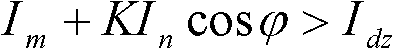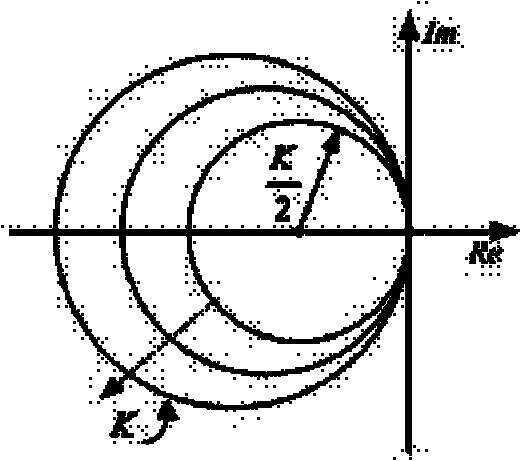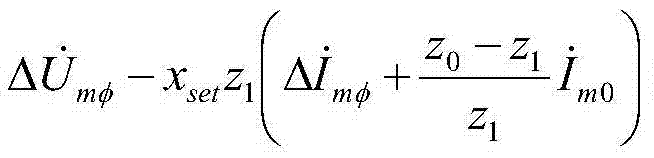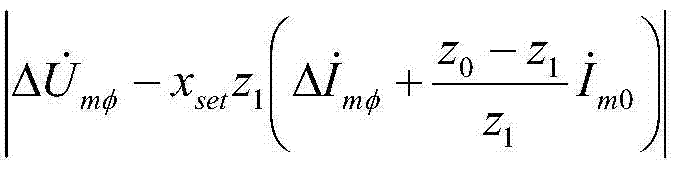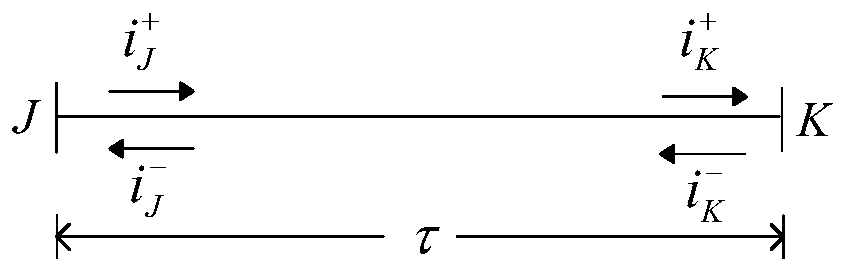Patents
Literature
43results about How to "Strong anti-transition resistance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for detecting fault of power transmission line based on random matrix
ActiveCN108828405AStrong anti-transition resistanceAccurate detectionFault location by conductor typesHigh resistanceOperation mode
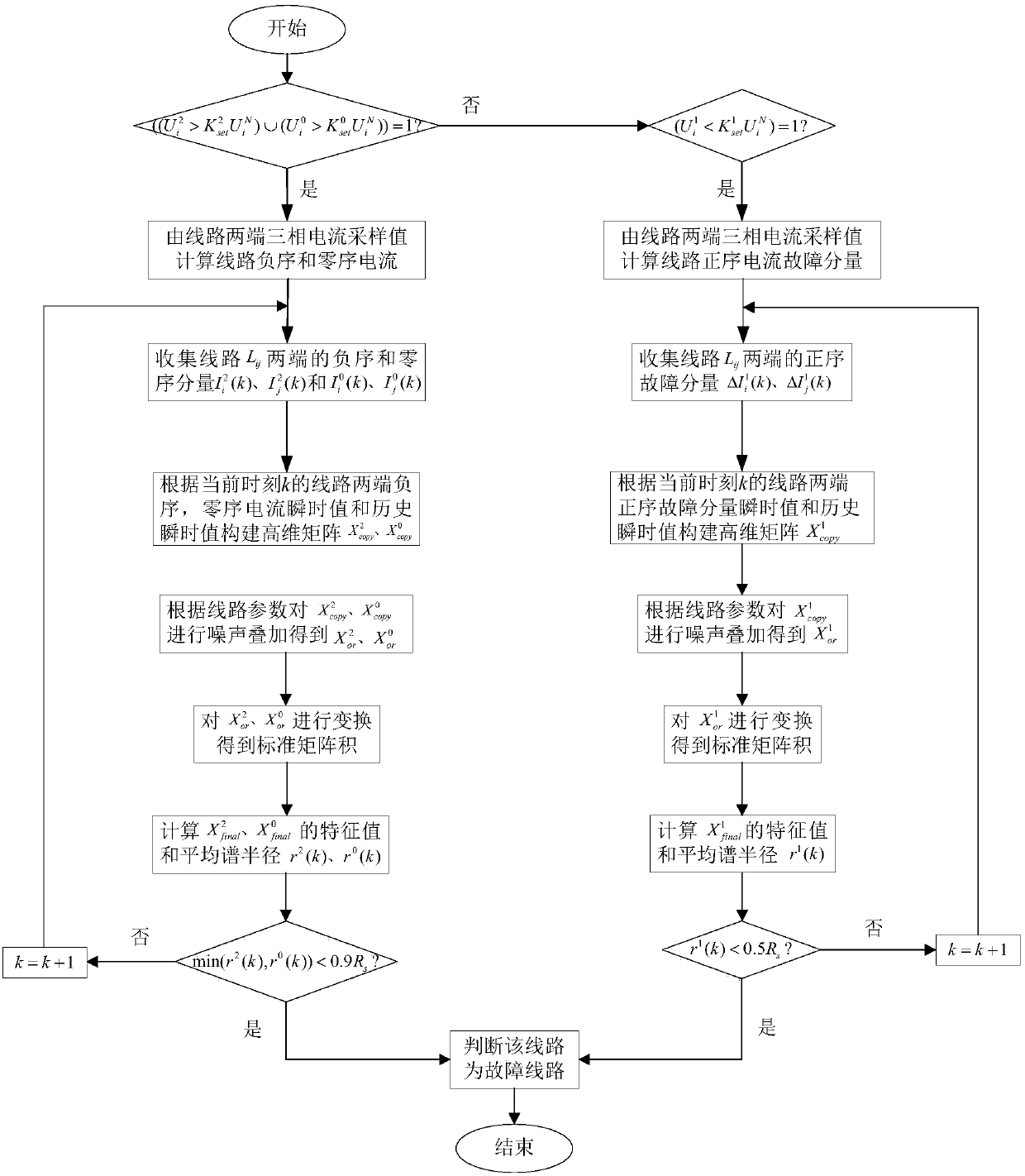
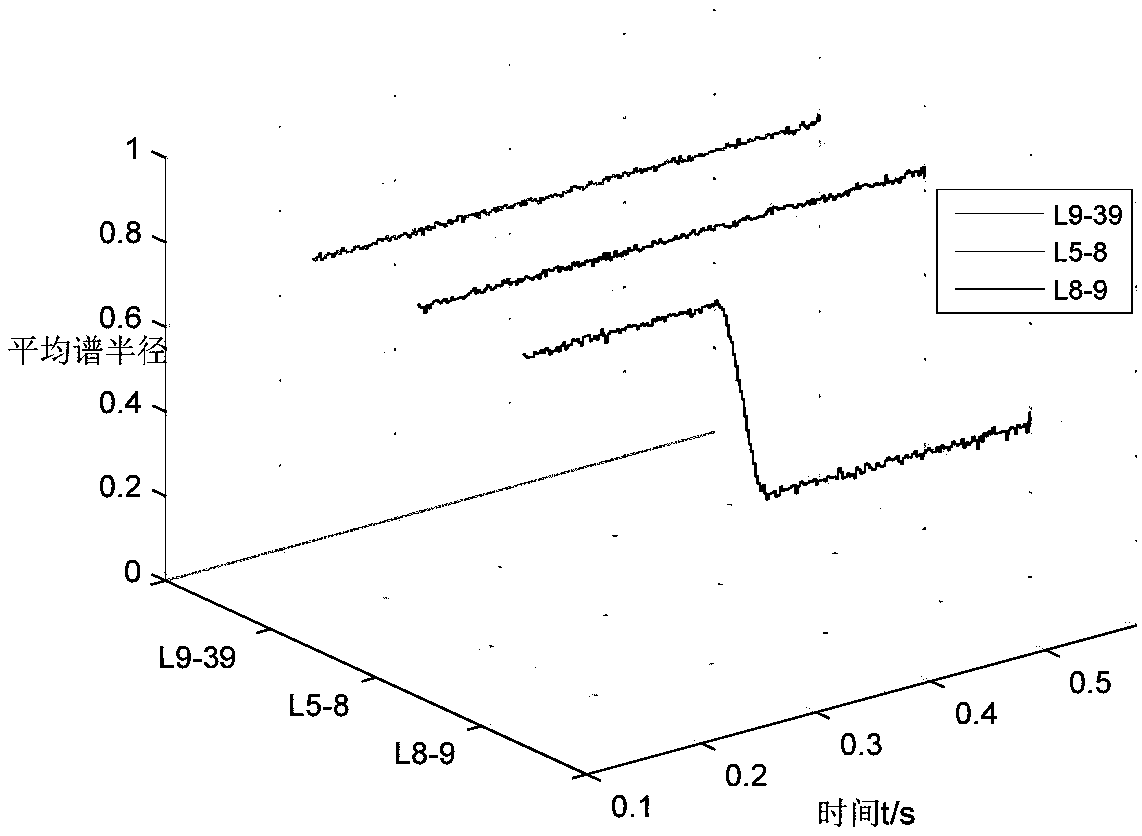
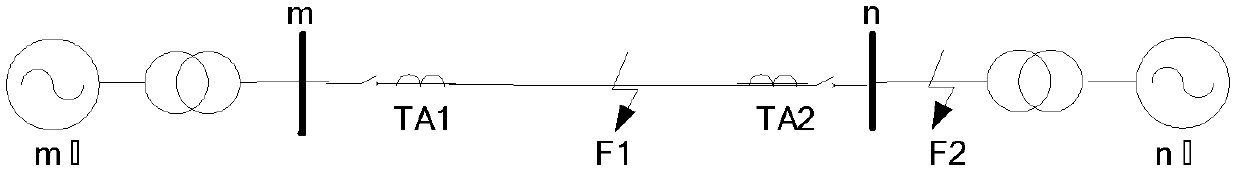
The invention discloses a method for detecting a fault of a power transmission line based on a random matrix, and the method comprises the steps: respectively obtaining three-phase currents of n sample values at two ends of the line, calculating and obtaining a sequences of positive sequence current fault components, negative sequence components and zero sequence components; respectively performing copying and translation processing of each sequence, and carrying out the expansion to form a matrix of each sequence, and then performing the superimposition of a noise matrix to form an original random matrix of each sequence; employing the random matrix theory for transforming the original random matrixes into a standard matrix product; calculating a complex eigenvalue of the standard matrixproduct, calculating and obtaining the average spectral radius of the current component sequence of the line according to the eigenvalue; constructing two criteria for fault detection of the power transmission line, determining a threshold value, and determining that the line whose average spectral radius is less than the threshold value as a faulty line. The method can accurately detect the faulty line, is not affected by the position of the fault point, the fault type, a system operation mode, power flow shift and the system oscillation, can identify a high-resistance ground fault, and has better resistance to abnormal data.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Current differential protection method based on fault component current amplitudes and phase differences
InactiveCN102324722ANot affected by load currentCriterion sensitivity is highEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionElectrical resistance and conductanceCapacitance
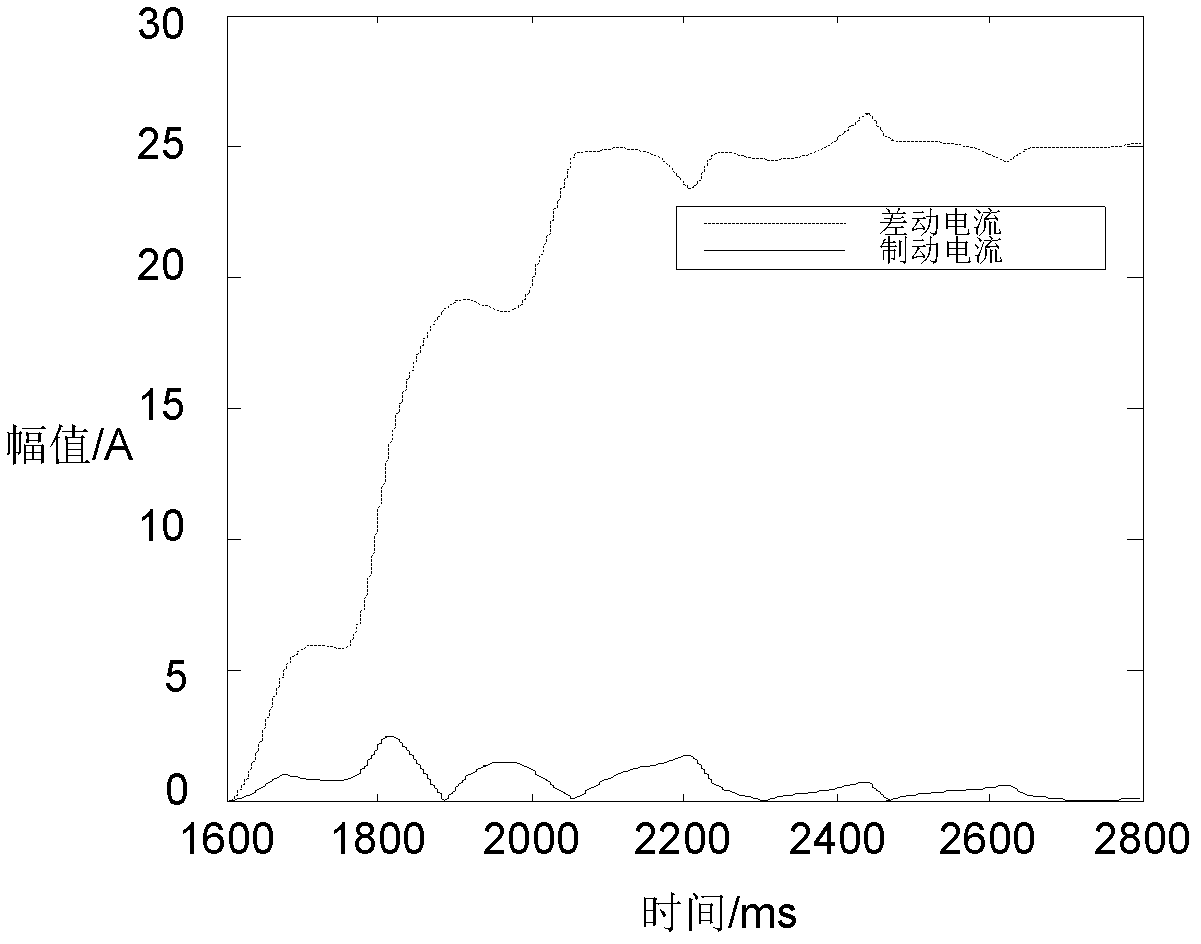
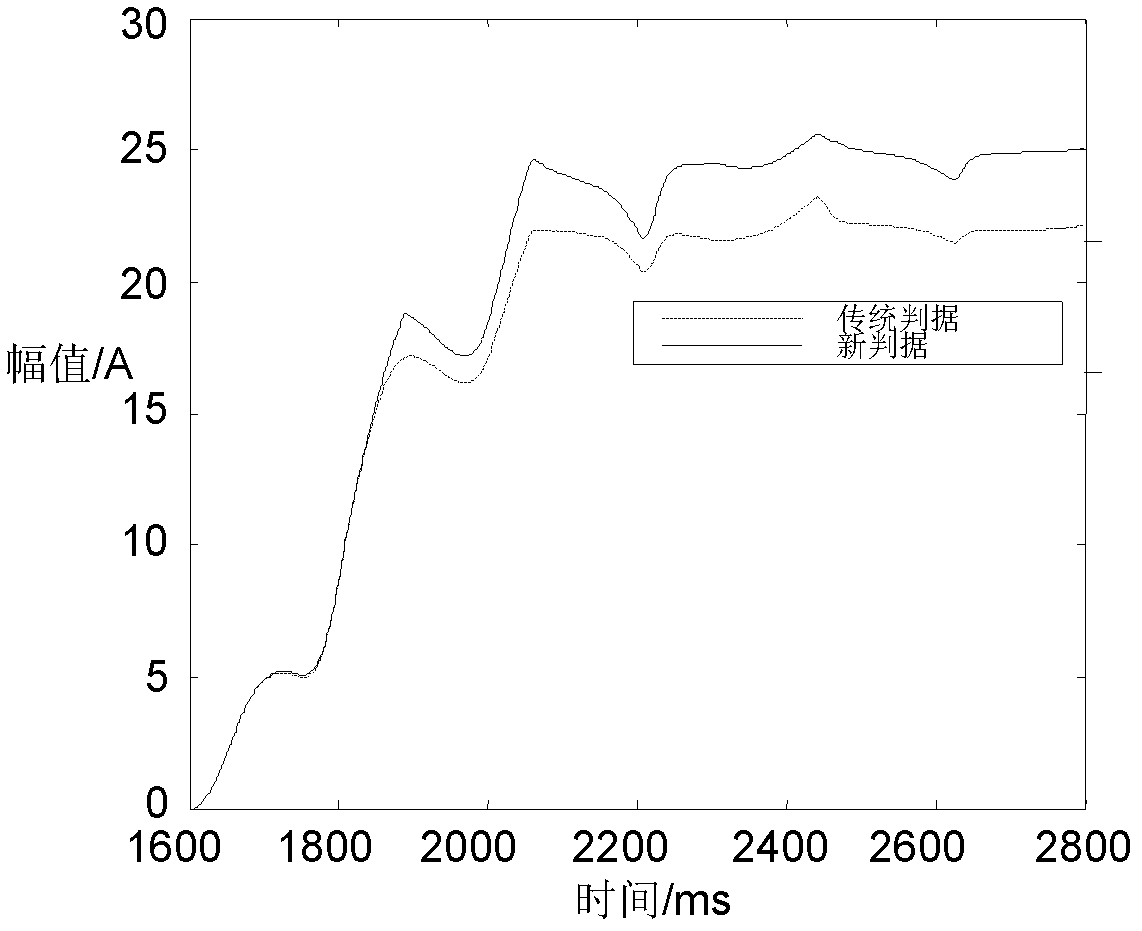
The invention relates to a current differential protection method based on fault component current amplitudes and phase differences. The current differential protection method is characterized in that: a differential protection criterion is formed by the adoption of the current fault component amplitudes at two sides of a protected line and the phase differences at the two sides of the protected line, wherein the differential current value (Icd) is equal to the sum of the current fault component amplitude (the absolute value of [delta]IM) at one side and the product of the current fault component amplitude (the absolute value of [delta]IN) at the opposite side and a cosine function of the phase difference ([phi]) between the absolute value of [delta]IM and the absolute value of [delta]IN, i.e. Icd= (the absolute value of [delta]IM)+(the absolute value of [delta]IN)cos[phi]; and the braking current (Ir) is equal to the difference between the absolute value of [delta]IM and the product of the absolute value of [delta]IN and the cos[phi], i.e. Ir= (the absolute value of [delta]IM)-(the absolute value of [delta]IN)cos[phi], and the differential protection criterion is the following inequation: Icd-KIr>= Idz, wherein K is a braking coefficient and Idz is an action current threshold. If the differential protection criterion is satisfied, an internal fault is determined and the differential protection acts; if the differential protection criterion is not satisfied, an external fault is determined and the differential protection does not act. The current differential protection method related to the invention has the advantages of higher sensitivity for internal faults, higher safety for external faults, fewer effects subjected from the factors, such as the transition resistance, the distributed capacitance, the TA saturation and the like, and good performances.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Single-phase grounding distance protection system and method on basis of voltage phase comparison
ActiveCN104682361AStrong anti-transition resistanceSolve protection problemsEmergency protective circuit arrangementsElectrical resistance and conductanceElectric power system
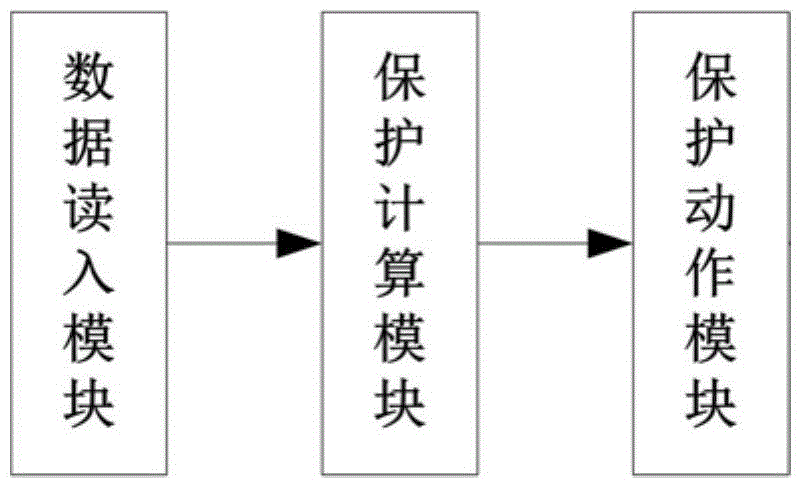
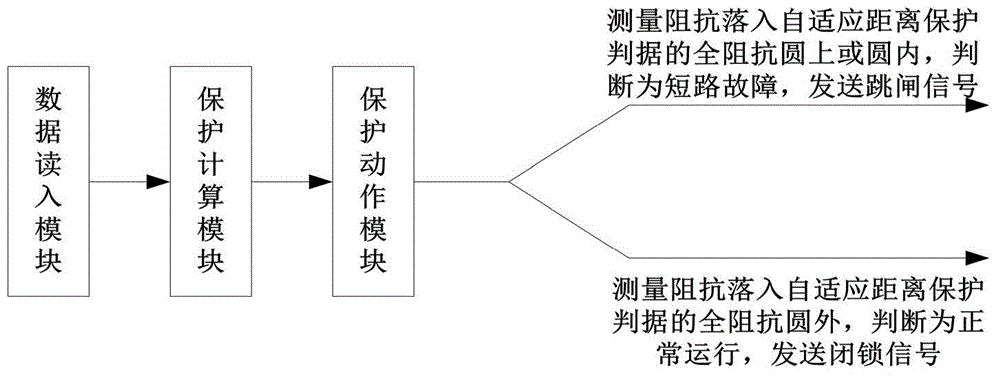
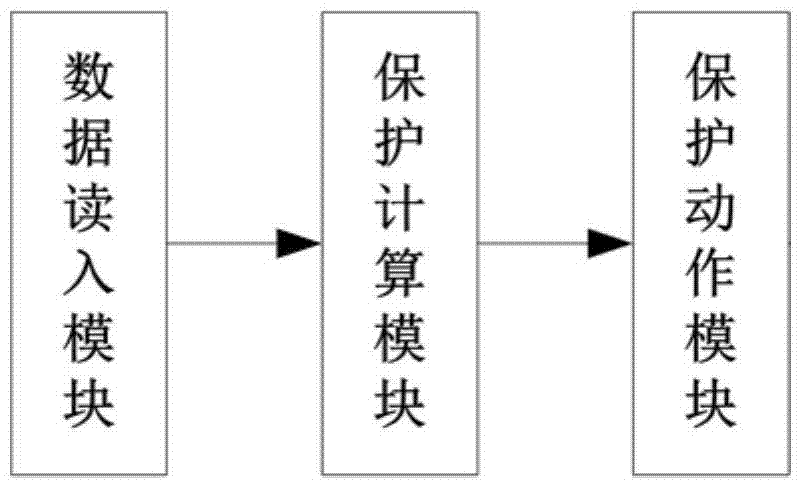
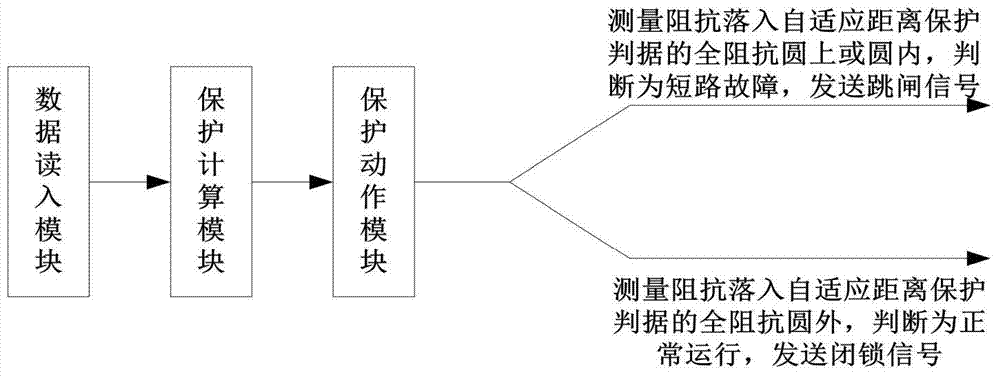
The invention belongs to the technical field of relay protection of a power system and particularly relates to a single-phase grounding distance protection system and method on the basis of voltage phase comparison. The system comprises a data reading module, a protection calculating module and a protection action module which are sequentially connected. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, calculating and measuring an included angle between a current and a fault voltage by using a relationship of a negative-sequence current phase at the protection mounting position and a negative-sequence current phase at a fault point; respectively calculating phase angles of a fault point voltage and a compensating voltage by using the measured voltage as a reference value; finally, according to the phase difference of the fault point voltage and the compensating voltage when an in-area or out-area fault occurs so as to construct a distance protection criterion. The single-phase grounding distance protection system has excellent resistance to transition resistance; the in-area and out-area faults can be correctly judged regardless of the transition resistance; meanwhile, protection action time and a fixed-value error meet the technical requirements of the grounding distance protection, the calculated amount is small and the single-phase grounding distance protection system has a higher practical engineering value.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Hierarchical location method for locating fault of active power distribution network by utilizing multi-source data
ActiveCN108152673APrecise positioningAccurate fault locationFault locationNODALElectrical resistance and conductance
The invention provides a hierarchical location method for locating the fault of an active power distribution network by utilizing multi-source data. The method comprises two levels of initial region layer positioning and accurate line layer positioning. According to the method, firstly, the information of a circuit breaker, a section switch and an interconnection switch monitoring terminal FTU, which is uploaded at a fault moment, is comprehensively utilized. The information is subjected to fault section area layer positioning, and then a line layer is positioned in the determined range of a fault section. The calculation is carried out by utilizing the electric quantity information of nodes at the two ends of the fault section and then an accurate fault position is obtained. The result ofthe verification shows that, the method is not influenced by the fault type and the position, and the fault positioning is rapidly realized. The adopted fault positioning principle is simple and reliable. The method is strong in anti-transition resistance capability and the sampling frequency requirement of the method is not high. Meanwhile, the fault positioning precision can be improved by increasing the sampling frequency, so that the method has higher practical application value.
Owner:JIANGSU ELECTRIC POWER CO +2
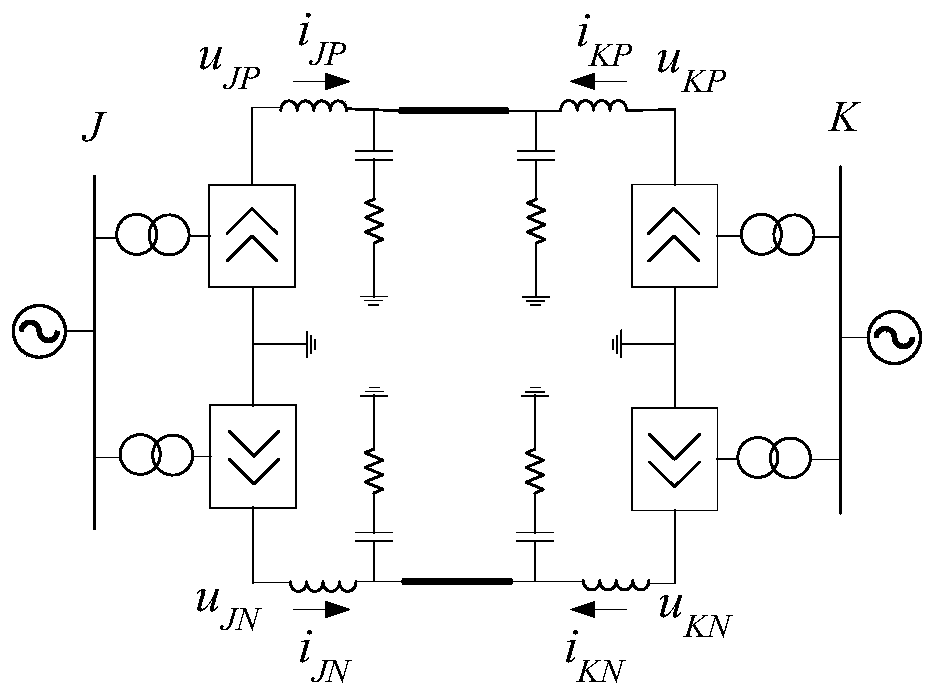
Single-end quantity protection method of a ring-shaped flexible power network line
ActiveCN109274079AQuick identificationReduce the impact of protection reliabilityEmergency protective circuit arrangementsFault location by conductor typesPower gridInductor
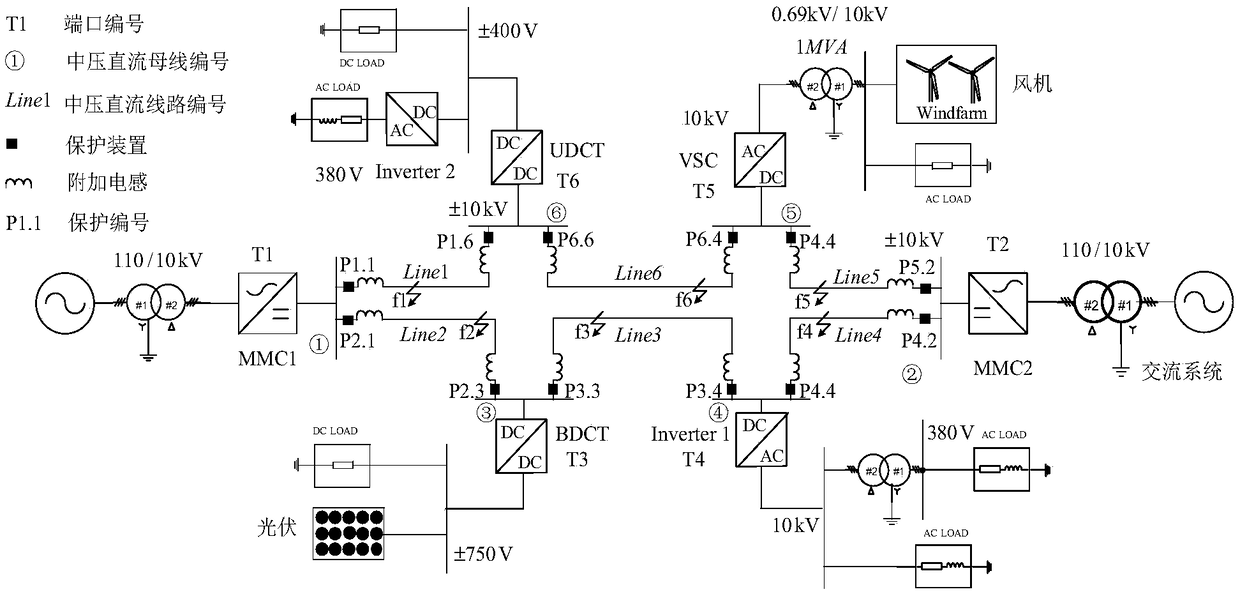
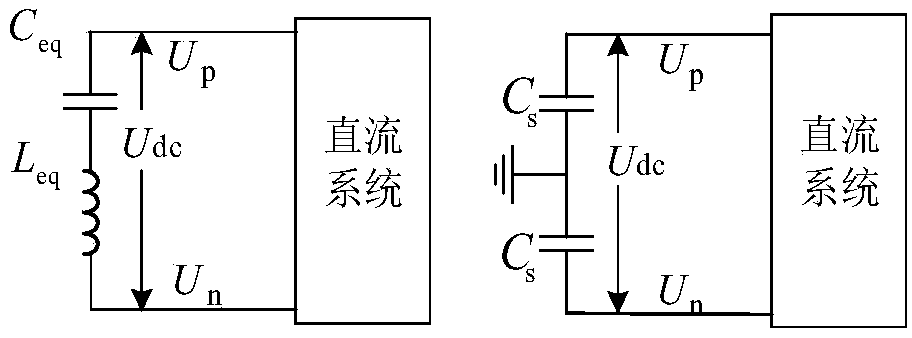
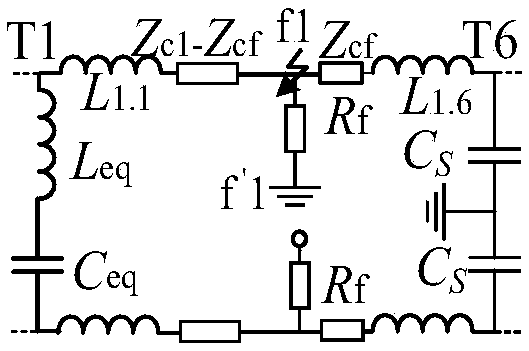
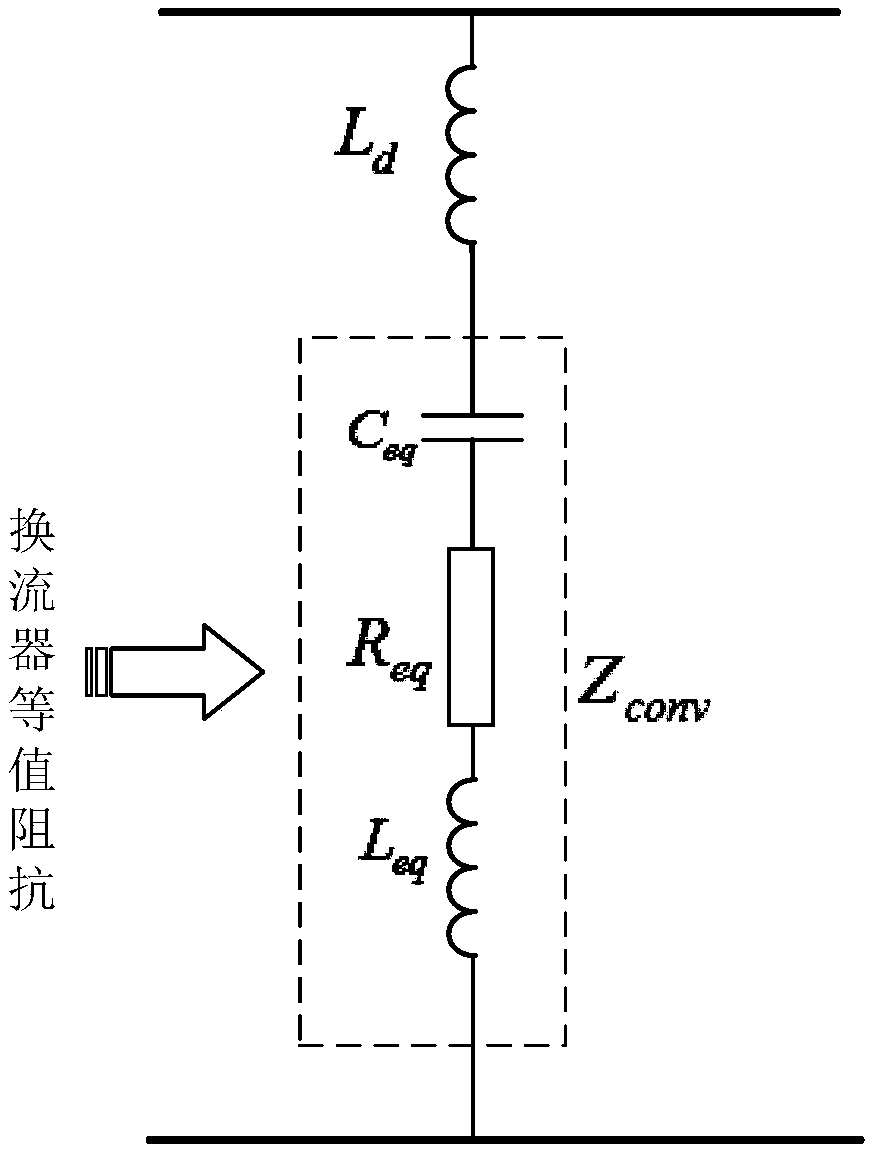
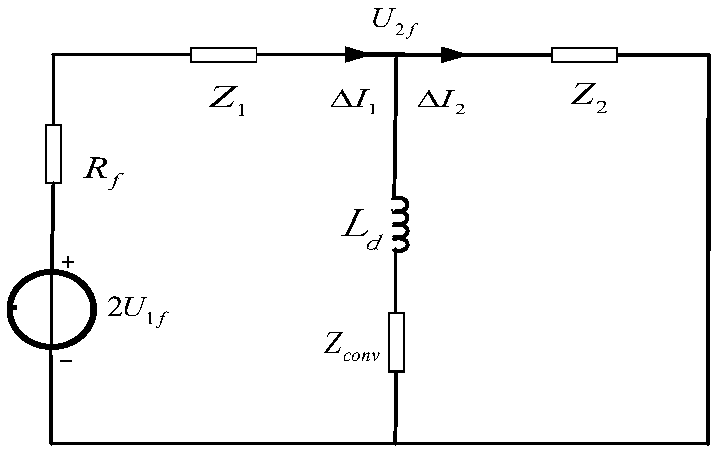
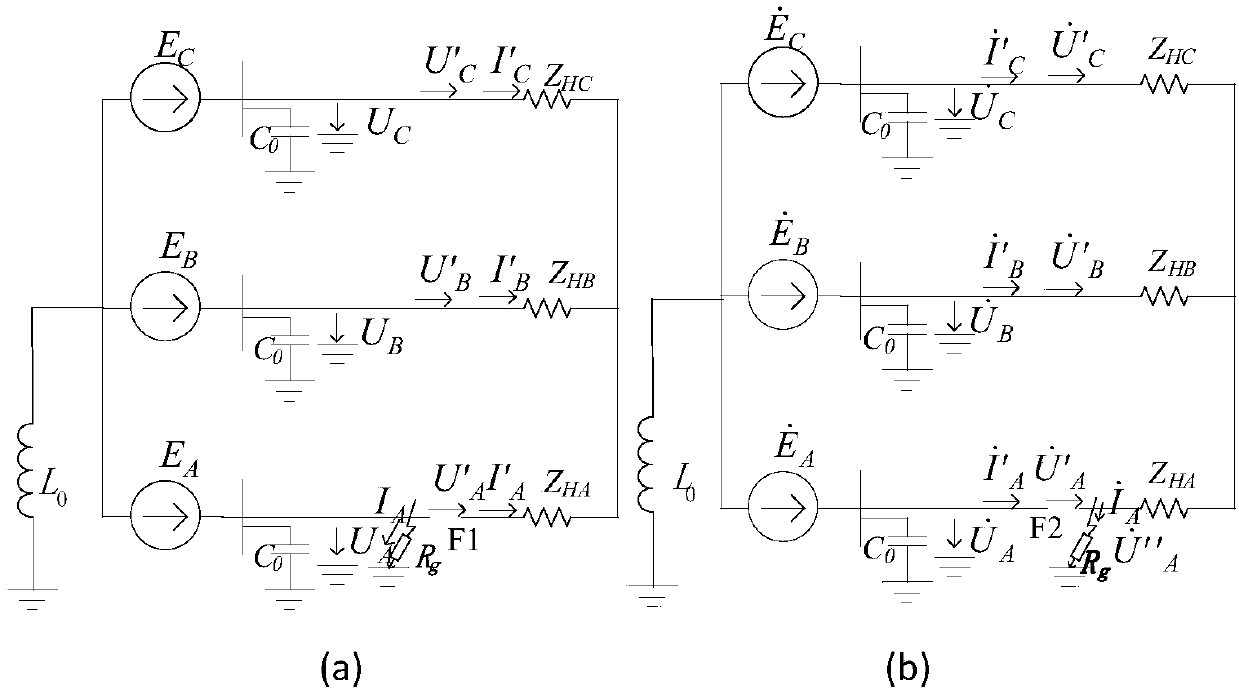
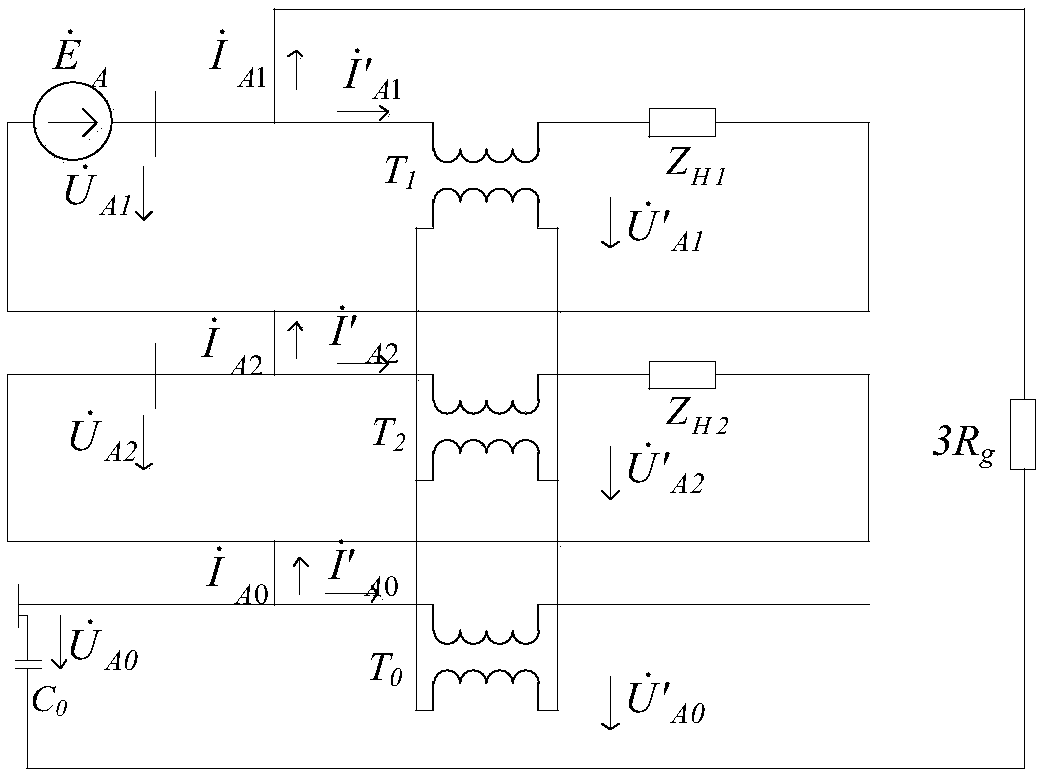
The invention belongs to the technical field of fault diagnosis of DC power network, in particular to a single-terminal quantity protection method of ring-shaped flexible power network line. The method comprises the following steps: measuring voltages of two terminals of additional inductors at the installation position of DC power line protection; The equivalent model of post-fault converter is established. The MMC is equivalent to the series circuit of capacitor and inductor, and the VSC and DCT are equivalent to the parallel capacitor on the DC side. The complex modulus network of DC line based on 0-modulus and 1-modulus is established. The initial value of the additional inductance voltage after the fault is obtained by solving the complex modulus network of the DC line. The relationship between the initial value of the additional inductor voltage and the fault types in and out of the region is obtained. The fault location identification criterion based on the initial value of additional inductance voltage is established and the fault location identification threshold is adjusted. Based on the initial value of the additional inductor voltage, the fault pole judgment criterion and the fault pole judgment threshold are established. Single-ended electrical quantity is used to identify faults quickly and accurately, and communication is not needed, and the reliability is high.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
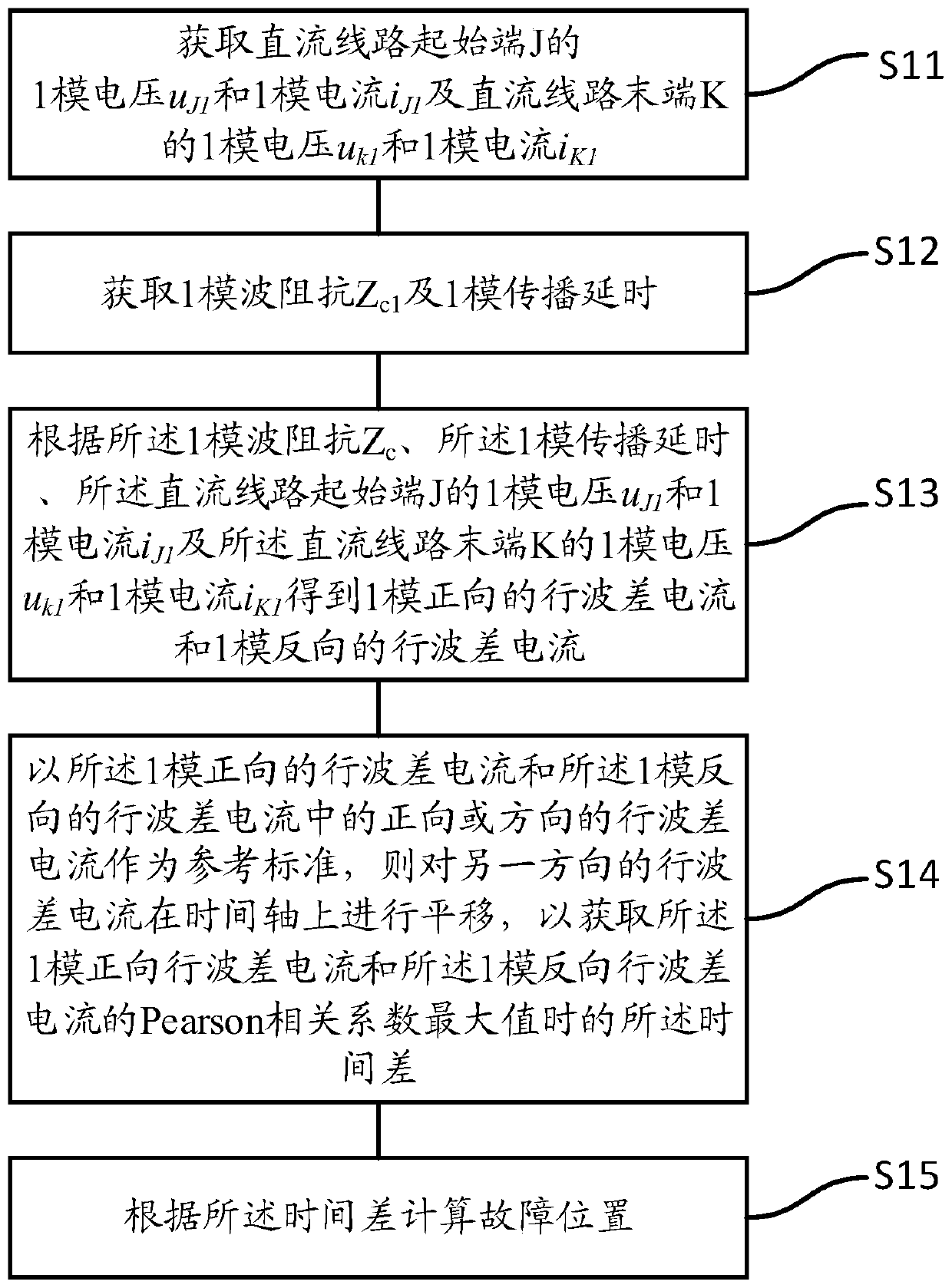
Fault location method based on traveling wave difference current, device, equipment and medium
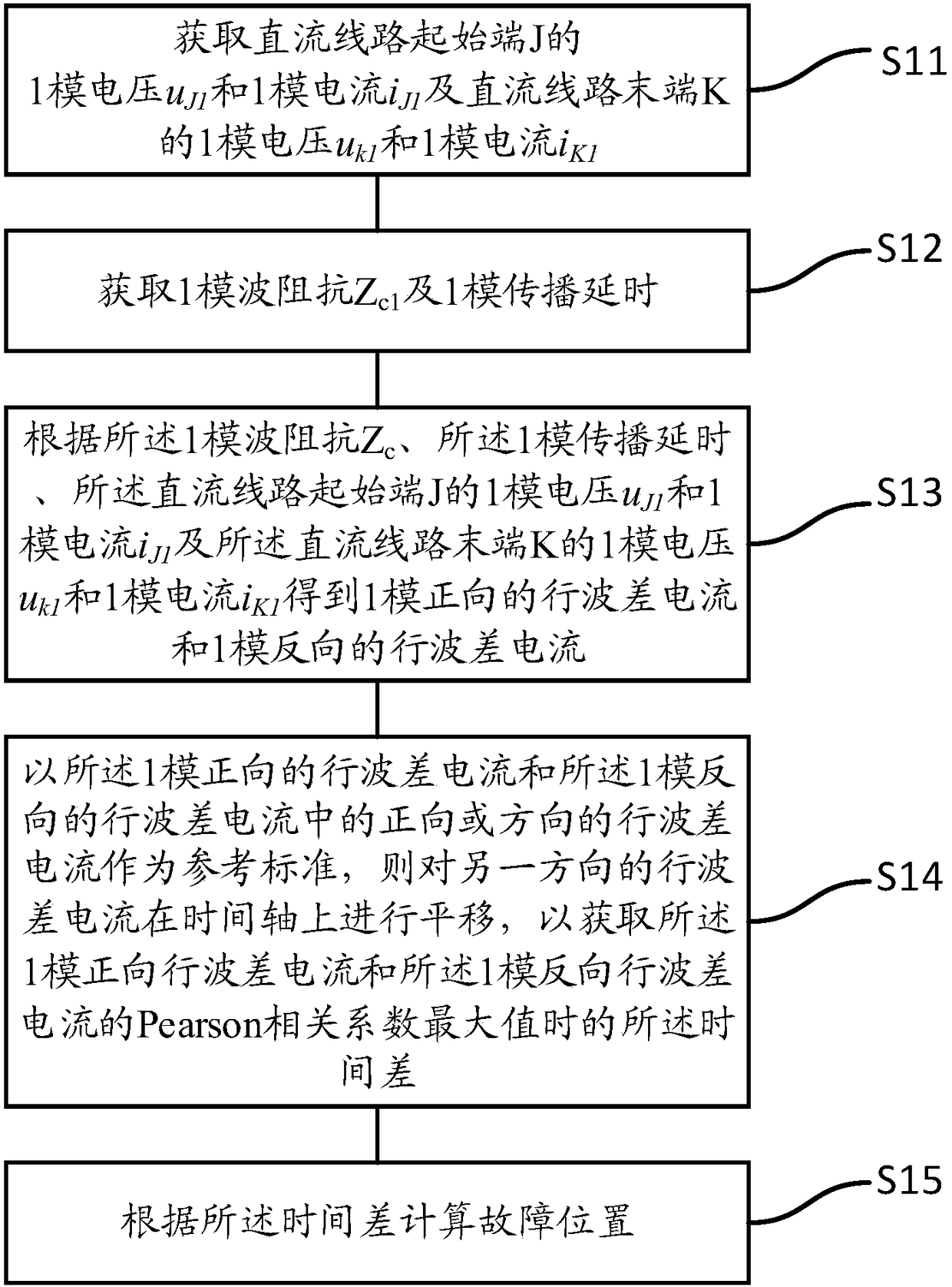
ActiveCN108445354AEasy and reliable to findNot affected by failure typeFault location by conductor typesInformation technology support systemCorrelation coefficientPropagation delay
The invention discloses a fault location method based on traveling wave difference current. The method comprises steps: one-mode voltage uJ1 and one-mode current iJ1 of a DC line starting end J and one-mode voltage uK1 and one-mode current iK1 of a DC line tail end K are acquired; 1-mode wave impedance Zc1 and 1-mode propagation delay tau1 are acquired; one-mode forward traveling wave difference current di<1><+>(t) and one-mode backward traveling wave difference current di<1><->(t) are obtained; forward or backward traveling wave difference current in the one-mode forward traveling wave difference current di<1><+>(t) and the one-mode backward traveling wave difference current di<1><->(t) is used as a reference standard, the traveling wave difference current in the other direction is translated, and the time difference deltat when a Pearson correlation coefficients are maximum of the one-mode forward traveling wave difference current di<1><+>(t) and the one-mode backward traveling wavedifference current di<1><->(t) is acquired, wherein deltat belongs to a range of -tau1 to tau1, the -tau1 is the propagation delay when the fault happens at the starting end J, and the tau1 is the propagation delay when the fault happens at the tail end K; and a fault location is calculated according to the time difference deltat. Thus, the fault location can be reliably judged, which is not influenced by a fault type, and the anti-transition resistance ability is strong.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE, CHINA SOUTHERN POWER GRID CO LTD +1
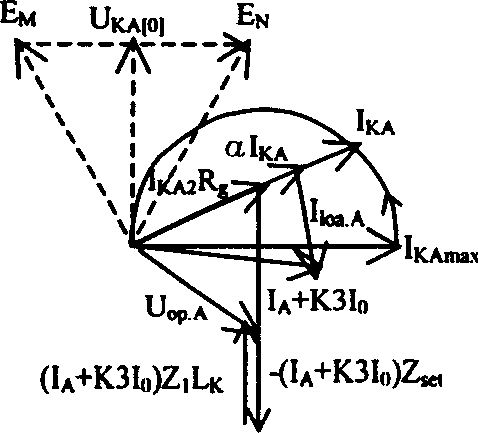
Adaptive earthing distance relay
InactiveCN1808822AStrong anti-transition resistanceImprove motor agilityEmergency protective circuit arrangementsElectrical resistance and conductanceHigh pressure
This invention relates to high voltage output circuit fault distance protection technique and to one self-adapting earth resistance relay, which forms the relay by fault protection fixing place negative voltage Um2 as electrode volume. This invention relay not only has strong transition resistance force and also with negative sequence volume protection integrated with good self-adapting relay.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Phase relevant current differential protection method
InactiveCN101814715ARealize dynamic adjustmentSolve protection problemsEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionPhase correlationEngineering
The invention relates to the power system relay protection field, in particular to a phase relevant current differential protection method. In order to improve the motion sensitivity of differential protection at the time of internal failure and the brake reliability at the time of external failure to the most extent, the invention adopts the technical scheme. A phase relevant current differential protection method adopts the circuital phase relevant current differential protection criterion: Im+KIn cos Phi>Idz. In the formula, Im and In respectively represent current phasor collected and calculated to be obtained at two sides in the current differential protection and Phi is an angle between Im<&> and In<&>. When the angle of Im<&> is larger than the angle of Im<&>, it is positive. The positive direction of Im<&> and In<&> is from busbar flow to a component to be protected. K is brake coefficient. Idz is the fixed threshold of the current differential protection. The invention is mainly applied to the power system relay protection.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Line fault region identification method
ActiveCN109061397AQuick identificationReliable identificationFault location by conductor typesTransient stateFrequency characteristic
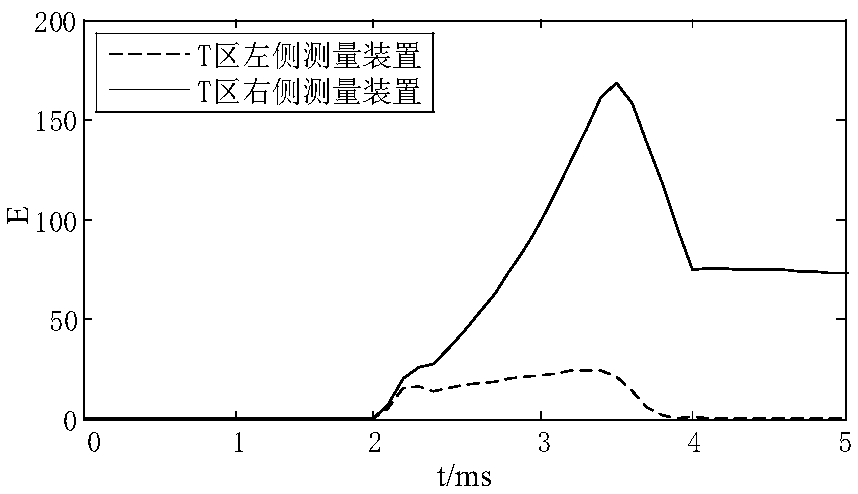
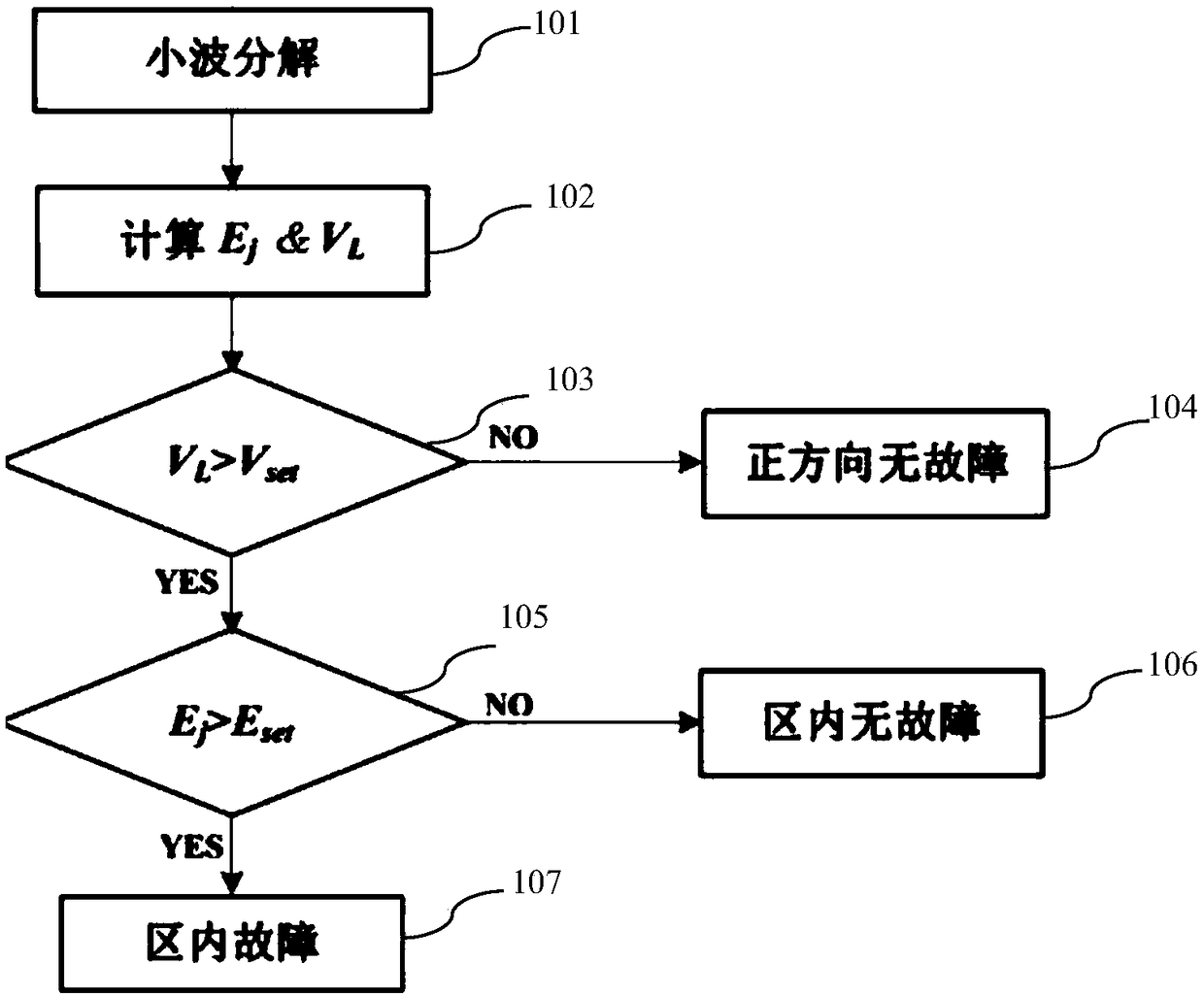
The invention discloses a line fault region identification method. The line fault region identification method comprises the following steps of calculating equivalent impedance Zeq of a T region; calculating current T region transfer functions on the non-fault side and the fault side of the T region when a line suffers from a fault, then obtaining an amplitude-frequency characteristic curve, and thereby determining the number J of layers of wavelet transform corresponding to a reduced frequency band; giving an initial value to a fault region judgment start setting value delta set1, wherein themaximum value of T region fault standard energy difference is delta EJset; measuring and working out line mode currents IL and IR; judging whether the fault region judgment protection needs action ornot; measuring and working out T region standard energy difference delta EJ; and by judging the relation between the standard energy difference delta EJ and the maximum value delta EJset, and then judging a fault region. According to the method, the difference of the fault transient state current energy on the two sides of the T region are extracted through wavelet transform according to the cutting-down effect to the low-frequency component in the fault transient state current energy by the T region, and quick and reliable identification of a fault position can be realized, so that fault region judgment is further realized by integrating fault direction position of each T region.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE, CHINA SOUTHERN POWER GRID CO LTD +1
Distance protection method and system
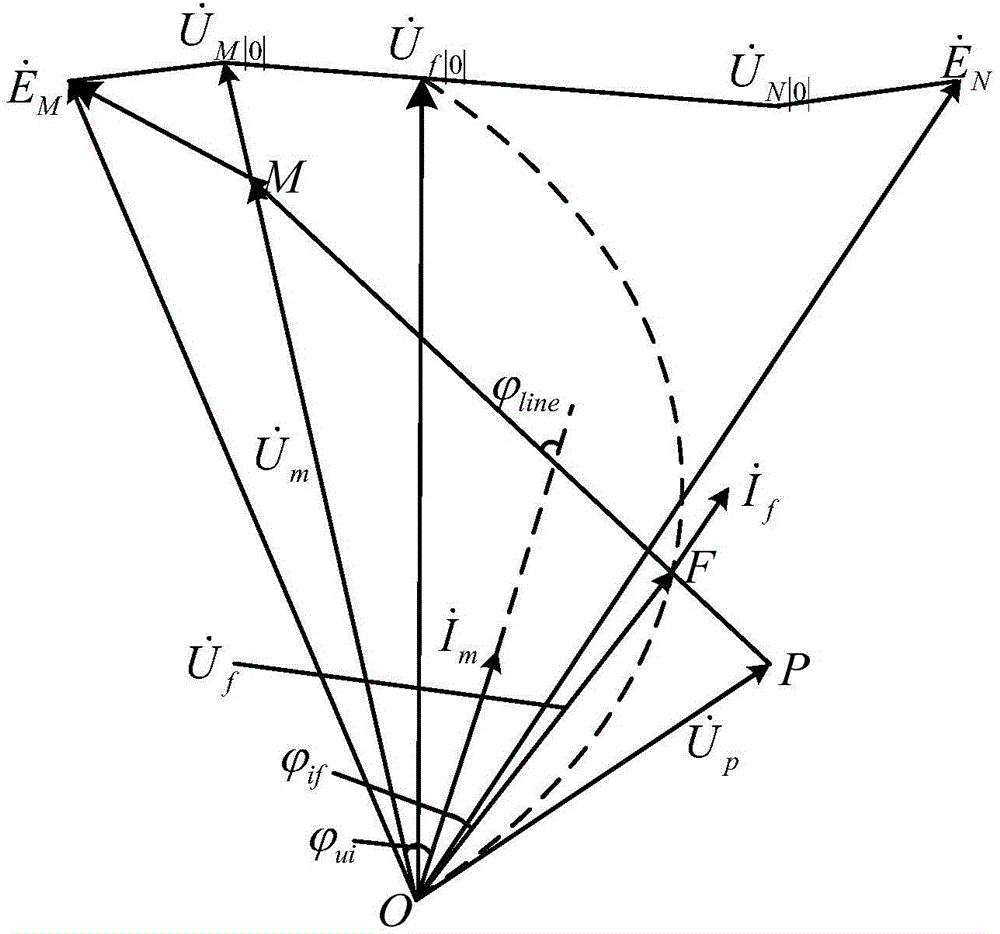
ActiveCN104466928AThe composition principle is simpleSmall amount of calculationEmergency protective circuit arrangementsElectrical resistance and conductancePower flow
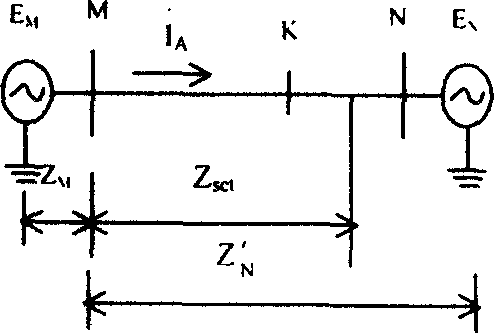
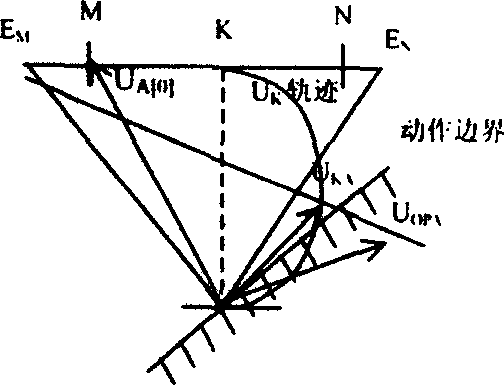
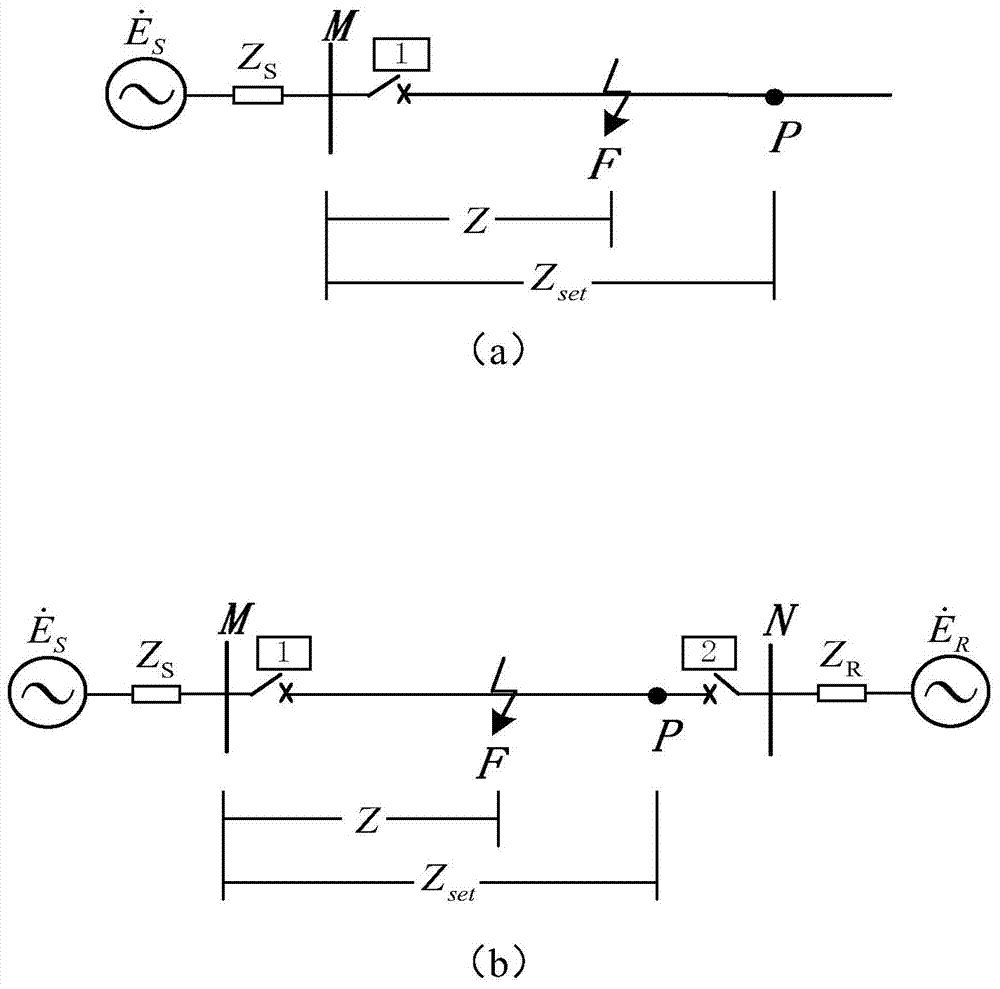
The invention discloses a distance protection method and system. The distance protection method includes the steps that A, the voltage Um at the distance protection installation position, the current Im at the distance protection installation position, the negative-sequence current Im2 at the distance protection installation position, a distance protection setting impedance boundary value ZMN and the impedance angle thetaline of a circuit where distance protection is located are collected; B, the measurement impedance Zm and self-adaptation distance protection setting impedance at the distance protection installation position are determined according to the collected signals in the step A; C, whether a trip signal or a blocking signal is sent is determined according to the measurement impedance Zm and self-adaptation distance protection setting impedance at the distance protection installation position. Through the distance protection method and system, influence of a transition resistor on distance protection can be eliminated, and correct actions of distance protection can be realized.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Method and system for judging fault section of multi-terminal DC transmission system based on polar wave energy
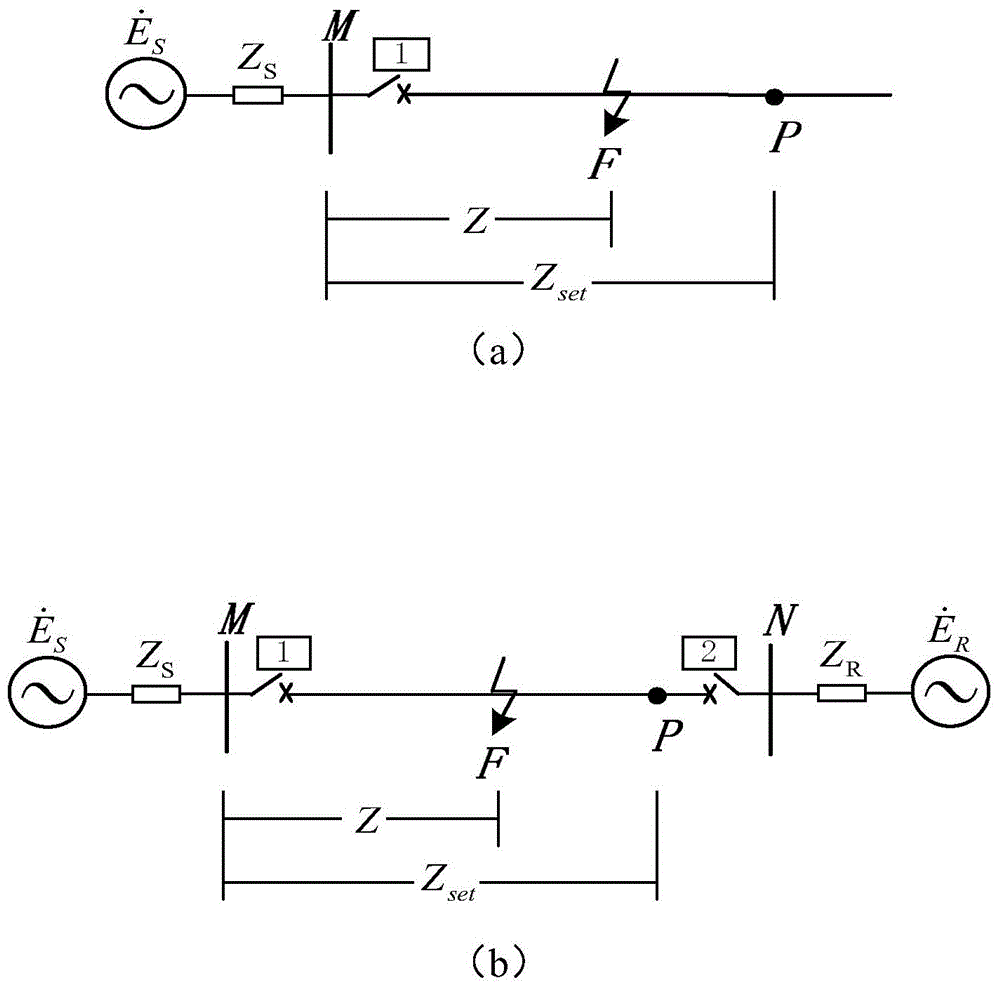
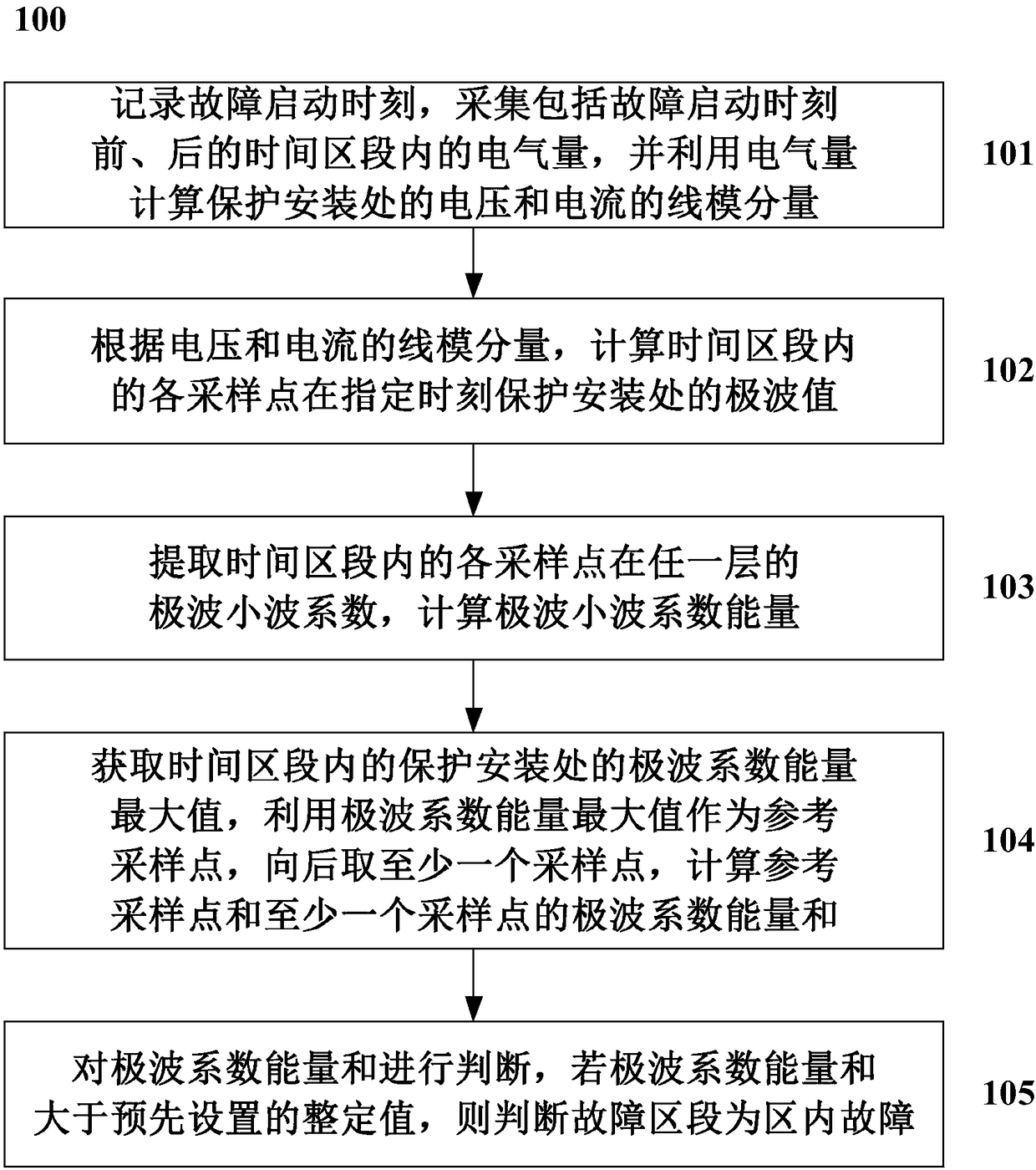
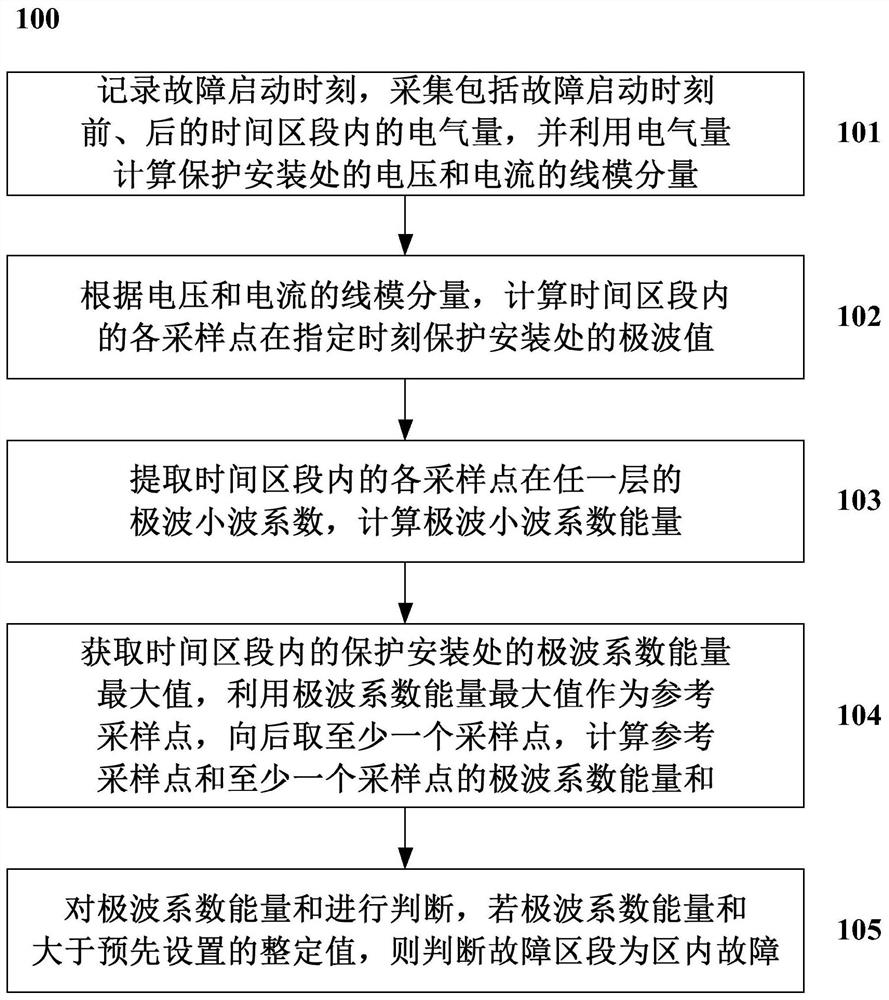
ActiveCN108551160AFast failureQuick identificationEmergency protection detectionFault location by conductor typesValue setTime segment
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +2
Single-phase earth fault relay protection method based on before-fault voltage actual-measurement line
InactiveCN103872663AStrong anti-transition resistanceStrong capability of load current influenceEmergency protective circuit arrangementsPhase currentsSingle phase
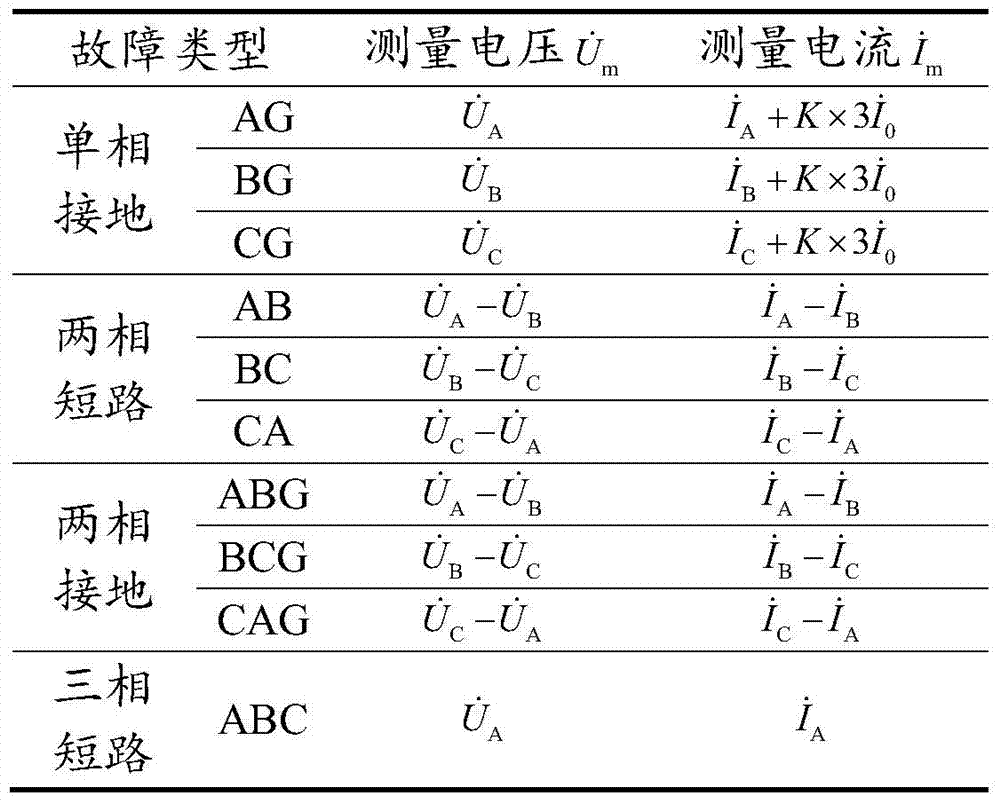
The invention discloses a single-phase earth fault relay protection method based on a before-fault voltage actual-measurement line. The method comprises the steps of firstly measuring fault phase voltage break variable, fault phase current break variable and zero sequence current at a protection mounting part of a power transmission line and two other normal phase voltages; calculating fault phase voltage before a line single-phase earth fault in real time by using the two normal phase voltage after the line single-phase earth fault; then judging whether the amplitude of the fault phase voltage during the normal operation of the power transmission line is greater than the amplitude of fault phase voltage at a protection setting range of the power transmission line or not, so as to determine whether to send an action trip signal or not. According to the method, memorizing the voltage before the line fault is not needed, and a voltage keeping loop before the line fault does not need to be arranged for relay protection hardware; an action characteristic circle corresponding to the method passes a third quadrant, and an origin of coordinates is in the action characteristic circle, so no protection dead zone for action characteristics exists when an exit single-phase earth fault is protected, and misoperation is avoided when a reverse-direction exit single-phase earth fault is protected.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
Adaptive impedance relay
InactiveCN1753267AImprove performanceStrong resistance to transition resistanceArrangements resposive to fault currentElectrical resistance and conductanceHigh pressure
This invention relates to an earth faulty distance protection technology of high voltage transmission line, which is an adaptive earth direction impedance relay taking the residual voltage Uo at the faulty protection installation place as the polarized volume, which not only has the strong ability of bearing the transient impedance, but also has the advantage of protecting residual component.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Method for protecting circuit interphase fault voltage phase based on fault overall-process transient characteristic
ActiveCN103779848AStrong anti-transition resistanceStrong capability of load current influenceEmergency protective circuit arrangementsTransient stateLoad following power plant
The invention discloses a method for protecting a circuit interphase fault voltage phase based on a fault overall-process transient characteristic. Whether a protection device transmits an action skip signal or not is determined according to whether the phase angle by which the fault inter-phase voltage before a circuit interphase short circuit fault occurs is ahead of the fault inter-phase voltage at a power transmission circuit protection setting range falls in the action characteristic zone (90 degrees and 270 degrees). The voltage before the circuit fault does not need to be memorized and a relay is used for protecting hardware without needing to set a voltage maintaining circuit before the circuit fault. An action characteristic circle corresponding to the method for protecting the circuit interphase fault voltage passes the third quadrant and the origin of coordinates is in the action characteristic circle. Thus, an action characteristic of the method is free of protection dead zones when an outlet interphase short circuit fault is protected and misoperation is avoided when a backward outlet interphase short circuit fault occurs. According to the method for protecting the circuit interphase fault voltage based on the fault overall-process transient characteristic, the action characteristic is the transient action characteristic in the whole circuit interphase short circuit fault process and the strong capacities of resisting influences of transition resistance and loaded currents are achieved.
Owner:STATE GRID PUTIAN ELECTRIC POWER SUPPLY +2
Direct-current transmission line distance measurement method and system
PendingCN114137356ALow ranging costStrong anti-noise abilityFault locationElectric power systemRanging
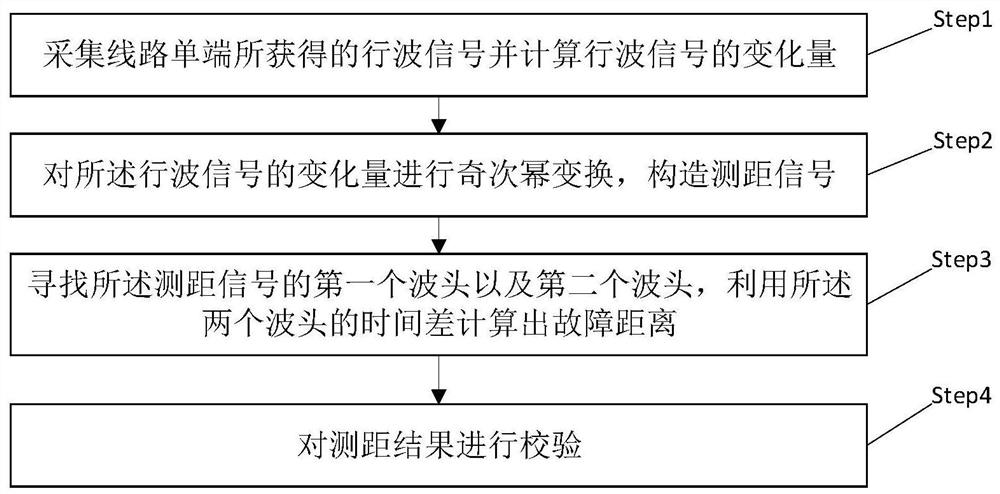
The invention relates to a direct-current power transmission line distance measurement method and system, and belongs to the technical field of power system relay protection. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a voltage signal obtained by a single end of a line and calculating the variable quantity of the voltage signal; odd power transformation is carried out on the variable quantity of the voltage signal, and a ranging signal is constructed; and searching a first wave head and a second wave head of the distance measurement signal, calculating a fault distance by using a time difference between the two wave heads, and verifying a distance measurement result. The invention further provides a direct-current transmission line distance measuring system. According to the method, only single-ended quantity is utilized, synchronous time synchronization is not needed, the anti-noise capability is high, and distance measurement can be accurately carried out.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Distance relay for reflecting single-phase ground short circuit and movement method and device
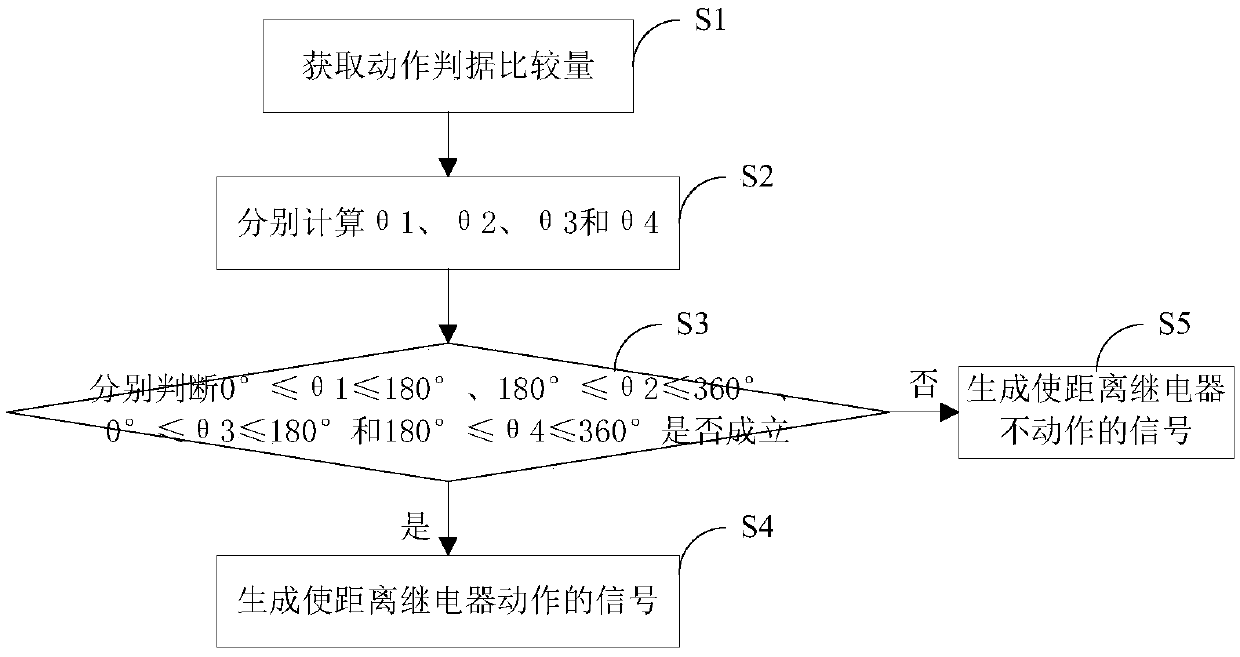
InactiveCN105514955AThe phase comparison criterion is simpleImprove reliabilityEmergency protective circuit arrangementsSimulationSingle phase
The invention discloses a method and device for movement of a distance relay and the distance relay for reflecting a single-phase ground short circuit. The method comprises the following steps of obtaining movement criterion comparative quantity, calculating theta 1, theta 2, theta 3 and theta 4 respectively, and judging whether it is true that 0 degree<=theta1<=180 degrees, 180 degrees<=theta 2<=360 degrees, 0 degree<=theta 3<=180 degrees and 180 degrees<=theta 4<=360 degrees; when 0 degree<=theta1<=180 degrees, 180 degrees<=theta 2<=360 degrees, 0 degree<=theta 3<=180 degrees and 180 degrees<=theta 4<=360 degrees, generating signals for enabling the distance relay to move. According to the method and device for movement of the distance relay and the distance relay for reflecting the single-phase ground short circuit, the phase comparison criterion is simple, the reliability is high, and the distance relay has very high transition resistance resisting capability and can automatically judge fault phases.
Owner:STATE GRID SHANDONG ELECTRIC POWER +1
Single-ended protection method for multi-terminal flexible DC grid system based on boundary characteristics
ActiveCN106253240BFast actionLow costEmergency protective circuit arrangementsTransient stateWavelet decomposition
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Ground distance relay and action method and device
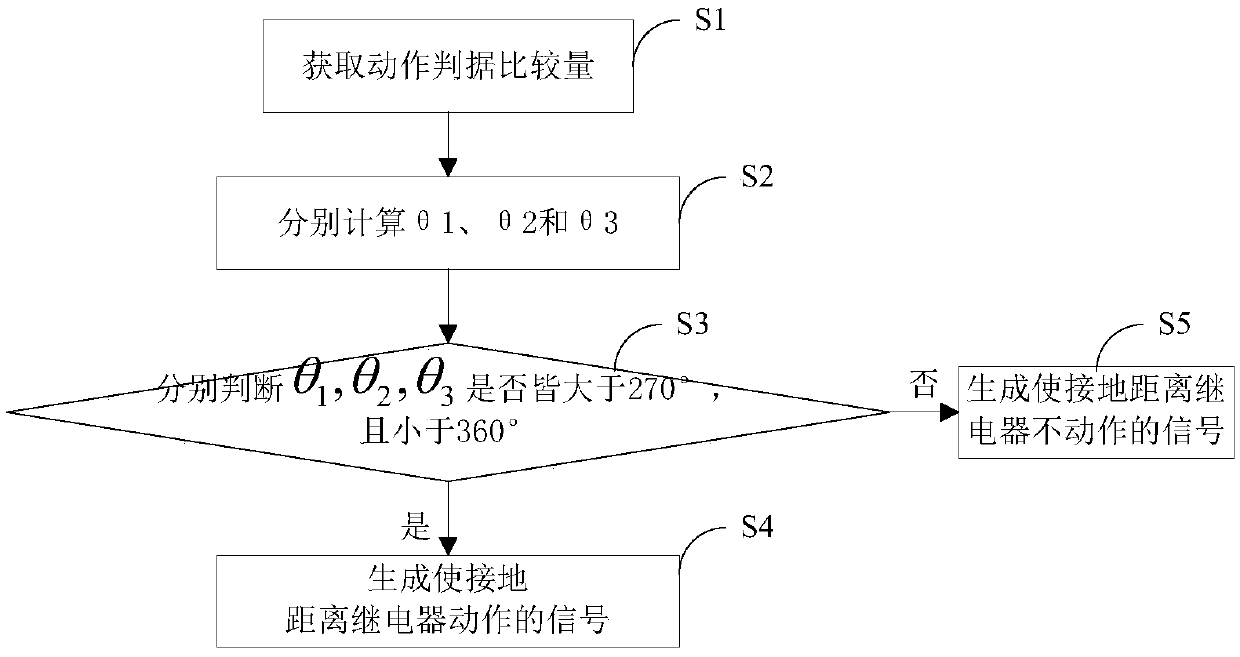
InactiveCN105514956AThe phase comparison criterion is simpleImprove reliabilityEmergency protective circuit arrangementsComputer scienceSingle phase
The invention discloses a ground distance relay action method and device and a ground distance relay reflecting a single-phase ground short circuit. The method comprises the following steps that the action criterion comparative quantity is obtained; theta1, theta2 and theta3 are calculated respectively; whether the conditions that the theta1 is larger than 270 degrees and smaller than 360 degrees, the theta2 is larger than 270 degrees and smaller than 360 degrees and the theta3 is larger than 270 degrees and smaller than 360 degrees are satisfied or not is judged respectively; when the theta1 is larger than 270 degrees and smaller than 360 degrees, the theta2 is larger than 270 degrees and smaller than 360 degrees and the theta3 is larger than 270 degrees and smaller than 360 degrees, a signal for making ground distance relay acted is generated. According to the ground distance relay action method and device and the ground distance relay reflecting the single-phase ground short circuit, a phase comparison criterion is simple, the reliability is high, the ground distance relay has strong transition resistance resistant capacity, and a fault phase can be automatically judged.
Owner:STATE GRID SHANDONG ELECTRIC POWER +1
Phase relevant current differential protection method
InactiveCN101814715BRealize dynamic adjustmentSolve protection problemsEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionPhase correlationEngineering
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Hybrid DC power transmission line single-end fault distance measurement method and system
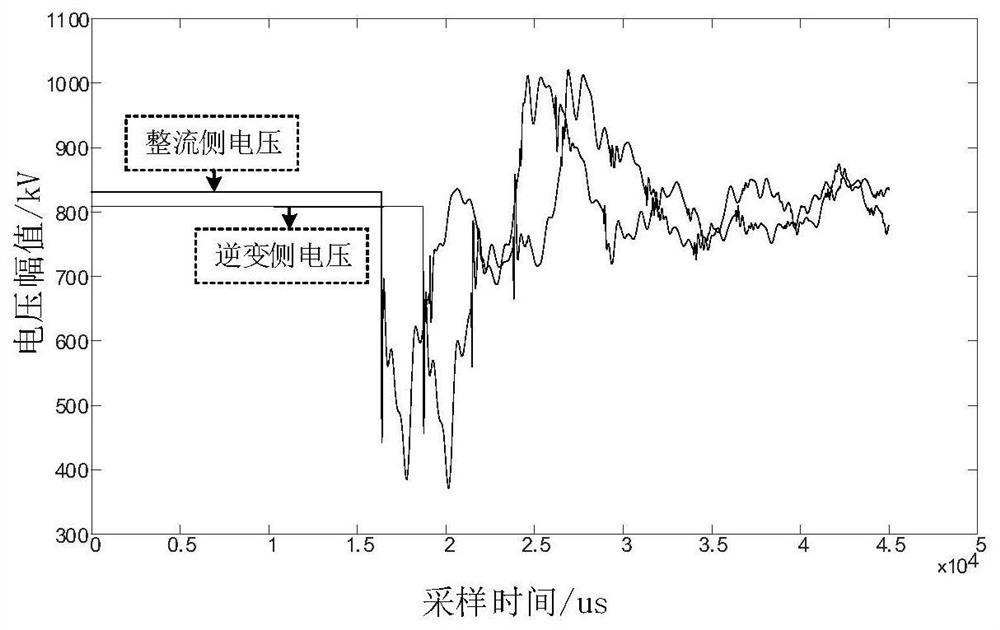
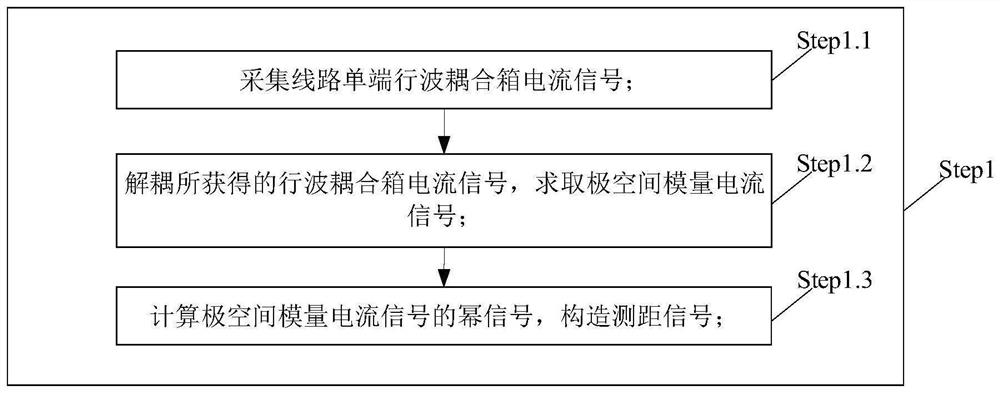
ActiveCN114184896AStrong anti-noise abilityStrong anti-transition resistanceFault locationInformation technology support systemTransmission lineEstimation result
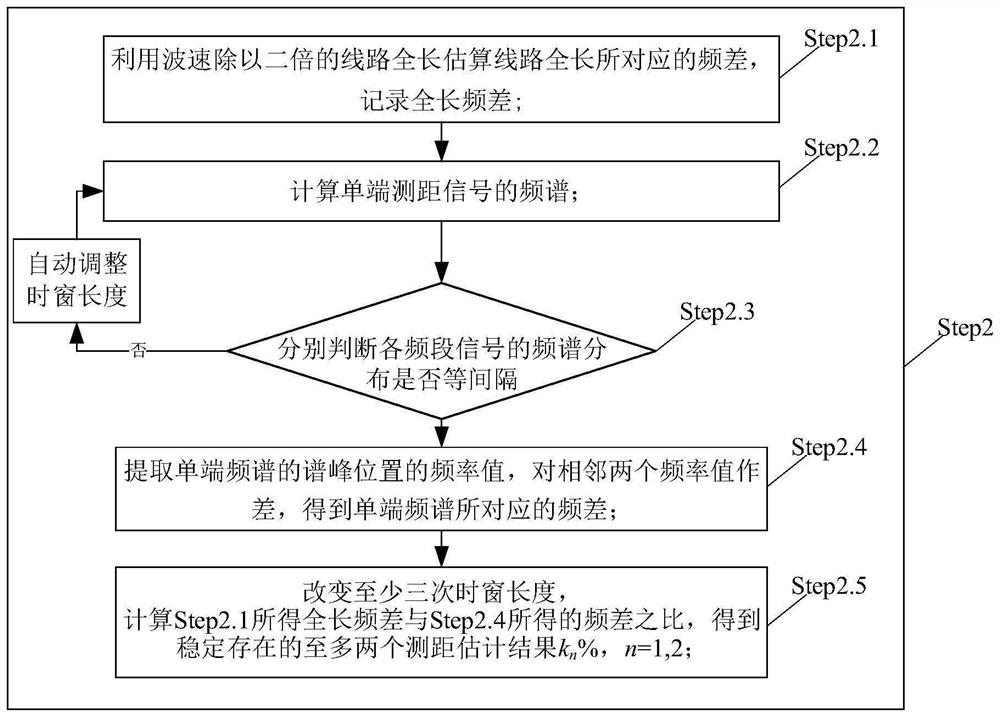
The invention relates to a hybrid direct current transmission line single-end fault distance measurement method and system, and belongs to the technical field of power system relay protection control. The method comprises the following steps: collecting a line single-end traveling wave coupling box current signal to obtain a ranging signal; calculating the frequency spectrum of a single-end ranging signal, judging whether a frequency difference stable value exists or not, if not, automatically adjusting the length of a data time window, returning to recalculate the single-end frequency spectrum, and if yes, performing fault ranging by using the frequency difference and changing the length of the time window for at least three times to obtain at most two ranging estimation results kn% which exist stably, n = 1, 2; calculating a single-end verification signal, and respectively calculating the deviation delta n% between the distance measurement estimation result and the verification signal, n = 1, 2; the deviation delta n% is compared with a verification threshold value, whether delta n% is smaller than or equal to a preset verification threshold value or not is judged, if yes, the distance measurement result is kn%, and if not, the distance measurement result is 1-kn%. The method is suitable for various complex working conditions of the hybrid direct current system, the distance measurement result is high in accuracy, high in reliability and high in robustness.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Single-phase grounding distance protection system and method based on voltage phase comparison
ActiveCN104682361BStrong anti-transition resistanceSolve protection problemsEmergency protective circuit arrangementsElectrical resistance and conductancePower-system protection
The invention belongs to the technical field of electric power system relay protection, and in particular relates to a single-phase grounding distance protection system based on voltage phase comparison and a method thereof. The system includes a sequentially connected data reading module, a protection calculation module and a protection action module; the method includes : First, use the relationship between the negative sequence current phase at the protection installation and the negative sequence current phase at the fault point to calculate the angle between the measured current and the fault voltage; then, use the measured voltage as a reference value to calculate the phase of the fault point voltage and the compensation voltage Finally, according to the phase difference between the fault point voltage and the compensation voltage when the fault is inside and outside the fault, the distance protection criterion is constructed. The invention has a good anti-transition resistance capability, and can correctly distinguish faults inside and outside the zone regardless of the size of the transition resistance; at the same time, the protection action time and fixed value error meet the technical requirements of grounding distance protection, and the calculation amount is small, which has a high engineering practical value.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Adaptive earthing distance relay
InactiveCN100444493CStrong anti-transition resistanceImprove motor agilityEmergency protective circuit arrangementsElectrical resistance and conductanceHigh pressure
This invention relates to high voltage output circuit fault distance protection technique and to one self-adapting earth resistance relay, which forms the relay by fault protection fixing place negative voltage Um2 as electrode volume. This invention relay not only has strong transition resistance force and also with negative sequence volume protection integrated with good self-adapting relay.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Diagnosis method of multiple fault types of single-phase disconnection and grounding in distribution network based on zero-sequence voltage
ActiveCN106872852BVersatileOffset angle characteristics are not affected by voltage levelFault location by conductor typesPhase differenceGround failure
The invention discloses a method for diagnosing multiple fault types of single-phase disconnection and grounding in a distribution network based on zero-sequence voltage. By determining the small current grounding mode, the starting value of zero-sequence voltage is set; The phase difference relationship between the fault phase voltage before the fault and the steady-state zero-sequence voltage phase after the fault and the reference function is obtained by calculating the phase voltage sampling data of N cycles after the fault moment by FFT and the symmetrical component algorithm as the judgment basis; judgment Whether the zero-sequence voltage exceeds the start-up value, if so, continue to extract, and judge whether the phase difference between the zero-sequence voltage phase and the fault phase voltage phase before the fault corresponds to the grounding range of the load side of the criterion, if yes, it is single-phase disconnection plus Ground fault on the load side, otherwise it is a single-phase disconnection plus a ground fault on the power side. The invention has good versatility, and is applicable to distribution networks with ungrounded neutral points or grounded through arc suppressing coils of various voltage levels, and the offset angle characteristics are not affected by voltage levels.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
A Method and System for Judging Fault Sections of Multi-Terminal Direct Current Transmission System Based on Polar Wave Energy
ActiveCN108551160BFast actionFast failureEmergency protection detectionFault location by conductor typesEngineeringComputational physics
The invention discloses a method for judging a fault section of a multi-terminal direct current transmission system based on polar wave energy: record the fault start time, collect the electric quantity in the time section including before and after the fault start time, and use the electric quantity to calculate the protection The linear mode components of the voltage and current at the installation site; according to the linear mode components of the voltage and current, calculate the extreme wave value of each sampling point in the time segment at the specified moment to protect the installation site; extract each sampling point in the time segment at any time Calculate the energy of the polar wavelet coefficient for the polar wavelet coefficient of the first layer; obtain the maximum energy value of the polar wave wavelet coefficient at the protection installation in the time zone, use the maximum energy value of the polar wave wavelet coefficient as a reference sampling point, and take at least One sampling point, calculate the energy sum of the polar wavelet coefficients of the reference sampling point and at least one sampling point; judge the energy sum of the polar wavelet coefficients, if the energy sum of the polar wavelet coefficients is greater than the preset setting value, then judge the faulty section In-zone failure.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +2
Current differential protection method based on fault component current amplitudes and phase differences
InactiveCN102324722BNot affected by load currentCriterion sensitivity is highEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionElectrical resistance and conductanceCapacitance
The invention relates to a current differential protection method based on fault component current amplitudes and phase differences. The current differential protection method is characterized in that: a differential protection criterion is formed by the adoption of the current fault component amplitudes at two sides of a protected line and the phase differences at the two sides of the protected line, wherein the differential current value (Icd) is equal to the sum of the current fault component amplitude (the absolute value of [delta]IM) at one side and the product of the current fault component amplitude (the absolute value of [delta]IN) at the opposite side and a cosine function of the phase difference ([phi]) between the absolute value of [delta]IM and the absolute value of [delta]IN, i.e. Icd= (the absolute value of [delta]IM)+(the absolute value of [delta]IN)cos[phi]; and the braking current (Ir) is equal to the difference between the absolute value of [delta]IM and the product of the absolute value of [delta]IN and the cos[phi], i.e. Ir= (the absolute value of [delta]IM)-(the absolute value of [delta]IN)cos[phi], and the differential protection criterion is the following inequation: Icd-KIr>= Idz, wherein K is a braking coefficient and Idz is an action current threshold. If the differential protection criterion is satisfied, an internal fault is determined and the differential protection acts; if the differential protection criterion is not satisfied, an external fault is determined and the differential protection does not act. The current differential protection method related to the invention has the advantages of higher sensitivity for internal faults, higher safety for external faults, fewer effects subjected from the factors, such as the transition resistance, the distributed capacitance, the TA saturation and the like, and good performances.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
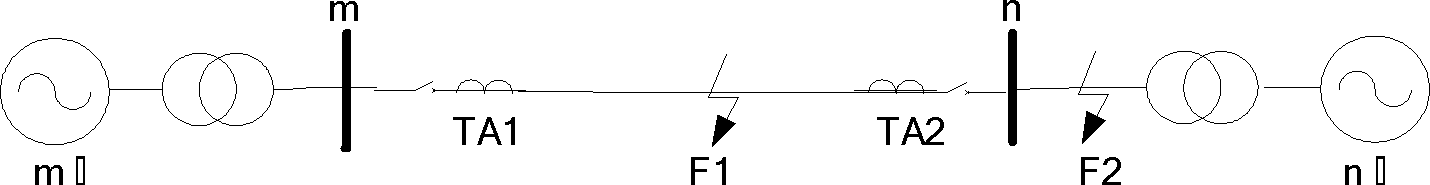
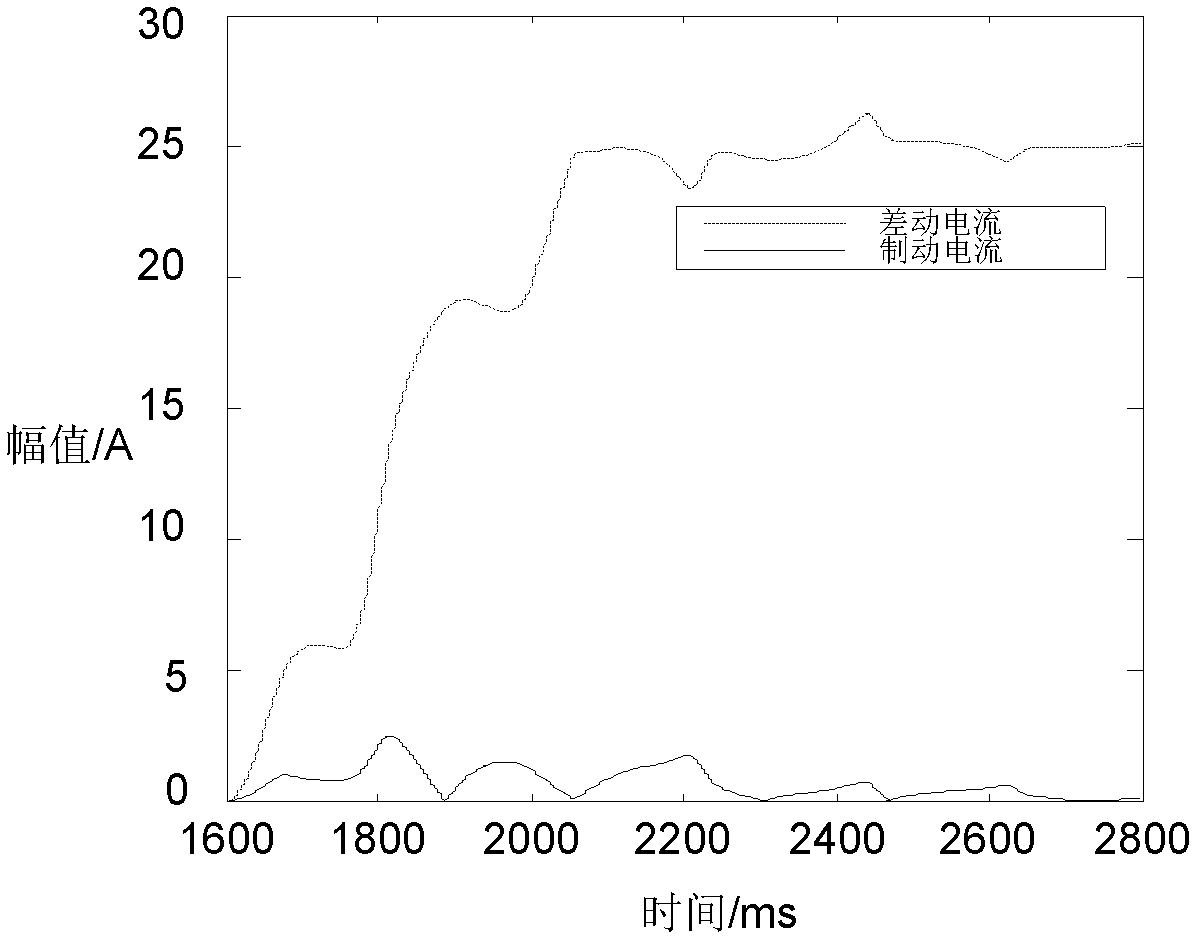
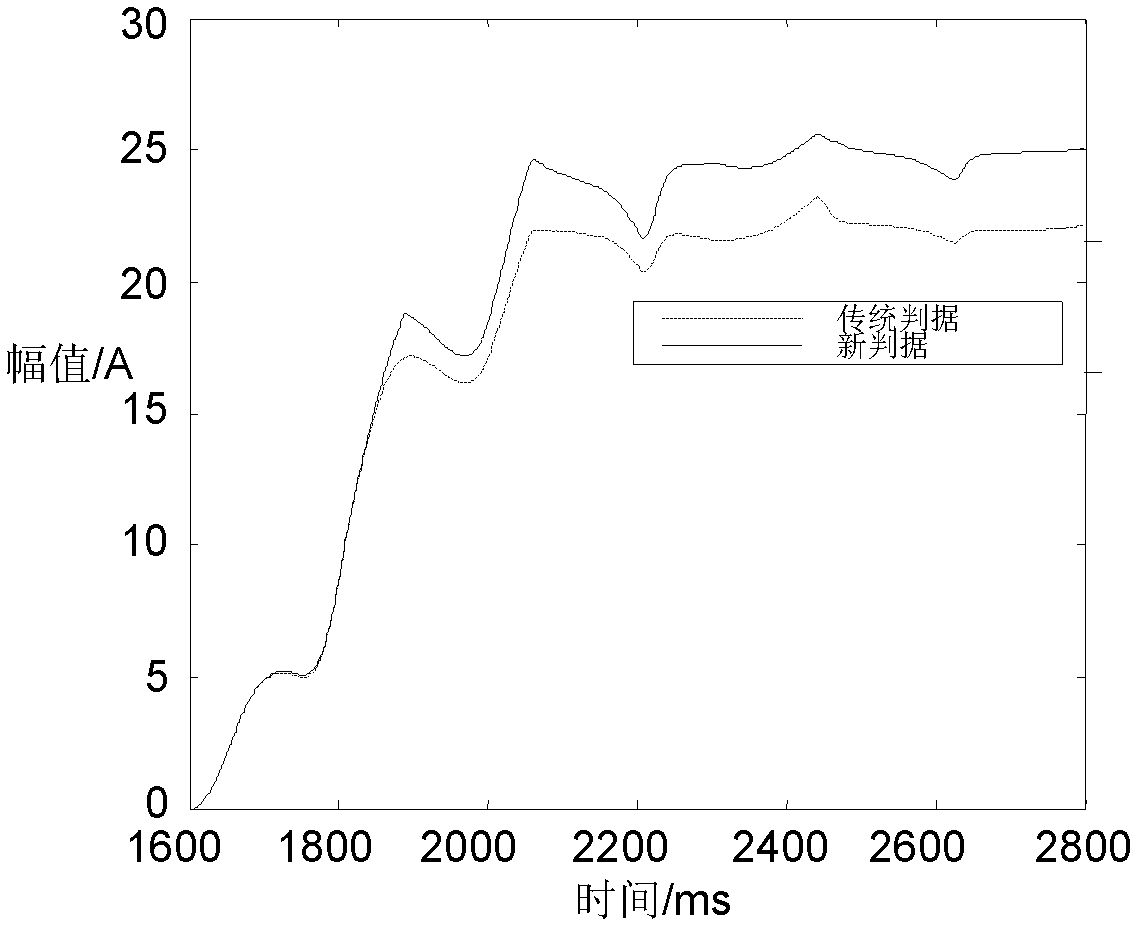
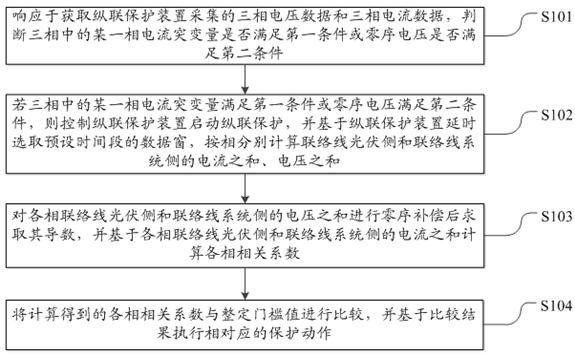
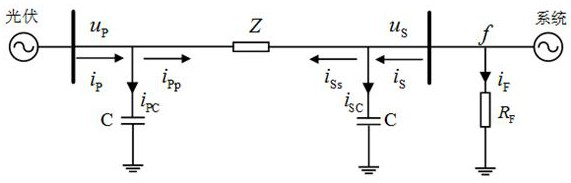
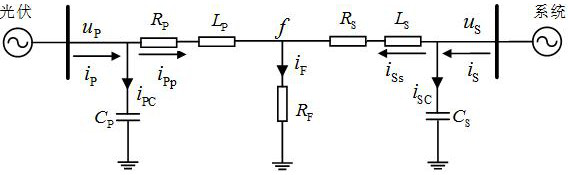
A photovoltaic power generation grid-connected tie line longitudinal protection method and system
ActiveCN113437732BMovement precisionStrong anti-transition resistanceEmergency protection data processing meansPhase currentsGrid network
The invention discloses a method and system for longitudinal protection of photovoltaic power generation grid-connected tie lines. The method includes: judging whether the sudden change in current of a certain phase in three phases satisfies the first condition or whether the zero-sequence voltage satisfies the second condition; If the sudden change of a certain phase current meets the first condition or the zero-sequence voltage meets the second condition, the longitudinal protection will be started, and the data window of the preset time period will be selected after a delay, and the PV side and the tie line of the tie line will be calculated separately by phase. The sum of the current and the voltage on the system side; the zero-sequence compensation is performed on the sum of the voltages on the photovoltaic side and the system side of the tie-line of each phase to obtain its derivative, and based on the photovoltaic side of the tie-line of each phase and the system side of the tie-line Calculate the correlation coefficient of each phase by the sum of the currents; compare the calculated correlation coefficient with the setting threshold, and execute the corresponding protection action based on the comparison result. Realized that it can act accurately in the case of different fault types at different fault locations.
Owner:STATE GRID JIANGXI ELECTRIC POWER CO LTD RES INST +2
Single-pole ground fault protection method for DC lines based on similarity of current mode components
ActiveCN112531658BStrong anti-transition resistanceEmergency protective circuit arrangementsShort-circuit testingElectrical resistance and conductanceCurrent mode
A DC line unipolar ground fault protection method based on the similarity of the current mode components, based on the similarity between the sum of the zero-mode components and the one-mode components of the current at both ends of the line According to the differences, a protection method for unipolar ground faults of DC lines is proposed, and the data window length can be flexibly selected according to actual needs. The protection method can reliably distinguish unipolar ground faults inside and outside the DC line area, and has a strong ability to resist transition resistance .
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF STATE GRID SHANDONG ELECTRIC POWER COMPANY +1
Fault location method, device, equipment and medium based on traveling wave difference current
ActiveCN108445354BEasy and reliable to findNot affected by failure typeFault location by conductor typesInformation technology support systemElectrical resistance and conductancePropagation delay
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE, CHINA SOUTHERN POWER GRID CO LTD +1
Self-adaptive reclosing method for single-phase earth fault in bipolar direct-current power grid
InactiveCN112072619AReduce threatGood quicknessEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionDc circuit breakerTransformer
The invention relates to a self-adaptive reclosing method for a single-phase earth fault in a bipolar direct-current power grid. The method comprises the following steps: (1) a fault clearing strategy: installing a direct-current circuit breaker (DCCB), i.e., a metal loop circuit breaker (MRCB), on a metal loop, and clearing a fault current through the switching-off of the DCCB and the MRCB afterthe overcurrent locking of a fault MMC; and (2) a self-adaptive reclosing method: based on the characteristics of the potential of a neutral point of a transformer valve side, namely a delta side, distinguishing the nature of the single-phase earth fault in the station so as to realize self-adaptive reclosing.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Distance protection method and system
ActiveCN104466928BThe composition principle is simpleSmall amount of calculationEmergency protective circuit arrangementsElectrical resistance and conductanceBoundary values
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com