Method for breeding rape self-incompatible hybrid seeds under assistance of S haplotype molecular markers
A molecular marker-assisted, haplotype technology, applied in the fields of botanical equipment and methods, biochemical equipment and methods, angiosperms/flowering plants, etc. Problems such as generating markers and inability to identify plant phenotypes can overcome the tediousness and blindness of combination configuration, reduce the workload of breeding, and shorten the breeding cycle.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
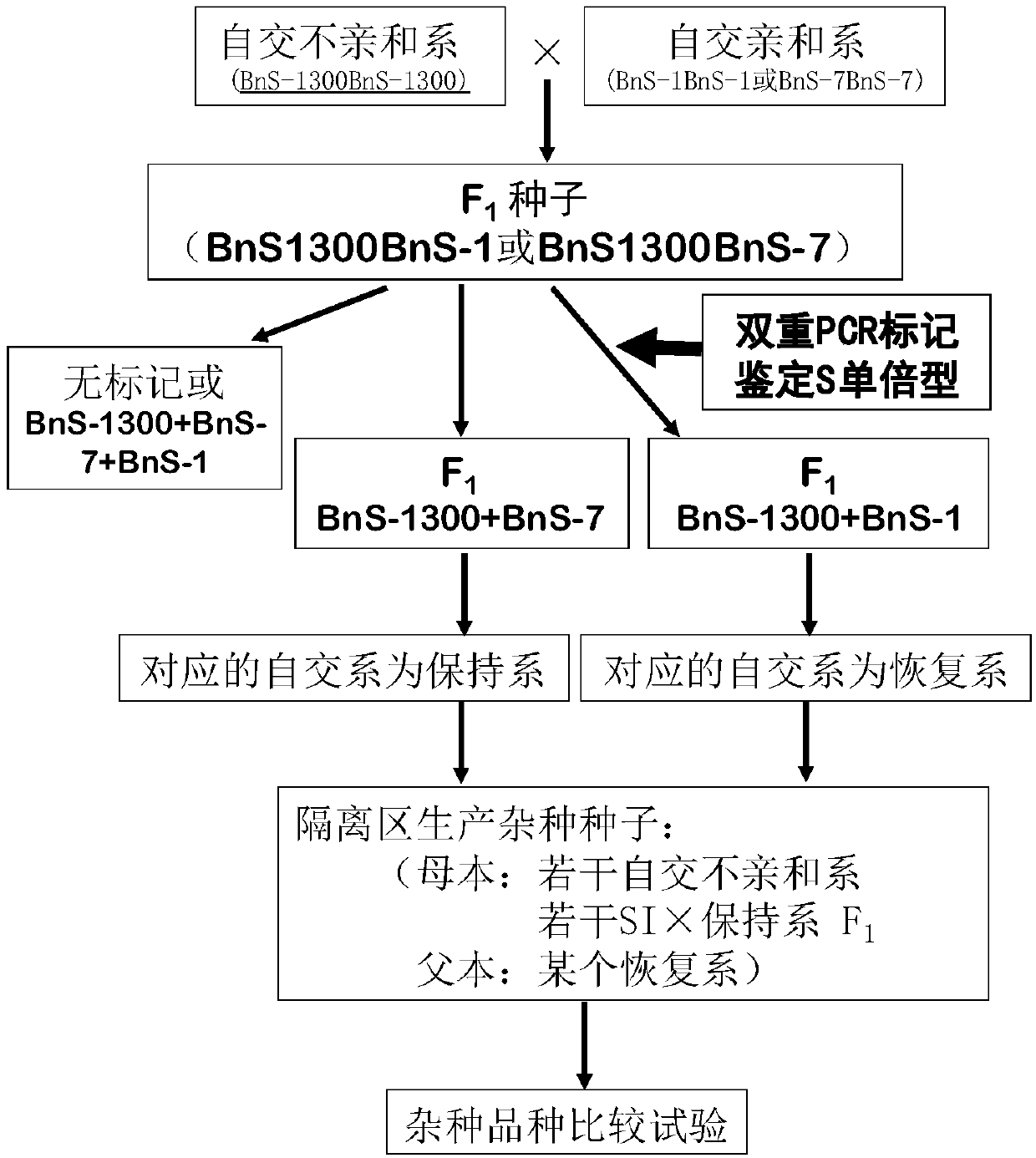
[0057] 1. F 1 acquisition of seeds
[0058] In the spring of 2015, the self-incompatibility line "S-1300" of Brassica napus was used in the experimental farm of Huazhong Agricultural University (see literature: Ma Chaozhi et al., Breeding of double-low self-incompatibility line of Brassica napus, Huazhong Agricultural University Acta Sinica, 1998, 17(3): 211-213) as the female parent, and conventional varieties "Hua Shuang No. 3" (approved by Hubei Province in 1998), "Hua Shuang No. You 18" (Zheyou 2006001), "Zheyou 28" (National You 2009014), "Zheyou 50" (National You 2011013) and "Zhongshuang No. 11" (National You 2008030) were used as male parents. Crossbreed to obtain the first generation of hybrids (F 1 )seed.
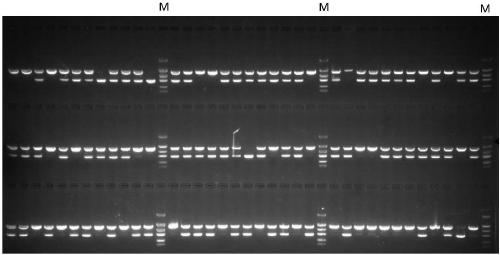
[0059] 2. Identification of the S haplotype of the inbred line
[0060] In the summer of 2015, "S-1300", the above six self-compatible varieties and their corresponding F 1 Seeds, 13 parts of materials in total, 10 grains per part; about 7 days, when the coty...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com