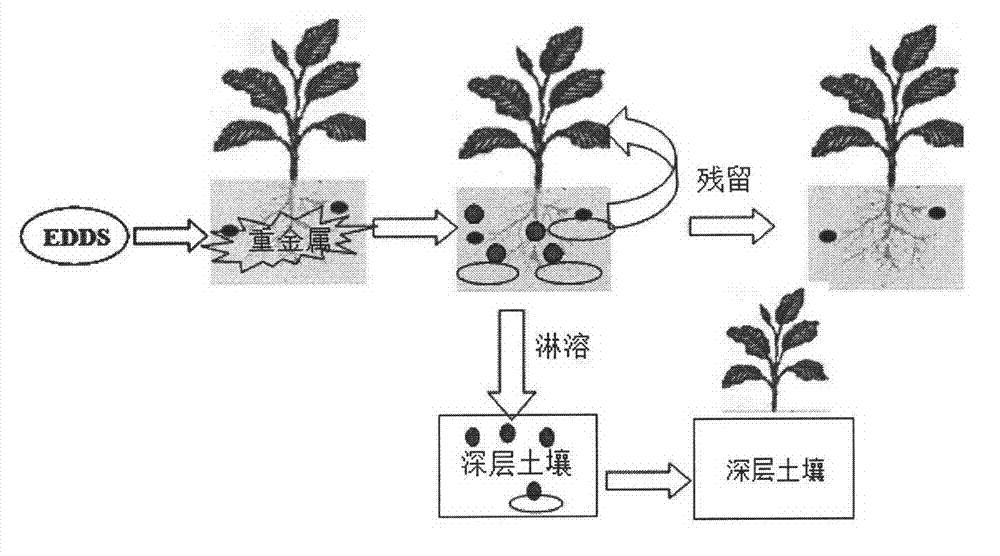
Residual and leaching risk evaluation technology of chelate-induced phytoremediation in heavy-metal contaminated soil
A technology for inducing plants and polluted soil, which is applied in the field of risk assessment of chelation-induced phytoremediation technology, and can solve the problems that there are no research reports on plant evaluation methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0008] Example 1: Experimental Design
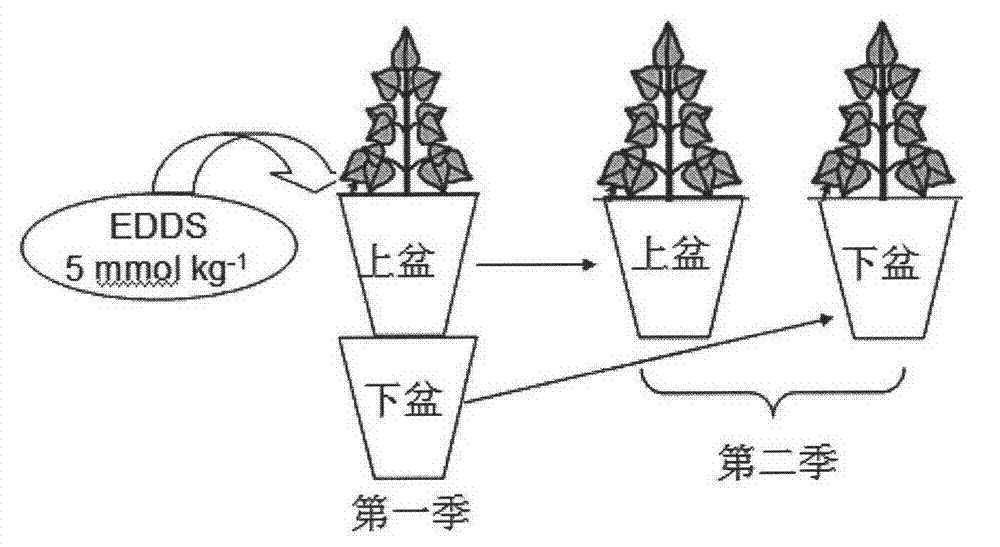
[0009] One pot was stacked on top of the other to simulate different depths of soil, and each pot contained 1.0 kg of heavy metal-contaminated soil (air-dried weight). The total copper content of the test soil is 453mgkg -1 , After the soil is naturally air-dried, pass through a 2mm sieve. Take no plants and no plants with EDDS as control, and monocot ryegrass and dicotyledon Chrysanthemum chrysanthemum with EDDS and no EDDS as treatments. Experimental design see figure 1 .
[0010] The first season: plant Chrysanthemum chrysanthemum and ryegrass in upper pots, and apply EDDS treatment after the seedlings grow for 42 days. The amount of EDDS applied is 5mmol kg -1 . On the 3rd and 4th days after the EDDS treatment, 200ml deionized water (equivalent to 15mm precipitation) was used to simulate a large amount of precipitation and poured into the soil of the upper pot, and the lower pot was poured with the solution. The seedlings were...
Embodiment 2
[0013] Embodiment 2: Harvested plant measures relevant index
[0014] 1. The effect of applying EDDS treatment on the biomass of upper and lower potted plants
[0015] When the plants were harvested, the shoots and roots were separated, dried at 80°C, and the dry weight was measured. In the first season without EDDS treatment, the two plants could grow normally and did not show obvious symptoms of heavy metal toxicity. And 5mmol Kg -1 The EDDS treatment had obvious toxic effects on Chrysanthemum chrysanthemum. The dry weight of aboveground part of Chrysanthemum Chrysanthemum treated with EDDS decreased by 30% compared with the control (without EDDS), which was a significant difference. However, the same amount of EDDS had no obvious toxic effect on the upper part of the ryegrass. There was no significant difference in dry weight of ryegrass shoots treated with EDDS compared with the control. The shoot dry weight of the two plants treated with EDDS in the first season was ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com