Method for extracting plasmodiophora brassicae DNA of cruciferae vegetables and application of method
A technology of cruciferous vegetables and an extraction method is applied in the field of isolating host-contaminated pathogenic bacteria DNA extraction, which can solve problems such as DNA molecular contamination of host plants, and achieve the effects of shortening the breeding cycle and speeding up the breeding process.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
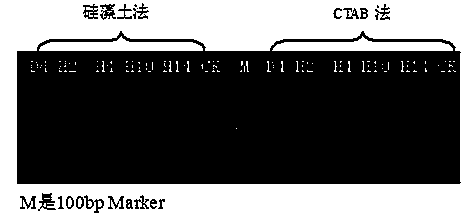
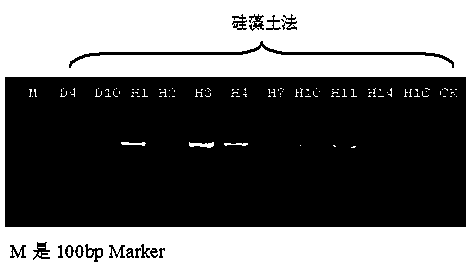
[0029] Embodiment 1: Chinese cabbage genome specific SSR marker detects CTAB method and diatomite method of the present invention extracts purity comparison
[0030] 1. Collection of clubroot pathogenic bacteria: 5 sources of clubroot pathogenic bacteria were collected from the diseased roots of the diseased plants in the main producing areas of cruciferous vegetables such as Yunnan, Liaoning, Shandong, etc., and the other material was from clubroot bacteria. Hosts include major cruciferous vegetables such as Chinese cabbage, cabbage, hybrids of black mustard and cauliflower, and radishes. The clubroot tissue sections were examined under a microscope, and dormant sporangia and swimming dormant spores were observed under the microscope, which was determined to be Plasmodium brassicae ( Plasmodiophora brassicae Wor.). The collected fresh mycorrhizae were washed, dried on the surface, and stored in a -20°C refrigerator.
[0031] Host identification: The identification of...
Embodiment 2
[0059] Comparison of the amplification results of the Genome Specific SSR Marker TCO1 of Plasmodium Plasmodium in the CTAB method and the diatomite method of the present invention.
[0060] 1. TC01 is based on the 18S rRNA (GenBank accession no. AF231027, 552bp) of the clubroot pathogen genome, which has the following nucleotide sequence:
[0061] 5’-gtggtcgaacttcattaaatttgggctcttagaagaagga gaagtcgtaacaaggtttccgtaggtgaacctgcagaagg atcattaaca cagtgggcgg ccctagcgct gcatcccaca
[0062] tcccaacccccaaccccatgtgaaccggtgacgtgcggcgta agctgcgtgtttcattttcgaaccatgctagccgaaacac aactgaagtt ccatacatac acatgttaca actcttagca
[0063] atggatatcttggttctcacaacgatgaagaacgcagcga actgcgatacgtagtgcgaattgcagaattcagtgaatca tcaaatcttt gaacgcaagt tgcgcttccg agataccctt
[0064] ggaagcatgcctctttgagtgtcggttcctgtttgtttgg gcgccccgcgcgcgcaagacaatgagctttgctgcggcat ggcttgaactagcgagacccgggaccgtgc gtgcattgttgagaacaccatcgagagaatgccggagcgg tccccgccga tctgcgcgca atcgaccacaa-3
[0065] Its specific amplification pr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com