Micro-fluidic chip for constructing brain function unit model and construction method
A technology of microfluidic chips and construction methods, applied in artificial cell constructs, biochemical equipment and methods, microorganisms, etc., to achieve the effects of strong versatility, weak in vitro proliferation ability, and easy regulation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Using an assembled and integrated microfluidic device, the in vitro neural-vascular unit is constructed to simulate the functional unit of the brain.
[0036] Design and preparation of functionalized microfluidic chips that mimic brain functional units:
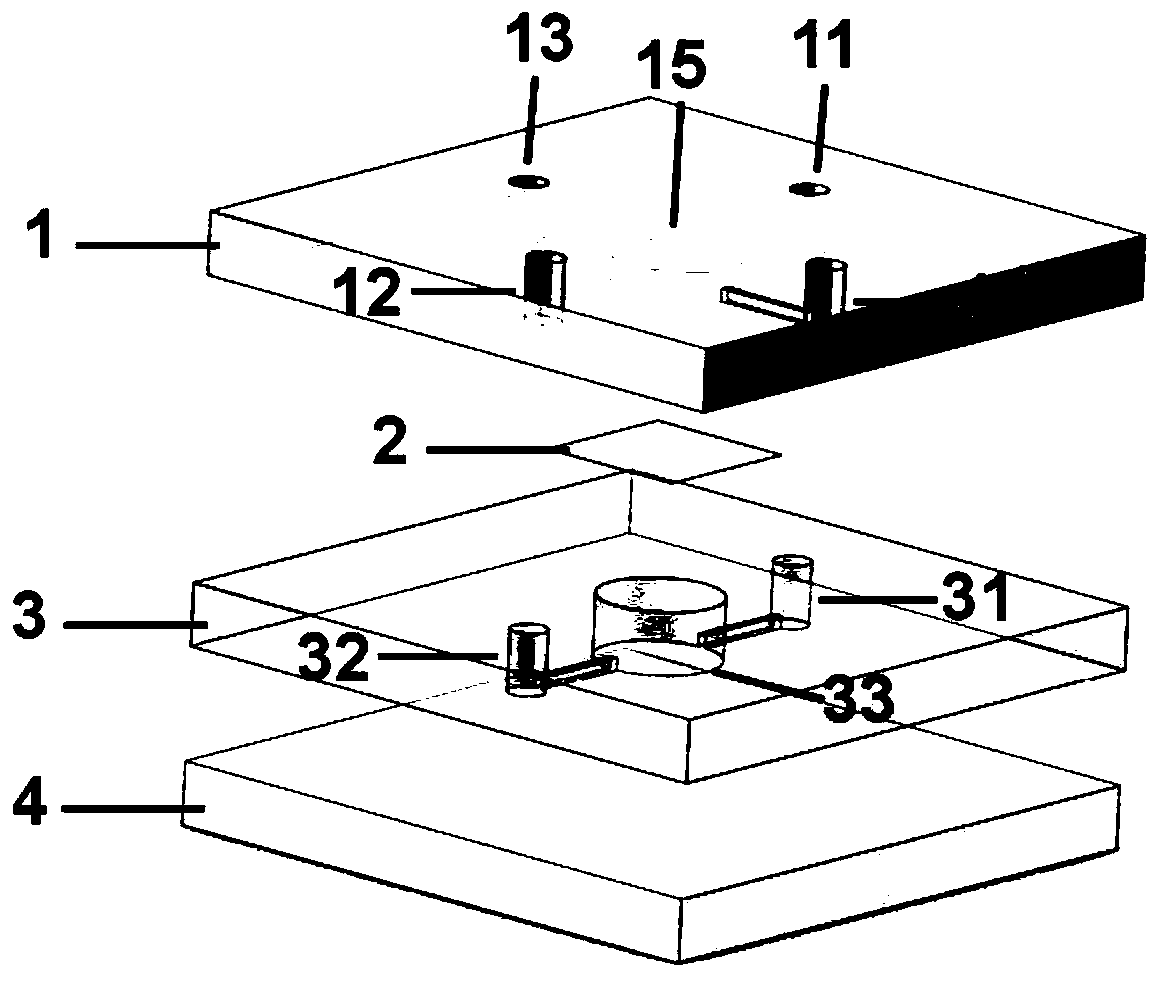
[0037] 1) Devices for functionalized microfluidic chips for simulating brain functional units, such as figure 1 , 2 shown. The whole device is composed of the first elastic layer 1 , the middle layer 2 , the second elastic layer 3 and the substrate 4 sequentially from the upper layer to the bottom layer. The first elastic layer 1 and the second elastic layer 3 are respectively PDMS layers, the intermediate layer 2 is a polycarbonate film, and the substrate 4 is a glass substrate.
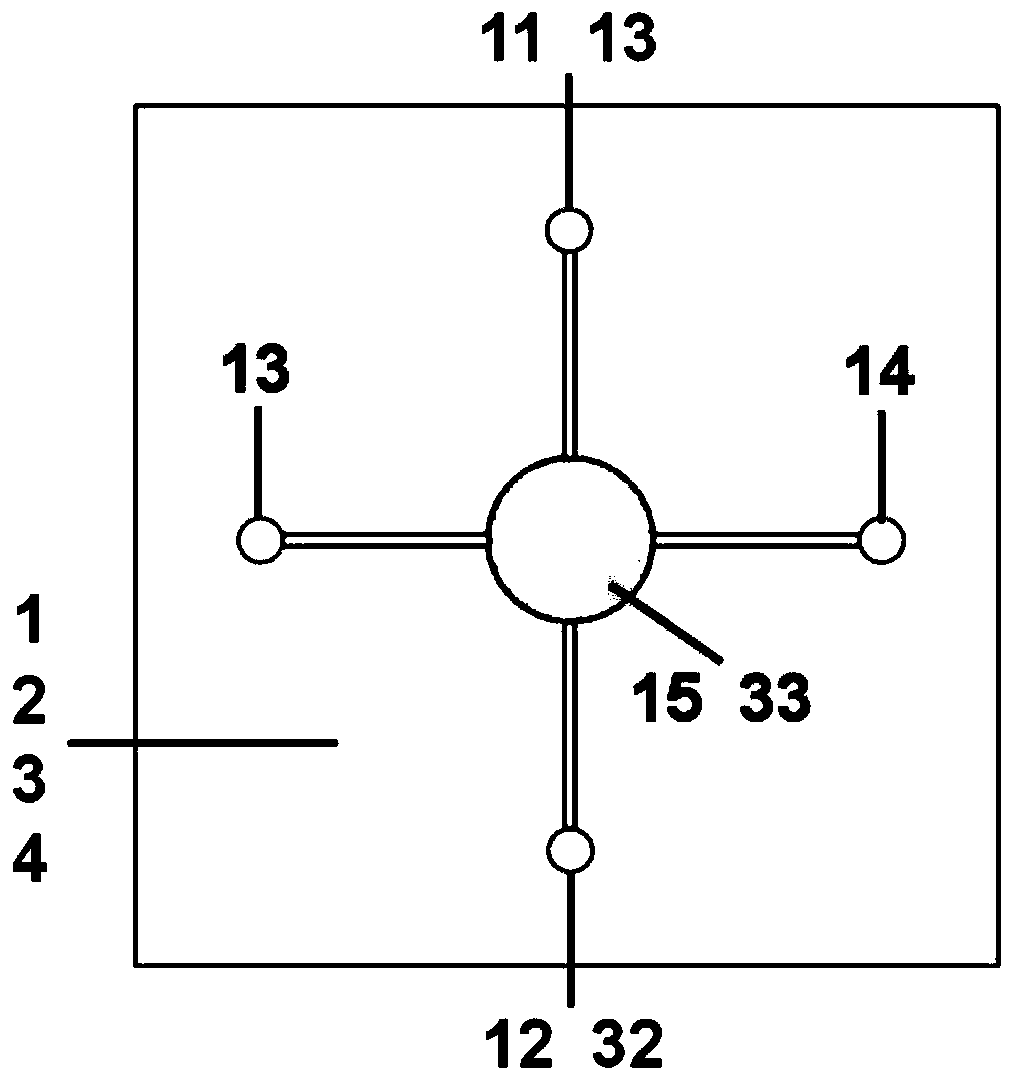
[0038] Wherein, the first elastic layer 1 is provided with a first liquid inlet 11, a first liquid outlet 12, a second liquid inlet 13, a second liquid outlet 14 and a first culture chamber 15 through it, the The first culture chamber 15...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Using microfluidic chips to construct models of brain functional units:
[0048] (1) Culture and identification of human brain microvascular endothelial cells and neural stem cells:
[0049] 1) Culture and identification of brain microvascular endothelial cells.
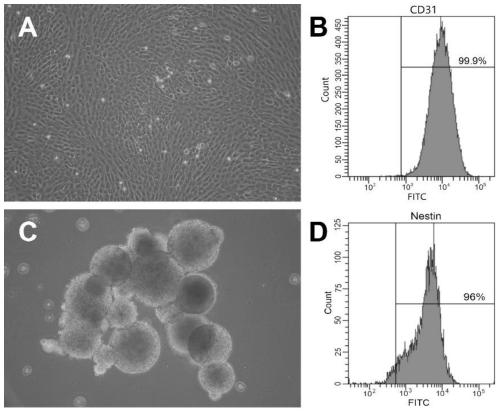
[0050] Human brain microvascular endothelial cells were cultured in DMEM medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum, and grown as a single layer adherently. After 90% of the cells were confluent, they were trypsinized and passaged. For phenotype identification, adherent cells were digested with trypsin to form a single-cell suspension, washed with PBS, then added with FITC-labeled CD31 antibody, and incubated in the dark. After washing with PBS, the cells were detected by flow cytometry. Cerebral microvascular endothelial cells image 3 As shown in A, the quantitative characterization by flow cytometry is as follows image 3 As shown in B, the positive rate of CD31 reached 99.9%.
[0051] 2) Primary extract...
Embodiment 3
[0060] Identification of the survival of each cell component in the brain functional unit model prepared in Example 2:
[0061] 1) Identification of microvascular endothelial cell activity in the brain functional unit model.
[0062] After 7 days of perfusion culture, the two PDMS layers were disassembled, and the polycarbonate membrane attached to the microvascular endothelial cells was carefully taken out and placed in a small dish. After washing with PBS, Calcein and PI dyes were added, and incubated in the dark. The dye was discarded and detected under a confocal fluorescence microscope after adding PBS. The sample was scanned in 20 slices, and the scanned images of 5 slices at equal intervals were taken, and the number of Calcein-expressing cells and PI-expressing cells were counted, and the percentage of living cells was calculated. The morphology of brain microvascular endothelial cells on the polycarbonate membrane is as follows: Figure 4 As shown in A, the survival...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com