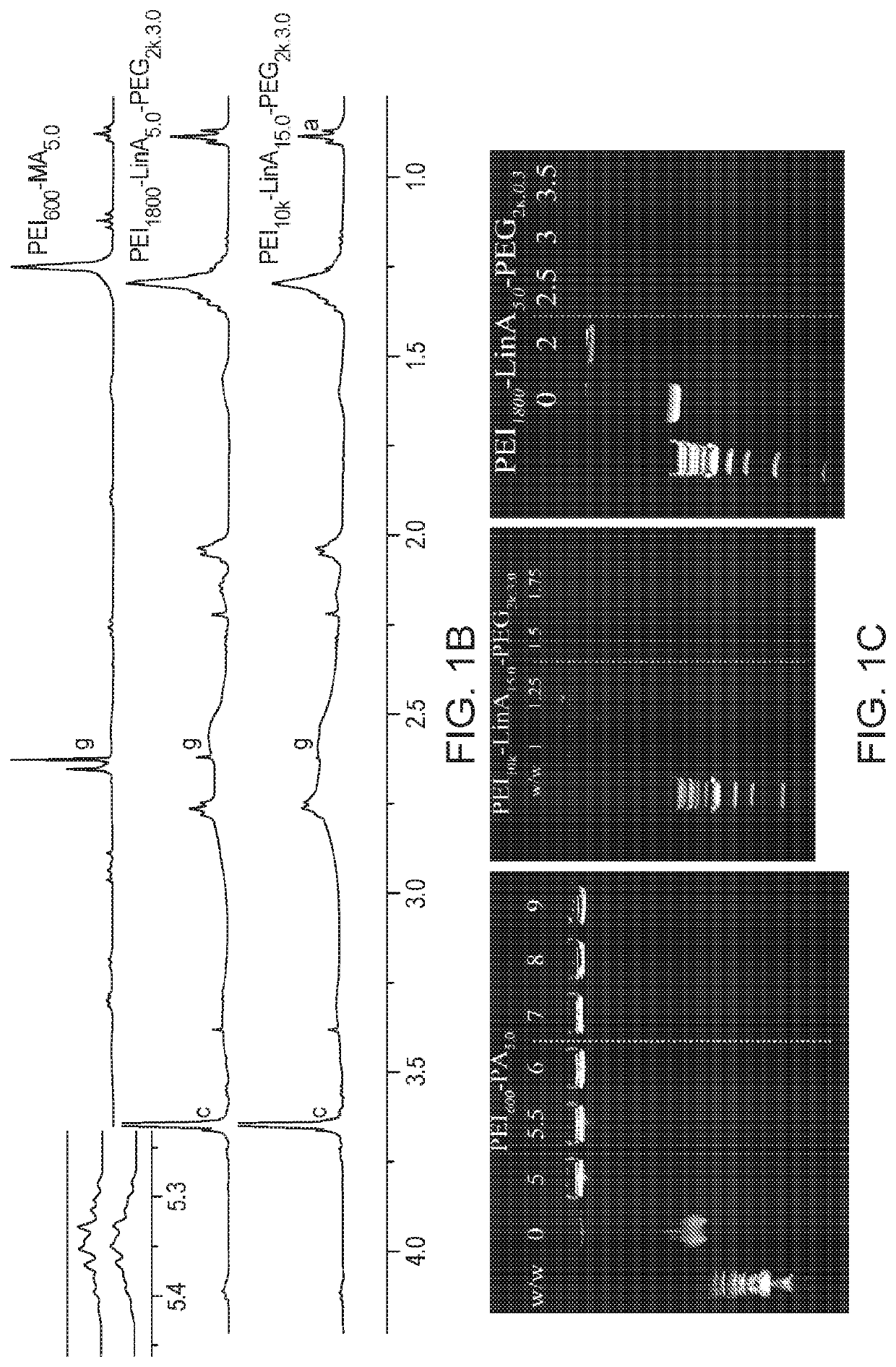
Disclosed herein are nanoparticle compositions containing that may be created by functionalizing polyethylenimine (PEI) with fatty acids and carboxylate terminated poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG). The disclosed compositions may be delivered to an individual in need thereof via delivery into blood circulation, where the nanoparticle compositions show an exceptionally high specificity to the pulmonary microvascular endothelium with minimal targeting of other cell types in the lung, to provide delivery of therapeutic agents such as stabilized nucleic acids. Methods of using the compositions are also disclosed.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL MEDICAL CENT CINCINNATI +1
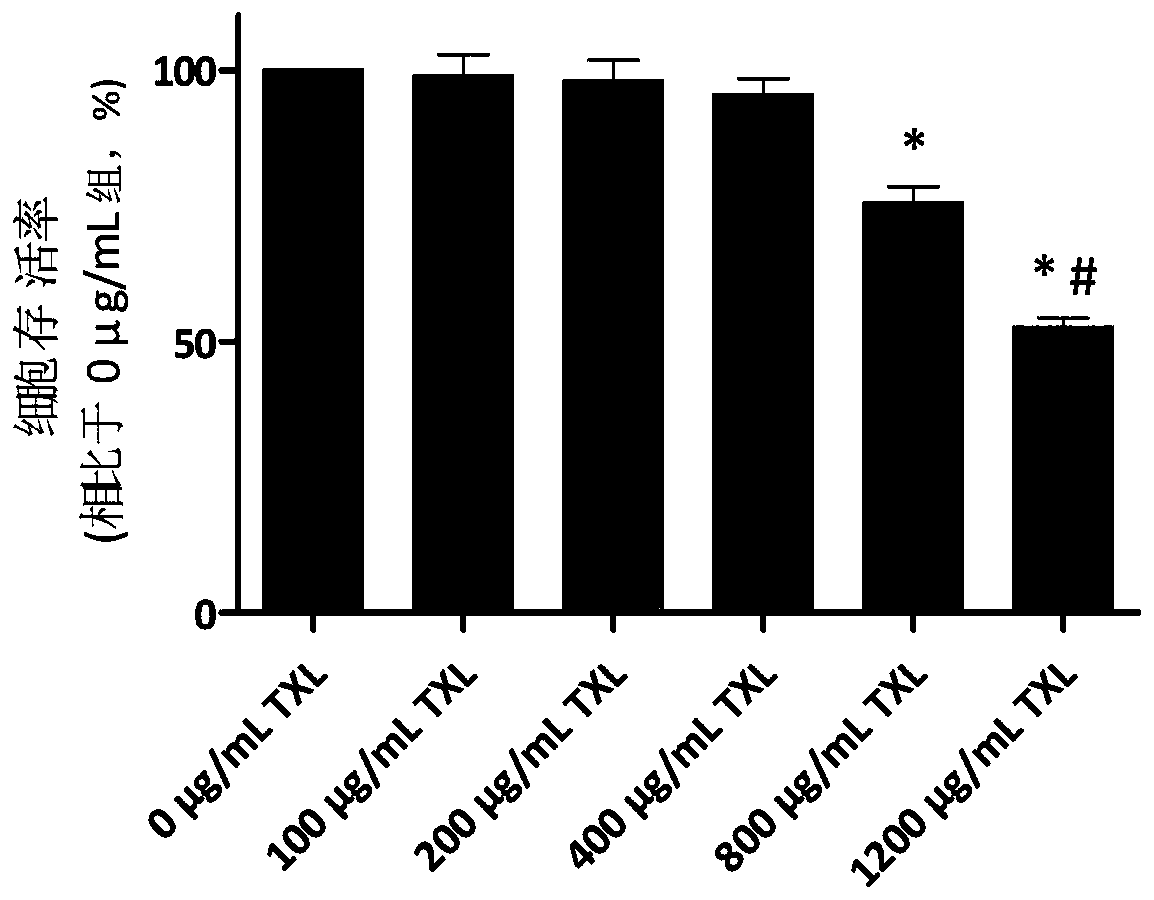
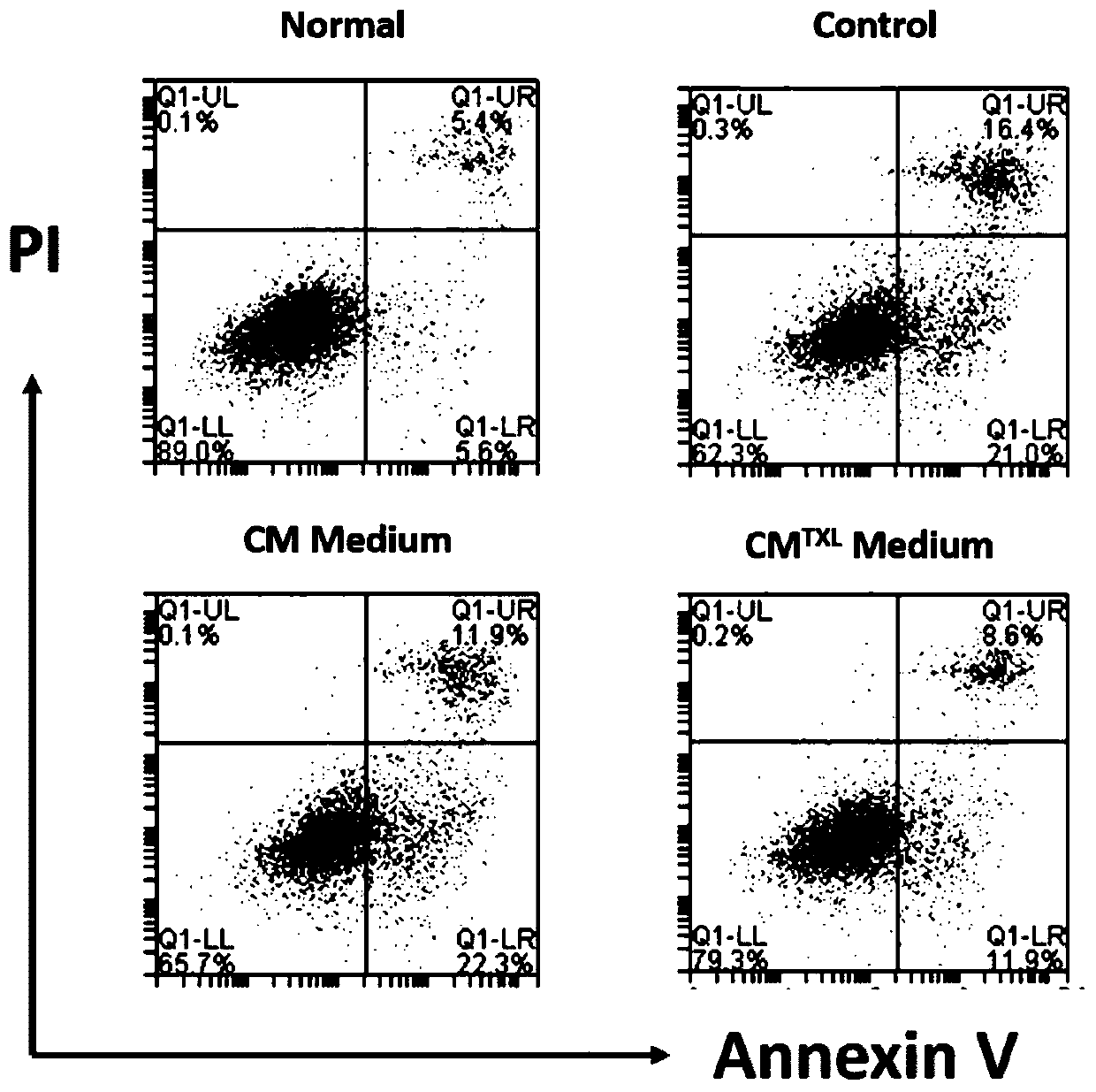
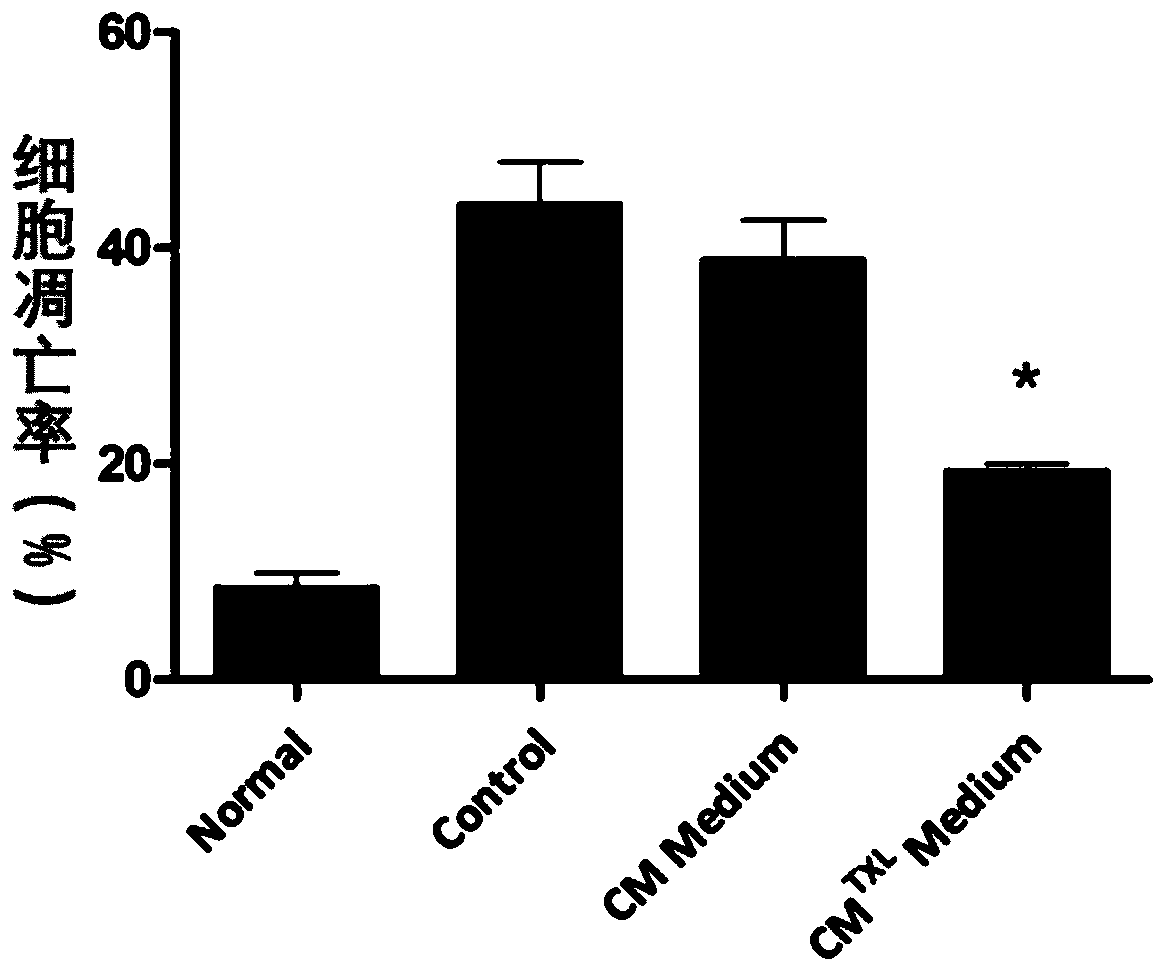
Myocardial-cell-derived exosome based on Tongxinluo pretreatment and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110257323AReduce reperfusion injuryHigh linc-ROR contentCell dissociation methodsCulture processReperfusion injuryMedicine
The invention provides a myocardial-cell-derived exosome based on Tongxinluo pretreatment and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises: pretreating myocardial cells with Tongxinluo, subjecting the pretreated myocardial cells to hypoxia / reoxygenation, and collecting an exosome secreted by the myocardial cells. The myocardial-cell-derived exosome effective in reducing the apoptosis of myocardial microvascular endothelial cells to alleviate myocardial Ischemia reperfusion injury can be prepared via the preparation method.
Owner:FUWAI HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI & PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE
Application of indirubin for preparing medicine for preventing blood vessel from regenerating
InactiveCN101284005AEnhanced inhibitory effectOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderDiseaseEmbryo
The invention relates to a new application of indirubin, particularly to an application of the indirubin in preparing drugs with angiogenesis inhibiting effect for treating angiogenesis diseases such as eye diseases, tumors, arthritis, hemangioma and psoriasis. In human microvascular endothelial cell-1 (HMEC-1) proliferation test, human umbilical vein endothelial cell (HUVEC) proliferation test, HUVEC in vitro scratch migration test, HUVEC-modified Boyden chamber migration test, HMEC-1 canalization test and chick embryo allantoic membrane test, the indirubin has evident inhibitory effect. Therefore, the indirubin can be used for preparing drugs with angiogenesis inhibiting effect.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Traditional Chinese medicine combination for treating diabetes mellitus and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a traditional Chinese medicine combination for treating diabetes mellitus and a preparation method thereof; the traditional Chinese medicine combination is formed by eleven Chinese medicinal crop raw materials, that is, salvia miltiorrhiza, root of common peony, angelica, achyranthes, safflower, peach kernel, yam, root of rehmannia, radix glehniae, lily and radix ophiopogonis; the traditional Chinese medicine combination has the efficiency of promoting blood circulation by removing blood stasis and nourishing Yin and moistening dryness, remarkably reduces blood sugar levels, increases bodymass of diabetics, regulates blood fat, improves pathological changes such as blood capillary basilar membrane incrassation and microvascular endothelial cell hyperplasia caused by diabetes mellitus, increases blood flow volume and improves microcirculatory disturbance.
Owner:BEIJING ZHONGKE RENHE SCI & TECH
Specification for hydrogen treatment of reperfusion injury of dermal microvascular endothelial cells
InactiveCN109913403AArtificial cell constructsVertebrate cellsReperfusion injuryCell-Extracellular Matrix
The invention discloses a manufacture method of a hydrogen saturated medium, comprising dissolving hydrogen in a serum-free ECM (extracellular matrix) medium for 2 hours under the pressure of 0.4 MPa,saturating the medium, depressurizing to allow hydrogen to be released, manufacturing O2 and CO2 saturated ECM media in the same way, and mixing in a ratio of (H2:O2:CO2=75%:20%:5%). The invention also discloses a specification for treating reperfusion injury of dermal microvascular endothelial cells by hydrogen saturated medium and hydrogen; in cell culture, the mixed medium is placed in a culture bottle, hydrogen concentration is detected immediately with a hydrogen measurer; a mixed gas having 75% of hydrogen, 20% of oxygen and 5% of carbon dioxide is introduced into a culture box; the concentrations of gases in the medium are kept balanced and stable; cells are added in the culture bottle and cultured in enclosed manner for 24 hours; the hydrogen content of the medium under the condition is about 0.6 MPa.
Owner:BEIJING ANZHEN HOSPITAL AFFILIATED TO CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV
Chinese pharmaceutical composition for treatment of diabetes and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a Chinese pharmaceutical composition for treatment of diabetes and a preparation method thereof. The pharmaceutical composition is prepared with eleven traditional Chinese medicinal materials as raw materials, including red sage roots, red peony roots, Chinese angelica roots, achyranthes roots, safflower, peach kernel, rhizoma dioscoreae, rehmannia roots, beach silvertop roots, lily, lilyturf roots and the like. The invention has the functions of promoting blood circulation to dispel blood stasis and nourishing yin to moisten dryness, significantly reduces blood glucose, improves the body condition of the patient with diabetes, adjusts the blood fat, prevents the pathologic changes such as the thickening of the basement membrane of the blood capillary and the hyperplasia of endothelial cells of the blood capillary caused by diabetes, increases the blood flow and eliminates the barrier in microcirculation.
Owner:BEIJING ZHONGKE RENHE SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com