Panicle size controlling gene, mutant and application thereof
A rice and gene technology, applied in the fields of application, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, etc., can solve the problems affecting the potential mining and improvement of hybrid rice combination yield of rice varieties, single genetic background of rice varieties, and narrow sources.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0072] Example 1: Phenotypic analysis of mutant ssp1
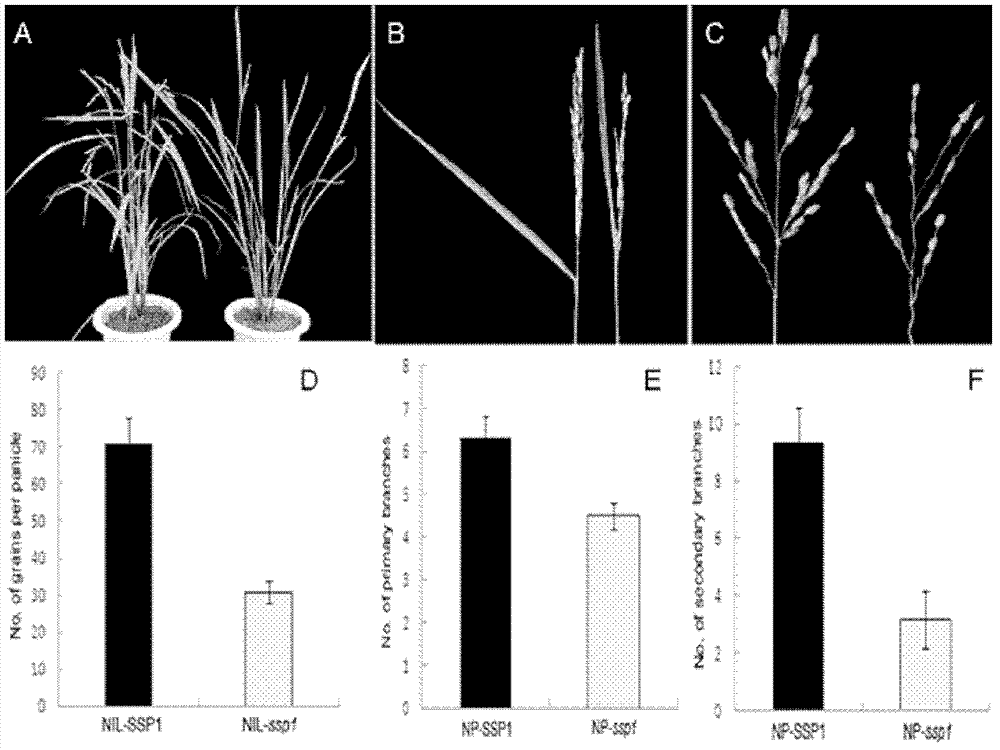
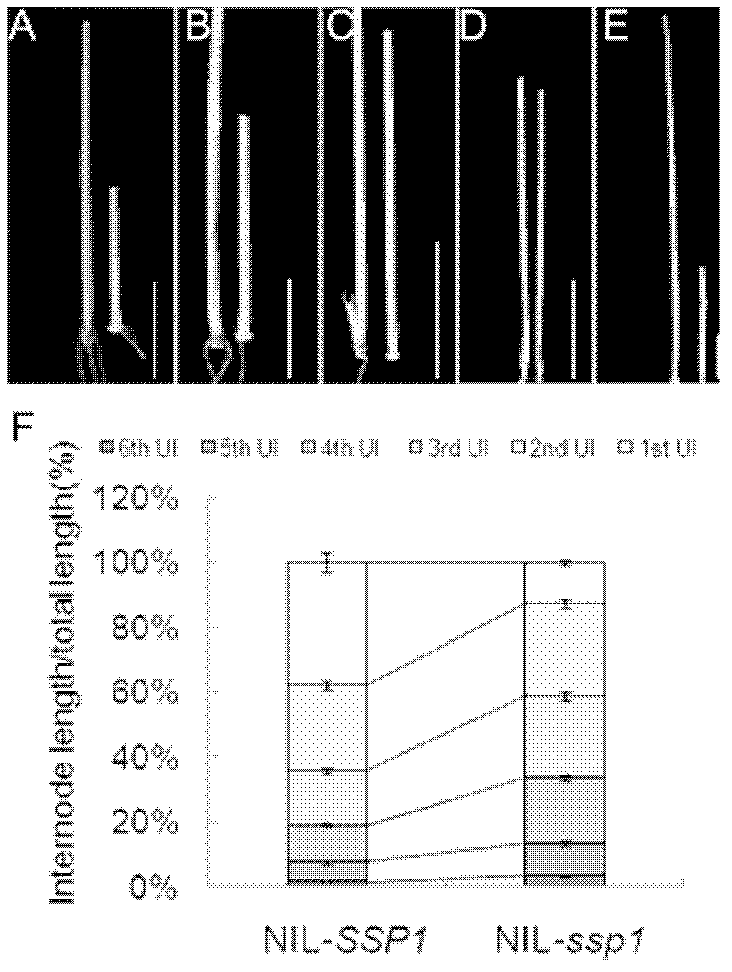
[0073] Through genetic hybridization, near-isogenic lines: NP-SSP1 and NIL-ssp1 were constructed and obtained in Nipponbare (japonica) and Nanjing 6 (indica) backgrounds. Such as figure 1 As shown, the NIL-ssp1 plants under the genetic background of Nanjing 6 showed phenotypes such as semi-dwarf, smaller leaf angle, dark green leaves, and changed panicle shape.
[0074] NIL-ssp1 rice panicle becomes smaller ( figure 1 , B, C), incomplete heading ( figure 1 B). Statistics found that the number of grains per panicle of NIL-ssp1 ( figure 1 D), the number of primary branches ( figure 1 E), the number of secondary branches ( figure 1 F) are significantly less than NIL-SSP1. In particular, the reduction in the number of secondary branches in NIL-ssp1 rice was more significant, indicating that the decrease in the number of grains per panicle was mainly caused by the reduction in the number of secondary branches. In additi...
Embodiment 2
[0075] Example 2: The ssp1 gene inhibits cell division and cell elongation
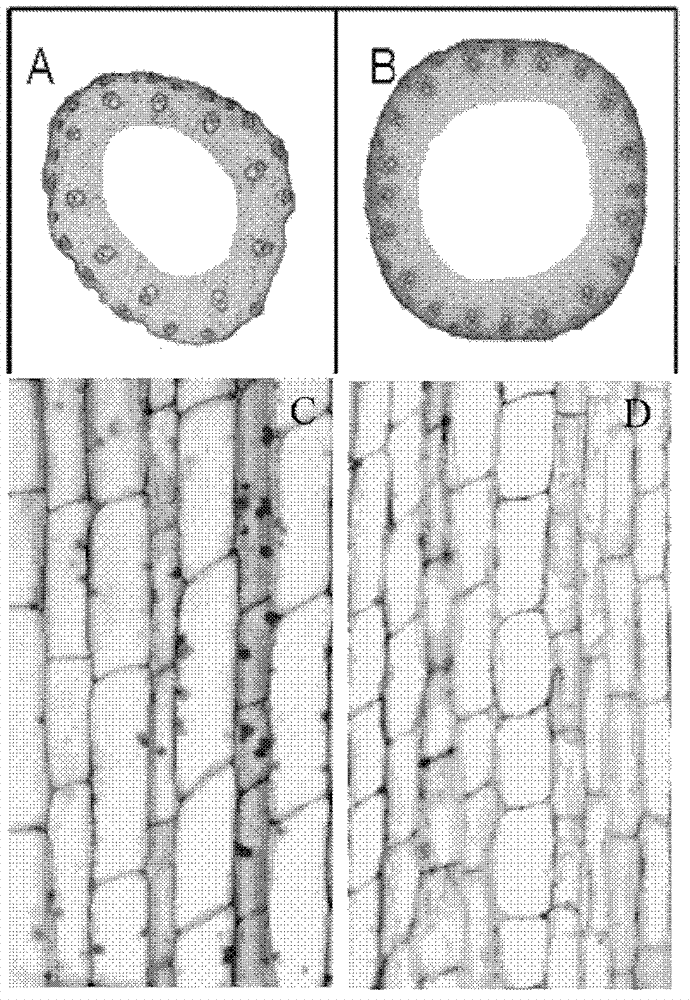
[0076] Tissues from the same part of the last stalk of the near isogenic line were selected and fixed, and the transverse and longitudinal tissue sections were observed, and it was found that the last stalk of NIL-ssp1 ( image 3 A) The number of vascular bundles in the medium was significantly less than that of NP-SSP1 ( image 3 B), indicating that the cell division of NIL-ssp1 is inhibited; at the same time, the number and size of longitudinal cells in the last stem of NIL-ssp1 ( image 3 D) significantly smaller than NP-SSP1 ( image 3 C), indicating that both cell division and cell elongation are significantly inhibited in NIL-ssp1.
Embodiment 3
[0077] Example 3: Map-based cloning of the SSP1 gene
[0078] The F1 and F2 offspring obtained from crossing ssp1 with Nanjing No. 6 were used for genetic analysis. Statistical data and Chi-square test found that the segregation ratio of the trait was 3:1, indicating that the trait was controlled by a dominant single gene.
[0079] The phenotype separation of the F2 generation of the mapping population constructed by crossing ssp1 with Nanjing No. 6 was used to segregate SSP1 roughly between Marker 337 and Marker 481 on the long arm of chromosome 1. Then, the phenotype of the F2 generation single plant constructed by crossing ssp1 and Zhonghua 11 was used to isolate, and it was finely mapped to the 109kb region on BAC AP002910 ( Figure 4 ). This region contains 15 ORFs, 11 of which have predicted protein products. Further sequencing revealed that there were two point mutations in one of the genes: G-C at 1360bp at the C-terminus, leading to Gly-Arg, and A-C at 1366bp, leadi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com