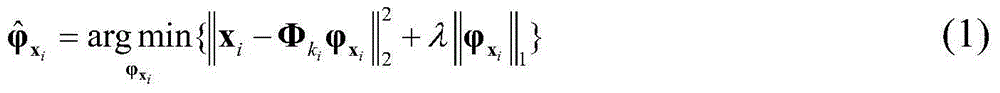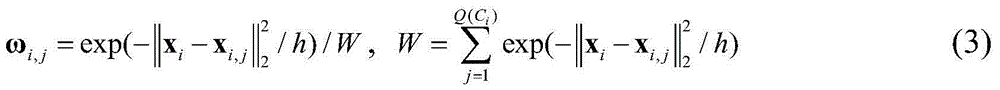Nuclear magnetic resonance image reconstruction method based on sparse representation and non-local similarity
A kind of nuclear magnetic resonance image, non-local similarity technology, applied in the field of image processing, can solve the problem of difficult reconstruction of image details, poor image reconstruction effect, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0041] The present invention is described in detail below in conjunction with embodiment:
[0042] Step (1) obtains the initial reference image for reconstruction, specifically:
[0043] Fourier transform is performed on the NMR grayscale image with a size of 256×256, and the Fourier transform coefficients are sampled by random downsampling with variable density, that is, the part of the Fourier coefficient corresponding to the low-frequency information of the image is more Sampling, less sampling of the part of the Fourier coefficient corresponding to the high-frequency information of the image; the amount of data obtained by sampling can account for 16%-30% of the total Fourier transform data, such as 20%; for the obtained sampled data matrix The missing part is filled with zero values, and then the initial reference image x for reconstruction is obtained by two-dimensional inverse Fourier transform (0) ;
[0044] Step (2) blocks the reference image and classifies the imag...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com