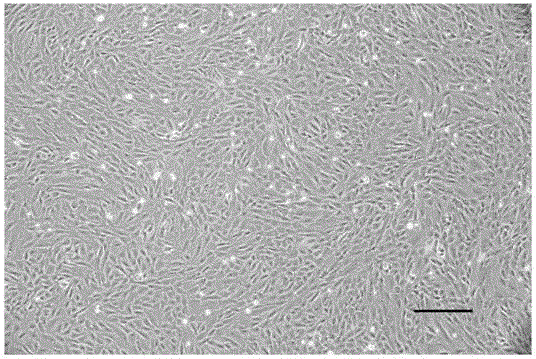
Method for separating and purifying mouse lung microvascular endothelial cell
An endothelial cell, separation and purification technology is applied in the field of separation and extraction of high-purity microvascular endothelial cells, which can solve the problems of difficult purification by manual operation, inability to determine the deblocking time, and difficulty in avoiding the pollution of pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0017] 1. Main experimental materials.
[0018] (1) Experimental animals: 7-day-old SD rats.
[0019] (2) Hank's solution: purchased from GIBCO Company, product number 14170-112.
[0020] (3) 0.01 M PBS: Take 8.0 g of NaCl, Na 2 HPO 4 2.9 g, KH 2 PO 4 0.2 g and 0.2 g KCl, dissolved in 1000 mL ultrapure water, sterilized by 0.22 μm filter, and stored in a refrigerator at 4°C.
[0021] (4) Digestive solution: prepared with 0.01 M PBS, containing 0.2% collagenase (purchased from Worthington, Cat. No. LS004176) and 0.1% neutral protease (purchased from Sigma, Cat. No. D4693-1G), sterilized by filtration with a 0.22 μm sterile filter.
[0022] (5) Complete medium: DMEM basal medium (purchased from GIBCO, product number 11960-044), containing 20% fetal bovine serum (purchased from GIBCO, product number 10099-141), 2 mM L-glutamine (purchased from GIBCO Company, product number 25030-081), 1% double antibody solution (100 IU / ml penicillin and 100 μg / ml streptomycin, purc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com