HO/LL canola with resistance to clubroot disease
A brassica and plant technology, applied in the field of HO/LL brassica which is resistant to clubroot, can solve the problems of hindering breeding, troublesome, time-consuming, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0218] Example 1: Materials and methods
[0219] plant material
[0220] Brassica varieties DMS100 (mutant type) and Quantum (wild type) were used in this study to clone the fad2 (fatty acid desaturase-2) and fad3 (fatty acid desaturase-3) alleles. DMS100 is a HO / LL (high oleic and low linolenic) line with an oleic acid content of about 77% and a linolenic acid content of about 3%. DMS100 is a single F derived from a sister line cross of Global xAG019 3 F for plant selection 4 Batch derivation. Quantum is a commercial variety and contains low oleic acid (-66%) and high linolenic acid (-7%) content. Double haploid (DH) populations through F to crosses between Brassica lines Quantum and DMS100 1 Formation of microspore cultures of plants. The DH population consisted of 604 lines. Complete fatty acid analysis of the seeds of the DH line and its parents was performed by using gas chromatography. Among the 604 DH lines, 183 were randomly selected for marker analysis and map...
Embodiment 2
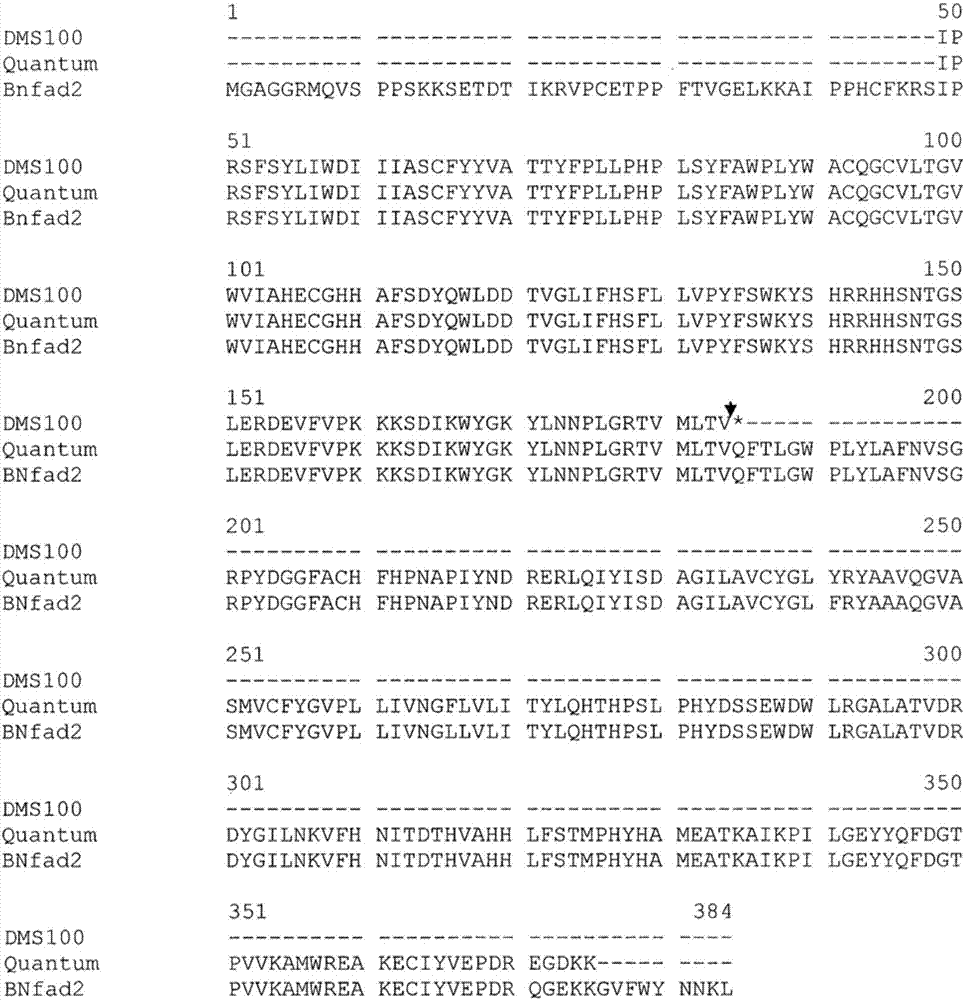
[0231] Example 2: Cloning of fad2 and fad3 alleles
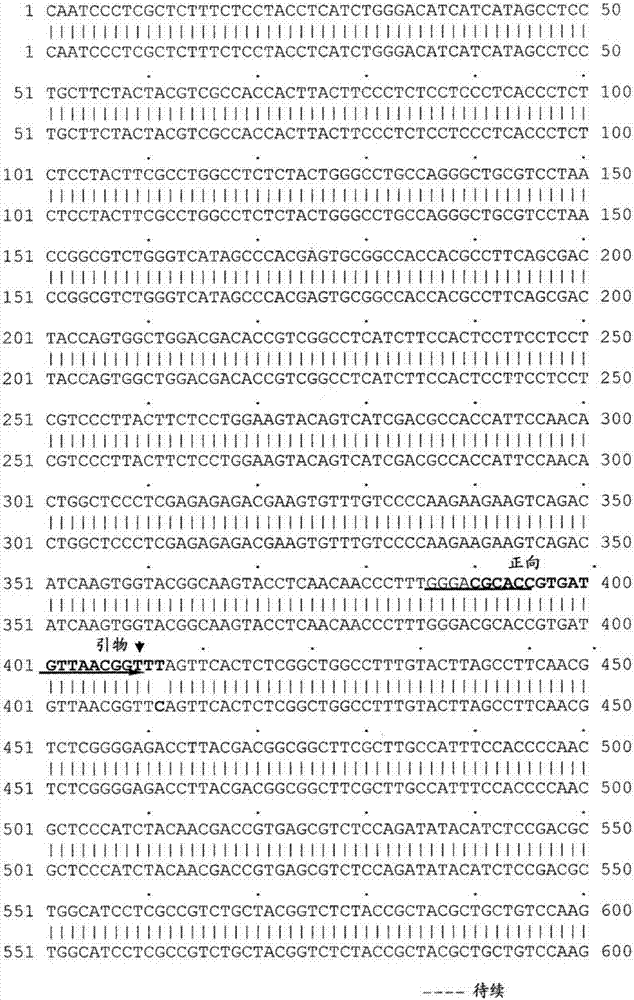
[0232] Genomic DNA fragments of the fad2 gene from the parental Brassica napus line DMS100 (mutant) and Quantum (wild type) were amplified by using primers homologous to the Arabidopsis or Brassica fad2 gene sequence. et al. (1998), see Figure 1 above. The fad2 fragment amplified from each parent by primers FAD2-2F and FAD2-6R was cloned and sequenced. This primer pair amplified fad2 fragments of the same length (986bp) from each of the two parents. The sequences of these two primers are:
[0233] FAD2-2F: CAATCCCTCGCTCTTTTCTCCTACC (SEQ ID NO: 1)
[0234] FAD2-6R: CCTTTCTTGTCACCTTCCCCTGTCC (SEQ ID NO: 2)
[0235]A single nucleotide substitution mutation was identified at position 411 of the fad2 gene between the two parental lines. figure 1. The wild-type Quantum fad2 gene contains a "C" nucleotide at position 411. However, the HO / LL DMS100 fad2 gene contained the SNP at the same position, where the nucleotide was ch...
Embodiment 3
[0240] Example 3: Mutant allele-specific SNP markers of fad2 and fad3 genes
[0241] Single nucleotide mutations present in the fad2 and fad3 genes were used as SNP markers to mark the fad2 and fad3 genes for selection of high C18:1 and low C18:3 in canola breeding. Mutant-specific primers (FAD2GM: CGCACCGTGATGGTTAACGGTTT (SEQ ID NO: 5); and FAD3cGM: ATAAATAATGTTGATCTACTTAT (SEQ ID NO: 15)) were designed to detect mutant alleles of fad2 and fad32 using PCR amplification. Primers were designed such that the mutated base (SNP) was at the 3' end of one primer for allele-specific PCR amplification. Figures 1 and 3.
[0242] Primers specific for fad2 amplified polymorphic bands that were present in DMS100 and DNA bulks (for high oleic acid (C18:1)), but not in Quantum and DNA bulks (for low oleic acid). Figure 4 . This gene-specific marker was tested on the DH population derived from the cross of Quantum and DMS100, where it was found that the allelic distribution was highly c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com