Fault moment determining and fault region location method based on random matrix theory
A technology of random matrix theory and fault time, applied in the field of power system, can solve problems such as bad data and interference of WAMS, and achieve the effect of timely detection of system anomalies and good practicability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
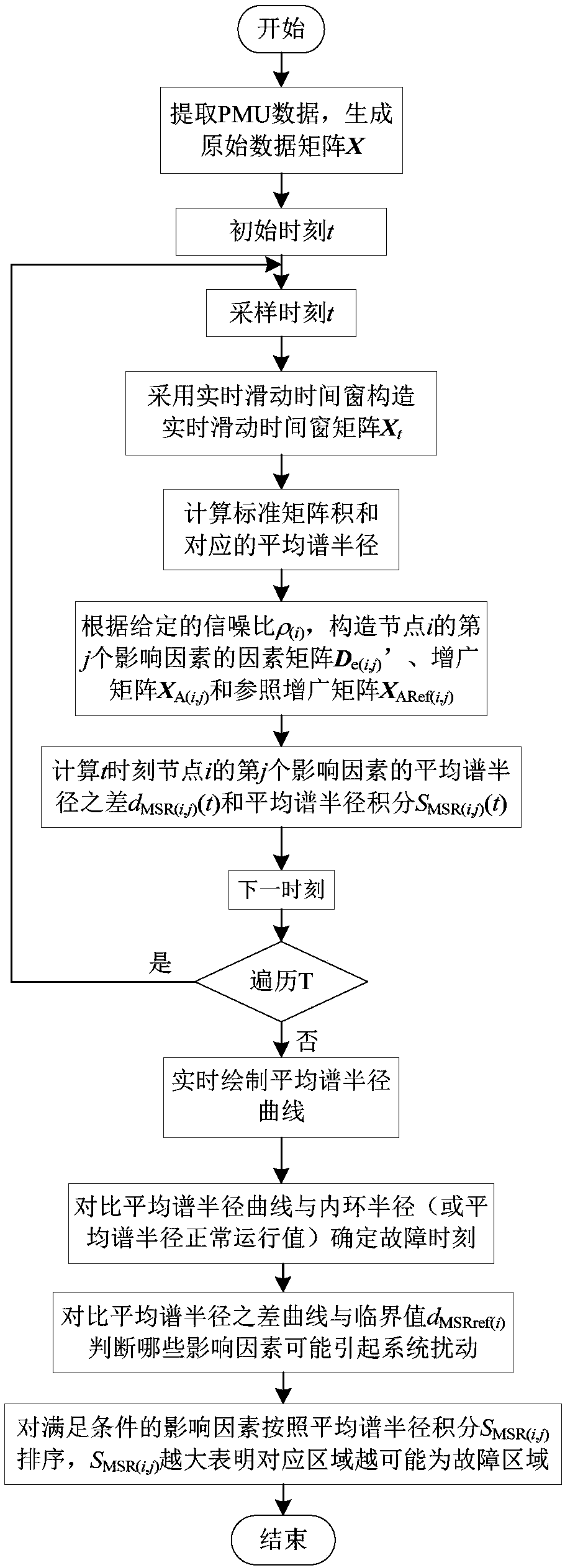
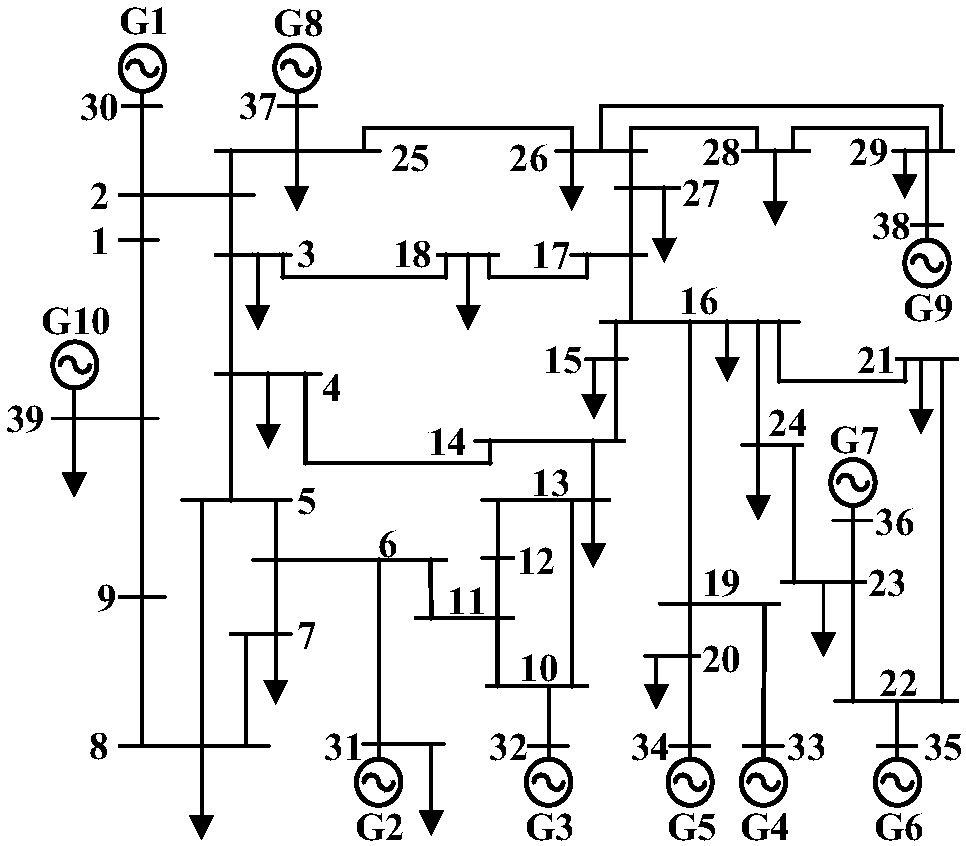
[0074] By applying the above method in the figure 2 The verification is carried out on the 10-machine 39-node system shown, and the calculation and analysis adopts the PSST software under Matlab / Simulink, and the simulation step length Δt=0.01s. The measurement data is obtained by adding the random error to the transient simulation calculation result, the random error is set to Gaussian white noise, the standard deviation of the amplitude is 1%, and the standard deviation of the phase angle is 1 degree. In Embodiment 1, all bus node voltage amplitudes (39 groups in total) are selected to form the original data matrix X, and the real-time sliding time window width is T w =80.
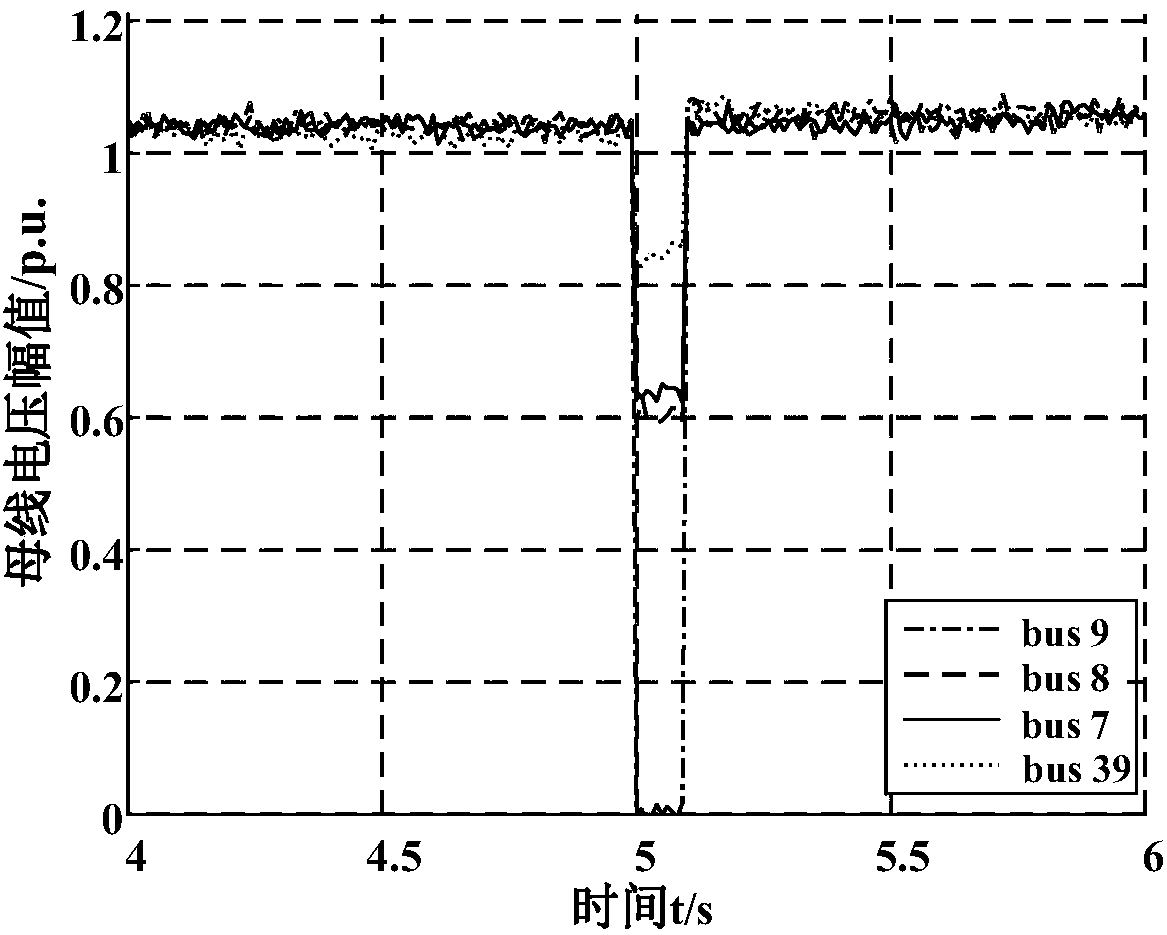
[0075] Set the line 9-39 close to the busbar 9 when an instantaneous three-phase short circuit occurs at t=5.00s, and the fault is eliminated at t=5.10s. After a short-circuit fault occurs on the line near node 9, the voltage change curves of each node are as follows: image 3As shown, the correspond...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com