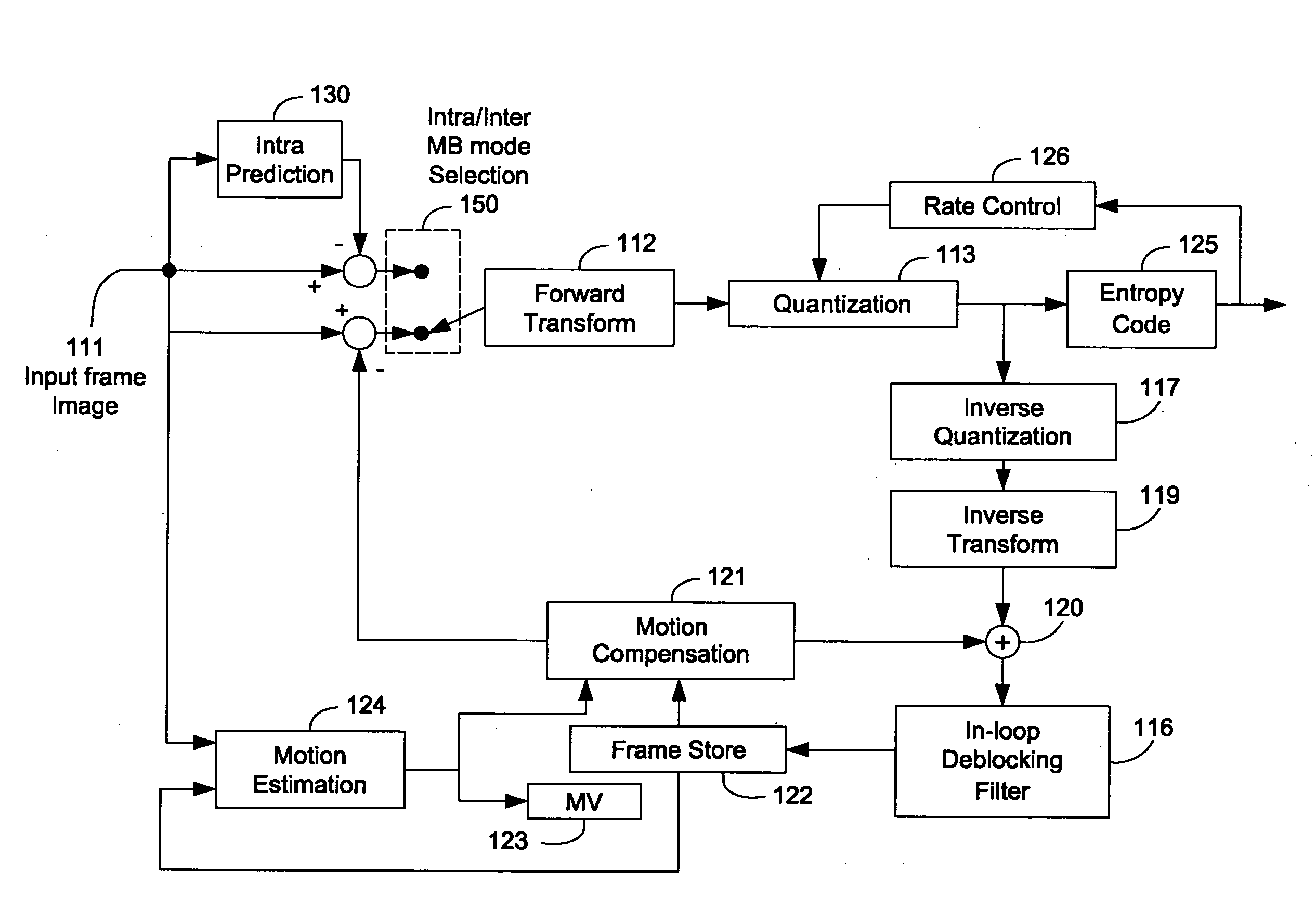
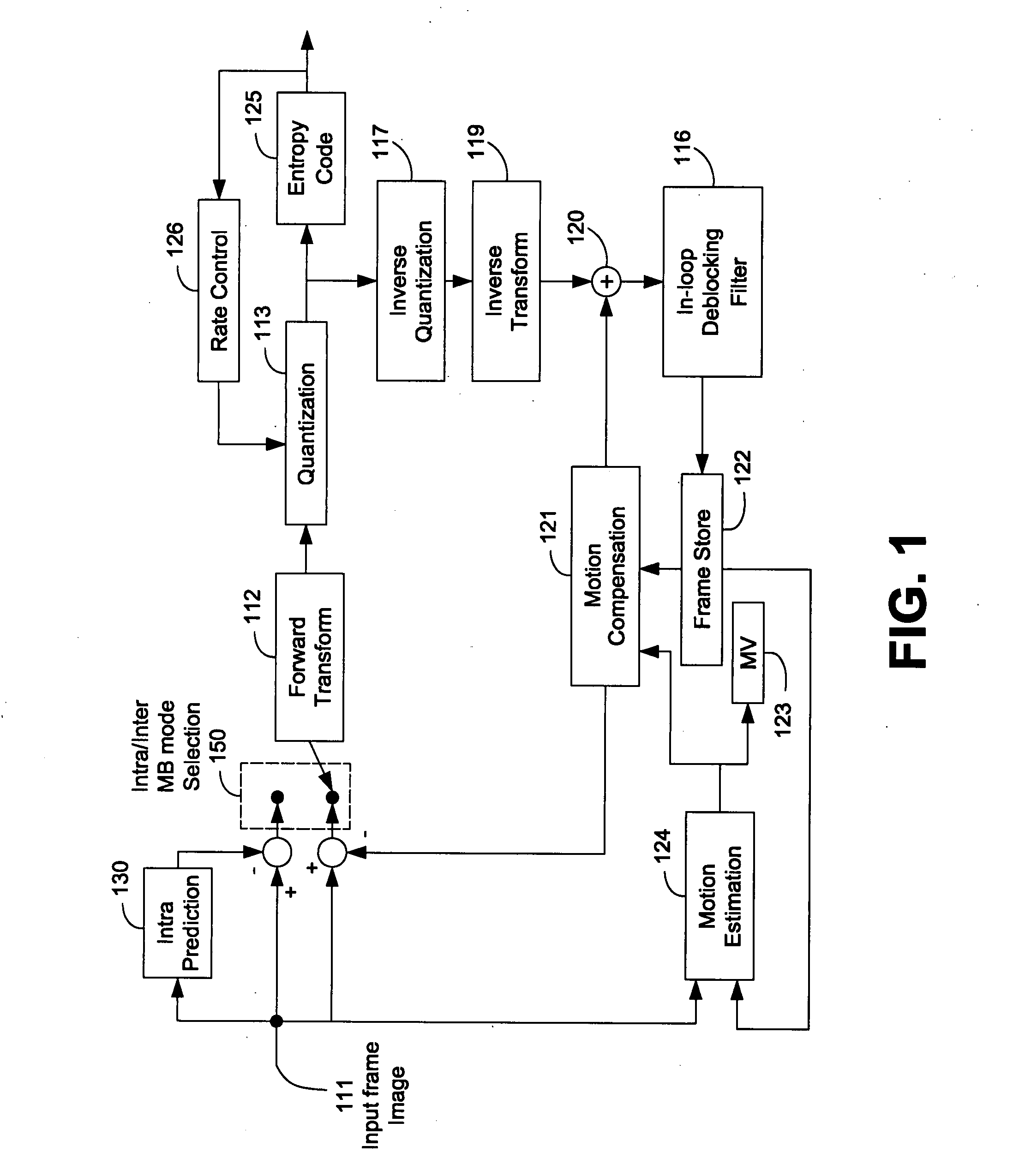
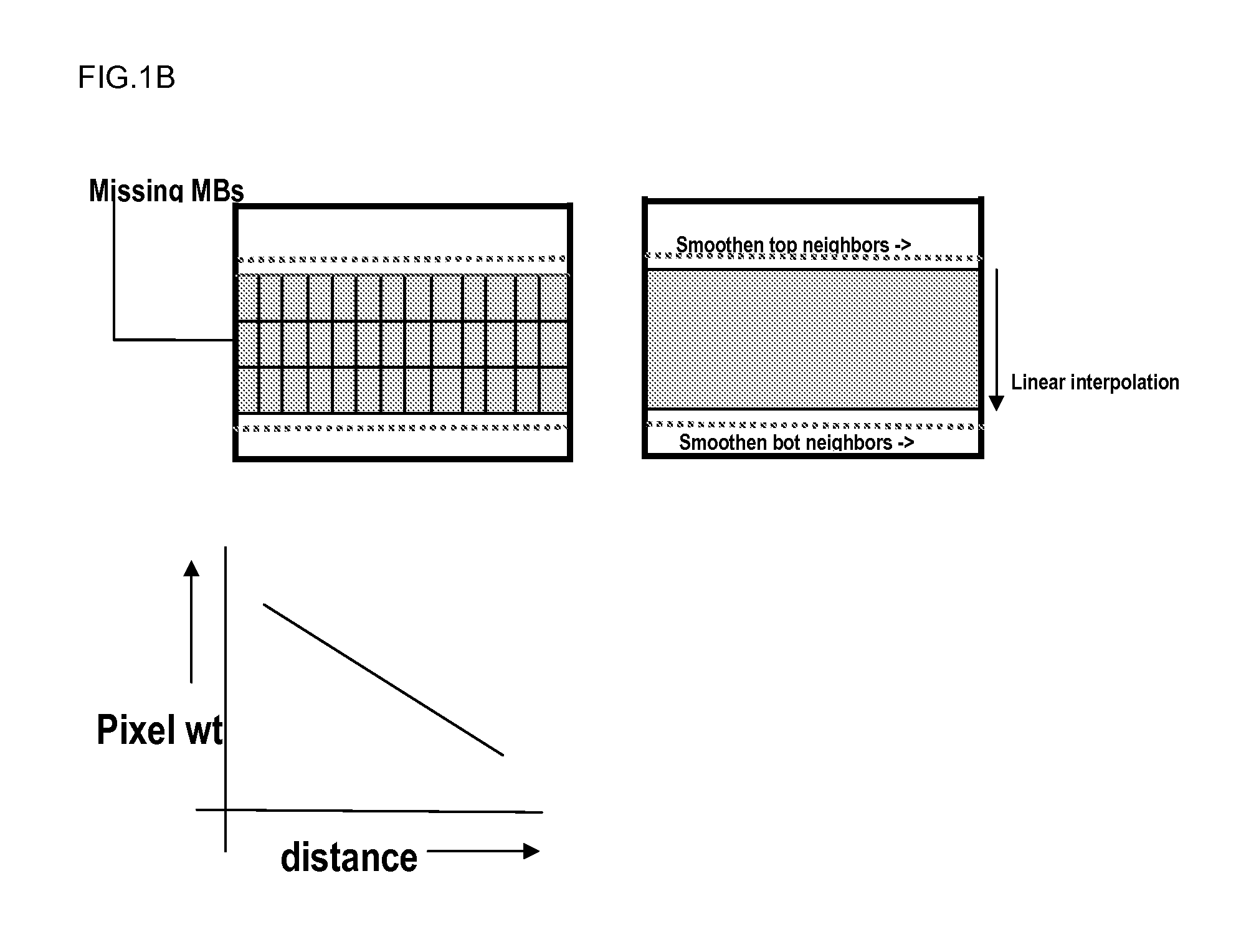
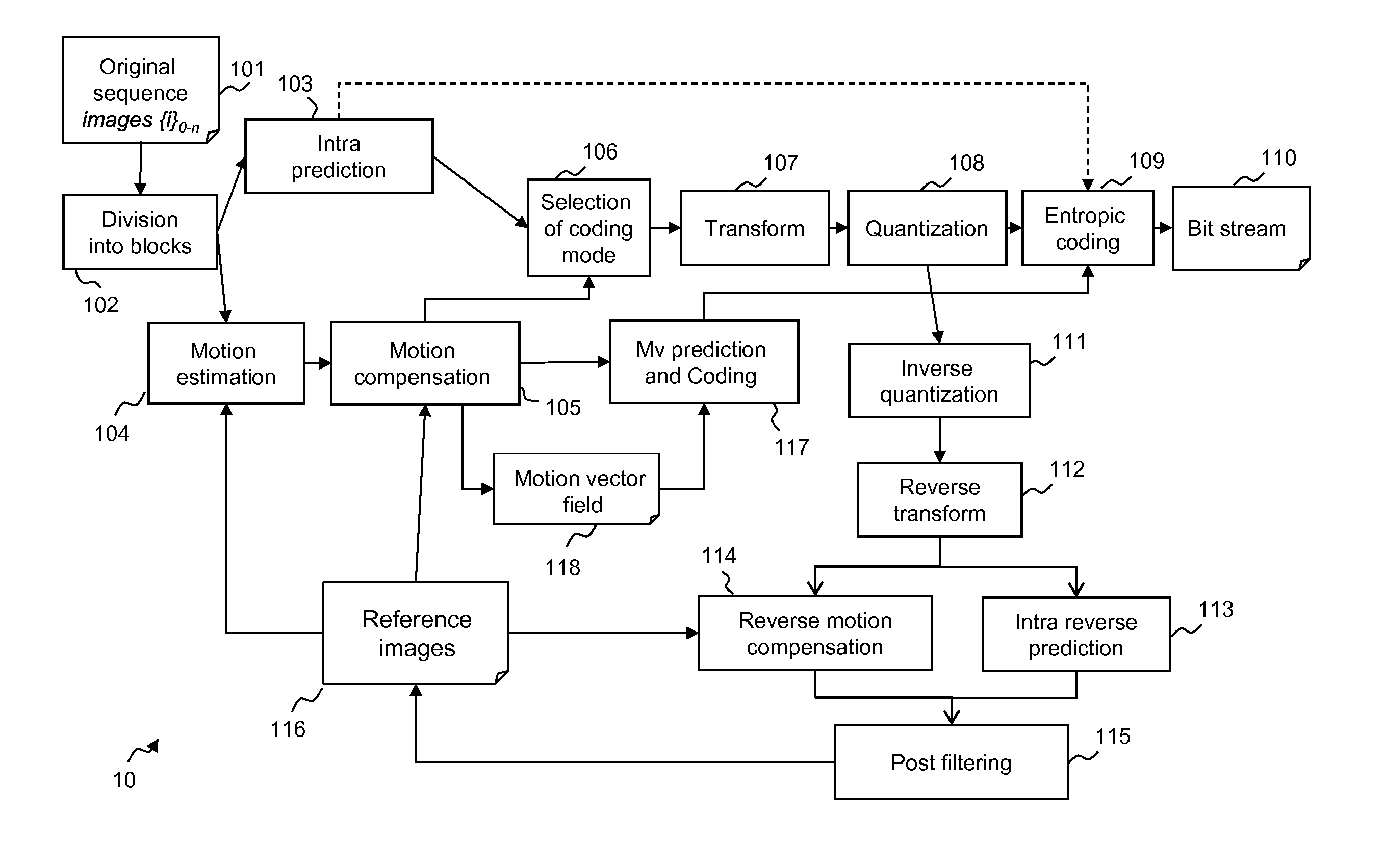
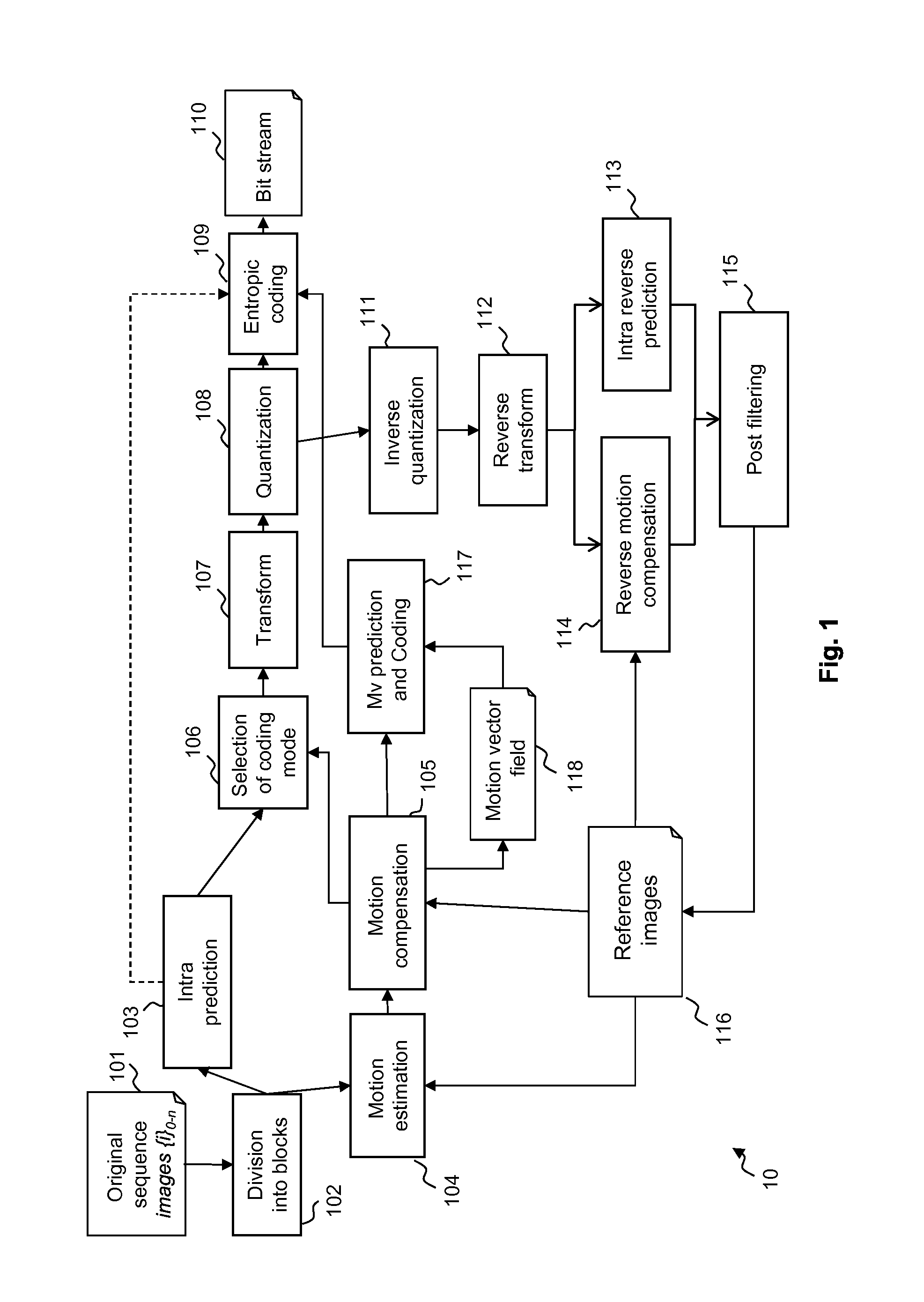
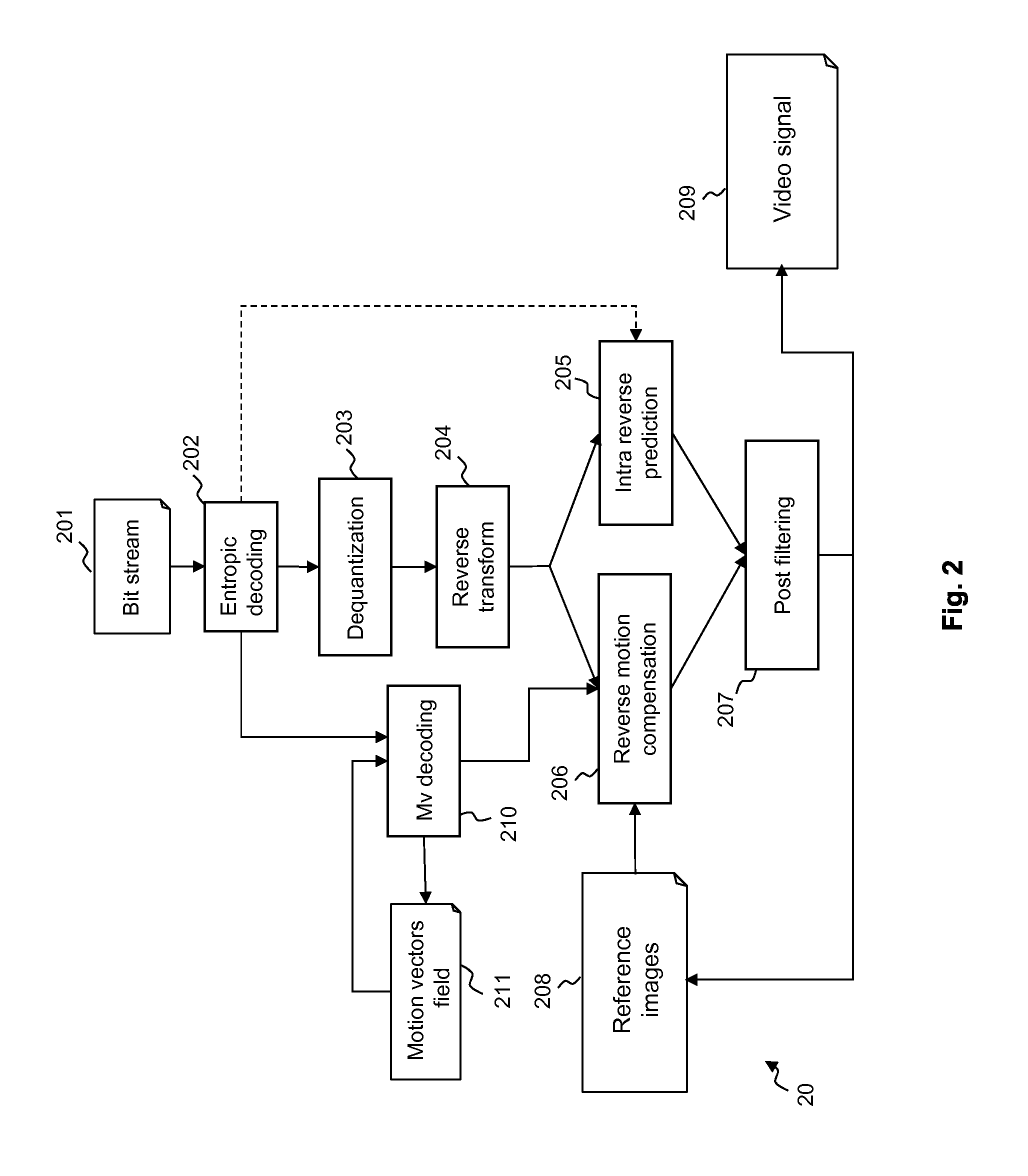
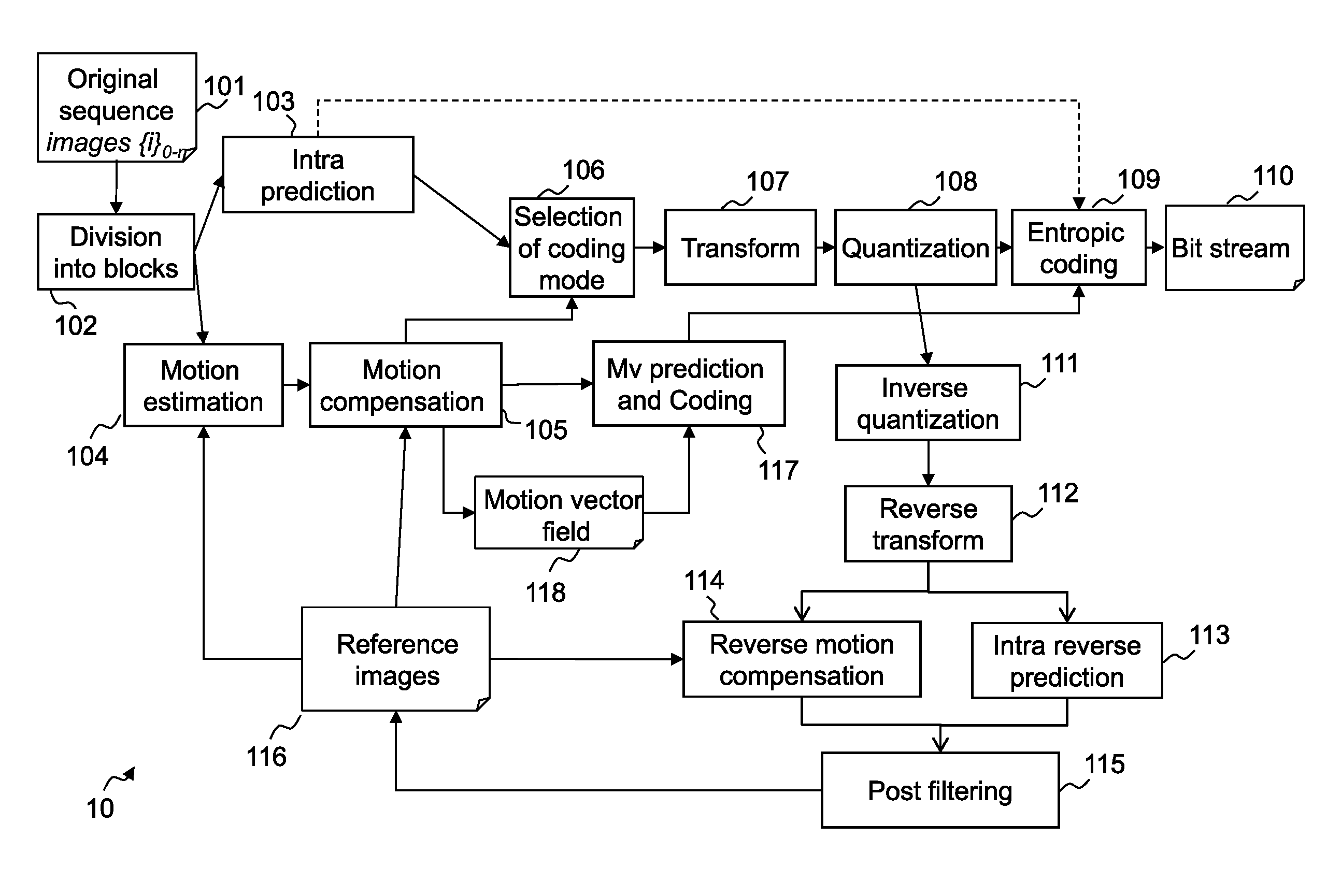
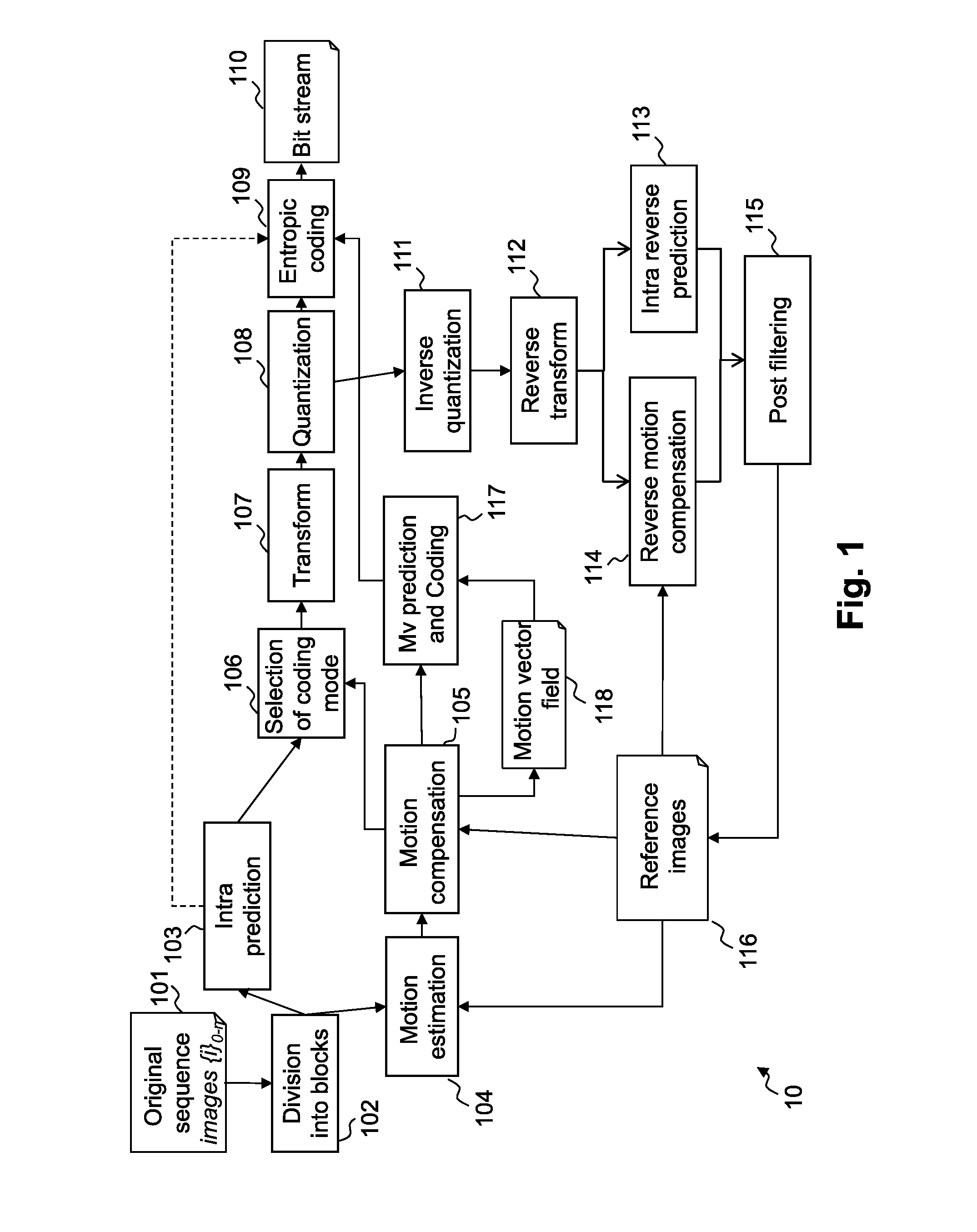
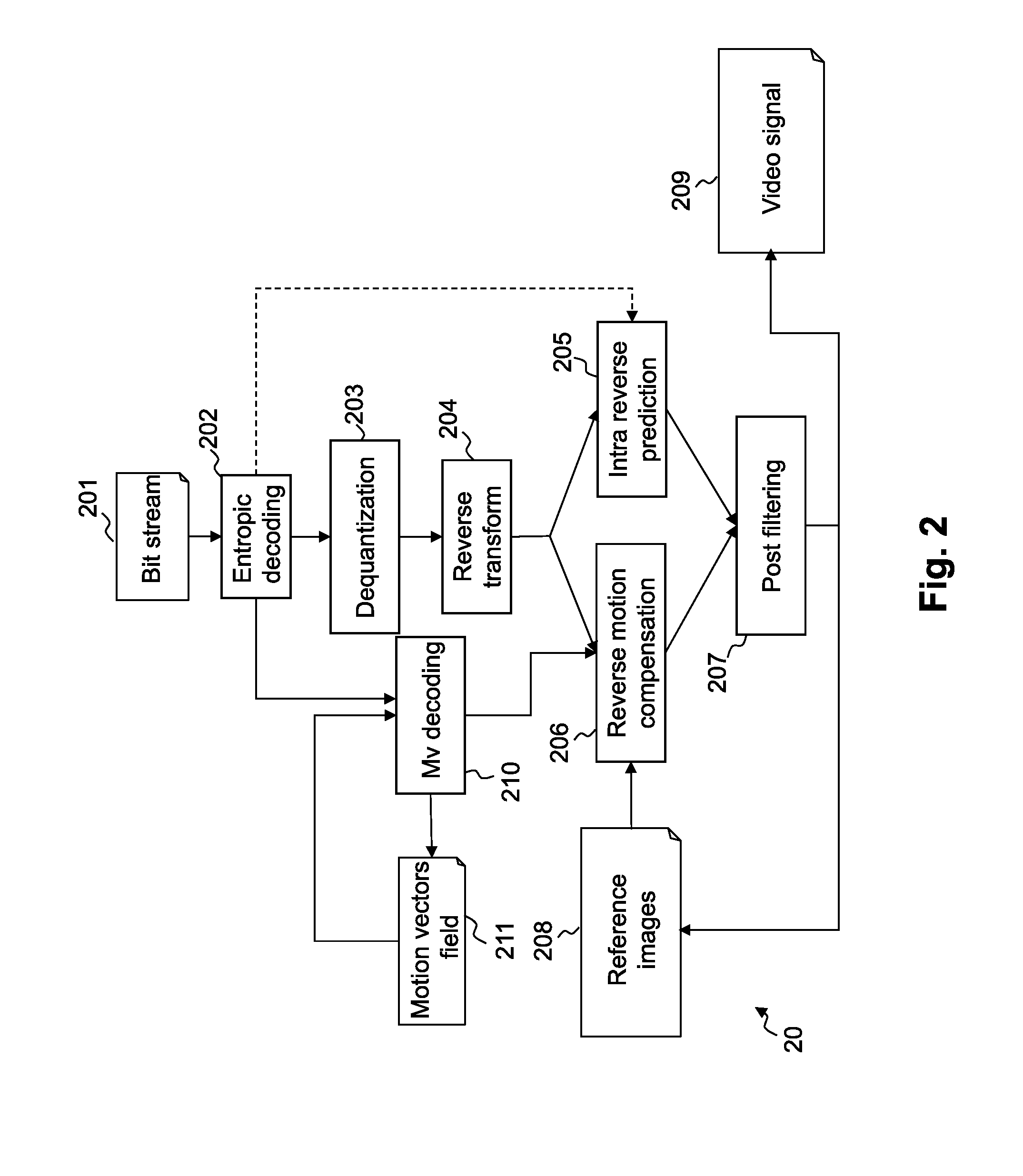
Patents
Literature
421 results about "Interframe coding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
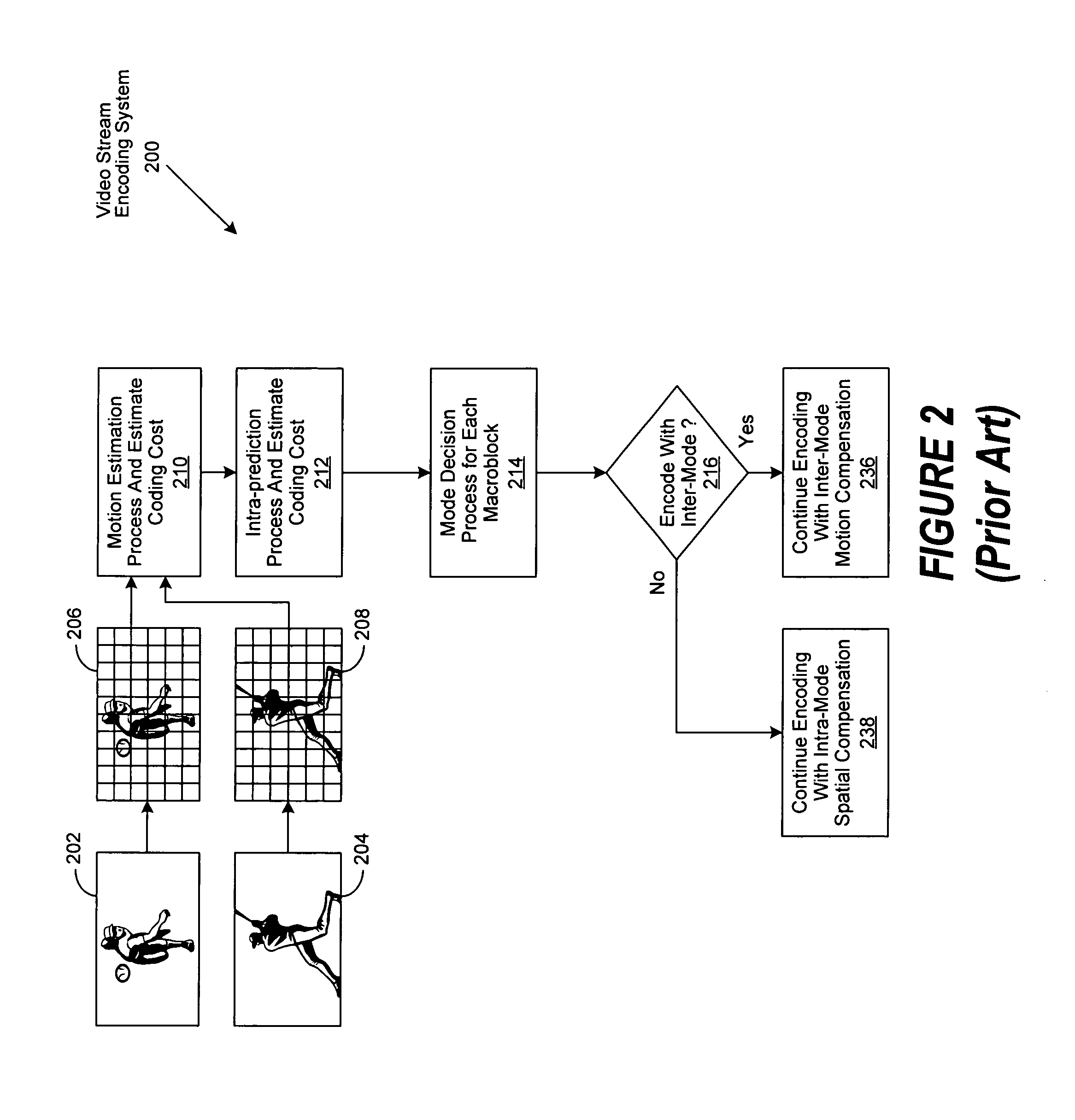
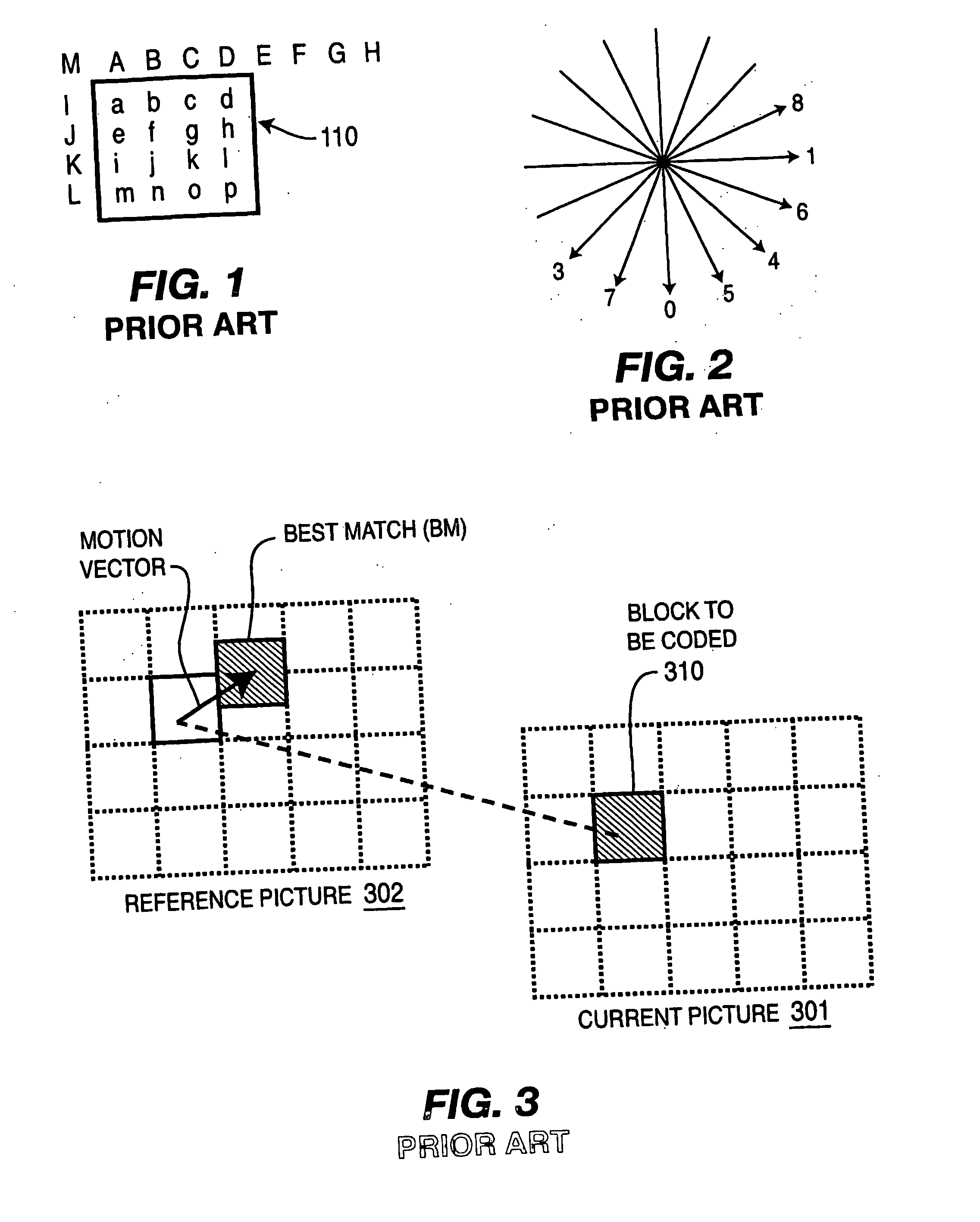
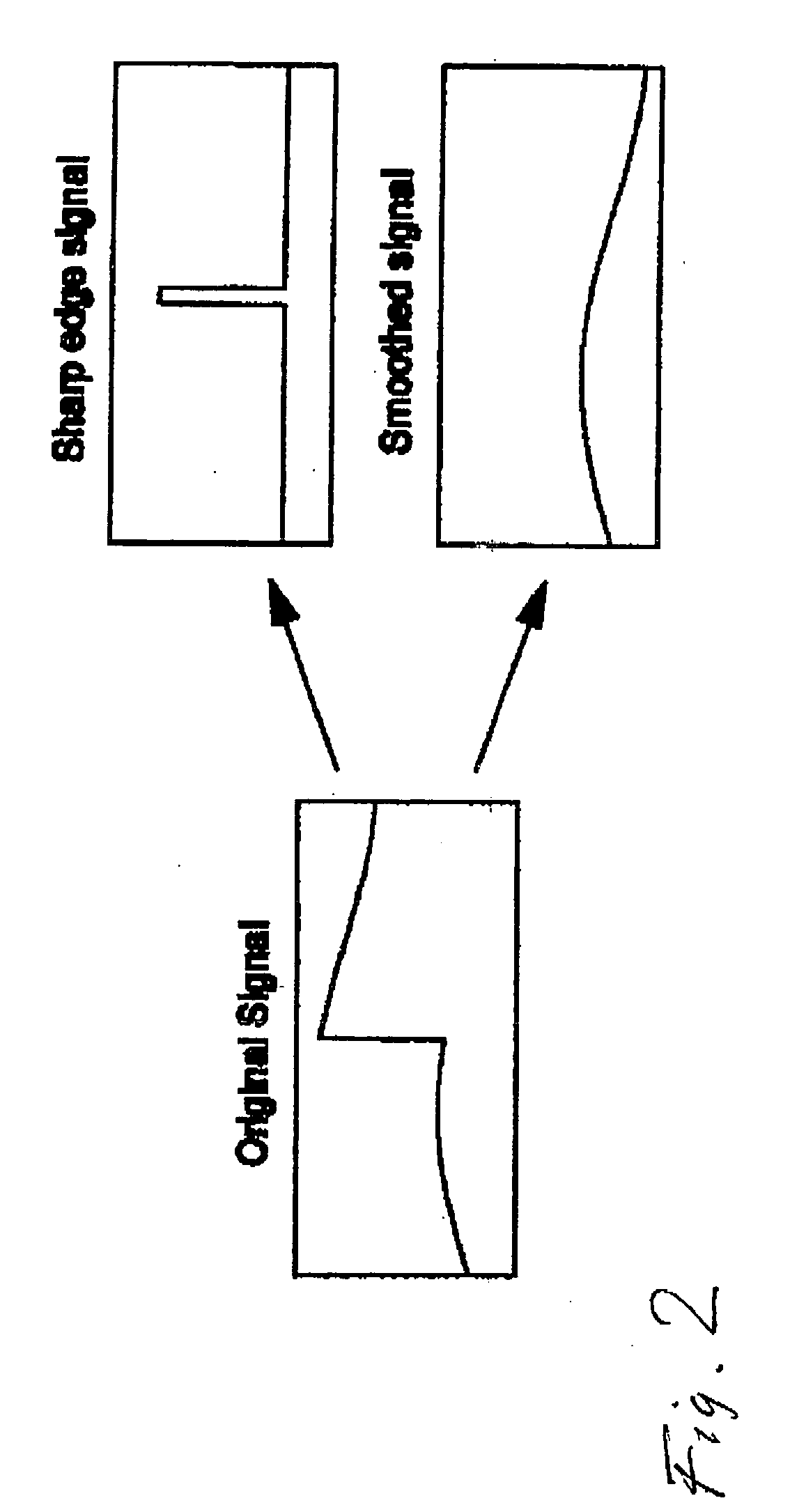
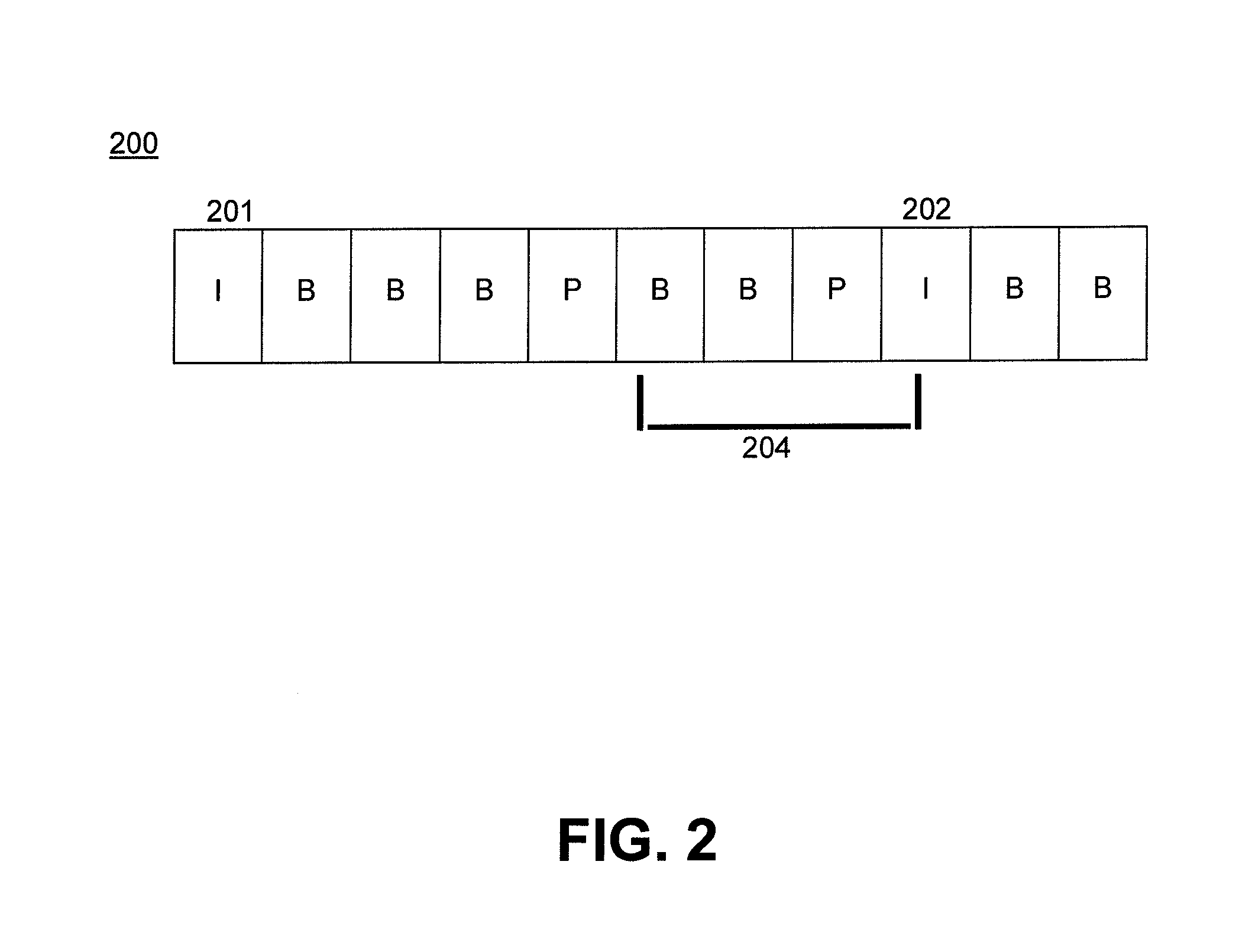
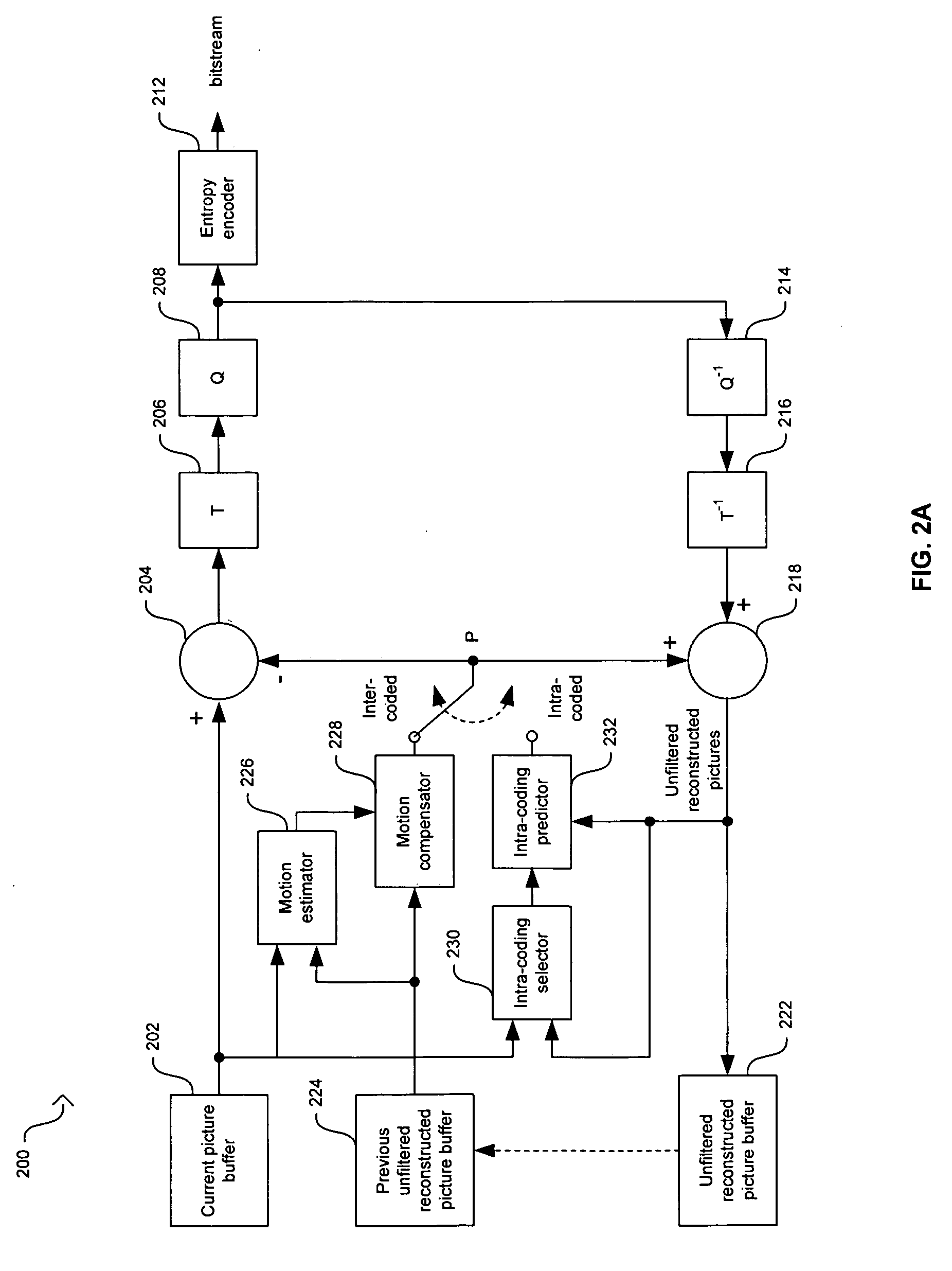
Interframe coding. In video compression, encoding the differences between frames rather than each full frame. Interframe coding often provides substantial compression because in many motion sequences, only a small percentage of the pixels are actually different from one frame to another.
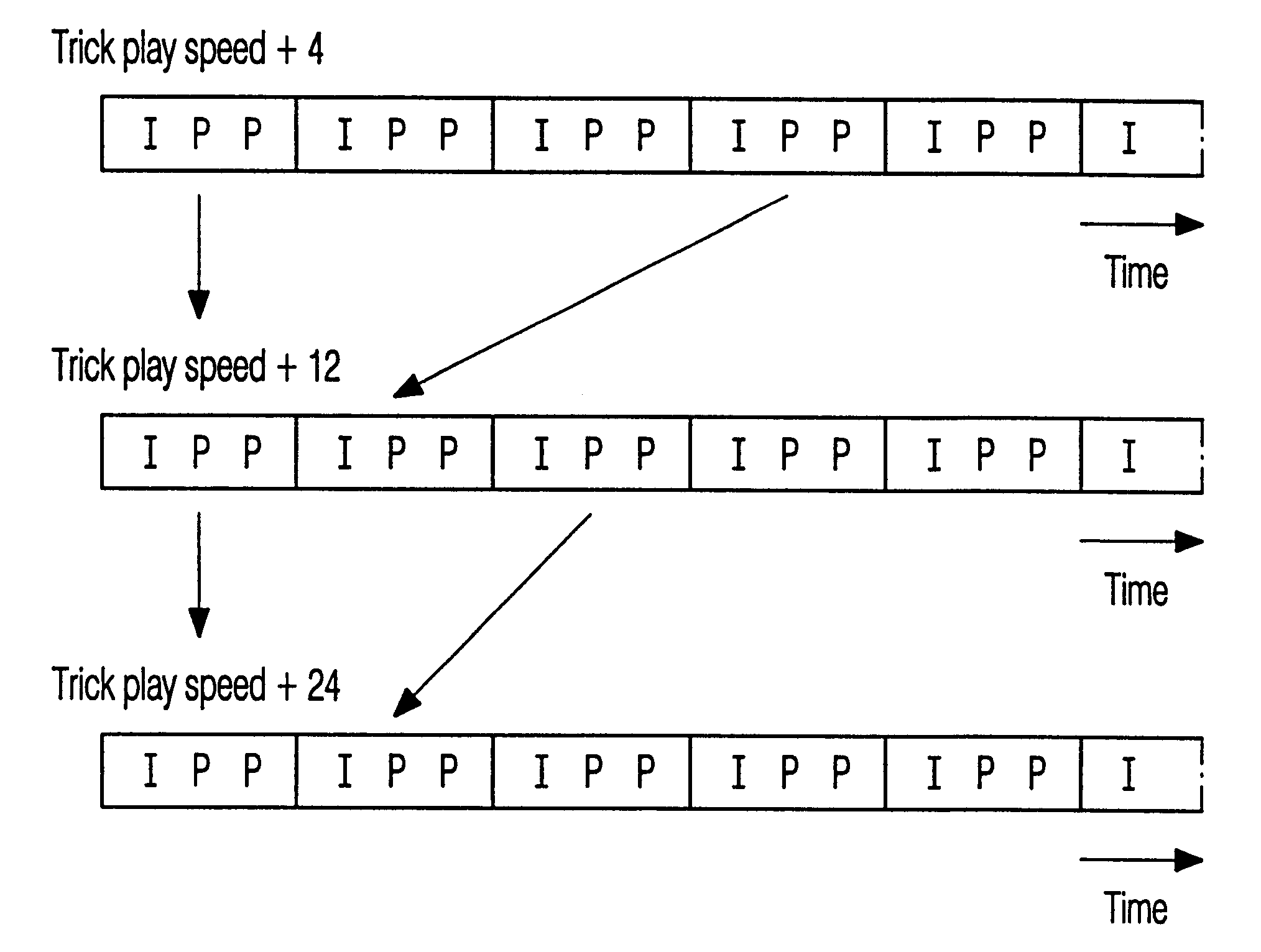
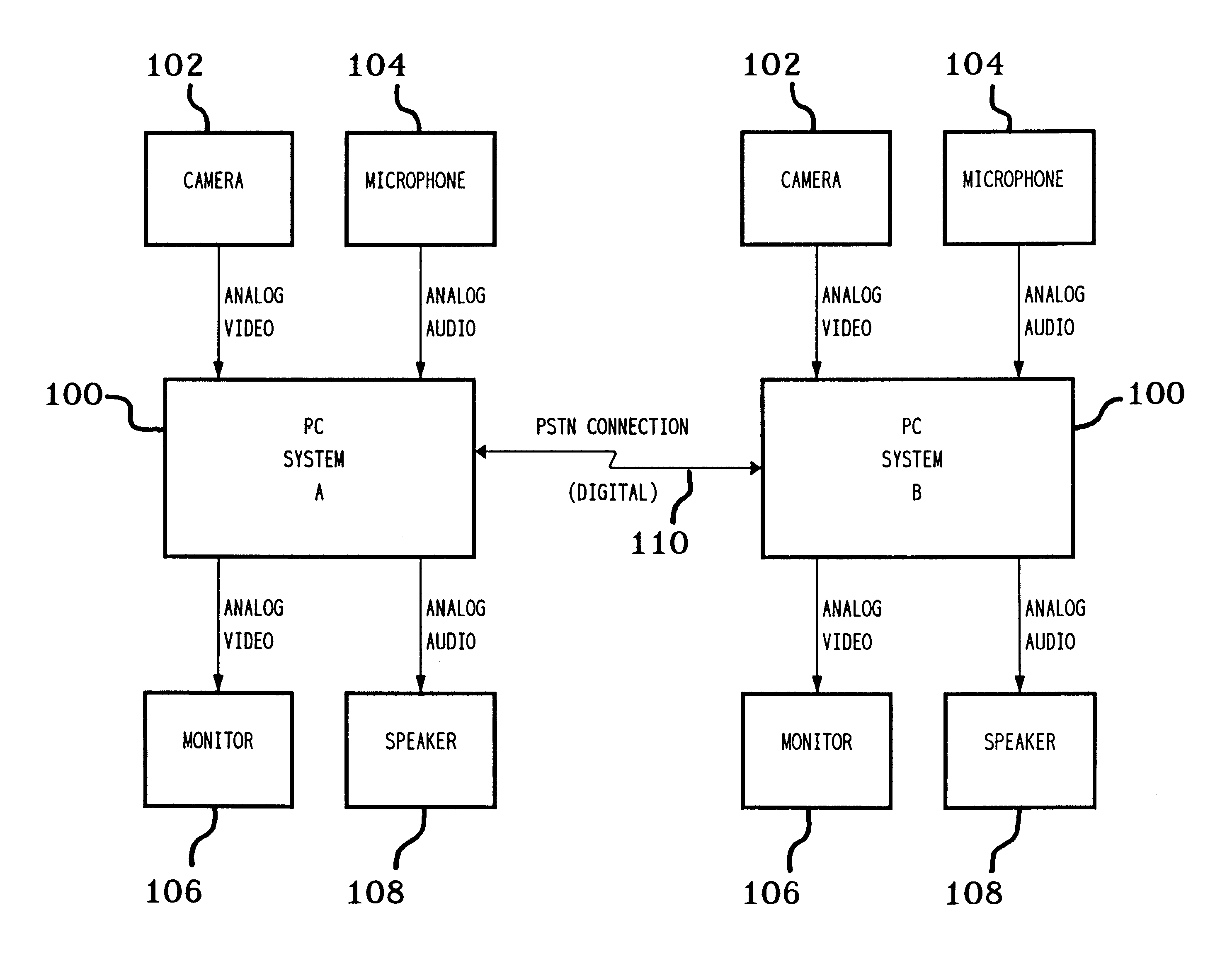
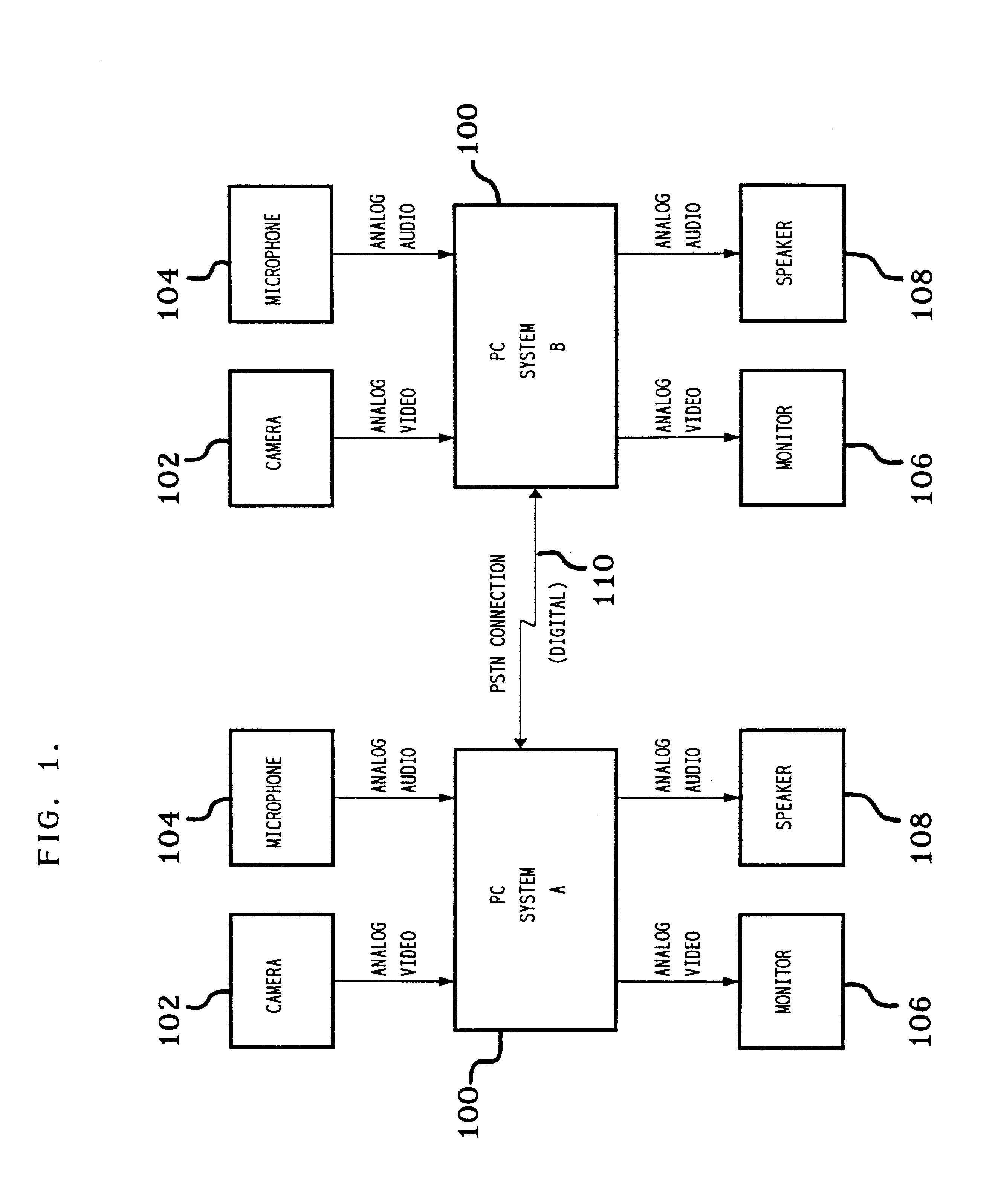
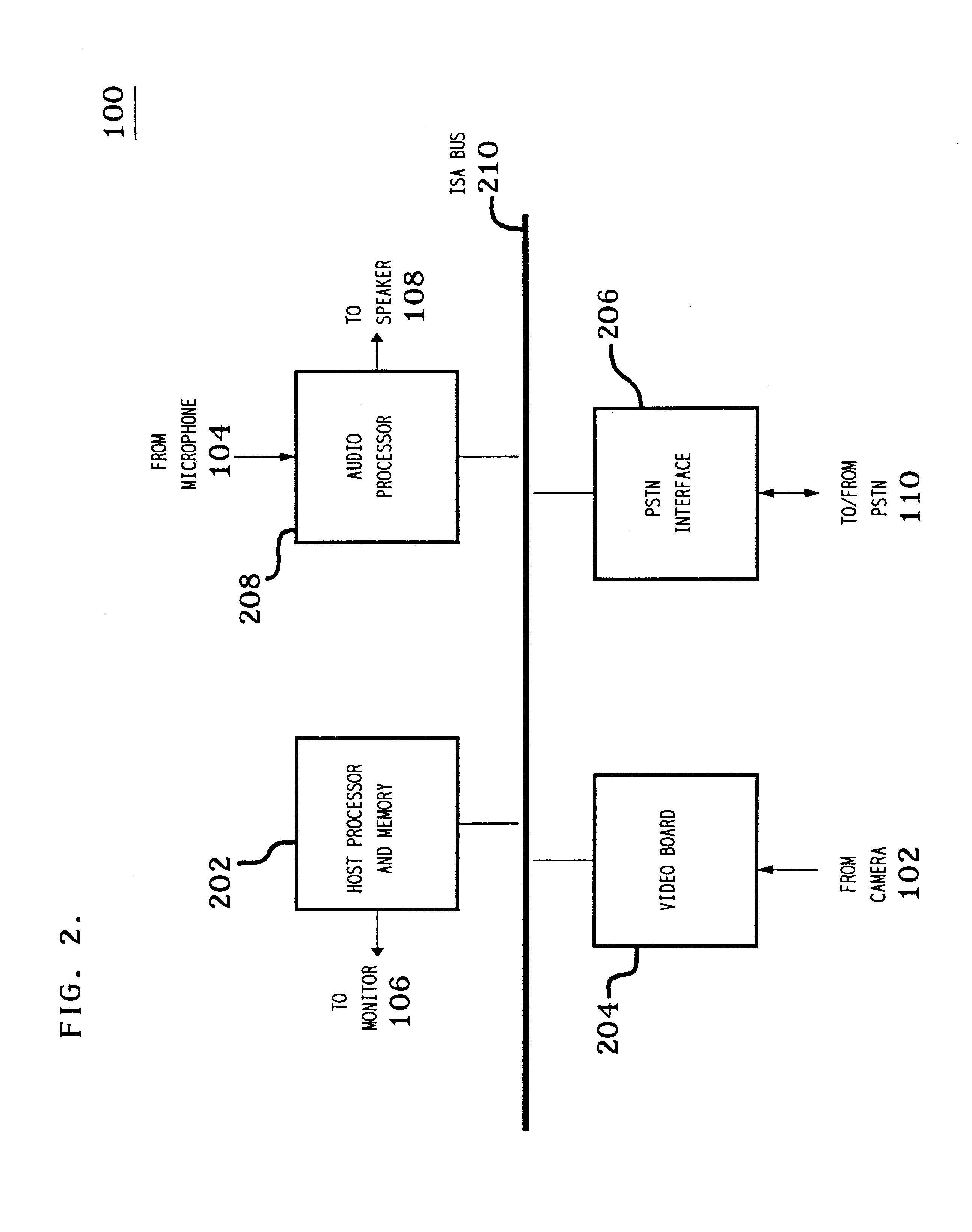
Trick play signal generation for a digital video recorder using retrieved intra-encoded pictures and generated inter-encoded pictures
InactiveUS6621979B1Constant bit-costIncrease speedTelevision system detailsColor television signals processingVisibilityDigital video
A trick play information stream is generated from a normal play information stream, so that they can be recorded together as a composite information stream on the record carrier, such that upon reproduction in a trick play reproduction mode, an information signal of sufficient quality, e.g., as regards visibility, can be obtained. GOPs are generated, each GOP including an I-frame retrieved from the original normal play information stream, and one or more so-called "empty P frames'. Another aspect is the requirement of generating GOPs for the trick play information stream that have a constant bitcost per GOP. Again, another aspect lies in the retrieval of the I-frame for the trick play information stream from the normal play information. More specifically, an I-frame is generated by retrieving, from an I-frame included in the normal play information, the DC coefficient of the I-frame and a number of AC coefficients from that I frame, and generating the I-frame for the trick play information stream therefrom. More specifically, the number of AC coefficients for an I-frame of the trick play information signal depends on the difference between the DC coefficients of two subsequent I-frames in the normal play information from which the I-frame to be generated and the just previously generated I-frame for the trick play information signal have been derived.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
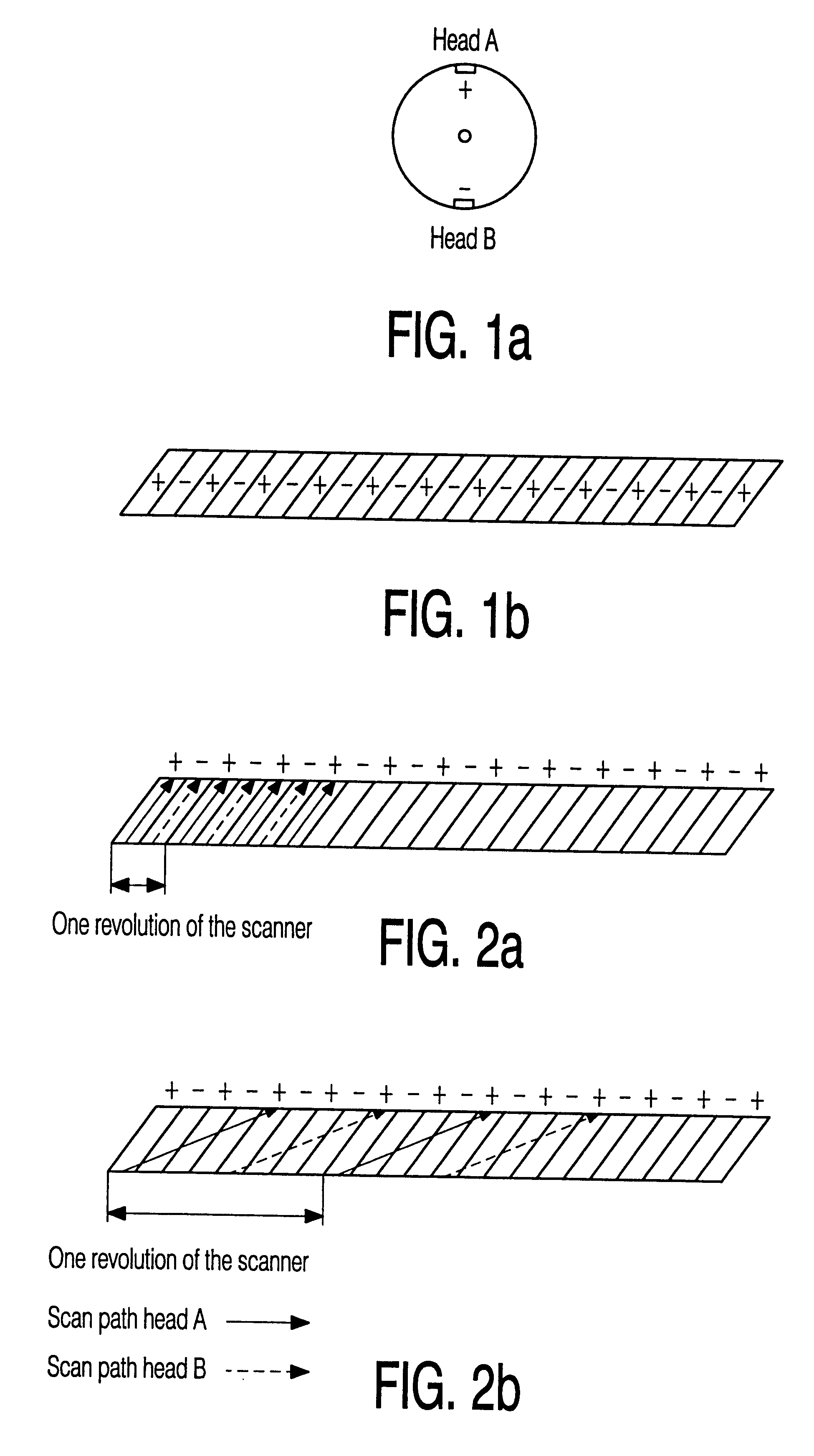
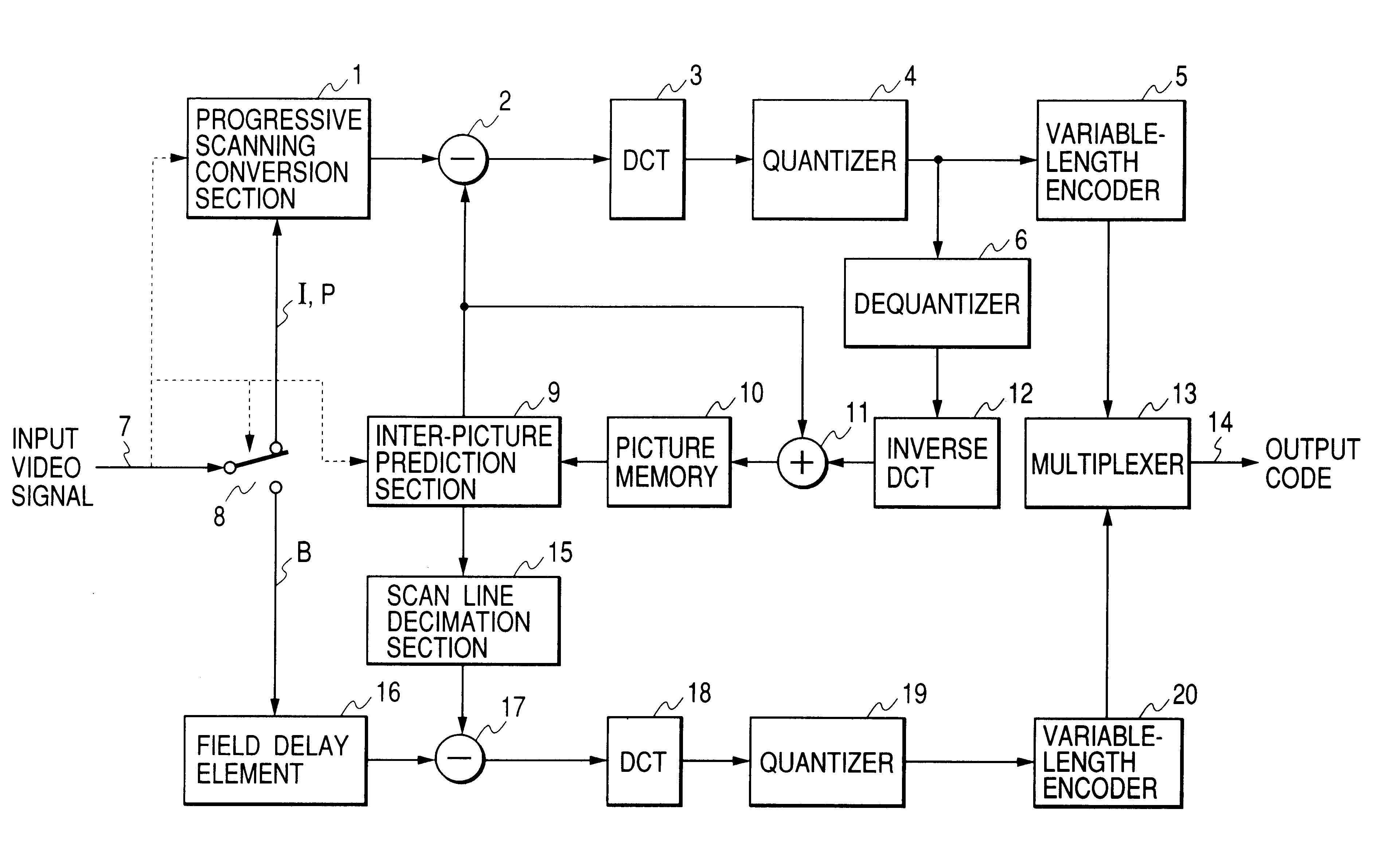
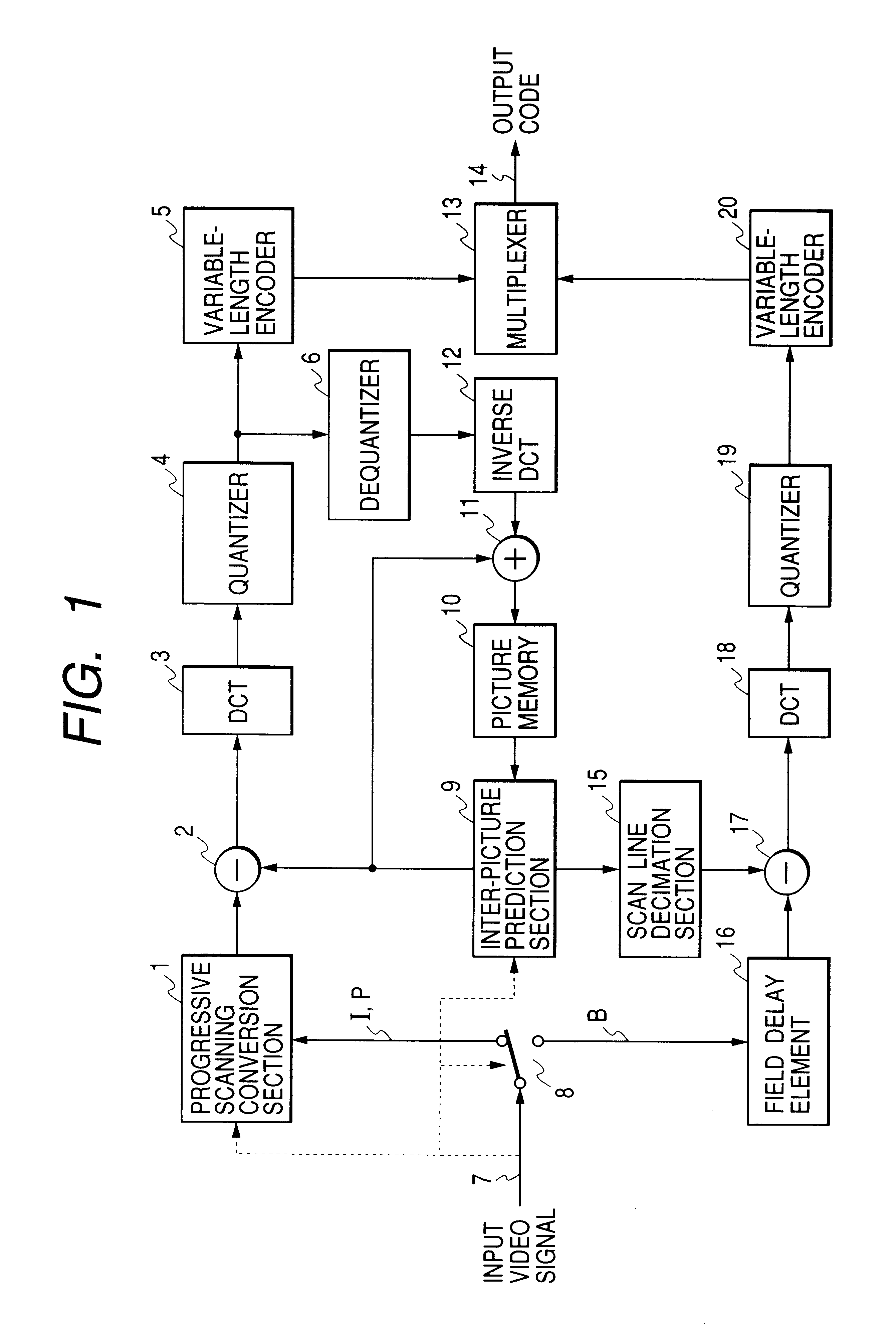
Interplaced video signal encoding and decoding method, and encoding apparatus and decoding apparatus utilizing the method, providing high efficiency of encoding by conversion of periodically selected fields to progressive scan frames which function as reference frames for predictive encoding
InactiveUS6188725B1Television system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesScan conversionInterlaced video
An encoding apparatus includes a selector for periodically selecting fields of an interlaced video signal to be converted to respective progressive scanning frames, by a scanning converter which doubles the number of scanning lines per field. The apparatus encodes these frames by intra-frame encoding or unidirectional predictive encoding using preceding ones of the frames, and encodes the remaining fields of the video signal by bidirectional prediction using preceding and succeeding ones of the progressive scanning frames for reference. The resultant code can be decoded by an inverse process to recover the interlaced video signal, or each decoded field can be converted to a progressive scanning frame to thereby enable output of a progressive scanning video signal. Enhanced accuracy of motion prediction for inter-frame encoding can thereby be achieved, and generation of encoded aliasing components suppressed, since all reference pictures are progressive scanning frames rather than pairs of fields constituting interlaced scanning frames.
Owner:RAKUTEN INC
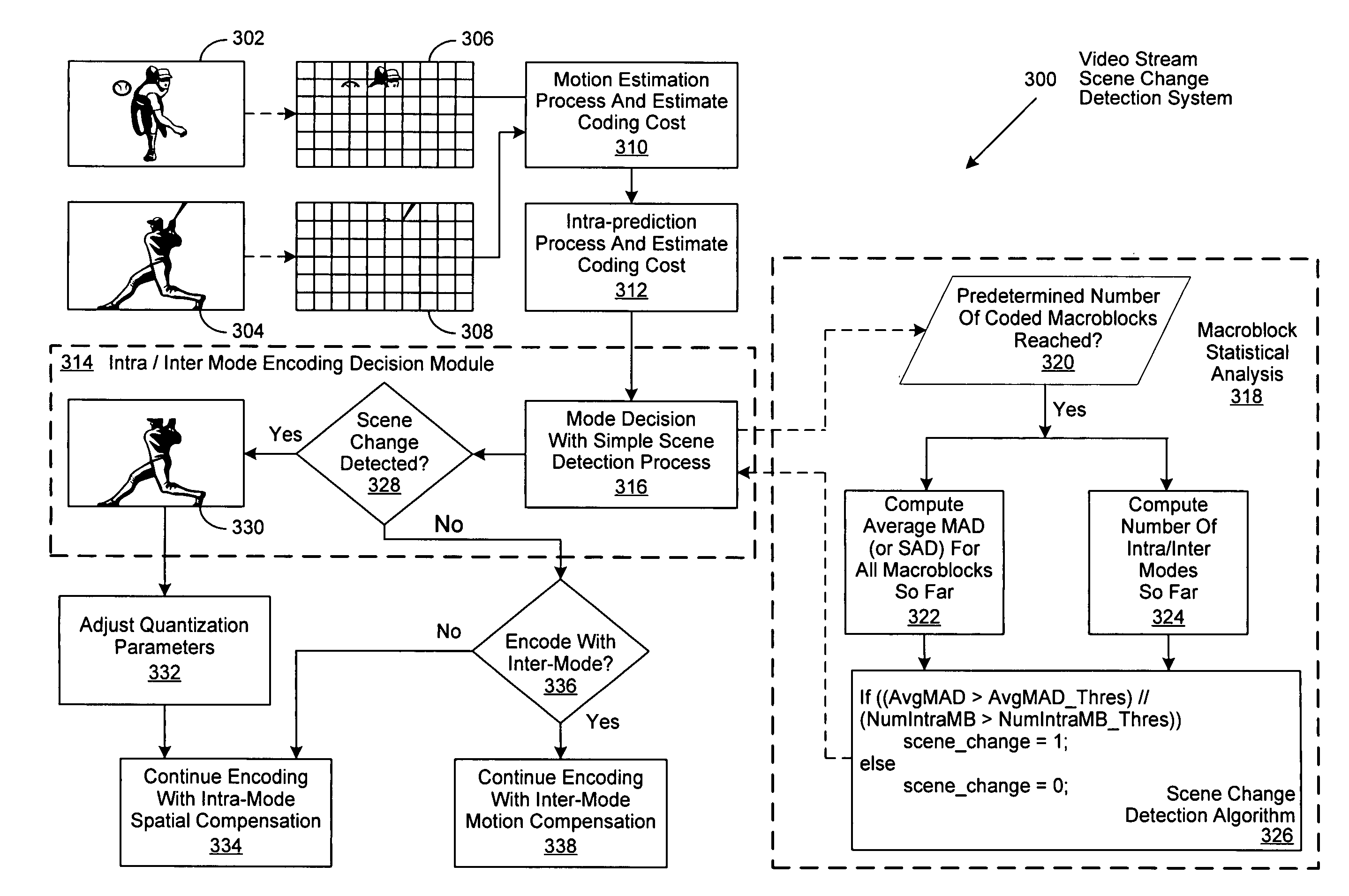
Method of increasing coding efficiency and reducing power consumption by on-line scene change detection while encoding inter-frame
InactiveUS20070274385A1Television system detailsColor television with pulse code modulationPattern recognitionComputation complexity
A system and method for on-the-fly detection of scene changes within a video stream through statistical analysis of a portion of the macroblocks comprising each video frame as they are processed using inter-frame coding. If the statistical analysis of the selected macroblocks of the current frame differs from the previous frame by exceeding predetermined thresholds, the current video frame is assumed to be a scene change. Once a scene change is detected, the remainder of the video frame is encoded as an intra-frame, intra-macroblocks, or intra slices, through implementation of one or more predetermined or adaptively adjusted quantization parameters to reduce computational complexity, decrease power consumption, and increase the resulting video image quality. As decoding is the inverse of encoding, these improvements are similarly recognized by a decoder as it decodes a resulting encoded video stream.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Method and apparatus for decoding hybrid intra-inter coded blocks
ActiveUS20070009044A1High gainImproved encoding efficiencyTelevision system detailsColor television with pulse code modulationCoding blockData stream
A hybrid intra-inter bi-predictive (or multi-predictive) coding mode allows both intraframe (intra) and interframe (inter) predictions to be combined together for hybrid-encoding a current macroblock or a subblock. Bi-prediction may be used also in I-pictures, combining two intra predictions that use two different intra prediction directions. A video encoder processes data representing a two-dimensional video image which has been produced by a conventional commercially available video camera. The video encoder is adapted to select, for coding a current macroblock, between an intra encoding mode, an P-frame inter encoding mode, a B-frame bi-predictive inter mode, and a hybrid intra-inter bi-predictive encoding mode. A video decoder receives and decodes a data stream that may contain a block / macroblock encoded in accordance with the hybrid intra-inter bi-predictive encoding mode.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL MADISON PATENT HLDG
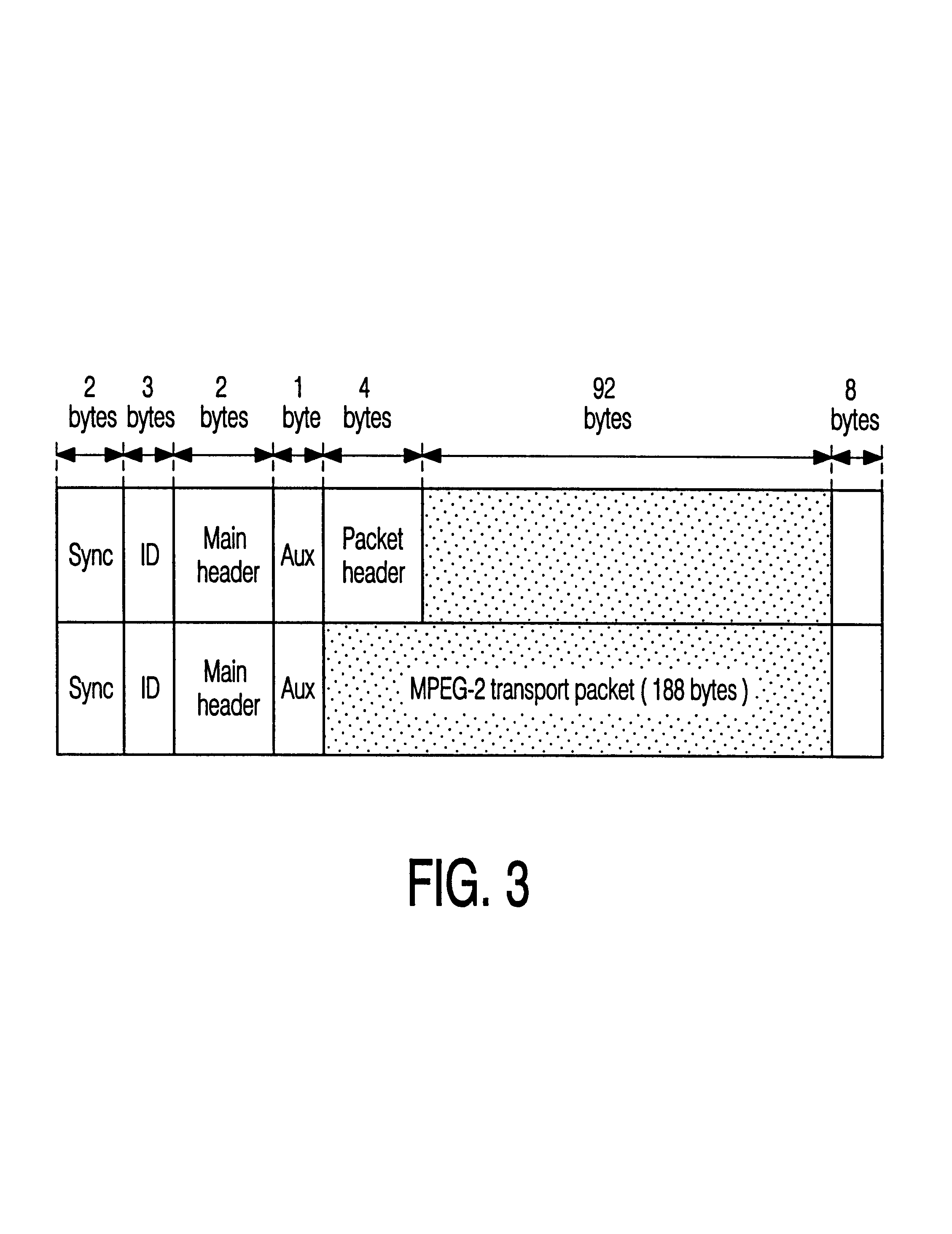
Method and apparatus for achieving video data reduction through the use of re-encoding
InactiveUS6023553AReduce the amount requiredReduce resolutionTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionVideocassette recorderData stream
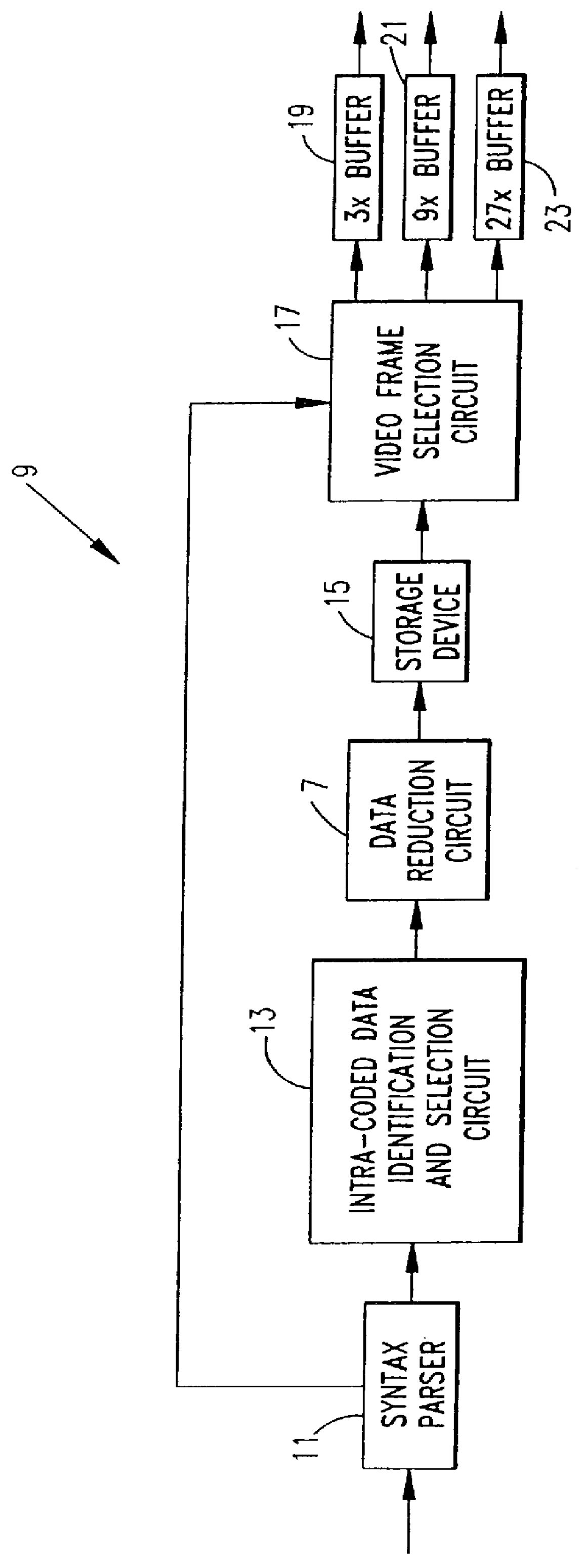
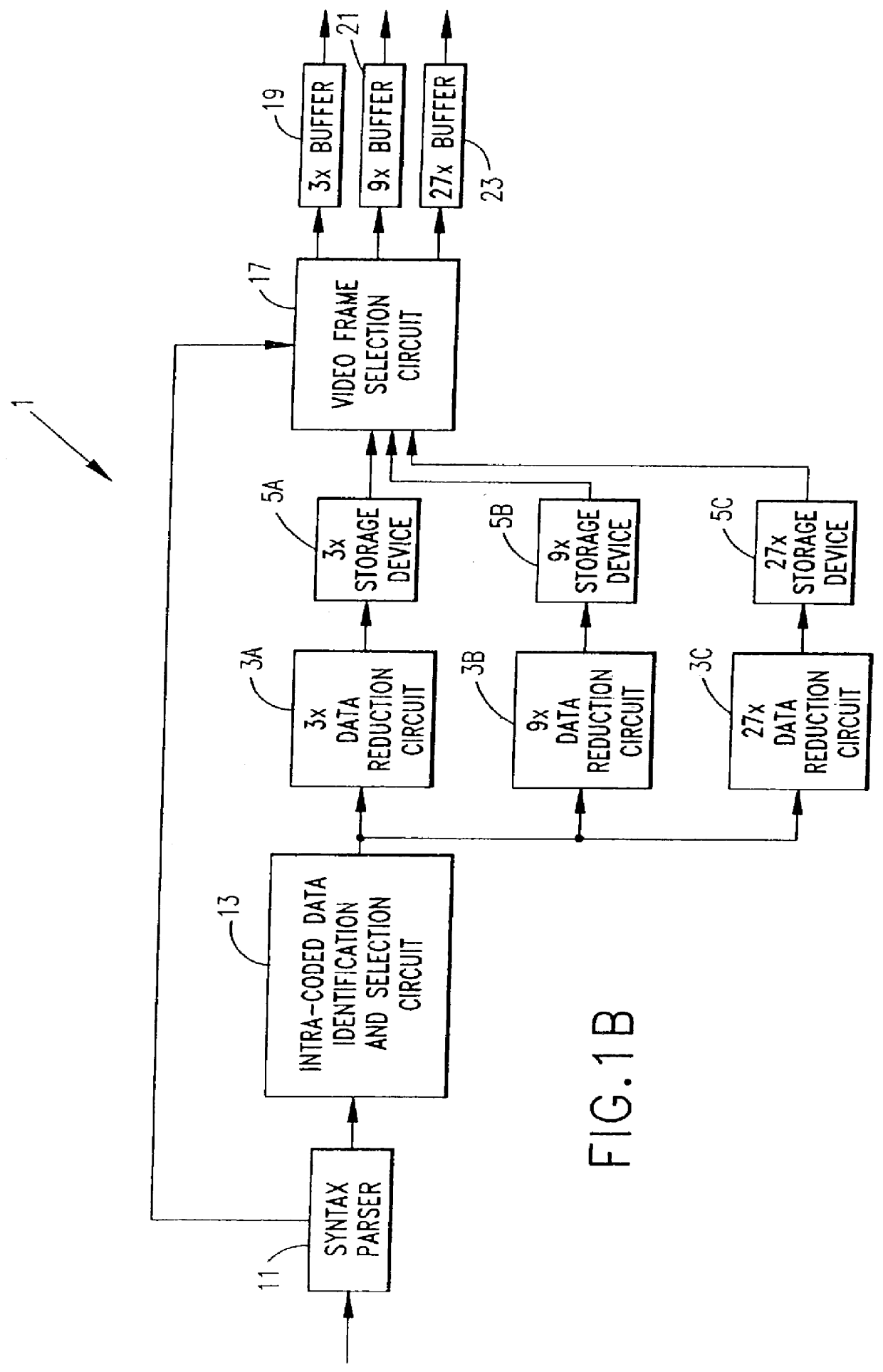
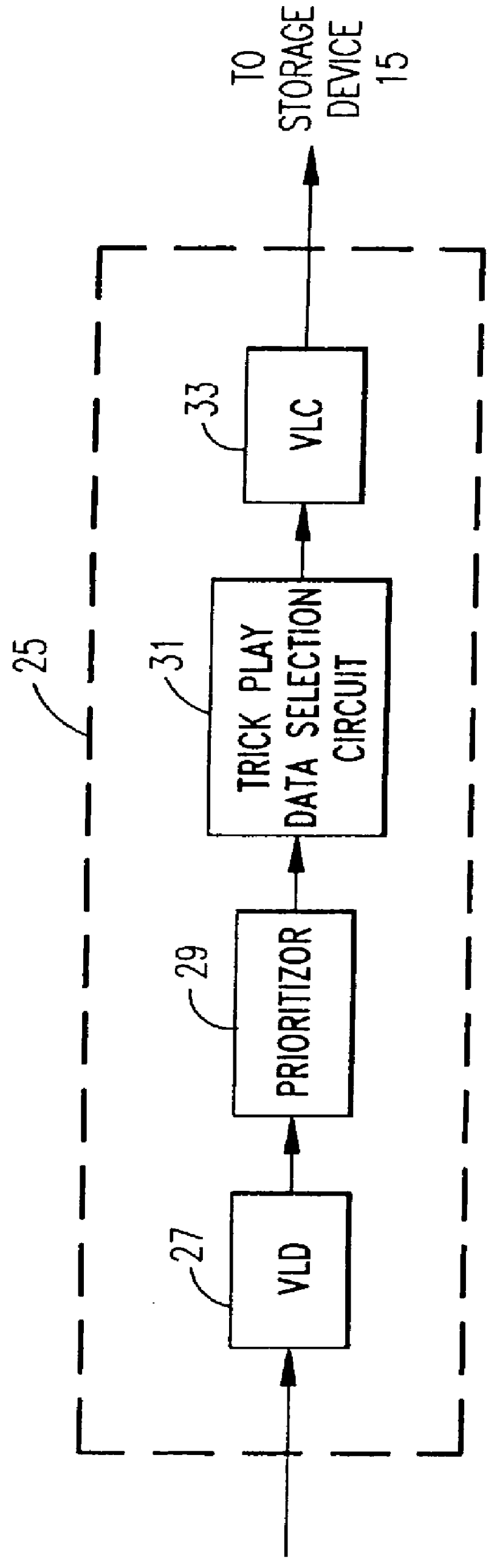
Method and apparatus for extracting intra-coded video frames from a video data stream including inter-coded video frames and intra-coded video frames to produce reduced resolution intra-coded video frames suitable for recording in trick play tape segments of a tape for later play back and display during video tape recorder trick play operation. A plurality of methods and apparatus for buffering and selecting received intra-coded video frames for recording in trick play tape segments to support a plurality of trick play modes of operation are disclosed. In addition, a plurality of different data reduction methods and apparatus are disclosed for generating reduced resolution intra-coded frames from the received full resolution intra-coded video frames.
Owner:HITACHI AMERICA
Method and apparatus for encoding hybrid intra-inter coded blocks
ActiveUS20070047648A1High gainImproved encoding efficiencyTelevision system detailsColor television with pulse code modulationCoding blockData stream
A hybrid intra-inter bi-predictive (or multi-predictive) coding mode allows both intraframe (intra) and interframe (inter) predictions to be combined together for hybrid-encoding a current macroblock or a subblock Bi-prediction may be used also in I-pictures, combining two intra predictions that use two different intra prediction directions. A video encoder processes data representing a two-dimensional video image which has been produced by a conventional commercially available video camera. The video encoder is adapted to select, for coding a current macroblock, between an intra encoding mode, an P-frame inter encoding mode, a B-frame bi-predictive inter mode, and a hybrid intra-inter bi-predictive encoding mode. A video decoder (800) receives and decodes a data stream that may contain a block / macroblock encoded in accordance with the hybrid intra-inter bi-predictive encoding mode.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL MADISON PATENT HLDG
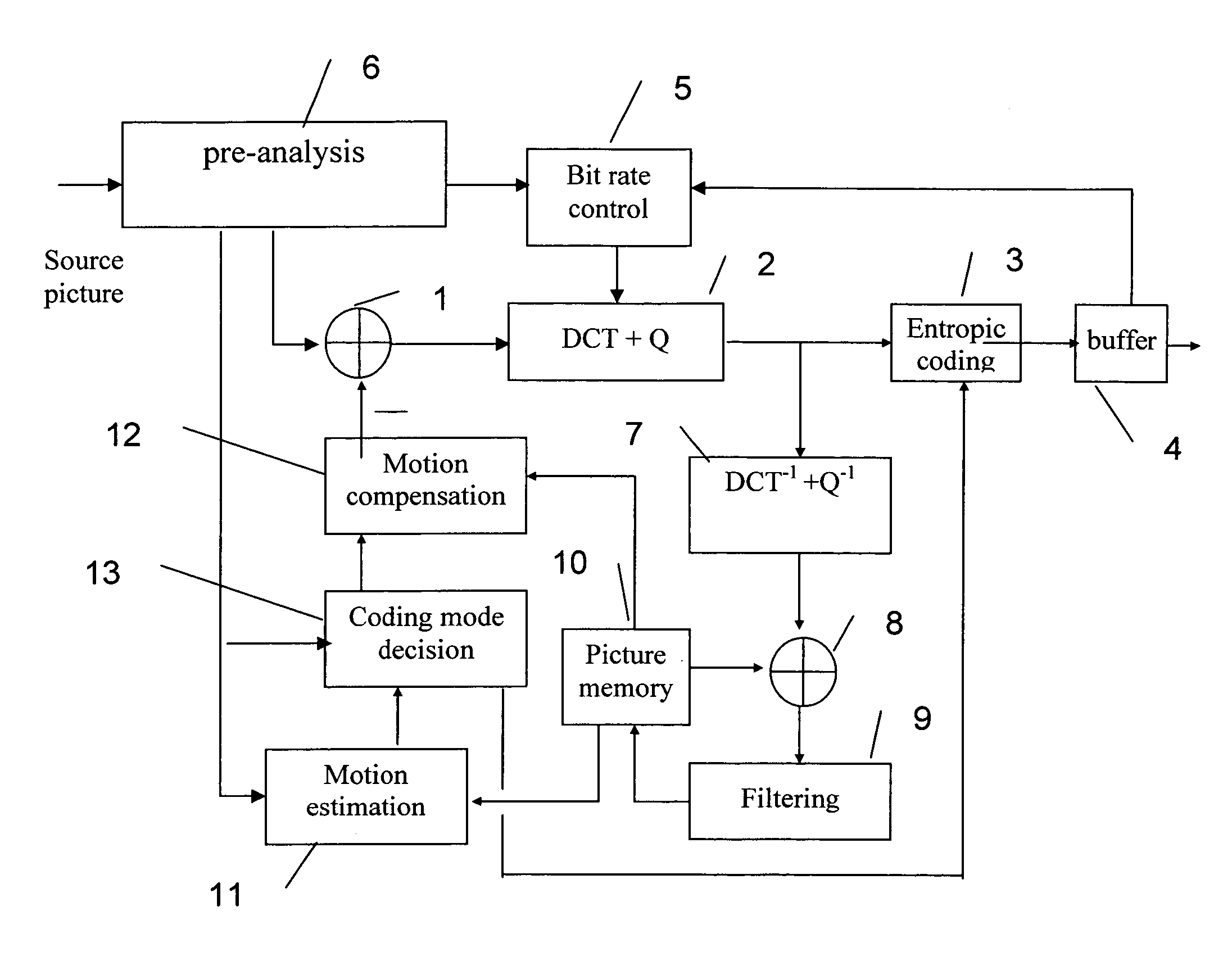
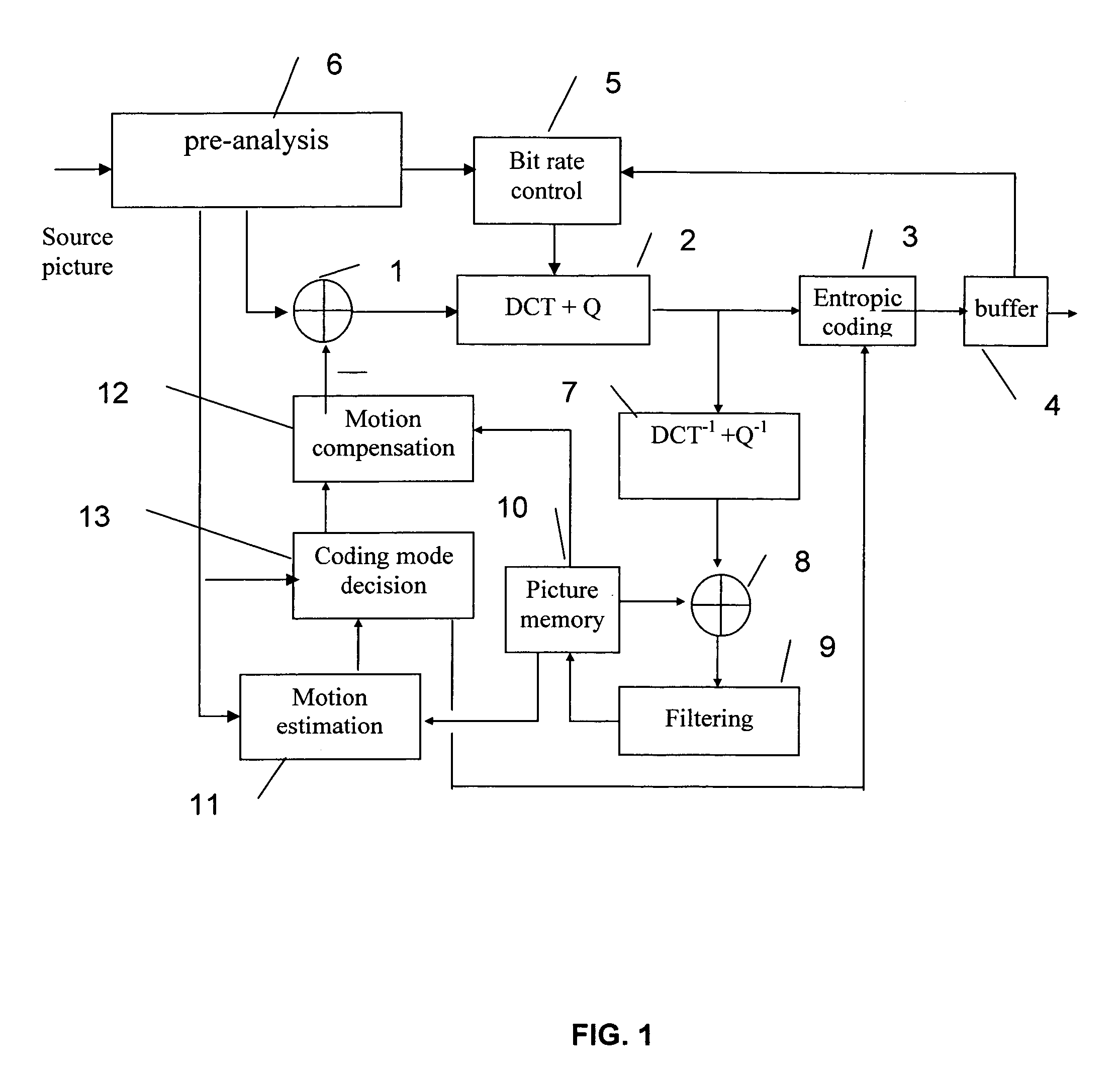
Method or device for coding a sequence of source pictures
InactiveUS20060013307A1Simple calculationReduce complexityTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPre analyticalComputer architecture
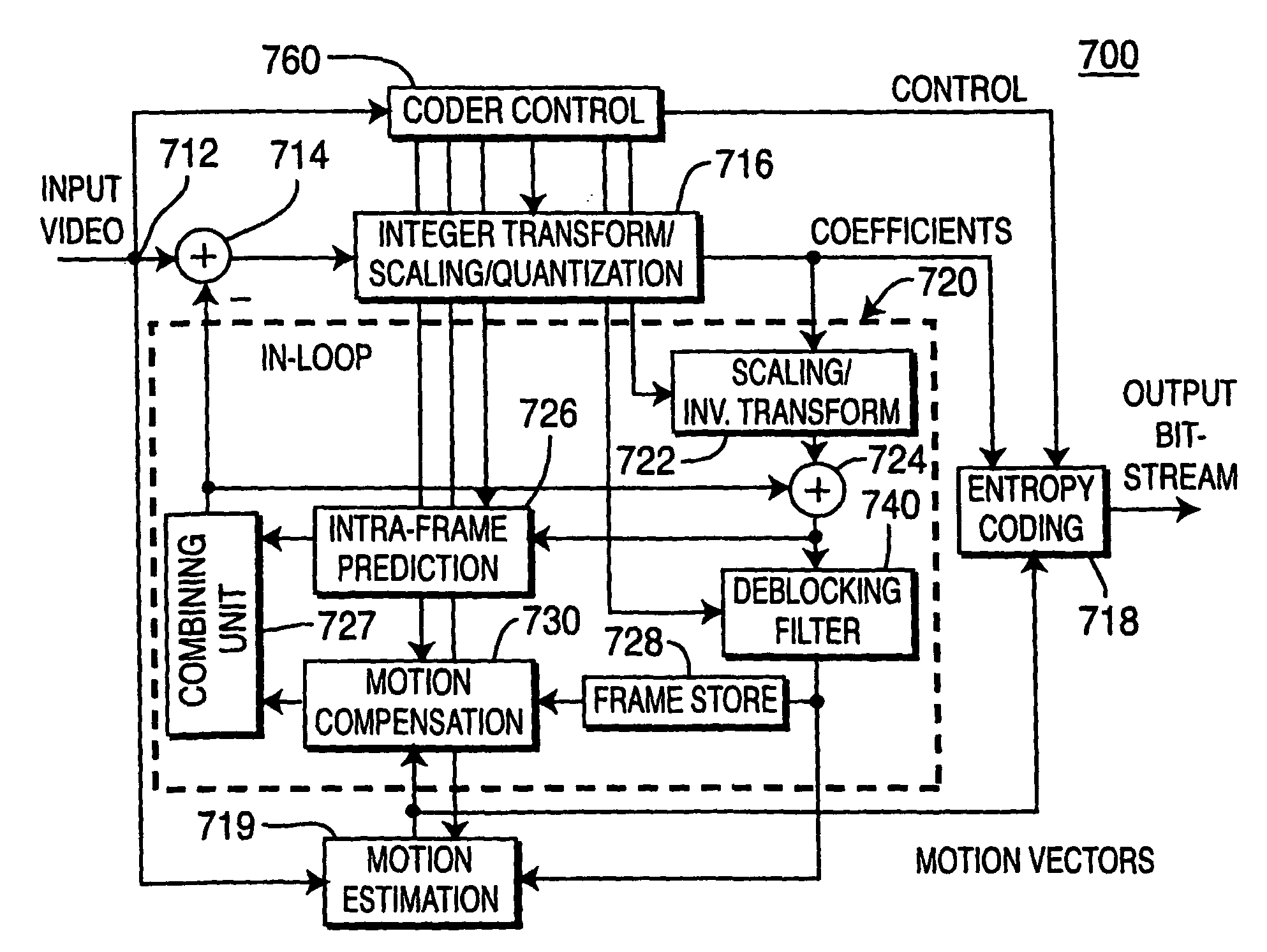
The method is characterized in that the pre-analysis phase performs correlation level calculations of the even and odd field blocks of the current picture with the even and odd blocks of the current picture with the even and odd field blocks of the reference picture based on motion vectors calculated during this phase and corresponding to the blocks to impose, during the coding mode decision stage and among the inter coding modes, the inter coding between fields of the same parity or of opposing parity or the inter coding between frames, according to the correlation levels.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL MADISON PATENT HLDG
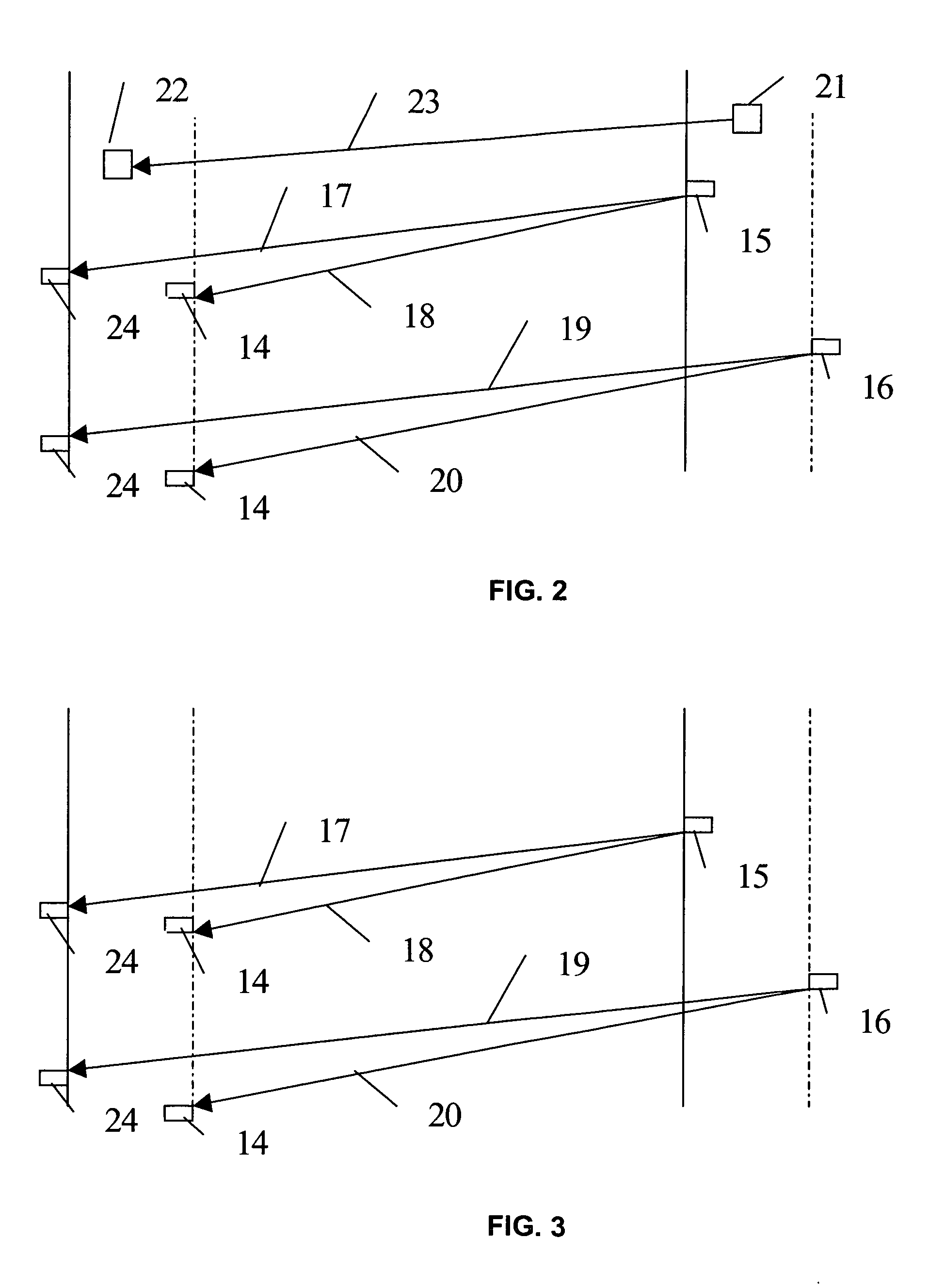
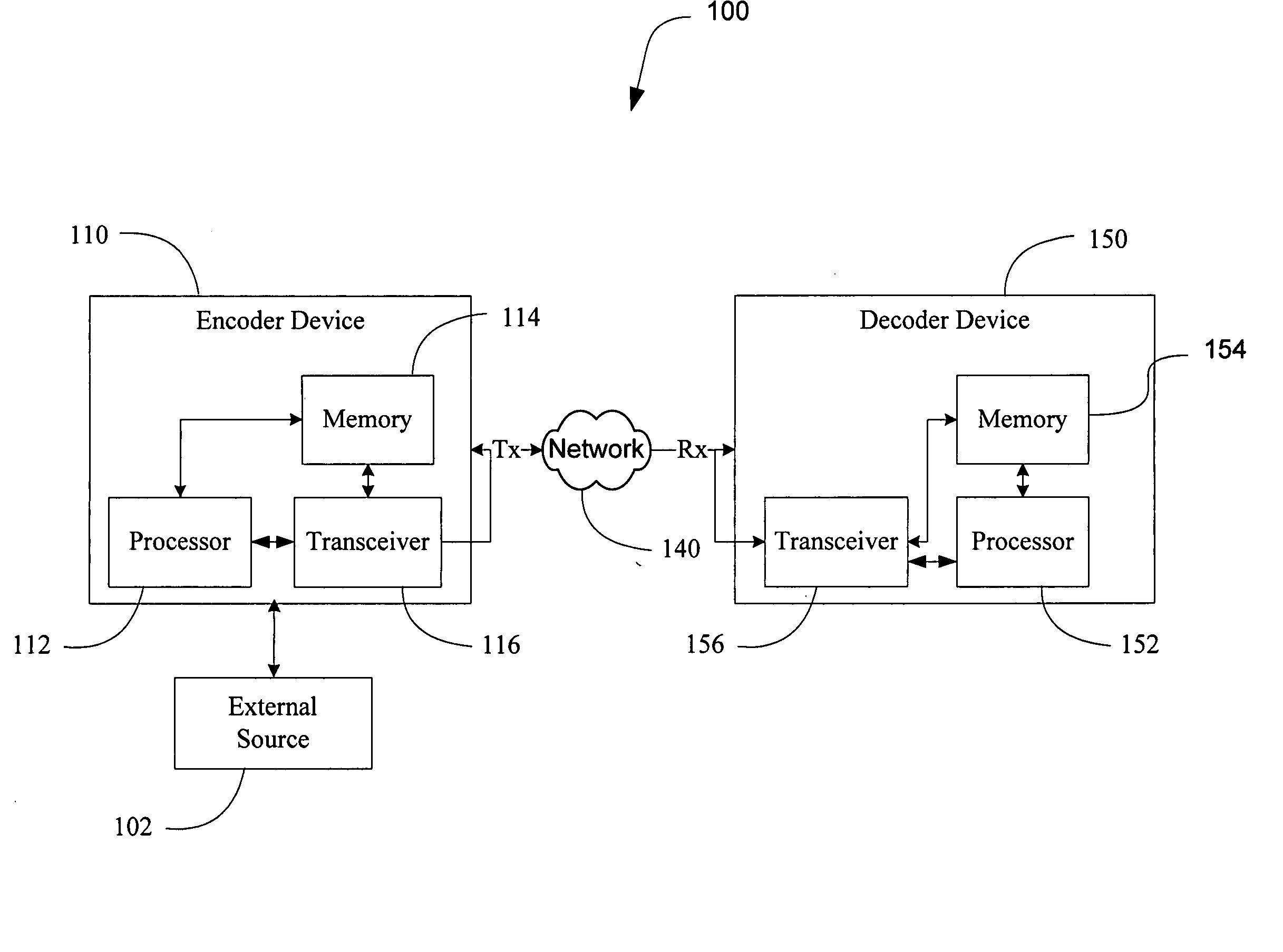
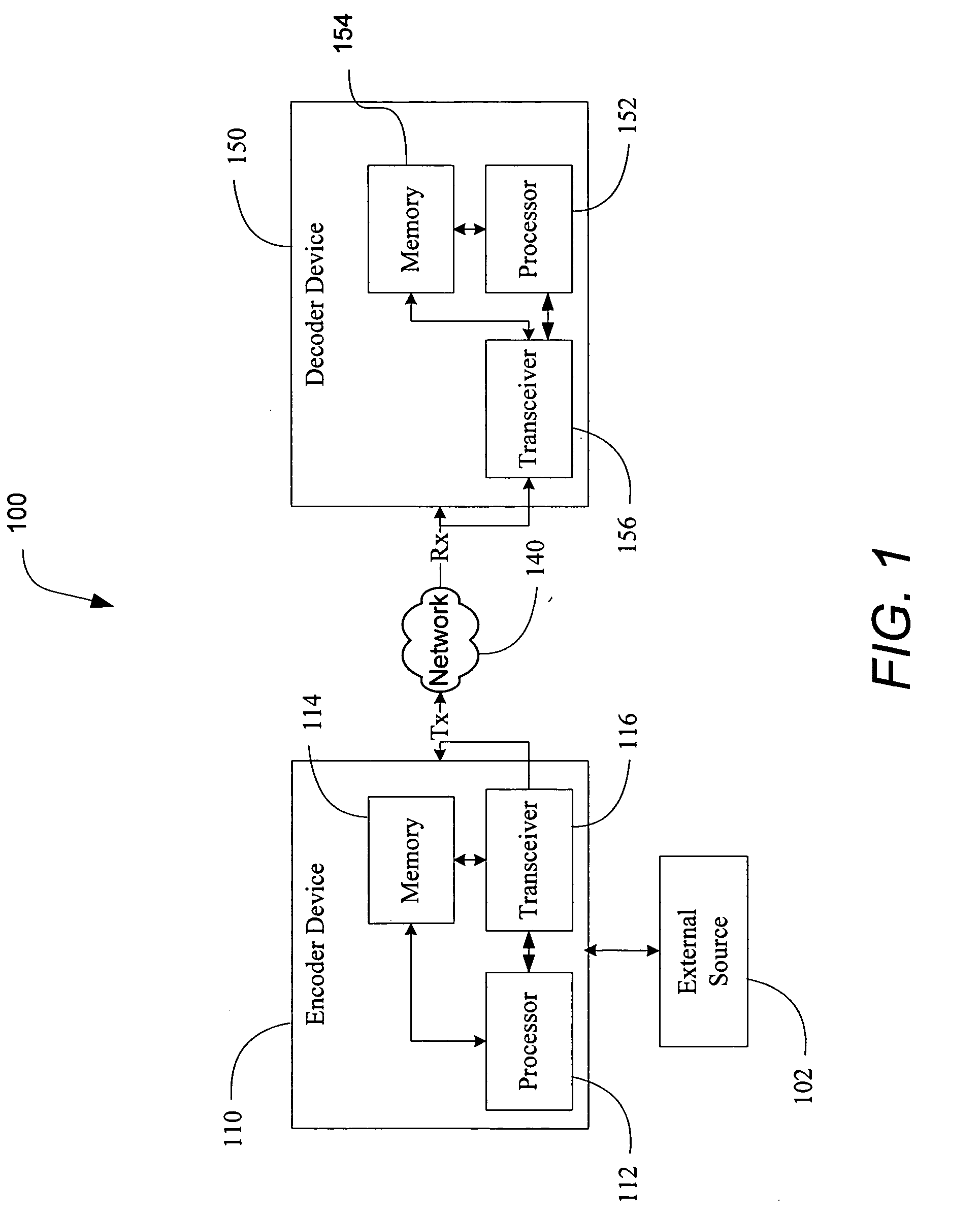
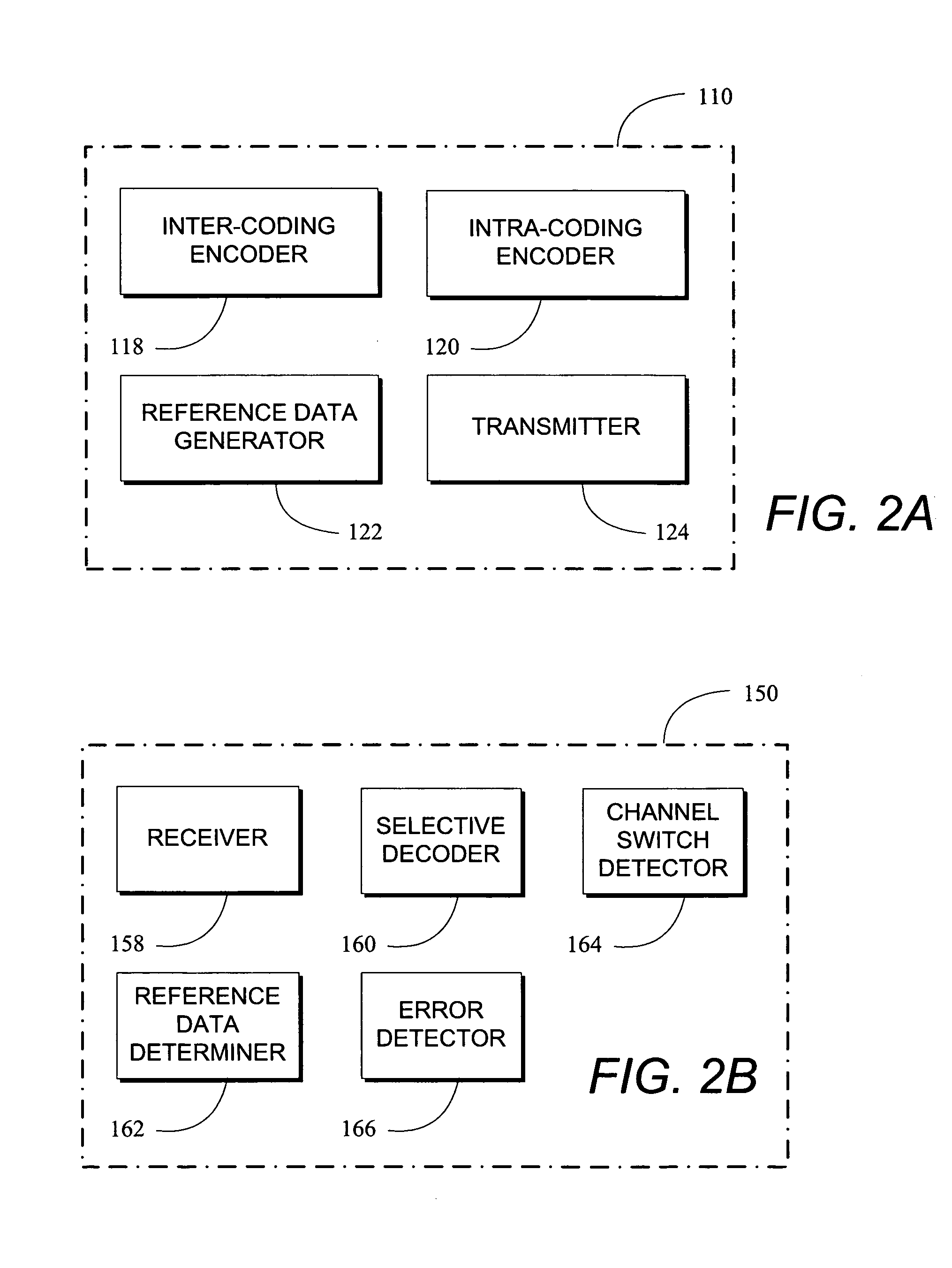
Channel switch frame
ActiveUS20070073779A1Easy accessError recoveryPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningComputer hardwareInterframe coding
Methods and apparatus to process multimedia data enabling faster channel acquisitions, improved error recovery and improved efficiency. An encoder device encodes a first portion of multimedia data using inter-coding to generate a first version, and encodes the first portion of multimedia data using intra-coding to generate a second version. A decoder device receives a first version of a first portion of multimedia data, wherein the first version is inter-coded, receives a second version of the first portion of multimedia data, wherein the second version is intra-coded, and selectively decodes the first and second received versions.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Using numbers of non-zero quantized transform signals and signal differences to determine when to encode video signals using inter-frame or intra-frame encoding
InactiveUS6222881B1Picture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningPattern recognitionInterframe coding
A transform is applied to a region of a current video frame to generate transform signals corresponding to the region. An activity measure is generated using the transform signals. The activity measure is then used to determine whether to encode the region as a skipped region. The region is encoded in accordance with that determination to generate an encoded bit stream for the region. In a preferred embodiment, the transform signals are DCT coefficients and the activity measure is a weighted sum of the DCT coefficients, where the weighting of the low-frequency DCT coefficients is greater than the weighting of the high-frequency DCT coefficients. The region is encoded as a skipped region if the activity measure is less than a threshold value; otherwise, the region is encoded as either an inter encoded region or an intra encoded region.
Owner:INTEL CORP
System and method for implementing fast tune-in with intra-coded redundant pictures
InactiveUS20080267287A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionBitstreamInterframe coding
A system and method by which instantaneous decoding refresh (IDR) / intra pictures that enable one to tune in or randomly access a media stream are included within a “normal” bitstream as redundant coded pictures. In various embodiments, each intra picture for tune-in is provided as a redundant coded picture, in addition to the corresponding primary inter-coded picture.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
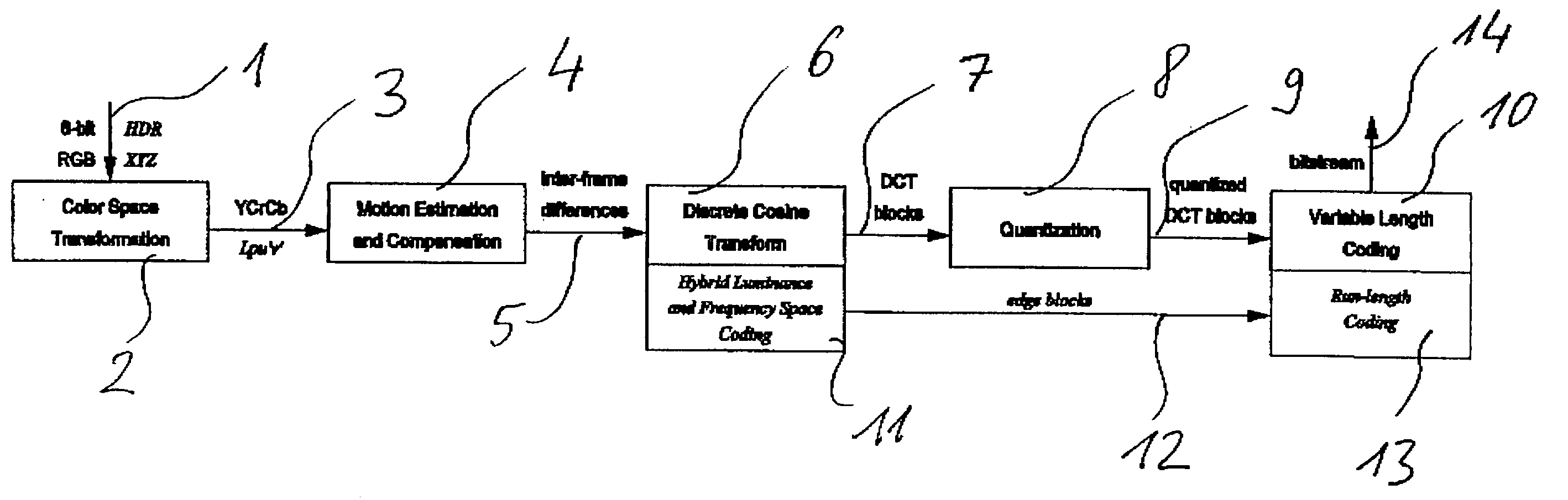
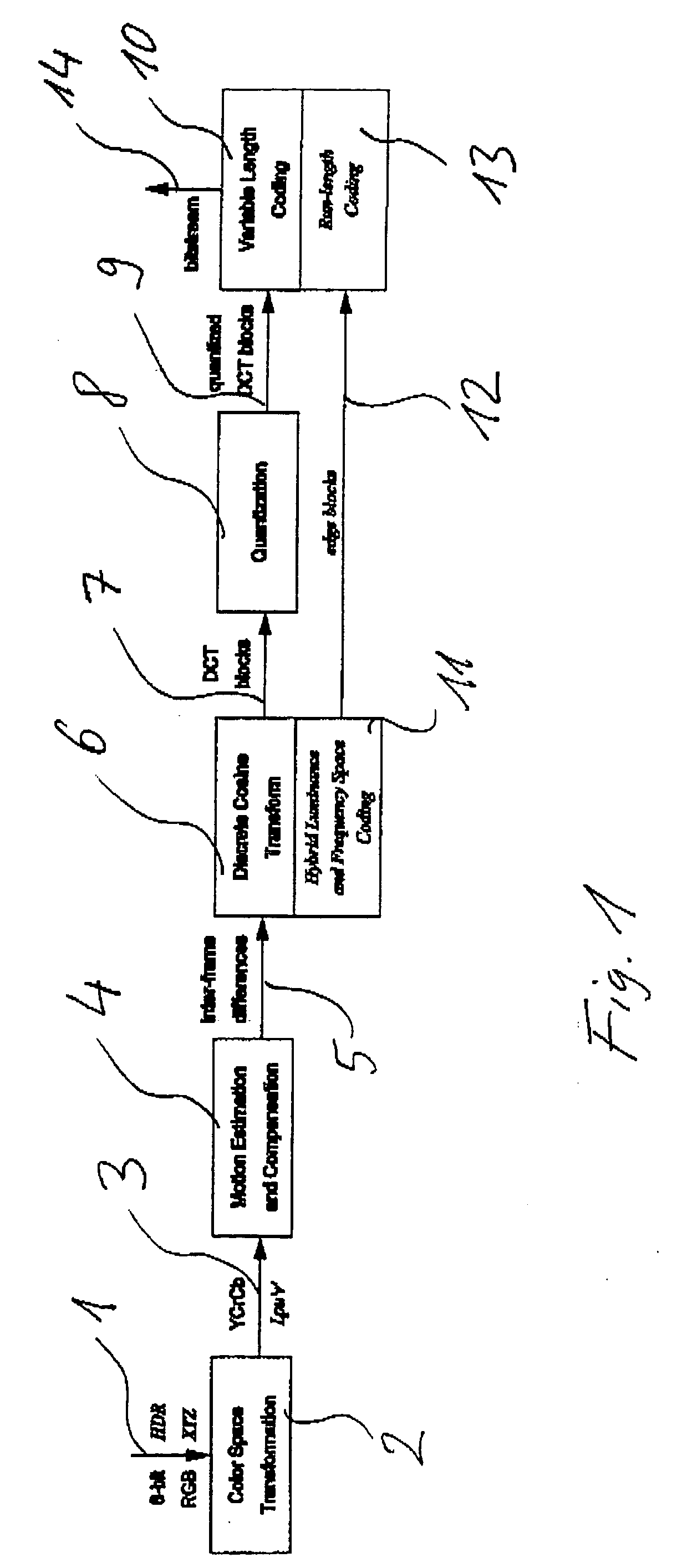
Method and apparatus for encoding high dynamic range video
InactiveUS20060002611A1Good colorIncrease rangeColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionData stream
A method and apparatus for encoding high dynamic range video by means of video compression is shown. The method comprises the steps of providing high dynamic range (HDR) tristimulus color data (XYZ) for each frame of the video and threshold versus intensity data for a human observer; constructing a perceptually conservative luminance transformation from continuous luminance data (Y) to discrete values (Lp) using said threshold versus intensity data for the human observer; transforming the HDR tristimulus color data into perceptually linear color data of three color channels (Lp, u′, v′) for obtaining visually lossless compressed frames; estimating motion vector of said consecutive frames of the video and compensating the difference of the tristimulus color data for performing an inter-frame encoding and an inter-frame compression; transforming the compensated differences of the tristimulus color data to frequency space data; quantizing said frequency space data; variable-length encoding of the quantized frequency space data and storing or transmitting a stream of visual data resulting from the encoded quantized frequency space data;
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
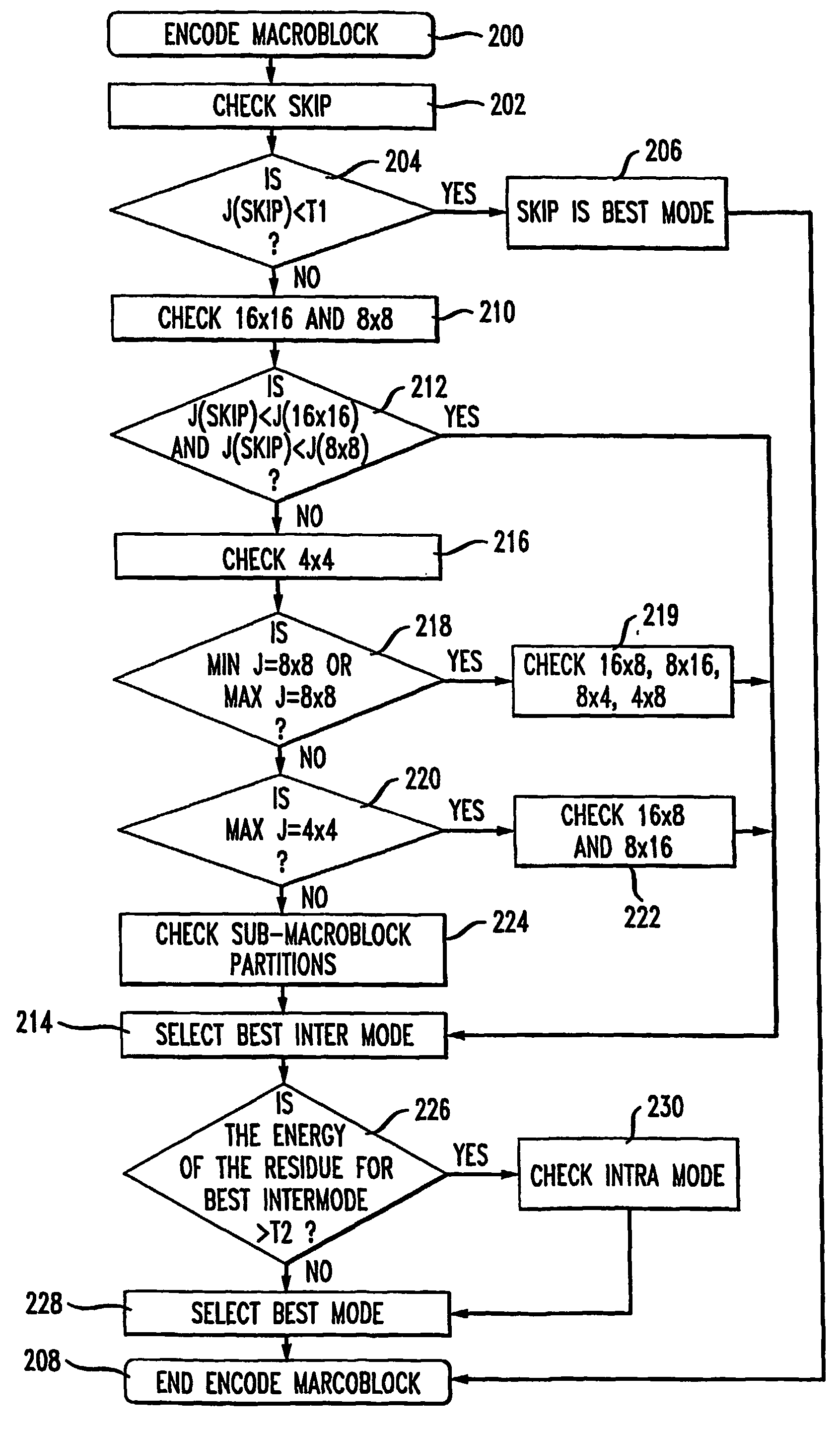
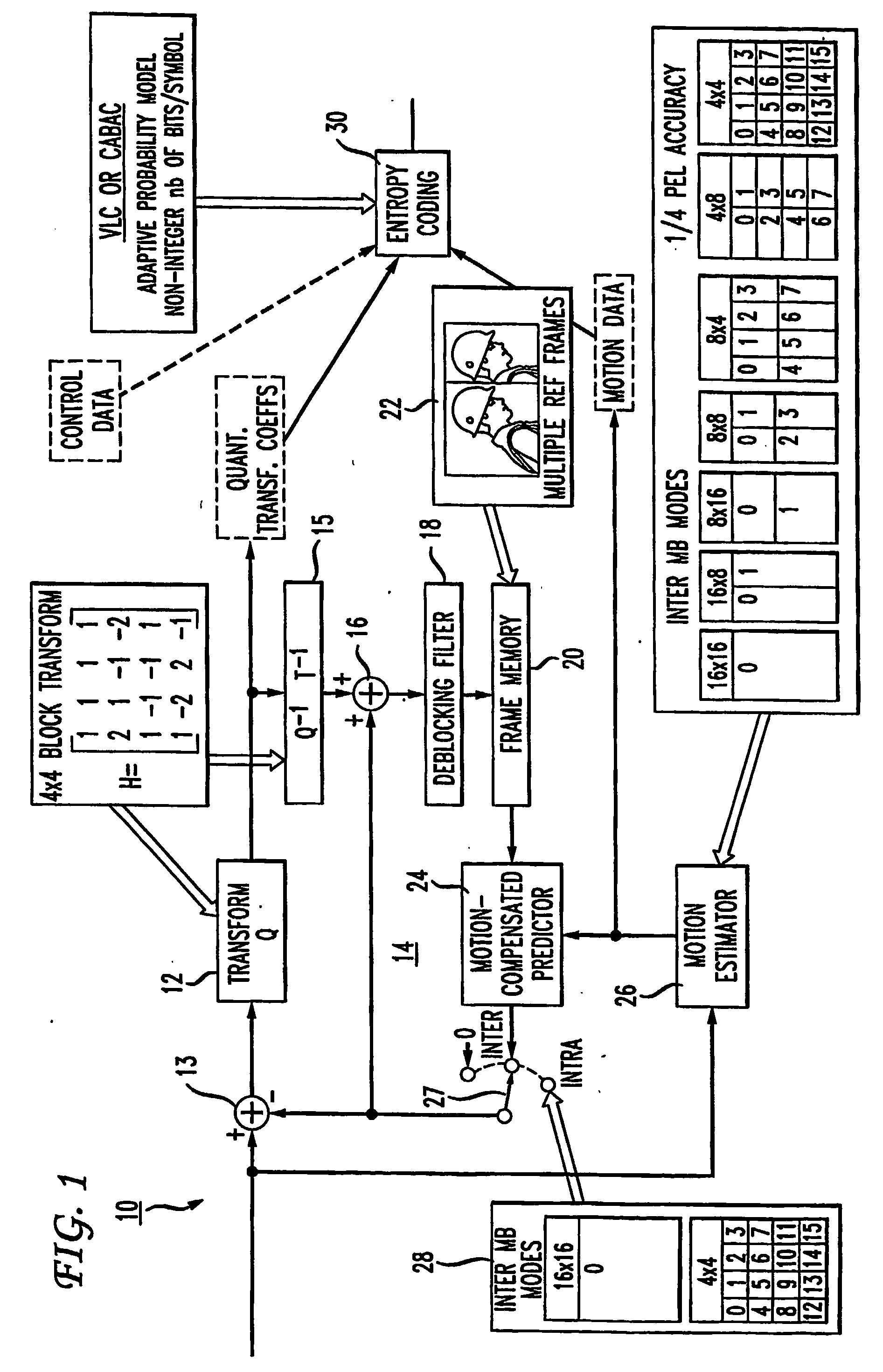
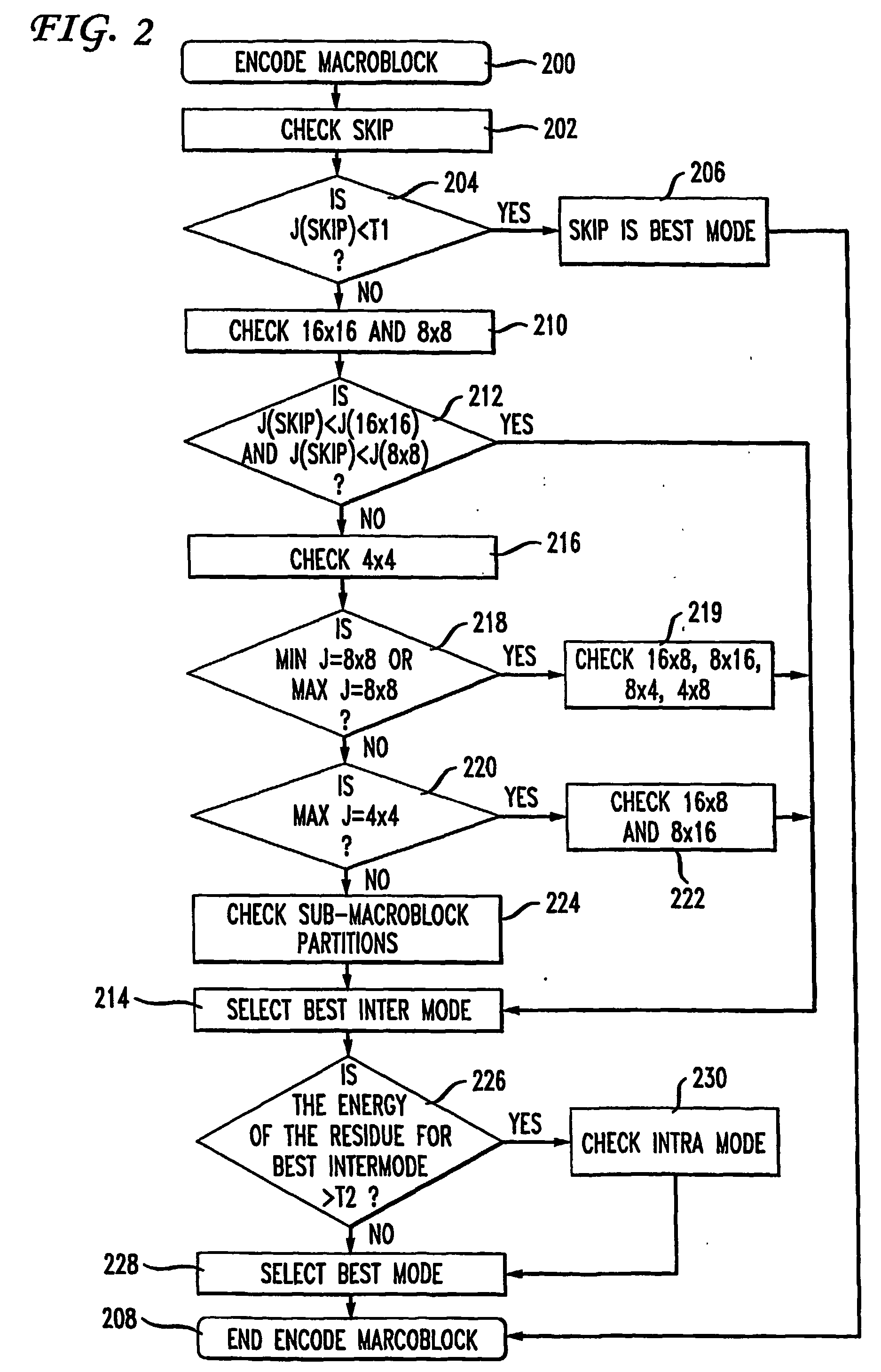
Fast mode decision making for interframe encoding
InactiveUS20060062302A1Television system detailsColor television with pulse code modulationMotion vectorInterframe coding
An encoder achieves improved encoding efficiency by initially limiting consideration of the potential modes (block sizes) to a prescribed sub-set and by performing mode estimation jointly with mode decision-making. An initial sub-set of modes is considered and an estimation of the motion for each block in the sub-set is made to establish a best motion vector. A distortion measure is also made for each sub-set. From the distortion measure, a determination is made whether or not to estimate the motion for other block sizes. If not, then an encoding mode is chosen in accordance with the estimated motion. In this way, motion estimation on all possible block sizes need not be undertaken.
Owner:THOMSON LICENSING SA
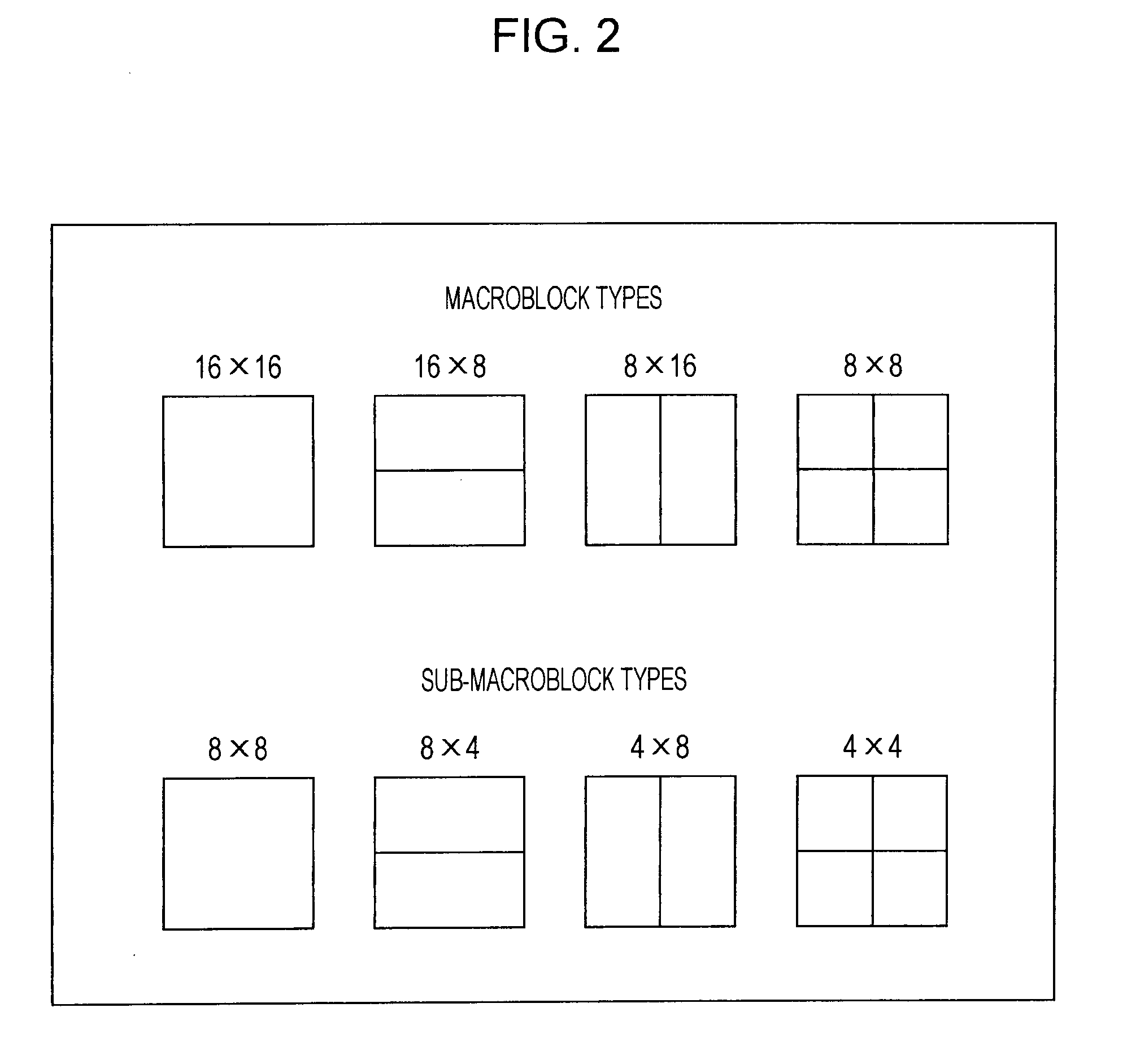
Mixed inter/intra video coding of macroblock partitions
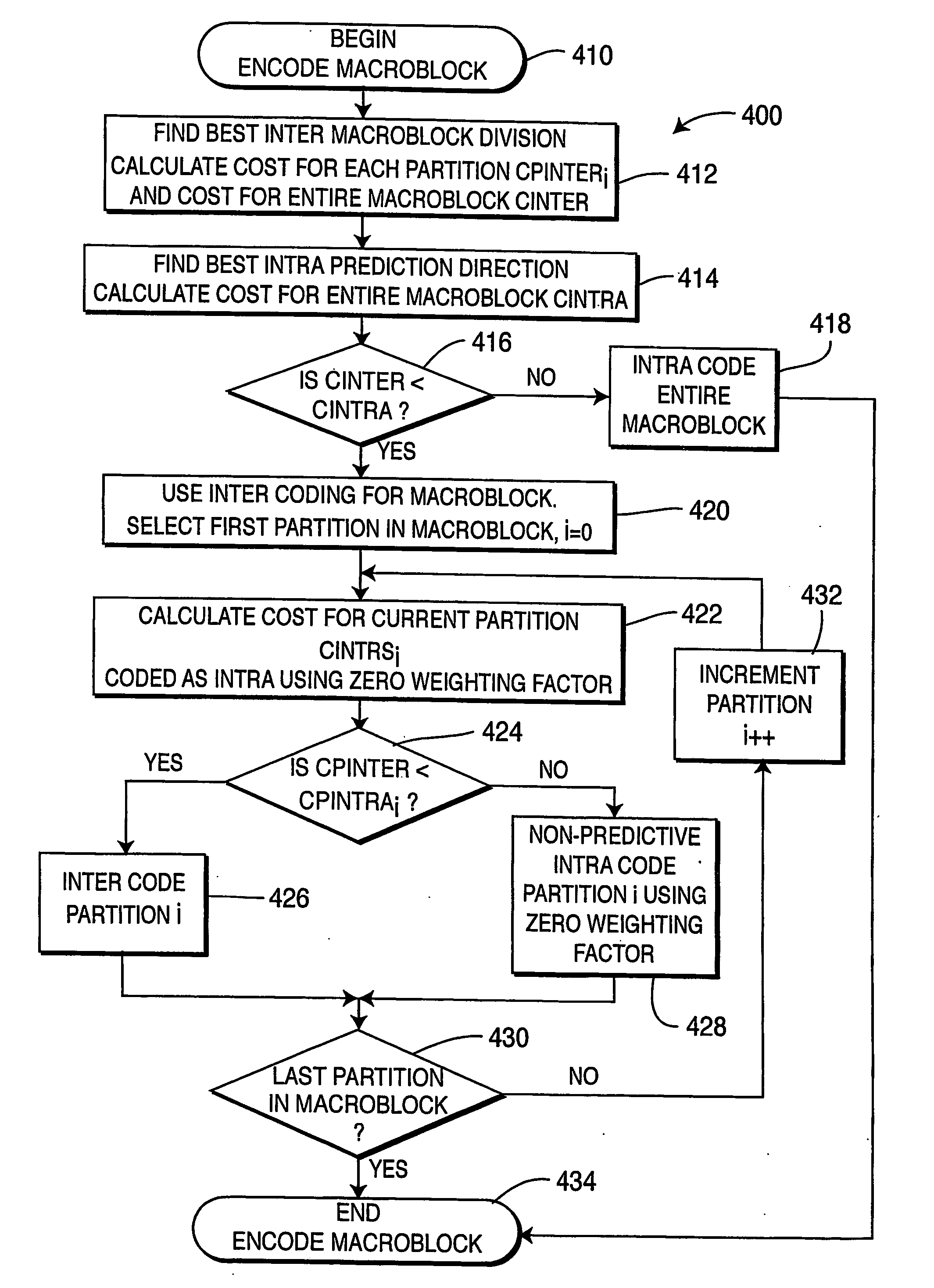
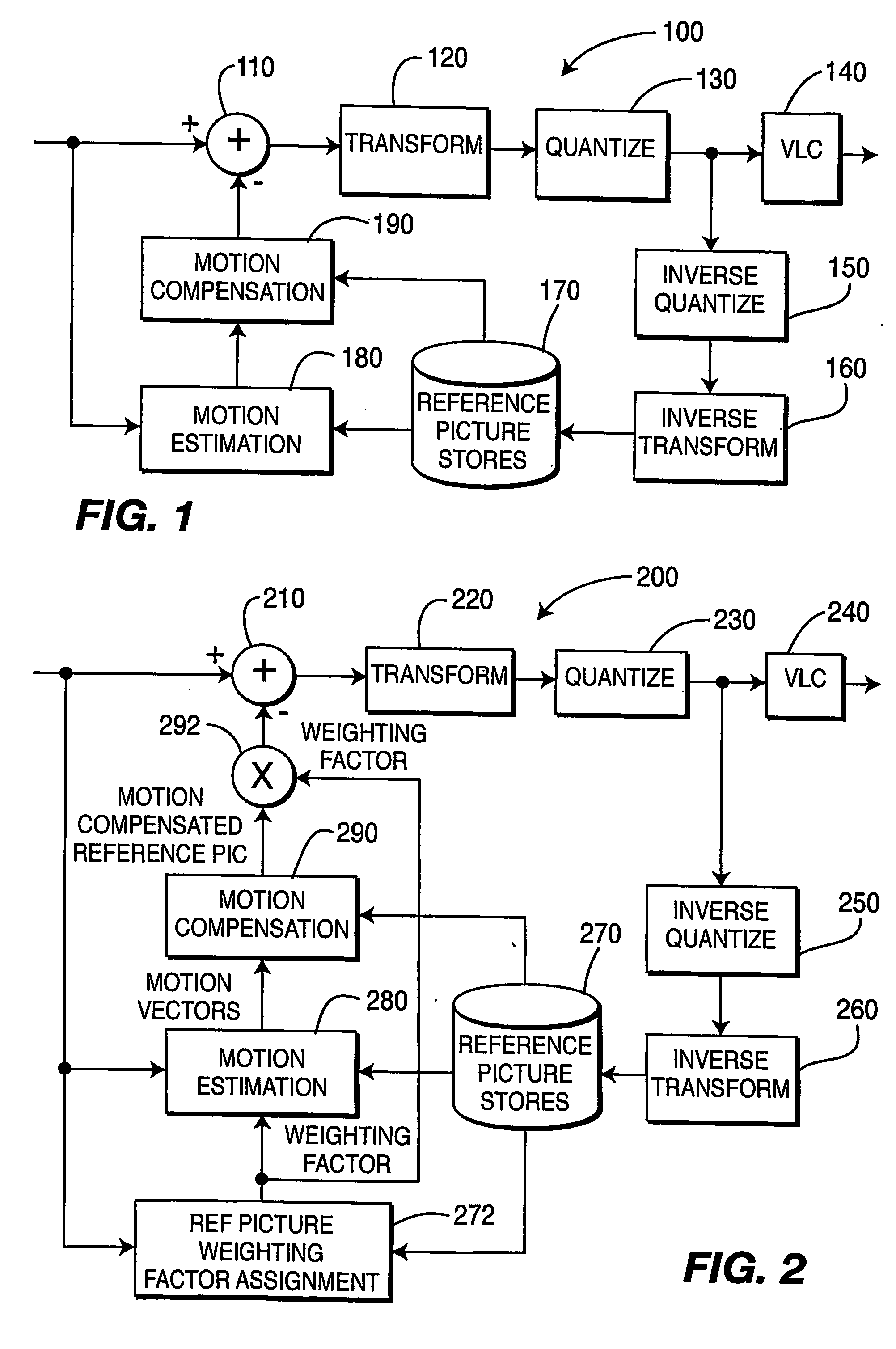
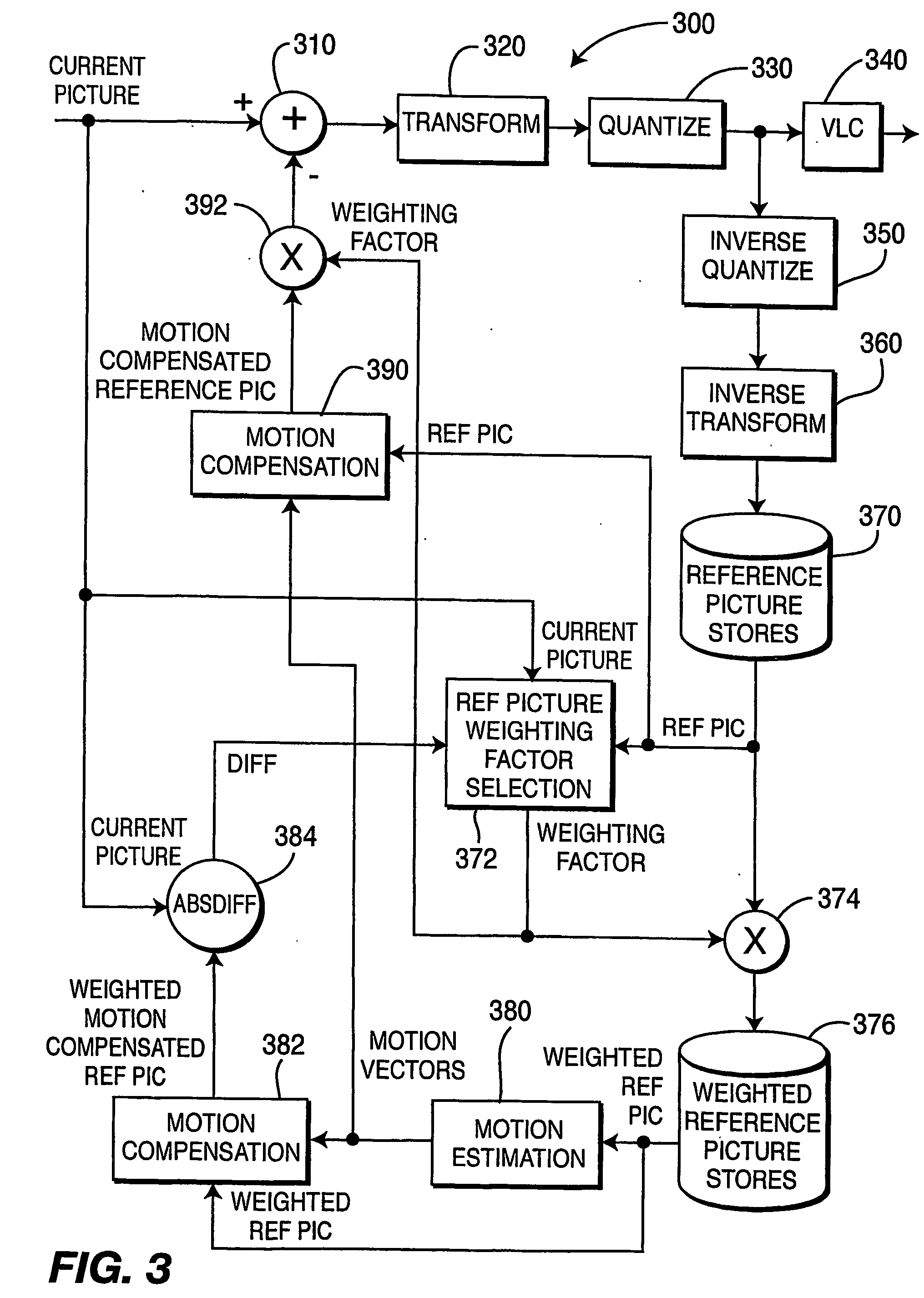
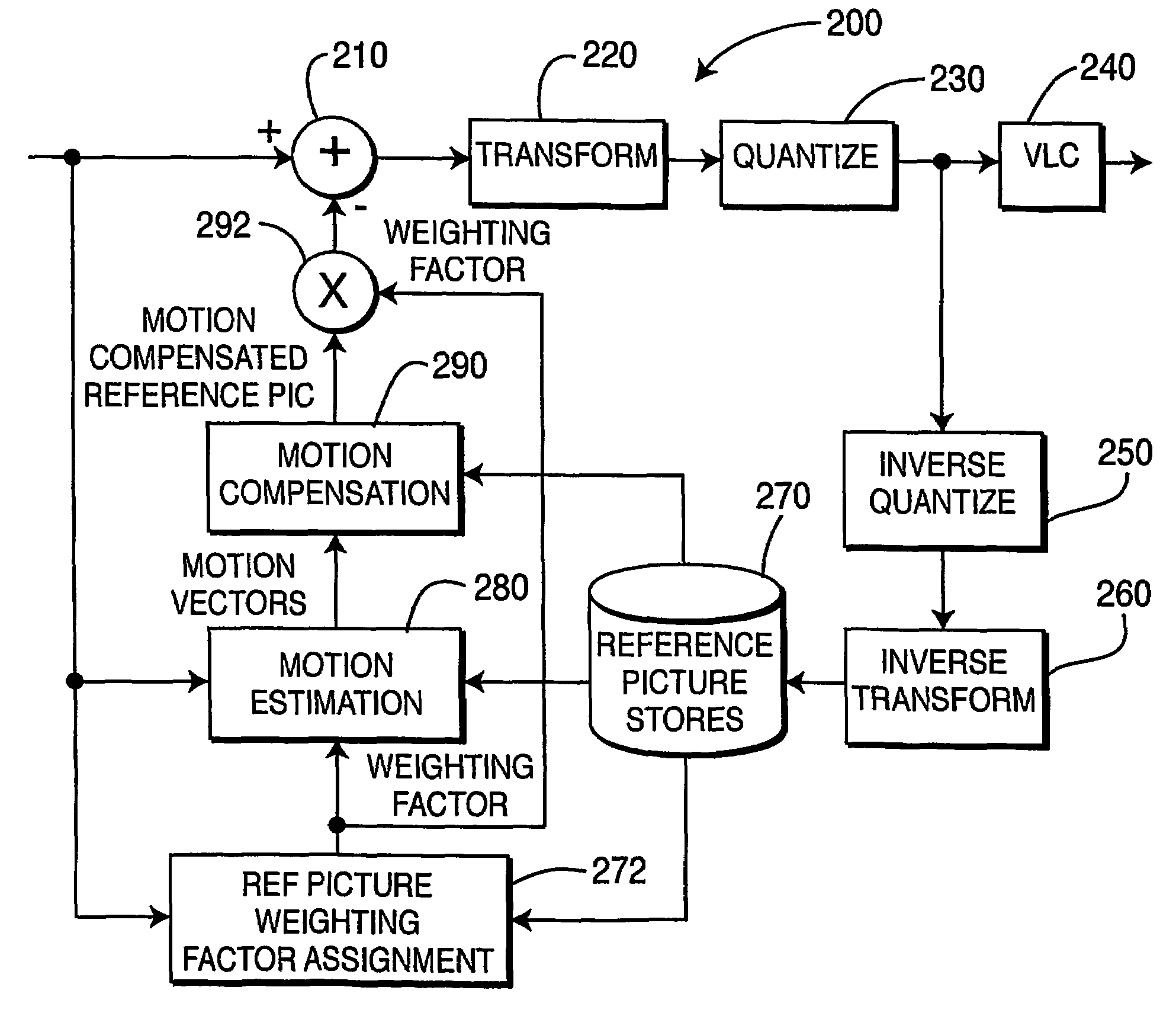
ActiveUS20060153297A1Improve coding efficiencyImprove subjective video qualityDigital variable displayPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPattern recognitionInterframe coding
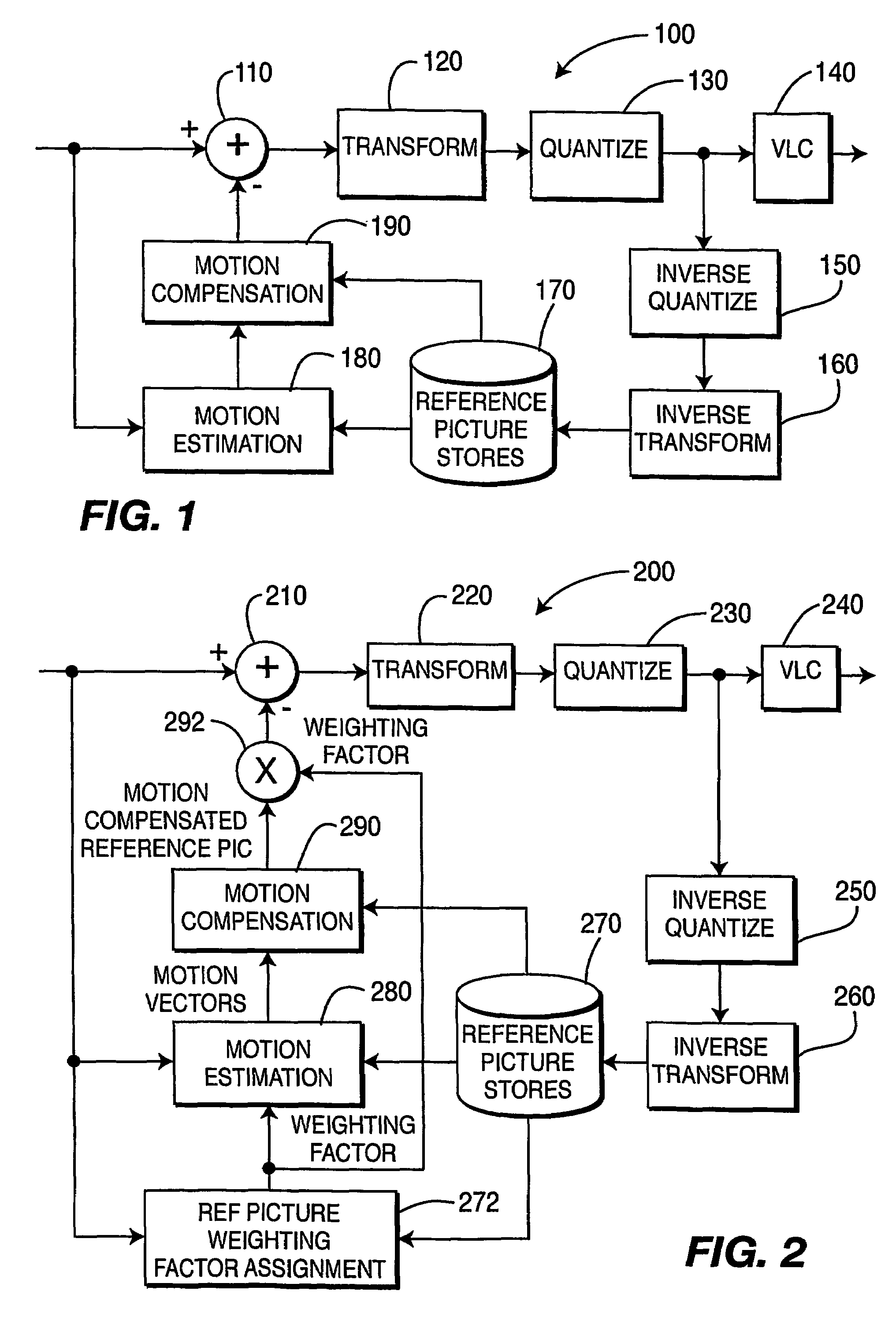
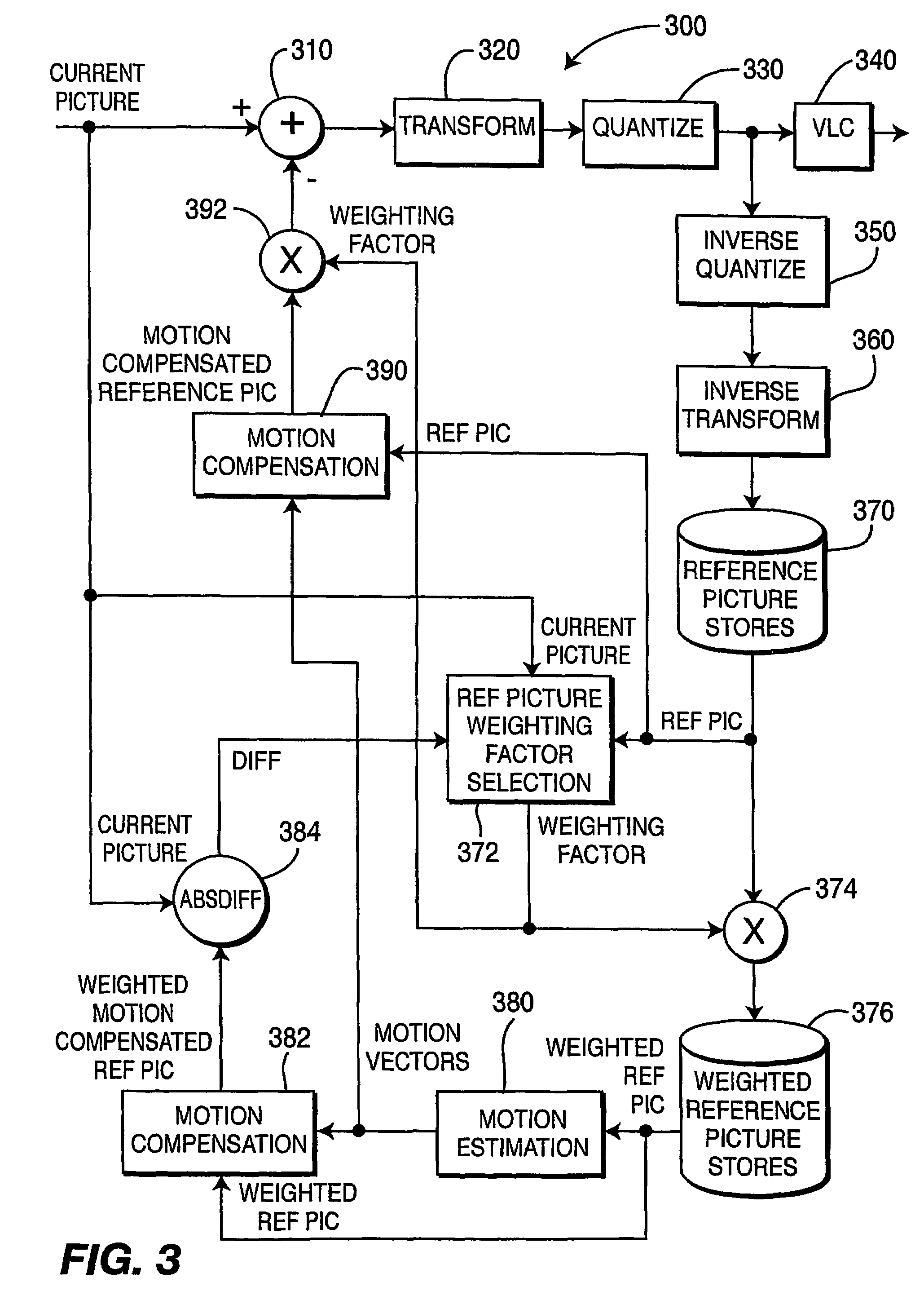
A video encoder and corresponding method are provided for mixed inter / intra encoding of a macroblock having a plurality of partitions, where the encoder includes a reference picture weighting applicator coupled with a reference picture weighting factor unit for assigning weighting factors corresponding to each of the inter and intra coded partitions, respectively; and the corresponding method for encoding a macroblock with several partitions includes inter-coding at least one partition and intra-coding at least a second partition.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL MADISON PATENT HLDG
Mixed inter/intra video coding of macroblock partitions
ActiveUS7466774B2Improve efficiencyQuality improvementDigital variable displayPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPattern recognitionVideo encoding
A video encoder and corresponding method are provided for mixed inter / intra encoding of a macroblock having a plurality of partitions, where the encoder includes a reference picture weighting applicator coupled with a reference picture weighting factor unit for assigning weighting factors corresponding to each of the inter and intra coded partitions, respectively; and the corresponding method for encoding a macroblock with several partitions includes inter-coding at least one partition and intra-coding at least a second partition.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL MADISON PATENT HLDG
Method and apparatus for encoding hybrid intra-inter coded blocks
ActiveUS8085845B2Improve efficiencyReduce data errorsTelevision system detailsColor television with pulse code modulationCoding blockData stream
A hybrid intra-inter bi-predictive (or multi-predictive) coding mode allows both intraframe (intra) and interframe (inter) predictions to be combined together for hybrid-encoding a current macroblock or a subblock. Bi-prediction may be used also in I-pictures, combining two intra predictions that use two different intra prediction directions. A video encoder processes data representing a two-dimensional video image which has been produced by a conventional commercially available video camera. The video encoder is adapted to select, for coding a current macroblock, between an intra encoding mode, an P-frame inter encoding mode, a B-frame bi-predictive inter mode, and a hybrid intra-inter bi-predictive encoding mode. A video decoder receives and decodes a data stream that may contain a block / macroblock encoded in accordance with the hybrid intra-inter bi-predictive encoding mode.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL MADISON PATENT HLDG
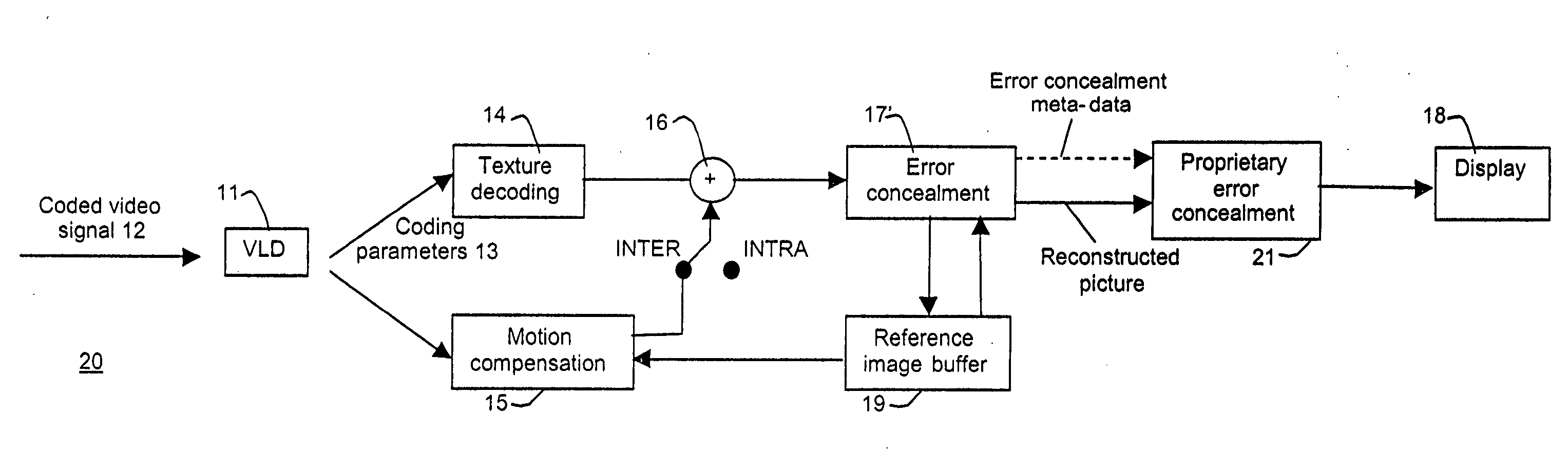
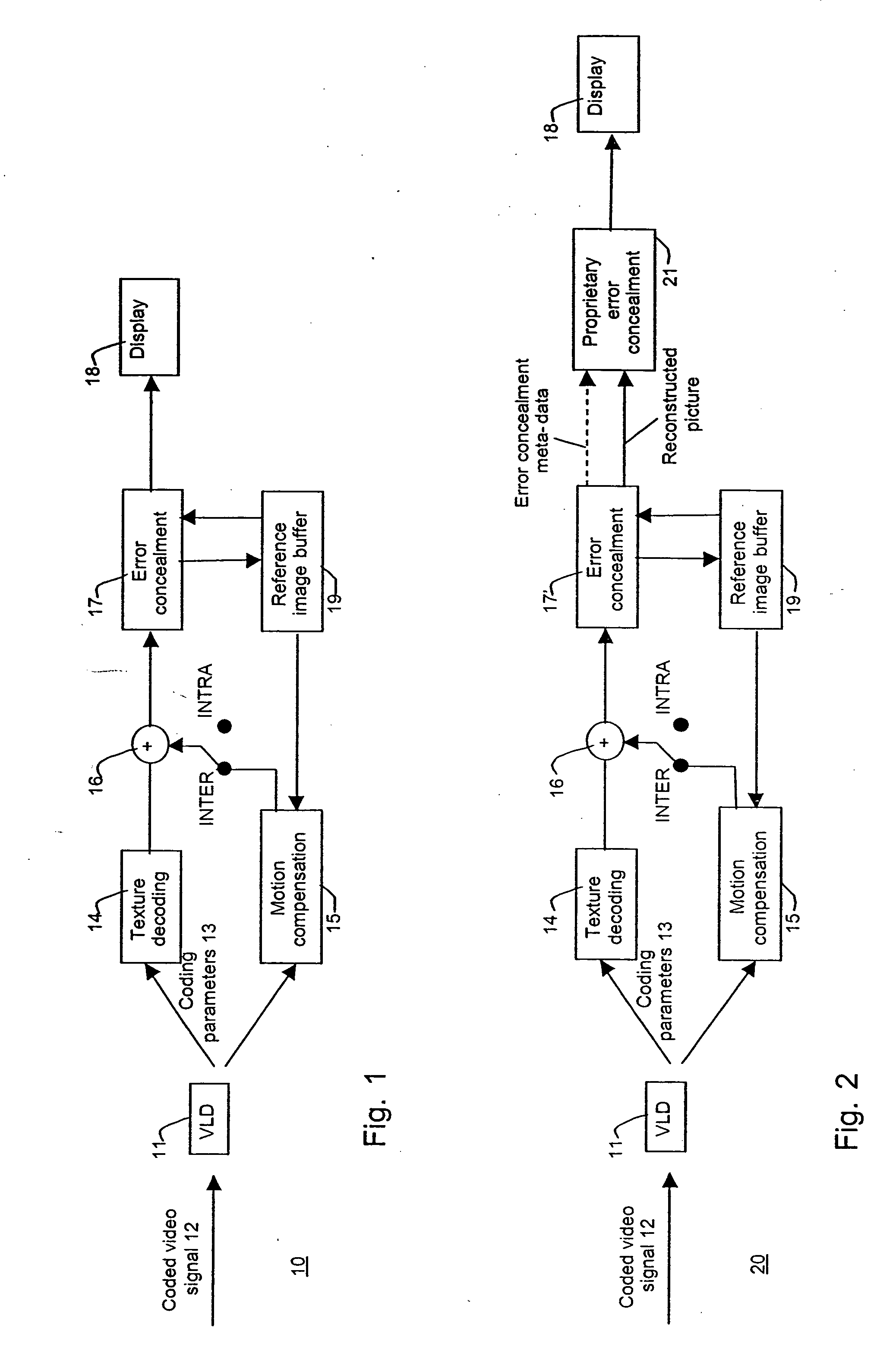
Error concealment
InactiveUS20060188025A1Reduce decreaseEliminate needColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer hardwareInterframe coding
An error concealment in decoding of inter-coded information, comprising normative error concealment within a decoding loop and proprietary error concealment outside the decoding loop. The normative error concealment provides meta-data and a reconstructed frame for the proprietary error concealment. Using these, the proprietary error concealment further enhances the reconstructed frame without effecting on the decoding of the inter-coded data. A mobile station, network element and a computer program product using the method have further been described.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
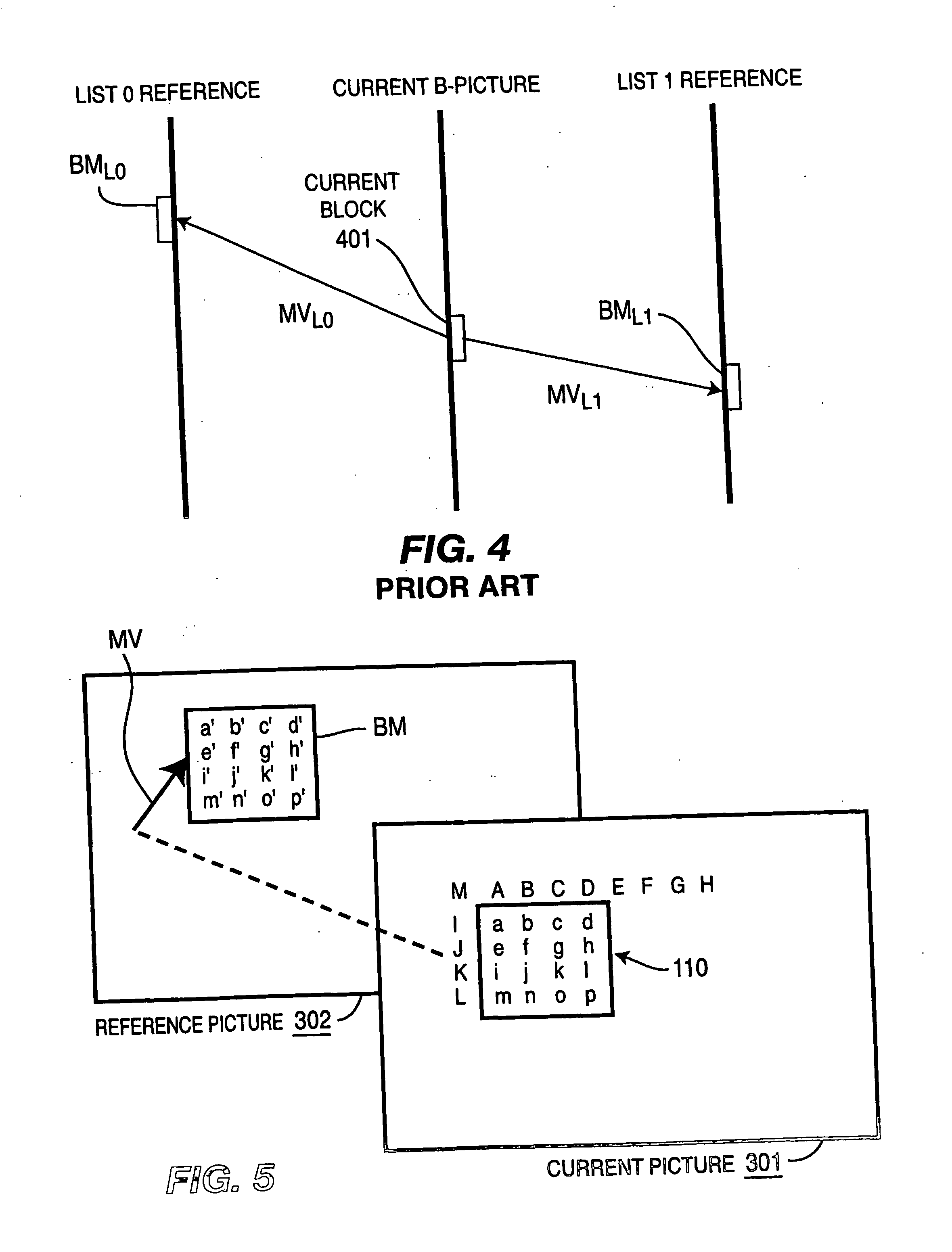
Motion vector predictive encoding method, motion vector decoding method, predictive encoding apparatus and decoding apparatus, and storage media storing motion vector predictive encoding and decoding programs
InactiveUS20030174776A1Reduce generationReduce the amount requiredColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionMotion vectorInterframe coding
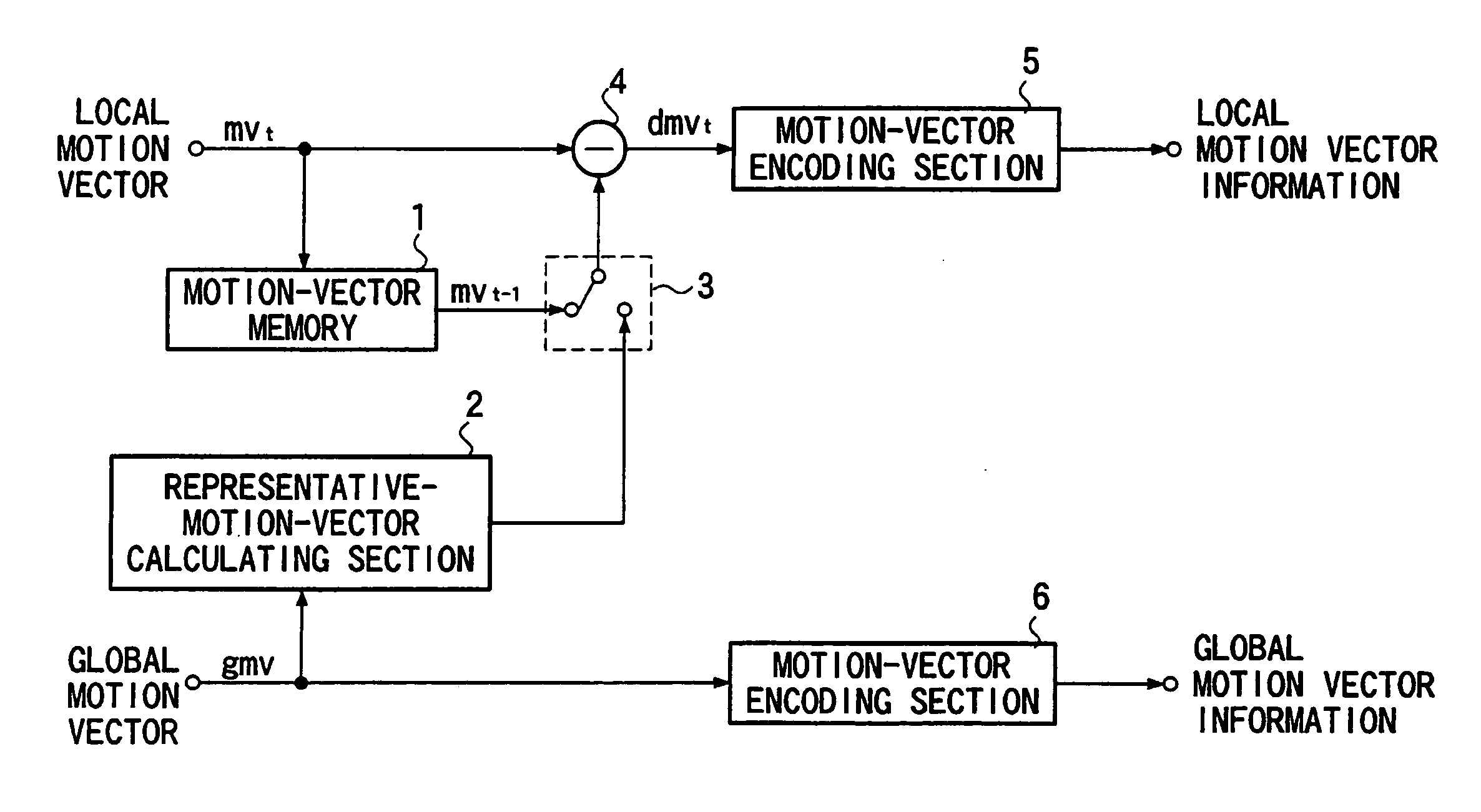
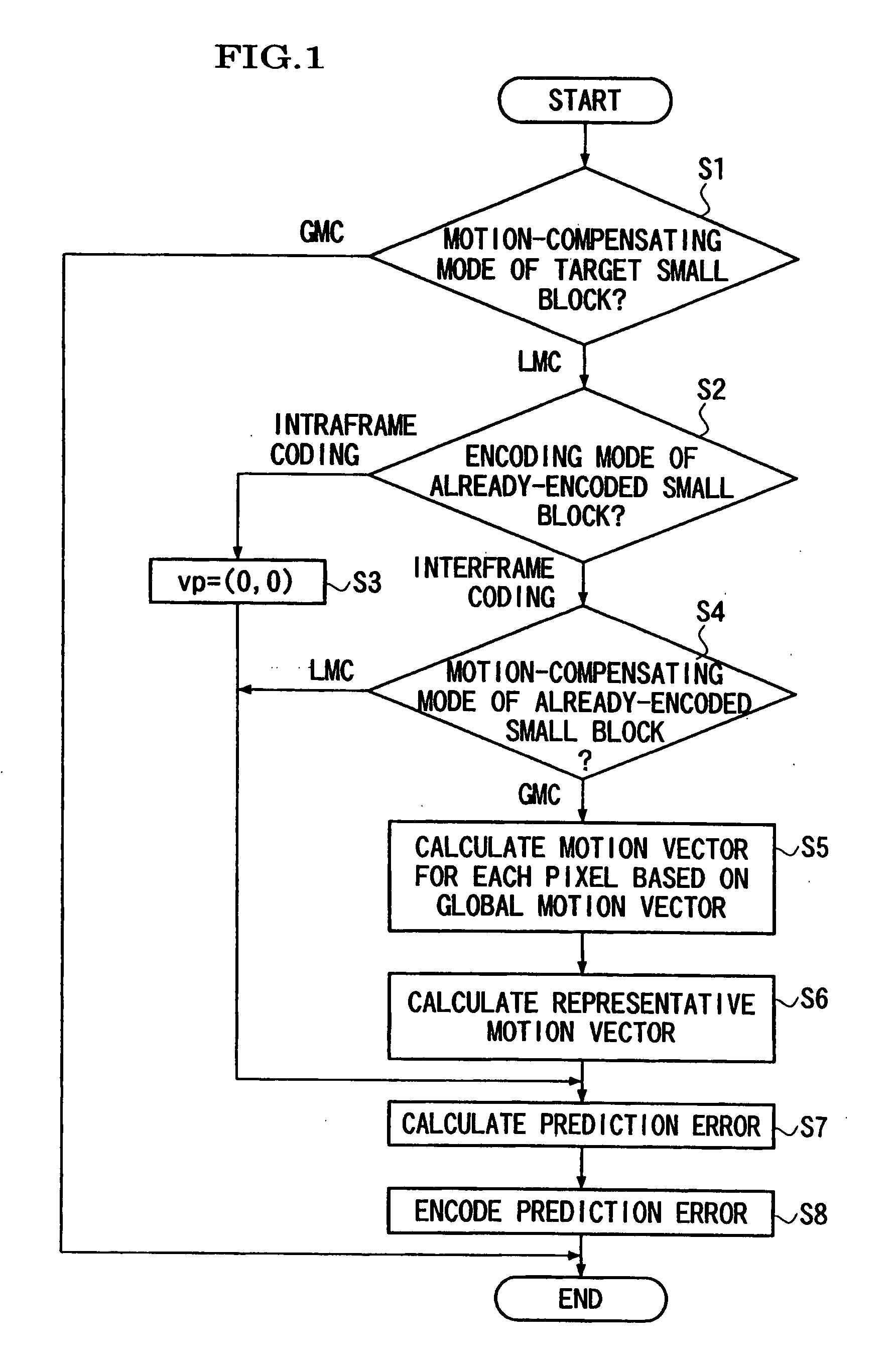
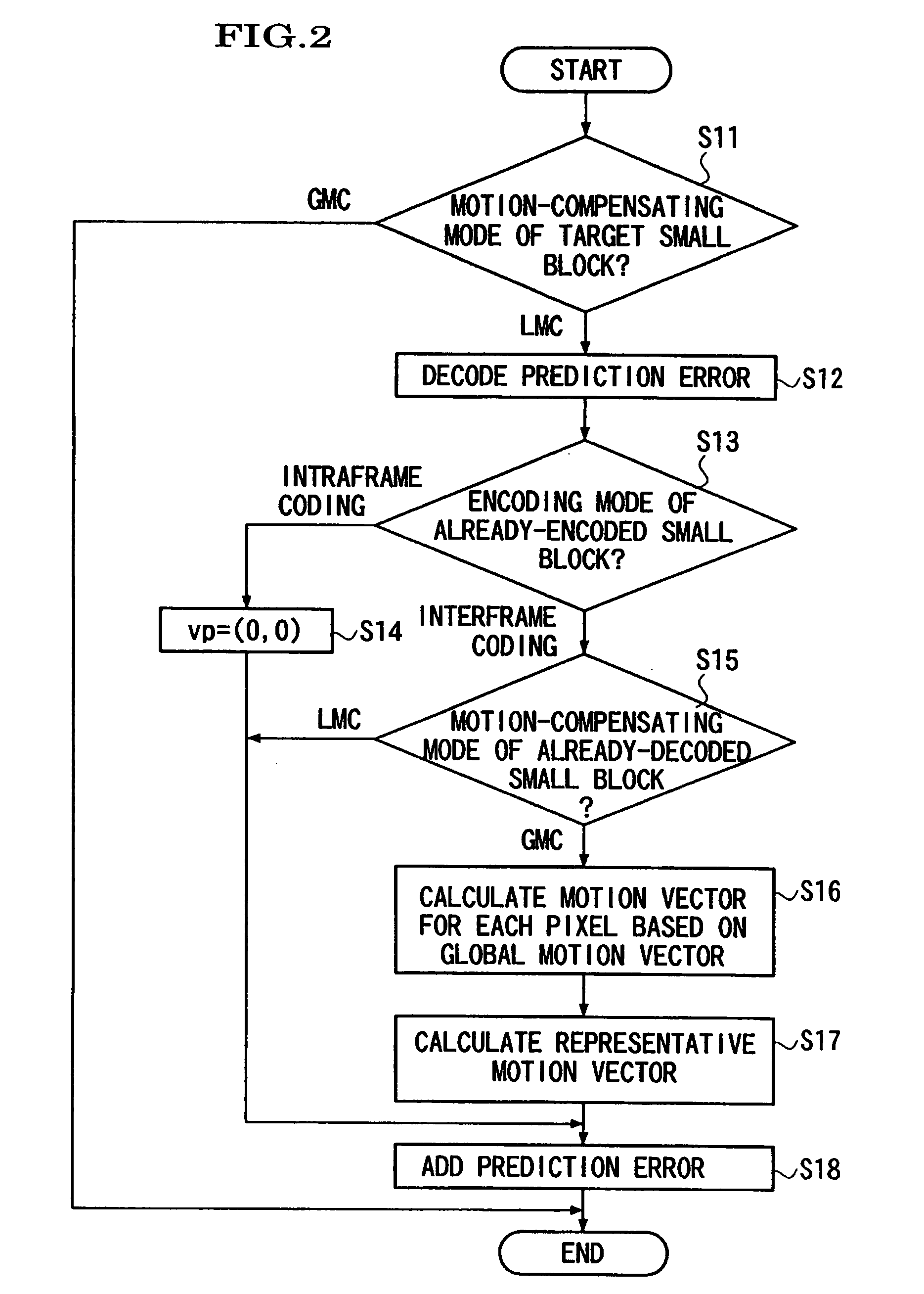
A motion vector predictive encoding method, a motion vector decoding method, a predictive encoding apparatus, a decoding apparatuses, and storage media storing motion vector predictive encoding and decoding programs are provided, thereby reducing the amount of generated code with respect to the motion vector, and improving the efficiency of the motion-vector prediction. If the motion-compensating mode of the target small block to be encoded is the global motion compensation, the encoding mode of an already-encoded small block is the interframe coding mode, and the motion-compensating mode of the already-encoded small block is the global motion compensation, then the motion vector of the translational motion model is determined for each pixel of the already-encoded small block, based on the global motion vector (steps S1-S5). Next, the representative motion vector is calculated as the predicted vector, based on the motion vector of each pixel of the already-encoded small block (step S6). Finally, the prediction error is calculated for each component of the motion vector and each prediction error is encoded (steps S7 and S8).
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
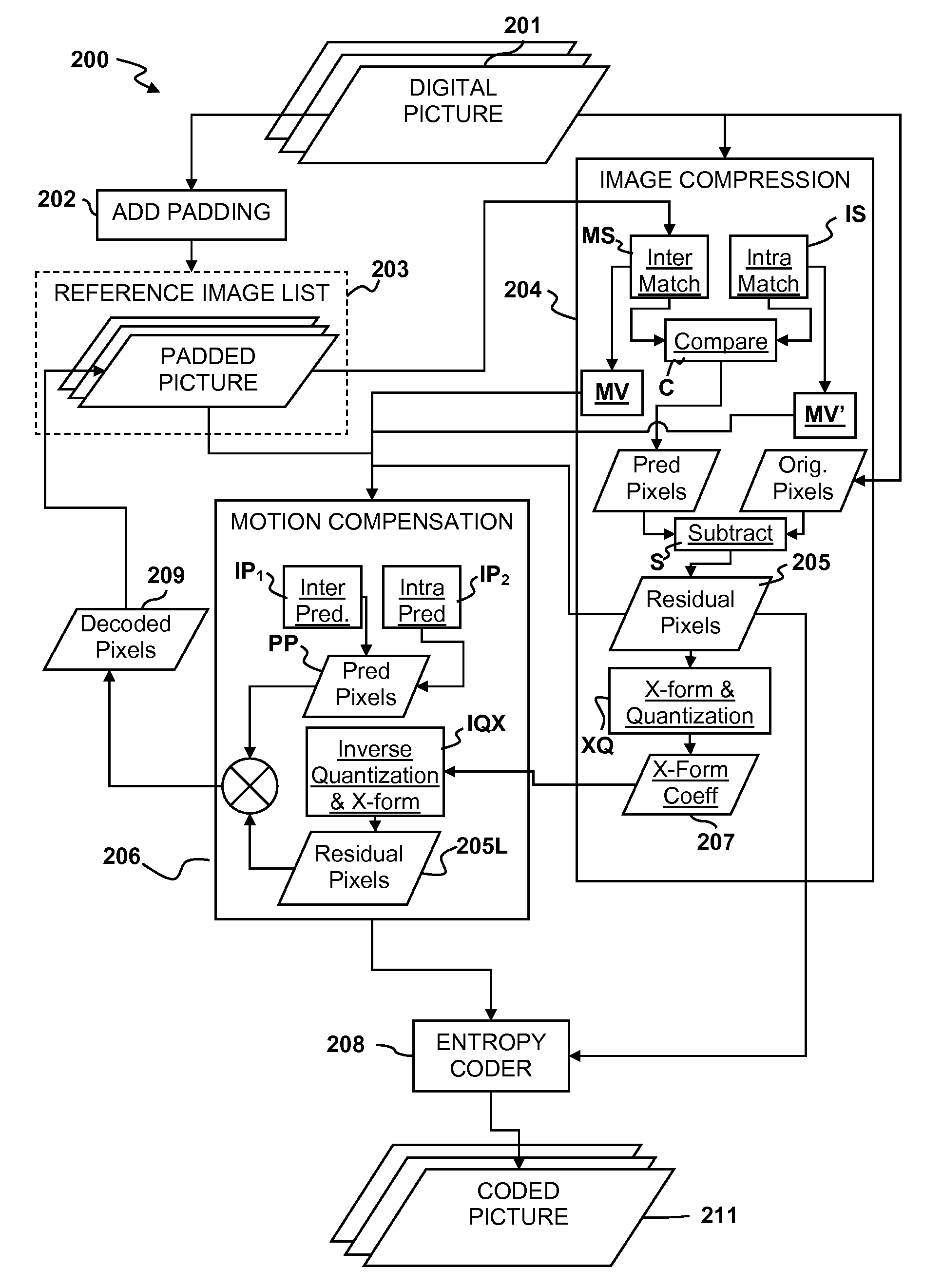
Picture encoding using same-picture reference for pixel reconstruction
ActiveUS20090010338A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionInterframe codingDigital pictures
Digital pictures may be encoded by padding all un-processed pixels within a currently processing picture with temporary pixel values; searching the picture for a matching section for use as a reference in pixel reconstruction of a section of the picture independent of whether the picture is intra-coded or inter-coded; and using the matching section to perform pixel prediction on the section to generate one or more predicted pixels for the section.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
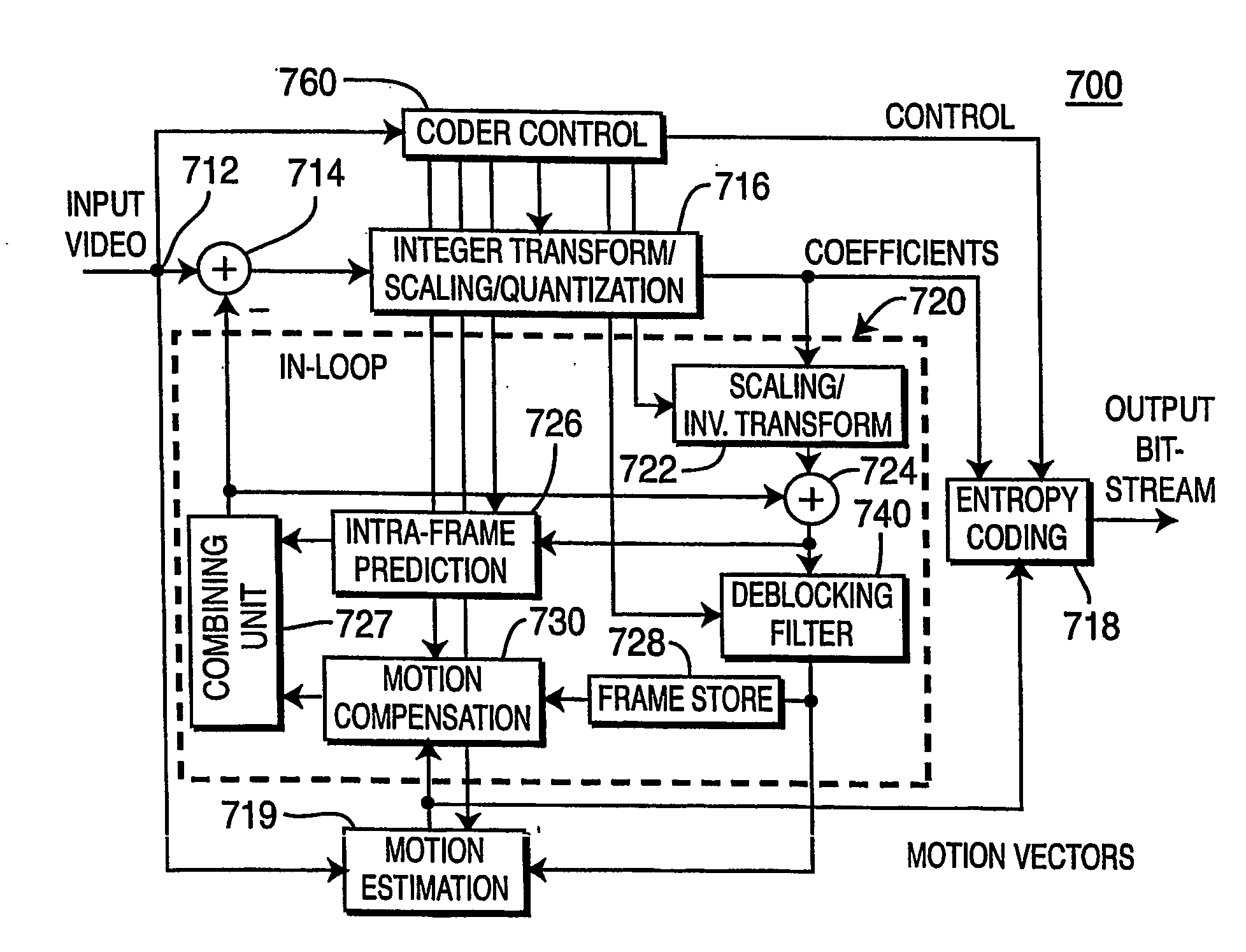
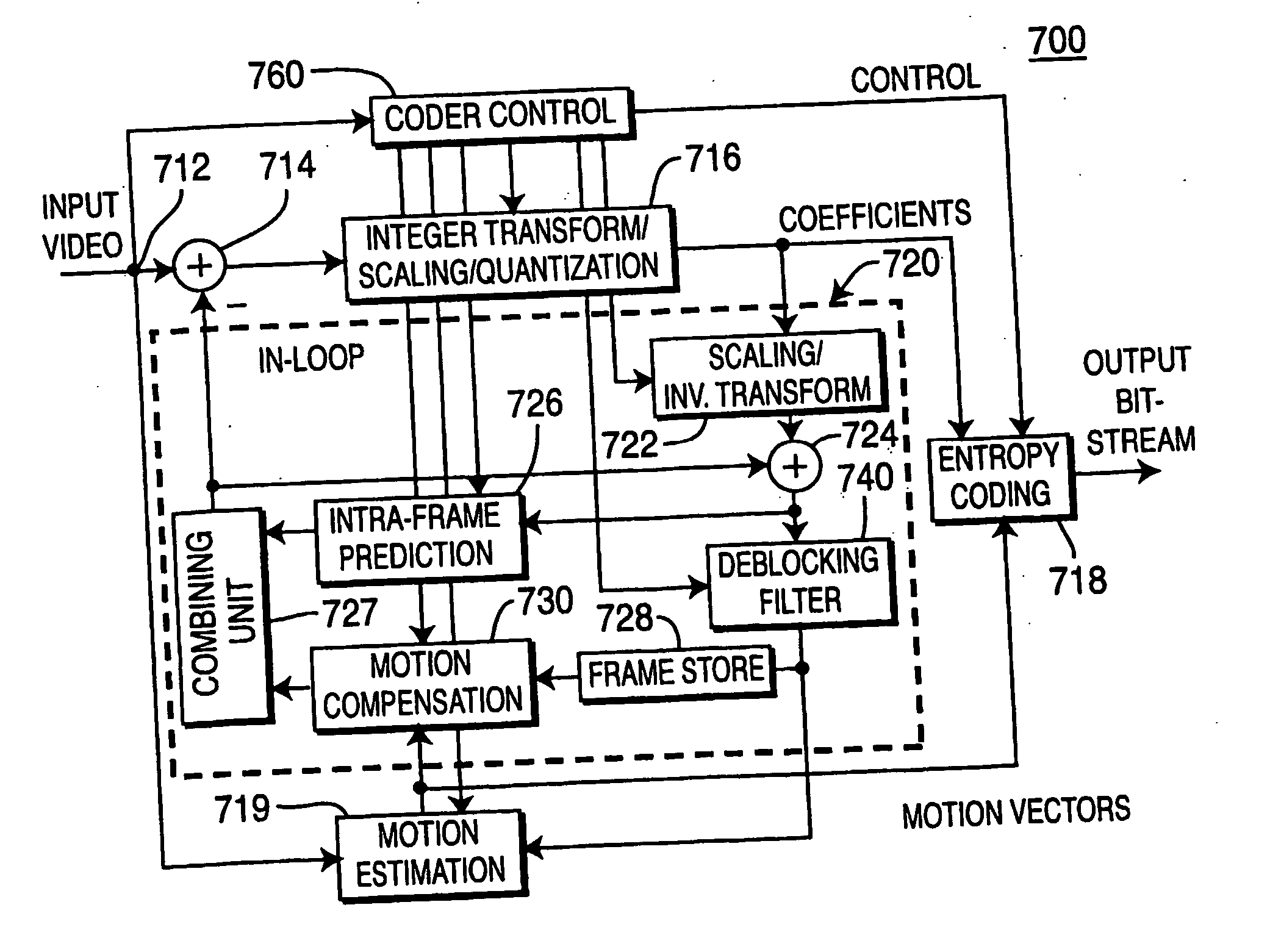
Video compression for high efficiency video coding
ActiveUS20130121401A1Reduce complexityValid choiceColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionVideo encoding
Encoding methods directed to making coding decisions and estimating coding parameters including searching for optimal angular prediction in intra-prediction mode; choosing the best intra block subdivision; and providing motion estimation for tree-structured inter coding. The methods are targeted to HEVC specifications of video compression, however, may be used with other video coding standards.
Owner:BEAMR IMAGING LTD
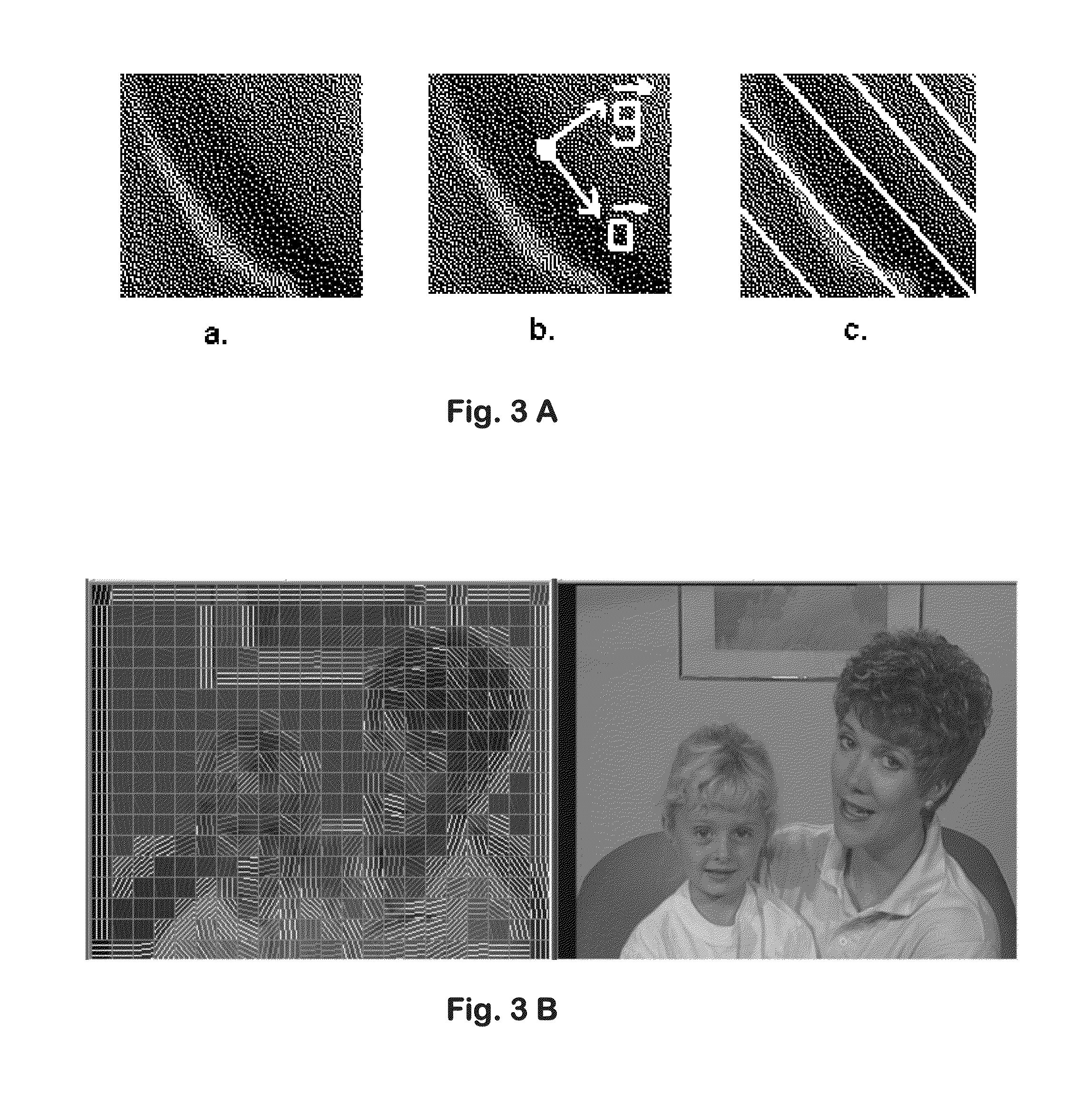
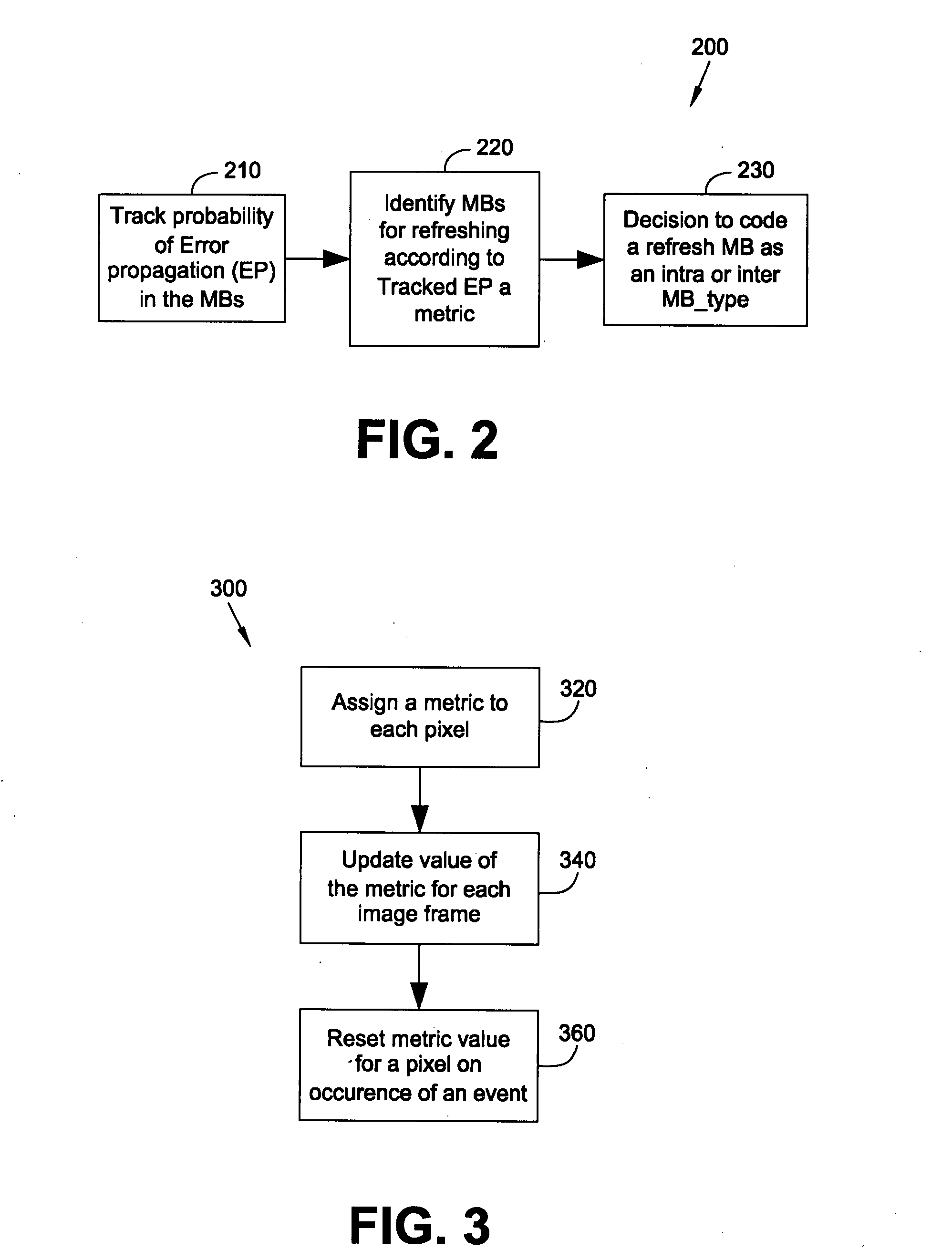
Method and device for tracking error propagation and refreshing a video stream
ActiveUS20080247469A1Reduce probabilityError propagationColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPacket lossInterframe coding
A method and device for tracking error propagation and refreshing a video stream is provided. The proposed subject matter comprises of an error propagation tracking method that works in the sub-sampled domain to reduce computational cycles and memory bandwidth. Further, the tracking based update of the error propagation metric is done differently for static and non-static regions to avoid unnecessary refresh of static areas. Through suitable thresholding of the metric at a macroblock (MB) level, a set of refresh MBs are selected for each frame. These refresh MBs are coded either as an intra MB or as an inter MB that is predicted from one or more reliable reference frames (—frames that are known to be available at the decoder with negligible errors—). Such inter coding of refresh MBs improves the compression efficiency when compared to pure intra coding of refresh MBs. Further, variants to the threshold selection are presented that result in temporally uniform distribution of the number of refresh MBs and a strict refresh scheme wherein all MBs are guaranteed to be with negligible errors following a packet loss within a committed refresh period. In addition, to using the error propagation metric, spatial connectivity to already chosen refresh MBs is used in the selection of additional refresh MBs within a frame and across frames; this reduces the rate of error propagation due to part of a macroblock predicting from older, erroneous neighboring MBs and in turn requiring more refresh MBs on the average per frame.
Owner:ITTIAM SYST P
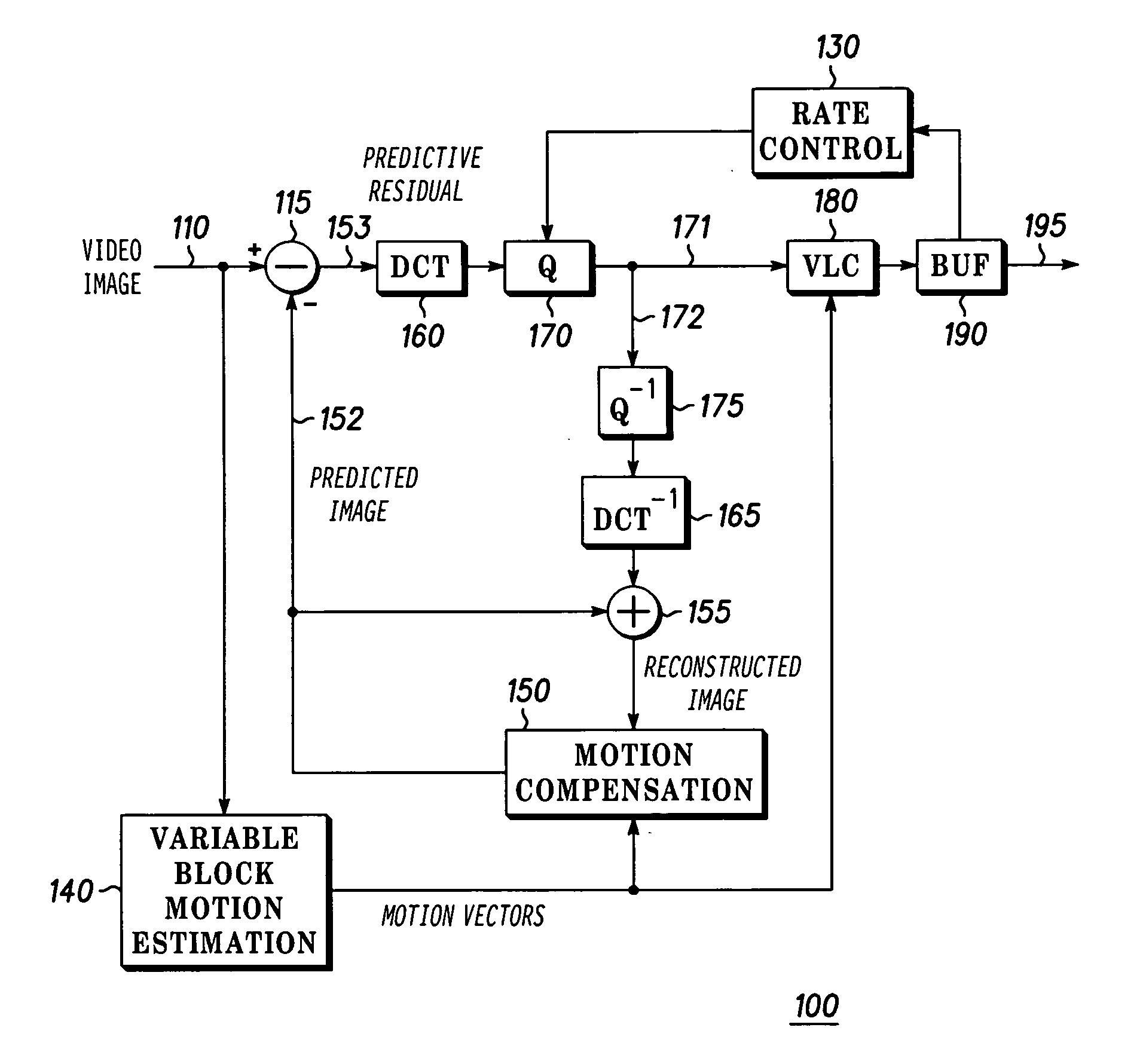
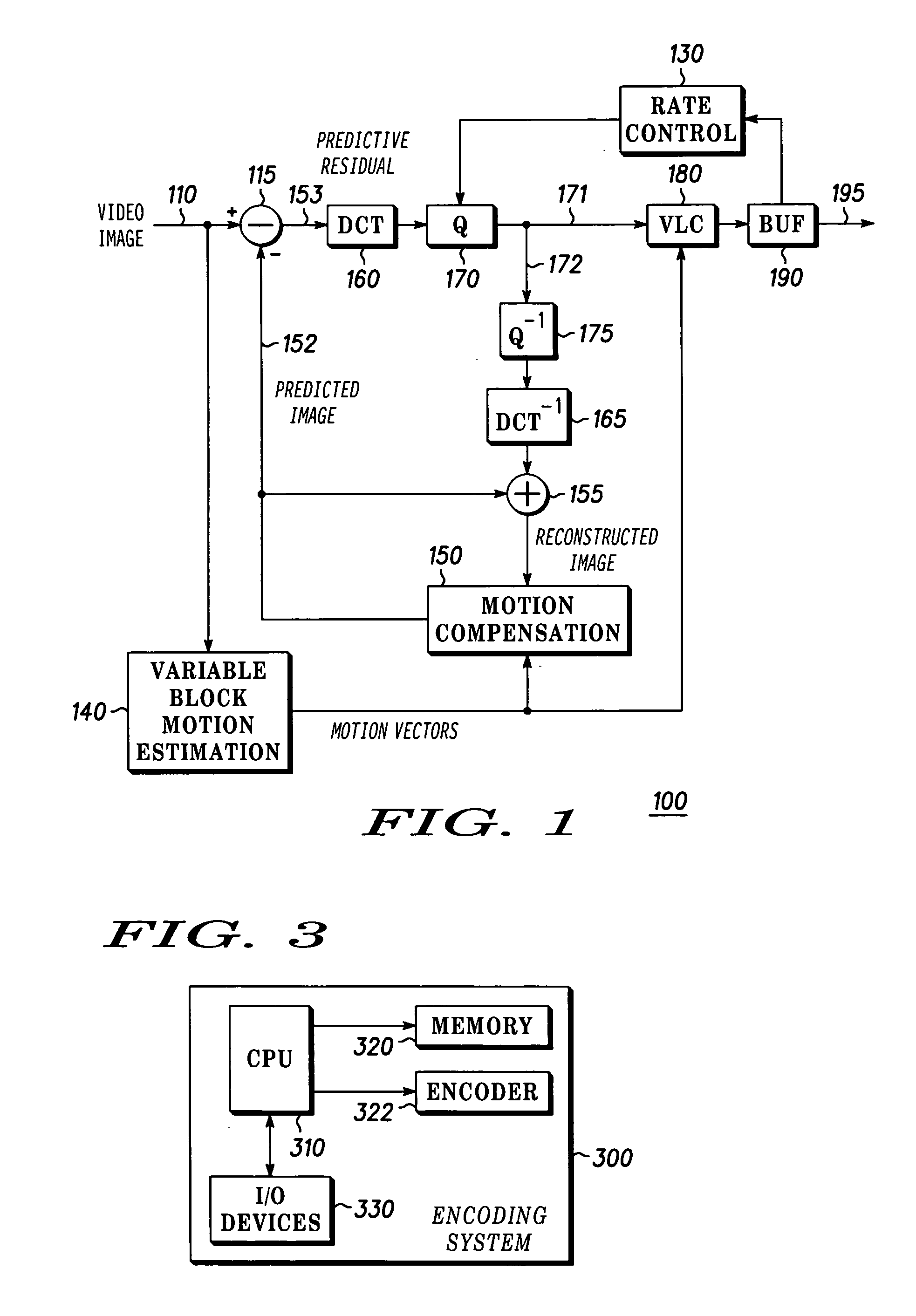
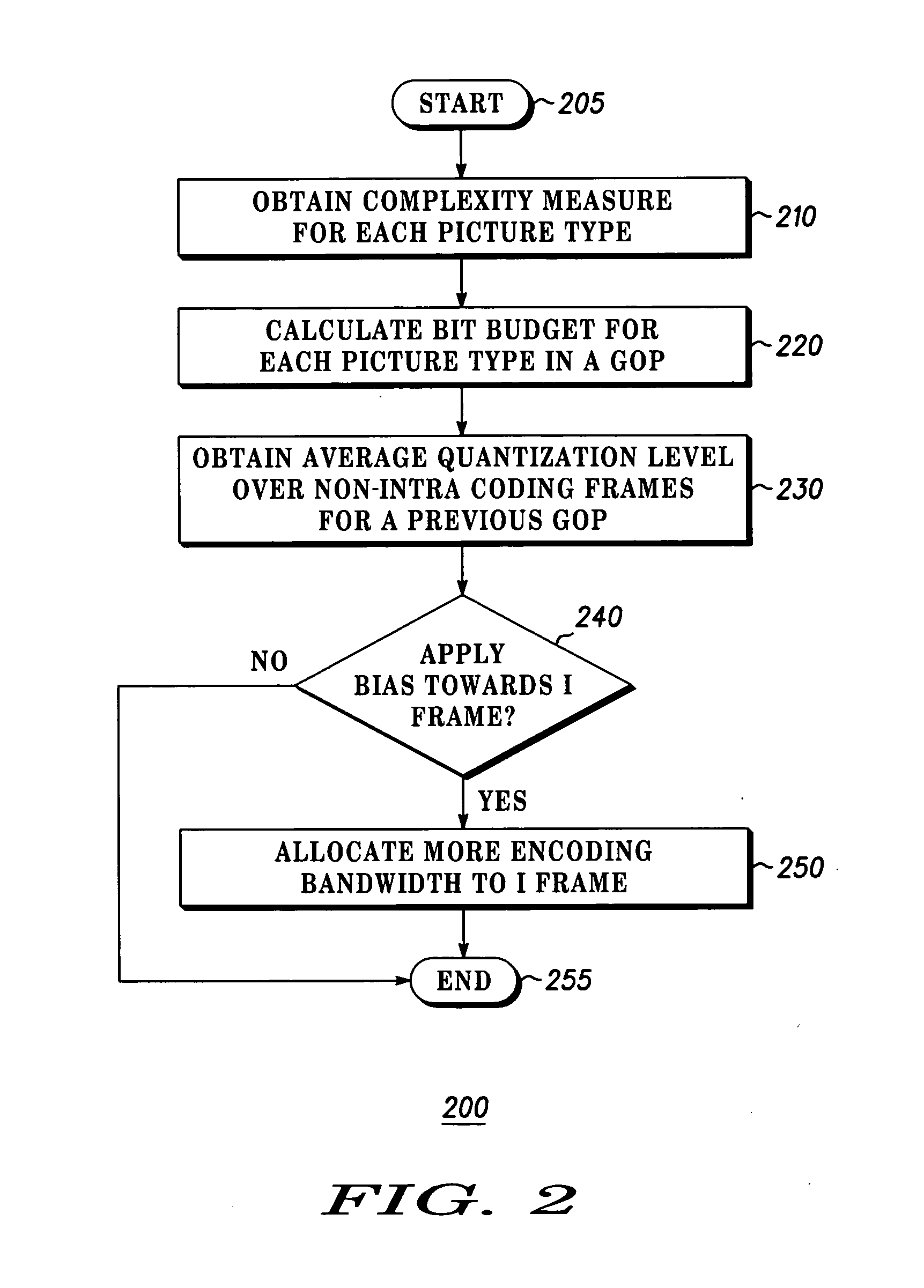
Method and apparatus for providing intra coding frame bit budget
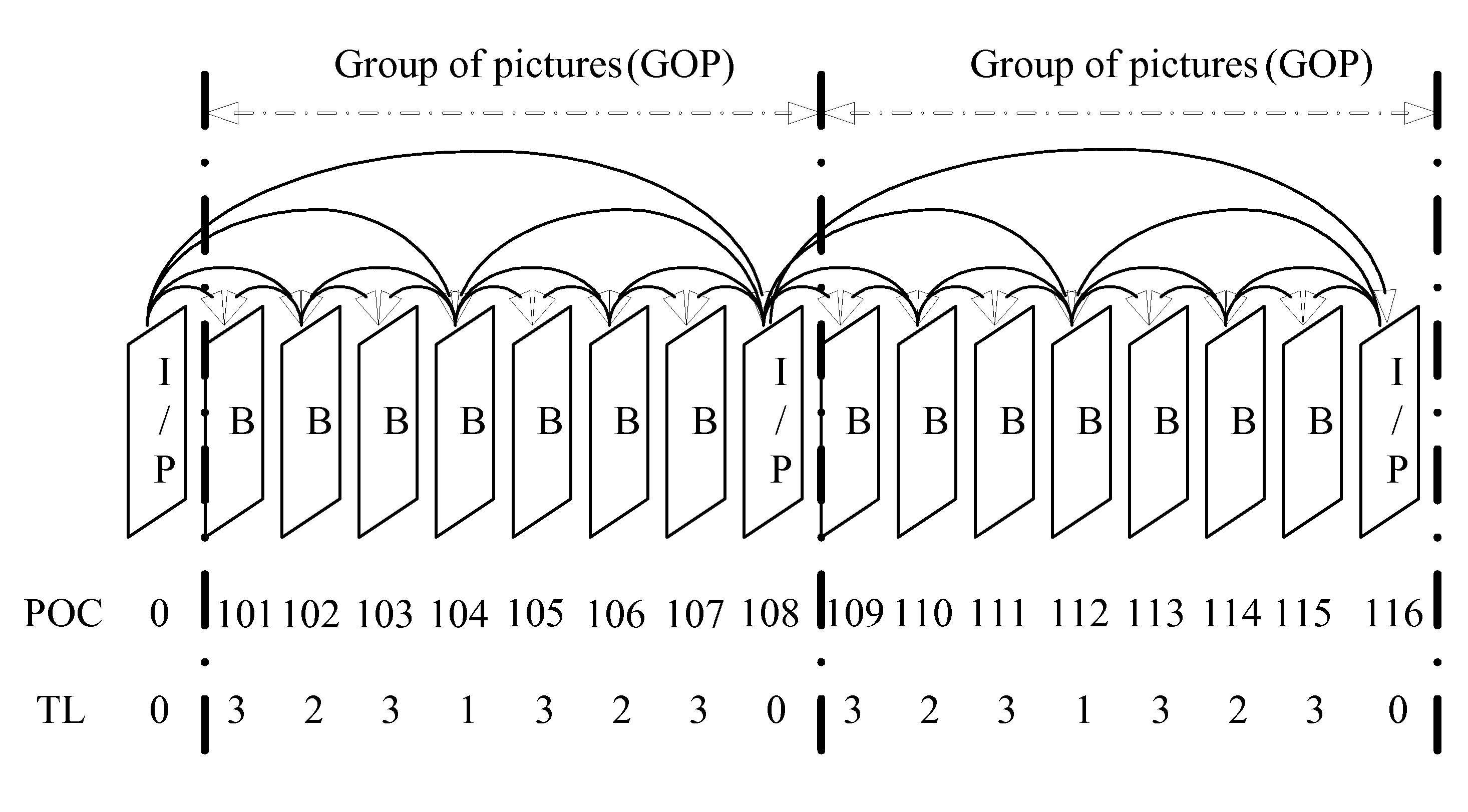
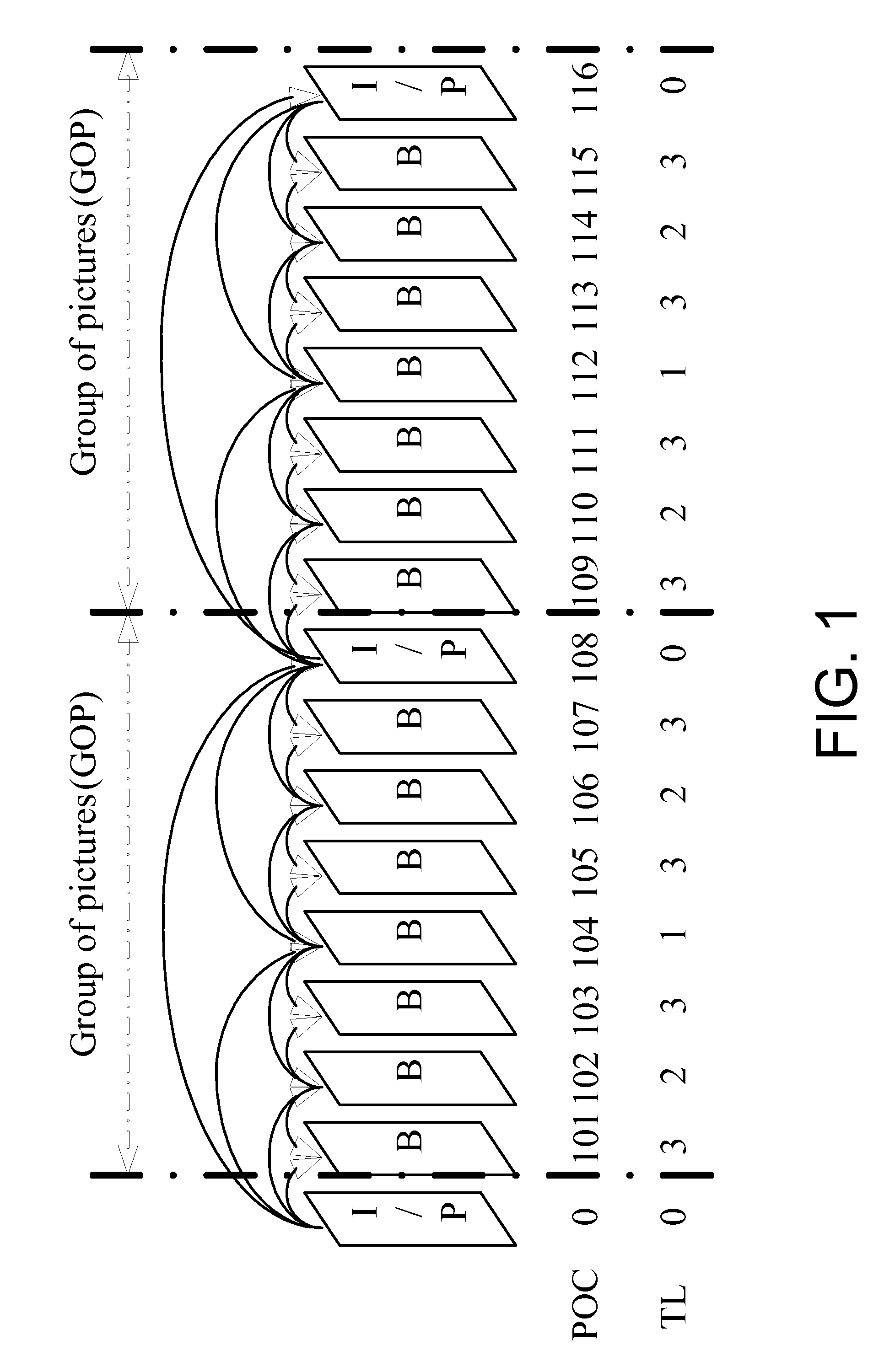
InactiveUS20060140267A1Improve picture qualityOptimizationColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer architectureGroup of pictures
The present invention discloses a system and method for adaptive adjustment of bit budget that favors the allocation of bits to intra coding frames (I frames). Namely, an encoder is able to dynamically adjust the bit budget for each picture type in an image sequence, thereby effecting proper usage of the available transmission bandwidth and improving the picture quality. In one embodiment, the present invention will allocate more encoding bandwidth to a current Intra coding frame when the average quantization level of inter coding frames (e.g., P and B frames) of a previous group of pictures is relatively high.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
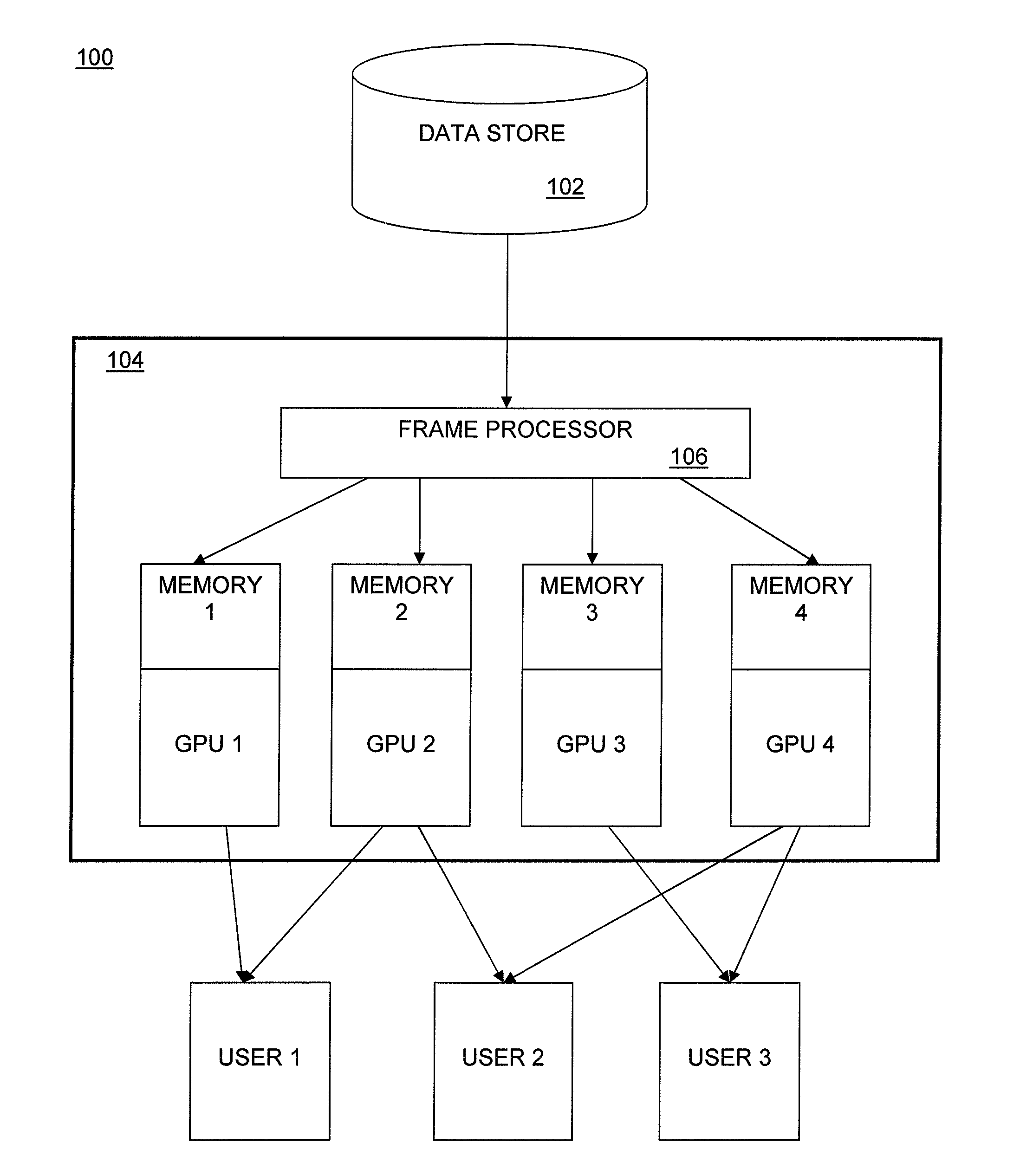
Efficient Video Decoding Migration For Multiple Graphics Processor Systems
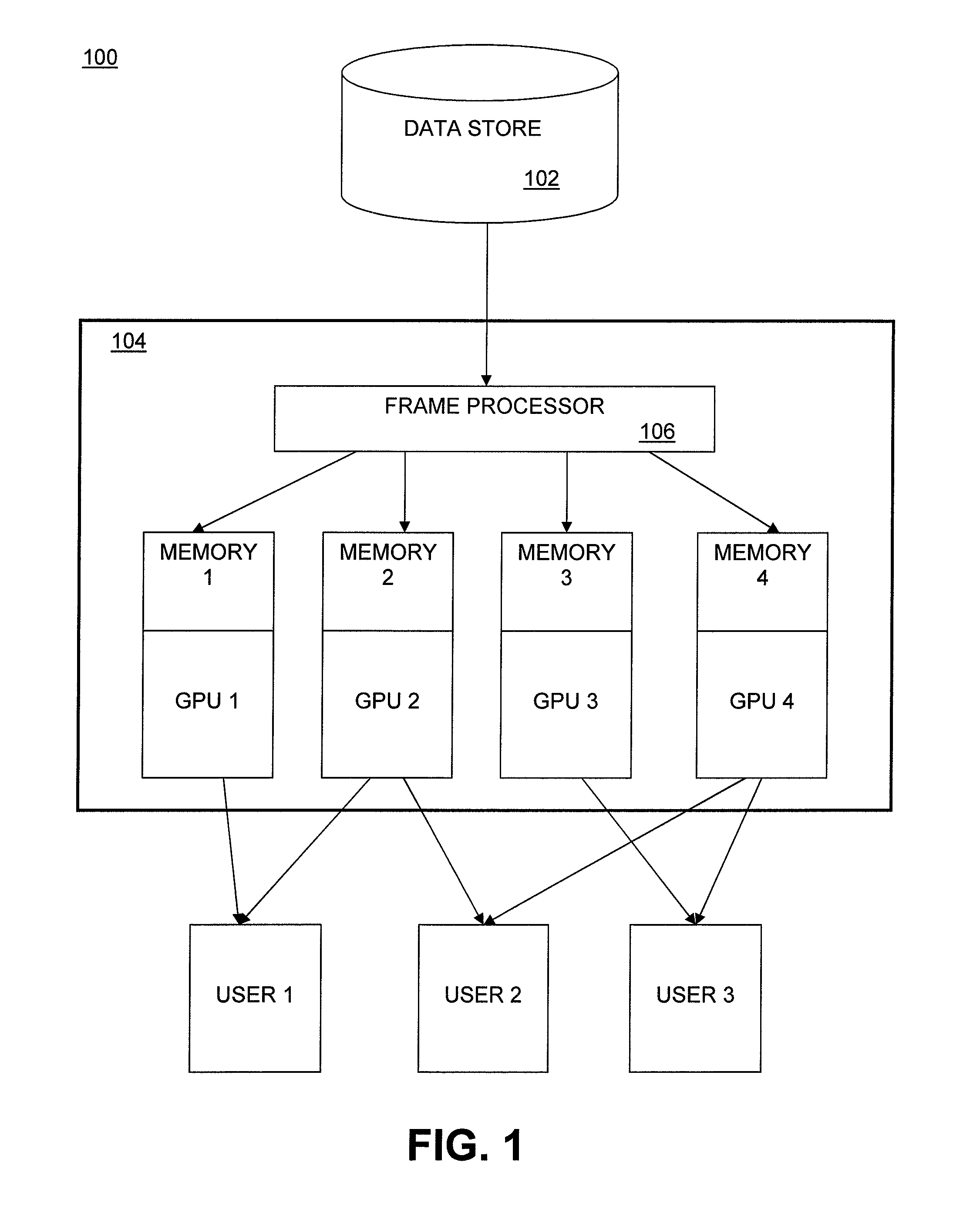
ActiveUS20090160865A1Color television signals processingMultiple digital computer combinationsComputational scienceGraphics
Embodiments of the invention as described herein provide a solution to the problems of conventional methods as stated above. In the following description, various examples are given for illustration, but none are intended to be limiting. Embodiments include a frame processor module in a graphics processing system that examines the intra-coded and inter-coded frames in an encoded video stream and initiates migration of decoding and rendering functions to a second graphics processor from a first graphics processor based on the location of intra-coded frames in a video stream and the composition of intermediate inter-coded frames.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
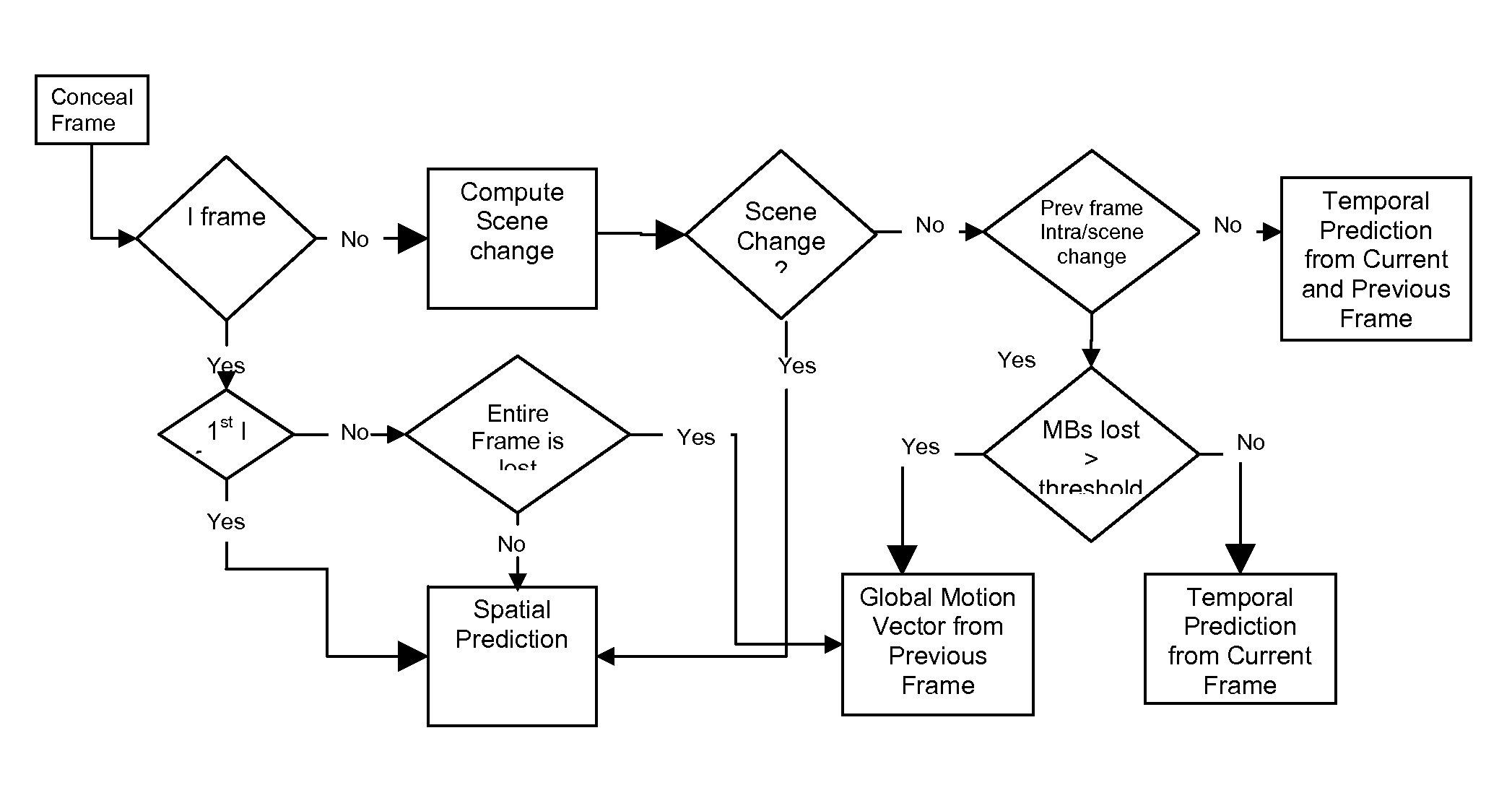
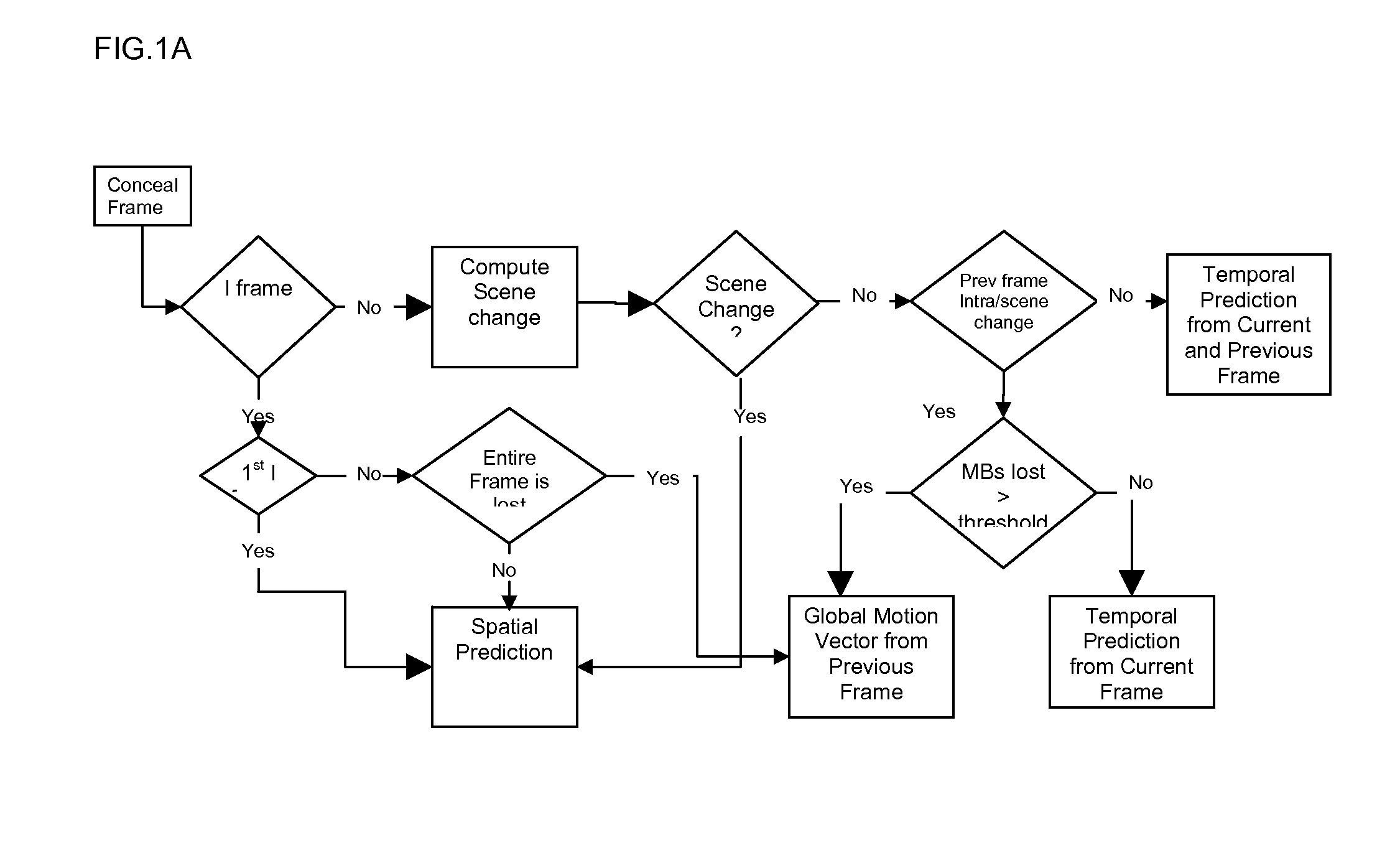
Video error concealment
ActiveUS20080084934A1Television system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionMotion vectorInterframe coding
Error concealment for video with a scene change detection based on inter-coded macroblock energy, spatial concealment for scene changes, and temporal concealment with predicted motion vectors as the global motion vector of the prior frame when half of the current frame macroblocks are corrupted.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Residual colour transform signalled at sequence level for specific coding modes
ActiveUS20160100175A1Improve coding efficiencyColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer architectureInterframe coding
The present invention is related to video coding and decoding, in particular HEVC RExt that define the adaptive residual colour transform, Adaptive RCT, of a residue of pixels. Compared to HEVC RExt where Adaptive RCT is signalled at Coding Unit level, embodiments of the invention propose to signal it in the bitstream in association with two or more coding units forming the image. In other words, it is signalled at a level higher than the CU level, for instance at sequence or frame or slice or tile or coding tree block level. In addition, various flags at this higher level make it possible to generically define the applying or not of RCT for various respective coding modes, for instance Inter coding mode, Intra Block Copy coding mode or Intra coding mode where Chroma and Luma modes are the same. Such approach makes it possible to reduce the amount of evaluations to be performed.
Owner:CANON KK
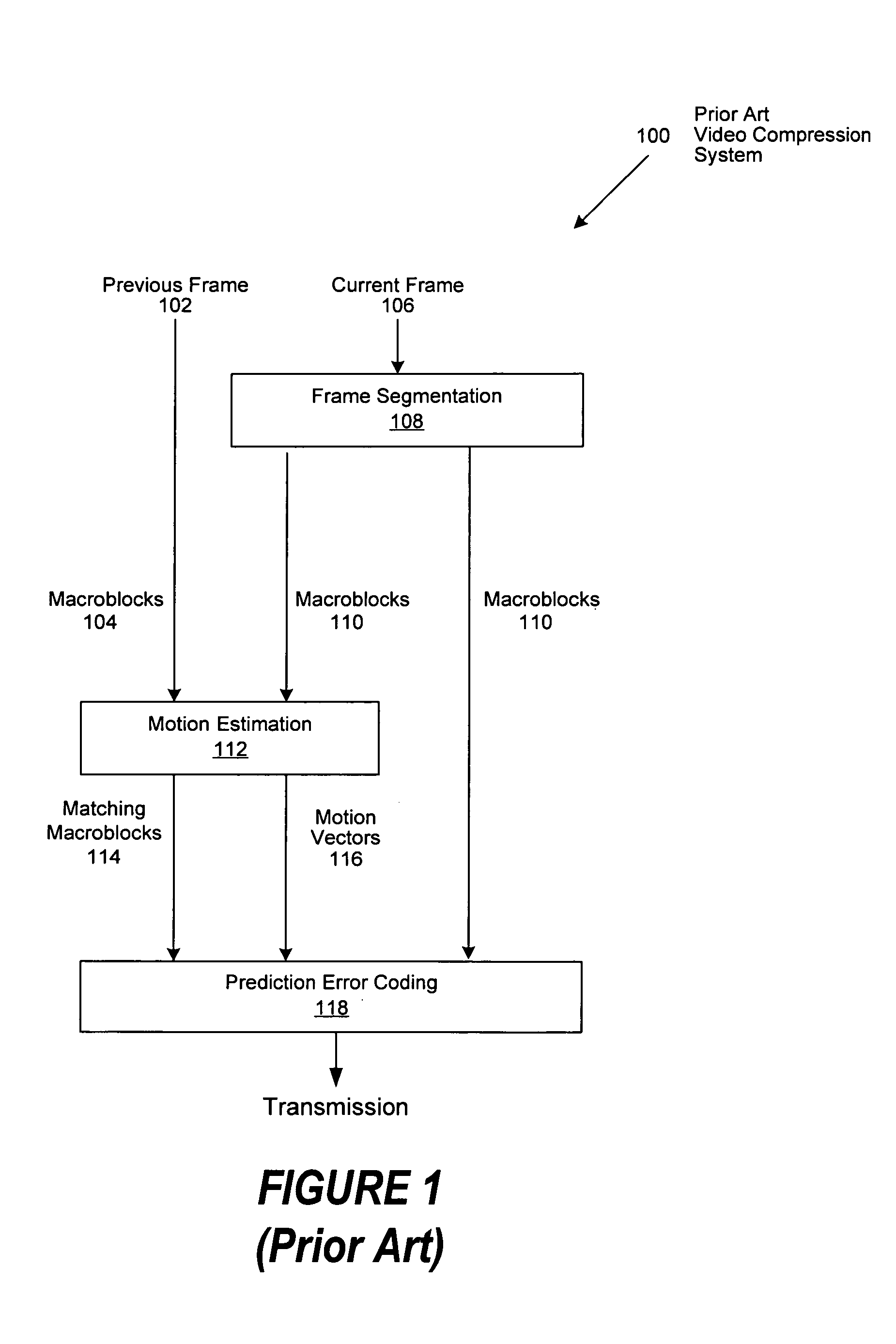
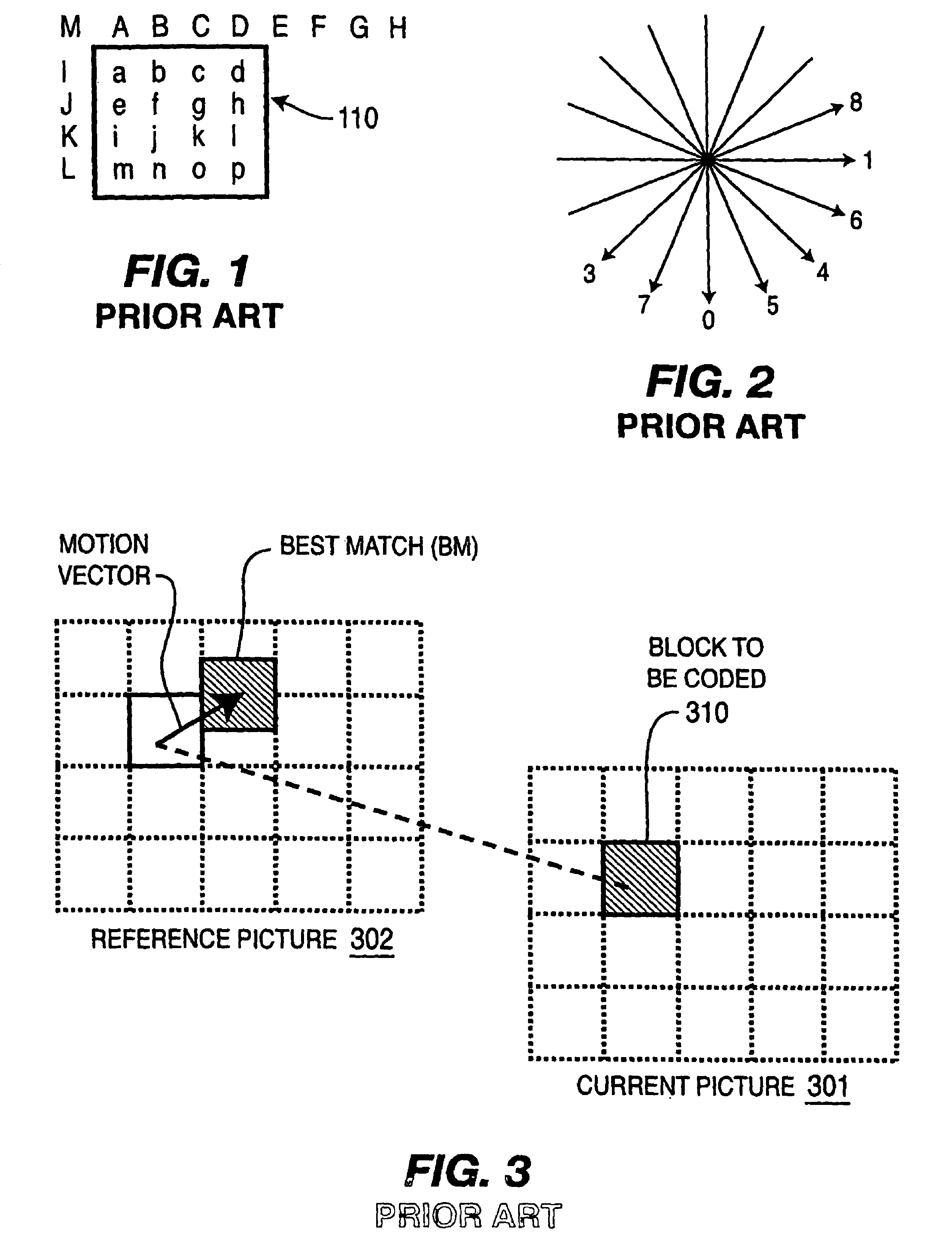
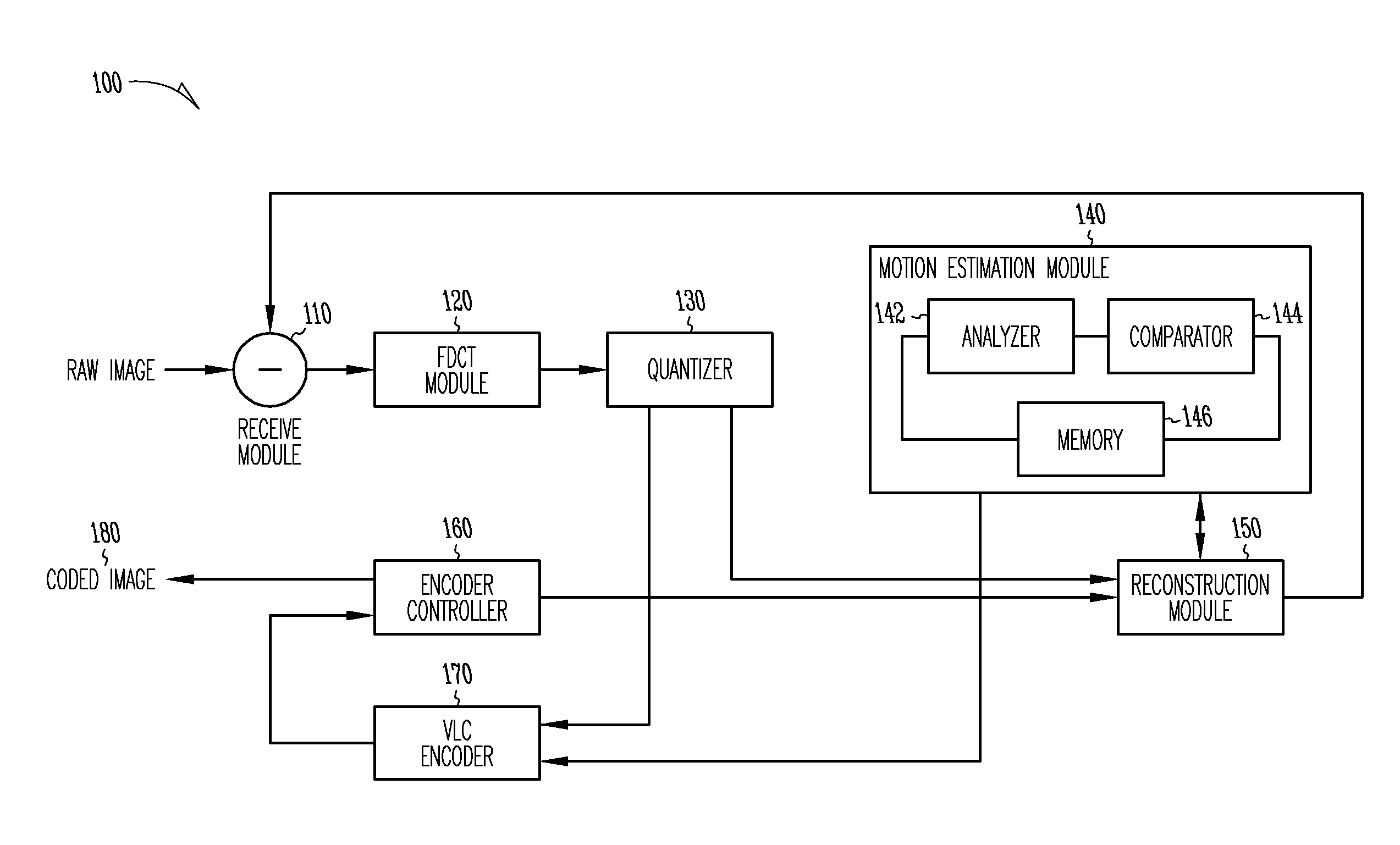
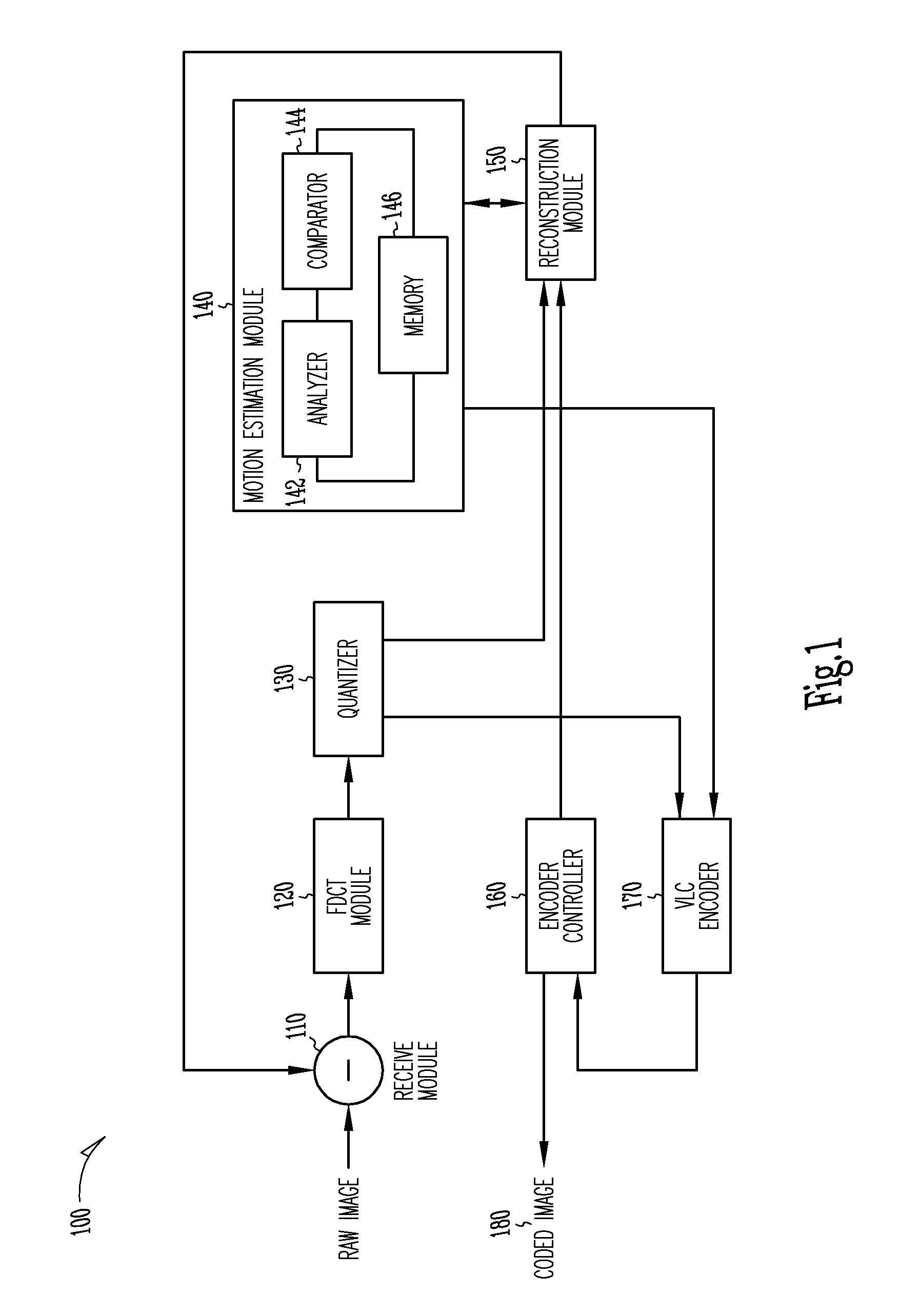
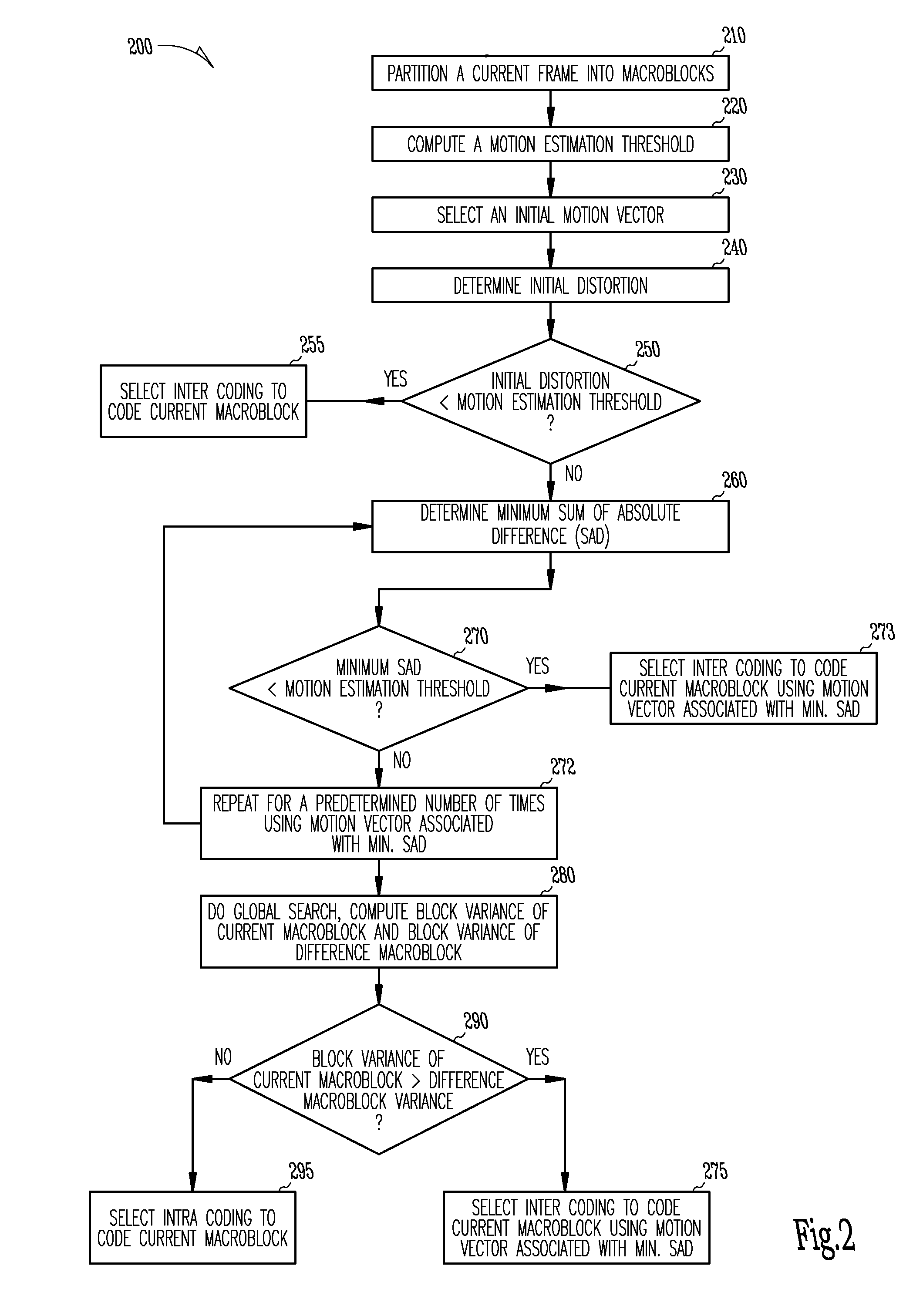
Motion estimation technique for digital video encoding applications
InactiveUS20100177826A1Television system detailsColor television with pulse code modulationPattern recognitionDigital video
The present invention provides an improved motion estimation encoder for digital video encoding applications. In one example embodiment, the improved encoder receives a raw image in the form of a current frame and estimates the macroblock motion vector with respect to a reference frame. The encoder then performs an initial local search around an initial motion vector candidate derived from spatio-temporal neighboring macroblock parameters. The encoder then compares the user-defined complexity scalable sum of absolute difference between the original and the associated reference macroblock against an adaptive threshold value for motion estimation convergence. The encoder introduces a global full search around a candidate from a coarser level, in case an initial local search fails. The encoder then selects an inter encoding mode for coding the current macroblock, when the first local search is successful, otherwise the encoder selects the inter or intra encoding mode for encoding the current macroblock by comparing variances of the original and difference macroblocks.
Owner:SASKEN COMMUNICATION TECHNOLOGIES
Scalable video coding
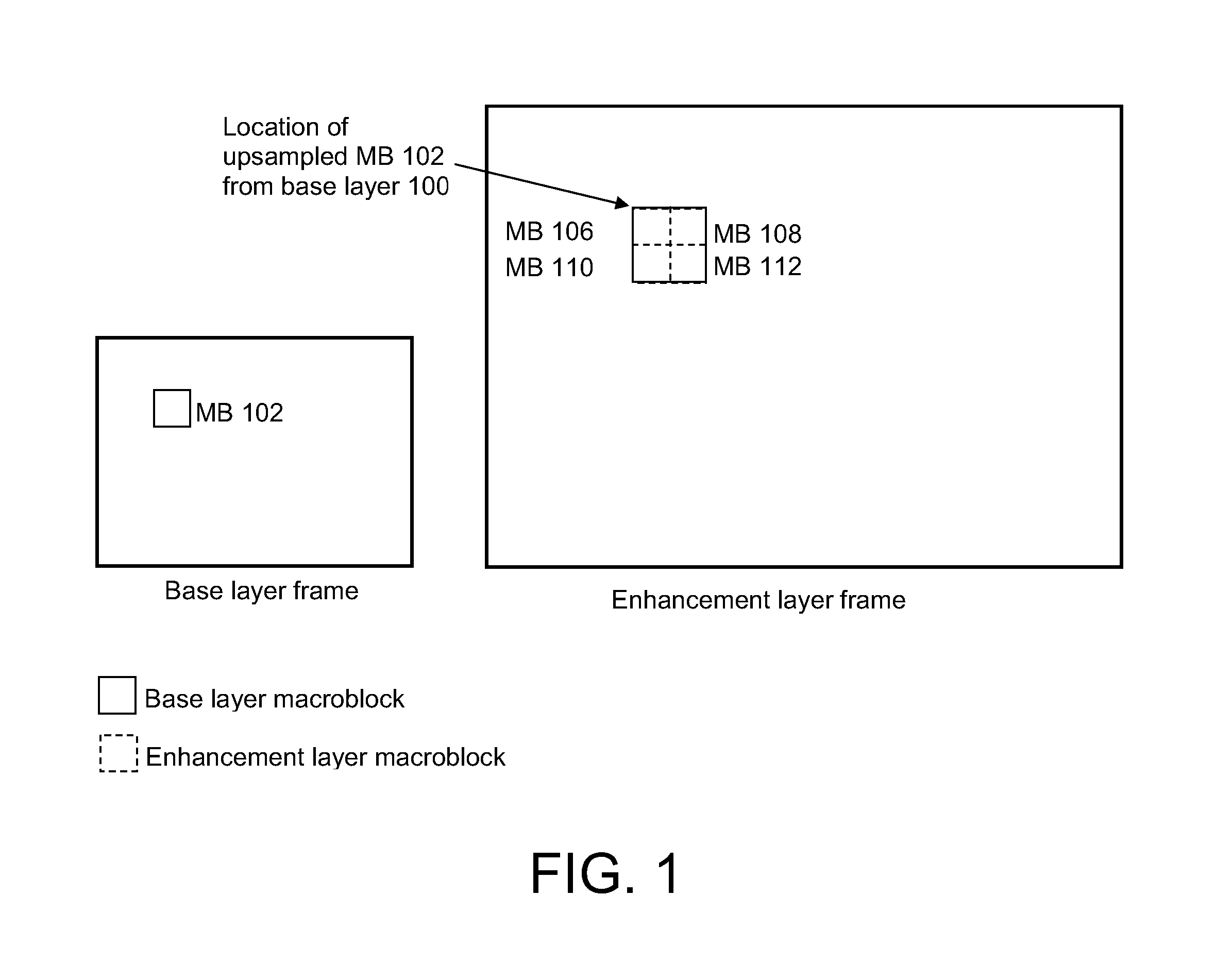
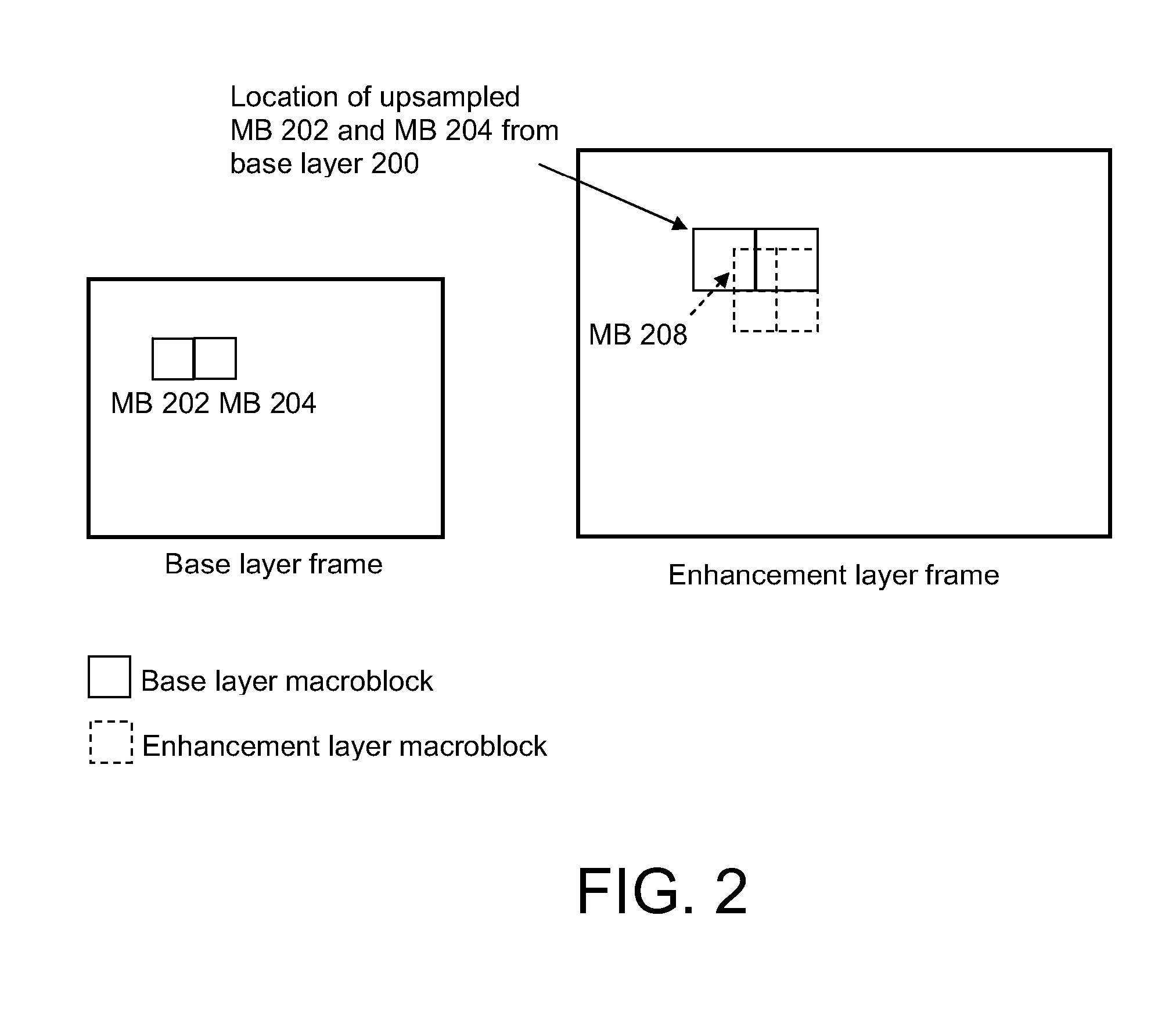
ActiveUS20080056356A1Smooth effectAccurate predictionColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionInter layerBoundary effects
A system and method for predicting an enhancement layer macroblock. A base layer frame is divided into intra-coded and inter-coded regions. If any portion of the enhancement layer macroblock is covered by both an intra-coded base layer macroblock and an inter-coded base layer macroblock, predictions utilizing the intra-coded and inter-coded macroblocks are established independently to generate at least two prediction values. The at least two prediction values are then combined to give a prediction from which the enhancement layer block is coded. Various embodiments serve to smooth the boundary effect between intra-coded regions and inter-coded regions inside the inter-layer prediction for extended spatial scalability.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
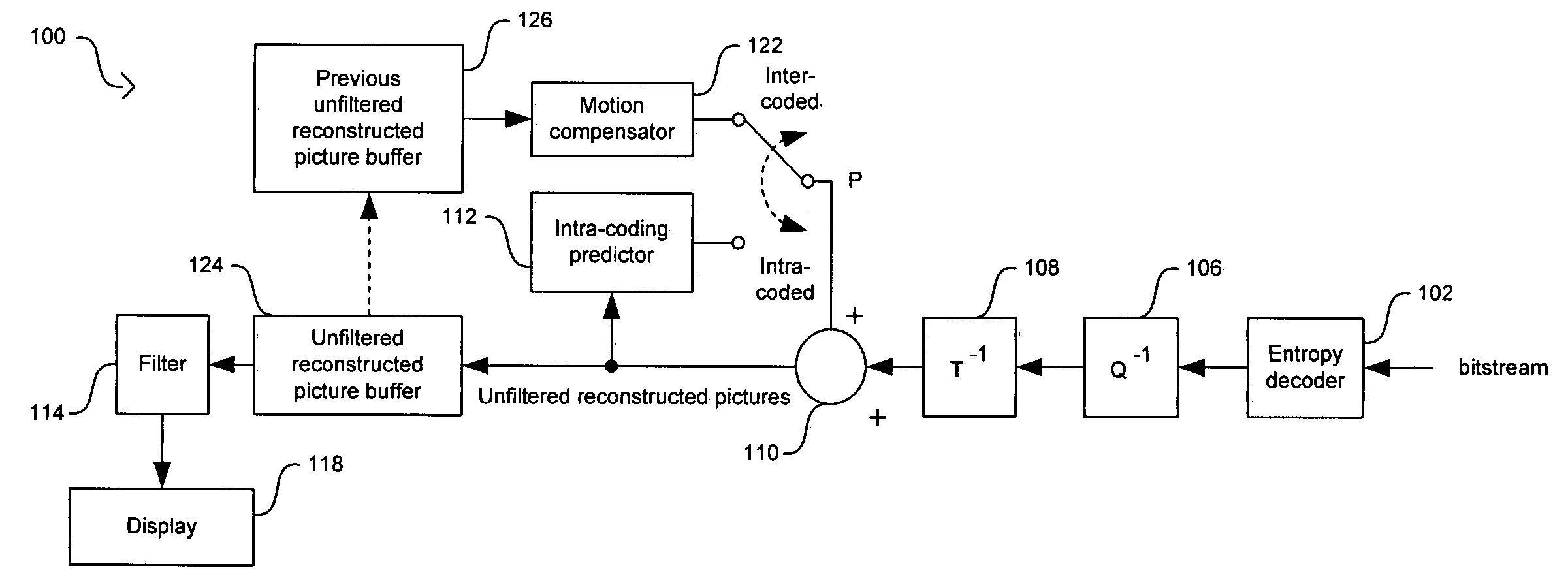
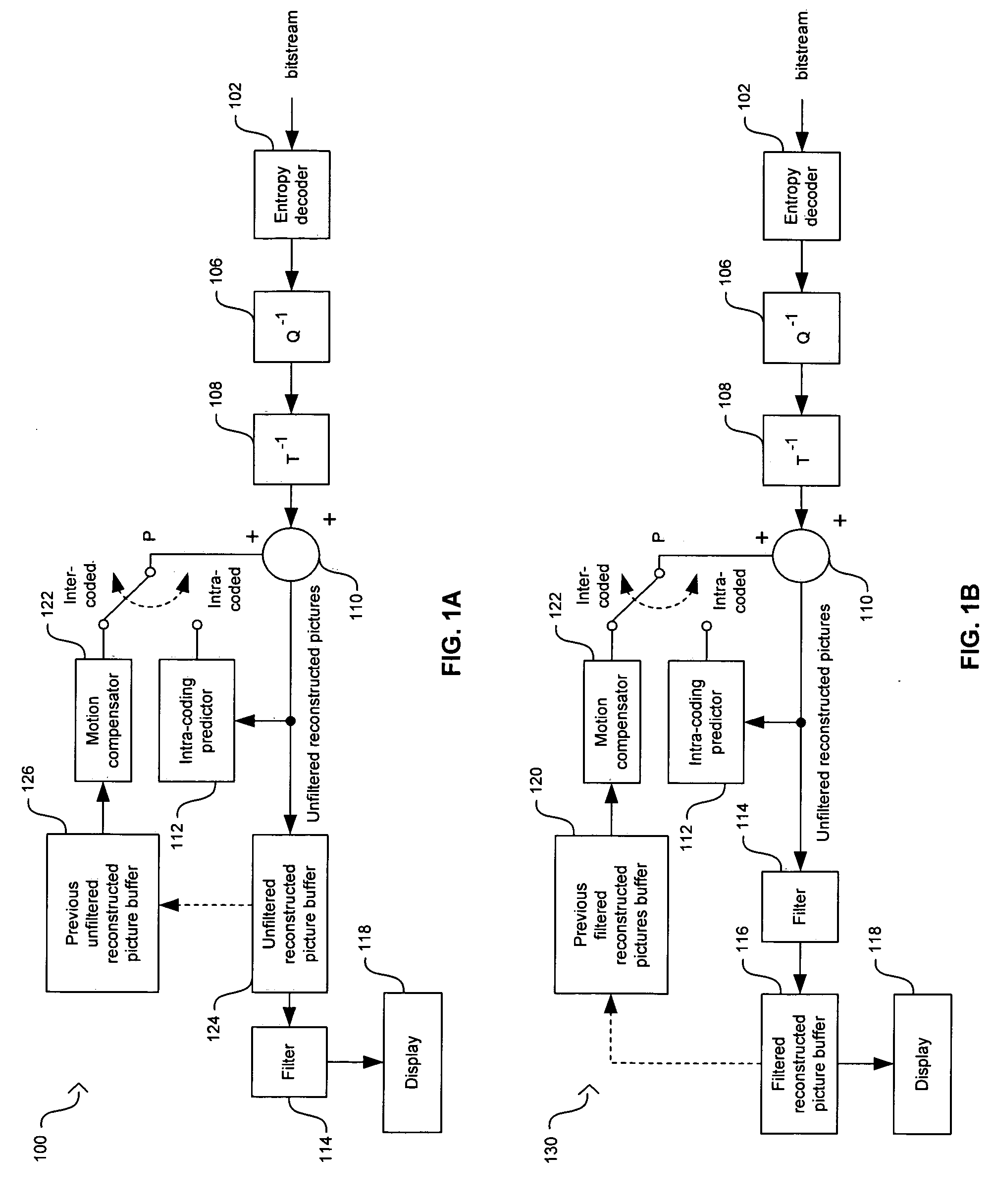
Method and system for a parametrized multi-standard deblocking filter for video compression systems
ActiveUS20060227881A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionInterframe codingSide information
In a video processing system, a method and system for a parametrized multi-standard deblocking filter for video compression systems are provided. A multi-standard deblocking filter may be configured to filter a reconstructed output stream based on a selected standard mode of operation. The configured multi-standard deblocking filter may be utilized in a decoder and / or in a decoding portion of an encoder. Filtered or unfiltered reconstructed pictures may be selected for storage in a picture buffer before further processing. Filtered or unfiltered reconstructed pictures may be selected for display in a decoder or for intra-coding and inter-coding processing in the decoding portion of the encoder. Filter parameters in the multi-standard deblocking filter may be configured based on a set of side information and the selected standard mode of operation.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Image Processing Apparatus and Method
InactiveUS20110103485A1Reduced compression efficiencyHigh computational complexityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputation complexityMotion vector
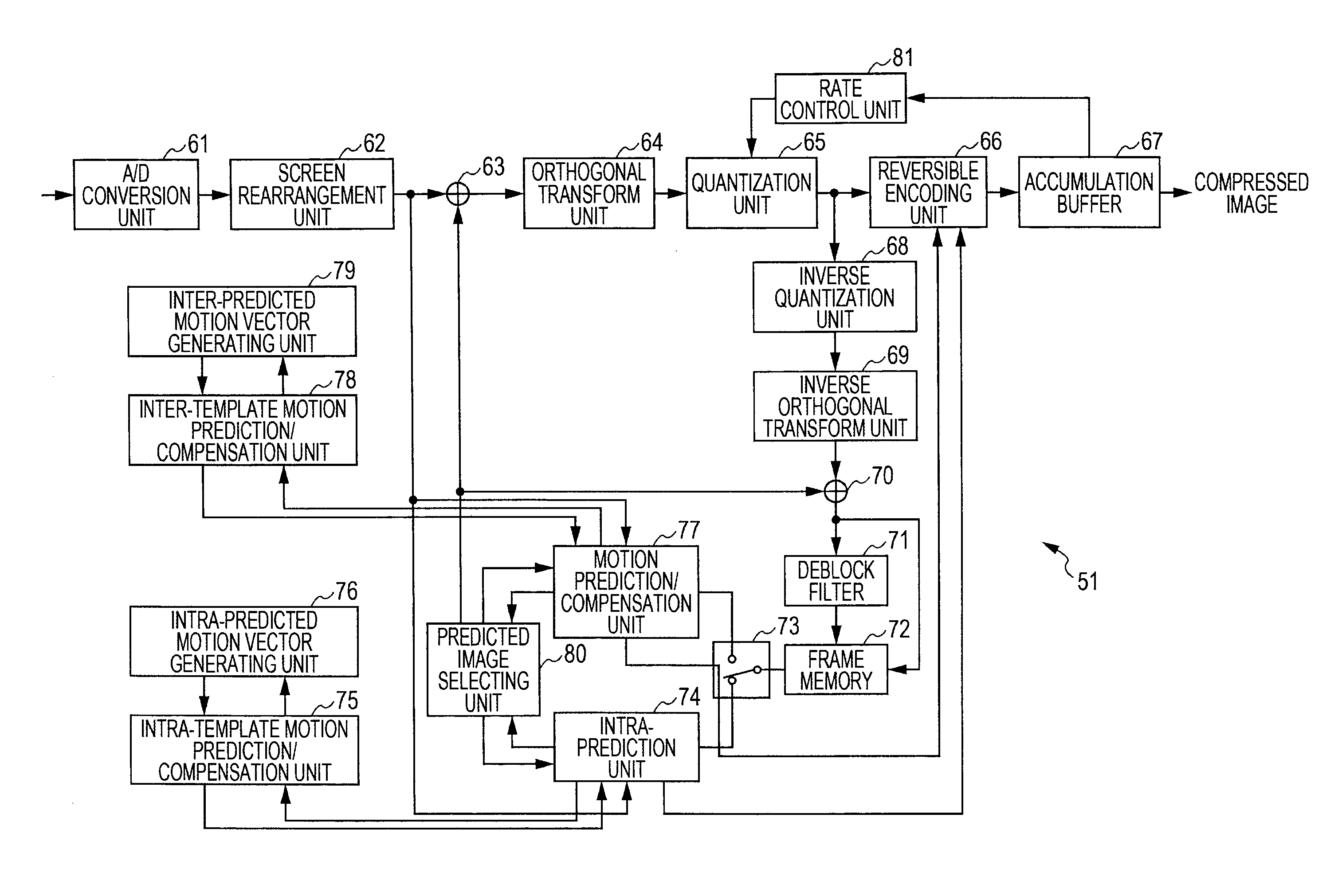
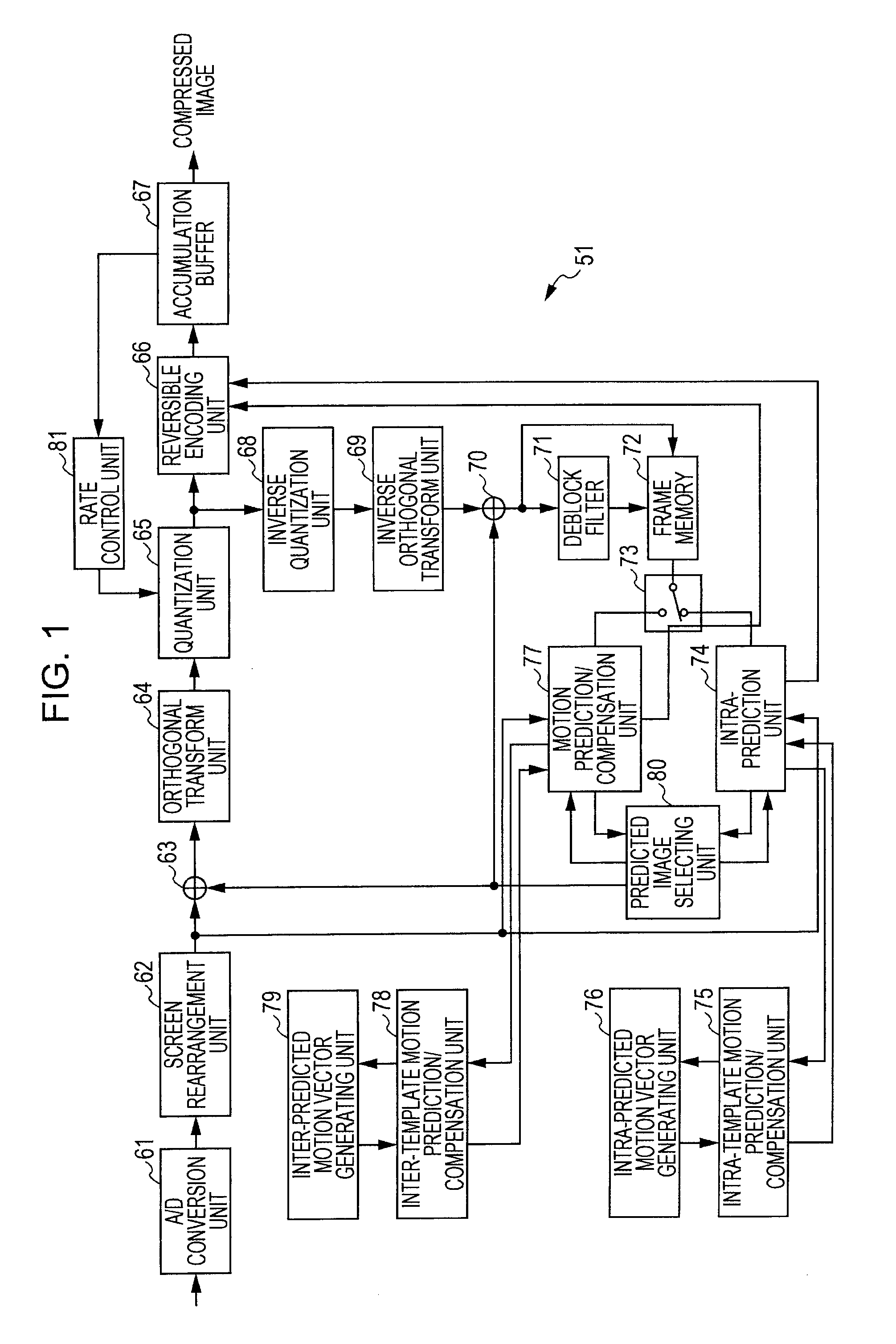
The present invention relates to image processing apparatus and method which make it possible to prevent a decrease in compression efficiency without increasing computational complexity.An intra-TP motion prediction / compensation unit 75 performs motion prediction within a predetermined search range by taking predicted motion vector information generated by an intra-predicted motion vector generating unit 76 as the center of search, on the basis of an image to be intra-predicted from a screen rearrangement buffer 62, and reference images from a frame memory 72. An inter-TP motion prediction / compensation unit 78 performs motion prediction within a predetermined search range by taking predicted motion vector information generated by an inter-predicted motion vector generating unit 79 as the center of search, on the basis of an image to be inter-encoded from the screen rearrangement buffer 62, and reference images from the frame memory 72. The present invention can be applied to, for example, an image encoding apparatus that performs encoding in H.264 / AVC format.
Owner:SONY CORP
Method and apparatus for vector encoding in video coding and decoding
ActiveUS20160100186A1SpeedCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationComputer architectureVideo encoding
The present invention concerns a method of encoding an image, the image comprising a plurality of coding elements made of blocks of pixels, each block of pixels being encoded according to a coding mode out of a plurality of coding modes, the method comprising for each block of pixel to be encoded determining the coding mode to be used for the encoding of a given block of pixels by sequentially evaluating some coding modes in the plurality of coding modes; wherein the method comprises evaluating Inter coding modes and fast IBC coding modes; and no residue-test is conducted between the evaluation of the Inter coding mode and the evaluation of the fast IBC mode. Accordingly, some good predictors may be found more rapidly and the whole encoding process is speed up.
Owner:CANON KK
Motion vector predictive encoding method, motion vector decoding method, predictive encoding apparatus and decoding apparatus, and storage media storing motion vector predictive encoding and decoding programs
InactiveUS20070183505A1Reduce generationReduce the amount requiredColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionDecoding methodsInterframe coding
A motion vector predictive encoding method, a motion vector decoding method, a predictive encoding apparatus, a decoding apparatuses, and storage media storing motion vector predictive encoding and decoding programs are provided, thereby reducing the amount of generated code with respect to the motion vector, and improving the efficiency of the motion-vector prediction. If the motion-compensating mode of the target small block to be encoded is the global motion compensation, the encoding mode of an already-encoded small block is the interframe coding mode, and the motion-compensating mode of the already-encoded small block is the global motion compensation, then the motion vector of the translational motion model is determined for each pixel of the already-encoded small block, based on the global motion vector (steps S1-S5). Next, the representative motion vector is calculated as the predicted vector, based on the motion vector of each pixel of the already-encoded small block (step S6). Finally, the prediction error is calculated for each component of the motion vector and each prediction error is encoded (steps S7 and S8).
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com