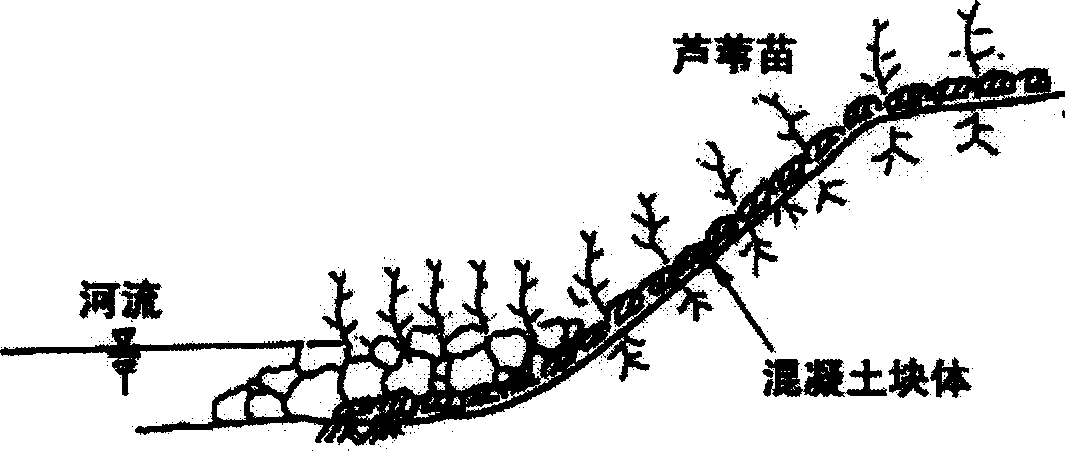
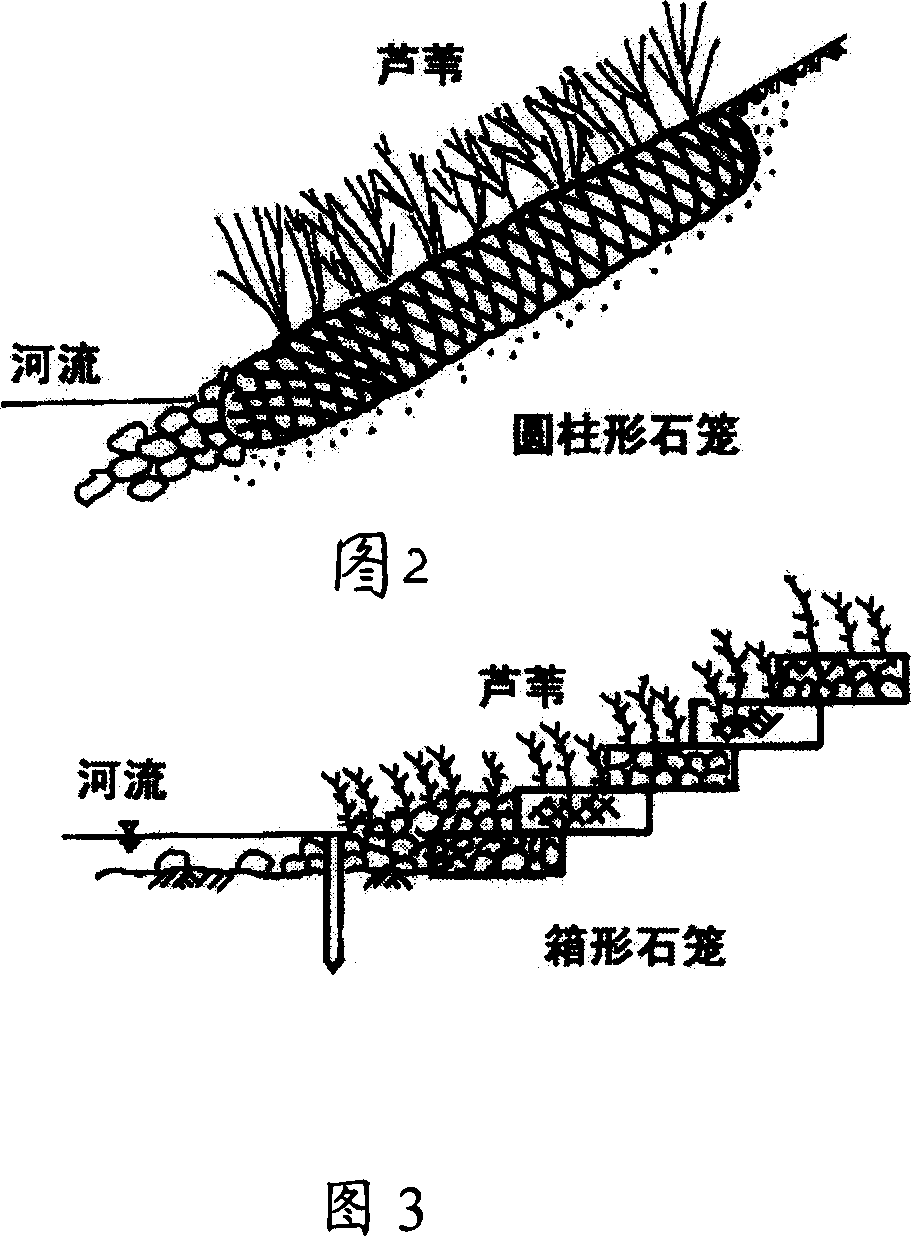
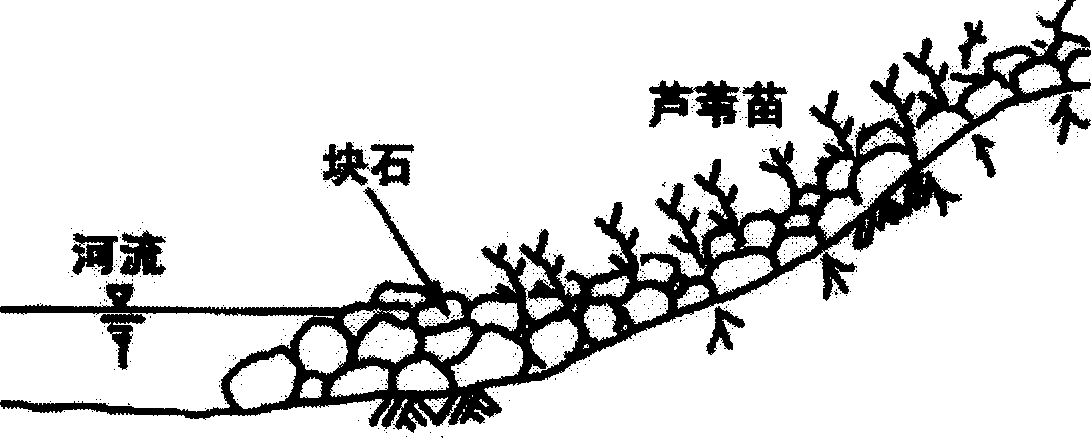
Engineering method of recovering degraduted river bank by reed
An engineering and reed technology, applied in the field of reed community restoration, can solve the problems of inconvenient transportation of reeds, damage to the original ecological environment of reeds, and high cost, and achieve the effects of preventing collapse and erosion, easy recovery, and reducing damage.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0097] 1. Reed collection: reeds are collected from the natural growth of reed communities;
[0098] Select reeds that grow well at the collection site and cut them off the ground, and cut off the reed leaves, then sort the thin rods: 2-3 mm in diameter, thick rods: 3-5 mm in diameter, and cut the thick and thin reed rods respectively into 30 cm long;
[0099] 2. Germination of reeds: germination under bundled conditions;
[0100] Bundle 10 thin reed stalks into 1 bundle or 5 thick reed stalks into 1 bundle, put them into the pool for soaking for 15 days; during this period, change the water once every 3 days to make the reed stalks germinate and cultivate reed seedlings;
[0101] 3. Seedlings of reeds
[0102] Cut the newly germinated reed seedlings on the reed stalks, plant them in rectangular plastic boxes filled with peat soil that are convenient for transportation, and cultivate them for 55 days. The rectangular plastic boxes are 35 cm long, 25 cm wide, and 10 cm high; ...
Embodiment 2
[0106] 1. Reed collection: reeds are collected from the natural growth of reed communities;
[0107] Select reeds that grow well at the collection site and cut them off the ground, and cut off the reed leaves, then sort the thin rods: 2-3 mm in diameter, thick rods: 3-5 mm in diameter, and cut the thick and thin reed rods respectively into 30 cm long;
[0108] 2. Germination of reeds: germination under bundled conditions;
[0109] Bundle 10 thin reed stalks into 1 bundle or 5 thick reed stalks into 1 bundle, put them into the pool for soaking for 15 days; during this period, change the water every 4 days to make the reed stalks germinate and cultivate reed seedlings;
[0110] 3. Seedlings of reeds
[0111] Cut the newly germinated reed seedlings on the reed stalks, plant them in a rectangular plastic box filled with peat soil that is convenient for transportation, and cultivate them for 60 days. The rectangular plastic box is 38 cm long, 27 cm wide, and 11 cm high; Water on...
Embodiment 3
[0115] 1. Reed collection: reeds are collected from the natural growth of reed communities;
[0116] Select reeds that grow well at the collection site and cut them off the ground, and cut off the reed leaves, then sort the thin rods: 2-3 mm in diameter, thick rods: 3-5 mm in diameter, and cut the thick and thin reed rods respectively into 30 cm long;
[0117] 2. Germination of reeds: germination under bundled conditions;
[0118] Bundle 10 thin reed stalks into 1 bundle or 5 thick reed stalks into 1 bundle, put them into the pool for soaking for 15 days; during this period, change the water every 5 days to make the reed stalks germinate and cultivate reed seedlings;
[0119] 3. Seedlings of reeds
[0120] Cut the newly germinated reed seedlings on the reed stalks, plant them in a rectangular plastic box filled with peat soil that is convenient for transportation, and cultivate them for 65 days. The rectangular plastic box is 40 cm long, 30 cm wide, and 12 cm high; Water on...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com