Patents
Literature
49 results about "Residual risk" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
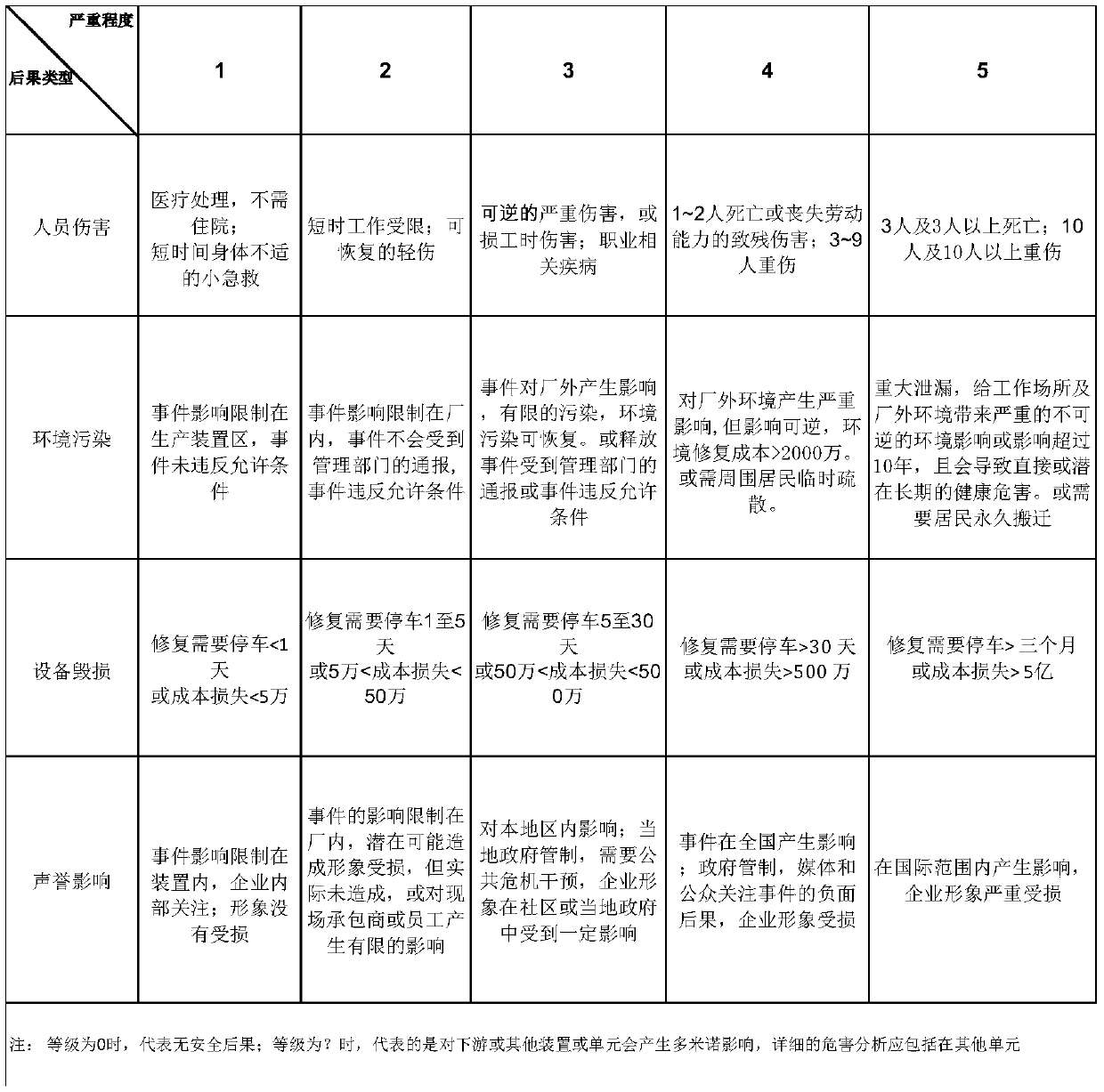
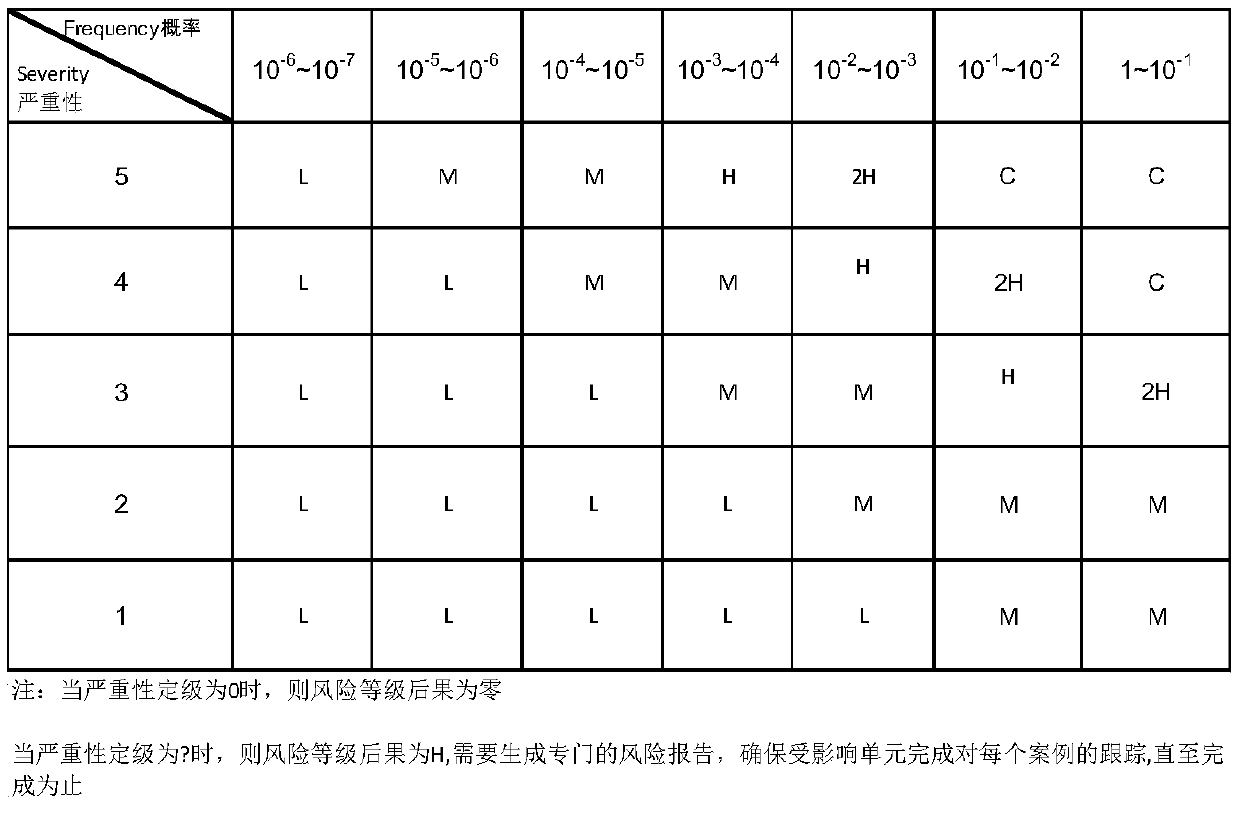
The residual risk is the amount of risk or danger associated with an action or event remaining after natural or inherent risks have been reduced by risk controls. The general formula to calculate residual risk is residual risk=(inherent risk)-(impact of risk controls) where the general concept of risk is (threats × vulnerability) or, alternatively, (severity × probability). An example of residual risk is given by the use of automotive seat-belts.
System and method for assessing compliance risk
InactiveUS20090319420A1Improve risk assessmentAugment mitigation processFinanceEngineeringBusiness activities
Institutional risk is calculated by collecting information about the products and services offered by an institution and assigning a risk value to each product and service. Other aspects and components of an institution are also assigned risk values. The various risk values are calculated along with institutional controls that are in place to mitigate risk in order to determine an overall residual risk assessment for the entity. Forecasts can be made for an institution by adding new or subtracting current business activities and / or institutional controls and calculating an alternative overall residual risk assessment.
Owner:COMPLIANCE COACH
Threat Modeling and Risk Forecasting Model
InactiveUS20090030751A1Reduce the impactReduce determined residual riskFinanceForecastingComputer scienceResidual risk
A system and method for determining residual business risks by correlating threats, controls, business continuity factors, and other general risk considerations is described. Requirements of an initiative of a project are mapped to a taxonomy, and the mapped requirements are rated with respect to its importance to the project. Projected changes in the mapped requirements are forecasted over a specified period of time, such as an eighteen month period. A threat to the project is mapped to the taxonomy, and the mapped threat is rated with respect to its impact on the project. Projected changes in the effectiveness of the control are forecasted based upon historical data, a maturity rating, and the rated effectiveness of the control. Residual risk associated with the project is then determined, and adjustments to one or more resources associated with the project may be made to reduce the determined residual risk.
Owner:BANK OF AMERICA CORP
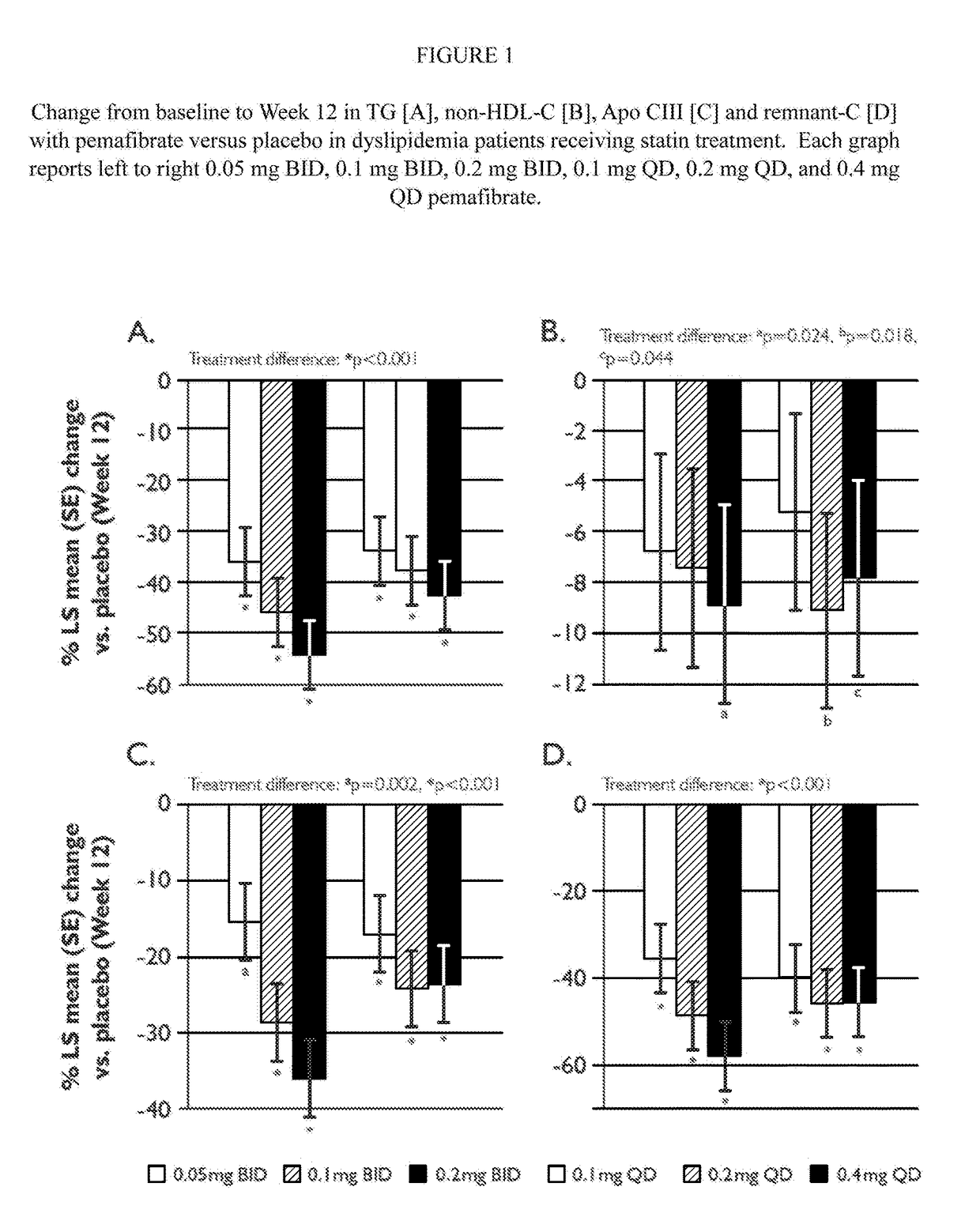
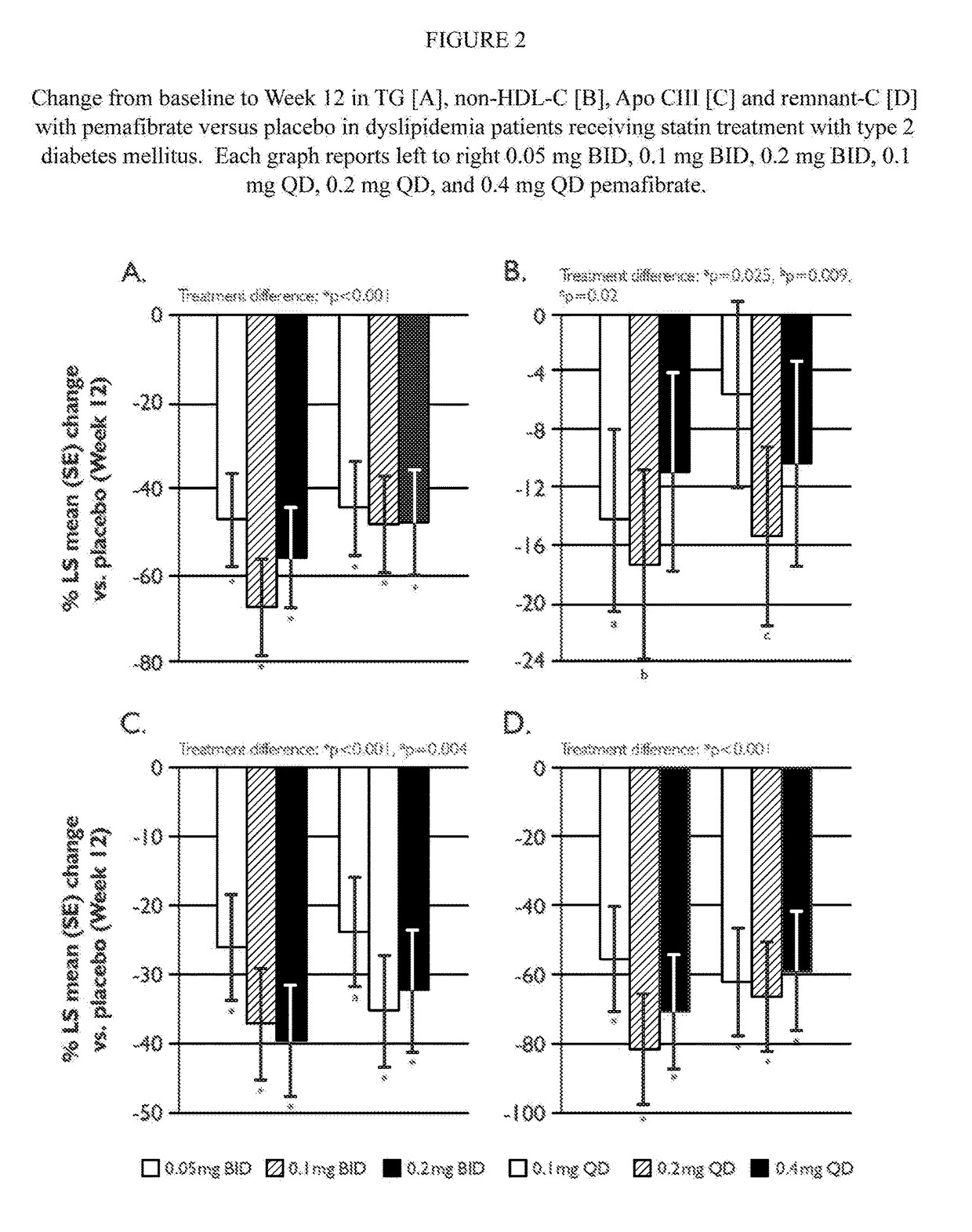
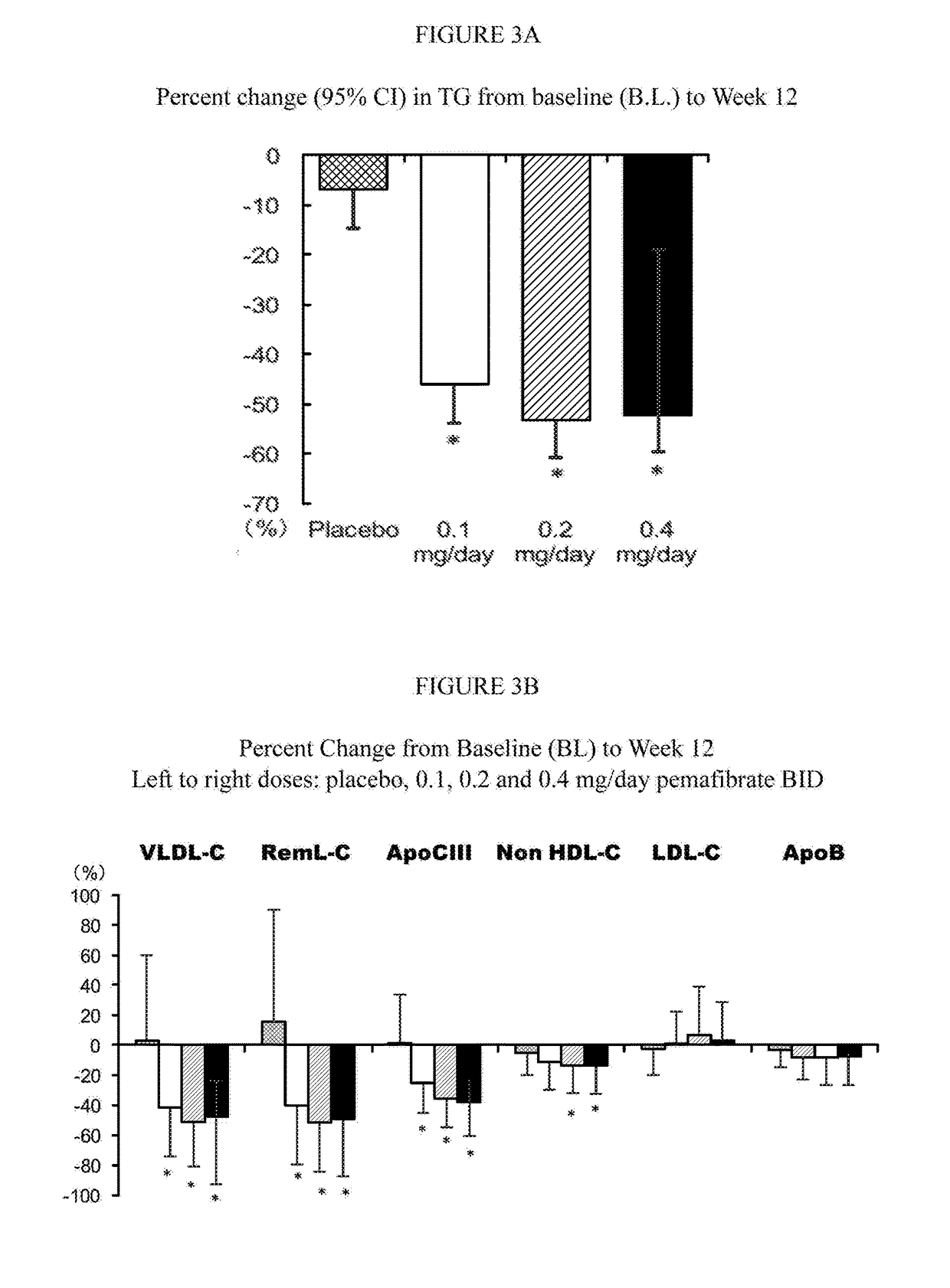
Methods of Preventing Cardiovascular Events in Residual Risk Dyslipidemic Populations
ActiveUS20180028505A1Reduce cardiovascular riskReduce riskMetabolism disorderPharmaceutical delivery mechanismDyslipidemiaPharmacological interventions
The present invention provides pharmacological interventions for the treatment of dyslipidemia, and to the reduction of residual risk of cardiovascular disease and adverse cardiovascular events in patients on intense statin use or with well-controlled LDL-C concentrations. In particular, the invention relates to the use of pemafibrate to prevent cardiovascular events in populations at-risk due to risk factors such as type 2 diabetes mellitus with dyslipidemia in spite of intense statin use or well-controlled LDL-C.
Owner:KOWA CO LTD
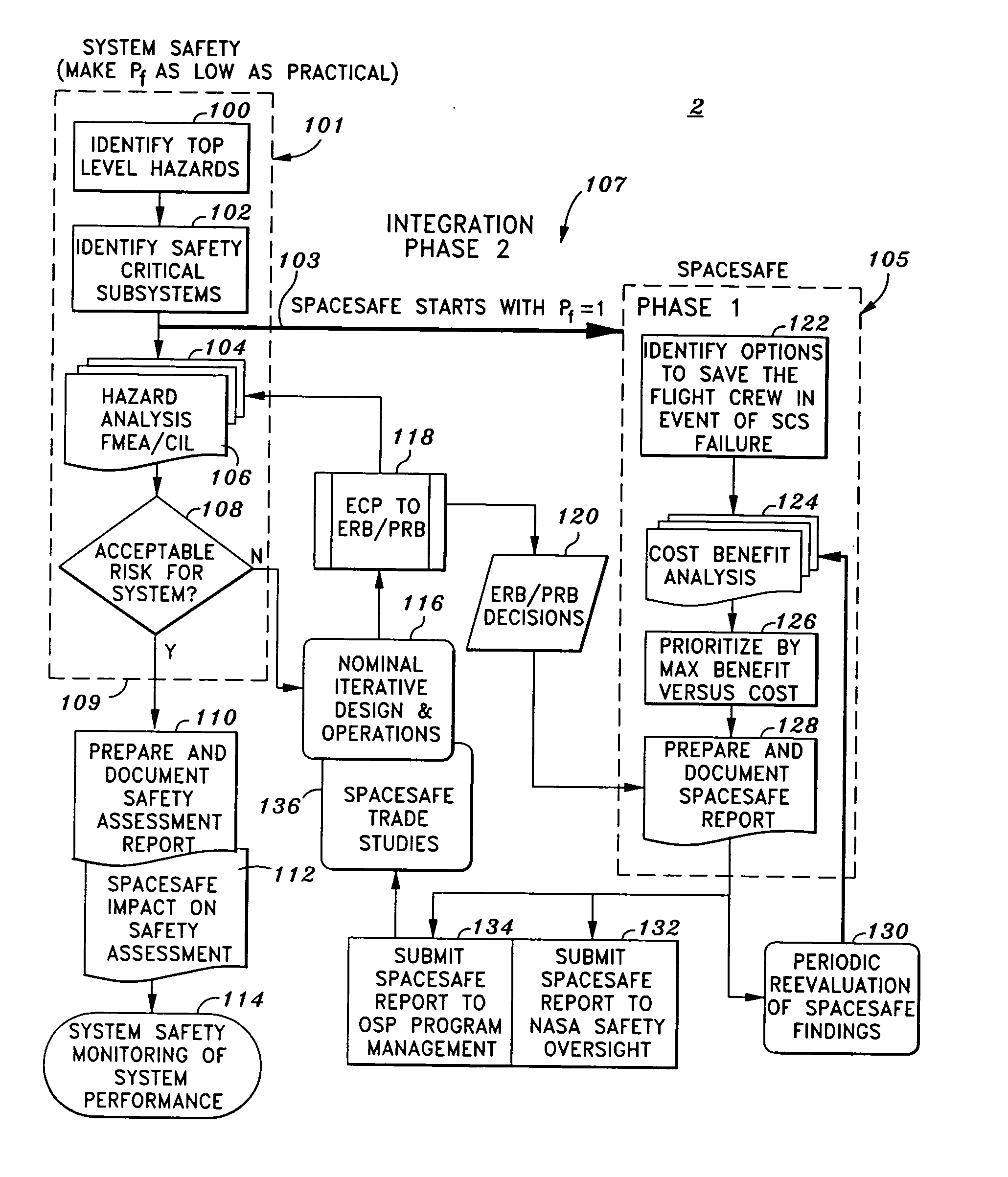
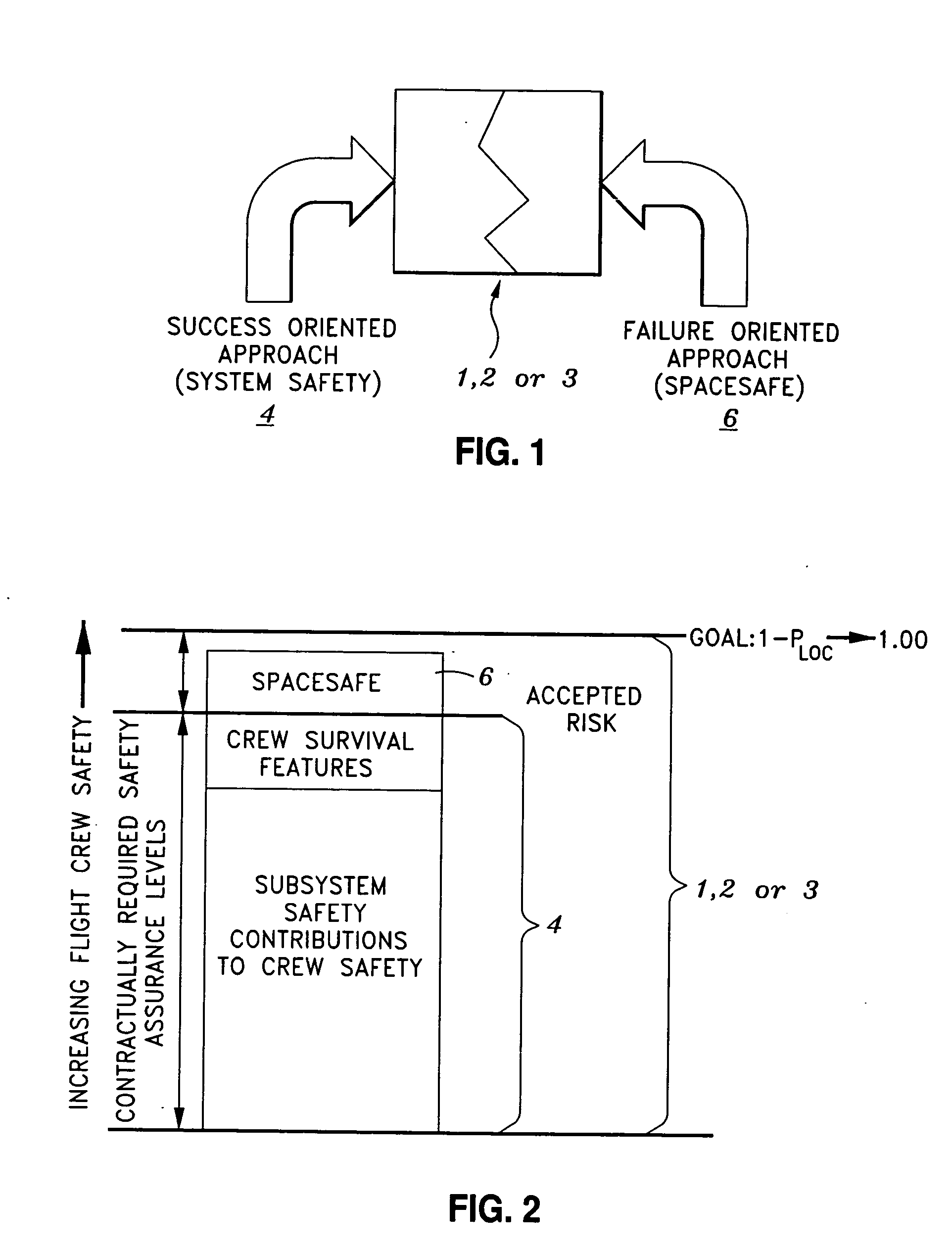
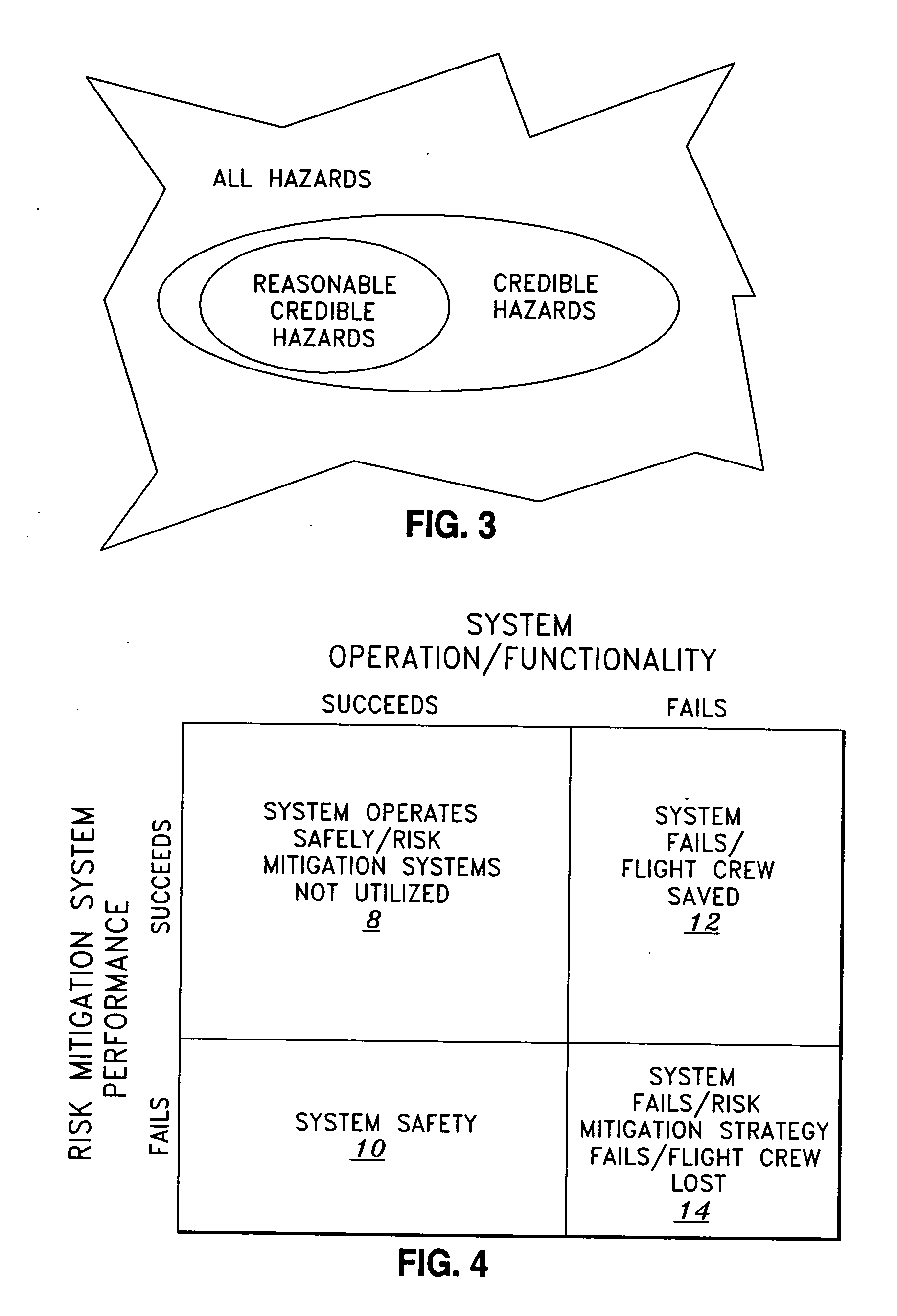
Method of evaluation of space systems for safety assurance and residual risk to flightcrew
InactiveUS20050256682A1Improve survival rateSignificant comprehensive benefitsNuclear monitoringDigital computer detailsEngineeringSafety assurance
A process for evaluating space systems for safety assurance and residual risk to the flight crew. The process includes a success oriented System Safety phase which attempts to reduce the probability of failure with respect to the loss of a crew member as low as practical; a failure oriented SPACESAFE phase which assumes that at least one Safety Critical Subsystem has failed and attempts to engineer a risk mitigation design minimize adverse effects on the crew; and an Integration phase which complimentary integrates the System Safety phase with the SPACESAFE phase. Such process allows for increased flight crew safety by minimizing risk of a failures that contribute to loss of a crew member.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMAN CORP
Industrial control system standard compliance evaluation system
InactiveCN107067179AReasonable designImprove the protective effectResourcesData switching networksTechnical standardUnit system
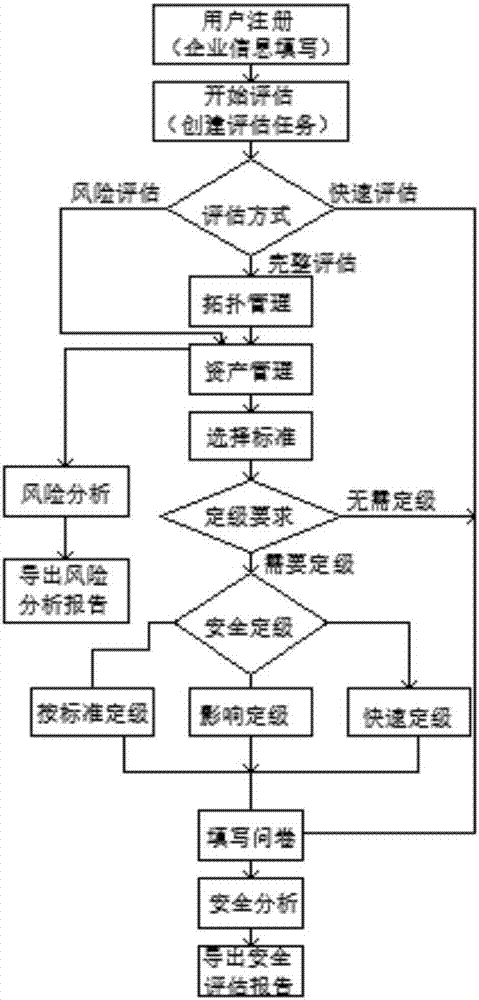
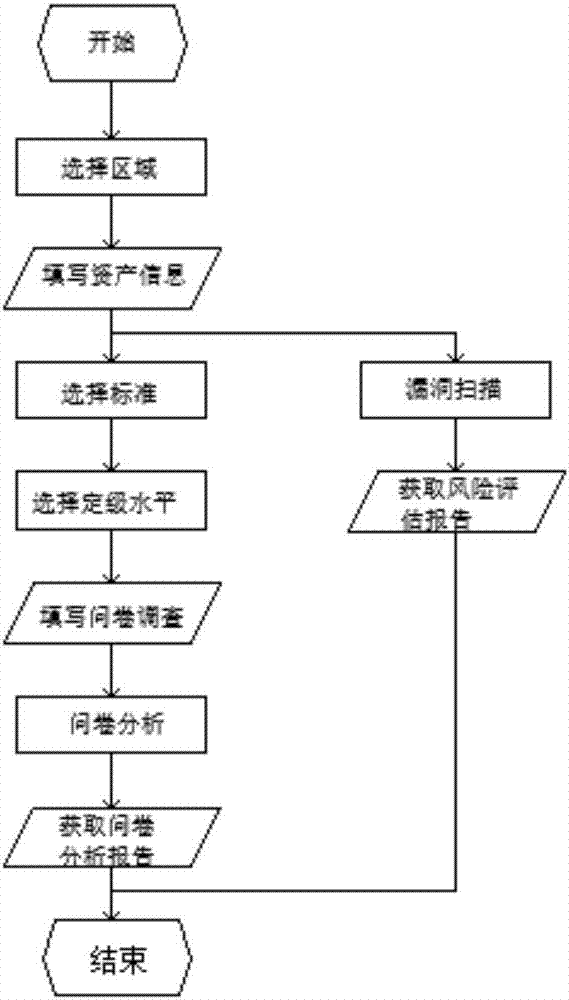
The invention discloses an industrial control system standard compliance evaluation system, which includes an evaluation module, a topology generation module, an asset management module and a report management module. The beneficial effect of the present invention is: carry out the conformity evaluation of relevant standards to the industrial control system, fully consider the particularity of the industrial control system and the safety requirements of different levels, carefully sort out the assets of the industrial control system system of the unit, and consider the environmental and human factors Analyze the threats faced by the industrial control system, analyze the vulnerability of the industrial control system from the aspects of technology and management, combine the existing security measures, analyze the existing risks of the industrial control system, balance the benefits and costs, formulate a risk treatment plan, and integrate the industrial The residual risk of the control system is controlled at an acceptable level, and the information security strategy is adjusted according to the evaluation results to help industrial enterprises improve their information security protection capabilities.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONICS STANDARDIZATION INST +1
Residual risk analysis system, method and computer program product therefor
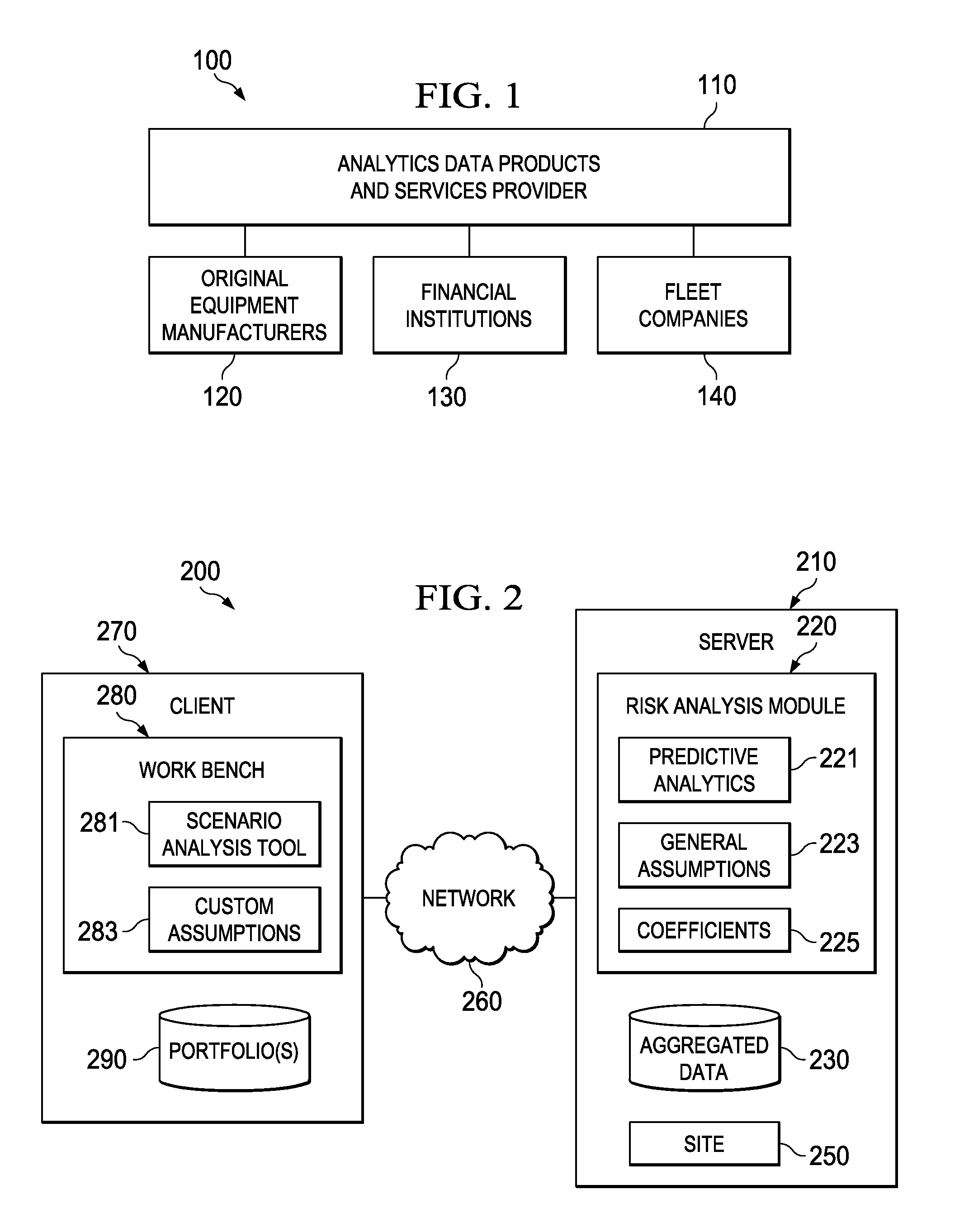
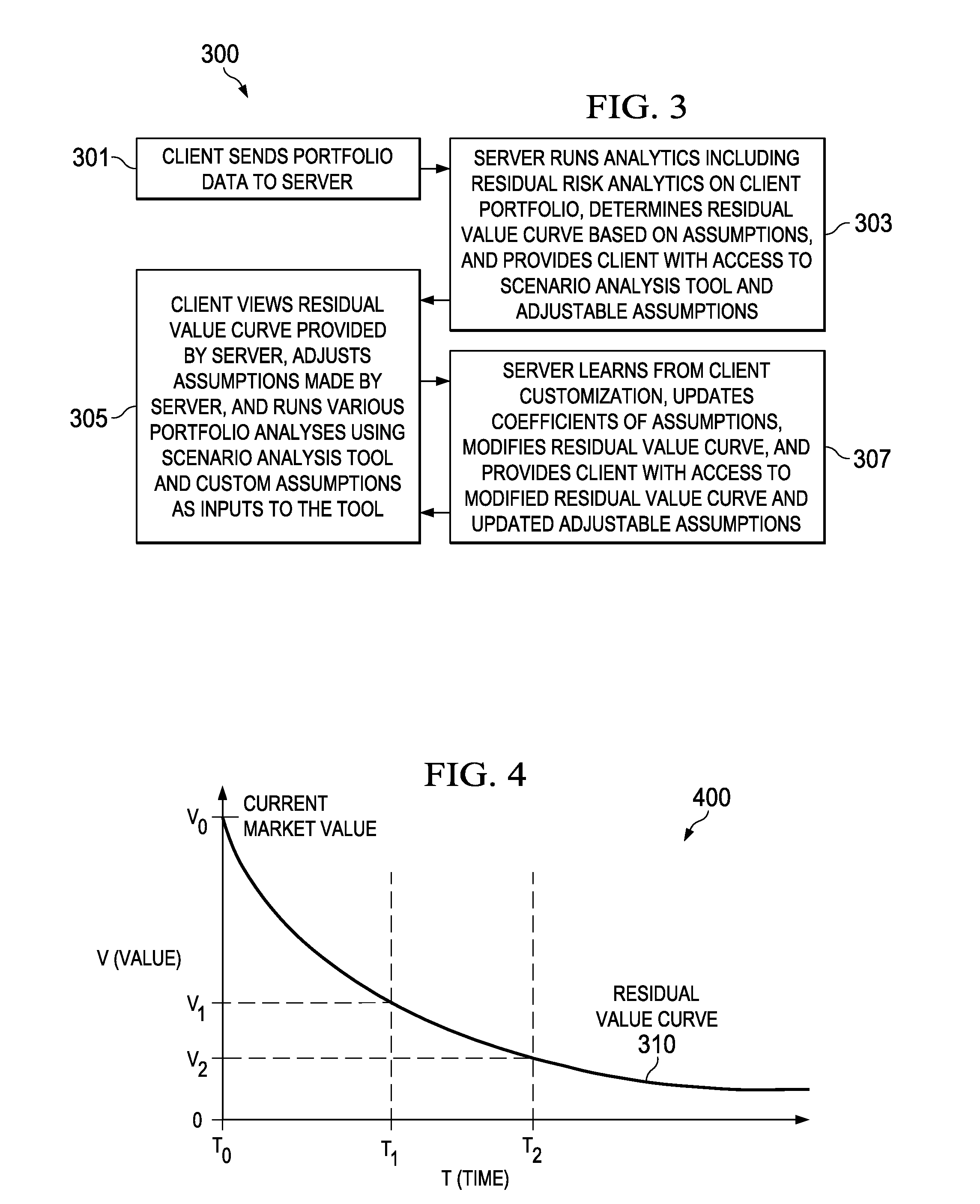
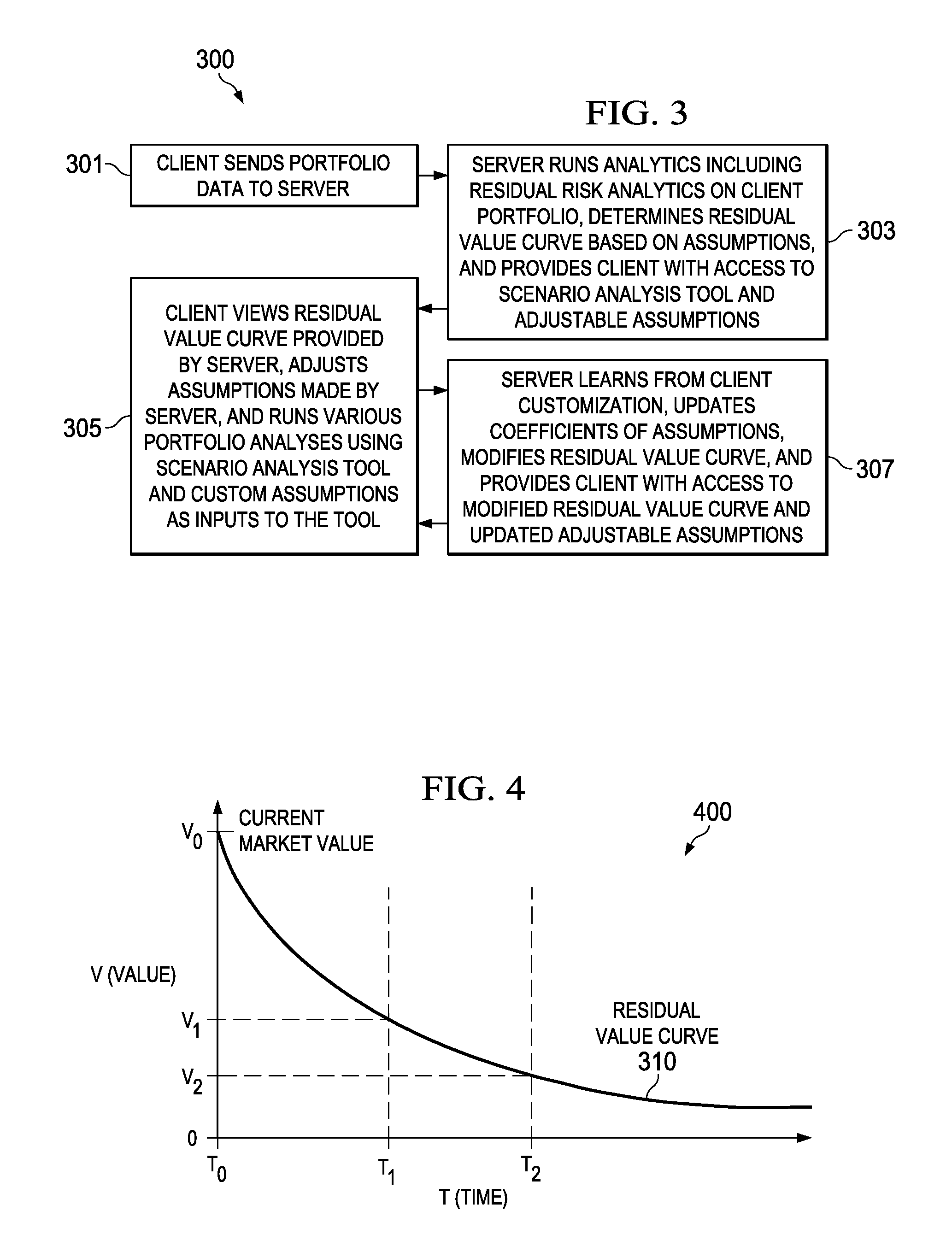
Systems, methods and products for determining residual values of asset portfolios are disclosed. In one embodiment, a system includes a server computer coupled to a network and to a data storage device. The server generates residual value curves for each of a set of item types and stores them. The server computer also receives and / or maintains information defining a set of items in a portfolio. When an assessment of the portfolio is initiated, the server determines a residual value for each item in the portfolio by identifying a corresponding one of the item types, retrieving the residual value curve corresponding to the identified item type, and determining a future value of the item based on the retrieved residual value curve for the corresponding item type. The server then aggregates the individual residual values into a residual value for the portfolio and enables access to this value.
Owner:ALG
Preparation method of medicinal calcium folinate
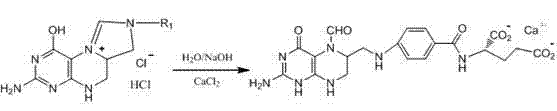
ActiveCN102399223AAvoid the risk of residual toxic substancesHigh yieldOrganic chemistryBulk chemical productionCarboxylic saltToxic material
The invention relates to the field of preparation of bulk pharmaceutical chemicals, in particular to a medicinal calcium folinate. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly reducing folic acid to generate tetrahydrofolic acid; then acylating tetrahydrofolic acid to generate leucovorin hydrochloride; and finally salifying leucovorin hydrochloride to generate calcium folinate. By the adoption of the method, the residual risk of toxic substances in medicines in the traditional process can be avoided completely; nontoxic organic acid zinc is used as a catalyst and nontoxic organic amine carboxylate servers as a reduzate and a protective group of aldehyde group, therefore the product is safer and the yield and purity of the product can be improved; a low-temperature and acidification condition is adopted in the method for keeping the leucovorin hydrochloride which serves as an intermediate stable, therefore the yield of the product can be improved, and impurities in the product can be reduced, and the yield of the finished calcium folinate product, based on calcium folinate, is improved to 30-38% from original 15-20%.
Owner:HUZHOU ZHANWANG PHARMA
Biodegradable blood vessel anastomosis ring/wheel and specialized surgical instrument thereof
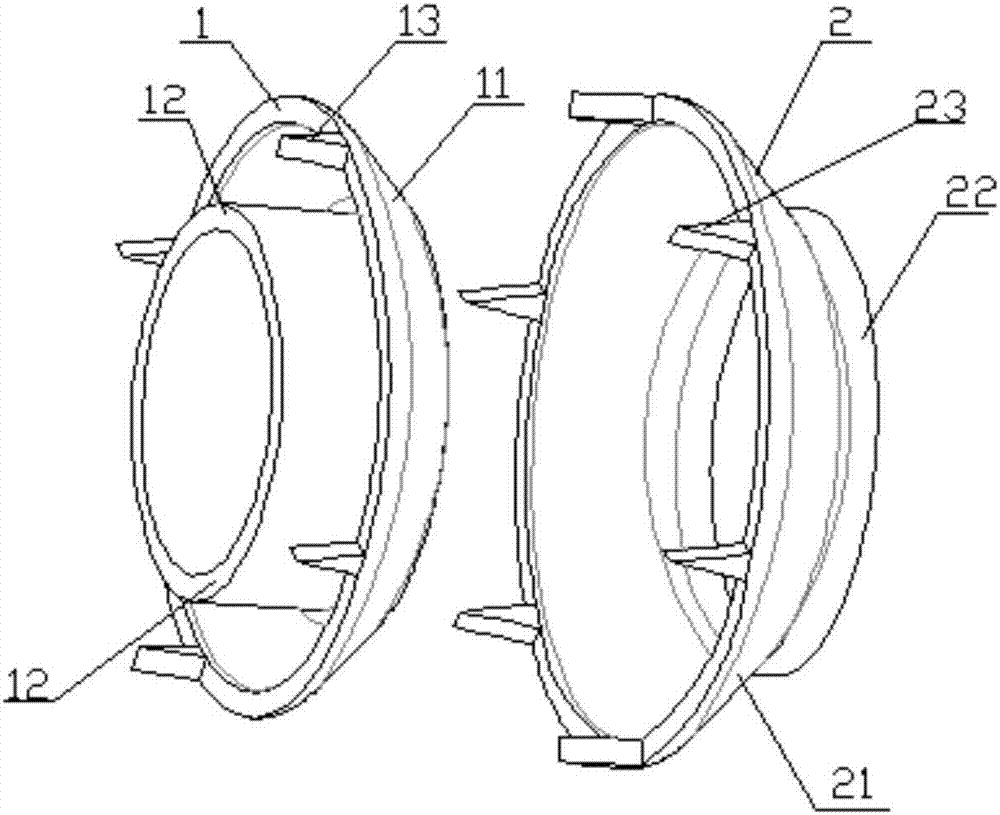
The invention discloses a biodegradable blood vessel anastomosis device, a special surgical instrument and a using method thereof which are used for the anastomosis between human blood vessels, between artificial blood vessels or between the human blood vessels and artificial blood vessels. The blood vessel anastomosis device is composed of a pair of coaxial first anastomosis ring / wheel and second anastomosis ring / wheel matched with each other; the anastomosis ring / wheel comprises a blood vessel support bracket, a clamping bracket, and anastomosis needles distributed circumferentially around a free end of the blood vessel support bracket. The anastomosis surface of the blood vessel anastomosis device is of a coaxial geometric structure, thus the blood vessel anastomosis device is high in anastomosis effect and wide in anastomosis area, improves the success rate of operations and reduces the collapse phenomenon of anastomosis positions. The blood vessel anastomosis is prepared by using biodegradable materials, through a reasonable structural design, the blood vessel anastomosis ring / wheel can be degraded by the human body after operations, and during the degradation process, a relatively complete structure is maintained, an appropriate effective support time is maintained after operations according to the conditions of different blood vessels to maintain the function of the blood vessel anastomosis ring / wheel, and the foreign body residual risk caused by the traditional mechanical anastomosis method is avoided. According to the special instrument, the clamping and anastomosis functions are integrated, the operation process is simplified, and the operation efficiency is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHANGHAI HOSPITAL
Method for preparing edible grade transparent concentrated soybean phospholipid
InactiveCN106866725ASolve the problem of deep color and poor transparencyImprove qualityGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsPhosphatide foodstuff compositionsOrganic solventSoybean Phospholipids
The invention provides a method for preparing edible grade transparent concentrated soybean phospholipid; the Gartner color of the phospholipid obtained by the method is less than 8, the transparency is high, the peroxide value is less than 10 meq / kg, the amount of a residual solvent is less than 50 mg / kg, and indicators meet the requirements of food phospholipid. Soybean crude oil is directly used as raw material, an organic solvent is not required to be added in the preparation process, no residual risk of the organic solvent exists, and at the same time, the potential safety hazard in the production process is reduced. In addition, the method solves the problems of deep color and poor transparency of concentrated soybean phospholipid in China and can realize industrialized production.
Owner:COFCO GROUP +3
Methods for assigning a price to an asset that is a derivative of a non-marketed variable
InactiveUS7613646B2Easy to implementFinanceElectric digital data processingComputer scienceResidual risk
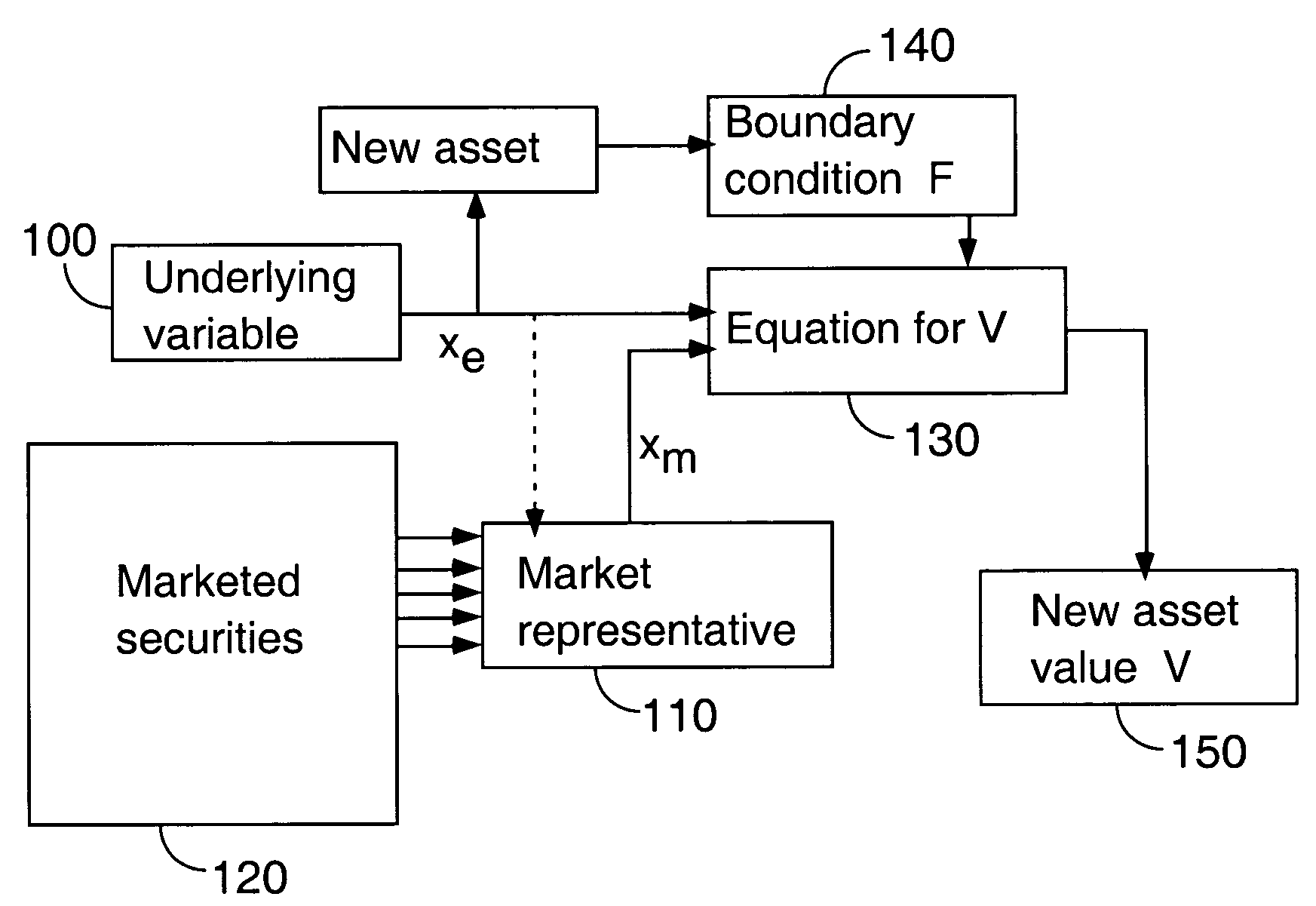
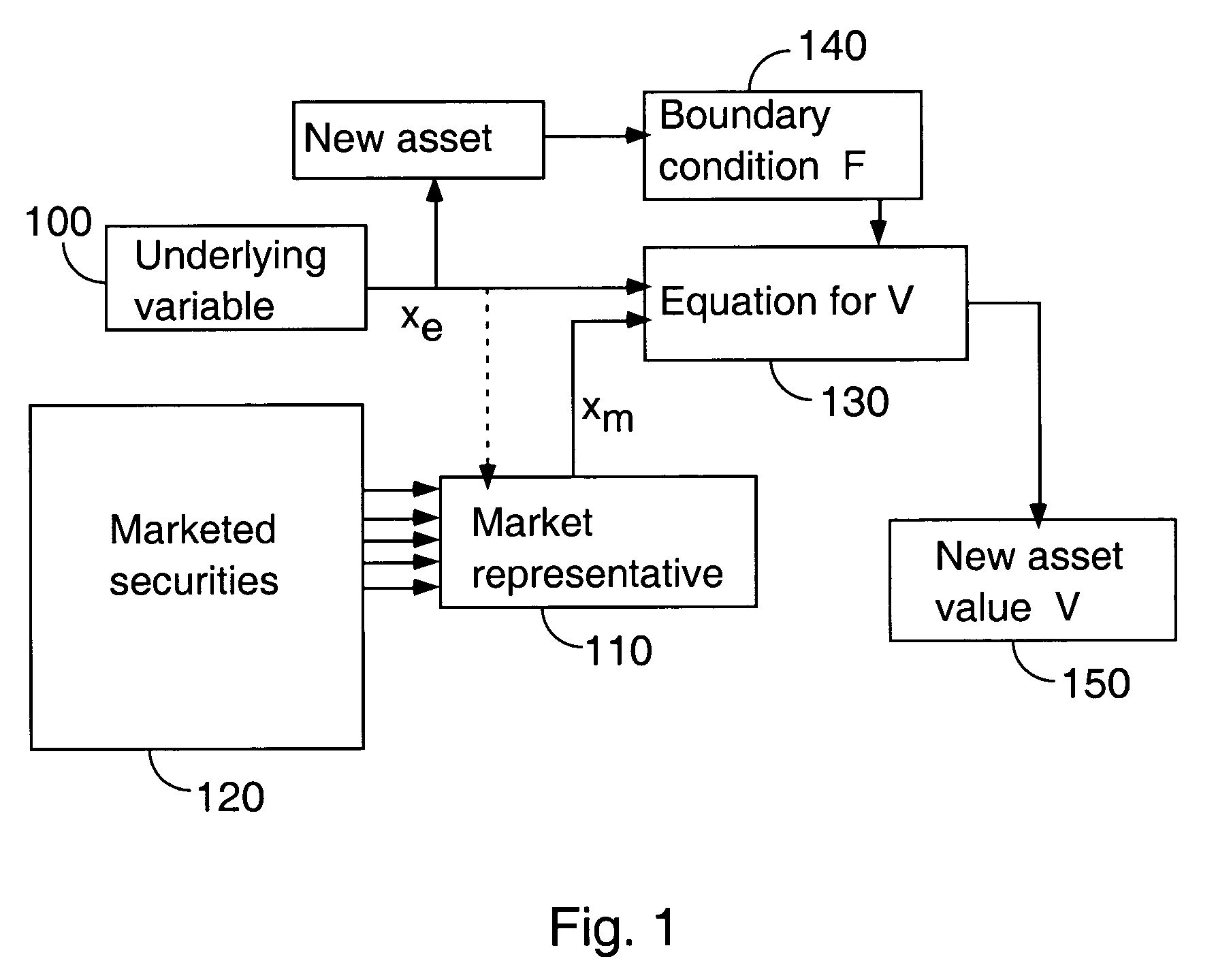
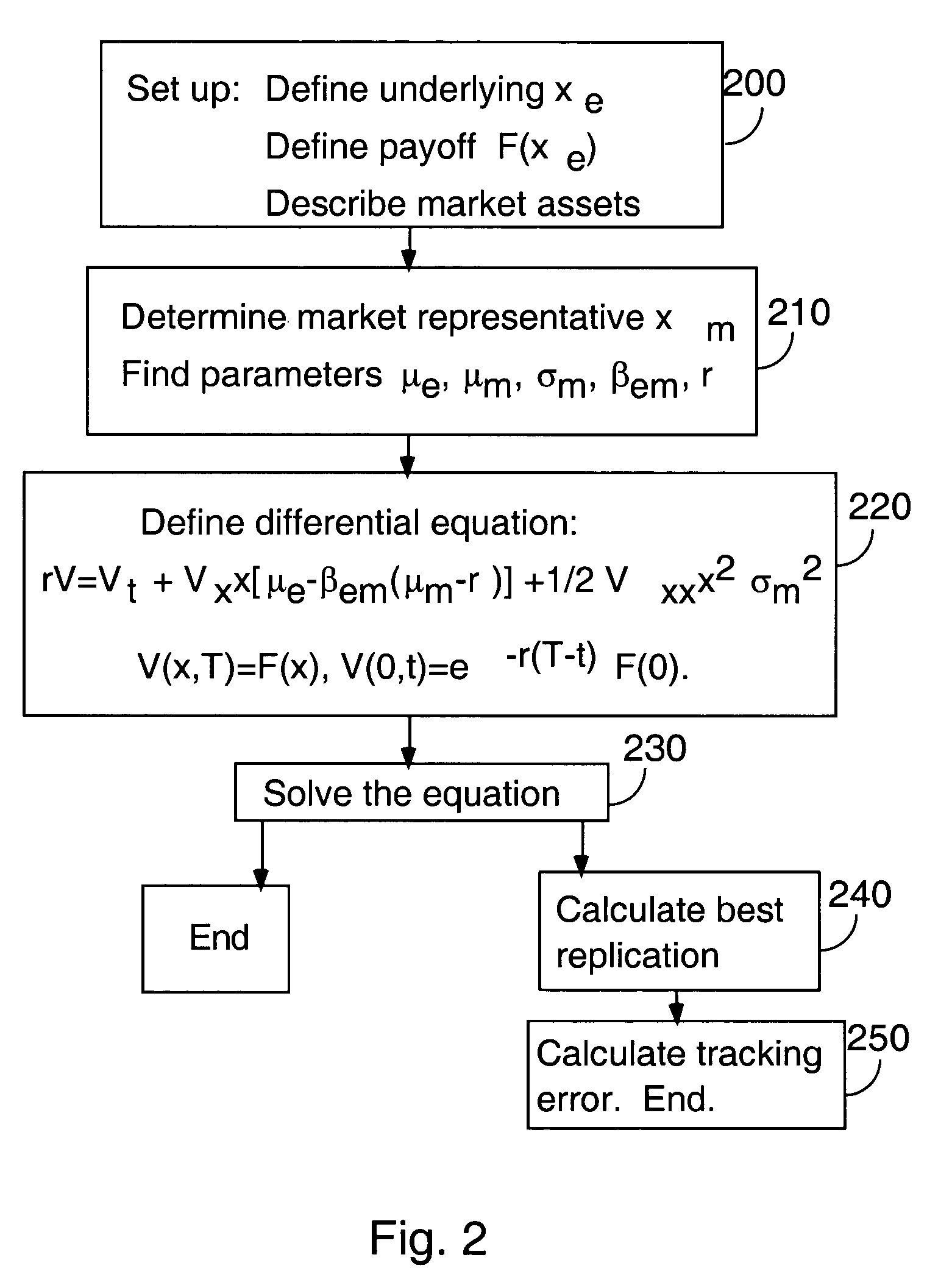
A computer-implemented method is provided for valuing and hedging payoffs that are determined by an underlying non-marketed variable that moves randomly. The value assigned is that which is obtained by projecting the instantaneous return of the future payoff onto the span of marketed assets. An explicit method is provided for determining this value by determining a suitable market representative. In a continuous-time embodiment, the methodology is based on an extended Black-Scholes equation that accounts for the correlation between the underlying non-tradable asset and marketed assets. Once this extended equation is solved, the value of the payoff, the optimal hedging strategy, and the residual risk of the optimal hedge can be determined. In alternate embodiments, the same value is determined as the discounted expected value of the payoff, using risk-neutral probabilities for the non-marketed variable. These risk-neutral probabilities are again determined by the relation of the underlying variable to the payoff of a most-correlated marketed asset. The risk-neutral version of the method applies in both continuous-time and discrete-time frameworks, providing asset valuation, optimal hedging, and evaluation of the minimum residual risk after hedging.
Owner:LUENBERGER DAVID G
Testing Process
InactiveUS20090036748A1Health-index calculationMicrobiological testing/measurementPregnancyClinical psychology
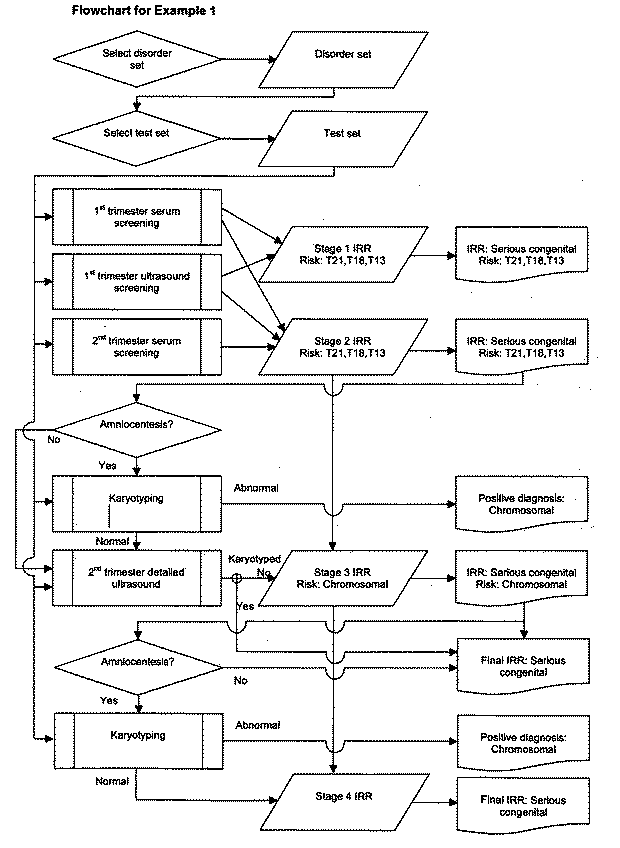
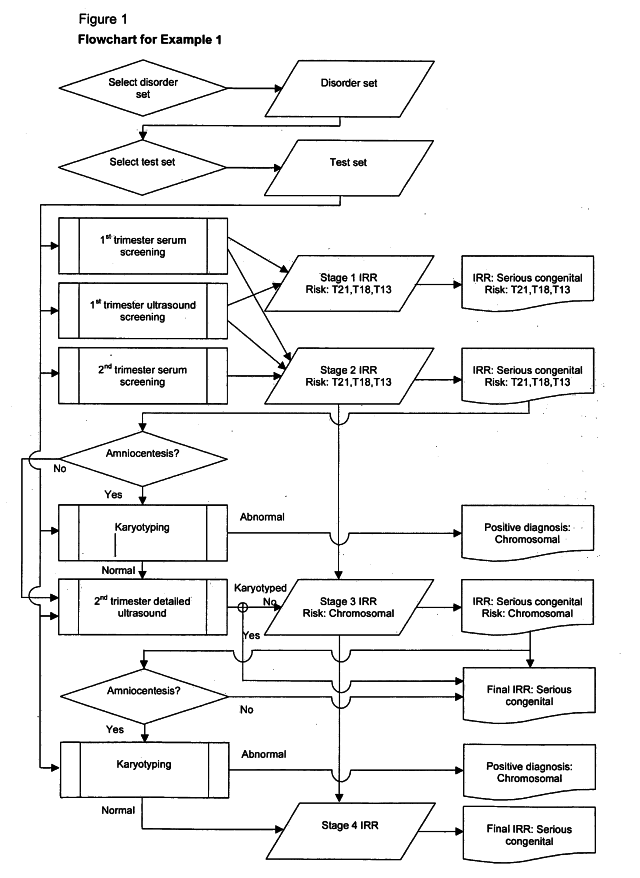
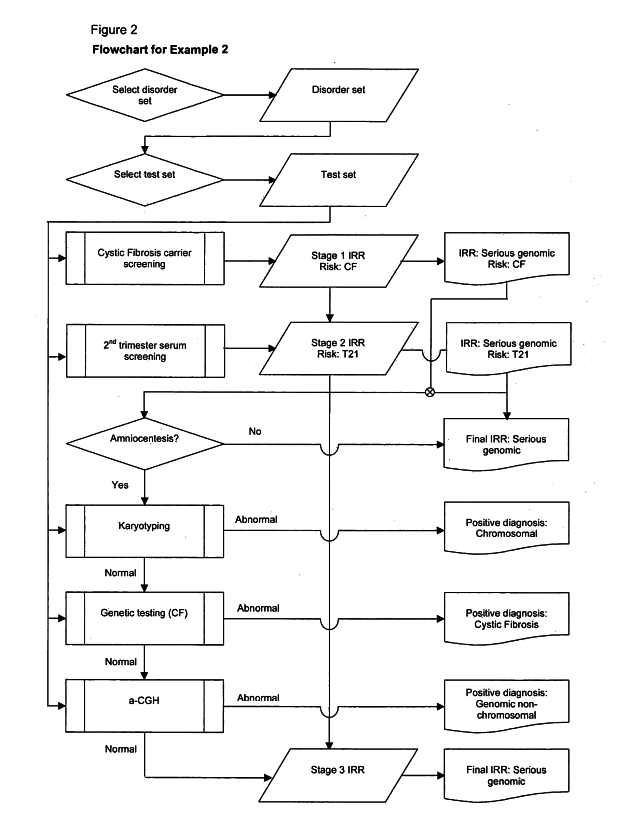
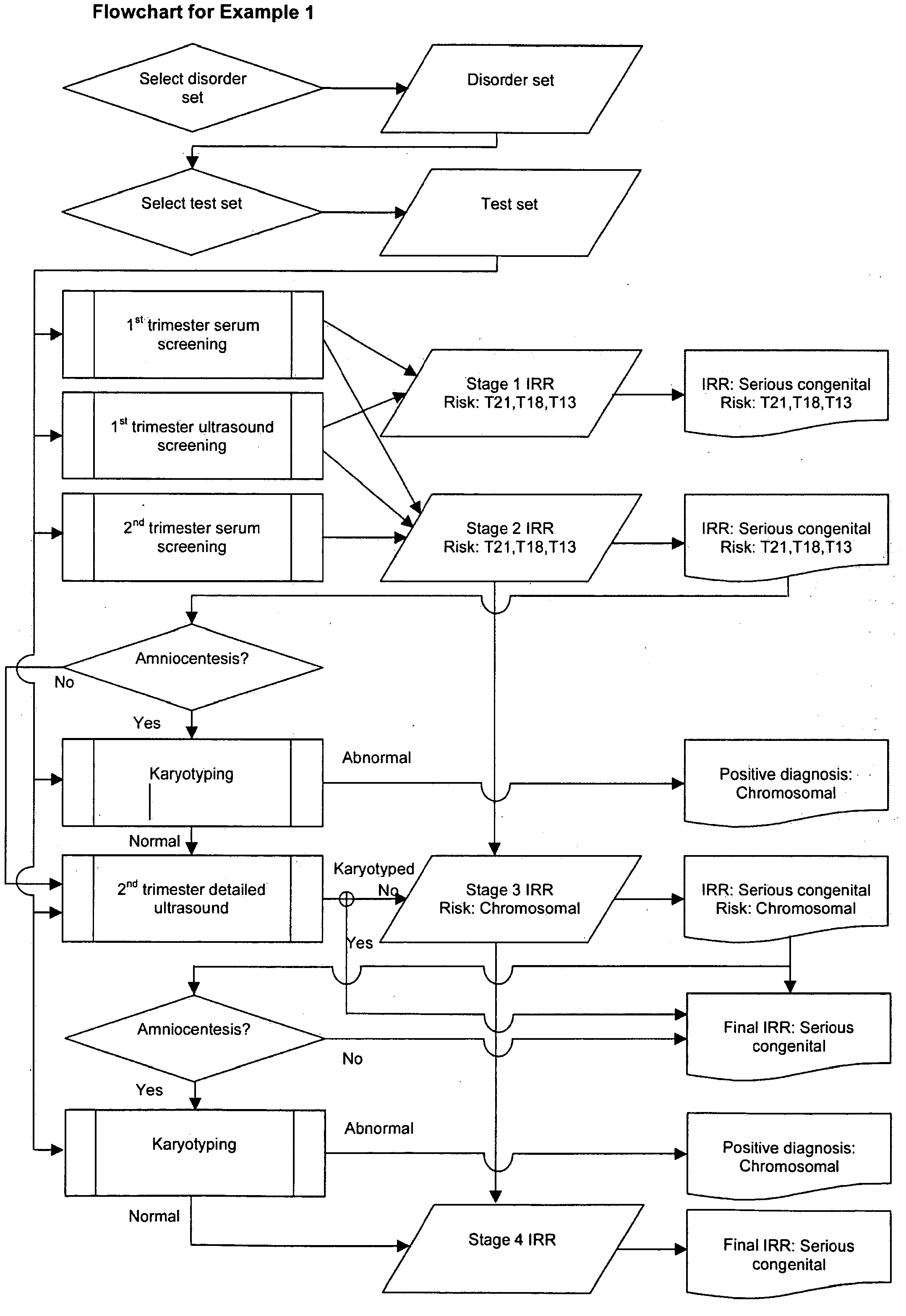
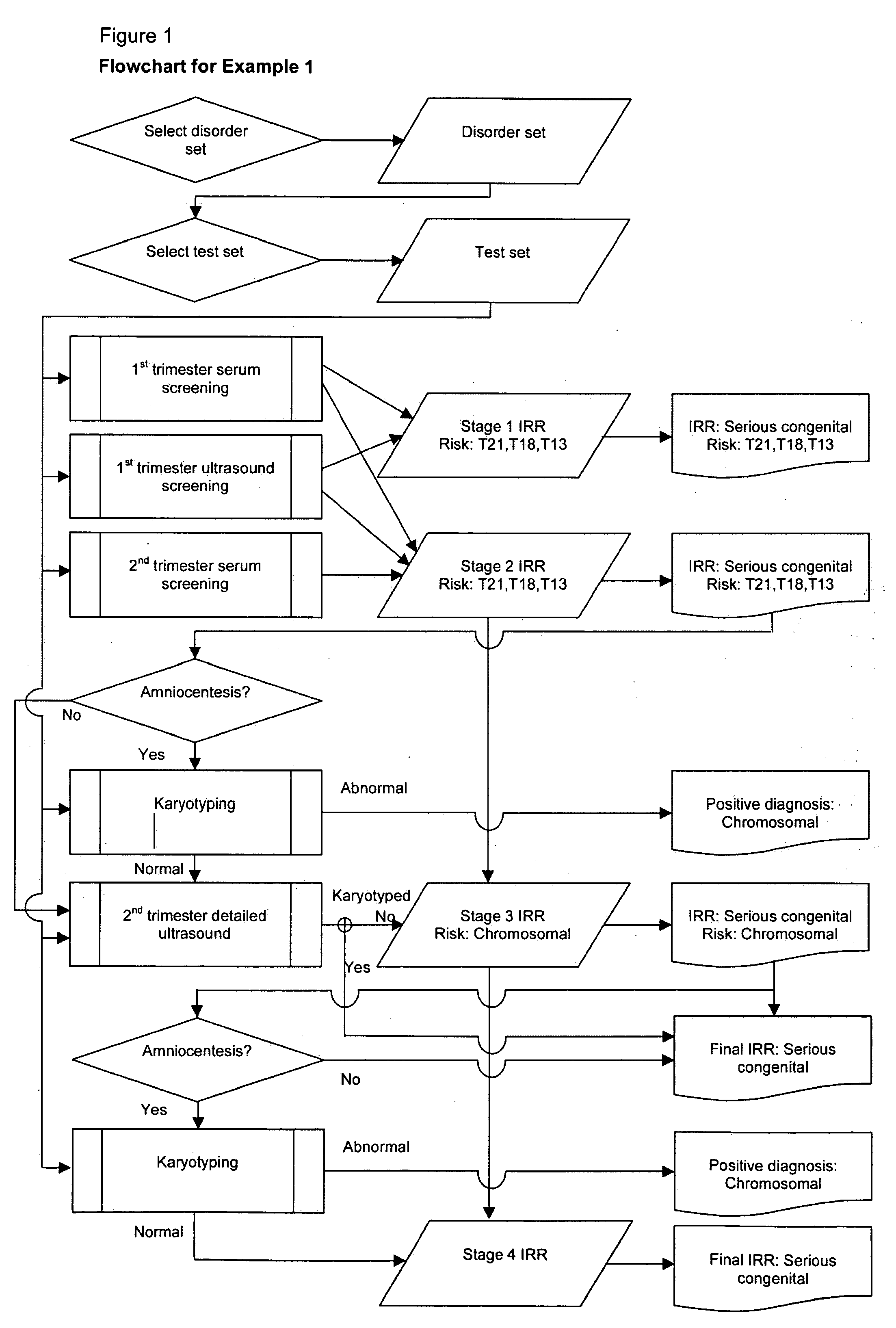
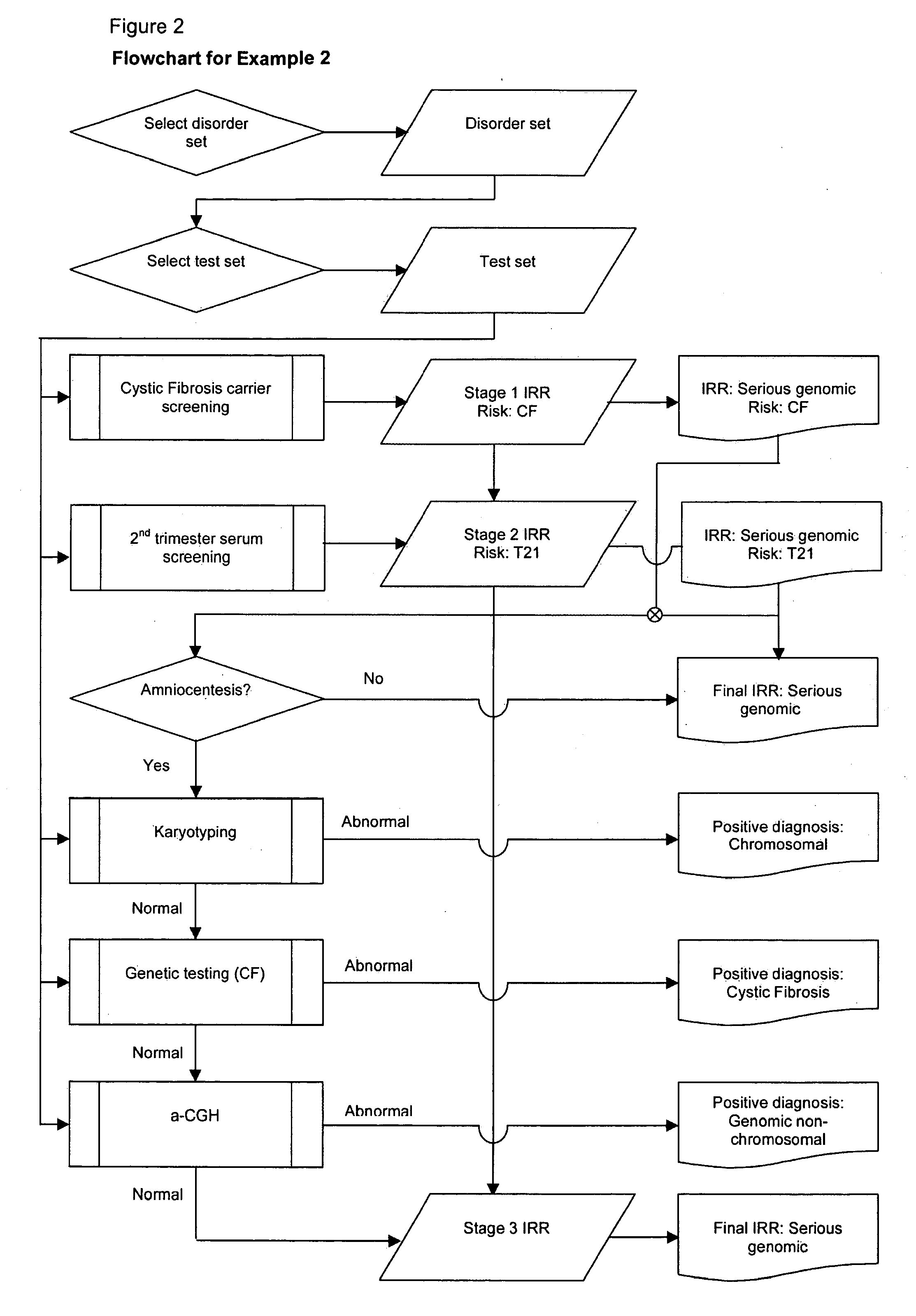
A method of determining an inclusive residual risk that a pregnancy is affected by at least one phenotypic disorder included in a disorder set is provided. The method includes calculating a prior risk for a disorder set, calculating posterior risks for the individual disorders or groups of disorders in the disorder set that can be screened for and / or diagnosed prenatally, and calculating an inclusive residual risk for the disorder set by combining the prior risks for disorders for which no tests have been performed and the individual posterior risks.
Owner:PERGAMENT EUGENE +3
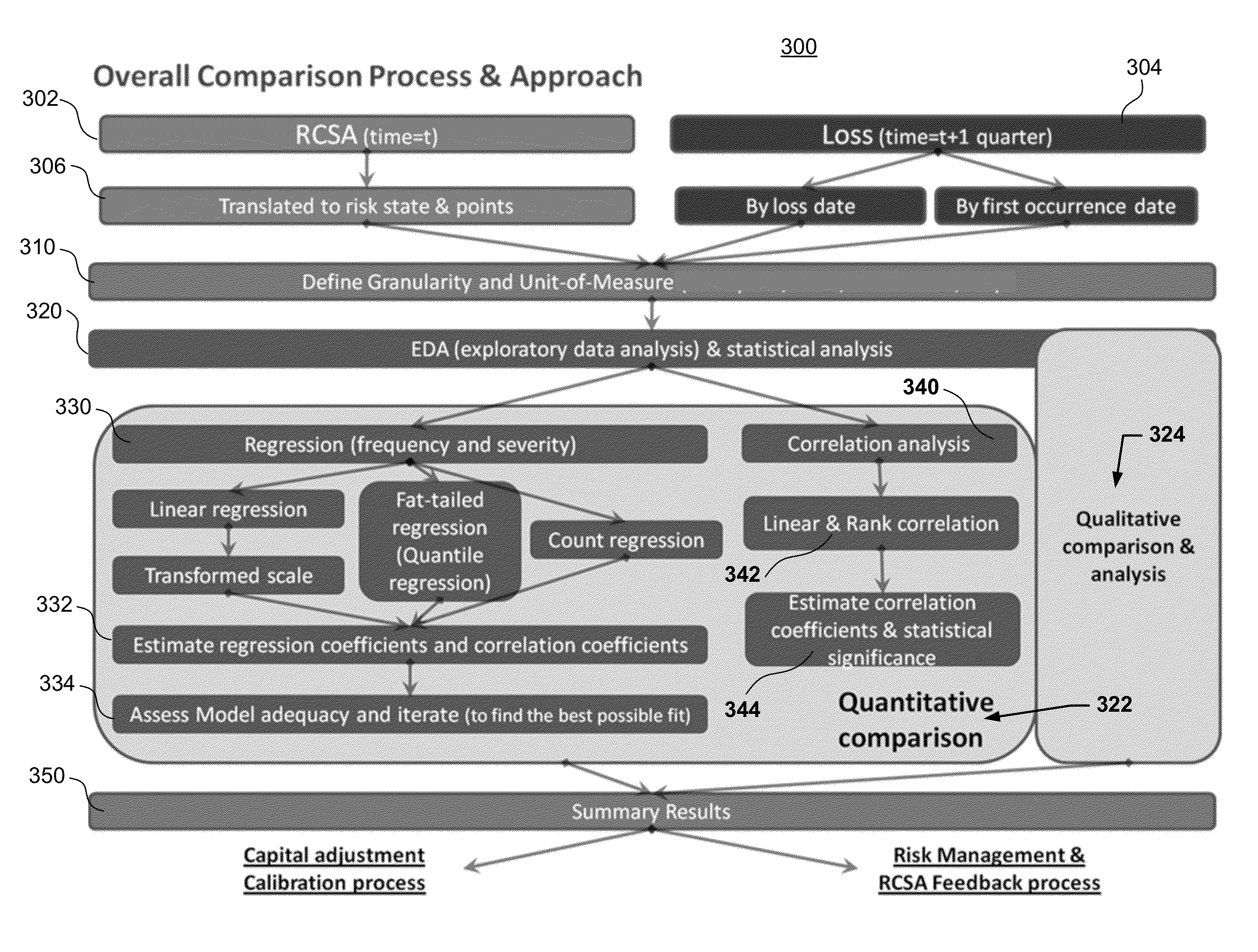
Operational Risk Back-Testing Process Using Quantitative Methods
Methods, computer-readable media, and apparatuses are disclosed for quantifying risk and control assessments. The risk includes both residual risk and direction of risk. Various aspects of the invention quantitatively compare the risk and control assessments against step-ahead losses using special regression models that are particularly applicable to this kind of data. The empirical comparison may be performed on both loss event frequency and severity in two different and separate dimensions. The empirical comparison may also be performed using losses extracted by even occurrence and event settlement dates in two separate dates.
Owner:BANK OF AMERICA CORP
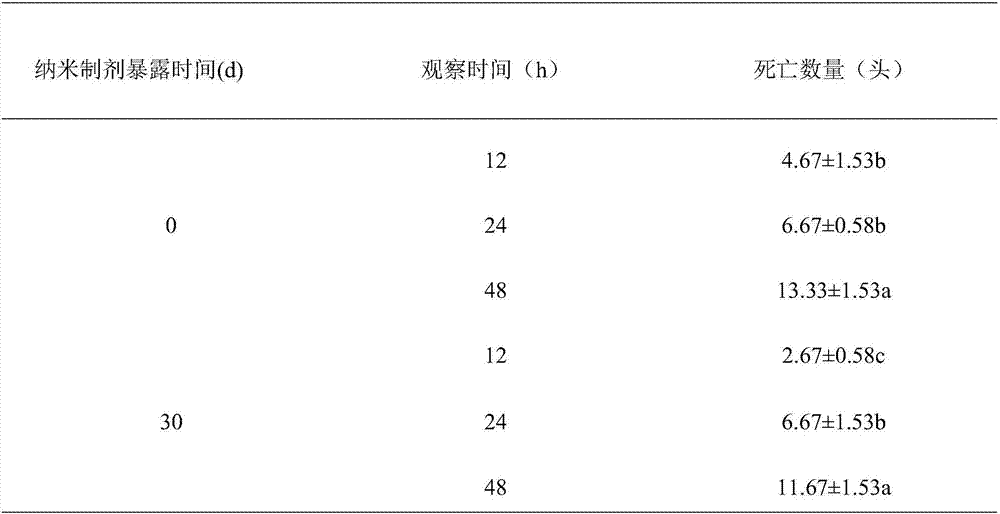
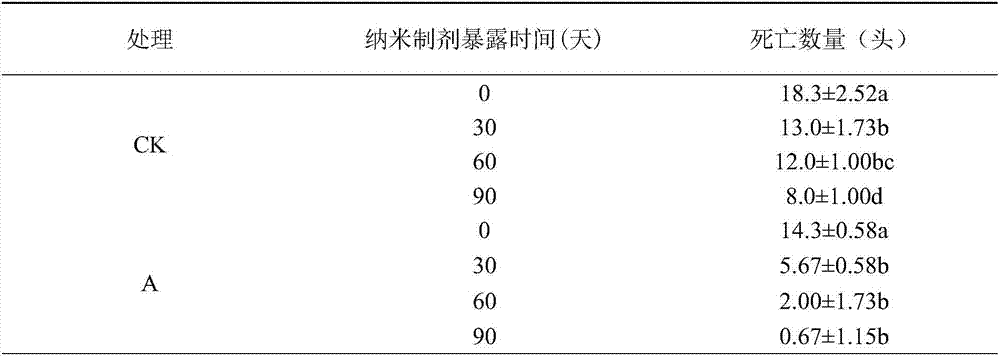
Scotogramma trifolii rottemberg attractant composition and preparation method of nano preparation thereof
ActiveCN107950529AGood environmental compatibilityImprove permeabilityBiocidePest attractantsCopolymerMicelle
The invention discloses scotogramma trifolii rottemberg attractant composition and a preparation method of a nano preparation thereof in the technical field of preparation of agricultural chemicals. According to the preparation method, an amphiphilic copolymer is adopted and subjected to self-assembly in an aqueous solution, nano-sized micelle with an obvious core-shell structure is formed, and anano-pesticide is prepared from the nano-sized micelle with an electrospinning technology. The preparation method is simple and convenient, the raw materials are easily available, the amphiphilic copolymer has quite good environmental compatibility, is biodegradable and is free of residual risk, and furthermore, a degradation product can be absorbed and used by crops; the prepared nano-pesticide is smaller and uniform in grain size and good in permeability and has certain slow-release effect, so that lasting period of scotogramma trifolii rottemberg sex pheromone and pyrethriods pesticides isprolonged, and the use dosage of the pesticide is reduced.
Owner:河北军星生物化工有限公司
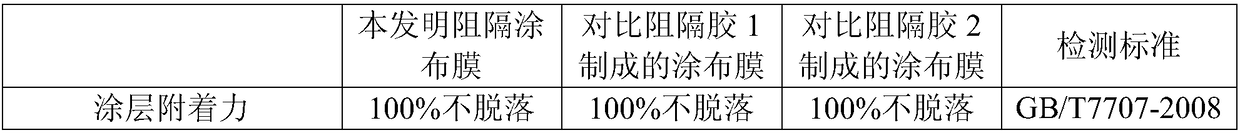
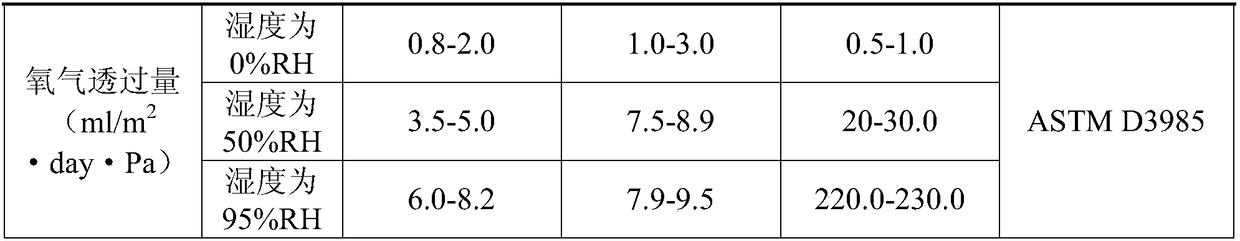
Barrier coating film without prime coat and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a barrier coating film without a prime coat and a preparation method thereof. By improving barrier coating liquid, a PVOH product having better barrier performance is added inPVDC latex, barrier performance (less than or equal to 2cc / m<2>, 24 hr) is increased, a polymerization technology is adjusted, the barrier coating film without the prime coat is finally prepared, under prerequisite that obstruct effect is good, a film prime coating process is reduced, an organic solvent generated during production can be avoided, and residual risk of a product solvent cannot be generated.
Owner:HAINAN SHINER IND
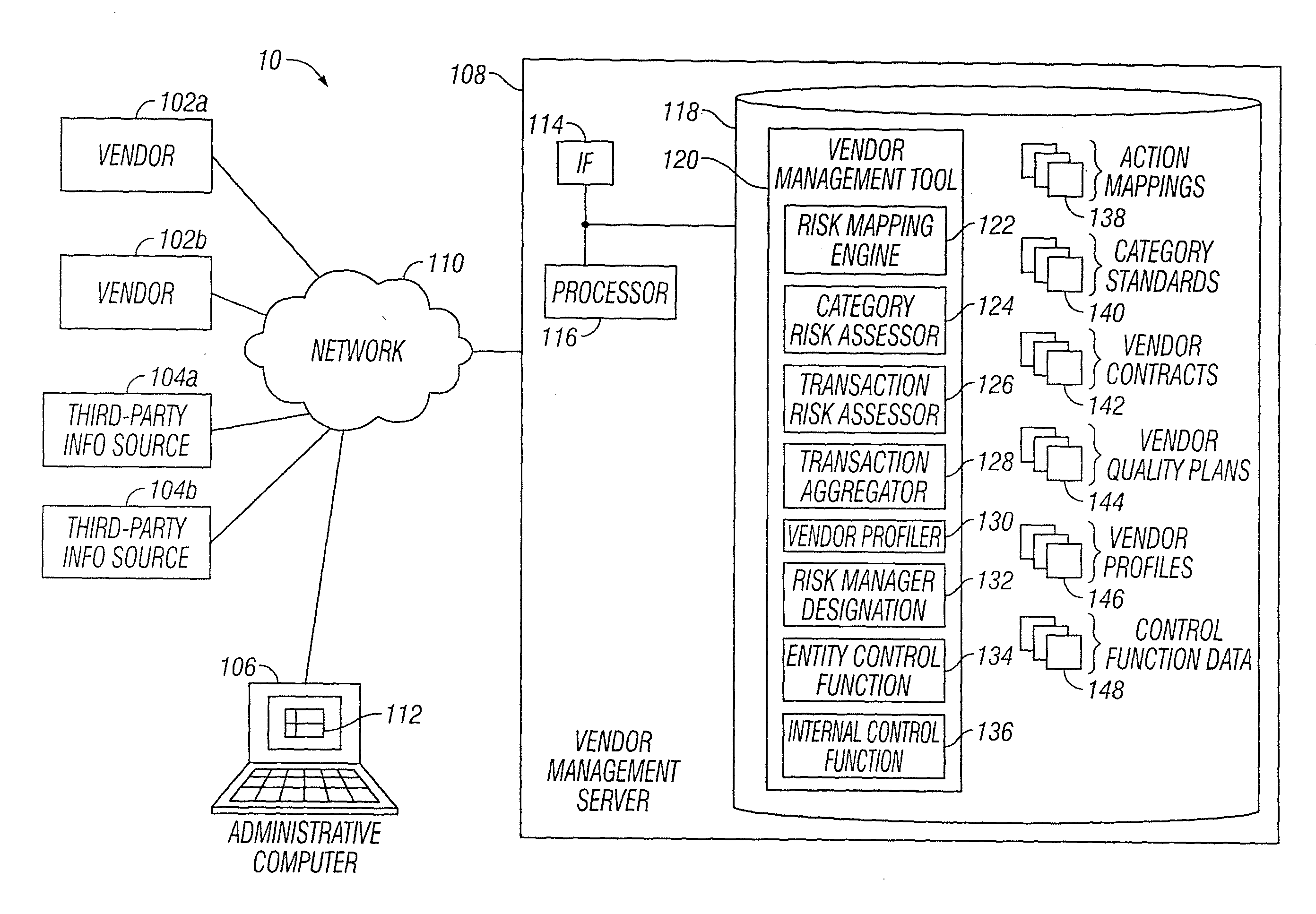
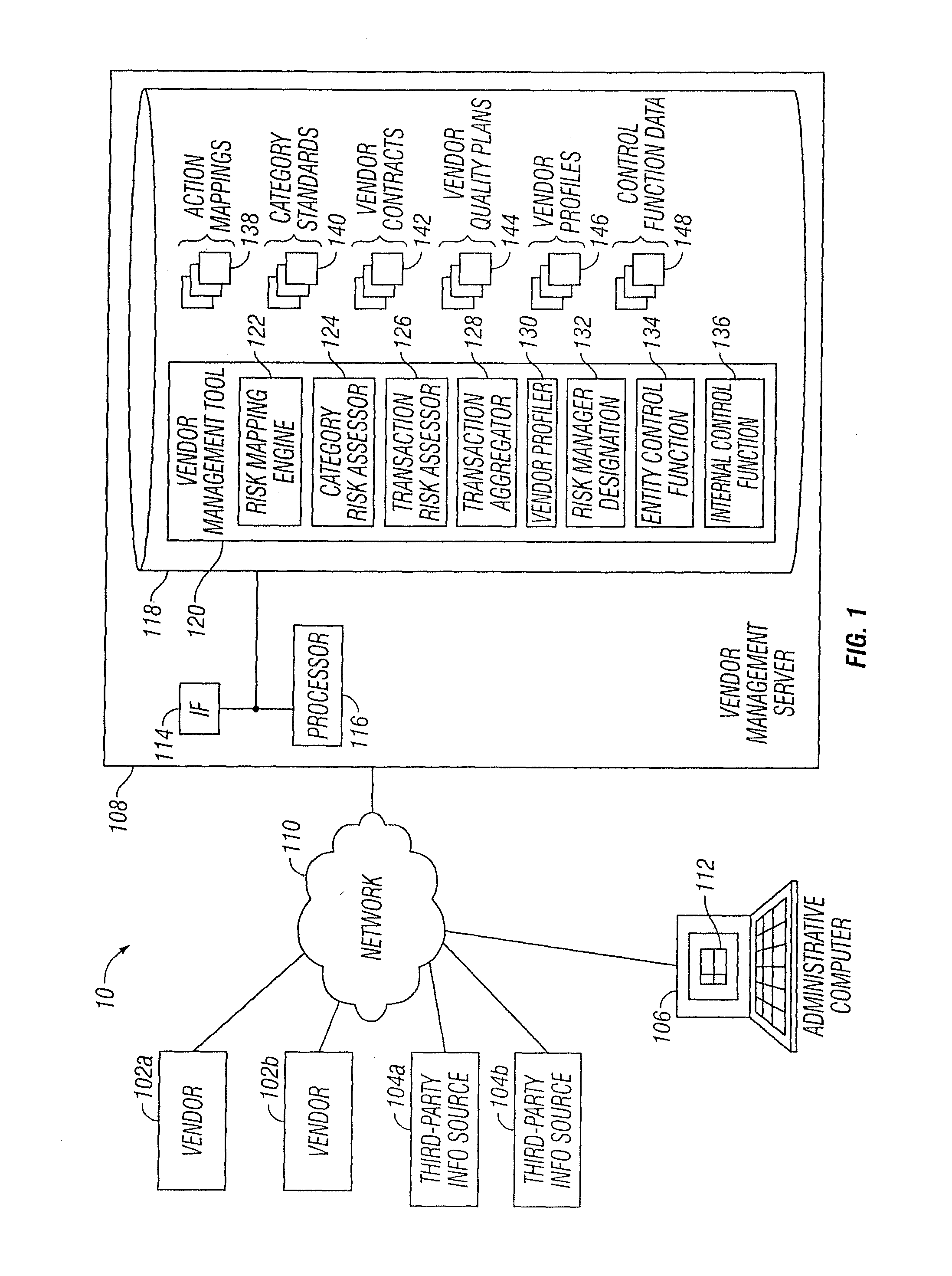
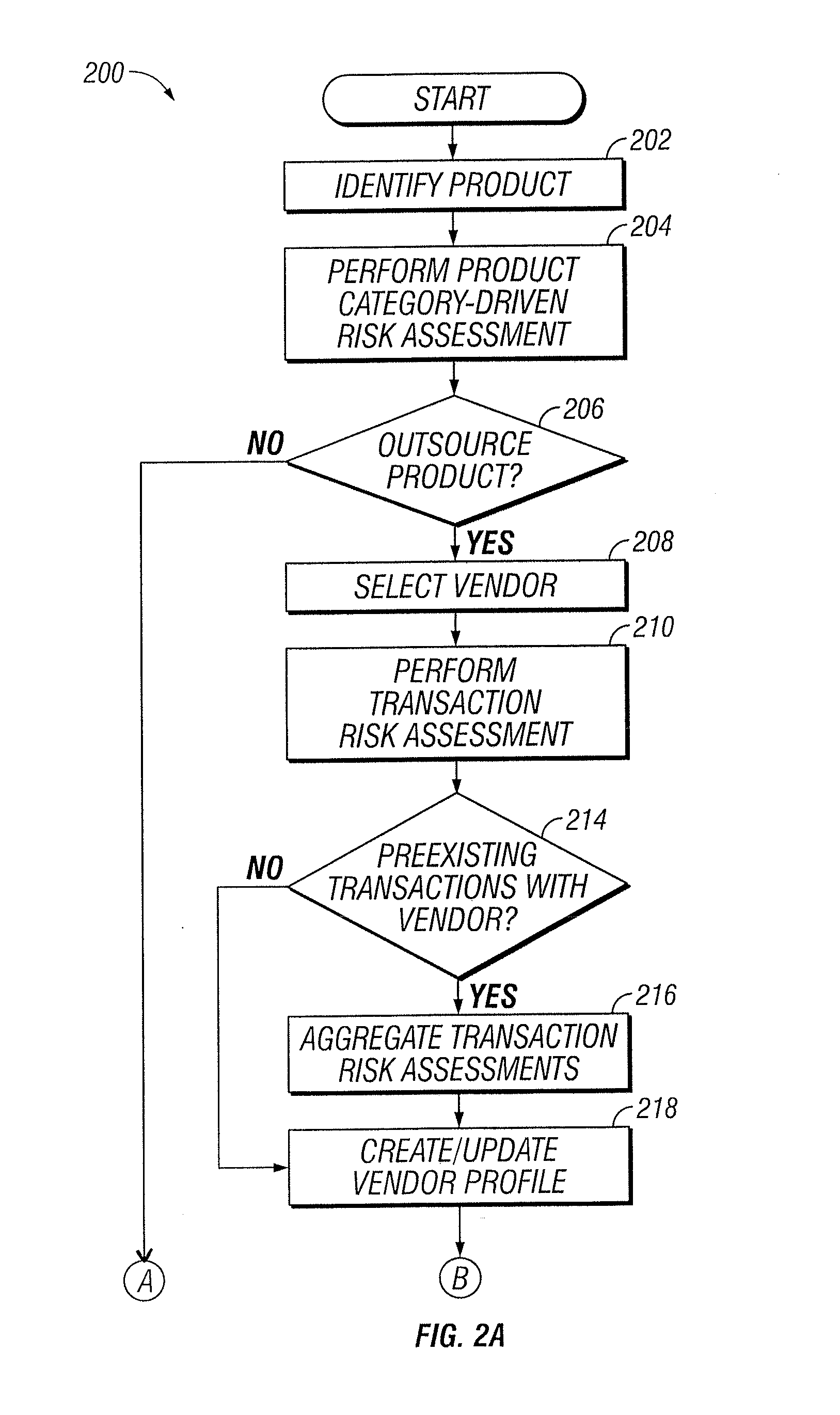
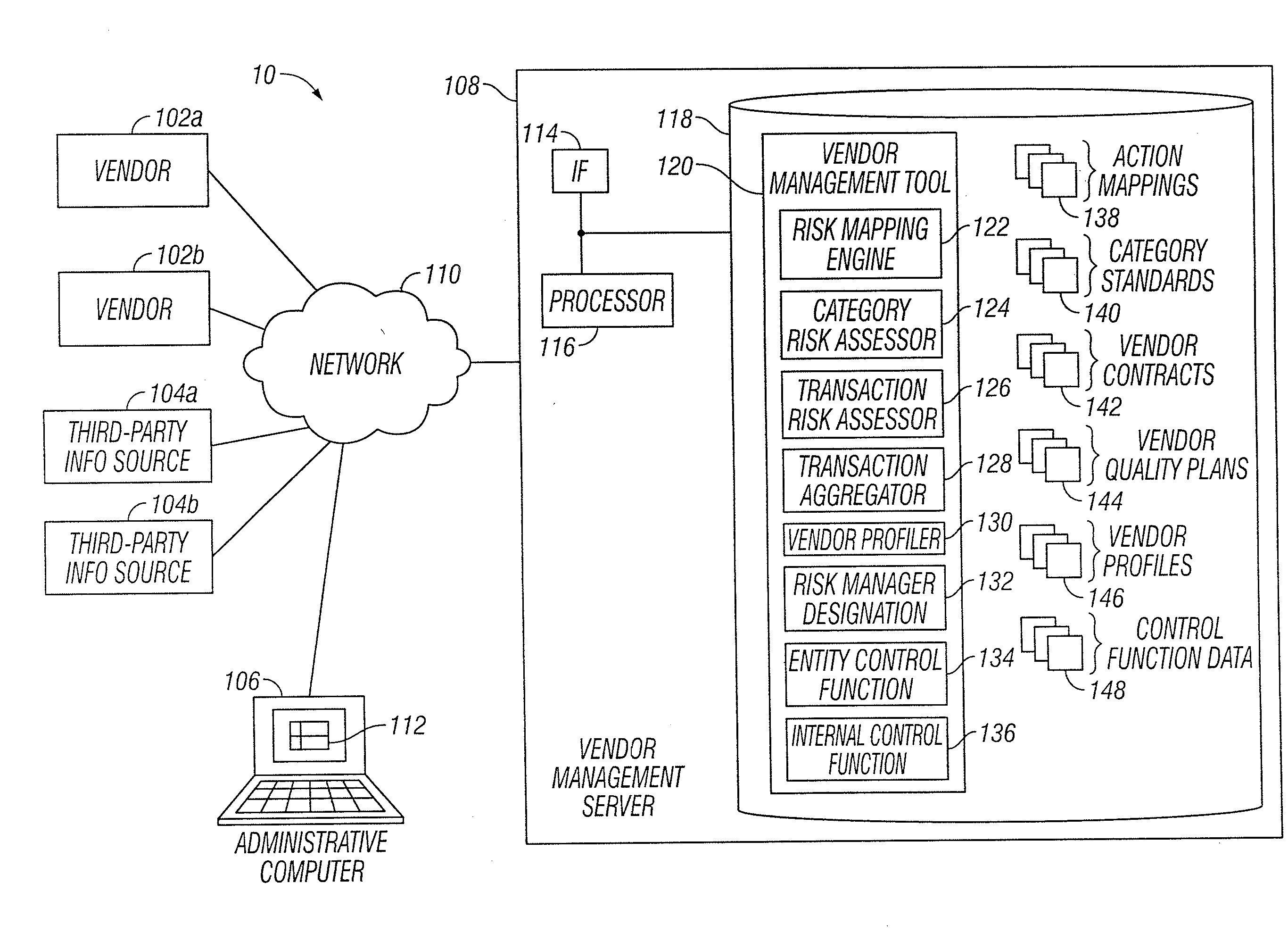
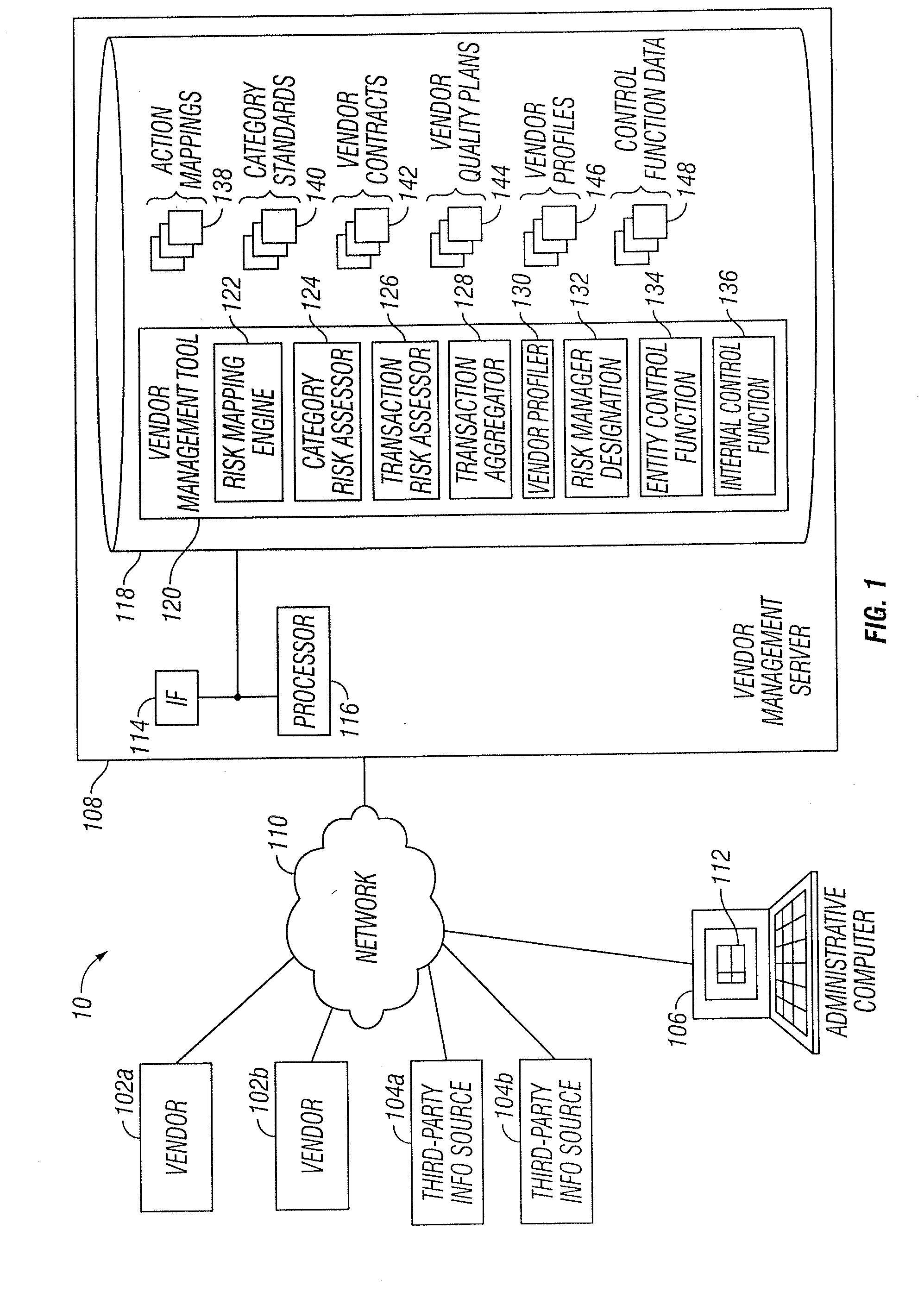
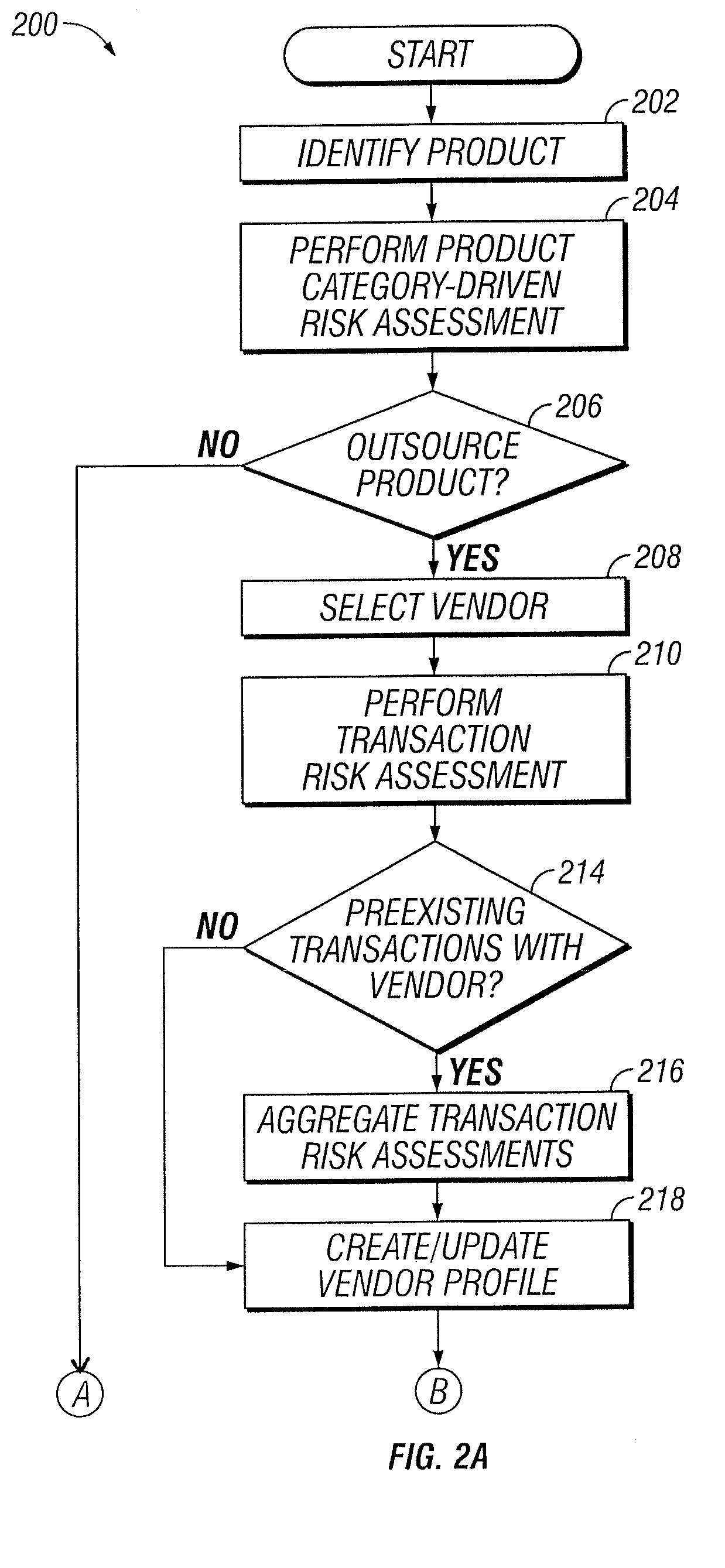
Vendor Risk And Performance Profile
InactiveUS20150242776A1Disadvantages can be reduced eliminatedProblems be reduced eliminatedFinanceResourcesEngineeringRisk element
Establishing a vendor profile may comprise identifying a plurality of risk elements associated with a vendor that supplies one or more products to an entity. Any completed management actions for the vendor that mitigate risk associated with any of the identified risk elements are identified. A performance requirement for the vendor associated with at least one of the products supplied by the vendor to the entity is identified. A performance measurement for the identified performance requirement for the vendor is identified. A residual risk for at least one of the identified risk elements is determined according to a completed management action that reduces risk associated with the at least one of the identified risk elements. A performance level is determined according to the performance requirement and the performance measurement. A vendor profile is created according to the identified risk elements, completed management actions, identified performance requirements, and performance measurement.
Owner:BANK OF AMERICA CORP
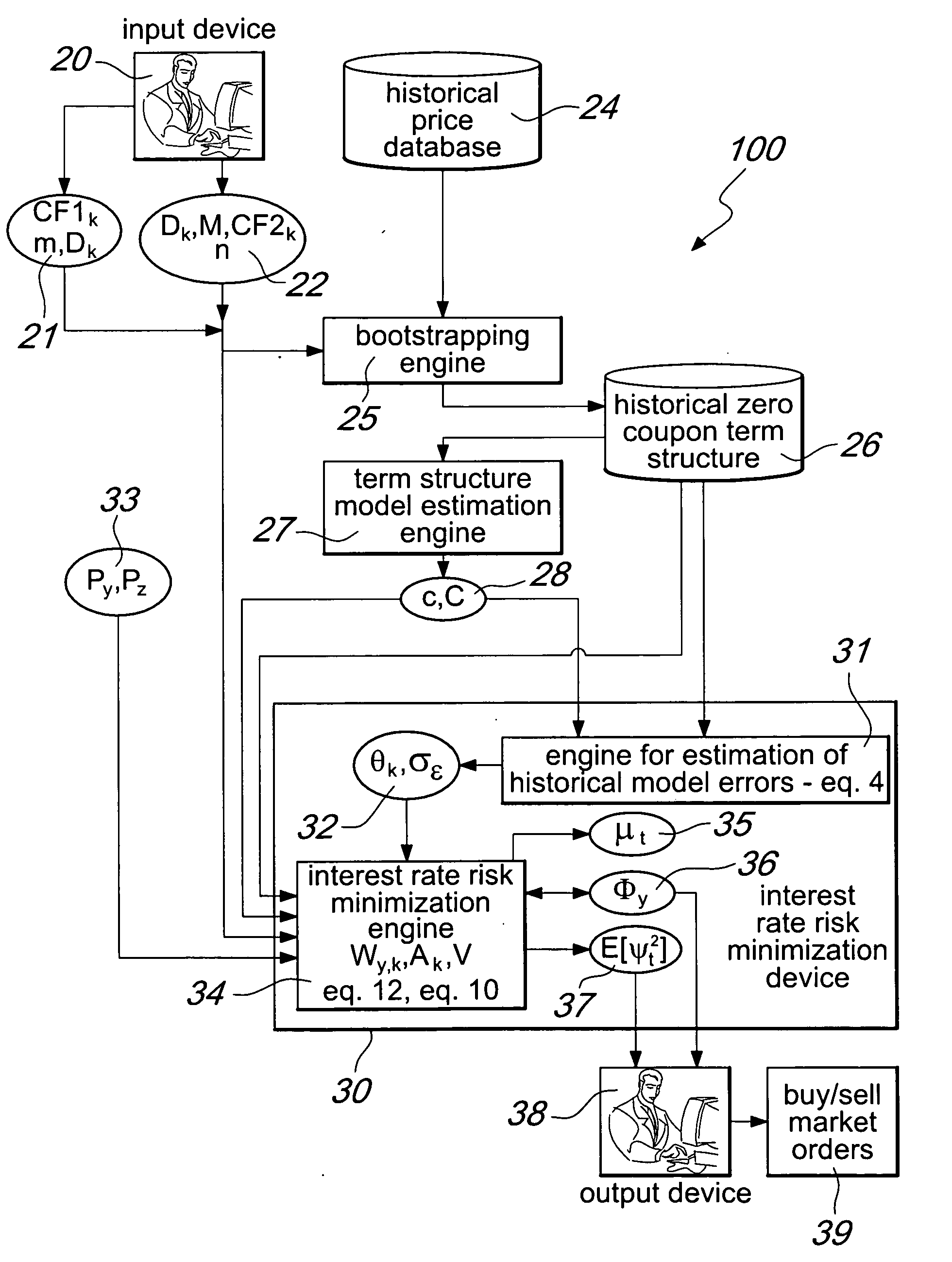
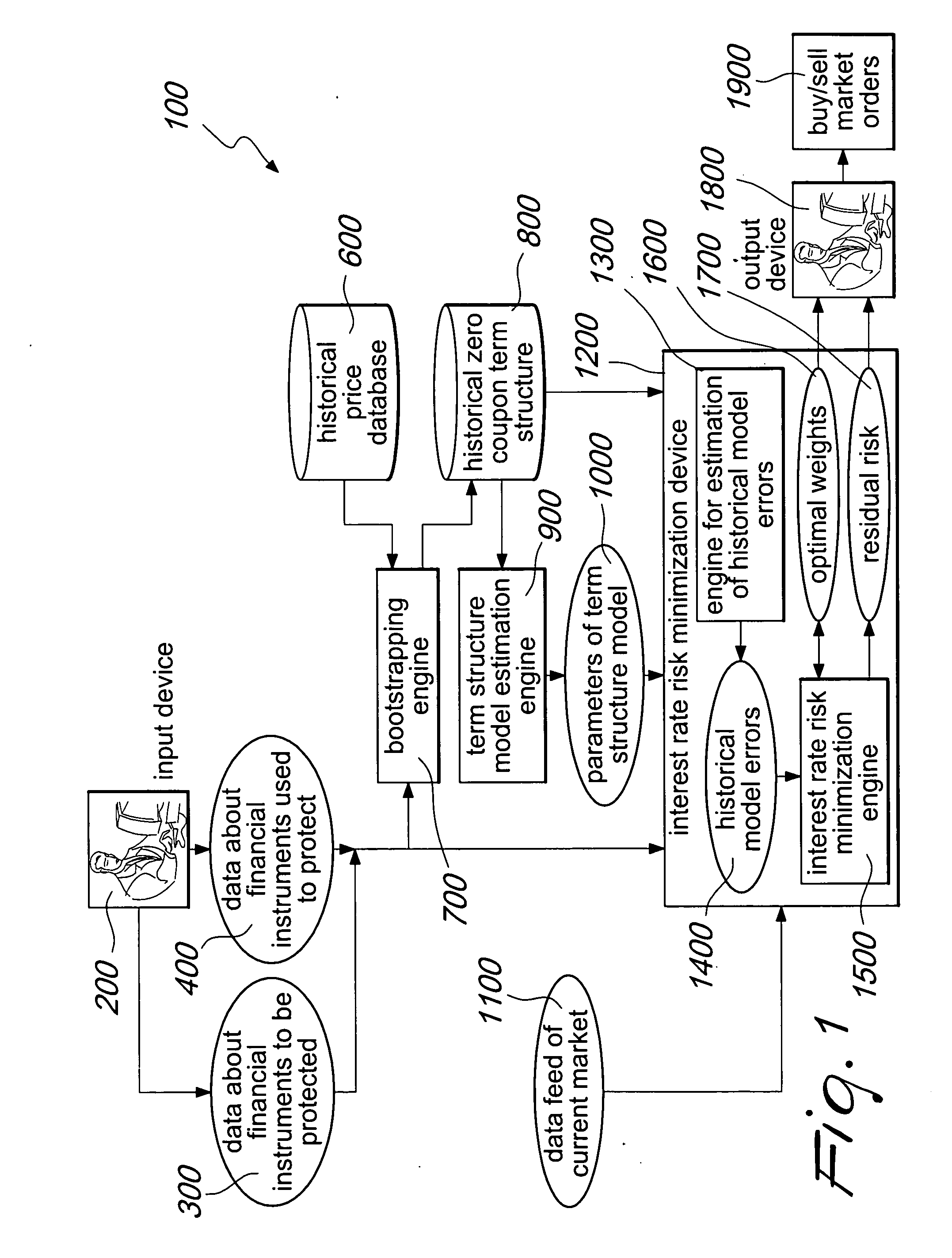
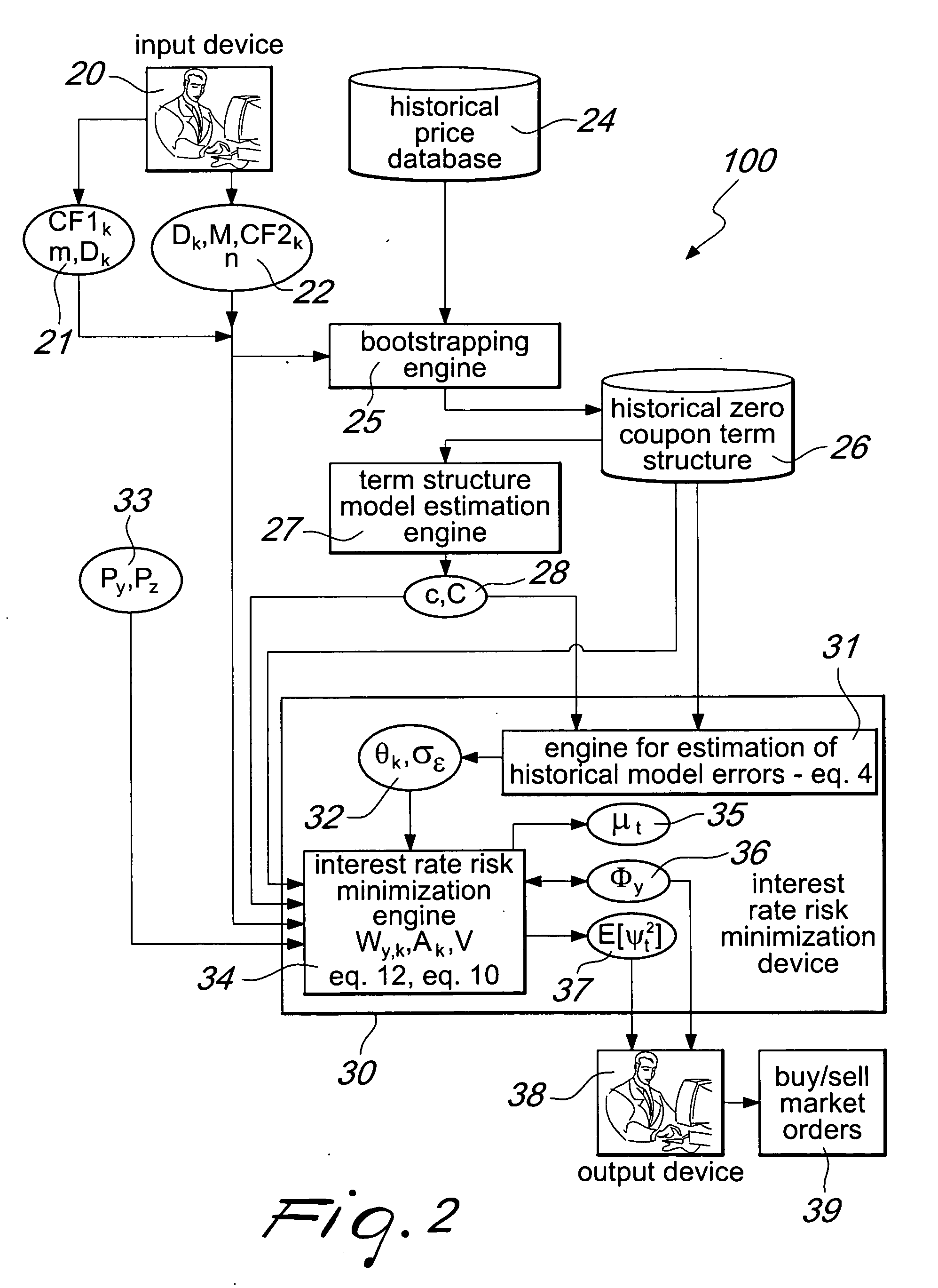
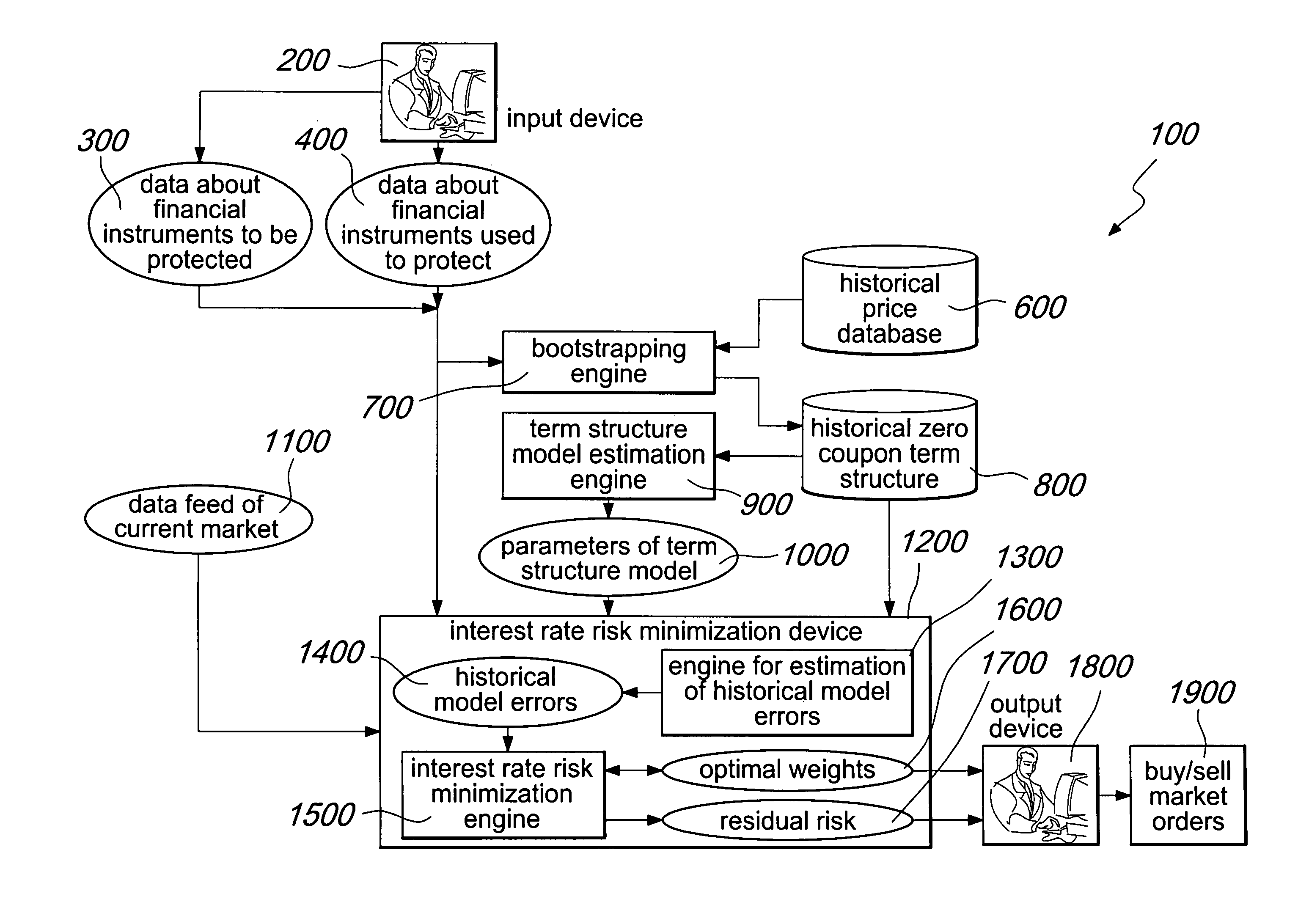
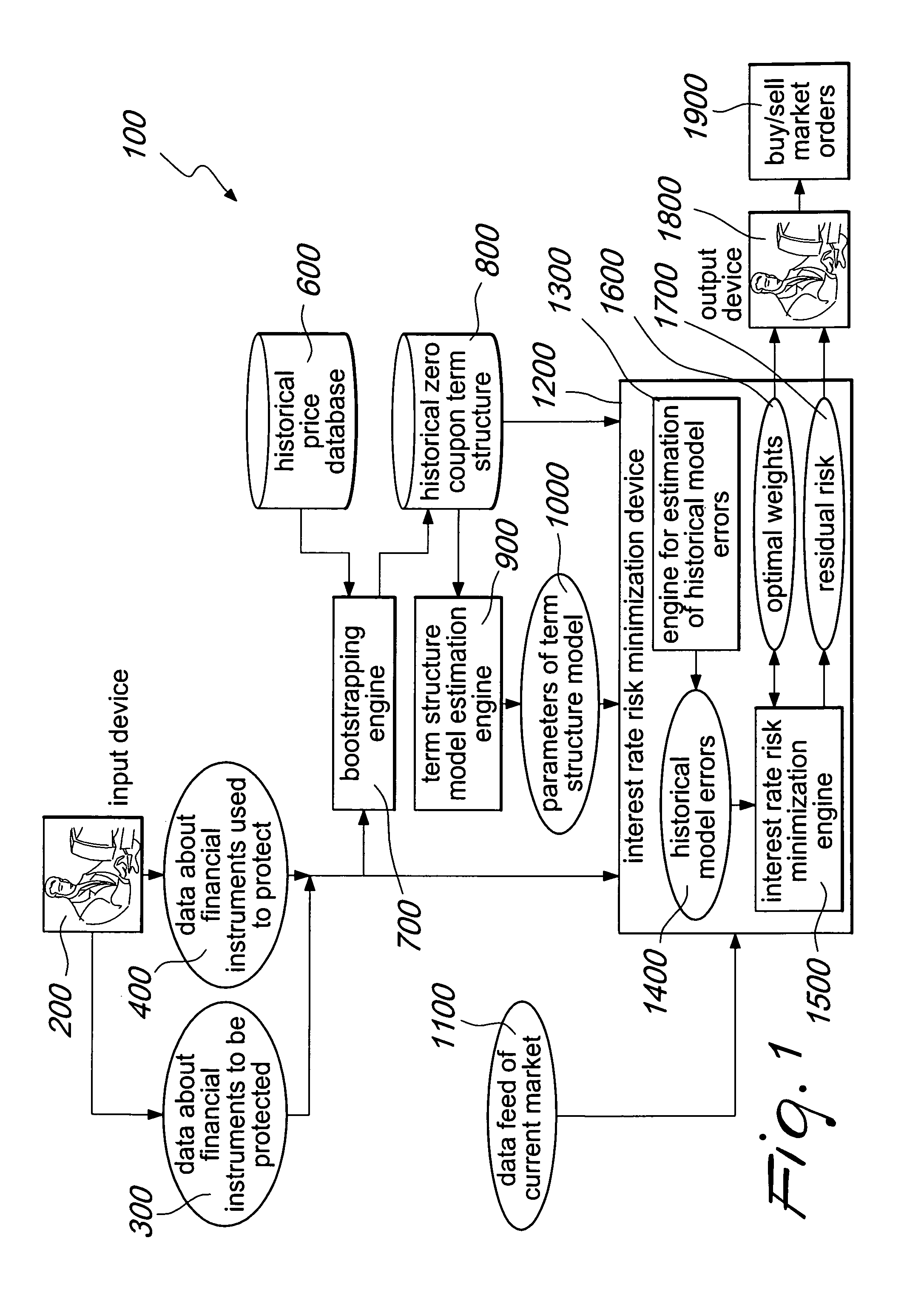
System and method for improving the minimization of the interest rate risk
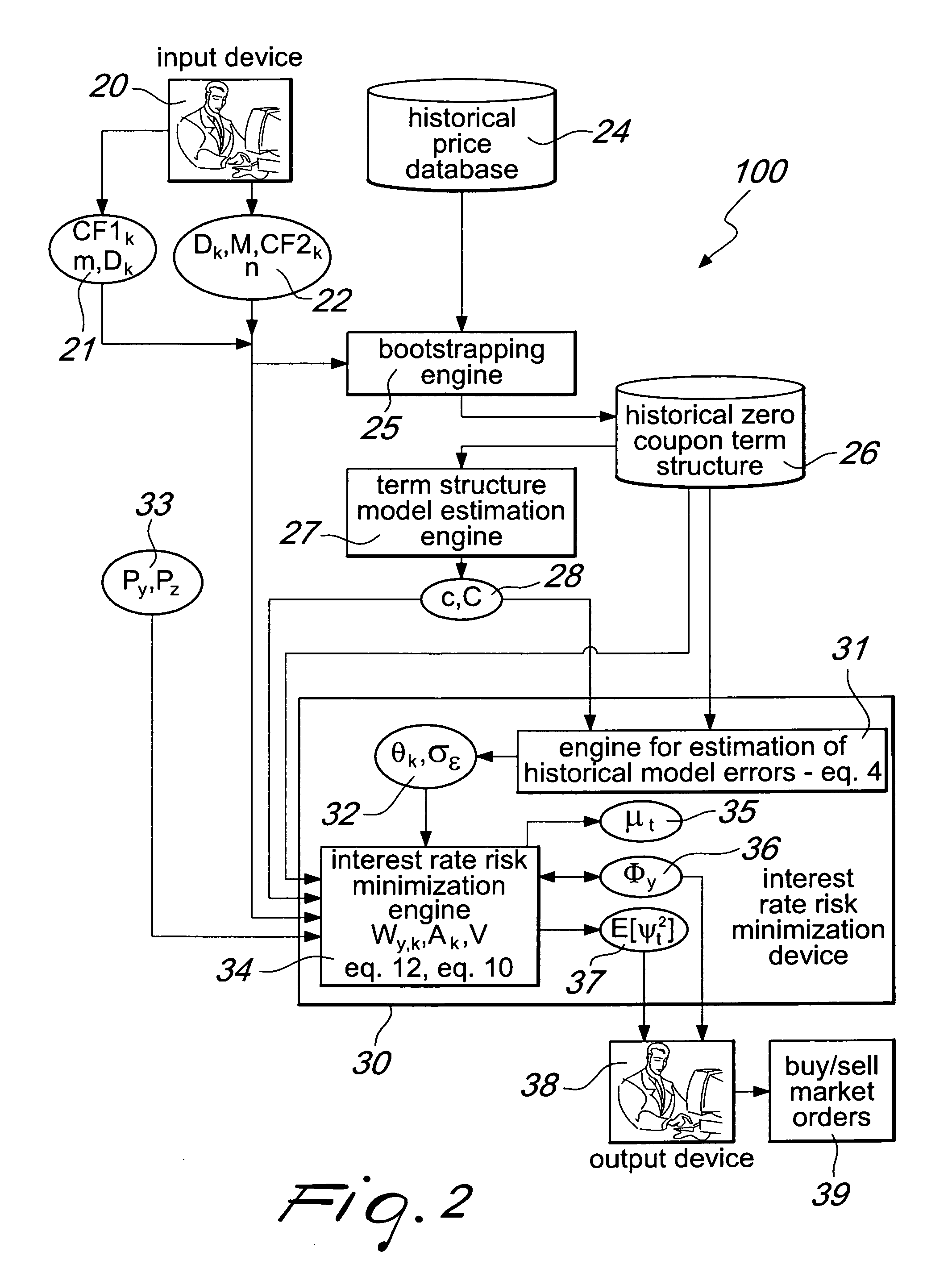
InactiveUS20110029452A1Reduce residual interest rate riskExposure was also limitedFinanceHistorical modelMachine learning
A system for interest rate risk management, comprising: an input device, configured to receive as input a first group of data indicative of a first group of financial instruments to be protected; a second group of data indicative of a second group of financial instruments aimed at protecting said first group of financial instruments; and an interest rate risk minimization device, connected to said input device, configured to receive as input said first and second group of data, a data feed of current market prices of said first and second group of financial instruments, a set of parameters of a term structure model, and historical zero-coupon term structures of interest rates, and to generate historical model errors and, considering these errors, the optimal amount to be invested in each financial instrument which shall be used to protect the balance sheet or portfolio. The interest rate risk minimization device is further configured to generate a residual risk estimation.
Owner:CARCANO NICOLA
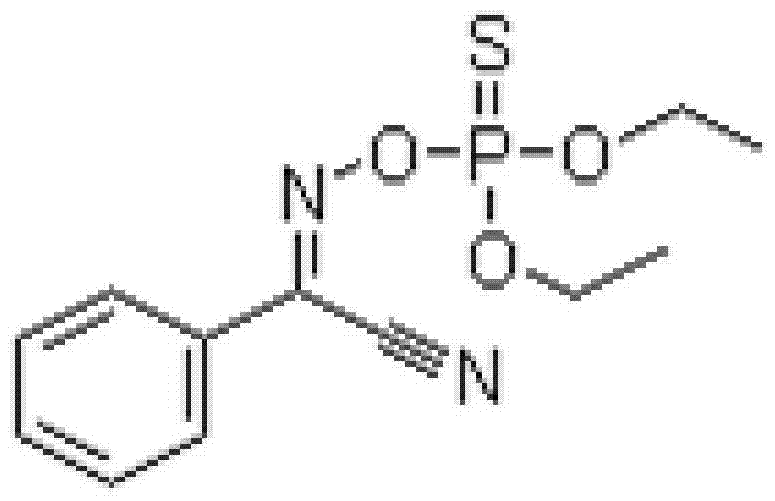
Efficient insecticide containing cypermethrin, phoxim, cyromazine and sulfur-fluorine oxime ether
InactiveCN104255779ABroad insecticidal spectrumStrong knockdownBiocideAnimal repellantsLiriomyza huidobrensisCypermethrin
The invention relates to an efficient insecticide composition used for killing agricultural insects. The efficient insecticide composition is composed of the following components in parts by weight: 20-50 parts of cypermethrin, 30-60 parts of phoxim, 10-40 parts of cyromazine, and 20-40 parts of sulfur-fluorine oxime ether. The efficient insecticide composition has the advantages of wide insecticidal spectrum, strong killing force and no systemic action; the efficient insecticide composition is decomposed rapidly since the efficient insecticide composition is unsteady under lights in a field, so that the residual period is short, and the residual risk is low; the efficient insecticide composition has outstanding killing effects on plutella xylostellas, asparagus caterpillars, cotton bollworms, striped rice borers, mealybugs and flies which mainly include liriomyza sativae, liriomyza huidobrensis, melanagromyza sojae, liriomyza chinensis and liriomyza trifolii.
Owner:QINGDAO RUNXIN WEIYE TECH & TRADE
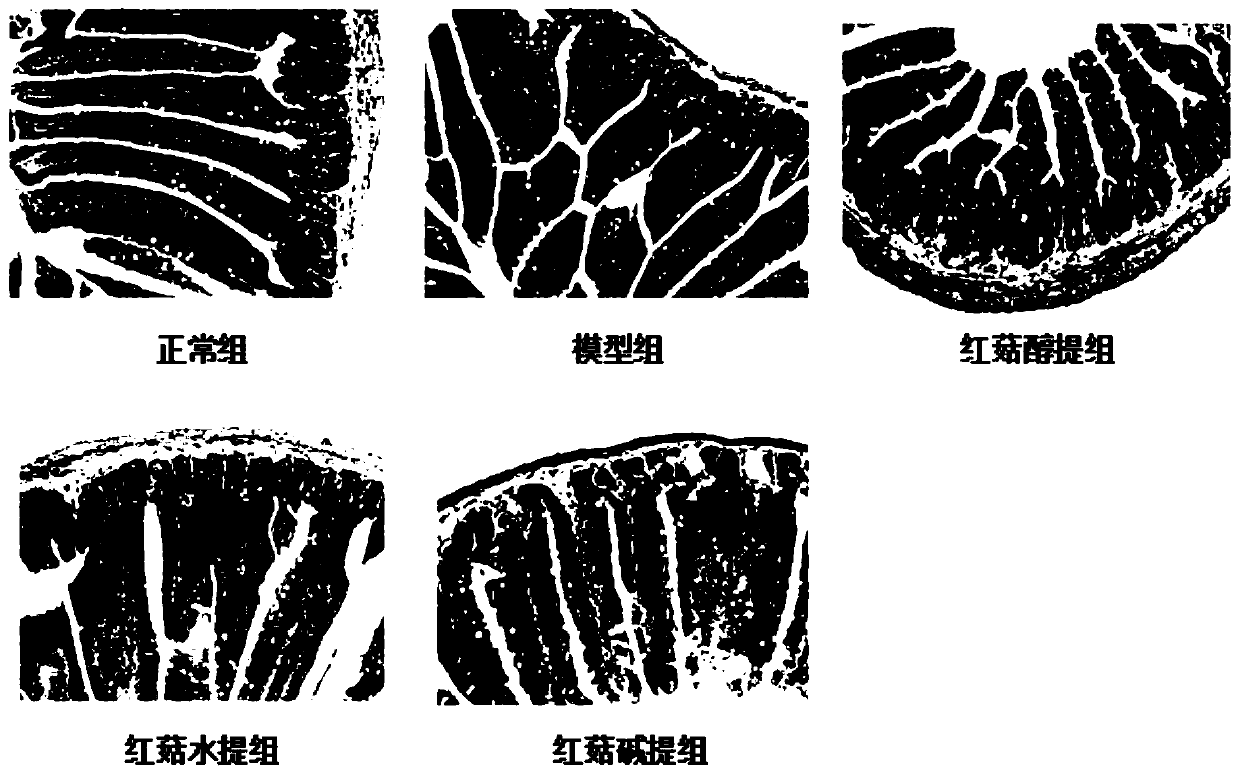
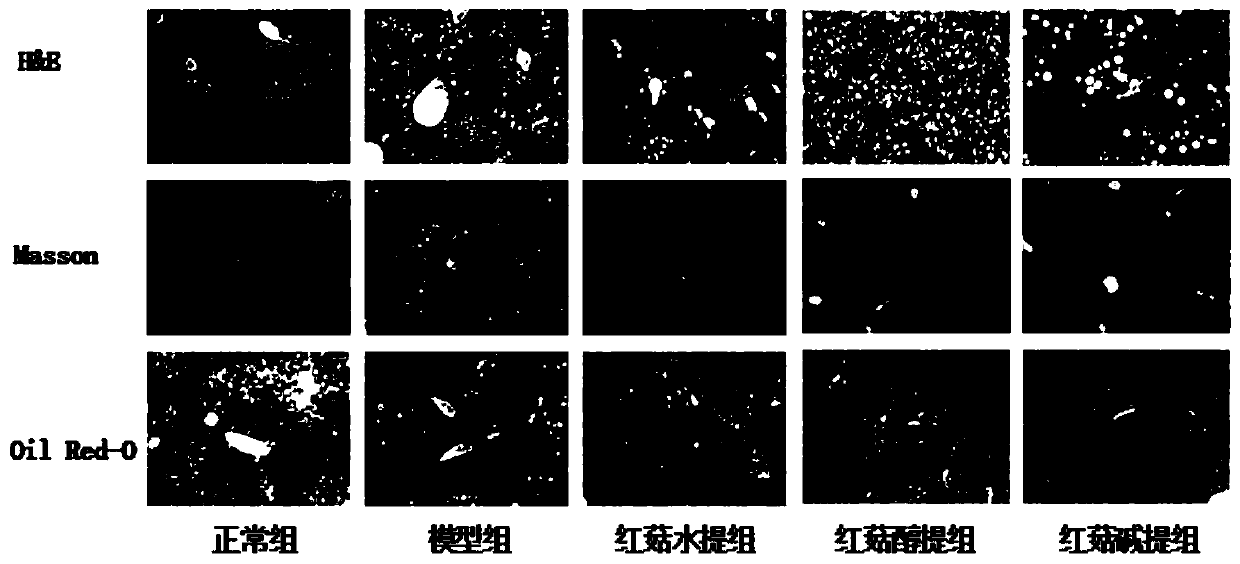
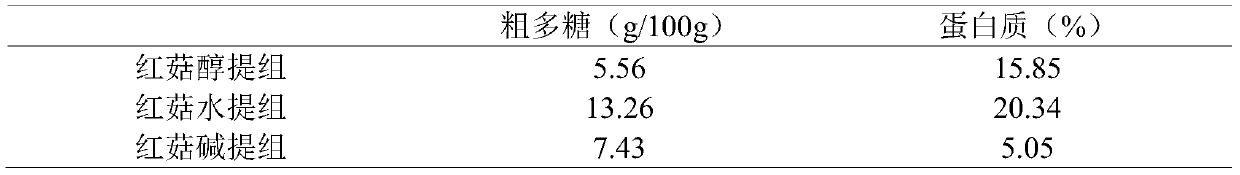
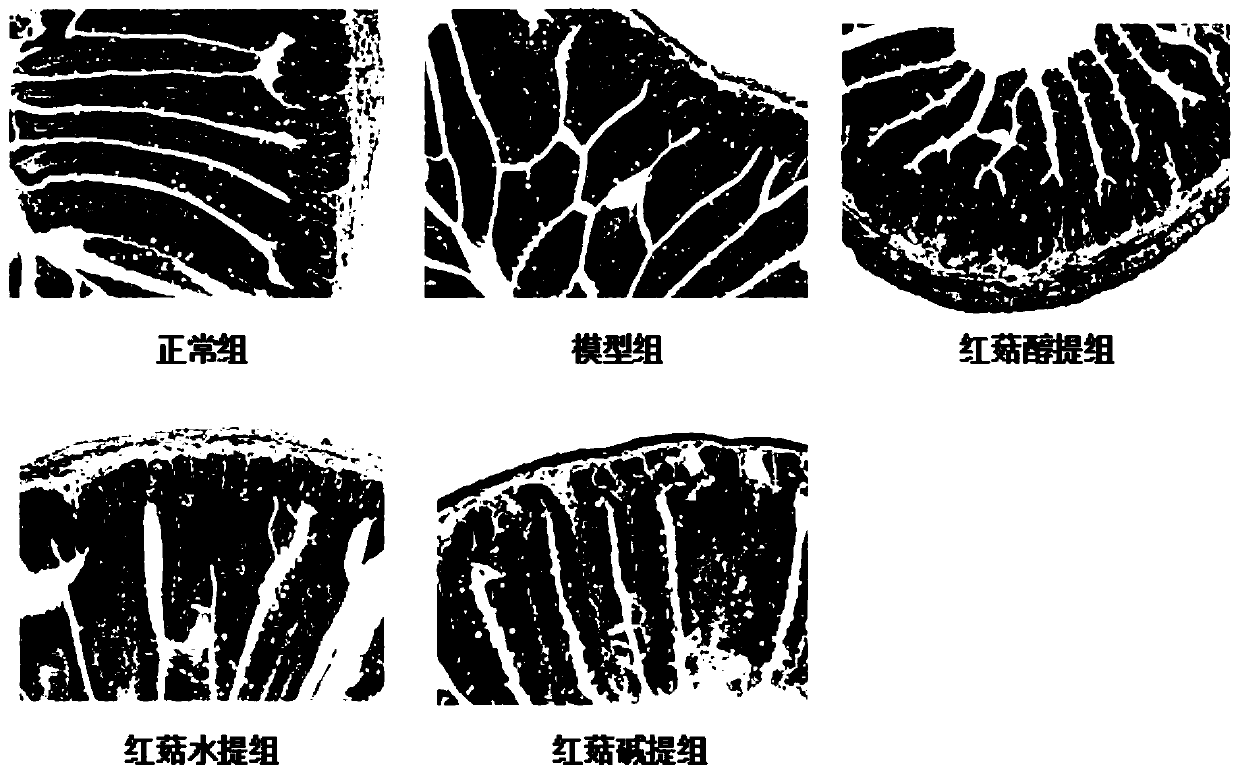
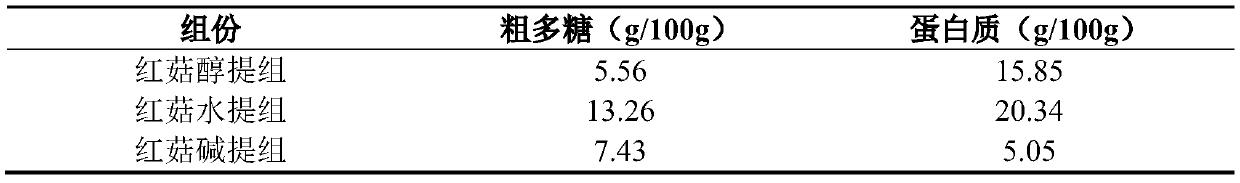
Application of red mushroom extracts in preparing preparation for treating and/ or preventing liver injury related diseases caused by high fat diet
InactiveCN109771457ANo residual riskKeep natural qualityDigestive systemFungi medical ingredientsDiseaseSolvent
The invention relates to an application of an edible fungus extract in preparing a preparation for treating and / or preventing liver injury related diseases caused by a high fat diet, in particular toan application of a red mushroom extract in preparing a preparation for treating and / or preventing liver injury related diseases caused by a high fat diet. The preparation method is simple and feasible, and low in operation cost; and an extraction solvent in the preparation method can be recycled, the residual risk of an organic reagent is avoided, the natural quality of the red mushroom extractis ensured, and the red mushroom extract is environment-friendly, and the method belongs to a green manufacturing technology. According to the invention, the raw materials are completely extracted, the raw materials are fully utilized, and the utilization rate of the raw materials is high on the basis of ensuring the effect of the extract. The red mushroom extract shows obvious treatment and / orprevention effects on liver injury related diseases, for example, the red mushroom extract can effectively relieve the deterioration of inflammation and improve various physiological and pathologicalindexes related to immunity, can be used in various fields such as medicines, health care products and the like, and has great economic and social values.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY +1
Use of russule extract in preparing preparation for treating and/or preventing intestinal flora disorder and related diseases
InactiveCN109758485ANo residual riskKeep natural qualityAntibacterial agentsMetabolism disorderDiseaseMedicine
The invention relates to a use of an edible fungus extract in preparing a preparation for treating and / or preventing intestinal flora disorder and related diseases, in particular to a use of a russuleextract in preparing a preparation for treating and / or preventing the intestinal flora disorder and related diseases. The preparation method is simple and easy to implement and low in operation cost;and an extraction solvent in the preparation method can be recycled, so that the residual risk of an organic reagent is avoided, the natural quality of the ressule extract is ensured, the preparationmethod is environment-friendly, and the preparation method belongs to a green manufacturing technology. According to the invention, the raw materials are completely extracted, the raw materials are fully utilized, and the utilization rate of the raw materials is high. The russule extract not only can obviously contribute to the recovery of the dominant flora structure in a intestinal tract and the diversity of the flora, but also has obvious treatment and / or prevention effects on diseases related to the flora structure of the intestinal tract, can be used in various fields such as medicines,health care products and the like, and has great economic and social values.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY +1
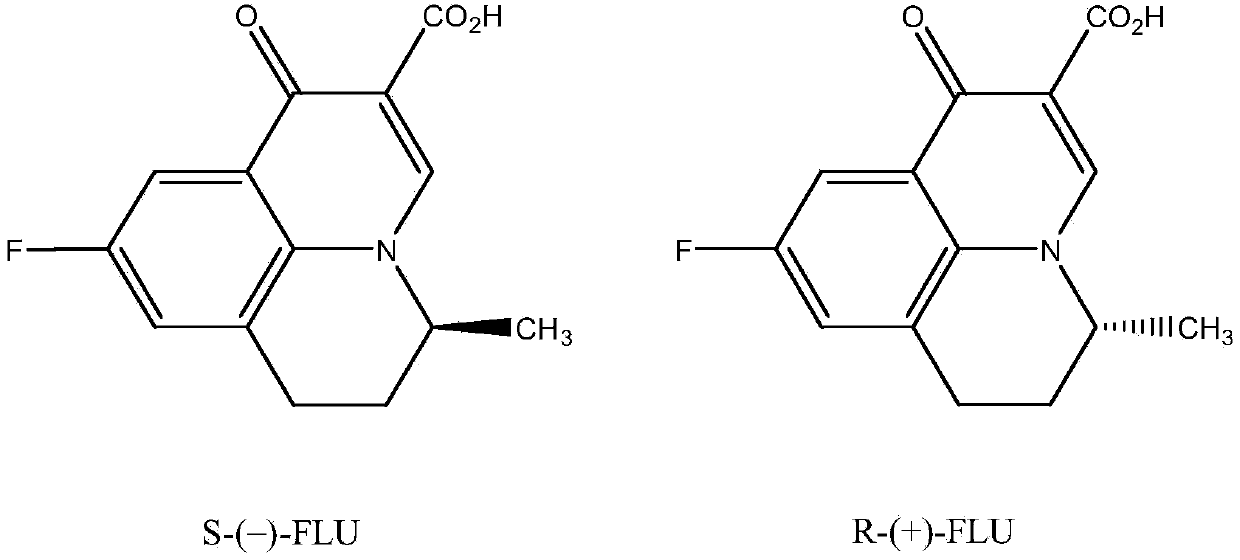
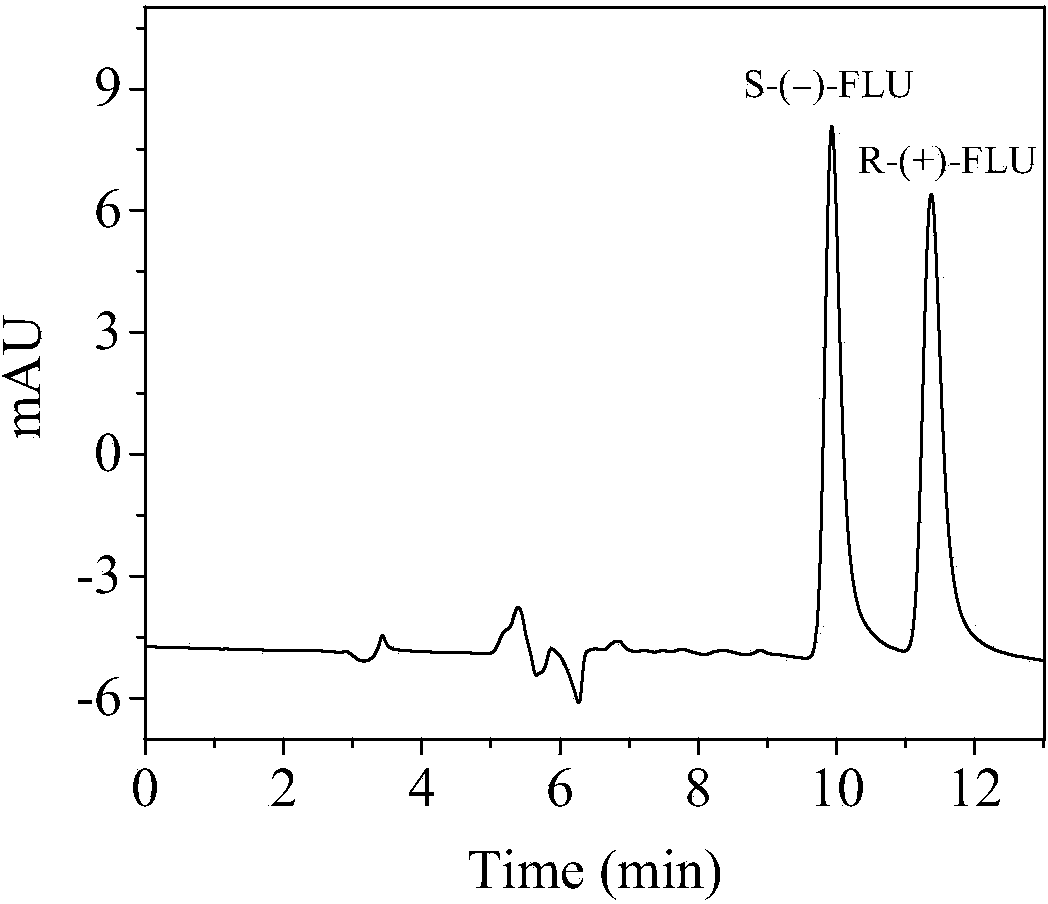
Detection method of flumequine chiral enantiomer in seawater
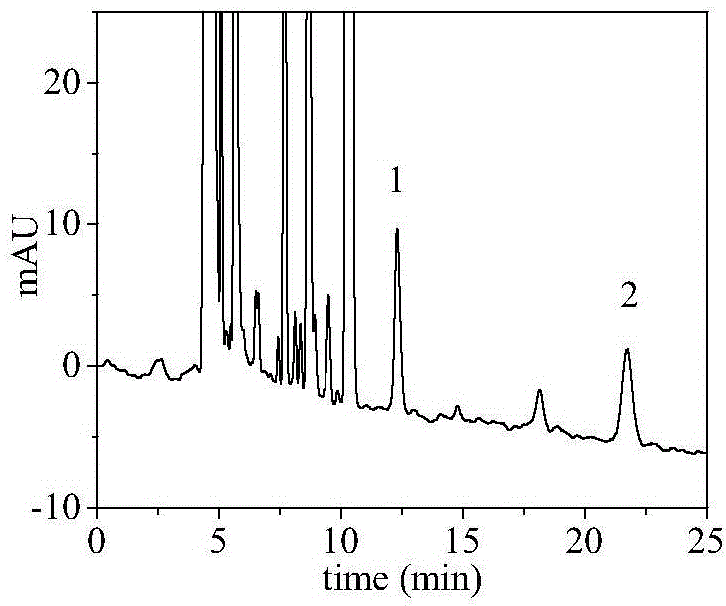
The invention discloses a detection method of a flumequine chiral enantiomer in seawater. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: taking 80-110mL of aquaculture seawater and adding in a beaker, adding 1mg-2mg of flumequine standard substance, performing ultrasonic treatment to completely dissolve the flumequine standard substance, taking 3-5mL of the obtained solution, treating by an HLB solid-phase extraction column, leaching by using 4-6mL of deionized water, and then eluting by using 5-10mL of methanol; nitrogen-blowing the eluent to nearly dry, redissolving by using ethanol, metering volume to 3mL, filtering by a millipore filter membrane with size of 0.22-0.45 micron to obtain a solution A; using n-hexane and ethanol in volume ratio of (10-40): (60-90) as a mobile phase, and adding methanoic acid with volume content of 0.1%-0.3% and ammonium acetate aqueous solution (5mmol / L) in the mobile phase to separate the flumequine chiral enantiomer; detecting the solution A by using high performance liquid chromatograph, wherein a CHIRALCEL OD-H chiral column is adopted, the column temperature is the room temperature, the flow velocity is 0.5mL / min to 0.7mL / min, and the wavelength is 254nm. By adopting the method disclosed by the invention, the flumequine chiral enantiomer can be successfully separated so that the residual quantity of the flumequine chiral enantiomer in the seawater can be detected, and basis is provided for the residual risk assessment and reasonable and safe use of flumequine in the seawater aquaculture.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
Detecting method for trichlorfon enantiomers in culture pond bottom mud
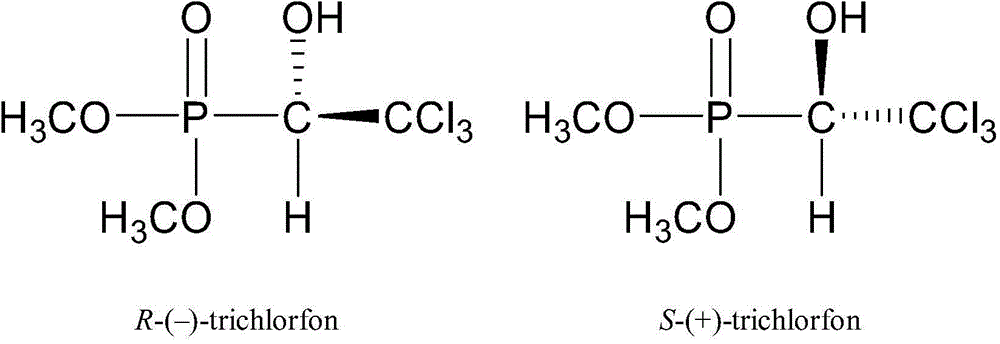
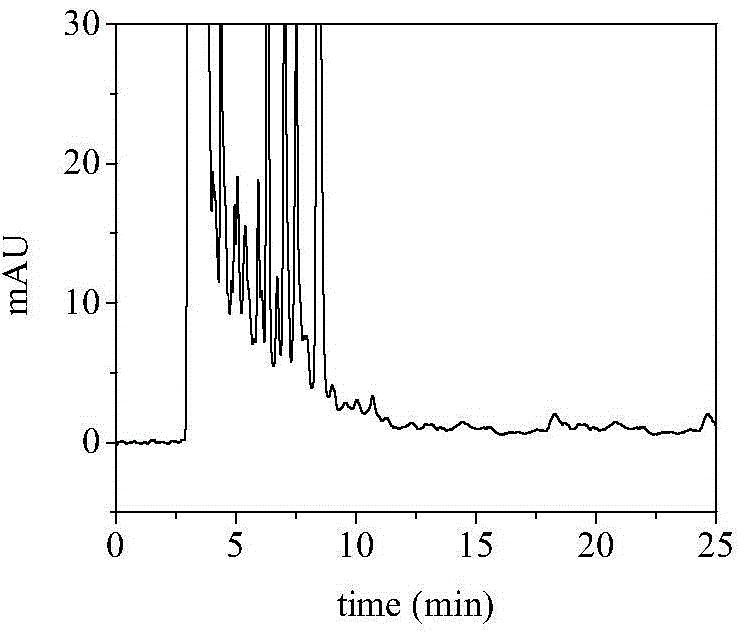
InactiveCN104990998AResidue achievedResidues, successfully realized the resolution of chiral enantiomers of trichlorfonComponent separationWater bathsEnantiomer
A detecting method for trichlorfon enantiomers in culture pond bottom mud includes the steps that a bottom mud sample is placed into a centrifugal tube, anhydrous sodium sulfate is added to remove water, acetic acid is added to acidize acetonitrile, centrifuging is performed after ultrasonic extraction is performed, an upper layer extracting solution is taken into a flask, the extracting process is repeated 2-3 times, extracting solutions are mixed, the mixed solution is subjected to rotary evaporation and concentration in a water bath at 27 DEG C, a concentrated solution is added into CARB / NH2 cartridges activated in advance, the acetonitrile is used for flushing the flask, flushing liquid passes through the CARB / NH2 cartridges, outflow liquid is collected, and the CARB / NH2 cartridges are blown through nitrogen to be almost dry, hexyl hydride / isopropanol is used for performing redissolving and volume constancy on the liquid to 1 mL, and then the liquid passes through a microporous filtering film of 0.22 micrometer to obtain a solution A; with the hexyl hydride / isopropanol being a moving phase, separation is performed on the trichlorfon enantiomers; a high-performance liquid chromatograph is used for detecting the solution A, (as shown in specifications) IC chiral columns are selected for usage, the temperature of the columns is 25 DEG C, the flow rate is 1 mL / min, and the wavelength is 207 nm. The trichlorfon chiral enantimoers can be successfully separated, in this way, the residual quantity of the trichlorfon enantiomers in the bottom mud is detected, and bases are provided for residual risk estimation and reasonable and safe using of trichlorfon in bottom mud culture.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
Operational risk back-testing process using quantitative methods
Methods, computer-readable media, and apparatuses are disclosed for quantifying risk and control assessments. The risk includes both residual risk and direction of risk. Various aspects of the invention quantitatively compare the risk and control assessments against step-ahead losses using special regression models that are particularly applicable to this kind of data. The empirical comparison may be performed on both loss event frequency and severity in two different and separate dimensions. The empirical comparison may also be performed using losses extracted by even occurrence and event settlement dates in two separate dates.
Owner:BANK OF AMERICA CORP
Usage of baicalin for preparing pharmaceuticals for preventing and treating aquatic livestock streptococcicosis
InactiveCN108066352ANo direct killing effectNo chance of resistance mutationAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsSide effectBacterial disease
The invention belongs to the field of the bacterial disease control and prevention of the aquatic livestock, and relates to a usage of baicalin for preparing pharmaceuticals for preventing and treating aquatic livestock streptococcicosis, and discloses a usage of the baicalin for inhibiting activity of tilapia-sourced streptococcus agalactiae Beta-hemolysis / cytolysin. The baicalin is applied for preparing the pharmaceuticals for preventing and treating the bacteriosis of aquatic culture animals, especially the prevention and control pharmaceuticals for tilapia streptococcus diseases, and the pharmaceuticals have the remarkable curative effect. The baicalin is a flavonoid active ingredient extracted and separated from dried roots of dicotyledonous labiate scutellaria baicalensis, and is developed as a new drug for preventing and treating the tilapia-sourced streptococcus. The baicalin has the advantages of abundant sources, low cost, low drug resistance probability, low residual risk, small toxic and side effect, environment-friendliness, no pollution, no harm and remarkable curative effect, and has the extensive application prospect.
Owner:HAINAN UNIVERSITY
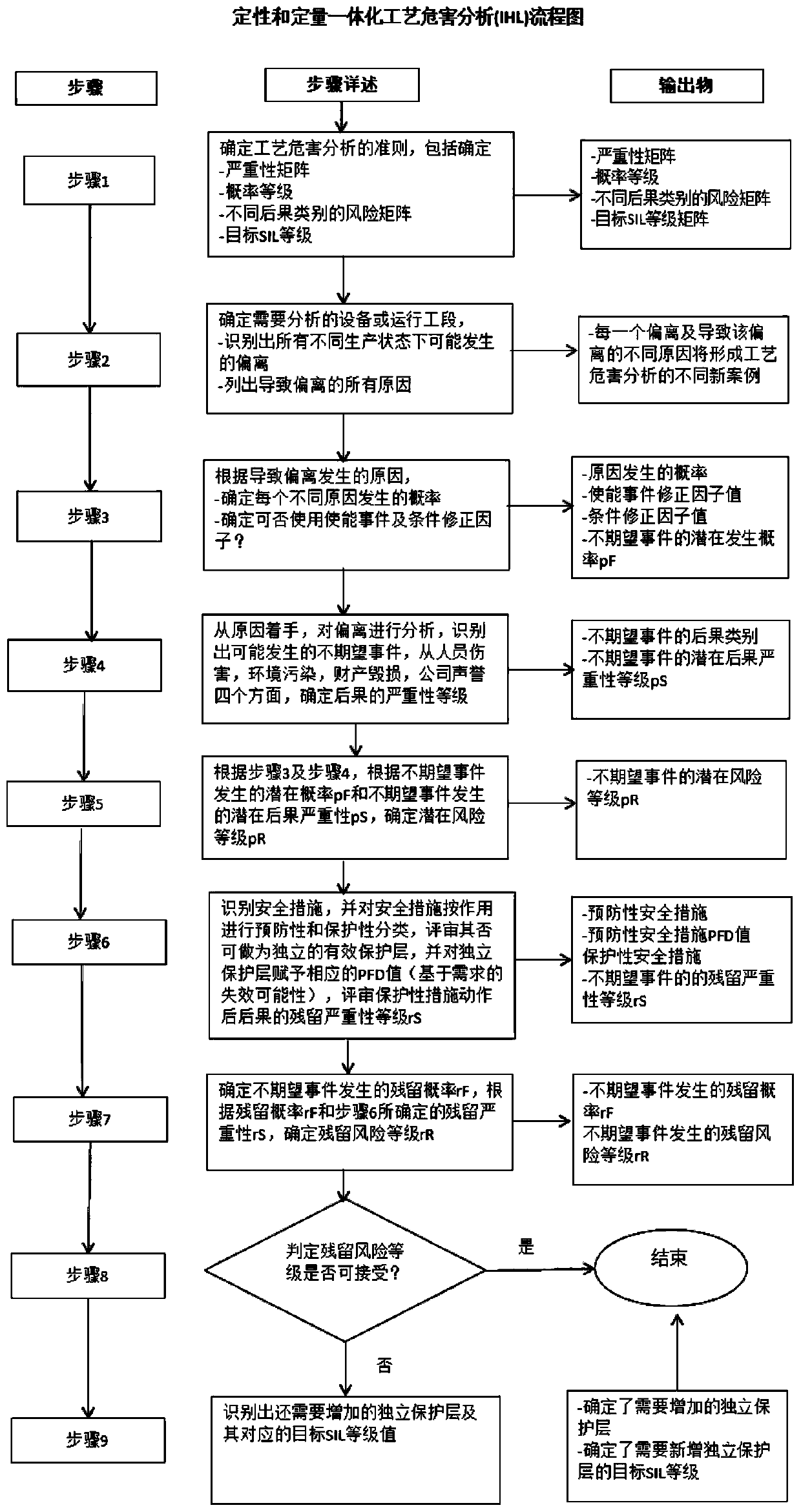
Integrated process hazard analysis method and system and storage medium
The invention discloses an integrated process hazard analysis method, an integrated process hazard analysis system and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring reasons causing deviation and causing deviation in different production states; correcting and calculating the potential probability of the unexpected event according to the probability of a deviation reason, anenabling event and condition; generating a consequence severity level of the unexpected event according to the reason of the deviation and the consequence severity matrix; performing preventive measure action on the unexpected event according to the potential risk level; obtaining the residual probability of the unexpected event after the preventive measure action is implemented; performing protective measure action on the unexpected event according to the potential risk level; obtaining the severity level of the residual consequence of the unexpected event after the protective measure actionis implemented; and generating a residual risk level according to the residual probability of the unexpected event, the residual consequence severity and the risk matrix. The defects of a traditionalanalysis method are effectively avoided.
Owner:顾敏
Designation Of A Vendor Manager
InactiveUS20150242775A1Disadvantages can be reduced eliminatedProblems be reduced eliminatedFinanceResourcesEngineeringRisk element
Determining vendor management requirements comprises identifying a plurality of risk elements associated with a vendor that supplies one or more products to an entity. Any completed management actions for the vendor that mitigate risk associated with any of the identified risk elements are identified. A residual risk is determined for at least one of the identified risk elements according to a completed management action that reduces risk associated with the at least one of the identified risk elements. A determination is made as to whether to assign a vendor manager to the vendor according to the residual risk for the at least one of the identified risk elements.
Owner:BANK OF AMERICA CORP
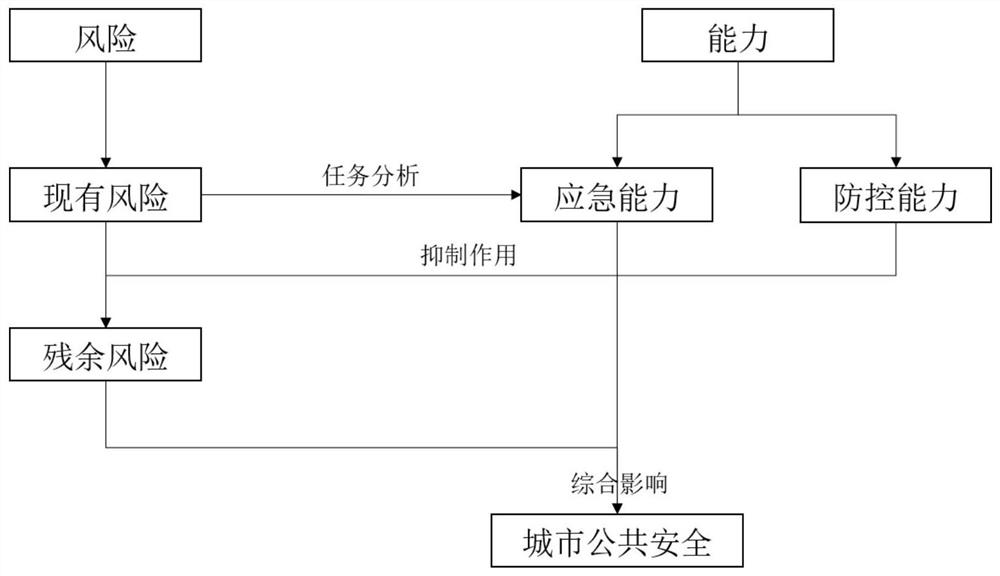
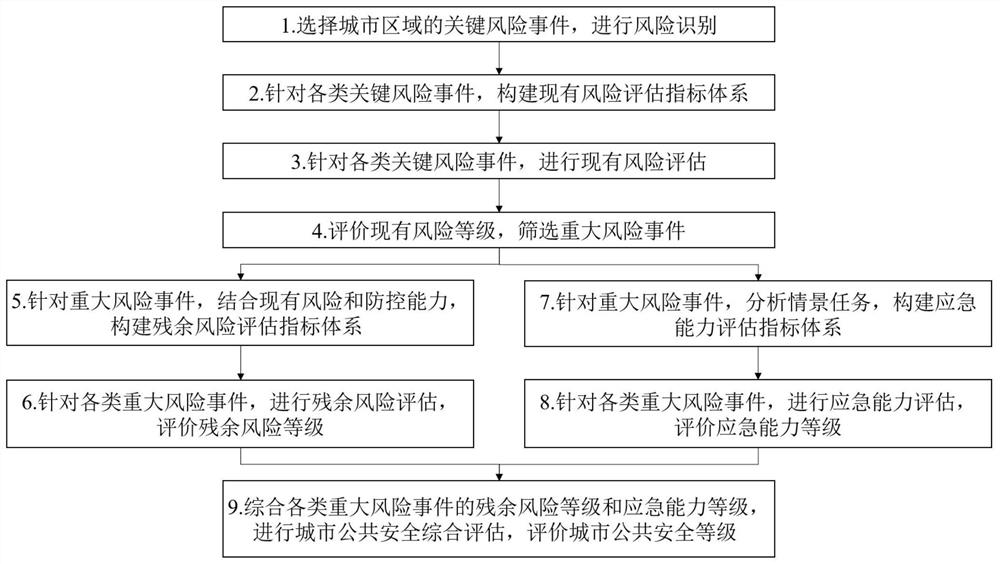
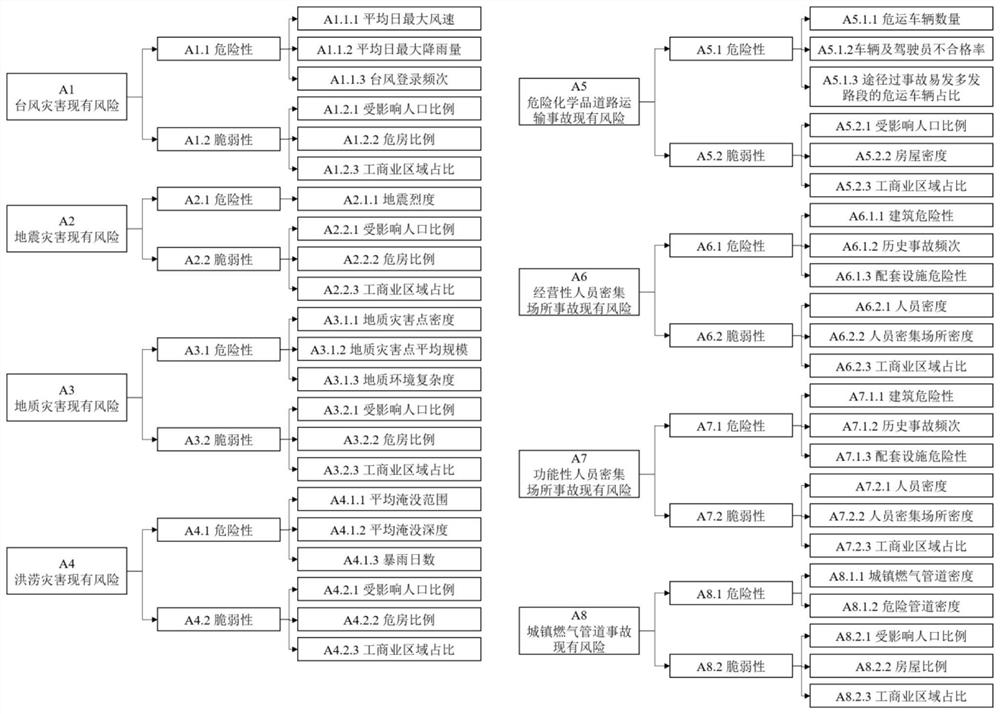
Urban public safety evaluation method based on risk and capability
The invention discloses an urban public safety evaluation method based on risk and capability, which divides urban public safety evaluation into four stages of existing risk evaluation, residual risk evaluation, emergency capability evaluation and urban public safety evaluation. The method considers the inhibition effect of the capability on the risk and the comprehensive influence effect of the capability and the risk on the urban public safety, carries out the existing risk evaluation, screens major risk event scenes, evaluates the residual risk in combination with the prevention and control capability, analyzes the scene task, evaluates the emergency capability, and carries out the safety evaluation based on the staggered influence of the risk and the capability. And comprehensively evaluating the urban public safety level. According to the embodiment of the invention, different management perspectives and different evaluation perspectives of the urban public safety are effectively fused, the inhibition effect of the capability on the risk and the comprehensive influence effect of the risk and the capability on the urban public safety are reflected, and systematic analysis and comprehensive evaluation of the urban public safety can be realized.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
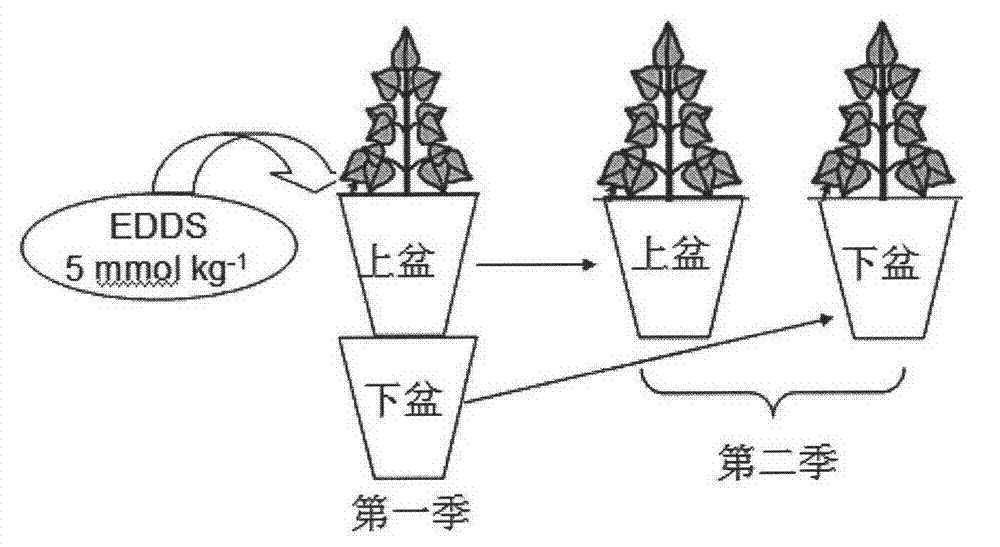
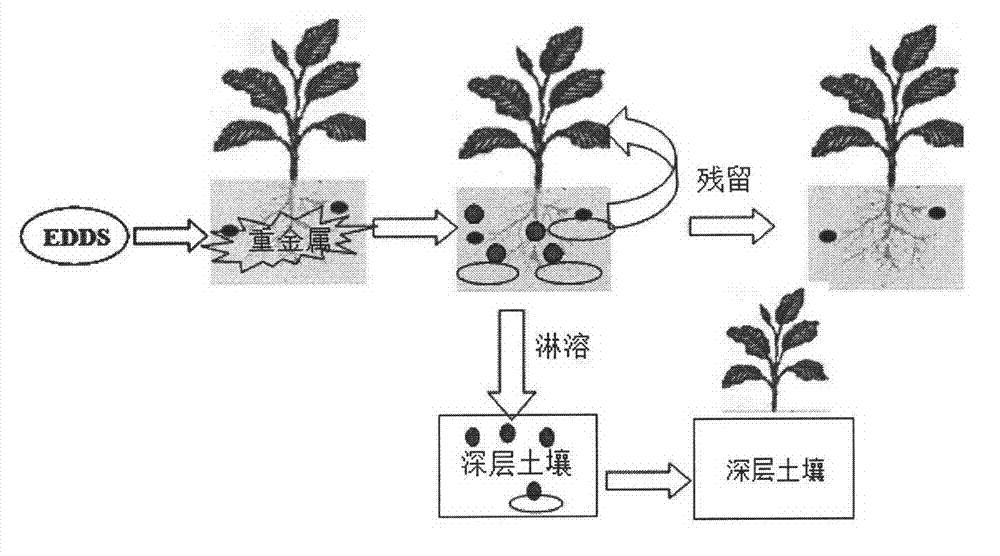
Residual and leaching risk evaluation technology of chelate-induced phytoremediation in heavy-metal contaminated soil
InactiveCN102921716AEasy plantingAccurate risk assessmentContaminated soil reclamationDestructive samplingMetal contamination
The invention belongs to the field of an evaluation technology of environmental pollution treatment, and relates to a leaching and residual risk evaluation technology of chelate-induced phytoremediation in heavy-metal contaminated soil. The technology provided by the invention is characterized by overlapping two pots up and down to simulate the soil at different depths, planting plants and analyzing the soil sample to precisely and conveniently evaluate a residual effect caused by using a chelating agent and the leaching risk on the soil on the lower layer. The design provided by the invention is capable of overcoming shortcomings of destructive sampling of traditional soil column experiments, conveniently simulating the soil on the deep layer to plant the plants and perform sample analysis. The invention provides a direct and reliable evaluation method for evaluating the residual effect of the chelating agent and the leaching risk in the chelate-induced phytoremediation process.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
System and method for improving the minimization of the interest rate risk
InactiveUS20130238529A1Reduce residual interest rate riskExposure was also limitedFinanceHistorical modelMachine learning
Owner:CARCANO NICOLA
Testing process
InactiveUS20120253685A1Health-index calculationMedical automated diagnosisPregnancyClinical psychology
A method of determining an inclusive residual risk that a pregnancy is affected by at least one phenotypic disorder included in a disorder set is provided. The method includes calculating a prior risk for a disorder set, calculating posterior risks for the individual disorders or groups of disorders in the disorder set that can be screened for and / or diagnosed prenatally, and calculating an inclusive residual risk for the disorder set by combining the prior risks for disorders for which no tests have been performed and the individual posterior risks.
Owner:PERGAMENT EUGENE +3
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com