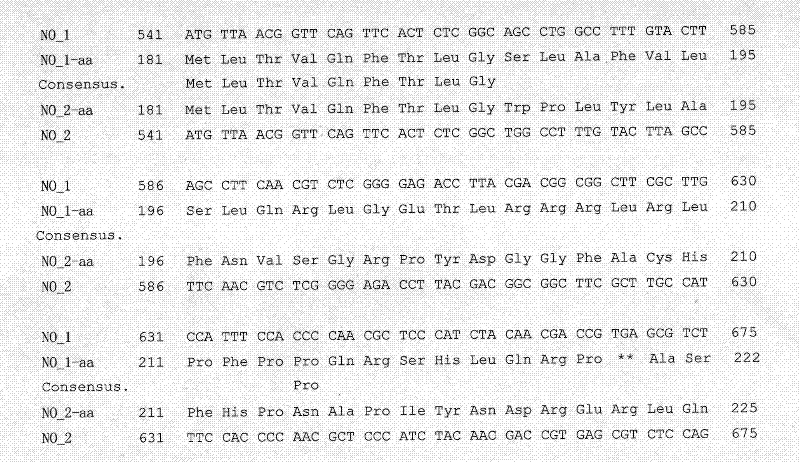Patents
Literature
71results about How to "Reduce breeding workload" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
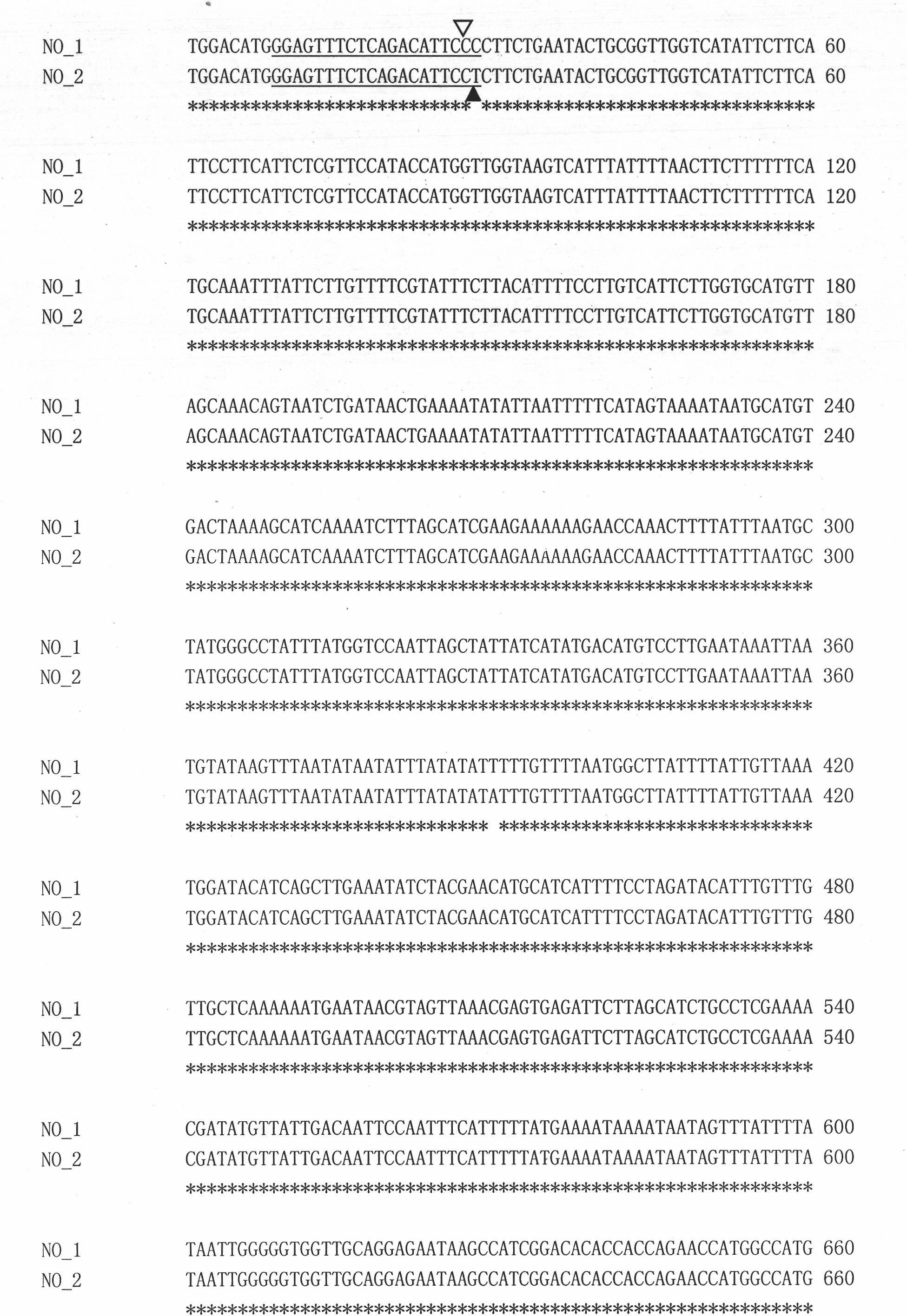
Specific molecular markers of related genes of brassica napus grain weight and application thereof
InactiveCN101962640ASpeed up the processOvercome the downside of choosingMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationAgricultural scienceCandidate Gene Association Study
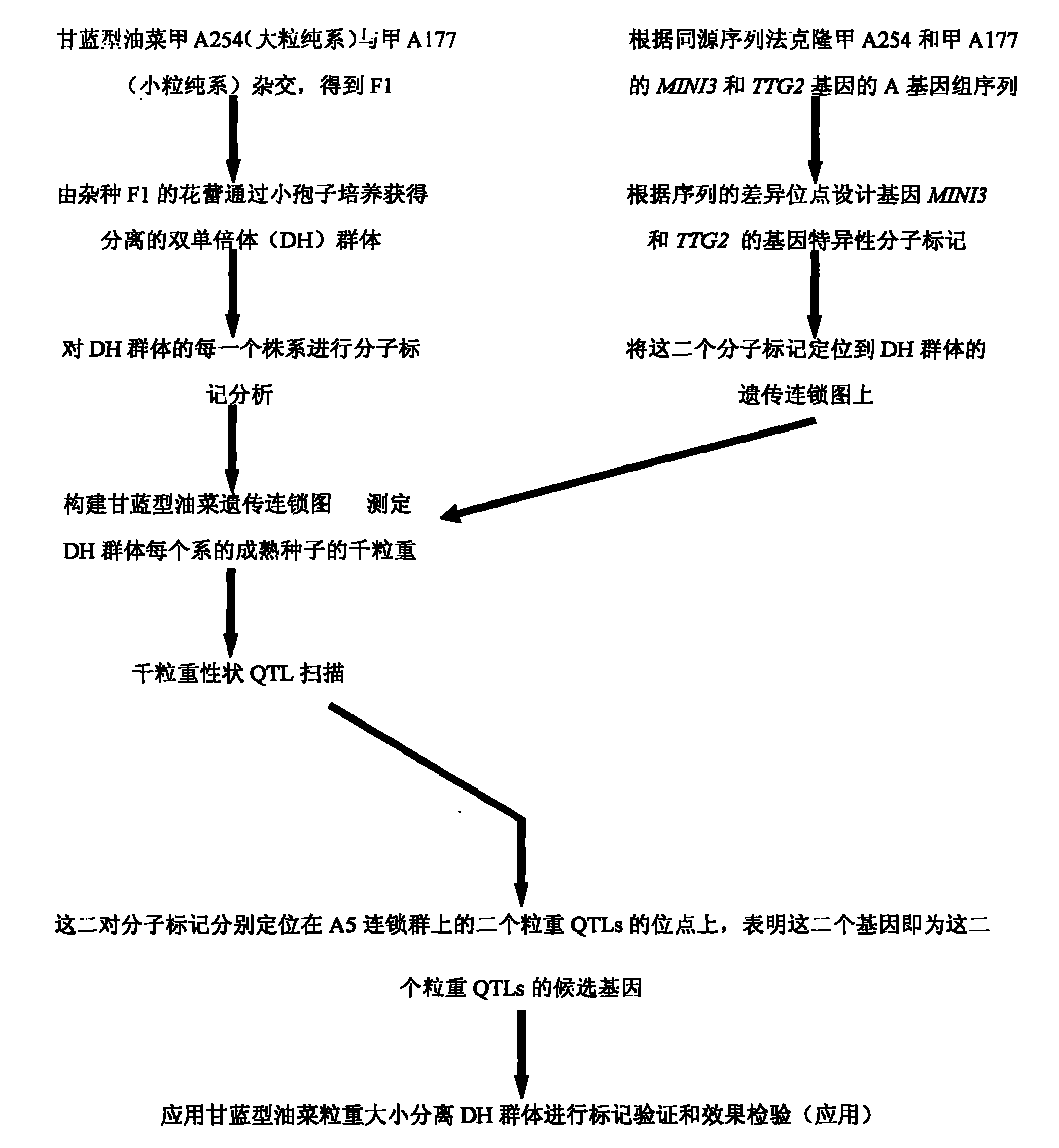
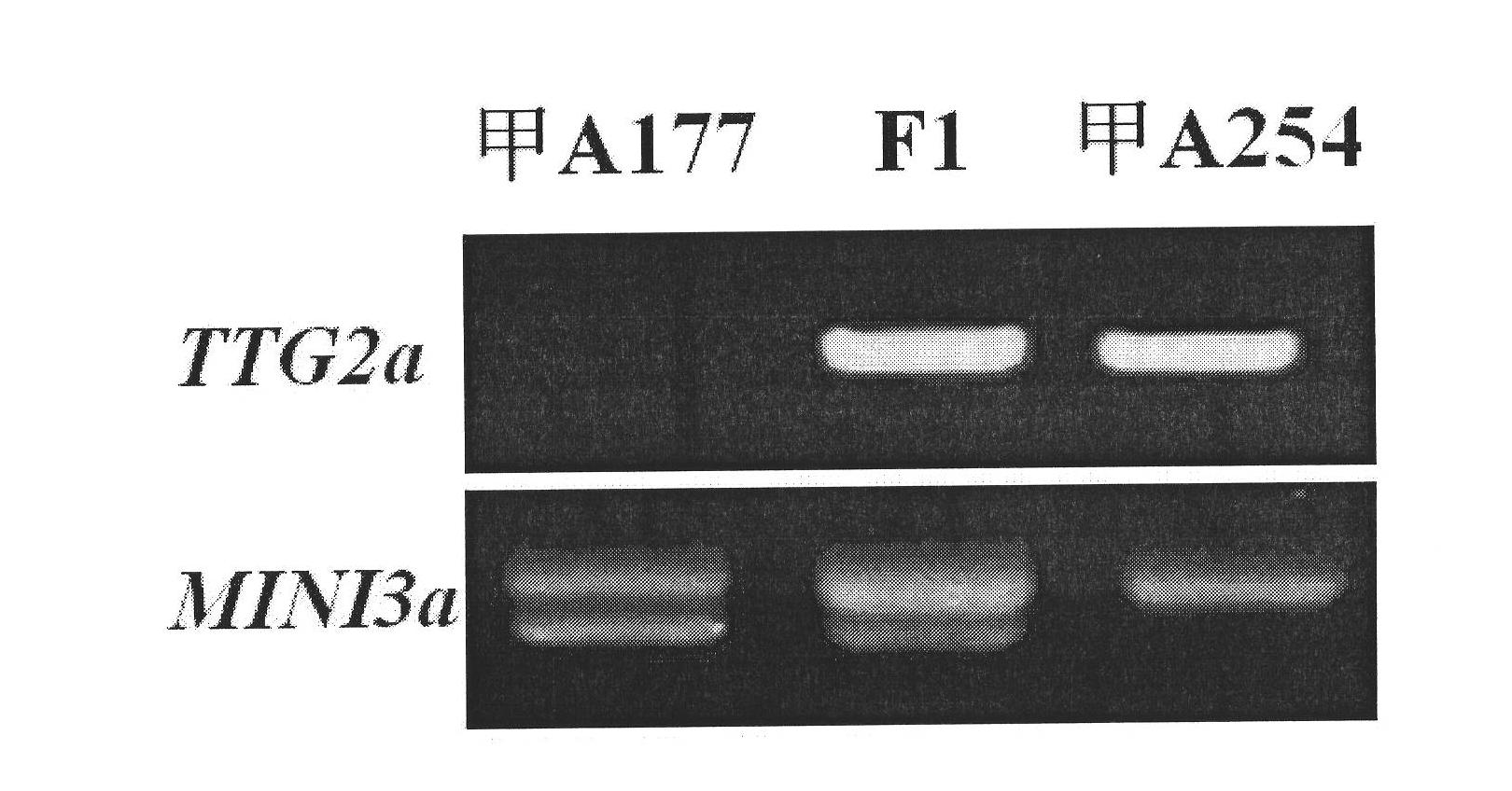
The invention belongs to the field of rape molecular breeding, and relates to preparation of specific molecular markers of related genes MINI3 and TTG2 of the brassica napus grain weight. Double haploid colony (DH) is constructed with brassica napus I A 254 as a female parent and a brassica napus I A 177 as a male parent through hybridization, and the DH colony genotype and the thousand seed weight data are analyzed to obtain a QTLs locus of grain weight character. The MINI3 and the TTG2 genes of the IA254 and the IA177 are cloned by using a homology based candidate gene method, specific molecular markers MINI3a and TTG2a of the MINI3 and the TTG2 genes are designed according to sequence different locuses, and the molecular markers MINI3a and TTG2a are located on two grain weight QTLs locus of an A5 linkage colony for related verification and application, which proves that the molecular marker prepared by the invention is a novel genetic marker. The gene sequence is obtained firstly. The invention provides a novel marker for the molecular breeding of the brassica napus grain weight, and also provides useful information for candidate gene clone and marker auxiliary selection of thethousand seed weight character locuses of the brassica napus.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Molecular marker closely linked with oil content QTL of cabbage type rape
ActiveCN105505925AImproved screening efficiency for oil content traitsImprove screening efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceNucleotide sequencing
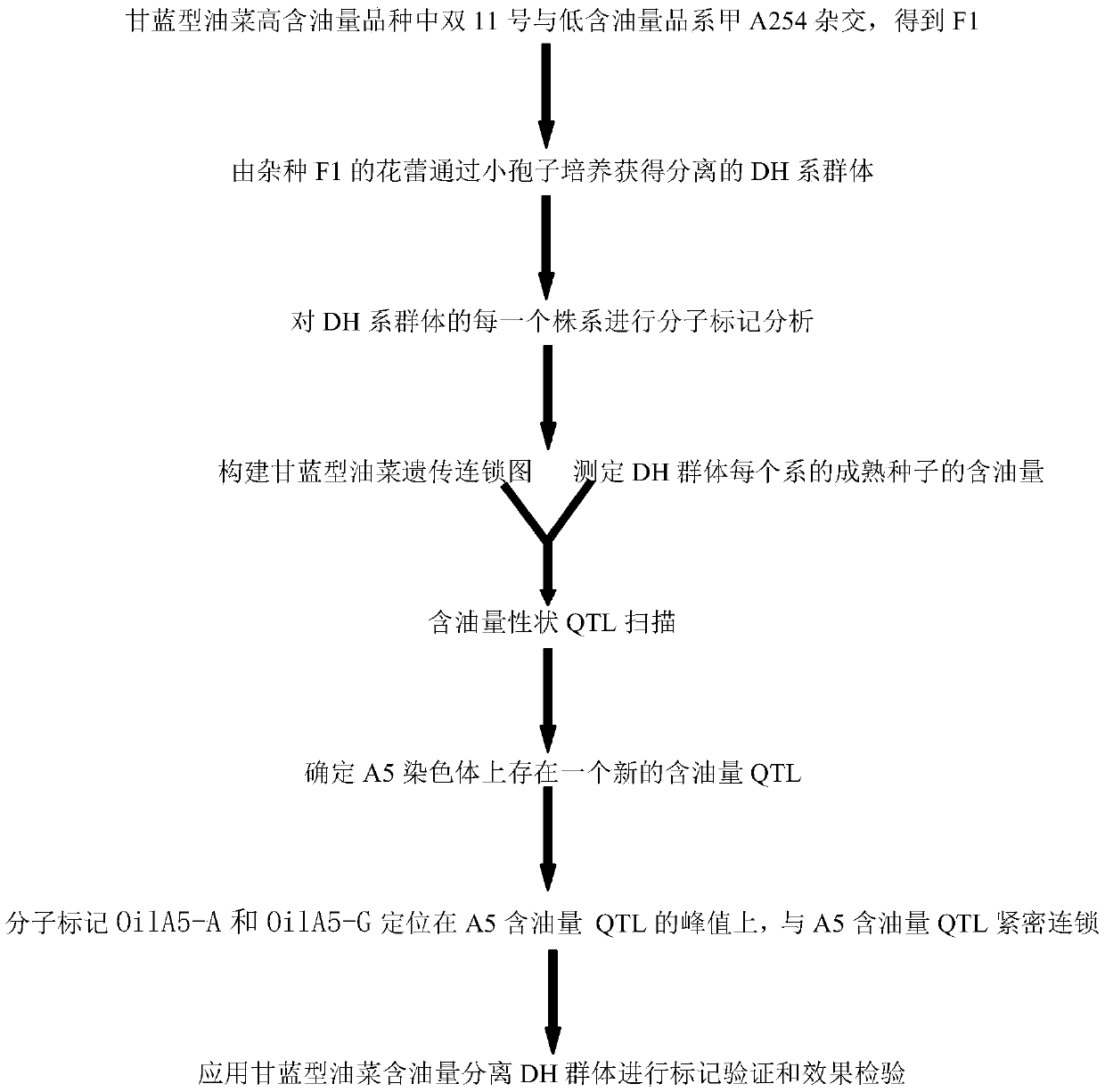
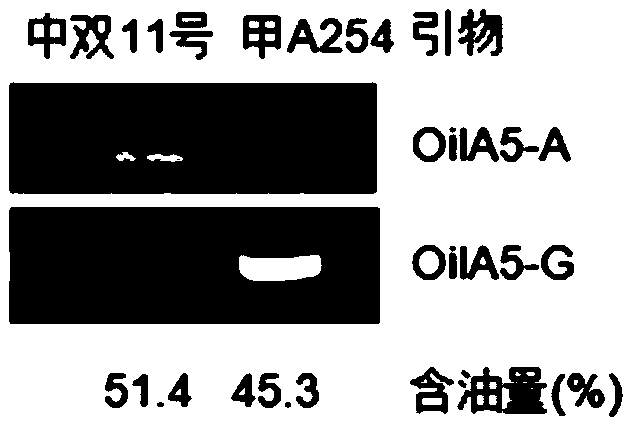
The invention belongs to the technical field of rape molecular marker preparation, and particularly relates to a molecular marker closely linked with the oil content QTL of cabbage type rape. The novel molecular marker OilA5 which is closely linked with the oil content QTL and can be used independently or / and used in combination is obtained through screening, and the nucleotide sequence of the molecular marker is shown in the sequence table SEQ ID NO:5 or 6. A primer pair OilA5-A and a primer pair OilA5-G for detecting the molecular marker OilA5 are constructed, and the nucleotide sequences of the primer pairs are shown in the sequence tables SEQ ID NO:1-4. The molecular marker can be applied to molecular marker auxiliary selection in cabbage type rape oil content character improvement and fine mapping and map-based cloning of oil content character sites.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Brassica napus L. grain weight major QTLs molecular marker and application thereof
InactiveCN102021235ASpeed up the processReduce breeding workloadMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationBrassicaGrain weight
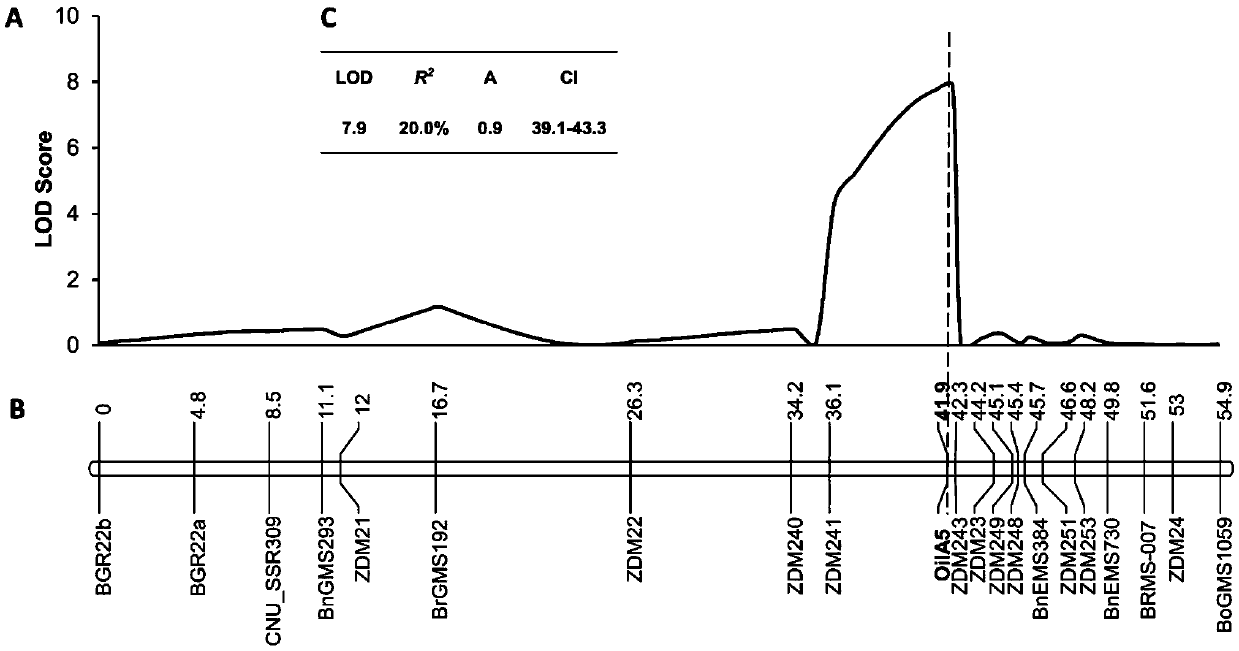
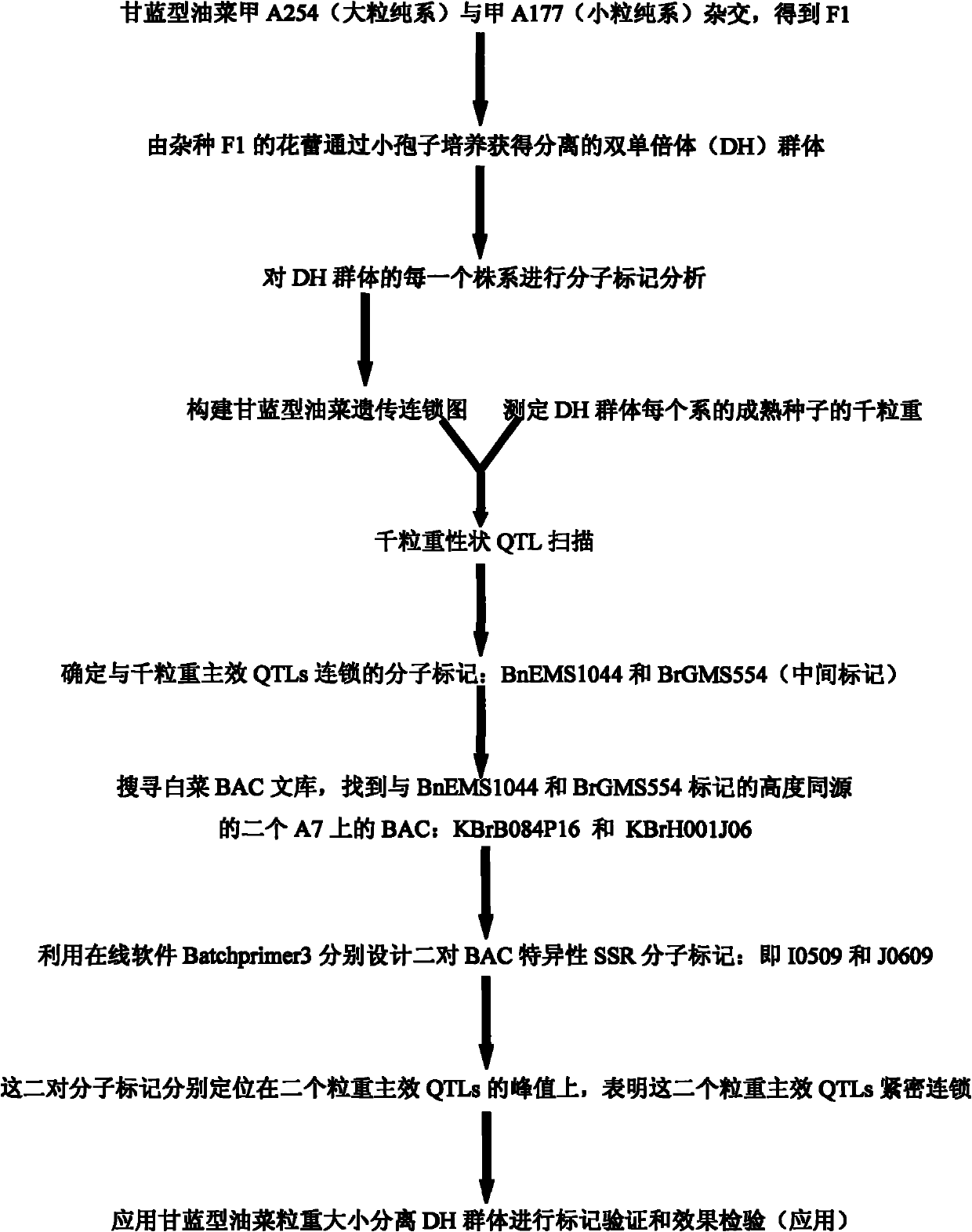
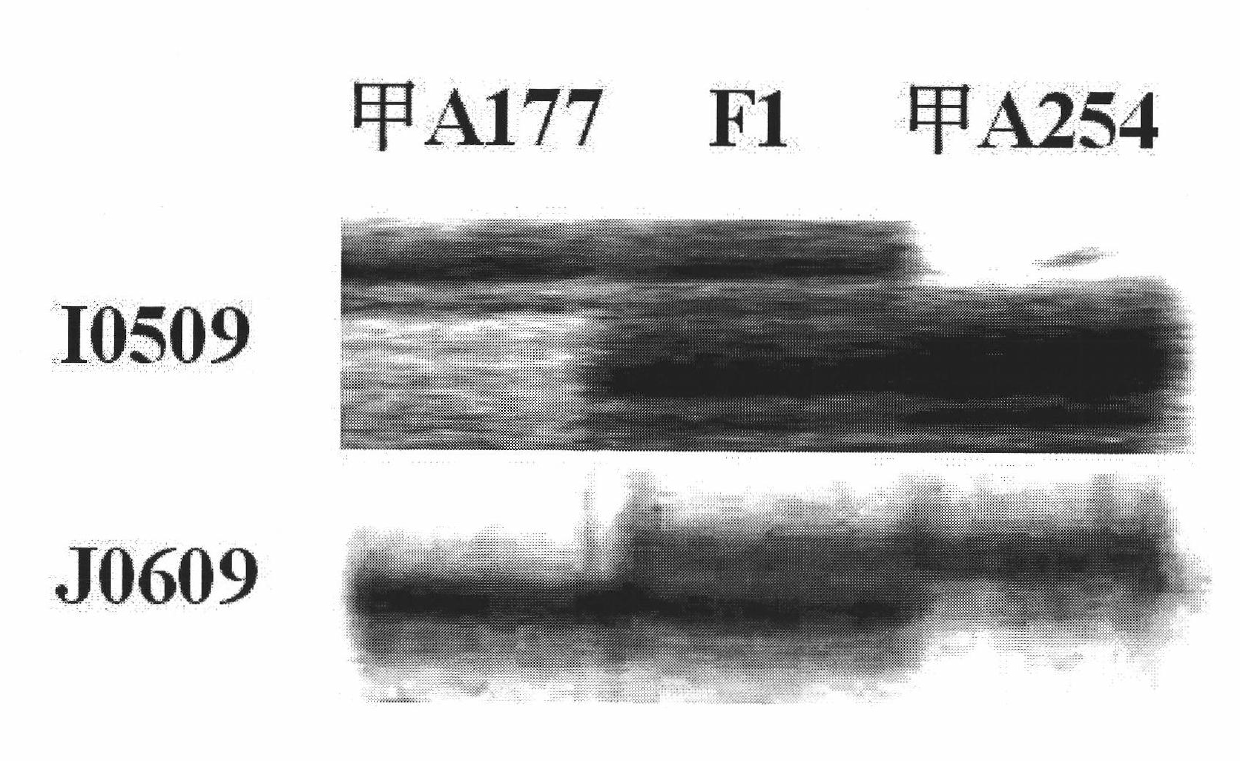
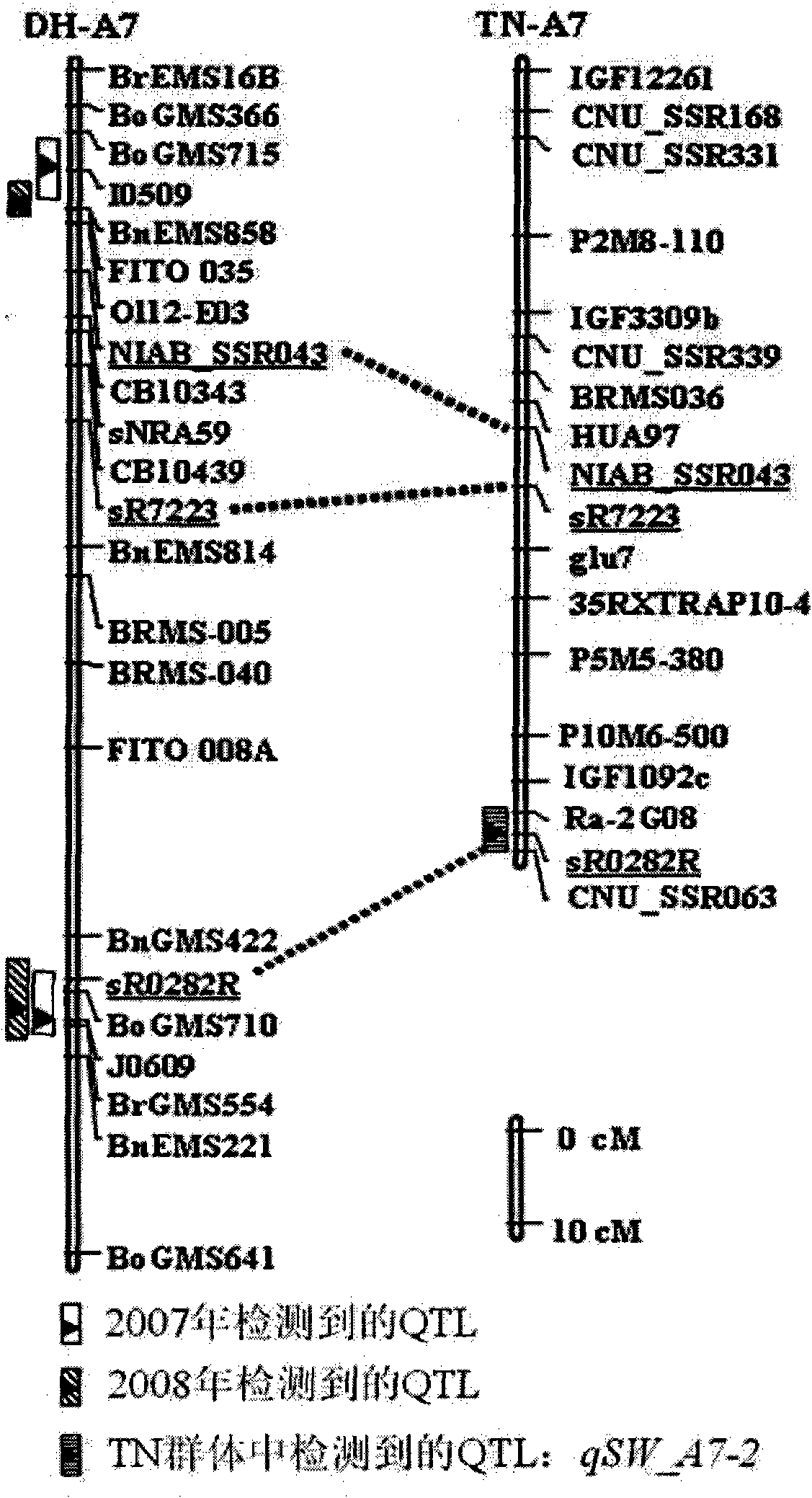
The invention belongs to the technical field of rape molecular breeding and preparation of molecular markers, and particularly relates to preparation of a brassica napus L. grain weight major QTLs locus specific molecular marker. The marker can be used for auxiliary selection of molecular markers, fine positioning of grain weight trait loci and based cloning in the improvement on brassica napus L. grain weight traits. The marker is characterized in that double haploid (DH) is constructed by hybridizing brassica napus L. first A254 (large-grain pure line materials) as a female parent and brassica napus L. first A177 (small-grain pure line materials) as a male parent, and the molecular marker which is tightly linked with the grain weight major QTLs is obtained by analyzing DH group genotypes and thousand grain weight data and is named I0509 and J0609, and is relatively verified and applied. A new genetic marker is provided for molecular breeding of rape grain weight and also useful information is provided for fine positioning of thousand grain weight trait loci of the brassica napus L. and based cloning of relative genes.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Molecular marker of brassica napus L. grain weight character and preparation method and application
InactiveCN102703438ASpeed up the processOvercome the downside of choosingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBrassicaGrain weight
The invention belongs to the field of rape molecular breeding, and relates to a specific molecular marker of brassica napus L. grain weight and a preparation method and an application. Hybridization is performed by using brassica napus L. A254 as a female parent and using brassica napus L. A177 as a male parent to construct a dihaploid colony (DH); data of the genotype and 1000-grain weight of the DH colony are analyzed to obtain QTLs loci of the grain weight character. MINI3 and TTG2 genes of A254 and A177 are cloned by a homologous sequencing method; specific molecular marker MINI3a and TTG2a of the MINI3 and TTG2 genes are designed according to sequence different loci; the molecular marker MINI3a and TTG2a are positioned on two grain weight QTLs loci of a A5 linkage group; related verification and application demonstrate that the molecular marker prepared by the invention is a new genetic marker. The invention provides a new genetic marker for rape grain weight molecular breeding.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Ma pomelo InDel (insertion-deletion) molecular marker, and application of molecular marker in differentiating rough bark Ma pomelo at early stage of citrus seed seedling
ActiveCN108660246AReduce breeding workloadEliminate distractionsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationInsertion deletionAgricultural science
The invention provides a Ma pomelo InDel (insertion-deletion) molecular marker, and an application of the molecular marker in differentiating a rough bark Ma pomelo at an early stage of a citrus seedseedling, and belongs to the field of genetic seed breeding. The Ma pomelo InDel molecular marker comprises a fragment obtained by amplification of a primer pair chr2.10-9584F / chr2.10-9584R, and a fragment obtained by amplification of a primer pair p-chr6.21-8689F / p-chr6.21-8689R. The molecular marker provides a novel molecular tool for identification and breeding of the genetically stable Ma pomelo seed seedling and early screening. The InDel molecular marker can be used for differentiating the rough bark Ma pomelo in a citrus variety at the early stage of the seed seedling, and has importantsignificance for identification of the citrus variety and risk control in Ma pomelo production.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Molecular marker for low linolenic acid of cabbage type rape, preparation method and application thereof
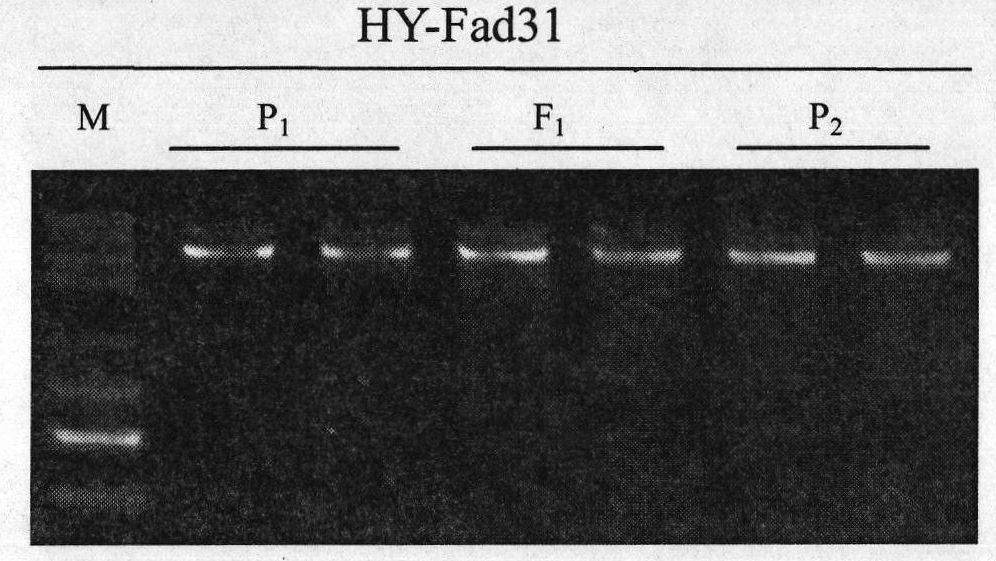
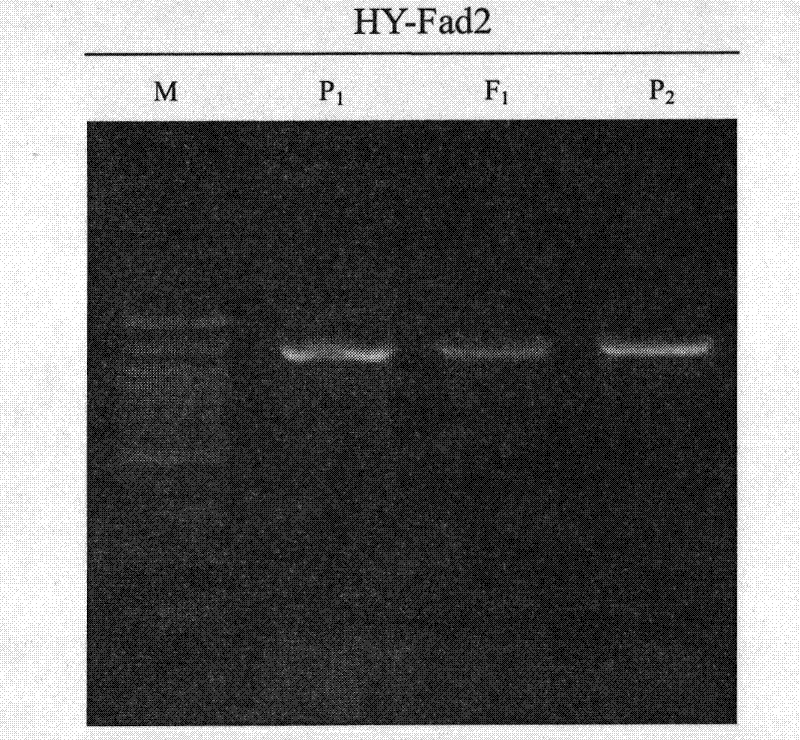
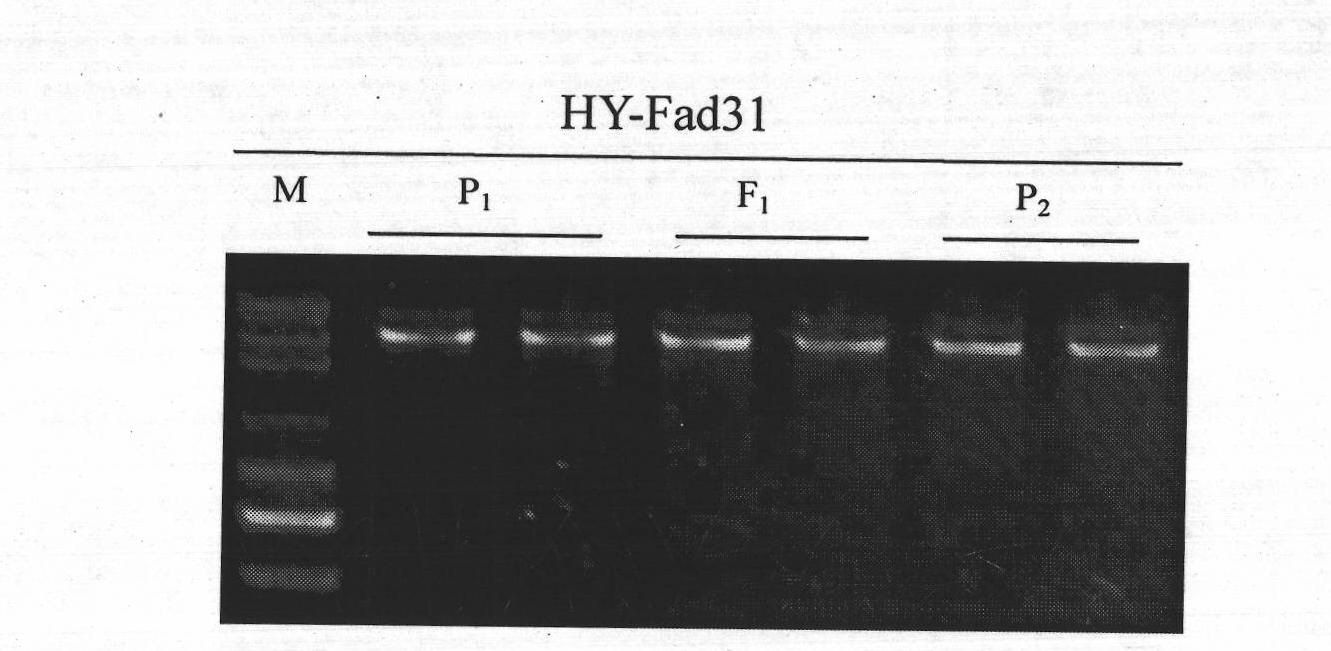
InactiveCN101818196AReduce breeding workloadShorten the breeding periodMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationHeterologousForward primer
The invention belongs to the technical field of rape molecular breeding, in particular relates to a preparation method of a codominant SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) molecular marker closely linked with the linolenic acid content of a cabbage type rape and application thereof as the marker in the auxiliary selection of the low linolenic acid cabbage type rape. The low linolenic acid cabbage type rape strain A254 and high linolenic acid cabbage type rape strain A177 genomes DNA are amplified by using primers to respectively obtain two DNA amplified fragments, then cloning, sequencing and nucleotide sequences comparison are carried out on the four DNA amplified fragments; according to the difference of the sequences, the second bases at 3'-end of a forward primer and a reverse primer are mispaired, primer pairs of YQ-fad31-1, YQ-fad31-2, YQ-fad32-1 and YQ-fad32-2 are designed, the PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification is carried out on the primer pairs of YQ-fad31-1, YQ-fad31-2, YQ-fad32-1 and YQ-fad32-2, and the PCR amplification and group detection effects are analyzed to obtain the codominant SNP molecular marker linked with low linolenic acid genes of the cabbage type rape. The invention provides a new marker for the rape molecular breeding. In the invention, a mispairing strategy of the 3'-end of the primer is firstly applied to the development and the detection of the SNP polymorphic marker of the cabbage type rape, and a means of synchronously mispairing the forward primer and the reverse primer is firstly adopted to develop the SNP marker based on the PCR amplification and an agarose gel electrophoresis in the cabbage type rape of an allopolyploid crop. The invention synchronously discloses a method for preparing the molecular marker and the application thereof.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
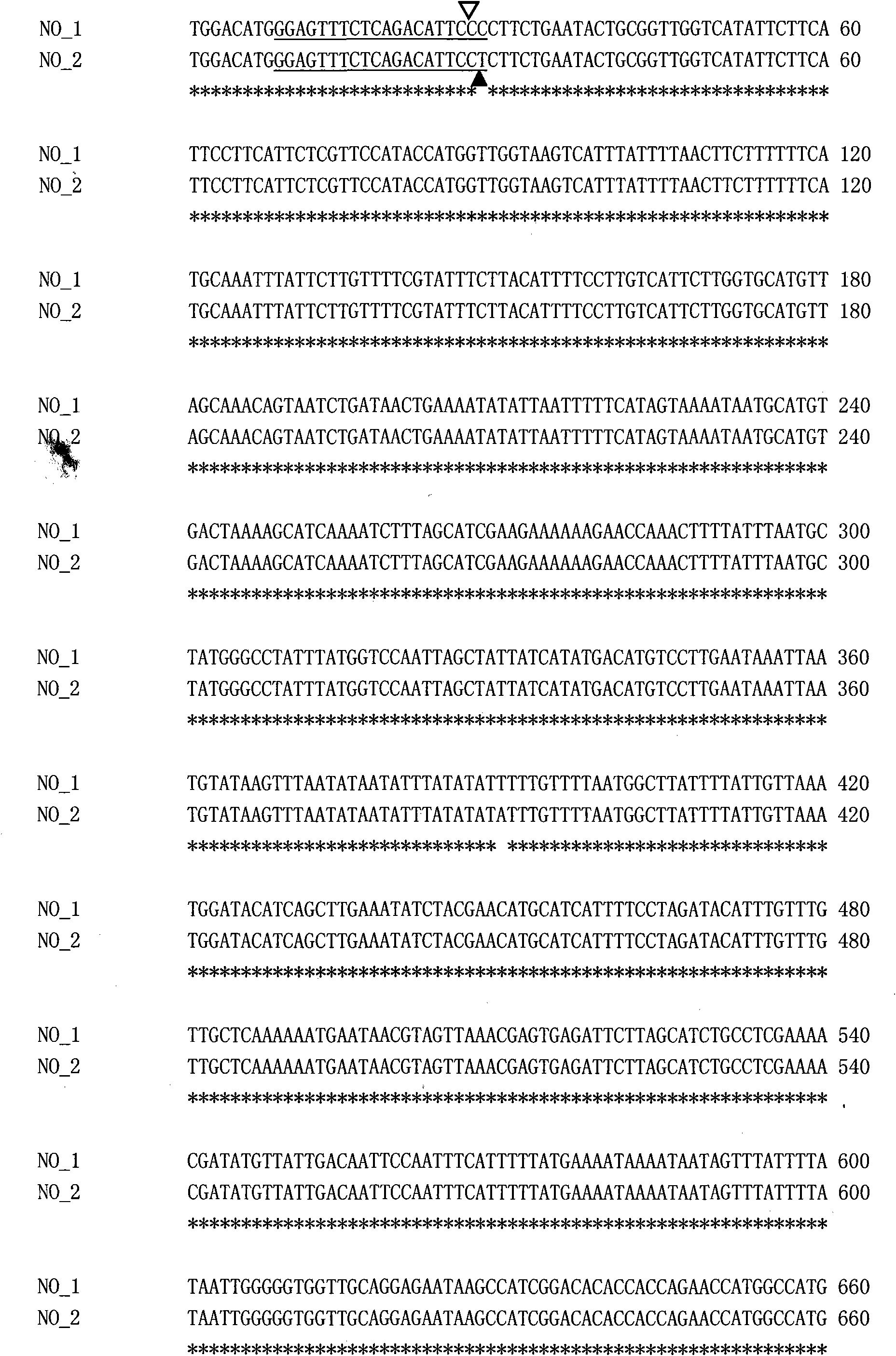
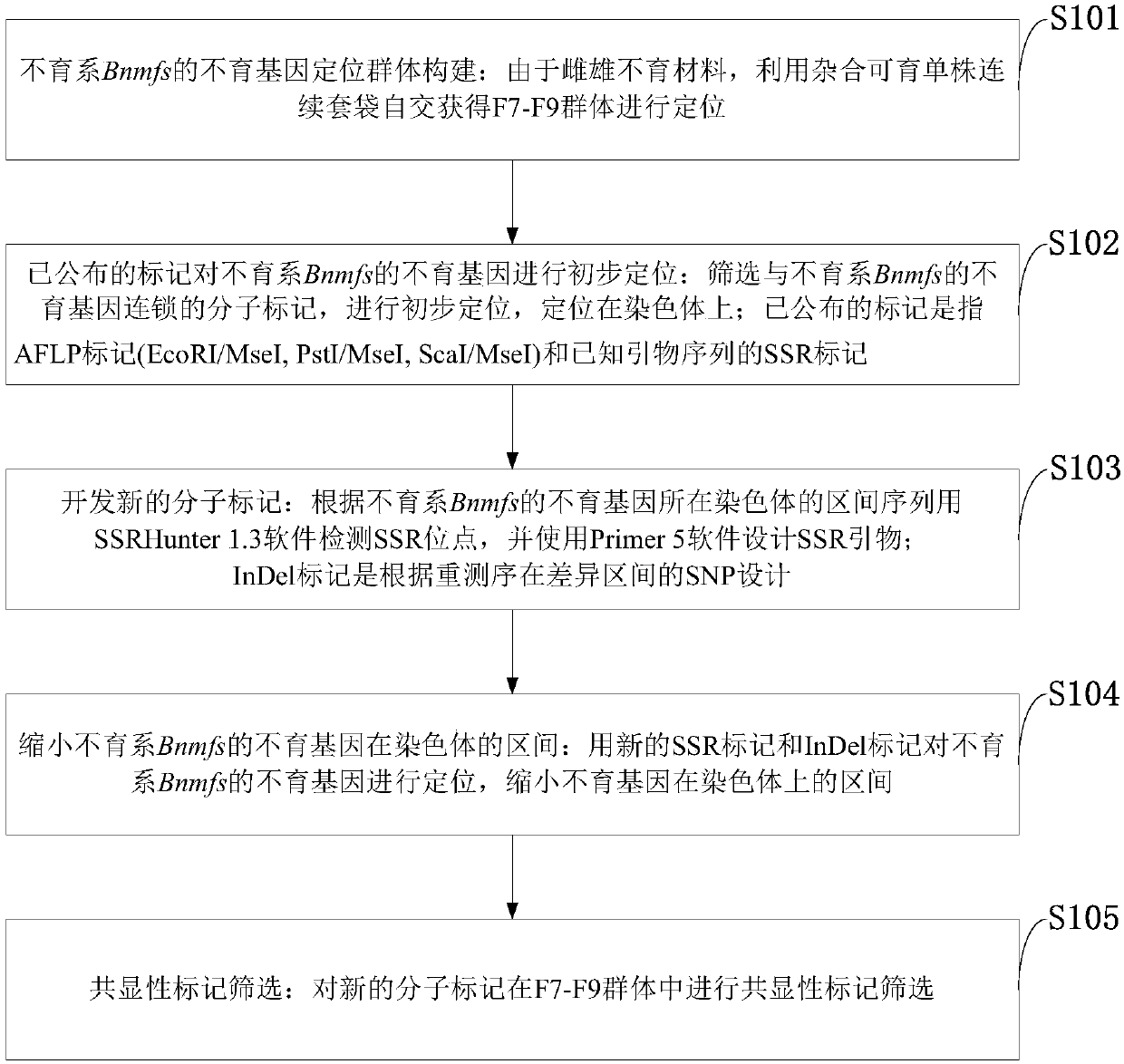
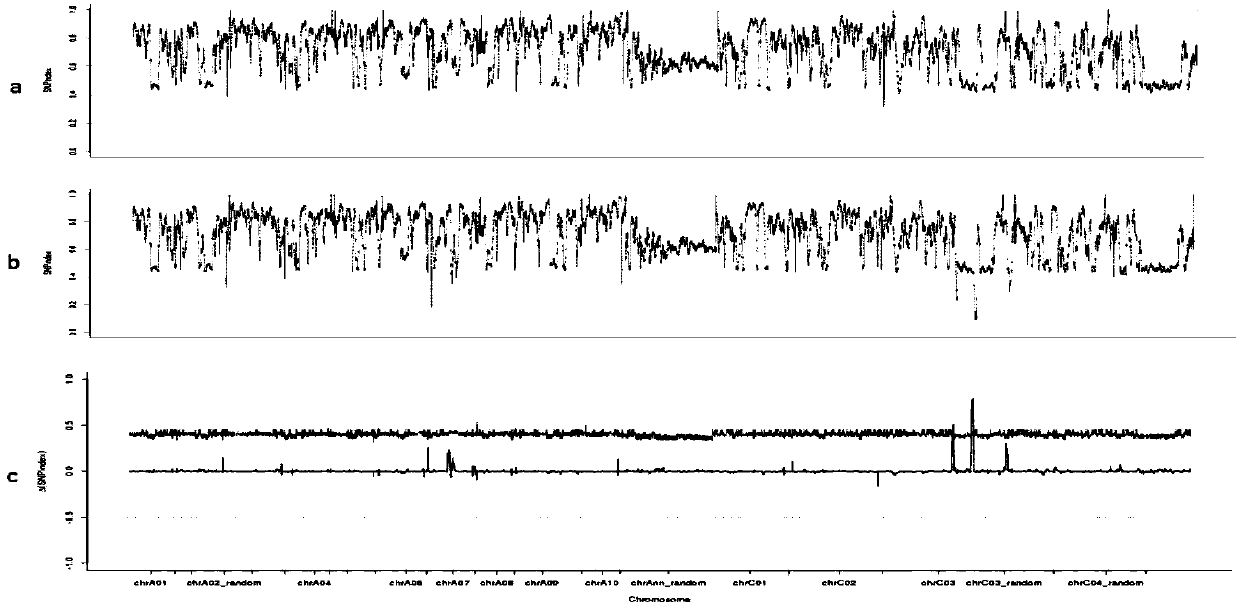
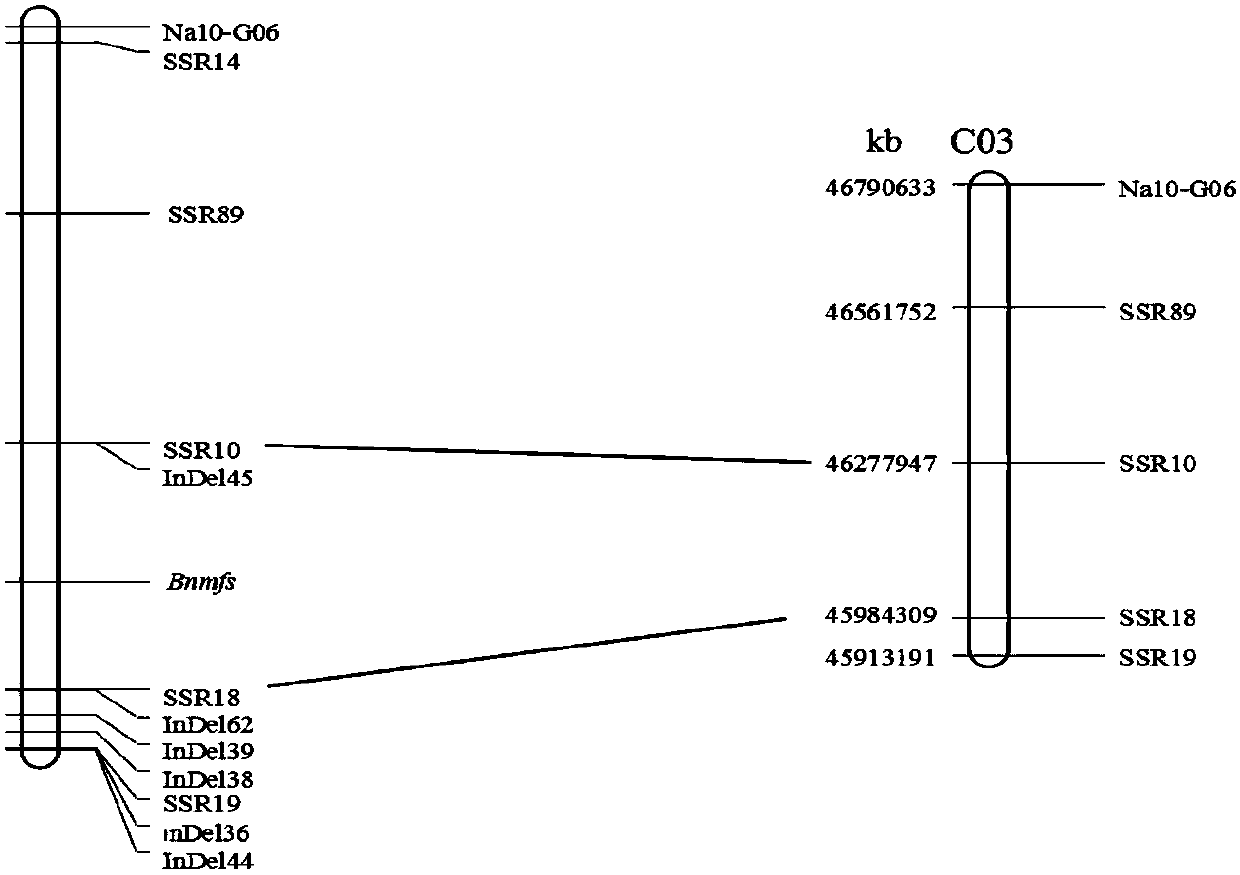
Cabbage type rape female and male sterile line Bnmfs molecular marker screening primer and method
ActiveCN107699631AReduce intervalStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceScreening method
The invention belongs to the technical field of rape breeding and discloses a cabbage type rape female and male sterile line Bnmfs molecular marker screening primer and a method. The sequence of the primer is as shown in SEQ ID NO:1 to SEQ ID NO:22. The molecular marker screening primer disclosed by the invention is a marker that two sides of a sterile gene of a sterile line Bnmfs are tightly interlinked, the interval of sterile genes in cabbage type rape chromosomes is reduced, and a base is made for later gene cloning; the molecular marker screening primer is good in specificity and stability, and in addition a marker screening method is simple to operate; a co-dominance marker is screened, dominant homozygosis, single plants of dominant heterozygosis and recessive homozygosis can be identified and separated, the characteristic that plants are screened according to phenotypes in conventional breeding is overcome, the breeding workload is reduced, the breeding years are reduced, and the breeding progress is accelerated.
Owner:QINGHAI UNIVERSITY
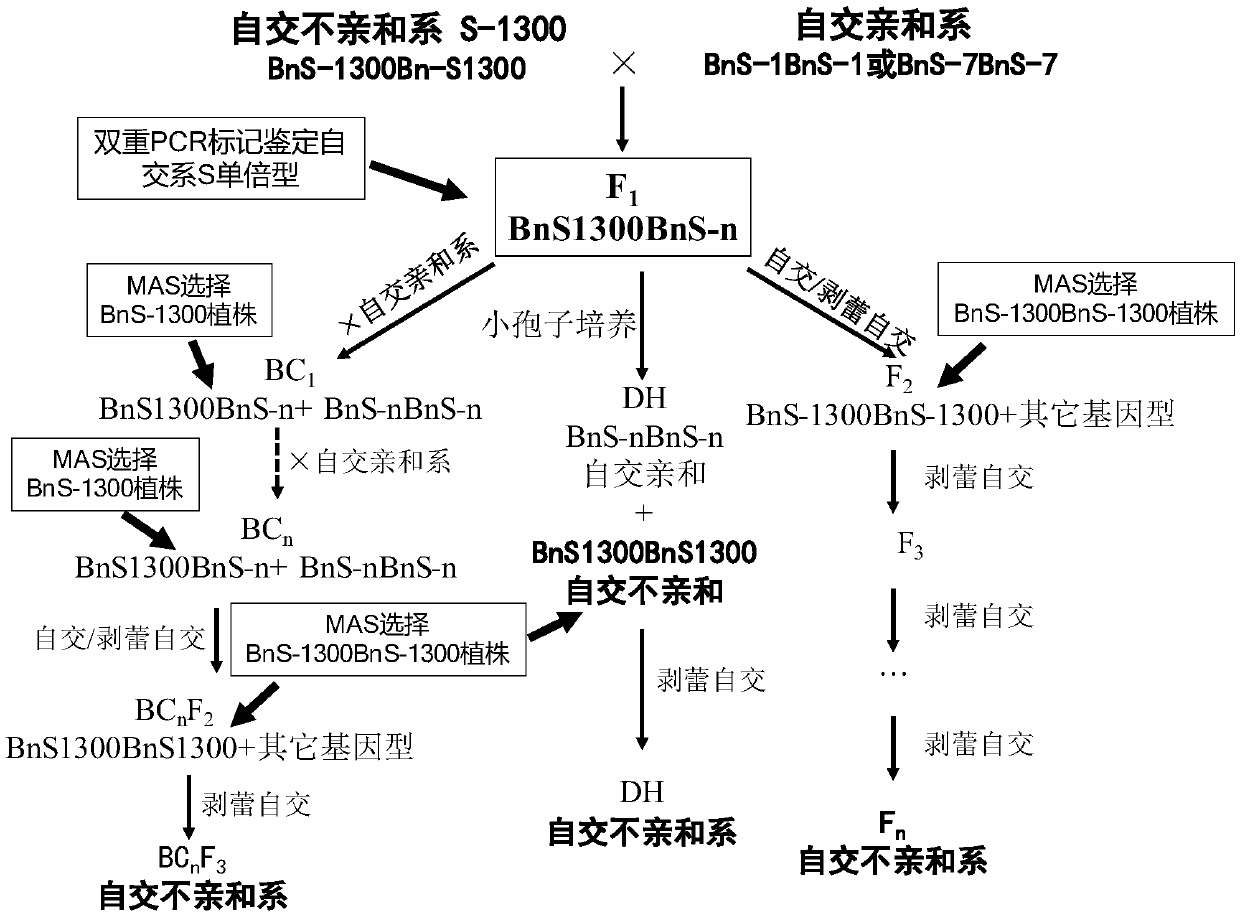
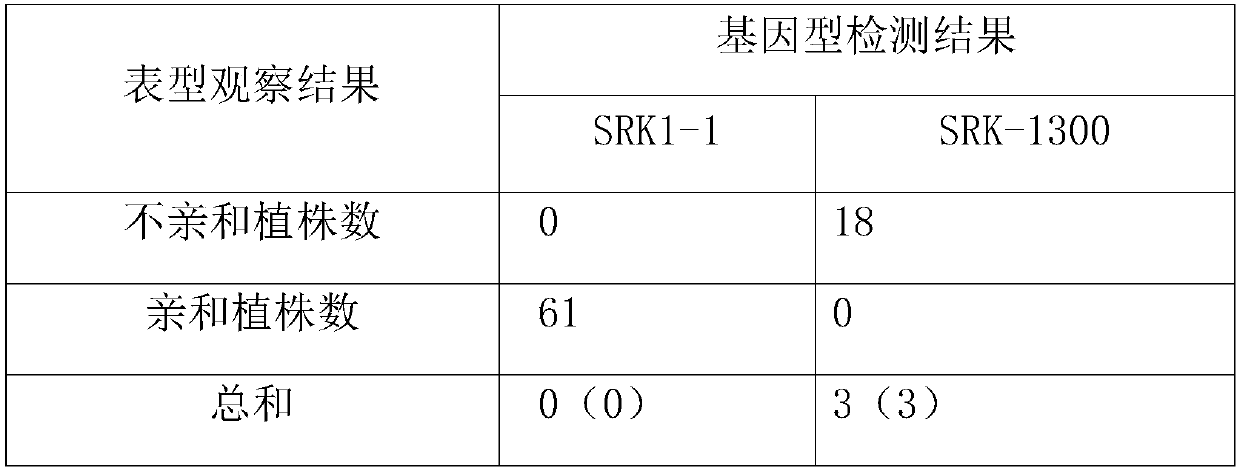
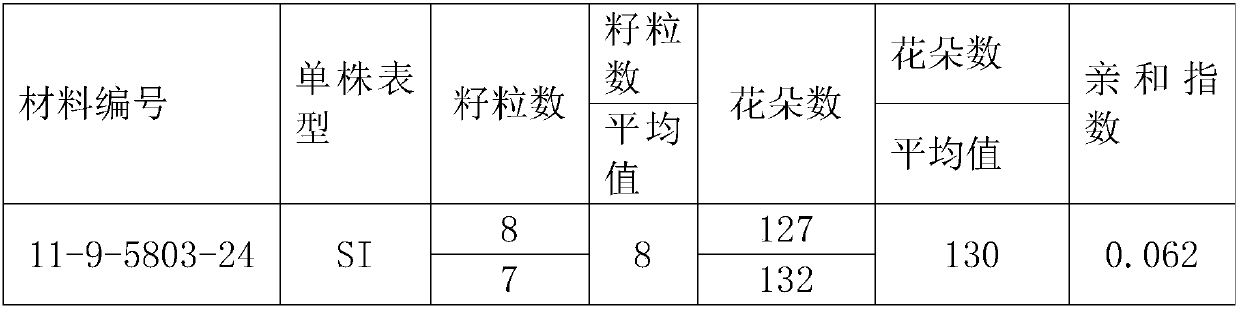
Method for breeding rape self-incompatible line assisted by S haplotype molecular markers
InactiveCN109566399AAvoid misjudgmentAccurate judgmentMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant tissue cultureAgricultural scienceBackcross population
The invention belongs to the technical field of rape molecular breeding, and discloses a method for breeding a rape self-incompatible line assisted by an S haplotype molecular marker, which comprisesthe following steps of: identifying an S haplotype of inbred line, double haploids of the self-incompatible line and inbred line, F2 populations of the self-incompatible line and inbred line, backcross populations of the self-incompatible line and inbred line and an S haplotype of the offspring by utilizing a molecular marker technology, the self-incompatible line of cabbage type rape is obtained,the method can overcome the defect of selection according to the self-incompatible phenotype in the rape breeding process, the breeding workload is greatly reduced, and the rapid cultivation of the self-incompatible line of the cabbage type rape is achieved, meanwhile, the S haplotype is detected by utilizing multiple PCR molecular markers, the error judgment on the result caused by the error ofthe experimental operation process is overcome, and the S haplotype of a plant can be accurately judged.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
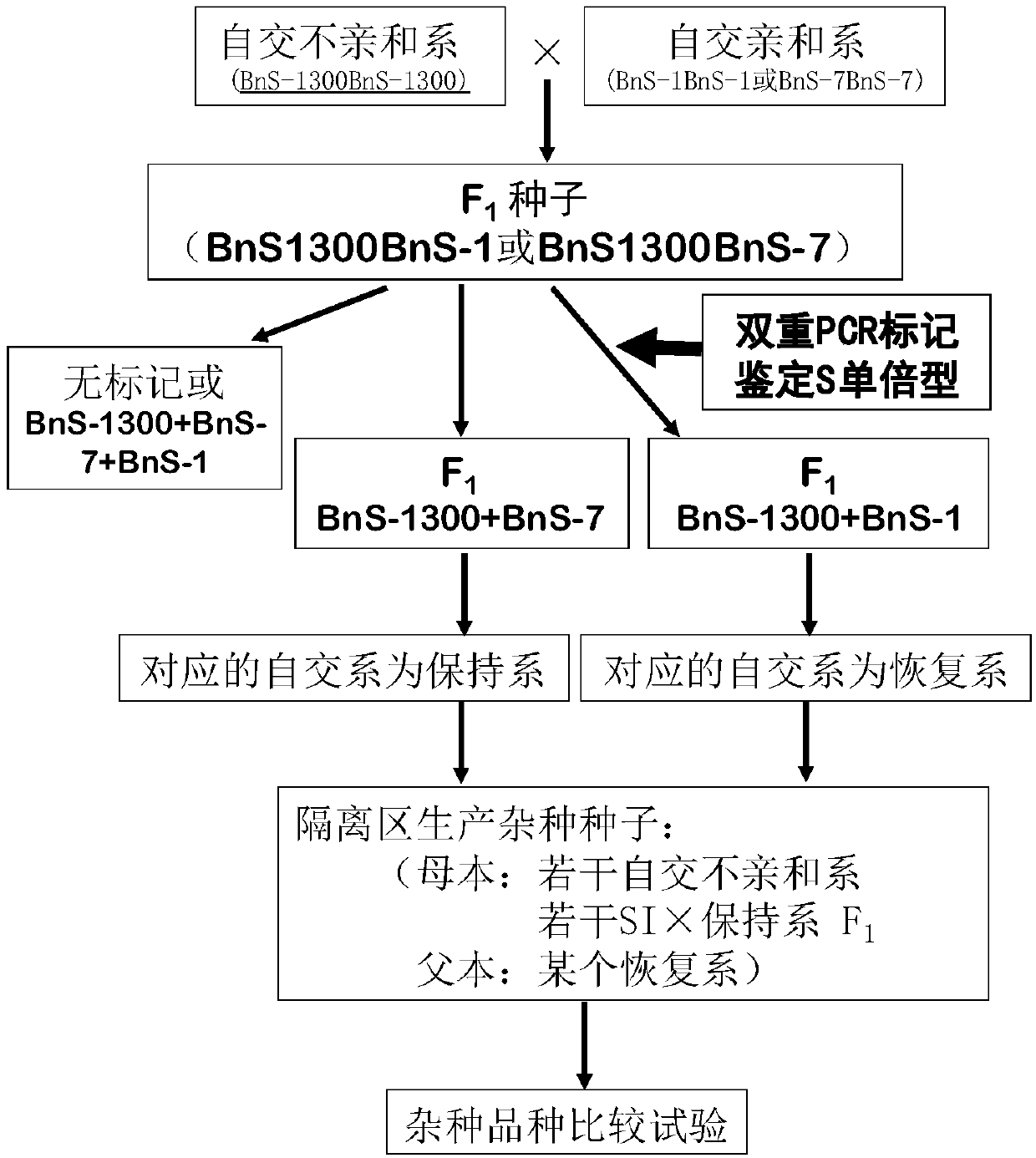
Method for breeding rape self-incompatible hybrid seeds under assistance of S haplotype molecular markers
InactiveCN109588306ABreed fastShorten the breeding cycleMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationDuplex pcrHybrid seed
The invention belongs to the technical field of rape molecular breeding, and discloses a method for breeding rape self-incompatible hybrid seeds under assistance of S haplotype molecular markers. Themethod comprises the following steps: obtaining F1 seeds, detecting S haplotype of a selfing line, obtaining self-incompatible two-line and three-line hybrid seeds, and arranging a variety screening test by the obtained two-line hybrid seeds and three-line hybrid seeds. The S haplotype of F1 is identified by double PCR markers, the technical defect that no marker is generated due to accidental factors in the experimental process is overcome, and the S haplotype of the selfing line and recovery or retention of the S haplotype can be accurately judged; fussiness of fertility identification and blindness of combination configuration in the breeding process of rape self-incompatible hybrids are overcome with the molecular marker technology, the breeding workload is greatly reduced, the breeding cycle is shortened, breeding efficiency is improved, and rapid cultivation of the cabbage type rape self-incompatible hybrids is promoted.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Cabbage type rape low erucic acid molecular marker, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101955930AReduce breeding workloadShorten the breeding periodMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationHeterologousReverse primer
The invention belongs to the rape molecular breeding field, which relates to a codominant SNP molecular marker closely linked with the content of a cabbage type rape erucic acid, a preparation method thereof and application in auxiliary selection of the low erucic acid cabbage type rape. A primer is used to amplify the genome DNA of the low erucic acid cabbage type rape and a high erucic acid cabbage type rape in order to obtain two amplified DNA fragments, and then cloning, sequencing and sequence alignment are carried out on the DNA fragments; according to the single nucleotide polymorphism of mutations 845C-845T in SEQ ID NO: 1 and SEQ ID NO:2, second bases at the 3' ends of forward and reverse primers are simultaneously used to carry out mismatch processing, and a primer pair is designed according to the sequence difference of SEQ ID NO: 3 and SEQ ID NO: 4; the primer pair is validated by PCR amplification and tested by group detection and effect analysis to obtain the codominant SNP molecular marker closely linked with the cabbage type rape low erucic acid gene. The invention can be applied to the development and detection of a cabbage type rape SNP polymorphic marker and the development of SNP markers by using forward and reverse primers simultaneously mismatched in allopolyploid crops such as the cabbage type rape.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Brassica napus high oleic acid molecular marker and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN101824472BSpeed up the breeding processReduce breeding workloadMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationBrassicaMarker-assisted selection
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Low-linolenic-acid molecular marker for brassica napus, and preparation method and application of low-linolenic-acid molecular marker
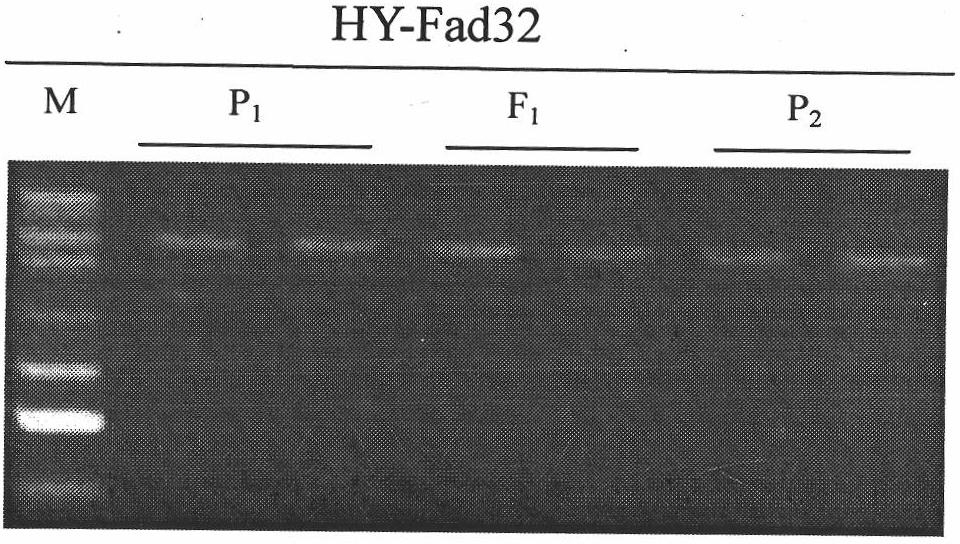
InactiveCN102433331AReduce breeding workloadShorten the breeding periodMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationForward primerNucleotide
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular breeding of rape, and particularly relates to a preparation method for a codominant single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) molecular marker which is closely linked with the content of linolenic acid of brassica napus, and application of the marker to the auxiliary selection of low-linolenic-acid brassica napus. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: amplifying genomic deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) of a low-linolenic-acid brassica napus line AA254 and a high-linolenic-acid brassica napus line AA177 by using primers to obtain two DNA-amplified fragments respectively, cloning the four DNA-amplified fragments, sequencing, and comparing nucleotide sequences; simultaneously mismatching 2nd basic groups of 3' terminals of a forward primer and a reverse primer according to the difference of the sequences so as to design a primer pair, namely YQ-fad32-1 and YQ-fad32-2; and performing polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification on the primer pair, namely the YQ-fad32-1 and the YQ-fad32-2 to obtain the codominant SNP molecular marker which is linked with a low linolenic acid gene of the brassica napus through PCR amplification and analysis of a population detection effect. The invention provides a novel marker for the molecular breeding of the rape. Nucleotide sequences of the novel marker are shown as SEQ ID NO:7 and SEQ ID NO:8.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Breeding method of slowly faded sweet pepper pigment restorer with high color value
InactiveCN109156336ADoes not affect normal growthReduce breeding workloadPlant genotype modificationSweet PeppersHybrid seed
The invention provides a breeding method of a slowly faded sweet pepper pigment restorer with a high color value. The method comprises plant breeding and primary selection, secondary selection and final selection of the restorer. In the method, a sweet pepper pigment material having a restoration gene linked marker is screened out by using a PR-CAPS molecular marker; by taking the sweet pepper pigment material as a male parent and taking a 100% cytoplasmic male sterile line as a female parent, a hybrid composition is prepared, and hybrid seeds are subjected to fertility identification; a restorer is bred through methods such as continuously back crossing; and meanwhile, the slowly faded restorer with the high color value is further bred according to the color value and a fading degree of afruit. The sweet pepper pigment restorer is bred in combination with technologies such as molecular marker aided screening, hybridization, continuously back crossing and pepper color value and fadingmeasuring methods. Sweet pepper pigment hybrid seeds which have the high color value and are difficult to fade and good in processing character can be prepared by taking the male sterile restorer bred according to the method provided by the invention as the male parent, and the method has significance for accelerating the breeding progress.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Daylily pollination method
InactiveCN106305409ALoss of pollinationImprove seed setting ratePlant genotype modificationDaylilyMedicine
The invention relates to a daylily pollination method. The method comprises the step of sleeving a hollow light tube on a daylily stigma to isolate the stigma, wherein one end of the tube is opened, the other end is closed, and the inner diameter thereof is slightly greater than the outer diameter of the daylily stigma. The pollination result cannot be influenced whether by wind or rain, the method is extremely suitable for the hybrid pollination of the daylily, the maturing rate of the pollination of the daylily under bad weather condition is greatly improved, and the pollination time is increased. Furthermore, the method is free from emasculation, and the breeding workload is lightened.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
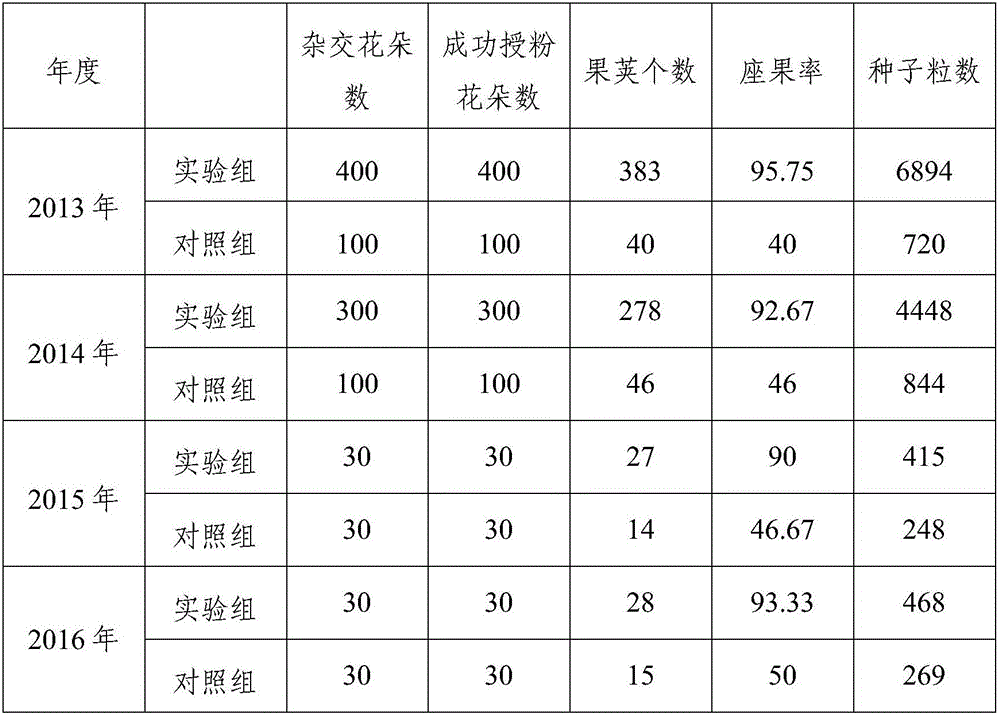
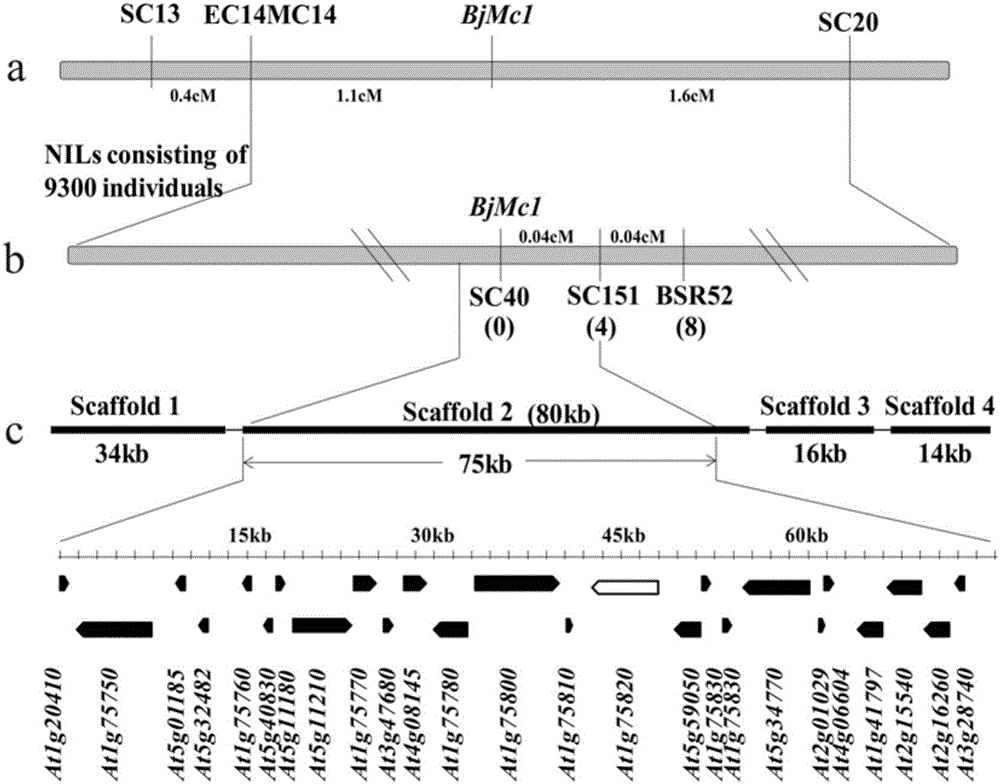
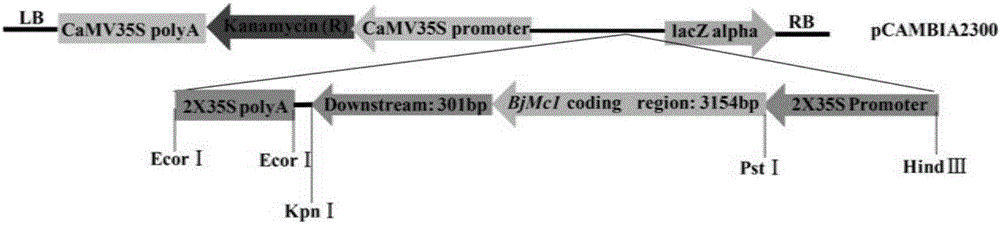
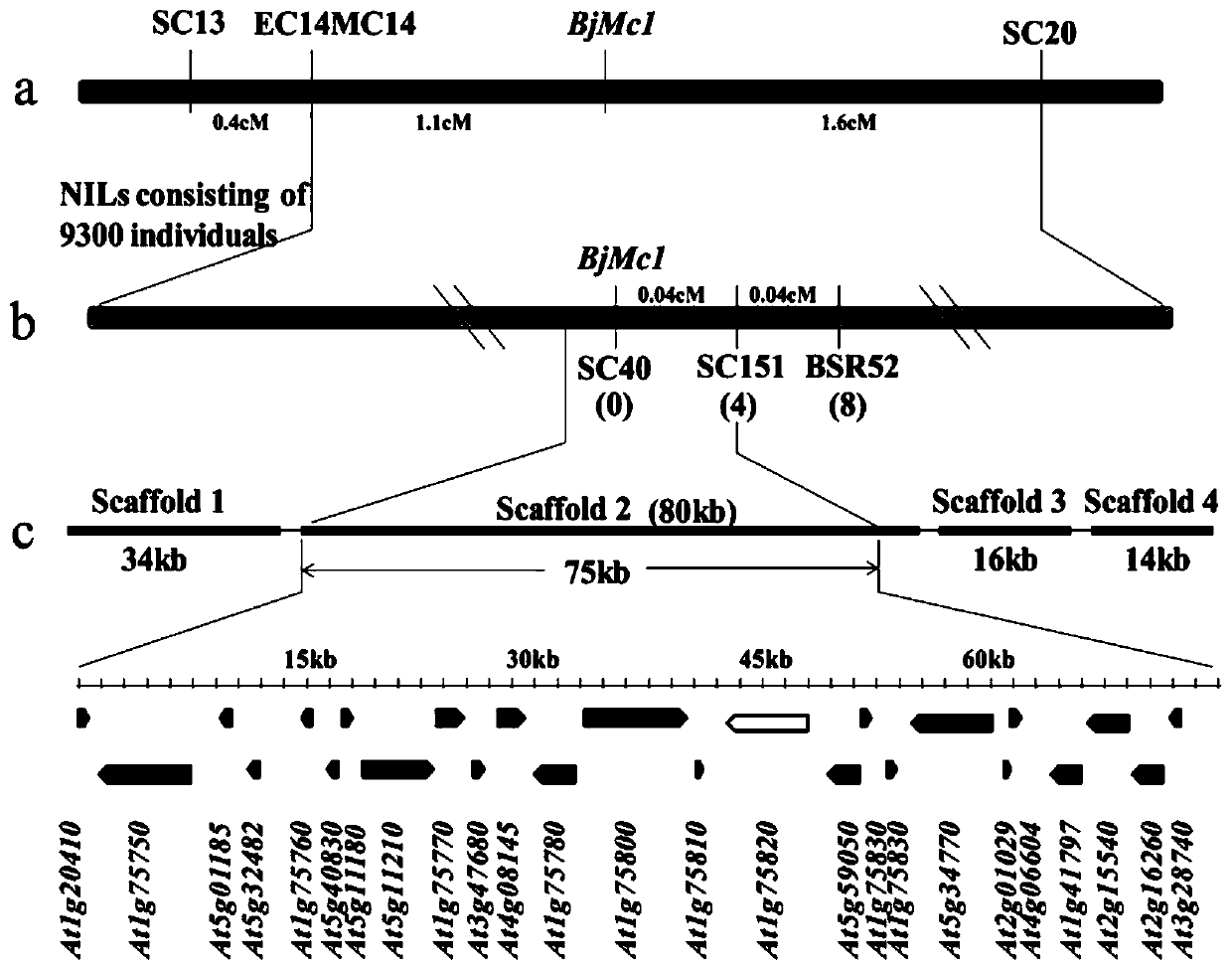
Two-room gene BjMc1 and three-room gene Bjmc1 which are related to multicapsular traits of mustard-type rapes and application of two-room gene BjMc1 and three-room gene Bjmc1
ActiveCN106279388ASpeed up the breeding processIncrease productionMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesGenetic engineeringPhenotype
The invention belongs to the technical field of rape breeding and particularly relates to a two-room gene BjMc1 and a three-room gene Bjmc1 which are relates to multiicapsular traits of mustard-type rapes and an application of the two-room gene BjMc1 and the three-room gene Bjmc1. The two-room gene BjMc1 and the three-room gene Bjmc1 of the mustard-type rapes are firstly obtained from clone of the mustard-type rapes, and the two-room gene of the rapes can be subjected to genetic engineering to obtain the three-room rapes high in yield by the aid of the technology. The two-room gene BjMc1 and the three-room gene Bjmc1 can be respectively and specifically amplified by provided molecular markers of M1-1, breeding work can be reduced by applying the molecular markers on assistant selection of the mustard-type rapes with the three-room traits to overcome the shortcoming of performing selection by relying phenotype in conventional breeding, breeding periods are shortened, and processing of the mustard-type rape breeding is fastened.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Main effect QTL related to mung bean early flowering stage, molecular marker and application thereof
ActiveCN112080579AAvoid time-consuming and labor-intensive disadvantagesReduce distractionsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyPhenotype
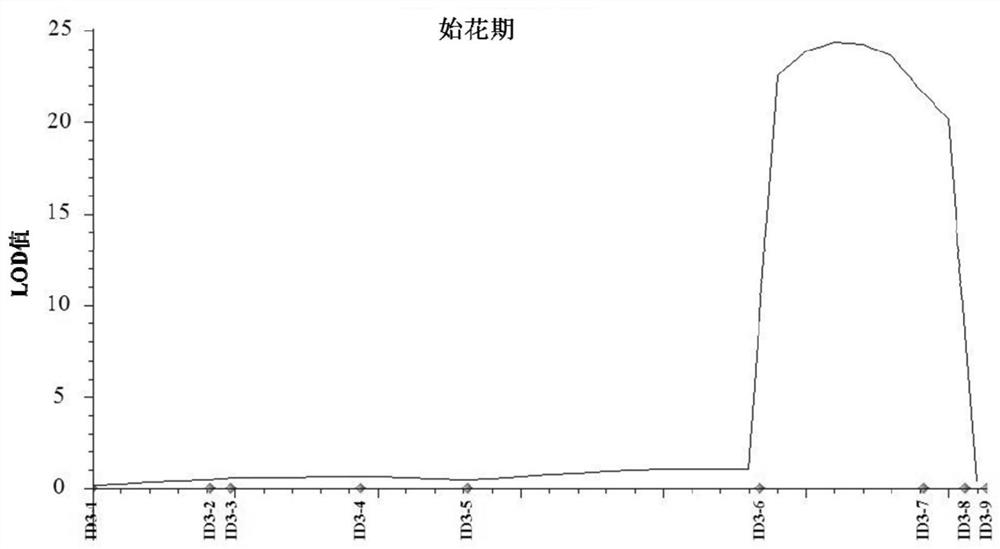
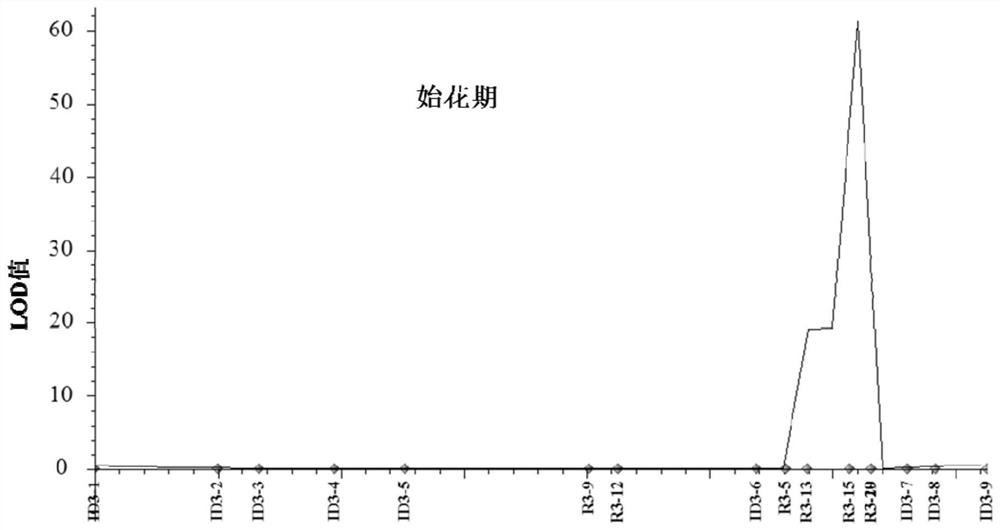
The invention discloses a main effect QTL related to a mung bean early flowering stage, a molecular marker and application thereof. The early flowering stage main effect QTL qDFF3 is located between InDel markers R3-15 and R3-19 on a third chromosome, the linkage marker R3-15 is located at 8504kb of the third chromosome, and the marker R3-19 is located at kb of the third chromosome. The two linkage markers are used for identifying the early flowering stage of mung bean resources, the phenotype and the markers show extremely significant correlation, the accuracy rate reaches 92.9%, and that thetwo markers can well identify the mung bean resource early flowering stage phenotype is indicated. The mung bean early flowering stage character is associated with the molecular marker, and the result is more stable and accurate. The two markers can be used for screening or identifying the mung bean resource early flowering stage, materials can be subjected to genetic typing in breeding low generations, the required early flowering stage phenotype materials are accurately screened, the breeding workload is reduced, and the selection efficiency is improved. On the other hand, fine positioningand gene cloning of the mung bean early flowering stage main effect QTL qDFF3 are facilitated, and the genetic regulation mechanism of the mung bean early flowering stage can be explained.
Owner:CROP INST ANHUI PROV ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Codominant RFP molecular marker applicable for breeding citrus grandis with red-peel characteristic and application of codominant RFP molecular marker
ActiveCN105132537ANew colorHigh nutritional valueMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAnthocyanin synthesisDna polymorphism
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular breeding of citrus, and particularly relates to a codominant RFP molecular marker applicable for breeding citrus grandis with a red-peel characteristic and application of the codominant RFP molecular marker. Most varieties of citrus grandis are light yellow in peel and single in color in China; the citrus grandis with the red-peel characteristic is novel in color and variety, thereby being more attractive to consumers. The method includes: starting from a unique material, the red-peel citrus grandis, using a primer pair MYB2F / R to amplify the red-peel citrus grandis and common citrus grandis for regulating promoters of anthocyanin synthesis key transcription factor CgMYB2 genes so as to obtain two DNA fragments, then subjecting DNA polymorphic regions to PCR amplification, cloning and sequencing, and comparing two obtained nucleotide sequences to find that one segment of insertion mutation of 162bp is between the two sequences, resulting in polymorphism of the sequence-characterized amplified region; designing primer pairs RFP F / R1 and RFP F / R2 according to differences of the two nucleotide sequences prior to PCR amplification to obtain the codominant RFP molecular marker capable of distinguishing the red-peel citrus grandis from the common citrus grandis (being light yellow in peel). The invention further discloses a method for preparing the molecular marker.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Gene related to thousand seed weight of rape as well as molecular marker and application of gene
ActiveCN113061616AHave pursuasive powerImprove relevanceMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesBiotechnologyGermplasm
The invention provides a gene related to thousand seed weight of rape as well as a molecular marker and application of the gene, and belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering and biology. In the invention, firstly, the difference of 15bp of thousand seed weight related genes BnaGRF7. C02 in different rape germplasms of different thousand seed weights is analyzed through comparison, then the correlation of the 15bp difference and the thousand seed weight of the rape is obtained through correlation analysis, and a molecular marker primer related to the thousand seed weight of the rape is also designed for screening whether the BnaGRF7. C02 genes of the rape contain 15bp or not, and if the BnaGRF7. C02 genes of the rape contain 15bp, the BnaGRF7. C02 genes of the rape contain 15bp, the BnaGRF7. C02 genes of the rape do not contain 15bp. The method is used for rape high-yield breeding.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
SNP molecular marker for column number of secondary milk ducts of rubber trees and application of SNP molecular marker
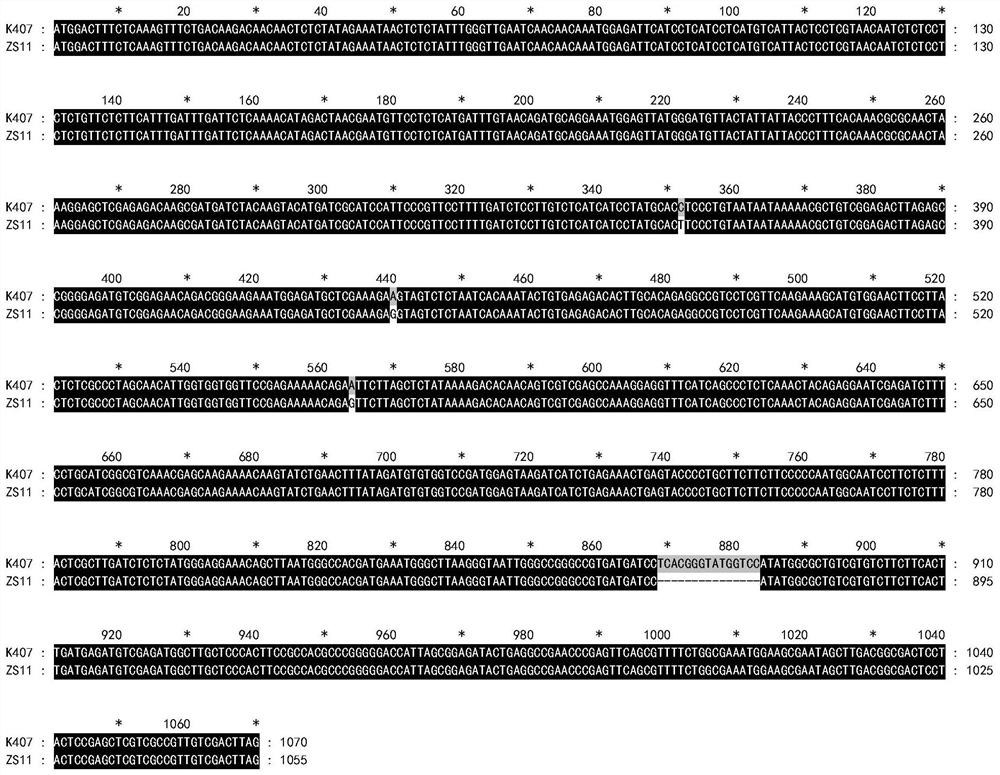
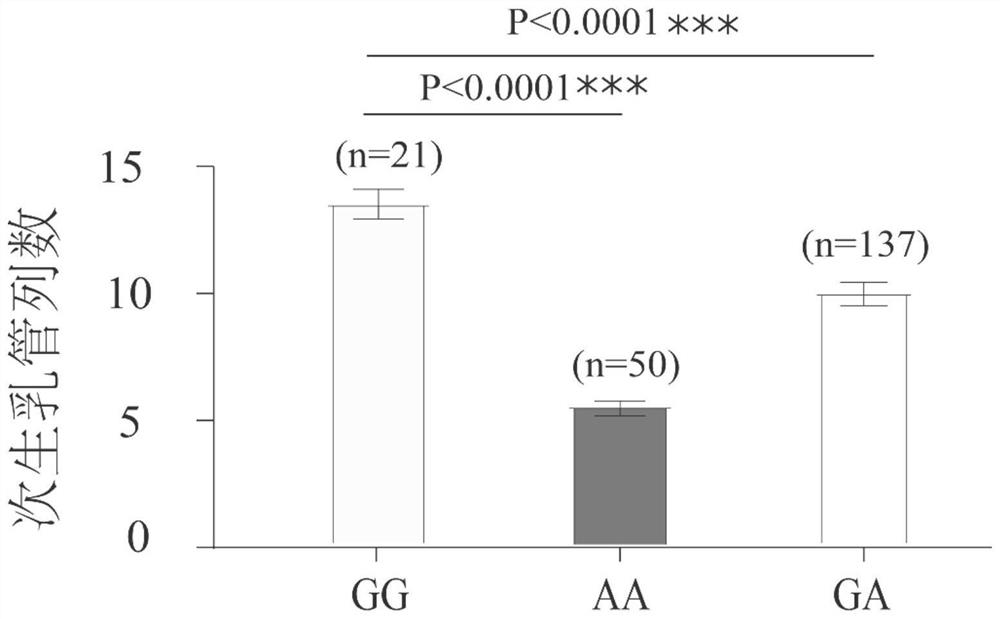
ActiveCN113846177AEasy to detectEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationAnimal scienceNucleotide
The invention discloses an SNP marker related to the column number of secondary milk ducts of a rubber tree. The SNP marker is as follows: the basic group from the 238th site from the 5'end of a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID No.1 is G or A. According to the SNP marker related to the column number of the secondary milk ducts of the rubber tree, from the big data level, it is identified that the number of SNP located at the 238th site of the nucleotide sequence SEQ ID NO.1 is closely associated with the number of rows of the secondary milk ducts for the first time, detection is facilitated, the accuracy and reliability are achieved, and operation is convenient; when the SNP marker is used for identifying the column number character of a secondary milk duct of a hybridized combination population, the accuracy reaches 91% or above; the SNP marker and a detection method are not influenced by the age of the rubber tree, can be selected in a seedling stage, greatly reduce the breeding workload, remarkably shorten the yield breeding selection period of the rubber tree, improve the breeding efficiency, and can be used for yield molecular marker-assisted breeding of the rubber tree in practice.
Owner:RUBBER RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
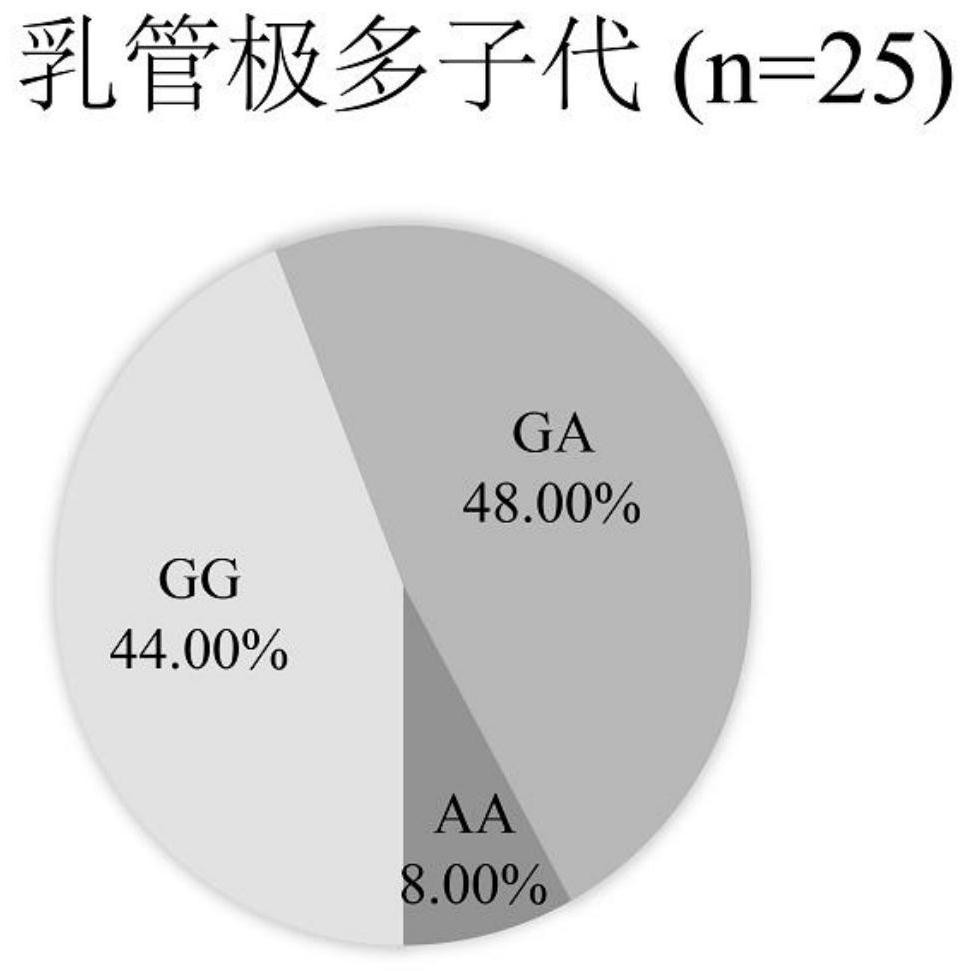
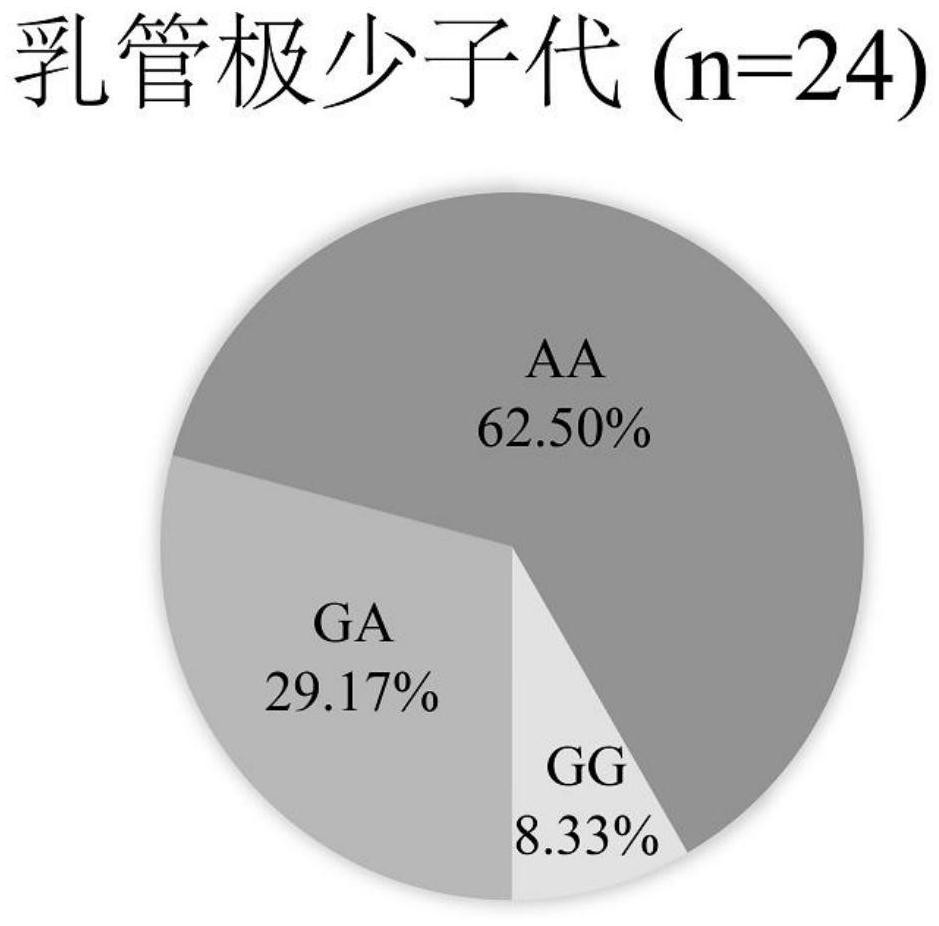
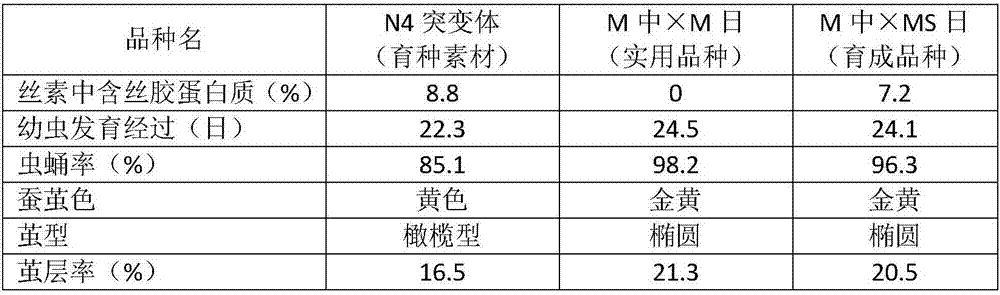
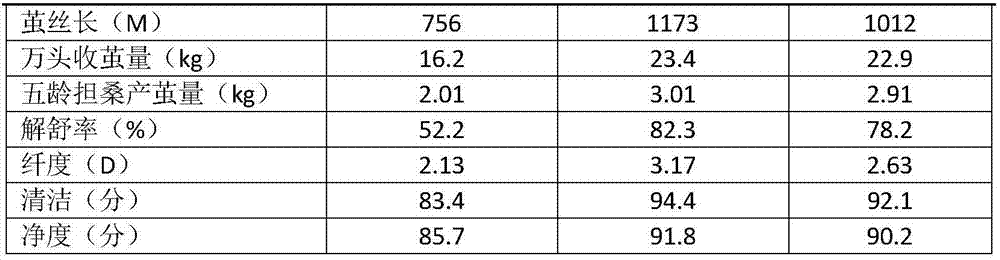
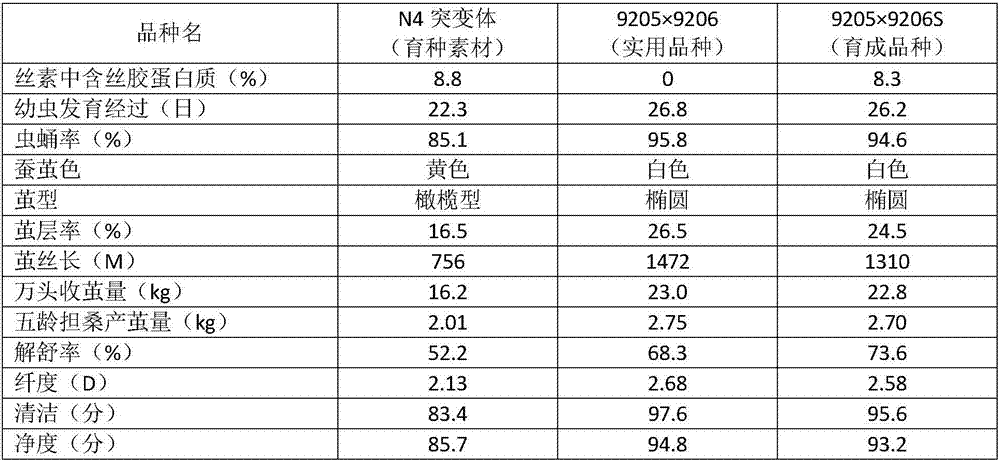
Breeding method for silkworm variety whose secreted fibroin fibril contains sericin protein
ActiveCN107484722ATo overcome the problem of intolerance to storage and the need for continuous breeding and conservation throughout the yearImprove short growth periodAnimal husbandryAnimal scienceFibril
The invention provides a breeding method for a silkworm variety whose secreted fibroin fibril contains sericin protein. The method comprises the following steps: using female moths of Japanese system variety transgenosis mutants which synthesize and secrete sericin by rear part sericteriums as female parents, mating with male months of a Japanese system silkworm variety of a digoneueism hybridization combination, further using selfing, backcross, marker gene tracking and other methods to breed a Japanese system protospecies whose rear part sericteriums efficiently express sericin; directly hybridizing the bred Japanese system protospecies with a Chinese system protospecies in the above digoneueism hybridization combination, to breed a silkworm hybridization combination variety whose secreted fibroin fibril contains sericin protein. The method can efficiently and rapidly breed the silkworm whose secreted fibroin fibril contains sericin protein by the silkworm hybrid variety which produces common silkworm cocoons, so as to obtain novel silk fibers whose fiber property is changed. The method is suitable for commercialized breeding requirement.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Breeding data collection and transmission method
InactiveCN105245832AGuaranteed accuracySo as not to confuseImage analysisClosed circuit television systemsData acquisitionComputer terminal
The invention discloses a breeding data collection and transmission method, and the method comprises the steps: 1, a plurality of plants are provided, wherein each plant is associated with a first machine reading identification; 2, a server is provided with a collection module, the collection module comprises an extracting module, a gathering module and mobile terminals, each mobile terminal is associated with a second machine reading identification, and the server sends a collection instruction to the mobile terminals and the gathering module at certain time intervals through the extracting module; 3, the mobile terminals read the collection instruction, and the data collection of a first machine reading identification plant is carried out through employing the mobile terminals, a rotating mechanism and an imaging device; 4, data is analyzed through the mobile terminals, and results are associated with first machine reading identification information of the plants; 5, the mobile terminals transmit collection data and results to the server; 6, the server receives collection data through the gathering module, the server judges the collection instruction and the second machine reading identification, and the gathering module receives the collection data from the mobile terminal if the collection instruction and the second machine reading identification are consistent.
Owner:JIANGSU VOCATION & TECHNICAL COLLEGE OF FINANCE & ECONOMICS
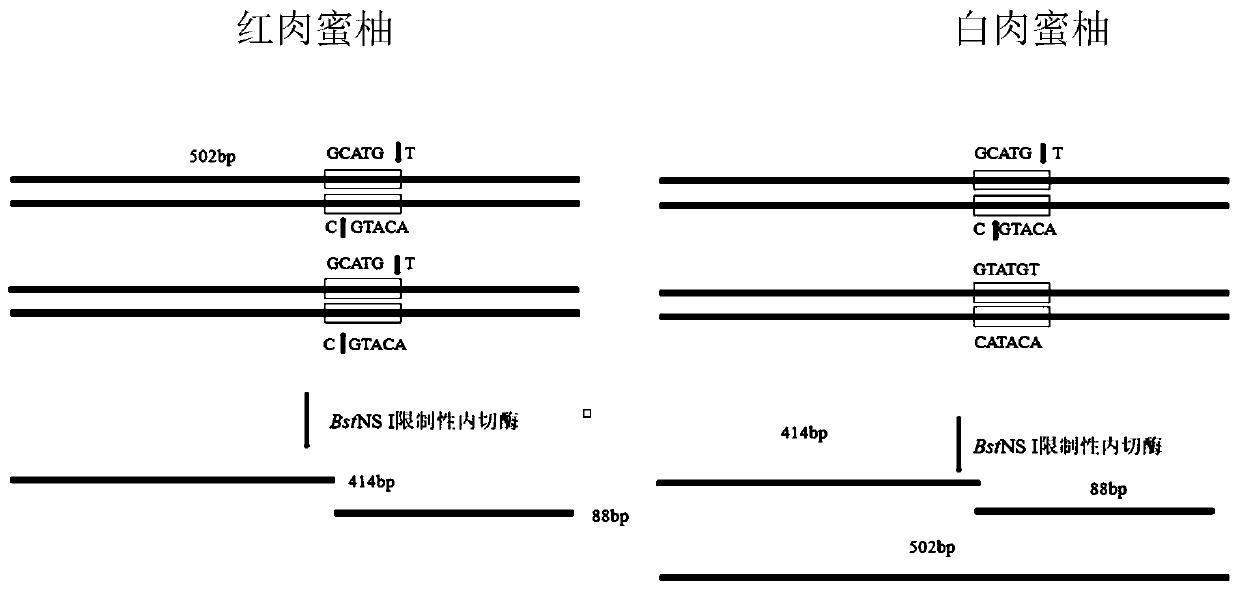
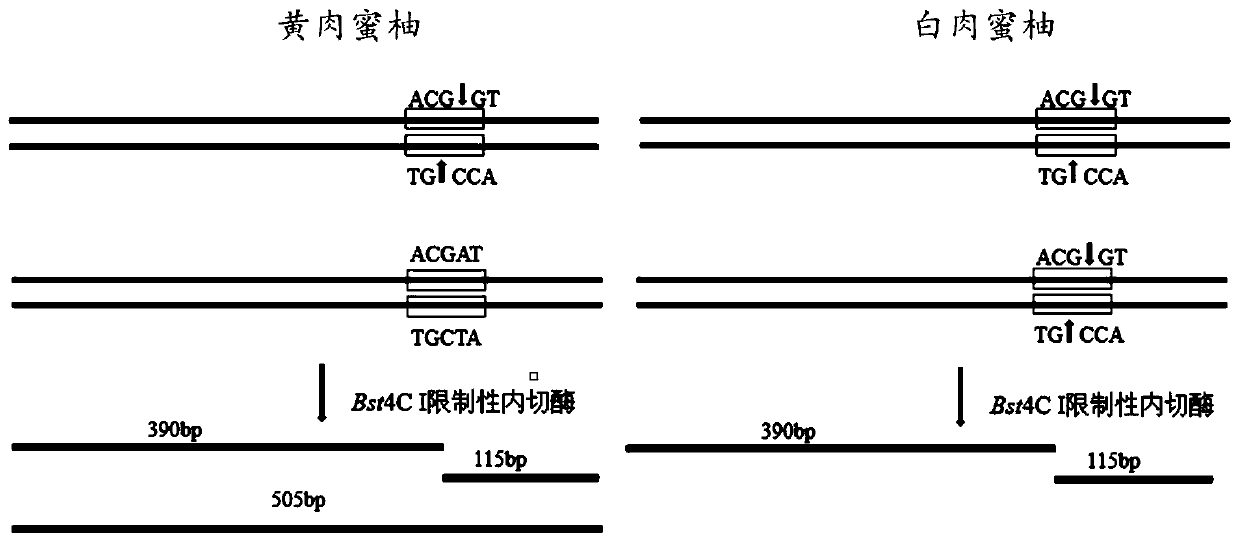
Cleaved amplified polymorphic sequence (CAPS) molecular marker suitable for identification of red pulp honey pomelo, white pulp honey pomelo and yellow pulp honey pomelo and application of CAPS molecular marker
ActiveCN110468127AReduce breeding workloadEnsure purityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationEnzymeMolecular breeding
The invention relates to the technical field of citrus molecular breeding, and discloses a cleaved amplified polymorphic sequence (CAPS) molecular marker suitable for identification of a red pulp honey pomelo, a white pulp honey pomelo and a yellow pulp honey pomelo and application of the CAPS molecular marker. The CAPS molecular marker and application of the CAPS molecular marker are suitable foridentification of Guanxi honey pomelo different bud varieties, and the CAPS molecular marker of the red pulp honey pomelo, the white pulp honey pomelo and the yellow pulp honey pomelo and applicationof the CAPS molecular marker are included. According to the CAPS molecular marker and application of the CAPS molecular marker, a set of specific PCR primers are designed by using DNA sequence information of a known site, then the primers are used for amplifying a certain DNA fragment at the site, an obtained amplified product is then incised with a specific restriction incision enzyme, separation of enzyme cleavage fragments is conducted by gel electrophoresis, and different materials are identified by analyzing electrophoresis results. The CAPS molecular marker is developed and can be usedfor identification of Guanxi honey pomelo nursery stock early varieties, and results are accurate and reliable.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
A method for directional breeding of flue-cured tobacco varieties resistant to black shank
ActiveCN106665328BHas fertility propertiesShorten breeding timePlant genotype modificationDiseaseBiotechnology
Owner:TOBACCO RES INST HENAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Indica rice target line for gene stacking of specific sites mediated by recombinase
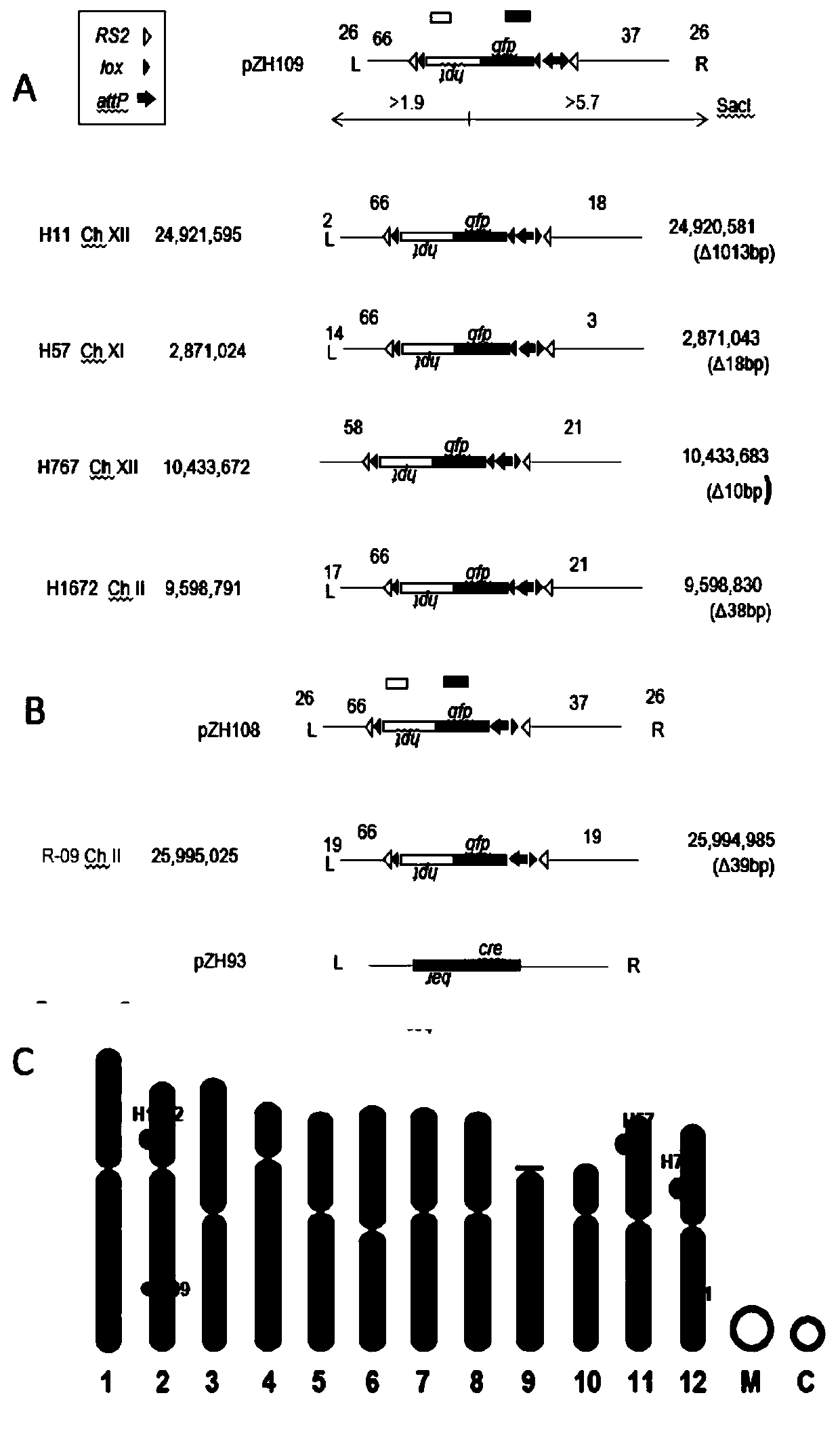
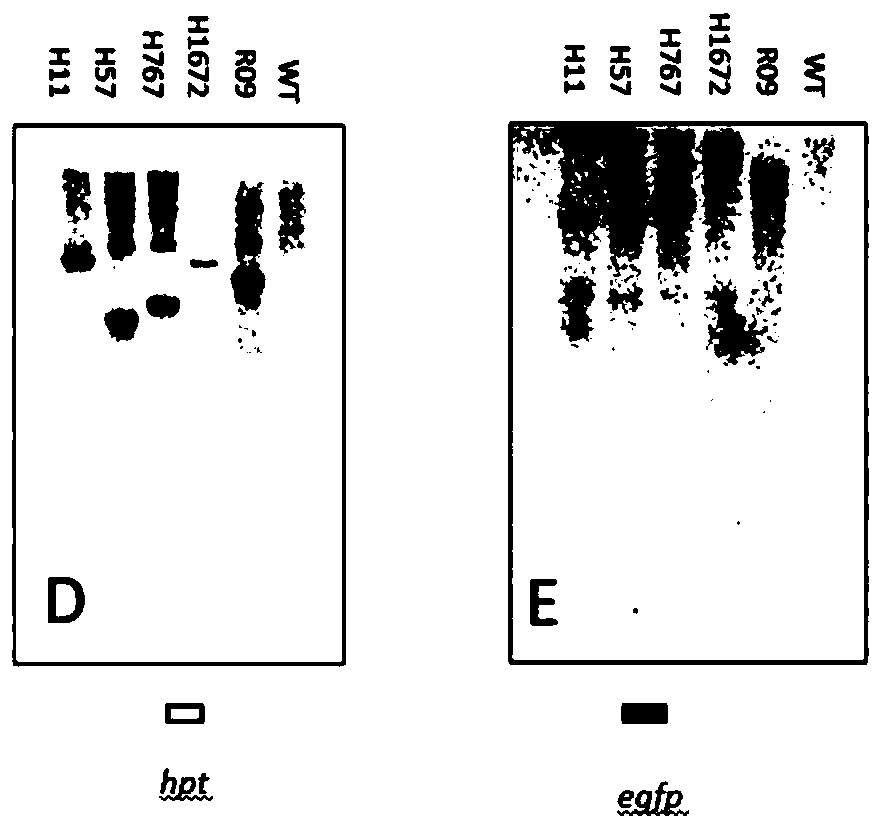
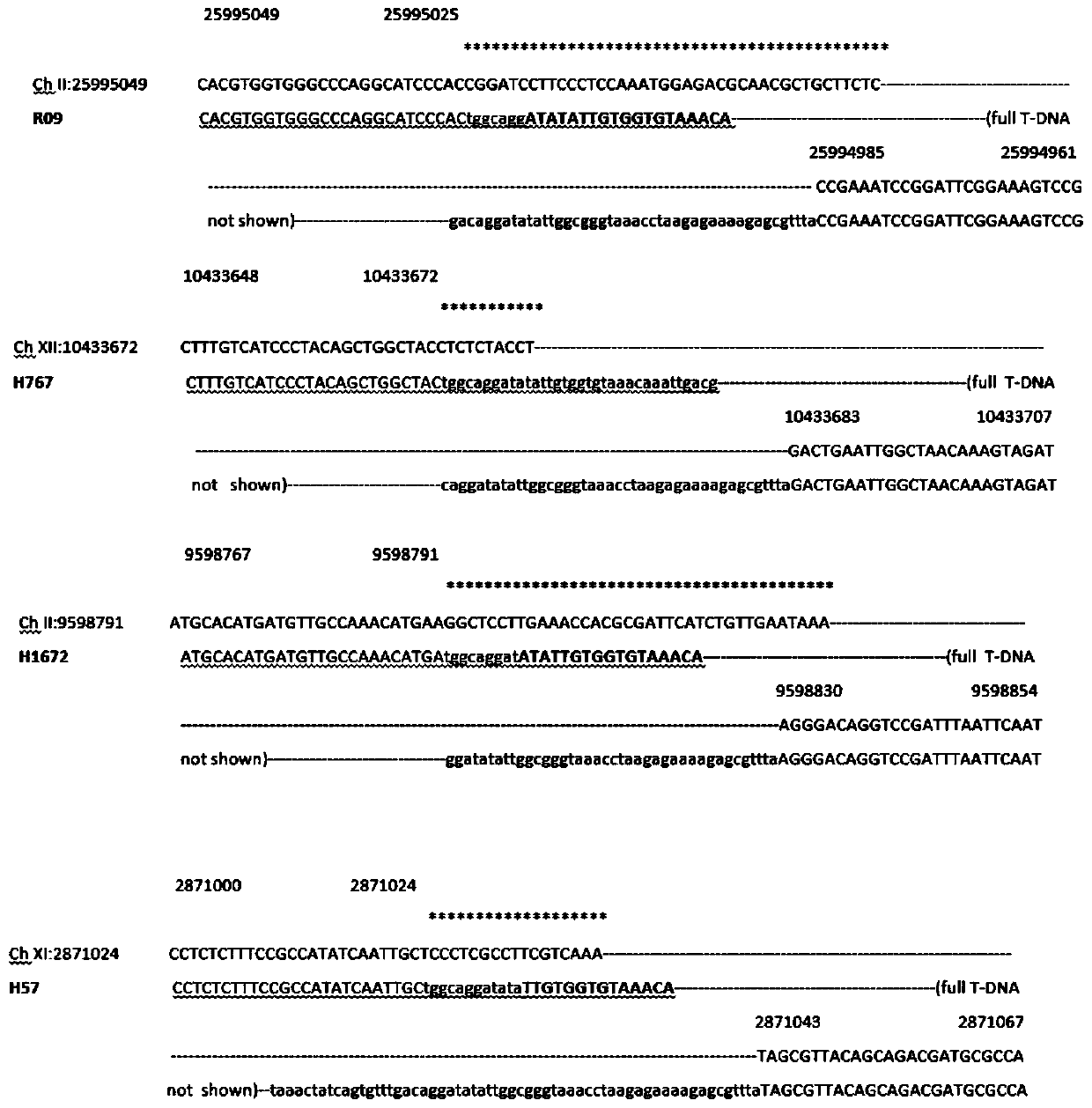
ActiveCN111118058ADoes not affect endogenous genesThe reporter gene GFP is well expressedVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsBiotechnologySite-specific recombination
The present invention discloses five starting target lines of gene stacking of specific sites mediated by recombinase suitable for indica rice. Each starting target line has an accurate single copy transgenic DNA, the DNA does not affect endogenous genes, an insertion site is at least 1 kb away from a nearest gene coding region, the DNA is far away from centromere, and a reporter gene gfp is wellexpressed. The target line contains attP and Lox recombination sites, which is conducive to stacking relevant functional genes on the gene sites through site-specific recombination fixed-point stacking. Therefore, the number of isolation sites can be reduced, and breeding workload of transgenic infiltration from experimental strains into local fine varieties can be greatly reduced. In addition, commercial product developers can also integrate the existing transgenic sites, thereby greatly reducing cost of release evaluation.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Breeding method of semiprostrate high-yield peanut variety
ActiveCN107079808AEasy to operateReduce breeding workloadMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationAgricultural scienceAgricultural mechanization
The invention provides a breeding method of a semiprostrate high-yield peanut variety. The breeding method is a method of screening male parent and female parent peanut varieties for hybridization by means of three yield trait related SSR marked primer units: GM1445, GM2531 and GM2589. The breeding method provided by the invention is a novel variety breeding method capable of predicting the yield condition of single strains on the premise of no need to wait for harvesting and polymerizing semiprostrate and high-yield trait to a same peanut plant. The method has the advantages of being simple in breeding method, clear in breeding target, small in blindness, high in efficiency and etc., and the output result can be suitable for the general orientation of agricultural mechanization in the future.
Owner:CROP RES INST GUANGDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) molecular marker closely linked with eggplant fruit color and application
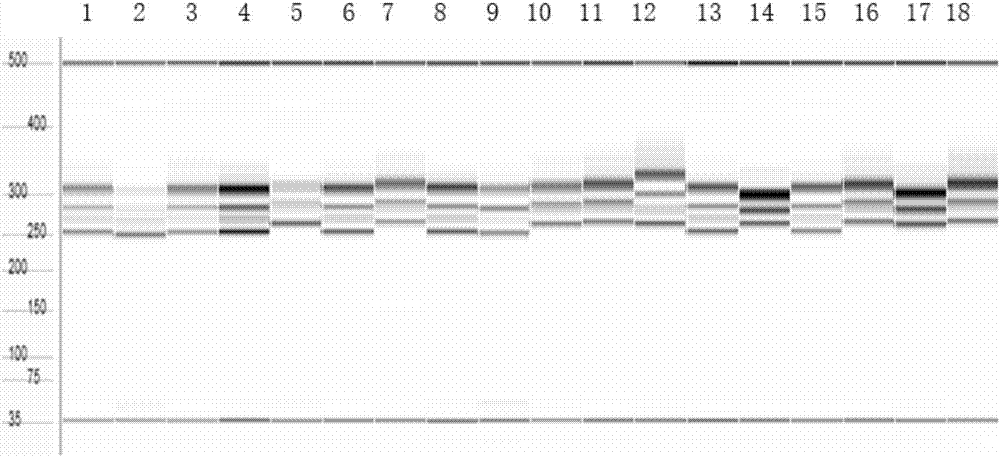
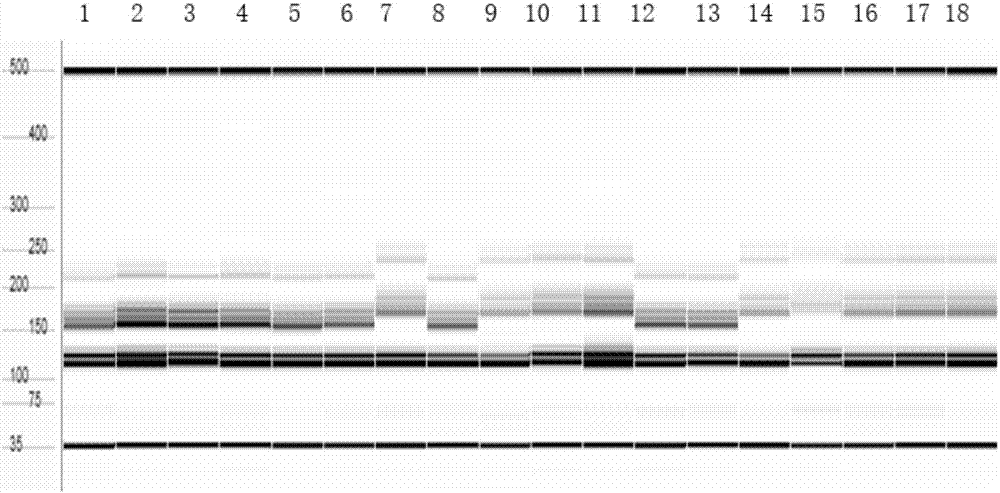
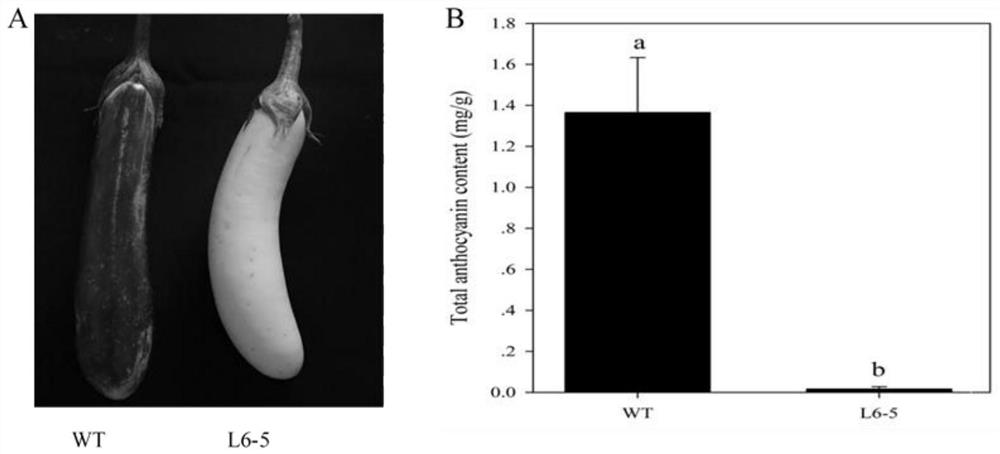
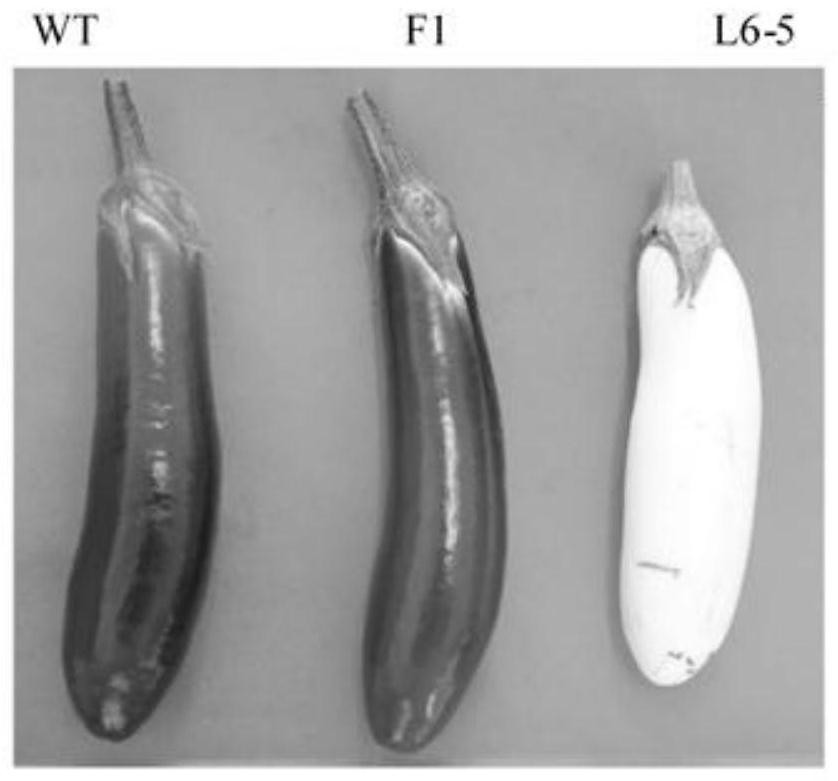
PendingCN114703312AHigh in anthocyaninsLow in anthocyaninsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideGenetics
The invention discloses an SNP molecular marker closely linked with eggplant fruit color and application, and belongs to the technical field of molecular genetic breeding, and the SNP molecular marker is characterized by comprising an SNP molecular marker I and an SNP molecular marker II; the SNP molecular marker I comprises a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1, and the 51st basic group from the 5'end of the nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 is an SNP site I; the SNP molecular marker II comprises a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.2, the 51st basic group of the nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.2 is the SNP site II from the 5'end, the SNP site I and the SNP site II are respectively positioned on the 95538422nd basic group and the 98266374th basic group of the eggplant chromosome 10, the 95538422nd basic group is C or T, the 98266374th basic group is C or T, the SEQ ID NO.1 is TACATAATTGATATTGATATTGATTACATAGGGGGGGA, and the SEQ ID NO.2 is
Owner:SOUTH SUBTROPICAL CROPS RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Two-chamber gene bjmc1 and three-chamber gene bjmc1 related to the multi-chamber trait of Brassica napus and its application
ActiveCN106279388BSpeed up the breeding processIncrease productionMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesBrassicaGenetic engineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of rape breeding and particularly relates to a two-room gene BjMc1 and a three-room gene Bjmc1 which are relates to multiicapsular traits of mustard-type rapes and an application of the two-room gene BjMc1 and the three-room gene Bjmc1. The two-room gene BjMc1 and the three-room gene Bjmc1 of the mustard-type rapes are firstly obtained from clone of the mustard-type rapes, and the two-room gene of the rapes can be subjected to genetic engineering to obtain the three-room rapes high in yield by the aid of the technology. The two-room gene BjMc1 and the three-room gene Bjmc1 can be respectively and specifically amplified by provided molecular markers of M1-1, breeding work can be reduced by applying the molecular markers on assistant selection of the mustard-type rapes with the three-room traits to overcome the shortcoming of performing selection by relying phenotype in conventional breeding, breeding periods are shortened, and processing of the mustard-type rape breeding is fastened.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Application of short n import fragments in tobacco and its screening and estimation methods
ActiveCN109517836BReduce in quantityReduce breeding workloadMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
The embodiment of the present invention discloses the application of a short N-introduced fragment in tobacco and its screening and estimation method. Compared with the N-introduced fragment of Coker176 type tobacco, the short N-introduced fragment reduces the right end of the N gene by at least 0.93Mb, preferably at least 1.56 The redundant gene component of Mb, the tobacco plants containing this short N-introduced fragment are highly resistant to TMV, and have no obvious yield and quality disadvantages, and the traits such as yield, yellowing and curing have been improved to the greatest extent. The method for estimating the number of missing redundant gene components in tobacco plants containing short N-imported fragments provided by the present invention can quickly and accurately select the plant with the shortest N-introduced fragment from plants with multiple short N-introduced fragments, and select one N-introduced The plants with the shortest fragments enter the breeding program, which can significantly reduce the breeding workload and improve the breeding efficiency.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI
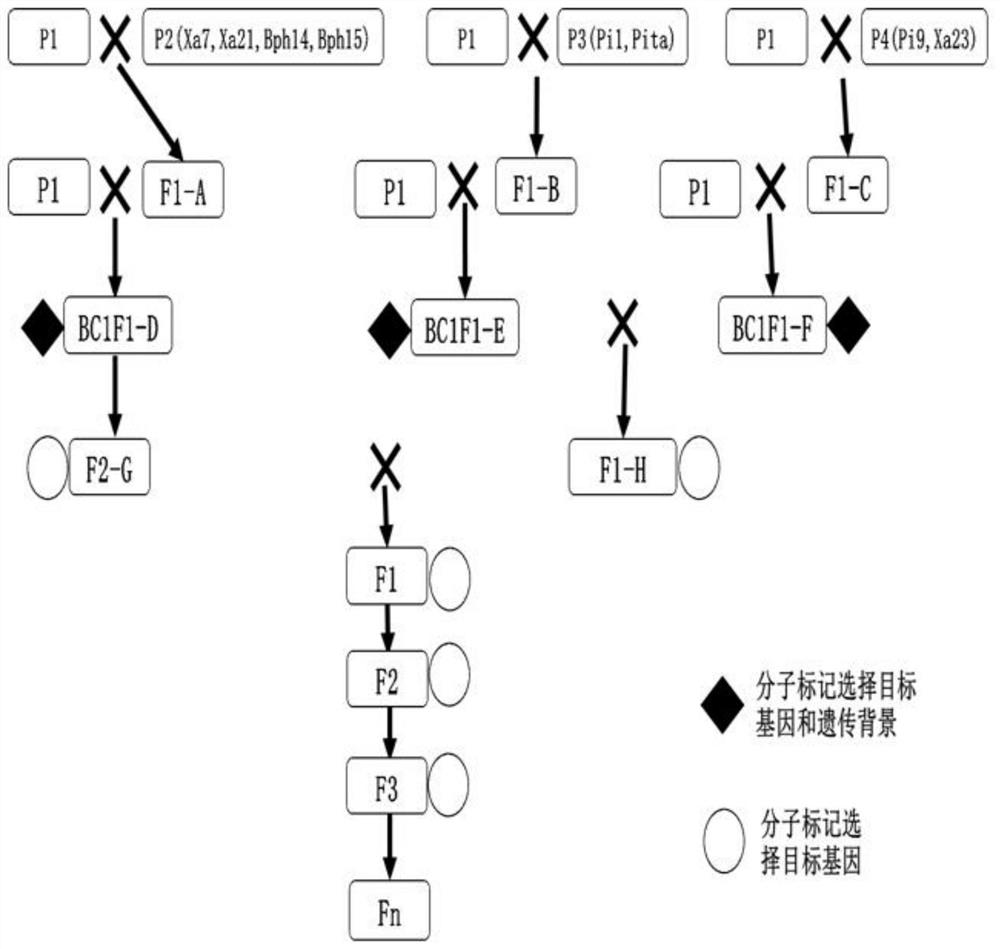
Method for creating novel multi-resistance rice germplasm by using molecular marker
ActiveCN112806252AImprove resistance to pests and diseasesBroaden the range of resistancePlant genotype modificationBacterial blightBiotechnology
The invention provides a method for creating a novel multi-resistant rice germplasm by using a molecular marker. The method comprises the following steps: according to a breeding target, carrying out multi-gene pyramiding breeding on a parent material, wherein the breeding target at least comprises pyramiding bacterial blight resistance, brown planthopper resistance and rice blast resistance. According to the method, a molecular marker-assisted selection technology is combined with a conventional breeding technology, and the polymerization of eight disease and pest resistant genes such as rice blast resistant genes Pi1, Pi9 and Pita, bacterial blight resistant genes Xa7, Xa21 and Xa23 and brown planthopper resistant genes Bph14 and Bph15 is rapidly realized, so that the breeding time is greatly shortened, and the breeding efficiency is improved.
Owner:HUAZHI RICE BIO TECH CO LTD
Molecular marker of brassica napus L. grain weight character and preparation method and application
InactiveCN102703438BSpeed up the processOvercome the downside of choosingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyBrassica
The invention belongs to the field of rape molecular breeding, and relates to a specific molecular marker of brassica napus L. grain weight and a preparation method and an application. Hybridization is performed by using brassica napus L. A254 as a female parent and using brassica napus L. A177 as a male parent to construct a dihaploid colony (DH); data of the genotype and 1000-grain weight of the DH colony are analyzed to obtain QTLs loci of the grain weight character. MINI3 and TTG2 genes of A254 and A177 are cloned by a homologous sequencing method; specific molecular marker MINI3a and TTG2a of the MINI3 and TTG2 genes are designed according to sequence different loci; the molecular marker MINI3a and TTG2a are positioned on two grain weight QTLs loci of a A5 linkage group; related verification and application demonstrate that the molecular marker prepared by the invention is a new genetic marker. The invention provides a new genetic marker for rape grain weight molecular breeding.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com