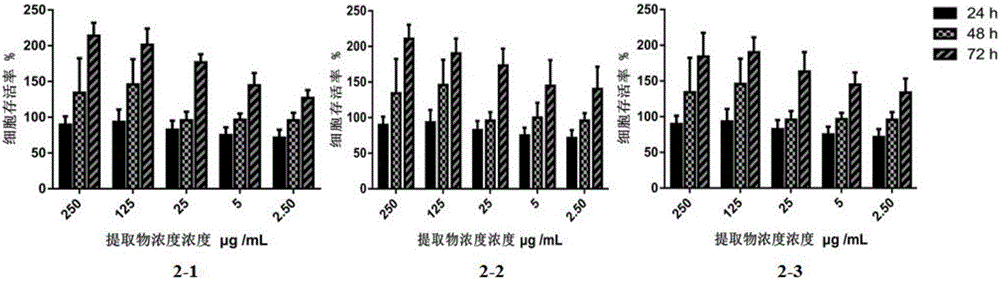
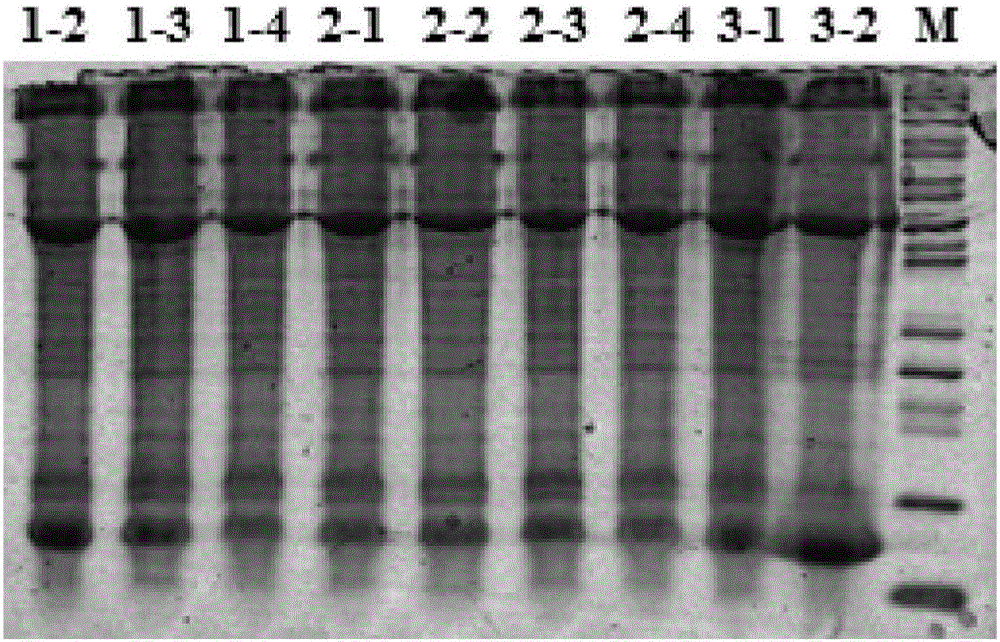
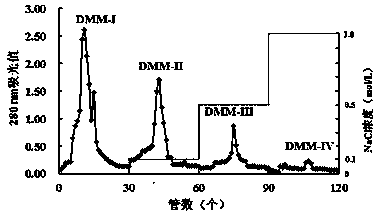
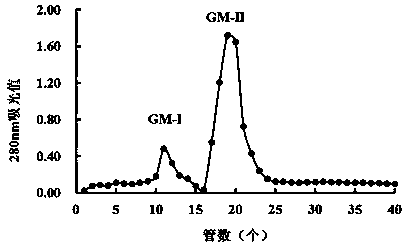
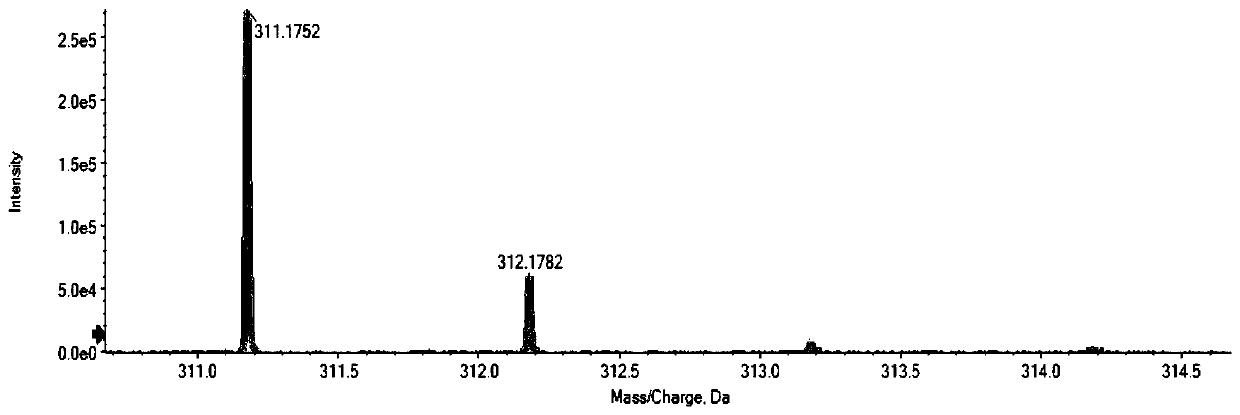
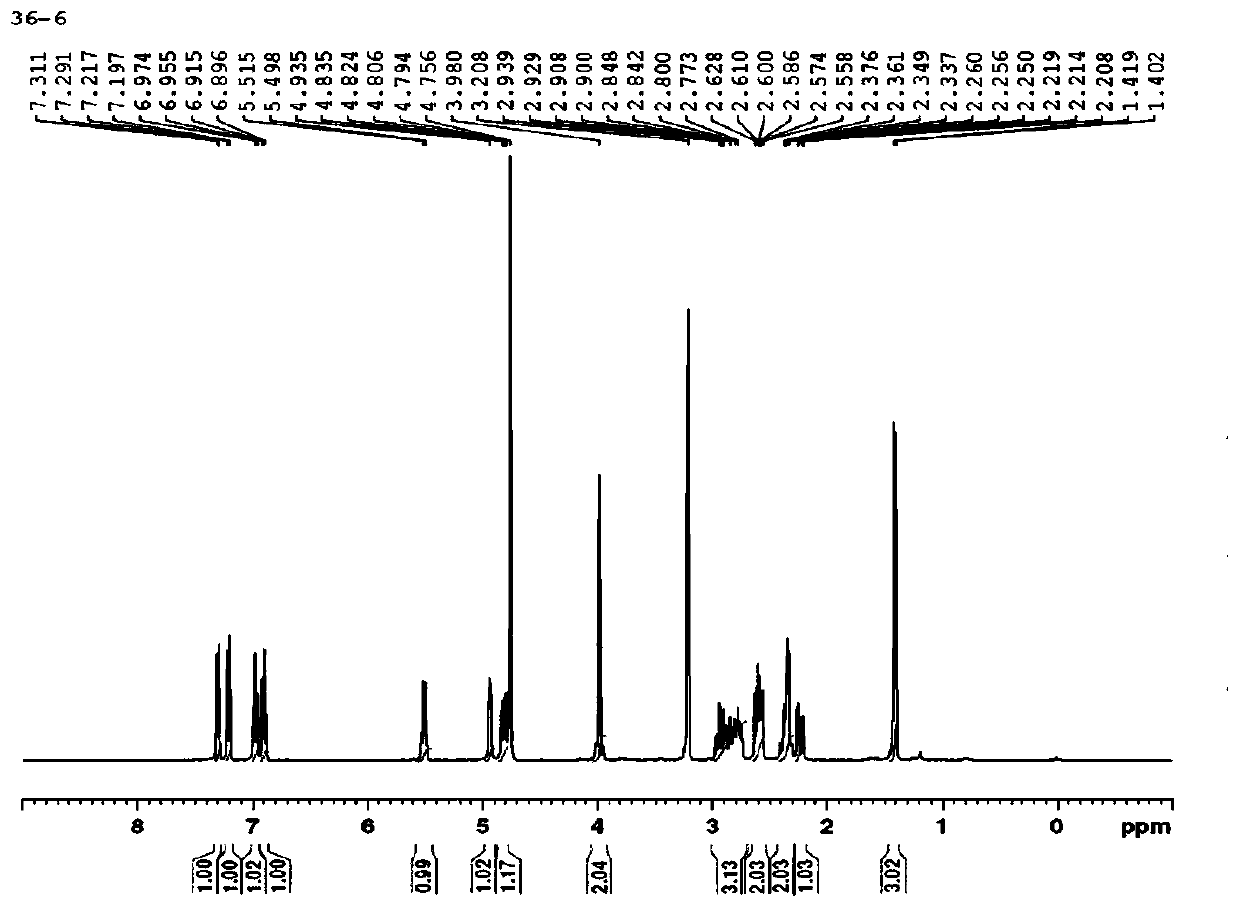
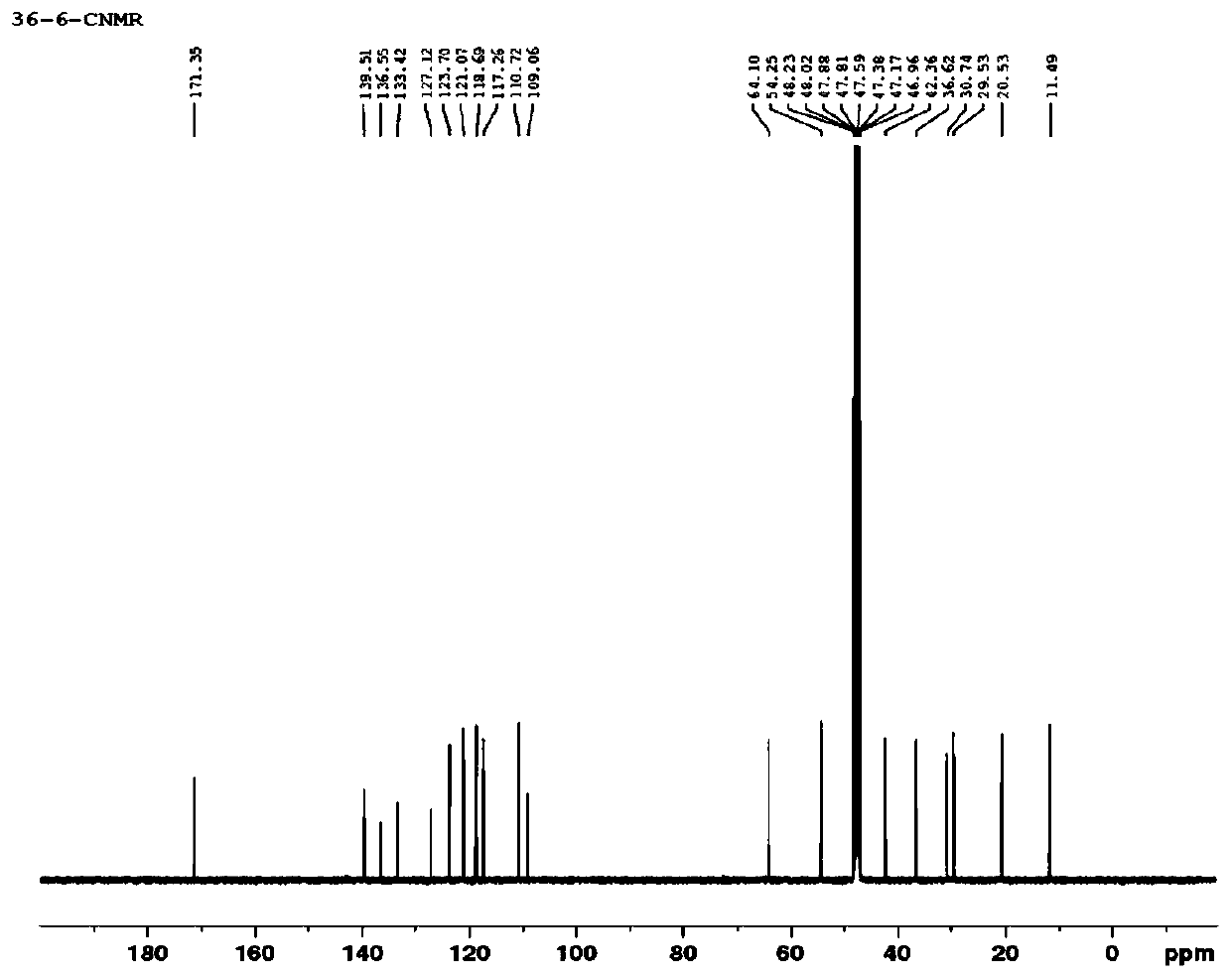
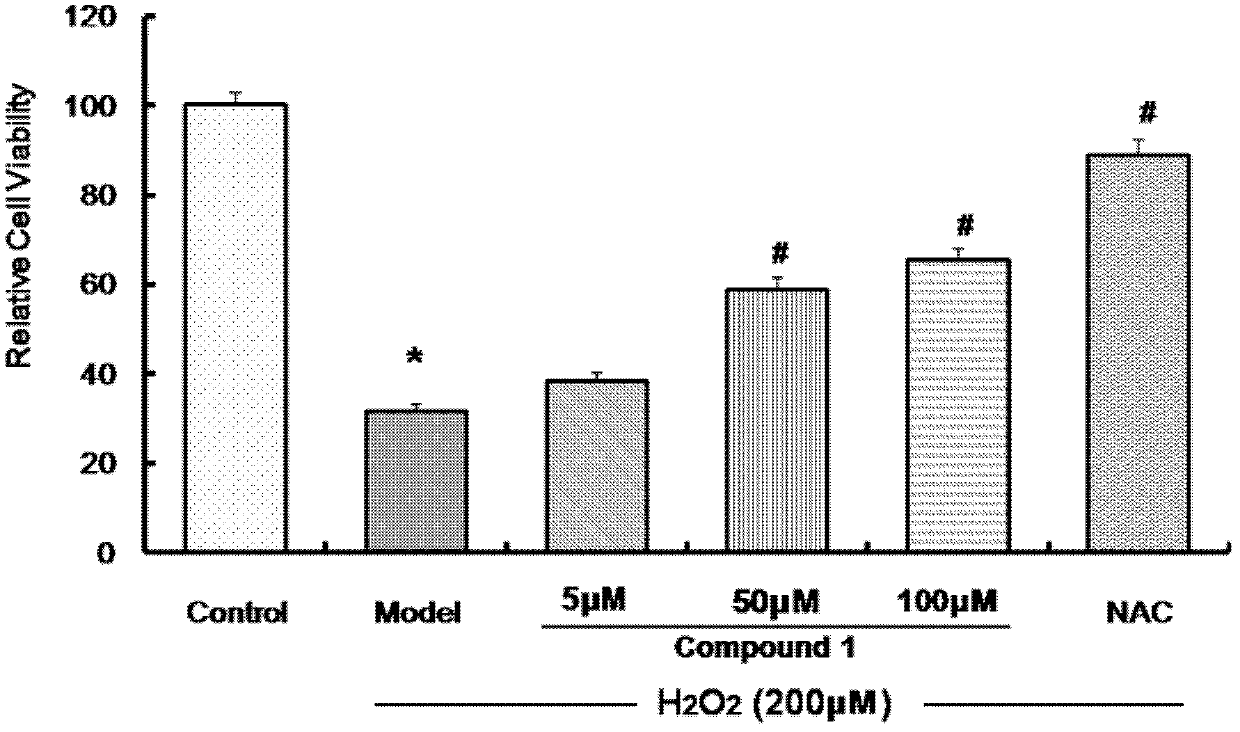
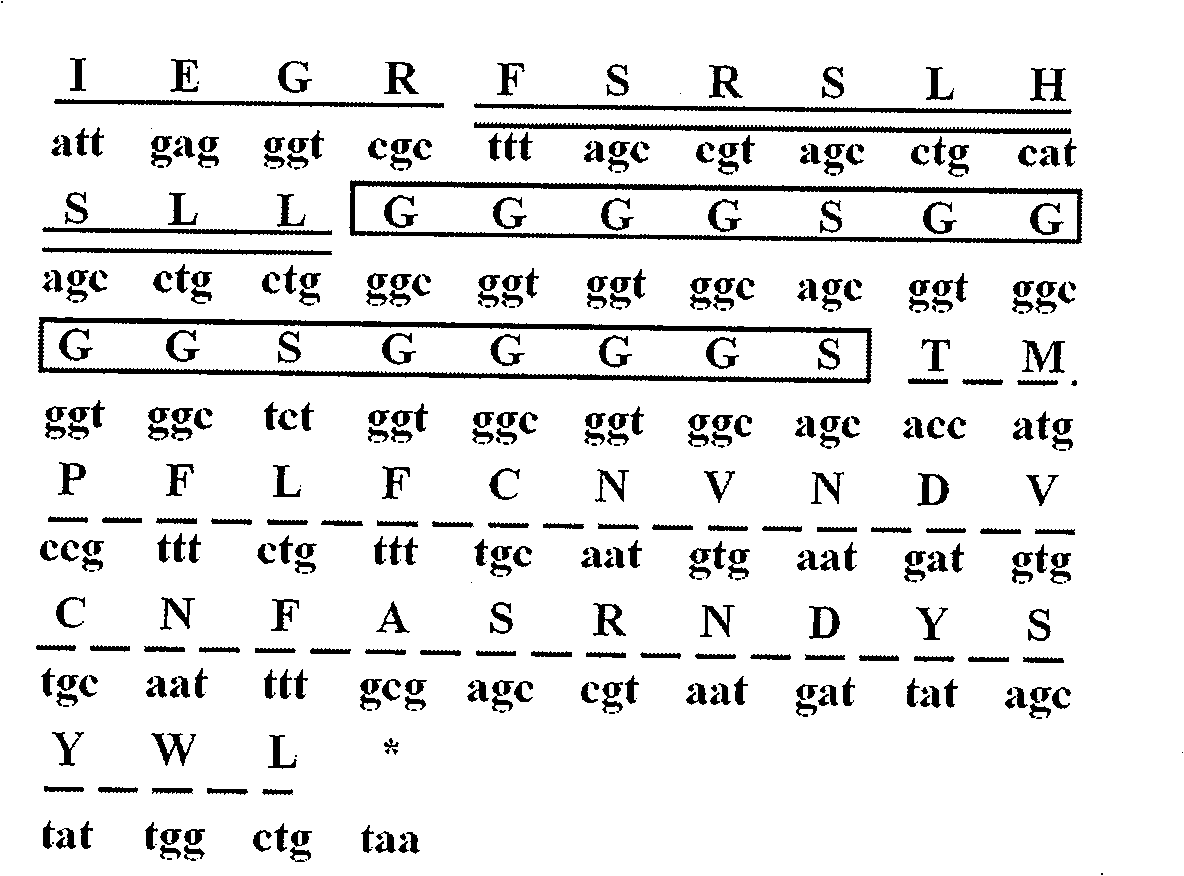Patents
Literature
148 results about "Human umbilical vein endothelial cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) are cells derived from the endothelium of veins from the umbilical cord. They are used as a laboratory model system for the study of the function and pathology of endothelial cells (e.g., angiogenesis). They are used due to their low cost, and simple techniques for isolating them from umbilical cords, which are normally resected after childbirth. HUVECs were first isolated and cultured in vitro in the 1970s by Jaffe and others. HUVECs can be easily made to proliferate in a laboratory setting. Like human umbilical artery endothelial cells they exhibit a cobblestone phenotype when lining vessel walls.
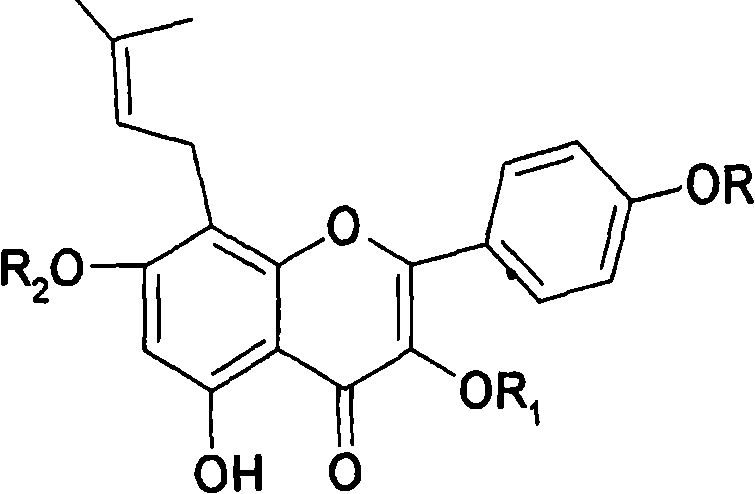
Application of icaritin in preparation of anti-angiogenic medicaments
InactiveCN101836976AOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsCytotoxicityAngiogenesis growth factor
The invention belongs to the field of traditional Chinese medicaments and relates to new medicinal application of a Chinese medicinal active ingredient icaritin, in particular to the application of the icaritin in preparation of anti-angiogenic medicaments. In the invention, the influence of the icaritin on cell proliferation and migration of human umbilical vein endothelial cells is observed through vitro experiments, the influence of the icaritin on the angiogenesis of a chick chorioallantoic membrane is observed through vivo experiments, and results demonstrate that the icaritin can effectively resist the angiogenesis and the anti-angiogenesis is not realized by cytotoxicity. The icaritin can be used as a medicinal active ingredient to be prepared, together with a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, into anti-angiogenic medicinal compositions.
Owner:AFFILIATED HUSN HOSPITAL OF FUDAN UNIV
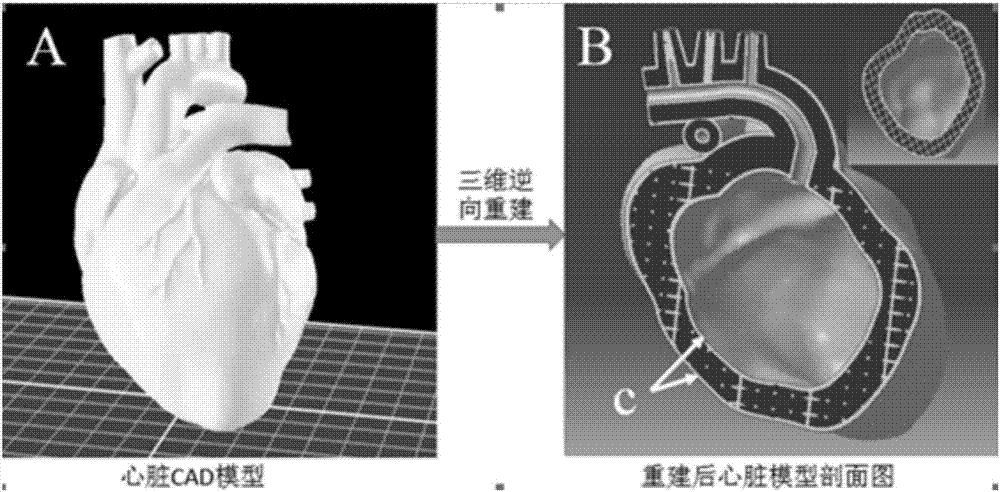
Method for building hollow vascularized heart based on 3D biological printing technology and hollow vascularized heart
ActiveCN107164318ASolve the poor effect of mechanical supportEasy to shapeCell culture supports/coatingSkeletal/connective tissue cellsCell activityReverse modeling
The invention provides a method for building a hollow vascularized heart based on the 3D biological printing technology and the hollow vascularized heart and relates to the technical field of tissue engineering and biology. The method includes: performing reverse modeling to build a heart three-dimensional grid model, importing the data of the heart three-dimensional grid model into a double-nozzle biological printing machine, and driving the nozzles of the printing machine to move according to a predesigned CAD digital model and selected forming parameters, wherein the nozzle 1 of the printing machine is loaded with sacrificial materials and used for printing a support framework, the nozzle 2 of the printing machine sprays biological ink to obtain building bodies, and the effective components of the biological ink comprise hydrogel, platelet-rich plasma, third-generation human umbilical vein endothelial cells and SD rat primary cardiomyocytes; crosslinking and cleaning the building bodies, and performing three-dimensional culture to form the hollow vascularized heart. The method has the advantages that the problem that a large-size hollow vascularized heart is hard in integrated printing, and the hollow vascularized heart built by the method is high in cell activity and has certain functions.
Owner:叶川 +2
HUVEC (human umbilical vein endothelial cell) separation, culture and subculture method
InactiveCN102827805AEasy to get materialsEasy to operateVertebrate cellsArtificial cell constructsWater bathsPenicillin
The invention relates to an HUVEC (human umbilical vein endothelial cell) separation, culture and subculture method belonging to the technical field of biology. The method comprises the following steps: (1) separation of HUVEC: taking a fresh umbilical cord, cleaning with a sterile PBS (phosphate buffer solution) containing penicillin-streptomycin, adding collagenase to perform water bath digestion at 37 DEG C, centrifuging the digestion solution, then adding an M199 culture medium, transferring into a gelatin-coated culture bottle, and culturing in a CO2 incubator at 37 DEG C; (2) culture of HUVEC: after the HUVEC is cultured at 37 DEG C for 24 hours, pouring out the culture medium, cleaning with the PBS, adding a fresh M199 culture medium, and afterwards, changing the culture medium once every two days, wherein the HUVEC can be subcultured generally after being cultured for 5-7 days; and (3) subculture of HUVEC: pouring out the culture medium, cleaning with the PBS, adding the digestion solution to digest the cell, adding a DMEM (dulbecco's modified eagle medium) containing serum to terminate the reaction once the cell is rounded, centrifuging the digested cell, and adding a fresh culture medium, wherein the HUVEC subcultured for 2-3 generations is used for experiments. The separated HUVEC is economical and practical, is simple and easy to use, and is beneficial to obtaining required in-vitro experimental model cells.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
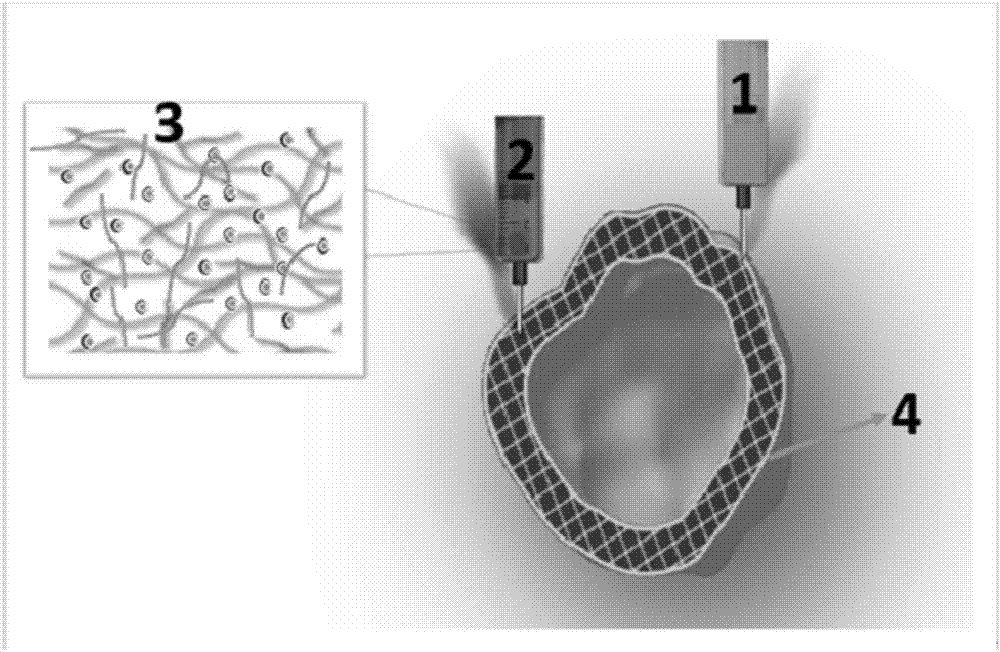
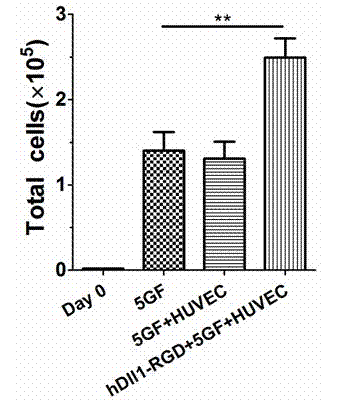
Expansion system in vitro for hematopoietic stem/progenitor cell
InactiveCN102643784AGood hematopoietic reconstruction abilityBlood/immune system cellsProgenitorVascular endothelium
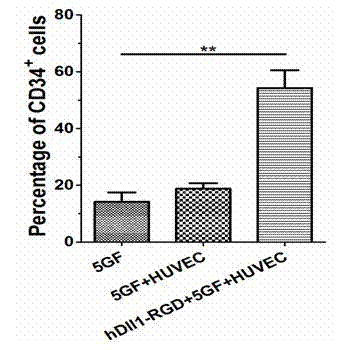
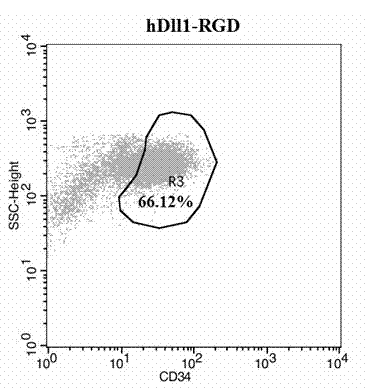
The invention provides an expansion system in vitro for hematopoietic stem / progenitor cells used for expanding human umbilical cord blood in vitro of soluble fusion protein Dll1-RGD (Hdll1-RGD) of notch ligand of a vascular endothelial cell target. The effective expansion system in vitro is formed by taking human umbilical vein endothelial cells as supporting cells of a cultivation system, jointly applying exogenous growth factors SCF, TOP, FL, IL-6, IL-3 and own developed hDLL1-RGD, and co-cultivating with the hematopoietic stem / progenitor cells. According to the expansion system, the hDll1-RGD target is combined to the surface of a human umbilical vein endothelial cell, activated stimulation aiming at a notch receptor is provided for the hematopoietic stem cells, and self-renewal and propagation of the hematopoietic stem cells are maintained, so that a satisfactory expansion effect and favorable implantation capacity are obtained.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
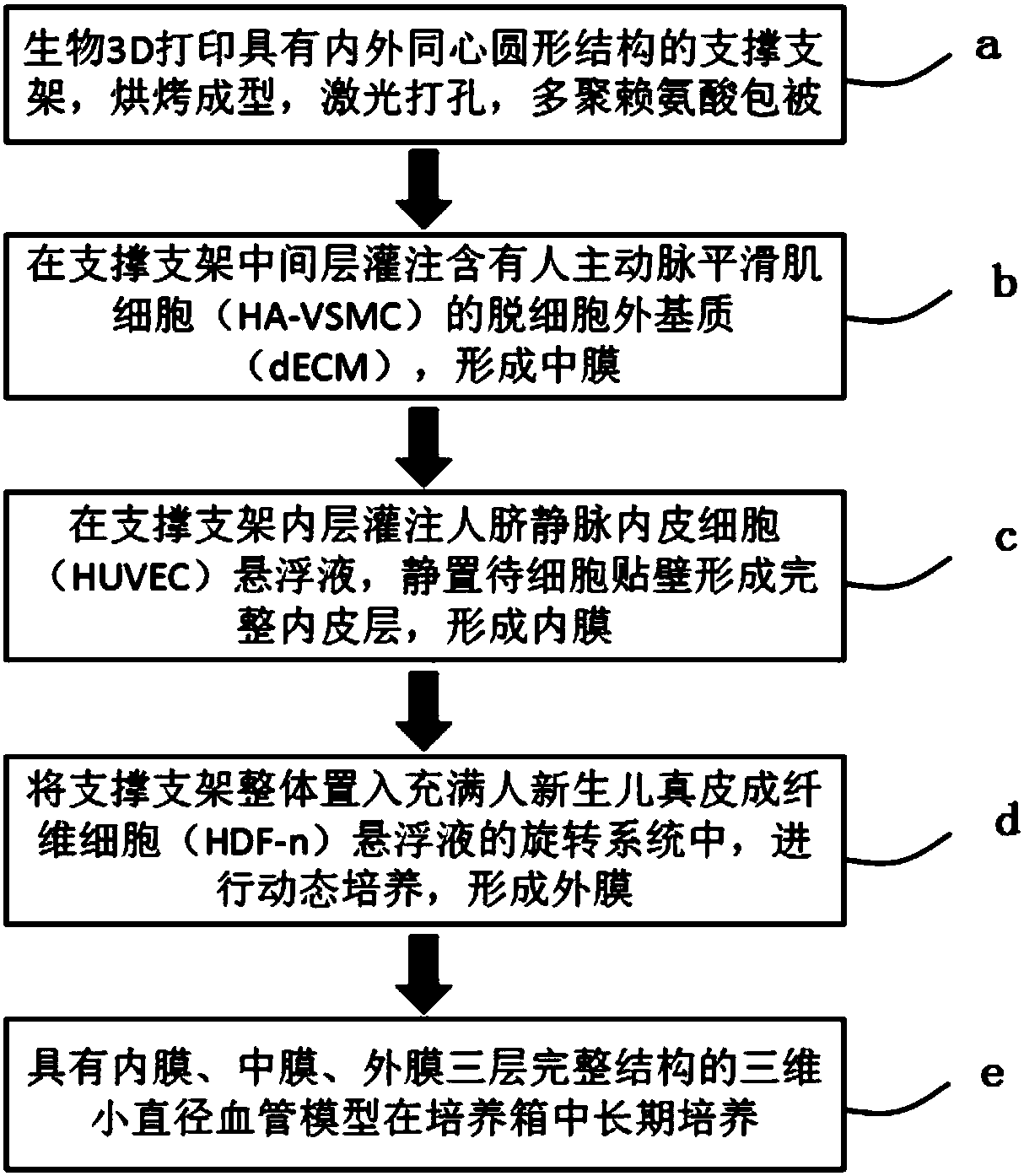
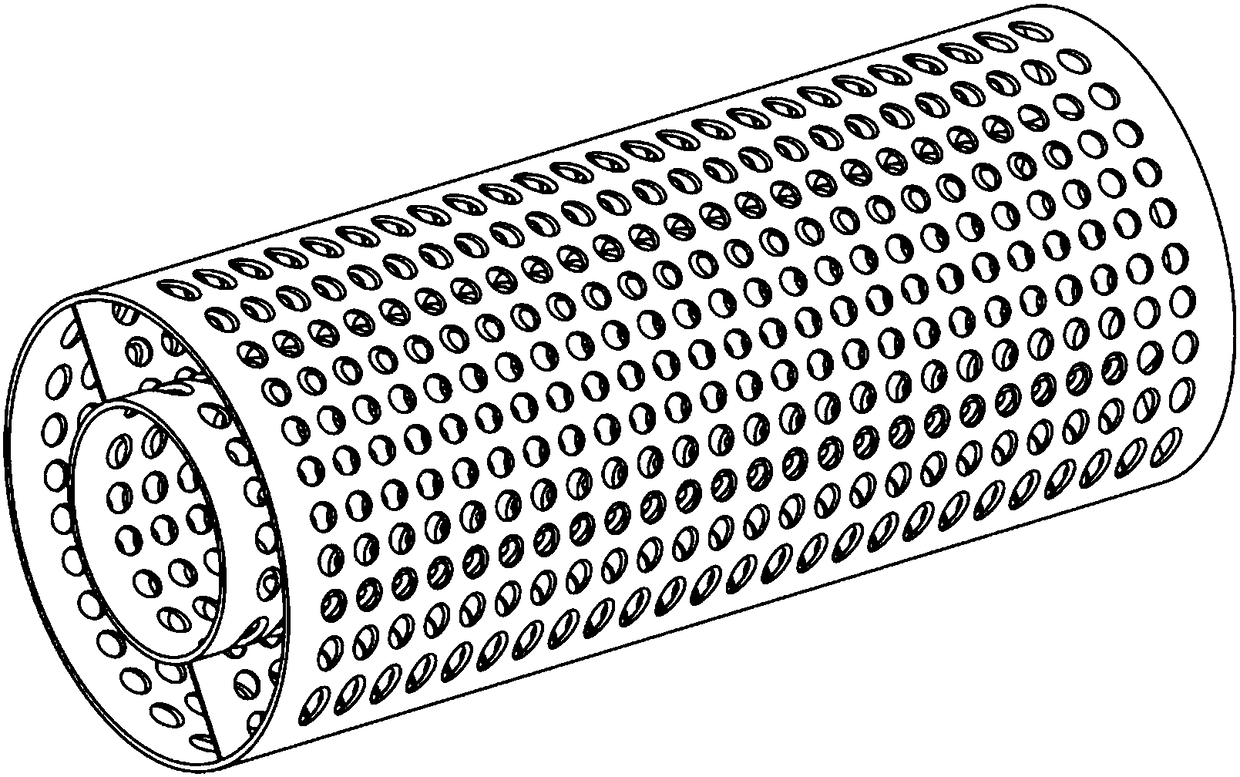
Method for manufacturing three-dimensional small-diameter vessel model
InactiveCN108498867AGood biocompatibilityStrong mechanical propertiesAdditive manufacturing apparatusProsthesisFiberBiocompatibility Testing
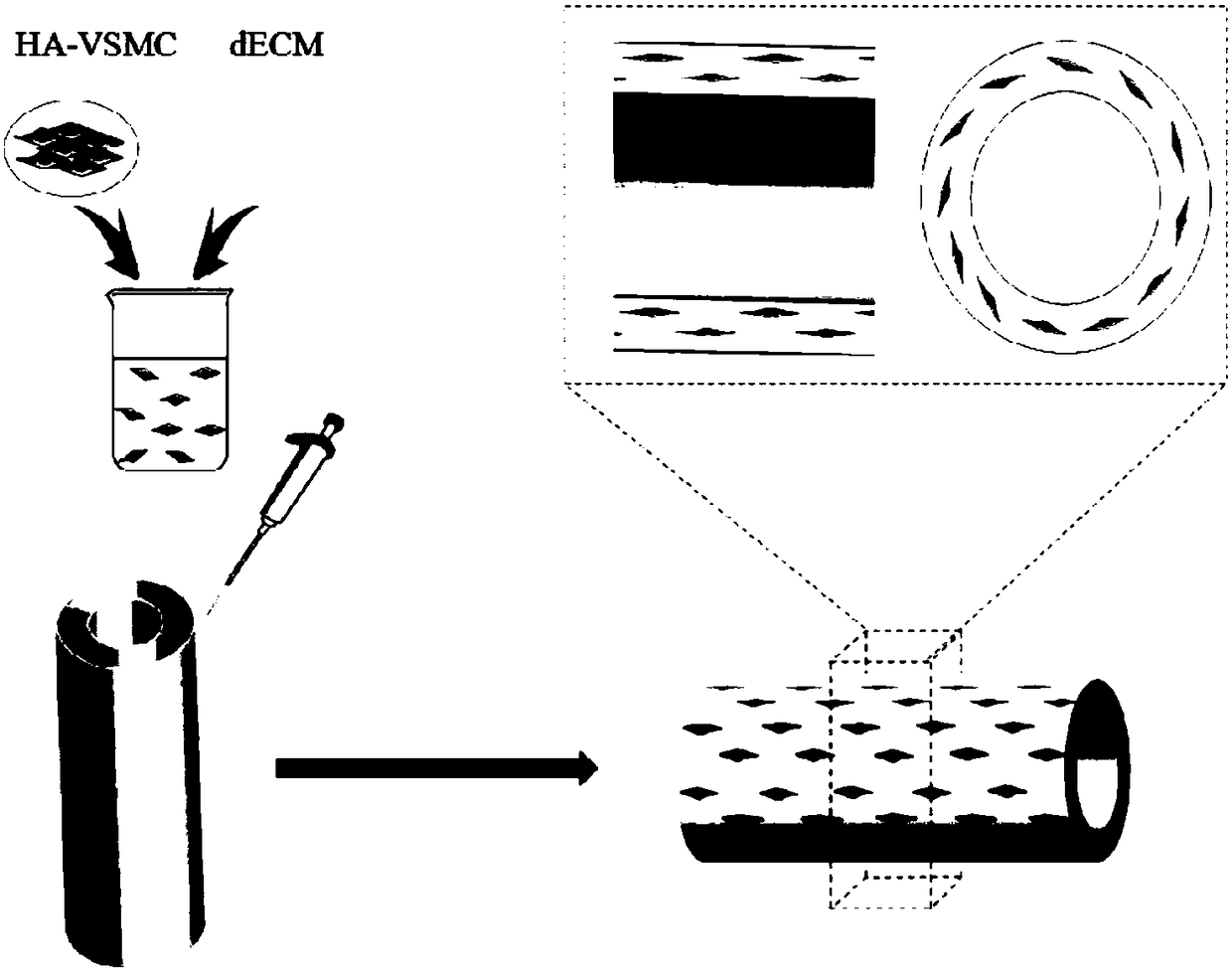
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing a three-dimensional small-diameter vessel model. The method comprises the following steps of a, preparation of a supporting bracket: utilizing a silica gel material to perform 3D printing of a supporting bracket with an inner and outer concentric circle shape structure; b, formation of a medial membrane: pouring an accellular extracellular matrixcontaining a human aortic smooth muscle cell into a middle layer of the supporting bracket to form the medial membrane; c, formation of an intima: pouring a human umbilical vein endothelial cell suspension into an inner layer of the supporting bracket to form the intima; and d, formation of an adventitia: wholly putting the supporting bracket in a dynamic culture system fully filled with human newbaby dermal fibroblast suspension to form the adventitia. The vessel model acquired with the method is good in biocompatibility, has relatively strong mechanical property and can be used for pathological model study and drug screening relevant to vessels.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
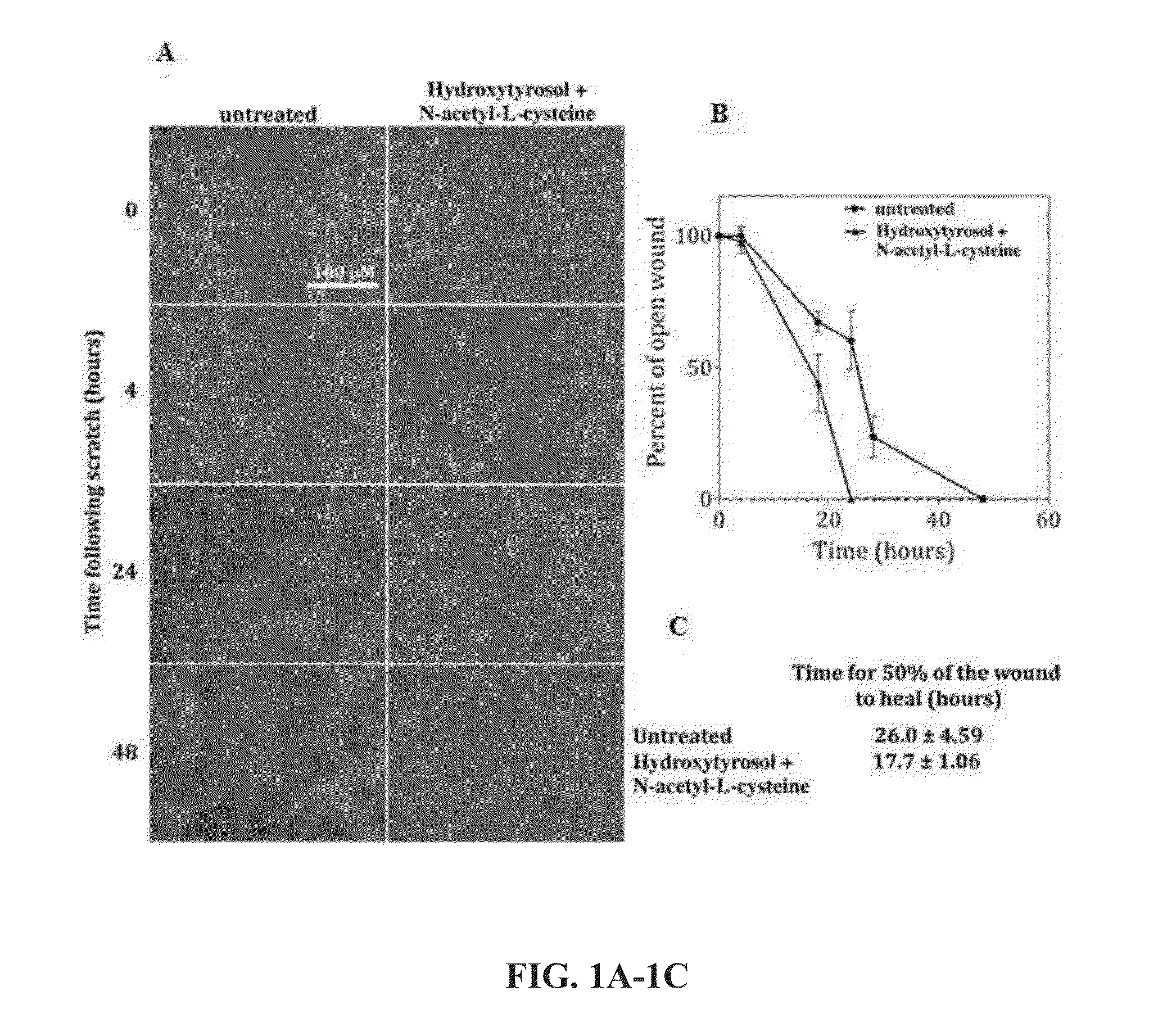
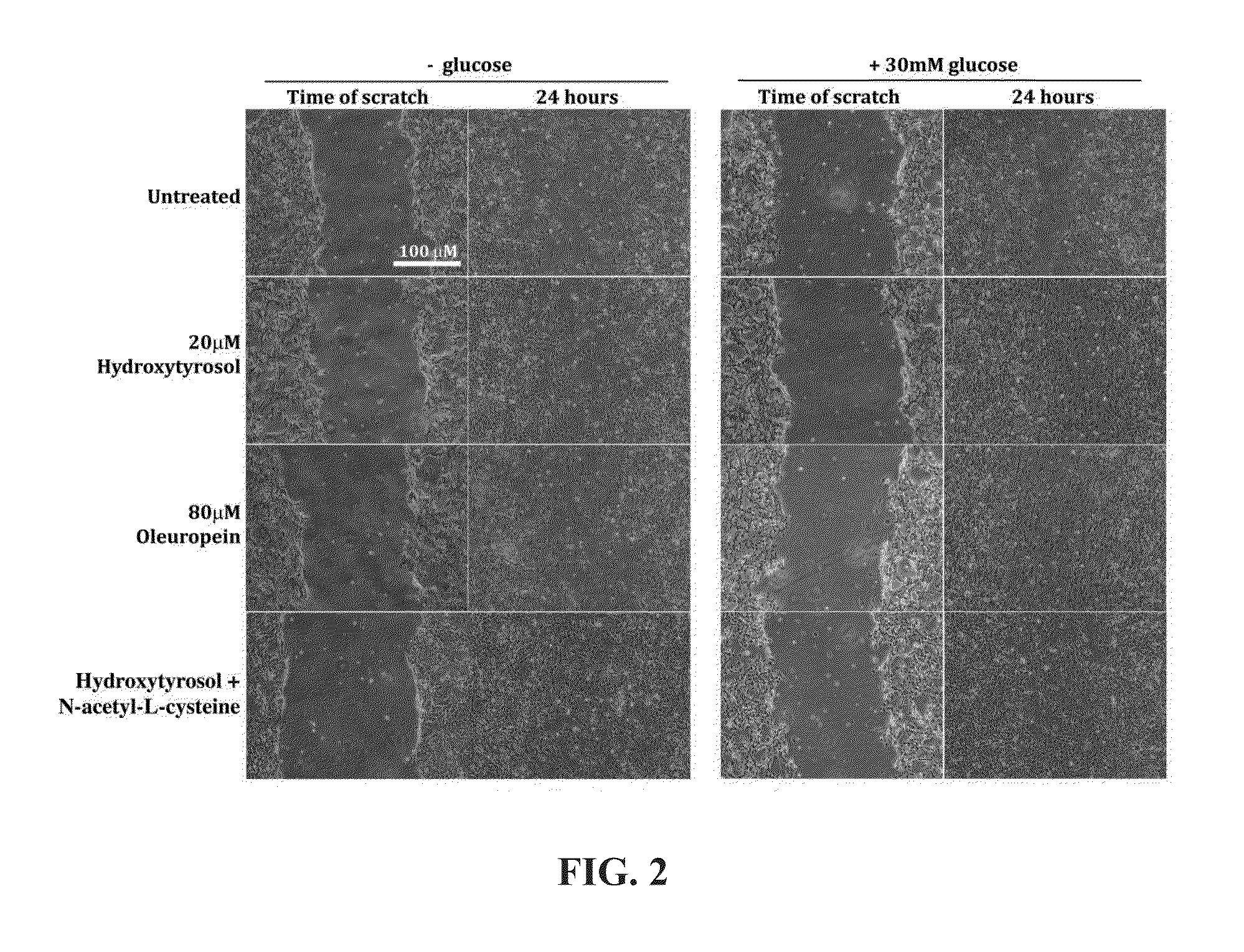
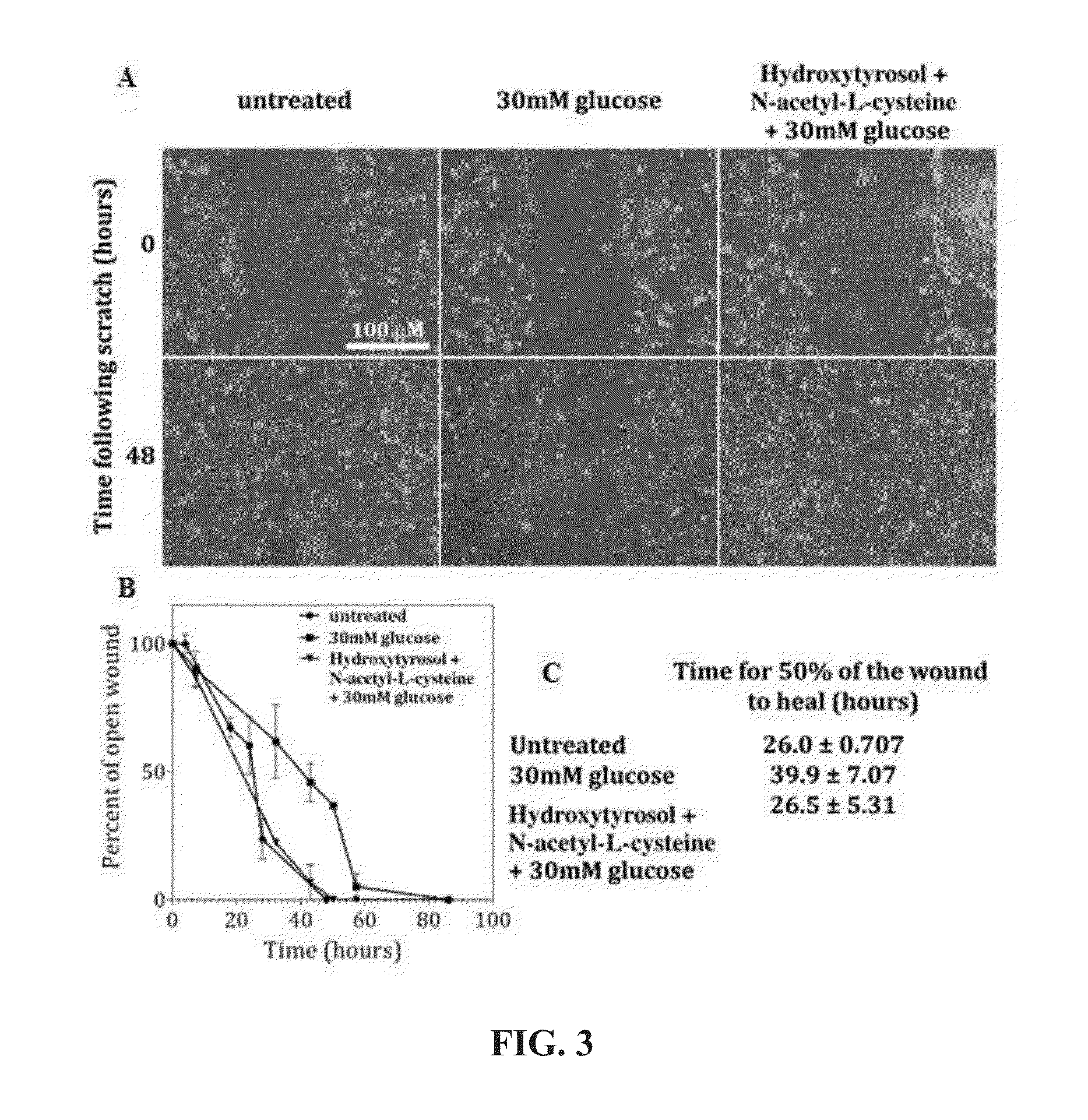
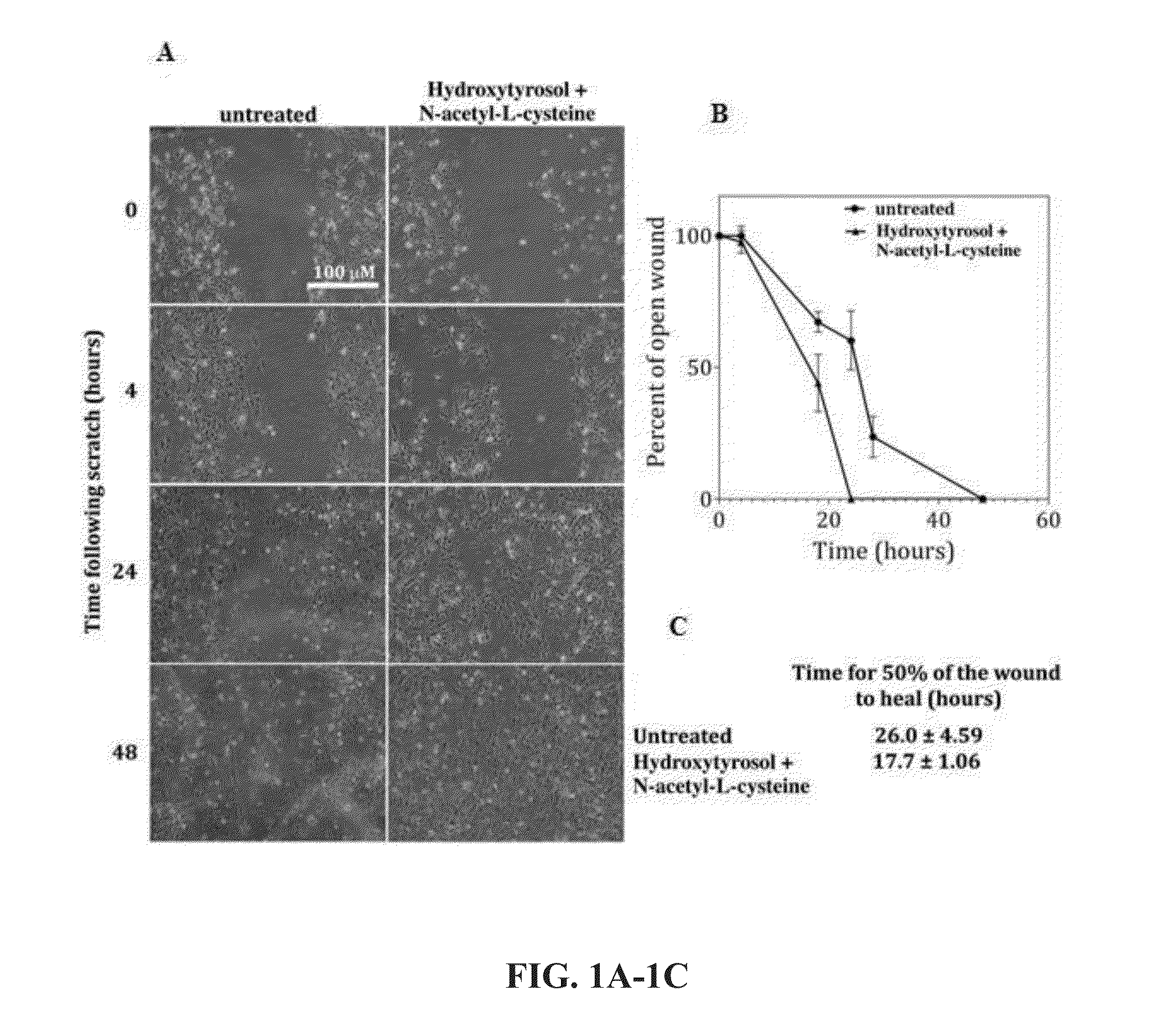
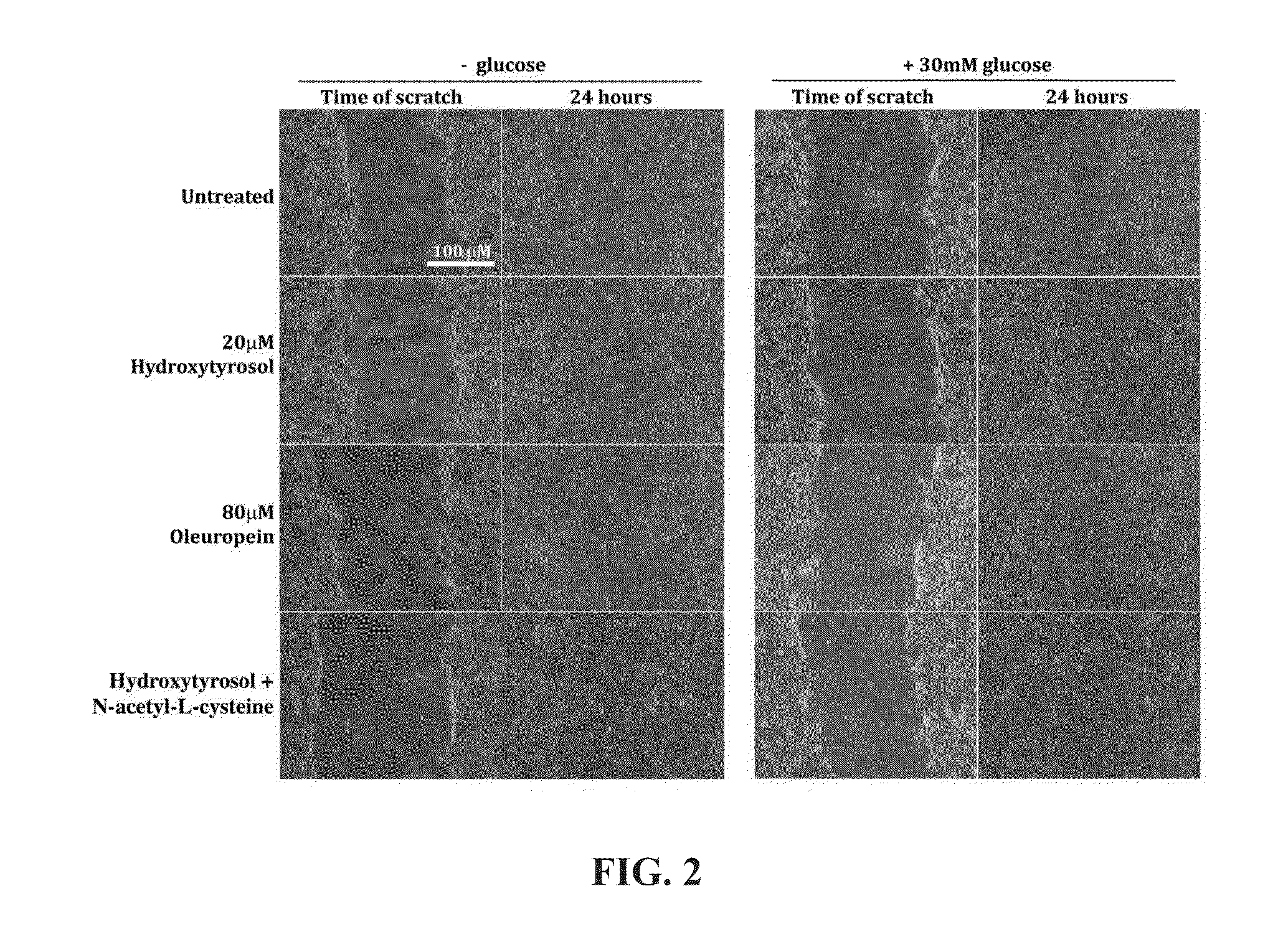
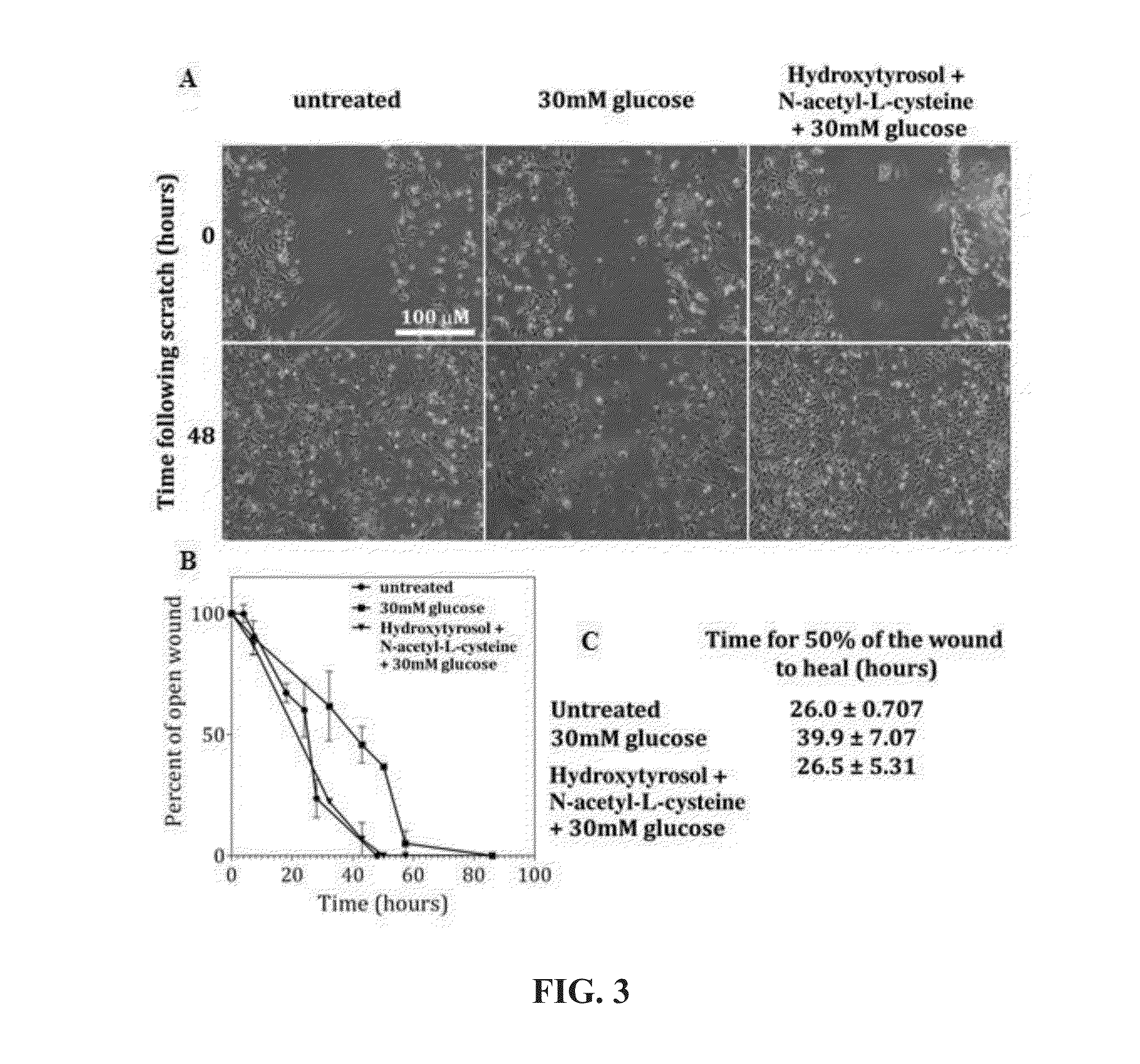
Methods for improved wound closure employing olivamine and human umbilical vein endothelial cells
ActiveUS8796315B2Time requiredPromote wound repairBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsHydroxytyrosolVein
Owner:MCCORD DARLENE E
Hyla simplex skin injury repair promotion polypeptides and genes as well as application thereof
InactiveCN102250217ASimple structureEasy to synthesizePeptide/protein ingredientsPeptidesVascular endotheliumCuticle
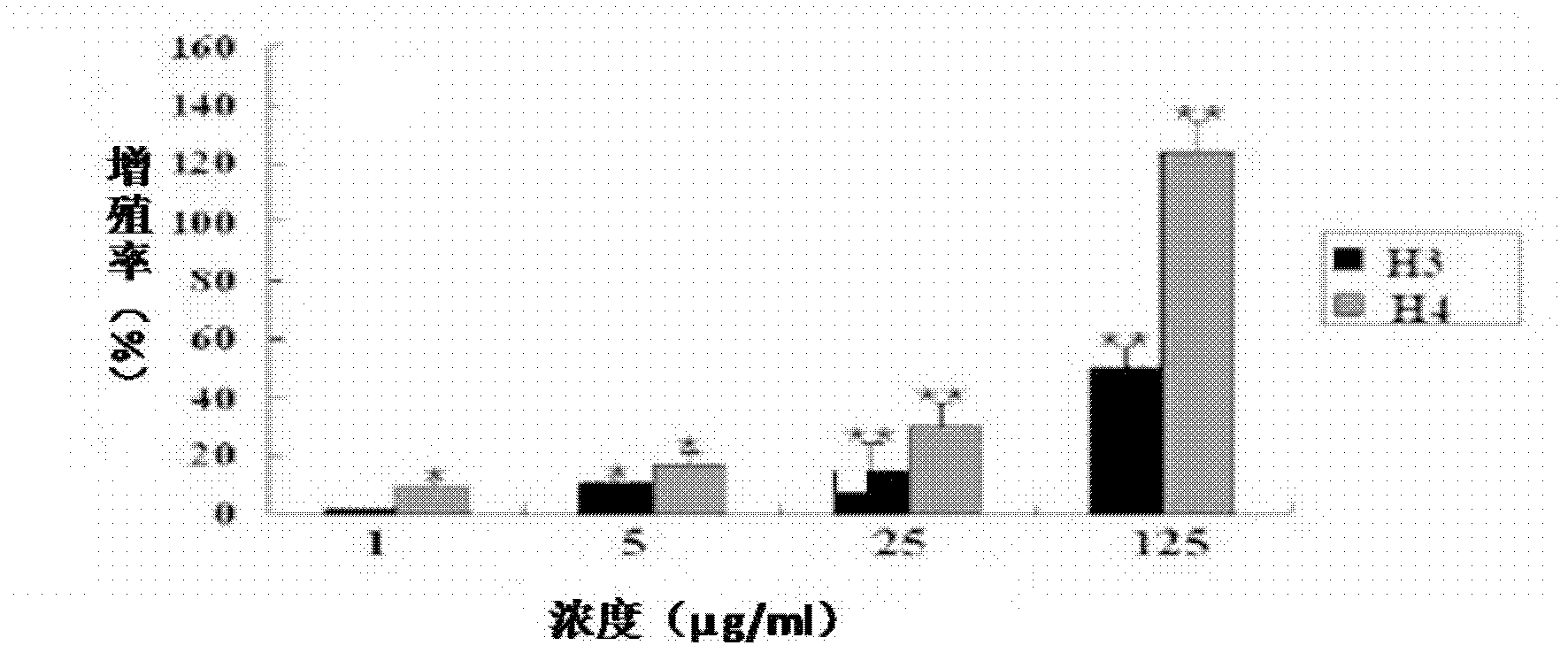
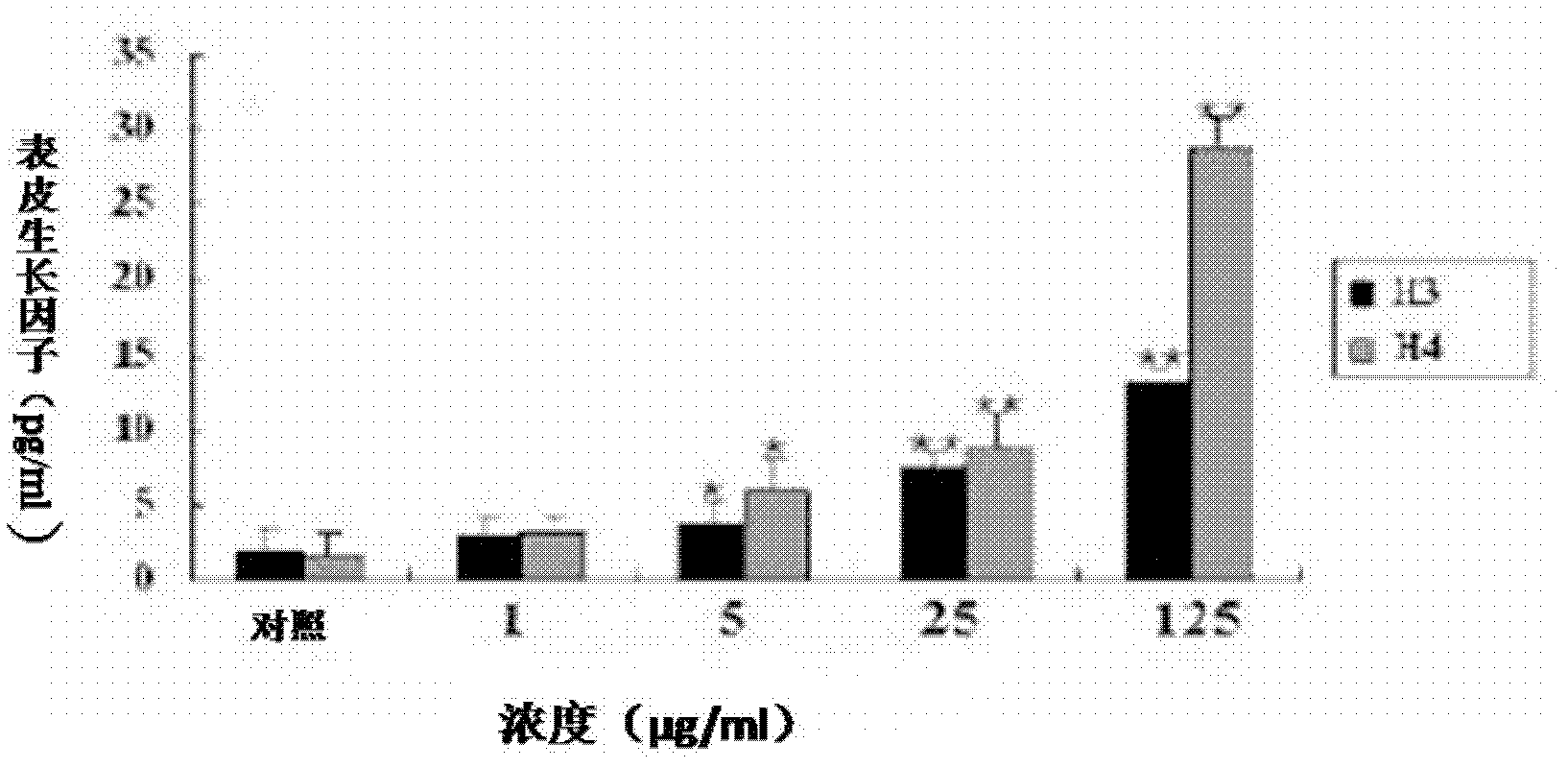
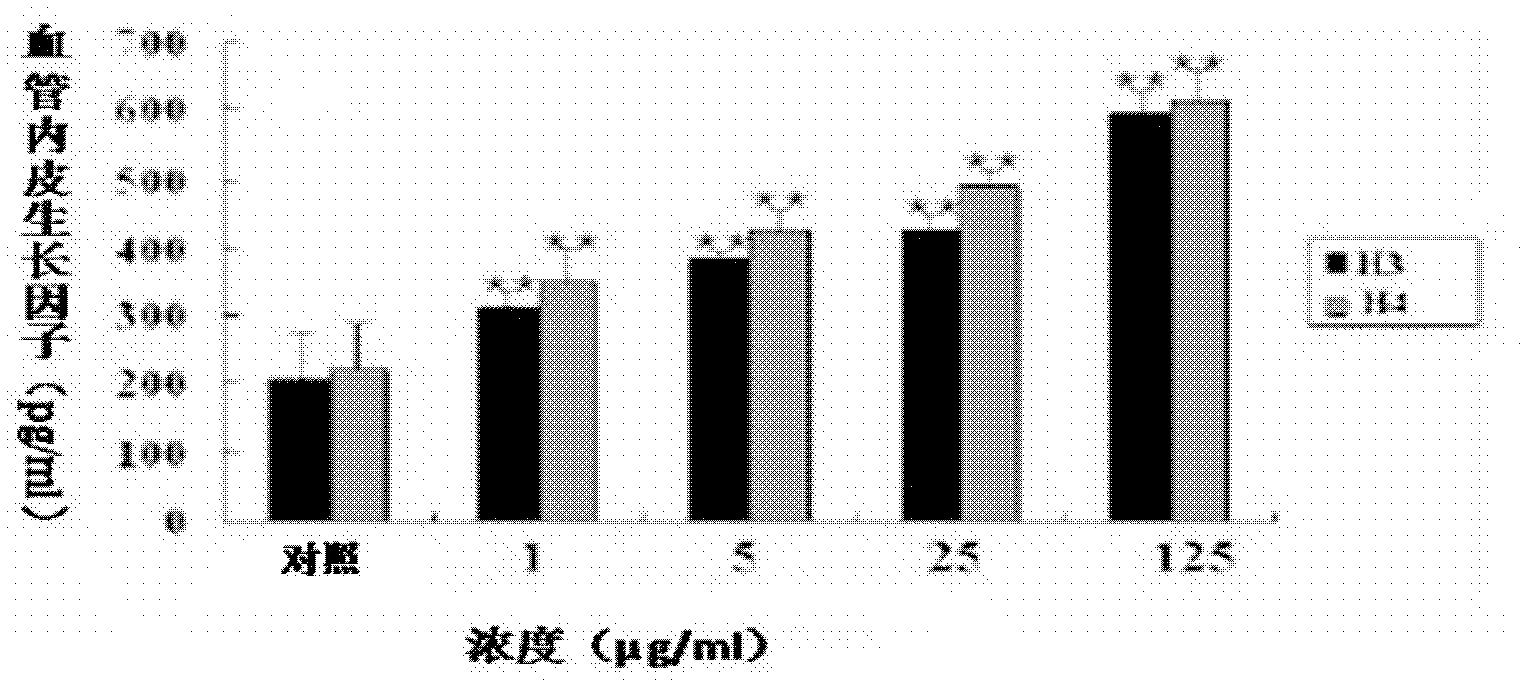
The invention relates to hyla simplex skin injury repair promotion polypeptides and genes as well as application thereof, and belongs to the field of biomedicine. The hyla simplex skin injury repair promotion polypeptides comprise Hylareleasin 3 and Hylareleasin 4, which are gene codes of hyla simplex, a Chinese amphibious animal, wherein the molecular weights of the Hylareleasin 3 and 4 are 1764.106 Daltons and 1707.05 Daltons respectively; the isoelectric points are 9.61 and 9.60 respectively; the complete sequences of the hyla simplex skin injury repair promotion polypeptides Hylareleasin 3 and Hylareleasin 4 are NH2-GLLDPVTHILGGFLRR-COOH and NH2-GLLDPVTNILGGLLRR-COOH respectively; the genes coded by both the polypeptides consist of 365 nucleotides; and the mature coding part comprises the nucleotides 217-264. The multiplication of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) and the activity of the HUVEC for releasing epidermal growth factor (EGF) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) are promoted by the synthetic hyla simplex skin injury repair promotion polypeptides; and the hyla simplex skin injury repair promotion polypeptides can be applied to preparing preparations for promoting multiplication and tissue regeneration of vascular endothelial cells and epidermic cells and treating wounds, burns and ulcers of the body surface. The hyla simplex skin injury repair promotion polypeptides also have the advantages of simple sequences and convenience for synthesis.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Gramicidin, isomer thereof and application thereof
The invention discloses gramicidin, isomer thereof and application thereof. The structure is Ac-Asp-Arg-Val-Tyr-Ile-His-Pro-NH2 and Ac-Asp-Arg-Val-Tyr(D)-Ile-His(D)-Pro. Two modified construction bodies have biological activity which is similar to angiotensin 1-7 and capable of promoting human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) to release nitrogen oxide (NO) for migration, forming a tubelet and restraining A549 cell growth. Simultaneously, the modified construction bodies have degradation capability of three degradation enzymes including ACE, NEP and AP, thereby ensuring that the modified construction bodies have longer half-life periods than the angiotensin 1-7. The modified construction bodies are simple to obtain and provide important application value for development of novel polypeptide drugs for treating cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Biological activity analysis method of recombinant anti-VEGFR2 monoclonal antibody and application thereof
PendingCN111024949AHigh sensitivityImprove accuracyArtificial cell constructsCell culture active agentsAntiendomysial antibodiesTiter
The invention relates to a biological activity analysis method of a recombinant anti-VEGFR2 monoclonal antibody and an application thereof. The biological activity analysis method comprises the following steps: co-culturing a recombinant anti-VEGFR2 monoclonal antibody, human umbilical vein endothelial cells and a VEGF reagent; adding a CCK8 chromogenic solution for continued culture; reading a light absorption value; carrying out 4-parameter fitting according to the dose-effect relationship between the concentration of the recombinant anti-VEGFR2 monoclonal antibody and the light absorption value, and carrying out biological activity evaluation according to an EC50 value of curve fitting. The method is a biological activity analysis method special for a recombinant anti-VEGFR2 monoclonalantibody, has the advantages of simple operation, high sensitivity, high accuracy and wide application range, can be used for detecting recombinant anti-VEGFR2 monoclonal antibodies with different titer levels, and can be used for detecting the biological activity of intermediates, stock solutions or finished products of the recombinant anti-VEGFR2 monoclonal antibodies.
Owner:MAB VENTURE BIOPHARM CO LTD
Decapeptide inhibiting angiogenesis and use thereof
InactiveCN101597324AEnhanced inhibitory effectSenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseVascular endothelium
The invention relates to a decapeptide inhibiting angiogenesis and use thereof, belonging to the technical field of biological medicine. The decapeptide inhibiting angiogenesis provided by the invention is deprived from human Homo sapien with an amino acid sequence of YNWNSFGLRF and the molecular weight of 1303.4, and is named as Kp-10. The invention further provides use of the decapeptide inhibiting angiogenesis for preparing medicines for inhibition of angiogenesis, in particular relevant use of Kp-10 for preparing medicines for inhibition of angiogenesis dependent diseases such as cancer, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, diabetes syndrome, and hemangioma. A series of experimental results in VEGF (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor) induction shows that Kp-10 has obvious inhibition function in the proliferation experiment of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC), transfer experiment, micro-tube forming experiment, angiogenesis experiment of chick embryo allantois and mouse cornea experiment, and the decapetide can be used for preparing medicines for inhibiting angiogenesis.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Use of oligosaccharide in preparing medicine for treating tumor and inhibiting tumor metastasis
InactiveCN101416979AInhibit migrationInhibition formationOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsVeinLymphatic Spread
The invention relates to the biological medicine, in particular to the application of chitosan oligosaccharide in preparing medicines used for treating tumors and restraining tumor metastasis, wherein, by taking a nutrient solution for tumor cells as an inducing factor and taking a human umbilical vein endothelial cell as an study object, the chitosan oligosaccharide can significantly restrain the human umbilical vein endothelial cell metastasis induced by the nutrient solution for tumor cells and the formation of tubular structure caused by the endothelial cell metastasis, but have no obvious restraining effect on the proliferation of the human umbilical vein endothelial cells metastasis induced by the nutrient solution for tumor cells.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing velvet antler protein extracts
ActiveCN104987358AMaintain biological activityMaintain extraction efficiencyPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsFreeze-dryingActive protein
The invention relates to the technical field of protein extraction, in particular to a method for preparing velvet antler active protein extracts. The method comprises the steps of conducting blood drawing, freeze-drying and smashing on fresh velvet antler to obtain velvet antler powder; mixing the velvet antler powder with a buffer solution, conducting ultrasonic extraction and centrifugation, collecting supernate, and conducting vacuum freeze drying to obtain the velvet antler protein extracts, wherein the pH value of the buffer solution is 7.0-8.0, and the concentration of the buffer solution is 10-50 mM. By the adoption of the method, the biological activity and extraction efficiency of velvet antler protein are maintained to the maximum degree. The velvet antler protein extracts prepared with the method can promote growth or proliferation of vascular cells, and particularly, the proliferation rate of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) reaches 200%.
Owner:吉林玉参医药科技有限公司
Miichthys miiuy meat antioxidative peptide
InactiveCN107602665AImprove cleanlinessPlay a protective effectPeptidesFermentationFood additiveDPPH
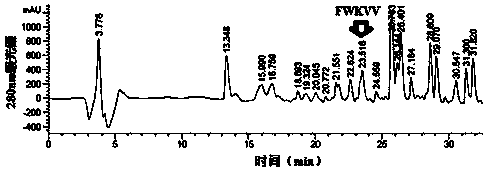
The invention discloses a miichthys miiuy meat antioxidative peptide. The preparation method comprises the following steps: performing degreasing and complex enzyme enzymolysis by using micchthy miiuymeat as a raw material to obtain enzymatic hydrolysate; and performing ultrafiltration, macroporous resin desalination, anionic exchange resin chromatography, gel column chromatography and reversed high performance liquid chromatography separation and purification on the enzymatic hydrolysate to obtain antioxidative peptide Phe-Trp-Lys-Val-Val(FWKVV); and detecting the molecular weight which is 677.84 Da with ESI-MS. The high-activity antioxidative peptide Phe-Trp-Lys-Val-Val (FWKVV) has an excellent cleaning effect for DPPH free radical, hydroxyl radical and superoxide anion free radical, and has a protective effect for hydrogen peroxide induced human umbilical vein endothelial cell-HUVEC cell oxidative damage, has the advantages of safety, no toxicity or side effect, strong antioxicative activity and the like, and can be used as medicines, health foods or food additives and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
Methods for improved wound closure employing olivamine and human umbilical vein endothelial cells
ActiveUS20130266545A1Shorten the timePromote wound repairBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsHydroxytyrosolVein
Owner:MCCORD DARLENE E
Recombination NuBCP-9 and Tumstatin(74-98) antitumor fusion polypetide
The invention relates to NuBCP-9 and Tumstatin(74-98) fusion genetic engineering antitumor peptide which is designed to be synthetic primer according to colon bacillus favorable codon, NuBCP-9 and Tumstation(74-98) fusion peptide gene order connected by flexible peptide (G4S3) is obtained by PCR through an SOE method, the NuBCP-9 and Tumstation(74-98) fusion peptide forms recombination expression plasmid after connecting with a carrier Pet 32A(+), the recombination expression plasmid is transferred to colon bacillus BL21 for performing the soluble efficient expression and purifying and enzyme-cutting to obtain the purpose peptide. The fusion peptide has better inhibition function to skin cell proliferation in umbilical vein and lung cancer cell, primarily shows the multitarget antitumor effect, and can have better clinical application prospect.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
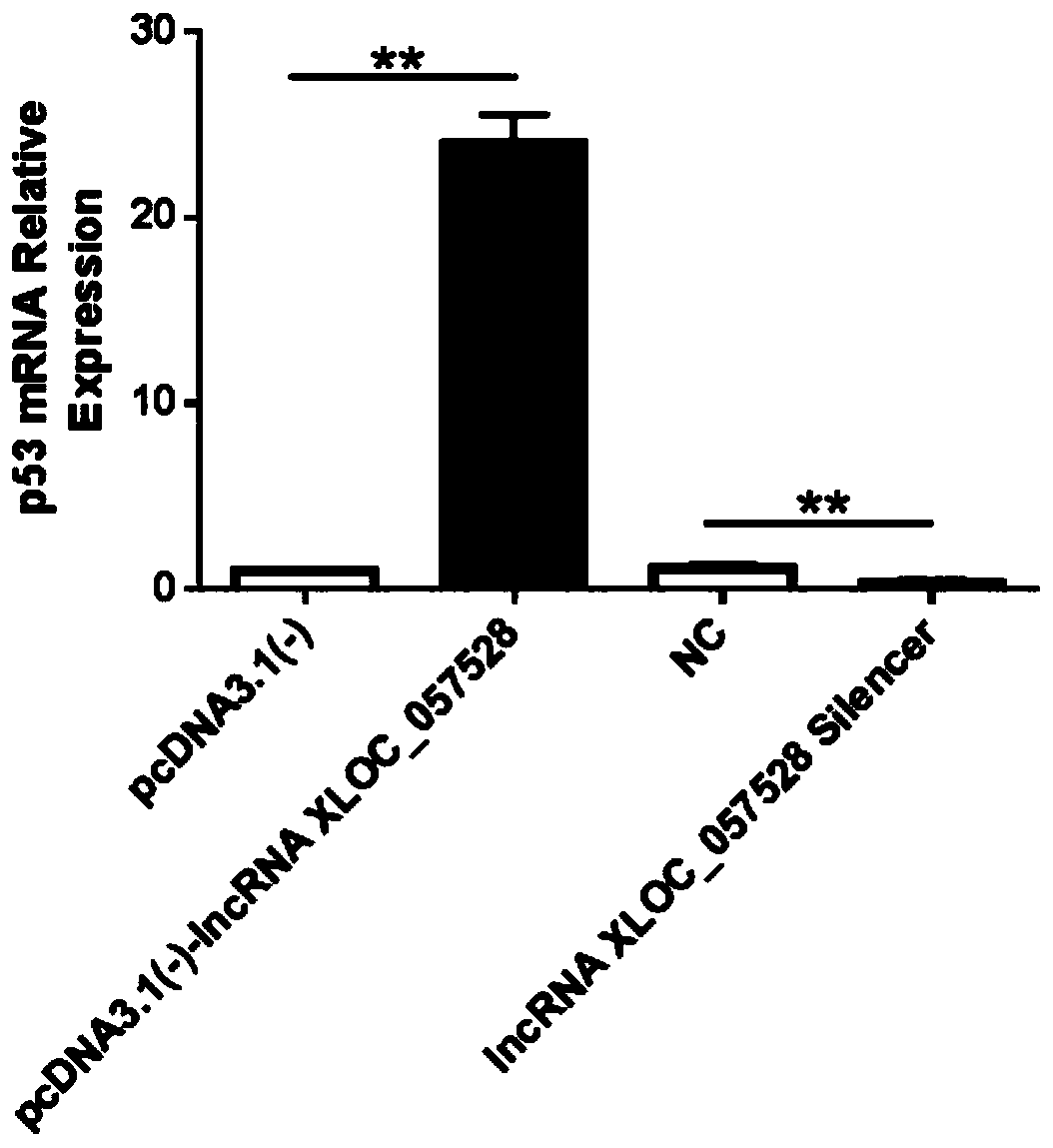
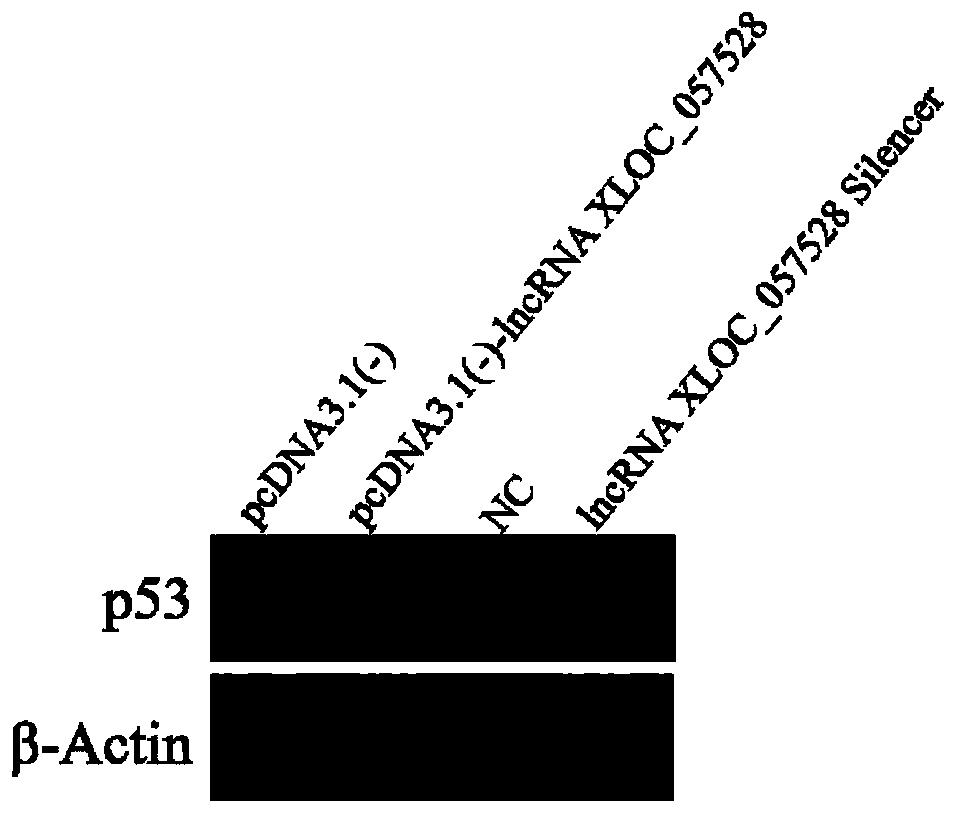
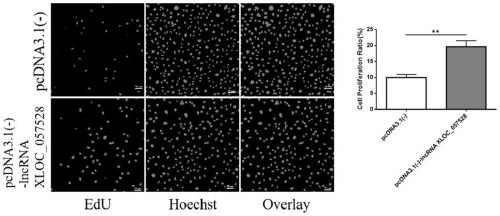
Application of LncRNA XLOC_057528 inhibitor to preparation of medicines for promoting blood vessel regeneration
ActiveCN110484614AReduce expressionHigh proliferation rateOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementVeinMedicine
The invention discloses an application of an LncRNA XLOC_057528 inhibitor to preparation of medicines for promoting blood vessel regeneration. Overexpression and silence of lncRNA XLOC_057528 confirmthat lncRNA XLOC_057528 can influence expression of a p53 gene and protein to human umbilical vein endothelial cells, and besides, confirm that the lncRNA XLOC_057528 participates in promotion of proliferation of the human umbilical vein endothelial cells, restraining of apoptosis of the human umbilical vein endothelial cells, and restraining of canaliculization of the human umbilical vein endothelial cells, and further confirm that the lncRNA XLOC_057528 can participate in restraining of blood vessel regeneration after miocardial infarction. Therefore, the lncRNA XLOC_057528 inhibitor can beused for preparing the medicines for promoting blood vessel regeneration, and particularly the lncRNA XLOC_057528 inhibitor can be used for preparing the medicines for promoting blood vessel regeneration after miocardial infarction.
Owner:GUANGDONG LAB ANIMALS MONITORING INST +1
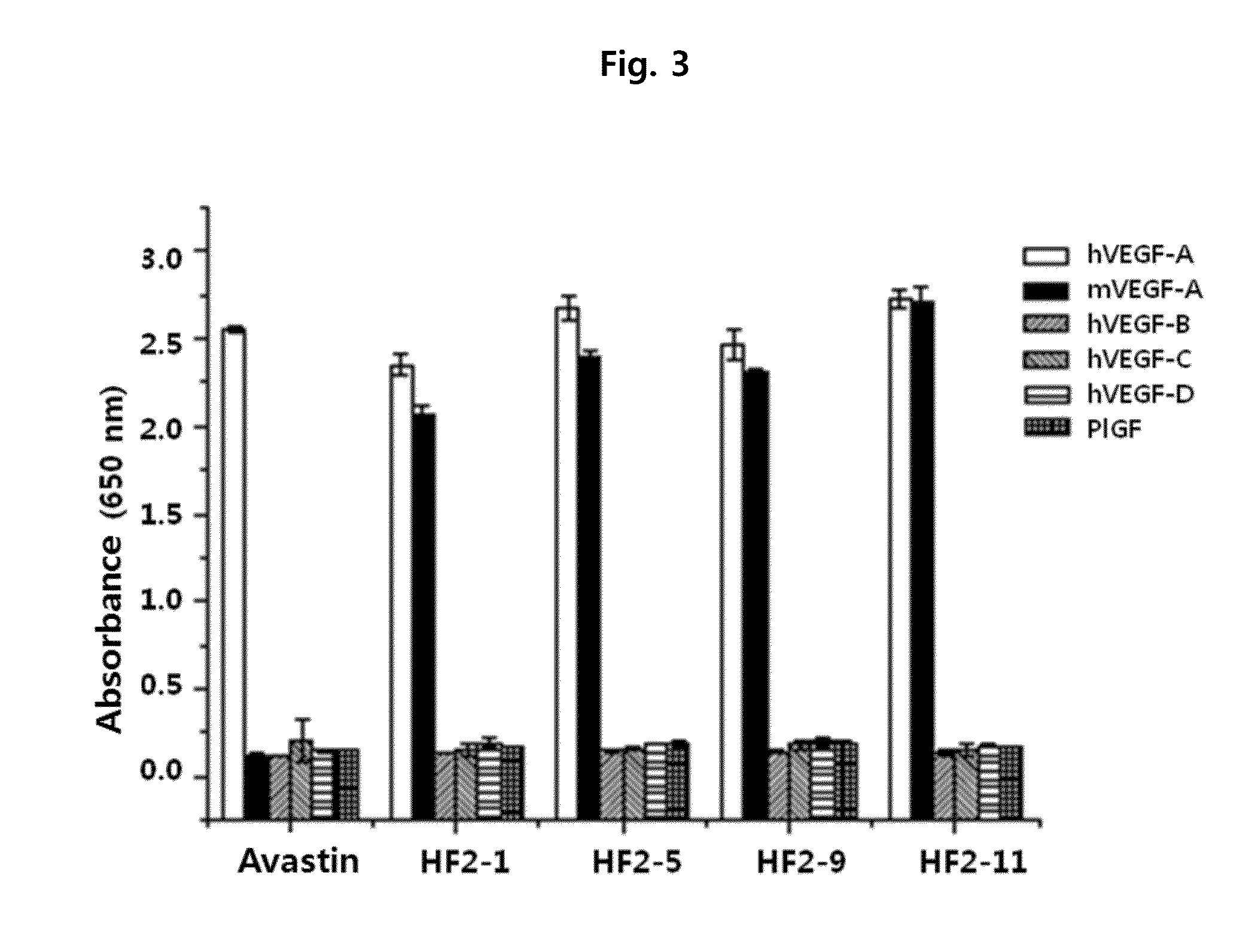
Anti-vegf antibody, and pharmaceutical composition for preventing, diagnosing or treating cancer or angiogenesis-related diseases, containing same
ActiveUS20160122426A1Remarkable binding propertySuppresses permeabilityAnimal cellsSenses disorderAnti vegf antibodyAngiogenesis growth factor
A novel anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) antibody having a strong binding affinity for VEGF and capable of inhibiting in vivo tumor growth and a composition for the treatment of cancer, containing the same. The antibody shows a remarkable binding property to human and mouse VEGF, suppresses the proliferation and permeability of a human umbilical vein endothelial cell (HUVEC) and inhibits tumor growth, and thus can be useful as an antibody for the treatment of cancer.
Owner:DONG A SOCIO HLDG CO LTD +1
Application of acetyl boswellic acid in preparing antitumor agent
InactiveCN1436533AIncrease or decrease contentOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsLymphatic SpreadBeta-boswellic acid
The present invention is the application of acetyl boswellic acid (BC-4) extracted from Boswellia carterii Birdw as antitumor medicine, a secondary application. It is found that BC-4 has the functions of resisting the proliferation of tumor cell, inducing malignant tumor cell to death, inhibiting the proliferation of human umbilical vein endothelial cell, inhibiting animal's grafted tumor, inhibiting metastasis of malignant tumor, etc. Both in vivo and vitro tests show that BC-4 has very low toxicity and is one excellent antitumor medicine and tumor metastasis inhibitor.
Owner:INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Method for differentiating and culturing mononuclear cells into mature dendritic cells
ActiveCN102443568AOptimizing the culture systemOvercoming complexityBlood/immune system cellsDendritic cellSecreting cell
The invention provides a method for differentiating and culturing CD 14<+> mononuclear cells into mature dendritic cells, which is characterized in that CD 14<+> cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells capable of secreting cell factors for promoting cell maturity and differentiation are simultaneously cultured, so the CD 14<+> cells become the mature dendritic cells. Compared with the traditional method, the method has the characteristics and advantages that the method is economic, the speed is high, and the mass culture can be realized.
Owner:FIELD OPERATION BLOOD TRANSFUSION INST OF PLA SCI ACAD OF MILITARY
Application of genipin in prevention or treatment of ischemic brain injury
The invention relates to application of genipin in prevention or treatment of ischemic brain injury. Brain injury is particularly related to injury of microglial cells or human umbilical vein endothelial cells. The invention further relates to a medicine composition containing genipin for preventing or treating ischemic brain injury.
Owner:INST OF CHINESE MATERIA MEDICA CHINA ACAD OF CHINESE MEDICAL SCI
Depolymerized holothurian glycosaminoglycan composition as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106349397AImproved degradation methodReasonable design of preparation processOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsSide effectOperability
The invention discloses a depolymerized holothurian glycosaminoglycan composition, as well as a preparation method and application of the depolymerized holothurian glycosaminoglycan composition. The depolymerized holothurian glycosaminoglycan composition is one or more of depolymerized holothurian glycosaminoglycan with the weight-average molecular weight between 2000Da and 12000Da, and the preparation method of the depolymerized holothurian glycosaminoglycan composition comprises extracting and purifying holothurian glycosaminoglycan, degrading the holothurian glycosaminoglycan and the like. Screened through a plurality of experiments, echinodermata holothurian is chosen as an object of study, and an extracting and purifying process of the holothurian glycosaminoglycan and a degrading process of the depolymerized holothurian glycosaminoglycan are chosen from a large quantity of experiments. The whole process is reasonable in design and strong in operability, and the industrial production is implemented. The anti-tumor study shows that the depolymerized holothurian glycosaminoglycan composition remarkably inhibits the generation of a lumen of a human umbilical vein endothelial cell in vitro, inhibits the transfer of melanin and a breast cancer in vivo, has an excellent anti-tumor effect, is expected to be developed into an efficient antitumor drug or healthcare product with low toxic or side effects, and has an important application prospect.
Owner:SUZHOU YI HUA BIOMEDICAL TECH CO LTD +1
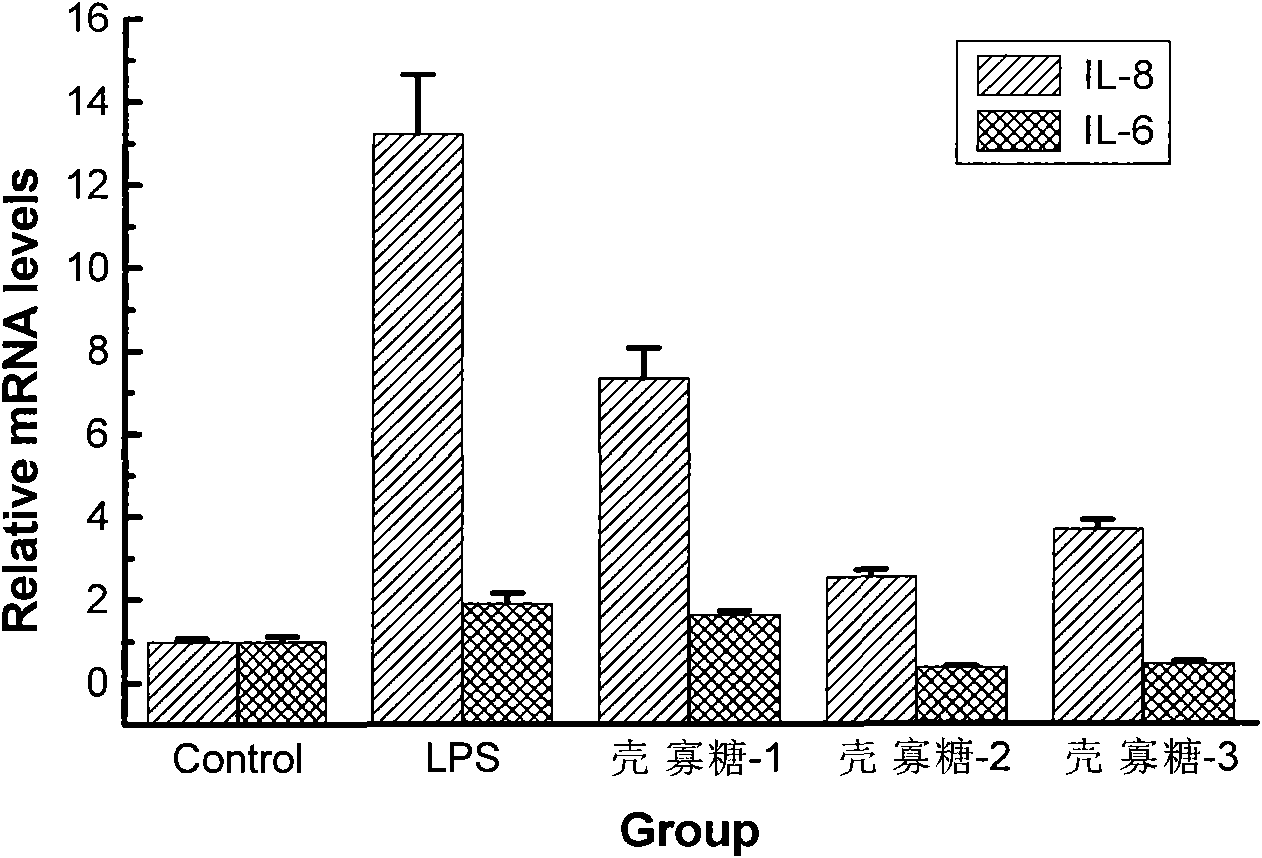
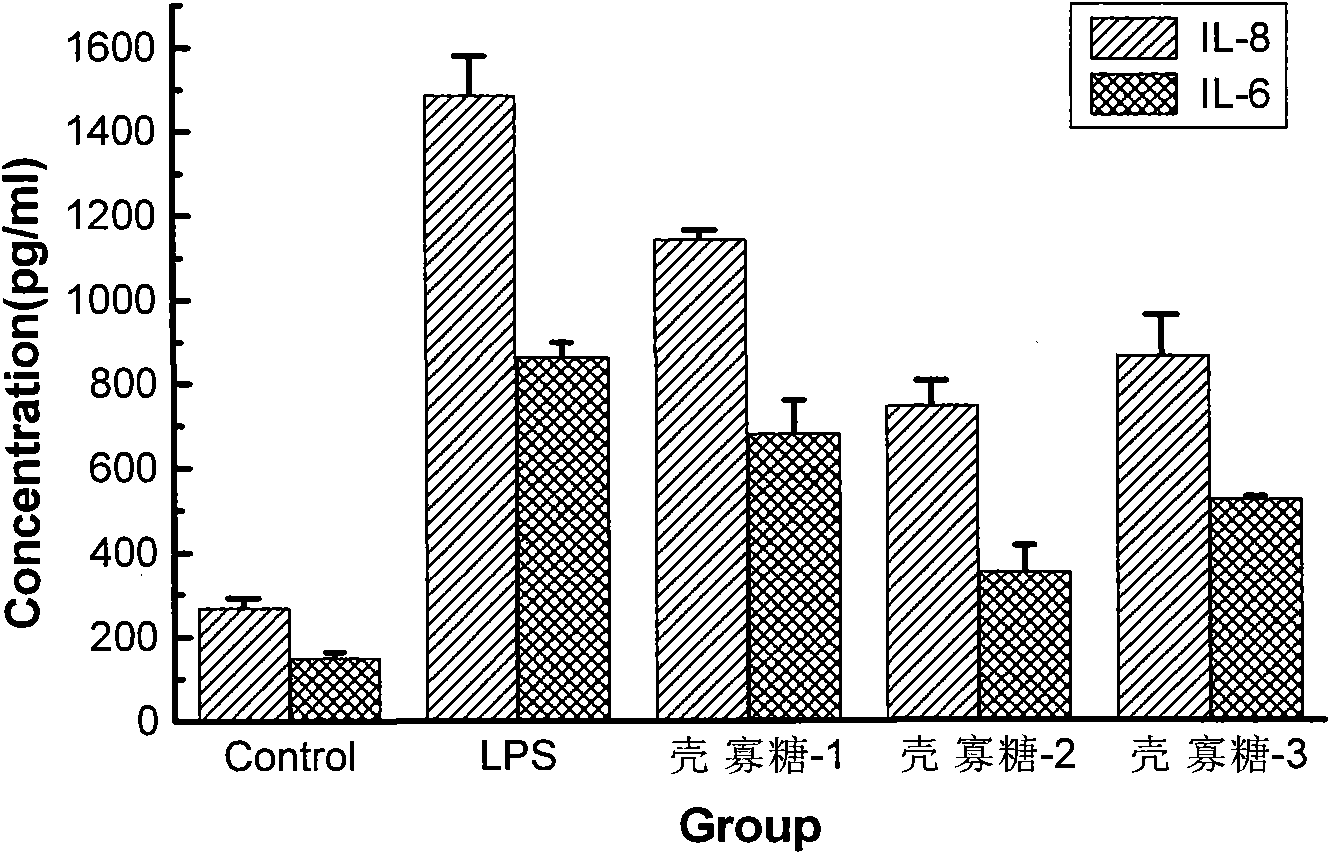
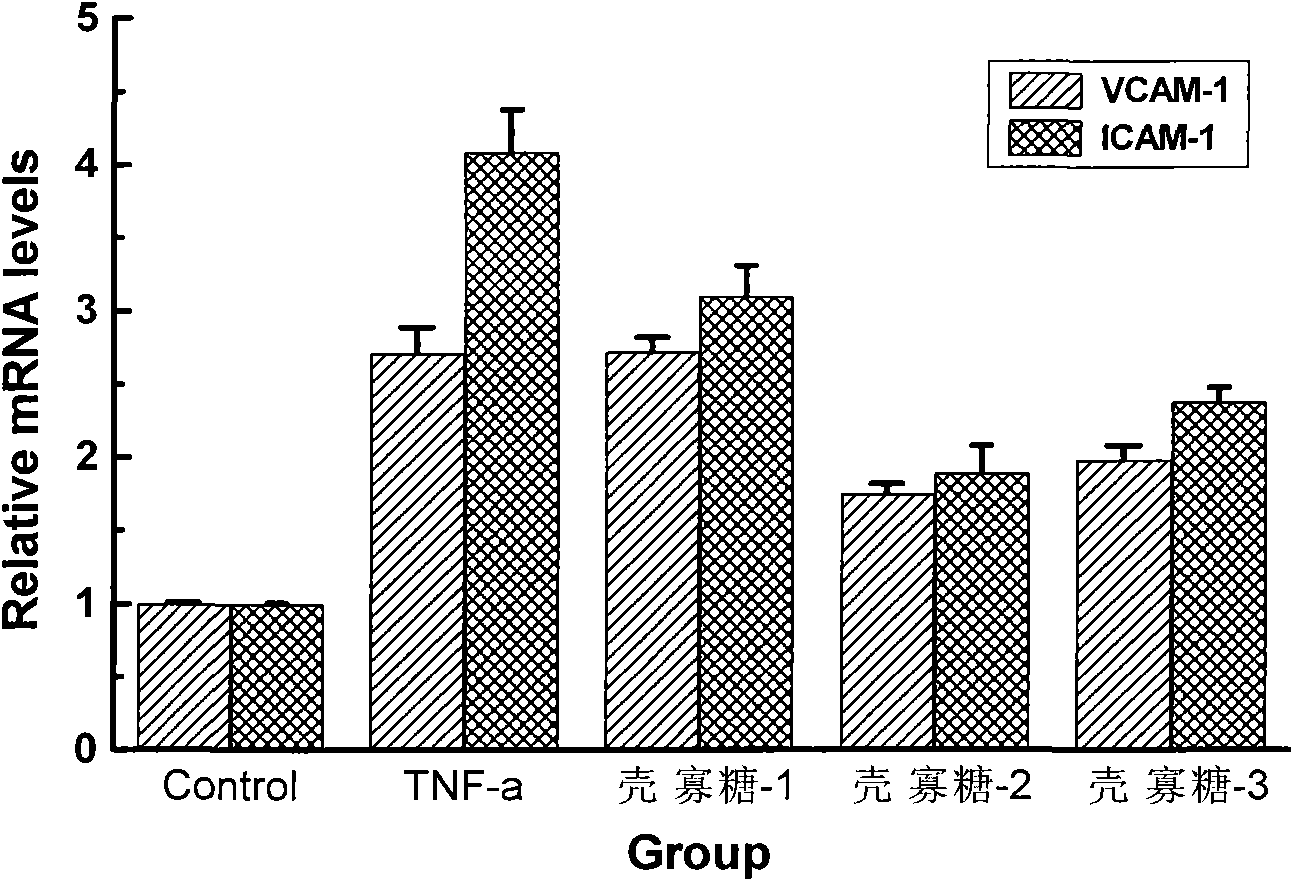
Application of oligochitosan in preparing medicine for preventing from formation of atherosclerosis
InactiveCN101849958APromote proliferationProtects against oxidative damageOrganic active ingredientsCardiovascular disorderVCAM-1Inflammatory factors
The invention relates to a medicine for curing atherosclerosis, in particular to application of oligochitosan in preparing a medicine for preventing from the formation of atherosclerosis. The application takes lipopolysaccharide (lipopolysaccharide) and humanized gene recombinant tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) as an induction factor, and takes human umbilical vein endothelial cell as a research object, thereby having the following results: (1) the oligochitosan can obviously restrain the expressions of IL-8, IL-6 and relevant inflammatory factors in the lipopolysaccharide-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cell; (2) the oligochitosan can obviously restrain the expressions of membrane surface molecules VCAM-1. ICAM-1 and relevant adhesion molecules family members of the TNF-alpha-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cell; and (3) the oligochitosan can obviously restrain the adhesion between the TNF-alpha-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cell and the human mononuclear cell.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
p66shc recombinant adenovirus vector as well as construction and application thereof
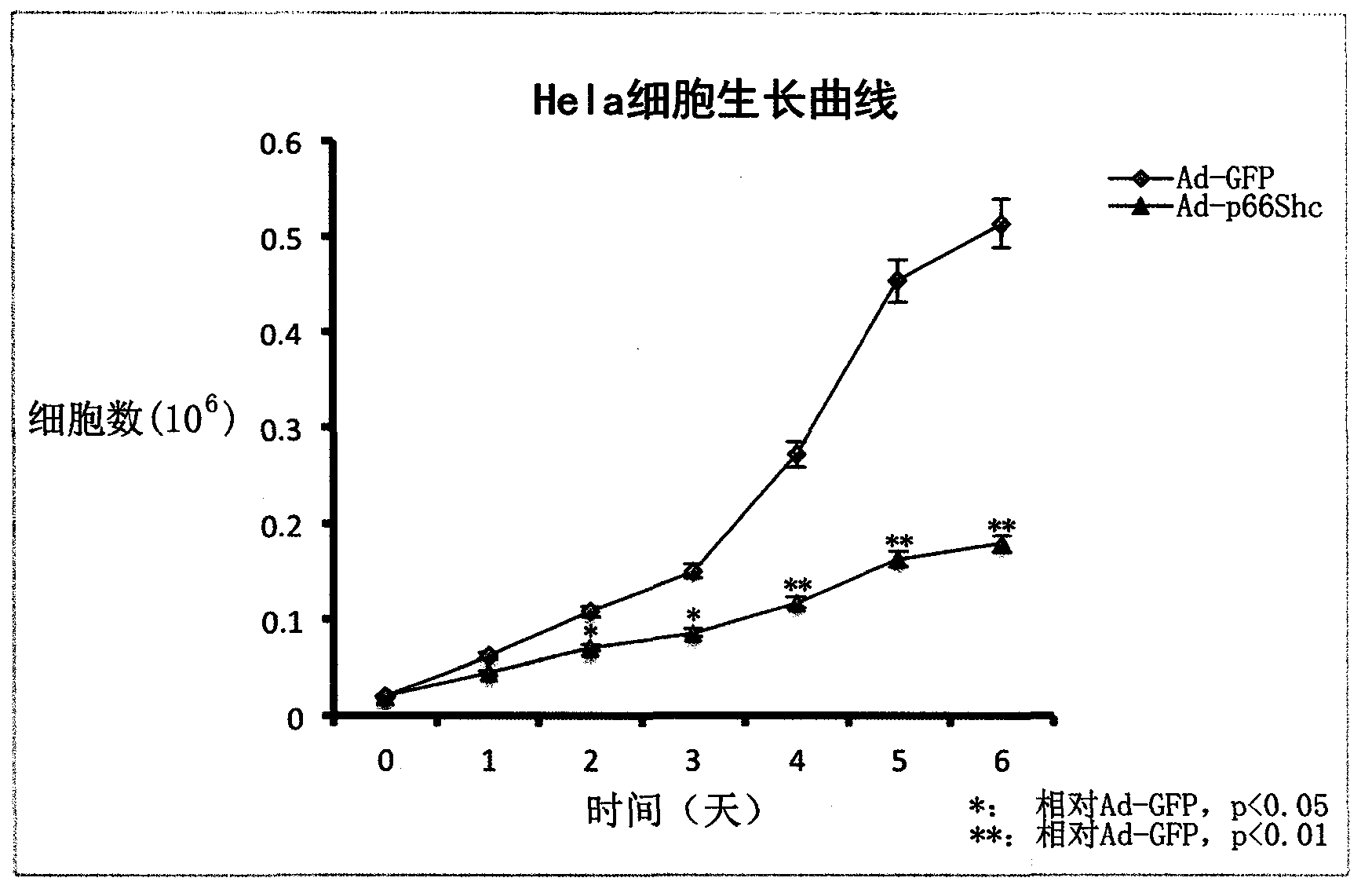
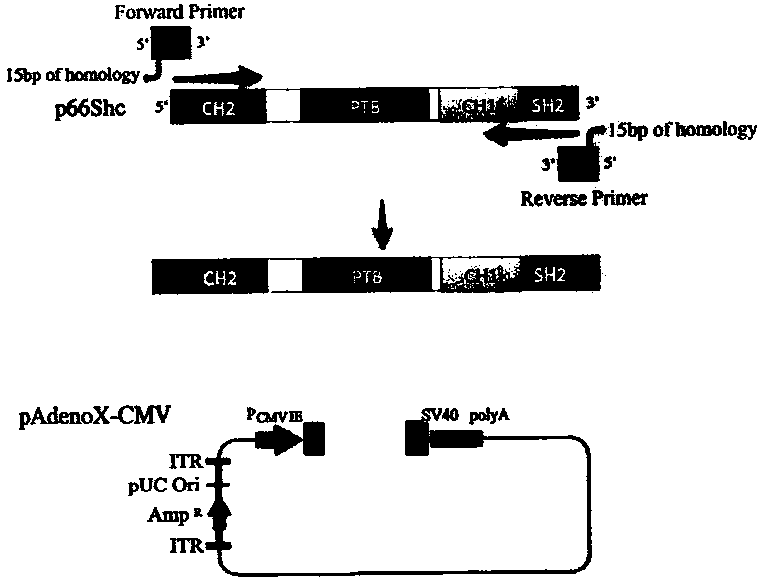
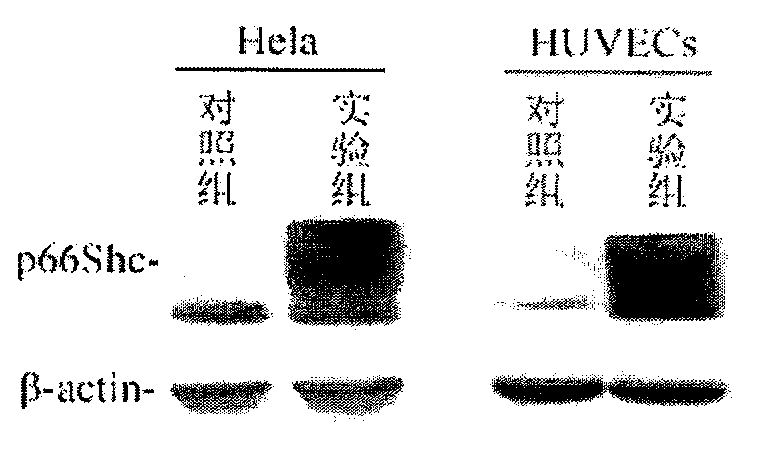
InactiveCN104073517AGrowth inhibitionGenetic material ingredientsFermentationHUVEC CellsGene engineering
The invention provides a p66Shc recombinant adenovirus vector. Homologous recombination in vitro of a human p66Shc fragment and a pAdeno X-CMV vector is realized by use of the gene engineering technology, and then competent bacteria are used for transformation to screen out correct recombinant adenoviruses; next, the recombinant adenoviruses are linearized and then used for transfecting HEK293A cells, and therefore, the recombinant adenoviruses are packaged and amplified largely in the HEK293A cells. After Hela cells are infected with the p66Shc recombinant adenovirus vectors, the growth and proliferation of the cells can be obviously inhibited; if human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) are in infected with the p66Shc recombinant adenovirus vectors, no obvious growth inhibition effect is caused. The p66Shc recombinant adenovirus vector is expected to achieve a special growth inhibition effect on tumor cells.
Owner:BEIJING HOSPITAL
Application of total triterpenes in preparing drugs inhibiting angiogenesis
InactiveCN102657660AGood inhibitory effectHas anti-angiogenic activityOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderDiseaseArthritis
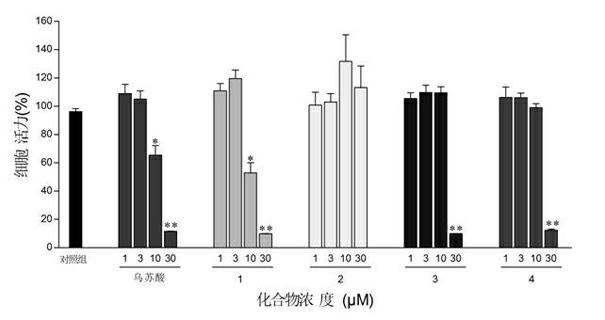
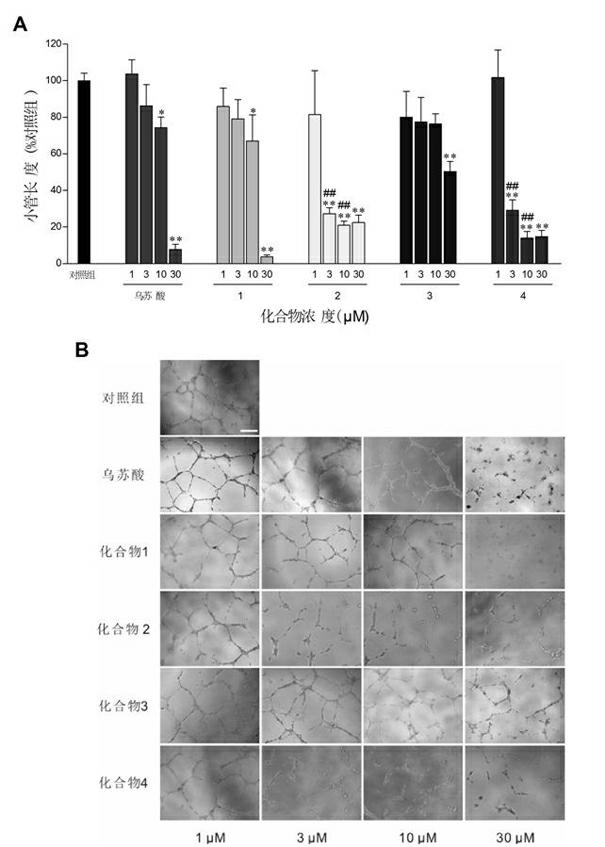
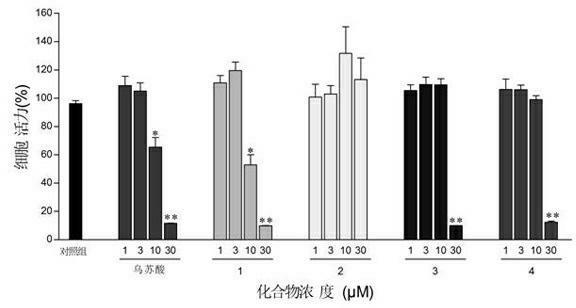
The invention relates to application of total triterpenes in preparing drugs inhibiting angiogenesis. The application has the advantages that novel application of the total triterpenes in extractive of Actinidia chinensis roots is provided. An experiment proves that the total triterpenes 1,2,3,4 have remarkable inhibiting effect on multiplication of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) and canaliculization of HUVEC, have anti-angiogenic activity, and can serve as angiogenesis inhibitors. By means of the application of the total triterpenes in preparing the drugs inhibiting the angiogenesis, the anti-angiogenesis effect of the total triterpenes in the extractive of Actinidia chinensis roots is firstly found out, and the total triterpenes can serve as the angiogenesis inhibitors to be applied to treat new blood vessel dependence and new vessel related diseases including tumors, arthritis, skin and eye diseases, atherosclerosis and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Heparin oligosaccharide and application thereof in preparation of anti-angiogenesis drugs
InactiveCN110845641APrevent proliferationInhibit migrationAntineoplastic agentsImmunoprecipitationOligosaccharide
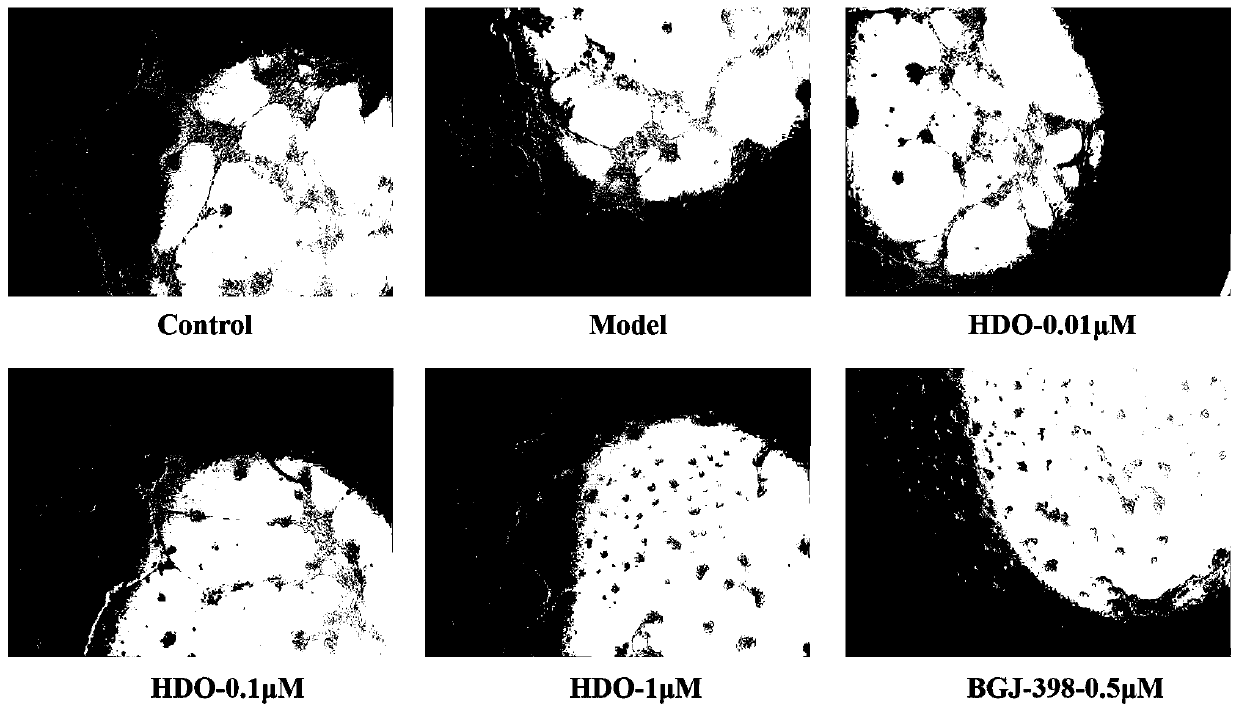
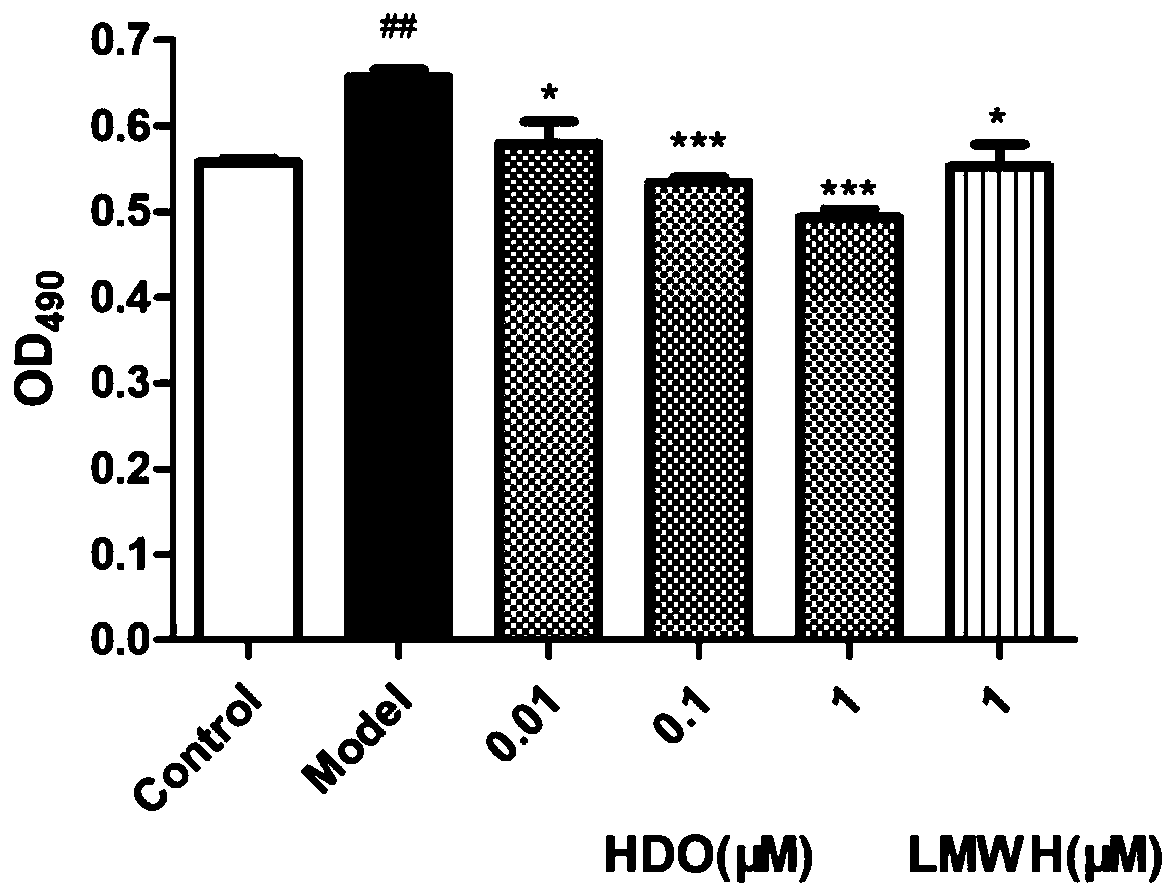
The invention discloses heparin oligosaccharide and application thereof in preparation of anti-angiogenesis drugs, belonging to the field of biomedicine. According to the invention, the basic fibroblast growth factor bFGF is adopted to stimulate human umbilical vein endothelial cells to establish a cell abnormality model; the influence and mechanism of heparin oligosaccharide on in-vitro angiogenesis of endothelial cells are studied through in-vitro angiogenesis, co-immunoprecipitation and other experiments, and results show that the heparin oligosaccharide destroys vascular formation of vascular endothelial cells and inhibits proliferation and migration of cells, and the heparin oligosaccharide with a concentration of 1 [mu]M has the best effect; meanwhile, the heparin oligosaccharide significantly reduces the mRNA and protein expression level of the cell surface receptor FGFR2, and inhibits the combination of bFGF and FGFR2, which indicates that FGFR2 is one of the important targetsof the anti-angiogenesis of the heparin oligosaccharide. The research can provide a new way for treating tumor growth and metastasis caused by abnormal generation of new vessels.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
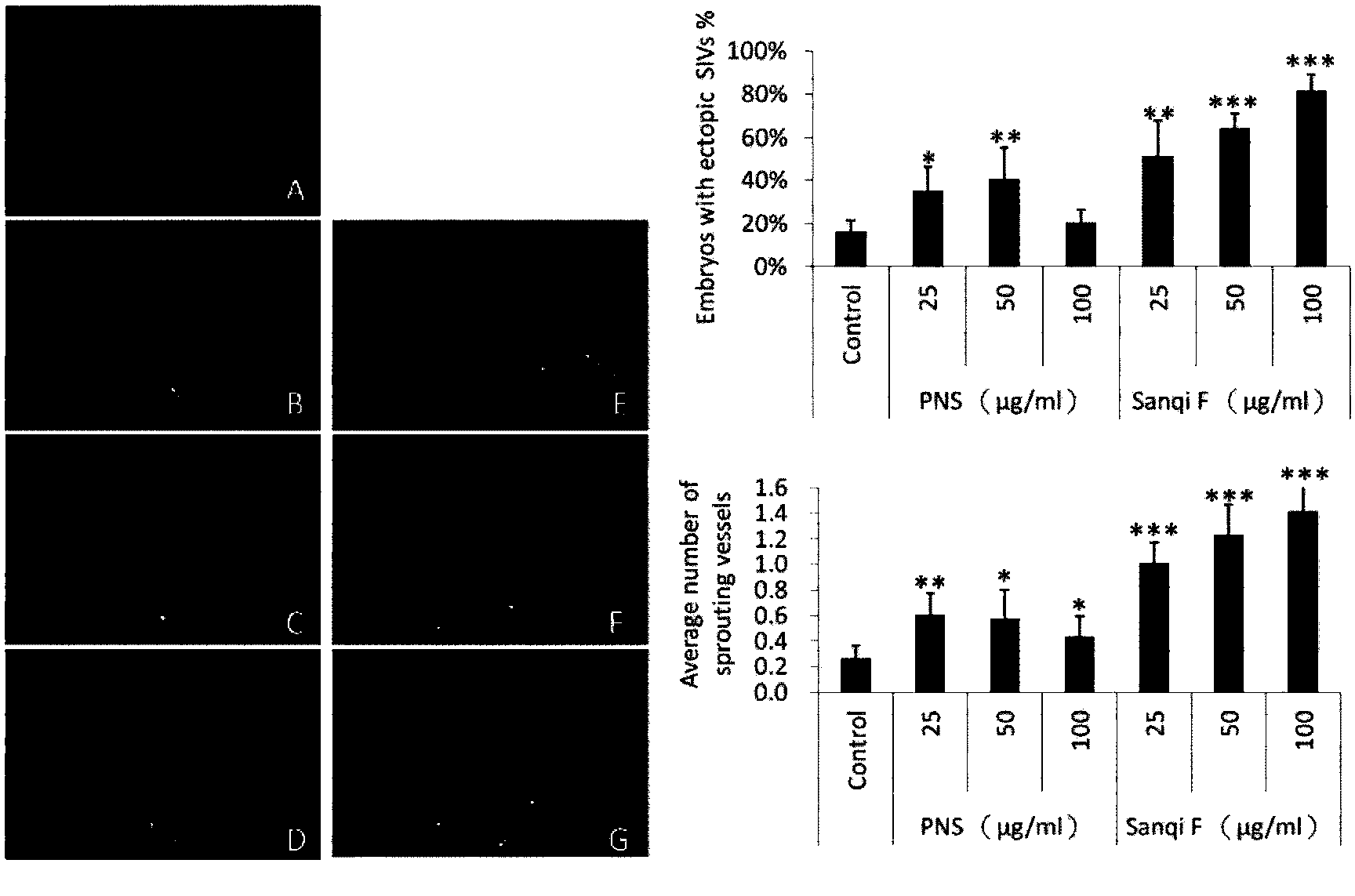
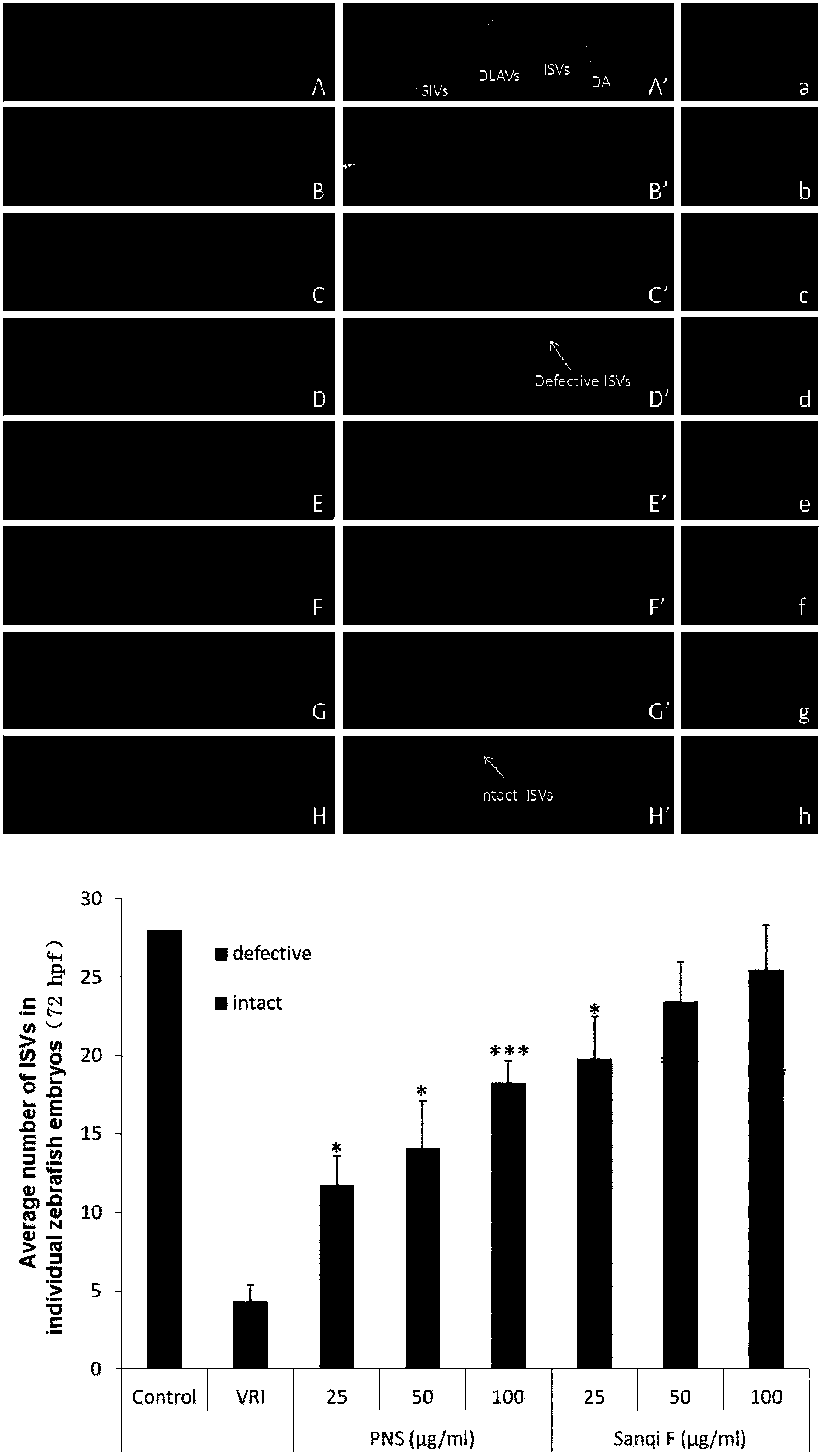
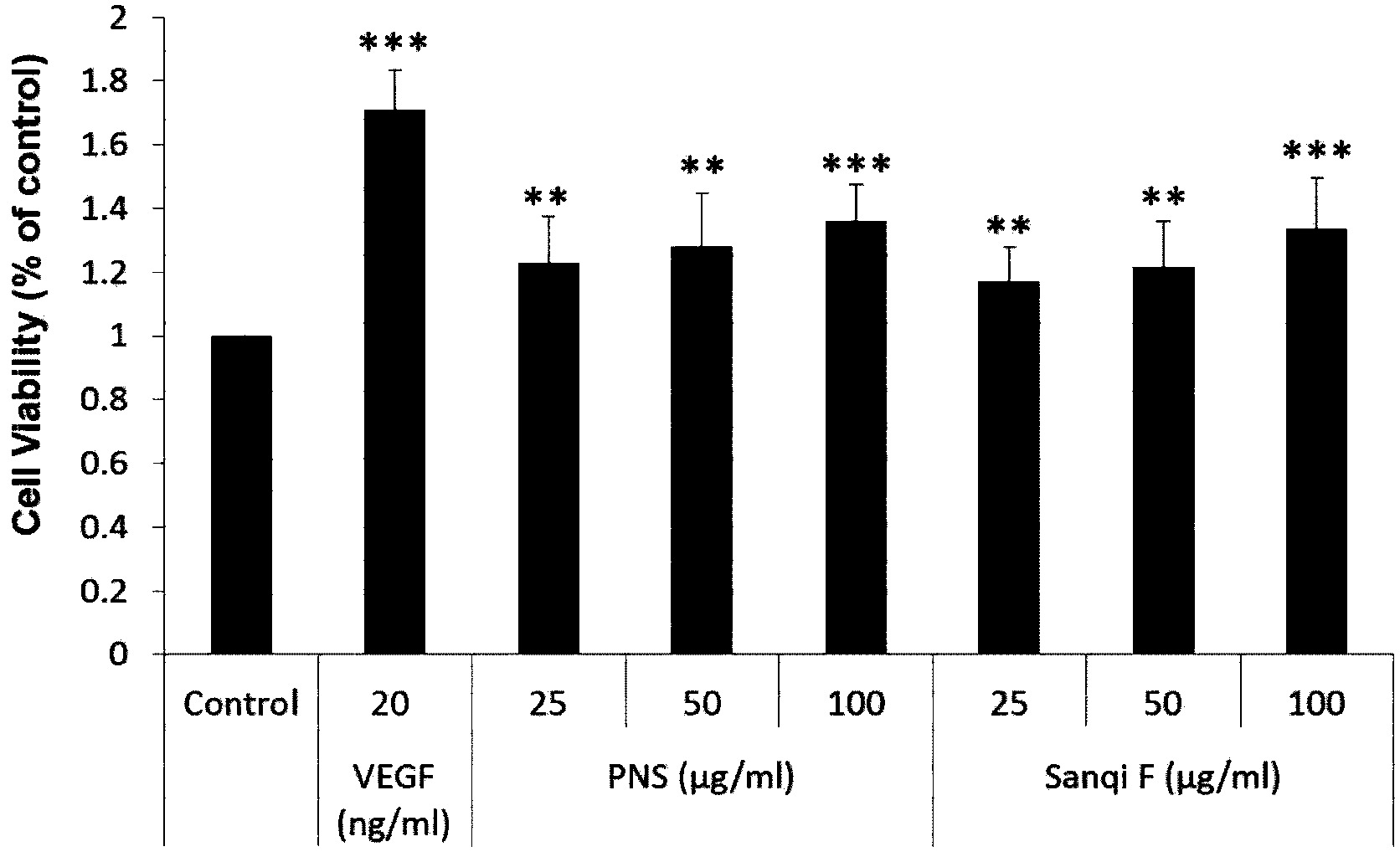
Application of panax notoginseng flos saponin in preparing medicine for promoting angiogenesis
The invention belongs to the field of preparing traditional Chinese medicines, and relates to application of panax notoginseng flos saponin, as an active part extracted from Chinese herbal notoginseng flos, in preparing a medicine for promoting angiogenesis. Experimental results show that the panax notoginseng flos saponin disclosed by the invention has a protective effect on VRI induced vascular injury in an early stage and has a recovery effect of promoting angiogenesis in a later vascular development process; the panax notoginseng flos saponin has a proliferation function on human umbilical vein endothelial cells; moreover, the panax notoginseng flos saponin is more significant in effects of promoting angiogenesis and protecting blood vessel compared with panax notoginseng (root) saponin. The panax notoginseng flos saponin disclosed by the invention can serve as a raw material to further prepare a pharmaceutical preparation for promoting angiogenesis, and the pharmaceutical preparation is used for preventing and treating such diseases related to angiogenesis deficiency as coronary heart disease, myocardial ischemia, insufficient construction of collateral circulation complementarity, slow trauma and fracture healing and thronboangitis obliterans.
Owner:LONGHUA HOSPITAL SHANGHAI UNIV OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
Medicinal fatheadtree branchlet or bark new compound with function of promoting endothelial injury repair, preparation method of compound and application of compound
ActiveCN110256430APromote repairImprove repair effectOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistrySolventEthyl acetate
The invention discloses a medicinal fatheadtree branchlet or bark alkaloid new compound with the function of promoting endothelial injury repair. The compound is prepared by a method including the steps: crushing medicinal fatheadtree branchlet or bark stems, adding water, performing soaking and extracting, collecting extraction liquid and performing vacuum concentration to obtain medicinal fatheadtree branchlet or bark extracts; extracting the extracts to obtain a dichloromethane portion and an ethyl acetate portion; feeding the ethyl acetate portion to a silica gel column; performing elution by taking dichloromethane-methanol with the volume ratio of 95:(5-10):90 as an elution solvent; combining similar portions by TLC (thin-layer chromatography) analysis; feeding a preparative liquid phase, taking methanol water as an eluent and performing liquid chromatography preparation to obtain the medicinal fatheadtree branchlet or bark new compound. Based on a cell repair related mechanism, under theoretical guidance, the proliferative activity of the medicinal fatheadtree branchlet or bark new compound is intensively studied, and experimental study indicates that the medicinal fatheadtree branchlet or bark new compound can obviously promote proliferation of HUVEC (human umbilical vein endothelial cell) cells and endothelial cell scratch repair and can be used for preparing a drug for controlling inflammatory endothelial injury.
Owner:HAINAN SENQI PHARMA CO LTD
Application of tanshinol derivatives in preparation of drug for preventing cardiovascular-related diseases
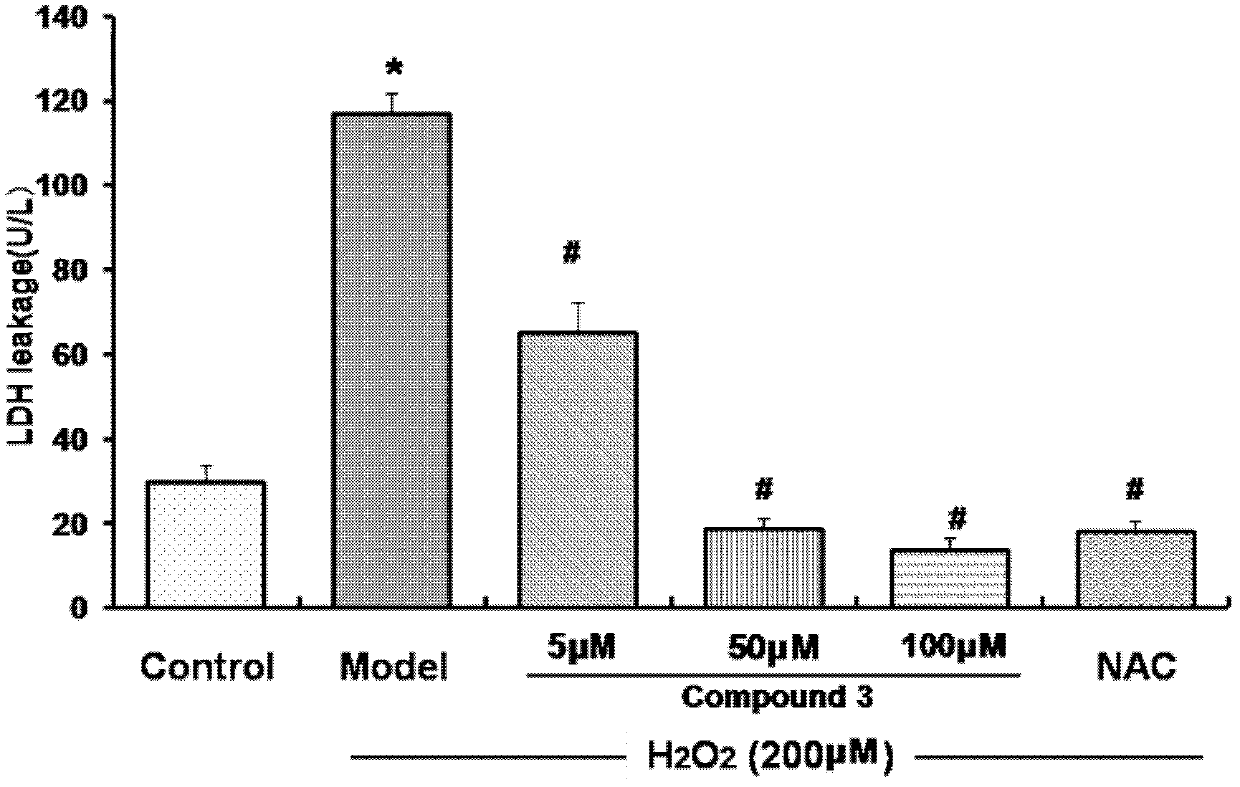
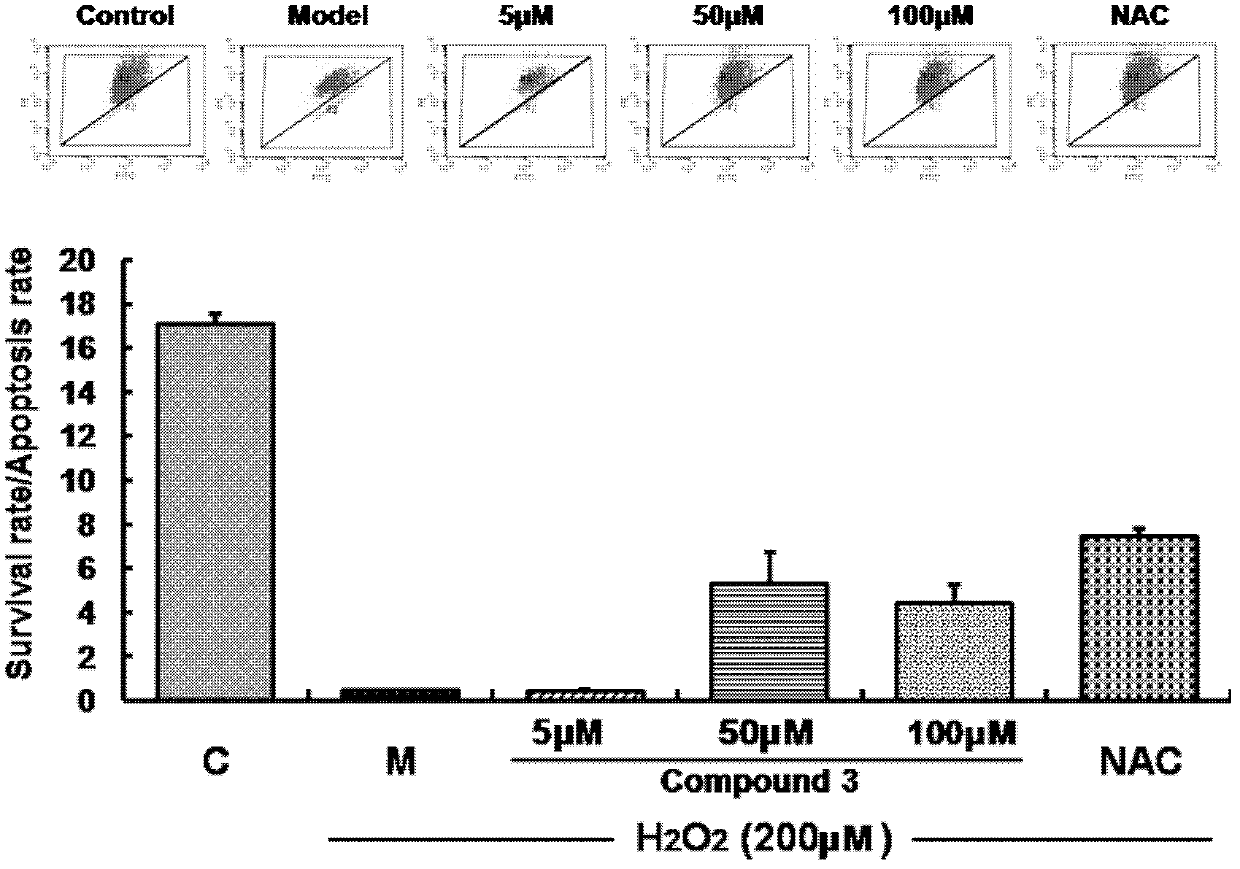
The invention belongs to the field of Chinese medicine production and relates to application of tanshinol derivatives in Chinese herbal medicine salvia in preparation of a pharmaceutical composition for preventing cardiovascular-related diseases. According to the in-vitro oxidation stress model experiment research, the result shows that the tanshinol derivatives can be used for preventing the cardiovascular-related diseases by protecting endothelial cells of a circulatory system. More specifically, the tanshinol derivatives can be used for achieving the effect of protecting endothelial cells by restraining transcriptional level of the cardiovascular-related diseases, restraining protein expression level of the cardiovascular-related diseases, restraining the production of reactive oxygen species and restraining the corresponding signal transduction pathway and transcription factor. According to the experimental result, the tanshinol derivatives have an obvious inbibitional effect on apoptosis of HUVEC (Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells) induced by H2O2 and have an obvious protection effect on cells damaged by oxidative stress, and can be used for further preparing a drug for preventing cardiovascular-related diseases.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Exogenous hydrogen sulfide donor, and preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN106928208ARelease stabilityPrecise control of contentOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryHuman umbilical vein endothelial cellTherapeutic action
The invention provides an exogenous hydrogen sulfide donor, and discloses a therapeutic action of an anethol trithione derivative used as the exogenous hydrogen sulfide donor on cardiovascular diseases. The exogenous hydrogen sulfide donor can release hydrogen sulfide, can promote the growth of an HUVEC (human umbilical vein endothelial cell) atherosclerosis cell model, has an antiatherosclerotic effect, and hopefully becomes a new target drug researched and developed by drugs with antiatherosclerotic effects.
Owner:川北医学院
Multi-wall carbon nanotube injected with NH<2+> ions and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102626527AHigh nitrogen contentGood biocompatibilitySurgeryVacuum evaporation coatingCarbon nanotubeMouse Lung
The invention relates to a multi-wall carbon nanotube injected with NH<2+> ions. NH<2+> ions are injected onto a sprayed carbon nanotube by using an ion injection method, wherein the dosage of the injected NH<2+> ions is 5*1,014-1*1,016 ions / cm<2>; and the energy of a NH<2+> ion beam is 40keV. The hydrophilicity of the multi-wall carbon nanotube injected with NH<2+> ions further disclosed by the invention is increased remarkably. As proved by an adhesion experiment of a mouse lung fibroblast and a human umbilical vein endothelial cell on the material, the cell compatibility of the multi-wall carbon nanotube can be enhanced through NH<2+> ion injection. As proved by a series of blood experiment results, the multi-wall carbon nanotube injected with NH<2+> ions has high blood compatibility, so that the material has high research and application values and wide application prospect in the fields of tissue scaffolds and the like.
Owner:TIANJIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com